STL - 常用算法
概述:
- 算法主要是由头文件
<algorithm><functional><numeric>组成 <algorithm>是所有STL头文件中最大的一个,范围涉及比较、 交换、查找、遍历操作、复制、修改等等<numeric>体积很小,只包括几个在序列上面进行简单数学运算的模板函数<functional>定义了一些模板类,用以声明函数对象。
5.1. 常用遍历算法
学习目标:
- 掌握常用的遍历算法
算法简介:
for_each//遍历容器transform//搬运容器到另一个容器中
5.1.1. for_each
功能描述:
- 实现遍历容器
- 在实际开发中最常用的遍历算法,必须熟练掌握
函数原型:
for_each(iterator beg, iterator end, _func);
// 遍历算法 遍历容器元素
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// _func 函数或者函数对象
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>// 普通函数
void Print01(int val)
{cout << val << ' ';
}// 仿函数
class Print02
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << ' ';}
};void Test01()
{vector<int> v;for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), Print01);cout << endl;for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), Print02());cout << endl;
}int main()
{Test01();return 0;
}输出:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 95.1.2. transform
功能描述:
- 搬运容器到另一个容器中
函数原型:
transform(iterator begl, iterator endl, iterator beg2, _func);
//beg1 源容器开始迭代器
//end1 源容器结束迭代器
//beg2 目标容器开始迭代器
//_func 函数或者函数对象
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>// 仿函数
class Transform
{
public:int operator()(int val){return val + 100;}
};class MyPrint
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << ' ';}
};void Test01()
{vector<int> v;for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}vector<int> vTarget;vTarget.resize(v.size()); // 目标容器需要提前开辟空间transform(v.begin(), v.end(), vTarget.begin(), Transform());for_each(vTarget.begin(), vTarget.end(), MyPrint());cout << endl;
}int main()
{Test01();return 0;
}输出:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 1095.2. 常用查找算法
学习目标:
- 掌握常用的查找算法
算法简介:
find//查找元素find_if//按条件查找元素adjacent_find//查找相邻重复元素binary_search//二分查找法count//统计元素个数count_if//按条件统计元素个数
5.2.1. find
功能描述:
- 查找指定元素,找到返回指定元素的迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器end()
- 利用find可以在容器中找到指定的元素,返回值是迭代器
函数原型:
find(iterator beg, iterator end, value);
// 按值查找元素,找到返回指定位置迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器位置
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// value 查找的元素
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>// 查找内置数据类型
void Test01()
{vector<int> v;for(int i = -5; i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}vector<int>::iterator it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 5);if (it == v.end()){cout << "not find!" << endl;}else{cout << "find-" << *it << endl;}}// 查找自定义数据类型
class Person
{
public:Person(string name, int age) : m_name(name), m_age(age){}// 重载 == ,让底层的find知道如何对比person数据类型bool operator==(const Person & p){if(this->m_name == p.m_name && this->m_age == p.m_age){return true;}else{return false;}}string m_name;int m_age;
};void Test02()
{vector<Person> v;Person p1("aaa", 10);Person p2("bbb", 20);Person p3("ccc", 30);Person p4("ddd", 40);v.push_back(p1);v.push_back(p2);v.push_back(p3);v.push_back(p4);vector<Person>::iterator it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), p2);if (it == v.end()){cout << "not find!" << endl;}else{cout << "find-name:" << it->m_name << " find-age:" << it->m_age << endl;}
}int main()
{Test01();Test02();return 0;
}输出:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
find-5
find-name:bbb find-age:205.2.2. find_if
功能描述:
- 按条件查找元素
函数原型:
find _if(iterator beg, iterator end, _pred);
// 按值查找元素,找到返回指定位置迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器位置
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// _Pred 函数或者谓词(返回bool类型的仿函数)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>class GreaterFive
{
public:bool operator()(int val){return val > 5;}
};class Person
{
public:Person(string name, int age) : m_name(name), m_age(age){}string m_name;int m_age;
};// 查找内置数据类型
void Test01()
{vector<int> v;for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}vector<int>::iterator it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), GreaterFive());if(it == v.end()){cout << "没有找到" << endl;}else{cout << "找到了大于5的数字为:" << *it << endl;}
}class Greater20
{
public:bool operator()(Person &p){return p.m_age > 20;}
};void Test02()
{vector<Person> v;Person p1("孙悟空", 100);Person p2("猪八戒", 80);Person p3("沙僧", 30);Person p4("唐僧", 10);v.push_back(p1);v.push_back(p2);v.push_back(p3);v.push_back(p4);vector<Person>::iterator it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Greater20());if(it == v.end()){cout << "没有找到" << endl;}else{cout << "找到了大于20岁的人:" << it->m_name << " " << it->m_age << endl;}}int main()
{Test01();Test02();return 0;
}输出:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
找到了大于5的数字为:6
找到了大于20岁的人:孙悟空 1005.2.3. adjacent_find
功能描述:
- 查找相邻重复元素
函数原型:
adjacent find(iterator beg, iterator end);
// 查找相邻重复元素,返回相邻元素的第一个位置的迭代器
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>// 查找内置数据类型
void Test01()
{vector<int> v;v.push_back(0);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(4);v.push_back(6);v.push_back(6);v.push_back(8);v.push_back(10);v.push_back(10);vector<int>::iterator it = adjacent_find(v.begin(), v.end());if(it == v.end()){cout << "没有找到" << endl;}else{cout << "找到的第一个相邻重复元素为:" << *it << endl;}
}int main()
{Test01();return 0;
}输出:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
找到的相邻重复元素为:65.2.4. binary_search
功能描述:
- 查找指定元素是否存在
- 二分查找,指数级运算,速度非常快
- 二分查找法查找效率很高,值得注意的是查找的容器中的元素必须是有序序列,否则结果不一定对
函数原型:
bool binary search(iterator beg, iterator end, value);
// 查找指定的元素,查到 返回true 否则false
// 注意:在无序序列中不可用
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// value 查找的元素
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>// 查找内置数据类型
void Test01()
{vector<int> v;v.push_back(0);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(4);v.push_back(6);v.push_back(6);v.push_back(8);v.push_back(10);v.push_back(10);bool ret = binary_search(v.begin(), v.end(), 9);if(!ret){cout << "没有找到" << endl;}else{cout << "成功找到" << endl;}
}int main()
{Test01();return 0;
}输出:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
没有找到5.2.5. count
功能描述:
- 统计元素个数
函数原型:
count(iterator beg, iterator end, value);
// 统计元素出现次数
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// value 统计的元素
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>class Person
{
public:Person(string name, int age) : m_name(name), m_age(age){}bool operator==(const Person & p){if(this->m_age == p.m_age){return true;}else{return false;}}string m_name;int m_age;
};
// 查找内置数据类型
void Test01()
{vector<int> v;v.push_back(0);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(4);v.push_back(6);v.push_back(6);v.push_back(8);v.push_back(10);v.push_back(10);v.push_back(10);int num = count(v.begin(), v.end(), 10);cout << "10的元素个数为:" << num << endl;
}void Test02()
{vector<Person> v;Person p1("刘备", 35);Person p2("关羽", 35);Person p3("张飞", 35);Person p4("赵云", 30);Person p5("曹操", 44);Person p("诸葛亮", 35);v.push_back(p1);v.push_back(p2);v.push_back(p3);v.push_back(p4);v.push_back(p5);int num = count(v.begin(), v.end(), p);cout << "和诸葛亮同岁的人有:" << num << "个" << endl;
}int main()
{Test01();Test02();return 0;
}输出:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
10的元素个数为:3
和诸葛亮同岁的人有:3个5.2.6. count_if
功能描述:
- 按条件统计元素个数
函数原型:
count_if(iterator beg, iterator end, _Pred);
// 按条件统计元素出现次数
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// _Pred 谓词
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>class Person
{
public:Person(string name, int age) : m_name(name), m_age(age){}bool operator==(const Person & p){if(this->m_age == p.m_age){return true;}else{return false;}}string m_name;int m_age;
};class Greater20
{
public:bool operator()(int v1){return v1 > 20;}
};// 查找内置数据类型
void Test01()
{vector<int> v;v.push_back(0);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(4);v.push_back(6);v.push_back(6);v.push_back(8);v.push_back(10);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(50);int num = count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Greater20());cout << "大于20的元素个数为:" << num << endl;
}class GreaterPerson
{
public:bool operator()(const Person & p){return p.m_age > 20;}
};void Test02()
{vector<Person> v;Person p1("刘备", 35);Person p2("关羽", 35);Person p3("张飞", 35);Person p4("赵云", 30);Person p5("曹操", 44);v.push_back(p1);v.push_back(p2);v.push_back(p3);v.push_back(p4);v.push_back(p5);int num = count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), GreaterPerson());cout << "年龄大于20的人数:" << num << endl;
}int main()
{Test01();Test02();return 0;
}输出:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
大于20的元素个数为:2
年龄大于20的人数:55.3. 常用排序算法
学习目标:
- 掌握常用的排序算法
算法简介:
sort// 对容器内元素进行排序random_shuffle// 洗牌,指定范围内的元素随机调整次序merge// 容器元素合并,并存储到另一容器中reverse// 反转指定范围的元素
5.3.1. sort
功能描述:
- 对容器内元素进行排序(默认从小到大)
函数原型:
sort(iterator beg, iterator end, _Pred);
// 按值查找元素,找到返回指定位置迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器位置
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// _Pred 谓词
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>void MyPrint(int val)
{cout << val << " ";
}// 查找内置数据类型
void Test01()
{vector<int> v;v.push_back(1);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(5);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(4);v.push_back(9);v.push_back(7);sort(v.begin(), v.end());for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), MyPrint);cout << endl;sort(v.begin(), v.end(), greater<int>());for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), MyPrint);cout << endl;
}int main()
{Test01();return 0;
}输出:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 2 3 4 5 7 9
9 7 5 4 3 2 15.3.2. random_shuffle
功能描述:
- 洗牌,指定范围内的元素随机调整次序
- 若想每次都不一样,要加随机数种子
函数原型:
random_shuffle(iterator_beg, iterator_end);
// 指定范围内的元素随机调整次序
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<ctime>void MyPrint(int val)
{cout << val << " ";
}void Test01()
{srand((unsigned int) time (NULL));vector<int> v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}random_shuffle(v.begin(), v.end());for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), MyPrint);cout << endl;random_shuffle(v.begin(), v.end());for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), MyPrint);cout << endl;
}int main()
{Test01();return 0;
}输出:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 8 6 4 5 1 7 2 3 9
0 3 1 2 4 6 8 9 7 55.3.3. merge
功能描述:
- 两个容器元素合并,并存储到另一容器中
- 目标容器需要提前开辟空间
- 合并后的序列还是一个有序序列
函数原型:
merge(iterator begl, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest);
// 容器元素合并,并存储到另一容器中
// 注意: 两个容器必须是有序的
// beg1 容器1开始迭代器
// end1 容器1结束迭代器
// beg2 容器2开始迭代器
// end2 容器2结束迭代器
// dest 目标容器开始迭代器
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>void MyPrint(int val)
{cout << val << " ";
}// 查找内置数据类型
void Test01()
{vector<int> v1;vector<int> v2;for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v1.push_back(i);v2.push_back(i+1);}vector<int> v3;v3.resize(v1.size() + v2.size());merge(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), v3.begin());for_each(v3.begin(), v3.end(), MyPrint);cout << endl;
}int main()
{Test01();return 0;
}输出:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 7 8 8 9 9 105.3.4. reverse
功能描述:
- 将容器内元素进行反转
函数原型:
reverse(iterator beg,iterator end);
// 反转指定范围的元素
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>void MyPrint(int val)
{cout << val << " ";
}// 查找内置数据类型
void Test01()
{vector<int> v;for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}reverse(v.begin(), v.end());for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), MyPrint);cout << endl;
}int main()
{Test01();return 0;
}输出:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 5.4. 常用拷贝和替换算法
学习目标:
- 掌握常用的拷贝和替换算法
算法简介:
copy// 容器内指定范围的元素拷贝到另一容器中replace// 将容器内指定范围的旧元素修改为新元素replace_if// 容器内指定范围满足条件的元素替换为新元素swap// 互换两个容器的元素
5.4.1. copy
功能描述:
- 容器内指定范围的元素拷贝到另一容器中
- 目标容器要提前开辟空间
函数原型:
copy(iterator beg,iterator end,iterator dest);
// 按值查找元素,找到返回指定位置迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器位置
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// dest 目标起始迭代器
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>void MyPrint(int val)
{cout << val << " ";
}// 查找内置数据类型
void Test01()
{vector<int> v;for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}vector<int> v2;v2.resize(v.size());copy(v.begin(), v.end(), v2.begin());for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), MyPrint);cout << endl;
}int main()
{Test01();return 0;
}输出:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 5.4.2. replace
功能描述:
- 将容器内指定范围所有的旧元素修改为新元素
函数原型:
replace(iterator beg,iterator end, oldvalue, newvalue);
// 将区间内旧元素 替换成 新元素
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// oldvalue 旧元素
// newvalue 新元素
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>class MyPrint
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};// 查找内置数据类型
void Test01()
{vector<int> v;for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}replace(v.begin(), v.end(), 3, 100);for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), MyPrint());cout << endl;
}int main()
{Test01();return 0;
}输出:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 1 2 100 4 5 6 7 8 95.4.3. replace_if
功能描述:
- 将区间内满足条件的元素,替换成指定元素
函数原型:
replace if(iterator beg, iterator end, _pred, newvalue);
// 按条件替换元素,满足条件的替换成指定元素
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// _pred 谓词
// newvalue 替换的新元素
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>class Greater5
{
public:bool operator()(int val){return val > 5;}
};class MyPrint
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};// 查找内置数据类型
void Test01()
{vector<int> v;for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}replace_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Greater5(), 100);for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), MyPrint());cout << endl;
}int main()
{Test01();return 0;
}输出:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 1 2 3 4 5 100 100 100 1005.4.4. swap
功能描述:
- 互换两个容器的元素
函数原型:
swap(container c1,container c2);
// 互换两个容器的元素
// c1容器1
// c2容器2
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>class MyPrint
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};// 查找内置数据类型
void Test01()
{vector<int> v1;vector<int> v2;for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v1.push_back(i);v2.push_back(i+100);}cout << "交换前:" << endl;for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), MyPrint());for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), MyPrint());cout << endl;swap(v1, v2);cout << "交换后:" << endl;for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), MyPrint());for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), MyPrint());cout << endl;
}int main()
{Test01();return 0;
}输出:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
交换前:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109
交换后:
100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 95.5. 常用算术生成算法
学习目标:
- 掌握常用的算术生成算法
注意:
- 算术生成算法属于小型算法,使用时包含的头文件为
#include<numeric>
算法简介:
accumulate// 计算容器元素累计总和fill// 向容器中添加元素
5.5.1. accumulate
功能描述:
- 计算区间内 容器元素累计总和
函数原型:
accumulate(iterator beg,iterator end,value);
// 计算容器元素累计总和
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// value 起始值
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<numeric>// 查找内置数据类型
void Test01()
{vector<int> v;for(int i = 0; i <= 100; i++){v.push_back(i);}int total = accumulate(v.begin(), v.end(), 0);cout << total << endl;
}int main()
{Test01();return 0;
}输出:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
50505.5.2. fill
功能描述:
- 向容器中填充指定的元素
函数原型:
fill(iterator beg,iterator end, value);
// 向容器中填充元素
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// value 填充的值
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<numeric>class MyPrint
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};void Test01()
{vector<int> v;// 初始化容器大小为10,并全部填充为0v.resize(10);for(vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++){cout << *it << ' ';}cout << endl;// 重新填充fill(v.begin(), v.end(), 100);for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), MyPrint());
}int main()
{Test01();return 0;
}输出:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 1005.6. 常用集合算法
学习目标:
- 掌握常用的集合算法
算法简介:
set_intersection// 求两个容器的交集set_union// 求两个容器的并集set_difference// 求两个容器的差集
5.6.1. set_intersection
功能描述:
- 求两个容器的交集
函数原型:
set_intersection(iterator begl, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest);
// 求两个集合的交集
// beg1 容器1开始迭代器
// end1 容器1结束迭代器
// beg2 容器2开始迭代器
// end2 容器2结束迭代器
// dest 目标容器开始迭代器
总结:
- 求交集的两个集合必须是有序序列
- 目标容器开辟的空间为两个容器中
size最小的哪一个 set_intersection的返回值是交集迭代器中最后一个元素的位置
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<numeric>class MyPrint
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};void Test01()
{vector<int> v1;vector<int> v2;for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v1.push_back(i); // 0~9v2.push_back(i + 5); // 5~14}vector<int> vTarget;// 目标容器需要提前开辟空间// 最特殊情况:大容器完全包含小容器,开辟空间时取小容器的size即可vTarget.resize(min(v1.size(), v2.size()));// 获取交集vector<int>::iterator itEnd = set_intersection(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vTarget.begin());for_each(vTarget.begin(), vTarget.end(), MyPrint());cout << endl;for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, MyPrint());
}int main()
{Test01();return 0;
}输出:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
5 6 7 8 9 0 0 0 0 0
5 6 7 8 95.6.2. set_union
功能描述:
- 求两个集合的并集
函数原型:
set_union(iterator begl, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest);
// 求两个集合的并集
// beg1 容器1开始迭代器
// end1 容器1结束迭代器
// beg2 容器2开始迭代器
// end2 容器2结束迭代器
// dest 目标容器开始迭代器
总结:
- 求并集的两个集合必须是有序序列
- 目标容器开辟的空间为两个容器的
size相加 set_intersection的返回值是交集迭代器中最后一个元素的位置
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<numeric>class MyPrint
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};void Test01()
{vector<int> v1;vector<int> v2;for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v1.push_back(i); // 0~9v2.push_back(i + 5); // 5~14}vector<int> vTarget;// 目标容器需要提前开辟空间// 最特殊情况:大容器与小容器完全不重合,开辟空间时取两个容器size之和vTarget.resize(v1.size() + v2.size());// 获取并集vector<int>::iterator itEnd = set_union(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vTarget.begin());for_each(vTarget.begin(), vTarget.end(), MyPrint());cout << endl;for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, MyPrint());
}int main()
{Test01();return 0;
}输出:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 0 0 0 0 0
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 145.6.3. set_difference
功能描述:
- 求两个集合的差集
函数原型:
set_difference(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest);
// 求两个集合的差集
// beg1 容器1开始迭代器
// end1 容器1结束迭代器
// beg2 容器2开始迭代器
// end2 容器2结束迭代器
// dest 目标容器开始迭代器
总结:
- 求并集的两个集合必须是有序序列
- 目标容器开辟的空间为两个容器的
size相加 set_intersection的返回值是交集迭代器中最后一个元素的位置
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<numeric>class MyPrint
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};void Test01()
{vector<int> v1;vector<int> v2;for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v1.push_back(i); // 0~9v2.push_back(i + 5); // 5~14}vector<int> vTarget;// 目标容器需要提前开辟空间// 最特殊情况:大容器与小容器完全不重合,开辟空间时取两个容器size之和vTarget.resize(max(v1.size(), v2.size()));// 获取并集vector<int>::iterator itEnd = set_difference(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vTarget.begin());cout << "v1和v2的差集为:" << endl;for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, MyPrint());cout << endl;cout << "v2和v1的差集为:" << endl;itEnd = set_difference(v2.begin(), v2.end(), v1.begin(), v1.end(), vTarget.begin());for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, MyPrint());
}int main()
{Test01();return 0;
}输出:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
v1和v2的差集为:
0 1 2 3 4
v2和v1的差集为:
10 11 12 13 14相关文章:

STL - 常用算法
概述: 算法主要是由头文件<algorithm><functional><numeric>组成<algorithm>是所有STL头文件中最大的一个,范围涉及比较、 交换、查找、遍历操作、复制、修改等等<numeric>体积很小,只包括几个在序列上面进行…...
)
Qt | QTextStream 类(文本流)
01、字符编码 1、怎样将字符转换为二进制形式进行存储,存在一个编码的问题,通常都需进行两次编码, 2、字符集:字符的第一次编码是将字符编码为与一个数值(如一个 10 进制整数)相对应,比如把字符 A 编码为 10 进制的 65,B 编码为 66 等。把每一个字符都编码为与一个数值…...

Python学习笔记7:入门知识(七)
前言 之前说过我更换了新的学习路线,现在是根据官方文档和书籍Python crash course来进行学习的,在目前的学习中,对于之前的知识有一些遗漏,这里进行补充。 学习资料有两个,书籍中文版PDF,关注我私信发送…...

如何翻译和本地化游戏?翻译访谈
如何翻译和本地化游戏?这个过程的技术细节有哪些?游戏翻译不同于电影翻译。Logrus IT游戏本地化部门负责人阿列克谢费奥多罗夫(Alexey Fedorov)在接受RUDN语言学系外语系教授和研究人员的采访时谈到了这一点,他是由尤利…...

[C++] 从零实现一个ping服务
💻文章目录 前言ICMP概念报文格式 Ping服务实现系统调用函数具体实现运行测试 总结 前言 ping命令,因为其简单、易用等特点,几乎所有的操作系统都内置了一个ping命令。如果你是一名C初学者,对网络编程、系统编程有所了解ÿ…...

2024网络安全学习路线 非常详细 推荐学习
关键词:网络安全入门、渗透测试学习、零基础学安全、网络安全学习路线 首先咱们聊聊,学习网络安全方向通常会有哪些问题 1、打基础时间太长 学基础花费很长时间,光语言都有几门,有些人会倒在学习 linux 系统及命令的路上&#…...
STM32F103ZET6_HAL_CAN
1定义时钟 2定义按键 按键上拉电阻 3开启串口 4打开CAN(具体什么意思上一篇讲了) 5生成代码 /* USER CODE BEGIN Header */ /********************************************************************************* file : main.c* brief …...

javaWeb项目-ssm+vue网上租车系统功能介绍
本项目源码:java-基于ssmvue的网上租车系统源码说明文档资料资源-CSDN文库 项目关键技术 开发工具:IDEA 、Eclipse 编程语言: Java 数据库: MySQL5.7 框架:ssm、Springboot 前端:Vue、ElementUI 关键技术:springboot、…...
Go模板页面浏览器显示HTML源码问题
<!--* Title: This is a file for ……* Author: JackieZheng* Date: 2024-06-09 17:00:01* LastEditTime: 2024-06-09 17:01:12* LastEditors: Please set LastEditors* Description:* FilePath: \\GoCode\\templates\\index.html --> <!DOCTYPE html> <html …...
弃用Docker Desktop:在WSL2中玩转Docker之Docker Engine 部署与WSL入门
Docker技术概论 在WSL2中玩转Docker之Docker Engine部署 - 文章信息 - Author: 李俊才 (jcLee95) Visit me at CSDN: https://jclee95.blog.csdn.netMy WebSite:http://thispage.tech/Email: 291148484163.com. Shenzhen ChinaAddress of this article:https://bl…...

Mac下载了docker,在终端使用docker命令时用不了
问题:在mac使用docker的时候,拉取docker镜像失败 原因:docker是需要用app使用的 ,所以在使用的时候必须打开这个桌面端软件才可以在终端上使用docker命令!!!...
Spring Security——基于MyBatis
目录 项目总结 新建一个项目 pom.xml application.properties配置文件 User实体类 UserMapper映射接口 UserService访问数据库中的用户信息 WebSecurityConfig配置类 MyAuthenticationFailureHandler登录失败后 MyAuthenticationSuccessHandlerw登录成功后 WebSecur…...
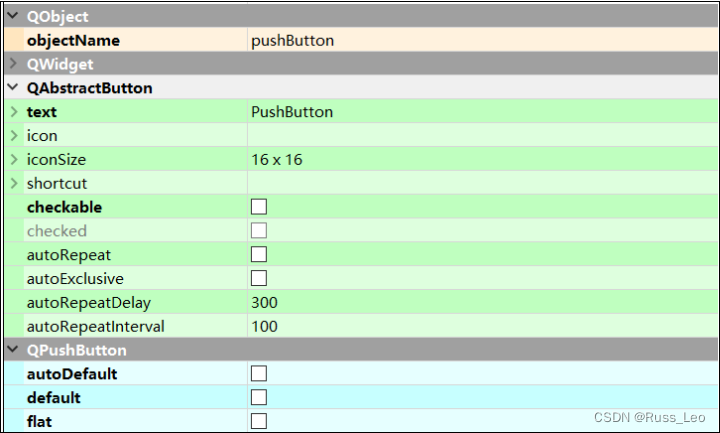
Qt——升级系列(Level Four):控件概述、QWidget 核心属性、按钮类控件
目录 控件概述 QWidget 核心属性 核心属性概览 enabled geometry windowTitle windowIcon windowOpacity cursor font toolTip focusPolicy styleSheet 按钮类控件 Push Button Radio Buttion Check Box Tool Button 控件概述 Widget 是 Qt 中的核⼼概念. 英⽂原义是 "…...
品质卓越为你打造App UI 风格
品质卓越为你打造App UI 风格...

ei期刊和sci期刊的区别
ei期刊和sci期刊的区别 ei期刊和sci期刊的区别是什么?Sci和ei都属于国际期刊的一种,但是二者之间存在一些区别,选择期刊投稿时需要注意这些区别。EI期刊刊物的审查周期短,SCI学术期刊的审查期长。难度要求不同,SCI期刊比EI期刊对…...

从零手写实现 nginx-20-placeholder 占位符 $
前言 大家好,我是老马。很高兴遇到你。 我们为 java 开发者实现了 java 版本的 nginx https://github.com/houbb/nginx4j 如果你想知道 servlet 如何处理的,可以参考我的另一个项目: 手写从零实现简易版 tomcat minicat 手写 nginx 系列 …...

leetcode290:单词规律
题目链接:290. 单词规律 - 力扣(LeetCode) class Solution { public:bool wordPattern(string pattern, string s) {unordered_map<char, string> s2t;unordered_map<string, char> t2s;int len pattern.size();int CountSpace…...

IDEA 2022
介绍 【尚硅谷IDEA安装idea实战教程(百万播放,新版来袭)】 jetbrains 中文官网 IDEA 官网 IDEA 从 IDEA 2022.1 版本开始支持 JDK 17,也就是说如果想要使用 JDK 17,那么就要下载 IDEA 2022.1 或之后的版本。 公司…...

Vue TypeScript 实战:掌握静态类型编程
title: Vue TypeScript 实战:掌握静态类型编程 date: 2024/6/10 updated: 2024/6/10 excerpt: 这篇文章介绍了如何在TypeScript环境下为Vue.js应用搭建项目结构,包括初始化配置、创建Vue组件、实现状态管理利用Vuex、配置路由以及性能优化的方法&#x…...

Hudi extraMetadata 研究总结
前言 研究总结 Hudi extraMetadata ,记录研究过程。主要目的是通过 extraMetadata 保存 source 表的 commitTime (checkpoint), 来实现增量读Hudi表写Hudi表时,保存增量读状态的事务性,实现类似于流任务中的 exactly-once 背景需求 有个需求:增量读Hudi表关联其他Hudi…...
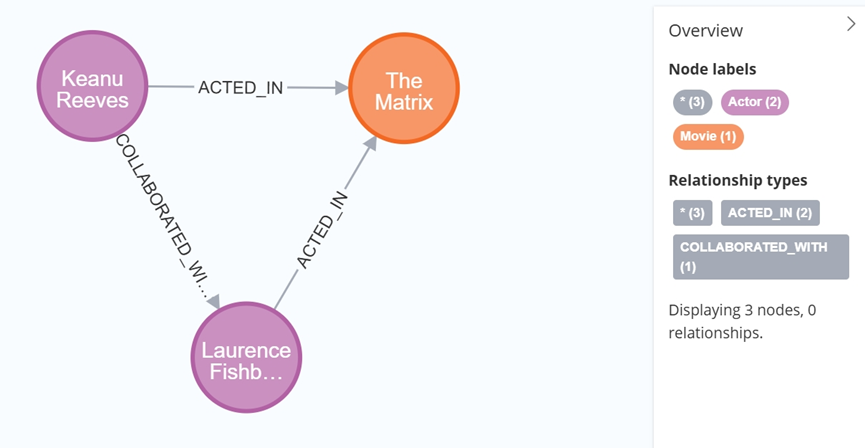
大数据学习栈记——Neo4j的安装与使用
本文介绍图数据库Neofj的安装与使用,操作系统:Ubuntu24.04,Neofj版本:2025.04.0。 Apt安装 Neofj可以进行官网安装:Neo4j Deployment Center - Graph Database & Analytics 我这里安装是添加软件源的方法 最新版…...

爬虫基础学习day2
# 爬虫设计领域 工商:企查查、天眼查短视频:抖音、快手、西瓜 ---> 飞瓜电商:京东、淘宝、聚美优品、亚马逊 ---> 分析店铺经营决策标题、排名航空:抓取所有航空公司价格 ---> 去哪儿自媒体:采集自媒体数据进…...
逻辑回归暴力训练预测金融欺诈
简述 「使用逻辑回归暴力预测金融欺诈,并不断增加特征维度持续测试」的做法,体现了一种逐步建模与迭代验证的实验思路,在金融欺诈检测中非常有价值,本文作为一篇回顾性记录了早年间公司给某行做反欺诈预测用到的技术和思路。百度…...

WebRTC从入门到实践 - 零基础教程
WebRTC从入门到实践 - 零基础教程 目录 WebRTC简介 基础概念 工作原理 开发环境搭建 基础实践 三个实战案例 常见问题解答 1. WebRTC简介 1.1 什么是WebRTC? WebRTC(Web Real-Time Communication)是一个支持网页浏览器进行实时语音…...
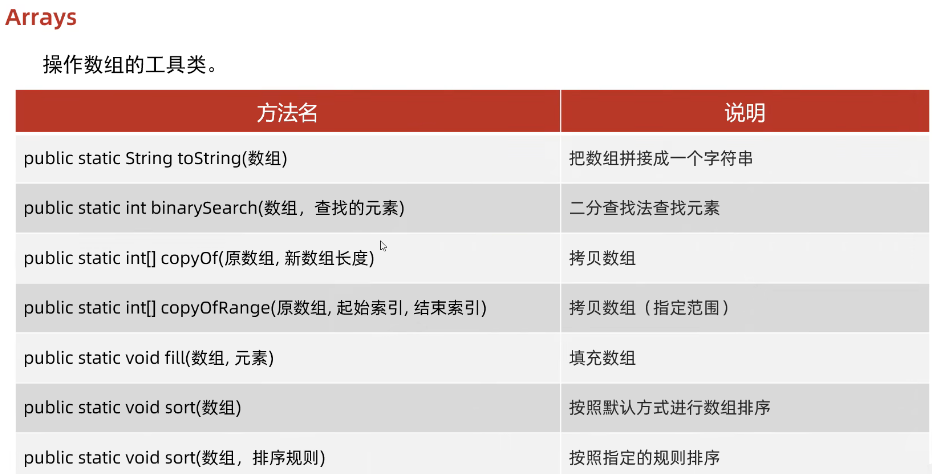
Java数组Arrays操作全攻略
Arrays类的概述 Java中的Arrays类位于java.util包中,提供了一系列静态方法用于操作数组(如排序、搜索、填充、比较等)。这些方法适用于基本类型数组和对象数组。 常用成员方法及代码示例 排序(sort) 对数组进行升序…...

SQL进阶之旅 Day 22:批处理与游标优化
【SQL进阶之旅 Day 22】批处理与游标优化 文章简述(300字左右) 在数据库开发中,面对大量数据的处理任务时,单条SQL语句往往无法满足性能需求。本篇文章聚焦“批处理与游标优化”,深入探讨如何通过批量操作和游标技术提…...
深入理解 C++ 左值右值、std::move 与函数重载中的参数传递
在 C 编程中,左值和右值的概念以及std::move的使用,常常让开发者感到困惑。特别是在函数重载场景下,如何合理利用这些特性来优化代码性能、确保语义正确,更是一个值得深入探讨的话题。 在开始之前,先提出几个问题&…...

STM32 低功耗设计全攻略:PWR 模块原理 + 睡眠 / 停止 / 待机模式实战(串口 + 红外 + RTC 应用全解析)
文章目录 PWRPWR(电源控制模块)核心功能 电源框图上电复位和掉电复位可编程电压监测器低功耗模式模式选择睡眠模式停止模式待机模式 修改主频一、准备工作二、修改主频的核心步骤:宏定义配置三、程序流程:时钟配置函数解析四、注意…...

ABB馈线保护 REJ601 BD446NN1XG
配电网基本量程数字继电器 REJ601是一种专用馈线保护继电器,用于保护一次和二次配电网络中的公用事业和工业电力系统。该继电器在一个单元中提供了保护和监控功能的优化组合,具有同类产品中最佳的性能和可用性。 REJ601是一种专用馈线保护继电器…...

NoSQL——Redis配置与优化
目录 关系型&非关系型数据库 一、核心原理对比 二、核心特性对比 三、关键区别剖析 四、典型产品示例 总结 Redis Redis核心原理 核心特性 技术意义 配置文件解析 1. 基础配置 2. 持久化配置 3. 内存管理 4. 高可用配置 5. 性能调优 6.…...
