tensorrt的安装和使用
安装
提前安装好 CUDA 和 CUDNN,登录 NVIDIA 官方网站下载和主机 CUDA 版本适配的 TensorRT 压缩包即可。
以 CUDA 版本是 10.2 为例,选择适配 CUDA 10.2 的 tar 包,然后执行类似如下的命令安装并测试:
#安装c++版本
cd /the/path/of/tensorrt/tar/gz/file
tar -zxvf TensorRT-8.2.5.1.linux.x86_64-gnu.cuda-10.2.cudnn8.2.tar.gz
export TENSORRT_DIR=$(pwd)/TensorRT-8.2.5.1
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$TENSORRT_DIR/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH #安装python版本
pip install TensorRT-8.2.5.1/python/tensorrt-8.2.5.1-cp37-none-linux_x86_64.whl
python -c "import tensorrt;print(tensorrt.__version__)" #打印8.2.5.1,则说明安装成功构建trt模型
手动搭建
使用python接口
import tensorrt as trt verbose = True
IN_NAME = 'input'
OUT_NAME = 'output'
IN_H = 224
IN_W = 224
BATCH_SIZE = 1 EXPLICIT_BATCH = 1 << (int)( trt.NetworkDefinitionCreationFlag.EXPLICIT_BATCH) TRT_LOGGER = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.VERBOSE) if verbose else trt.Logger()
with trt.Builder(TRT_LOGGER) as builder, builder.create_builder_config(
) as config, builder.create_network(EXPLICIT_BATCH) as network: # define network input_tensor = network.add_input( name=IN_NAME, dtype=trt.float32, shape=(BATCH_SIZE, 3, IN_H, IN_W)) pool = network.add_pooling( input=input_tensor, type=trt.PoolingType.MAX, window_size=(2, 2)) pool.stride = (2, 2) pool.get_output(0).name = OUT_NAME network.mark_output(pool.get_output(0)) # serialize the model to engine file profile = builder.create_optimization_profile() profile.set_shape_input('input', *[[BATCH_SIZE, 3, IN_H, IN_W]]*3) builder.max_batch_size = 1 config.max_workspace_size = 1 << 30 engine = builder.build_engine(network, config) with open('model_python_trt.engine', mode='wb') as f: f.write(bytearray(engine.serialize())) print("generating file done!")使用c++接口
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream> #include <NvInfer.h>
#include <../samples/common/logger.h> using namespace nvinfer1;
using namespace sample; const char* IN_NAME = "input";
const char* OUT_NAME = "output";
static const int IN_H = 224;
static const int IN_W = 224;
static const int BATCH_SIZE = 1;
static const int EXPLICIT_BATCH = 1 << (int)(NetworkDefinitionCreationFlag::kEXPLICIT_BATCH); int main(int argc, char** argv)
{ // Create builder Logger m_logger; IBuilder* builder = createInferBuilder(m_logger); IBuilderConfig* config = builder->createBuilderConfig(); // Create model to populate the network INetworkDefinition* network = builder->createNetworkV2(EXPLICIT_BATCH); ITensor* input_tensor = network->addInput(IN_NAME, DataType::kFLOAT, Dims4{ BATCH_SIZE, 3, IN_H, IN_W }); IPoolingLayer* pool = network->addPoolingNd(*input_tensor, PoolingType::kMAX, DimsHW{ 2, 2 }); pool->setStrideNd(DimsHW{ 2, 2 }); pool->getOutput(0)->setName(OUT_NAME); network->markOutput(*pool->getOutput(0)); // Build engine IOptimizationProfile* profile = builder->createOptimizationProfile(); profile->setDimensions(IN_NAME, OptProfileSelector::kMIN, Dims4(BATCH_SIZE, 3, IN_H, IN_W)); profile->setDimensions(IN_NAME, OptProfileSelector::kOPT, Dims4(BATCH_SIZE, 3, IN_H, IN_W)); profile->setDimensions(IN_NAME, OptProfileSelector::kMAX, Dims4(BATCH_SIZE, 3, IN_H, IN_W)); config->setMaxWorkspaceSize(1 << 20); ICudaEngine* engine = builder->buildEngineWithConfig(*network, *config); // Serialize the model to engine file IHostMemory* modelStream{ nullptr }; assert(engine != nullptr); modelStream = engine->serialize(); std::ofstream p("model.engine", std::ios::binary); if (!p) { std::cerr << "could not open output file to save model" << std::endl; return -1; } p.write(reinterpret_cast<const char*>(modelStream->data()), modelStream->size()); std::cout << "generating file done!" << std::endl; // Release resources modelStream->destroy(); network->destroy(); engine->destroy(); builder->destroy(); config->destroy(); return 0;
} onnx模型转换
trtexec
使用python接口
import torch
import onnx
import tensorrt as trt onnx_model = 'model.onnx' class NaiveModel(torch.nn.Module): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.pool = torch.nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2) def forward(self, x): return self.pool(x) device = torch.device('cuda:0') # generate ONNX model
torch.onnx.export(NaiveModel(), torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224), onnx_model, input_names=['input'], output_names=['output'], opset_version=11)
onnx_model = onnx.load(onnx_model) # create builder and network
logger = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.ERROR)
builder = trt.Builder(logger)
EXPLICIT_BATCH = 1 << (int)( trt.NetworkDefinitionCreationFlag.EXPLICIT_BATCH)
network = builder.create_network(EXPLICIT_BATCH) # parse onnx
parser = trt.OnnxParser(network, logger) if not parser.parse(onnx_model.SerializeToString()): error_msgs = '' for error in range(parser.num_errors): error_msgs += f'{parser.get_error(error)}\n' raise RuntimeError(f'Failed to parse onnx, {error_msgs}') config = builder.create_builder_config()
config.max_workspace_size = 1<<20
profile = builder.create_optimization_profile() profile.set_shape('input', [1,3 ,224 ,224], [1,3,224, 224], [1,3 ,224 ,224])
config.add_optimization_profile(profile)
# create engine
with torch.cuda.device(device): engine = builder.build_engine(network, config) with open('model.engine', mode='wb') as f: f.write(bytearray(engine.serialize())) print("generating file done!") 使用c++接口
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream> #include <NvInfer.h>
#include <NvOnnxParser.h>
#include <../samples/common/logger.h> using namespace nvinfer1;
using namespace nvonnxparser;
using namespace sample; int main(int argc, char** argv)
{ // Create builder Logger m_logger; IBuilder* builder = createInferBuilder(m_logger); const auto explicitBatch = 1U << static_cast<uint32_t>(NetworkDefinitionCreationFlag::kEXPLICIT_BATCH); IBuilderConfig* config = builder->createBuilderConfig(); // Create model to populate the network INetworkDefinition* network = builder->createNetworkV2(explicitBatch); // Parse ONNX file IParser* parser = nvonnxparser::createParser(*network, m_logger); bool parser_status = parser->parseFromFile("model.onnx", static_cast<int>(ILogger::Severity::kWARNING)); // Get the name of network input Dims dim = network->getInput(0)->getDimensions(); if (dim.d[0] == -1) // -1 means it is a dynamic model { const char* name = network->getInput(0)->getName(); IOptimizationProfile* profile = builder->createOptimizationProfile(); profile->setDimensions(name, OptProfileSelector::kMIN, Dims4(1, dim.d[1], dim.d[2], dim.d[3])); profile->setDimensions(name, OptProfileSelector::kOPT, Dims4(1, dim.d[1], dim.d[2], dim.d[3])); profile->setDimensions(name, OptProfileSelector::kMAX, Dims4(1, dim.d[1], dim.d[2], dim.d[3])); config->addOptimizationProfile(profile); } // Build engine config->setMaxWorkspaceSize(1 << 20); ICudaEngine* engine = builder->buildEngineWithConfig(*network, *config); // Serialize the model to engine file IHostMemory* modelStream{ nullptr }; assert(engine != nullptr); modelStream = engine->serialize(); std::ofstream p("model.engine", std::ios::binary); if (!p) { std::cerr << "could not open output file to save model" << std::endl; return -1; } p.write(reinterpret_cast<const char*>(modelStream->data()), modelStream->size()); std::cout << "generate file success!" << std::endl; // Release resources modelStream->destroy(); network->destroy(); engine->destroy(); builder->destroy(); config->destroy(); return 0;
} 模型推理
使用python接口
#输入一个 1x3x224x224 的张量,输出一个 1x3x112x112 的张量
from typing import Union, Optional, Sequence,Dict,Any import torch
import tensorrt as trt class TRTWrapper(torch.nn.Module): def __init__(self,engine: Union[str, trt.ICudaEngine], output_names: Optional[Sequence[str]] = None) -> None: super().__init__() self.engine = engine if isinstance(self.engine, str): with trt.Logger() as logger, trt.Runtime(logger) as runtime: with open(self.engine, mode='rb') as f: engine_bytes = f.read() self.engine = runtime.deserialize_cuda_engine(engine_bytes) self.context = self.engine.create_execution_context() names = [_ for _ in self.engine] input_names = list(filter(self.engine.binding_is_input, names)) self._input_names = input_names self._output_names = output_names if self._output_names is None: output_names = list(set(names) - set(input_names)) self._output_names = output_names def forward(self, inputs: Dict[str, torch.Tensor]): assert self._input_names is not None assert self._output_names is not None bindings = [None] * (len(self._input_names) + len(self._output_names)) profile_id = 0 for input_name, input_tensor in inputs.items(): # check if input shape is valid profile = self.engine.get_profile_shape(profile_id, input_name) assert input_tensor.dim() == len( profile[0]), 'Input dim is different from engine profile.' for s_min, s_input, s_max in zip(profile[0], input_tensor.shape, profile[2]): assert s_min <= s_input <= s_max, \ 'Input shape should be between ' \ + f'{profile[0]} and {profile[2]}' \ + f' but get {tuple(input_tensor.shape)}.' idx = self.engine.get_binding_index(input_name) # All input tensors must be gpu variables assert 'cuda' in input_tensor.device.type input_tensor = input_tensor.contiguous() if input_tensor.dtype == torch.long: input_tensor = input_tensor.int() self.context.set_binding_shape(idx, tuple(input_tensor.shape)) bindings[idx] = input_tensor.contiguous().data_ptr() # create output tensors outputs = {} for output_name in self._output_names: idx = self.engine.get_binding_index(output_name) dtype = torch.float32 shape = tuple(self.context.get_binding_shape(idx)) device = torch.device('cuda') output = torch.empty(size=shape, dtype=dtype, device=device) outputs[output_name] = output bindings[idx] = output.data_ptr() self.context.execute_async_v2(bindings, torch.cuda.current_stream().cuda_stream) return outputs model = TRTWrapper('model.engine', ['output'])
output = model(dict(input = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224).cuda()))
print(output) c++接口
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream> #include <NvInfer.h>
#include <../samples/common/logger.h> #define CHECK(status) \ do\ {\ auto ret = (status);\ if (ret != 0)\ {\ std::cerr << "Cuda failure: " << ret << std::endl;\ abort();\ }\ } while (0) using namespace nvinfer1;
using namespace sample; const char* IN_NAME = "input";
const char* OUT_NAME = "output";
static const int IN_H = 224;
static const int IN_W = 224;
static const int BATCH_SIZE = 1;
static const int EXPLICIT_BATCH = 1 << (int)(NetworkDefinitionCreationFlag::kEXPLICIT_BATCH); void doInference(IExecutionContext& context, float* input, float* output, int batchSize)
{ const ICudaEngine& engine = context.getEngine(); // Pointers to input and output device buffers to pass to engine. // Engine requires exactly IEngine::getNbBindings() number of buffers. assert(engine.getNbBindings() == 2); void* buffers[2]; // In order to bind the buffers, we need to know the names of the input and output tensors. // Note that indices are guaranteed to be less than IEngine::getNbBindings() const int inputIndex = engine.getBindingIndex(IN_NAME); const int outputIndex = engine.getBindingIndex(OUT_NAME); // Create GPU buffers on device CHECK(cudaMalloc(&buffers[inputIndex], batchSize * 3 * IN_H * IN_W * sizeof(float))); CHECK(cudaMalloc(&buffers[outputIndex], batchSize * 3 * IN_H * IN_W /4 * sizeof(float))); // Create stream cudaStream_t stream; CHECK(cudaStreamCreate(&stream)); // DMA input batch data to device, infer on the batch asynchronously, and DMA output back to host CHECK(cudaMemcpyAsync(buffers[inputIndex], input, batchSize * 3 * IN_H * IN_W * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice, stream)); context.enqueue(batchSize, buffers, stream, nullptr); CHECK(cudaMemcpyAsync(output, buffers[outputIndex], batchSize * 3 * IN_H * IN_W / 4 * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost, stream)); cudaStreamSynchronize(stream); // Release stream and buffers cudaStreamDestroy(stream); CHECK(cudaFree(buffers[inputIndex])); CHECK(cudaFree(buffers[outputIndex]));
} int main(int argc, char** argv)
{ // create a model using the API directly and serialize it to a stream char *trtModelStream{ nullptr }; size_t size{ 0 }; std::ifstream file("model.engine", std::ios::binary); if (file.good()) { file.seekg(0, file.end); size = file.tellg(); file.seekg(0, file.beg); trtModelStream = new char[size]; assert(trtModelStream); file.read(trtModelStream, size); file.close(); } Logger m_logger; IRuntime* runtime = createInferRuntime(m_logger); assert(runtime != nullptr); ICudaEngine* engine = runtime->deserializeCudaEngine(trtModelStream, size, nullptr); assert(engine != nullptr); IExecutionContext* context = engine->createExecutionContext(); assert(context != nullptr); // generate input data float data[BATCH_SIZE * 3 * IN_H * IN_W]; for (int i = 0; i < BATCH_SIZE * 3 * IN_H * IN_W; i++) data[i] = 1; // Run inference float prob[BATCH_SIZE * 3 * IN_H * IN_W /4]; doInference(*context, data, prob, BATCH_SIZE); // Destroy the engine context->destroy(); engine->destroy(); runtime->destroy(); return 0;
} 相关文章:

tensorrt的安装和使用
安装 提前安装好 CUDA 和 CUDNN,登录 NVIDIA 官方网站下载和主机 CUDA 版本适配的 TensorRT 压缩包即可。 以 CUDA 版本是 10.2 为例,选择适配 CUDA 10.2 的 tar 包,然后执行类似如下的命令安装并测试: #安装c版本 cd /the/pat…...
电压放大器在电子测试中的应用有哪些方面
电压放大器是一种常见的电子设备,广泛应用于各种测试和测量应用中。以下是电压放大器在电子测试中的几个主要方面应用的简要介绍。 信号采集与处理:电压放大器通常用于信号采集和处理,在测试过程中将低电平信号放大到适合进一步处理或分析的水…...

39.地址算术运算
如果p是一个指向数组中某个元素的指针,那么p将会对p进行自增运算并指向下一个元素,而pi将对p进行加i的增量运算,使其指向指针p当前所指向的元素之后的第i个元素。这类运算时指针或地址算术运算中最简单的形式。 allocbuf中的空间使用状况也是…...

没有外网的麒麟系统上搭建GitLab服务并且无需客户端账号密码验证
要在没有外网的麒麟系统上搭建GitLab服务并且无需客户端账号密码验证,可以按照以下步骤进行操作: 安装必要的依赖包和软件 sudo yum install curl policycoreutils-python openssh-server openssh-clients sudo systemctl enable sshd sudo systemctl …...

微服务生态系统:使用Spring Cloud构建分布式系统
文章目录 什么是微服务?为什么选择Spring Cloud?Spring Cloud的关键组件示例:构建一个简单的微服务步骤1:创建Spring Boot项目步骤2:配置Eureka服务发现步骤3:创建REST控制器步骤4:运行项目步骤…...
DIY 一个汽车方向盘游戏外设(MMOS OSW DIY)
OSW-MMOS直驱方向盘DIY过程记录 - 简书 (jianshu.com) DIY 一个汽车方向盘游戏外设(MMOS OSW DIY) 首先讲一下这个直驱系统大概的框架,首先是电脑,电脑里装MMOS的软件(这个软件国内高手把它汉化了的),电脑通过USB线&a…...

校园网络技术需求分析
路由技术: 路由协议工作在 OSI 参考模型的第 3 层,因此它的作用主要是在通信 子网间路由数据包。路由器具有在网络中传递数据时选择最佳路径的能力。 除了可以完成主要的路由任务,利用访问控制列表(Access Control List&#x…...
计算机网络(二):TCP篇
文章目录 1. TCP头部包含哪些内容?2. 为什么需要 TCP 协议? TCP 工作在哪一层?3. 什么是 TCP ?4. 什么是 TCP 连接?5. 如何唯一确定一个 TCP 连接呢?6. UDP头部大小是多少?包含哪些内容…...

测试登录界面:Python
import unittest from selenium import webdriver class LoginTest(unittest.TestCase): def setUp(self): self.driver webdriver.Chrome() def test_login(self): # 打开登录页面 self.driver.get("http://example.com/login") # 输入用户名和密码 user…...

Rust踩雷笔记(7)——两个链表题例子初识裸指针
目录 leetcode 234leetcode 19 leetcode 234 题目在这https://leetcode.cn/problems/palindrome-linked-list/,leetcode 234的回文链表,思路很简单,就是fast和slow两个指针,fast一次移动两个、slow一次一个,最后slow指…...

用什么命令看Linux系统的体系架构
要查看Linux系统的体系架构,可以使用uname命令。在终端中运行以下命令: uname -m该命令将返回系统的体系架构,例如x86_64表示64位系统,i686表示32位系统。 uname 使用方法 uname命令用于获取操作系统的相关信息。它可以用于显示…...

消息中间件大揭秘:选择之前你必须知道的关键信息
Hello大家好!我是小米,很高兴再次和大家见面!今天的话题非常精彩,我们将深入探讨消息中间件,并了解一些常见的消息队列:RabbitMQ、RocketMQ、Kafka以及Redis。如果你正在准备面试,或者只是对这些…...

【Unity基础】4.动画Animation
【Unity基础】4.动画Animation 大家好,我是Lampard~~ 欢迎来到Unity基础系列博客,所学知识来自B站阿发老师~感谢 (一)Unity动画编辑器 (1)Animation组件 这一张我们要学习如何在unity编辑器中&…...
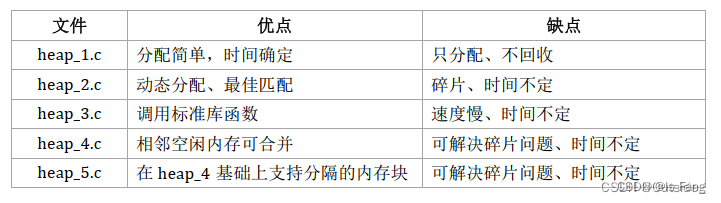
FreeRTOS移植以及核心功能
文章目录 freertos和ucos区别,优缺点比较移植步骤核心功能内存管理(5种内存管理策略)FreeRTOS任务调度算法有三种时间管理通信管理 栈管理 freertos和ucos区别,优缺点比较 FreeRTOS(Free Real-Time Operating System&…...
重装系统(配置环境)
这里写目录标题 0.重装系统1.python1.1 anaconda1.2 pycharm1.3 深度学习环境配置 2.java2.1.安装JDK2.2.配置JDK环境变量2.3IDEA2.4 Maven 3.大数据3.1 虚拟机3.2 Hadoop平台3.3 存储3.4 采集3.5 计算3.6 查询3.7 可视化 0.重装系统 // An highlighted block var foo bar;1.…...

docker系列-报错以及解决指南
1. windows运行docker报错Windows Hypervisor is not presentDocker Desktop is unable to detect a Hypervisor.Hardware assisted virtualization and data execution protection must be enabled in the BIOS. Docker Desktop - Windows Hypervisor is not presentDocker D…...

Vue3快速上手
1.Vue3简介 2020年9月18日,Vue.js发布3.0版本,代号:One Piece(海贼王)耗时2年多、2600次提交、30个RFC、600次PR、99位贡献者github上的tags地址:Release v3.0.0 One Piece vuejs/core GitHub 2.Vue3带…...
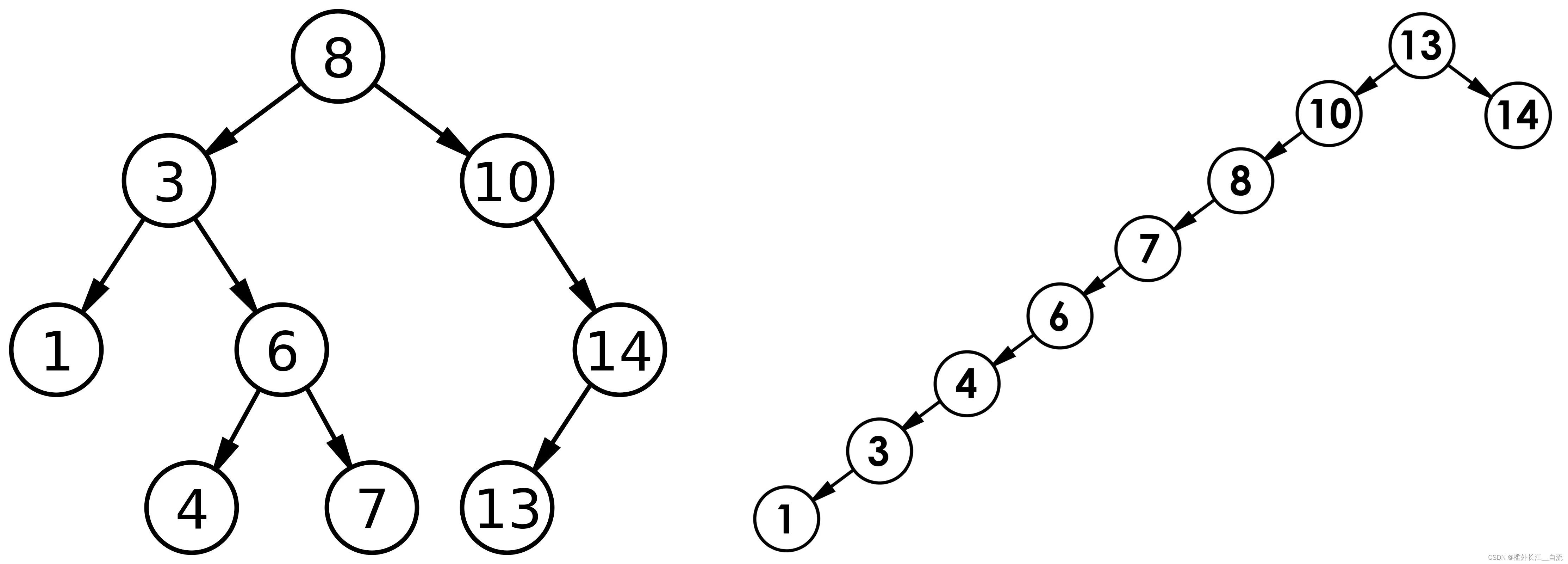
二叉搜索树(BST,Binary Search Tree)
文章目录 1. 二叉搜索树1.1 二叉搜索树概念1.2 二叉搜索树的查找1.3 二叉搜索树的插入1.4 二叉搜索树的删除 2 二叉搜索树的实现3 二叉搜索树的应用3.1二叉搜索树的性能分析 1. 二叉搜索树 1.1 二叉搜索树概念 二叉搜索树又称二叉排序树,它或者是一棵空树…...
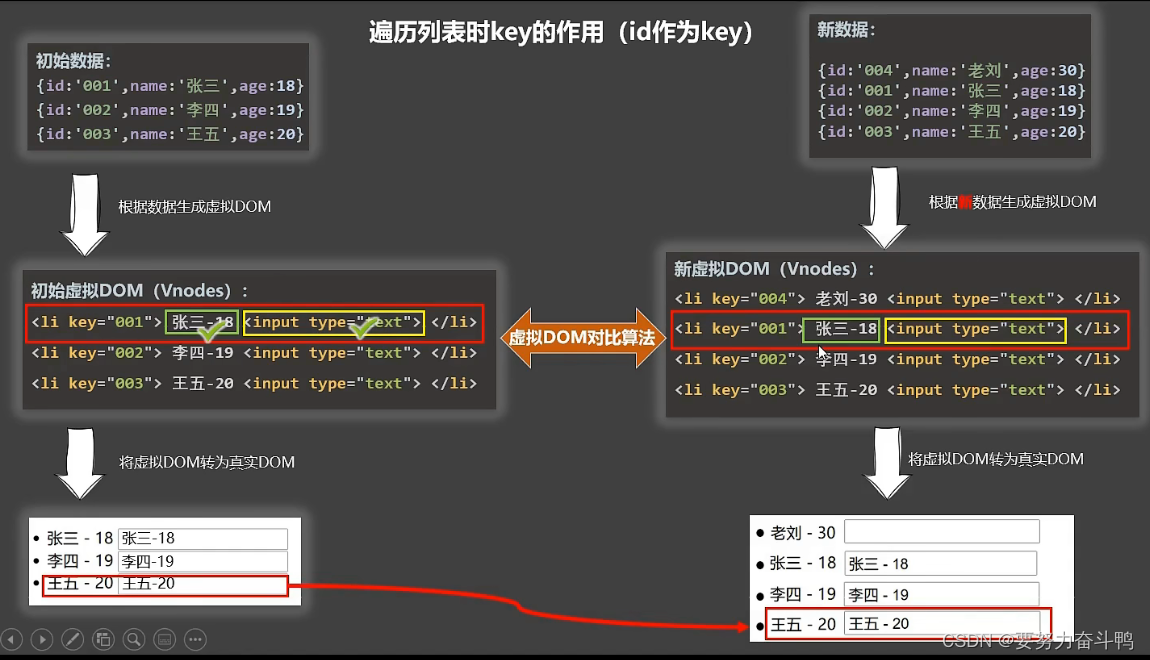
分析key原理
总结: key是虚拟dom对象的标识,当数据发生变化时,vue会根据新数据生成新的虚拟dom,随后vue进行新虚拟dom与旧虚拟dom的差异比较 比较规则: ①旧虚拟dom中找到了与新虚拟dom相同的key 若虚拟dom中的内容没变,…...
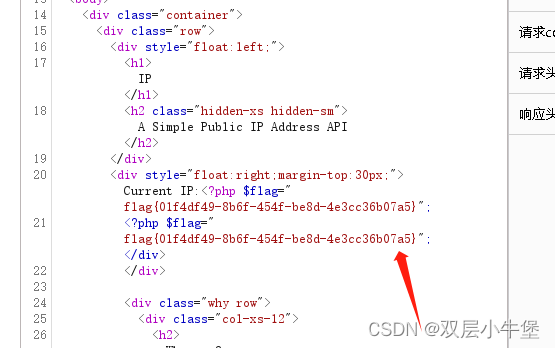
[CISCN2019 华东南赛区]Web11 SSTI
这道SSTI 差点给我渗透的感觉了 全是API 我还想去访问API看看 发现这里读取了我们的ip 我们抓包看看是如何做到的 没有东西 我们看看还有什么提示 欸 那我们可不可以直接修改参数呢 我们传递看看 发现成功了 是受控的 这里我就开始没有思路了 于是看了wp 说是ssti 那我们看…...
相机Camera日志实例分析之二:相机Camx【专业模式开启直方图拍照】单帧流程日志详解
【关注我,后续持续新增专题博文,谢谢!!!】 上一篇我们讲了: 这一篇我们开始讲: 目录 一、场景操作步骤 二、日志基础关键字分级如下 三、场景日志如下: 一、场景操作步骤 操作步…...

将对透视变换后的图像使用Otsu进行阈值化,来分离黑色和白色像素。这句话中的Otsu是什么意思?
Otsu 是一种自动阈值化方法,用于将图像分割为前景和背景。它通过最小化图像的类内方差或等价地最大化类间方差来选择最佳阈值。这种方法特别适用于图像的二值化处理,能够自动确定一个阈值,将图像中的像素分为黑色和白色两类。 Otsu 方法的原…...

Qwen3-Embedding-0.6B深度解析:多语言语义检索的轻量级利器
第一章 引言:语义表示的新时代挑战与Qwen3的破局之路 1.1 文本嵌入的核心价值与技术演进 在人工智能领域,文本嵌入技术如同连接自然语言与机器理解的“神经突触”——它将人类语言转化为计算机可计算的语义向量,支撑着搜索引擎、推荐系统、…...

sqlserver 根据指定字符 解析拼接字符串
DECLARE LotNo NVARCHAR(50)A,B,C DECLARE xml XML ( SELECT <x> REPLACE(LotNo, ,, </x><x>) </x> ) DECLARE ErrorCode NVARCHAR(50) -- 提取 XML 中的值 SELECT value x.value(., VARCHAR(MAX))…...

成都鼎讯硬核科技!雷达目标与干扰模拟器,以卓越性能制胜电磁频谱战
在现代战争中,电磁频谱已成为继陆、海、空、天之后的 “第五维战场”,雷达作为电磁频谱领域的关键装备,其干扰与抗干扰能力的较量,直接影响着战争的胜负走向。由成都鼎讯科技匠心打造的雷达目标与干扰模拟器,凭借数字射…...

智能分布式爬虫的数据处理流水线优化:基于深度强化学习的数据质量控制
在数字化浪潮席卷全球的今天,数据已成为企业和研究机构的核心资产。智能分布式爬虫作为高效的数据采集工具,在大规模数据获取中发挥着关键作用。然而,传统的数据处理流水线在面对复杂多变的网络环境和海量异构数据时,常出现数据质…...
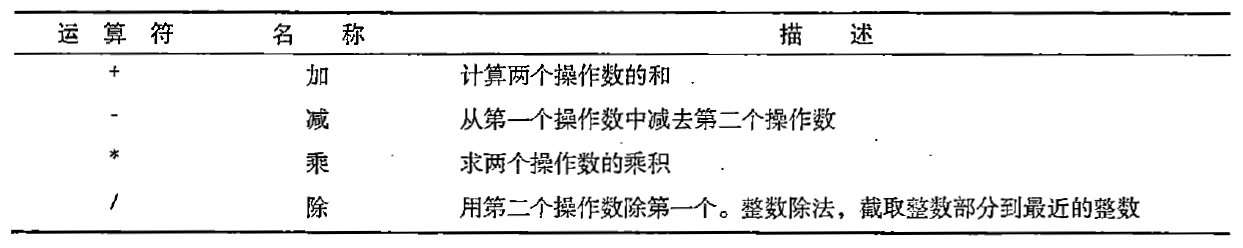
C# 表达式和运算符(求值顺序)
求值顺序 表达式可以由许多嵌套的子表达式构成。子表达式的求值顺序可以使表达式的最终值发生 变化。 例如,已知表达式3*52,依照子表达式的求值顺序,有两种可能的结果,如图9-3所示。 如果乘法先执行,结果是17。如果5…...
STM32---外部32.768K晶振(LSE)无法起振问题
晶振是否起振主要就检查两个1、晶振与MCU是否兼容;2、晶振的负载电容是否匹配 目录 一、判断晶振与MCU是否兼容 二、判断负载电容是否匹配 1. 晶振负载电容(CL)与匹配电容(CL1、CL2)的关系 2. 如何选择 CL1 和 CL…...

手机平板能效生态设计指令EU 2023/1670标准解读
手机平板能效生态设计指令EU 2023/1670标准解读 以下是针对欧盟《手机和平板电脑生态设计法规》(EU) 2023/1670 的核心解读,综合法规核心要求、最新修正及企业合规要点: 一、法规背景与目标 生效与强制时间 发布于2023年8月31日(OJ公报&…...
通过MicroSip配置自己的freeswitch服务器进行调试记录
之前用docker安装的freeswitch的,启动是正常的, 但用下面的Microsip连接不上 主要原因有可能一下几个 1、通过下面命令可以看 [rootlocalhost default]# docker exec -it freeswitch fs_cli -x "sofia status profile internal"Name …...
