ESIM实战文本匹配
引言
今天我们来实现ESIM文本匹配,这是一个典型的交互型文本匹配方式,也是近期第一个测试集准确率超过80%的模型。
我们来看下是如何实现的。
模型架构
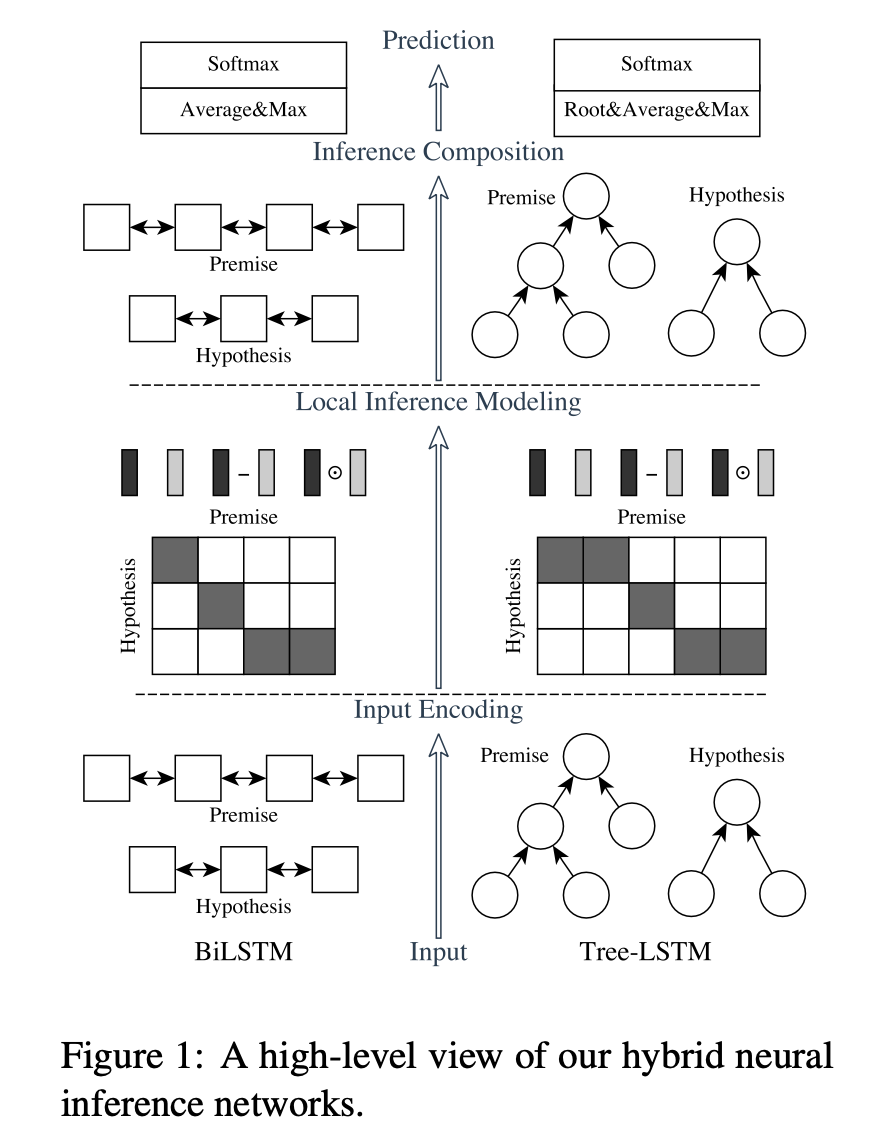
我们主要实现左边的ESIM网络。
从下往上看,分别是
- 输入编码层(Input Ecoding)
对前提和假设进行编码
把语句中的单词转换为词向量,得到一个向量序列
把两句话的向量序列分别送入各自的Bi-LSTM网络进行语义特征抽取 - 局部推理建模层(Local Inference Modeling)
就是注意力层
通过注意力层捕获LSTM输出向量间的局部特征
然后通过元素级方法构造了一些特征 - 推理组合层(Inference Composition)
和输入编码层一样,也是Bi-LSTM
在捕获了文本间的注意力特征后,进一步做的融合/提取语义特征工作 - 预测层(Prediction)
拼接平均池化和最大池化后得到的向量
接Softmax进行分类
模型实现
class ESIM(nn.Module):def __init__(self,vocab_size: int,embedding_size: int,hidden_size: int,num_classes: int,lstm_dropout: float = 0.1,dropout: float = 0.5,) -> None:"""_summary_Args:vocab_size (int): the size of the Vocabularyembedding_size (int): the size of each embedding vectorhidden_size (int): the size of the hidden layernum_classes (int): the output sizelstm_dropout (float, optional): dropout ratio in lstm layer. Defaults to 0.1.dropout (float, optional): dropout ratio in linear layer. Defaults to 0.5."""super().__init__()self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_size)# lstm for input embeddingself.lstm_a = nn.LSTM(hidden_size,hidden_size,batch_first=True,bidirectional=True,dropout=lstm_dropout,)self.lstm_b = nn.LSTM(hidden_size,hidden_size,batch_first=True,bidirectional=True,dropout=lstm_dropout,)
首先有一个嵌入层,然后对于输入的两个句子分别有一个Bi-LSTM。
然后定义推理组合层:
# lstm for augment inference vectorself.lstm_v_a = nn.LSTM(8 * hidden_size,hidden_size,batch_first=True,bidirectional=True,dropout=lstm_dropout,)self.lstm_v_b = nn.LSTM(8 * hidden_size,hidden_size,batch_first=True,bidirectional=True,dropout=lstm_dropout,)完了就是最后的预测层,这里是一个多层前馈网络:
self.predict = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(8 * hidden_size, 2 * hidden_size),nn.ReLU(),nn.Dropout(dropout),nn.Linear(2 * hidden_size, hidden_size),nn.ReLU(),nn.Dropout(dropout),nn.Linear(hidden_size, num_classes),)
初始化函数的完整实现为:
class ESIM(nn.Module):def __init__(self,vocab_size: int,embedding_size: int,hidden_size: int,num_classes: int,lstm_dropout: float = 0.1,dropout: float = 0.5,) -> None:"""_summary_Args:vocab_size (int): the size of the Vocabularyembedding_size (int): the size of each embedding vectorhidden_size (int): the size of the hidden layernum_classes (int): the output sizelstm_dropout (float, optional): dropout ratio in lstm layer. Defaults to 0.1.dropout (float, optional): dropout ratio in linear layer. Defaults to 0.5."""super().__init__()self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_size)# lstm for input embeddingself.lstm_a = nn.LSTM(hidden_size,hidden_size,batch_first=True,bidirectional=True,dropout=lstm_dropout,)self.lstm_b = nn.LSTM(hidden_size,hidden_size,batch_first=True,bidirectional=True,dropout=lstm_dropout,)# lstm for augment inference vectorself.lstm_v_a = nn.LSTM(8 * hidden_size,hidden_size,batch_first=True,bidirectional=True,dropout=lstm_dropout,)self.lstm_v_b = nn.LSTM(8 * hidden_size,hidden_size,batch_first=True,bidirectional=True,dropout=lstm_dropout,)self.predict = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(8 * hidden_size, 2 * hidden_size),nn.ReLU(),nn.Dropout(dropout),nn.Linear(2 * hidden_size, hidden_size),nn.ReLU(),nn.Dropout(dropout),nn.Linear(hidden_size, num_classes),)
使用ReLU激活函数,在激活函数后都有一个Dropout。
重点是forward方法:
def forward(self, a: torch.Tensor, b: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:"""Args:a (torch.Tensor): input sequence a with shape (batch_size, a_seq_len)b (torch.Tensor): input sequence b with shape (batch_size, b_seq_len)Returns:torch.Tensor:"""# a (batch_size, a_seq_len, embedding_size)a_embed = self.embedding(a)# b (batch_size, b_seq_len, embedding_size)b_embed = self.embedding(b)# a_bar (batch_size, a_seq_len, 2 * hidden_size)a_bar, _ = self.lstm_a(a_embed)# b_bar (batch_size, b_seq_len, 2 * hidden_size)b_bar, _ = self.lstm_b(b_embed)# score (batch_size, a_seq_len, b_seq_len)score = torch.matmul(a_bar, b_bar.permute(0, 2, 1))# softmax (batch_size, a_seq_len, b_seq_len) x (batch_size, b_seq_len, 2 * hidden_size)# a_tilde (batch_size, a_seq_len, 2 * hidden_size)a_tilde = torch.matmul(torch.softmax(score, dim=2), b_bar)# permute (batch_size, b_seq_len, a_seq_len) x (batch_size, a_seq_len, 2 * hidden_size)# b_tilde (batch_size, b_seq_len, 2 * hidden_size)b_tilde = torch.matmul(torch.softmax(score, dim=1).permute(0, 2, 1), a_bar)# m_a (batch_size, a_seq_len, 8 * hidden_size)m_a = torch.cat([a_bar, a_tilde, a_bar - a_tilde, a_bar * a_tilde], dim=-1)# m_b (batch_size, b_seq_len, 8 * hidden_size)m_b = torch.cat([b_bar, b_tilde, b_bar - b_tilde, b_bar * b_tilde], dim=-1)# v_a (batch_size, a_seq_len, 2 * hidden_size)v_a, _ = self.lstm_v_a(m_a)# v_b (batch_size, b_seq_len, 2 * hidden_size)v_b, _ = self.lstm_v_b(m_b)# (batch_size, 2 * hidden_size)avg_a = torch.mean(v_a, dim=1)avg_b = torch.mean(v_b, dim=1)max_a, _ = torch.max(v_a, dim=1)max_b, _ = torch.max(v_b, dim=1)# (batch_size, 8 * hidden_size)v = torch.cat([avg_a, max_a, avg_b, max_b], dim=-1)return self.predict(v)标注出每个向量的维度就挺好理解的。
首先分别为两个输入得到嵌入向量;
其次喂给各自的LSTM层,得到每个时间步的输出,注意由于是双向LSTM,因此最后的维度是2 * hidden_size;
接着对它两计算注意力分数score (batch_size, a_seq_len, b_seq_len);
然后分别计算a对b和b对a的注意力,这里要注意softmax中dim的维度。在计算a的注意力输出时,是利用b每个输入的加权和,所以softmax(score, dim=2)在b_seq_len维度上间求和;
然后是增强的局部推理,差、乘各种拼接,得到一个8 * hidden_size的维度,所以lstm_v_a的输入维度是8 * hidden_size;
接下来就是对得到的a和b进行平均池化和最大池化,然后把它们拼接起来,也得到了8 * hidden_size的一个维度;
最后经过我们的预测层,多层前馈网络,进行了一些非线性变换后变成了输出维度大小,比较最后一个维度的值哪个大当成对哪个类的一个预测;
数据准备
和前面几篇几乎一样,这里直接贴代码:
from collections import defaultdict
from tqdm import tqdm
import numpy as np
import json
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
import pandas as pd
from typing import TupleUNK_TOKEN = "<UNK>"
PAD_TOKEN = "<PAD>"class Vocabulary:"""Class to process text and extract vocabulary for mapping"""def __init__(self, token_to_idx: dict = None, tokens: list[str] = None) -> None:"""Args:token_to_idx (dict, optional): a pre-existing map of tokens to indices. Defaults to None.tokens (list[str], optional): a list of unique tokens with no duplicates. Defaults to None."""assert any([tokens, token_to_idx]), "At least one of these parameters should be set as not None."if token_to_idx:self._token_to_idx = token_to_idxelse:self._token_to_idx = {}if PAD_TOKEN not in tokens:tokens = [PAD_TOKEN] + tokensfor idx, token in enumerate(tokens):self._token_to_idx[token] = idxself._idx_to_token = {idx: token for token, idx in self._token_to_idx.items()}self.unk_index = self._token_to_idx[UNK_TOKEN]self.pad_index = self._token_to_idx[PAD_TOKEN]@classmethoddef build(cls,sentences: list[list[str]],min_freq: int = 2,reserved_tokens: list[str] = None,) -> "Vocabulary":"""Construct the Vocabulary from sentencesArgs:sentences (list[list[str]]): a list of tokenized sequencesmin_freq (int, optional): the minimum word frequency to be saved. Defaults to 2.reserved_tokens (list[str], optional): the reserved tokens to add into the Vocabulary. Defaults to None.Returns:Vocabulary: a Vocubulary instane"""token_freqs = defaultdict(int)for sentence in tqdm(sentences):for token in sentence:token_freqs[token] += 1unique_tokens = (reserved_tokens if reserved_tokens else []) + [UNK_TOKEN]unique_tokens += [tokenfor token, freq in token_freqs.items()if freq >= min_freq and token != UNK_TOKEN]return cls(tokens=unique_tokens)def __len__(self) -> int:return len(self._idx_to_token)def __getitem__(self, tokens: list[str] | str) -> list[int] | int:"""Retrieve the indices associated with the tokens or the index with the single tokenArgs:tokens (list[str] | str): a list of tokens or single tokenReturns:list[int] | int: the indices or the single index"""if not isinstance(tokens, (list, tuple)):return self._token_to_idx.get(tokens, self.unk_index)return [self.__getitem__(token) for token in tokens]def lookup_token(self, indices: list[int] | int) -> list[str] | str:"""Retrive the tokens associated with the indices or the token with the single indexArgs:indices (list[int] | int): a list of index or single indexReturns:list[str] | str: the corresponding tokens (or token)"""if not isinstance(indices, (list, tuple)):return self._idx_to_token[indices]return [self._idx_to_token[index] for index in indices]def to_serializable(self) -> dict:"""Returns a dictionary that can be serialized"""return {"token_to_idx": self._token_to_idx}@classmethoddef from_serializable(cls, contents: dict) -> "Vocabulary":"""Instantiates the Vocabulary from a serialized dictionaryArgs:contents (dict): a dictionary generated by `to_serializable`Returns:Vocabulary: the Vocabulary instance"""return cls(**contents)def __repr__(self):return f"<Vocabulary(size={len(self)})>"class TMVectorizer:"""The Vectorizer which vectorizes the Vocabulary"""def __init__(self, vocab: Vocabulary, max_len: int) -> None:"""Args:vocab (Vocabulary): maps characters to integersmax_len (int): the max length of the sequence in the dataset"""self.vocab = vocabself.max_len = max_lendef _vectorize(self, indices: list[int], vector_length: int = -1, padding_index: int = 0) -> np.ndarray:"""Vectorize the provided indicesArgs:indices (list[int]): a list of integers that represent a sequencevector_length (int, optional): an arugment for forcing the length of index vector. Defaults to -1.padding_index (int, optional): the padding index to use. Defaults to 0.Returns:np.ndarray: the vectorized index array"""if vector_length <= 0:vector_length = len(indices)vector = np.zeros(vector_length, dtype=np.int64)if len(indices) > vector_length:vector[:] = indices[:vector_length]else:vector[: len(indices)] = indicesvector[len(indices) :] = padding_indexreturn vectordef _get_indices(self, sentence: list[str]) -> list[int]:"""Return the vectorized sentenceArgs:sentence (list[str]): list of tokensReturns:indices (list[int]): list of integers representing the sentence"""return [self.vocab[token] for token in sentence]def vectorize(self, sentence: list[str], use_dataset_max_length: bool = True) -> np.ndarray:"""Return the vectorized sequenceArgs:sentence (list[str]): raw sentence from the datasetuse_dataset_max_length (bool): whether to use the global max vector lengthReturns:the vectorized sequence with padding"""vector_length = -1if use_dataset_max_length:vector_length = self.max_lenindices = self._get_indices(sentence)vector = self._vectorize(indices, vector_length=vector_length, padding_index=self.vocab.pad_index)return vector@classmethoddef from_serializable(cls, contents: dict) -> "TMVectorizer":"""Instantiates the TMVectorizer from a serialized dictionaryArgs:contents (dict): a dictionary generated by `to_serializable`Returns:TMVectorizer:"""vocab = Vocabulary.from_serializable(contents["vocab"])max_len = contents["max_len"]return cls(vocab=vocab, max_len=max_len)def to_serializable(self) -> dict:"""Returns a dictionary that can be serializedReturns:dict: a dict contains Vocabulary instance and max_len attribute"""return {"vocab": self.vocab.to_serializable(), "max_len": self.max_len}def save_vectorizer(self, filepath: str) -> None:"""Dump this TMVectorizer instance to fileArgs:filepath (str): the path to store the file"""with open(filepath, "w") as f:json.dump(self.to_serializable(), f)@classmethoddef load_vectorizer(cls, filepath: str) -> "TMVectorizer":"""Load TMVectorizer from a fileArgs:filepath (str): the path stored the fileReturns:TMVectorizer:"""with open(filepath) as f:return TMVectorizer.from_serializable(json.load(f))class TMDataset(Dataset):"""Dataset for text matching"""def __init__(self, text_df: pd.DataFrame, vectorizer: TMVectorizer) -> None:"""Args:text_df (pd.DataFrame): a DataFrame which contains the processed data examplesvectorizer (TMVectorizer): a TMVectorizer instance"""self.text_df = text_dfself._vectorizer = vectorizerdef __getitem__(self, index: int) -> Tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray, int]:row = self.text_df.iloc[index]return (self._vectorizer.vectorize(row.sentence1),self._vectorizer.vectorize(row.sentence2),row.label,)def get_vectorizer(self) -> TMVectorizer:return self._vectorizerdef __len__(self) -> int:return len(self.text_df)模型训练
定义辅助函数和指标:
def make_dirs(dirpath):if not os.path.exists(dirpath):os.makedirs(dirpath)def tokenize(sentence: str):return list(jieba.cut(sentence))def build_dataframe_from_csv(dataset_csv: str) -> pd.DataFrame:df = pd.read_csv(dataset_csv,sep="\t",header=None,names=["sentence1", "sentence2", "label"],)df.sentence1 = df.sentence1.apply(tokenize)df.sentence2 = df.sentence2.apply(tokenize)return dfdef metrics(y: torch.Tensor, y_pred: torch.Tensor) -> Tuple[float, float, float, float]:TP = ((y_pred == 1) & (y == 1)).sum().float() # True PositiveTN = ((y_pred == 0) & (y == 0)).sum().float() # True NegativeFN = ((y_pred == 0) & (y == 1)).sum().float() # False NegatvieFP = ((y_pred == 1) & (y == 0)).sum().float() # False Positivep = TP / (TP + FP).clamp(min=1e-8) # Precisionr = TP / (TP + FN).clamp(min=1e-8) # RecallF1 = 2 * r * p / (r + p).clamp(min=1e-8) # F1 scoreacc = (TP + TN) / (TP + TN + FP + FN).clamp(min=1e-8) # Accuraryreturn acc, p, r, F1定义评估函数和训练函数:
def evaluate(data_iter: DataLoader, model: nn.Module
) -> Tuple[float, float, float, float]:y_list, y_pred_list = [], []model.eval()for x1, x2, y in tqdm(data_iter):x1 = x1.to(device).long()x2 = x2.to(device).long()y = torch.LongTensor(y).to(device)output = model(x1, x2)pred = torch.argmax(output, dim=1).long()y_pred_list.append(pred)y_list.append(y)y_pred = torch.cat(y_pred_list, 0)y = torch.cat(y_list, 0)acc, p, r, f1 = metrics(y, y_pred)return acc, p, r, f1def train(data_iter: DataLoader,model: nn.Module,criterion: nn.CrossEntropyLoss,optimizer: torch.optim.Optimizer,print_every: int = 500,verbose=True,
) -> None:model.train()for step, (x1, x2, y) in enumerate(tqdm(data_iter)):x1 = x1.to(device).long()x2 = x2.to(device).long()y = torch.LongTensor(y).to(device)output = model(x1, x2)loss = criterion(output, y)optimizer.zero_grad()loss.backward()optimizer.step()if verbose and (step + 1) % print_every == 0:pred = torch.argmax(output, dim=1).long()acc, p, r, f1 = metrics(y, pred)print(f" TRAIN iter={step+1} loss={loss.item():.6f} accuracy={acc:.3f} precision={p:.3f} recal={r:.3f} f1 score={f1:.4f}")参数定义:
args = Namespace(dataset_csv="text_matching/data/lcqmc/{}.txt",vectorizer_file="vectorizer.json",model_state_file="model.pth",save_dir=f"{os.path.dirname(__file__)}/model_storage",reload_model=False,cuda=True,learning_rate=4e-4,batch_size=128,num_epochs=10,max_len=50,embedding_dim=300,hidden_size=300,num_classes=2,lstm_dropout=0.8,dropout=0.5,min_freq=2,print_every=500,verbose=True,)这个模型非常简单,但效果是非常不错的,可以作为一个很好的baseline。在训练过程中发现对训练集的准确率达到了100%,有点过拟合了,因此最后把lstm的dropout加大到0.8,最后看一下训练效果如何:
make_dirs(args.save_dir)if args.cuda:device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")else:device = torch.device("cpu")print(f"Using device: {device}.")vectorizer_path = os.path.join(args.save_dir, args.vectorizer_file)train_df = build_dataframe_from_csv(args.dataset_csv.format("train"))test_df = build_dataframe_from_csv(args.dataset_csv.format("test"))dev_df = build_dataframe_from_csv(args.dataset_csv.format("dev"))if os.path.exists(vectorizer_path):print("Loading vectorizer file.")vectorizer = TMVectorizer.load_vectorizer(vectorizer_path)args.vocab_size = len(vectorizer.vocab)else:print("Creating a new Vectorizer.")train_sentences = train_df.sentence1.to_list() + train_df.sentence2.to_list()vocab = Vocabulary.build(train_sentences, args.min_freq)args.vocab_size = len(vocab)print(f"Builds vocabulary : {vocab}")vectorizer = TMVectorizer(vocab, args.max_len)vectorizer.save_vectorizer(vectorizer_path)train_dataset = TMDataset(train_df, vectorizer)test_dataset = TMDataset(test_df, vectorizer)dev_dataset = TMDataset(dev_df, vectorizer)train_data_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=True)dev_data_loader = DataLoader(dev_dataset, batch_size=args.batch_size)test_data_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=args.batch_size)print(f"Arguments : {args}")model = ESIM(args.vocab_size,args.embedding_dim,args.hidden_size,args.num_classes,args.lstm_dropout,args.dropout,)print(f"Model: {model}")model_saved_path = os.path.join(args.save_dir, args.model_state_file)if args.reload_model and os.path.exists(model_saved_path):model.load_state_dict(torch.load(args.model_saved_path))print("Reloaded model")else:print("New model")model = model.to(device)optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=args.learning_rate)criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()for epoch in range(args.num_epochs):train(train_data_loader,model,criterion,optimizer,print_every=args.print_every,verbose=args.verbose,)print("Begin evalute on dev set.")with torch.no_grad():acc, p, r, f1 = evaluate(dev_data_loader, model)print(f"EVALUATE [{epoch+1}/{args.num_epochs}] accuracy={acc:.3f} precision={p:.3f} recal={r:.3f} f1 score={f1:.4f}")model.eval()acc, p, r, f1 = evaluate(test_data_loader, model)print(f"TEST accuracy={acc:.3f} precision={p:.3f} recal={r:.3f} f1 score={f1:.4f}")python .\text_matching\esim\train.py
Using device: cuda:0.
Building prefix dict from the default dictionary ...
Loading model from cache C:\Users\ADMINI~1\AppData\Local\Temp\jieba.cache
Loading model cost 0.563 seconds.
Prefix dict has been built successfully.
Loading vectorizer file.
Arguments : Namespace(dataset_csv='text_matching/data/lcqmc/{}.txt', vectorizer_file='vectorizer.json', model_state_file='model.pth', save_dir='D:\\workspace\\nlp-in-action\\text_matching\\esim/model_storage', reload_model=False, cuda=True, learning_rate=0.0004, batch_size=128, num_epochs=10, max_len=50, embedding_dim=300, hidden_size=300, num_classes=2, lstm_dropout=0.8, dropout=0.5, min_freq=2, print_every=500, verbose=True, vocab_size=35925)
D:\workspace\nlp-in-action\.venv\lib\site-packages\torch\nn\modules\rnn.py:67: UserWarning: dropout option adds dropout after all but last recurrent layer, so non-zero dropout expects num_layers greater than 1, but got dropout=0.8 and num_layers=1warnings.warn("dropout option adds dropout after all but last "
Model: ESIM((embedding): Embedding(35925, 300)(lstm_a): LSTM(300, 300, batch_first=True, dropout=0.8, bidirectional=True)(lstm_b): LSTM(300, 300, batch_first=True, dropout=0.8, bidirectional=True)(lstm_v_a): LSTM(2400, 300, batch_first=True, dropout=0.8, bidirectional=True)(lstm_v_b): LSTM(2400, 300, batch_first=True, dropout=0.8, bidirectional=True)(predict): Sequential((0): Linear(in_features=2400, out_features=600, bias=True)(1): ReLU()(2): Dropout(p=0.5, inplace=False)(3): Linear(in_features=600, out_features=300, bias=True)(4): ReLU()(5): Dropout(p=0.5, inplace=False)(6): Linear(in_features=300, out_features=2, bias=True))
)
New model27%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████▋ | 499/1866 [01:33<04:13, 5.40it/s]
TRAIN iter=500 loss=0.500601 accuracy=0.750 precision=0.714 recal=0.846 f1 score=0.774654%|███████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████▌ | 999/1866 [03:04<02:40, 5.41it/s]
TRAIN iter=1000 loss=0.250350 accuracy=0.883 precision=0.907 recal=0.895 f1 score=0.900780%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████▌ | 1499/1866 [04:35<01:07, 5.43it/s]
TRAIN iter=1500 loss=0.311494 accuracy=0.844 precision=0.868 recal=0.868 f1 score=0.8684
100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 1866/1866 [05:42<00:00, 5.45it/s]
Begin evalute on dev set.
100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 69/69 [00:04<00:00, 17.10it/s]
EVALUATE [1/10] accuracy=0.771 precision=0.788 recal=0.741 f1 score=0.7637
...
TRAIN iter=500 loss=0.005086 accuracy=1.000 precision=1.000 recal=1.000 f1 score=1.0000
...
EVALUATE [10/10] accuracy=0.815 precision=0.807 recal=0.829 f1 score=0.8178
100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 98/98 [00:05<00:00, 17.38it/s]
TEST accuracy=0.817 precision=0.771 recal=0.903 f1 score=0.8318
可以看到,训练集上的损失第一次降到了0.005级别,准确率甚至达到了100%,但最终在测试集上的准确率相比训练集还是逊色了一些,只有81.7%,不过相比前面几个模型已经很不错了。
相关文章:

ESIM实战文本匹配
引言 今天我们来实现ESIM文本匹配,这是一个典型的交互型文本匹配方式,也是近期第一个测试集准确率超过80%的模型。 我们来看下是如何实现的。 模型架构 我们主要实现左边的ESIM网络。 从下往上看,分别是 输入编码层(Input Ecoding) 对前…...
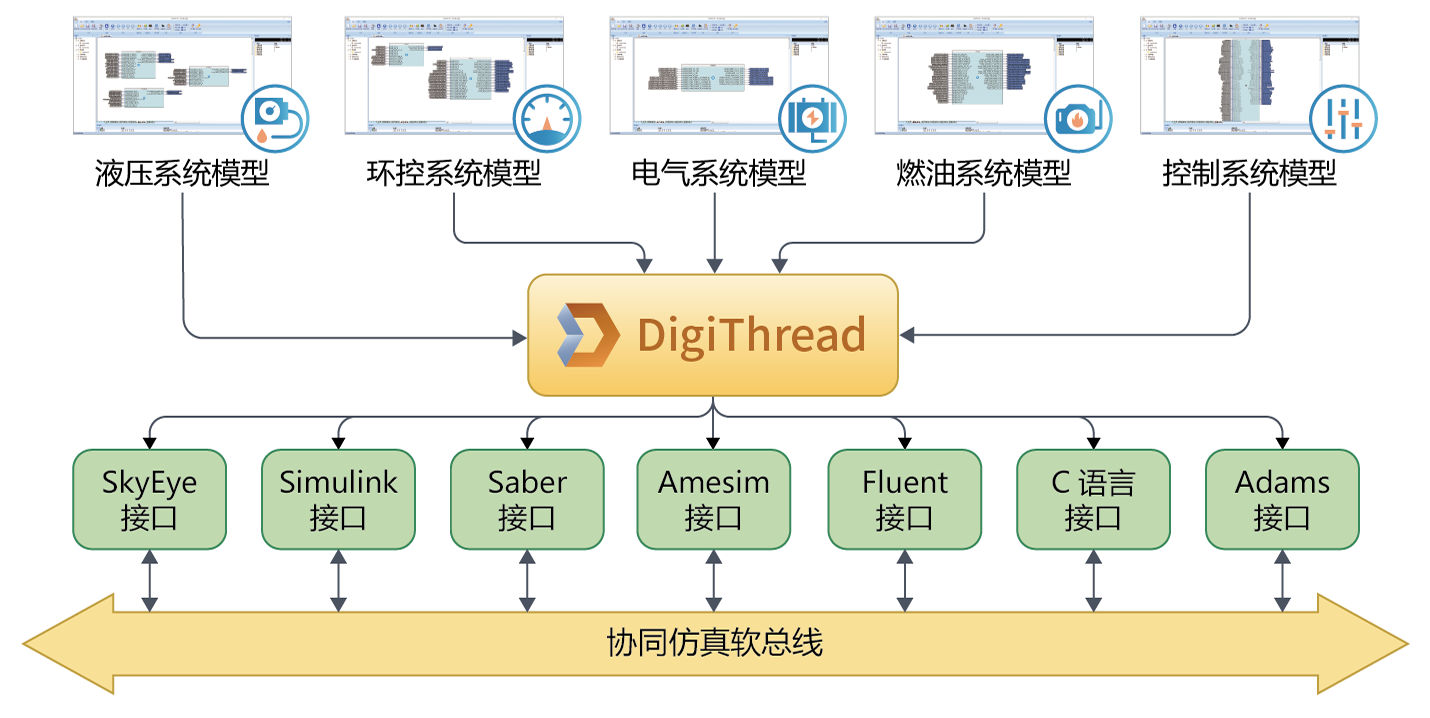
基于虚拟仿真技术的汽车燃油泵控制
在当前激烈的竞争环境下,汽车行业正在加速产业和技术更迭,整车厂对大型ECU嵌入式控制系统和软件的需求迫在眉睫。 然而,复杂而庞大的汽车系统往往由多个物理系统组成,系统所对应的模型都需要在不同的领域实现:发动机、…...

angular:HtmlElement的子节点有Shadow dom时奇怪的现象
描述: 这样写时,会自动跳过shadow dom节点的遍历 const cloneElement this.contentElement.cloneNode(true) as HTMLElement; for(let childNodeIndex 0; childNodeIndex < cloneElement.childNodes.length; childNodeIndex) {element.appendChild…...

栈与队列--删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项
给出由小写字母组成的字符串 S,重复项删除操作会选择两个相邻且相同的字母,并删除它们。 在 S 上反复执行重复项删除操作,直到无法继续删除。 在完成所有重复项删除操作后返回最终的字符串。答案保证唯一。 示例: 输入&#x…...
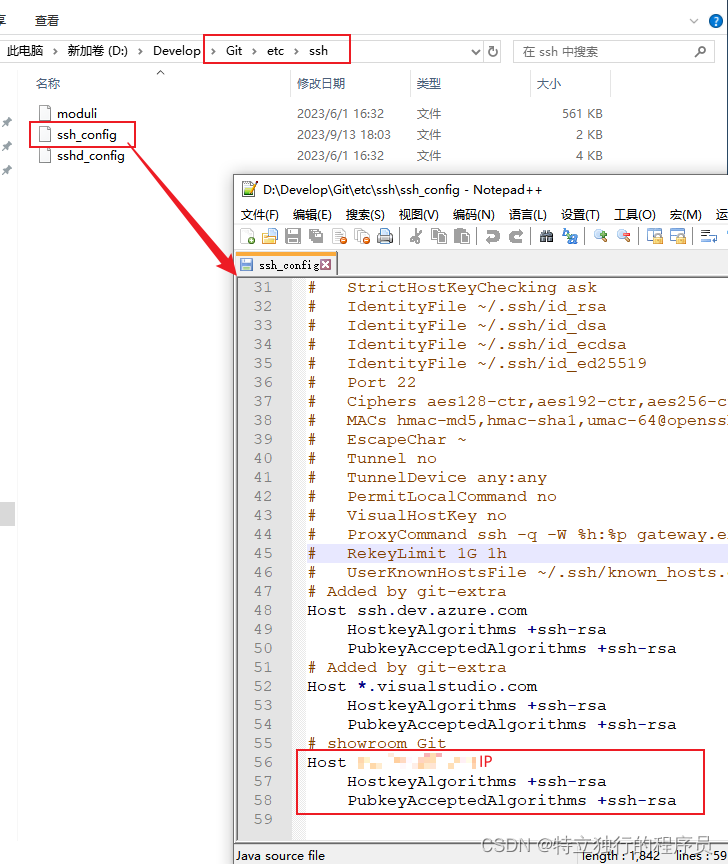
使用SSH地址拉取远程仓库代码报下面的错误
说明:配置了SSH秘钥后,使用SSH地址克隆代码,依旧无法拉取代码,提示下面这个信息。 Their offer:ssh-rsa,ssh-dss fatal:Could not read from remote repository. Please make sure you have the…...
easycms v5.5 分析 | Bugku S3 AWD排位赛
前言 这个awd打的悲,后台默认用户名密码为admin:admin,但是几乎所有人都改了 而且一进去看到这个cms就有点懵逼,都不知道这个cms是干嘛的(没用过相似的cms) 虽然网上找出了很多相关的漏洞,但是不知道为什…...
成都营运《乡村振兴战略下传统村落文化旅游设计》许少辉八一著作
成都营运《乡村振兴战略下传统村落文化旅游设计》许少辉八一著作...
创邻科技Galaxybase助力SPG推动知识图谱应用落地
1. 知识图谱实践应用:从理论到落地的全景视角 知识图谱,作为一种先进的数据模型和信息表示策略,极大地提升了信息检索与分析的能力。该模型利用图结构,将不同领域、层次和类别的信息有机整合,令复杂的数据关系变得清晰…...
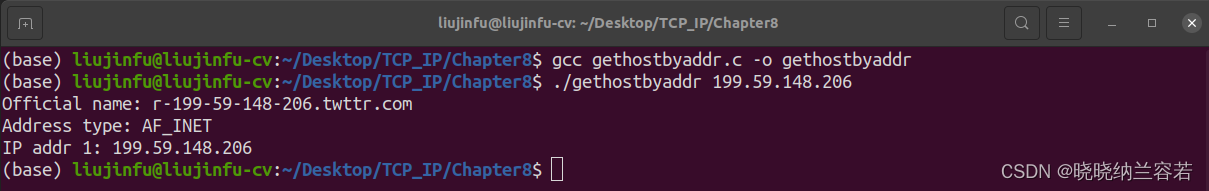
《TCP/IP网络编程》阅读笔记--域名及网络地址
目录 1--域名系统 2--域名与 IP 地址的转换 2-1--利用域名来获取 IP 地址 2-2--利用 IP 地址获取域名 3--代码实例 3-1--gethostbyname() 3-2--gethostbyaddr() 1--域名系统 域名系统(Domain Name System,DNS)是对 IP 地址和域名进行相…...
我的C#基础
using System; namespace HelloWorldApplication }TOC 欢迎使用Markdown编辑器 你好! 这是你第一次使用 Markdown编辑器 所展示的欢迎页。 为帮助您在CSDN创作的文章获得更多曝光和关注,我们为您提供了专属福利: 已注册且未在CSDN平台发布过…...
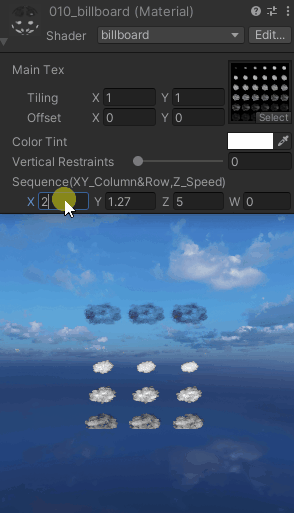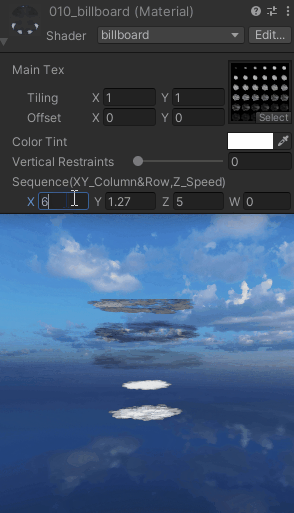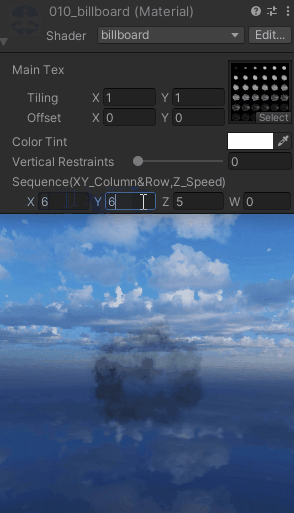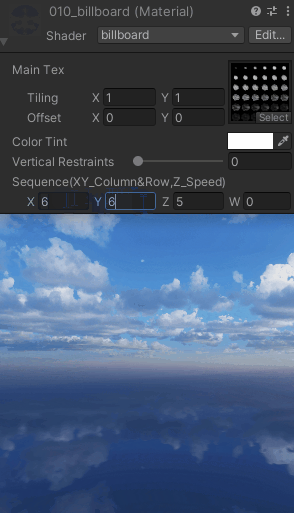
【UnityShaderLab实现“Billboard“始终面向相机_播放序列图的效果_案例分享(内附源码)】
"Billboard"始终面向相机 Shader "billboard" {Properties{_MainTex ("Main Tex", 2D) = "white" {}_Color (...
Ceph入门到精通-S3 基准测试工具warp使用入门
S3 基准测试工具。 下载 下载适用于各种平台的二进制版本。 配置 可以使用命令行参数或环境变量配置 Warp。 可以使用 、 在命令行上指定要使用的 S3 服务器,也可以选择指定 TLS 和自定义区域。--host--access-key--secret-key--tls--region 也可以使用 、、 和…...

Docker--未完结
一.Docker是干什么的 在没亲自使用过之前,再多的术语也仅仅是抽象,只有写的人或者使用过的人能看懂。 所以,作为新手来说,只要知道Docker是用于部署项目就够了,下面展示如何用Docker部署项目及Docker常用命令。 二、…...
string的使用和模拟实现
💓博主个人主页:不是笨小孩👀 ⏩专栏分类:数据结构与算法👀 C👀 刷题专栏👀 C语言👀 🚚代码仓库:笨小孩的代码库👀 ⏩社区:不是笨小孩👀 🌹欢迎大…...

基础算法---区间合并
直接上题目,不废话! 题目 给定 n 个区间 [l,r],要求合并所有有交集的区间。 注意如果在端点处相交,也算有交集。 输出合并完成后的区间个数。 例如:[1,3] 和 [2,6] 可以合并为一个区间 [1,6]。 输入格式 第一行包含整数 n。 接下来 n 行&am…...
C++(day4)
思维导图 封装Mystring #include <iostream> #include<cstring>using namespace std;class Mystring{ public://无参构造函数Mystring():size(10){strnew char[size];strcpy(str,"");cout<<"无参构造函数"<<endl;}//有参构造函数…...
docker 部署 node.js(express) 服务
1、在 express 项目根目录下新增 Dockerfile 文件,内容如下: 创建服务容器的方法,可以根据自己的情况选择: 1、以下示例为宿主机没有安装 node 环境的写法; 2、先在本地构建包含 node 和 express 的基础镜像࿰…...

商城系统开发,如何确保用户数据的安全性?
确保用户数据的安全性是商城系统开发中至关重要的一项任务。随着数字化时代的到来,用户的个人信息和交易数据已成为黑客和不法分子的重要目标,因此保护用户数据的安全性对于商城系统的成功运营至关重要。在开发商城系统时,以下几个方面是确保…...

黑客必备工具Kali Linux,安装与使用教程全包含,从入门到精通,全网最详细全面的Kali Linux教程
Kali Linux是一个高级渗透测试和安全审计Linux发行版,目前可以说是网络安全人员的专用系统。 Kali Linux功能非常强大,能够进行信息取证、渗透测试、攻击WPA / WPA2保护的无线网络、离线破解哈希密码、将android、Java、C编写的程序反编译成代码等等&am…...
)
2024滴滴校招面试真题汇总及其讲解(二)
4.【基础题】HashMap了解吗?介绍一下它对应的线程安全版本。 HashMap 是 Java 中一种键值对映射的集合,它使用哈希表来存储键值对。HashMap 具有插入和删除元素效率高的优势,但不是线程安全的。 ConcurrentHashMap 是 Java 中一种线程安全的 HashMap,它使用分段锁来保证线…...
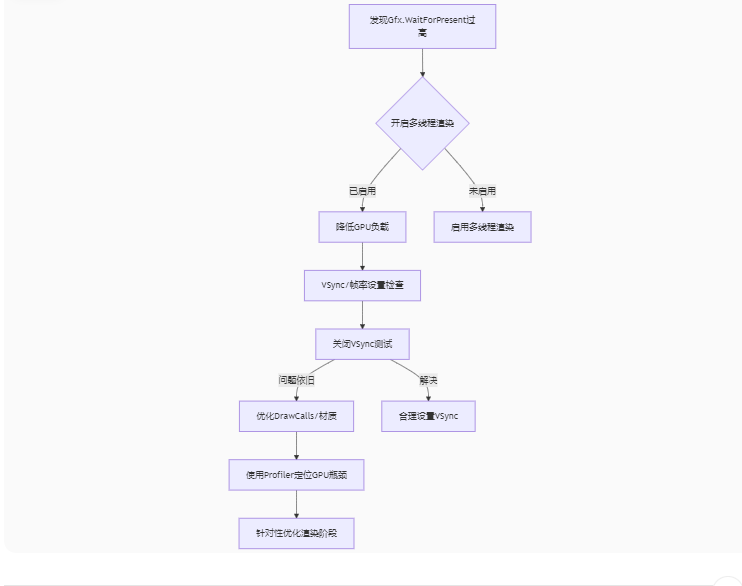
Unity3D中Gfx.WaitForPresent优化方案
前言 在Unity中,Gfx.WaitForPresent占用CPU过高通常表示主线程在等待GPU完成渲染(即CPU被阻塞),这表明存在GPU瓶颈或垂直同步/帧率设置问题。以下是系统的优化方案: 对惹,这里有一个游戏开发交流小组&…...
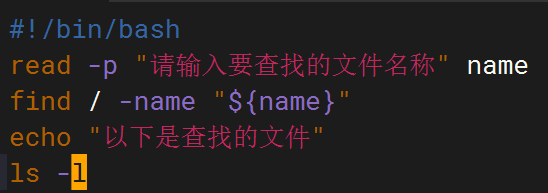
shell脚本--常见案例
1、自动备份文件或目录 2、批量重命名文件 3、查找并删除指定名称的文件: 4、批量删除文件 5、查找并替换文件内容 6、批量创建文件 7、创建文件夹并移动文件 8、在文件夹中查找文件...
ESP32 I2S音频总线学习笔记(四): INMP441采集音频并实时播放
简介 前面两期文章我们介绍了I2S的读取和写入,一个是通过INMP441麦克风模块采集音频,一个是通过PCM5102A模块播放音频,那如果我们将两者结合起来,将麦克风采集到的音频通过PCM5102A播放,是不是就可以做一个扩音器了呢…...
2025盘古石杯决赛【手机取证】
前言 第三届盘古石杯国际电子数据取证大赛决赛 最后一题没有解出来,实在找不到,希望有大佬教一下我。 还有就会议时间,我感觉不是图片时间,因为在电脑看到是其他时间用老会议系统开的会。 手机取证 1、分析鸿蒙手机检材&#x…...

今日科技热点速览
🔥 今日科技热点速览 🎮 任天堂Switch 2 正式发售 任天堂新一代游戏主机 Switch 2 今日正式上线发售,主打更强图形性能与沉浸式体验,支持多模态交互,受到全球玩家热捧 。 🤖 人工智能持续突破 DeepSeek-R1&…...
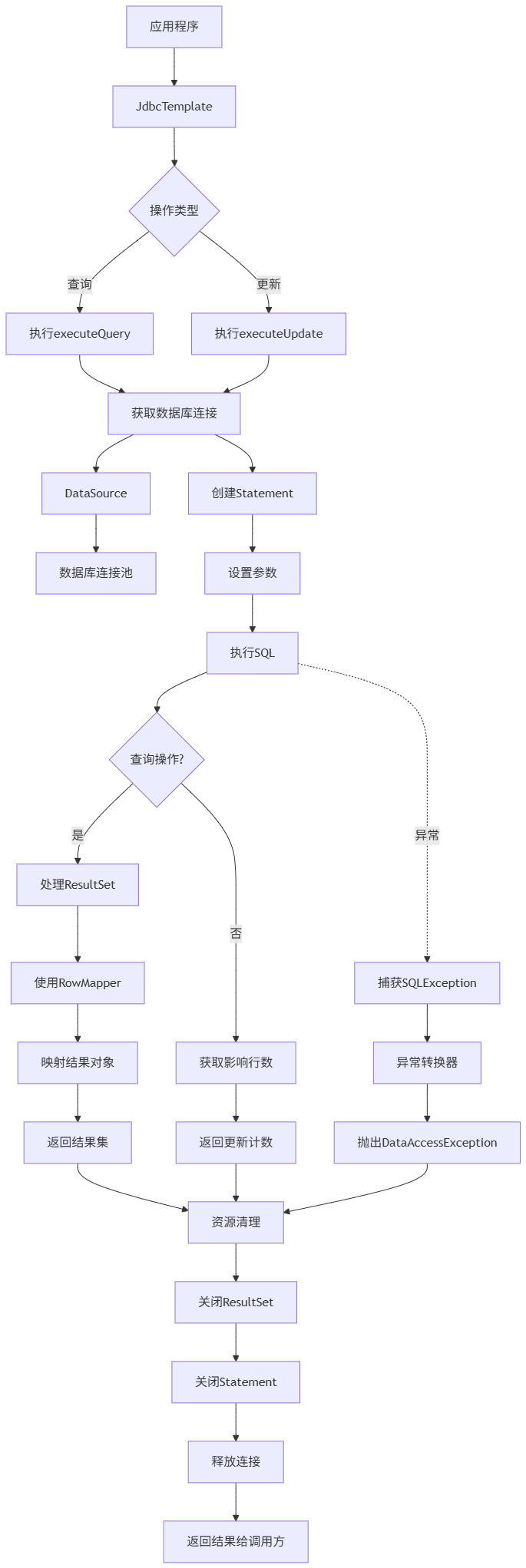
Spring数据访问模块设计
前面我们已经完成了IoC和web模块的设计,聪明的码友立马就知道了,该到数据访问模块了,要不就这俩玩个6啊,查库势在必行,至此,它来了。 一、核心设计理念 1、痛点在哪 应用离不开数据(数据库、No…...
C++:多态机制详解
目录 一. 多态的概念 1.静态多态(编译时多态) 二.动态多态的定义及实现 1.多态的构成条件 2.虚函数 3.虚函数的重写/覆盖 4.虚函数重写的一些其他问题 1).协变 2).析构函数的重写 5.override 和 final关键字 1&#…...
【深度学习新浪潮】什么是credit assignment problem?
Credit Assignment Problem(信用分配问题) 是机器学习,尤其是强化学习(RL)中的核心挑战之一,指的是如何将最终的奖励或惩罚准确地分配给导致该结果的各个中间动作或决策。在序列决策任务中,智能体执行一系列动作后获得一个最终奖励,但每个动作对最终结果的贡献程度往往…...

【Kafka】Kafka从入门到实战:构建高吞吐量分布式消息系统
Kafka从入门到实战:构建高吞吐量分布式消息系统 一、Kafka概述 Apache Kafka是一个分布式流处理平台,最初由LinkedIn开发,后成为Apache顶级项目。它被设计用于高吞吐量、低延迟的消息处理,能够处理来自多个生产者的海量数据,并将这些数据实时传递给消费者。 Kafka核心特…...
C++_哈希表
本篇文章是对C学习的哈希表部分的学习分享 相信一定会对你有所帮助~ 那咱们废话不多说,直接开始吧! 一、基础概念 1. 哈希核心思想: 哈希函数的作用:通过此函数建立一个Key与存储位置之间的映射关系。理想目标:实现…...
