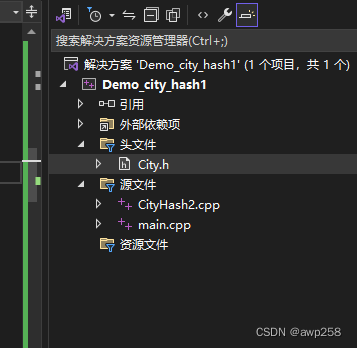
Android 移动端编译 cityhash动态库
最近做项目, 硬件端 需要 用 cityhash 编译一个 动态库 提供给移动端使用,l
记录一下 编译过程
city .cpp
//
// Created by Administrator on 2023/12/12.
//
// Copyright (c) 2011 Google, Inc.
//
// Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
// of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
// in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
// to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
// copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
// furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
//
// The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in
// all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
//
// THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
// IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
// FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
// AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
// LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
// OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN
// THE SOFTWARE.
//
// CityHash, by Geoff Pike and Jyrki Alakuijala
//
// This file provides CityHash64() and related functions.
//
// It's probably possible to create even faster hash functions by
// writing a program that systematically explores some of the space of
// possible hash functions, by using SIMD instructions, or by
// compromising on hash quality.#include "city.h"#include <algorithm>
/*#include <string.h>*/
#include "string.h"using namespace std;static uint64 UNALIGNED_LOAD64(const char *p) {uint64 result;memcpy(&result, p, sizeof(result));return result;
}static uint32 UNALIGNED_LOAD32(const char *p) {uint32 result;memcpy(&result, p, sizeof(result));return result;
}#ifndef __BIG_ENDIAN__#define uint32_in_expected_order(x) (x)
#define uint64_in_expected_order(x) (x)#else#ifdef _MSC_VER
#include <stdlib.h>
#define bswap_32(x) _byteswap_ulong(x)
#define bswap_64(x) _byteswap_uint64(x)#elif defined(__APPLE__)
// Mac OS X / Darwin features
#include <libkern/OSByteOrder.h>
#define bswap_32(x) OSSwapInt32(x)
#define bswap_64(x) OSSwapInt64(x)#else
#include <byteswap.h>
#endif#define uint32_in_expected_order(x) (bswap_32(x))
#define uint64_in_expected_order(x) (bswap_64(x))#endif // __BIG_ENDIAN__#if !defined(LIKELY)
#if defined(__GNUC__) || defined(__INTEL_COMPILER)
#define LIKELY(x) (__builtin_expect(!!(x), 1))
#else
#define LIKELY(x) (x)
#endif
#endifstatic uint64 Fetch64(const char *p) {return uint64_in_expected_order(UNALIGNED_LOAD64(p));
}static uint32 Fetch32(const char *p) {return uint32_in_expected_order(UNALIGNED_LOAD32(p));
}// Some primes between 2^63 and 2^64 for various uses.
static const uint64 k0 = 0xc3a5c85c97cb3127ULL;
static const uint64 k1 = 0xb492b66fbe98f273ULL;
static const uint64 k2 = 0x9ae16a3b2f90404fULL;
static const uint64 k3 = 0xc949d7c7509e6557ULL;// Bitwise right rotate. Normally this will compile to a single
// instruction, especially if the shift is a manifest constant.
static uint64 Rotate(uint64 val, int shift) {// Avoid shifting by 64: doing so yields an undefined result.return shift == 0 ? val : ((val >> shift) | (val << (64 - shift)));
}// Equivalent to Rotate(), but requires the second arg to be non-zero.
// On x86-64, and probably others, it's possible for this to compile
// to a single instruction if both args are already in registers.
static uint64 RotateByAtLeast1(uint64 val, int shift) {return (val >> shift) | (val << (64 - shift));
}static uint64 ShiftMix(uint64 val) {return val ^ (val >> 47);
}static uint64 HashLen16(uint64 u, uint64 v) {return Hash128to64(uint128(u, v));
}static uint64 HashLen0to16(const char *s, size_t len) {if (len > 8) {uint64 a = Fetch64(s);uint64 b = Fetch64(s + len - 8);return HashLen16(a, RotateByAtLeast1(b + len, len)) ^ b;}if (len >= 4) {uint64 a = Fetch32(s);return HashLen16(len + (a << 3), Fetch32(s + len - 4));}if (len > 0) {uint8 a = s[0];uint8 b = s[len >> 1];uint8 c = s[len - 1];uint32 y = static_cast<uint32>(a) + (static_cast<uint32>(b) << 8);uint32 z = len + (static_cast<uint32>(c) << 2);return ShiftMix(y * k2 ^ z * k3) * k2;}return k2;
}// This probably works well for 16-byte strings as well, but it may be overkill
// in that case.
static uint64 HashLen17to32(const char *s, size_t len) {uint64 a = Fetch64(s) * k1;uint64 b = Fetch64(s + 8);uint64 c = Fetch64(s + len - 8) * k2;uint64 d = Fetch64(s + len - 16) * k0;return HashLen16(Rotate(a - b, 43) + Rotate(c, 30) + d,a + Rotate(b ^ k3, 20) - c + len);
}// Return a 16-byte hash for 48 bytes. Quick and dirty.
// Callers do best to use "random-looking" values for a and b.
static pair<uint64, uint64> WeakHashLen32WithSeeds(uint64 w, uint64 x, uint64 y, uint64 z, uint64 a, uint64 b) {a += w;b = Rotate(b + a + z, 21);uint64 c = a;a += x;a += y;b += Rotate(a, 44);return make_pair(a + z, b + c);
}// Return a 16-byte hash for s[0] ... s[31], a, and b. Quick and dirty.
static pair<uint64, uint64> WeakHashLen32WithSeeds(const char* s, uint64 a, uint64 b) {return WeakHashLen32WithSeeds(Fetch64(s),Fetch64(s + 8),Fetch64(s + 16),Fetch64(s + 24),a,b);
}// Return an 8-byte hash for 33 to 64 bytes.
static uint64 HashLen33to64(const char *s, size_t len) {uint64 z = Fetch64(s + 24);uint64 a = Fetch64(s) + (len + Fetch64(s + len - 16)) * k0;uint64 b = Rotate(a + z, 52);uint64 c = Rotate(a, 37);a += Fetch64(s + 8);c += Rotate(a, 7);a += Fetch64(s + 16);uint64 vf = a + z;uint64 vs = b + Rotate(a, 31) + c;a = Fetch64(s + 16) + Fetch64(s + len - 32);z = Fetch64(s + len - 8);b = Rotate(a + z, 52);c = Rotate(a, 37);a += Fetch64(s + len - 24);c += Rotate(a, 7);a += Fetch64(s + len - 16);uint64 wf = a + z;uint64 ws = b + Rotate(a, 31) + c;uint64 r = ShiftMix((vf + ws) * k2 + (wf + vs) * k0);return ShiftMix(r * k0 + vs) * k2;
}uint64 CityHash64(const char *s, size_t len) {if (len <= 32) {if (len <= 16) {return HashLen0to16(s, len);} else {return HashLen17to32(s, len);}} else if (len <= 64) {return HashLen33to64(s, len);}// For strings over 64 bytes we hash the end first, and then as we// loop we keep 56 bytes of state: v, w, x, y, and z.uint64 x = Fetch64(s + len - 40);uint64 y = Fetch64(s + len - 16) + Fetch64(s + len - 56);uint64 z = HashLen16(Fetch64(s + len - 48) + len, Fetch64(s + len - 24));pair<uint64, uint64> v = WeakHashLen32WithSeeds(s + len - 64, len, z);pair<uint64, uint64> w = WeakHashLen32WithSeeds(s + len - 32, y + k1, x);x = x * k1 + Fetch64(s);// Decrease len to the nearest multiple of 64, and operate on 64-byte chunks.len = (len - 1) & ~static_cast<size_t>(63);do {x = Rotate(x + y + v.first + Fetch64(s + 8), 37) * k1;y = Rotate(y + v.second + Fetch64(s + 48), 42) * k1;x ^= w.second;y += v.first + Fetch64(s + 40);z = Rotate(z + w.first, 33) * k1;v = WeakHashLen32WithSeeds(s, v.second * k1, x + w.first);w = WeakHashLen32WithSeeds(s + 32, z + w.second, y + Fetch64(s + 16));std::swap(z, x);s += 64;len -= 64;} while (len != 0);return HashLen16(HashLen16(v.first, w.first) + ShiftMix(y) * k1 + z,HashLen16(v.second, w.second) + x);
}uint64 CityHash64WithSeed(const char *s, size_t len, uint64 seed) {return CityHash64WithSeeds(s, len, k2, seed);
}uint64 CityHash64WithSeeds(const char *s, size_t len,uint64 seed0, uint64 seed1) {return HashLen16(CityHash64(s, len) - seed0, seed1);
}// A subroutine for CityHash128(). Returns a decent 128-bit hash for strings
// of any length representable in signed long. Based on City and Murmur.
static uint128 CityMurmur(const char *s, size_t len, uint128 seed) {uint64 a = Uint128Low64(seed);uint64 b = Uint128High64(seed);uint64 c = 0;uint64 d = 0;signed long l = len - 16;if (l <= 0) { // len <= 16a = ShiftMix(a * k1) * k1;c = b * k1 + HashLen0to16(s, len);d = ShiftMix(a + (len >= 8 ? Fetch64(s) : c));} else { // len > 16c = HashLen16(Fetch64(s + len - 8) + k1, a);d = HashLen16(b + len, c + Fetch64(s + len - 16));a += d;do {a ^= ShiftMix(Fetch64(s) * k1) * k1;a *= k1;b ^= a;c ^= ShiftMix(Fetch64(s + 8) * k1) * k1;c *= k1;d ^= c;s += 16;l -= 16;} while (l > 0);}a = HashLen16(a, c);b = HashLen16(d, b);return uint128(a ^ b, HashLen16(b, a));
}uint128 CityHash128WithSeed(const char *s, size_t len, uint128 seed) {if (len < 128) {return CityMurmur(s, len, seed);}// We expect len >= 128 to be the common case. Keep 56 bytes of state:// v, w, x, y, and z.pair<uint64, uint64> v, w;uint64 x = Uint128Low64(seed);uint64 y = Uint128High64(seed);uint64 z = len * k1;v.first = Rotate(y ^ k1, 49) * k1 + Fetch64(s);v.second = Rotate(v.first, 42) * k1 + Fetch64(s + 8);w.first = Rotate(y + z, 35) * k1 + x;w.second = Rotate(x + Fetch64(s + 88), 53) * k1;// This is the same inner loop as CityHash64(), manually unrolled.do {x = Rotate(x + y + v.first + Fetch64(s + 8), 37) * k1;y = Rotate(y + v.second + Fetch64(s + 48), 42) * k1;x ^= w.second;y += v.first + Fetch64(s + 40);z = Rotate(z + w.first, 33) * k1;v = WeakHashLen32WithSeeds(s, v.second * k1, x + w.first);w = WeakHashLen32WithSeeds(s + 32, z + w.second, y + Fetch64(s + 16));std::swap(z, x);s += 64;x = Rotate(x + y + v.first + Fetch64(s + 8), 37) * k1;y = Rotate(y + v.second + Fetch64(s + 48), 42) * k1;x ^= w.second;y += v.first + Fetch64(s + 40);z = Rotate(z + w.first, 33) * k1;v = WeakHashLen32WithSeeds(s, v.second * k1, x + w.first);w = WeakHashLen32WithSeeds(s + 32, z + w.second, y + Fetch64(s + 16));std::swap(z, x);s += 64;len -= 128;} while (LIKELY(len >= 128));x += Rotate(v.first + z, 49) * k0;z += Rotate(w.first, 37) * k0;// If 0 < len < 128, hash up to 4 chunks of 32 bytes each from the end of s.for (size_t tail_done = 0; tail_done < len; ) {tail_done += 32;y = Rotate(x + y, 42) * k0 + v.second;w.first += Fetch64(s + len - tail_done + 16);x = x * k0 + w.first;z += w.second + Fetch64(s + len - tail_done);w.second += v.first;v = WeakHashLen32WithSeeds(s + len - tail_done, v.first + z, v.second);}// At this point our 56 bytes of state should contain more than// enough information for a strong 128-bit hash. We use two// different 56-byte-to-8-byte hashes to get a 16-byte final result.x = HashLen16(x, v.first);y = HashLen16(y + z, w.first);return uint128(HashLen16(x + v.second, w.second) + y,HashLen16(x + w.second, y + v.second));
}uint128 CityHash128(const char *s, size_t len) {if (len >= 16) {return CityHash128WithSeed(s + 16,len - 16,uint128(Fetch64(s) ^ k3,Fetch64(s + 8)));} else if (len >= 8) {return CityHash128WithSeed(NULL,0,uint128(Fetch64(s) ^ (len * k0),Fetch64(s + len - 8) ^ k1));} else {return CityHash128WithSeed(s, len, uint128(k0, k1));}
}#if defined(__SSE4_2__) && defined(__x86_64__)
#include <nmmintrin.h>// Requires len >= 240.
static void CityHashCrc256Long(const char *s, size_t len,uint32 seed, uint64 *result) {uint64 a = Fetch64(s + 56) + k0;uint64 b = Fetch64(s + 96) + k0;uint64 c = result[0] = HashLen16(b, len);uint64 d = result[1] = Fetch64(s + 120) * k0 + len;uint64 e = Fetch64(s + 184) + seed;uint64 f = seed;uint64 g = 0;uint64 h = 0;uint64 i = 0;uint64 j = 0;uint64 t = c + d;// 240 bytes of input per iter.size_t iters = len / 240;len -= iters * 240;do {
#define CHUNK(multiplier, z) \{ \uint64 old_a = a; \a = Rotate(b, 41 ^ z) * multiplier + Fetch64(s); \b = Rotate(c, 27 ^ z) * multiplier + Fetch64(s + 8); \c = Rotate(d, 41 ^ z) * multiplier + Fetch64(s + 16); \d = Rotate(e, 33 ^ z) * multiplier + Fetch64(s + 24); \e = Rotate(t, 25 ^ z) * multiplier + Fetch64(s + 32); \t = old_a; \} \f = _mm_crc32_u64(f, a); \g = _mm_crc32_u64(g, b); \h = _mm_crc32_u64(h, c); \i = _mm_crc32_u64(i, d); \j = _mm_crc32_u64(j, e); \s += 40CHUNK(1, 1); CHUNK(k0, 0);CHUNK(1, 1); CHUNK(k0, 0);CHUNK(1, 1); CHUNK(k0, 0);} while (--iters > 0);while (len >= 40) {CHUNK(k0, 0);len -= 40;}if (len > 0) {s = s + len - 40;CHUNK(k0, 0);}j += i << 32;a = HashLen16(a, j);h += g << 32;b += h;c = HashLen16(c, f) + i;d = HashLen16(d, e + result[0]);j += e;i += HashLen16(h, t);e = HashLen16(a, d) + j;f = HashLen16(b, c) + a;g = HashLen16(j, i) + c;result[0] = e + f + g + h;a = ShiftMix((a + g) * k0) * k0 + b;result[1] += a + result[0];a = ShiftMix(a * k0) * k0 + c;result[2] = a + result[1];a = ShiftMix((a + e) * k0) * k0;result[3] = a + result[2];
}// Requires len < 240.
static void CityHashCrc256Short(const char *s, size_t len, uint64 *result) {char buf[240];memcpy(buf, s, len);memset(buf + len, 0, 240 - len);CityHashCrc256Long(buf, 240, ~static_cast<uint32>(len), result);
}void CityHashCrc256(const char *s, size_t len, uint64 *result) {if (LIKELY(len >= 240)) {CityHashCrc256Long(s, len, 0, result);} else {CityHashCrc256Short(s, len, result);}
}uint128 CityHashCrc128WithSeed(const char *s, size_t len, uint128 seed) {if (len <= 900) {return CityHash128WithSeed(s, len, seed);} else {uint64 result[4];CityHashCrc256(s, len, result);uint64 u = Uint128High64(seed) + result[0];uint64 v = Uint128Low64(seed) + result[1];return uint128(HashLen16(u, v + result[2]),HashLen16(Rotate(v, 32), u * k0 + result[3]));}
}}#endifcity.h 头文件
// Created by Administrator on 2023/12/12.
//// Copyright (c) 2011 Google, Inc.
//
// Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
// of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
// in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
// to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
// copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
// furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
//
// The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in
// all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
//
// THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
// IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
// FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
// AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
// LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
// OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN
// THE SOFTWARE.
//
// CityHash, by Geoff Pike and Jyrki Alakuijala
//
// This file provides a few functions for hashing strings. On x86-64
// hardware in 2011, CityHash64() is faster than other high-quality
// hash functions, such as Murmur. This is largely due to higher
// instruction-level parallelism. CityHash64() and CityHash128() also perform
// well on hash-quality tests.
//
// CityHash128() is optimized for relatively long strings and returns
// a 128-bit hash. For strings more than about 2000 bytes it can be
// faster than CityHash64().
//
// Functions in the CityHash family are not suitable for cryptography.
//
// WARNING: This code has not been tested on big-endian platforms!
// It is known to work well on little-endian platforms that have a small penalty
// for unaligned reads, such as current Intel and AMD moderate-to-high-end CPUs.
//
// By the way, for some hash functions, given strings a and b, the hash
// of a+b is easily derived from the hashes of a and b. This property
// doesn't hold for any hash functions in this file.#ifndef CITY_HASH_H_
#define CITY_HASH_H_#include <stdlib.h> // for size_t.
#include <utility>// Microsoft Visual Studio may not have stdint.h.
#if defined(_MSC_VER) && (_MSC_VER < 1600)
typedef unsigned char uint8_t;
typedef unsigned int uint32_t;
typedef unsigned __int64 uint64_t;
#else // defined(_MSC_VER)
#include <stdint.h>
#endif // !defined(_MSC_VER)typedef uint8_t uint8;
typedef uint32_t uint32;
typedef uint64_t uint64;
typedef std::pair<uint64, uint64> uint128;inline uint64 Uint128Low64(const uint128& x) { return x.first; }
inline uint64 Uint128High64(const uint128& x) { return x.second; }// Hash function for a byte array.
uint64 CityHash64(const char *buf, size_t len);// Hash function for a byte array. For convenience, a 64-bit seed is also
// hashed into the result.
uint64 CityHash64WithSeed(const char *buf, size_t len, uint64 seed);// Hash function for a byte array. For convenience, two seeds are also
// hashed into the result.
uint64 CityHash64WithSeeds(const char *buf, size_t len,uint64 seed0, uint64 seed1);// Hash function for a byte array.
uint128 CityHash128(const char *s, size_t len);// Hash function for a byte array. For convenience, a 128-bit seed is also
// hashed into the result.
uint128 CityHash128WithSeed(const char *s, size_t len, uint128 seed);// Hash 128 input bits down to 64 bits of output.
// This is intended to be a reasonably good hash function.
inline uint64 Hash128to64(const uint128& x) {// Murmur-inspired hashing.const uint64 kMul = 0x9ddfea08eb382d69ULL;uint64 a = (Uint128Low64(x) ^ Uint128High64(x)) * kMul;a ^= (a >> 47);uint64 b = (Uint128High64(x) ^ a) * kMul;b ^= (b >> 47);b *= kMul;return b;
}// Conditionally include declarations for versions of City that require SSE4.2
// instructions to be available.
#if defined(__SSE4_2__) && defined(__x86_64__)// Hash function for a byte array.
uint128 CityHashCrc128(const char *s, size_t len);// Hash function for a byte array. For convenience, a 128-bit seed is also
// hashed into the result.
uint128 CityHashCrc128WithSeed(const char *s, size_t len, uint128 seed);// Hash function for a byte array. Sets result[0] ... result[3].
void CityHashCrc256(const char *s, size_t len, uint64 *result);#endif // __SSE4_2__#endif // CITY_HASH_H_在这里插入代码片
我在vs 编译一下
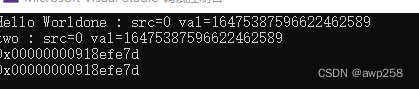 编译通过
编译通过
直接移植到Android 上
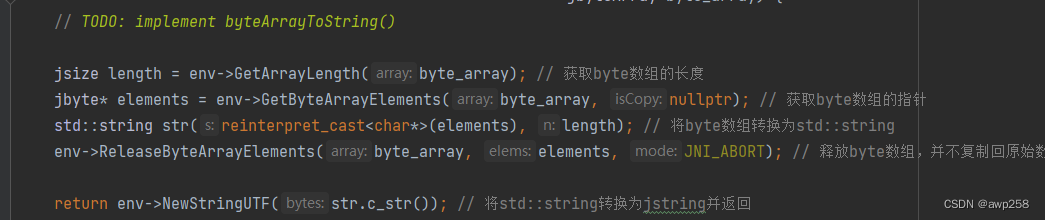 调用
调用
byte[] byteArray ={(byte) 0x8E, (byte) 0xE8,(byte)0x6D, (byte) 0xD6};String result1 = googleCity.getCityCode(byteArray);tv.setText(result1+"");在这里插入代码片
```搞定 需要代码的小伙伴 点击这里:相关文章:

Android 移动端编译 cityhash动态库
最近做项目, 硬件端 需要 用 cityhash 编译一个 动态库 提供给移动端使用,l 记录一下 编译过程 city .cpp // // Created by Administrator on 2023/12/12. // // Copyright (c) 2011 Google, Inc. // // Permission is hereby granted, free of charg…...
IO流学习
IO流:存储和读取数据的解决方案 import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//1.创建对象//写出 输入流 OutputStream//本地文件fileFileOutputStream fos new FileOutputS…...

新手HTML和CSS的常见知识点
目录 1.HTML标题标签(到)用于定义网页中的标题,并按照重要性递减排列。例如: 2.HTML段落标签()用于定义网页中的段落。例如: 3.HTML链接标签()用于创建链接…...
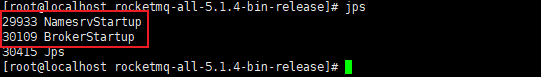
RocketMQ系统性学习-RocketMQ领域模型及Linux下单机安装
MQ 之间的对比 三种常用的 MQ 对比,ActiveMQ、Kafka、RocketMQ 性能方面: 三种 MQ 吞吐量级别为:万,百万,十万消息发送时延:毫秒,毫秒,微秒可用性:主从,分…...
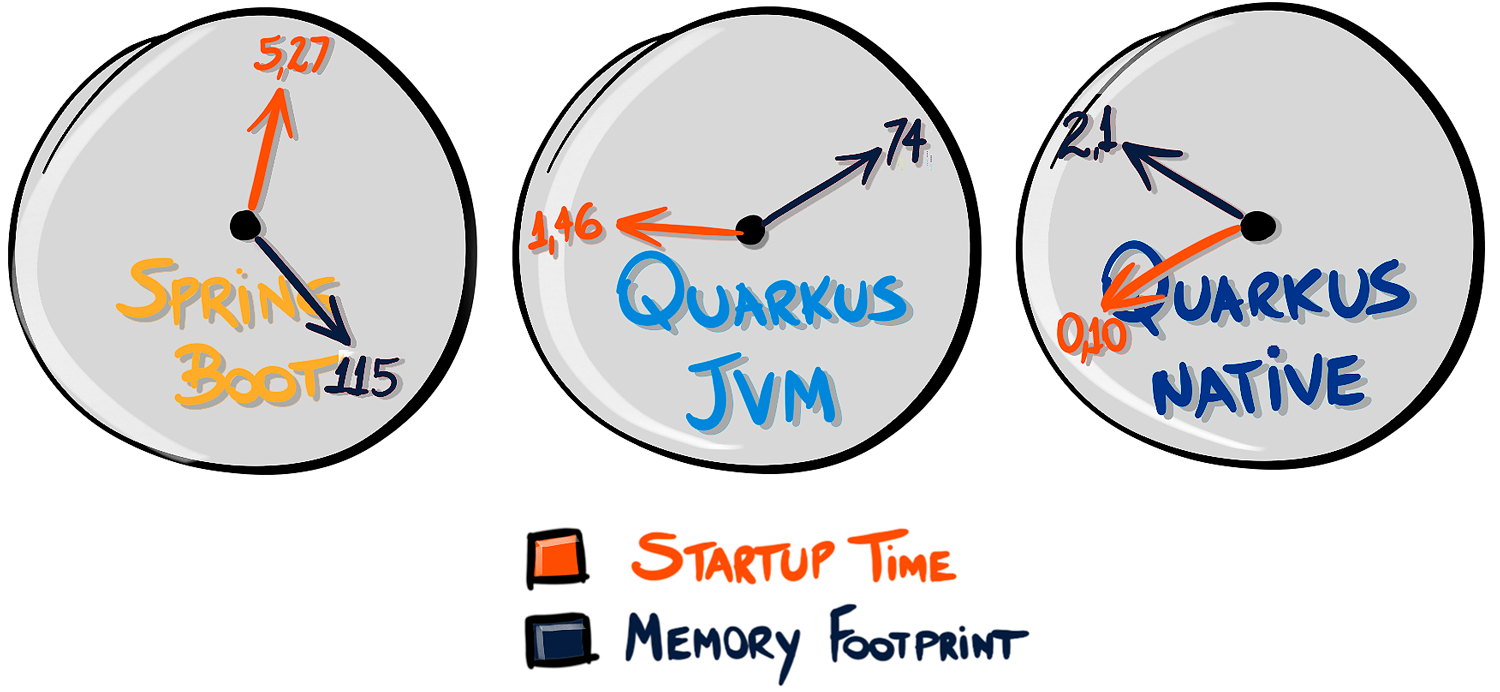
微服务架构之争:Quarkus VS Spring Boot
在容器时代(“Docker时代”),无论如何,Java仍然活着。Java在性能方面一直很有名,主要是因为代码和真实机器之间的抽象层,多平台的成本(一次编写,随处运行——还记得吗?&a…...
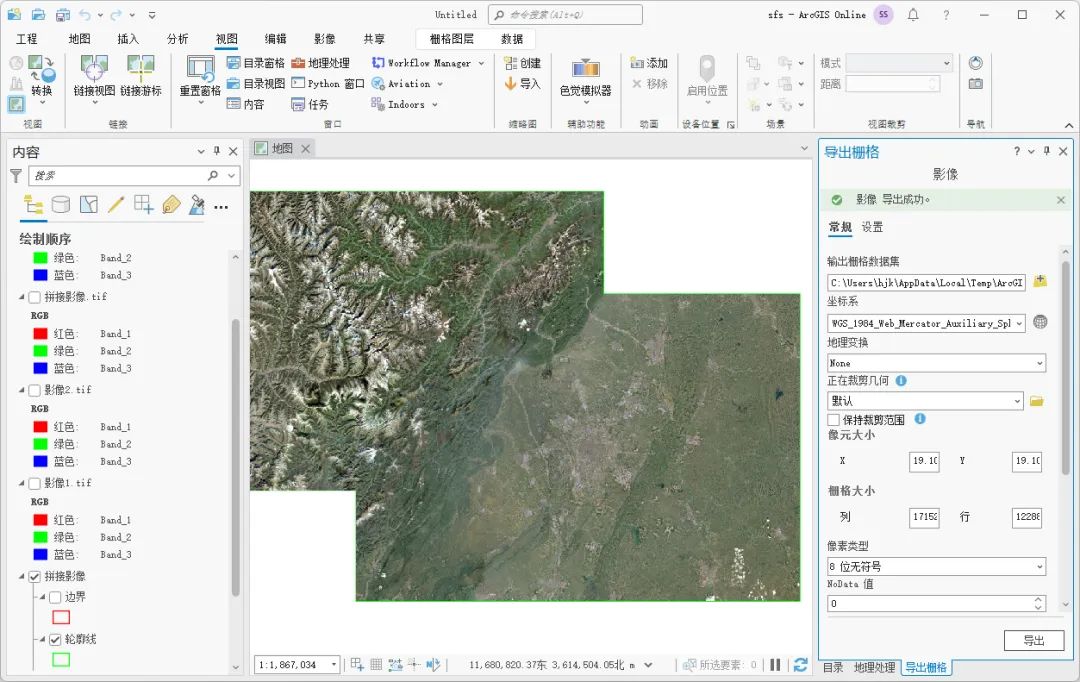
如何使用ArcGIS Pro拼接影像
为了方便数据的存储和传输,我们在网上获取到的影像一般都是分块的,正式使用之前需要对这些影像进行拼接,这里为大家介绍一下ArcGIS Pro中拼接影像的方法,希望能对你有所帮助。 数据来源 本教程所使用的数据是从水经微图中下载的…...
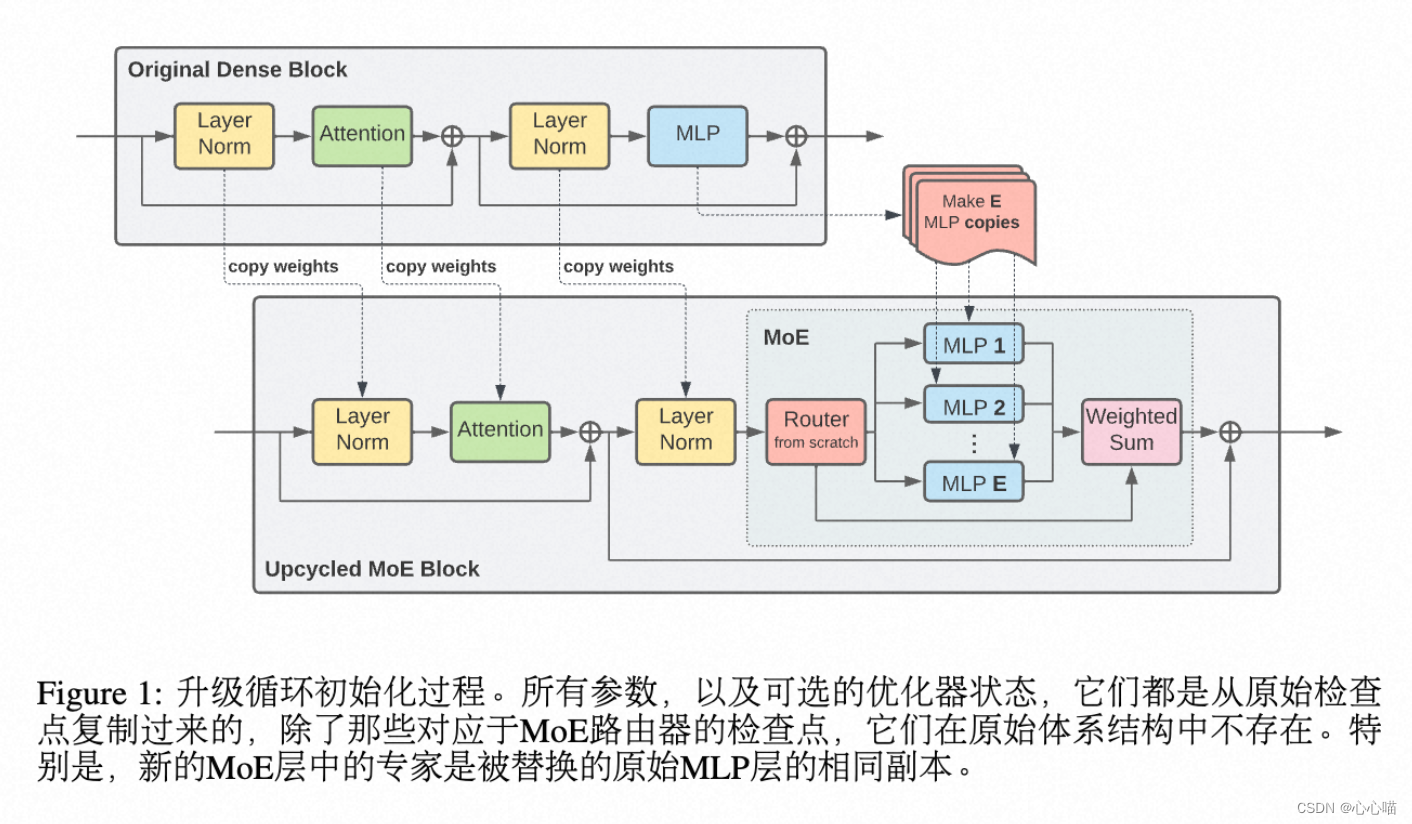
[论文笔记] chatgpt系列 SparseMOE—GPT4的MOE结构
SparseMOE: 稀疏激活的MOE Swtich MOE,所有token要在K个专家网络中,选择一个专家网络。 显存增加。 Experts Choice:路由MOE: 由专家选择token。这样不同的专家都选择到某个token,也可以不选择该token。 由于FFN层的时间复杂度和attention层不同,FFN层的时…...
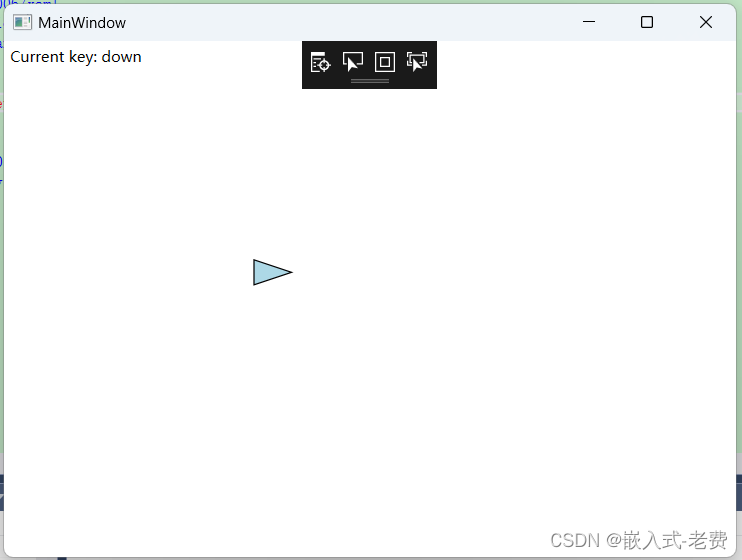
C# WPF上位机开发(键盘绘图控制)
【 声明:版权所有,欢迎转载,请勿用于商业用途。 联系信箱:feixiaoxing 163.com】 在软件开发中,如果存在canvas图像的话,一般有几种控制方法。一种是鼠标控制;一种是键盘控制;还有一…...
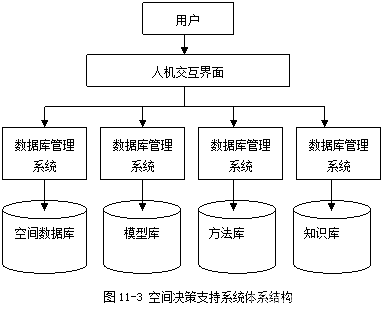
《地理信息系统原理》笔记/期末复习资料(10. 空间数据挖掘与空间决策支持系统)
目录 10. 空间数据挖掘与空间决策支持系统 10.1. 空间数据挖掘 10.1.1. 空间数据挖掘的概念 10.1.2. 空间数据挖掘的方法与过程 10.1.3. 空间数据挖掘的应用 10.2. 空间决策支持系统 10.2.1. 空间决策支持系统的概念 10.2.2. 空间决策支持系统的结构 10.2.3. 空间决策…...
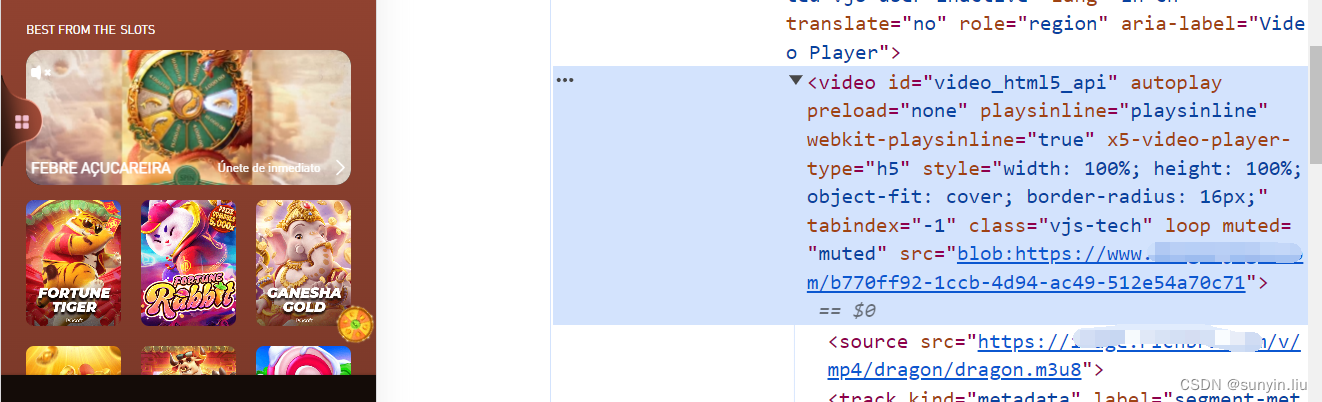
uniapp播放 m3u8格式视频 兼容pc和移动端
支持全自动播放、设置参数 自己摸索出来的,花了一天时间,给点订阅支持下,订阅后,不懂的地方可以私聊我。 代码实现 代码实现 1.安装dplayer组件 npm i dplayer2. static/index.html下引入 hls 引入hls.min.js 可以存放在static项目hls下面<script src="/static…...
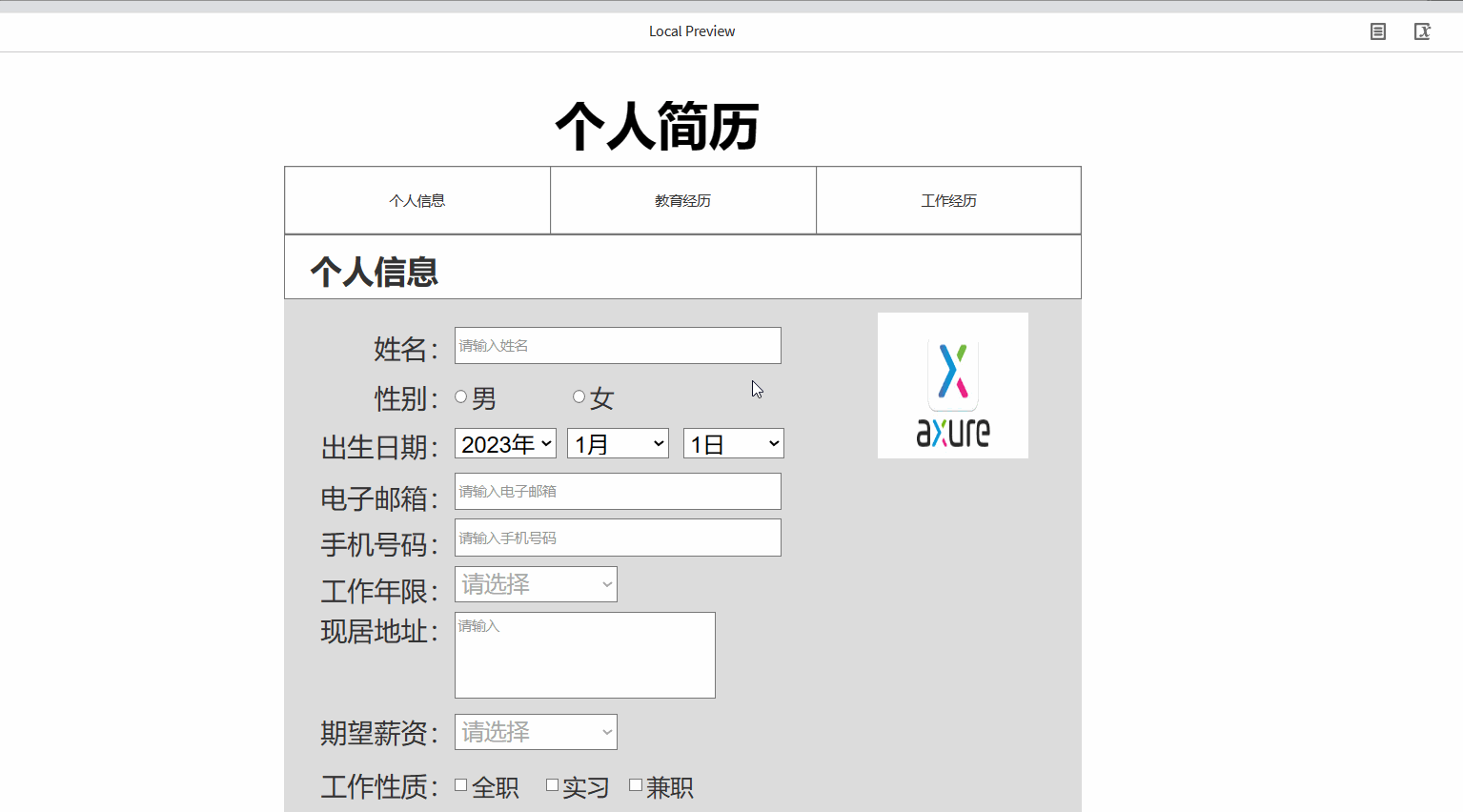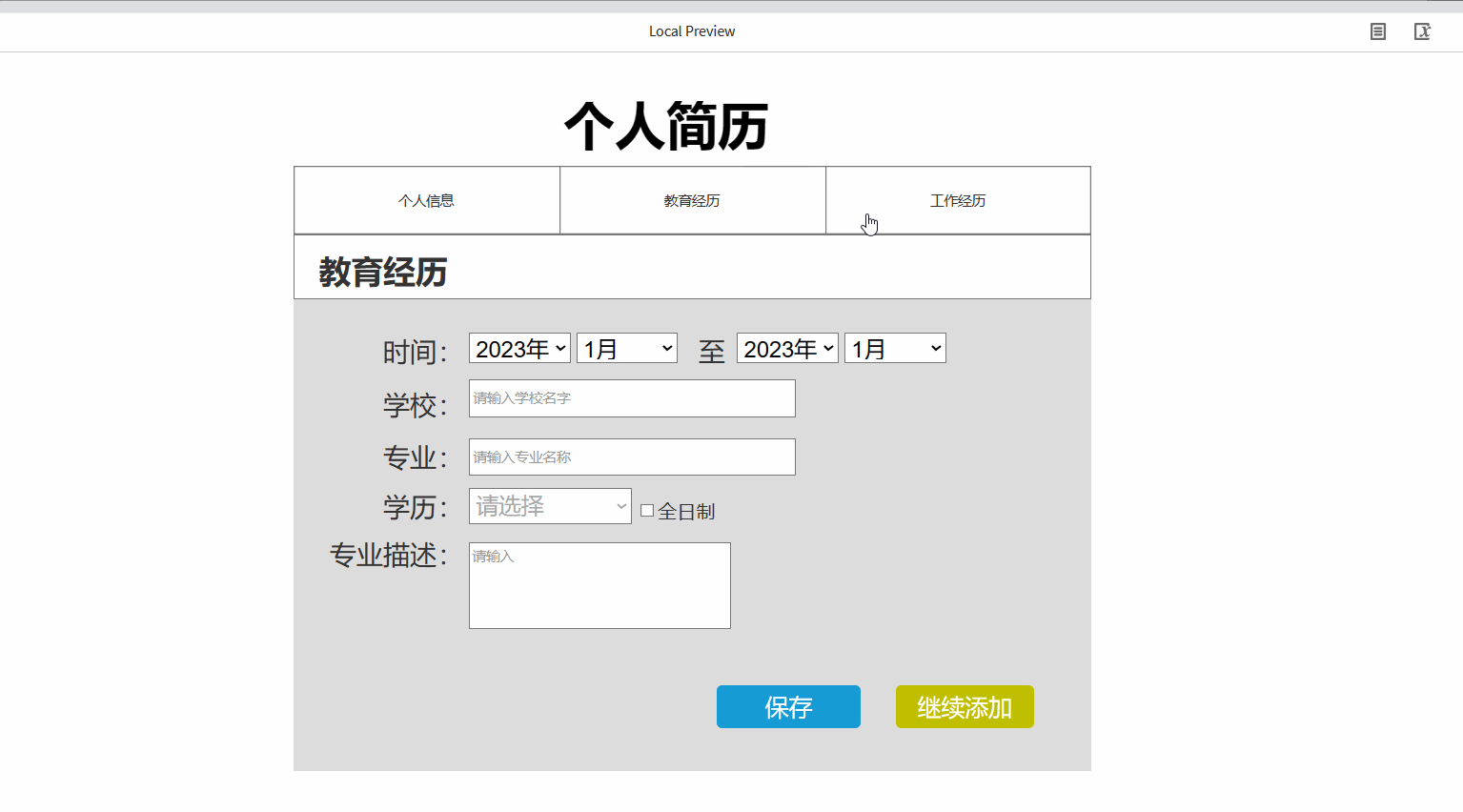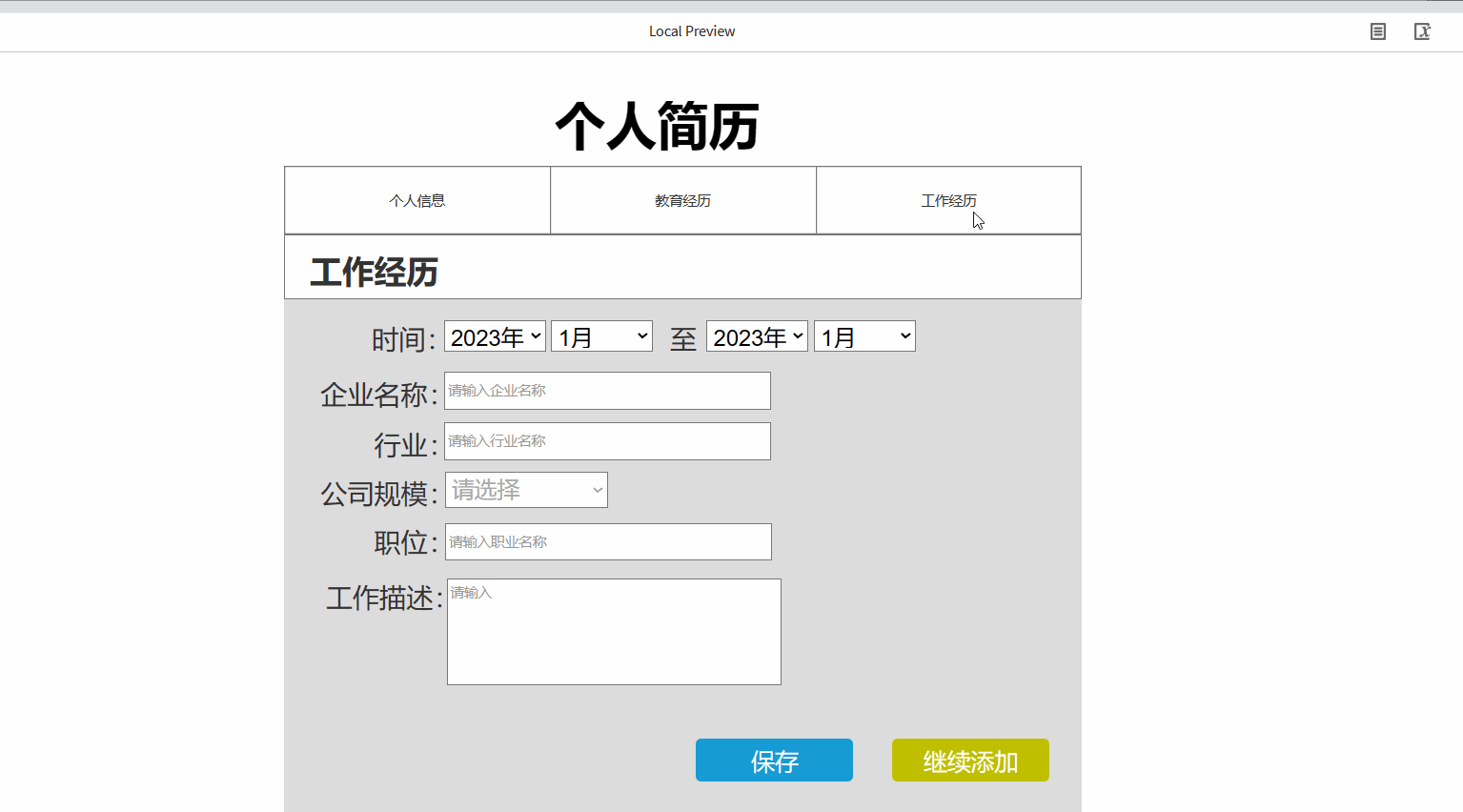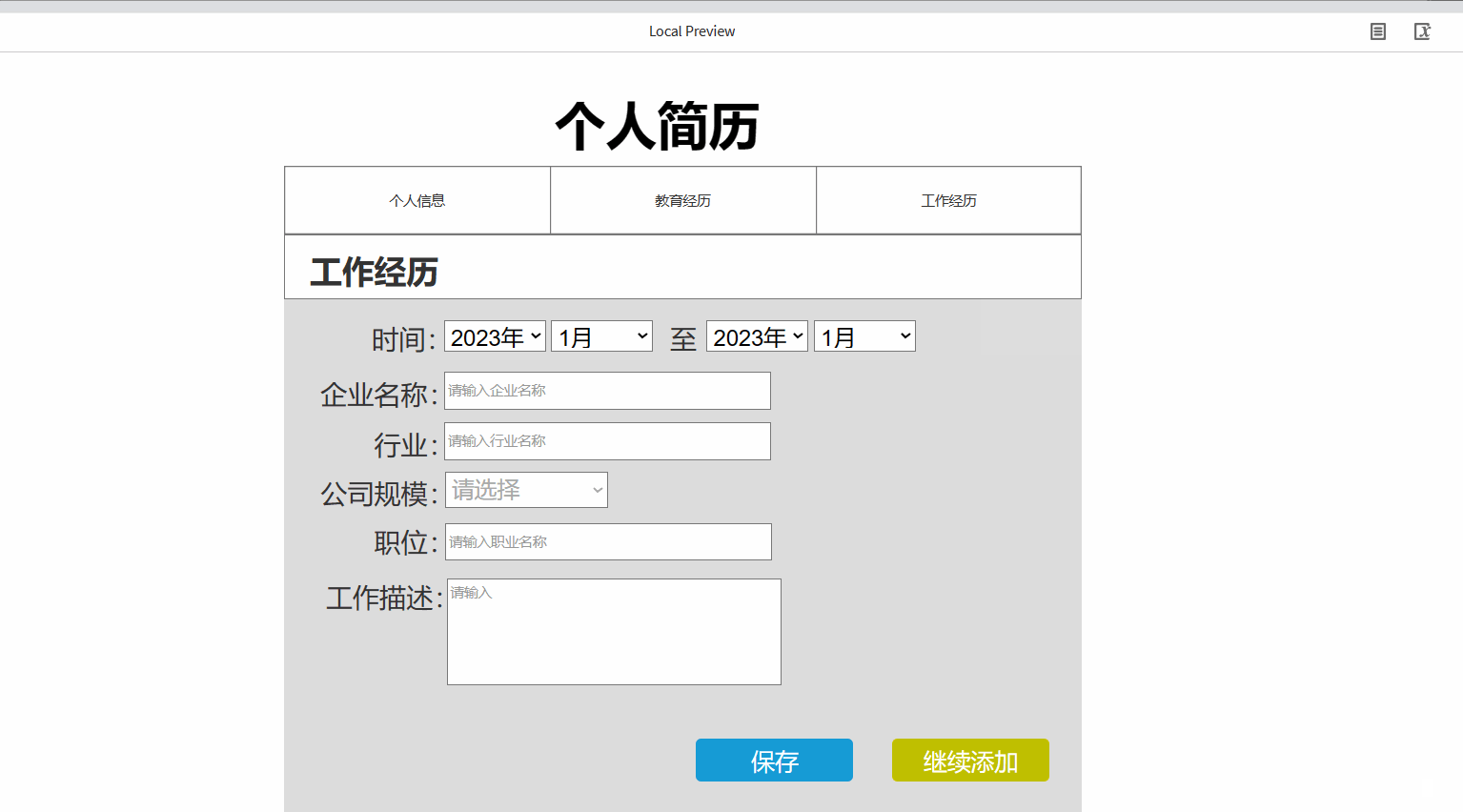
产品经理之Axure的元件库使用详细案例
⭐⭐ 产品经理专栏:产品专栏 ⭐⭐ 个人主页:个人主页 目录 前言 一.Axure的元件库的使用 1.1 元件介绍 1.2 基本元件的使用 1.2.1 矩形、按钮、标题的使用 1.2.2 图片及热区的使用 1.3 表单元件及表格元件的使用 1.3.1表单元件的使用 1.3.…...
数字化转型对企业有什么好处?
引言 数字化转型已经成为当今商业领域中的一股强大力量,它不仅仅是简单的技术更新,更是企业发展的重要战略转变。随着科技的迅猛发展和全球化竞争的加剧,企业们正在积极探索如何将数字化的力量融入到他们的运营和战略中。 数字化转型不仅是传…...

微信小程序:按钮禁用,避免按钮重复提交
wxml <view class"modal-buttons"><view class"one_btn" bindtap"submit">确认</view><view class"two_btn" bindtap"cancel">取消</view> </view> wxss /* 按钮 */ .modal-buttons…...
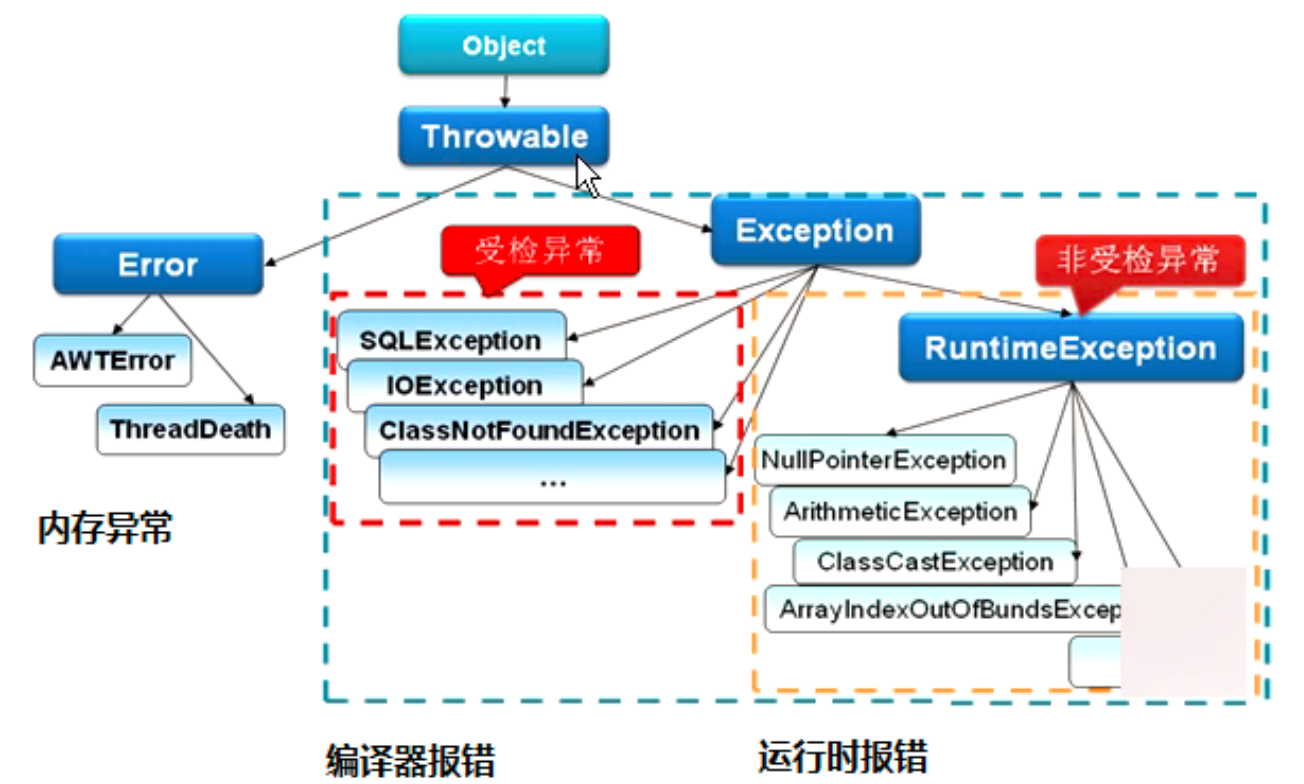
JAVA 异常分类及处理
JAVA 异常分类及处理 概念 如果某个方法不能按照正常的途径完成任务,就可以通过另一种路径退出方法。在这种情况下会抛出一个封装了错误信息的对象。此时,这个方法会立刻退出同时不返回任何值。另外,调用这个方法的其他代码也无法继续执行&…...
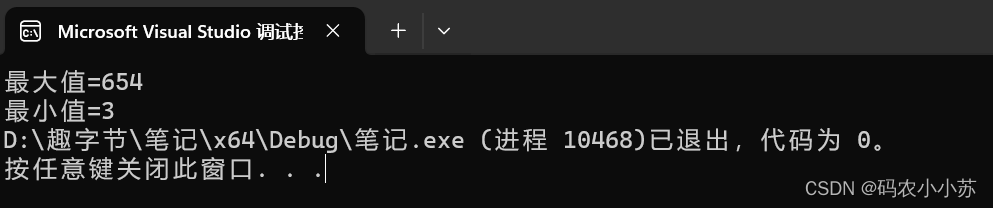
C语言--求数组的最大值和最小值【两种方法】
🍗方法一:用for循环遍历数组,找出最大值与最小值 🍗方法二:用qsort排序,让数组成为升序的有序数组,第一个值就是最小值,最后一个是最大值 完整代码: 方法一: …...
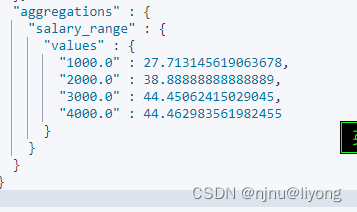
ES-组合与聚合
ES组合查询 1 must 满足两个match才会被命中 GET /mergeindex/_search {"query": {"bool": {"must": [{"match": {"name": "liyong"}},{"match_phrase": {"desc": "liyong"}}]}}…...
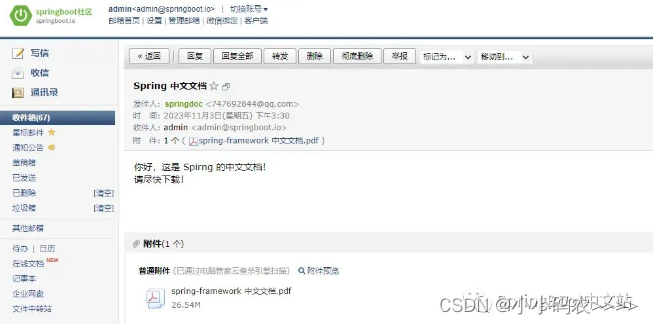
在 Spring Boot 中发送邮件简单实现
Spring Boot 对于发送邮件这种常用功能也提供了开箱即用的 Starter:spring-boot-starter-mail。 通过这个 starter,只需要简单的几行配置就可以在 Spring Boot 中实现邮件发送,可用于发送验证码、账户激活等等业务场景。 本文将通过实际的案…...
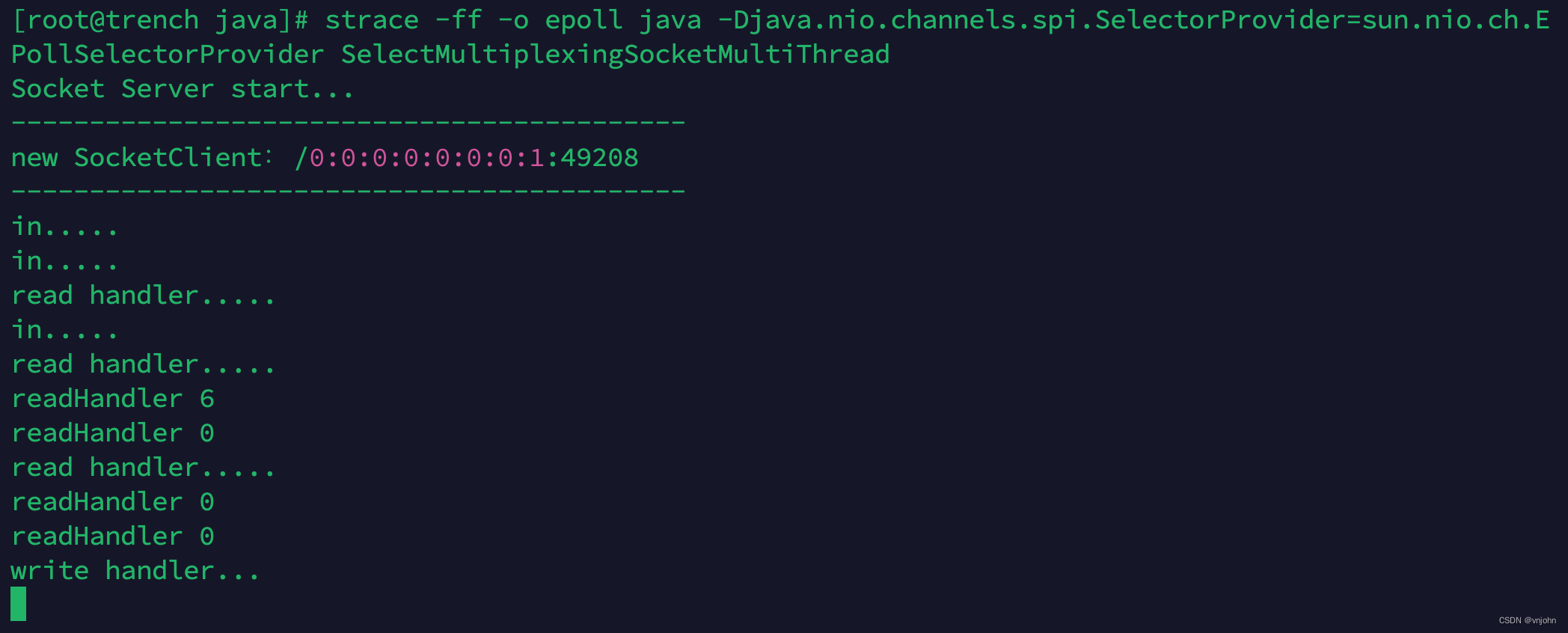
深入理解网络 I/O:单 Selector 多线程|单线程模型
🔭 嗨,您好 👋 我是 vnjohn,在互联网企业担任 Java 开发,CSDN 优质创作者 📖 推荐专栏:Spring、MySQL、Nacos、Java,后续其他专栏会持续优化更新迭代 🌲文章所在专栏&…...

Kafka Avro序列化之三:使用Schema Register实现
为什么需要Schema Register 注册表 无论是使用传统的Avro API自定义序列化类和反序列化类 还是 使用Twitter的Bijection类库实现Avro的序列化与反序列化,这两种方法都有一个缺点:在每条Kafka记录里都嵌入了schema,这会让记录的大小成倍地增加。但是不管怎样,在读取记录时…...
EasyExcel
概述 GitHub - alibaba/easyexcel: 快速、简洁、解决大文件内存溢出的java处理Excel工具 EasyExcel官方文档 - 基于Java的Excel处理工具 | Easy Excel EasyExcel是一个基于Java的、快速、简洁、解决大文件内存溢出的Excel处理工具。 他能让你在不用考虑性能、内存的等因素的…...

铭豹扩展坞 USB转网口 突然无法识别解决方法
当 USB 转网口扩展坞在一台笔记本上无法识别,但在其他电脑上正常工作时,问题通常出在笔记本自身或其与扩展坞的兼容性上。以下是系统化的定位思路和排查步骤,帮助你快速找到故障原因: 背景: 一个M-pard(铭豹)扩展坞的网卡突然无法识别了,扩展出来的三个USB接口正常。…...
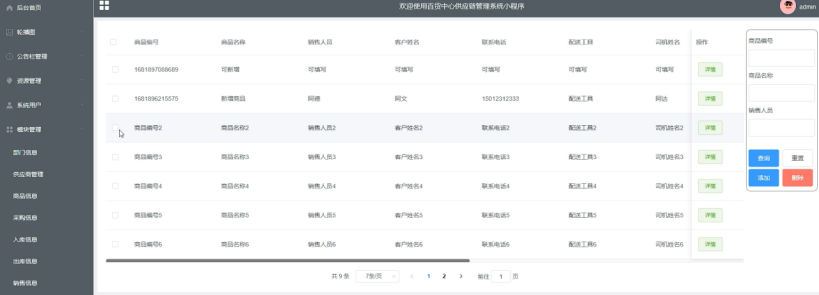
springboot 百货中心供应链管理系统小程序
一、前言 随着我国经济迅速发展,人们对手机的需求越来越大,各种手机软件也都在被广泛应用,但是对于手机进行数据信息管理,对于手机的各种软件也是备受用户的喜爱,百货中心供应链管理系统被用户普遍使用,为方…...

Leetcode 3577. Count the Number of Computer Unlocking Permutations
Leetcode 3577. Count the Number of Computer Unlocking Permutations 1. 解题思路2. 代码实现 题目链接:3577. Count the Number of Computer Unlocking Permutations 1. 解题思路 这一题其实就是一个脑筋急转弯,要想要能够将所有的电脑解锁&#x…...

vue3 定时器-定义全局方法 vue+ts
1.创建ts文件 路径:src/utils/timer.ts 完整代码: import { onUnmounted } from vuetype TimerCallback (...args: any[]) > voidexport function useGlobalTimer() {const timers: Map<number, NodeJS.Timeout> new Map()// 创建定时器con…...
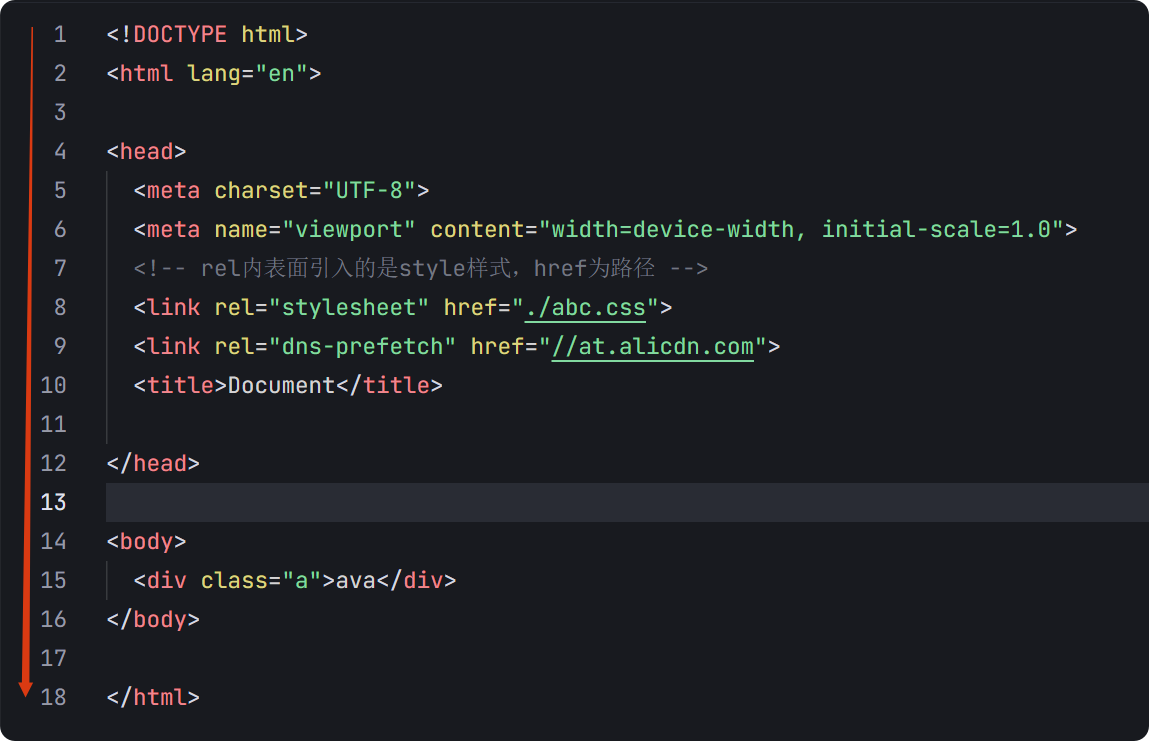
04-初识css
一、css样式引入 1.1.内部样式 <div style"width: 100px;"></div>1.2.外部样式 1.2.1.外部样式1 <style>.aa {width: 100px;} </style> <div class"aa"></div>1.2.2.外部样式2 <!-- rel内表面引入的是style样…...
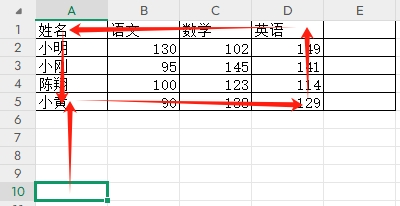
3-11单元格区域边界定位(End属性)学习笔记
返回一个Range 对象,只读。该对象代表包含源区域的区域上端下端左端右端的最后一个单元格。等同于按键 End 向上键(End(xlUp))、End向下键(End(xlDown))、End向左键(End(xlToLeft)End向右键(End(xlToRight)) 注意:它移动的位置必须是相连的有内容的单元格…...

管理学院权限管理系统开发总结
文章目录 🎓 管理学院权限管理系统开发总结 - 现代化Web应用实践之路📝 项目概述🏗️ 技术架构设计后端技术栈前端技术栈 💡 核心功能特性1. 用户管理模块2. 权限管理系统3. 统计报表功能4. 用户体验优化 🗄️ 数据库设…...
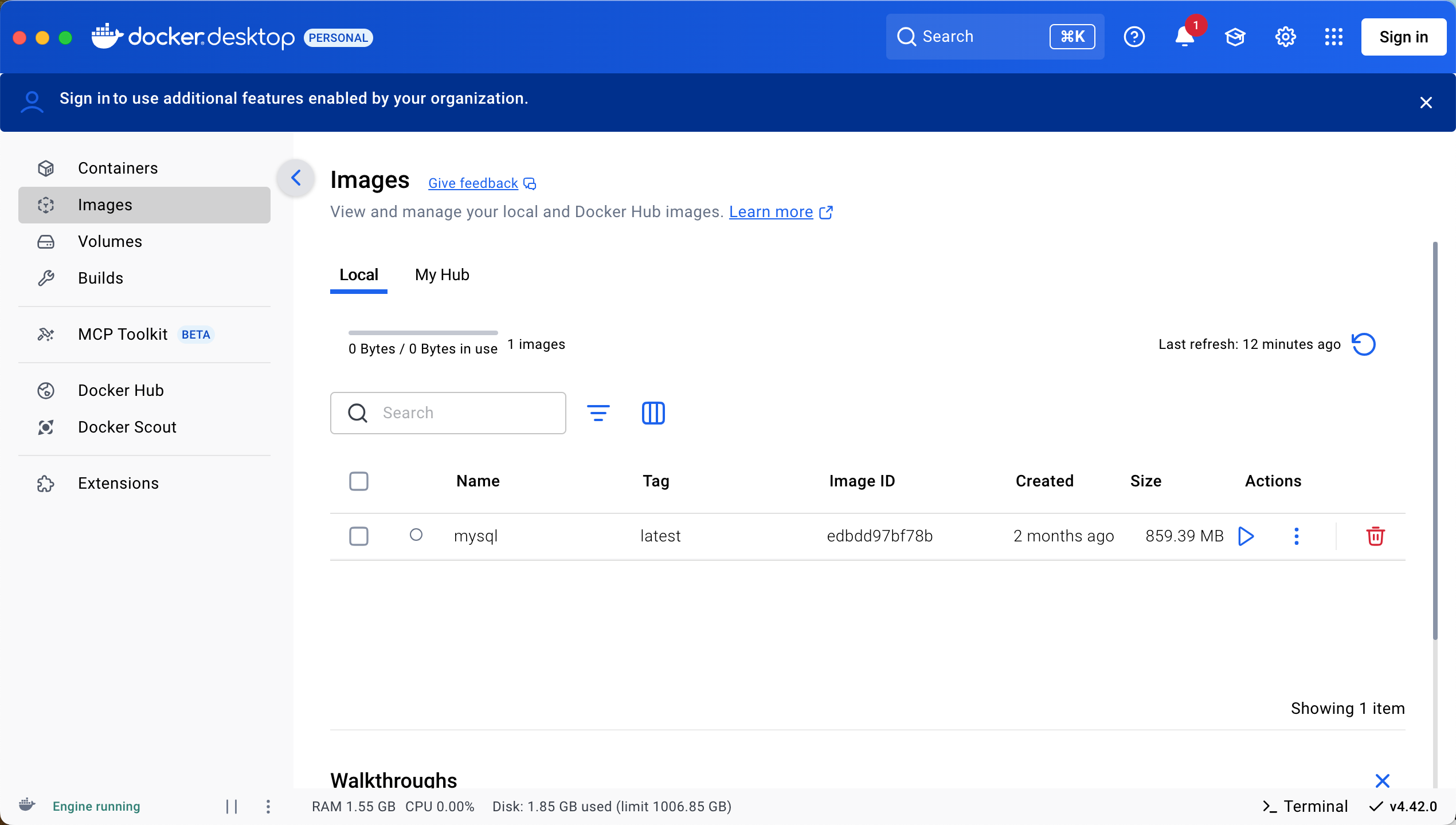
Docker 本地安装 mysql 数据库
Docker: Accelerated Container Application Development 下载对应操作系统版本的 docker ;并安装。 基础操作不再赘述。 打开 macOS 终端,开始 docker 安装mysql之旅 第一步 docker search mysql 》〉docker search mysql NAME DE…...

return this;返回的是谁
一个审批系统的示例来演示责任链模式的实现。假设公司需要处理不同金额的采购申请,不同级别的经理有不同的审批权限: // 抽象处理者:审批者 abstract class Approver {protected Approver successor; // 下一个处理者// 设置下一个处理者pub…...
【C++特殊工具与技术】优化内存分配(一):C++中的内存分配
目录 一、C 内存的基本概念 1.1 内存的物理与逻辑结构 1.2 C 程序的内存区域划分 二、栈内存分配 2.1 栈内存的特点 2.2 栈内存分配示例 三、堆内存分配 3.1 new和delete操作符 4.2 内存泄漏与悬空指针问题 4.3 new和delete的重载 四、智能指针…...
