C++ -- 学习系列 关联式容器 set 与 map
一 关联式容器是什么?
c++ 中有两种容器类型:关联式容器与序列式容器(顺序容器)
关联式中的容器是按照关键字来存储与访问的,序列式容器(顺序容器)则是元素在容器中的相对位置来存储与访问的。
c++ 中的关联式容器主要是 set 与 map.
二 底层原理与源码
1. 红黑树
红黑树是一种平衡二叉搜索树(balanced binary search tree),即插入或者删除元素后,依然能够保证树是平衡的,所谓平衡意味着任意一个父节点,其左右子树的深度相差不会太多。
平衡树也称 AVL 树,任意节点的左右个子树的高度差不超过1。
这一特性也保证了在插入元素与查找元素时的效率。
红黑树核心法则:
1. 每个节点要么是红色,要么是黑色
2. 红黑树中的任意节点到达其每个叶子节点的黑色高度是相同的(黑色高度值得是某个节点到达叶子节点的黑色节点的个数,因叶子节点是黑色的,所以也包括叶子节点)
3. 两个红色节点之间不能相邻,即对于任意一个红色节点而言,其左右子节点定不是红色
4. 根节点必须是黑色的
5. 每个红色节点的两个子节点一定是黑色的
【红黑树】的详细实现(C++)附代码 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)

c++ 中的红黑树源代码位置
#include <bits/stl_tree.h
template<typename _Key, typename _Val, typename _KeyOfValue,typename _Compare, typename _Alloc = allocator<_Val> >class _Rb_tree{typedef typename __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Alloc>::templaterebind<_Rb_tree_node<_Val> >::other _Node_allocator;typedef __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Node_allocator> _Alloc_traits;protected:typedef _Rb_tree_node_base* _Base_ptr;typedef const _Rb_tree_node_base* _Const_Base_ptr;typedef _Rb_tree_node<_Val>* _Link_type;typedef const _Rb_tree_node<_Val>* _Const_Link_type;......};源码中的模板参数解释如下:
1. Key 为存储在红黑树中的关键字类型
2. Value 实际存储数据的类型
3. KeyOfValue 表示如何通过 Value 获取到 Key,通常是一个函数
4. Compare 则为比较元素大小的函数,可自定义实现
5. Alloc 分配内存的方式
#include<iostream>
#include <bits/stl_tree.h>int main()
{
// template<typename _Tp>
// struct _Identity
// : public unary_function<_Tp,_Tp>
// {
// _Tp&
// operator()(_Tp& __x) const
// { return __x; }// const _Tp&
// operator()(const _Tp& __x) const
// { return __x; }
// };std::_Rb_tree<int, int, std::_Identity<int>, std::less<int>> rb_tree;std::cout << rb_tree.empty() << std::endl;std::cout << rb_tree.size() << std::endl;// 1. 插入元素不允许重复.rb_tree._M_insert_unique(1);rb_tree._M_insert_unique(2);rb_tree._M_insert_unique(3);rb_tree._M_insert_unique(4);rb_tree._M_insert_unique(5);std::cout << rb_tree.size() << std::endl;rb_tree._M_insert_unique(1);std::cout << rb_tree.size() << std::endl;std::cout << "------" << std::endl;// 2. 插入元素允许重复.rb_tree._M_insert_equal(1);rb_tree._M_insert_equal(1);rb_tree._M_insert_equal(1);std::cout << rb_tree.size() << std::endl;for(auto iter = rb_tree.begin(); iter != rb_tree.end(); iter++){std::cout << *iter <<" ";}std::cout <<""<<std::endl;return 0;
}
2. 基于红黑树的关联式容器
2.1 set/multiset
set/multiset 是以红黑树为底层结构的,因此存入的元素具有自动排序的特性,排序的依据是 key ,而 set/miltiset 元素的 key 与 value是合二为一的,其value 就是 key;
set/multiset 提供遍历操作与迭代器 iterator, 通过 不断的 iterator++ 遍历可以获取到已经排好序的元素;
我们无法通过 迭代器来改变 set/multiset 的值,这样设计的原因是 若是可以随意修改值,那么按照key 排好的顺序便有可能不存在了,从代码上来讲,set/multiset 用的迭代器是底层红黑树类 _Rb_tree 的 const iterator ,禁止使用者赋值。
2.1.1 set 源代码
template<typename _Key, typename _Compare = std::less<_Key>,typename _Alloc = std::allocator<_Key> >class set{public:// typedefs://@{/// Public typedefs.typedef _Key key_type;typedef _Key value_type;typedef _Compare key_compare;typedef _Compare value_compare;typedef _Alloc allocator_type;private:typedef typename __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Alloc>::templaterebind<_Key>::other _Key_alloc_type;typedef _Rb_tree<key_type, value_type, _Identity<value_type>,key_compare, _Key_alloc_type> _Rep_type;_Rep_type _M_t; // Red-black tree representing set.typedef __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Key_alloc_type> _Alloc_traits;.....iteratorinsert(const_iterator __position, const value_type& __x){ return _M_t._M_insert_unique_(__position, __x); }.....
};通过源码可以看出,set 底层使用的是 _Rb_tree , insert 函数底层调用的是 _Rb_tree 的 insert_unique 函数,即 _Rb_tree 中的元素不重复。
2.1.2 multiset 源码
template <typename _Key, typename _Compare = std::less<_Key>,typename _Alloc = std::allocator<_Key> >class multiset{
#ifdef _GLIBCXX_CONCEPT_CHECKS// concept requirementstypedef typename _Alloc::value_type _Alloc_value_type;
# if __cplusplus < 201103L__glibcxx_class_requires(_Key, _SGIAssignableConcept)
# endif__glibcxx_class_requires4(_Compare, bool, _Key, _Key,_BinaryFunctionConcept)__glibcxx_class_requires2(_Key, _Alloc_value_type, _SameTypeConcept)
#endifpublic:// typedefs:typedef _Key key_type;typedef _Key value_type;typedef _Compare key_compare;typedef _Compare value_compare;typedef _Alloc allocator_type;private:/// This turns a red-black tree into a [multi]set.typedef typename __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Alloc>::templaterebind<_Key>::other _Key_alloc_type;typedef _Rb_tree<key_type, value_type, _Identity<value_type>,key_compare, _Key_alloc_type> _Rep_type;/// The actual tree structure._Rep_type _M_t;typedef __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Key_alloc_type> _Alloc_traits;......iteratorinsert(const value_type& __x){ return _M_t._M_insert_equal(__x); }......};通过源码可以看出,multiset 底层使用的是 _Rb_tree , insert 函数底层调用的是 _Rb_tree 的 insert_equal 函数,即 _Rb_tree 中的元素允许重复。
2.2 map/multimap
map/multimap 是以红黑树为底层结构的,因此存入的元素具有自动排序的特性,排序的依据是 key;
map/multimap 提供遍历操作与迭代器 iterator, 通过 不断的 iterator++ 遍历可以获取到已经按照 key 排好序的元素;
我们无法通过 迭代器来改变 map/multimap 的值,这样设计的原因是 若是可以随意修改值,那么按照 key 排好的顺序便有可能不存在了,但是我们可以修改 key 对应的 data 值。因而 map/multimap 内部将 key type 设为 const ,如此可以避免对 key 的随意修改。
map 的key 是独一无二的,所以底层使用 _Rb_tree 的 insert_unique 函数;
multimap 的key允许重复,所以底层使用 _Rb_tree 的 insert_equal 函数
2.2.1 map 源码
template <typename _Key, typename _Tp, typename _Compare = std::less<_Key>,typename _Alloc = std::allocator<std::pair<const _Key, _Tp> > >class map{public:typedef _Key key_type;typedef _Tp mapped_type;typedef std::pair<const _Key, _Tp> value_type;typedef _Compare key_compare;typedef _Alloc allocator_type;private:/// This turns a red-black tree into a [multi]map.typedef typename __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Alloc>::templaterebind<value_type>::other _Pair_alloc_type;typedef _Rb_tree<key_type, value_type, _Select1st<value_type>,key_compare, _Pair_alloc_type> _Rep_type;/// The actual tree structure._Rep_type _M_t;typedef __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Pair_alloc_type> _Alloc_traits;.....std::pair<iterator, bool>insert(const value_type& __x){ return _M_t._M_insert_unique(__x); }.....
};通过源码可以看到 map 的 insert 函数底层调用的是 insert_unique 函数,所以 map 的 key 是唯一的。
2.2.2 multimap 源码
template <typename _Key, typename _Tp,typename _Compare = std::less<_Key>,typename _Alloc = std::allocator<std::pair<const _Key, _Tp> > >class multimap{public:typedef _Key key_type;typedef _Tp mapped_type;typedef std::pair<const _Key, _Tp> value_type;typedef _Compare key_compare;typedef _Alloc allocator_type;private:/// This turns a red-black tree into a [multi]map.typedef typename __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Alloc>::templaterebind<value_type>::other _Pair_alloc_type;typedef _Rb_tree<key_type, value_type, _Select1st<value_type>,key_compare, _Pair_alloc_type> _Rep_type;/// The actual tree structure._Rep_type _M_t;typedef __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Pair_alloc_type> _Alloc_traits;......iteratorinsert(const value_type& __x){ return _M_t._M_insert_equal(__x); }......
};通过源码可以看到 multimap 的 insert 函数底层调用的是 insert_equal 函数,所以 map 的 key 是可以重复的。
2.2.3 Select1st
前面的源码中提到了 Select1st,该函数的作用是获取 pair 中的第一个元素,应用在 map 中,获取的就是 key
Select1st 源码如下:
template<typename _Pair>struct _Select1st: public unary_function<_Pair, typename _Pair::first_type>{typename _Pair::first_type&operator()(_Pair& __x) const{ return __x.first; }const typename _Pair::first_type&operator()(const _Pair& __x) const{ return __x.first; }
};三 使用
1. set/multiset
1.1 set 函数
std::set - cppreference.com
1.1.1 构造函数
| 函数 | 说明 |
| set() | 空构造函数 |
template<typename _InputIterator> set(_InputIterator __first, _InputIterator __last) | range 构造函数 |
1.1.2 容器修改
| 函数 | 说明 |
| clear() | 清空容器 |
| insert | 插入元素 |
| emplace | 插入元素,可以只传入元素类的构造函数所需参数 |
| erase | 移除指定位置的元素 |
1.1.3 容器查找
| 函数 | 说明 |
| count | 返回指定元素的个数 |
| begin() | 返回首元素的 iterator |
| end() | 返回尾元素下一地址的 iterator,该 iterator 不能获取元素 |
| find | 查找指定元素,若是存在返回指向该元素的 iterator;若是不存在,则返回尾 iterator |
| lower_bound | Iterator pointing to the first element that is not less than key. If no such element is found, a past-the-end iterator (see end()) is returned. |
| uppser_bound | Iterator pointing to the first element that is greater than key. If no such element is found, past-the-end (see end()) iterator is returned. |
1.1.4 容器容量
| 函数 | 说明 |
| empty() | 判断 set 是否为空 |
| size() | 返回 set 中的元素个数 |
1.1.5 示例
#include<iostream>
#include<set>int main()
{// 1. 构造函数std::set<int> unique_set1;int nums[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};std::set<int> unique_set2(nums, nums+6);std::set<int> unique_set3(unique_set2.begin(), unique_set2.end());// 2. 容器修改unique_set1.insert(1);unique_set1.insert(2);unique_set1.insert(3);unique_set1.emplace(4);unique_set1.emplace(5);unique_set1.erase(4);// 3. 容器查找std::cout << unique_set1.count(3) << std::endl; // 1auto item1_iter = unique_set1.find(3);std::cout << (item1_iter == unique_set1.end()) << ", " << *item1_iter << std::endl; // 0 , 3auto item2_iter = unique_set1.lower_bound(4);std::cout << (item2_iter == unique_set1.end()) << ", " << *item2_iter << std::endl; // 0 , 3auto item3_iter = unique_set1.upper_bound(5);std::cout << (item3_iter == unique_set1.end()) << ", " << *item3_iter << std::endl;// 0 , 5for(auto iter = unique_set1.begin(); iter != unique_set1.end(); iter++){std::cout << *iter << " "; // 1. 2, 3, 5}std::cout << "" << std::endl;// 4. 容器容量std::cout << unique_set1.size() << std::endl; // 4std::cout << unique_set1.empty() << std::endl; // 0unique_set1.clear();std::cout << unique_set1.size() << std::endl; // 0std::cout << unique_set1.empty() << std::endl; // 1return 0;
}1.2 multiset 函数
std::multiset - cppreference.com
1.2.1 构造函数
| 函数 | 说明 |
| set() | 空构造函数 |
template<typename _InputIterator> set(_InputIterator __first, _InputIterator __last) | range 构造函数 |
1.2.2 容器修改
| 函数 | 说明 |
| clear() | 清空容器 |
| insert | 插入元素 |
| emplace | 插入元素,可以只传入元素类的构造函数所需参数 |
| erase | 移除指定位置的元素 |
1.2.3 容器查找
| 函数 | 说明 |
| count | 返回指定元素的个数 |
| begin() | 返回首元素的 iterator |
| end() | 返回尾元素下一地址的 iterator,该 iterator 不能获取元素 |
| find | 查找指定元素,若是存在返回指向该元素的 iterator;若是不存在,则返回尾 iterator |
| lower_bound | Iterator pointing to the first element that is not less than key. If no such element is found, a past-the-end iterator (see end()) is returned. |
| uppser_bound | Iterator pointing to the first element that is greater than key. If no such element is found, past-the-end (see end()) iterator is returned. |
1.2.4 容器容量
| 函数 | 说明 |
| empty() | 判断 set 是否为空 |
| size() | 返回 set 中的元素个数 |
1.2.5 示例
#include<iostream>
#include<set>int main()
{// 1. 构造函数std::multiset<int> multi_set1;int nums1[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};std::multiset<int> multi_set2(nums1, nums1+6);std::multiset<int> multi_set3(multi_set2.begin(), multi_set2.end());// 2. 容器修改multi_set1.insert(1);multi_set1.insert(2);multi_set1.insert(3);multi_set1.insert(3);multi_set1.insert(3);multi_set1.emplace(4);multi_set1.emplace(5);multi_set1.erase(4);// 3. 容器查找std::cout << multi_set1.count(3) << std::endl; // 3auto item1_iter = multi_set1.find(3);std::cout << (item1_iter == multi_set1.end()) << ", " << *item1_iter << std::endl; // 0, 3auto item2_iter = multi_set1.lower_bound(4);std::cout << (item2_iter == multi_set1.end()) << ", " << *item2_iter << std::endl; // 0, 5auto item3_iter = multi_set1.upper_bound(4);std::cout << (item3_iter == multi_set1.end()) << ", " << *item3_iter << std::endl; // 0, 5for(auto iter = multi_set1.begin(); iter != multi_set1.end(); iter++){std::cout << *iter << " "; // 1 2 3 3 3 5}std::cout << "" << std::endl;// 4. 容器容量std::cout << multi_set1.size() << std::endl; // 6std::cout << multi_set1.empty() << std::endl; // 0multi_set1.clear();std::cout << multi_set1.size() << std::endl; // 0std::cout << multi_set1.empty() << std::endl; // 1return 0;
}2. map/multimap
2.1 map 函数
2.1.1 构造函数
| 函数 | 说明 |
| map | 默认构造函数 |
| template< class InputIt > map( InputIt first, InputIt last) | range 构造函数 |
| map( std::initializer_list<value_type> init) | initializer list 构造函数 |
2.1.2 容器修改
| 函数 | 说明 |
| clear() | 清空容器 |
| insert | 插入元素 |
| emplace | 插入元素,可以只传入元素类的构造函数所需参数 |
| erase | 移除指定位置的元素 |
2.1.3 容器访问
| 函数 | 说明 |
| count | 返回指定 key 元素的个数 |
| begin() | 返回首元素的 iterator |
| end() | 返回尾元素下一地址的 iterator,该 iterator 不能获取元素 |
| find | 查找指定元素,若是存在返回指向该元素的 iterator;若是不存在,则返回尾 iterator |
| lower_bound | Iterator pointing to the first element that is not less than key. If no such element is found, a past-the-end iterator (see end()) is returned. |
| uppser_bound | Iterator pointing to the first element that is greater than key. If no such element is found, past-the-end (see end()) iterator is returned. |
| at | Returns a reference to the mapped value of the element with key equivalent to key. If no such element exists, an exception of type std::out_of_range is thrown. |
| operator[] | Returns a reference to the value that is mapped to a key equivalent to key, performing an insertion if such key does not already exist. |
2.1.4 容器容量
| 函数 | 说明 |
| empty() | 判断 set 是否为空 |
| size() | 返回 set 中的元素个数 |
2.1.5 示例
#include<iostream>
#include<map>int main()
{// 1. 构造函数std::map<int, std::string> unique_map1;std::map<int, std::string> unique_map2 = {{1, "a"}, {22, "bb"}, {3, "c"}};std::map<int, std::string> unique_map3(unique_map2.begin(), unique_map2.end());// 2. 容器修改unique_map1.insert({5, "e"});unique_map1.insert({6, "f"});unique_map1.emplace(7, "g");unique_map1.emplace(8, "h");unique_map1.insert({16, "ff"});unique_map1.erase(16);// 3. 容器访问std::cout << unique_map1.count(6) << std::endl; // 1auto item_iter1 = unique_map1.find(6);std::cout << (item_iter1 == unique_map1.end()) << std::endl; // 0std::cout << item_iter1->first << ", " << item_iter1->second << std::endl; // 6, fauto item_iter2 = unique_map1.lower_bound(6);std::cout << item_iter2->first << ", " << item_iter2->second << std::endl; // 6, fauto item_iter3 = unique_map1.upper_bound(7);std::cout << item_iter3->first << ", " << item_iter3->second << std::endl; // 8, hstd::cout << unique_map1.at(7) << std::endl; // gstd::cout << unique_map1[7] << std::endl; // g// 4. 容器容量std::cout << unique_map1.empty() << std::endl; // 0std::cout << unique_map1.size() << std::endl; // 4unique_map1.clear();std::cout << unique_map1.empty() << std::endl; // 1std::cout << unique_map1.size() << std::endl; // 0 return 0;
}2.2 multimap 函数
2.1.1 构造函数
| 函数 | 说明 |
| map | 默认构造函数 |
| template< class InputIt > map( InputIt first, InputIt last) | range 构造函数 |
| map( std::initializer_list<value_type> init) | initializer list 构造函数 |
2.1.2 容器修改
| 函数 | 说明 |
| clear() | 清空容器 |
| insert | 插入元素 |
| emplace | 插入元素,可以只传入元素类的构造函数所需参数 |
| erase | 移除指定位置的元素 |
2.1.3 容器访问
| 函数 | 说明 |
| count | 返回指定 key 元素的个数 |
| begin() | 返回首元素的 iterator |
| end() | 返回尾元素下一地址的 iterator,该 iterator 不能获取元素 |
| find | 查找指定元素,若是存在返回指向该元素的 iterator;若是不存在,则返回尾 iterator |
| lower_bound | Iterator pointing to the first element that is not less than key. If no such element is found, a past-the-end iterator (see end()) is returned. |
| uppser_bound | Iterator pointing to the first element that is greater than key. If no such element is found, past-the-end (see end()) iterator is returned. |
2.1.4 容器容量
| 函数 | 说明 |
| empty() | 判断 set 是否为空 |
| size() | 返回 set 中的元素个数 |
2.1.5 示例
#include<iostream>
#include<map>int main()
{// 1. 构造函数std::multimap<int, std::string> multi_map1;std::multimap<int, std::string> multi_map2 = {{1, "a"}, {22, "bb"}, {3, "c"}};std::multimap<int, std::string> multi_map3(multi_map2.begin(), multi_map2.end());// 2. 容器修改multi_map1.insert({5, "e"});multi_map1.insert({6, "f"});multi_map1.emplace(7, "g1");multi_map1.emplace(7, "g2");multi_map1.emplace(7, "g3");multi_map1.emplace(8, "h");multi_map1.insert({16, "ff"});multi_map1.erase(16);// 3. 容器访问std::cout << multi_map1.count(6) << std::endl; // 1auto item_iter1 = multi_map1.find(6);std::cout << (item_iter1 == multi_map1.end()) << std::endl; // 0std::cout << item_iter1->first << ", " << item_iter1->second << std::endl; // 6, fauto item_iter2 = multi_map1.lower_bound(6);std::cout << item_iter2->first << ", " << item_iter2->second << std::endl; // 6, fauto item_iter3 = multi_map1.upper_bound(7);std::cout << item_iter3->first << ", " << item_iter3->second << std::endl; // 8, h// 4. 容器容量std::cout << multi_map1.empty() << std::endl; // 0std::cout << multi_map1.size() << std::endl; // 6multi_map1.clear();std::cout << multi_map1.empty() << std::endl; // 1std::cout << multi_map1.size() << std::endl; // 0return 0;
}四 简单实现
1. my_set
// my_set.h#include <bits/stl_tree.h>template<typename T>
class my_set
{typedef T ValueType;typedef T KeyType;typedef std::_Rb_tree<KeyType, ValueType, std::_Identity<ValueType>, std::less<KeyType>> Rb_type;typedef typename std::_Rb_tree<T, T, std::_Identity<T>, std::less<T>>::const_iterator const_Iterator;public:my_set(){}template<typename InputIterator>my_set(InputIterator first, InputIterator last){rb_tree._M_insert_unique(first, last);}~my_set(){}const_Iterator begin(){return rb_tree.begin();}const_Iterator end(){return rb_tree.end();}void clear(){rb_tree.clear();}void insert(ValueType& val){rb_tree._M_insert_unique(val);}void insert(ValueType&& val){rb_tree._M_insert_unique(val);}template<typename ... Args>void emplace(Args&& ... args){rb_tree._M_emplace_unique(std::forward<Args>(args)...);}template<typename ... Args>void emplace(Args& ... args){rb_tree._M_emplace_unique(std::forward<Args>(args)...);}void erase(ValueType& val){rb_tree.erase(val);}void erase(ValueType&& val){rb_tree.erase(val);}std::size_t count(ValueType& val){return rb_tree.count(val);}std::size_t count(ValueType&& val){return rb_tree.count(val);}const_Iterator find(ValueType& val){return rb_tree.find(val);}const_Iterator find(ValueType&& val){return rb_tree.find(val);}bool empty(){return rb_tree.empty();}std::size_t size(){return rb_tree.size();}private:Rb_type rb_tree;};// main.cpp
int main()
{// 1. 构造函数my_set<int> unique_set1;int nums[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};my_set<int> unique_set2(nums, nums+6);my_set<int> unique_set3(unique_set2.begin(), unique_set2.end());// 2. 容器修改unique_set1.insert(1);unique_set1.insert(2);unique_set1.insert(3);unique_set1.emplace(4);unique_set1.emplace(5);unique_set1.erase(4);// 3. 容器查找std::cout << unique_set1.count(3) << std::endl; // 1auto item1_iter = unique_set1.find(3);std::cout << (item1_iter == unique_set1.end()) << ", " << *item1_iter << std::endl; // 0. 3for(auto iter = unique_set1.begin(); iter != unique_set1.end(); iter++){std::cout << *iter << " "; // 1 2 3 5}std::cout << "" << std::endl;// 4. 容器容量std::cout << unique_set1.size() << std::endl; // 4std::cout << unique_set1.empty() << std::endl; // 0unique_set1.clear();std::cout << unique_set1.size() << std::endl; // 0std::cout << unique_set1.empty() << std::endl; // 1return 0;
}2. my_multiset
// my_multiset.h#include <bits/stl_tree.h>template<typename T>
class my_multiset
{typedef T ValueType;typedef T KeyType;typedef std::_Rb_tree<KeyType, ValueType, std::_Identity<ValueType>, std::less<KeyType>> Rb_type;typedef typename std::_Rb_tree<T, T, std::_Identity<T>, std::less<T>>::const_iterator const_Iterator;public:my_multiset(){}template<typename InputIterator>my_multiset(InputIterator first, InputIterator last){rb_tree._M_insert_equal(first, last);}~my_multiset(){}const_Iterator begin(){return rb_tree.begin();}const_Iterator end(){return rb_tree.end();}void clear(){rb_tree.clear();}void insert(ValueType& val){rb_tree._M_insert_equal(val);}void insert(ValueType&& val){rb_tree._M_insert_equal(val);}template<typename ... Args>void emplace(Args&& ... args){rb_tree._M_emplace_unique(std::forward<Args>(args)...);}template<typename ... Args>void emplace(Args& ... args){rb_tree._M_emplace_unique(std::forward<Args>(args)...);}void erase(ValueType& val){rb_tree.erase(val);}void erase(ValueType&& val){rb_tree.erase(val);}std::size_t count(ValueType& val){return rb_tree.count(val);}std::size_t count(ValueType&& val){return rb_tree.count(val);}const_Iterator find(ValueType& val){return rb_tree.find(val);}const_Iterator find(ValueType&& val){return rb_tree.find(val);}bool empty(){return rb_tree.empty();}std::size_t size(){return rb_tree.size();}private:Rb_type rb_tree;};// main.cpp
#include<iostream>
#include"my_multiset.h"int main()
{// 1. 构造函数my_multiset<int> multi_set1;int nums[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};my_multiset<int> multi_set2(nums, nums+6);my_multiset<int> multi_set3(multi_set2.begin(), multi_set2.end());// 2. 容器修改multi_set1.insert(1);multi_set1.insert(2);multi_set1.insert(3);multi_set1.insert(3);multi_set1.insert(3);multi_set1.emplace(4);multi_set1.emplace(5);multi_set1.erase(4);// 3. 容器查找std::cout << multi_set1.count(3) << std::endl; // 1auto item1_iter = multi_set1.find(3);std::cout << (item1_iter == multi_set1.end()) << ", " << *item1_iter << std::endl; // 0, 3for(auto iter = multi_set1.begin(); iter != multi_set1.end(); iter++){std::cout << *iter << " "; // 1 2 3 3 3 5}std::cout << "" << std::endl;// 4. 容器容量std::cout << multi_set1.size() << std::endl; // 6std::cout << multi_set1.empty() << std::endl; // 0multi_set1.clear();std::cout << multi_set1.size() << std::endl; // 0std::cout << multi_set1.empty() << std::endl; // 1return 0;
}3. my_map
// my_map.h
#include <bits/stl_tree.h>
#include<initializer_list>template<typename Key, typename Value>
class my_map
{typedef std::pair<Key, Value> ValueType;typedef std::_Rb_tree<Key, ValueType, std::_Select1st<ValueType>, std::less<Key>> Rb_type;typedef typename Rb_type::iterator Iterator;public:my_map(){}template<typename InputIterator>my_map(InputIterator first, InputIterator last){rb_tree._M_insert_unique(first, last);}my_map(std::initializer_list<ValueType> init_list){rb_tree._M_insert_unique(init_list.begin(), init_list.end());}~my_map(){}Iterator begin(){return rb_tree.begin();}Iterator end(){return rb_tree.end();}void clear(){rb_tree.clear();}void insert(ValueType& val){rb_tree._M_insert_unique(val);}void insert(ValueType&& val){rb_tree._M_insert_unique(val);}template<typename ... Args>void emplace(Args&& ... args){rb_tree._M_emplace_unique(std::forward<Args>(args)...);}void erase(Iterator iter){rb_tree.erase(iter);}std::size_t count(Key& key){return rb_tree.count(key);}std::size_t count(Key&& key){return rb_tree.count(key);}Iterator find(Key& key){return rb_tree.find(key);}Iterator find(Key&& key){return rb_tree.find(key);}Value& at(Key& key){return (*rb_tree.lower_bound(key)).second;}Value& at(Key&& key){return (*rb_tree.lower_bound(key)).second;}Value& operator[](Key& key){return (*rb_tree.lower_bound(key)).second;}Value& operator[](Key&& key){return (*rb_tree.lower_bound(key)).second;}bool empty(){return rb_tree.empty();}std::size_t size(){return rb_tree.size();}void erase(Key& key){rb_tree.erase(key);}void erase(Key&& key){rb_tree.erase(key);}private:Rb_type rb_tree;
};// main.cppint main()
{// 1. 构造函数my_map<int, std::string> unique_map1;my_map<int, std::string> unique_map2 = {{1, "a"}, {22, "bb"}, {3, "c"}};my_map<int, std::string> unique_map3(unique_map2.begin(), unique_map2.end());// 2. 容器修改unique_map1.insert({5, "e"});unique_map1.insert({6, "f"});unique_map1.emplace(7, "g");unique_map1.emplace(8, "h");unique_map1.insert({16, "ff"});unique_map1.erase(16);// 3. 容器访问std::cout << unique_map1.count(6) << std::endl; // 1auto item_iter1 = unique_map1.find(6);std::cout << (item_iter1 == unique_map1.end()) << std::endl; // 0std::cout << item_iter1->first << ", " << item_iter1->second << std::endl; // 6, fstd::cout << unique_map1.at(7) << std::endl; // gstd::cout << unique_map1[7] << std::endl; // g// 4. 容器容量std::cout << unique_map1.empty() << std::endl; // 0std::cout << unique_map1.size() << std::endl; // 4unique_map1.clear();std::cout << unique_map1.empty() << std::endl; // 1std::cout << unique_map1.size() << std::endl; // 0return 0;
}4. my_multimap
// my_multimap.h#include <bits/stl_tree.h>
#include<initializer_list>template<typename Key, typename Value>
class my_multimap
{typedef std::pair<Key, Value> ValueType;typedef std::_Rb_tree<Key, ValueType, std::_Select1st<ValueType>, std::less<Key>> Rb_type;typedef typename Rb_type::iterator Iterator;public:my_multimap(){}template<typename InputIterator>my_multimap(InputIterator first, InputIterator last){rb_tree._M_insert_equal(first, last);}my_multimap(std::initializer_list<ValueType> init_list){rb_tree._M_insert_equal(init_list.begin(), init_list.end());}~my_multimap(){}Iterator begin(){return rb_tree.begin();}Iterator end(){return rb_tree.end();}void clear(){rb_tree.clear();}void insert(ValueType& val){rb_tree._M_insert_equal(val);}void insert(ValueType&& val){rb_tree._M_insert_equal(val);}template<typename ... Args>void emplace(Args&& ... args){rb_tree._M_emplace_equal(std::forward<Args>(args)...);}void erase(Iterator iter){rb_tree.erase(iter);}std::size_t count(Key& key){return rb_tree.count(key);}std::size_t count(Key&& key){return rb_tree.count(key);}Iterator find(Key& key){return rb_tree.find(key);}Iterator find(Key&& key){return rb_tree.find(key);}bool empty(){return rb_tree.empty();}std::size_t size(){return rb_tree.size();}void erase(Key& key){rb_tree.erase(key);}void erase(Key&& key){rb_tree.erase(key);}private:Rb_type rb_tree;
};// main.cpp#include<iostream>
#include"my_multimap.h"int main()
{// 1. 构造函数my_multimap<int, std::string> multi_map1;my_multimap<int, std::string> multi_map2 = {{1, "a"}, {22, "bb"}, {3, "c"}};my_multimap<int, std::string> multi_map3(multi_map2.begin(), multi_map2.end());// 2. 容器修改multi_map1.insert({5, "e"});multi_map1.insert({6, "f"});multi_map1.emplace(7, "g");multi_map1.emplace(7, "g");multi_map1.emplace(7, "g");multi_map1.emplace(8, "h");multi_map1.insert({16, "ff"});multi_map1.erase(16);// 3. 容器访问std::cout << multi_map1.count(6) << std::endl; // 1auto item_iter1 = multi_map1.find(6);std::cout << (item_iter1 == multi_map1.end()) << std::endl; // 0std::cout << item_iter1->first << ", " << item_iter1->second << std::endl; // 6, f// 4. 容器容量std::cout << multi_map1.empty() << std::endl; // 0std::cout << multi_map1.size() << std::endl; // 6multi_map1.clear();std::cout << multi_map1.empty() << std::endl; // 1std::cout << multi_map1.size() << std::endl; // 0return 0;
}
相关文章:

C++ -- 学习系列 关联式容器 set 与 map
一 关联式容器是什么? c 中有两种容器类型:关联式容器与序列式容器(顺序容器) 关联式中的容器是按照关键字来存储与访问的,序列式容器(顺序容器)则是元素在容器中的相对位置来存储与访问的。…...

Day 04 python学习笔记
Python数据容器 元组 元组的声明 变量名称(元素1,元素2,元素3,元素4…….) (元素类型可以不同) eg: tuple_01 ("hello", 1, 2,-20,[11,22,33]) print(type(tuple_01))结果&#x…...
Moonbeam Ignite强势回归
参与Moonbeam上最新的流动性计划 还记得新一轮的流动性激励计划吗?Moonbeam Ignite社区活动带着超过300万枚GLMR奖励来啦!体验新项目,顺便薅一把GLMR羊毛。 本次Moonbeam Ignite活动的参与项目均为第二批Moonbeam生态系统Grant资助提案中获…...

【改造后序遍历算法】95. 不同的二叉搜索树 II
95. 不同的二叉搜索树 II 解题思路 遍历每一个节点查看以k为根节点的二叉搜索树储存所有左子树的根节点储存所有右子树的根节点将左子树和右子树组装起来 将根节点储存在向量中 /*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeN…...
)
栈的基本操作(数据结构)
顺序栈的基本操作 #include <stdlib.h> #include <iostream> #include <stdio.h> #define MaxSize 10typedef struct{int data[MaxSize];int top; }SqStack;//初始化栈 void InitStack(SqStack &S){S.top -1; } //判断栈空 bool StackEmpty(SqStack S)…...
)
D. Jellyfish and Mex Codeforces Round 901 (Div. 2)
Problem - D - Codeforces 题目大意:有一个n个数的数组a,数m初始为0,每次操作可以删除任意一个数,然后m加上那个数,求n次操作和m的最小值 1<n<5000;0<a[i]<1e9 思路:可以发现&am…...
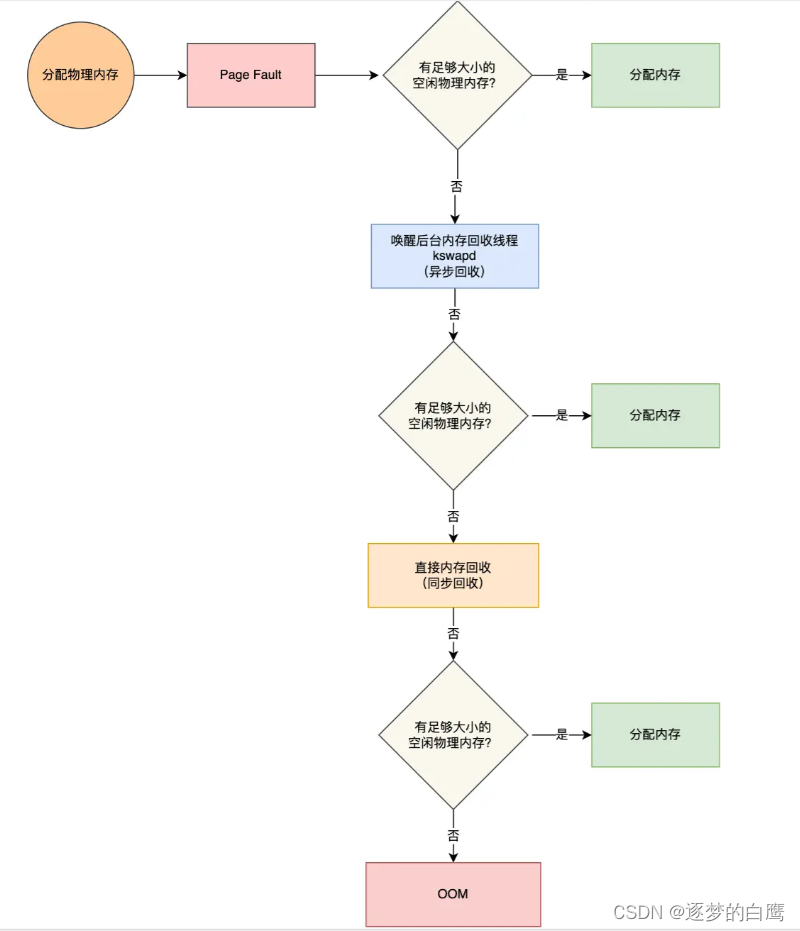
操作系统内存管理相关
1. 虚拟内存 1.1 什么是虚拟内存 虚拟内存是计算机系统内存管理的一种技术,我们可以手动设置自己电脑的虚拟内存。不要单纯认为虚拟内存只是“使用硬盘空间来扩展内存“的技术。虚拟内存的重要意义是它定义了一个连续的虚拟地址空间,并且 把内存扩展到硬…...

Sui流动性质押黑客松获胜者公布,助力资产再流通
Sui流动质押黑客松于日前结束Demo Day演示,其中有五个团队获奖、六个团队荣誉提名,共有超过30个项目获得参赛资格。此外,有两个团队赢得了Sui上DeFi协议提供的赏金。 本次黑客松的目的是挖掘并奖励将流动质押功能集成到其apps和产品中的开发…...
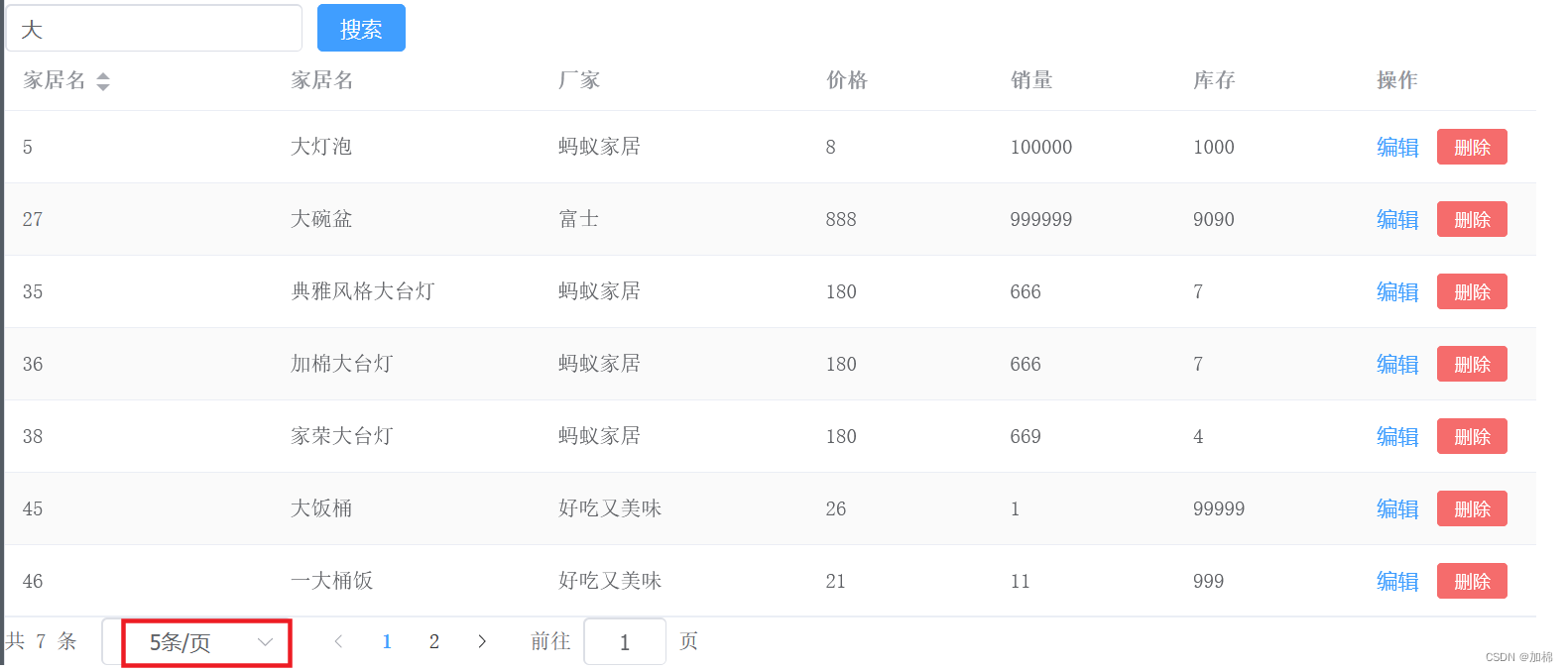
为什么在使用PageHelper插件时,指定的每页记录数大小失效?显示所有的记录数
1.问题现象: 这里指定每页显示5条,却把所有的记录数都显示出来了 2.分析: 之前是可以的,然后发现:PageHelper.startPage(pageNum,pageSize) 和执行sql的语句 顺序颠倒了,然后就出错了。 3.验证…...

XML文档基础
什么是XML XML (eXtensible Markup Language,可扩展标记语言) 是一种用于存储和传输数据的文本文件格式。用户可以按照XML规则自定义标记,XML 的设计目标是传输数据,而不是显示数据,因此它是一种通用的标记语言,可用于…...

软考知识汇总-软件工程
软件工程 1 能力成熟度模型(CMM)2 能力成熟度模型集成(CMMI)2.1阶段式模型2.2 连续式模型 3 软件过程模型 1 能力成熟度模型(CMM) 将软件工程成熟度分为5个级别 初始级:杂乱无章,很…...
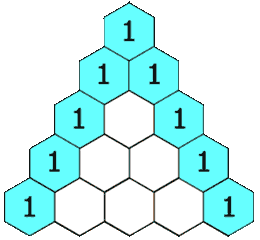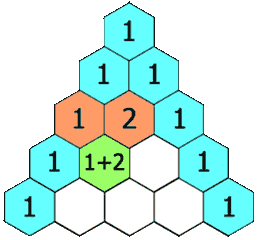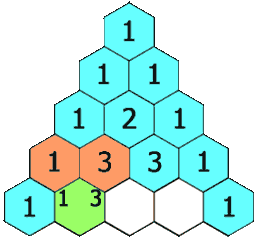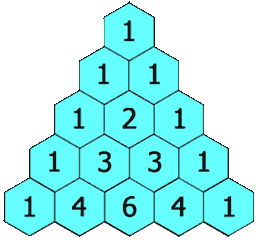
力扣:119. 杨辉三角 II(Python3)
题目: 给定一个非负索引 rowIndex,返回「杨辉三角」的第 rowIndex 行。 在「杨辉三角」中,每个数是它左上方和右上方的数的和。 来源:力扣(LeetCode) 链接:力扣(LeetCode)…...
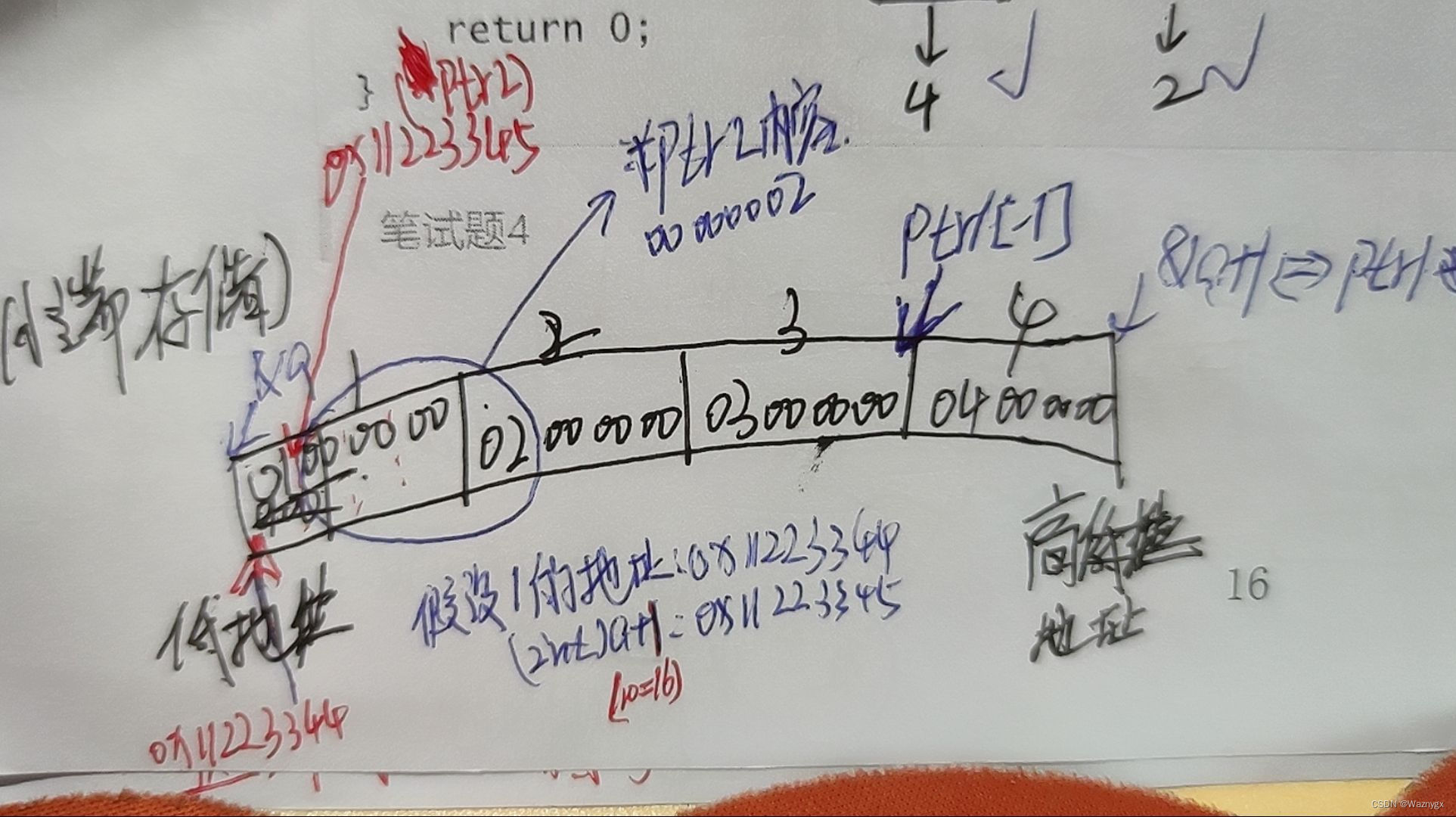
指针笔试题(带解析版)
题目2: struct MyStruct {int num;char* pcname;short sdate;char cha[2];short sba[4]; }*p; //结构体大小为32字节 //p0x100000 int main() {p 0x100000;printf("%p\n", p 0x1);//p:结构体指针,1下一个结构体指针,…...
服务器搭建(TCP套接字)-libevent版(服务端)
Libevent 是一个开源的事件驱动库,用于开发高性能、并发的网络应用程序。它提供了跨平台的事件处理和网络编程功能,具有高性能、可扩展性和可移植性。下面详细讲解 Libevent 的主要组成部分和使用方法。 一、事件基础结构(event_base&#x…...
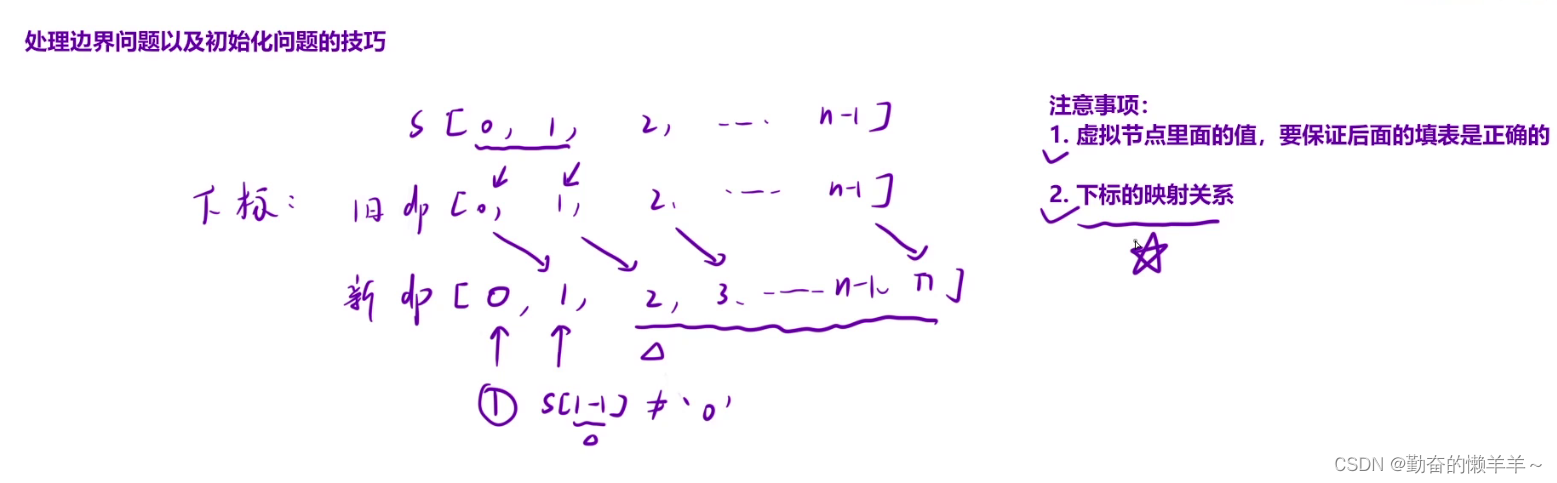
斐波那契模型系列【动态规划】
动态规划步骤 1、状态表示 是什么:dp表(可能是一维或二维数组)里的值所表示的含义。 怎么来: 1、题目要求 2、经验题目要求 3、发现重复子问题 2、状态转移方程 dp[i]... 3、初始化 保证填表不越界 4、填表顺序 5、返回值 写代码时…...

【Java】微服务——Nacos注册中心
目录 1.Nacos快速入门1.1.服务注册到nacos1)引入依赖2)配置nacos地址3)重启 2.服务分级存储模型2.1.给user-service配置集群2.2.同集群优先的负载均衡 3.权重配置4.环境隔离4.1.创建namespace4.2.给微服务配置namespace 5.Nacos与Eureka的区别…...

Redis Cluster Gossip Protocol: PING, PONG, MEET
返回目录 PING / PONG / MEET 的发送 过程 计算freshNodes。freshNodes表示在消息中能携带的,在cluster节点字典中的节点总数,但需要减去myself和对端节点,因为myself的信息会存储在消息头中。实际上,并非所有在cluster节点字典…...
httpserver 下载服务器demo 以及libevent版本的 httpserver
实现效果如下: 图片可以直接显示 cpp h 这些可以直接显示 其他的 则是提示是否要下载 单线程 还有bug 代码如下 先放上来 #include "httpserver.h" #include "stdio.h" #include <stdlib.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> #include…...

构建强大的RESTful API:@RestController与@Controller的对比与应用
构建强大的RESTful API:RestController与Controller的对比与应用 前言什么是RESTful APIRestController,Controller,ResponseBody1. Controller注解:2. RestController注解:3. ResponseBody注解: 示例非thy…...
-当不存在一个简单的正确答案时)
【Java-LangChain:使用 ChatGPT API 搭建系统-10】评估(下)-当不存在一个简单的正确答案时
第十章,评估(下)-当不存在一个简单的正确答案时 在上一章中,了解了如何评估 LLM 模型在 有明确正确答案 的情况下的输出,我们可以编写一个函数来判断 LLM 输出是否正确地分类并列出产品。 然而,如果 LLM …...
: K8s 核心概念白话解读(上):Pod 和 Deployment 究竟是什么?)
云原生核心技术 (7/12): K8s 核心概念白话解读(上):Pod 和 Deployment 究竟是什么?
大家好,欢迎来到《云原生核心技术》系列的第七篇! 在上一篇,我们成功地使用 Minikube 或 kind 在自己的电脑上搭建起了一个迷你但功能完备的 Kubernetes 集群。现在,我们就像一个拥有了一块崭新数字土地的农场主,是时…...

ES6从入门到精通:前言
ES6简介 ES6(ECMAScript 2015)是JavaScript语言的重大更新,引入了许多新特性,包括语法糖、新数据类型、模块化支持等,显著提升了开发效率和代码可维护性。 核心知识点概览 变量声明 let 和 const 取代 var…...

Golang dig框架与GraphQL的完美结合
将 Go 的 Dig 依赖注入框架与 GraphQL 结合使用,可以显著提升应用程序的可维护性、可测试性以及灵活性。 Dig 是一个强大的依赖注入容器,能够帮助开发者更好地管理复杂的依赖关系,而 GraphQL 则是一种用于 API 的查询语言,能够提…...

渲染学进阶内容——模型
最近在写模组的时候发现渲染器里面离不开模型的定义,在渲染的第二篇文章中简单的讲解了一下关于模型部分的内容,其实不管是方块还是方块实体,都离不开模型的内容 🧱 一、CubeListBuilder 功能解析 CubeListBuilder 是 Minecraft Java 版模型系统的核心构建器,用于动态创…...

什么是EULA和DPA
文章目录 EULA(End User License Agreement)DPA(Data Protection Agreement)一、定义与背景二、核心内容三、法律效力与责任四、实际应用与意义 EULA(End User License Agreement) 定义: EULA即…...
selenium学习实战【Python爬虫】
selenium学习实战【Python爬虫】 文章目录 selenium学习实战【Python爬虫】一、声明二、学习目标三、安装依赖3.1 安装selenium库3.2 安装浏览器驱动3.2.1 查看Edge版本3.2.2 驱动安装 四、代码讲解4.1 配置浏览器4.2 加载更多4.3 寻找内容4.4 完整代码 五、报告文件爬取5.1 提…...
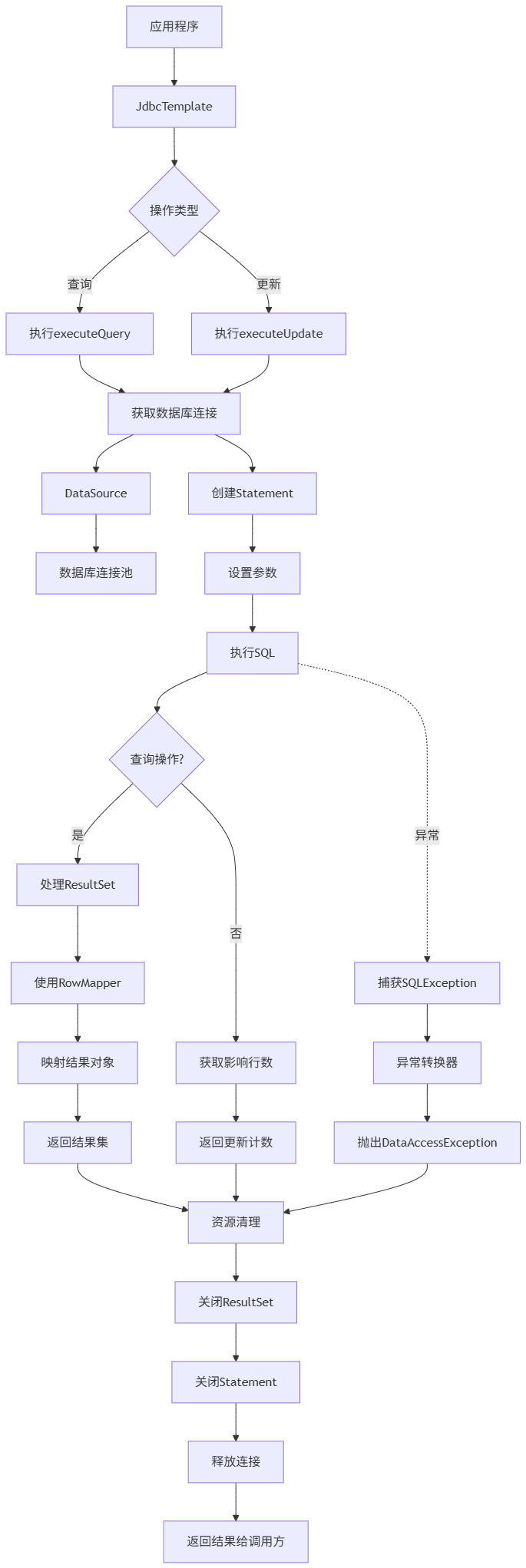
Spring数据访问模块设计
前面我们已经完成了IoC和web模块的设计,聪明的码友立马就知道了,该到数据访问模块了,要不就这俩玩个6啊,查库势在必行,至此,它来了。 一、核心设计理念 1、痛点在哪 应用离不开数据(数据库、No…...

2023赣州旅游投资集团
单选题 1.“不登高山,不知天之高也;不临深溪,不知地之厚也。”这句话说明_____。 A、人的意识具有创造性 B、人的认识是独立于实践之外的 C、实践在认识过程中具有决定作用 D、人的一切知识都是从直接经验中获得的 参考答案: C 本题解…...

网站指纹识别
网站指纹识别 网站的最基本组成:服务器(操作系统)、中间件(web容器)、脚本语言、数据厍 为什么要了解这些?举个例子:发现了一个文件读取漏洞,我们需要读/etc/passwd,如…...
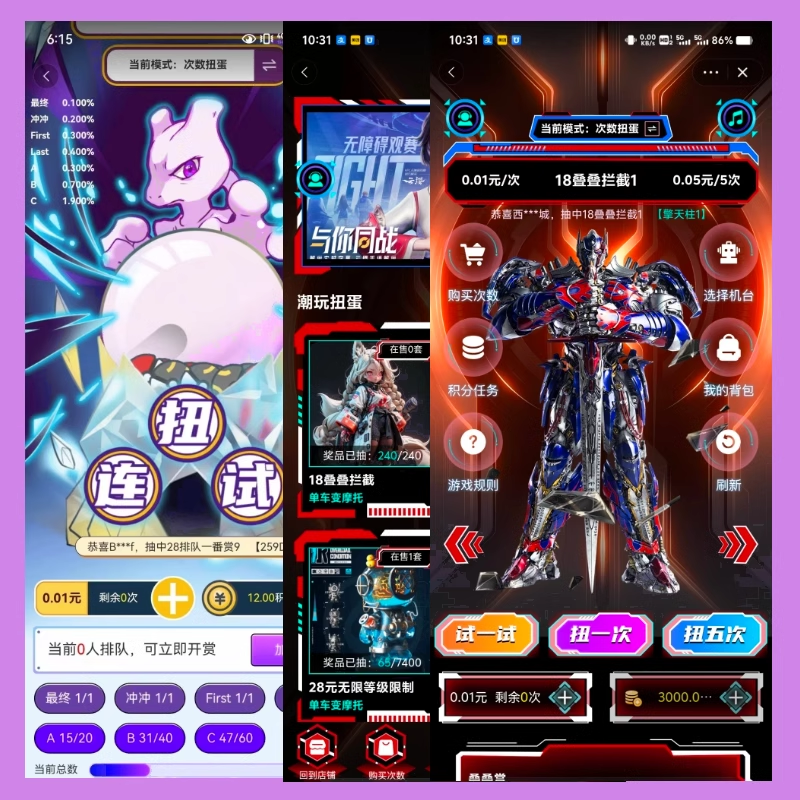
淘宝扭蛋机小程序系统开发:打造互动性强的购物平台
淘宝扭蛋机小程序系统的开发,旨在打造一个互动性强的购物平台,让用户在购物的同时,能够享受到更多的乐趣和惊喜。 淘宝扭蛋机小程序系统拥有丰富的互动功能。用户可以通过虚拟摇杆操作扭蛋机,实现旋转、抽拉等动作,增…...
