【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PIECEWISE_JERK_SPEED_OPTIMIZER
文章目录
- TASK系列解析文章
- 前言
- PIECEWISE_JERK_SPEED_OPTIMIZER功能简介
- PIECEWISE_JERK_SPEED_OPTIMIZER相关配置
- PIECEWISE_JERK_SPEED_OPTIMIZER流程
- QP问题的标准类型定义:
- 优化变量
- 设计目标函数
- 约束条件
- 相关矩阵
- 二次项系数矩阵 H H H
- 一次项系数向量 q q q
- 设定OSQP求解参数
- Process
- 设置相关参数
- 更新STBoundary
- 更新速度边界和参考s
- 速度优化
- 输出
TASK系列解析文章
1.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之LANE_CHANGE_DECIDER
2.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PATH_REUSE_DECIDER
3.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PATH_BORROW_DECIDER
4.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PATH_BOUNDS_DECIDER
5.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PIECEWISE_JERK_PATH_OPTIMIZER
6.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PATH_ASSESSMENT_DECIDER
7.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PATH_DECIDER
8.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之RULE_BASED_STOP_DECIDER
9.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之SPEED_BOUNDS_PRIORI_DECIDER&&SPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDER
10.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之SPEED_HEURISTIC_OPTIMIZER
11.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之SPEED_DECIDER
12.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PIECEWISE_JERK_SPEED_OPTIMIZER
13.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PIECEWISE_JERK_NONLINEAR_SPEED_OPTIMIZER(一)
14.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PIECEWISE_JERK_NONLINEAR_SPEED_OPTIMIZER(二)
前言
在Apollo星火计划学习笔记——Apollo路径规划算法原理与实践与【Apollo学习笔记】——Planning模块讲到……Stage::Process的PlanOnReferenceLine函数会依次调用task_list中的TASK,本文将会继续以LaneFollow为例依次介绍其中的TASK部分究竟做了哪些工作。由于个人能力所限,文章可能有纰漏的地方,还请批评斧正。
在modules/planning/conf/scenario/lane_follow_config.pb.txt配置文件中,我们可以看到LaneFollow所需要执行的所有task。
stage_config: {stage_type: LANE_FOLLOW_DEFAULT_STAGEenabled: truetask_type: LANE_CHANGE_DECIDERtask_type: PATH_REUSE_DECIDERtask_type: PATH_LANE_BORROW_DECIDERtask_type: PATH_BOUNDS_DECIDERtask_type: PIECEWISE_JERK_PATH_OPTIMIZERtask_type: PATH_ASSESSMENT_DECIDERtask_type: PATH_DECIDERtask_type: RULE_BASED_STOP_DECIDERtask_type: SPEED_BOUNDS_PRIORI_DECIDERtask_type: SPEED_HEURISTIC_OPTIMIZERtask_type: SPEED_DECIDERtask_type: SPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDERtask_type: PIECEWISE_JERK_SPEED_OPTIMIZER# task_type: PIECEWISE_JERK_NONLINEAR_SPEED_OPTIMIZERtask_type: RSS_DECIDER
本文将继续介绍LaneFollow的第13个TASK——PIECEWISE_JERK_SPEED_OPTIMIZER
PIECEWISE_JERK_SPEED_OPTIMIZER功能简介
产生平滑速度规划曲线


根据ST图的可行驶区域,优化出一条平滑的速度曲线。满足一阶导、二阶导平滑(速度加速度平滑);满足道路限速;满足车辆动力学约束。
PIECEWISE_JERK_SPEED_OPTIMIZER相关配置
modules/planning/conf/planning_config.pb.txt
default_task_config: {task_type: PIECEWISE_JERK_SPEED_OPTIMIZERpiecewise_jerk_speed_optimizer_config {acc_weight: 1.0jerk_weight: 3.0kappa_penalty_weight: 2000.0ref_s_weight: 10.0ref_v_weight: 10.0}
}
PIECEWISE_JERK_SPEED_OPTIMIZER流程
动态规划得到的轨迹还比较粗糙,需要用优化的方法对轨迹进行进一步的平滑。基于二次规划的速度规划的方法与路径规划基本一致。
原理可以参考这篇论文:
《Optimal Trajectory Generation for Autonomous Vehicles UnderCentripetal Acceleration Constraints for In-lane Driving Scenarios》
QP问题的标准类型定义:
m i n i m i z e 1 2 ⋅ x T ⋅ H ⋅ x + f T ⋅ x s . t . L B ≤ x ≤ U B A e q x = b e q A x ≤ b minimize \frac{1}{2} \cdot x^T \cdot H \cdot x + f^T \cdot x \\ s.t. LB \leq x \leq UB \\ A_{eq}x = b_{eq} \\ Ax \leq b minimize21⋅xT⋅H⋅x+fT⋅xs.t.LB≤x≤UBAeqx=beqAx≤b
优化变量

注意:速度规划的 s s s沿着轨迹的方向,路径规划的 s s s沿着参考线的方向。
 优化变量 x x x, x x x有三个部分组成:从 s 0 s_0 s0, s 1 s_1 s1, s 2 s_2 s2到 s n − 1 s_{n-1} sn−1,从 s ˙ 0 \dot s_0 s˙0, s ˙ 1 \dot s_1 s˙1, s ˙ 2 \dot s_2 s˙2到 s ˙ n − 1 \dot s_{n-1} s˙n−1,从 s ¨ 0 \ddot s_0 s¨0, s ¨ 1 \ddot s_1 s¨1, s ¨ 2 \ddot s_2 s¨2到 s ¨ n − 1 \ddot s_{n-1} s¨n−1.
优化变量 x x x, x x x有三个部分组成:从 s 0 s_0 s0, s 1 s_1 s1, s 2 s_2 s2到 s n − 1 s_{n-1} sn−1,从 s ˙ 0 \dot s_0 s˙0, s ˙ 1 \dot s_1 s˙1, s ˙ 2 \dot s_2 s˙2到 s ˙ n − 1 \dot s_{n-1} s˙n−1,从 s ¨ 0 \ddot s_0 s¨0, s ¨ 1 \ddot s_1 s¨1, s ¨ 2 \ddot s_2 s¨2到 s ¨ n − 1 \ddot s_{n-1} s¨n−1.
x = { s 0 , s 1 , … , s n − 1 , s 0 ˙ , s 1 ˙ , … , s n − 1 ˙ , s 0 ¨ , s 1 ¨ , … , s n − 1 ¨ } x=\{s_0,s_1,\ldots,s_{n-1},\dot{s_0},\dot{s_1},\ldots,\dot{s_{n-1}},\ddot{s_0},\ddot{s_1},\ldots,\ddot{s_{n-1}}\} x={s0,s1,…,sn−1,s0˙,s1˙,…,sn−1˙,s0¨,s1¨,…,sn−1¨}
ps:三阶导的求解方式为: s ′ ′ ′ = s ′ ′ i + 1 − s ′ ′ i Δ t s^{'''}=\frac{{{{s''}_{i + 1}} - {{s''}_i}}}{{\Delta t}} s′′′=Δts′′i+1−s′′i
设计目标函数
对于目标函数的设计,我们需要明确以下目标:
- 尽可能贴合决策时制定的st曲线: ∣ s i − s i − r e f ∣ ↓ \left| {{s_i} - {s_{i - ref}}} \right| \downarrow ∣si−si−ref∣↓
- 确保舒适的体感,尽可能降低加速度/加加速度: ∣ s ¨ i + 1 ∣ ↓ \left| {{{\ddot s}_{i + 1}}} \right| \downarrow ∣s¨i+1∣↓, ∣ s ′ ′ ′ i → i + 1 ∣ ↓ \left| {{{s'''}_{i \to i + 1}}} \right| \downarrow ∣s′′′i→i+1∣↓
- 尽可能按照巡航速度行驶: ∣ s ˙ i − v r e f ∣ ↓ \left| {{{\dot s}_i} - {v_{ref}}} \right| \downarrow ∣s˙i−vref∣↓
- 在转弯时减速行驶, 曲率越大,速度越小,减小向心加速度: ∣ s ˙ i 2 κ s i ∣ ↓ \left| \dot{s}_i^2\kappa_{s_i} \right| \downarrow s˙i2κsi ↓
- 末端惩罚项,使末端 s , v , a s,v,a s,v,a趋于预期
最后会得到以下目标函数:
m i n f = ∑ i = 0 n − 1 w s ( s i − s i − r e f ) 2 + w v ( s ˙ i − v r e f ) 2 + w i s ˙ i 2 κ s i + w a s ¨ i 2 + ∑ i = 0 n − 2 w j s ′ ′ ′ i → i + 1 2 + w e n d − s ( s n − 1 − s e n d ) 2 + w e n d − d s ( s n − 1 ˙ − s e n d ˙ ) 2 + w e n d − d d s ( s n − 1 ¨ − s e n d ¨ ) 2 \begin{aligned} minf&=\sum_{i=0}^{n-1}w_s(s_i-s_{i-ref})^2+w_v(\dot{s}_i-v_{ref})^2+w_i\dot{s}_i^2\kappa_{s_i}+w_a\ddot{s}_i^2+\sum_{i=0}^{n-2}w_j{s^{'''}}_{i \to i + 1}^2\\ & +w_{end-s}(s_{n-1}-s_{end})^2+w_{end-ds}(\dot{s_{n-1}}-\dot{s_{end}})^2+w_{end-dds}(\ddot{s_{n-1}}-\ddot{s_{end}})^2 \end{aligned} minf=i=0∑n−1ws(si−si−ref)2+wv(s˙i−vref)2+wis˙i2κsi+was¨i2+i=0∑n−2wjs′′′i→i+12+wend−s(sn−1−send)2+wend−ds(sn−1˙−send˙)2+wend−dds(sn−1¨−send¨)2
w s w_s ws——位置的权重
w v w_v wv——速度的权重
w i w_i wi——曲率的权重
w a w_a wa——加速度的权重
w j w_j wj——加加速度的权重
为了统一格式,方便与代码对照,在此对目标函数进行变换:
m i n f = ∑ i = 0 n − 1 w s − r e f ( s i − s i − r e f ) 2 + w d s − r e f ( s ˙ i − s ˙ r e f ) 2 + p i s ˙ i 2 + w d d s s ¨ i 2 + ∑ i = 0 n − 2 w d d d s s ′ ′ ′ i → i + 1 2 + w e n d − s ( s n − 1 − s e n d ) 2 + w e n d − d s ( s n − 1 ˙ − s e n d ˙ ) 2 + w e n d − d d s ( s n − 1 ¨ − s e n d ¨ ) 2 \begin{aligned} minf&=\sum_{i=0}^{n-1}w_{s-ref}(s_i-s_{i-ref})^2+w_{ds-ref}(\dot{s}_i-\dot s_{ref})^2+p_i\dot{s}_i^2+w_{dds}\ddot{s}_i^2+\sum_{\color{red}i=0}^{\color{red}n-2}w_{ddds}{s^{'''}}_{i \to i + 1}^2\\ & +w_{end-s}(s_{n-1}-s_{end})^2+w_{end-ds}(\dot{s_{n-1}}-\dot{s_{end}})^2+w_{end-dds}(\ddot{s_{n-1}}-\ddot{s_{end}})^2 \end{aligned} minf=i=0∑n−1ws−ref(si−si−ref)2+wds−ref(s˙i−s˙ref)2+pis˙i2+wddss¨i2+i=0∑n−2wdddss′′′i→i+12+wend−s(sn−1−send)2+wend−ds(sn−1˙−send˙)2+wend−dds(sn−1¨−send¨)2
注: p i p_i pi代表penalty,为曲率 κ \kappa κ与曲率的权重 w i w_i wi的乘积。
接着,对目标函数按阶次整理可得:
m i n f = ∑ i = 0 n − 1 w s − r e f ( s i − s i − r e f ) 2 + w e n d − s ( s n − 1 − s e n d ) 2 + ∑ i = 0 n − 1 w d s − r e f ( s ˙ i − s ˙ r e f ) 2 + p i s ˙ i 2 + w e n d − d s ( s n − 1 ˙ − s e n d ˙ ) 2 + ∑ i = 0 n − 1 w d d s s ¨ i 2 + w e n d − d d s ( s n − 1 ¨ − s e n d ¨ ) 2 + ∑ i = 0 n − 2 w d d d s s ′ ′ ′ i → i + 1 2 \begin{aligned} minf&=\sum_{i=0}^{n-1}w_{s-ref}(s_i-s_{i-ref})^2+w_{end-s}(s_{n-1}-s_{end})^2\\ &+\sum_{i=0}^{n-1}w_{ds-ref}(\dot{s}_i-\dot s_{ref})^2+p_i\dot{s}_i^2+w_{end-ds}(\dot{s_{n-1}}-\dot{s_{end}})^2\\ &+\sum_{i=0}^{n-1}w_{dds}\ddot{s}_i^2+w_{end-dds}(\ddot{s_{n-1}}-\ddot{s_{end}})^2\\ &+\sum_{\color{red}i=0}^{\color{red}n-2}w_{ddds}{s^{'''}}_{i \to i + 1}^2 \end{aligned} minf=i=0∑n−1ws−ref(si−si−ref)2+wend−s(sn−1−send)2+i=0∑n−1wds−ref(s˙i−s˙ref)2+pis˙i2+wend−ds(sn−1˙−send˙)2+i=0∑n−1wddss¨i2+wend−dds(sn−1¨−send¨)2+i=0∑n−2wdddss′′′i→i+12
用 s ′ ′ ′ = s ′ ′ i + 1 − s ′ ′ i Δ t s^{'''}=\frac{{{{s''}_{i + 1}} - {{s''}_i}}}{{\Delta t}} s′′′=Δts′′i+1−s′′i代入目标函数,
∑ i = 0 n − 2 ( s i ′ ′ ′ ) 2 = ( s 1 ′ ′ − s 0 ′ ′ Δ t ) 2 + ( s 2 ′ ′ − s 1 ′ ′ Δ t ) 2 + ⋯ + ( s n − 2 ′ ′ − s n − 3 ′ ′ Δ t ) 2 + ( s n − 1 ′ ′ − s n − 2 ′ ′ Δ t ) 2 = ( s 0 ′ ′ ) 2 Δ t 2 + 2 ⋅ ∑ i = 1 n − 2 ( s i ′ ′ ) 2 Δ t 2 + ( s n − 1 ′ ′ ) 2 Δ t 2 − 2 ⋅ ∑ i = 0 n − 2 s i ′ ′ ⋅ s i + 1 ′ ′ Δ t 2 \begin{aligned} \sum_{\color{red}{i=0}}^{\color{red}{n-2}}(s_i^{\prime\prime\prime})^2& =\left(\frac{s_{1}^{\prime\prime}-s_{0}^{\prime\prime}}{\Delta t}\right)^2+\left(\frac{s_{2}^{\prime\prime}-s_{1}^{\prime\prime}}{\Delta t}\right)^2+\cdots+\left(\frac{s_{n-2}^{\prime\prime}-s_{n-3}^{\prime\prime}}{\Delta t}\right)^2+\left(\frac{s_{n-1}^{\prime\prime}-s_{n-2}^{\prime\prime}}{\Delta t}\right)^2 \\ &=\frac{\left(s_0^{\prime\prime}\right)^2}{\Delta t^2}+{2}\cdot\sum_{\color{red}i=1}^{\color{red}n-2}\frac{\left(s_i^{\prime\prime}\right)^2}{\Delta t^2}+\frac{\left(s_{n-1}^{\prime\prime}\right)^2}{\Delta t^2}-{2}\cdot\sum_{\color{red}i=0}^{\color{red}n-2}\frac{s_i^{\prime\prime}\cdot s_{i+1}^{\prime\prime}}{\Delta t^2} \end{aligned} i=0∑n−2(si′′′)2=(Δts1′′−s0′′)2+(Δts2′′−s1′′)2+⋯+(Δtsn−2′′−sn−3′′)2+(Δtsn−1′′−sn−2′′)2=Δt2(s0′′)2+2⋅i=1∑n−2Δt2(si′′)2+Δt2(sn−1′′)2−2⋅i=0∑n−2Δt2si′′⋅si+1′′
m i n f = ∑ i = 0 n − 1 w s − r e f ( s i − s i − r e f ) 2 + w e n d − s ( s n − 1 − s e n d ) 2 + ∑ i = 0 n − 1 w d s − r e f ( s ˙ i − s ˙ r e f ) 2 + p i s ˙ i 2 + w e n d − d s ( s n − 1 ˙ − s e n d ˙ ) 2 + ∑ i = 0 n − 1 w d d s s ¨ i 2 + w e n d − d d s ( s n − 1 ¨ − s e n d ¨ ) 2 + w d d d s [ ( s 0 ′ ′ ) 2 Δ t 2 + 2 ⋅ ∑ i = 1 n − 2 ( s i ′ ′ ) 2 Δ t 2 + ( s n − 1 ′ ′ ) 2 Δ t 2 − 2 ⋅ ∑ i = 0 n − 2 s i ′ ′ ⋅ s i + 1 ′ ′ Δ t 2 ] \begin{aligned} minf&=\sum_{i=0}^{n-1}w_{s-ref}(s_i-s_{i-ref})^2+w_{end-s}(s_{n-1}-s_{end})^2\\ &+\sum_{i=0}^{n-1}w_{ds-ref}(\dot{s}_i-\dot s_{ref})^2+p_i\dot{s}_i^2+w_{end-ds}(\dot{s_{n-1}}-\dot{s_{end}})^2\\ &+\sum_{i=0}^{n-1}w_{dds}\ddot{s}_i^2+w_{end-dds}(\ddot{s_{n-1}}-\ddot{s_{end}})^2\\ &+w_{ddds}[\frac{\left(s_0^{\prime\prime}\right)^2}{\Delta t^2}+{2}\cdot\sum_{\color{red}i=1}^{\color{red}n-2}\frac{\left(s_i^{\prime\prime}\right)^2}{\Delta t^2}+\frac{\left(s_{n-1}^{\prime\prime}\right)^2}{\Delta t^2}-{2}\cdot\sum_{\color{red}i=0}^{\color{red}n-2}\frac{s_i^{\prime\prime}\cdot s_{i+1}^{\prime\prime}}{\Delta t^2}] \end{aligned} minf=i=0∑n−1ws−ref(si−si−ref)2+wend−s(sn−1−send)2+i=0∑n−1wds−ref(s˙i−s˙ref)2+pis˙i2+wend−ds(sn−1˙−send˙)2+i=0∑n−1wddss¨i2+wend−dds(sn−1¨−send¨)2+wddds[Δt2(s0′′)2+2⋅i=1∑n−2Δt2(si′′)2+Δt2(sn−1′′)2−2⋅i=0∑n−2Δt2si′′⋅si+1′′]
约束条件
接下来谈谈约束的设计。
要满足的约束条件:
• 主车必须在道路边界内,同时不能和障碍物有碰撞 s i ∈ ( s min i , s max i ) {s_i} \in (s_{\min }^i,s_{\max }^i) si∈(smini,smaxi)• 根据当前状态,主车的横向速度/加速度/加加速度有特定运动学限制:
s i ′ ∈ ( s m i n i ′ ( t ) , s m a x i ′ ( t ) ) , s i ′ ′ ∈ ( s m i n i ′ ′ ( t ) , s m a x i ′ ′ ( t ) ) , s i ′ ′ ′ ∈ ( s m i n i ′ ′ ′ ( t ) , s m a x i ′ ′ ′ ( t ) ) s_{i}^{\prime}\in\left(s_{min}^{i}{}^{\prime}(t),s_{max}^{i}{}^{\prime}(t)\right)\text{,}s_{i}^{\prime\prime}\in\left(s_{min}^{i}{}^{\prime\prime}(t),s_{max}^{i}{}^{\prime\prime}(t)\right)\text{,}s_{i}^{\prime\prime\prime}\in\left(s_{min}^{i}{}^{\prime\prime\prime}(t),s_{max}^{i}{}^{\prime\prime\prime}(t)\right) si′∈(smini′(t),smaxi′(t)),si′′∈(smini′′(t),smaxi′′(t)),si′′′∈(smini′′′(t),smaxi′′′(t))
• 连续性约束:
s i + 1 ′ ′ = s i ′ ′ + ∫ 0 Δ t s i → i + 1 ′ ′ ′ d t = s i ′ ′ + s i → i + 1 ′ ′ ′ ∗ Δ t s i + 1 ′ = s i ′ + ∫ 0 Δ t s ′ ′ ( t ) d t = s i ′ + s i ′ ′ ∗ Δ t + 1 2 ∗ s i → i + 1 ′ ′ ′ ∗ Δ t 2 = s i ′ + 1 2 ∗ s i ′ ′ ∗ Δ t + 1 2 ∗ s i + 1 ′ ′ ∗ Δ t s i + 1 = s i + ∫ 0 Δ t s ′ ( t ) d t = s i + s i ′ ∗ Δ t + 1 2 ∗ s i ′ ′ ∗ Δ t 2 + 1 6 ∗ s i → i + 1 ′ ′ ′ ∗ Δ t 3 = s i + s i ′ ∗ Δ t + 1 3 ∗ s i ′ ′ ∗ Δ t 2 + 1 6 ∗ s i + 1 ′ ′ ∗ Δ t 2 \begin{aligned} s_{i+1}^{\prime\prime} &=s_i''+\int_0^{\Delta t}s_{i\to i+1}^{\prime\prime\prime}dt=s_i''+s_{i\to i+1}^{\prime\prime\prime}*\Delta t \\ s_{i+1}^{\prime} &=s_i^{\prime}+\int_0^{\Delta t}\boldsymbol{s''}(t)dt=s_i^{\prime}+s_i^{\prime\prime}*\Delta t+\frac12*s_{i\to i+1}^{\prime\prime\prime}*\Delta t^2 \\ &= s_i^{\prime}+\frac12*s_i^{\prime\prime}*\Delta t+\frac12*s_{i+1}^{\prime\prime}*\Delta t\\ s_{i+1} &=s_i+\int_0^{\Delta t}\boldsymbol{s'}(t)dt \\ &=s_i+s_i^{\prime}*\Delta t+\frac12*s_i^{\prime\prime}*\Delta t^2+\frac16*s_{i\to i+1}^{\prime\prime\prime}*\Delta t^3\\ &=s_i+s_i^{\prime}*\Delta t+\frac13*s_i^{\prime\prime}*\Delta t^2+\frac16*s_{i+1}^{\prime\prime}*\Delta t^2 \end{aligned} si+1′′si+1′si+1=si′′+∫0Δtsi→i+1′′′dt=si′′+si→i+1′′′∗Δt=si′+∫0Δts′′(t)dt=si′+si′′∗Δt+21∗si→i+1′′′∗Δt2=si′+21∗si′′∗Δt+21∗si+1′′∗Δt=si+∫0Δts′(t)dt=si+si′∗Δt+21∗si′′∗Δt2+61∗si→i+1′′′∗Δt3=si+si′∗Δt+31∗si′′∗Δt2+61∗si+1′′∗Δt2
• 起点约束: s 0 = s i n i t s_0=s_{init} s0=sinit, s ˙ 0 = s ˙ i n i t \dot s_0=\dot s_{init} s˙0=s˙init, s ¨ 0 = s ¨ i n i t \ddot s_0=\ddot s_{init} s¨0=s¨init满足的是起点的约束,即为实际车辆规划起点的状态。
可以看到和路径规划部分的约束条件基本一致,因此在约束矩阵 A A A部分,路径规划和速度规划矩阵一致,不用再次编写。
相关矩阵
回到代码中,PiecewiseJerkSpeedOptimizer的主流程依旧在Process中,我们暂且不关注其他细节,先关注与二次规划主体部分。
以下代码创建了一个类为PiecewiseJerkSpeedProblem的对象piecewise_jerk_problem,PiecewiseJerkSpeedProblem继承自PiecewiseJerkProblem。其中参数意义如下:
num_of_knots:表示采样点的数量。
delta_t:表示每个采样点之间的时间间隔。
init_s:表示起点位置。
// 分段加加速度速度优化算法PiecewiseJerkSpeedProblem piecewise_jerk_problem(num_of_knots, delta_t,init_s);
接着看下一段代码:
通过调用Optimize,进行二次规划问题的解决
// Solve the problemif (!piecewise_jerk_problem.Optimize()) {const std::string msg = "Piecewise jerk speed optimizer failed!";AERROR << msg;speed_data->clear();return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);}
Optimize这部分代码和路径规划部分一致,具体可参考【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PIECEWISE_JERK_PATH_OPTIMIZER
速度规划部分约束矩阵 A A A, u p p e r b o u n d upperbound upperbound, l o w e r b o u n d lowerbound lowerbound均和路径规划部分一致:
l b = [ s l b [ 0 ] ⋮ s l b [ n − 1 ] s ′ l b [ 0 ] ⋮ s ′ l b [ n − 1 ] s ′ ′ l b [ 0 ] ⋮ s ′ ′ l b [ n − 1 ] s ′ ′ ′ l b [ 0 ] ⋅ Δ t ⋮ s ′ ′ ′ l b [ n − 2 ] ⋅ Δ t 0 ⋮ 0 s i n i t s ′ i n i t s ′ ′ i n i t ] , u b = [ s u b [ 0 ] ⋮ s u b [ n − 1 ] s ′ u b [ 0 ] ⋮ s ′ u b [ n − 1 ] s ′ ′ u b [ 0 ] ⋮ s ′ ′ u b [ n − 1 ] s ′ ′ ′ u b [ 0 ] ⋅ Δ t ⋮ s ′ ′ ′ u b [ n − 2 ] ⋅ Δ t 0 ⋮ 0 s i n i t s ′ i n i t s ′ ′ i n i t ] lb = \left[ {\begin{array}{ccccccccccccccc}{{s_{lb}}[0]}\\ \vdots \\{{s_{lb}}[n - 1]}\\{{{s'}_{lb}}[0]}\\ \vdots \\{{{s'}_{lb}}[n - 1]}\\{{{s''}_{lb}}[0]}\\ \vdots \\{{{s''}_{lb}}[n - 1]}\\{{{s'''}_{lb}}[0] \cdot \Delta t}\\ \vdots \\{{{s'''}_{lb}}[n - 2] \cdot \Delta t}\\0\\ \vdots \\0\\{{s_{init}}}\\{{{s'}_{init}}}\\{{{s''}_{init}}}\end{array}} \right],ub = \left[ {\begin{array}{ccccccccccccccc}{{s_{ub}}[0]}\\ \vdots \\{{s_{ub}}[n - 1]}\\{{{s'}_{ub}}[0]}\\ \vdots \\{{{s'}_{ub}}[n - 1]}\\{{{s''}_{ub}}[0]}\\ \vdots \\{{{s''}_{ub}}[n - 1]}\\{{{s'''}_{ub}}[0] \cdot \Delta t}\\ \vdots \\{{{s'''}_{ub}}[n - 2] \cdot \Delta t}\\0\\ \vdots \\0\\{{s_{init}}}\\{{{s'}_{init}}}\\{{{s''}_{init}}}\end{array}} \right] lb= slb[0]⋮slb[n−1]s′lb[0]⋮s′lb[n−1]s′′lb[0]⋮s′′lb[n−1]s′′′lb[0]⋅Δt⋮s′′′lb[n−2]⋅Δt0⋮0sinits′inits′′init ,ub= sub[0]⋮sub[n−1]s′ub[0]⋮s′ub[n−1]s′′ub[0]⋮s′′ub[n−1]s′′′ub[0]⋅Δt⋮s′′′ub[n−2]⋅Δt0⋮0sinits′inits′′init
A = [ 1 0 ⋯ 0 0 ⋱ ⋮ ⋮ ⋱ 0 0 ⋯ 0 1 1 0 ⋯ 0 0 ⋱ ⋮ ⋮ ⋱ 0 0 ⋯ 0 1 1 0 ⋯ 0 0 ⋱ ⋮ ⋮ ⋱ 0 0 ⋯ 0 1 − 1 1 ⋱ ⋱ − 1 1 − 1 1 ⋱ ⋱ − 1 1 − Δ t 2 − Δ t 2 ⋱ ⋱ − Δ t 2 − Δ t 2 − 1 1 ⋱ ⋱ − 1 1 − Δ t ⋱ − Δ t − Δ t 2 3 − Δ t 2 6 ⋱ ⋱ − Δ t 2 3 − Δ t 2 6 1 1 1 ] A = \left[ {\begin{array}{ccccccccccccccc}{\begin{array}{ccccccccccccccc}1&0& \cdots &0\\0& \ddots &{}& \vdots \\ \vdots &{}& \ddots &0\\0& \cdots &0&1\end{array}}&{}&{}\\{}&{\begin{array}{ccccccccccccccc}1&0& \cdots &0\\0& \ddots &{}& \vdots \\ \vdots &{}& \ddots &0\\0& \cdots &0&1\end{array}}&{}\\{}&{}&{\begin{array}{ccccccccccccccc}1&0& \cdots &0\\0& \ddots &{}& \vdots \\ \vdots &{}& \ddots &0\\0& \cdots &0&1\end{array}}\\{}&{}&{\begin{array}{ccccccccccccccc}{ - 1}&1&{}&{}\\{}& \ddots & \ddots &{}\\{}&{}&{ - 1}&1\end{array}}\\{}&{\begin{array}{ccccccccccccccc}{ - 1}&1&{}&{}\\{}& \ddots & \ddots &{}\\{}&{}&{ - 1}&1\end{array}}&{\begin{array}{ccccccccccccccc}{ - \frac{{\Delta t}}{2}}&{ - \frac{{\Delta t}}{2}}&{}&{}\\{}& \ddots & \ddots &{}\\{}&{}&{ - \frac{{\Delta t}}{2}}&{ - \frac{{\Delta t}}{2}}\end{array}}\\{\begin{array}{ccccccccccccccc}{ - 1}&1&{}&{}\\{}& \ddots & \ddots &{}\\{}&{}&{ - 1}&1\end{array}}&{\begin{array}{ccccccccccccccc}{ - \Delta t}&{}&{}&{}\\{}& \ddots &{}&{}\\{}&{}&{ - \Delta t}&{}\end{array}}&{\begin{array}{ccccccccccccccc}{ - \frac{{\Delta {t^2}}}{3}}&{ - \frac{{\Delta {t^2}}}{6}}&{}&{}\\{}& \ddots & \ddots &{}\\{}&{}&{ - \frac{{\Delta {t^2}}}{3}}&{ - \frac{{\Delta {t^2}}}{6}}\end{array}}\\{\begin{array}{ccccccccccccccc}1&{}&{}&{}\\{}&{}&{}&{}\\{}&{}&{}&{}\end{array}}&{\begin{array}{ccccccccccccccc}{}&{}&{}&{}\\1&{}&{}&{}\\{}&{}&{}&{}\end{array}}&{\begin{array}{ccccccccccccccc}{}&{}&{}&{}\\{}&{}&{}&{}\\1&{}&{}&{}\end{array}}\end{array}} \right] A= 10⋮00⋱⋯⋯⋱00⋮01−11⋱⋱−11110⋮00⋱⋯⋯⋱00⋮01−11⋱⋱−11−Δt⋱−Δt110⋮00⋱⋯⋯⋱00⋮01−11⋱⋱−11−2Δt−2Δt⋱⋱−2Δt−2Δt−3Δt2−6Δt2⋱⋱−3Δt2−6Δt21
不同之处在于二次项系数矩阵 H H H与一次项系数向量 q q q
二次项系数矩阵 H H H
H = 2 ⋅ [ w s − r e f 0 ⋯ 0 0 ⋱ ⋮ ⋮ w s − r e f 0 0 ⋯ 0 w s − r e f + w e n d − s w d s − r e f + p 0 0 ⋯ 0 0 ⋱ ⋮ ⋮ w d s − r e f + p n − 2 0 0 ⋯ 0 w d s − r e f + p n − 1 + w e n d − s w d d s + w d d d s Δ t 2 0 ⋯ ⋯ 0 − 2 ⋅ w d d d s Δ t 2 w d d s + 2 ⋅ w d d d s Δ t 2 ⋮ 0 − 2 ⋅ w d d d s Δ t 2 ⋱ ⋮ ⋮ ⋱ w d d s + 2 ⋅ w d d d s Δ t 2 0 0 ⋯ 0 − 2 ⋅ w d d d s Δ t 2 w d d s + w d d d s Δ t 2 + w e n d − d d s ] H = 2 \cdot \left[ {\begin{array}{ccccccccccccccc}{\begin{array}{ccccccccccccccc}{{w_{s - ref}}}&0& \cdots &0\\0& \ddots &{}& \vdots \\ \vdots &{}&{{w_{s - ref}}}&0\\0& \cdots &0&{{w_{s - ref}} + {w_{end - s}}}\end{array}}&{}&{}\\{}&{\begin{array}{ccccccccccccccc}{{w_{ds - ref}} + {p_0}}&0& \cdots &0\\0& \ddots &{}& \vdots \\ \vdots &{}&{{w_{ds - ref}} + {p_{n - 2}}}&0\\0& \cdots &0&{{w_{ds - ref}} + {p_{n - 1}} + {w_{end - s}}}\end{array}}&{}\\{}&{}&{\begin{array}{ccccccccccccccc}{{w_{dds}} + \frac{{{w_{ddds}}}}{{\Delta {t^2}}}}&0& \cdots & \cdots &0\\{ - 2 \cdot \frac{{{w_{ddds}}}}{{\Delta {t^2}}}}&{{w_{dds}} + 2 \cdot \frac{{{w_{ddds}}}}{{\Delta {t^2}}}}&{}&{}& \vdots \\0&{ - 2 \cdot \frac{{{w_{ddds}}}}{{\Delta {t^2}}}}& \ddots &{}& \vdots \\ \vdots &{}& \ddots &{{w_{dds}} + 2 \cdot \frac{{{w_{ddds}}}}{{\Delta {t^2}}}}&0\\0& \cdots &0&{ - 2 \cdot \frac{{{w_{ddds}}}}{{\Delta {t^2}}}}&{{w_{dds}} + \frac{{{w_{ddds}}}}{{\Delta {t^2}}} + {w_{end - dds}}}\end{array}}\end{array}} \right] H=2⋅ ws−ref0⋮00⋱⋯⋯ws−ref00⋮0ws−ref+wend−swds−ref+p00⋮00⋱⋯⋯wds−ref+pn−200⋮0wds−ref+pn−1+wend−swdds+Δt2wddds−2⋅Δt2wddds0⋮00wdds+2⋅Δt2wddds−2⋅Δt2wddds⋯⋯⋱⋱0⋯wdds+2⋅Δt2wddds−2⋅Δt2wddds0⋮⋮0wdds+Δt2wddds+wend−dds
void PiecewiseJerkSpeedProblem::CalculateKernel(std::vector<c_float>* P_data,std::vector<c_int>* P_indices,std::vector<c_int>* P_indptr) {const int n = static_cast<int>(num_of_knots_);const int kNumParam = 3 * n;const int kNumValue = 4 * n - 1;std::vector<std::vector<std::pair<c_int, c_float>>> columns;columns.resize(kNumParam);int value_index = 0;// x(i)^2 * w_x_reffor (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) {columns[i].emplace_back(i, weight_x_ref_ / (scale_factor_[0] * scale_factor_[0]));++value_index;}// x(n-1)^2 * (w_x_ref + w_end_x)columns[n - 1].emplace_back(n - 1, (weight_x_ref_ + weight_end_state_[0]) /(scale_factor_[0] * scale_factor_[0]));++value_index;// x(i)'^2 * (w_dx_ref + penalty_dx)for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) {columns[n + i].emplace_back(n + i,(weight_dx_ref_ + penalty_dx_[i]) /(scale_factor_[1] * scale_factor_[1]));++value_index;}// x(n-1)'^2 * (w_dx_ref + penalty_dx + w_end_dx)columns[2 * n - 1].emplace_back(2 * n - 1, (weight_dx_ref_ + penalty_dx_[n - 1] + weight_end_state_[1]) /(scale_factor_[1] * scale_factor_[1]));++value_index;auto delta_s_square = delta_s_ * delta_s_;// x(i)''^2 * (w_ddx + 2 * w_dddx / delta_s^2)columns[2 * n].emplace_back(2 * n,(weight_ddx_ + weight_dddx_ / delta_s_square) /(scale_factor_[2] * scale_factor_[2]));++value_index;for (int i = 1; i < n - 1; ++i) {columns[2 * n + i].emplace_back(2 * n + i, (weight_ddx_ + 2.0 * weight_dddx_ / delta_s_square) /(scale_factor_[2] * scale_factor_[2]));++value_index;}columns[3 * n - 1].emplace_back(3 * n - 1,(weight_ddx_ + weight_dddx_ / delta_s_square + weight_end_state_[2]) /(scale_factor_[2] * scale_factor_[2]));++value_index;// -2 * w_dddx / delta_s^2 * x(i)'' * x(i + 1)''for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) {columns[2 * n + i].emplace_back(2 * n + i + 1,-2.0 * weight_dddx_ / delta_s_square /(scale_factor_[2] * scale_factor_[2]));++value_index;}CHECK_EQ(value_index, kNumValue);int ind_p = 0;for (int i = 0; i < kNumParam; ++i) {P_indptr->push_back(ind_p);for (const auto& row_data_pair : columns[i]) {P_data->push_back(row_data_pair.second * 2.0);P_indices->push_back(row_data_pair.first);++ind_p;}}P_indptr->push_back(ind_p);
}
一次项系数向量 q q q
q = [ − 2 ⋅ w s − r e f ⋅ s 0 − r e f ⋮ − 2 ⋅ w s − r e f ⋅ s ( n − 2 ) − r e f − 2 ⋅ w s − r e f ⋅ s ( n − 1 ) − r e f − 2 ⋅ w e n d − s ⋅ s e n d − 2 ⋅ w d s − r e f ⋅ s ˙ r e f ⋮ − 2 ⋅ w d s − r e f ⋅ s ˙ r e f − 2 ⋅ w e n d − d s ⋅ s ¨ e n d − 2 ⋅ w d s − r e f ⋅ s ˙ r e f 0 ⋮ 0 − 2 ⋅ w e n d − d d s ⋅ s ¨ e n d ] q = \left[ {\begin{array}{ccccccccccccccc}{ - 2 \cdot {w_{s - ref}} \cdot {s_{0 - ref}}}\\ \vdots \\{ - 2 \cdot {w_{s - ref}} \cdot {s_{(n - 2) - ref}}}\\{ - 2 \cdot {w_{s - ref}} \cdot {s_{(n - 1) - ref}} - {\rm{2}} \cdot {w_{end - s}} \cdot {s_{end }}}\\- 2 \cdot {w_{ds - ref}} \cdot {\dot s_{ref}}\\ \vdots \\- 2 \cdot {w_{ds - ref}} \cdot {\dot s_{ref}}\\{ - {\rm{2}} \cdot {w_{end - ds}} \cdot {\ddot s_{end}}}- 2 \cdot {w_{ds - ref}} \cdot {\dot s_{ref}}\\0\\ \vdots \\0\\{ - {\rm{2}} \cdot {w_{end - dds}} \cdot {\ddot s_{end }}}\end{array}} \right] q= −2⋅ws−ref⋅s0−ref⋮−2⋅ws−ref⋅s(n−2)−ref−2⋅ws−ref⋅s(n−1)−ref−2⋅wend−s⋅send−2⋅wds−ref⋅s˙ref⋮−2⋅wds−ref⋅s˙ref−2⋅wend−ds⋅s¨end−2⋅wds−ref⋅s˙ref0⋮0−2⋅wend−dds⋅s¨end
void PiecewiseJerkSpeedProblem::CalculateOffset(std::vector<c_float>* q) {CHECK_NOTNULL(q);const int n = static_cast<int>(num_of_knots_);const int kNumParam = 3 * n;q->resize(kNumParam);for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {if (has_x_ref_) {q->at(i) += -2.0 * weight_x_ref_ * x_ref_[i] / scale_factor_[0];}if (has_dx_ref_) {q->at(n + i) += -2.0 * weight_dx_ref_ * dx_ref_ / scale_factor_[1];}}if (has_end_state_ref_) {q->at(n - 1) +=-2.0 * weight_end_state_[0] * end_state_ref_[0] / scale_factor_[0];q->at(2 * n - 1) +=-2.0 * weight_end_state_[1] * end_state_ref_[1] / scale_factor_[1];q->at(3 * n - 1) +=-2.0 * weight_end_state_[2] * end_state_ref_[2] / scale_factor_[2];}
}
设定OSQP求解参数
OSQPSettings* PiecewiseJerkSpeedProblem::SolverDefaultSettings() {// Define Solver default settingsOSQPSettings* settings =reinterpret_cast<OSQPSettings*>(c_malloc(sizeof(OSQPSettings)));osqp_set_default_settings(settings);settings->eps_abs = 1e-4;settings->eps_rel = 1e-4;settings->eps_prim_inf = 1e-5;settings->eps_dual_inf = 1e-5;settings->polish = true;settings->verbose = FLAGS_enable_osqp_debug;settings->scaled_termination = true;return settings;
}
Process
Process便是基于二次规划的速度优化算法的主流程了,主要包含以下步骤:
- 判断是否抵达终点,如果抵达终点,直接return。
- 检查路径是否为空
- 设置相关参数
- 更新STBoundary
- 更新速度边界和参考s
- 速度优化
- 输出
输入:
const PathData& path_data,const SpeedData& speed_data,const common::TrajectoryPoint& init_point.
输出:
得到最优的速度,信息包括 o p t _ s , o p t _ d s , o p t _ d d s opt\_s,opt\_ds,opt\_dds opt_s,opt_ds,opt_dds。在Process函数中最终结果保存到了speed_data中。
设置相关参数
StGraphData& st_graph_data = *reference_line_info_->mutable_st_graph_data();const auto& veh_param =common::VehicleConfigHelper::GetConfig().vehicle_param();// 起始点(s,v,a)std::array<double, 3> init_s = {0.0, st_graph_data.init_point().v(),st_graph_data.init_point().a()};double delta_t = 0.1;double total_length = st_graph_data.path_length();double total_time = st_graph_data.total_time_by_conf();int num_of_knots = static_cast<int>(total_time / delta_t) + 1;// 分段加加速度速度优化算法PiecewiseJerkSpeedProblem piecewise_jerk_problem(num_of_knots, delta_t,init_s);// 设置相关参数const auto& config = config_.piecewise_jerk_speed_optimizer_config();piecewise_jerk_problem.set_weight_ddx(config.acc_weight());piecewise_jerk_problem.set_weight_dddx(config.jerk_weight());piecewise_jerk_problem.set_x_bounds(0.0, total_length);piecewise_jerk_problem.set_dx_bounds(0.0, std::fmax(FLAGS_planning_upper_speed_limit,st_graph_data.init_point().v()));piecewise_jerk_problem.set_ddx_bounds(veh_param.max_deceleration(),veh_param.max_acceleration());piecewise_jerk_problem.set_dddx_bound(FLAGS_longitudinal_jerk_lower_bound,FLAGS_longitudinal_jerk_upper_bound);piecewise_jerk_problem.set_dx_ref(config.ref_v_weight(),reference_line_info_->GetCruiseSpeed());
这部分需要注意一下:
可以看到,在速度规划方面, s s s的约束为 0 ≤ s ≤ p a t h l e n g t h 0\leq s \leq pathlength 0≤s≤pathlength,此时还未考虑ST boundary; s ˙ \dot s s˙的约束为 0 ≤ s ˙ ≤ v m a x 0\leq \dot s \leq v_{max} 0≤s˙≤vmax, v m a x v_{max} vmax选出FLAGS_planning_upper_speed_limit和起始点速度之中最大的一个; s ¨ \ddot s s¨的约束为 a d e c − m a x ≤ s ¨ ≤ a a c c − m a x a_{dec-max}\leq \ddot s \leq a_{acc-max} adec−max≤s¨≤aacc−max,即在最大减速度和最大加速度范围内; s ′ ′ ′ s^{'''} s′′′的约束为 s l b ′ ′ ′ ≤ s ′ ′ ′ ≤ s u b ′ ′ ′ s^{'''}_{lb}\leq s^{'''} \leq s^{'''}_{ub} slb′′′≤s′′′≤sub′′′, j e r k jerk jerk的约束由FLAGS_longitudinal_jerk_lower_bound和FLAGS_longitudinal_jerk_upper_bound两个参数决定; s ˙ r e f \dot s_{ref} s˙ref参考速度取决于当前路径的巡航速度。
更新STBoundary
遍历每个点,根据不同障碍物类型,更新STBoundary 。
// Update STBoundarystd::vector<std::pair<double, double>> s_bounds;for (int i = 0; i < num_of_knots; ++i) {double curr_t = i * delta_t;double s_lower_bound = 0.0;double s_upper_bound = total_length;for (const STBoundary* boundary : st_graph_data.st_boundaries()) {double s_lower = 0.0;double s_upper = 0.0;if (!boundary->GetUnblockSRange(curr_t, &s_upper, &s_lower)) {continue;}switch (boundary->boundary_type()) {case STBoundary::BoundaryType::STOP:case STBoundary::BoundaryType::YIELD:s_upper_bound = std::fmin(s_upper_bound, s_upper);break;case STBoundary::BoundaryType::FOLLOW:// TODO(Hongyi): unify follow buffer on decision sides_upper_bound = std::fmin(s_upper_bound, s_upper - 8.0);break;case STBoundary::BoundaryType::OVERTAKE:s_lower_bound = std::fmax(s_lower_bound, s_lower);break;default:break;}}if (s_lower_bound > s_upper_bound) {const std::string msg ="s_lower_bound larger than s_upper_bound on STGraph";AERROR << msg;speed_data->clear();return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);}s_bounds.emplace_back(s_lower_bound, s_upper_bound);}piecewise_jerk_problem.set_x_bounds(std::move(s_bounds));
其中涉及到这个函数GetUnblockSRange,用途是获取未被阻塞段的s的范围。
bool STBoundary::GetUnblockSRange(const double curr_time, double* s_upper,double* s_lower) const {CHECK_NOTNULL(s_upper);CHECK_NOTNULL(s_lower);// FLAGS_speed_lon_decision_horizon: Longitudinal horizon for speed decision making (meter) 200m;*s_upper = FLAGS_speed_lon_decision_horizon;*s_lower = 0.0;// 若不在boundary的范围内,说明未被阻塞if (curr_time < min_t_ || curr_time > max_t_) {return true;}size_t left = 0;size_t right = 0;// Given time t, find a segment denoted by left and right idx, that contains the time t. // - If t is less than all or larger than all, return false.if (!GetIndexRange(lower_points_, curr_time, &left, &right)) {AERROR << "Fail to get index range.";return false;}if (curr_time > upper_points_[right].t()) {return true;}// 求出curr_time在segment中所占比例const double r =(left == right? 0.0: (curr_time - upper_points_[left].t()) /(upper_points_[right].t() - upper_points_[left].t()));// 线性插值double upper_cross_s =upper_points_[left].s() +r * (upper_points_[right].s() - upper_points_[left].s());double lower_cross_s =lower_points_[left].s() +r * (lower_points_[right].s() - lower_points_[left].s());// 根据障碍物类型,更新s_upper或s_lowerif (boundary_type_ == BoundaryType::STOP ||boundary_type_ == BoundaryType::YIELD ||boundary_type_ == BoundaryType::FOLLOW) {*s_upper = lower_cross_s;} else if (boundary_type_ == BoundaryType::OVERTAKE) {*s_lower = std::fmax(*s_lower, upper_cross_s);} else {ADEBUG << "boundary_type is not supported. boundary_type: "<< static_cast<int>(boundary_type_);return false;}return true;
}
更新速度边界和参考s
// Update SpeedBoundary and ref_sstd::vector<double> x_ref;std::vector<double> penalty_dx;std::vector<std::pair<double, double>> s_dot_bounds;const SpeedLimit& speed_limit = st_graph_data.speed_limit();for (int i = 0; i < num_of_knots; ++i) {double curr_t = i * delta_t;// get path_sSpeedPoint sp;reference_speed_data.EvaluateByTime(curr_t, &sp);const double path_s = sp.s();x_ref.emplace_back(path_s);// get curvaturePathPoint path_point = path_data.GetPathPointWithPathS(path_s);penalty_dx.push_back(std::fabs(path_point.kappa()) *config.kappa_penalty_weight());// get v_upper_boundconst double v_lower_bound = 0.0;double v_upper_bound = FLAGS_planning_upper_speed_limit;v_upper_bound = speed_limit.GetSpeedLimitByS(path_s);s_dot_bounds.emplace_back(v_lower_bound, std::fmax(v_upper_bound, 0.0));}piecewise_jerk_problem.set_x_ref(config.ref_s_weight(), std::move(x_ref));piecewise_jerk_problem.set_penalty_dx(penalty_dx);piecewise_jerk_problem.set_dx_bounds(std::move(s_dot_bounds));
速度优化
// Solve the problemif (!piecewise_jerk_problem.Optimize()) {const std::string msg = "Piecewise jerk speed optimizer failed!";AERROR << msg;speed_data->clear();return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);}
输出
// Extract outputconst std::vector<double>& s = piecewise_jerk_problem.opt_x();const std::vector<double>& ds = piecewise_jerk_problem.opt_dx();const std::vector<double>& dds = piecewise_jerk_problem.opt_ddx();for (int i = 0; i < num_of_knots; ++i) {ADEBUG << "For t[" << i * delta_t << "], s = " << s[i] << ", v = " << ds[i]<< ", a = " << dds[i];}speed_data->clear();speed_data->AppendSpeedPoint(s[0], 0.0, ds[0], dds[0], 0.0);for (int i = 1; i < num_of_knots; ++i) {// Avoid the very last points when already stoppedif (ds[i] <= 0.0) {break;}speed_data->AppendSpeedPoint(s[i], delta_t * i, ds[i], dds[i],(dds[i] - dds[i - 1]) / delta_t);}SpeedProfileGenerator::FillEnoughSpeedPoints(speed_data);RecordDebugInfo(*speed_data, st_graph_data.mutable_st_graph_debug());return Status::OK();
相关文章:

【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PIECEWISE_JERK_SPEED_OPTIMIZER
文章目录 TASK系列解析文章前言PIECEWISE_JERK_SPEED_OPTIMIZER功能简介PIECEWISE_JERK_SPEED_OPTIMIZER相关配置PIECEWISE_JERK_SPEED_OPTIMIZER流程QP问题的标准类型定义:优化变量设计目标函数约束条件相关矩阵二次项系数矩阵 H H H一次项系数向量 q q q设定OSQP求…...

CNI、CSI 和 CRI在 Docker 中的角色和作用
摘要 CNI(Container Network Interface): CNI 是用于容器网络的接口标准,它定义了容器和网络插件之间的通信协议。CNI 的主要作用是为容器创建和管理网络接口。当创建一个容器时,CNI 插件会被调用来为容器创建一个网络…...

「Docker」M1 Pro 打包docker image问题合集
运行docker 遇到 The requested images platform (linux/arm64/v8) does not match the detected host platform (linux/amd64/v4) and no specific platform was requested 说明打包的镜像没有 linux/amd64 解决方案:重新打包镜像 docker buildx build --platfor…...
Android发布依赖到 Jitpack
前言 我们在日常开发中,经常会用到第三方开源的库文件,有的来自JCenter,Maven Central,google等。但是随着JCenter的弃用,现在用的最多的还是Maven Central,google。今天我们就自己亲自发布一个依赖。 现…...
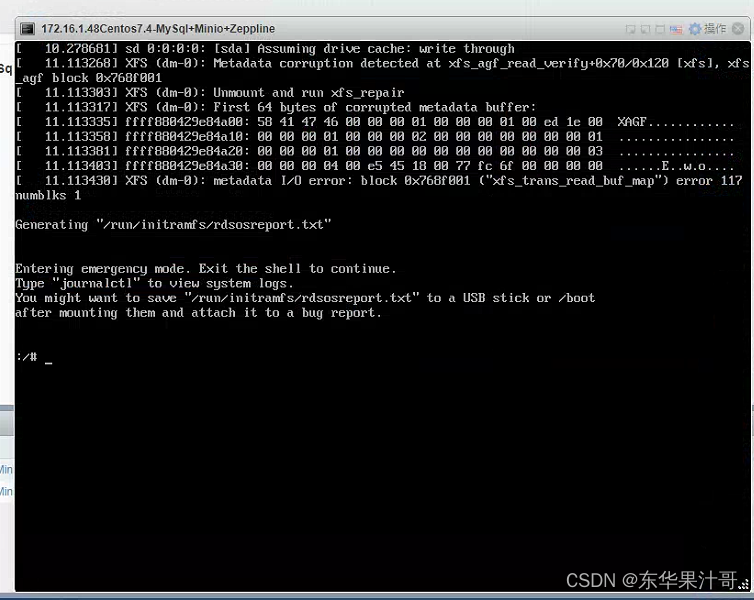
【虚拟机开不了】linux、centOS虚拟机出现entering emergency mode解决方案
按他的操作输入journalctl之后输入shiftg到日志最后查看报错发现是xfs(dm-0有问题) xfs_repair -v -L /dev/dm-0 reboot解决问题...

嘉泰实业举行“互联网金融知识社区”“安全理财风险讲座”等活动
每一次暖心的沟通都是一次公益,真诚不会因为它的渺小而被忽略;每一声问候都是一次公益,善意不会因为它的普通而被埋没。熟悉嘉泰实业的人都知道,这家企业不但擅长在金融理财领域里面呼风唤雨,同时也非常擅长在公益事业当中践行,属于企业的责任心,为更多有困难的群体带来大爱的传…...

《C++设计模式》——结构型
前言 结构模式可以让我们把很多小的东西通过结构模式组合起来成为一个打的结构,但是又不影响各自的独立性,尽可能减少各组件之间的耦合。 Adapter Class/Object(适配器) Bridge(桥接) Composite(组合) Decorator(装饰) 动态…...
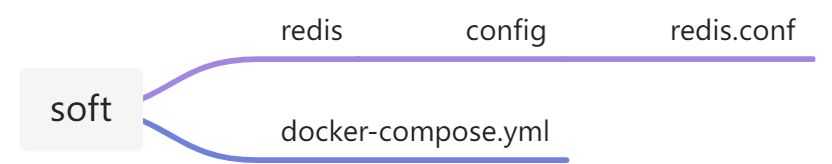
docker-compose安装redis
基于docker-compose快速安装redis 目录 一、目录结构 1、docker-compose.yml 2、redis.conf 二、连接使用 一、目录结构 1、docker-compose.yml version: 3 services:redis:image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/zhengqing/redis:6.0.8 # 镜像red…...
机器学习基础之《分类算法(6)—决策树》
一、决策树 1、认识决策树 决策树思想的来源非常朴素,程序设计中的条件分支结构就是if-else结构,最早的决策树就是利用这类结构分割数据的一种分类学习方法 2、一个对话的例子 想一想这个女生为什么把年龄放在最上面判断!!&…...

2023国赛数学建模C题思路模型 - 蔬菜类商品的自动定价与补货决策
# 1 赛题 在生鲜商超中,一般蔬菜类商品的保鲜期都比较短,且品相随销售时间的增加而变差, 大部分品种如当日未售出,隔日就无法再售。因此, 商超通常会根据各商品的历史销售和需 求情况每天进行补货。 由于商超销售的蔬菜…...

【Docker】Docker网络与存储(三)
前言: Docker网络与存储的作用是实现容器之间的通信和数据持久化,以便有效地部署、扩展和管理容器化应用程序。 文章目录 Docker网络桥接网络容器之间的通信 覆盖网络创建一个覆盖网络 Docker存储卷 总结 Docker网络 Docker网络是在容器之间提供通信的机…...

python面向对象的一个简单实例
#发文福利# #!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*-students {id001: {name: serena, age: 18, address: beijing},id002: {name: fanbingbing, age: 42, address: anhui},id003: {name: kahn, age: 20, address: shanghai}}class Student:def __init__(self, xid, na…...

微信小程序通过npm引入tdesign包进行构建的时候报错
问题 在通过npm 引入 tdesign时:https://tdesign.tencent.com/miniprogram/getting-started 通过微信小程序IDE进行npm构建的时候出现:无法构建,应该怎么办? 解决方法: 1 输入: npm init -y命令 2 重新点…...

三次握手四次挥手
TCP协议是一种面向连接的、可靠的、基于字节流的运输层通信协议。它通过三次握手来建立连接,通过四次挥手来断开连接。 三次握手 所谓三次握手,是指建立一个TCP连接时,需要客户端和服务器总共发送3个报文。三次握手的目的是连接服务器指定端…...

Redis持久化、主从与哨兵架构详解
Redis持久化 RDB快照(snapshot) 在默认情况下, Redis 将内存数据库快照保存在名字为 dump.rdb 的二进制文件中。 你可以对 Redis 进行设置, 让它在“ N 秒内数据集至少有 M 个改动”这一条件被满足时, 自动保存一次数…...

SQLITE_BUSY 是指 SQLite 数据库返回的错误码,表示数据库正在被其他进程或线程使用,因此当前操作无法完成。
SQLITE_BUSY 当多个进程或线程同时尝试对同一个 SQLite 数据库进行写操作时,就可能出现 SQLITE_BUSY 错误。这是为了确保数据库的数据完整性和一致性而设计的并发控制机制。 如果你在使用 SQLite 时遇到 SQLITE_BUSY 错误,可以考虑以下解决方法&#x…...

matlab求解方程组-求解过程中限制解的取值范围
文章目录 问题背景代码my_fun.mmain.m 结果展示:不加入F(4)加入F(4) 问题背景 求解方程组的时候,对某些未知数的求解结果的取值范围有要求。例如在某些物理问题求解中,要求待求解量大于0。 代码 一共两个文件: my_fun.m main.mmy_fun.m function Fm…...

【正则表达式】正则表达式常见匹配模式
目录 常见匹配模式re.match 从字符串的起始位置匹配一个模式泛匹配匹配目标贪婪匹配非贪婪匹配匹配模式转义 re.search 扫描整个字符串并返回第一个成功的匹配re.findall 以列表形式返回全部能匹配的子串re.sub 替换字符串中每一个匹配的子串后返回替换后的字符串 re.compile 将…...

Docker搭建RK3568建模环境
推荐:Ubuntu 20.04 版本 Docker加速 # 编辑 Docker 配置文件 $ sudo vim /etc/docker/daemon.json# 加入以下配置项 {"registry-mirrors": ["https://dockerproxy.com","https://hub-mirror.c.163.com","https://mirror.baidu…...
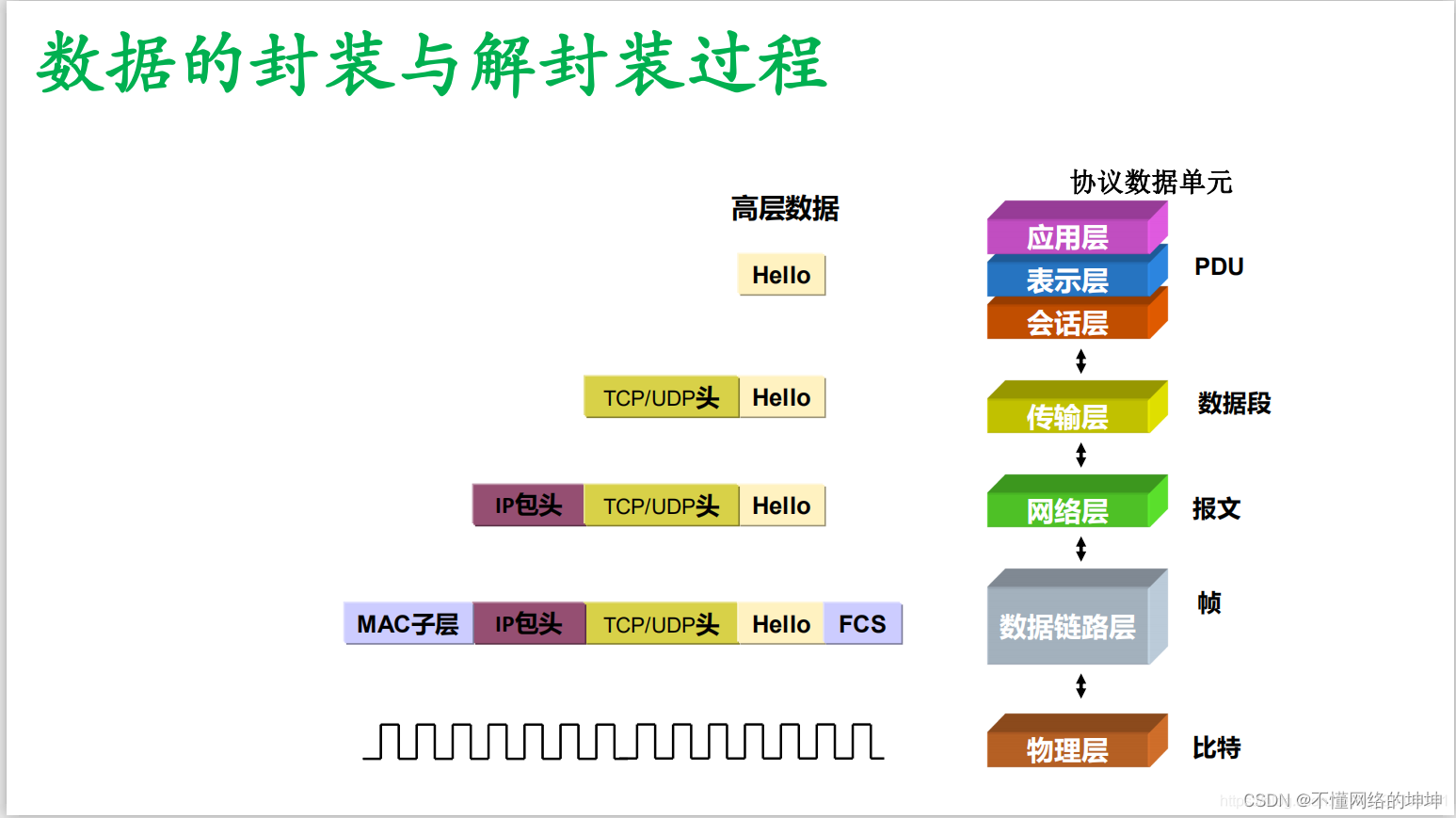
TCP/IP基础
前言: TCP/IP协议是计算机网络领域中最基本的协议之一,它被广泛应用于互联网和局域网中,实现了不同类型、不同厂家、运行不同操作系统的计算机之间的相互通信。本文将介绍TCP/IP协议栈的层次结构、各层功能以及数据封装过程,帮助您…...
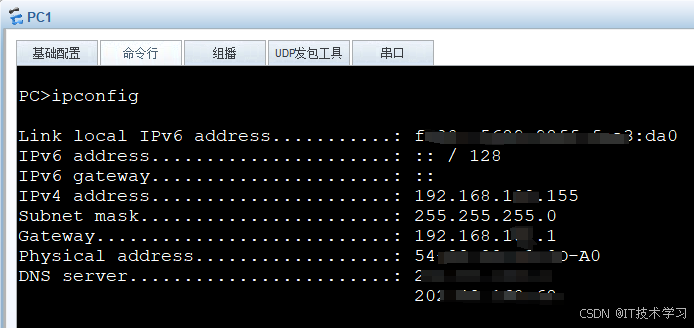
eNSP-Cloud(实现本地电脑与eNSP内设备之间通信)
说明: 想象一下,你正在用eNSP搭建一个虚拟的网络世界,里面有虚拟的路由器、交换机、电脑(PC)等等。这些设备都在你的电脑里面“运行”,它们之间可以互相通信,就像一个封闭的小王国。 但是&#…...
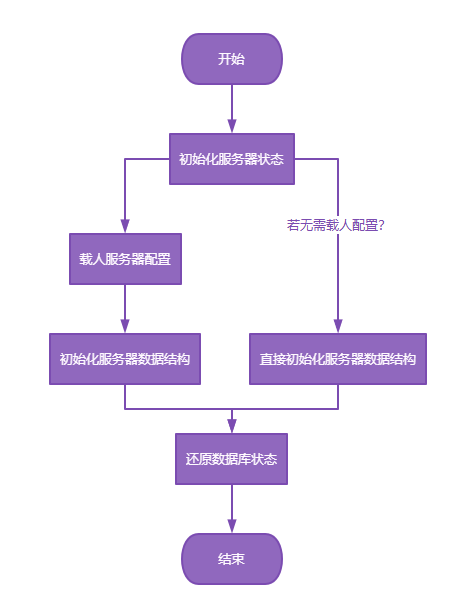
【Redis技术进阶之路】「原理分析系列开篇」分析客户端和服务端网络诵信交互实现(服务端执行命令请求的过程 - 初始化服务器)
服务端执行命令请求的过程 【专栏简介】【技术大纲】【专栏目标】【目标人群】1. Redis爱好者与社区成员2. 后端开发和系统架构师3. 计算机专业的本科生及研究生 初始化服务器1. 初始化服务器状态结构初始化RedisServer变量 2. 加载相关系统配置和用户配置参数定制化配置参数案…...
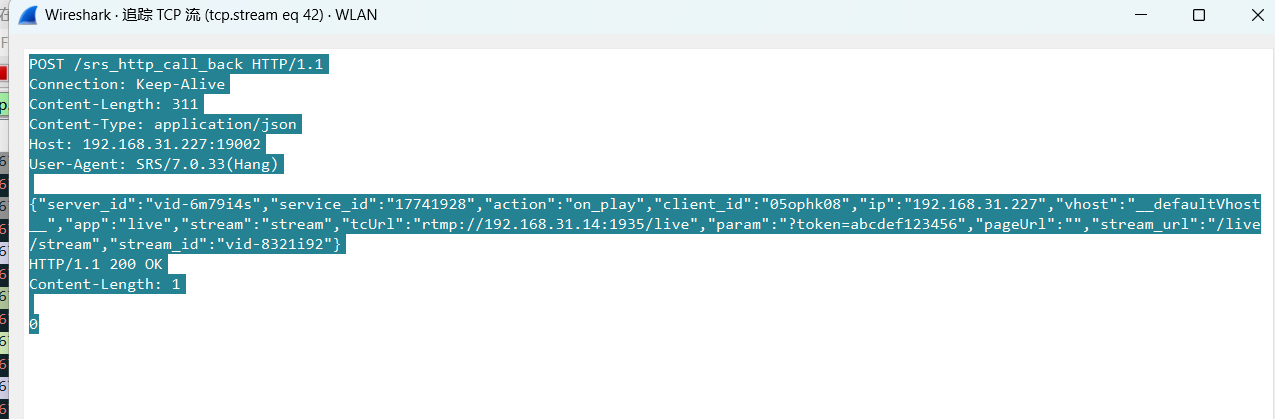
srs linux
下载编译运行 git clone https:///ossrs/srs.git ./configure --h265on make 编译完成后即可启动SRS # 启动 ./objs/srs -c conf/srs.conf # 查看日志 tail -n 30 -f ./objs/srs.log 开放端口 默认RTMP接收推流端口是1935,SRS管理页面端口是8080,可…...
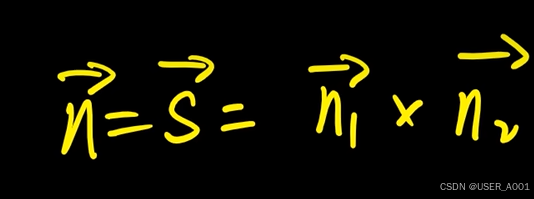
高等数学(下)题型笔记(八)空间解析几何与向量代数
目录 0 前言 1 向量的点乘 1.1 基本公式 1.2 例题 2 向量的叉乘 2.1 基础知识 2.2 例题 3 空间平面方程 3.1 基础知识 3.2 例题 4 空间直线方程 4.1 基础知识 4.2 例题 5 旋转曲面及其方程 5.1 基础知识 5.2 例题 6 空间曲面的法线与切平面 6.1 基础知识 6.2…...

ios苹果系统,js 滑动屏幕、锚定无效
现象:window.addEventListener监听touch无效,划不动屏幕,但是代码逻辑都有执行到。 scrollIntoView也无效。 原因:这是因为 iOS 的触摸事件处理机制和 touch-action: none 的设置有关。ios有太多得交互动作,从而会影响…...

力扣-35.搜索插入位置
题目描述 给定一个排序数组和一个目标值,在数组中找到目标值,并返回其索引。如果目标值不存在于数组中,返回它将会被按顺序插入的位置。 请必须使用时间复杂度为 O(log n) 的算法。 class Solution {public int searchInsert(int[] nums, …...

在web-view 加载的本地及远程HTML中调用uniapp的API及网页和vue页面是如何通讯的?
uni-app 中 Web-view 与 Vue 页面的通讯机制详解 一、Web-view 简介 Web-view 是 uni-app 提供的一个重要组件,用于在原生应用中加载 HTML 页面: 支持加载本地 HTML 文件支持加载远程 HTML 页面实现 Web 与原生的双向通讯可用于嵌入第三方网页或 H5 应…...

A2A JS SDK 完整教程:快速入门指南
目录 什么是 A2A JS SDK?A2A JS 安装与设置A2A JS 核心概念创建你的第一个 A2A JS 代理A2A JS 服务端开发A2A JS 客户端使用A2A JS 高级特性A2A JS 最佳实践A2A JS 故障排除 什么是 A2A JS SDK? A2A JS SDK 是一个专为 JavaScript/TypeScript 开发者设计的强大库ÿ…...

LangChain知识库管理后端接口:数据库操作详解—— 构建本地知识库系统的基础《二》
这段 Python 代码是一个完整的 知识库数据库操作模块,用于对本地知识库系统中的知识库进行增删改查(CRUD)操作。它基于 SQLAlchemy ORM 框架 和一个自定义的装饰器 with_session 实现数据库会话管理。 📘 一、整体功能概述 该模块…...
Unity UGUI Button事件流程
场景结构 测试代码 public class TestBtn : MonoBehaviour {void Start(){var btn GetComponent<Button>();btn.onClick.AddListener(OnClick);}private void OnClick(){Debug.Log("666");}}当添加事件时 // 实例化一个ButtonClickedEvent的事件 [Formerl…...
