Python酷库之旅-第三方库Pandas(064)
目录
一、用法精讲
251、pandas.Series.tz_localize方法
251-1、语法
251-2、参数
251-3、功能
251-4、返回值
251-5、说明
251-6、用法
251-6-1、数据准备
251-6-2、代码示例
251-6-3、结果输出
252、pandas.Series.at_time方法
252-1、语法
252-2、参数
252-3、功能
252-4、返回值
252-5、说明
252-6、用法
252-6-1、数据准备
252-6-2、代码示例
252-6-3、结果输出
253、pandas.Series.between_time方法
253-1、语法
253-2、参数
253-3、功能
253-4、返回值
253-5、说明
253-6、用法
253-6-1、数据准备
253-6-2、代码示例
253-6-3、结果输出
254、pandas.Series.str方法
254-1、语法
254-2、参数
254-3、功能
254-3-1、转换大小写
254-3-2、字符串匹配和搜索
254-3-3、字符串替换和去除
254-3-4、字符串分割和连接
254-3-5、提取和访问子串
254-3-6、格式化和填充
254-3-7、长度和计数
254-4、返回值
254-5、说明
254-6、用法
254-6-1、数据准备
254-6-2、代码示例
254-6-3、结果输出
255、pandas.Series.cat方法
255-1、语法
255-2、参数
255-3、功能
255-4、返回值
255-5、说明
255-6、用法
255-6-1、数据准备
255-6-2、代码示例
255-6-3、结果输出
二、推荐阅读
1、Python筑基之旅
2、Python函数之旅
3、Python算法之旅
4、Python魔法之旅
5、博客个人主页



一、用法精讲
251、pandas.Series.tz_localize方法
251-1、语法
# 251、pandas.Series.tz_localize方法
pandas.Series.tz_localize(tz, axis=0, level=None, copy=None, ambiguous='raise', nonexistent='raise')
Localize tz-naive index of a Series or DataFrame to target time zone.This operation localizes the Index. To localize the values in a timezone-naive Series, use Series.dt.tz_localize().Parameters:
tzstr or tzinfo or None
Time zone to localize. Passing None will remove the time zone information and preserve local time.axis{0 or ‘index’, 1 or ‘columns’}, default 0
The axis to localizelevelint, str, default None
If axis ia a MultiIndex, localize a specific level. Otherwise must be None.copybool, default True
Also make a copy of the underlying data.NoteThe copy keyword will change behavior in pandas 3.0. Copy-on-Write will be enabled by default, which means that all methods with a copy keyword will use a lazy copy mechanism to defer the copy and ignore the copy keyword. The copy keyword will be removed in a future version of pandas.You can already get the future behavior and improvements through enabling copy on write pd.options.mode.copy_on_write = Trueambiguous‘infer’, bool-ndarray, ‘NaT’, default ‘raise’
When clocks moved backward due to DST, ambiguous times may arise. For example in Central European Time (UTC+01), when going from 03:00 DST to 02:00 non-DST, 02:30:00 local time occurs both at 00:30:00 UTC and at 01:30:00 UTC. In such a situation, the ambiguous parameter dictates how ambiguous times should be handled.‘infer’ will attempt to infer fall dst-transition hours based on orderbool-ndarray where True signifies a DST time, False designates a non-DST time (note that this flag is only applicable for ambiguous times)‘NaT’ will return NaT where there are ambiguous times‘raise’ will raise an AmbiguousTimeError if there are ambiguous times.nonexistentstr, default ‘raise’
A nonexistent time does not exist in a particular timezone where clocks moved forward due to DST. Valid values are:‘shift_forward’ will shift the nonexistent time forward to the closest existing time‘shift_backward’ will shift the nonexistent time backward to the closest existing time‘NaT’ will return NaT where there are nonexistent timestimedelta objects will shift nonexistent times by the timedelta‘raise’ will raise an NonExistentTimeError if there are nonexistent times.Returns:
Series/DataFrame
Same type as the input.Raises:
TypeError
If the TimeSeries is tz-aware and tz is not None.251-2、参数
251-2-1、tz(必须):字符串或pytz.timezone对象,指定要本地化的时区,可以是时区的名称(如'US/Eastern')或一个pytz时区对象。
251-2-2、axis(可选,默认值为0):整数或字符串,指定沿着哪个轴进行本地化,对于Series,这个参数通常被忽略,因为Series只有一个轴,即轴0。
251-2-3、level(可选,默认值为None):整数或字符串,当处理多级索引(MultiIndex)时,此参数指定要本地化的级别,对普通的Series对象通常不需要使用。
251-2-4、copy(可选,默认值为None):布尔值,如果设置为False,会尝试在原地修改Series;如果为True,则会返回一个新的Series;默认值为None时,会自动选择合适的策略。
251-2-5、ambiguous(可选,默认值为'raise'):字符串,处理夏令时切换期间的模糊时间,如果设置为'raise',则在出现模糊时间时抛出异常;如果设置为'NaT',则将这些时间标记为NaT(Not a Time);如果设置为'ignore',则保持原样。
251-2-6、nonexistent(可选,默认值为'raise'):字符串,处理由于时区转换而不存在的时间,如果设置为'raise',则在出现不存在的时间时抛出异常;如果设置为'NaT',则将这些时间标记为NaT(Not a Time);如果设置为'shift',则将这些时间移到最近的存在时间。
251-3、功能
用于将一个没有时区的Series对象的时间戳本地化到指定的时区。
251-4、返回值
返回一个新的Series对象,其中时间戳已经被本地化到指定的时区,如果copy=False,可能会修改原始Series对象(具体取决于是否需要复制),新Series的时间戳将带有时区信息,格式为DatetimeIndex。
251-5、说明
无
251-6、用法
251-6-1、数据准备
无251-6-2、代码示例
# 251、pandas.Series.tz_localize方法
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series(range(7),index=pd.DatetimeIndex(['2024-8-2 01:30:00','2024-8-2 02:00:00','2024-8-2 02:30:00','2024-8-2 03:00:00','2024-8-2 03:30:00','2024-8-2 04:00:00','2024-8-2 04:30:00']))
data = s.tz_localize('CET', ambiguous='infer')
print(data)251-6-3、结果输出
# 251、pandas.Series.tz_localize方法
# 2024-08-02 01:30:00+02:00 0
# 2024-08-02 02:00:00+02:00 1
# 2024-08-02 02:30:00+02:00 2
# 2024-08-02 03:00:00+02:00 3
# 2024-08-02 03:30:00+02:00 4
# 2024-08-02 04:00:00+02:00 5
# 2024-08-02 04:30:00+02:00 6
# dtype: int64252、pandas.Series.at_time方法
252-1、语法
# 252、pandas.Series.at_time方法
pandas.Series.at_time(time, asof=False, axis=None)
Select values at particular time of day (e.g., 9:30AM).Parameters:
time
datetime.time or str
The values to select.axis
{0 or ‘index’, 1 or ‘columns’}, default 0
For Series this parameter is unused and defaults to 0.Returns:
Series or DataFrame
Raises:
TypeError
If the index is not a DatetimeIndex252-2、参数
252-2-1、time(必须):字符串或datetime.time,指定要提取的时间,这个时间应当是datetime.time对象或符合时间格式的字符串(如'06:18')。
252-2-2、asof(可选,默认值为False):布尔值,如果设置为True,方法将返回在指定时间点之前最近的时间;如果为False,则方法仅返回与指定时间完全匹配的时间点的数据。
252-2-3、axis(可选,默认值为None):整数或字符串,指定沿着哪个轴进行操作,在Series中,通常可以忽略这个参数,因为Series只有一个轴(即轴0)。
252-3、功能
用于从Series中筛选出指定时间点的数据,该方法将时间与Series的索引进行匹配,提取出符合指定时间的数据行,可以用来获取一天中某个特定时间点的数据,忽略具体的日期信息。
252-4、返回值
返回一个新的Series对象,其中包含了在指定时间点的数据,返回的Series中的索引是与指定时间匹配的时间戳。
252-5、说明
无
252-6、用法
252-6-1、数据准备
无252-6-2、代码示例
# 252、pandas.Series.at_time方法
import pandas as pd
# 创建一个时间序列
idx = pd.date_range('2024-01-01', periods=4, freq='h')
data = pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4], index=idx)
# 提取每天的'02:00'数据
result = data.at_time('02:00')
print("提取的时间点数据:")
print(result)252-6-3、结果输出
# 252、pandas.Series.at_time方法
# 提取的时间点数据:
# 2024-01-01 02:00:00 3
# Freq: h, dtype: int64253、pandas.Series.between_time方法
253-1、语法
# 253、pandas.Series.between_time方法
pandas.Series.between_time(start_time, end_time, inclusive='both', axis=None)
Select values between particular times of the day (e.g., 9:00-9:30 AM).By setting start_time to be later than end_time, you can get the times that are not between the two times.Parameters:
start_time
datetime.time or str
Initial time as a time filter limit.end_time
datetime.time or str
End time as a time filter limit.inclusive
{“both”, “neither”, “left”, “right”}, default “both”
Include boundaries; whether to set each bound as closed or open.axis
{0 or ‘index’, 1 or ‘columns’}, default 0
Determine range time on index or columns value. For Series this parameter is unused and defaults to 0.Returns:
Series or DataFrame
Data from the original object filtered to the specified dates range.Raises:
TypeError
If the index is not a DatetimeIndex253-2、参数
253-2-1、start_time(必须):字符串或datetime.time,指定时间范围的开始时间,应当是datetime.time对象或符合时间格式的字符串(如'06:18')。
253-2-2、end_time(必须):字符串或datetime.time,指定时间范围的结束时间,应当是datetime.time对象或符合时间格式的字符串(如'17:30')。
253-2-3、inclusive(可选,默认值为'both'):{'both','neither','left','right'},指定时间范围的边界条件,可以选择以下四个值:
- 'both':包括开始时间和结束时间。
- 'neither':不包括开始时间和结束时间。
- 'left':包括开始时间,但不包括结束时间。
- 'right':不包括开始时间,但包括结束时间。
253-2-4、axis(可选,默认值为None):整数或字符串,指定沿着哪个轴进行操作,在Series中,通常可以忽略这个参数,因为Series只有一个轴(即轴0)。
253-3、功能
用于从Series中筛选出在指定时间范围内的数据,它将时间与Series的索引进行匹配,提取出在开始时间和结束时间之间的数据,该方法可以用来获取一天中某个时间段的数据,忽略日期信息。
253-4、返回值
返回一个新的Series对象,其中包含了在指定时间范围内的数据,返回的Series中的索引是与指定时间范围匹配的时间戳。
253-5、说明
无
253-6、用法
253-6-1、数据准备
无253-6-2、代码示例
# 253、pandas.Series.between_time方法
import pandas as pd
# 创建一个时间序列
idx = pd.date_range('2024-08-01', periods=24, freq='h')
data = pd.Series(range(24), index=idx)
# 提取每天的'09:00'到'17:00'之间的数据
result = data.between_time('09:00', '17:00')
print("提取的时间范围数据:")
print(result)253-6-3、结果输出
# 253、pandas.Series.between_time方法
# 提取的时间范围数据:
# 2024-08-01 09:00:00 9
# 2024-08-01 10:00:00 10
# 2024-08-01 11:00:00 11
# 2024-08-01 12:00:00 12
# 2024-08-01 13:00:00 13
# 2024-08-01 14:00:00 14
# 2024-08-01 15:00:00 15
# 2024-08-01 16:00:00 16
# 2024-08-01 17:00:00 17
# Freq: h, dtype: int64254、pandas.Series.str方法
254-1、语法
# 254、pandas.Series.str方法
pandas.Series.str()
Vectorized string functions for Series and Index.NAs stay NA unless handled otherwise by a particular method. Patterned after Python’s string methods, with some inspiration from R’s stringr package.254-2、参数
无
254-3、功能
254-3-1、转换大小写
254-3-1-1、str.lower():将每个字符串转换为小写。
254-3-1-2、str.upper():将每个字符串转换为大写。
254-3-2、字符串匹配和搜索
254-3-2-1、str.contains(pattern):检查每个字符串是否包含指定的模式,返回布尔值的 Series。
254-3-2-2、str.startswith(prefix):检查每个字符串是否以指定的前缀开头,返回布尔值的 Series。
254-3-2-3、str.endswith(suffix):检查每个字符串是否以指定的后缀结尾,返回布尔值的 Series。
254-3-3、字符串替换和去除
254-3-3-1、str.replace(old,new):将每个字符串中的指定内容替换为新的内容。
254-3-3-2、str.strip():去除每个字符串的前后空白字符。
254-3-4、字符串分割和连接
254-3-4-1、str.split(separator):按照指定分隔符将字符串分割为列表。
254-3-4-2、str.join(sep):使用指定的分隔符连接列表中的元素。
254-3-5、提取和访问子串
254-3-5-1、str.extract(pattern):使用正则表达式提取匹配的子字符串。
254-3-5-2、str.get(i):获取每个字符串的第i个字符。
254-3-6、格式化和填充
254-3-6-1、str.pad(width,side='left',fillchar=''):使用指定字符填充字符串,使其达到指定宽度。可以选择在左、右或两侧填充。
254-3-6-2、str.zfill(width):在左侧填充零,使字符串达到指定宽度。
254-3-7、长度和计数
254-3-7-1、str.len():返回每个字符串的长度。
254-3-7-2、str.count(pattern):计算每个字符串中匹配模式的出现次数。
254-4、返回值
功能不同,产生了不同的返回值。
254-5、说明
无
254-6、用法
254-6-1、数据准备
无254-6-2、代码示例
# 254、pandas.Series.str方法
# 254-1、转换大小写
# 254-1-1、str.lower():将每个字符串转换为小写
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series(['Hello', 'World', 'Pandas'])
s_lower = s.str.lower()
print(s_lower, end='\n\n')# 254-1-2、str.upper():将每个字符串转换为大写
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series(['Hello', 'World', 'Pandas'])
s_upper = s.str.upper()
print(s_upper, end='\n\n')# 254-2、字符串匹配和搜索
# 254-2-1、str.contains(pattern):检查每个字符串是否包含指定的模式,返回布尔值的Series
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series(['Hello', 'World', 'Pandas'])
s_contains = s.str.contains('o')
print(s_contains, end='\n\n')# 254-2-2、str.startswith(prefix):检查每个字符串是否以指定的前缀开头,返回布尔值的Series
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series(['Hello', 'World', 'Pandas'])
s_startswith = s.str.startswith('P')
print(s_startswith, end='\n\n')# 254-2-3、str.endswith(suffix):检查每个字符串是否以指定的后缀结尾,返回布尔值的Series
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series(['Hello', 'World', 'Pandas'])
s_endswith = s.str.endswith('s')
print(s_endswith, end='\n\n')# 254-3、字符串替换和去除
# 254-3-1、str.replace(old, new):将每个字符串中的指定内容替换为新的内容
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series(['Hello', 'World', 'Pandas'])
s_replace = s.str.replace('o', '0')
print(s_replace, end='\n\n')# 254-3-2、str.strip():去除每个字符串的前后空白字符
import pandas as pd
s_with_spaces = pd.Series([' Hello ', ' World ', ' Pandas '])
s_strip = s_with_spaces.str.strip()
print(s_strip, end='\n\n')# 254-4、字符串分割和连接
# 254-4-1、str.split(separator):按照指定分隔符将字符串分割为列表
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series(['Hello', 'World', 'Pandas'])
s_split = s.str.split('l')
print(s_split, end='\n\n')# 254-4-2、str.join(sep):使用指定的分隔符连接列表中的元素
import pandas as pd
s_join = pd.Series([['a', 'b', 'c'], ['d', 'e'], ['f']])
s_joined = s_join.str.join('-')
print(s_joined, end='\n\n')# 254-5、提取和访问子串
# 254-5-1、str.extract(pattern):使用正则表达式提取匹配的子字符串
import pandas as pd
s_dates = pd.Series(['2022-08-01', '2023-07-06', '2024-08-03'])
s_extract = s_dates.str.extract(r'(\d{4})-(\d{2})-(\d{2})')
print(s_extract, end='\n\n')# 254-5-2、str.get(i):获取每个字符串的第i个字符
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series(['Hello', 'World', 'Pandas'])
s_get = s.str.get(1)
print(s_get, end='\n\n')# 254-6、格式化和填充
# 254-6-1、str.pad(width, side='left', fillchar=' '):使用指定字符填充字符串,使其达到指定宽度。可以选择在左、右或两侧填充
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series(['Hello', 'World', 'Pandas'])
s_pad = s.str.pad(10, side='right', fillchar='*')
print(s_pad, end='\n\n')# 254-6-2、str.zfill(width):在左侧填充零,使字符串达到指定宽度
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series(['Hello', 'World', 'Pandas'])
s_zfill = s.str.zfill(10)
print(s_zfill, end='\n\n')# 254-7、长度和计数
# 254-7-1、str.len():返回每个字符串的长度
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series(['Hello', 'World', 'Pandas'])
s_len = s.str.len()
print(s_len, end='\n\n')# 254-7-2、str.count(pattern):计算每个字符串中匹配模式的出现次数
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series(['Hello', 'World', 'Pandas'])
s_count = s.str.count('l')
print(s_count, end='\n\n')# 254-8、综合案例
import pandas as pd
# 创建一个包含混合文本数据的Series
data = pd.Series([' Myelsa ', 'bob123', 'C@r0l', 'DAVID'])
# 清洗和标准化文本数据
cleaned_data = data.str.strip().str.lower().str.replace(r'\d+', '').str.replace(r'[^a-z]', '')
print(cleaned_data)254-6-3、结果输出
# 254、pandas.Series.str方法
# 254-1、转换大小写
# 254-1-1、str.lower():将每个字符串转换为小写
# 0 hello
# 1 world
# 2 pandas
# dtype: object# 254-1-2、str.upper():将每个字符串转换为大写
# 0 HELLO
# 1 WORLD
# 2 PANDAS
# dtype: object# 254-2、字符串匹配和搜索
# 254-2-1、str.contains(pattern):检查每个字符串是否包含指定的模式,返回布尔值的Series
# 0 True
# 1 True
# 2 False
# dtype: bool# 254-2-2、str.startswith(prefix):检查每个字符串是否以指定的前缀开头,返回布尔值的Series
# 0 False
# 1 False
# 2 True
# dtype: bool# 254-2-3、str.endswith(suffix):检查每个字符串是否以指定的后缀结尾,返回布尔值的Series
# 0 False
# 1 False
# 2 True
# dtype: bool# 254-3、字符串替换和去除
# 254-3-1、str.replace(old, new):将每个字符串中的指定内容替换为新的内容
# 0 Hell0
# 1 W0rld
# 2 Pandas
# dtype: object# 254-3-2、str.strip():去除每个字符串的前后空白字符
# 0 Hello
# 1 World
# 2 Pandas
# dtype: object# 254-4、字符串分割和连接
# 254-4-1、str.split(separator):按照指定分隔符将字符串分割为列表
# 0 [He, , o]
# 1 [Wor, d]
# 2 [Pandas]
# dtype: object# 254-4-2、str.join(sep):使用指定的分隔符连接列表中的元素
# 0 a-b-c
# 1 d-e
# 2 f
# dtype: object# 254-5、提取和访问子串
# 254-5-1、str.extract(pattern):
# 0 1 2
# 0 2022 08 01
# 1 2023 07 06
# 2 2024 08 03# 254-5-2、str.get(i):获取每个字符串的第i个字符
# 0 e
# 1 o
# 2 a
# dtype: object# 254-6、格式化和填充
# 254-6-1、str.pad(width, side='left', fillchar=' '):使用指定字符填充字符串,使其达到指定宽度。可以选择在左、右或两侧填充
# 0 Hello*****
# 1 World*****
# 2 Pandas****
# dtype: object# 254-6-2、str.zfill(width):在左侧填充零,使字符串达到指定宽度
# 0 00000Hello
# 1 00000World
# 2 0000Pandas
# dtype: object# 254-7、长度和计数
# 254-7-1、str.len():返回每个字符串的长度
# 0 5
# 1 5
# 2 6
# dtype: int64# 254-7-2、str.count(pattern):计算每个字符串中匹配模式的出现次数
# 0 2
# 1 1
# 2 0
# dtype: int64# 254-8、综合案例
# 0 myelsa
# 1 bob123
# 2 c@r0l
# 3 david
# dtype: object255、pandas.Series.cat方法
255-1、语法
# 255、pandas.Series.cat方法
pandas.Series.cat()
Accessor object for categorical properties of the Series values.Parameters:
data
Series or CategoricalIndex255-2、参数
无
255-3、功能
提供了对类别数据的创建、修改、重命名和管理等功能,使得处理数据时可以利用类别数据的特性进行更加细致的操作和分析。
255-4、返回值
返回值是一个Categorical对象,它提供了关于类别数据的详细信息,包括类别的列表、类别的顺序(如果有的话)等,该对象使得对类别数据的进一步操作和分析更加灵活和高效。
255-5、说明
无
255-6、用法
255-6-1、数据准备
无255-6-2、代码示例
# 255、pandas.Series.cat方法
import pandas as pd
# 创建一个包含类别数据的 Series
data = pd.Series(['apple', 'banana', 'apple', 'orange', 'banana'], dtype='category')
# 输出原始数据及其类别
print("Original Series:")
print(data)
print("Categories:")
print(data.cat.categories, end='\n\n')# 255-1、设置类别的顺序
data = data.cat.set_categories(['banana', 'apple', 'orange'], ordered=True)
print("Ordered Categories:")
print(data.cat.categories, end='\n\n')# 255-2、 添加新类别
data = data.cat.add_categories(['grape'])
print("Categories after Adding 'grape':")
print(data.cat.categories, end='\n\n')# 255-3、 删除类别
data = data.cat.remove_categories(['orange'])
print("Categories after Removing 'orange':")
print(data.cat.categories, end='\n\n')# 255-4、 重命名类别
data = data.cat.rename_categories({'banana': 'yellow_banana', 'apple': 'green_apple'})
print("Categories after Renaming:")
print(data.cat.categories, end='\n\n')# 255-5、 获取类别的整数编码
print("Integer Encoding of the Series:")
print(data.cat.codes, end='\n\n')# 255-6、查看数据和类别编码
print("Data with Integer Encoding:")
print(data)255-6-3、结果输出
# 255、pandas.Series.cat方法
# Original Series:
# 0 apple
# 1 banana
# 2 apple
# 3 orange
# 4 banana
# dtype: category
# Categories (3, object): ['apple', 'banana', 'orange']
# Categories:
# Index(['apple', 'banana', 'orange'], dtype='object')# 255-1、设置类别的顺序
# Ordered Categories:
# Index(['banana', 'apple', 'orange'], dtype='object')# 255-2、 添加新类别
# Categories after Adding 'grape':
# Index(['banana', 'apple', 'orange', 'grape'], dtype='object')# 255-3、 删除类别
# Categories after Removing 'orange':
# Index(['banana', 'apple', 'grape'], dtype='object')# 255-4、 重命名类别
# Categories after Renaming:
# Index(['yellow_banana', 'green_apple', 'grape'], dtype='object')# 255-5、 获取类别的整数编码
# Integer Encoding of the Series:
# 0 1
# 1 0
# 2 1
# 3 -1
# 4 0
# dtype: int8# 255-6、查看数据和类别编码
# Data with Integer Encoding:
# 0 green_apple
# 1 yellow_banana
# 2 green_apple
# 3 NaN
# 4 yellow_banana
# dtype: category
# Categories (3, object): ['yellow_banana' < 'green_apple' < 'grape']二、推荐阅读
1、Python筑基之旅
2、Python函数之旅
3、Python算法之旅
4、Python魔法之旅
5、博客个人主页
相关文章:

Python酷库之旅-第三方库Pandas(064)
目录 一、用法精讲 251、pandas.Series.tz_localize方法 251-1、语法 251-2、参数 251-3、功能 251-4、返回值 251-5、说明 251-6、用法 251-6-1、数据准备 251-6-2、代码示例 251-6-3、结果输出 252、pandas.Series.at_time方法 252-1、语法 252-2、参数 252-3…...
)
MATLAB基础操作(二)
11.求方程2x^5-3x^371x^2-9x130的全部跟 >> p[2,0,-3,71,-9,13]; >> xroots(p); 12.求解线性方程组2x3y-z2 8x2y3z4 45x3y9z23 >> a[2,3,-1;8,2,3;45,3,9];%建立系数矩阵a >> b[2,4,23]%建立列向量b >> …...

win10 繁体简体字切换
1. 使用快捷键 Ctrl Shift F 2. 在语言设置中更改 | 点击任务栏上的“开始”按钮。 | 选择“设置”(齿轮图标)。 | 在弹出的“Windows 设置”窗口中,点击“时间和语言”。 | 选择“语言”选项。 | 在右侧找到您正在使用的输入法ÿ…...

R语言统计分析——描述性统计
参考资料:R语言实战【第2版】 1、整体统计 对于R语言基础安装,可以使用summary()函数来获取描述性统计量。summary()函数提供了最小值、最大值、四分位数、中位数和算术平均数,以及因子向量和逻辑向量的频数统计。 myvars<-c("mpg&…...

为什么需要合成数据进行机器学习
为什么需要合成数据进行机器学习 文章目录 一、说明二、数据缩放问题三、合成数据的前景与进展四、将合成数据与 LLM 结合使用的最佳实践五、通过合成数据释放创新 一、说明 数据是人工智能的命脉。如果没有高质量的、具有代表性的训练数据,我们的机器学习模型将毫无…...
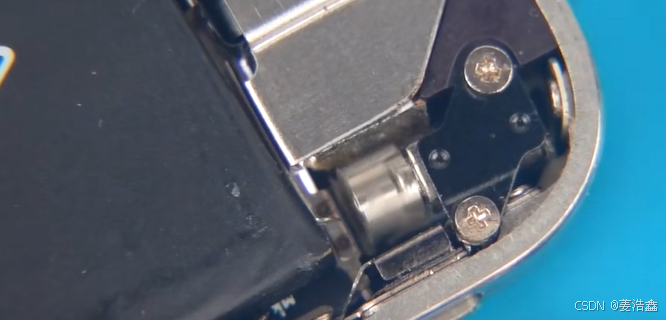
传统CS网络的新生——基于2G网络的远程灌溉实现
概述:iphone 实现远程电话触发,实现灌溉绿植的一般方法 方法一: 远程电话触发,音频线左右声道会产生一个信号,可以在后端利用SR锁存器暂存信号,后级可以接相应的控制电路实现灌溉。 方法二: 同…...
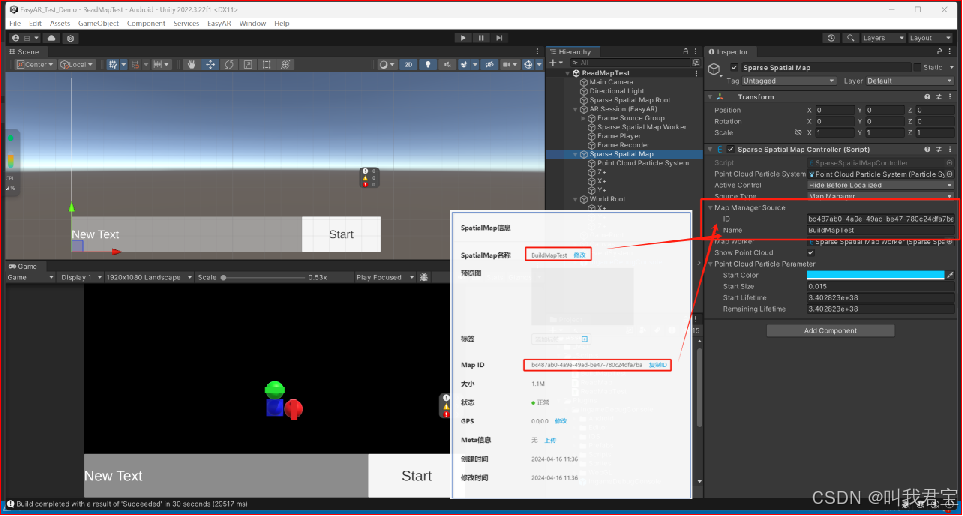
EasyAR_稀疏空间图
EasyAR_稀疏空间图 EasyAR4.6.3 丨 Unity2020.3.15f2 1.创建稀疏空间地图 在EasyAR开发中心后台创建Scene许可证密钥,并且使用稀疏空间地图 2.设置稀疏空间地图库名,对稀疏空间地图进行管理,设置密钥 3.复制密钥到Unity中 添加Spatial Map Ap…...

设计模式 - Singleton pattern 单例模式
文章目录 定义单例模式的实现构成构成UML图 单例模式的六种实现懒汉式-线程不安全懒汉式-线程安全饿汉式-线程安全双重校验锁-线程安全静态内部类实现枚举实现 总结其他设计模式文章:最后 定义 单例模式是一种创建型设计模式,它用来保证一个类只有一个实…...
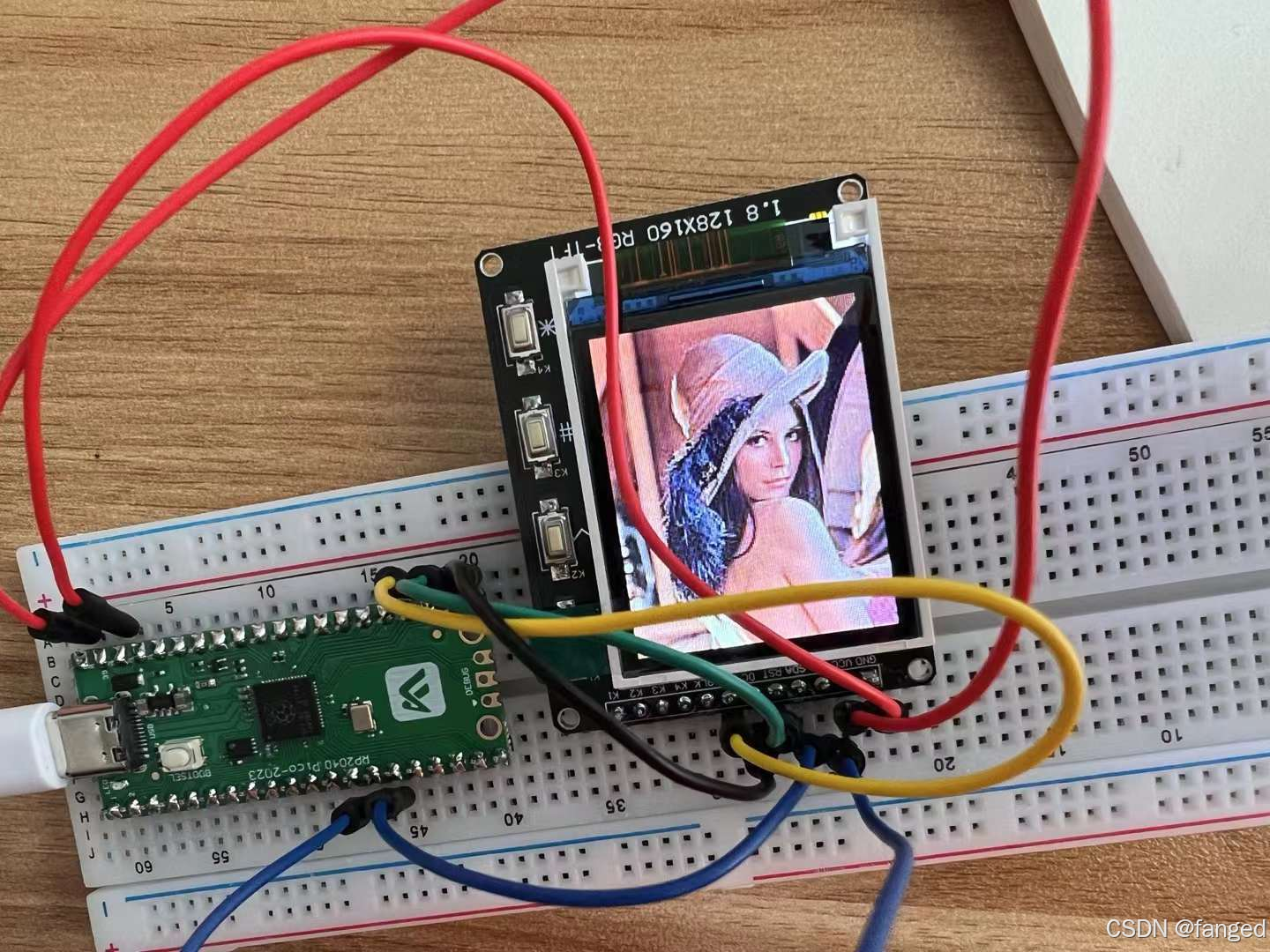
显示学习5(基于树莓派Pico) -- 彩色LCD的驱动
和这篇也算是姊妹篇,只是一个侧重SPI协议,一个侧重显示驱动。 总线学习3--SPI-CSDN博客 驱动来自:https://github.com/boochow/MicroPython-ST7735 所以这里主要还是学习。 代码Init def __init__( self, spi, aDC, aReset, aCS) :"&…...

ros vscode配置gdb调试
ros工程vscode下配置gdb的调试环境需要添加几个配置文件,下面贴一下用得到的几个配置文件。 c_cpp_properties.json,这个配置作用是方便代码跳转。 {"configurations": [{"browse": {"databaseFilename": "${defau…...

C 环境设置
C 环境设置 C语言作为一种广泛使用的编程语言,其环境设置是每个开发者必须掌握的基本技能。本文将详细介绍如何在不同的操作系统上设置C语言开发环境,包括Windows、macOS和Linux系统。我们将涵盖安装编译器、配置开发环境以及编写和运行第一个C程序。 Windows系统上的C环境…...

Linux-ubuntu操作系统装机步骤
1、下载iso镜像 方法一、访问Ubuntu官网 方法二、163镜像 2、制作U盘启动盘 方法一、UltraISO(软碟通)写入硬盘映像,参考该 [链接] 方法二、Rufus,参考该 [链接] 3、安装 参考该 [链接] 4、相关配置 Ubuntu 换源 参考链接…...

马尔科夫毯:信息屏障与状态独立性的守护者
马尔科夫毯(Markov Blanket)是概率图模型中的一个重要概念,用于描述某一节点在网络中的信息独立性和条件依赖关系。马尔科夫毯定义了一个节点的“信息屏障”,即给定马尔科夫毯中节点的状态,该节点与网络中其他节点的状…...

Pandas的30个高频函数使用介绍
Pandas是Python中用于数据分析的一个强大的库,它提供了许多功能丰富的函数。本文介绍其中高频使用的30个函数。 read_csv(): 从CSV文件中读取数据并创建DataFrame对象。 import pandas as pd df pd.read_csv(data.csv) read_excel(): 从Excel文件中读取数据…...

1. protobuf学习
文章目录 1. protobuf介绍1.1 ProtoBuf使用场景说明2. 其他序列化介绍2.1 Json2.1.1 使用Json序列化2.1.2 Json反序列化2.2 其他可选地序列化和反序列化3. protoBuf3.1 protobuf数据类型3.2 protobuf使用步骤3.2.1 定义proto文件3.2.2 编译proto文件3.2.2.1 安装protocol buffe…...

Java面试题:SpringBean的生命周期
SpringBean的生命周期 BeanDefinition Spring容器在进行实例化时,会将xml配置的信息封装成BeanDefinition对象 Spring根据BeanDefinition来创建Bean对象 包含很多属性来描述Bean 包括 beanClassName:bean的类名,通过类名进行反射 initMethodName:初始化方法名称 proper…...
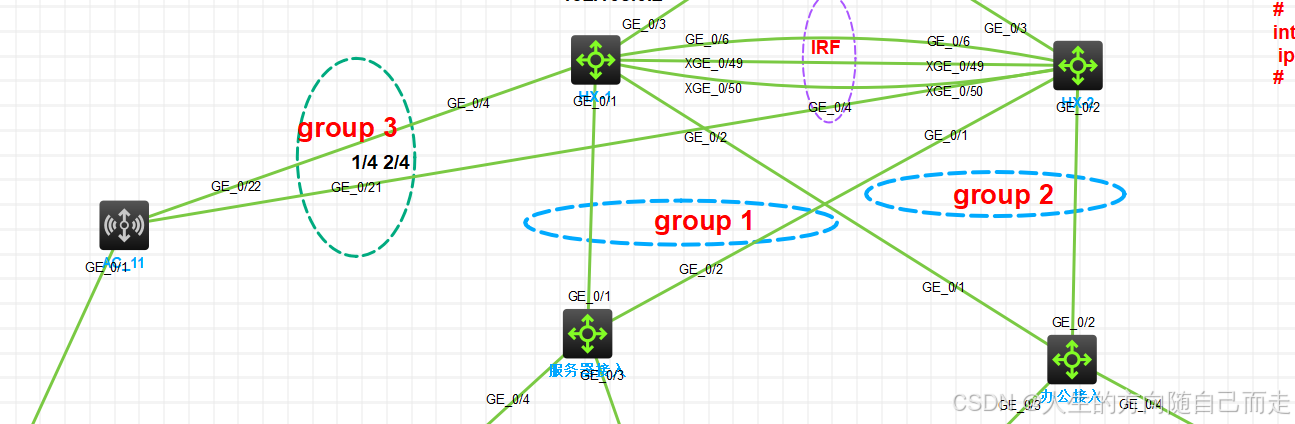
50 IRF检测MAD-BFD
IRF 检测MAD-BFD IRF配置思路 网络括谱图 主 Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/49 Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/50 Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/51 备 Ten-GigabitEthernet 2/0/49 Ten-GigabitEthernet 2/0/50 Ten-GigabitEthernet 2/0/51 1 利用console线进入设备的命令行页…...
SpringSecurity-1(认证和授权+SpringSecurity入门案例+自定义认证+数据库认证)
SpringSecurity 1 初识权限管理1.1 权限管理的概念1.2 权限管理的三个对象1.3 什么是SpringSecurity 2 SpringSecurity第一个入门程序2.1 SpringSecurity需要的依赖2.2 创建web工程2.2.1 使用maven构建web项目2.2.2 配置web.xml2.2.3 创建springSecurity.xml2.2.4 加载springSe…...

Java高级
类变量/静态变量package com.study.static_; 通过static关键词声明,是该类所有对象共享的对象,任何一个该类的对象去访问他的时候,取到的都是相同的词,同样任何一个该类的对象去修改,所修改的也是同一个对象. 如何定义及访问? 遵循相关访问权限 访问修饰符 static 数据类型…...

python实现图像分割算法3
python实现区域增长算法 算法原理基本步骤数学模型Python实现详细解释优缺点应用领域区域增长算法是一种经典的图像分割技术,它的目标是将图像划分为多个互不重叠的区域。该算法通过迭代地合并与种子区域相似的邻域像素来实现分割。区域增长算法通常用于需要精确分割的场景,如…...

Docker 离线安装指南
参考文章 1、确认操作系统类型及内核版本 Docker依赖于Linux内核的一些特性,不同版本的Docker对内核版本有不同要求。例如,Docker 17.06及之后的版本通常需要Linux内核3.10及以上版本,Docker17.09及更高版本对应Linux内核4.9.x及更高版本。…...

前端倒计时误差!
提示:记录工作中遇到的需求及解决办法 文章目录 前言一、误差从何而来?二、五大解决方案1. 动态校准法(基础版)2. Web Worker 计时3. 服务器时间同步4. Performance API 高精度计时5. 页面可见性API优化三、生产环境最佳实践四、终极解决方案架构前言 前几天听说公司某个项…...
无法与IP建立连接,未能下载VSCode服务器
如题,在远程连接服务器的时候突然遇到了这个提示。 查阅了一圈,发现是VSCode版本自动更新惹的祸!!! 在VSCode的帮助->关于这里发现前几天VSCode自动更新了,我的版本号变成了1.100.3 才导致了远程连接出…...

iPhone密码忘记了办?iPhoneUnlocker,iPhone解锁工具Aiseesoft iPhone Unlocker 高级注册版分享
平时用 iPhone 的时候,难免会碰到解锁的麻烦事。比如密码忘了、人脸识别 / 指纹识别突然不灵,或者买了二手 iPhone 却被原来的 iCloud 账号锁住,这时候就需要靠谱的解锁工具来帮忙了。Aiseesoft iPhone Unlocker 就是专门解决这些问题的软件&…...
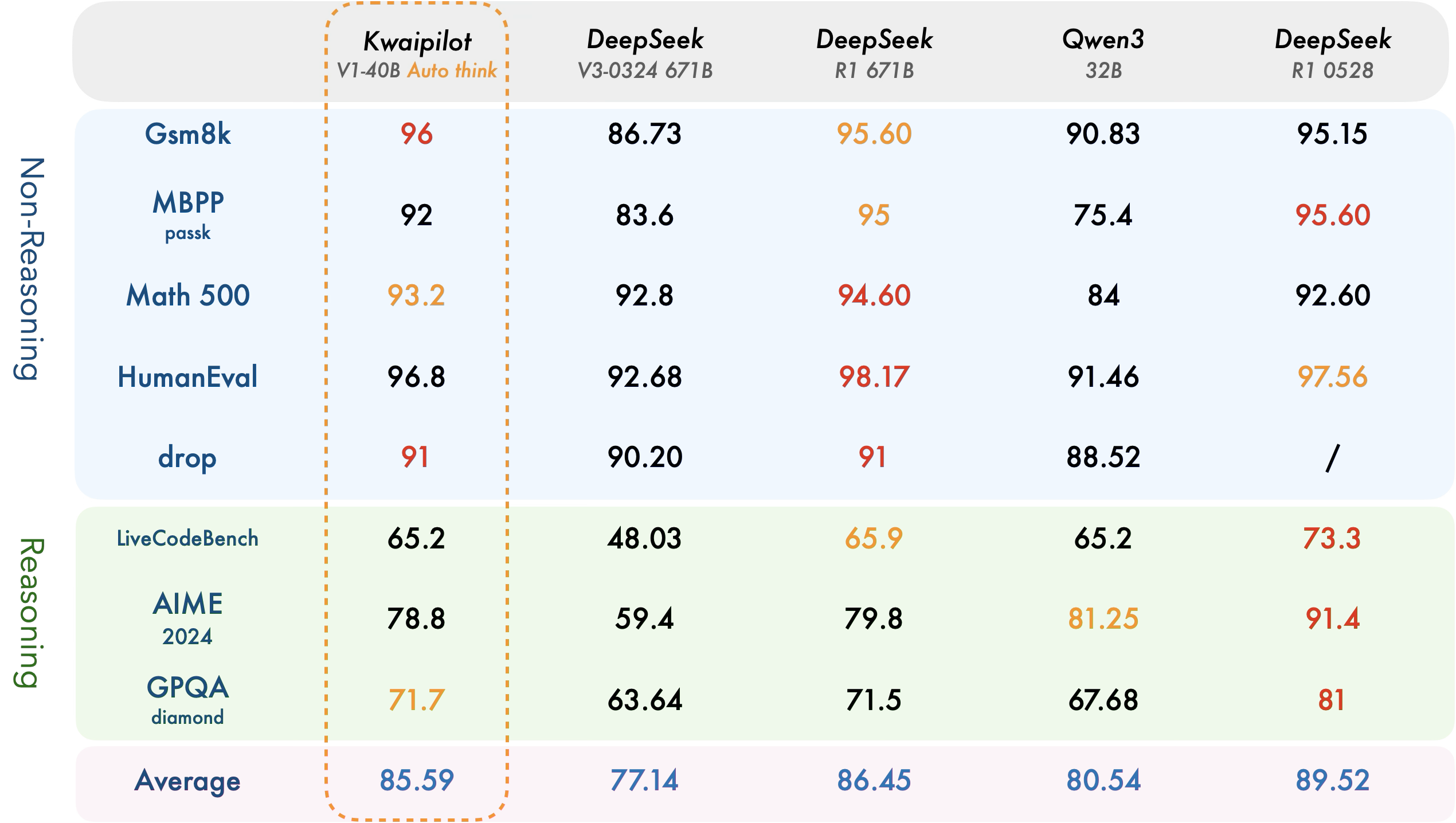
【快手拥抱开源】通过快手团队开源的 KwaiCoder-AutoThink-preview 解锁大语言模型的潜力
引言: 在人工智能快速发展的浪潮中,快手Kwaipilot团队推出的 KwaiCoder-AutoThink-preview 具有里程碑意义——这是首个公开的AutoThink大语言模型(LLM)。该模型代表着该领域的重大突破,通过独特方式融合思考与非思考…...

C++八股 —— 单例模式
文章目录 1. 基本概念2. 设计要点3. 实现方式4. 详解懒汉模式 1. 基本概念 线程安全(Thread Safety) 线程安全是指在多线程环境下,某个函数、类或代码片段能够被多个线程同时调用时,仍能保证数据的一致性和逻辑的正确性…...
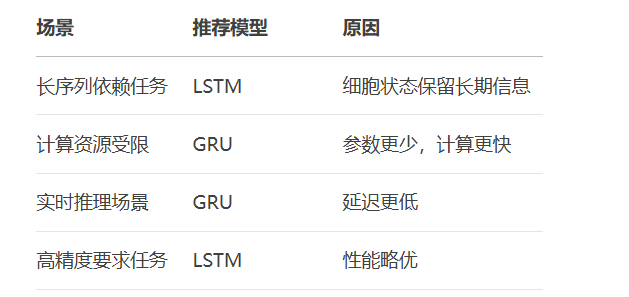
RNN避坑指南:从数学推导到LSTM/GRU工业级部署实战流程
本文较长,建议点赞收藏,以免遗失。更多AI大模型应用开发学习视频及资料,尽在聚客AI学院。 本文全面剖析RNN核心原理,深入讲解梯度消失/爆炸问题,并通过LSTM/GRU结构实现解决方案,提供时间序列预测和文本生成…...
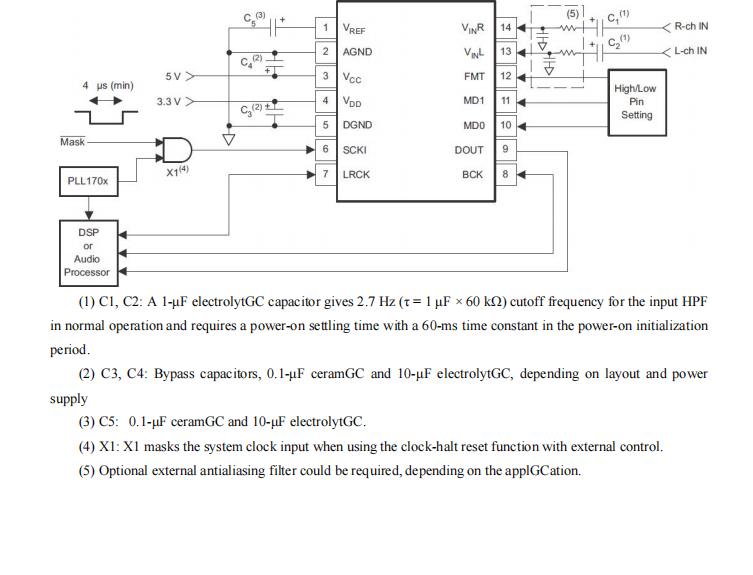
GC1808高性能24位立体声音频ADC芯片解析
1. 芯片概述 GC1808是一款24位立体声音频模数转换器(ADC),支持8kHz~96kHz采样率,集成Δ-Σ调制器、数字抗混叠滤波器和高通滤波器,适用于高保真音频采集场景。 2. 核心特性 高精度:24位分辨率,…...
GruntJS-前端自动化任务运行器从入门到实战
Grunt 完全指南:从入门到实战 一、Grunt 是什么? Grunt是一个基于 Node.js 的前端自动化任务运行器,主要用于自动化执行项目开发中重复性高的任务,例如文件压缩、代码编译、语法检查、单元测试、文件合并等。通过配置简洁的任务…...

在鸿蒙HarmonyOS 5中使用DevEco Studio实现企业微信功能
1. 开发环境准备 安装DevEco Studio 3.1: 从华为开发者官网下载最新版DevEco Studio安装HarmonyOS 5.0 SDK 项目配置: // module.json5 {"module": {"requestPermissions": [{"name": "ohos.permis…...
