spring高级源码50讲-43-50(spring续)
其它
43) FactoryBean
演示 - FactoryBean
代码参考
package com.itheima.a43;import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;@ComponentScan
public class A43 {public static void main(String[] args) {AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(A43.class);Bean1 bean1 = (Bean1) context.getBean("bean1");Bean1 bean2 = (Bean1) context.getBean("bean1");Bean1 bean3 = (Bean1) context.getBean("bean1");System.out.println(bean1);System.out.println(bean2);System.out.println(bean3);System.out.println(context.getBean(Bean1.class));System.out.println(context.getBean(Bean1FactoryBean.class));System.out.println(context.getBean("&bean1"));context.close();/*学到了什么: 一个在 Spring 发展阶段中重要, 但目前已经很鸡肋的接口 FactoryBean 的使用要点说它鸡肋有两点:1. 它的作用是用制造创建过程较为复杂的产品, 如 SqlSessionFactory, 但 @Bean 已具备等价功能2. 使用上较为古怪, 一不留神就会用错a. 被 FactoryBean 创建的产品- 会认为创建、依赖注入、Aware 接口回调、前初始化这些都是 FactoryBean 的职责, 这些流程都不会走- 唯有后初始化的流程会走, 也就是产品可以被代理增强- 单例的产品不会存储于 BeanFactory 的 singletonObjects 成员中, 而是另一个 factoryBeanObjectCache 成员中b. 按名字去获取时, 拿到的是产品对象, 名字前面加 & 获取的是工厂对象就说恶心不?但目前此接口的实现仍被大量使用, 想被全面废弃很难*/}}package com.itheima.a43;import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;public class Bean1 implements BeanFactoryAware {private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Bean1.class);private Bean2 bean2;@Autowiredpublic void setBean2(Bean2 bean2) {log.debug("setBean2({})", bean2);this.bean2 = bean2;}public Bean2 getBean2() {return bean2;}@PostConstructpublic void init() {log.debug("init");}@Overridepublic void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {log.debug("setBeanFactory({})", beanFactory);}
}package com.itheima.a43;import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component("bean1")
public class Bean1FactoryBean implements FactoryBean<Bean1> {private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Bean1FactoryBean.class);// 决定了根据【类型】获取或依赖注入能否成功@Overridepublic Class<?> getObjectType() {return Bean1.class;}// 决定了 getObject() 方法被调用一次还是多次@Overridepublic boolean isSingleton() {return true;}@Overridepublic Bean1 getObject() throws Exception {Bean1 bean1 = new Bean1();log.debug("create bean: {}", bean1);return bean1;}
}收获💡
- 它的作用是用制造创建过程较为复杂的产品, 如 SqlSessionFactory, 但 @Bean 已具备等价功能
- 使用上较为古怪, 一不留神就会用错
- 被 FactoryBean 创建的产品
- 会认为创建、依赖注入、Aware 接口回调、前初始化这些都是 FactoryBean 的职责, 这些流程都不会走
- 唯有后初始化的流程会走, 也就是产品可以被代理增强
- 单例的产品不会存储于 BeanFactory 的 singletonObjects 成员中, 而是另一个 factoryBeanObjectCache 成员中
- 按名字去获取时, 拿到的是产品对象, 名字前面加 & 获取的是工厂对象
- 被 FactoryBean 创建的产品
44) @Indexed 原理
真实项目中,只需要加入以下依赖即可
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-context-indexer</artifactId><optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
演示 - @Indexed
代码参考
package com.itheima.a44;import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner;import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;/*做这个试验前, 先在 target/classes 创建 META-INF/spring.components, 内容为com.itheima.a44.Bean1=org.springframework.stereotype.Componentcom.itheima.a44.Bean2=org.springframework.stereotype.Component做完实现建议删除, 避免影响其它组件扫描的结果真实项目中, 这个步骤可以自动完成, 加入以下依赖<dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-context-indexer</artifactId><optional>true</optional></dependency>*/
public class A44 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();// 组件扫描的核心类ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(beanFactory);scanner.scan(A44.class.getPackageName());for (String name : beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {System.out.println(name);}/*学到了什么a. @Indexed 的原理, 在编译时就根据 @Indexed 生成 META-INF/spring.components 文件扫描时1. 如果发现 META-INF/spring.components 存在, 以它为准加载 bean definition2. 否则, 会遍历包下所有 class 资源 (包括 jar 内的)*/}
}收获💡
- 在编译时就根据 @Indexed 生成 META-INF/spring.components 文件
- 扫描时
- 如果发现 META-INF/spring.components 存在, 以它为准加载 bean definition
- 否则, 会遍历包下所有 class 资源 (包括 jar 内的)
- 解决的问题,在编译期就找到 @Component 组件,节省运行期间扫描 @Component 的时间
45) 代理进一步理解
演示 - 代理
代码参考
package com.itheima.a45;import org.springframework.aop.framework.Advised;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;import java.lang.reflect.Method;@SpringBootApplication
public class A45 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(A45.class, args);Bean1 proxy = context.getBean(Bean1.class);/*1.演示 spring 代理的设计特点依赖注入和初始化影响的是原始对象代理与目标是两个对象,二者成员变量并不共用数据*/
// showProxyAndTarget(proxy);
//
// System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");
// System.out.println(proxy.getBean2());
// System.out.println(proxy.isInitialized());/*2.演示 static 方法、final 方法、private 方法均无法增强*/proxy.m1();proxy.m2();proxy.m3();Method m4 = Bean1.class.getDeclaredMethod("m1");m4.setAccessible(true);m4.invoke(proxy);context.close();}public static void showProxyAndTarget(Bean1 proxy) throws Exception {System.out.println(">>>>> 代理中的成员变量");System.out.println("\tinitialized=" + proxy.initialized);System.out.println("\tbean2=" + proxy.bean2);if (proxy instanceof Advised advised) {System.out.println(">>>>> 目标中的成员变量");Bean1 target = (Bean1) advised.getTargetSource().getTarget();System.out.println("\tinitialized=" + target.initialized);System.out.println("\tbean2=" + target.bean2);}}}收获💡
-
spring 代理的设计特点
-
依赖注入和初始化影响的是原始对象
- 因此 cglib 不能用 MethodProxy.invokeSuper()
-
代理与目标是两个对象,二者成员变量并不共用数据
-
-
static 方法、final 方法、private 方法均无法增强
- 进一步理解代理增强基于方法重写
46) @Value 装配底层
按类型装配的步骤
- 查看需要的类型是否为 Optional,是,则进行封装(非延迟),否则向下走
- 查看需要的类型是否为 ObjectFactory 或 ObjectProvider,是,则进行封装(延迟),否则向下走
- 查看需要的类型(成员或参数)上是否用 @Lazy 修饰,是,则返回代理,否则向下走
- 解析 @Value 的值
- 如果需要的值是字符串,先解析 ${ },再解析 #{ }
- 不是字符串,需要用 TypeConverter 转换
- 看需要的类型是否为 Stream、Array、Collection、Map,是,则按集合处理,否则向下走
- 在 BeanFactory 的 resolvableDependencies 中找有没有类型合适的对象注入,没有向下走
- 在 BeanFactory 及父工厂中找类型匹配的 bean 进行筛选,筛选时会考虑 @Qualifier 及泛型
- 结果个数为 0 抛出 NoSuchBeanDefinitionException 异常
- 如果结果 > 1,再根据 @Primary 进行筛选
- 如果结果仍 > 1,再根据成员名或变量名进行筛选
- 结果仍 > 1,抛出 NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException 异常
演示 - @Value 装配过程
代码参考
package com.itheima.a46;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanExpressionContext;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.DependencyDescriptor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import java.lang.reflect.Field;// 本章节作为第四讲的延续
@Configuration
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class A46 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(A46.class);DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getDefaultListableBeanFactory();ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver resolver = new ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver();resolver.setBeanFactory(beanFactory);// test1(context, resolver, Bean1.class.getDeclaredField("home"));
// test2(context, resolver, Bean1.class.getDeclaredField("age"));
// test3(context, resolver, Bean2.class.getDeclaredField("bean3"));test3(context, resolver, Bean4.class.getDeclaredField("value"));}private static void test3(AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context, ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver resolver, Field field) {DependencyDescriptor dd1 = new DependencyDescriptor(field, false);// 获取 @Value 的内容String value = resolver.getSuggestedValue(dd1).toString();System.out.println(value);// 解析 ${}value = context.getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(value);System.out.println(value);System.out.println(value.getClass());// 解析 #{} @bean3Object bean3 = context.getBeanFactory().getBeanExpressionResolver().evaluate(value, new BeanExpressionContext(context.getBeanFactory(), null));// 类型转换Object result = context.getBeanFactory().getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean3, dd1.getDependencyType());System.out.println(result);}private static void test2(AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context, ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver resolver, Field field) {DependencyDescriptor dd1 = new DependencyDescriptor(field, false);// 获取 @Value 的内容String value = resolver.getSuggestedValue(dd1).toString();System.out.println(value);// 解析 ${}value = context.getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(value);System.out.println(value);System.out.println(value.getClass());Object age = context.getBeanFactory().getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(value, dd1.getDependencyType());System.out.println(age.getClass());}private static void test1(AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context, ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver resolver, Field field) {DependencyDescriptor dd1 = new DependencyDescriptor(field, false);// 获取 @Value 的内容String value = resolver.getSuggestedValue(dd1).toString();System.out.println(value);// 解析 ${}value = context.getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(value);System.out.println(value);}public class Bean1 {@Value("${JAVA_HOME}")private String home;@Value("18")private int age;}public class Bean2 {@Value("#{@bean3}") // SpringEL #{SpEL}private Bean3 bean3;}@Component("bean3")public class Bean3 {}static class Bean4 {@Value("#{'hello, ' + '${JAVA_HOME}'}")private String value;}
}收获💡
- ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver 作用之一,获取 @Value 的值
- 了解 ${ } 对应的解析器
- 了解 #{ } 对应的解析器
- TypeConvert 的一项体现
47) @Autowired 装配底层
演示 - @Autowired 装配过程
代码参考
package com.itheima.a47;import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.ObjectFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.DependencyDescriptor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Lazy;
import org.springframework.core.MethodParameter;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Optional;@Configuration
public class A47_1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, NoSuchMethodException {AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(A47_1.class);DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getDefaultListableBeanFactory();System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");// 1. 根据成员变量的类型注入DependencyDescriptor dd1 = new DependencyDescriptor(Bean1.class.getDeclaredField("bean2"), false);System.out.println(beanFactory.doResolveDependency(dd1, "bean1", null, null));System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");// 2. 根据参数的类型注入Method setBean2 = Bean1.class.getDeclaredMethod("setBean2", Bean2.class);DependencyDescriptor dd2 = new DependencyDescriptor(new MethodParameter(setBean2, 0), false);System.out.println(beanFactory.doResolveDependency(dd2, "bean1", null, null));System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");// 3. 结果包装为 Optional<Bean2>DependencyDescriptor dd3 = new DependencyDescriptor(Bean1.class.getDeclaredField("bean3"), false);if (dd3.getDependencyType() == Optional.class) {dd3.increaseNestingLevel();Object result = beanFactory.doResolveDependency(dd3, "bean1", null, null);System.out.println(Optional.ofNullable(result));}System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");// 4. 结果包装为 ObjectProvider,ObjectFactoryDependencyDescriptor dd4 = new DependencyDescriptor(Bean1.class.getDeclaredField("bean4"), false);if (dd4.getDependencyType() == ObjectFactory.class) {dd4.increaseNestingLevel();ObjectFactory objectFactory = new ObjectFactory() {@Overridepublic Object getObject() throws BeansException {return beanFactory.doResolveDependency(dd4, "bean1", null, null);}};System.out.println(objectFactory.getObject());}System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");// 5. 对 @Lazy 的处理DependencyDescriptor dd5 = new DependencyDescriptor(Bean1.class.getDeclaredField("bean2"), false);ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver resolver = new ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver();resolver.setBeanFactory(beanFactory);Object proxy = resolver.getLazyResolutionProxyIfNecessary(dd5, "bean1");System.out.println(proxy);System.out.println(proxy.getClass());/*学到了什么1. Optional 及 ObjectFactory 对于内嵌类型的处理, 源码参考 ResolvableType2. ObjectFactory 懒惰的思想3. @Lazy 懒惰的思想下一节, 继续学习 doResolveDependency 内部处理*/}static class Bean1 {@Autowired @Lazy private Bean2 bean2;@Autowired public void setBean2(Bean2 bean2) {this.bean2 = bean2;}@Autowired private Optional<Bean2> bean3;@Autowired private ObjectFactory<Bean2> bean4;}@Component("bean2")static class Bean2 {/*@Overridepublic String toString() {return super.toString();}*/}
}package com.itheima.a47;import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinitionHolder;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.DependencyDescriptor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;@SuppressWarnings("all")
@Configuration
public class A47_2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(A47_2.class);DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getDefaultListableBeanFactory();System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 1. 数组类型");testArray(beanFactory);System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 2. List 类型");testList(beanFactory);System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 3. applicationContext");testApplicationContext(beanFactory);System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 4. 泛型");testGeneric(beanFactory);System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 5. @Qualifier");testQualifier(beanFactory);/*学到了什么1. 如何获取数组元素类型2. Spring 如何获取泛型中的类型3. 特殊对象的处理, 如 ApplicationContext, 并注意 Map 取值时的类型匹配问题 (另见 TestMap)4. 谁来进行泛型匹配 (另见 TestGeneric)5. 谁来处理 @Qualifier6. 刚开始都只是按名字处理, 等候选者确定了, 才会创建实例*/}private static void testQualifier(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws NoSuchFieldException {DependencyDescriptor dd5 = new DependencyDescriptor(Target.class.getDeclaredField("service"), true);Class<?> type = dd5.getDependencyType();ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver resolver = new ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver();resolver.setBeanFactory(beanFactory);for (String name : BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(beanFactory, type)) {BeanDefinition bd = beanFactory.getMergedBeanDefinition(name);// @Qualifier("service2")if (resolver.isAutowireCandidate(new BeanDefinitionHolder(bd,name), dd5)) {System.out.println(name);System.out.println(dd5.resolveCandidate(name, type, beanFactory));}}}private static void testGeneric(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws NoSuchFieldException {DependencyDescriptor dd4 = new DependencyDescriptor(Target.class.getDeclaredField("dao"), true);Class<?> type = dd4.getDependencyType();ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver resolver = new ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver();resolver.setBeanFactory(beanFactory);for (String name : BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(beanFactory, type)) {BeanDefinition bd = beanFactory.getMergedBeanDefinition(name);// 对比 BeanDefinition 与 DependencyDescriptor 的泛型是否匹配if (resolver.isAutowireCandidate(new BeanDefinitionHolder(bd,name), dd4)) {System.out.println(name);System.out.println(dd4.resolveCandidate(name, type, beanFactory));}}}private static void testApplicationContext(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {DependencyDescriptor dd3 = new DependencyDescriptor(Target.class.getDeclaredField("applicationContext"), true);Field resolvableDependencies = DefaultListableBeanFactory.class.getDeclaredField("resolvableDependencies");resolvableDependencies.setAccessible(true);Map<Class<?>, Object> dependencies = (Map<Class<?>, Object>) resolvableDependencies.get(beanFactory);
// dependencies.forEach((k, v) -> {
// System.out.println("key:" + k + " value: " + v);
// });for (Map.Entry<Class<?>, Object> entry : dependencies.entrySet()) {// 左边类型 右边类型if (entry.getKey().isAssignableFrom(dd3.getDependencyType())) {System.out.println(entry.getValue());break;}}}private static void testList(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws NoSuchFieldException {DependencyDescriptor dd2 = new DependencyDescriptor(Target.class.getDeclaredField("serviceList"), true);if (dd2.getDependencyType() == List.class) {Class<?> resolve = dd2.getResolvableType().getGeneric().resolve();System.out.println(resolve);List<Object> list = new ArrayList<>();String[] names = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(beanFactory, resolve);for (String name : names) {Object bean = dd2.resolveCandidate(name, resolve, beanFactory);list.add(bean);}System.out.println(list);}}private static void testArray(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws NoSuchFieldException {DependencyDescriptor dd1 = new DependencyDescriptor(Target.class.getDeclaredField("serviceArray"), true);if (dd1.getDependencyType().isArray()) {Class<?> componentType = dd1.getDependencyType().getComponentType();System.out.println(componentType);String[] names = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(beanFactory, componentType);List<Object> beans = new ArrayList<>();for (String name : names) {System.out.println(name);Object bean = dd1.resolveCandidate(name, componentType, beanFactory);beans.add(bean);}Object array = beanFactory.getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(beans, dd1.getDependencyType());System.out.println(array);}}static class Target {@Autowired private Service[] serviceArray;@Autowired private List<Service> serviceList;@Autowired private ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext;@Autowired private Dao<Teacher> dao;@Autowired @Qualifier("service2") private Service service;}interface Dao<T> {}@Component("dao1") static class Dao1 implements Dao<Student> {}@Component("dao2") static class Dao2 implements Dao<Teacher> {}static class Student {}static class Teacher {}interface Service {}@Component("service1")static class Service1 implements Service {}@Component("service2")static class Service2 implements Service {}@Component("service3")static class Service3 implements Service {}
}package com.itheima.a47;import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.DependencyDescriptor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionBuilder;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Configuration
public class A47_3 {public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException {AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(A47_3.class);DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getDefaultListableBeanFactory();testPrimary(beanFactory);testDefault(beanFactory);/*学到了什么1. @Primary 的处理, 其中 @Primary 会在 @Bean 解析或组件扫描时被解析 (另见 TestPrimary)2. 最后的防线, 通过属性或参数名匹配*/}private static void testDefault(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws NoSuchFieldException {DependencyDescriptor dd = new DependencyDescriptor(Target2.class.getDeclaredField("service3"), false);Class<?> type = dd.getDependencyType();for (String name : BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(beanFactory, type)) {if(name.equals(dd.getDependencyName())) {System.out.println(name);}}}private static void testPrimary(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws NoSuchFieldException {DependencyDescriptor dd = new DependencyDescriptor(Target1.class.getDeclaredField("service"), false);Class<?> type = dd.getDependencyType();for (String name : BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(beanFactory, type)) {if (beanFactory.getMergedBeanDefinition(name).isPrimary()) {System.out.println(name);}}}static class Target1 {@Autowired private Service service;}static class Target2 {@Autowired private Service service3;}interface Service {}@Component("service1") static class Service1 implements Service {}@Component("service2") static class Service2 implements Service {}@Component("service3") static class Service3 implements Service {}
}收获💡
- @Autowired 本质上是根据成员变量或方法参数的类型进行装配
- 如果待装配类型是 Optional,需要根据 Optional 泛型找到 bean,再封装为 Optional 对象装配
- 如果待装配的类型是 ObjectFactory,需要根据 ObjectFactory 泛型创建 ObjectFactory 对象装配
- 此方法可以延迟 bean 的获取
- 如果待装配的成员变量或方法参数上用 @Lazy 标注,会创建代理对象装配
- 此方法可以延迟真实 bean 的获取
- 被装配的代理不作为 bean
- 如果待装配类型是数组,需要获取数组元素类型,根据此类型找到多个 bean 进行装配
- 如果待装配类型是 Collection 或其子接口,需要获取 Collection 泛型,根据此类型找到多个 bean
- 如果待装配类型是 ApplicationContext 等特殊类型
- 会在 BeanFactory 的 resolvableDependencies 成员按类型查找装配
- resolvableDependencies 是 map 集合,key 是特殊类型,value 是其对应对象
- 不能直接根据 key 进行查找,而是用 isAssignableFrom 逐一尝试右边类型是否可以被赋值给左边的 key 类型
- 如果待装配类型有泛型参数
- 需要利用 ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver 按泛型参数类型筛选
- 如果待装配类型有 @Qualifier
- 需要利用 ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver 按注解提供的 bean 名称筛选
- 有 @Primary 标注的 @Component 或 @Bean 的处理
- 与成员变量名或方法参数名同名 bean 的处理
48) 事件监听器
演示 - 事件监听器
代码参考
package com.itheima.a48;import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisher;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.event.ApplicationEventMulticaster;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;// 事件解耦例子
@Configuration
public class A48_1 {public static void main(String[] args) {AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(A48_1.class);context.getBean(MyService.class).doBusiness();context.close();}static class MyEvent extends ApplicationEvent {public MyEvent(Object source) {super(source);}}@Componentstatic class MyService {private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyService.class);@Autowiredprivate ApplicationEventPublisher publisher; // applicationContextpublic void doBusiness() {log.debug("主线业务");// 主线业务完成后需要做一些支线业务,下面是问题代码publisher.publishEvent(new MyEvent("MyService.doBusiness()"));}}// @Componentstatic class SmsApplicationListener implements ApplicationListener<MyEvent> {private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SmsApplicationListener.class);@Overridepublic void onApplicationEvent(MyEvent event) {log.debug("发送短信");}}@Componentstatic class EmailApplicationListener implements ApplicationListener<MyEvent> {private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(EmailApplicationListener.class);@Overridepublic void onApplicationEvent(MyEvent event) {log.debug("发送邮件");}}}
package com.itheima.a48;import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisher;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.event.EventListener;
import org.springframework.context.event.SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;@Configuration
public class A48_2 {public static void main(String[] args) {AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(A48_2.class);context.getBean(MyService.class).doBusiness();context.close();}static class MyEvent extends ApplicationEvent {public MyEvent(Object source) {super(source);}}@Componentstatic class MyService {private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyService.class);@Autowiredprivate ApplicationEventPublisher publisher; // applicationContextpublic void doBusiness() {log.debug("主线业务");// 主线业务完成后需要做一些支线业务,下面是问题代码publisher.publishEvent(new MyEvent("MyService.doBusiness()"));}}@Componentstatic class SmsService {private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SmsService.class);@EventListenerpublic void listener(MyEvent myEvent) {log.debug("发送短信");}}@Componentstatic class EmailService {private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(EmailService.class);@EventListenerpublic void listener(MyEvent myEvent) {log.debug("发送邮件");}}@Beanpublic ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor() {ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();executor.setCorePoolSize(3);executor.setMaxPoolSize(10);executor.setQueueCapacity(100);return executor;}@Beanpublic SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster applicationEventMulticaster(ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor) {SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster multicaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster();multicaster.setTaskExecutor(executor);return multicaster;}}
package com.itheima.a48;import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.SmartInitializingSingleton;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisher;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;@Configuration
public class A48_3 {public static void main(String[] args) {AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(A48_3.class);context.getBean(MyService.class).doBusiness();context.close();}@Beanpublic SmartInitializingSingleton smartInitializingSingleton(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {return () -> {for (String name : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {Object bean = context.getBean(name);for (Method method : bean.getClass().getMethods()) {if (method.isAnnotationPresent(MyListener.class)) {context.addApplicationListener((event) -> {System.out.println(event);Class<?> eventType = method.getParameterTypes()[0];// 监听器方法需要的事件类型if (eventType.isAssignableFrom(event.getClass())) {try {method.invoke(bean, event);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}});}}}};}@Componentstatic class MyService {private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyService.class);@Autowiredprivate ApplicationEventPublisher publisher; // applicationContextpublic void doBusiness() {log.debug("主线业务");// 主线业务完成后需要做一些支线业务,下面是问题代码publisher.publishEvent(new MyEvent("MyService.doBusiness()"));}}@Componentstatic class SmsService {private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SmsService.class);@MyListenerpublic void listener(MyEvent myEvent) {log.debug("发送短信");}}@Componentstatic class EmailService {private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(EmailService.class);@MyListenerpublic void listener(MyEvent myEvent) {log.debug("发送邮件");}}@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Target(ElementType.METHOD)@interface MyListener {}static class MyEvent extends ApplicationEvent {public MyEvent(Object source) {super(source);}}
}
收获💡
事件监听器的两种方式
- 实现 ApplicationListener 接口
- 根据接口泛型确定事件类型
- @EventListener 标注监听方法
- 根据监听器方法参数确定事件类型
- 解析时机:在 SmartInitializingSingleton(所有单例初始化完成后),解析每个单例 bean
49) 事件发布器
演示 - 事件发布器
代码参考
package com.itheima.a49;import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisher;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.event.ApplicationEventMulticaster;
import org.springframework.context.event.GenericApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.core.ResolvableType;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.function.Predicate;@Configuration
public class A49 {public static void main(String[] args) {AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(A49.class);context.getBean(MyService.class).doBusiness();context.close();}static class MyEvent extends ApplicationEvent {public MyEvent(Object source) {super(source);}}@Componentstatic class MyService {private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyService.class);@Autowiredprivate ApplicationEventPublisher publisher; // applicationContextpublic void doBusiness() {log.debug("主线业务");// 主线业务完成后需要做一些支线业务,下面是问题代码publisher.publishEvent(new MyEvent("MyService.doBusiness()"));}}@Componentstatic class SmsApplicationListener implements ApplicationListener<MyEvent> {private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SmsApplicationListener.class);@Overridepublic void onApplicationEvent(MyEvent event) {log.debug("发送短信");}}@Componentstatic class EmailApplicationListener implements ApplicationListener<MyEvent> {private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(EmailApplicationListener.class);@Overridepublic void onApplicationEvent(MyEvent event) {log.debug("发送邮件");}}@Beanpublic ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor() {ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();executor.setCorePoolSize(3);executor.setMaxPoolSize(10);executor.setQueueCapacity(100);return executor;}@Beanpublic ApplicationEventMulticaster applicationEventMulticaster(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor) {return new AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster() {private List<GenericApplicationListener> listeners = new ArrayList<>();// 收集监听器public void addApplicationListenerBean(String name) {ApplicationListener listener = context.getBean(name, ApplicationListener.class);System.out.println(listener);// 获取该监听器支持的事件类型ResolvableType type = ResolvableType.forClass(listener.getClass()).getInterfaces()[0].getGeneric();System.out.println(type);// 将原始的 listener 封装为支持事件类型检查的 listenerGenericApplicationListener genericApplicationListener = new GenericApplicationListener() {// 是否支持某事件类型 真实的事件类型public boolean supportsEventType(ResolvableType eventType) {return type.isAssignableFrom(eventType);}public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {executor.submit(() -> listener.onApplicationEvent(event));}};listeners.add(genericApplicationListener);}// 发布事件public void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event, ResolvableType eventType) {for (GenericApplicationListener listener : listeners) {if (listener.supportsEventType(ResolvableType.forClass(event.getClass()))) {listener.onApplicationEvent(event);}}}};}abstract static class AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster implements ApplicationEventMulticaster {@Overridepublic void addApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener) {}@Overridepublic void addApplicationListenerBean(String listenerBeanName) {}@Overridepublic void removeApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener) {}@Overridepublic void removeApplicationListenerBean(String listenerBeanName) {}@Overridepublic void removeApplicationListeners(Predicate<ApplicationListener<?>> predicate) {}@Overridepublic void removeApplicationListenerBeans(Predicate<String> predicate) {}@Overridepublic void removeAllListeners() {}@Overridepublic void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {}@Overridepublic void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event, ResolvableType eventType) {}}
}
package com.itheima.a49;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.context.PayloadApplicationEvent;
import org.springframework.context.event.ApplicationEventMulticaster;
import org.springframework.context.event.GenericApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.ResolvableType;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.function.Predicate;// 演示事件发布器实现要点
public class TestEventPublisher {public static void main(String[] args) {GenericApplicationContext context = new GenericApplicationContext();context.registerBean("applicationEventMulticaster", MyApplicationEventMulticaster.class);context.refresh();context.publishEvent(new Object());context.publishEvent("aaaa");context.publishEvent(new Bean1());}interface Inter {}static class Bean1 implements Inter{}static class MyApplicationEventMulticaster implements ApplicationEventMulticaster {private List<ApplicationListener> listeners = new ArrayList<>();{listeners.add(new GenericApplicationListener() {@Overridepublic void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {if (event instanceof PayloadApplicationEvent payloadApplicationEvent) {System.out.println(payloadApplicationEvent.getPayload());}}@Overridepublic boolean supportsEventType(ResolvableType eventType) {System.out.println(eventType);// eventType --> PayloadApplicationEvent<Object>, PayloadApplicationEvent<String>return (Inter.class.isAssignableFrom(eventType.getGeneric().toClass()));}});}@Overridepublic void addApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener) {}@Overridepublic void addApplicationListenerBean(String listenerBeanName) {}@Overridepublic void removeApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener) {}@Overridepublic void removeApplicationListenerBean(String listenerBeanName) {}@Overridepublic void removeApplicationListeners(Predicate<ApplicationListener<?>> predicate) {}@Overridepublic void removeApplicationListenerBeans(Predicate<String> predicate) {}@Overridepublic void removeAllListeners() {}@Overridepublic void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {multicastEvent(event, null);}@SuppressWarnings("all")@Overridepublic void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event, ResolvableType eventType) {listeners.stream().filter(applicationListener -> {if (eventType == null) {return false;}if (applicationListener instanceof GenericApplicationListener genericApplicationListener) {return genericApplicationListener.supportsEventType(eventType);}return false;}).forEach(applicationListener -> {applicationListener.onApplicationEvent(event);});}}
}
收获💡
事件发布器模拟实现
- addApplicationListenerBean 负责收集容器中的监听器
- 监听器会统一转换为 GenericApplicationListener 对象,以支持判断事件类型
- multicastEvent 遍历监听器集合,发布事件
- 发布前先通过 GenericApplicationListener.supportsEventType 判断支持该事件类型才发事件
- 可以利用线程池进行异步发事件优化
- 如果发送的事件对象不是 ApplicationEvent 类型,Spring 会把它包装为 PayloadApplicationEvent 并用泛型技术解析事件对象的原始类型
- 视频中未讲解
相关文章:
)
spring高级源码50讲-43-50(spring续)
其它 43) FactoryBean 演示 - FactoryBean 代码参考 package com.itheima.a43;import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;ComponentScan public class A43 {publi…...
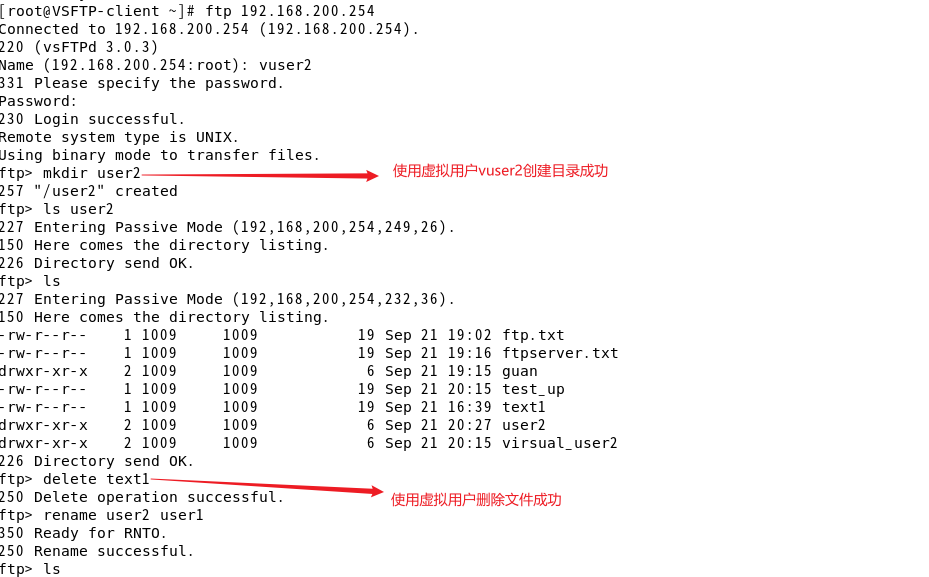
FTP文件传输服务器
目录 一、FTP协议两种工作模式 二、FTP数据两种传输模式 三、FTP用户分类 四、VSFTP配置案例 4.1匿名开放模式 4.2本地用户模式 4.3虚拟用户模式 五、实验总结 一、FTP协议两种工作模式 主动模式: 1、客户端主动向ftp服务器发送控制连接,三次握手控制连接…...
)
【LeetCode - 每日一题】2240. 买钢笔和铅笔的方案数(23.09.1)
2240. 买钢笔和铅笔的方案数 题意 两种价格的笔返回所有可以买的方案数可以为 0 解法 注意这道题的复杂度比较高,O(N2) 是过不了的。一开始是这样写的: // tle 代码 class Solution { public:long long waysToBuyPensPencils(int total, int cost1,…...
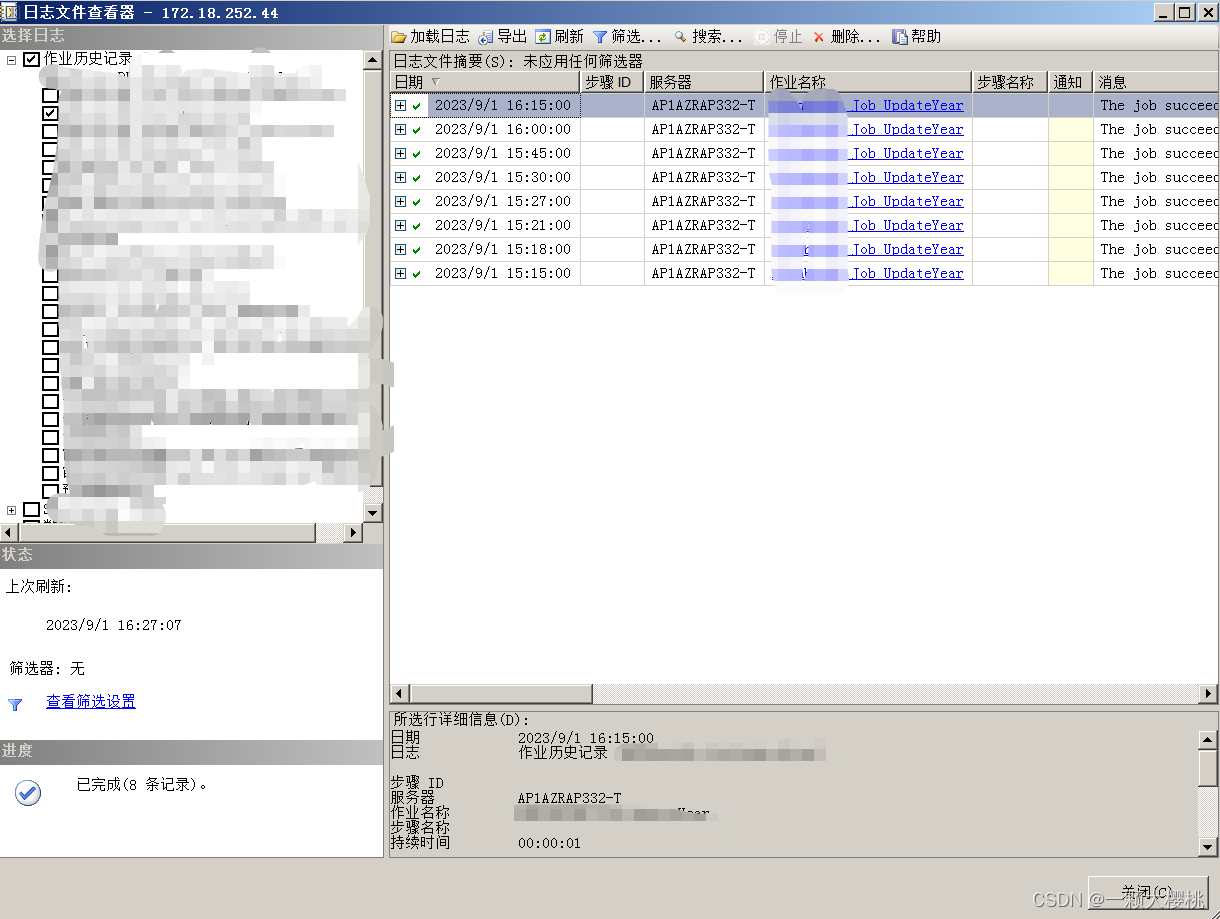
SQL Server如何新建作业
作业: 在 SQL Server 中,作业(Job)是一组可以在预定时间自动执行的任务。可以将作业看作是一个可以在后台运行的程序或脚本。作业由一系列步骤组成,每个步骤都是一个独立的任务,可以执行诸如执行 SQL 查询…...

【计算机网络】CDN 内容分发
CDN(Content Delivery Network)是一种用于加速网站内容传输的分布式网络架构。它的目标是通过在全球多个位置分布服务器来存储和分发网站的静态资源,从而减少用户访问这些资源的延迟,提高网站的加载速度和性能。以下是CDN内容分发…...
Yjs + Quill 实现文档多人协同编辑器开发(基础+实战)
前言 多人协同开发确实是比较难的知识点,在技术实现上有一定挑战,但随着各种技术库的发展,目前已经有了比较成熟的解决方案。今介绍 Yjs 基于CRDT算法,用于构建自动同步的协作应用程序,与Quill富文本编辑器,…...

个性化定制界面还是极简版原装界面?我的选择是……
个性化定制界面和极简版原装界面,哪一个你用起来更加顺手呢,相比之下你更喜欢哪一个?来聊一聊原因吧! 一、我的观点和选择 个性化定制界面和极简版原装界面,二者各有优缺点。 (一)极简版原装…...

C++ STL list容器使用教程
文章目录 引用头文件初始化赋值遍历 list 容器迭代器list 常用方法删除元素插入元素 合并列表 list 翻译为列表,列表容器被实现为双向链表,因此它提供了对其数据的双向顺序访问。 List 不提供快速随机访问,它只支持双向顺序访问。 List 允许…...

go web之一:hello world快速上手+handle(http.Handle和http.HandleFunc的区别与联系)
前情提要: 需要安装好go的环境和VSCode的go插件。 hello world快速上手 1、创建go.mod 在项目根目录下打开命令行,或者直接用VSCode中的终端。输入命令 go mod init github.com/solenovex/web-tutorial 然后就能看到项目结构中多了一个go.mod 2、…...
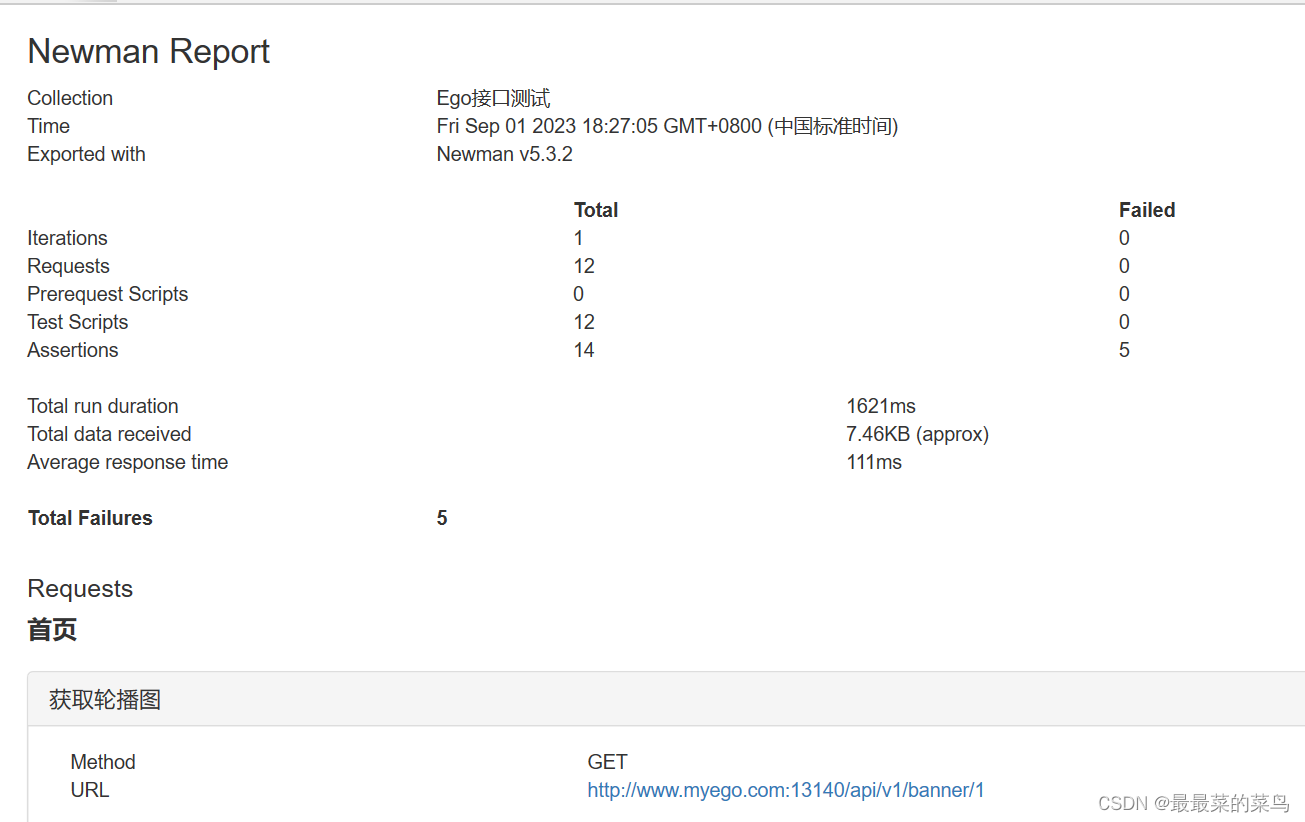
【Postman】postman生成测试报告完整步骤(包含命令与newman安装教程链接)
文章目录 一、前提二、导出Postman脚本三、生成测试报告 一、前提 前提准备: 已安装好Newman 指引文章:Newman安装与环境配置完整版文章 Newman是一款基于nodejs开发的可以运行Postman脚本的工具,并可以生成测试报告。 二、导出Postman脚本…...
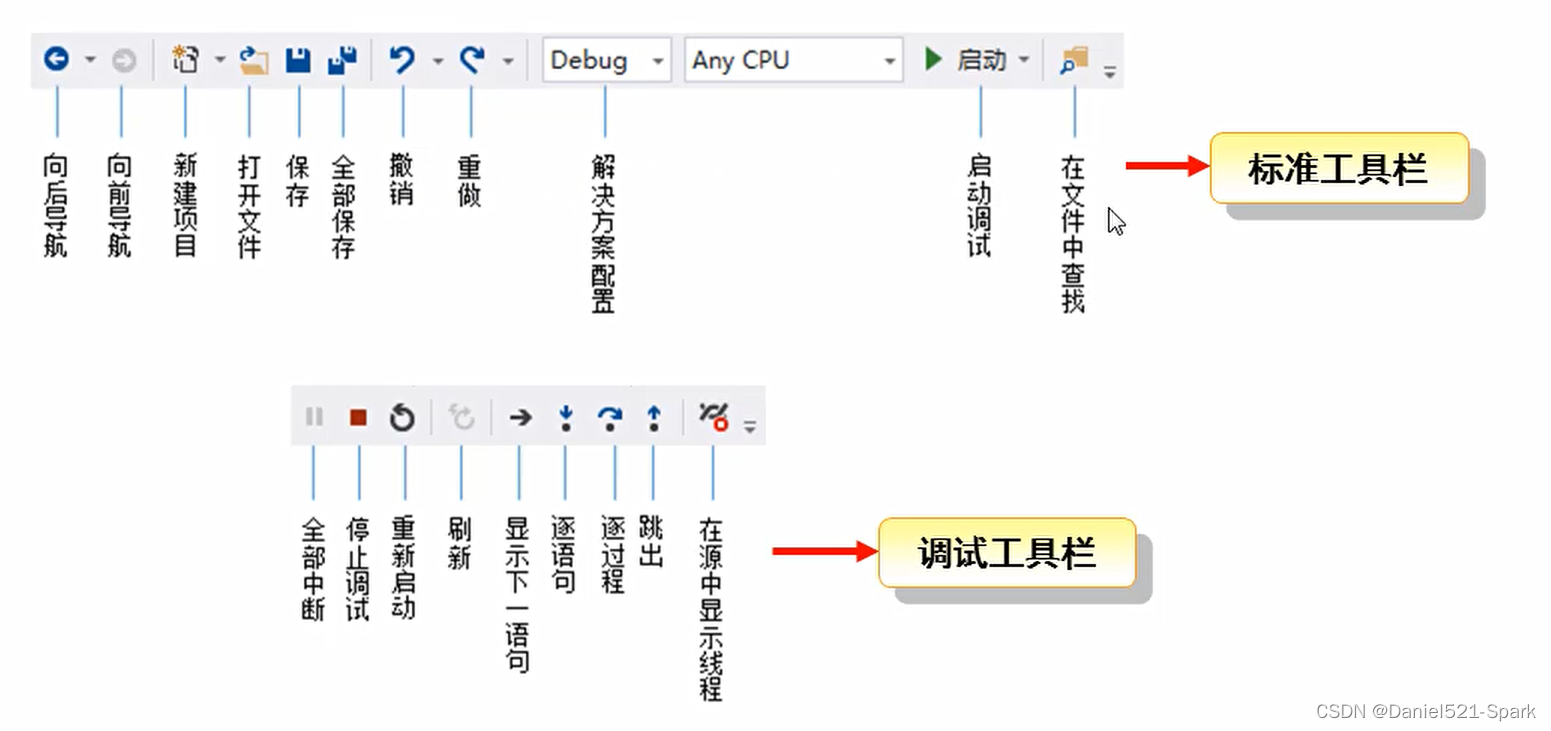
一、C#—概述环境安装(1)
🌻🌻 目录 一、 C#概述1.1 为啥学习C#1.2 TIBOE编程语言排行榜1.3 IEEE编程语言排行榜1.4 什么是C#1.5 C#创始人1.6 C#发展历史1.7 C#特点1.8 C#与Java1.9 .NET Framework1.10 C# 与 .NET Framework1.11 C#得应用领域1.12 C#能做什么 二、开发环境得安装…...

C# 实现ComboBox下拉框控件
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Data; using System.Drawing; using System...

leetcode做题笔记119. 杨辉三角 II
给定一个非负索引 rowIndex,返回「杨辉三角」的第 rowIndex 行。 在「杨辉三角」中,每个数是它左上方和右上方的数的和。 思路一:模拟题意 int* getRow(int rowIndex, int* returnSize){int* ret malloc(sizeof(int)*(rowIndex1));ret[0]…...
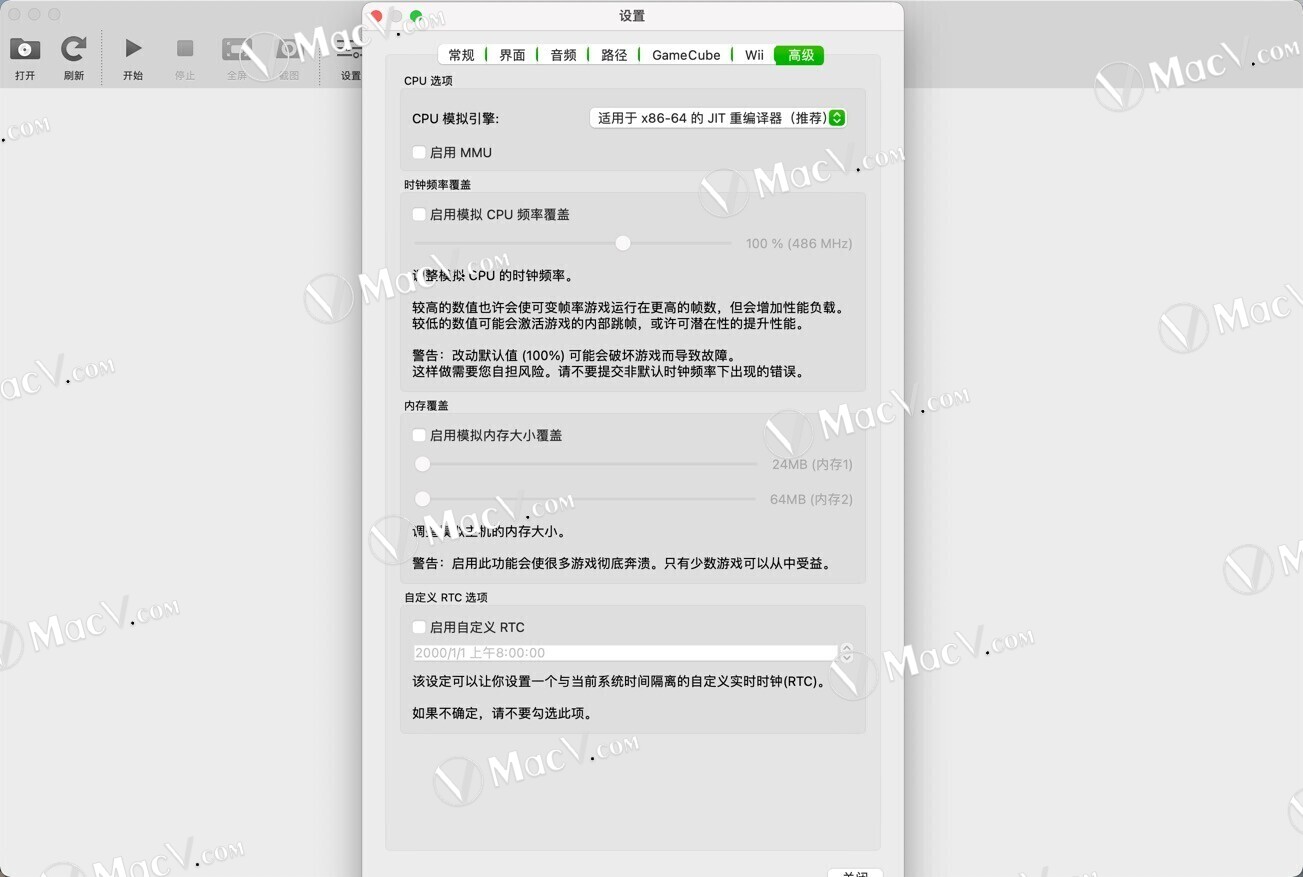
Dolphin for Mac(Wii游戏模拟器)配置指南
Wii模拟器Dolphin Mac是款适合Mac电脑中的游戏玩家们使用的模拟器工具。Wii模拟器Dolphin Mac官方版支持直接运行游戏镜像文件,玩家可以将游戏ISO拷贝到某一个文件夹中统一进行管理。Wii模拟器Dolphin Mac除了键盘和鼠标外,还支持配合原版的Wii遥控器操作…...

Java,Linux,Mysql小白入门
Java入门 java后端__阿伟_的博客-CSDN博客 Linux与Git入门 Linux与Git入门教程__阿伟_的博客-CSDN博客 Mysql入门 Linux与Git入门教程__阿伟_的博客-CSDN博客...
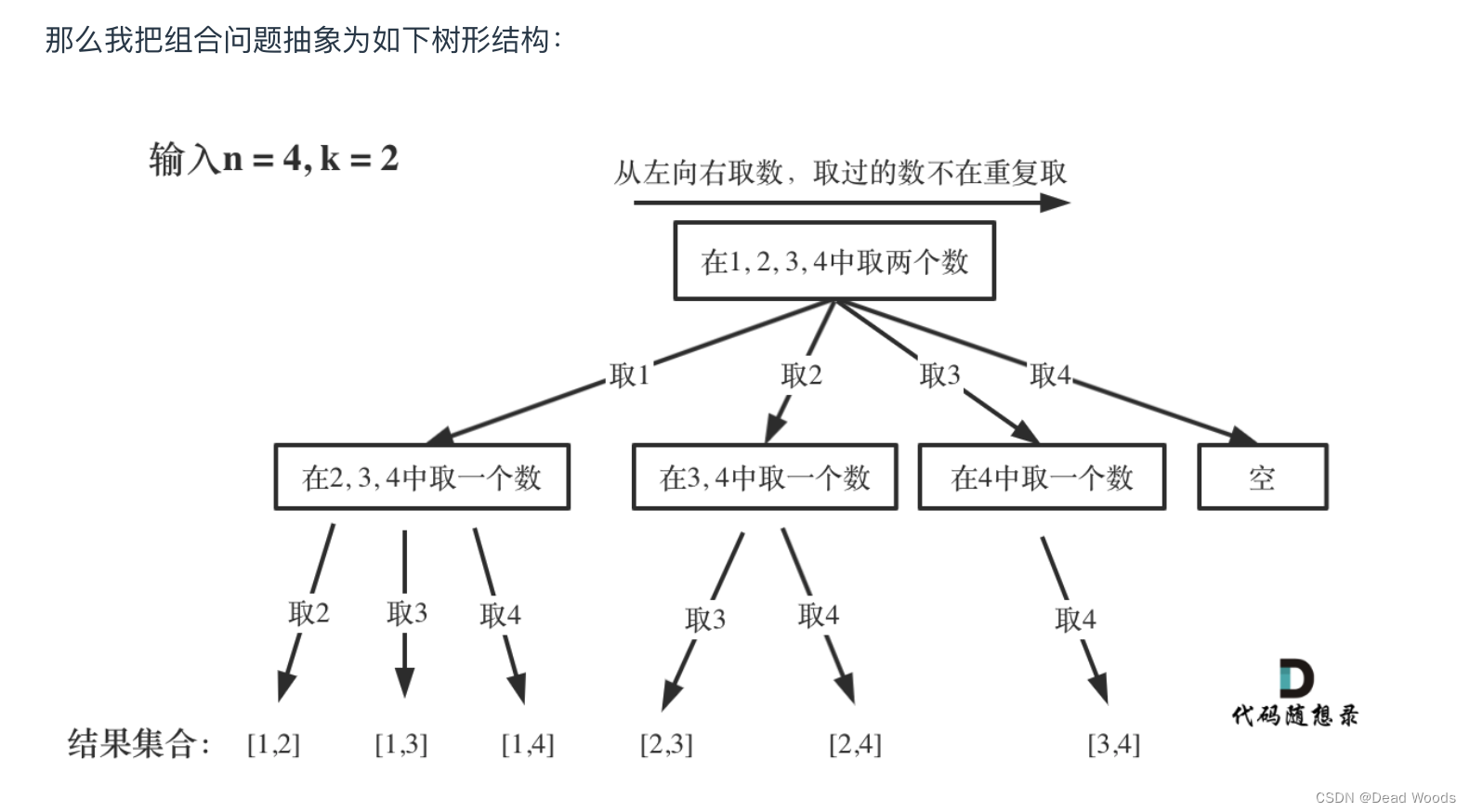
代码随想录算法训练营第二十四天|理论基础 77. 组合
理论基础 其实在讲解二叉树的时候,就给大家介绍过回溯,这次正式开启回溯算法,大家可以先看视频,对回溯算法有一个整体的了解。 题目链接/文章讲解:代码随想录 视频讲解:带你学透回溯算法(理论篇…...

macos安装zsh
https://www.cnblogs.com/xuLessReigns/p/11005435.html mac下安装autojump brew install autojump 1,安装zsh,执行 sh -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.github.com/robbyrussell/oh-my-zsh/master/tools/install.sh)" 2,将zsh设置…...
克隆体问题)
【Unity】预制体材质变(Clone)克隆体问题
1、排查代码是否存在直接修改预制体的材质为克隆体。 解决:删了这段代码。 2、双击Prefab文件进入预制体编辑模式时,会执行预制体身上的脚本方法Awake、Start等(生命周期方法),所以要排查这些方法里是否有克隆…...
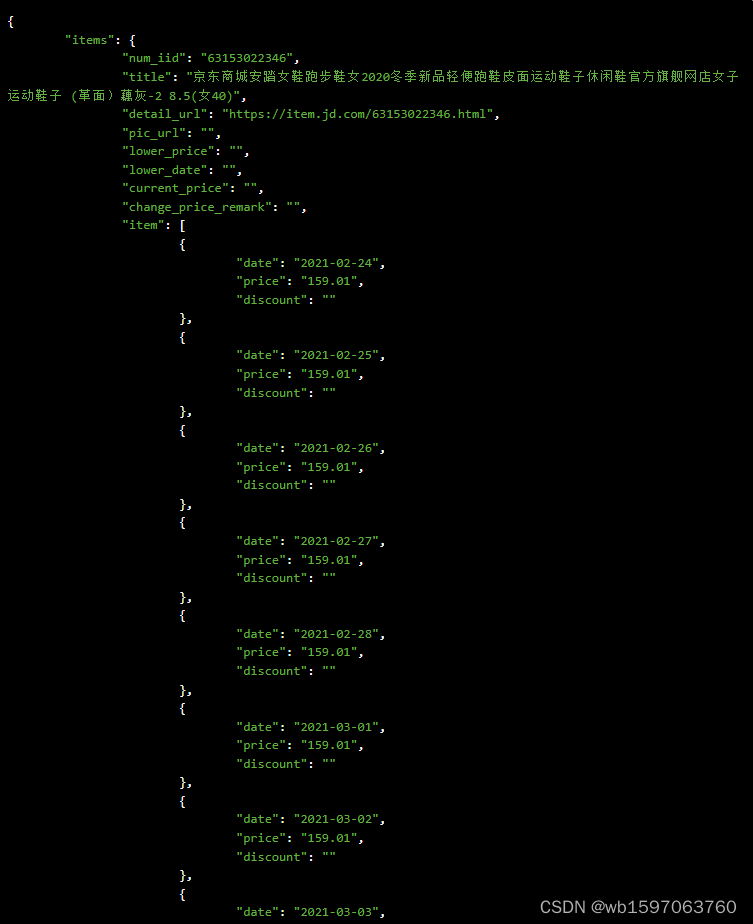
python“魂牵”京东商品历史价格数据接口(含代码示例)
要通过京东的API获取商品详情历史价格数据,您可以使用京东开放平台提供的接口来实现。以下是一种使用Java编程语言实现的示例,展示如何通过京东开放平台API获取商品详情历史价格数据: 首先,确保您已注册成为京东开放平台的开发者…...
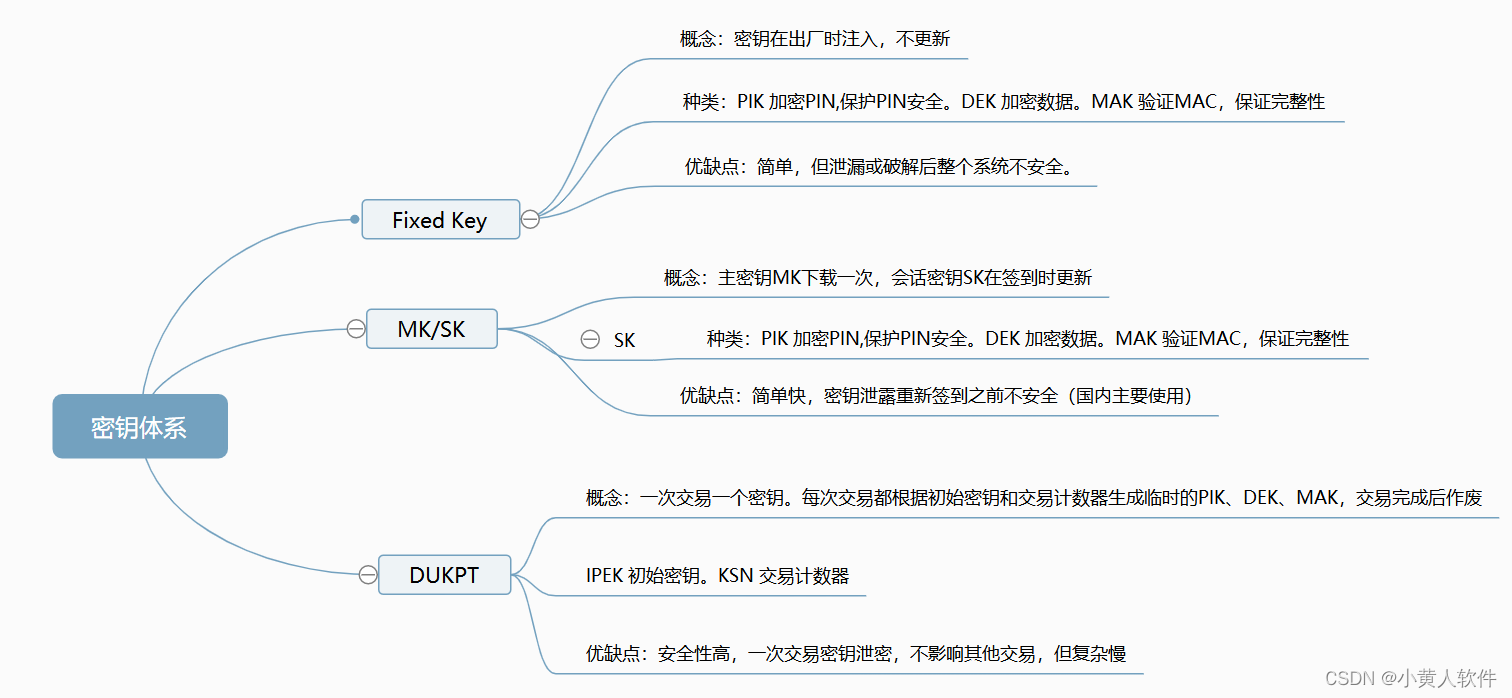
密码算法、密钥体系---安全行业基础篇1
一、密码算法 密码算法是一种数学和计算方法,用于保护数据的机密性和安全性。不同的密码算法使用不同的数学原理和技术来加密和解密数据。以下是一些常见的密码算法类型: 1. **对称密码算法:** 特点:相同的密钥用于加密和解密数…...

《Qt C++ 与 OpenCV:解锁视频播放程序设计的奥秘》
引言:探索视频播放程序设计之旅 在当今数字化时代,多媒体应用已渗透到我们生活的方方面面,从日常的视频娱乐到专业的视频监控、视频会议系统,视频播放程序作为多媒体应用的核心组成部分,扮演着至关重要的角色。无论是在个人电脑、移动设备还是智能电视等平台上,用户都期望…...
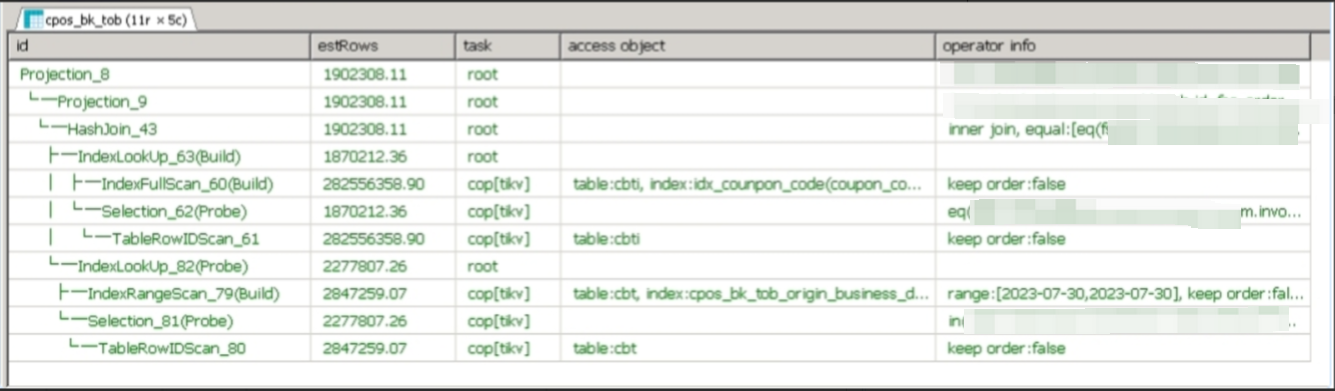
【入坑系列】TiDB 强制索引在不同库下不生效问题
文章目录 背景SQL 优化情况线上SQL运行情况分析怀疑1:执行计划绑定问题?尝试:SHOW WARNINGS 查看警告探索 TiDB 的 USE_INDEX 写法Hint 不生效问题排查解决参考背景 项目中使用 TiDB 数据库,并对 SQL 进行优化了,添加了强制索引。 UAT 环境已经生效,但 PROD 环境强制索…...

HTML 列表、表格、表单
1 列表标签 作用:布局内容排列整齐的区域 列表分类:无序列表、有序列表、定义列表。 例如: 1.1 无序列表 标签:ul 嵌套 li,ul是无序列表,li是列表条目。 注意事项: ul 标签里面只能包裹 li…...

基础测试工具使用经验
背景 vtune,perf, nsight system等基础测试工具,都是用过的,但是没有记录,都逐渐忘了。所以写这篇博客总结记录一下,只要以后发现新的用法,就记得来编辑补充一下 perf 比较基础的用法: 先改这…...

2025年渗透测试面试题总结-腾讯[实习]科恩实验室-安全工程师(题目+回答)
安全领域各种资源,学习文档,以及工具分享、前沿信息分享、POC、EXP分享。不定期分享各种好玩的项目及好用的工具,欢迎关注。 目录 腾讯[实习]科恩实验室-安全工程师 一、网络与协议 1. TCP三次握手 2. SYN扫描原理 3. HTTPS证书机制 二…...

关于uniapp展示PDF的解决方案
在 UniApp 的 H5 环境中使用 pdf-vue3 组件可以实现完整的 PDF 预览功能。以下是详细实现步骤和注意事项: 一、安装依赖 安装 pdf-vue3 和 PDF.js 核心库: npm install pdf-vue3 pdfjs-dist二、基本使用示例 <template><view class"con…...

【AI教我写网站-ECG datacenter】
阶段性总结:后端用户管理基础 在项目管理和协作中,清晰地阐述“为什么做”比“怎么做”更能凝聚共识和提供方向。我们不仅要理解技术实现,更要明白其背后的动机和意义。 让我们重新回顾并总结我们到目前为止的工作,这次会更侧重…...

ubuntu 系统分区注意事项
ubuntu 系统分区大小,注意事项: 安装ubuntu系统时,需要进行分区,手动分区时,有一点需要注意。一开始我也没有注意,长时间使用后才发现的问题。 需要注意一点,如果不对 /usr 进行单独分区&…...

笔记:算法题目中需要处理 int 某个位的三种方法:for、while、to_string
int n; cin >> n; 1. 使用for观察高位、低位、本位 for(int i 1; i < n; i * 10){ //i 1 当前位为个位, i 10 为十位,以此类推 high n / (i * 10); //这是相对于 i 的高位,例如 i 为个位…...

26考研——数据的表示和运算_整数和实数的表示(2)
408答疑 文章目录 二、整数和实数的表示1、整数的表示1.1、无符号整数的表示1.2、有符号整数的表示1.3、C 语言中的整数类型及类型转换1.3.1、C 语言中的整型数据类型1.3.2、有符号数和无符号数的转换1.3.3、不同字长整数之间的转换 2、实数的表示2.1、浮点数的相关概念2.2、浮…...
