MongoDB - 查询操作符:比较查询、逻辑查询、元素查询、数组查询
文章目录
- 1. 构造数据
- 2. MongoDB 比较查询操作符
- 1. $eq 等于
- 1.1 等于指定值
- 1.2 嵌入式文档中的字段等于某个值
- 1.3 数组元素等于某个值
- 1.4 数组元素等于数组值
- 2. $ne 不等于
- 3. $gt 大于
- 3.1 匹配文档字段
- 3.2 根据嵌入式文档字段执行更新
- 4. $gte 大于等于
- 5. $lt 小于
- 6. $lte 小于等于
- 7. $in
- 8. $nin
- 3. MongoDB 逻辑查询操作符
- 1. $and
- 2. $or
- 3. $not
- 4. $nor
- 4. 元素查询操作符
- 1. $exists
- 2. $type
- 5. MongoDB 数组查询操作符
- 1. $elemMatch
- 1.1 元素匹配
- 1.2 嵌入式文档数组
- 2. $size
- 3. $all
参考官方文档:https://www.mongodb.com/zh-cn/docs/manual/reference/operator/query/and/
1. 构造数据
① 批量插入4个文档到user集合:
db.user.insertMany([{ name: "Alice", age: 25, email: "alice@example.com", hobbies: ["reading", "writing", "music"] },{ name: "John", age: 30, email: "John@qq.com", hobbies: ["reading", "gaming", "traveling"] },{ name: "Jane", age: 25, email: "Jane@qq.com", hobbies: ["sports", "music", "cooking"] },{ name: "Mike", age: 35, email: "Mike@qq.com", hobbies: ["reading", "writing", "painting"] }
]);
② SpringBoot整合MongoDB实现批量插入文档:
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId>
</dependency>
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Data
@Document(collection = "user")
public class User {@Idprivate String id;private String name;private Integer age;private String email;private List<String> hobbies;public User(String name,Integer age,String email,List<String> hobbies){this.name = name;this.age = age;this.email = email;this.hobbies = hobbies;}
}
@SpringBootTest
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
public class BeanLoadServiceTest {@Autowiredprivate MongoTemplate mongoTemplate;@Testpublic void insertUser() {List<User> users = Arrays.asList(new User("Alice", 25, "alice@example.com",Arrays.asList("reading", "writing", "music")),new User("John", 30, "John@qq.com", Arrays.asList("reading", "gaming", "traveling")),new User("Jane", 25, "Jane@qq.com", Arrays.asList("sports", "music", "cooking")),new User("Mike", 35, "Mike@qq.com", Arrays.asList("reading", "writing", "painting")));mongoTemplate.insertAll(users);}
}

2. MongoDB 比较查询操作符
比较操作符根据数值比较返回数据。MongoDB提供了一些比较查询操作符,用于在查询中进行条件比较。以下是一些常用的比较查询操作符:
$eq:等于,用于匹配字段值等于指定值的文档。
例如:db.collection.find({ field: { $eq: value } })
$ne:不等于,用于匹配字段值不等于指定值的文档。
例如:db.collection.find({ field: { $ne: value } })
$gt:大于,用于匹配字段值大于指定值的文档。
例如:db.collection.find({ field: { $gt: value } })
$gte:大于等于,用于匹配字段值大于等于指定值的文档。
例如:db.collection.find({ field: { $gte: value } })
$lt:小于,用于匹配字段值小于指定值的文档。
例如:db.collection.find({ field: { $lt: value } })
$lte:小于等于,用于匹配字段值小于等于指定值的文档。
例如:db.collection.find({ field: { $lte: value } })
$in:在指定值数组中,用于匹配字段值在指定值数组中的文档。
例如:db.collection.find({ field: { $in: [value1, value2, …] } })
$nin:不在指定值数组中,用于匹配字段值不在指定值数组中的文档。
例如:db.collection.find({ field: { $nin: [value1, value2, …] } })
这些比较查询操作符可以与逻辑操作符(如 a n d 、 and、 and、or、$not等)结合使用,以构建更复杂的查询条件。
1. $eq 等于
用于匹配字段值等于指定值的文档:
db.collection.find({ field: { $eq: value } })
# 相当于
db.collection.find({ field : value})
1.1 等于指定值
查询user集合中name等于Alice的文档:
db.user.find({ name: { $eq: "Alice" } })
@Test
public void findUser1() {// 创建查询条件Criteria criteria = Criteria.where("name").is("Alice");// 创建查询对象Query query = new Query(criteria);// 执行查询List<User> users = mongoTemplate.find(query, User.class);users.forEach(System.out::println); // User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0096, name=Alice, age=25, email=alice@example.com, hobbies=[reading, writing, music])
}
1.2 嵌入式文档中的字段等于某个值
db.inventory.insertMany( [{ _id: 1, item: { name: "ab", code: "123" }, qty: 15, tags: [ "A", "B", "C" ] },{ _id: 2, item: { name: "cd", code: "123" }, qty: 20, tags: [ "B" ] },{ _id: 3, item: { name: "ij", code: "456" }, qty: 25, tags: [ "A", "B" ] },{ _id: 4, item: { name: "xy", code: "456" }, qty: 30, tags: [ "B", "A" ] },{ _id: 5, item: { name: "mn", code: "000" }, qty: 20, tags: [ [ "A", "B" ], "C" ] }
] )
查询 inventory 集合中 item 文档的 name 等于 "ab" 的所有文档。要对嵌入式文档中的字段指定条件,使用点符号:
db.inventory.find( { "item.name": { $eq: "ab" } } )
@Data
@Document(collection = "inventory")
public class Inventory {@Idprivate String id;private Item item;private int qty;private List<Object> tags;@Datapublic static class Item {private String name;private String code;}
}@Test
public void findUser1() {// 创建查询条件Criteria criteria = Criteria.where("item.name").is("ab");// 创建查询对象Query query = new Query(criteria);List<Inventory> inventoryList = mongoTemplate.find(query, Inventory.class);inventoryList.forEach(System.out::println);// Inventory(id=1.0, item=Inventory.Item(name=ab, code=123), qty=15, tags=[A, B, C])
}
1.3 数组元素等于某个值
查询 inventory 集合中 tags 数组包含值为 "C" 的元素的所有文档:
db.inventory.find( { tags: { $eq: "B" } } )
@Test
public void findUser1() {// 创建查询条件Criteria criteria = Criteria.where("tags").is("C");// 创建查询对象Query query = new Query(criteria);List<Inventory> inventoryList = mongoTemplate.find(query, Inventory.class);inventoryList.forEach(System.out::println);// Inventory(id=1.0, item=Inventory.Item(name=ab, code=123), qty=15, tags=[A, B, C])// Inventory(id=5.0, item=Inventory.Item(name=mn, code=000), qty=20, tags=[[A, B], C])
}
1.4 数组元素等于数组值
查询 inventory 集合中 tags 数组与指定数组完全相同或 tags 数组包含数组 [ "A", "B" ] 的所有文档:
db.inventory.find( { tags: { $eq: [ "A", "B" ] } } )
db.inventory.find( { tags: [ "A", "B" ] } )
@Test
public void findUser1() {// 创建查询条件Criteria criteria = Criteria.where("tags").is(Arrays.asList("A","B"));// 创建查询对象Query query = new Query(criteria);List<Inventory> inventoryList = mongoTemplate.find(query, Inventory.class);inventoryList.forEach(System.out::println);// Inventory(id=3.0, item=Inventory.Item(name=ij, code=456), qty=25, tags=[A, B])// Inventory(id=5.0, item=Inventory.Item(name=mn, code=000), qty=20, tags=[[A, B], C])
}
2. $ne 不等于
用于匹配字段值不等于指定值的文档:
db.collection.find({ field: { $ne: value } })
查询user集合中name不等于Alice的文档:
db.user.find({ name: { $ne: "Alice" } })
@Test
public void findUser2() {// 创建查询条件Criteria criteria = Criteria.where("name").ne("Alice");// 创建查询对象Query query = new Query(criteria);// 执行查询List<User> users = mongoTemplate.find(query, User.class);users.forEach(System.out::println);// User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0097, name=John, age=30, email=John@qq.com, hobbies=[reading, gaming, traveling])// User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0098, name=Jane, age=25, email=Jane@qq.com, hobbies=[sports, music, cooking])// User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0099, name=Mike, age=35, email=Mike@qq.com, hobbies=[reading, writing, painting])
}
3. $gt 大于
用于匹配字段值大于指定值的文档:
db.collection.find({ field: { $gt: value } })
3.1 匹配文档字段
查询user集合中age大于30的文档:
@Test
public void findUser2() {// 创建查询条件Criteria criteria = Criteria.where("age").gt(30);// 创建查询对象Query query = new Query(criteria);// 执行查询List<User> users = mongoTemplate.find(query, User.class);users.forEach(System.out::println);// User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0099, name=Mike, age=35, email=Mike@qq.com, hobbies=[reading, writing, painting])
}
3.2 根据嵌入式文档字段执行更新
db.inventory.insertMany( [{"item": "nuts", "quantity": 30,"carrier": { "name": "Shipit", "fee": 3 }},{"item": "bolts", "quantity": 50,"carrier": { "name": "Shipit", "fee": 4 }},{"item": "washers", "quantity": 10,"carrier": { "name": "Shipit", "fee": 1 }}
] )
查询 inventory 集合中 carrier 文档的 fee 大于 2 的第一个文档,并设置文档的price等于9.99:
db.inventory.updateOne({ "carrier.fee": { $gt: 2 } }, { $set: { "price": 9.99 } }
)
@Data
@Document(collection = "inventory")
public class Inventory {@Idprivate String id;private String item;private int quantity;private Carrier carrier;@Datapublic static class Carrier {private String name;private int fee;}
}@Test
public void updateUser(){// 创建查询条件Criteria criteria = Criteria.where("carrier.fee").gt(2);// 创建更新对象Update update = new Update();update.set("price", 9.99);// 创建查询对象Query query = new Query(criteria);// 执行更新操作UpdateResult updateResult = mongoTemplate.updateFirst(query, update, Inventory.class);
}
对应查询结果为:
{_id: ObjectId("61ba3ec9fe687fce2f042417"),item: 'nuts',quantity: 30,carrier: { name: 'Shipit', fee: 3 },price: 9.99
},
{_id: ObjectId("61ba3ec9fe687fce2f042418"),item: 'bolts',quantity: 50,carrier: { name: 'Shipit', fee: 4 }
},
{_id: ObjectId("61ba3ec9fe687fce2f042419"),item: 'washers',quantity: 10,carrier: { name: 'Shipit', fee: 1 }
}
要在carrier.fee 所有大于 2 的文档中设置 price 字段的值,请使用 updateMany()。
4. $gte 大于等于
用于匹配字段值大于等于指定值的文档:
db.collection.find({ field: { $gte: value } })
查询user集合中age大于等于30的文档:
@Test
public void findUser2() {// 创建查询条件Criteria criteria = Criteria.where("age").gte(30);// 创建查询对象Query query = new Query(criteria);// 执行查询List<User> users = mongoTemplate.find(query, User.class);users.forEach(System.out::println);// User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0097, name=John, age=30, email=John@qq.com, hobbies=[reading, gaming, traveling])// User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0099, name=Mike, age=35, email=Mike@qq.com, hobbies=[reading, writing, painting])
}
5. $lt 小于
用于匹配字段值小于指定值的文档:
db.collection.find({ field: { $lt: value } })
查询user集合中age小于30的文档:
@Test
public void findUser1() {// 创建查询条件Criteria criteria = Criteria.where("age").lt(30);// 创建查询对象Query query = new Query(criteria);// 执行查询List<User> users = mongoTemplate.find(query, User.class);users.forEach(System.out::println);// User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0096, name=Alice, age=25, email=alice@example.com, hobbies=[reading, writing, music])// User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0098, name=Jane, age=25, email=Jane@qq.com, hobbies=[sports, music, cooking])
}
6. $lte 小于等于
用于匹配字段值小于等于指定值的文档:
db.collection.find({ field: { $lte: value } })
查询user集合中age小于等于30的文档:
@Test
public void findUser2() {// 创建查询条件Criteria criteria = Criteria.where("age").lte(30);// 创建查询对象Query query = new Query(criteria);// 执行查询List<User> users = mongoTemplate.find(query, User.class);users.forEach(System.out::println);// User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0096, name=Alice, age=25, email=alice@example.com, hobbies=[reading, writing, music])// User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0097, name=John, age=30, email=John@qq.com, hobbies=[reading, gaming, traveling])// User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0098, name=Jane, age=25, email=Jane@qq.com, hobbies=[sports, music, cooking])
}
7. $in
在指定值数组中,用于匹配字段值在指定值数组中的文档:
db.collection.find({ field: { $in: [value1, value2, ...] } })
查询user集合中name等于Alice或Jone或Jane的文档:
db.user.find({ name: { $in: ["Alice", "John", "Jane"] } })
@Test
public void findUser2() {// 创建查询条件Criteria criteria = Criteria.where("name").in(Arrays.asList("Alice","John","Jane"));// 创建查询对象Query query = new Query(criteria);// 执行查询List<User> users = mongoTemplate.find(query, User.class);users.forEach(System.out::println);// User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0096, name=Alice, age=25, email=alice@example.com, hobbies=[reading, writing, music])// User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0097, name=John, age=30, email=John@qq.com, hobbies=[reading, gaming, traveling])// User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0098, name=Jane, age=25, email=Jane@qq.com, hobbies=[sports, music, cooking])
}
8. $nin
不在指定值数组中,用于匹配字段值不在指定值数组中的文档:
db.collection.find({ field: { $nin: [value1, value2, ...] } })
查询user集合中name不等于Alice、Jone、Jane的文档:
db.user.find({ name: { $nin: ["Alice", "John", "Jane"] } })
@Test
public void findUser2() {// 创建查询条件Criteria criteria = Criteria.where("name").nin(Arrays.asList("Alice","John","Jane"));// 创建查询对象Query query = new Query(criteria);// 执行查询List<User> users = mongoTemplate.find(query, User.class);users.forEach(System.out::println);// User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0099, name=Mike, age=35, email=Mike@qq.com, hobbies=[reading, writing, painting])
}
3. MongoDB 逻辑查询操作符
逻辑操作符根据计算结果为 ture 或 false 的表达式来返回数据。MongoDB提供了丰富的逻辑查询操作符,用于在查询中进行逻辑运算和条件判断。以下是一些常用的逻辑查询操作符:
$and:用于同时满足多个条件的查询。
例如:db.collection.find({ $and: [ { condition1 }, { condition2 } ] })
$or:用于满足多个条件中的任意一个的查询。
例如:db.collection.find({ $or: [ { condition1 }, { condition2 } ] })
$not:用于否定一个条件的查询。
例如:db.collection.find({ field: { $not: { condition } } })
$nor:用于满足多个条件都不成立的查询。
例如:db.collection.find({ $nor: [ { condition1 }, { condition2 } ] })
这些逻辑查询操作符可以与其他查询条件结合使用,以实现更复杂的查询逻辑。
1. $and
用于同时满足多个条件的查询。
db.collection.find({ $and: [ { condition1 }, { condition2 } ] })
查询user集合中age大于等于18,并且name等于Alice的文档:
db.user.find({ $and: [ { age: { $gte: 18 } }, { name: "Alice" } ] })
@Test
public void findUser1() {// 创建查询条件:首先创建了一个Criteria对象,并使用andOperator方法来添加多个条件Criteria criteria = new Criteria();criteria.andOperator(Criteria.where("age").gte(18),Criteria.where("name").is("Alice"));// 创建查询对象Query query = new Query(criteria);// 执行查询List<User> users = mongoTemplate.find(query, User.class);users.forEach(System.out::println);// User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0096, name=Alice, age=25, email=alice@example.com, hobbies=[reading, writing, music])
}
@Test
public void findUser1() {// 查询条件Criteria criteria = Criteria.where("age").gte(18).and("name").is("Alice");// 查询对象Query query = new Query();query.addCriteria(criteria);// 执行查询List<User> users = mongoTemplate.find(query, User.class);users.forEach(System.out::println);// User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0096, name=Alice, age=25, email=alice@example.com, hobbies=[reading, writing, music])
}
2. $or
用于满足多个条件中的任意一个的查询。
db.collection.find({ $or: [ { condition1 }, { condition2 } ] })
查询user集合中age小于30,或者name等于Alice的文档:
db.user.find({ $or: [ { age: { gt: 30 } }, { name: "Alice" } ] })
@Test
public void findUser1() {// 创建查询条件Criteria criteria = new Criteria();// 首先创建了一个Criteria对象,并使用orOperator方法来添加多个条件criteria.orOperator(Criteria.where("age").gt(30),Criteria.where("name").is("Alice"));// 创建查询对象Query query = new Query(criteria);// 执行查询List<User> users = mongoTemplate.find(query, User.class);users.forEach(System.out::println);// User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0096, name=Alice, age=25, email=alice@example.com, hobbies=[reading, writing, music])// User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0099, name=Mike, age=35, email=Mike@qq.com, hobbies=[reading, writing, painting])
}
3. $not
用于否定一个条件的查询。
db.collection.find({ field: { $not: { condition } } })
查询user集合中age小于30的文档:
db.user.find({ age: { $not: { $gte: 30 } } })
@Test
public void findUser1() {// 创建查询对象Query query = new Query(Criteria.where("age").not().gte(30));// 执行查询List<User> users = mongoTemplate.find(query, User.class);users.forEach(System.out::println);// User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0096, name=Alice, age=25, email=alice@example.com, hobbies=[reading, writing, music])// User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0098, name=Jane, age=25, email=Jane@qq.com, hobbies=[sports, music, cooking])
}
4. $nor
用于满足多个条件都不成立的查询。
db.collection.find({ $nor: [ { condition1 }, { condition2 } ] })
查询user集合中age小于30,并且name不等于Alice的文档
db.users.find({ $nor: [ { age: { $gte: 30 } }, { name: "Alice" } ] })
@Test
public void findUser1() {Criteria criteria = new Criteria();criteria.norOperator(Criteria.where("age").gte(30),Criteria.where("name").is("Alice"));// 创建查询对象Query query = new Query(criteria);// 执行查询List<User> users = mongoTemplate.find(query, User.class);users.forEach(System.out::println);// User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0098, name=Jane, age=25, email=Jane@qq.com, hobbies=[sports, music, cooking])
}
4. 元素查询操作符
元素操作符根据字段是否存在或数据类型返回数据。
$exists:用于检查字段是否存在的查询。
例如:db.collection.find({ field: { $exists: true } })
$type:用于检查字段类型的查询。
例如:db.collection.find({ field: { $type: “string” } })
数据构造:向user集合中name等于Alice的文档新增一个字段
db.user.updateOne( { name: "Alice" },{$set: {city: "ShangHai"}}
)
@Test
public void updateUser(){// 构建查询条件Criteria criteria = Criteria.where("name").is("Alice");Query query = Query.query(criteria);// 构建更新操作Update update = new Update();update.set("city", "ShangHai");// 执行更新操作mongoTemplate.updateMulti(query, update, "user");
}

1. $exists
用于检查字段是否存在的查询
db.collection.find({ field: { $exists: true } })
查询user集合中city字段是否存在:
db.user.find({ city: { $exists: true } })
@Test
public void findUser1() {// 查询条件Criteria criteria = Criteria.where("city").exists(true);// 查询对象Query query = new Query(criteria);// 执行查询List<User> users = mongoTemplate.find(query, User.class);users.forEach(System.out::println);// User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0096, name=Alice, age=25, email=alice@example.com, hobbies=[reading, writing, music])
}
2. $type
用于检查字段类型的查询
db.collection.find({ field: { $type: "string" } })
$type 运算符接受的字段类型:
| 类型 | 数值 | 别名 | 注意 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 双精度 | 1 | “double” | |
| 字符串 | 2 | “string” | |
| 对象 | 3 | “object” | |
| 阵列 | 4 | “array” | |
| 二进制数据 | 5 | “binData” | |
| ObjectId | 7 | “objectId” | |
| 布尔 | 8 | “bool” | |
| Date | 9 | “date” | |
| null | 10 | “null” | |
| 正则表达式 | 11 | “regex” | |
| JavaScript | 13 | “javascript” | |
| 32 位整数 | 16 | “int” | |
| 时间戳 | 17 | “timestamp” | |
| 64 位整型 | 18 | “long” | |
| Decimal128 | 19 | “decimal” | |
| Min key | -1 | “minKey” | |
| Max key | 127 | “maxKey” |
查询user集合中name的字段类型是否为string:
db.user.find({ name: { $type: "string" } })
db.user.find( { name : { $type : 2 } } )
@Test
public void findUser1() {// 查询条件Criteria criteria = Criteria.where("name").type(2);// 查询对象Query query = new Query(criteria);// 执行查询List<User> users = mongoTemplate.find(query, User.class);users.forEach(System.out::println);// User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0096, name=Alice, age=25, email=alice@example.com, hobbies=[reading, writing, music])// User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0097, name=John, age=30, email=John@qq.com, hobbies=[reading, gaming, traveling])// User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0098, name=Jane, age=25, email=Jane@qq.com, hobbies=[sports, music, cooking])// User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0099, name=Mike, age=35, email=Mike@qq.com, hobbies=[reading, writing, painting])
}
5. MongoDB 数组查询操作符
数组操作符根据数组条件返回数据。MongoDB提供了多种数组查询操作符,用于在查询中对数组字段进行操作和匹配。以下是一些常用的数组查询操作符:
$elemMatch:用于在数组字段中匹配满足多个条件的元素的查询。
db.collection.find({ field: { $elemMatch: { condition1, condition2 } } })
$size:用于匹配数组字段的长度的查询。
db.collection.find({ field: { $size: 3 } })
$all:用于匹配数组字段中包含所有指定元素的查询。
db.collection.find({ field: { $all: [ element1, element2 ] } })
$in:用于匹配数组字段中包含指定元素的查询。例如:
db.collection.find({ field: { $in: [ element1, element2 ] } })
$nin:用于匹配数组字段中不包含指定元素的查询。例如:
db.collection.find({ field: { $nin: [ element1, element2 ] } })
$slice:用于返回数组字段的子集。例如:
db.collection.find({ field: { $slice: 5 } })
$addToSet:用于向数组字段添加唯一的元素。例如:
db.collection.updateOne({ _id: ObjectId(“…”) }, { $addToSet: { field: element } })
这些数组查询操作符可以与其他查询条件结合使用,以实现更复杂的查询逻辑。请注意,以上示例中的"collection"和"field"应替换为实际的集合名和字段名。
1. $elemMatch
用于在数组字段中匹配满足多个条件的元素的查询。
db.collection.find({ arrayField: { $elemMatch: { condition1, condition2 } } })
1.1 元素匹配
查询user集合中age大于等于30并且hobbies包含reading的文档:
db.user.find({ age: { $gte: 30 }, hobbies: { $elemMatch: { $eq: "reading" } } })
@Test
public void findUser1() {// 查询条件Criteria criteria = Criteria.where("age").gte(30).and("hobbies").elemMatch(Criteria.where("$eq").is("reading"));// 查询对象Query query = new Query(criteria);// 执行查询List<User> users = mongoTemplate.find(query, User.class);users.forEach(System.out::println);// User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0097, name=John, age=30, email=John@qq.com, hobbies=[reading, gaming, traveling])// User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0099, name=Mike, age=35, email=Mike@qq.com, hobbies=[reading, writing, painting])
}
@Test
public void findUser1() {// 查询条件Criteria criteria = new Criteria();criteria.andOperator(Criteria.where("age").gte(30),Criteria.where("hobbies").elemMatch(Criteria.where("$eq").is("reading")));// 查询对象Query query = new Query();query.addCriteria(criteria);// 执行查询List<User> users = mongoTemplate.find(query, User.class);users.forEach(System.out::println);// User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0097, name=John, age=30, email=John@qq.com, hobbies=[reading, gaming, traveling])// User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0099, name=Mike, age=35, email=Mike@qq.com, hobbies=[reading, writing, painting])
}
查询user集合中hobbies数组包含reading的文档:
db.user.find( hobbies: { $elemMatch: { $eq: "reading" } } })
@Test
public void findUser1() {// 查询条件Criteria criteria = Criteria.where("hobbies").elemMatch(Criteria.where("$eq").is("reading"));// 查询对象Query query = new Query();query.addCriteria(criteria);// 执行查询List<User> users = mongoTemplate.find(query, User.class);users.forEach(System.out::println);// User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0096, name=Alice, age=25, email=alice@example.com, hobbies=[reading, writing, music])//User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0097, name=John, age=30, email=John@qq.com, hobbies=[reading, gaming, traveling])//User(id=668f53342e9dde5bccea0099, name=Mike, age=35, email=Mike@qq.com, hobbies=[reading, writing, painting])
}
1.2 嵌入式文档数组
① 查询survey集合中product为"xyz"且score大于或等于8 的文档:
db.survey.insertMany( [{ "_id": 1, "results": [ { "product": "abc", "score": 10 },{ "product": "xyz", "score": 5 } ] },{ "_id": 2, "results": [ { "product": "abc", "score": 8 },{ "product": "xyz", "score": 7 } ] },{ "_id": 3, "results": [ { "product": "abc", "score": 7 },{ "product": "xyz", "score": 8 } ] },{ "_id": 4, "results": [ { "product": "abc", "score": 7 },{ "product": "def", "score": 8 } ] },{ "_id": 5, "results": { "product": "xyz", "score": 9 } }
] )
注意,_id 为 5 的文档不包含数组。
db.survey.find( { results: { $elemMatch: { product: "xyz", score: { $gte: 8 } } } } )
@Data
@Document(collection = "survey")
public class Survey {@Idprivate int _id;private List<Result> results;
}@Data
public class Result {private String product;private int score;
}@Test
public void findUser1() {// 查询条件Query query = new Query();query.addCriteria(Criteria.where("results").elemMatch(Criteria.where("product").is("xyz").and("score").gte(8)));List<Survey> surveyList = mongoTemplate.find(query, Survey.class, "survey");surveyList.forEach(System.out::println);// Survey(_id=3, results=[Result(product=abc, score=7), Result(product=xyz, score=8)])
}
② 使用$elemMatch进行单一查询条件:
db.survey.find({ results: { $elemMatch: { product: "xyz" } } }
)
此查询会返回 results 中的任一 product 为 "xyz" 的文档。
③ 不使用$elemMatch进行单一查询条件:
db.survey.find({ "results.product": "xyz" }
)
此查询结果还包括 _id 为 5 的文档(不包含数组)
④ 查询student集合中所有数学成绩高于90分的学生:
db.student.insertMany( [{"_id": 1,"name": "Alice","grades": [{ "subject": "Math", "score": 90 },{ "subject": "English", "score": 85 },{ "subject": "Science", "score": 95 }]},{"_id": 2,"name": "Bob","grades": [{ "subject": "Math", "score": 80 },{ "subject": "English", "score": 75 },{ "subject": "Science", "score": 85 }]},{"_id": 3, "name": "Charlie","grades": [{ "subject": "Math", "score": 95 },{ "subject": "English", "score": 90 },{ "subject": "Science", "score": 92 }]}]
)
db.students.find({ grades: { $elemMatch: { subject: "Math", score: { $gt: 90 } } } })
@Data
@Document(collection = "student")
public class Student {@Idprivate int _id;private String name;private List<Grade> grades;
}@Data
public class Grade {private String subject;private int score;
}@Test
public void findUser1() {// 查询条件Query query = new Query();query.addCriteria(Criteria.where("grades").elemMatch(Criteria.where("subject").is("Math").and("score").gte(90)));List<Student> studentList = mongoTemplate.find(query, Student.class, "student");studentList.forEach(System.out::println);// Student(_id=1, name=Alice, grades=[Grade(subject=Math, score=90), Grade(subject=English, score=85), Grade(subject=Science, score=95)])// Student(_id=3, name=Charlie, grades=[Grade(subject=Math, score=95), Grade(subject=English, score=90), Grade(subject=Science, score=92)])
}
2. $size
用于匹配数组字段的长度的查询。
db.collection.find({ arrayField: { $size: 3 } })
查询user集合中hobbies数组包含2个元素的所有文档:
db.user.insertMany([{ name: "Alice", age: 25, email: "alice@example.com", hobbies: ["writing"] },{ name: "John", age: 30, email: "John@qq.com", hobbies: ["reading", "gaming",] },{ name: "Jane", age: 25, email: "Jane@qq.com", hobbies: ["sports", "music"] },{ name: "Mike", age: 35, email: "Mike@qq.com", hobbies: ["reading", "writing", "painting", "cooking"] }
]);
db.user.find( { hobbies: { $size: 2 } } );
@Test
public void findUser1() {// 查询条件Query query = new Query();Criteria criteria = Criteria.where("hobbies").size(2);query.addCriteria(criteria);List<User> users = mongoTemplate.find(query, User.class, "user");users.forEach(System.out::println);// User(id=66906798197700004d003dcd, name=John, age=30, email=John@qq.com, hobbies=[reading, gaming])//User(id=66906798197700004d003dce, name=Jane, age=25, email=Jane@qq.com, hobbies=[sports, music])
}
此查询返回 collection 中 field 为包含 2 个元素的数组的所有文档。
3. $all
用于匹配数组字段中包含所有指定元素的查询。
db.collection.find({ field: { $all: [ element1, element2 ] } })
db.user.insertMany([{ name: "Alice", age: 25, email: "alice@example.com", hobbies: ["reading", "writing", "music"] },{ name: "John", age: 30, email: "John@qq.com", hobbies: ["reading", "gaming", "traveling"] },{ name: "Jane", age: 25, email: "Jane@qq.com", hobbies: ["sports", "music", "cooking"] },{ name: "Mike", age: 35, email: "Mike@qq.com", hobbies: ["reading", "writing", "painting"] }
]);
查询user集合中hobbies数组包含 “writing” 和 “music” 的文档:
db.user.find({ hobbies: { $all: [ "writing" , "music" ] } })
# 相当于
db.user.find({ $and: [ { hobbies: "writing" }, { hobbies: "music" } ] })
@Test
public void findUser1() {// 查询条件Query query = new Query();Criteria criteria = Criteria.where("hobbies").all("music","writing");query.addCriteria(criteria);List<User> users = mongoTemplate.find(query, User.class, "user");users.forEach(System.out::println);// User(id=6690693d197700004d003dd0, name=Alice, age=25, email=alice@example.com, hobbies=[reading, writing, music])
}
相关文章:

MongoDB - 查询操作符:比较查询、逻辑查询、元素查询、数组查询
文章目录 1. 构造数据2. MongoDB 比较查询操作符1. $eq 等于1.1 等于指定值1.2 嵌入式文档中的字段等于某个值1.3 数组元素等于某个值1.4 数组元素等于数组值 2. $ne 不等于3. $gt 大于3.1 匹配文档字段3.2 根据嵌入式文档字段执行更新 4. $gte 大于等于5. $lt 小于6. $lte 小于…...

html5——CSS高级选择器
目录 属性选择器 E[att^"value"] E[att$"http"] E[att*"http"] 关系选择器 子代: 相邻兄弟: 普通兄弟: 结构伪类选择器 链接伪类选择器 伪元素选择器 CSS的继承与层叠 CSS的继承性 CSS的层叠性 …...
)
Python-数据爬取(爬虫)
~~~理性爬取~~~ 杜绝从入门到入狱 1.简要描述一下Python爬虫的工作原理,并介绍几个常用的Python爬虫库。 Python爬虫的工作原理 发送请求:爬虫向目标网站发送HTTP请求,通常使用GET请求来获取网页内容。解析响应:接收并解析HTTP响…...

虚幻引擎ue5如何调节物体锚点
当发现锚点不在物体上时,如何调节瞄点在物体上。 步骤1:按住鼠标中键拖动锚点,在透视图中多次调节锚点位置。 步骤2:在物体上点击鼠标右键点击-》锚定--》“设置为枢轴偏移”即可。...

Xcode持续集成之道:自动化构建与部署的精粹
标题:Xcode持续集成之道:自动化构建与部署的精粹 在快节奏的软件开发中,持续集成(Continuous Integration, CI)是提升开发效率和软件质量的关键实践。Xcode作为苹果生态中的核心开发工具,提供了与多种持续…...

Java高频面试基础知识点整理13
干货分享,感谢您的阅读!背景高频面试题基本总结回顾(含笔试高频算法整理) 最全文章见:Java高频面试基础知识点整理 (一)Java基础高频知识考点 针对人员: 1.全部人员都…...

css画半圆画圆弧
利用border-radius和border完成: <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset"utf-8"> <title>test</title> <style> .semicircle {width: 100px;height: 50px;border-radius: 0 0 50px 50px;background:…...

LeetCode HOT100(四)字串
和为 K 的子数组(mid) 给你一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数 k ,请你统计并返回 该数组中和为 k 的子数组的个数 。 子数组是数组中元素的连续非空序列。 输入:nums [1,1,1], k 2 输出:2 解法1:前缀和Map 这…...
 #按需引入)
uniapp引入 uview( HBuilder 和 npm 两种安装方式) #按需引入
方式一、HBuilder 安装 uview 1.1. HBuider安装-链接-》》 1.2. 在uni.scss 中引入 import "uni_modules/uview-ui/theme.scss";1.3. main.js 引入(import Vue from ‘vue’ 下面) import uView from "uni_modules/uview-ui"; V…...

使用uni-app和Golang开发影音类小程序
在数字化时代,影音内容已成为人们日常生活中不可或缺的一部分。个人开发者如何快速构建一个功能丰富、性能优越的影音类小程序?本文将介绍如何使用uni-app前端框架和Golang后端语言来实现这一目标。 项目概述 本项目旨在开发一个个人影音类小程序&#…...

基于Go1.19的站点模板爬虫详细介绍
构建一个基于Go1.19的站点模板爬虫是一项有趣且具有挑战性的任务。这个爬虫将能够从网站上提取数据,并按照指定的模板进行格式化。以下是详细的介绍和实现步骤。 1. 准备工作 工具和库: Go 1.19colly:一个强大的Go爬虫库goquery࿱…...

永恒之蓝:一场网络风暴的启示
引言 在网络安全的漫长历史中,“永恒之蓝”(EternalBlue)是一个不可忽视的里程碑事件。它不仅揭示了网络世界的脆弱性,还促使全球范围内对网络安全的重视达到了前所未有的高度。本文将深入探讨“永恒之蓝”漏洞的起源、影响及其对…...

AI绘画:艺术与科技的交融,创新浪潮与无限可能
在科技日新月异的当下,AI 绘画作为人工智能领域的一颗璀璨新星,正以惊人的速度在国内崭露头角,引发了艺术与技术交融的全新变革。随着人工智能技术的飞速发展,AI绘画已成为艺术与科技交融的新宠。2024年,AI绘画行业在国…...

医疗健康信息的安全挑战与隐私保护最佳实践
医疗健康信息的安全挑战 医疗健康信息的安全挑战主要包括数据规模庞大、管理困难、数据类型多样导致的安全风险高、以及法律法规与伦理约束带来的挑战。随着医疗信息化的发展,医疗健康数据呈现出爆炸式的增长,医院信息系统、电子病历、健康管理等产生了海…...
)
《C++并发编程实战》笔记(一、二)
一、简介 抽象损失:对于实现某个功能时,可以使用高级工具,也可以直接使用底层工具。这两种方式运行的开销差异称为抽象损失。 二、线程管控 2.1 线程的基本控制 1. 创建线程 线程相关的管理函数和类在头文件: #include <…...

【日常bug记录】el-checkbox 绑定对象数组
版本说明 "vue": "2.6.10", "element-ui": "2.13.2", 这个写法很怪异哦,但确实管用。el-checkbox 绑定的 label 是双向绑定的值,也就是选中之后传到表单数据里面的值,一般设置为 id,然后…...

单元测试Mockito笔记
文章目录 单元测试Mockito1. 入门1.1 什么是Mockito1.2 优势1.3 原理 2. 使用2.0 环境准备2.1 Mock1) Mock对象创建2) 配置Mock对象的行为(打桩)3) 验证方法调用4) 参数匹配5) 静态方法 2.2 常用注解1) Mock2) BeforeEach 与 BeforeAfter3) InjectMocks4) Spy5) Captor6) RunWi…...

基于SpringBoot+VueJS+微信小程序技术的图书森林共享小程序设计与实现:7000字论文+源代码参考
博主介绍:硕士研究生,专注于信息化技术领域开发与管理,会使用java、标准c/c等开发语言,以及毕业项目实战✌ 从事基于java BS架构、CS架构、c/c 编程工作近16年,拥有近12年的管理工作经验,拥有较丰富的技术架…...

GitHub连接超时问题 Recv failure: Connection was reset
用手机热点WIF拉取git项目的时候,遇到Recv failure: Connection was reset问题。 解决办法 一、手动开启本地代理 二、在终端(cmd)输入命令 git config --global http.proxy http://127.0.0.1:7890 git config --global https.proxy https:…...

浅谈PostCSS
1. 背景 css的预处理器语言(比如 sass, less, stylus)的扩展性不好,你可以使用它们已有的功能,但如果想做扩展就没那么容易。 sass是很常用的css预处理器语言,在webpack中要使用它,…...
详解)
后进先出(LIFO)详解
LIFO 是 Last In, First Out 的缩写,中文译为后进先出。这是一种数据结构的工作原则,类似于一摞盘子或一叠书本: 最后放进去的元素最先出来 -想象往筒状容器里放盘子: (1)你放进的最后一个盘子(…...
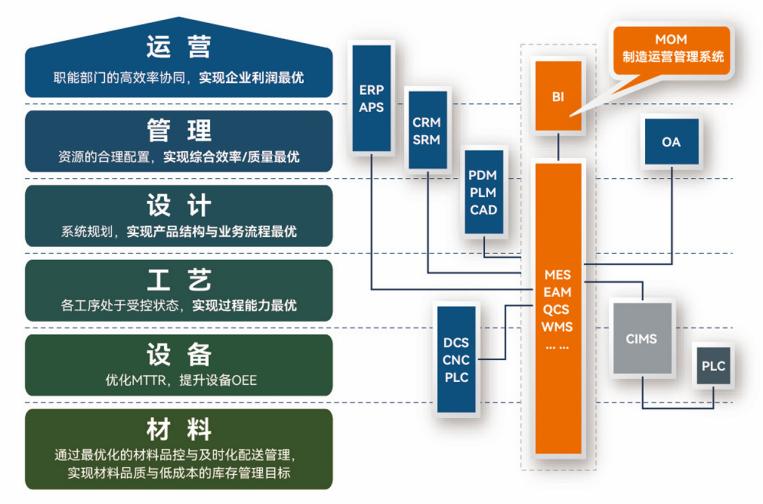
盘古信息PCB行业解决方案:以全域场景重构,激活智造新未来
一、破局:PCB行业的时代之问 在数字经济蓬勃发展的浪潮中,PCB(印制电路板)作为 “电子产品之母”,其重要性愈发凸显。随着 5G、人工智能等新兴技术的加速渗透,PCB行业面临着前所未有的挑战与机遇。产品迭代…...

Qt Widget类解析与代码注释
#include "widget.h" #include "ui_widget.h"Widget::Widget(QWidget *parent): QWidget(parent), ui(new Ui::Widget) {ui->setupUi(this); }Widget::~Widget() {delete ui; }//解释这串代码,写上注释 当然可以!这段代码是 Qt …...
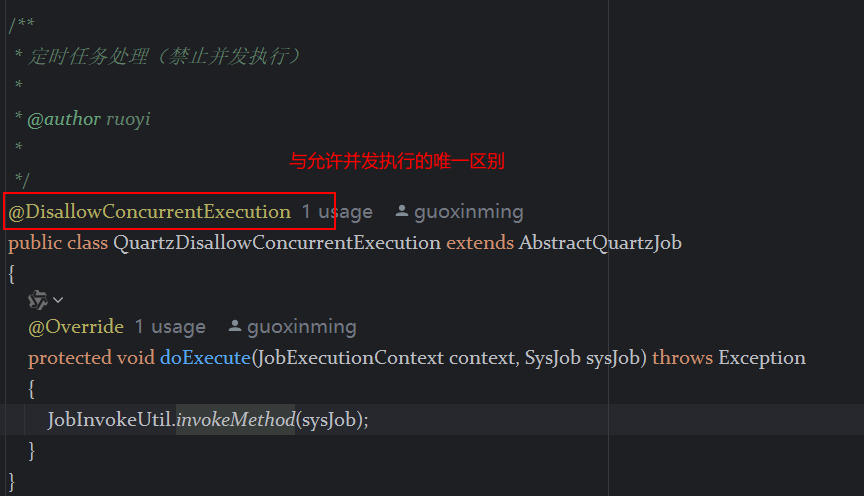
定时器任务——若依源码分析
分析util包下面的工具类schedule utils: ScheduleUtils 是若依中用于与 Quartz 框架交互的工具类,封装了定时任务的 创建、更新、暂停、删除等核心逻辑。 createScheduleJob createScheduleJob 用于将任务注册到 Quartz,先构建任务的 JobD…...

对WWDC 2025 Keynote 内容的预测
借助我们以往对苹果公司发展路径的深入研究经验,以及大语言模型的分析能力,我们系统梳理了多年来苹果 WWDC 主题演讲的规律。在 WWDC 2025 即将揭幕之际,我们让 ChatGPT 对今年的 Keynote 内容进行了一个初步预测,聊作存档。等到明…...

Axios请求超时重发机制
Axios 超时重新请求实现方案 在 Axios 中实现超时重新请求可以通过以下几种方式: 1. 使用拦截器实现自动重试 import axios from axios;// 创建axios实例 const instance axios.create();// 设置超时时间 instance.defaults.timeout 5000;// 最大重试次数 cons…...
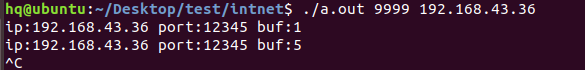
网络编程(UDP编程)
思维导图 UDP基础编程(单播) 1.流程图 服务器:短信的接收方 创建套接字 (socket)-----------------------------------------》有手机指定网络信息-----------------------------------------------》有号码绑定套接字 (bind)--------------…...

多模态图像修复系统:基于深度学习的图片修复实现
多模态图像修复系统:基于深度学习的图片修复实现 1. 系统概述 本系统使用多模态大模型(Stable Diffusion Inpainting)实现图像修复功能,结合文本描述和图片输入,对指定区域进行内容修复。系统包含完整的数据处理、模型训练、推理部署流程。 import torch import numpy …...
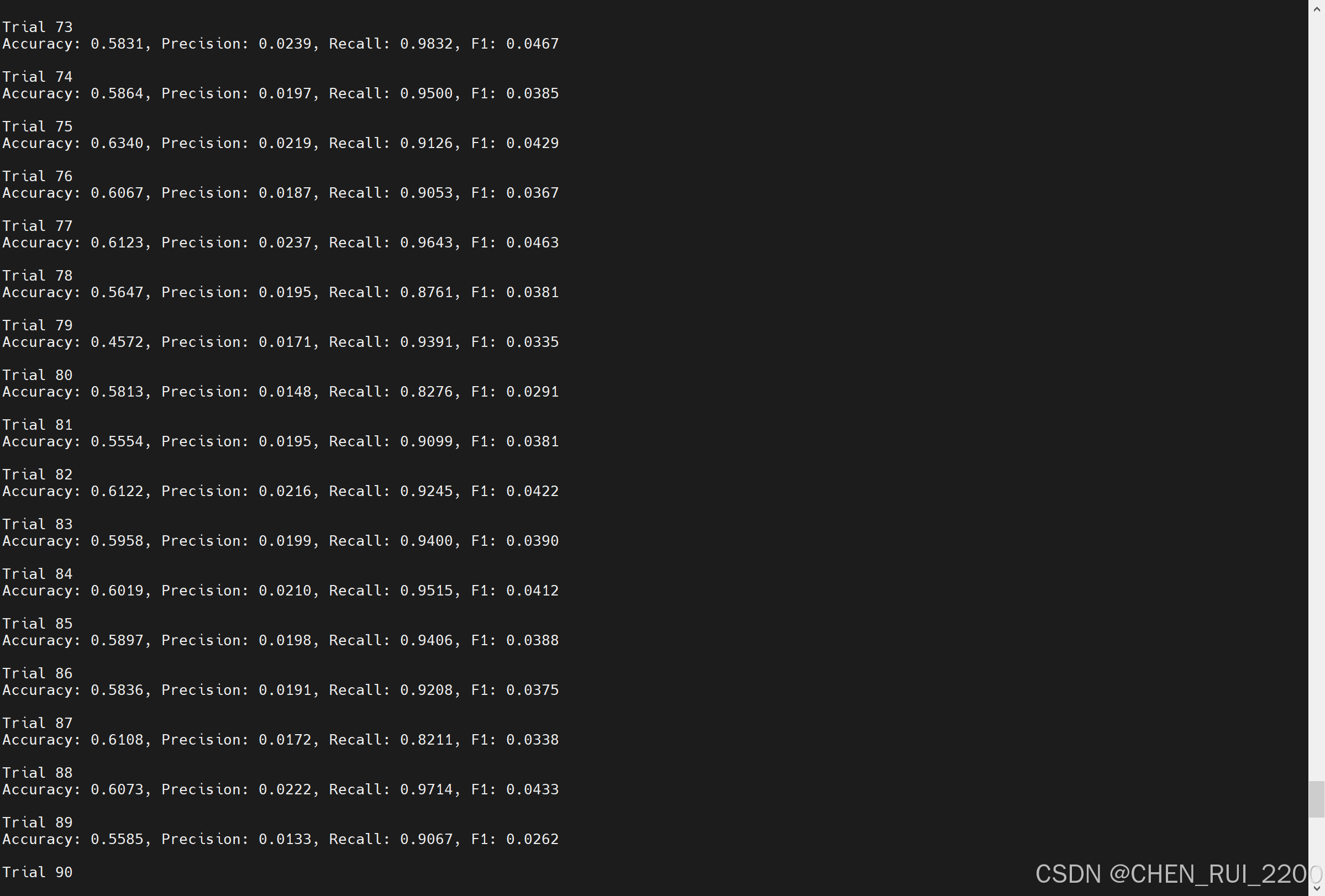
逻辑回归暴力训练预测金融欺诈
简述 「使用逻辑回归暴力预测金融欺诈,并不断增加特征维度持续测试」的做法,体现了一种逐步建模与迭代验证的实验思路,在金融欺诈检测中非常有价值,本文作为一篇回顾性记录了早年间公司给某行做反欺诈预测用到的技术和思路。百度…...
基于Java+VUE+MariaDB实现(Web)仿小米商城
仿小米商城 环境安装 nodejs maven JDK11 运行 mvn clean install -DskipTestscd adminmvn spring-boot:runcd ../webmvn spring-boot:runcd ../xiaomi-store-admin-vuenpm installnpm run servecd ../xiaomi-store-vuenpm installnpm run serve 注意:运行前…...
