Python typing函式庫和torch.types
Python typing函式庫和torch.types
- 前言
- typing
- Sequence vs Iterable
- Callable
- Union
- Optional
- Functions
- Callable
- Iterator/generator
- 位置參數 & 關鍵字參數
- Classes
- self
- 自定義類別
- ClassVar
- \_\_setattr\_\_ 與 \__getattr\_\_
- torch.types
- builtins
- 參數前的*
前言
在PyTorch的torch/_C/_VariableFunctions.pyi中有如下代碼:
@overload
def rand(size: Sequence[Union[_int, SymInt]], *, generator: Optional[Generator], names: Optional[Sequence[Union[str, ellipsis, None]]], dtype: Optional[_dtype] = None, layout: Optional[_layout] = None, device: Optional[Union[_device, str, None]] = None, pin_memory: Optional[_bool] = False, requires_grad: Optional[_bool] = False) -> Tensor: ...
@overload
def rand(*size: _int, generator: Optional[Generator], names: Optional[Sequence[Union[str, ellipsis, None]]], dtype: Optional[_dtype] = None, layout: Optional[_layout] = None, device: Optional[Union[_device, str, None]] = None, pin_memory: Optional[_bool] = False, requires_grad: Optional[_bool] = False) -> Tensor: ...
@overload
def rand(size: Sequence[Union[_int, SymInt]], *, generator: Optional[Generator], out: Optional[Tensor] = None, dtype: Optional[_dtype] = None, layout: Optional[_layout] = None, device: Optional[Union[_device, str, None]] = None, pin_memory: Optional[_bool] = False, requires_grad: Optional[_bool] = False) -> Tensor: ...
@overload
def rand(*size: _int, generator: Optional[Generator], out: Optional[Tensor] = None, dtype: Optional[_dtype] = None, layout: Optional[_layout] = None, device: Optional[Union[_device, str, None]] = None, pin_memory: Optional[_bool] = False, requires_grad: Optional[_bool] = False) -> Tensor: ...
@overload
def rand(size: Sequence[Union[_int, SymInt]], *, out: Optional[Tensor] = None, dtype: Optional[_dtype] = None, layout: Optional[_layout] = None, device: Optional[Union[_device, str, None]] = None, pin_memory: Optional[_bool] = False, requires_grad: Optional[_bool] = False) -> Tensor: ...
@overload
def rand(*size: _int, out: Optional[Tensor] = None, dtype: Optional[_dtype] = None, layout: Optional[_layout] = None, device: Optional[Union[_device, str, None]] = None, pin_memory: Optional[_bool] = False, requires_grad: Optional[_bool] = False) -> Tensor: ...
@overload
def rand(size: Sequence[Union[_int, SymInt]], *, names: Optional[Sequence[Union[str, ellipsis, None]]], dtype: Optional[_dtype] = None, layout: Optional[_layout] = None, device: Optional[Union[_device, str, None]] = None, pin_memory: Optional[_bool] = False, requires_grad: Optional[_bool] = False) -> Tensor: ...
@overload
def rand(*size: _int, names: Optional[Sequence[Union[str, ellipsis, None]]], dtype: Optional[_dtype] = None, layout: Optional[_layout] = None, device: Optional[Union[_device, str, None]] = None, pin_memory: Optional[_bool] = False, requires_grad: Optional[_bool] = False) -> Tensor: ...
當中的Sequence, Iterable, Optional, Union以及_int, _bool都是什麼意思呢?可以從torch/_C/_VariableFunctions.pyi.in中一窺端倪:
from torch import Tensor, Generator, strided, memory_format, contiguous_format, strided, inf
from typing import List, Tuple, Optional, Union, Any, ContextManager, Callable, overload, Iterator, NamedTuple, Sequence, Literal, TypeVarfrom torch.types import _int, _float, _bool, Number, _dtype, _device, _qscheme, _size, _layout, SymInt, Device
所以Sequence, Iterable, Optional, Union等是從一個叫做typing的庫中導入的。typing是Python的標準庫之一,作用是提供對類型提示的運行時支持。
_int, _bool等則是PyTorch中自行定義的類型。
typing
Sequence vs Iterable
根據Type hints cheat sheet - Standard “duck types”,Sequence代表的是支持__len__及__getitem__方法的序列類型,例如list, tuple和str。dict和set則不屬於此類型。
# Use Iterable for generic iterables (anything usable in "for"),
# and Sequence where a sequence (supporting "len" and "__getitem__") is
# required
根據Python Iterable vs Sequence:
Iterable代表的是支持__iter__或__getitem__的類型,如range和reversed。
r = range(4)
r.__getitem__(0) # 0
r.__iter__() # <range_iterator object at 0x0000015AE7945D30>
l = [1, 2, 3]
rv = reversed(l)
rv.__iter__() # <list_reverseiterator object at 0x0000015AE7980E20>
rv.__getitem__() # 不支援__getitem__方法,但因為支持__iter__所以依然可以歸類為Iterable
# Traceback (most recent call last):
# File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
# AttributeError: 'list_reverseiterator' object has no attribute '__getitem__'
因為Sequence也具有__iter__和__getitem__,所以根據定義,所有的Sequence都是Iterable。
l = []
l.__iter__ # <method-wrapper '__iter__' of list object at 0x7f15bb50b5c0>
l.__getitem__ # <built-in method __getitem__ of list object at 0x7f15bb50b5c0>
Callable
typing - Callable
Callable
Frameworks expecting callback functions of specific signatures might be type hinted using Callable[[Arg1Type, Arg2Type], ReturnType].
文檔寫得很淺顯易懂,不過有一點要注意的是入參型別要用[]括起來。
Type hints cheat sheet - Functions中給出了例子:
# This is how you annotate a callable (function) value
x: Callable[[int, float], float] = f
如果先不看類型提示的代碼,這句其實就是x = f,把x這個變數設定為f這個函數。當中的Callable[[int, float], float]說明了f是一個接受int, float,輸出float的函數。
Union
typing - Union
typing.Union
Union type; Union[X, Y] is equivalent to X | Y and means either X or Y.To define a union, use e.g. Union[int, str] or the shorthand int | str. Using that shorthand is recommended.
Union[X, Y]表示型別可以是X或Y,從Python 3.10以後,可以使用X | Y這種更簡潔的寫法。
Type hints cheat sheet - Useful built-in types中給出的例子:
# On Python 3.10+, use the | operator when something could be one of a few types
x: list[int | str] = [3, 5, "test", "fun"] # Python 3.10+
# On earlier versions, use Union
x: list[Union[int, str]] = [3, 5, "test", "fun"]
Optional
typing - Optional
Optional type.Optional[X] is equivalent to X | None (or Union[X, None]).
Optional[X]表示該變數可以是X型別或是None型別。
Type hints cheat sheet - Useful built-in types中給出了一個很好的例子:
# Use Optional[X] for a value that could be None
# Optional[X] is the same as X | None or Union[X, None]
x: Optional[str] = "something" if some_condition() else None
這裡x根據some_condition()的回傳值有可能是一個字串或是None,所以此處選用Optional[str]的類型提示。
Functions
mypy - Functions
指定參數和回傳值型別:
from typing import Callable, Iterator, Union, Optional# This is how you annotate a function definition
def stringify(num: int) -> str:return str(num)
多個參數:
# And here's how you specify multiple arguments
def plus(num1: int, num2: int) -> int:return num1 + num2
無回傳值的函數以None為回傳型別,並且參數的預設值應寫在參數型別後面:
# If a function does not return a value, use None as the return type
# Default value for an argument goes after the type annotation
def show(value: str, excitement: int = 10) -> None:print(value + "!" * excitement)
可以接受任意型別參數的函數則不必指定參數型別:
# Note that arguments without a type are dynamically typed (treated as Any)
# and that functions without any annotations not checked
def untyped(x):x.anything() + 1 + "string" # no errors
Callable
將Callable當作參數的函數:
# This is how you annotate a callable (function) value
x: Callable[[int, float], float] = f
def register(callback: Callable[[str], int]) -> None: ...
Iterator/generator
generator函數相當於一個Iterator:
# A generator function that yields ints is secretly just a function that
# returns an iterator of ints, so that's how we annotate it
def gen(n: int) -> Iterator[int]:i = 0while i < n:yield ii += 1
將function annotation分成多行:
# You can of course split a function annotation over multiple lines
def send_email(address: Union[str, list[str]],sender: str,cc: Optional[list[str]],bcc: Optional[list[str]],subject: str = '',body: Optional[list[str]] = None) -> bool:...
位置參數 & 關鍵字參數
# Mypy understands positional-only and keyword-only arguments
# Positional-only arguments can also be marked by using a name starting with
# two underscores
def quux(x: int, /, *, y: int) -> None:passquux(3, y=5) # Ok
quux(3, 5) # error: Too many positional arguments for "quux"
quux(x=3, y=5) # error: Unexpected keyword argument "x" for "quux"
注意到此處參數列表中有/和*兩個符號,參考What Are Python Asterisk and Slash Special Parameters For?:
| Left side | Divider | Right side |
|---|---|---|
| Positional-only arguments | / | Positional or keyword arguments |
| Positional or keyword arguments | * | Keyword-only arguments |
Python的參數分為三種:位置參數,關鍵字參數及可變參數(可以透過位置或關鍵字的方式傳遞)。
/符號的左邊必須是位置參數,*符號的右邊則必須是關鍵字參數。
所以上例中x必須以位置參數的方式傳遞,y必須以關鍵字參數的方式傳遞。
一次指定多個參數的型別:
# This says each positional arg and each keyword arg is a "str"
def call(self, *args: str, **kwargs: str) -> str:reveal_type(args) # Revealed type is "tuple[str, ...]"reveal_type(kwargs) # Revealed type is "dict[str, str]"request = make_request(*args, **kwargs)return self.do_api_query(request)
Classes
mypy - Classes
self
class BankAccount:# The "__init__" method doesn't return anything, so it gets return# type "None" just like any other method that doesn't return anythingdef __init__(self, account_name: str, initial_balance: int = 0) -> None:# mypy will infer the correct types for these instance variables# based on the types of the parameters.self.account_name = account_nameself.balance = initial_balance# For instance methods, omit type for "self"def deposit(self, amount: int) -> None:self.balance += amountdef withdraw(self, amount: int) -> None:self.balance -= amount
成員函數self參數的型別不需指定。
自定義類別
可以將變數型別指定為自定義的類別:
# User-defined classes are valid as types in annotations
account: BankAccount = BankAccount("Alice", 400)
def transfer(src: BankAccount, dst: BankAccount, amount: int) -> None:src.withdraw(amount)dst.deposit(amount)
# Functions that accept BankAccount also accept any subclass of BankAccount!
class AuditedBankAccount(BankAccount):# You can optionally declare instance variables in the class bodyaudit_log: list[str]def __init__(self, account_name: str, initial_balance: int = 0) -> None:super().__init__(account_name, initial_balance)self.audit_log: list[str] = []def deposit(self, amount: int) -> None:self.audit_log.append(f"Deposited {amount}")self.balance += amountdef withdraw(self, amount: int) -> None:self.audit_log.append(f"Withdrew {amount}")self.balance -= amountaudited = AuditedBankAccount("Bob", 300)
transfer(audited, account, 100) # type checks!
transfer函數的第一個參數型別應為BankAccount,而AuditedBankAccount是BankAccount的子類別,所以在做類型檢查時不會出錯。
ClassVar
Python中類別的變數有類別變數別實例變數兩種。如果想要將成員變數標記為類別變數,可以用ClassVar[type]。
# You can use the ClassVar annotation to declare a class variable
class Car:seats: ClassVar[int] = 4passengers: ClassVar[list[str]]
__setattr__ 與 __getattr__
# If you want dynamic attributes on your class, have it
# override "__setattr__" or "__getattr__"
class A:# This will allow assignment to any A.x, if x is the same type as "value"# (use "value: Any" to allow arbitrary types)def __setattr__(self, name: str, value: int) -> None: ...# This will allow access to any A.x, if x is compatible with the return typedef __getattr__(self, name: str) -> int: ...a.foo = 42 # Works
a.bar = 'Ex-parrot' # Fails type checking
__setattr__函數可以為類別新增實體變數。
torch.types
PyTorch中自定義的類型。
torch/types.py
import torch
from typing import Any, List, Sequence, Tuple, Unionimport builtins# Convenience aliases for common composite types that we need
# to talk about in PyTorch_TensorOrTensors = Union[torch.Tensor, Sequence[torch.Tensor]]# In some cases, these basic types are shadowed by corresponding
# top-level values. The underscore variants let us refer to these
# types. See https://github.com/python/mypy/issues/4146 for why these
# workarounds is necessary
_int = builtins.int
_float = builtins.float
_bool = builtins.bool_dtype = torch.dtype
_device = torch.device
_qscheme = torch.qscheme
_size = Union[torch.Size, List[_int], Tuple[_int, ...]]
_layout = torch.layout
_dispatchkey = Union[str, torch._C.DispatchKey]class SymInt:pass# Meta-type for "numeric" things; matches our docs
Number = Union[builtins.int, builtins.float, builtins.bool]# Meta-type for "device-like" things. Not to be confused with 'device' (a
# literal device object). This nomenclature is consistent with PythonArgParser.
# None means use the default device (typically CPU)
Device = Union[_device, str, _int, None]# Storage protocol implemented by ${Type}StorageBase classesclass Storage(object):_cdata: intdevice: torch.devicedtype: torch.dtype_torch_load_uninitialized: booldef __deepcopy__(self, memo) -> 'Storage':...def _new_shared(self, int) -> 'Storage':...def _write_file(self, f: Any, is_real_file: _bool, save_size: _bool, element_size: int) -> None:...def element_size(self) -> int:...def is_shared(self) -> bool:...def share_memory_(self) -> 'Storage':...def nbytes(self) -> int:...def cpu(self) -> 'Storage':...def data_ptr(self) -> int:...def from_file(self, filename: str, shared: bool = False, nbytes: int = 0) -> 'Storage':...def _new_with_file(self, f: Any, element_size: int) -> 'Storage':......
torch.types中的_int, _float, _bool就是Python內建的builtins.int, builtins.float, builtins.bool。
PyTorch中定義的Number則是_int, _float, _bool中的其中一個。
builtins
builtins — Built-in objects
This module provides direct access to all ‘built-in’ identifiers of Python; for example, builtins.open is the full name for the built-in function open().
可以透過builtins這個模組存取Python內建的identifier,例如Python中的open()函數可以使用builtins.open來存取。
參數前的*
參考What does the Star operator mean in Python?
Single asterisk as used in function declaration allows variable number of arguments passed from calling environment. Inside the function it behaves as a tuple.
在函數參數前加上*表示可以接受任意個參數,在函數內部,該參數會被當成一個tuple。
def function(*arg):print (type(arg))for i in arg:print (i)
function(1,2,3)
# <class 'tuple'>
# 1
# 2
# 3
相关文章:

Python typing函式庫和torch.types
Python typing函式庫和torch.types 前言typingSequence vs IterableCallableUnionOptionalFunctionsCallableIterator/generator位置參數 & 關鍵字參數 Classesself自定義類別ClassVar\_\_setattr\_\_ 與 \__getattr\_\_ torch.typesbuiltins 參數前的* …...

UE5 编程规范
官方文档 使用现代C编程标准, 使用前沿C标准库版本. 1. 类中按照先 Public 后 Private 去写 2. 继承自 UObject 的类都以 U 前缀 3. 继承自 AActor 的类都以 A 前缀 4. 继承自 SWidget 的类都以 S 前缀 5. 模板以 T 前缀 6. 接口以 I 前缀 7. 枚举以 E 前缀 8. 布尔值…...
交互消息式IMessage扩展开发记录
IMessage扩展简介 iOS10新加入的基于iMessage的应用扩展,可以丰富发送消息的内容。(分享表情、图片、文字、视频、动态消息;一起完成任务或游戏。) 简单的将发送的数据内型分为三种: 1.贴纸Stickers; 2.交…...

软件团队降本增效-建立需求评估体系
需求对于软件开发来说是非常重要的输入,它们直接决定了软件的产品形态、代码数量和质量。如果需求不清晰、不完善,或者存在逻辑冲突,将会导致软件质量迅速下降,增加代码耦合性和开发成本。 在开发过程中,对需求的产品…...

npm yarn pnpm 命令集
npm 安装依赖 npm install 安装某个依赖 npm install xxx7.6.3 安装到全局(dependencies) npm install xxx7.6.3 -S 安装到线下(devDependencies) npm install xxx7.6.3 -D 卸载某个依赖 npm uninstall xxx 卸载全局依…...
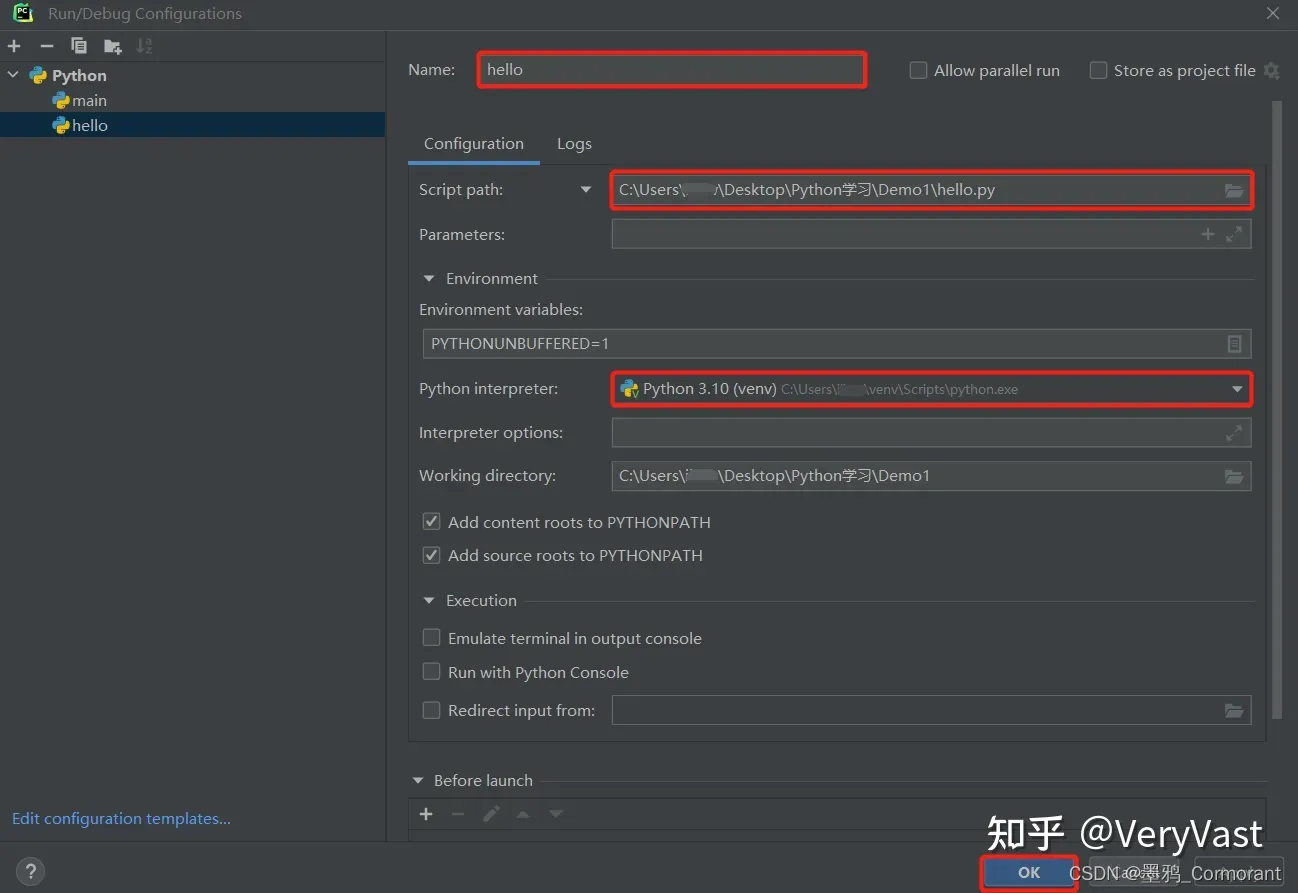
python 开发环境(PyCharm)搭建指南
Python 的下载并安装 参考:Python基础教程——搭建Python编程环境 下载 Python Python 下载地址:官网 (1)点击【Downloads】>>>点击【Windows】>>>点击【Python 3.x.x】下载最新版 Python; Pyt…...
springboot里 运用 easyexcel 导出
引入pom <dependency><groupId>com.alibaba</groupId><artifactId>easyexcel</artifactId><version>2.2.6</version> </dependency>运用 import com.alibaba.excel.EasyExcel; import org.springframework.stereotype.Contr…...

一“码”当先,PR大征集!2023 和RT-Thread一起赋能开源!
活动地址:https://club.rt-thread.org/ask/article/3c7cf7345ca47a18.html 活动介绍 「一“码”当先,PR大征集!」是一项为了鼓励开发者积极参与开源软件开发维护的活动。 你可在Github RT-Thread( https://github.com/RT-Thread …...
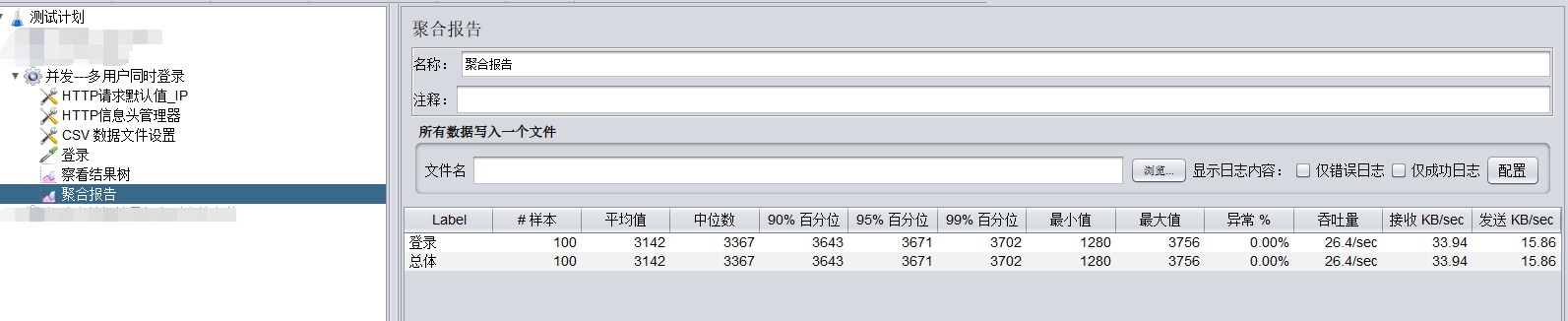
jmeter模拟多用户并发
一、100个真实的用户 1、一个账号模拟100虚拟用户同时登录和100账号同时登录 区别 (1)1个账号100个人用,同时登录; (2)100个人100个账号,同时登录。 相同 (1)两个都…...

澎峰科技|邀您关注2023 RISC-V中国峰会!
峰会概览 2023 RISC-V中国峰会(RISC-V Summit China 2023)将于8月23日至25日在北京香格里拉饭店举行。本届峰会将以“RISC-V生态共建”为主题,结合当下全球新形势,把握全球新时机,呈现RISC-V全球新观点、新趋势。 本…...
【系统架构】系统架构设计之数据同步策略
文章目录 一、介绍1.1、分布式系统中的数据同步定义1.2、为何数据同步如此关键1.3、数据同步策略简介 二、为什么需要数据同步2.1、提高系统可用性2.2、备份与灾难恢复2.3、提高性能2.4、考虑地理位置(如使用CDN) 三、同步备份3.1、定义和概述3.2、工作原…...

Linux内核学习笔记——ACPI命名空间
所有定义块都加载到单个命名空间中。命名空间 是由名称和路径标识的对象层次结构。 以下命名约定适用于 ACPI 中的对象名称 命名空间: 所有名称的长度均为 32 位。 名称的第一个字节必须是“A”-“Z”、“_”之一。 名称的每个剩余字节必须是“A”-“Z”、“0”之…...

使用 OpenCV Python 实现自动图像注释工具的详细步骤--附完整源码
注释是深度学习项目中最关键的部分。它是模型学习效果的决定因素。然而,这是非常乏味且耗时的。一种解决方案是使用自动图像注释工具,这大大缩短了时间。 本文是pyOpenAnnotate系列的一部分,其中包括以下内容。 1、使用 OpenCV 进行图像注释的路线图。 2、pyOpenAnnotate工…...
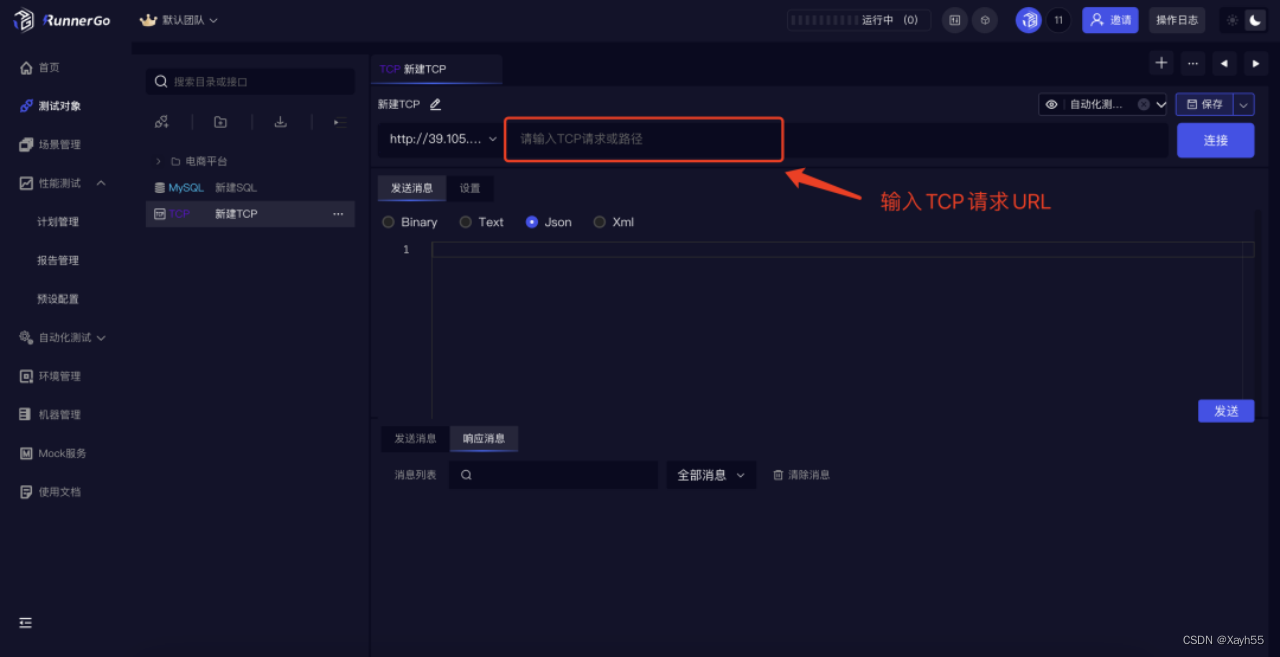
RunnerGo中WebSocket、Dubbo、TCP/IP三种协议接口测试详解
大家好,RunnerGo作为一款一站式测试平台不断为用户提供更好的使用体验,最近得知RunnerGo新增对,WebSocket、Dubbo、TCP/IP,三种协议API的测试支持,本篇文章跟大家分享一下使用方法。 WebSocket协议 WebSocket 是一种…...
【Java 动态数据统计图】动态数据统计思路案例(动态,排序,数组)一(112)
需求:: 有一个List<Map<String.Object>>,存储了某年某月的数据, 数据是根据用户查询条件进行显示的;所以查询的数据是动态的;需按月份统计每个年月数据出现的次数,并且按照月份排序࿱…...

kafka踩坑
问题:项目中用到kafka作为消息中间件,因为现在是开发阶段,试了一次没问题之后就没在管,今天又要测试kafka相关功能,发现消息发送者能够正常发送消息,但是消费者怎么也就收不到数据。然后经过各种百度进行了…...

让你专注于工作的电脑桌面日程提醒软件
在现代职场中,上班族们常常在繁忙的工作中会遇到各种各样的事情干扰。比如,当我们专注于完成重要的报告时,却又有同事来询问问题;在准备去会议事项时,手机却突然收到了一系列的短信和通知。这些干扰不仅浪费了我们的时…...

62页智慧产业园区数字化综合解决方案PPT
导读:原文《62页智慧产业园区数字化综合解决方案PPT》(获取来源见文尾),本文精选其中精华及架构部分,逻辑清晰、内容完整,为快速形成售前方案提供参考。 喜欢文章,您可以关注评论转发本文&#…...

苹果开发者账号注册方法简明指南
注册苹果开发者账号的方法 在2020年以前,注册苹果开发者账号后,就可以生成证书。 但2020年后,因为注册苹果开发者账号需要使用Apple Developer app注册开发者账号,所以需要缴费才能创建ios证书了。 所以新政策出来后,…...
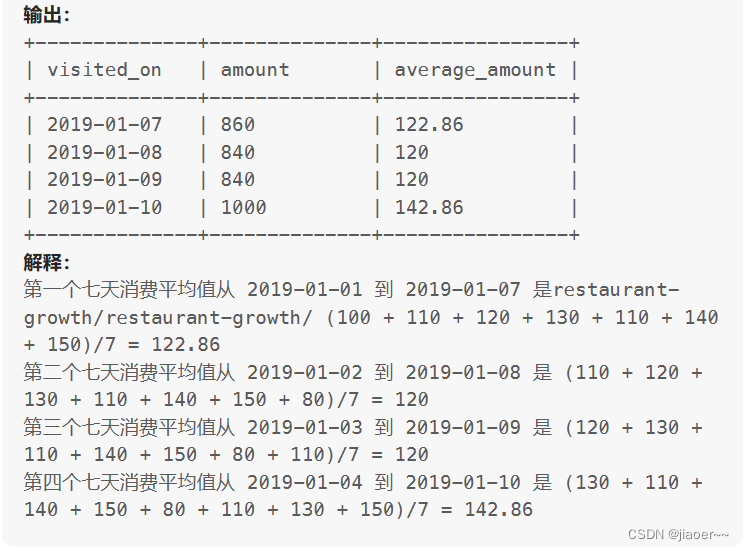
SQL-每日一题【1321. 餐馆营业额变化增长】
题目 表: Customer 你是餐馆的老板,现在你想分析一下可能的营业额变化增长(每天至少有一位顾客)。 计算以 7 天(某日期 该日期前的 6 天)为一个时间段的顾客消费平均值。average_amount 要 保留两位小数。 结果按 …...

在鸿蒙HarmonyOS 5中实现抖音风格的点赞功能
下面我将详细介绍如何使用HarmonyOS SDK在HarmonyOS 5中实现类似抖音的点赞功能,包括动画效果、数据同步和交互优化。 1. 基础点赞功能实现 1.1 创建数据模型 // VideoModel.ets export class VideoModel {id: string "";title: string ""…...
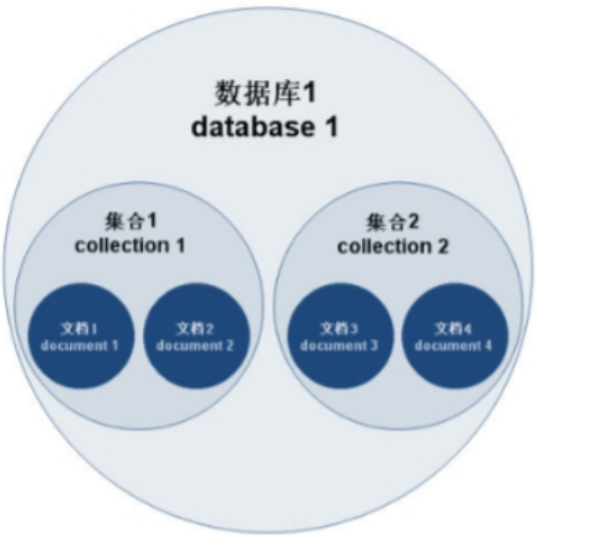
MongoDB学习和应用(高效的非关系型数据库)
一丶 MongoDB简介 对于社交类软件的功能,我们需要对它的功能特点进行分析: 数据量会随着用户数增大而增大读多写少价值较低非好友看不到其动态信息地理位置的查询… 针对以上特点进行分析各大存储工具: mysql:关系型数据库&am…...
使用分级同态加密防御梯度泄漏
抽象 联邦学习 (FL) 支持跨分布式客户端进行协作模型训练,而无需共享原始数据,这使其成为在互联和自动驾驶汽车 (CAV) 等领域保护隐私的机器学习的一种很有前途的方法。然而,最近的研究表明&…...

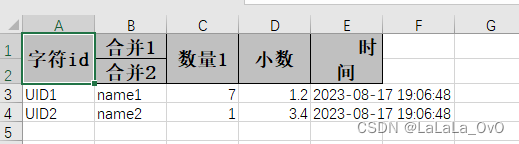
前端导出带有合并单元格的列表
// 导出async function exportExcel(fileName "共识调整.xlsx") {// 所有数据const exportData await getAllMainData();// 表头内容let fitstTitleList [];const secondTitleList [];allColumns.value.forEach(column > {if (!column.children) {fitstTitleL…...

pam_env.so模块配置解析
在PAM(Pluggable Authentication Modules)配置中, /etc/pam.d/su 文件相关配置含义如下: 配置解析 auth required pam_env.so1. 字段分解 字段值说明模块类型auth认证类模块,负责验证用户身份&am…...

Opencv中的addweighted函数
一.addweighted函数作用 addweighted()是OpenCV库中用于图像处理的函数,主要功能是将两个输入图像(尺寸和类型相同)按照指定的权重进行加权叠加(图像融合),并添加一个标量值&#x…...

Auto-Coder使用GPT-4o完成:在用TabPFN这个模型构建一个预测未来3天涨跌的分类任务
通过akshare库,获取股票数据,并生成TabPFN这个模型 可以识别、处理的格式,写一个完整的预处理示例,并构建一个预测未来 3 天股价涨跌的分类任务 用TabPFN这个模型构建一个预测未来 3 天股价涨跌的分类任务,进行预测并输…...
)
相机Camera日志分析之三十一:高通Camx HAL十种流程基础分析关键字汇总(后续持续更新中)
【关注我,后续持续新增专题博文,谢谢!!!】 上一篇我们讲了:有对最普通的场景进行各个日志注释讲解,但相机场景太多,日志差异也巨大。后面将展示各种场景下的日志。 通过notepad++打开场景下的日志,通过下列分类关键字搜索,即可清晰的分析不同场景的相机运行流程差异…...

全面解析各类VPN技术:GRE、IPsec、L2TP、SSL与MPLS VPN对比
目录 引言 VPN技术概述 GRE VPN 3.1 GRE封装结构 3.2 GRE的应用场景 GRE over IPsec 4.1 GRE over IPsec封装结构 4.2 为什么使用GRE over IPsec? IPsec VPN 5.1 IPsec传输模式(Transport Mode) 5.2 IPsec隧道模式(Tunne…...
)
Android第十三次面试总结(四大 组件基础)
Activity生命周期和四大启动模式详解 一、Activity 生命周期 Activity 的生命周期由一系列回调方法组成,用于管理其创建、可见性、焦点和销毁过程。以下是核心方法及其调用时机: onCreate() 调用时机:Activity 首次创建时调用。…...
