olap/clickhouse-编译器优化与向量化
本文主要结合15721和clickhouse源码来聊聊向量化,正好我最近也在用Eigen做算子加速,了解下还是有好处的。
提示编译器
提示编译器而不是复杂化简单的代码
什么时候使用汇编,什么时候使用SIMD?下面有几个基本原则:
- 如果编译器能知道怎么优化是最好的(绝大多数情况下),那么不要复杂化代码。
- 编译器的优势是聪明,但你的优势是知道的多,因此提示编译器而不是手写汇编/SIMD。
- 99%的情况下不要使用SIMD,如果你发现无法成功提示编译器,并且这里的性能_真的_很重要,那么可以使用SIMD,但是要注意跨平台的问题,并测试你的代码真的超过了-O3下的编译器(因为流水线和CPU性能问题,性能可能并没有提高)。
- 不要使用汇编,除非你找到了SIMD库的问题(https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/docs/intrinsics-guide/index.html)
Clickhouse目前的代码量超过百万行,使用SIMD的地方也只有七个文件,只有极少的处理跨平台的汇编代码:

编译器能进行的优化
下面就说一下最常用的Release(O2)和O3级别编译器采取的优化,这些优化都是可以被关闭的。
O2
-fauto-inc-dec:对自增和自减操作进行优化,将其转换为更高效的指令序列。
-fbranch-count-reg:使用寄存器来统计分支指令的执行次数,用于分支预测优化。
-fcombine-stack-adjustments:合并连续的堆栈调整操作,以减少不必要的指令。
-fcompare-elim:消除不必要的比较操作,减少程序的运行时间。
-fcprop-registers:通过寄存器传播常量的值,以减少内存访问。
-fdce:删除未使用的代码。
-fdefer-pop:推迟对堆栈的调整操作,以减少指令的数量。
-fdelayed-branch:推迟分支指令的执行,以减少流水线的停顿。
-fdse:进行死代码消除优化,删除不可达的代码。
-fforward-propagate:进行常量传播优化,将常量传播到使用该常量的代码中。
-fguess-branch-probability:根据先前的执行信息猜测分支指令的概率,以优化分支预测。
-fif-conversion:对if语句进行优化,将条件表达式转换为更简单的形式。
-fif-conversion2:进行更复杂的if语句优化,包括通过更改条件的计算顺序来提高性能。
-finline-functions-called-once:对只被调用一次的函数进行内联展开。
-fipa-modref:进行模块间引用分析优化,减少不必要的内存操作。
-fipa-profile:根据程序的执行信息进行优化。
-fipa-pure-const:将纯函数和常量传播进行优化。
-fipa-reference:进行引用分析优化,减少不必要的内存操作。
-fipa-reference-addressable:进行可寻址引用分析优化,减少不必要的内存操作。
-fmerge-constants:合并重复的常量,以减少内存的使用。
-fmove-loop-invariants:将循环不变式移动到循环外部,以减少循环迭代次数。
-fomit-frame-pointer:优化代码以减少堆栈帧的使用。
-freorder-blocks:重新排序基本块以优化执行路径。
-fshrink-wrap:将变量的生命周期范围缩小到最小,以减少内存的使用。
-fshrink-wrap-separate:在函数中单独进行缩小作用域的操作。
-fsplit-wide-types:将宽类型的变量分割为多个较窄的变量,以减少内存的使用。
-fssa-backprop:通过SSA(静态单赋值)形式的数据流分析来优化代码。
-fssa-phiopt:通过SSA形式的Phi函数优化来优化代码。
-ftree-bit-ccp:进行位级的常量传播优化。
-ftree-ccp:进行常量传播优化。
-ftree-ch:进行复杂表达式优化。
-ftree-coalesce-vars:合并变量来减少内存的使用。
-ftree-copy-prop:进行复制传播优化。
-ftree-dce:进行死代码消除优化。
-ftree-dominator-opts:进行支配关系优化。
-ftree-dse:进行死存储消除优化。
-ftree-forwprop:进行常量传播和复制传播的优化。
-ftree-fre:进行冗余表达式消除优化。
-ftree-phiprop:对Phi函数进行优化。
-ftree-pta:进行指针分析优化。
-ftree-scev-cprop:进行简单标量表达式和常量传播优化。
-ftree-sink:将表达式移动到循环外部,以减少循环迭代次数。
-ftree-slsr:进行简单局部标量替换优化。
-ftree-sra:进行标量寄存器分配优化。
-ftree-ter:进行三元表达式优化。
-falign-functions:强制函数在内存中按指定的对齐方式对齐。
-falign-jumps:强制跳转指令在内存中按指定的对齐方式对齐。
-falign-labels:强制标签在内存中按指定的对齐方式对齐。
-falign-loops:强制循环开始地址在内存中按指定的对齐方式对齐。
-fcaller-saves:在函数调用时,保存调用者寄存器的值,以便被调用函数可以修改这些寄存器的值。
-fcode-hoisting:将可能的计算移动到循环外部,以减少循环迭代次数。
-fcrossjumping:在不同的控制流路径中查找重复的代码块,并将其合并为一个共享的代码块。
-fcse-follow-jumps:在跳转指令后面的代码中进行公共子表达式消除。
-fcse-skip-blocks:跳过指定数量的基本块,以提高公共子表达式消除的效率。
-fdelete-null-pointer-checks:删除空指针检查,以提高代码的执行速度。
-fdevirtualize:对虚函数调用进行优化,将虚函数调用转化为直接调用。
-fdevirtualize-speculatively:假设虚函数调用的目标是唯一的,并将其转化为直接调用。
-fexpensive-optimizations:进行一些代价较高的优化,可能会增加编译时间。
-ffinite-loops:假设循环最多执行有限次数,进行一些循环优化。
-fgcse:进行全局公共子表达式消除,删除重复计算的代码。
-fgcse-lm:对循环进行公共子表达式消除,删除循环内重复计算的代码。
-fhoist-adjacent-loads:将相邻的加载指令移动到循环外部,以减少循环迭代次数。
-finline-functions:对函数进行内联展开,将函数调用处替换为函数体。
-finline-small-functions:对小函数进行内联展开。
-findirect-inlining:对间接函数调用进行内联展开。
-fipa-bit-cp:进行位级的常量传播优化。
-fipa-cp:进行常量传播优化。
-fipa-icf:进行间接代码优化,合并相似的间接调用。
-fipa-ra:进行间接寄存器分配优化。
-fipa-sra:进行间接寄存器分配优化,同时进行标量寄存器分配优化。
-fipa-vrp:进行值范围传播优化。
-fisolate-erroneous-paths-dereference:对错误路径上的指针解引用进行隔离。
-flra-remat:在循环中重新材料化值范围,以减少循环迭代次数。
-foptimize-sibling-calls:对兄弟函数调用进行优化。
-foptimize-strlen:对strlen函数进行优化。
-fpartial-inlining:对函数进行部分内联展开。
-fpeephole2:进行指令级别的优化。
-freorder-blocks-algorithm=stc:按指定的算法对基本块进行重新排序。
-freorder-blocks-and-partition:对基本块进行重新排序和分区,以提高指令级优化效果。
-freorder-functions:对函数进行重新排序,以提高指令级优化效果。
-frerun-cse-after-loop:在循环后重新运行公共子表达式消除。
-fschedule-insns:对指令进行调度以提高执行效率。
-fschedule-insns2 -fsched-interblock:对指令进行调度以提高执行效率。
-fstore-merging:合并存储操作,减少存储操作的数量。
-fstrict-aliasing:启用严格别名规则,优化代码对内存的访问。
-fthread-jumps:在多线程环境中,对线程间的跳转进行优化。
-ftree-builtin-call-dce:删除未使用的内建函数调用。
-ftree-pre:进行部分复写消除优化。
-ftree-switch-conversion:对switch语句进行转换优化。
-ftree-tail-merge:合并尾递归函数的调用。
-ftree-vrp:进行值范围传播优化。
O3
-fgcse-after-reload:在寄存器分配之后进行全局公共子表达式消除(GCSE)优化。
-fipa-cp-clone:通过复制函数来进行间接代码传播优化。
-floop-interchange:进行循环交换优化,改变循环的顺序。
-floop-unroll-and-jam:进行循环展开和循环合并的优化。
-fpeel-loops:将循环分解成多个部分,以减少循环迭代次数。
-fpredictive-commoning:通过提前计算和共享结果来进行预测性共享优化。
-fsplit-loops:将循环分割为多个部分,以便更好地利用指令级并行性。
-fsplit-paths:将控制流路径分割为多个部分,以便更好地利用指令级并行性。
-ftree-loop-distribution:将循环分布到多个线程或处理器上,以进行并行化处理。
-ftree-loop-vectorize:对循环进行向量化优化,以利用SIMD指令。
-ftree-partial-pre:进行局部部分预测优化,提前计算和共享部分结果。
-ftree-slp-vectorize:对循环进行超标量指令优化,将多条指令合并为一条指令。
-funswitch-loops:对循环进行开关优化,将循环展开成多个版本,通过开关语句来选择执行哪个版本。
-fvect-cost-model:使用向量化优化的成本模型进行优化。
-fvect-cost-model=dynamic:使用动态的向量化优化成本模型进行优化。
-fversion-loops-for-strides:对循环进行版本化优化,根据迭代步长来选择不同的版本进行执行。
直观感受一下
计算一个数字的二进制中有多少个 1
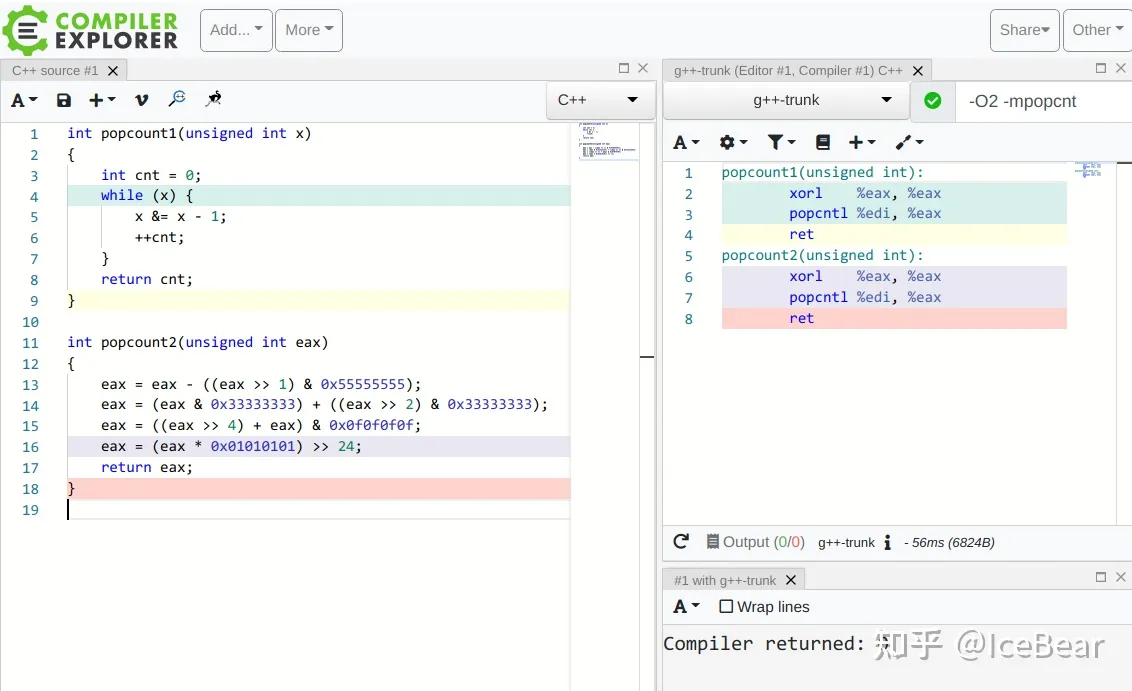
唯一的内存访问

显式告诉编译器数组是内存中的不同位置
void f(int *a, int *b, int *c)
{*a += *c;*b += *c;
}// f(int*, int*, int*):
// movl (%rdx), %eax
// addl %eax, (%rdi)
// movl (%rdx), %eax
// addl %eax, (%rsi)
// retvoid f(int * __restrict__ a, int* __restrict__ b, int* __restrict__ c)
{*a += *c;*b += *c;
}// f(int*, int*, int*):
// movl (%rdx), %eax
// addl %eax, (%rdi)
// addl %eax, (%rsi)
// ret
显式告诉编译器忽略向量的循环依赖关系,作用和上面是一样的

除了可以用 __restrict 让编译器放心做 SIMD 优化外,还可以用 OpenMP 的这条指令来迫使编译器无视指针别名的问题,并启用 SIMD 优化。不过得给编译器打开 -fopenmp 这个选项。:


循环展开
循环展开现在编译器都会自动做了,有时候可能需要限制循环展开。
比如clickhouse里面的一段:
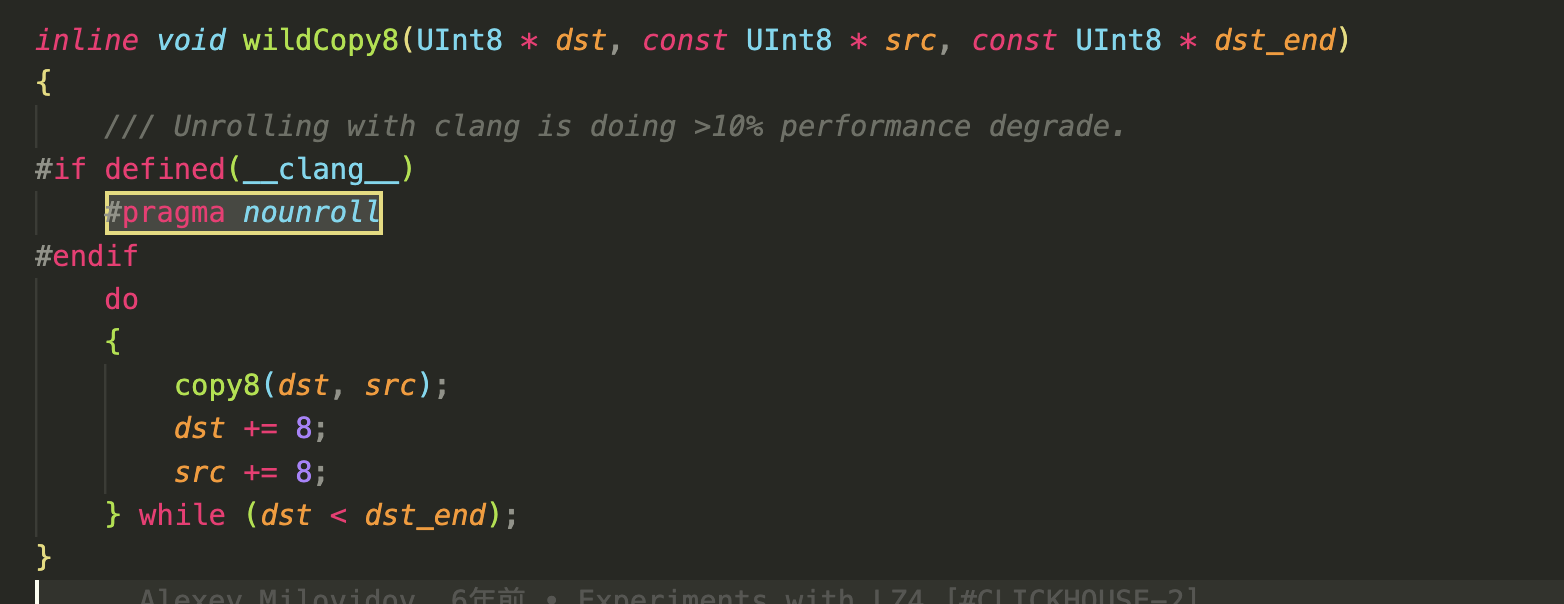
对小的循环体进行 unroll 可能是划算的,但最好不要 unroll 大的循环体,否则会造成指令缓存的压力反而变慢。
对齐
对齐的主要作用是使用SIMD向量化指令进行复杂的向量运算。
比如使用avx-512,将数据与64个字节对齐时可以通过_mm512_load_pd将数据直接加载到zmmm寄存器中,并在其上应用SIMD指令,然后通过_mm512 _stream_pd将其存储回。如果不进行大量的向量化计算,只会造成内存浪费。
相反,大多数情况下需要的是1字节填充来节省内存。
比如:
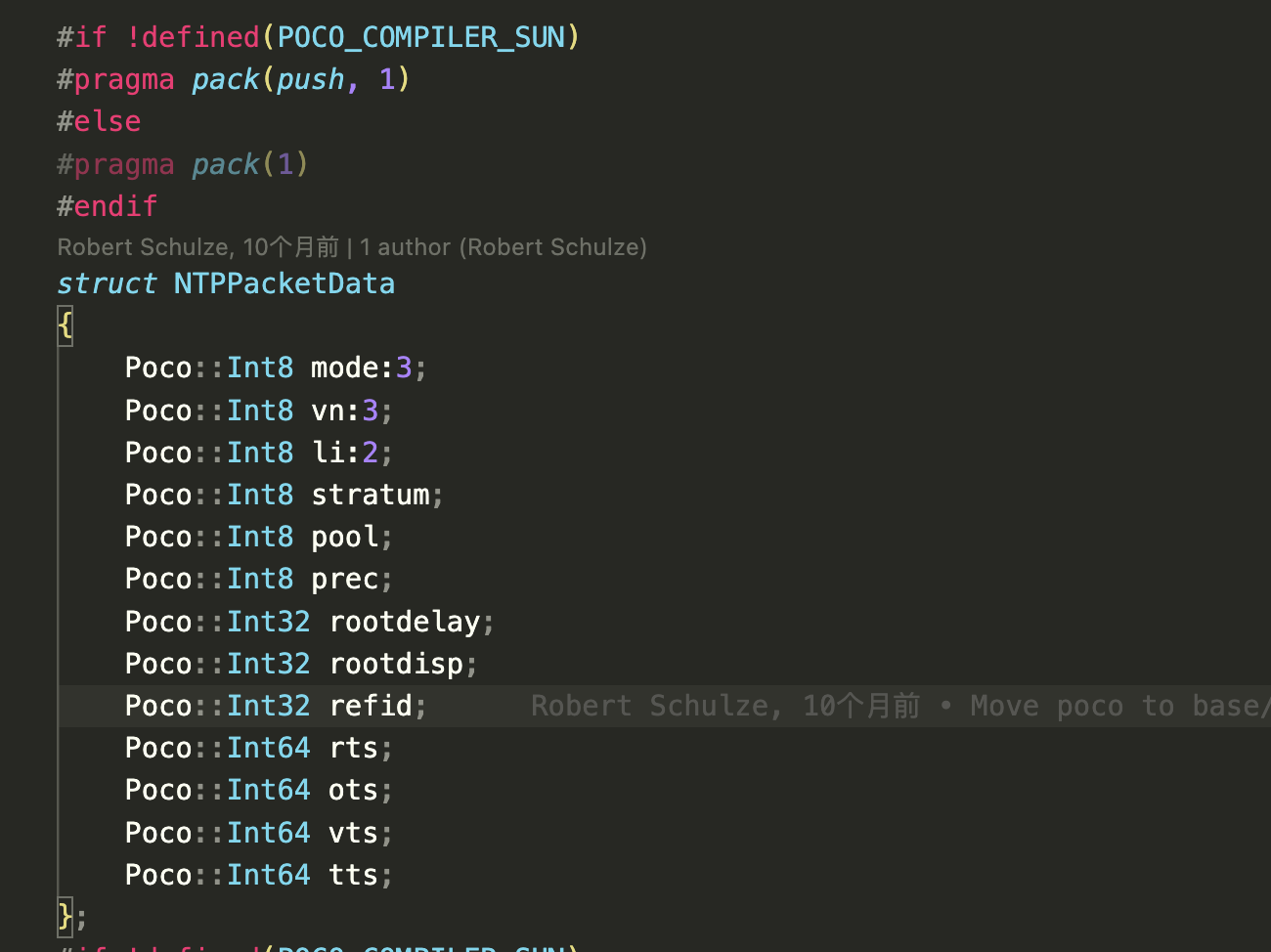
-ffast-math
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/7420665/what-does-gccs-ffast-math-actually-do
OLAP经常使用的SIMD操作
所谓的SIMD,就是用MMX指令集(64位SIMD寄存器)或者SSE/AVX/AVX512指令集(128位SIMD寄存器),做数据的并行化处理。
- 遮罩 Masking
- 排列
- 选择性加载 / 存储
- 压缩 / 扩展
- 选择性聚集 / 散开
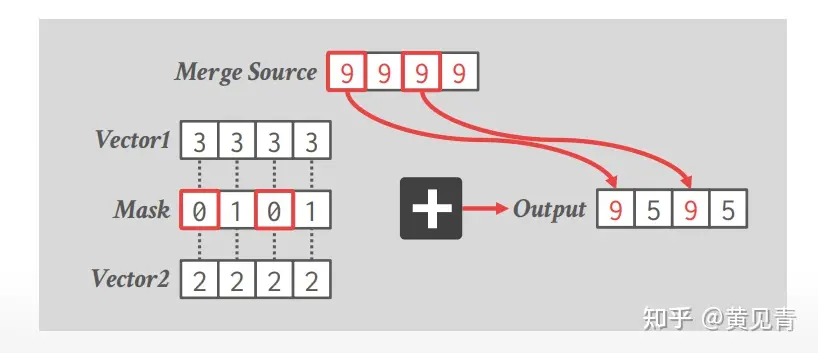
遮罩
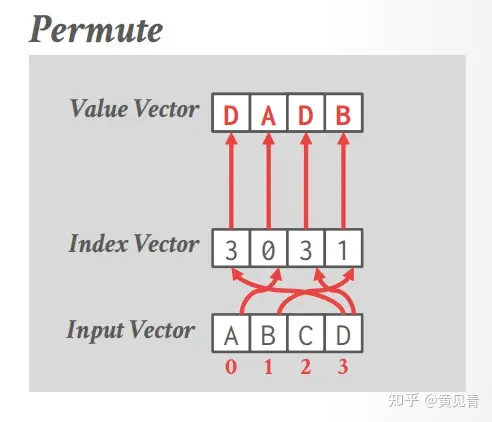
排列
对于每个通道,将索引向量中指定的偏移量处的输入向量的值复制到目标向量中。在 AVX-512 之前,数据库管理系统必须将数据从 SIMD 寄存器写入内存,然后再写回 SIMD 寄存器。而 AVX-512 指令集引入了新的 PERMUTE 操作,可以直接在 SIMD 寄存器内部完成元素重排,大大提高了性能。
blend:
在SIMD(Single Instruction, Multiple Data)编程中,Blend(混合)是一种操作,用于将两个向量按照指定的规则进行混合。混合操作通常是将两个向量的对应元素进行混合,生成一个新的向量。
选择性加载 / 存储
选择性加载从内存中读取满足特定条件的数据元素,而选择性存储将数据元素写回内存
压缩 / 扩展
用于减少数据存储需求和提高内存访问效率。
压缩操作将数据集中的冗余信息删除,减小数据的存储空间。扩展操作则是压缩的逆过程,将压缩后的数据还原为原始格式
这两种指令
选择性聚集 / 散开
用于重组数据的技术。
选择性聚集从一个数据集中提取满足特定条件的元素,并将它们组合成一个新的、更紧凑的数据集。
选择性散开是选择性聚集的逆操作,它将数据集中的元素根据特定条件分散到一个更大的数据集中。
这两种操作可以提高数据处理效率,特别是在需要对数据进行过滤、合并或分组等操作时。
Make the most out of your SIMD investments: counter control flow divergence in compiled query pipelines
Clickhouse
clickhouse里面针对三种SIMD指令集进行了优化,分别是__SSE2__、AVX、NEON
#ifdef __SSE2__
#include <emmintrin.h>
#endif#if USE_MULTITARGET_CODE
#include <immintrin.h>
#endif#if defined(__aarch64__) && defined(__ARM_NEON)
# include <arm_neon.h>
# pragma clang diagnostic ignored "-Wreserved-identifier"
#endif
一共在代码里出现了17处。
所以,就算是OLAP这种CPU密集型的应用,手写SIMD也只是小部分情况。
memcpy
clickhouse重写了glibc的memcpy,这里作者提到:
- 如果用 -ftree-loop-distribute-patterns可能会导致编译器优化为自带的memcpy,而又会重新调用到重写的memcpy,导致递归调用,所以必须禁用掉。
- 用AVX512有两个问题:一个是降频,第二个是SSE切换AVX512的性能开销。
- 然后作者列了几个影响性能的因素:
- 预取指令,因为预取指令的大小不确定,而且在ARM中性能比较差,所以这里没有预取
- 对齐,这里使用不对齐的加载和对齐的存储
- 循环展开次数,这里固定为8次
- attribute((no_sanitize(“coverage”)))禁用行数统计
- 最后作者提到memcpy可能会在编译时被优化为循环赋值,使用**-fbuiltin-memcpy**
#include <stddef.h>#include <emmintrin.h>/** Custom memcpy implementation for ClickHouse.* It has the following benefits over using glibc's implementation:* 1. Avoiding dependency on specific version of glibc's symbol, like memcpy@@GLIBC_2.14 for portability.* 2. Avoiding indirect call via PLT due to shared linking, that can be less efficient.* 3. It's possible to include this header and call inline_memcpy directly for better inlining or interprocedural analysis.* 4. Better results on our performance tests on current CPUs: up to 25% on some queries and up to 0.7%..1% in average across all queries.** Writing our own memcpy is extremely difficult for the following reasons:* 1. The optimal variant depends on the specific CPU model.* 2. The optimal variant depends on the distribution of size arguments.* 3. It depends on the number of threads copying data concurrently.* 4. It also depends on how the calling code is using the copied data and how the different memcpy calls are related to each other.* Due to vast range of scenarios it makes proper testing especially difficult.* When writing our own memcpy there is a risk to overoptimize it* on non-representative microbenchmarks while making real-world use cases actually worse.** Most of the benchmarks for memcpy on the internet are wrong.** Let's look at the details:** For small size, the order of branches in code is important.* There are variants with specific order of branches (like here or in glibc)* or with jump table (in asm code see example from Cosmopolitan libc:* https://github.com/jart/cosmopolitan/blob/de09bec215675e9b0beb722df89c6f794da74f3f/libc/nexgen32e/memcpy.S#L61)* or with Duff device in C (see https://github.com/skywind3000/FastMemcpy/)** It's also important how to copy uneven sizes.* Almost every implementation, including this, is using two overlapping movs.** It is important to disable -ftree-loop-distribute-patterns when compiling memcpy implementation,* otherwise the compiler can replace internal loops to a call to memcpy that will lead to infinite recursion.** For larger sizes it's important to choose the instructions used:* - SSE or AVX or AVX-512;* - rep movsb;* Performance will depend on the size threshold, on the CPU model, on the "erms" flag* ("Enhansed Rep MovS" - it indicates that performance of "rep movsb" is decent for large sizes)* https://stackoverflow.com/questions/43343231/enhanced-rep-movsb-for-memcpy** Using AVX-512 can be bad due to throttling.* Using AVX can be bad if most code is using SSE due to switching penalty* (it also depends on the usage of "vzeroupper" instruction).* But in some cases AVX gives a win.** It also depends on how many times the loop will be unrolled.* We are unrolling the loop 8 times (by the number of available registers), but it not always the best.** It also depends on the usage of aligned or unaligned loads/stores.* We are using unaligned loads and aligned stores.** It also depends on the usage of prefetch instructions. It makes sense on some Intel CPUs but can slow down performance on AMD.* Setting up correct offset for prefetching is non-obvious.** Non-temporary (cache bypassing) stores can be used for very large sizes (more than a half of L3 cache).* But the exact threshold is unclear - when doing memcpy from multiple threads the optimal threshold can be lower,* because L3 cache is shared (and L2 cache is partially shared).** Very large size of memcpy typically indicates suboptimal (not cache friendly) algorithms in code or unrealistic scenarios,* so we don't pay attention to using non-temporary stores.** On recent Intel CPUs, the presence of "erms" makes "rep movsb" the most beneficial,* even comparing to non-temporary aligned unrolled stores even with the most wide registers.** memcpy can be written in asm, C or C++. The latter can also use inline asm.* The asm implementation can be better to make sure that compiler won't make the code worse,* to ensure the order of branches, the code layout, the usage of all required registers.* But if it is located in separate translation unit, inlining will not be possible* (inline asm can be used to overcome this limitation).* Sometimes C or C++ code can be further optimized by compiler.* For example, clang is capable replacing SSE intrinsics to AVX code if -mavx is used.** Please note that compiler can replace plain code to memcpy and vice versa.* - memcpy with compile-time known small size is replaced to simple instructions without a call to memcpy;* it is controlled by -fbuiltin-memcpy and can be manually ensured by calling __builtin_memcpy.* This is often used to implement unaligned load/store without undefined behaviour in C++.* - a loop with copying bytes can be recognized and replaced by a call to memcpy;* it is controlled by -ftree-loop-distribute-patterns.* - also note that a loop with copying bytes can be unrolled, peeled and vectorized that will give you* inline code somewhat similar to a decent implementation of memcpy.** This description is up to date as of Mar 2021.** How to test the memcpy implementation for performance:* 1. Test on real production workload.* 2. For synthetic test, see utils/memcpy-bench, but make sure you will do the best to exhaust the wide range of scenarios.** TODO: Add self-tuning memcpy with bayesian bandits algorithm for large sizes.* See https://habr.com/en/company/yandex/blog/457612/*/__attribute__((no_sanitize("coverage")))
static inline void * inline_memcpy(void * __restrict dst_, const void * __restrict src_, size_t size)
{/// We will use pointer arithmetic, so char pointer will be used./// Note that __restrict makes sense (otherwise compiler will reload data from memory/// instead of using the value of registers due to possible aliasing).char * __restrict dst = reinterpret_cast<char * __restrict>(dst_);const char * __restrict src = reinterpret_cast<const char * __restrict>(src_);/// Standard memcpy returns the original value of dst. It is rarely used but we have to do it./// If you use memcpy with small but non-constant sizes, you can call inline_memcpy directly/// for inlining and removing this single instruction.void * ret = dst;tail:/// Small sizes and tails after the loop for large sizes./// The order of branches is important but in fact the optimal order depends on the distribution of sizes in your application./// This order of branches is from the disassembly of glibc's code./// We copy chunks of possibly uneven size with two overlapping movs./// Example: to copy 5 bytes [0, 1, 2, 3, 4] we will copy tail [1, 2, 3, 4] first and then head [0, 1, 2, 3].// 不对齐的加载 两个重叠的movsif (size <= 16){if (size >= 8){/// Chunks of 8..16 bytes.__builtin_memcpy(dst + size - 8, src + size - 8, 8);__builtin_memcpy(dst, src, 8);}else if (size >= 4){/// Chunks of 4..7 bytes.__builtin_memcpy(dst + size - 4, src + size - 4, 4);__builtin_memcpy(dst, src, 4);}else if (size >= 2){/// Chunks of 2..3 bytes.__builtin_memcpy(dst + size - 2, src + size - 2, 2);__builtin_memcpy(dst, src, 2);}else if (size >= 1){/// A single byte.*dst = *src;}/// No bytes remaining.}else{// 这里src和dst不可能同时128对齐,因此/// Medium and large sizes.if (size <= 128){/// Medium size, not enough for full loop unrolling./// We will copy the last 16 bytes._mm_storeu_si128(reinterpret_cast<__m128i *>(dst + size - 16), _mm_loadu_si128(reinterpret_cast<const __m128i *>(src + size - 16)));/// Then we will copy every 16 bytes from the beginning in a loop./// The last loop iteration will possibly overwrite some part of already copied last 16 bytes./// This is Ok, similar to the code for small sizes above.while (size > 16){_mm_storeu_si128(reinterpret_cast<__m128i *>(dst), _mm_loadu_si128(reinterpret_cast<const __m128i *>(src)));dst += 16;src += 16;size -= 16;}}else{/// Large size with fully unrolled loop./// Align destination to 16 bytes boundary.size_t padding = (16 - (reinterpret_cast<size_t>(dst) & 15)) & 15;/// If not aligned - we will copy first 16 bytes with unaligned stores.if (padding > 0){__m128i head = _mm_loadu_si128(reinterpret_cast<const __m128i*>(src));_mm_storeu_si128(reinterpret_cast<__m128i*>(dst), head);dst += padding;src += padding;size -= padding;}/// Aligned unrolled copy. We will use half of available SSE registers./// It's not possible to have both src and dst aligned./// So, we will use aligned stores and unaligned loads.__m128i c0, c1, c2, c3, c4, c5, c6, c7;while (size >= 128){c0 = _mm_loadu_si128(reinterpret_cast<const __m128i*>(src) + 0);c1 = _mm_loadu_si128(reinterpret_cast<const __m128i*>(src) + 1);c2 = _mm_loadu_si128(reinterpret_cast<const __m128i*>(src) + 2);c3 = _mm_loadu_si128(reinterpret_cast<const __m128i*>(src) + 3);c4 = _mm_loadu_si128(reinterpret_cast<const __m128i*>(src) + 4);c5 = _mm_loadu_si128(reinterpret_cast<const __m128i*>(src) + 5);c6 = _mm_loadu_si128(reinterpret_cast<const __m128i*>(src) + 6);c7 = _mm_loadu_si128(reinterpret_cast<const __m128i*>(src) + 7);src += 128;_mm_store_si128((reinterpret_cast<__m128i*>(dst) + 0), c0);_mm_store_si128((reinterpret_cast<__m128i*>(dst) + 1), c1);_mm_store_si128((reinterpret_cast<__m128i*>(dst) + 2), c2);_mm_store_si128((reinterpret_cast<__m128i*>(dst) + 3), c3);_mm_store_si128((reinterpret_cast<__m128i*>(dst) + 4), c4);_mm_store_si128((reinterpret_cast<__m128i*>(dst) + 5), c5);_mm_store_si128((reinterpret_cast<__m128i*>(dst) + 6), c6);_mm_store_si128((reinterpret_cast<__m128i*>(dst) + 7), c7);dst += 128;size -= 128;}/// The latest remaining 0..127 bytes will be processed as usual.goto tail;}}return ret;
}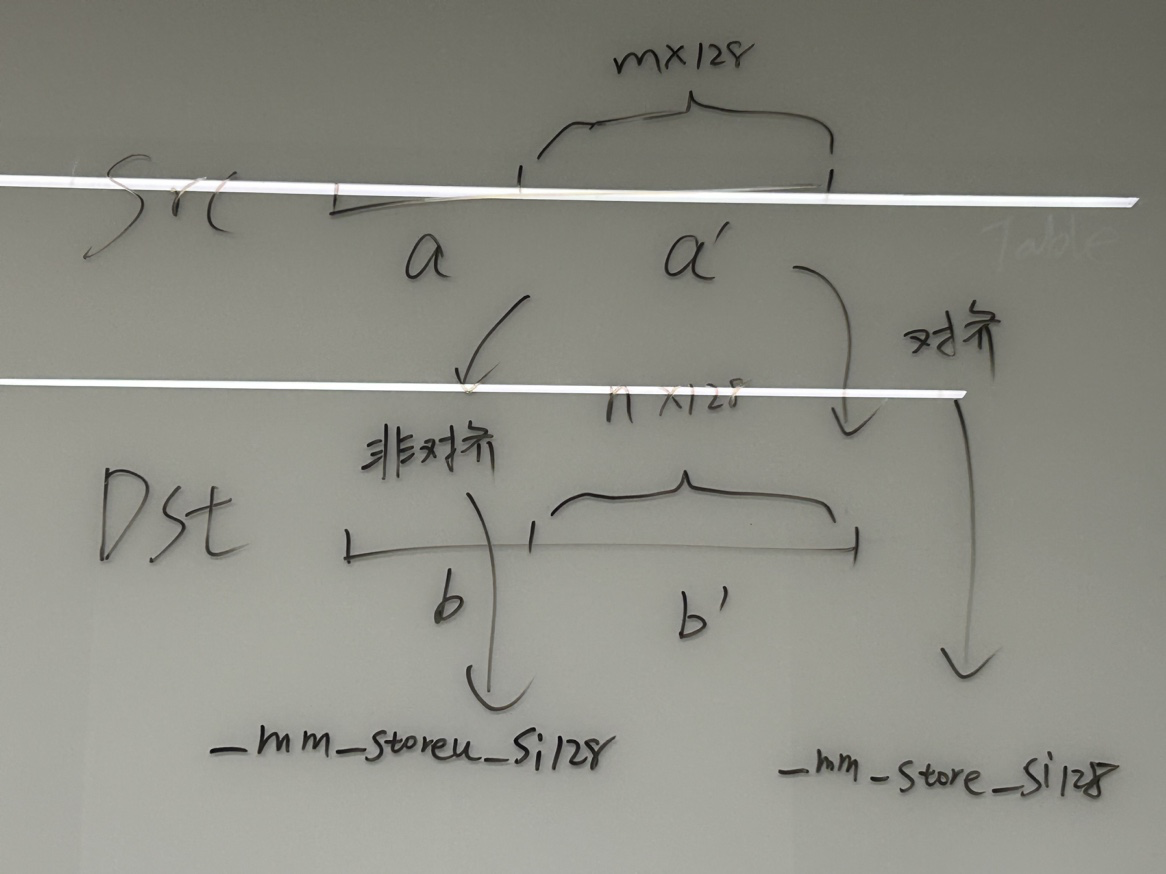
这里使用了一半的SSE寄存器(8个)来做,可能是考虑到32位平台上只有8个,而64位平台则可以进行展开。
有些实现还会用预取指令,比如韦大佬写的FastMemcpy,clickhouse里面也有完整代码作为benchmark https://github.com/skywind3000/FastMemcpy/blob/master/FastMemcpy.h

MergeTreeRangeReader
mergetree是clickhouse的列式存储结构,跟ORC很像,不过索引是分开存的(而且没有bloomfilter)。具体可以看https://bohutang.me/2020/06/26/clickhouse-and-friends-merge-tree-disk-layout/
这段代码是 ClickHouse 项目中的一段,它定义了一个名为 optimize 的方法,该方法在读取 ClickHouse 表的数据时优化读取的顺序和方式。具体来说,它在读取 ClickHouse 的 MergeTree 表时,对表中的数据进行预过滤,以减少读取的数据量,从而提高查询性能。https://github.com/ClickHouse/ClickHouse/blob/4279dd2bf11841d8f68bdea78f3d8668a2c4289b/src/Storages/MergeTree/MergeTreeRangeReader.cpp#L495
首先,它将 current_filter 和已有的 final_filter (如果存在)进行组合,创建一个新的过滤条件 filter,这个过滤条件将被应用在每个数据块的开头。
filter是一个PODArray
using Filter = PaddedPODArray<UInt8>;
使用向量化的代码在https://github.com/ClickHouse/ClickHouse/blob/4279dd2bf11841d8f68bdea78f3d8668a2c4289b/src/Storages/MergeTree/MergeTreeRangeReader.cpp#L730
这段代码的作用就是计算两个地址之间0位的大小。
使用godbolt分析下:
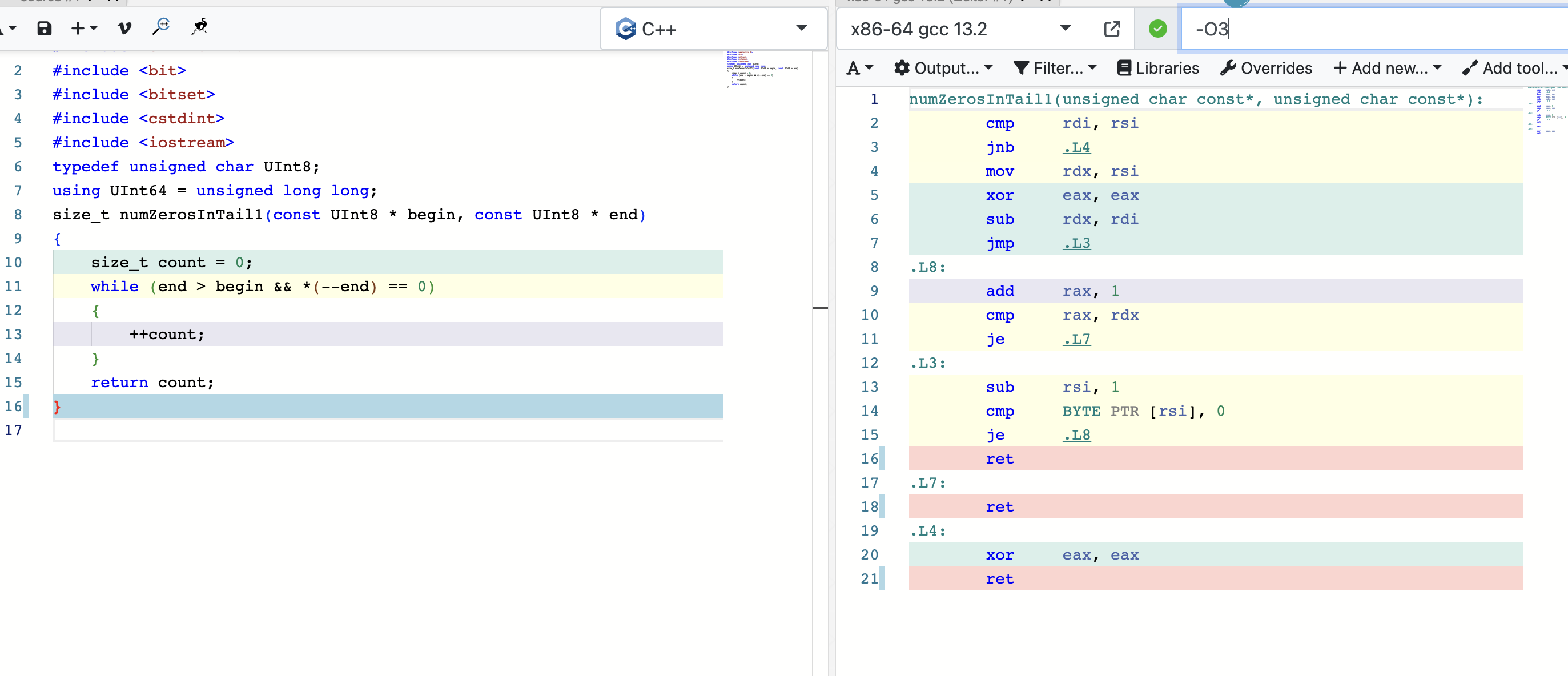
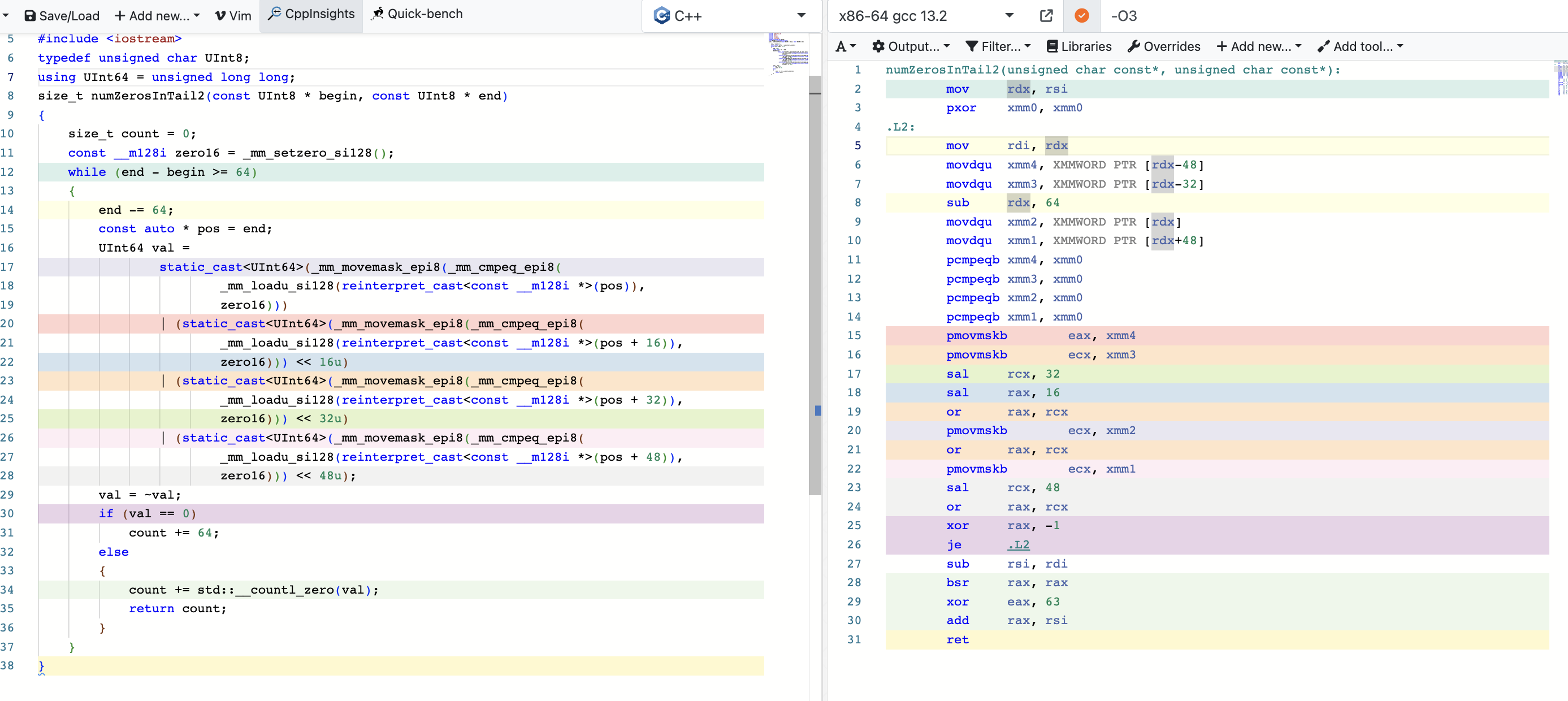
这里很明显,因为是逐位次比较,编译器不知道中间位数的多少,如果引入表跳转会导致缓存行失效的问题,所以编译器只使用普通寄存器进行。
但是在clickhouse场景下,这两个地址之间往往差距很大,所以这里加了分支。
处理流程如下所示,每次处理128*4位
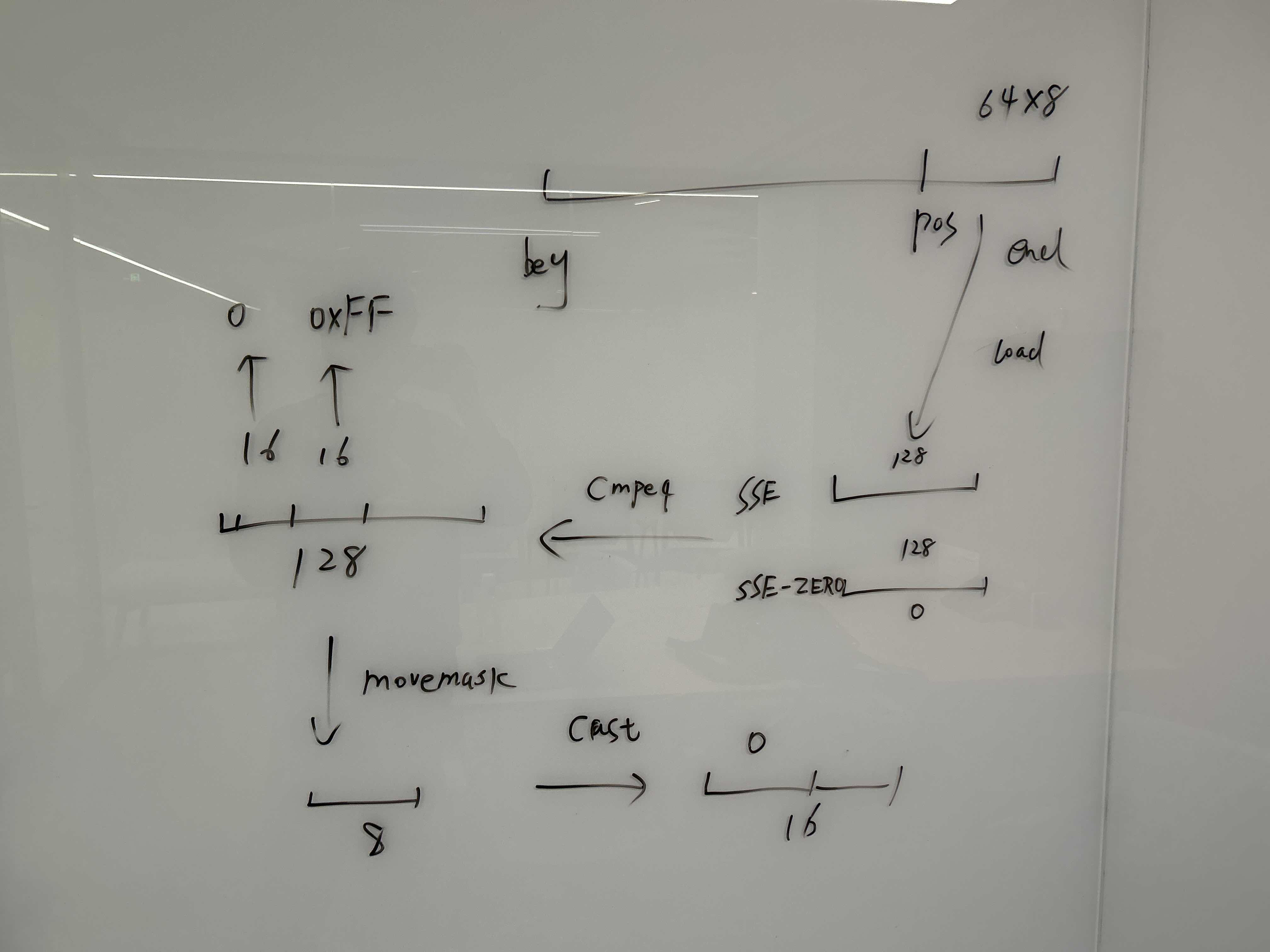
bytes64MaskToBits64Mask
https://github.com/ClickHouse/ClickHouse/blob/fc67d2c0e984098e492c1111c8b5e3c705a80e86/src/Columns/ColumnsCommon.h#L27C1-L27C1
这段代码就很简单,取64*64位的掩码到64位中。
/// Transform 64-byte mask to 64-bit mask
inline UInt64 bytes64MaskToBits64Mask(const UInt8 * bytes64)
{
#if defined(__AVX512F__) && defined(__AVX512BW__)const __m512i vbytes = _mm512_loadu_si512(reinterpret_cast<const void *>(bytes64));UInt64 res = _mm512_testn_epi8_mask(vbytes, vbytes);
#elif defined(__AVX__) && defined(__AVX2__)const __m256i zero32 = _mm256_setzero_si256();UInt64 res =(static_cast<UInt64>(_mm256_movemask_epi8(_mm256_cmpeq_epi8(_mm256_loadu_si256(reinterpret_cast<const __m256i *>(bytes64)), zero32))) & 0xffffffff)| (static_cast<UInt64>(_mm256_movemask_epi8(_mm256_cmpeq_epi8(_mm256_loadu_si256(reinterpret_cast<const __m256i *>(bytes64+32)), zero32))) << 32);
#elif defined(__SSE2__)const __m128i zero16 = _mm_setzero_si128();UInt64 res =(static_cast<UInt64>(_mm_movemask_epi8(_mm_cmpeq_epi8(_mm_loadu_si128(reinterpret_cast<const __m128i *>(bytes64)), zero16))) & 0xffff)| ((static_cast<UInt64>(_mm_movemask_epi8(_mm_cmpeq_epi8(_mm_loadu_si128(reinterpret_cast<const __m128i *>(bytes64 + 16)), zero16))) << 16) & 0xffff0000)| ((static_cast<UInt64>(_mm_movemask_epi8(_mm_cmpeq_epi8(_mm_loadu_si128(reinterpret_cast<const __m128i *>(bytes64 + 32)), zero16))) << 32) & 0xffff00000000)| ((static_cast<UInt64>(_mm_movemask_epi8(_mm_cmpeq_epi8(_mm_loadu_si128(reinterpret_cast<const __m128i *>(bytes64 + 48)), zero16))) << 48) & 0xffff000000000000);
#elif defined(__aarch64__) && defined(__ARM_NEON)const uint8x16_t bitmask = {0x01, 0x02, 0x4, 0x8, 0x10, 0x20, 0x40, 0x80, 0x01, 0x02, 0x4, 0x8, 0x10, 0x20, 0x40, 0x80};const auto * src = reinterpret_cast<const unsigned char *>(bytes64);const uint8x16_t p0 = vceqzq_u8(vld1q_u8(src));const uint8x16_t p1 = vceqzq_u8(vld1q_u8(src + 16));const uint8x16_t p2 = vceqzq_u8(vld1q_u8(src + 32));const uint8x16_t p3 = vceqzq_u8(vld1q_u8(src + 48));uint8x16_t t0 = vandq_u8(p0, bitmask);uint8x16_t t1 = vandq_u8(p1, bitmask);uint8x16_t t2 = vandq_u8(p2, bitmask);uint8x16_t t3 = vandq_u8(p3, bitmask);uint8x16_t sum0 = vpaddq_u8(t0, t1);uint8x16_t sum1 = vpaddq_u8(t2, t3);sum0 = vpaddq_u8(sum0, sum1);sum0 = vpaddq_u8(sum0, sum0);UInt64 res = vgetq_lane_u64(vreinterpretq_u64_u8(sum0), 0);
#elseUInt64 res = 0;for (size_t i = 0; i < 64; ++i)res |= static_cast<UInt64>(0 == bytes64[i]) << i;
#endifreturn ~res;
}
从这个里面我们可以看出来,编译器对SIMD的支持确实弱了点,也难怪clickhouse向量化有这么大优势。
这里无论我用STL容器还是指针,加什么编译选项,都无法优化为SIMD指令。
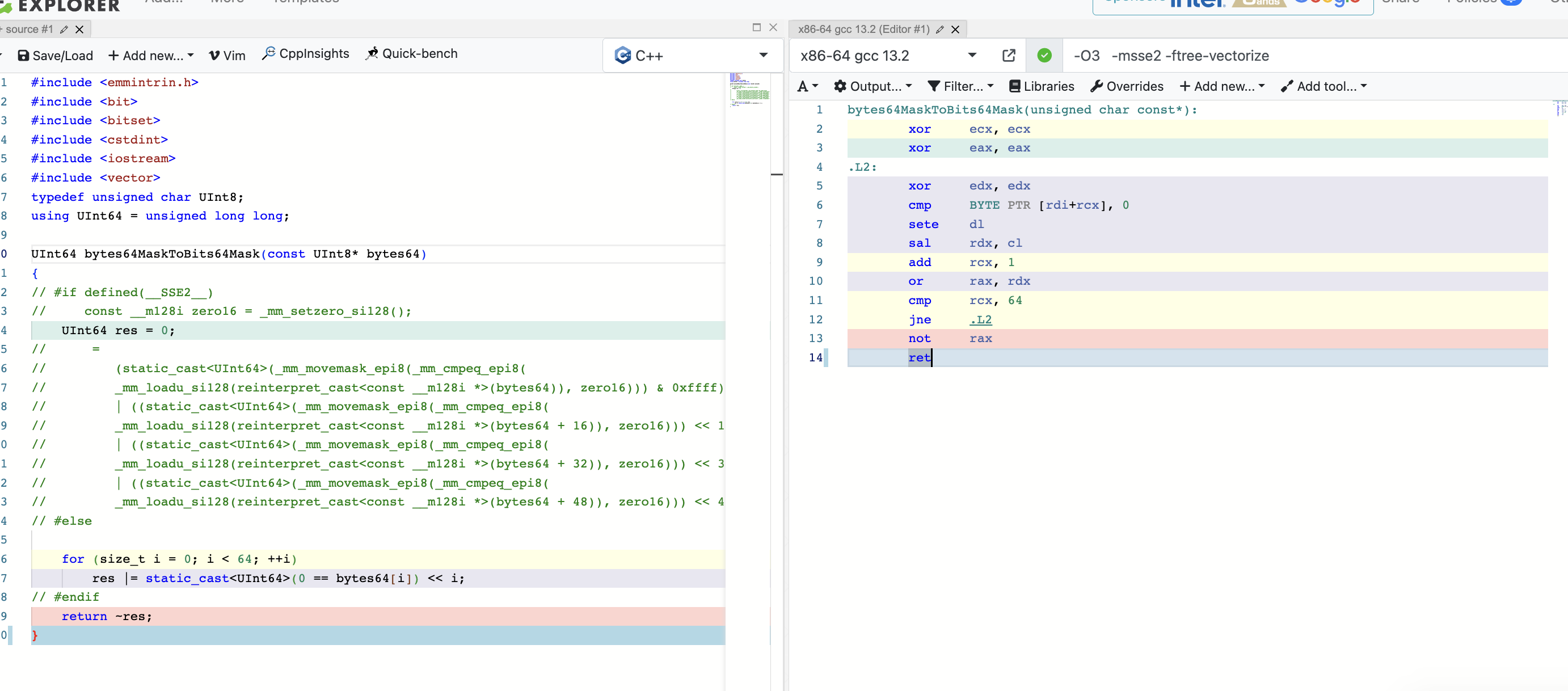
Hash64Long
这段代码在
https://github.com/ClickHouse/ClickHouse/blob/7f675ddf80b60445c769797b73353f32a6ff6ce5/contrib/libfarmhash/farmhash.cc#L796
这段代码实现了farmhashxo::Hash64算法,用于给定输入字符串生成64位哈希值的哈希函数。
相关文章:

olap/clickhouse-编译器优化与向量化
本文主要结合15721和clickhouse源码来聊聊向量化,正好我最近也在用Eigen做算子加速,了解下还是有好处的。 提示编译器 提示编译器而不是复杂化简单的代码 什么时候使用汇编,什么时候使用SIMD?下面有几个基本原则: …...
RK3399平台开发系列讲解(内核入门篇)网络协议的分层
🚀返回专栏总目录 文章目录 一、应用层二、传输层三、网络层四、数据链路层(Data Link Layer)五、物理层沉淀、分享、成长,让自己和他人都能有所收获!😄 📢对于多数的应用和用户而言,使用互联网的一个基本要求就是数据可以无损地到达。用户通过应用进行网络通信...
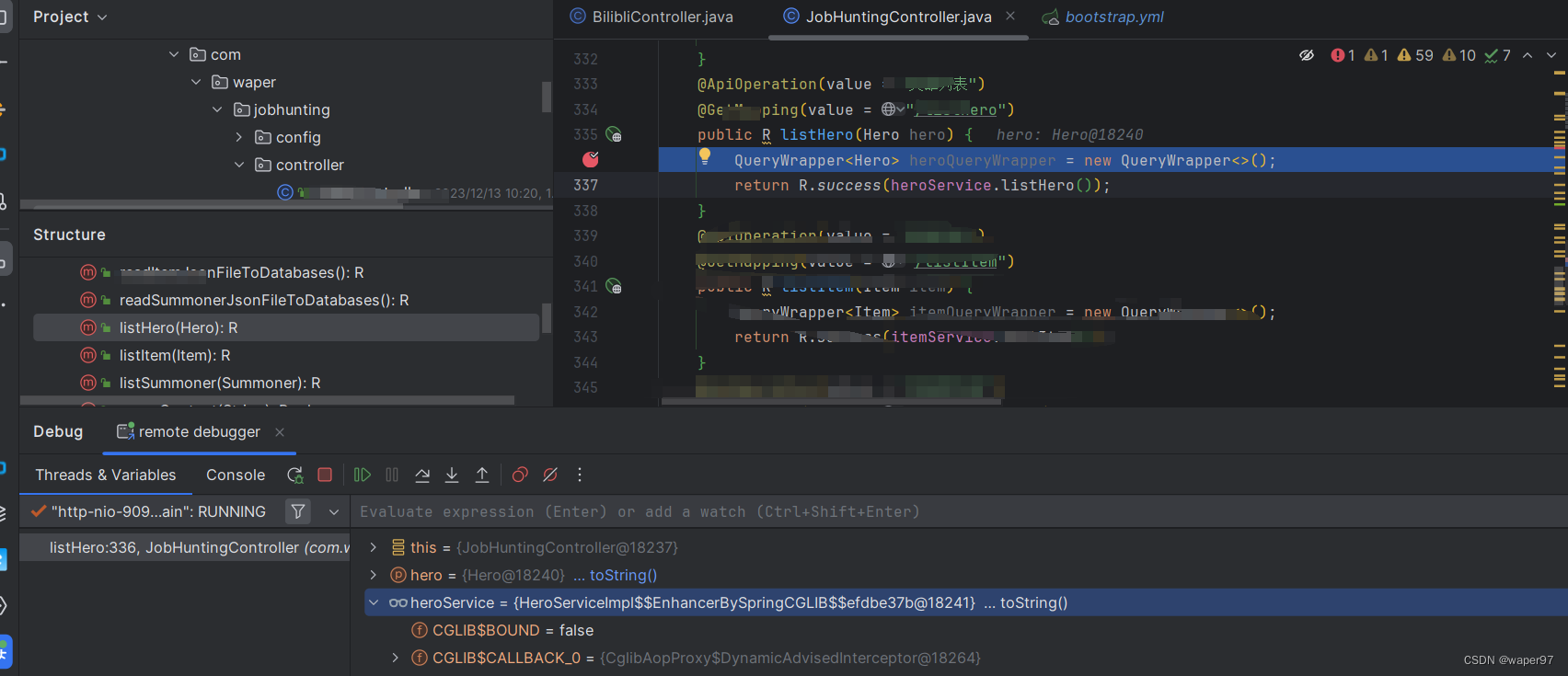
Idea远程debugger调试
当我们服务部署在服务器上,我们想要像在本地一样debug,就可以使用idea自带的Remote JVM Debug 创建Remote JVM Debug服务器启动jar打断点进入断点 当我们服务部署在服务器上,我们想要像在本地一样debug,就可以使用idea自带的 Remote JVM Debug) 创建Rem…...
MATLAB - Gazebo 仿真环境
系列文章目录 前言 机器人系统工具箱(Robotics System Toolbox™)为使用 Gazebo 模拟器可视化的模拟环境提供了一个界面。通过 Gazebo,您可以在真实模拟的物理场景中使用机器人进行测试和实验,并获得高质量的图形。 Gazebo 可在…...
selenium自动化webdriver下载及安装
1、确认浏览器的版本 在浏览器的地址栏,输入chrome://version/,回车后即可查看到对应版本 2、找到对应的chromedriver版本 2.1 114及之前的版本可以通过点击下载chromedriver,根据版本号(只看大版本)下载对应文件 2.2 116版本通过…...
网络基础介绍
1.网线制作 1.1 网线制作需要的工具 网线 网线钳 水晶头 测试仪 编辑 1.2 网线的标准 1.3 网线的做法 2.集线器&交换机&路由器的介绍 3.OSI七层模型 4.路由器的设置 4.1 常见的路由器设置地址 4.2 常见的路由器账号密码 4.3 登录路由器 设置访客网…...

Java中四种引用类型(强、软、弱、虚)
目录 引言 强引用(Strong References) 软引用(Soft References) 弱引用(Weak References) 虚引用(Phantom References) 引用类型的应用场景 总结 引言 Java中的引用类型是管理…...
【MyBatis学习笔记】MyBatis基础学习
MyBatis基础 MyBatis简介MyBatis特性MyBatis下载和其他持久化层技术对比 核心配置文件详解默认的类型别名 搭建MyBatis开发环境创建maven工程创建MyBatis的核心配置文件创建mapper接口创建MyBatis的映射文件通过junit测试功能加入log4j日志功能 MyBatis获取参数值的两种方式&am…...
还在为论文焦虑?免费AI写作大师帮你搞定
先来看1分钟的视频,对于要写论文的你来说,绝对有所值! 还在为写论文焦虑?免费AI写作大师来帮你三步搞定 第一步:输入关键信息 第二步:生成大纲 稍等片刻后,专业大纲生成(由于举例&am…...
)
3.10【窗口】窗口使用示例(窗口缩放 三)
五,从窗口所有者放大 要从窗口的所有者本身进行放大,可以将源图像矩形设置得比窗口小。可以想象我们在一张图片中选取一部分进行放大的操作。 屏幕使用默认位置 (0,0) 作为源矩形、窗口和显示器显示的左上角。要放大源图形的特定区域,必须设置源矩形的大小。 源矩形由这些…...
【机器学习】密度聚类:从底层手写实现DBSCAN
【机器学习】Building-DBSCAN-from-Scratch 概念代码数据导入实现DBSCAN使用样例及其可视化 补充资料 概念 DBSCAN(Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise,具有噪声的基于密度的聚类方法)是一种基于密度的空间聚类算…...
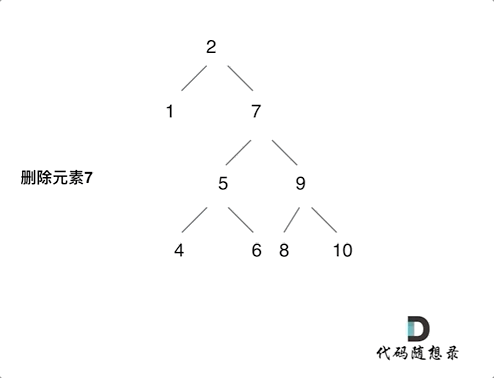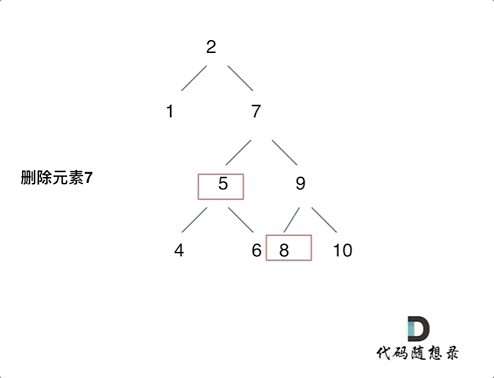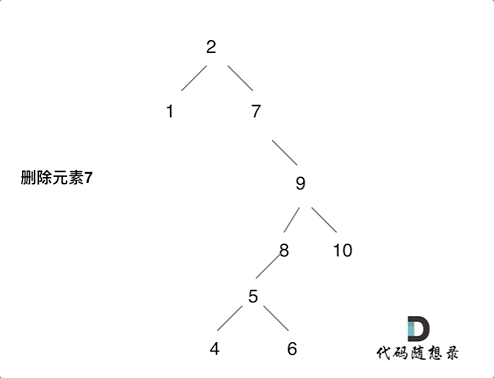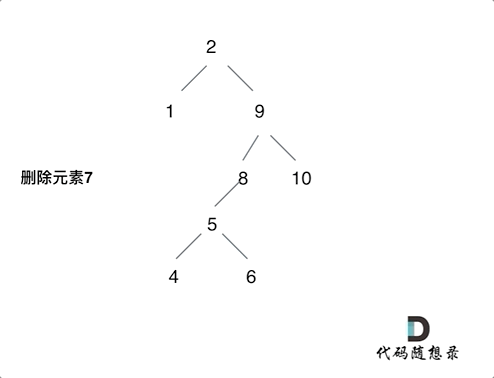
2023-12-20 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先和二叉搜索树中的插入操作和删除二叉搜索树中的节点
235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先 思想:和二叉树的公共最近祖先节点的思路基本一致的!就是不用从下往上遍历处理!可以利用的二叉搜索树的特点从上往下处理了!而且最近公共节点肯定是第一个出现在【q,p】这个区间的内的&…...
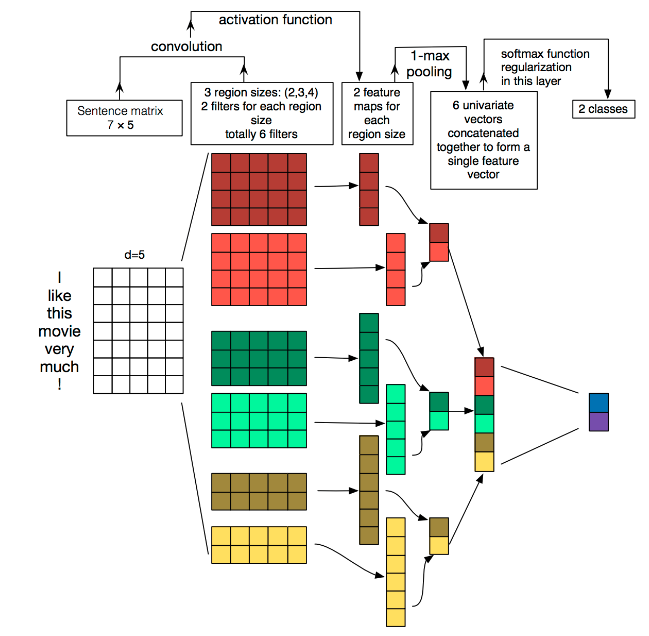
pytorch文本分类(三)模型框架(DNNtextCNN)
pytorch文本分类(三)模型框架(DNN&textCNN) 原任务链接 目录 pytorch文本分类(三)模型框架(DNN&textCNN)1. 背景知识深度学习 2. DNN2.1 从感知器到神经网络2.2 DNN的基本…...
<长篇文章!!>数据结构与算法的重要知识点与概要总结 ( •̀ ω •́ )✧✧临近考试和查漏补缺的小伙伴看这一篇就都懂啦~
目录 一、数据结构概论二、算法概论三、线性表四、栈五、队列六、串七、多维数组与矩阵八、广义表九、树与二叉树十、图 一、数据结构概论 1、数据元素和数据项 数据由数据元素组成,即数据元素是数据的基本单位,而数据元素又由若干个数据项组成…...

【安全】audispd调研
audispd调研 1 问题背景 在Linux中,当某个进程调用audit_set_pid将自己的pid保存到内核的audit模块后,如果有日志生成,kaudit内核线程就会通过netlink通信机制将审计日志发送给audit_pid,因此,只能有一个进程占用aud…...
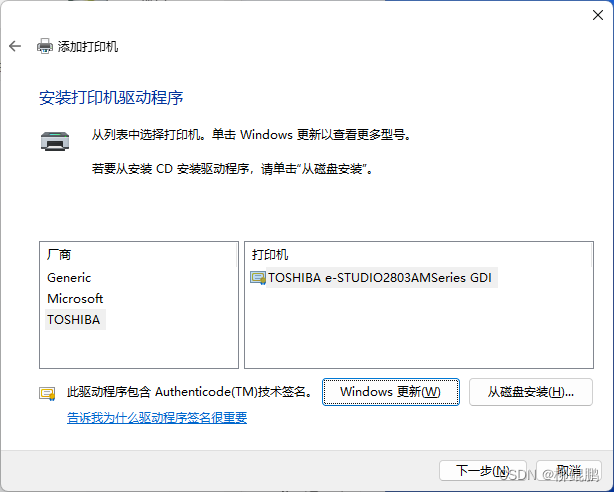
WINDOWS(WIN11)通过IP添加网络打印机
点击添加设备 点击手动添加 使用IP地址或主机名添加打印机 选择TCP/IP设备,输入打印机地址 如果有正确驱动就安装,没有就取消。 通过手动设置添加本地打印机或网络打印机 使用现有的端口 根据打印机IP,选择标准端口。 成功! 到…...

华为数通试题
选择题 华为数通推出的面向企业的云计算平台是? A) FusionSphere B) CloudEngine C) Agile Controller D) eSight 下面哪个不是华为数通的核心交换机系列? A) S12700 B) S5700 C) S9300 D) CloudEngine 华为数通的企业级路由器系列包括哪个?…...
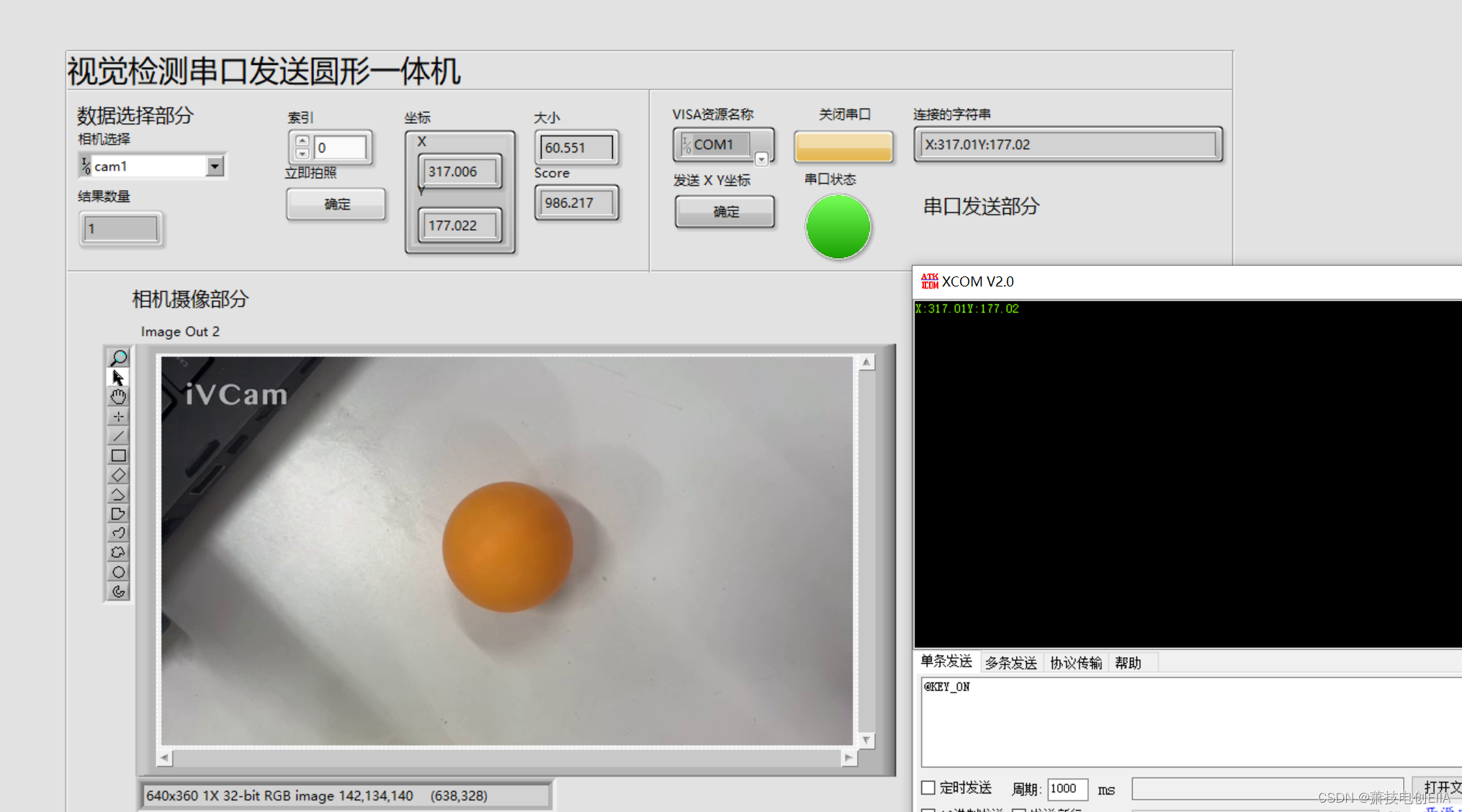
Labview Vision 机器视觉使用,从下载程序安装应用,到实战找硬币并输出值
1.前言 大家好,今天我要和机器人一起配合来打算 做机器视觉 用Labview 和 Vision 联动实现机器的视觉 2.下载软件-软件的安装 我们除了基础款的labview软件 还要安装视觉四件套 1.Labview 编程平台(我是 2023 q3) 2. NI - IMAQdx (驱动软…...

【delphi11】delphi基础探索【三、基础组件和事件】
目录 基础组件 1. TButton(按钮) 2. TLabel(标签) 3. TEdit(编辑框) 4. TMemo(多行编辑框) 5. TComboBox(组合框) 6. TCheckBox(复选框&…...

react hooks浅谈
一.useEffect useEffect是hooks中的生命周期函数 1.只要页面更新就触发回调: useEffect(() > { // 执行逻辑 }) 2.只运行一次(组件挂载和卸载时执行),第二个参数传空数组[]: useEffect(() > { // },[]) 3. 条件…...

09期:电池端高压和母线端高压
在新能源汽车(包括长安启源系列)的高压系统中,电池端高压和母线端高压是两个关键但不同的电压测量点。它们的区别主要体现在物理位置、数值状态以及控制逻辑上。简单来说:电池端高压 电池包“源头”的电压(始终有电&a…...

Cosmos-Reason1-7B环境配置:CUDA版本兼容性检查与日志排查方法
Cosmos-Reason1-7B环境配置:CUDA版本兼容性检查与日志排查方法 1. 引言 最近在部署NVIDIA开源的Cosmos-Reason1-7B模型时,我遇到了一个挺典型的问题:模型加载失败,WebUI界面一直卡在“加载中”的状态。这其实是一个多模态视觉语…...

CLIP-GmP-ViT-L-14图文匹配测试工具部署避坑指南:C盘空间与Docker环境管理
CLIP-GmP-ViT-L-14图文匹配测试工具部署避坑指南:C盘空间与Docker环境管理 你是不是也遇到过这种情况:兴致勃勃地准备部署一个AI工具,比如这个CLIP-GmP-ViT-L-14图文匹配模型,结果第一步就被卡住了——C盘红了,空间告…...

Windows 开发者的 WSL 生存指南:用 Systemd 实现服务自启的 3 种实战方案
Windows 开发者的 WSL 生存指南:用 Systemd 实现服务自启的 3 种实战方案 对于习惯在 Windows 环境下开发的工程师来说,WSL(Windows Subsystem for Linux)已经成为不可或缺的工具。它完美融合了 Windows 的易用性和 Linux 的强大功…...

小程序内嵌H5页面的如何交互?
目录一、微信小程序介绍二、什么是内嵌H5页面三、小程序内嵌H5页面的如何交互四、微信小程序的应用场景一、微信小程序介绍 微信小程序是一种基于微信平台的轻量级应用,它无需下载安装,用户只需通过微信扫一扫或搜索即可快速打开使用。与传统的APP相比&…...

Qwen3-ForcedAligner-0.6B在嵌入式开发板上的部署:STM32F103C8T6实战
Qwen3-ForcedAligner-0.6B在嵌入式开发板上的部署:STM32F103C8T6实战 1. 引言 想象一下,你正在开发一款智能语音设备,需要实时生成精确到词级的字幕。传统方案要么依赖云端服务带来延迟,要么需要昂贵的专用芯片增加成本。现在&a…...

Cyanine 5 TSA,Cy5 酪胺,1431148-26-3:该试剂可实现荧光标记物的局部沉积和信号放大。
基础试剂介绍英文名称:Cyanine 5 TSA,Sulfo-Cyanine5 tyramide中文名称:水溶Cy5 tyramide,Cy5 酪胺CAS 号:1431148-26-3分子式:C41H49N3O8S2分子量:775.97纯度:>95%外观性状&…...

Flutter 三方库 regexed_validator 的鸿蒙适配指南 - 实现结构化正则表达式校验、在 OpenHarmony 上打造极致严谨的表单输入实战
欢迎加入开源鸿蒙跨平台社区:https://openharmonycrossplatform.csdn.net Flutter 三方库 regexed_validator 的鸿蒙适配指南 - 实现结构化正则表达式校验、在 OpenHarmony 上打造极致严谨的表单输入实战 前言 在鸿蒙(OpenHarmony)应用开发…...
强缓存、协商缓存和启发式缓存)
WHAT - 浏览器缓存机制系列(二)强缓存、协商缓存和启发式缓存
目录 一、介绍 二、强缓存 三、协商缓存 三、html & js 缓存策略 四、启发式缓存 启发式缓存什么时候发生 浏览器的推算规则 如果没有 Last-Modified DevTools 里怎么看出是启发式缓存 启发式缓存的风险 1. 浏览器行为不一致 2. 更新不可控 3. CDN 行为不同 总结 今天主要介…...

深入解析STM32的电源管理、复位机制与时钟配置实战
1. 电源供电:不只是接上VCC和GND那么简单 很多刚接触STM32的朋友,包括当年的我自己,拿到开发板或者画完第一版原理图,最容易犯的一个错误就是:把电源部分想得太简单了。不就是接个3.3V和地吗?结果板子焊好&…...
