【Sentinel】Sentinel原码分析
本文内容来自【黑马】Sentinel从使用到源码解读笔记,做了部分修改和补充
目录
Sentinel 基本概念
基本流程
Node
Entry
定义资源的两种方式
使用try-catch定义资源
使用注解标记资源
基于注解标记资源的实现原理
Context
什么是Context
Context的初始化
ContextUtil
ProcessorSlotChain执行流程
入口
NodeSelectorSlot
ClusterBuilderSlot
LogSlot
StatisticSlot
AuthoritySlot
SystemSlot
ParamFlowSlot
令牌桶
FlowSlot
滑动时间窗口
时间窗口请求量统计
滑动窗口QPS计算
DegradeSlot
触发断路器
Sentinel 基本概念
基本流程
在 Sentinel 里面,所有的资源都对应一个资源名称以及一个 Entry。Entry 可以通过对主流框架的适配自动创建,也可以通过注解的方式或调用 API 显式创建;每一个 Entry 创建的时候,同时也会创建一系列功能插槽(slot chain)。这些插槽有不同的职责:
NodeSelectorSlot负责收集资源的路径,并将这些资源的调用路径,以树状结构存储起来,用于根据调用路径来限流降级;ClusterBuilderSlot用于存储资源的统计信息以及调用者信息,例如该资源的 RT, QPS, thread count 等等,这些信息将用作为多维度限流,降级的依据;LogSlot用于响应日志记录块异常,以提供用于故障排除的具体日志;StatisticSlot用于记录、统计不同纬度的 runtime 指标监控信息;AuthoritySlot根据配置的黑白名单和调用来源信息,来做黑白名单控制;SystemSlot通过系统的状态,例如 load1 等,来控制总的入口流量;ParamFlowSlot负责通过频繁(“热点”)参数进行流控制的处理器插槽;FlowSlot则用于根据预设的限流规则以及前面 slot 统计的状态,来进行流量控制;DegradeSlot通过统计信息以及预设的规则,来做熔断降级;
总体的框架如下(旧版,未更新):
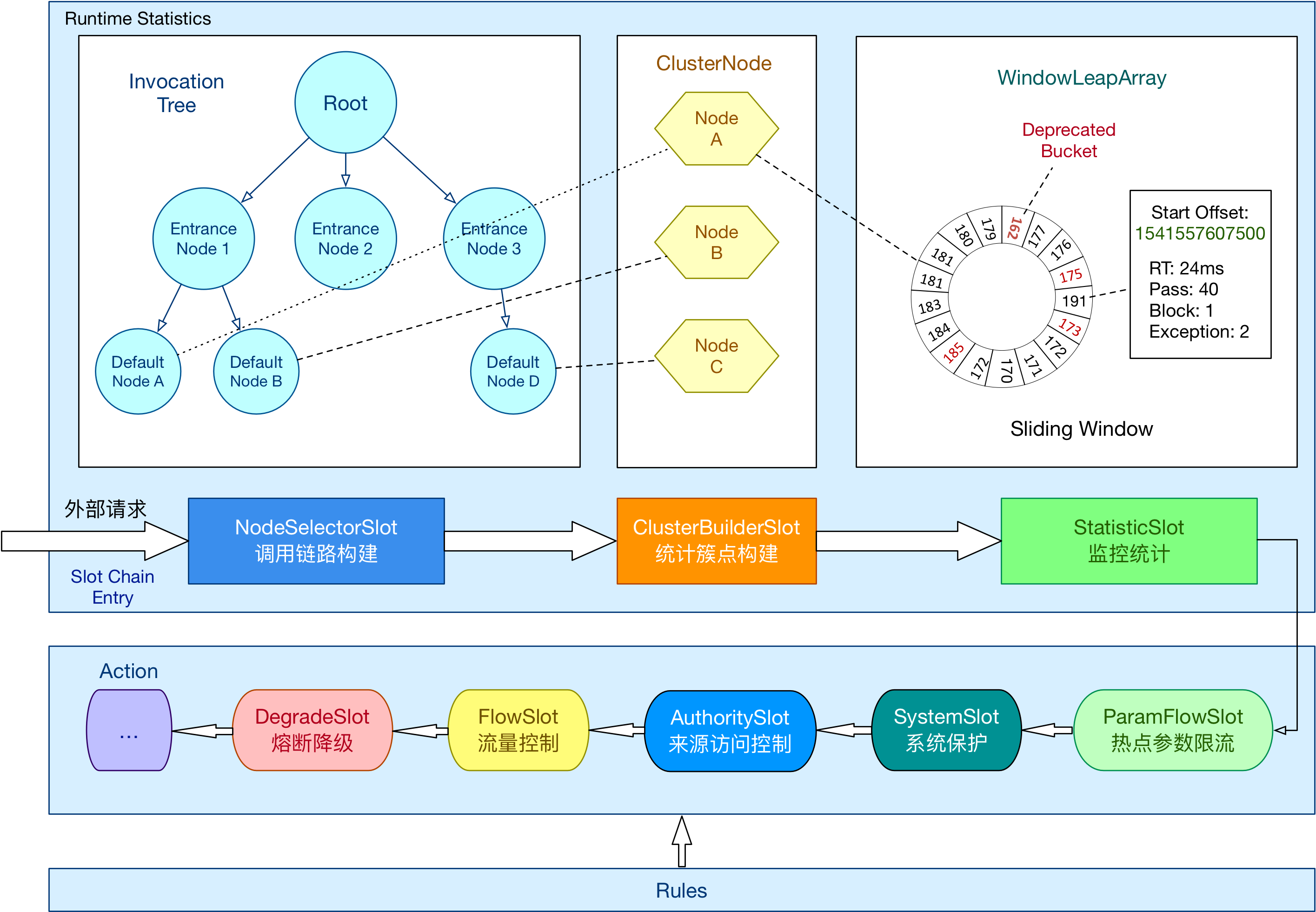
Sentinel 将 ProcessorSlot 作为 SPI 接口进行扩展(1.7.2 版本以前 SlotChainBuilder 作为 SPI),使得 Slot Chain 具备了扩展的能力。可以自行加入自定义的 slot 并编排 slot 间的顺序,从而可以给 Sentinel 添加自定义的功能。

Slot也为两大类:
- 统计数据构建部分(statistic)
-
- NodeSelectorSlot
- ClusterBuilderSlot
- LogSlot
- StatisticSlot
- 规则判断部分(rule checking)
-
- AuthoritySlot
- SystemSlot
- ParamFlowSlot
- FlowSlot
- DegradeSlot
Node
Sentinel中的簇点链路是由一个个的Node组成的,Node是一个接口,包括下面的实现:

所有的节点都可以记录对资源的访问统计数据,所以都是StatisticNode的子类。
按照作用分为两类Node:
DefaultNode:代表链路树中的每一个资源,一个资源出现在不同链路中时,会创建不同的DefaultNode节点。而树的入口节点叫EntranceNode,是一种特殊的DefaultNodeClusterNode:代表资源,一个资源不管出现在多少链路中,只会有一个ClusterNode。记录的是当前资源被访问的所有统计数据之和。
DefaultNode记录的是资源在当前链路中的访问数据,用来实现基于链路模式的限流规则。
ClusterNode记录的是资源在所有链路中的访问数据,实现默认模式、关联模式的限流规则。
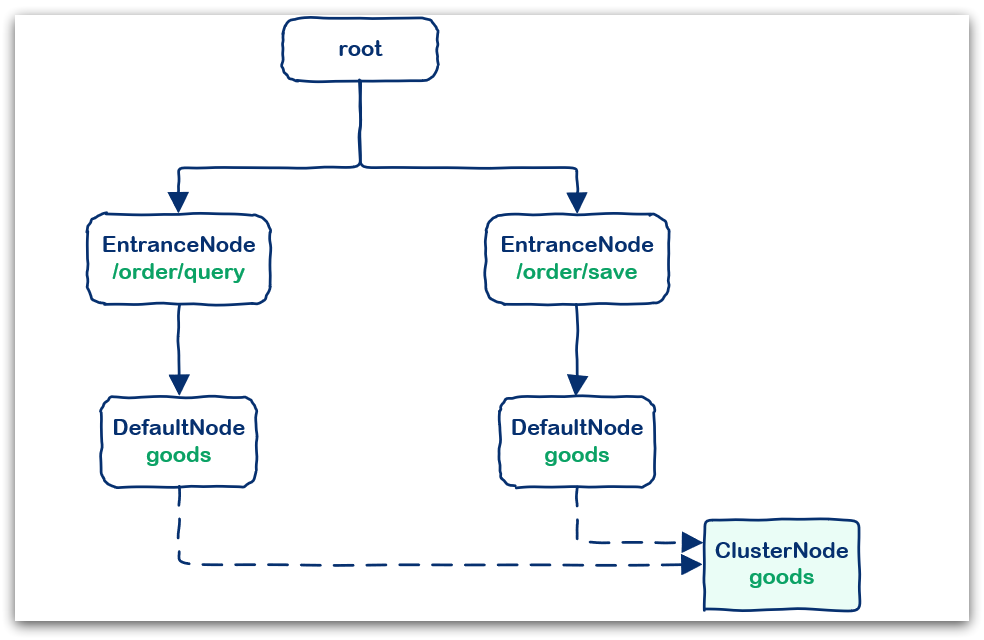
例如:在一个SpringMVC项目中,有两个业务:
- 业务1:controller中的资源/order/query访问了service中的资源/goods
- 业务2:controller中的资源/order/save访问了service中的资源/goods
创建的链路图如下:
Entry
默认情况下,Sentinel会将controller中的方法作为被保护资源,如果想定义自己的资源,则需显示定义。
Sentinel中的资源用Entry来表示。
定义资源的两种方式
使用try-catch定义资源
// 资源名可使用任意有业务语义的字符串,比如方法名、接口名或其它可唯一标识的字符串。
try (Entry entry = SphU.entry("resourceName")) {// 被保护的业务逻辑// do something here...
} catch (BlockException ex) {// 资源访问阻止,被限流或被降级// 在此处进行相应的处理操作
}public Order queryOrderById(Long orderId) {// 创建Entry,标记资源,资源名为resource1try (Entry entry = SphU.entry("resource1")) {// 1.查询订单,这里是假数据Order order = Order.build(101L, 4999L, "小米 MIX4", 1, 1L, null);// 2.查询用户,基于Feign的远程调用User user = userClient.findById(order.getUserId());// 3.设置order.setUser(user);// 4.返回return order;}catch (BlockException e){log.error("被限流或降级", e);return null;}
}使用注解标记资源
@SentinelResource("orderResource")
public Order queryOrderById(Long orderId) {// 1.查询订单Order order = orderMapper.findById(orderId);// 2.用Feign远程调用User user = userClient.findById(order.getUserId());// 3.封装user到Orderorder.setUser(user);// 4.返回return order;
}
基于注解标记资源的实现原理
Sentinel的stater中,spring.factories声明需要就是自动装配的配置类

在SentinelAutoConfiguration类中声明了一个SentinelResourceAspectbean
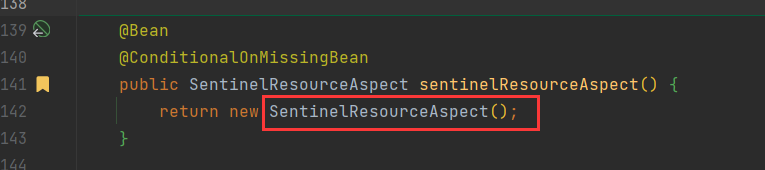
在SentinelResourceAspect中基于AOP实现了增强。
@Aspect
public class SentinelResourceAspect extends AbstractSentinelAspectSupport {// 切点是添加了 @SentinelResource注解的类@Pointcut("@annotation(com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.annotation.SentinelResource)")public void sentinelResourceAnnotationPointcut() {}// 环绕增强@Around("sentinelResourceAnnotationPointcut()")public Object invokeResourceWithSentinel(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {// 获取受保护的方法Method originMethod = resolveMethod(pjp);// 获取 @SentinelResource注解// @SentinelResource("resource1")SentinelResource annotation = originMethod.getAnnotation(SentinelResource.class);if (annotation == null) {// Should not go through here.throw new IllegalStateException("Wrong state for SentinelResource annotation");}// 获取注解上的资源名称String resourceName = getResourceName(annotation.value(), originMethod);EntryType entryType = annotation.entryType();int resourceType = annotation.resourceType();Entry entry = null;try {// 创建资源 Entryentry = SphU.entry(resourceName, resourceType, entryType, pjp.getArgs());// 执行受保护的方法Object result = pjp.proceed();return result;} catch (BlockException ex) {return handleBlockException(pjp, annotation, ex);} catch (Throwable ex) {Class<? extends Throwable>[] exceptionsToIgnore = annotation.exceptionsToIgnore();// The ignore list will be checked first.if (exceptionsToIgnore.length > 0 && exceptionBelongsTo(ex, exceptionsToIgnore)) {throw ex;}if (exceptionBelongsTo(ex, annotation.exceptionsToTrace())) {traceException(ex);return handleFallback(pjp, annotation, ex);}// No fallback function can handle the exception, so throw it out.throw ex;} finally {if (entry != null) {entry.exit(1, pjp.getArgs());}}}
}@SentinelResource注解就是一个标记,而Sentinel基于AOP思想,对被标记的方法做环绕增强,完成资源(Entry)的创建。
Context
在上面的簇点链路中除了controller方法、service方法两个资源外,还多了一个默认的入口节点:
sentinel_spring_web_context,这是一个EntranceNode类型的节点。
这个节点是在初始化Context的时候由Sentinel创建的。
什么是Context
- Context 代表调用链路上下文,贯穿一次调用链路中的所有资源(
Entry),基于ThreadLocal。 - Context 维持着入口节点(
entranceNode)、本次调用链路的curNode(当前资源节点)、调用来源(origin)等信息。 - 后续的Slot都可以通过
Context拿到DefaultNode或者ClusterNode,从而获取统计数据,完成规则判断 Context初始化的过程中,会创建EntranceNode,contextName就是EntranceNode的名称
对应的API如下:
// 创建context,包含两个参数:context名称、 来源名称
ContextUtil.enter("contextName", "originName");Context的初始化

在SentinelWebAutoConfiguration中,添加了SentinelWebInterceptor
@Autowired
private Optional<SentinelWebInterceptor> sentinelWebInterceptorOptional;
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {if (!sentinelWebInterceptorOptional.isPresent()) {return;}SentinelProperties.Filter filterConfig = properties.getFilter();// 添加一个SentinelWebInterceptor拦截器registry.addInterceptor(sentinelWebInterceptorOptional.get()).order(filterConfig.getOrder()).addPathPatterns(filterConfig.getUrlPatterns());log.info("[Sentinel Starter] register SentinelWebInterceptor with urlPatterns: {}.",filterConfig.getUrlPatterns());
}SentinelWebInterceptor继承自AbstractSentinelInterceptor,而AbstractSentinelInterceptor实现了HandlerInterceptor接口,会拦截一切进入controller的方法,执行preHandle前置拦截方法,而Context的初始化就是在这里完成的。
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {try {// 获取资源名称,一般是controller方法的@RequestMapping路径,例如/order/{orderId}String resourceName = getResourceName(request);if (StringUtil.isEmpty(resourceName)) {return true;}if (increaseReferece(request, this.baseWebMvcConfig.getRequestRefName(), 1) != 1) {return true;}// Parse the request origin using registered origin parser.// 从request中获取请求来源,将来做 授权规则 判断时会用String origin = parseOrigin(request);// 获取 contextName,默认是sentinel_spring_web_contextString contextName = getContextName(request);// 创建 ContextContextUtil.enter(contextName, origin);// 创建资源,名称就是当前请求的controller方法的映射路径Entry entry = SphU.entry(resourceName, ResourceTypeConstants.COMMON_WEB, EntryType.IN);request.setAttribute(baseWebMvcConfig.getRequestAttributeName(), entry);return true;} catch (BlockException e) {try {handleBlockException(request, response, e);} finally {ContextUtil.exit();}return false;}
}如果要关闭使用sentinel_spring_web_context作为默认的root,只需要在application.yml文件中关闭即可
spring: cloud: sentinel:web-context-unify: false # 关闭context整合ContextUtil
创建Context的方法就是ContextUtil.enter(contextName, origin);
public static Context enter(String name, String origin) {if (Constants.CONTEXT_DEFAULT_NAME.equals(name)) {throw new ContextNameDefineException("The " + Constants.CONTEXT_DEFAULT_NAME + " can't be permit to defined!");}return trueEnter(name, origin);
}protected static Context trueEnter(String name, String origin) {// 尝试获取contextContext context = contextHolder.get();// 判空if (context == null) {// 如果为空,开始初始化Map<String, DefaultNode> localCacheNameMap = contextNameNodeMap;// 尝试获取入口节点DefaultNode node = localCacheNameMap.get(name);if (node == null) {// 判断缓存数量是否上限if (localCacheNameMap.size() > Constants.MAX_CONTEXT_NAME_SIZE) {setNullContext();return NULL_CONTEXT;} else {// 加锁,确保线程安全LOCK.lock();try {node = contextNameNodeMap.get(name);if (node == null) {if (contextNameNodeMap.size() > Constants.MAX_CONTEXT_NAME_SIZE) {setNullContext();return NULL_CONTEXT;} else {node = new EntranceNode(new StringResourceWrapper(name, EntryType.IN), null);// 添加入口节点到 ROOTConstants.ROOT.addChild(node);// 将入口节点放入缓存Map<String, DefaultNode> newMap = new HashMap<>(contextNameNodeMap.size() + 1);newMap.putAll(contextNameNodeMap);newMap.put(name, node);contextNameNodeMap = newMap;}}} finally {LOCK.unlock();}}}// 创建Context,参数为:入口节点 和 contextNamecontext = new Context(node, name);// 设置请求来源 origincontext.setOrigin(origin);// 放入ThreadLocalcontextHolder.set(context);}// 返回return context;
}ProcessorSlotChain执行流程
入口
从上面的分析中可以知道,资源可以分为两种类型
- sentinel自己对所有的controller接口创建的资源
-
- 这种资源的创建位于
AbstractSentinelInterceptor的preHandle方法中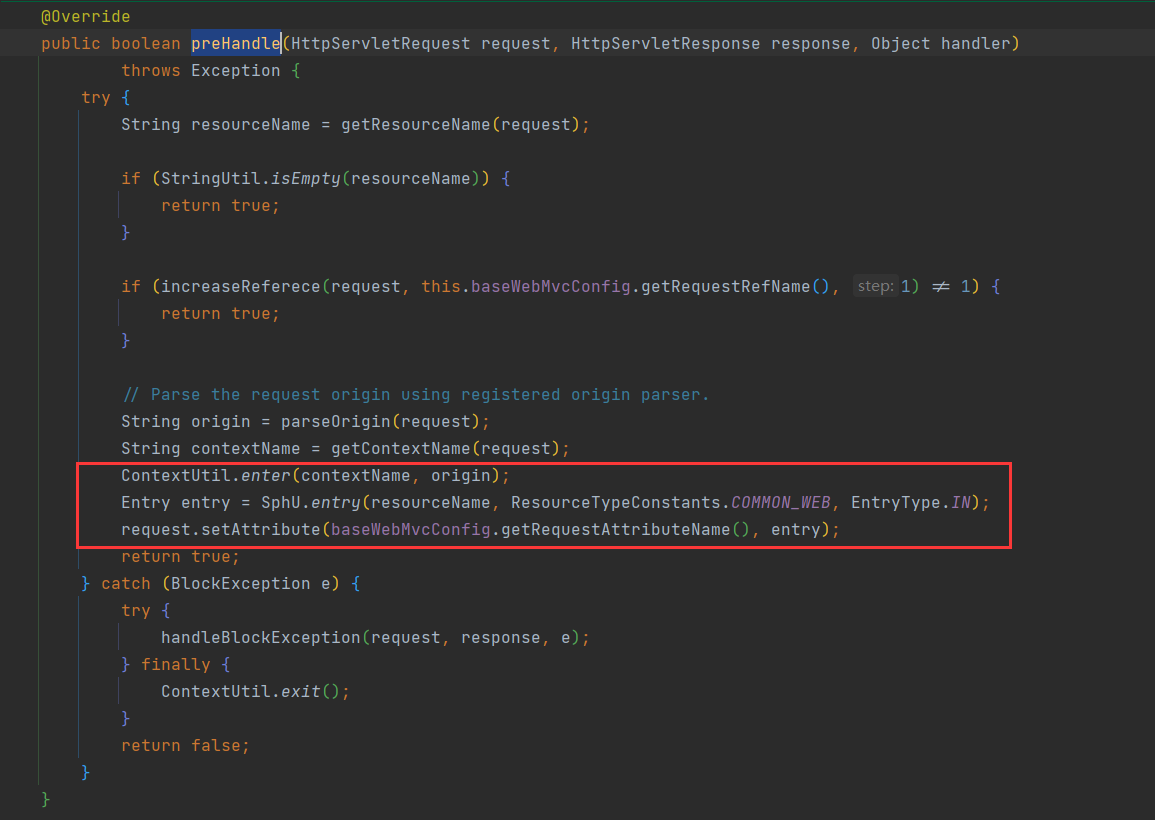
- 这种资源的创建位于
- 我们自己使用注解或者try-cache创建的声明的资源
-
- 这种资源的创建位于
SentinelResourceAspect的环绕通知中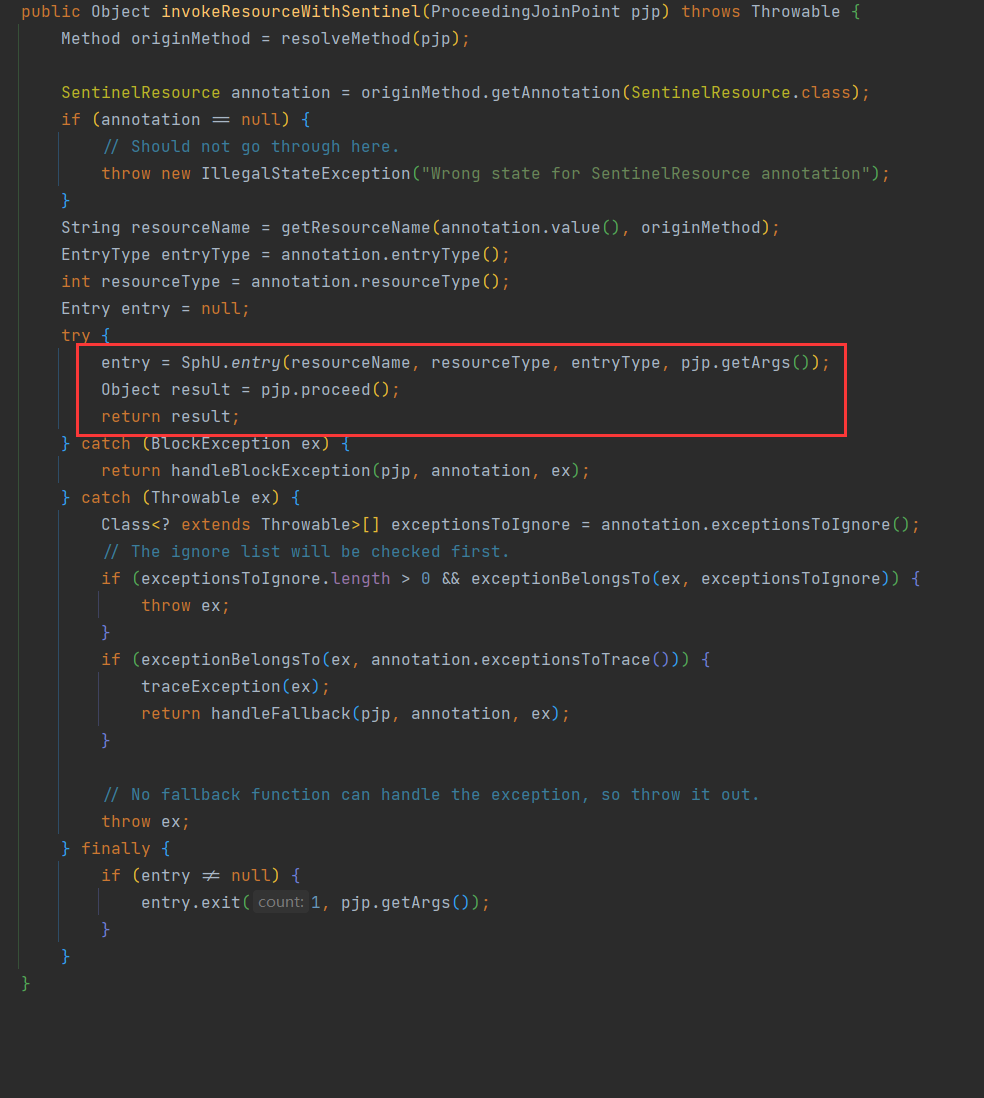
- 这种资源的创建位于
这两种方式都是用了SphU.entry();这个方法
public static Entry entry(String name, int resourceType, EntryType trafficType, Object[] args)
throws BlockException {return Env.sph.entryWithType(name, resourceType, trafficType, 1, args);
}@Override
public Entry entryWithType(String name, int resourceType, EntryType entryType, int count, Object[] args)throws BlockException {return entryWithType(name, resourceType, entryType, count, false, args);
}@Override
public Entry entryWithType(String name, int resourceType, EntryType entryType, int count, boolean prioritized,Object[] args) throws BlockException {// 将 资源名称等基本信息 封装为一个 StringResourceWrapper对象StringResourceWrapper resource = new StringResourceWrapper(name, entryType, resourceType);return entryWithPriority(resource, count, prioritized, args);
}private Entry entryWithPriority(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws BlockException {// 获取 ContextContext context = ContextUtil.getContext();if (context instanceof NullContext) {// The {@link NullContext} indicates that the amount of context has exceeded the threshold,// so here init the entry only. No rule checking will be done.return new CtEntry(resourceWrapper, null, context);}if (context == null) {// Using default context.context = InternalContextUtil.internalEnter(Constants.CONTEXT_DEFAULT_NAME);}// Global switch is close, no rule checking will do.if (!Constants.ON) {return new CtEntry(resourceWrapper, null, context);}// 获取 Slot执行链,同一个资源,会创建一个执行链,放入缓存// 这里是创建 DefaultProcessorSlotChain子类ProcessorSlot<Object> chain = lookProcessChain(resourceWrapper);/** Means amount of resources (slot chain) exceeds {@link Constants.MAX_SLOT_CHAIN_SIZE},* so no rule checking will be done.*/if (chain == null) {return new CtEntry(resourceWrapper, null, context);}// 创建 Entry,并将 resource、chain、context 记录在 Entry中Entry e = new CtEntry(resourceWrapper, chain, context);try {// 执行 slotChainchain.entry(context, resourceWrapper, null, count, prioritized, args);} catch (BlockException e1) {e.exit(count, args);throw e1;} catch (Throwable e1) {// This should not happen, unless there are errors existing in Sentinel internal.RecordLog.info("Sentinel unexpected exception", e1);}return e;
}在这段代码中,会获取ProcessorSlotChain对象,然后基于chain.entry()开始执行slotChain中的每一个Slot。 而这里创建的是其实现类:DefaultProcessorSlotChain。
获取ProcessorSlotChain后会保存到Map中,key是ResourceWrapper,值是ProcessorSlotChain。
所以,一个资源只会有一个ProcessorSlotChain。
此时在DefaultProcessorSlotChain的entry()方法中,first是DefaultProcessorSlotChain,之后基于责任链模式,后续slot作为上一个slot的next执行。
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, Object t, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {first.transformEntry(context, resourceWrapper, t, count, prioritized, args);
}@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
void transformEntry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, Object o, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {T t = (T)o;entry(context, resourceWrapper, t, count, prioritized, args);
}AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot中的entry()方法调用顺序如下
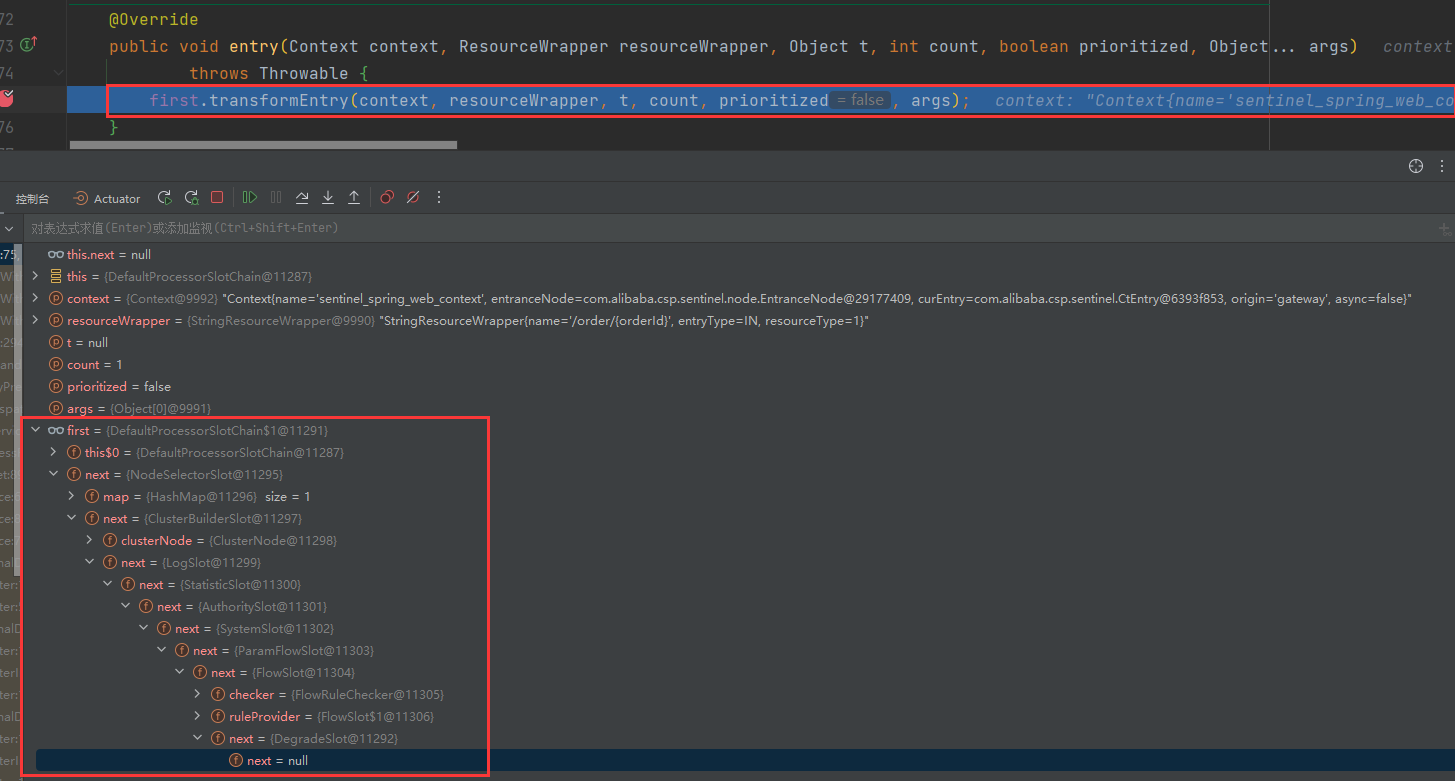
NodeSelectorSlot
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, Object obj, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args)
throws Throwable {DefaultNode node = map.get(context.getName());if (node == null) {synchronized (this) {node = map.get(context.getName());if (node == null) {// 创建DefaultNodenode = new DefaultNode(resourceWrapper, null);// 将DefaultNode放入缓存中,key是contextName,// 这样不同链路入口的请求,将会创建多个DefaultNode,相同链路则只有一个DefaultNodeHashMap<String, DefaultNode> cacheMap = new HashMap<String, DefaultNode>(map.size());cacheMap.putAll(map);cacheMap.put(context.getName(), node);map = cacheMap;// Build invocation tree// 将当前资源的DefaultNode设置为上一个资源的childNode((DefaultNode) context.getLastNode()).addChild(node);}}}// 将当前资源的DefaultNode设置为Context中的curNode(当前节点)context.setCurNode(node);fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
}这个Slot完成了这么几件事情:
- 为当前资源创建 DefaultNode
- 将DefaultNode放入缓存中,key是contextName,这样不同链路入口的请求,将会创建多个DefaultNode,相同链路则只有一个DefaultNode
- 将当前资源的DefaultNode设置为上一个资源的childNode
- 将当前资源的DefaultNode设置为Context中的curNode(当前节点)
下一个slot,就是ClusterBuilderSlot
ClusterBuilderSlot
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {// 判空,注意ClusterNode是共享的成员变量,也就是说一个资源只有一个ClusterNode,与链路无关if (clusterNode == null) {synchronized (lock) {if (clusterNode == null) {// Create the cluster node.clusterNode = new ClusterNode(resourceWrapper.getName(), resourceWrapper.getResourceType());HashMap<ResourceWrapper, ClusterNode> newMap = new HashMap<>(Math.max(clusterNodeMap.size(), 16));newMap.putAll(clusterNodeMap);// 放入缓存newMap.put(node.getId(), clusterNode);clusterNodeMap = newMap;}}}// 将资源的 DefaultNode与 ClusterNode关联node.setClusterNode(clusterNode);/** if context origin is set, we should get or create a new {@link Node} of the specific origin.*/if (!"".equals(context.getOrigin())) {// 记录请求来源 origin 将 origin放入 entryNode originNode = node.getClusterNode().getOrCreateOriginNode(context.getOrigin());context.getCurEntry().setOriginNode(originNode);}// 继续下一个slotfireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
}LogSlot
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode obj, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args)
throws Throwable {try {// 执行下一个slot,如果有异常则记录并抛出fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, obj, count, prioritized, args);} catch (BlockException e) {EagleEyeLogUtil.log(resourceWrapper.getName(), e.getClass().getSimpleName(), e.getRuleLimitApp(), context.getOrigin(), count);throw e;} catch (Throwable e) {RecordLog.warn("Unexpected entry exception", e);}}StatisticSlot
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count,boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {try {// 执行下一个slot,做限流、降级等判断fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);// 请求通过了, 线程计数器 +1 ,用作线程隔离node.increaseThreadNum();// 请求计数器 +1 用作限流node.addPassRequest(count);if (context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode() != null) {// 如果有 origin,来源计数器也都要 +1context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode().increaseThreadNum();context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode().addPassRequest(count);}if (resourceWrapper.getEntryType() == EntryType.IN) {// 如果是入口资源,还要给全局计数器 +1.Constants.ENTRY_NODE.increaseThreadNum();Constants.ENTRY_NODE.addPassRequest(count);}// 请求通过后的回调.for (ProcessorSlotEntryCallback<DefaultNode> handler : StatisticSlotCallbackRegistry.getEntryCallbacks()) {handler.onPass(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, args);}} catch (PriorityWaitException ex) {异常处理......throw e;}
}另外,需要注意的是,所有的计数+1动作都包括两部分,以node.addPassRequest(count);为例:
@Override
public void addPassRequest(int count) {// DefaultNode的计数器,代表当前链路的 计数器super.addPassRequest(count);// ClusterNode计数器,代表当前资源的 总计数器this.clusterNode.addPassRequest(count);
}AuthoritySlot
负责请求来源origin的授权规则判断,如图:
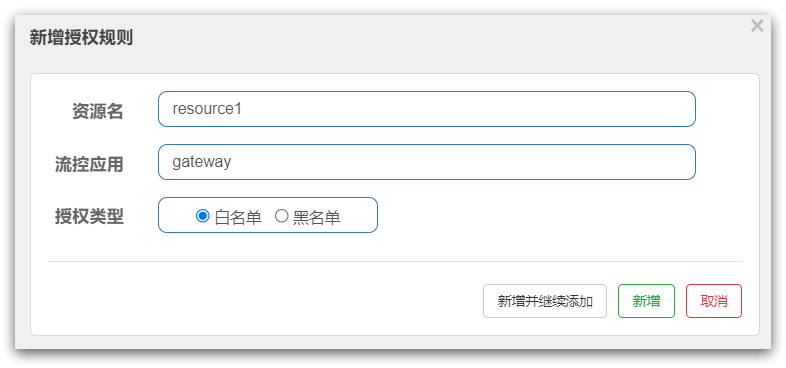
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args)throws Throwable {// 校验黑白名单checkBlackWhiteAuthority(resourceWrapper, context);// 进入下一个 slotfireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
}void checkBlackWhiteAuthority(ResourceWrapper resource, Context context) throws AuthorityException {// 获取授权规则Map<String, Set<AuthorityRule>> authorityRules = AuthorityRuleManager.getAuthorityRules();if (authorityRules == null) {return;}Set<AuthorityRule> rules = authorityRules.get(resource.getName());if (rules == null) {return;}// 遍历规则并判断for (AuthorityRule rule : rules) {if (!AuthorityRuleChecker.passCheck(rule, context)) {// 规则不通过,直接抛出异常throw new AuthorityException(context.getOrigin(), rule);}}
}static boolean passCheck(AuthorityRule rule, Context context) {String requester = context.getOrigin();// Empty origin or empty limitApp will pass.if (StringUtil.isEmpty(requester) || StringUtil.isEmpty(rule.getLimitApp())) {return true;}// Do exact match with origin name.int pos = rule.getLimitApp().indexOf(requester);boolean contain = pos > -1;// 如果包含,做精确匹配if (contain) {boolean exactlyMatch = false;// 使用逗号分割String[] appArray = rule.getLimitApp().split(",");for (String app : appArray) {if (requester.equals(app)) {exactlyMatch = true;break;}}contain = exactlyMatch;}// 获取校验方式。0:白名单;1:黑名单int strategy = rule.getStrategy();if (strategy == RuleConstant.AUTHORITY_BLACK && contain) {return false;}if (strategy == RuleConstant.AUTHORITY_WHITE && !contain) {return false;}return true;
}默认的请求头是空的(""),所以需要使用gateway或者重写RequestOriginParser的parseOrigin()方法对请求头进行处理,都则空的origin会直接通过
重写RequestOriginParser
@Component
public class HeaderOriginParser implements RequestOriginParser {@Overridepublic String parseOrigin(HttpServletRequest request) {// 1.获取请求头String origin = request.getHeader("origin");// 2.非空判断,给空请求头附默认值if (StringUtils.isEmpty(origin)) {origin = "blank";}return origin;}
}在gateway中对请求头做处理
spring: cloud:gateway:default-filters:# 给经过网关的请求添加请求头,格式为 xxx,yyy- AddRequestHeader=Truth,Itcast is freaking awesome!- AddRequestHeader=origin,gatewaySystemSlot
SystemSlot是对系统保护的规则校验:

@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count,boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {SystemRuleManager.checkSystem(resourceWrapper);fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
}public static void checkSystem(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper) throws BlockException {if (resourceWrapper == null) {return;}// Ensure the checking switch is on.if (!checkSystemStatus.get()) {return;}// 只针对入口资源做校验,其它直接返回if (resourceWrapper.getEntryType() != EntryType.IN) {return;}// total qpsdouble currentQps = Constants.ENTRY_NODE == null ? 0.0 : Constants.ENTRY_NODE.successQps();if (currentQps > qps) {throw new SystemBlockException(resourceWrapper.getName(), "qps");}// total threadint currentThread = Constants.ENTRY_NODE == null ? 0 : Constants.ENTRY_NODE.curThreadNum();if (currentThread > maxThread) {throw new SystemBlockException(resourceWrapper.getName(), "thread");}// 全局平均 RT校验double rt = Constants.ENTRY_NODE == null ? 0 : Constants.ENTRY_NODE.avgRt();if (rt > maxRt) {throw new SystemBlockException(resourceWrapper.getName(), "rt");}// 全局 系统负载 校验if (highestSystemLoadIsSet && getCurrentSystemAvgLoad() > highestSystemLoad) {if (!checkBbr(currentThread)) {throw new SystemBlockException(resourceWrapper.getName(), "load");}}// 全局 CPU使用率 校验if (highestCpuUsageIsSet && getCurrentCpuUsage() > highestCpuUsage) {throw new SystemBlockException(resourceWrapper.getName(), "cpu");}
}ParamFlowSlot
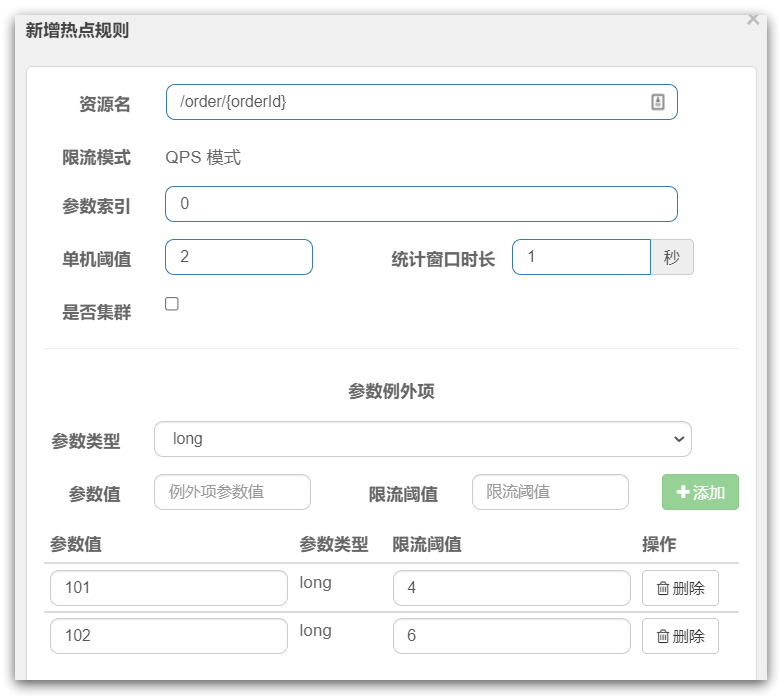
是针对进入资源的请求,针对不同的请求参数值分别统计QPS的限流方式。
- 这里的单机阈值,就是最大令牌数量:maxCount
- 这里的统计窗口时长,就是统计时长:duration
含义是每隔duration时间长度内,最多生产maxCount个令牌,上图配置的含义是每1秒钟生产2个令牌。
这里在配置资源名时,默认的controller资源是不生效的,
需要写@SentinelResource("orderResource")中的资源名。
比如对于下面的controller应该写hot而不是/order/{orderId}
@SentinelResource("hot")
@GetMapping("{orderId}")
public Order queryOrderByUserId(@PathVariable("orderId") Long orderId) {// 根据id查询订单并返回return orderService.queryOrderById(orderId);
}这是因为
// AbstractSentinelInterceptor
// 这里没有传入参数
Entry entry = SphU.entry(resourceName, ResourceTypeConstants.COMMON_WEB, EntryType.IN);// SentinelResourceAspect
// 这里在最后传入的参数pjp.getArgs()
entry = SphU.entry(resourceName, resourceType, entryType, pjp.getArgs());在dispatchServerlet中的doDispatch方法内部可以看到,先执行applyPreHandle(controller资源),然后执行handle(注解资源)
所以一个请求会创建两次资源(如果这个请求controller方法添加了@SentinelResource("hot"))
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);try {ModelAndView mv = null;Exception dispatchException = null;try {processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);// Determine handler for the current request.mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);if (mappedHandler == null) {noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);return;}// Determine handler adapter for the current request.HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.String method = request.getMethod();boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {return;}}// 前置处理,在这里进行controller接口的资源创建,创建的资源不支持热点参数限流if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {return;}// 执行真正的处理,在这里对添加注解的方法创建资源,支持热点参数限流// 因此,对于热点参数限流的controller方法,第一次请求进入到ParamFlowSlot的entry// 方法中时,不会进行checkFlow,因为没有传入热点参数// 第二次进入时,才会进行热点参数限流// Actually invoke the handler.mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {return;}applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);}catch (Exception ex) {异常处理。。。。。。
}核心API:
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count,boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {// 如果没有热点规则,直接放行if (!ParamFlowRuleManager.hasRules(resourceWrapper.getName())) {fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);return;}// 检查热点规则checkFlow(resourceWrapper, count, args);fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
}void checkFlow(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args) throws BlockException {// 检查args是否为nullif (args == null) {return;}// 检查ParamFlowRuleManager中是否定义了与给定资源名称相关的流量规则if (!ParamFlowRuleManager.hasRules(resourceWrapper.getName())) {return;}// 从ParamFlowRuleManager中获取与给定资源名称相关的所有流量规则,并将它们存储在rules列表中List<ParamFlowRule> rules = ParamFlowRuleManager.getRulesOfResource(resourceWrapper.getName());// 遍历rules列表中的每个流量规则rulefor (ParamFlowRule rule : rules) {// 应用实际的参数索引paramIdxapplyRealParamIdx(rule, args.length);// 初始化参数指标ParameterMetricStorageParameterMetricStorage.initParamMetricsFor(resourceWrapper, rule);// 使用ParamFlowChecker检查资源是否满足流量规则if (!ParamFlowChecker.passCheck(resourceWrapper, rule, count, args)) {// 获取触发异常的参数值和规则String triggeredParam = "";if (args.length > rule.getParamIdx()) {Object value = args[rule.getParamIdx()];triggeredParam = String.valueOf(value);}throw new ParamFlowException(resourceWrapper.getName(), triggeredParam, rule);}}
}public static boolean passCheck(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, /*@Valid*/ ParamFlowRule rule, /*@Valid*/ int count,Object... args) {if (args == null) {return true;}int paramIdx = rule.getParamIdx();if (args.length <= paramIdx) {return true;}// Get parameter value.Object value = args[paramIdx];// Assign value with the result of paramFlowKey methodif (value instanceof ParamFlowArgument) {value = ((ParamFlowArgument) value).paramFlowKey();}// If value is null, then passif (value == null) {return true;}if (rule.isClusterMode() && rule.getGrade() == RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS) {return passClusterCheck(resourceWrapper, rule, count, value);}return passLocalCheck(resourceWrapper, rule, count, value);
}private static boolean passLocalCheck(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, ParamFlowRule rule, int count,Object value) {try {if (Collection.class.isAssignableFrom(value.getClass())) {for (Object param : ((Collection)value)) {if (!passSingleValueCheck(resourceWrapper, rule, count, param)) {return false;}}} else if (value.getClass().isArray()) {int length = Array.getLength(value);for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {Object param = Array.get(value, i);if (!passSingleValueCheck(resourceWrapper, rule, count, param)) {return false;}}} else {return passSingleValueCheck(resourceWrapper, rule, count, value);}} catch (Throwable e) {RecordLog.warn("[ParamFlowChecker] Unexpected error", e);}return true;
}static boolean passSingleValueCheck(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, ParamFlowRule rule, int acquireCount,Object value) {if (rule.getGrade() == RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS) {if (rule.getControlBehavior() == RuleConstant.CONTROL_BEHAVIOR_RATE_LIMITER) {return passThrottleLocalCheck(resourceWrapper, rule, acquireCount, value);} else {// 走这里return passDefaultLocalCheck(resourceWrapper, rule, acquireCount, value);}} else if (rule.getGrade() == RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_THREAD) {Set<Object> exclusionItems = rule.getParsedHotItems().keySet();long threadCount = getParameterMetric(resourceWrapper).getThreadCount(rule.getParamIdx(), value);if (exclusionItems.contains(value)) {int itemThreshold = rule.getParsedHotItems().get(value);return ++threadCount <= itemThreshold;}long threshold = (long)rule.getCount();return ++threadCount <= threshold;}return true;
}令牌桶
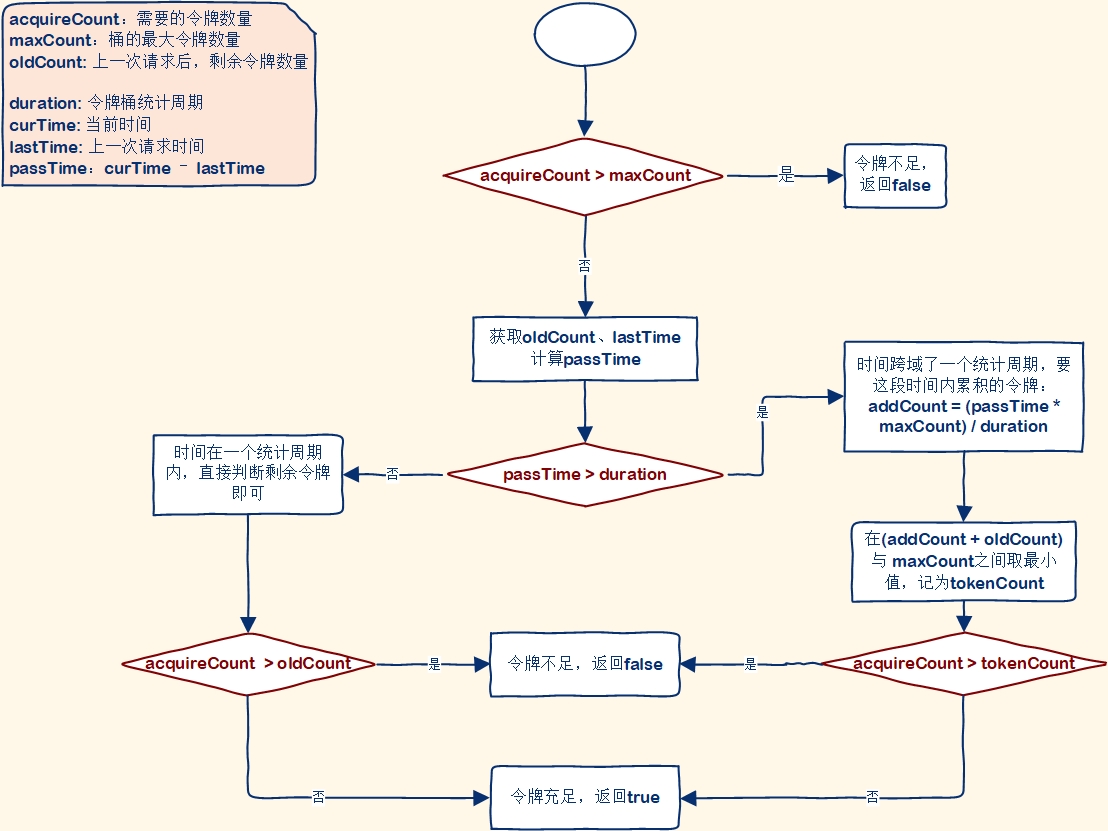
热点规则判断采用了令牌桶算法来实现参数限流,为每一个不同参数值设置令牌桶,Sentinel的令牌桶有两部分组成:

这两个Map的key都是请求的参数值,value却不同,其中:
- tokenCounters:用来记录剩余令牌数量
- timeCounters:用来记录上一个请求的时间
当一个携带参数的请求到来后,基本判断流程是这样的:
/*** 检查资源是否过载,基于给定的resourceWrapper、rule、acquireCount和value。* * @param resourceWrapper 资源包装器* @param rule 参数流规则* @param acquireCount 要获得的令牌数量* @param value 当前请求的标识符,热点参数* @return 如果资源没有过载,返回true,否则返回false*/
static boolean passDefaultLocalCheck(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, ParamFlowRule rule, int acquireCount, Object value) {// 获取参数指标ParameterMetric metric = getParameterMetric(resourceWrapper);// 获取令牌计数器和时间计数器从指标CacheMap<Object, AtomicLong> tokenCounters = metric == null ? null : metric.getRuleTokenCounter(rule);CacheMap<Object, AtomicLong> timeCounters = metric == null ? null : metric.getRuleTimeCounter(rule);// 检查令牌计数器和时间计数器是否为空if (tokenCounters == null || timeCounters == null) {return true;}// exclusionItems存放单独配置热点限流规则的参数值,对这部分参数做自定义的限流Set<Object> exclusionItems = rule.getParsedHotItems().keySet();long tokenCount = (long)rule.getCount();if (exclusionItems.contains(value)) {tokenCount = rule.getParsedHotItems().get(value);}// 检查令牌数量是否为0if (tokenCount == 0) {return false;}// 计算最大计数(阈值),getBurstCount()允许的突发阈值,一般为0long maxCount = tokenCount + rule.getBurstCount();if (acquireCount > maxCount) {return false;}// Token bucket算法while (true) {// 获取当前时间long currentTime = TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis();// 获取上次添加令牌的时间AtomicLong lastAddTokenTime = timeCounters.putIfAbsent(value, new AtomicLong(currentTime));// 如果上次添加令牌的时间为空,说明令牌从未添加if (lastAddTokenTime == null) {// 令牌未添加,只需补充令牌并消耗 acquireCount 立即返回 truetokenCounters.putIfAbsent(value, new AtomicLong(maxCount - acquireCount));return true;}// 计算自上次添加令牌以来时间间隔long passTime = currentTime - lastAddTokenTime.get();// 一个简化版的 token bucket 算法,当统计窗口已过时,才会补充令牌// 如果当前经过的时间大于一个统计窗口的时长if (passTime > rule.getDurationInSec() * 1000) {AtomicLong oldQps = tokenCounters.putIfAbsent(value, new AtomicLong(maxCount - acquireCount));if (oldQps == null) {// Might not be accurate here.lastAddTokenTime.set(currentTime);return true;} else {long restQps = oldQps.get();// 计算累计令牌数量: 经过时间*每秒生成令牌数/(统计窗口时长*1000)long toAddCount = (passTime * tokenCount) / (rule.getDurationInSec() * 1000);// 去最大令牌数量和累计令牌数量最小值long newQps = toAddCount + restQps > maxCount ? (maxCount - acquireCount) : (restQps + toAddCount - acquireCount);// 如果没有令牌直接返回if (newQps < 0) {return false;}if (oldQps.compareAndSet(restQps, newQps)) {lastAddTokenTime.set(currentTime);return true;}Thread.yield();}} else {// 获取剩余的令牌AtomicLong oldQps = tokenCounters.get(value);// 如果剩余的令牌不为空,比较并设置旧令牌值if (oldQps != null) {long oldQpsValue = oldQps.get();if (oldQpsValue - acquireCount >= 0) {if (oldQps.compareAndSet(oldQpsValue, oldQpsValue - acquireCount)) {return true;}} else {return false;}}// 释放线程Thread.yield();}}
}FlowSlot
包括:
- 三种流控模式:直接模式、关联模式、链路模式
- 三种流控效果:快速失败、warm up、排队等待
三种流控模式,从底层数据统计角度,分为两类:
- 对进入资源的所有请求(ClusterNode)做限流统计:直接模式、关联模式
- 对进入资源的部分链路(DefaultNode)做限流统计:链路模式
三种流控效果,从限流算法来看,分为两类:
- 滑动时间窗口算法:快速失败、warm up
- 漏桶算法:排队等待效果
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count,boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {checkFlow(resourceWrapper, context, node, count, prioritized);fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
}void checkFlow(ResourceWrapper resource, Context context, DefaultNode node, int count, boolean prioritized)
throws BlockException {checker.checkFlow(ruleProvider, resource, context, node, count, prioritized);
}public void checkFlow(Function<String, Collection<FlowRule>> ruleProvider, ResourceWrapper resource,Context context, DefaultNode node, int count, boolean prioritized) throws BlockException {if (ruleProvider == null || resource == null) {return;}Collection<FlowRule> rules = ruleProvider.apply(resource.getName());if (rules != null) {for (FlowRule rule : rules) {if (!canPassCheck(rule, context, node, count, prioritized)) {throw new FlowException(rule.getLimitApp(), rule);}}}
}public boolean canPassCheck(/*@NonNull*/ FlowRule rule, Context context, DefaultNode node, int acquireCount,boolean prioritized) {String limitApp = rule.getLimitApp();if (limitApp == null) {return true;}if (rule.isClusterMode()) {return passClusterCheck(rule, context, node, acquireCount, prioritized);}return passLocalCheck(rule, context, node, acquireCount, prioritized);
}private static boolean passLocalCheck(FlowRule rule, Context context, DefaultNode node, int acquireCount,boolean prioritized) {// 根绝请求和策略选择nodeNode selectedNode = selectNodeByRequesterAndStrategy(rule, context, node);if (selectedNode == null) {return true;}// 这里的canPass根据不同的策略采用不同的算法实现return rule.getRater().canPass(selectedNode, acquireCount, prioritized);
}static Node selectNodeByRequesterAndStrategy(/*@NonNull*/ FlowRule rule, Context context, DefaultNode node) {// The limit app should not be empty.String limitApp = rule.getLimitApp();// public static final int STRATEGY_DIRECT = 0;// public static final int STRATEGY_RELATE = 1;// public static final int STRATEGY_CHAIN = 2;int strategy = rule.getStrategy(); String origin = context.getOrigin();if (limitApp.equals(origin) && filterOrigin(origin)) {if (strategy == RuleConstant.STRATEGY_DIRECT) {// Matches limit origin, return origin statistic node.return context.getOriginNode();}return selectReferenceNode(rule, context, node);} else if (RuleConstant.LIMIT_APP_DEFAULT.equals(limitApp)) {if (strategy == RuleConstant.STRATEGY_DIRECT) {// Return the cluster node.// 直连模式和关联模式都采用clusterNodereturn node.getClusterNode();}return selectReferenceNode(rule, context, node);} else if (RuleConstant.LIMIT_APP_OTHER.equals(limitApp)&& FlowRuleManager.isOtherOrigin(origin, rule.getResource())) {if (strategy == RuleConstant.STRATEGY_DIRECT) {return context.getOriginNode();}return selectReferenceNode(rule, context, node);}return null;
}static Node selectReferenceNode(FlowRule rule, Context context, DefaultNode node) {String refResource = rule.getRefResource();int strategy = rule.getStrategy();if (StringUtil.isEmpty(refResource)) {return null;}// 如果是关联模式,返回clusterNodeif (strategy == RuleConstant.STRATEGY_RELATE) {return ClusterBuilderSlot.getClusterNode(refResource);}// 如果是链路模式,返回当前的node(defaultNode)if (strategy == RuleConstant.STRATEGY_CHAIN) {if (!refResource.equals(context.getName())) {return null;}return node;}// No node.return null;
}滑动时间窗口
时间窗口请求量统计
这里canPass()对规则的判断先要通过FlowRule#getRater()获取流量控制器TrafficShapingController,然后再做限流
而TrafficShapingController有3种实现:
DefaultController:快速失败,默认的方式,基于滑动时间窗口算法WarmUpController:预热模式,基于滑动时间窗口算法,只不过阈值是动态的RateLimiterController:排队等待模式,基于漏桶算法
最终的限流判断都在TrafficShapingController的canPass方法中。

这里进入了DefaultNode内部:
发现同时对DefaultNode和ClusterNode在做QPS统计,DefaultNode和ClusterNode都是StatisticNode的子类,这里调用addPassRequest()方法,最终都会进入StatisticNode中。随便跟入一个:
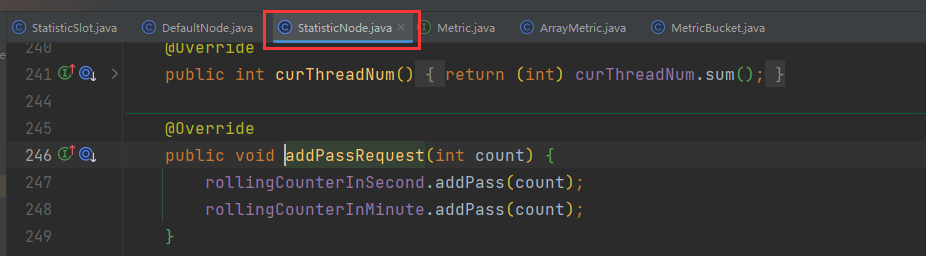
这里有秒、分两种纬度的统计,对应两个计数器。找到对应的成员变量,可以看到:

两个计数器都是ArrayMetric类型,并且传入了两个参数:
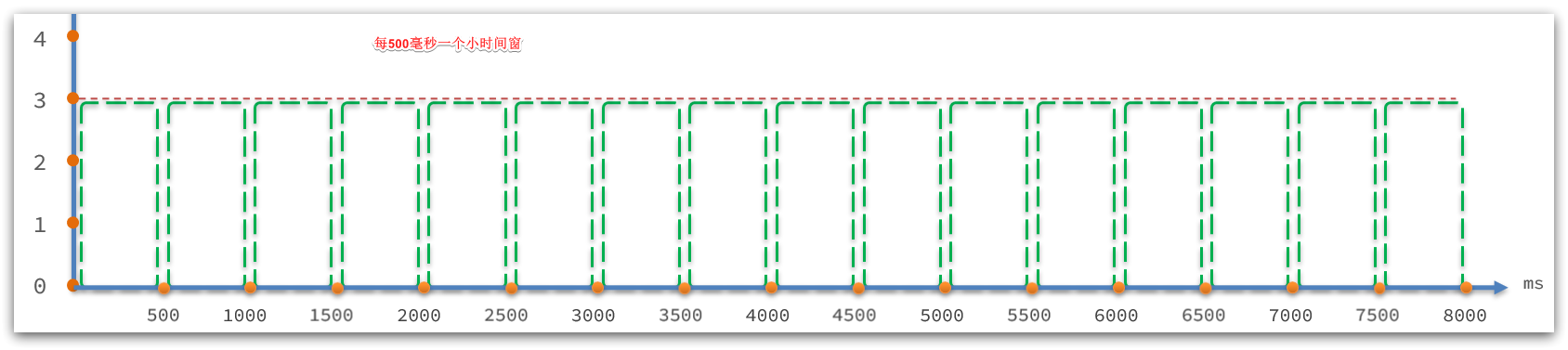
// intervalInMs:是滑动窗口的时间间隔,默认为 1 秒
// sampleCount: 时间窗口的分隔数量,默认为 2,就是把 1秒分为 2个小时间窗
public ArrayMetric(int sampleCount, int intervalInMs) {this.data = new OccupiableBucketLeapArray(sampleCount, intervalInMs);
}如图:
接下来,我们进入ArrayMetric类的addPass方法:
@Override
public void addPass(int count) {// 获取当前时间所在的时间窗WindowWrap<MetricBucket> wrap = data.currentWindow();// 计数器 +1wrap.value().addPass(count);
}这里的data是一个LeapArray:
private final LeapArray<MetricBucket> data;LeapArray的四个属性:
public abstract class LeapArray<T> {// 小窗口的时间长度,默认是500ms ,值 = intervalInMs / sampleCountprotected int windowLengthInMs;// 滑动窗口内的 小窗口 数量,默认为 2protected int sampleCount;// 滑动窗口的时间间隔,默认为 1000msprotected int intervalInMs;// 滑动窗口的时间间隔,单位为秒,默认为 1private double intervalInSecond;
}LeapArray是一个环形数组,因为时间是无限的,数组长度不可能无限,因此数组中每一个格子放入一个时间窗(window),当数组放满后,角标归0,覆盖最初的window。
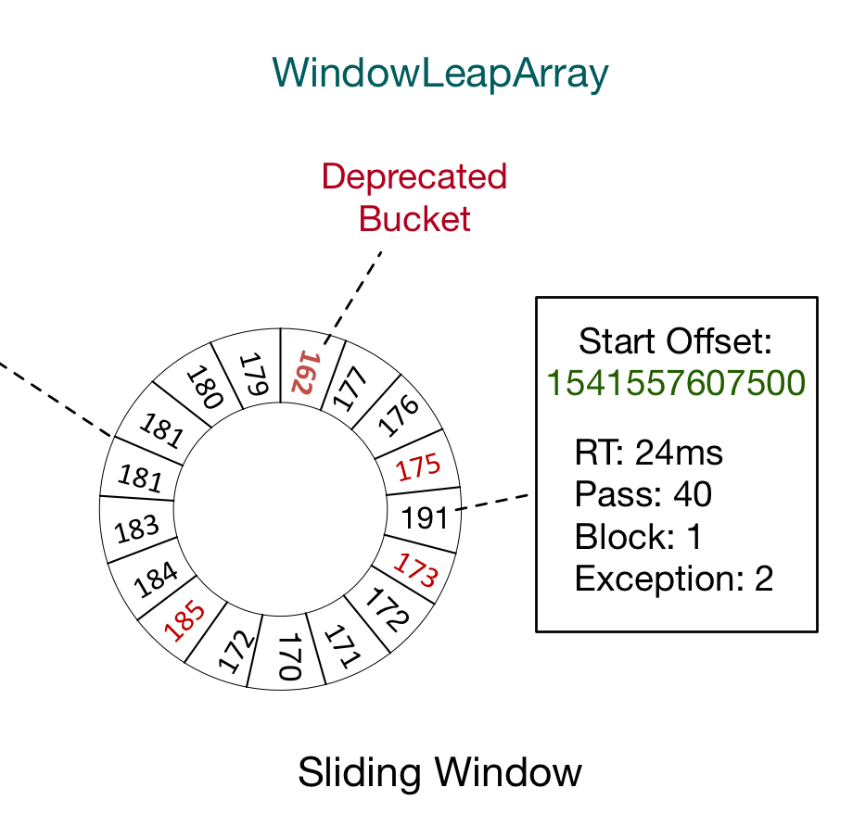
因为滑动窗口最多分成sampleCount数量的小窗口,因此数组长度只要大于sampleCount,那么最近的一个滑动窗口内的2个小窗口就永远不会被覆盖,就不用担心旧数据被覆盖的问题了。
data.currentWindow()方法:
public WindowWrap<T> currentWindow(long timeMillis) {if (timeMillis < 0) {return null;}// 计算当前时间对应的数组角标int idx = calculateTimeIdx(timeMillis);// 计算当前时间所在窗口的开始时间.long windowStart = calculateWindowStart(timeMillis);/*** 先根据角标获取数组中保存的 oldWindow 对象,可能是旧数据,需要判断.** (1) oldWindow 不存在, 说明是第一次,创建新 window并存入,然后返回即可* (2) oldWindow的 starTime = 本次请求的 windowStar, 说明正是要找的窗口,直接返回.* (3) oldWindow的 starTime < 本次请求的 windowStar, 说明是旧数据,需要被覆盖,创建 * 新窗口,覆盖旧窗口*/while (true) {WindowWrap<T> old = array.get(idx);if (old == null) {// 创建新 windowWindowWrap<T> window = new WindowWrap<T>(windowLengthInMs, windowStart, newEmptyBucket(timeMillis));// 基于CAS写入数组,避免线程安全问题if (array.compareAndSet(idx, null, window)) {// 写入成功,返回新的 windowreturn window;} else {// 写入失败,说明有并发更新,等待其它人更新完成即可Thread.yield();}} else if (windowStart == old.windowStart()) {return old;} else if (windowStart > old.windowStart()) {if (updateLock.tryLock()) {try {// 获取并发锁,覆盖旧窗口并返回return resetWindowTo(old, windowStart);} finally {updateLock.unlock();}} else {// 获取锁失败,等待其它线程处理就可以了Thread.yield();}} else if (windowStart < old.windowStart()) {// 这种情况不应该存在,写这里只是以防万一。return new WindowWrap<T>(windowLengthInMs, windowStart, newEmptyBucket(timeMillis));}}
}找到当前时间所在窗口(WindowWrap)后,只要调用WindowWrap对象中的add方法,计数器+1即可。
这里只负责统计每个窗口的请求量,不负责拦截。限流拦截要看FlowSlot中的逻辑。
滑动窗口QPS计算
FlowSlot的限流判断最终都由TrafficShapingController接口中的canPass方法来实现。该接口有三个实现类:
DefaultController:快速失败,默认的方式,基于滑动时间窗口算法WarmUpController:预热模式,基于滑动时间窗口算法,只不过阈值是动态的RateLimiterController:排队等待模式,基于漏桶算法
跟入默认的DefaultController中的canPass方法来分析:
@Override
public boolean canPass(Node node, int acquireCount, boolean prioritized) {// 计算目前为止滑动窗口内已经存在的请求量int curCount = avgUsedTokens(node);// 判断:已使用请求量 + 需要的请求量(1) 是否大于 窗口的请求阈值if (curCount + acquireCount > count) {// 大于,说明超出阈值,返回falseif (prioritized && grade == RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS) {long currentTime;long waitInMs;currentTime = TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis();waitInMs = node.tryOccupyNext(currentTime, acquireCount, count);if (waitInMs < OccupyTimeoutProperty.getOccupyTimeout()) {node.addWaitingRequest(currentTime + waitInMs, acquireCount);node.addOccupiedPass(acquireCount);sleep(waitInMs);// PriorityWaitException indicates that the request will pass after waiting for {@link @waitInMs}.throw new PriorityWaitException(waitInMs);}}return false;}// 小于等于,说明在阈值范围内,返回truereturn true;
}因此,判断的关键就是int curCount = avgUsedTokens(node);
private int avgUsedTokens(Node node) {if (node == null) {return DEFAULT_AVG_USED_TOKENS;}return grade == RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_THREAD ? node.curThreadNum() : (int)(node.passQps());
}因为采用的是限流,走node.passQps()逻辑:
// 这里又进入了 StatisticNode类
@Override
public double passQps() {// 请求量 ÷ 滑动窗口时间间隔 ,得到的就是QPSreturn rollingCounterInSecond.pass() / rollingCounterInSecond.getWindowIntervalInSec();
}rollingCounterInSecond.pass()得到请求量
// rollingCounterInSecond 本质是ArrayMetric
@Override
public long pass() {// 获取当前窗口data.currentWindow();long pass = 0;// 获取当前时间的滑动窗口范围内的所有小窗口List<MetricBucket> list = data.values();// 遍历for (MetricBucket window : list) {// 累加求和pass += window.pass();}// 返回return pass;
}data.values()如何获取滑动窗口范围内的所有小窗口:
// 此处进入LeapArray类中:
public List<T> values(long timeMillis) {if (timeMillis < 0) {return new ArrayList<T>();}// 创建空集合,大小等于 LeapArray长度int size = array.length();List<T> result = new ArrayList<T>(size);// 遍历 LeapArrayfor (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {// 获取每一个小窗口WindowWrap<T> windowWrap = array.get(i);// 判断这个小窗口是否在滑动窗口时间范围内(1秒内)if (windowWrap == null || isWindowDeprecated(timeMillis, windowWrap)) {// 不在范围内,则跳过continue;}// 在范围内,则添加到集合中result.add(windowWrap.value());}// 返回集合return result;
}isWindowDeprecated(timeMillis, windowWrap)判断窗口是否符合要求
public boolean isWindowDeprecated(long time, WindowWrap<T> windowWrap) {// 当前时间 - 窗口开始时间 是否大于 滑动窗口的最大间隔(1秒)// 也就是说,我们要统计的时 距离当前时间1秒内的小窗口的 count之和return time - windowWrap.windowStart() > intervalInMs;
}DegradeSlot
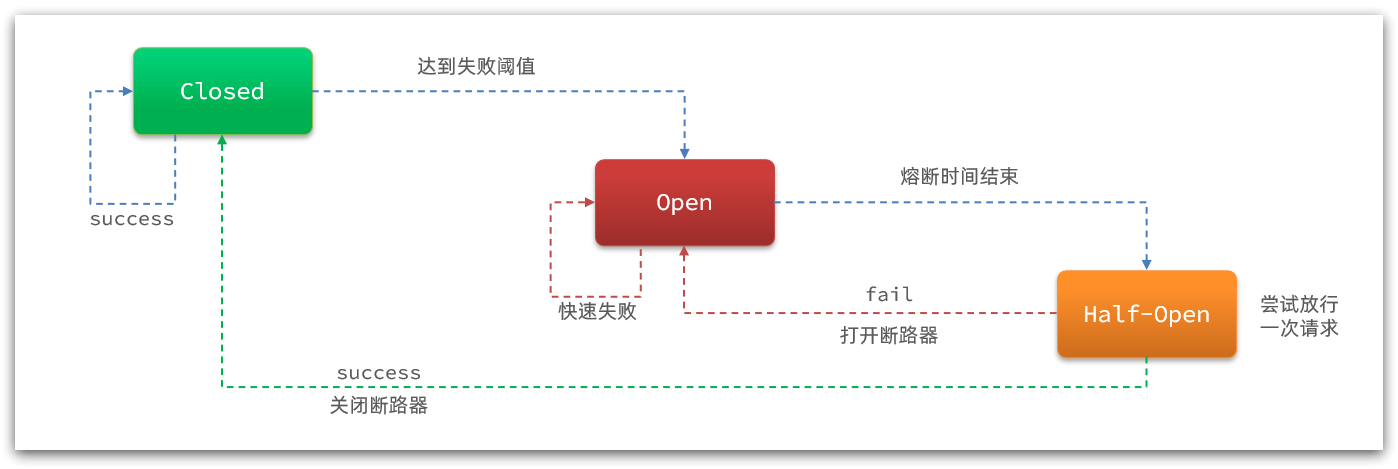
Sentinel的熔断是基于状态机实现的。当达到失败阈值时,断路器会打开,按照配置规则进行熔断。当熔断时间结束后,断路器会进入到 half-open 状态,尝试放行一次请求。当请求成功时断路器会关闭,否则重新回到打开状态。
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count,boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {performChecking(context, resourceWrapper);fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
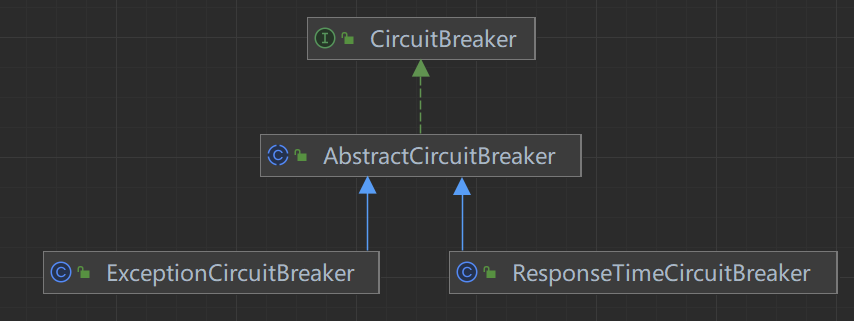
}void performChecking(Context context, ResourceWrapper r) throws BlockException {List<CircuitBreaker> circuitBreakers = DegradeRuleManager.getCircuitBreakers(r.getName());if (circuitBreakers == null || circuitBreakers.isEmpty()) {return;}for (CircuitBreaker cb : circuitBreakers) {if (!cb.tryPass(context)) {throw new DegradeException(cb.getRule().getLimitApp(), cb.getRule());}}
}
@Override
public boolean tryPass(Context context) {// 判断状态机状态if (currentState.get() == State.CLOSED) {// 如果是closed状态,直接放行return true;}if (currentState.get() == State.OPEN) {// 如果是OPEN状态,断路器打开// 继续判断OPEN时间窗是否结束,如果是则把状态从OPEN切换到 HALF_OPEN,返回truereturn retryTimeoutArrived() && fromOpenToHalfOpen(context);}// OPEN状态,并且时间窗未到,返回falsereturn false;
}protected boolean retryTimeoutArrived() {// 当前时间 大于 下一次 HalfOpen的重试时间return TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis() >= nextRetryTimestamp;
}protected boolean fromOpenToHalfOpen(Context context) {// 基于CAS修改状态,从 OPEN到 HALF_OPENif (currentState.compareAndSet(State.OPEN, State.HALF_OPEN)) {// 状态变更的事件通知notifyObservers(State.OPEN, State.HALF_OPEN, null);// 得到当前资源Entry entry = context.getCurEntry();// 给资源设置监听器,在资源Entry销毁时(资源业务执行完毕时)触发entry.whenTerminate(new BiConsumer<Context, Entry>() {@Overridepublic void accept(Context context, Entry entry) {// 判断 资源业务是否异常if (entry.getBlockError() != null) {// 如果异常,则再次进入OPEN状态currentState.compareAndSet(State.HALF_OPEN, State.OPEN);notifyObservers(State.HALF_OPEN, State.OPEN, 1.0d);}}});return true;}return false;
}这里出现了从OPEN到HALF_OPEN、从HALF_OPEN到OPEN的变化,但是还有几个没有:
- 从CLOSED到OPEN
- 从HALF_OPEN到CLOSED
触发断路器
请求经过所有插槽 后,一定会执行exit方法,而在DegradeSlot的exit方法中:

会调用CircuitBreaker的onRequestComplete()方法。而CircuitBreaker有两个实现:
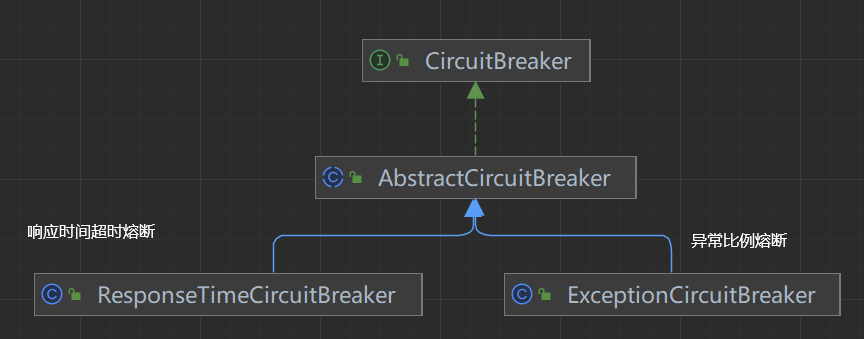
@Override
public void onRequestComplete(Context context) {// 获取资源 EntryEntry entry = context.getCurEntry();if (entry == null) {return;}// 尝试获取 资源中的 异常Throwable error = entry.getError();// 获取计数器,同样采用了滑动窗口来计数SimpleErrorCounter counter = stat.currentWindow().value();if (error != null) {// 如果出现异常,则 error计数器 +1counter.getErrorCount().add(1);}// 不管是否出现异常,total计数器 +1counter.getTotalCount().add(1);// 判断异常比例是否超出阈值handleStateChangeWhenThresholdExceeded(error);
}阈值判断的方法:
private void handleStateChangeWhenThresholdExceeded(Throwable error) {// 如果当前已经是OPEN状态,不做处理if (currentState.get() == State.OPEN) {return;}// 如果已经是 HALF_OPEN 状态,判断是否需求切换状态if (currentState.get() == State.HALF_OPEN) {if (error == null) {// 没有异常,则从 HALF_OPEN 到 CLOSEDfromHalfOpenToClose();} else {// 有一次,再次进入OPENfromHalfOpenToOpen(1.0d);}return;}// 说明当前是CLOSE状态,需要判断是否触发阈值List<SimpleErrorCounter> counters = stat.values();long errCount = 0;long totalCount = 0;// 累加计算 异常请求数量、总请求数量for (SimpleErrorCounter counter : counters) {errCount += counter.errorCount.sum();totalCount += counter.totalCount.sum();}// 如果总请求数量未达到阈值(最小请求数),什么都不做if (totalCount < minRequestAmount) {return;}double curCount = errCount;// 按照异常比例统计if (strategy == DEGRADE_GRADE_EXCEPTION_RATIO) {// 计算请求的异常比例curCount = errCount * 1.0d / totalCount;}// 按照异常数统计// 如果比例超过阈值,切换到 OPENif (curCount > threshold) {transformToOpen(curCount);}
}相关文章:

【Sentinel】Sentinel原码分析
本文内容来自【黑马】Sentinel从使用到源码解读笔记,做了部分修改和补充 目录 Sentinel 基本概念 基本流程 Node Entry 定义资源的两种方式 使用try-catch定义资源 使用注解标记资源 基于注解标记资源的实现原理 Context 什么是Context Context的初始化 …...

计算机竞赛 题目:基于深度学习的人脸表情识别 - 卷积神经网络 竞赛项目 代码
文章目录 0 简介1 项目说明2 数据集介绍:3 思路分析及代码实现3.1 数据可视化3.2 数据分离3.3 数据可视化3.4 在pytorch下创建数据集3.4.1 创建data-label对照表3.4.2 重写Dataset类3.4.3 数据集的使用 4 网络模型搭建4.1 训练模型4.2 模型的保存与加载 5 相关源码6…...
)
基于aarch64分析kernel源码 五:idle进程(0号进程)
一、参考 linux — 0号进程,1号进程,2号进程 - 流水灯 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com) Linux0号进程,1号进程,2号进程_0号进程和1号进程-CSDN博客 二、idle进程的创建流程 start_kernel --> arch_call_rest_init --> rest_init…...
【Linux】 vi / vim 使用
天天用vim 或者vi 。看着大佬用的很6 。我们却用的很少。今天咱们一起系统学习一下。 vi / vim 发展史 vi 是一款由加州大学伯克利分校,Bill Joy研究开发的文本编辑器。 vim Vim是一个类似于Vi的高度可定制的文本编辑器,在Vi的基础上改进和增加了很多…...
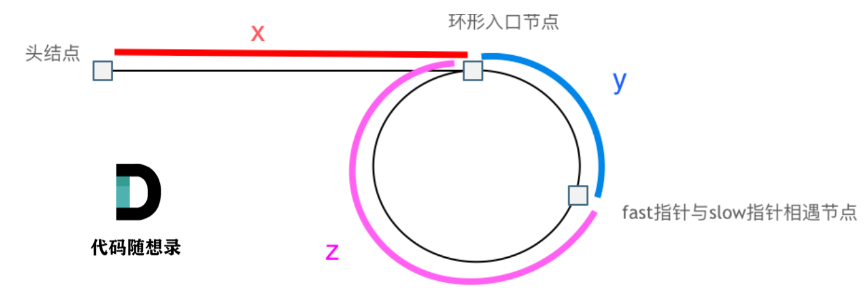
Leetcode hot 100之双指针(快慢指针、滑动窗口)
目录 数组 有序的平方仍有序 删除/覆盖元素 移动零:交换slow和fast 滑动窗口:最短的连续子串(r可行解->l--最短解) 最小长度的子数组 求和:sort、l i 1, r len - 1 三数之和abctarget 四数之和abcdtarg…...

Bridge Champ助力我国桥牌阔步亚运, Web3游戏为传统项目注入创新活力
本届杭州亚运会,中国桥牌队表现杰出,共斩获1金1银1铜佳绩,其中女子团体夺得冠军,混合团体获得亚军。这充分展现了我国桥牌的实力,也彰显了桥牌作为亚运会体育竞技项目的影响力。与此同时,Web3游戏Bridge Champ为传统桥牌项目带来创新模式,将有望推动桥牌运动在亚运舞台上焕发新…...
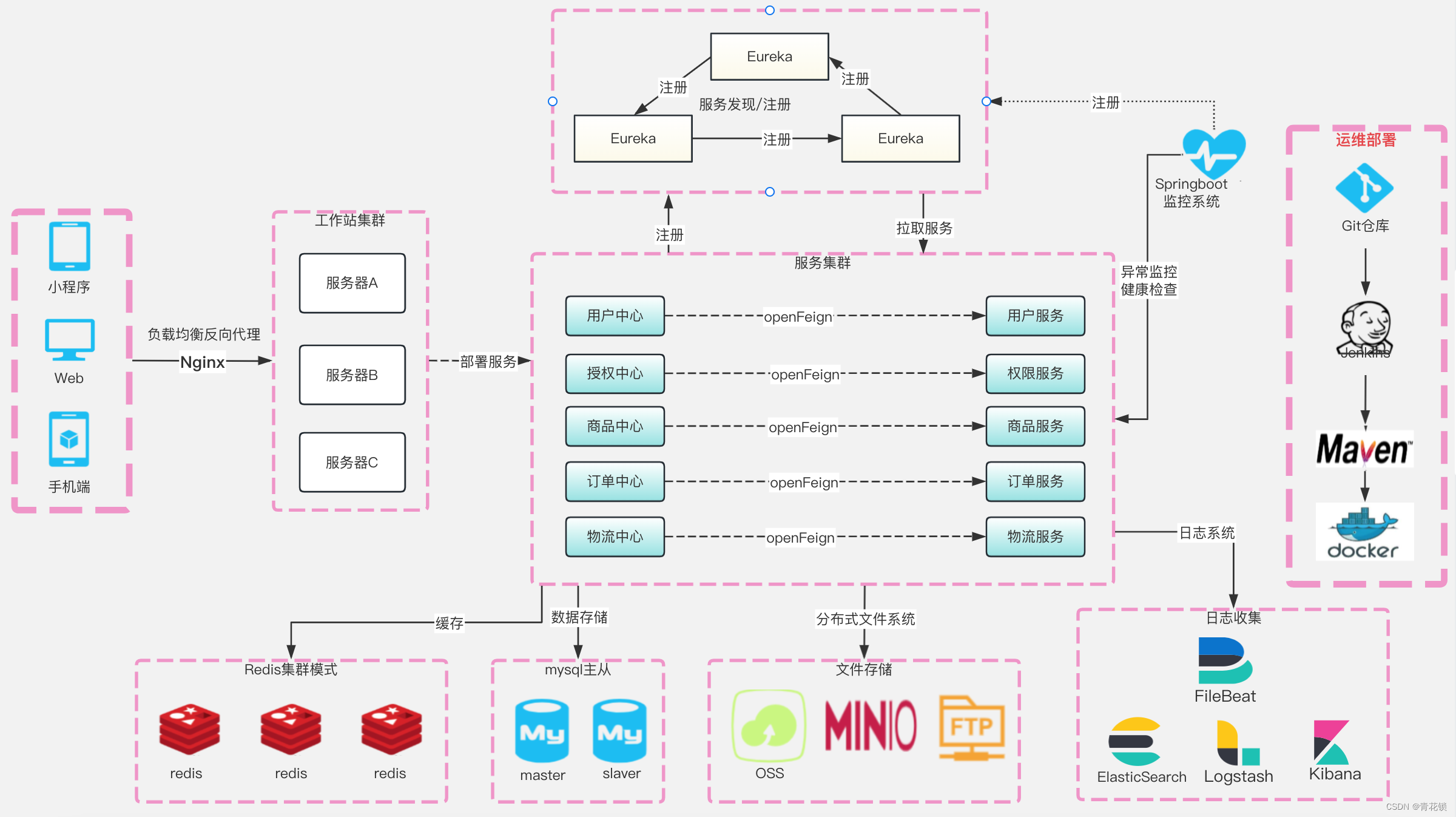
云原生微服务 第六章 Spring Cloud中使用OpenFeign
系列文章目录 第一章 Java线程池技术应用 第二章 CountDownLatch和Semaphone的应用 第三章 Spring Cloud 简介 第四章 Spring Cloud Netflix 之 Eureka 第五章 Spring Cloud Netflix 之 Ribbon 第六章 Spring Cloud 之 OpenFeign 文章目录 系列文章目录前言1、OpenFeign的实现…...
)
uniapp-vue3 抖音小程序开发(上线项目开源)
最近公司临时接一个项目来接手别人的流量,项目比较小,时间比较赶。 需求:一个答题小程序,通过答题来实现性格测算和分析。 之前开发过支付宝小程序和微信小程序,这次是首次开发抖音小程序,老板要求只能下…...
基于微信小程序的个人健康数据管理平台设计与实现(源码+lw+部署文档+讲解等)
文章目录 前言具体实现截图论文参考详细视频演示为什么选择我自己的网站自己的小程序(小蔡coding)有保障的售后福利 代码参考源码获取 前言 💗博主介绍:✌全网粉丝10W,CSDN特邀作者、博客专家、CSDN新星计划导师、全栈领域优质创作…...
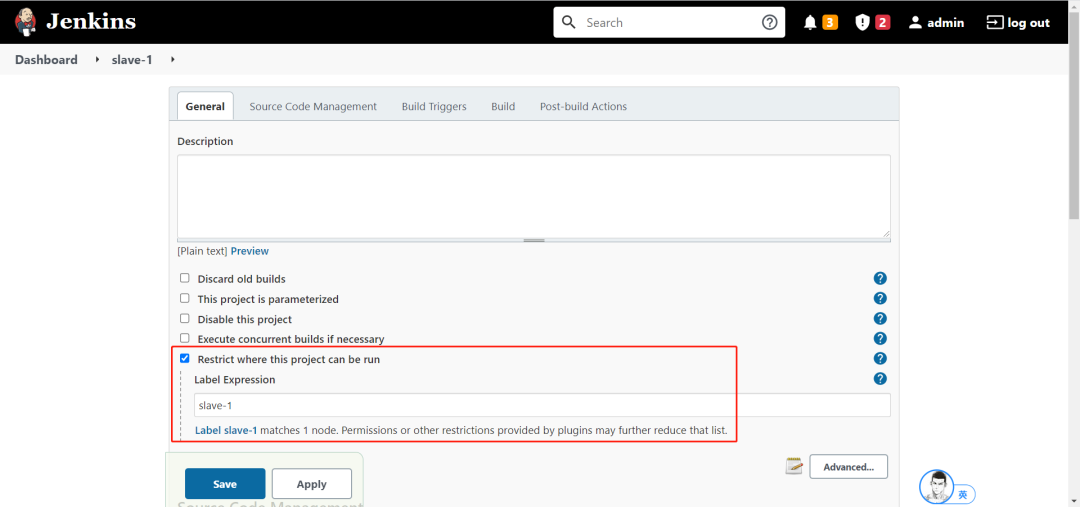
真香!Jenkins 主从模式解决问题So Easy~
01.Jenkins 能干什么 Jenkins 是一个开源软件项目,是基于 Java 开发的一种持续集成工具,用于监控持续重复的工作,旨在提供一个开放易用的软件平台,使软件项目可以进行持续集成。 中文官网:https://jenkins.io/zh/ 0…...
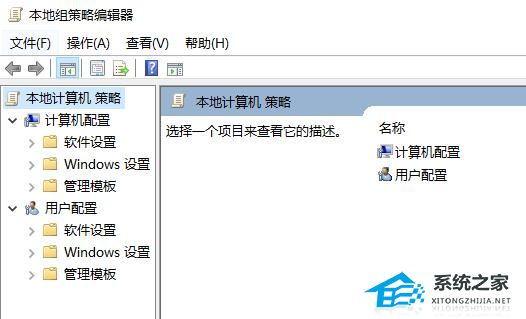
Win10系统打开组策略编辑器的两种方法
组策略编辑器是Win10电脑中很实用的工具,它可以帮助用户管理和设置计算机的安全性、网络连接、软件安装等各种策略。但是,很多新手用户不知道打开Win10电脑中组策略编辑器的方法步骤,下面小编给大家介绍两种简单的方法,帮助打开快…...

git 的行结束符
CR (Carriage Return) 表示<回车>LF (Line Feed) 表示<换行> 1. 不同系统的行结束符 系统名称行结束符意义释义git line endings选项DOS / Windows\r\nCRLF‘\r’是使光标移动到行首 ’\n’是使光标下移一行Windows-styleMacOS\rCRreturnAs-isUNIX / Linux\nLFne…...
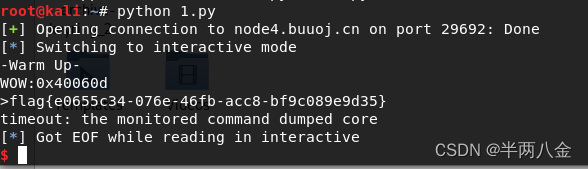
buuctf PWN warmup_csaw_2016
下载附件,IDA查看 发现直接有显示flag函数 int sub_40060D() {return system("cat flag.txt"); }查看程序起始地址0x40060D ; Attributes: bp-based framesub_40060D proc near ; __unwind { push rbp mov rbp, rsp mov edi, offset comman…...

C++中的对象切割(Object slicing)问题
在C中,当我们把派生类对象向上强制转型为基类对象时,会造成对象切割(Object slicing)问题。 请看下面示例代码: #include <iostream> using namespace std;class CBase { public:virtual ~CBase() default;v…...
VxeTable 表格组件推荐
VxeTable 表格组件推荐 https://vxetable.cn 在前端开发中,表格组件是不可或缺的一部分,它们用于展示和管理数据,为用户提供了重要的数据交互功能。VxeTable 是一个优秀的 Vue 表格组件,它提供了丰富的功能和灵活的配置选项&…...

好消息:用 vue3+layui 共同铸造我们新的项目
前言: layui这个框架不知道多少人还在关注着,记得第一次接触它是在18年,后来随着vue,react的盛行,jquerylayui的模式受到了特别大的冲击,后来作者都放弃维护他的官方网站,转而在github/gitee上做…...
 和 split(‘ ‘)的区别以及split()详细解法,字符串分割正则用法)
JS中 split(/s+/) 和 split(‘ ‘)的区别以及split()详细解法,字符串分割正则用法
博主: http://t.csdnimg.cn/e4gDi split用法详解: http://t.csdnimg.cn/6logr...

MySQL性能调优
🙈作者简介:练习时长两年半的Java up主 🙉个人主页:程序员老茶 🙊 ps:点赞👍是免费的,却可以让写博客的作者开兴好久好久😎 📚系列专栏:Java全栈,…...
如何解决openal32.dll丢失,有什么办法解决
你第一次知道openal32.dll文件是在什么情况下,你了解过openal32.dll文件吗?如果电脑中openal32.dll丢失有什么办法可以解决,今天就教大家如何解决openal32.dll丢失,都有哪些办法可以解决openal32.dll丢失。 一.openal3…...
)
Nginx 如何配置http server 、负载均衡(反向代理)
目录 1. 关于 Nginx2. 配置http server3. 配置负载均衡 本文主要介绍 Nginx中如何配置 http server,负载均衡(反向代理)。 1. 关于 Nginx Nginx是一个开源的、高性能的、稳定的、简单的、功能丰富的HTTP和反向代理服务器,也可以用作IMAP/POP3/SMTP代理…...

synchronized 学习
学习源: https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1aJ411V763?spm_id_from333.788.videopod.episodes&vd_source32e1c41a9370911ab06d12fbc36c4ebc 1.应用场景 不超卖,也要考虑性能问题(场景) 2.常见面试问题: sync出…...
:OpenBCI_GUI:从环境搭建到数据可视化(下))
脑机新手指南(八):OpenBCI_GUI:从环境搭建到数据可视化(下)
一、数据处理与分析实战 (一)实时滤波与参数调整 基础滤波操作 60Hz 工频滤波:勾选界面右侧 “60Hz” 复选框,可有效抑制电网干扰(适用于北美地区,欧洲用户可调整为 50Hz)。 平滑处理&…...

【Java学习笔记】Arrays类
Arrays 类 1. 导入包:import java.util.Arrays 2. 常用方法一览表 方法描述Arrays.toString()返回数组的字符串形式Arrays.sort()排序(自然排序和定制排序)Arrays.binarySearch()通过二分搜索法进行查找(前提:数组是…...
8k长序列建模,蛋白质语言模型Prot42仅利用目标蛋白序列即可生成高亲和力结合剂
蛋白质结合剂(如抗体、抑制肽)在疾病诊断、成像分析及靶向药物递送等关键场景中发挥着不可替代的作用。传统上,高特异性蛋白质结合剂的开发高度依赖噬菌体展示、定向进化等实验技术,但这类方法普遍面临资源消耗巨大、研发周期冗长…...
什么是库存周转?如何用进销存系统提高库存周转率?
你可能听说过这样一句话: “利润不是赚出来的,是管出来的。” 尤其是在制造业、批发零售、电商这类“货堆成山”的行业,很多企业看着销售不错,账上却没钱、利润也不见了,一翻库存才发现: 一堆卖不动的旧货…...

在web-view 加载的本地及远程HTML中调用uniapp的API及网页和vue页面是如何通讯的?
uni-app 中 Web-view 与 Vue 页面的通讯机制详解 一、Web-view 简介 Web-view 是 uni-app 提供的一个重要组件,用于在原生应用中加载 HTML 页面: 支持加载本地 HTML 文件支持加载远程 HTML 页面实现 Web 与原生的双向通讯可用于嵌入第三方网页或 H5 应…...
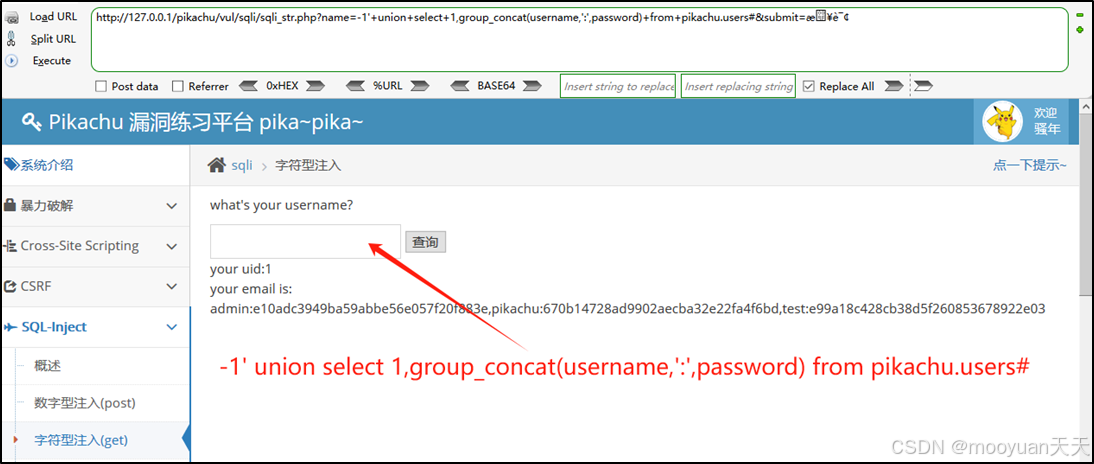
pikachu靶场通关笔记19 SQL注入02-字符型注入(GET)
目录 一、SQL注入 二、字符型SQL注入 三、字符型注入与数字型注入 四、源码分析 五、渗透实战 1、渗透准备 2、SQL注入探测 (1)输入单引号 (2)万能注入语句 3、获取回显列orderby 4、获取数据库名database 5、获取表名…...

Cilium动手实验室: 精通之旅---13.Cilium LoadBalancer IPAM and L2 Service Announcement
Cilium动手实验室: 精通之旅---13.Cilium LoadBalancer IPAM and L2 Service Announcement 1. LAB环境2. L2公告策略2.1 部署Death Star2.2 访问服务2.3 部署L2公告策略2.4 服务宣告 3. 可视化 ARP 流量3.1 部署新服务3.2 准备可视化3.3 再次请求 4. 自动IPAM4.1 IPAM Pool4.2 …...
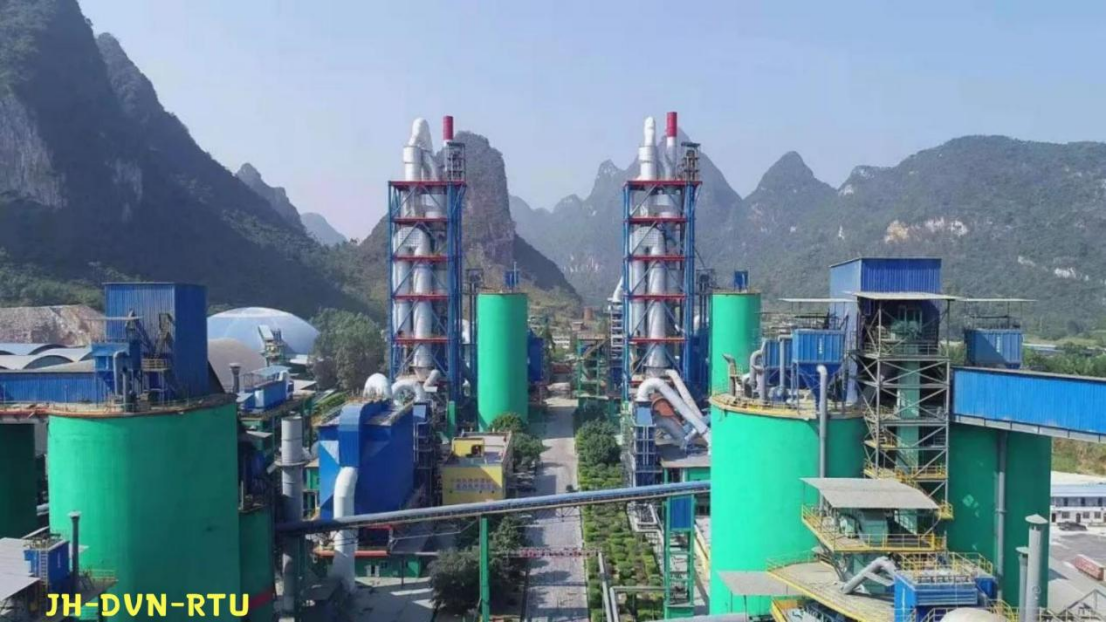

水泥厂自动化升级利器:Devicenet转Modbus rtu协议转换网关
在水泥厂的生产流程中,工业自动化网关起着至关重要的作用,尤其是JH-DVN-RTU疆鸿智能Devicenet转Modbus rtu协议转换网关,为水泥厂实现高效生产与精准控制提供了有力支持。 水泥厂设备众多,其中不少设备采用Devicenet协议。Devicen…...
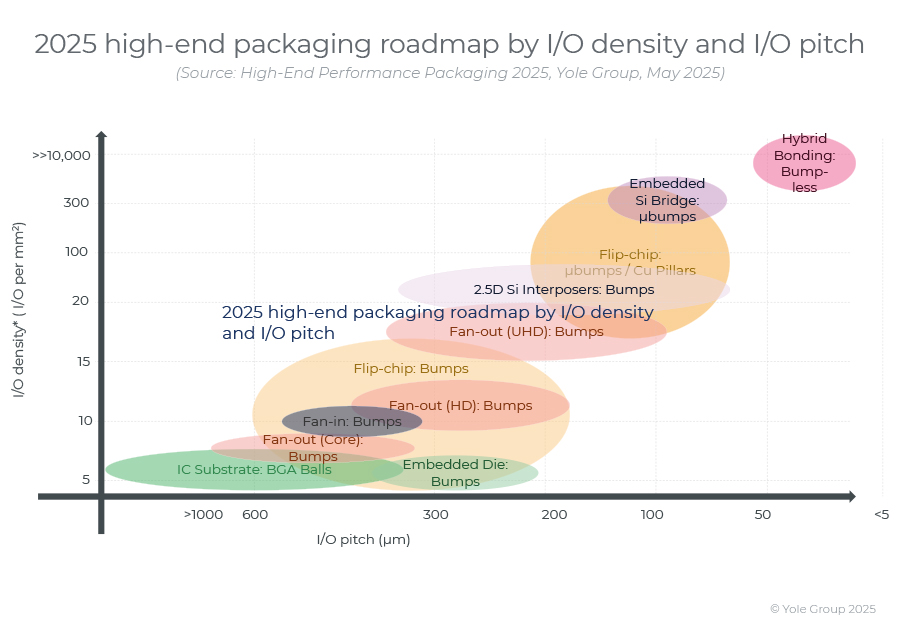
高端性能封装正在突破性能壁垒,其芯片集成技术助力人工智能革命。
2024 年,高端封装市场规模为 80 亿美元,预计到 2030 年将超过 280 亿美元,2024-2030 年复合年增长率为 23%。 细分到各个终端市场,最大的高端性能封装市场是“电信和基础设施”,2024 年该市场创造了超过 67% 的收入。…...
