C++编程:实现简单的高精度时间日志记录小程序
0. 概述
为了检查是否存在系统时间跳变,本文使用C++实现了一个简单的高精度时间日志记录小程序。该程序能够每隔指定时间(默认40毫秒)记录一次系统时间到文件中,并具备以下功能:
- 自定义时间间隔和文件名:通过命令行参数设置时间间隔和输出文件名,默认值为40毫秒和
timestamps.txt。 - 高精度定时:采用
std::chrono::steady_clock和sleep_until确保时间间隔的准确性,避免std::this_thread::sleep_for带来的时间漂移。 - 缓存队列:使用线程安全的队列缓存时间戳,减少频繁的文件I/O操作。
- 日志轮转:当日志文件大小超过100MB时,自动进行日志轮转。
- 时间跳变检测:使用
[TIME_JUMP]标记日志中发生的时间跳变(即后续时间戳小于前一个时间戳的情况)。
默认仅记录跳变前后的10个时间戳,避免日志文件中充斥过多正常的时间记录,突出异常事件。
1. 代码实现
1.1. 线程安全队列(ThreadSafeQueue)
实现了一个简单的线程安全队列类ThreadSafeQueue,使用std::mutex和std::condition_variable来确保并发访问的安全性。
// Thread-safe queue for storing timestamps
class ThreadSafeQueue {
public:// Push a new timestamp into the queuevoid push(const std::string& value) {std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mtx_);queue_.push(value);cv_.notify_one();}// Retrieve and clear all timestamps from the queuestd::queue<std::string> popAll() {std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mtx_);std::queue<std::string> temp;std::swap(temp, queue_);return temp;}private:std::queue<std::string> queue_;std::mutex mtx_;std::condition_variable cv_;
};
1.2. 获取当前时间的字符串表示
使用gettimeofday获取系统当前时间,并将其格式化为字符串,精确到微秒。
// Function to get the current time as a formatted string
std::string getCurrentTimeString() {struct timeval tv;gettimeofday(&tv, nullptr);struct tm* tm_info = localtime(&tv.tv_sec);char buffer[64];strftime(buffer, sizeof(buffer), "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", tm_info);// Append microsecondschar currentTime[100];snprintf(currentTime, sizeof(currentTime), "%s.%06ld", buffer, tv.tv_usec);return std::string(currentTime);
}
1.3. 文件大小获取
使用stat函数获取指定文件的大小,以便在日志轮转时进行判断。
// Function to get the size of a file in bytes
std::size_t getFileSize(const std::string& filename) {struct stat stat_buf;int rc = stat(filename.c_str(), &stat_buf);return rc == 0 ? stat_buf.st_size : 0;
}
1.4. 时间戳解析
将时间戳字符串解析为自纪元以来的微秒数,方便进行时间比较以检测时间跳变。
// Function to parse timestamp string to microseconds since epoch
uint64_t parseTimestamp(const std::string& timestamp_str) {struct tm tm_info;int microseconds = 0;// Split the timestamp into datetime and microsecondssize_t dot_pos = timestamp_str.find('.');if (dot_pos == std::string::npos) {// If no microseconds part, parse as isif (strptime(timestamp_str.c_str(), "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", &tm_info) == nullptr) {return 0;}} else {std::string datetime_str = timestamp_str.substr(0, dot_pos);std::string micro_str = timestamp_str.substr(dot_pos + 1);// Parse datetime partif (strptime(datetime_str.c_str(), "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", &tm_info) == nullptr) {return 0;}// Parse microseconds parttry {microseconds = std::stoi(micro_str);} catch (...) {microseconds = 0;}}time_t seconds = mktime(&tm_info);if (seconds == -1) {return 0;}uint64_t total_microseconds = static_cast<uint64_t>(seconds) * 1000000 + microseconds;return total_microseconds;
}
1.5. 主函数实现
主函数负责解析命令行参数,启动生产者和消费者线程,并控制程序的运行时间和日志轮转。
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {// Default valuesint interval_ms = 40; // Default interval of 40 millisecondsstd::string filename = "timestamps.txt"; // Default filenameint run_time_seconds = 3600; // Default run time of 1 hour (3600 seconds)const std::size_t max_file_size = 100 * 1024 * 1024; // 100MB// Parse command-line argumentsfor(int i = 1; i < argc; ++i) {std::string arg = argv[i];if((arg == "-i" || arg == "--interval") && i + 1 < argc) {interval_ms = std::atoi(argv[++i]);if(interval_ms <= 0) {std::cerr << "Invalid interval. Using default value of 40 milliseconds." << std::endl;interval_ms = 40;}}else if((arg == "-f" || arg == "--file") && i + 1 < argc) {filename = argv[++i];}else if((arg == "-t" || arg == "--time") && i + 1 < argc) {run_time_seconds = std::atoi(argv[++i]);if(run_time_seconds <= 0) {std::cerr << "Invalid run time. Using default value of 3600 seconds (1 hour)." << std::endl;run_time_seconds = 3600;}}else if(arg == "-h" || arg == "--help") {std::cout << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " [options]\n"<< "Options:\n"<< " -i, --interval <milliseconds> Set the time interval, default is 40 milliseconds\n"<< " -f, --file <filename> Set the output filename, default is timestamps.txt\n"<< " -t, --time <seconds> Set the run time in seconds, default is 3600 seconds (1 hour)\n"<< " -h, --help Show this help message\n";return 0;}else {std::cerr << "Unknown argument: " << arg << "\nUse -h or --help to see available options." << std::endl;return 1;}}std::cout << "Time Interval: " << interval_ms << " milliseconds" << std::endl;std::cout << "Output File: " << filename << std::endl;std::cout << "Run Time: " << run_time_seconds << " seconds" << std::endl;ThreadSafeQueue timeQueue;std::atomic<bool> running(true);std::atomic<int> file_index(1); // For log rotation// Producer thread: collects timestamps at specified intervalsstd::thread producer([&timeQueue, &running, interval_ms]() {using clock = std::chrono::steady_clock;auto next_time = clock::now();while (running.load()) {// Get current time and push to queuestd::string currentTime = getCurrentTimeString();timeQueue.push(currentTime);// Calculate next time pointnext_time += std::chrono::milliseconds(interval_ms);// Sleep until the next time pointstd::this_thread::sleep_until(next_time);// Adjust next_time if we're behind scheduleauto now = clock::now();if (now > next_time) {next_time = now;}}});// Consumer thread: writes timestamps to the file, handles log rotation, and detects time jumpsstd::thread consumer([&timeQueue, &running, &filename, &file_index, max_file_size]() {std::ofstream outFile(filename, std::ios::out | std::ios::app);if (!outFile.is_open()) {std::cerr << "Unable to open file for writing: " << filename << std::endl;running.store(false);return;}uint64_t last_timestamp_us = 0; // To store the last timestamp in microsecondswhile (running.load()) {// Wait for 1 second before writing to the filestd::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(1));// Retrieve all timestamps from the queuestd::queue<std::string> tempQueue = timeQueue.popAll();// Write timestamps to the filewhile (!tempQueue.empty()) {std::string current_timestamp_str = tempQueue.front();tempQueue.pop();uint64_t current_timestamp_us = parseTimestamp(current_timestamp_str);bool time_jump = false;if (last_timestamp_us != 0 && current_timestamp_us < last_timestamp_us) {time_jump = true;}if (time_jump) {outFile << current_timestamp_str << " [TIME_JUMP]" << std::endl;} else {outFile << current_timestamp_str << std::endl;}last_timestamp_us = current_timestamp_us;}outFile.flush(); // Ensure data is written to the file// Check if file size exceeds the maximum limitstd::size_t current_size = getFileSize(filename);if (current_size >= max_file_size) {outFile.close();// Generate a new filename with an indexstd::ostringstream new_filename;new_filename << filename << "." << file_index++;// Rename the current fileif (std::rename(filename.c_str(), new_filename.str().c_str()) != 0) {std::cerr << "Failed to rotate log file." << std::endl;} else {std::cout << "Rotated log file to " << new_filename.str() << std::endl;}// Open a new fileoutFile.open(filename, std::ios::out | std::ios::app);if (!outFile.is_open()) {std::cerr << "Unable to open new file for writing: " << filename << std::endl;running.store(false);return;}// Reset last_timestamp_us after rotationlast_timestamp_us = 0;}}// Write any remaining timestamps before exitingstd::queue<std::string> tempQueue = timeQueue.popAll();while (!tempQueue.empty()) {std::string current_timestamp_str = tempQueue.front();tempQueue.pop();uint64_t current_timestamp_us = parseTimestamp(current_timestamp_str);bool time_jump = false;if (last_timestamp_us != 0 && current_timestamp_us < last_timestamp_us) {time_jump = true;}if (time_jump) {outFile << current_timestamp_str << " [TIME_JUMP]" << std::endl;} else {outFile << current_timestamp_str << std::endl;}last_timestamp_us = current_timestamp_us;}outFile.flush();outFile.close();});std::cout << "Program will run for " << run_time_seconds << " seconds and then exit." << std::endl;// Let the program run for the specified durationstd::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(run_time_seconds));running.store(false);// Wait for threads to finishproducer.join();consumer.join();std::cout << "Program has ended." << std::endl;return 0;
}
2. 编译与运行
2.1 编译
g++ -std=c++11 -pthread -o time_logger time_logger.cpp
运行
-
使用默认设置(40毫秒间隔,输出文件为
timestamps.txt,运行1小时):./time_logger -
自定义设置(例如,100毫秒间隔,输出文件为
output.txt,运行2小时):./time_logger -i 100 -f output.txt -t 7200
2.2 示例日志文件
以下是日志文件timestamps.txt的一部分示例内容,其中标记了时间跳变:
2024-04-27 12:34:56.789123
2024-04-27 12:34:56.829456
2024-04-27 12:34:56.869789
2024-04-27 12:34:56.809012 [TIME_JUMP]
2024-04-27 12:34:56.849345
...
3. 附完整代码
// g++ -std=c++11 -pthread -o time_logger time_logger.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <queue>
#include <deque>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>
#include <chrono>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <atomic>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iomanip>
#include <sstream>
#include <sys/stat.h>// Thread-safe queue for storing timestamps
class ThreadSafeQueue {
public:// Push a new timestamp into the queuevoid push(const std::string& value) {std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mtx_);queue_.push(value);cv_.notify_one();}// Retrieve and clear all timestamps from the queuestd::queue<std::string> popAll() {std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mtx_);std::queue<std::string> temp;std::swap(temp, queue_);return temp;}private:std::queue<std::string> queue_;std::mutex mtx_;std::condition_variable cv_;
};// Function to get the current time as a formatted string
std::string getCurrentTimeString() {struct timeval tv;gettimeofday(&tv, nullptr);struct tm* tm_info = localtime(&tv.tv_sec);char buffer[64];strftime(buffer, sizeof(buffer), "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", tm_info);// Append microsecondschar currentTime[100];snprintf(currentTime, sizeof(currentTime), "%s.%06ld", buffer, tv.tv_usec);return std::string(currentTime);
}// Function to get the size of a file in bytes
std::size_t getFileSize(const std::string& filename) {struct stat stat_buf;int rc = stat(filename.c_str(), &stat_buf);return rc == 0 ? stat_buf.st_size : 0;
}// Function to parse timestamp string to microseconds since epoch
uint64_t parseTimestamp(const std::string& timestamp_str) {struct tm tm_info;int microseconds = 0;// Split the timestamp into datetime and microsecondssize_t dot_pos = timestamp_str.find('.');if (dot_pos == std::string::npos) {// If no microseconds part, parse as isif (strptime(timestamp_str.c_str(), "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", &tm_info) == nullptr) {return 0;}} else {std::string datetime_str = timestamp_str.substr(0, dot_pos);std::string micro_str = timestamp_str.substr(dot_pos + 1);// Parse datetime partif (strptime(datetime_str.c_str(), "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", &tm_info) == nullptr) {return 0;}// Parse microseconds parttry {microseconds = std::stoi(micro_str);} catch (...) {microseconds = 0;}}time_t seconds = mktime(&tm_info);if (seconds == -1) {return 0;}uint64_t total_microseconds = static_cast<uint64_t>(seconds) * 1000000 + microseconds;return total_microseconds;
}int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {// Default valuesint interval_ms = 40; // Default interval of 40 millisecondsstd::string filename = "timestamps.txt"; // Default filenameint run_time_seconds = 3600; // Default run time of 1 hour (3600 seconds)const std::size_t max_file_size = 100 * 1024 * 1024; // 100MBbool selective_logging = true; // Default: enable selective logging// Parse command-line argumentsfor(int i = 1; i < argc; ++i) {std::string arg = argv[i];if((arg == "-i" || arg == "--interval") && i + 1 < argc) {interval_ms = std::atoi(argv[++i]);if(interval_ms <= 0) {std::cerr << "Invalid interval. Using default value of 40 milliseconds." << std::endl;interval_ms = 40;}}else if((arg == "-f" || arg == "--file") && i + 1 < argc) {filename = argv[++i];}else if((arg == "-t" || arg == "--time") && i + 1 < argc) {run_time_seconds = std::atoi(argv[++i]);if(run_time_seconds <= 0) {std::cerr << "Invalid run time. Using default value of 3600 seconds (1 hour)." << std::endl;run_time_seconds = 3600;}}else if(arg == "--disable_selective_logging") {selective_logging = false;}else if(arg == "-h" || arg == "--help") {std::cout << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " [options]\n"<< "Options:\n"<< " -i, --interval <milliseconds> Set the time interval, default is 40 milliseconds\n"<< " -f, --file <filename> Set the output filename, default is timestamps.txt\n"<< " -t, --time <seconds> Set the run time in seconds, default is 3600 seconds (1 hour)\n"<< " --disable_selective_logging Disable selective logging feature\n"<< " -h, --help Show this help message\n";return 0;}else {std::cerr << "Unknown argument: " << arg << "\nUse -h or --help to see available options." << std::endl;return 1;}}std::cout << "Time Interval: " << interval_ms << " milliseconds" << std::endl;std::cout << "Output File: " << filename << std::endl;std::cout << "Run Time: " << run_time_seconds << " seconds" << std::endl;std::cout << "Selective Logging: " << (selective_logging ? "Enabled" : "Disabled") << std::endl;ThreadSafeQueue timeQueue;std::atomic<bool> running(true);std::atomic<int> file_index(1); // For log rotation// Producer thread: collects timestamps at specified intervalsstd::thread producer([&timeQueue, &running, interval_ms]() {using clock = std::chrono::steady_clock;auto next_time = clock::now();while (running.load()) {// Get current time and push to queuestd::string currentTime = getCurrentTimeString();timeQueue.push(currentTime);// Calculate next time pointnext_time += std::chrono::milliseconds(interval_ms);// Sleep until the next time pointstd::this_thread::sleep_until(next_time);// Adjust next_time if we're behind scheduleauto now = clock::now();if (now > next_time) {next_time = now;}}});// Consumer thread: writes timestamps to the file, handles log rotation, and detects time jumpsstd::thread consumer([&timeQueue, &running, &filename, &file_index, max_file_size, selective_logging]() {std::ofstream outFile(filename, std::ios::out | std::ios::app);if (!outFile.is_open()) {std::cerr << "Unable to open file for writing: " << filename << std::endl;running.store(false);return;}uint64_t last_timestamp_us = 0; // To store the last timestamp in microsecondsstd::deque<std::string> recent_timestamps; // To store recent timestamps for bufferconst size_t buffer_size = 10; // Number of timestamps to keep before a time jumpsize_t normal_count = 0; // Counter for normal timestampsconst size_t normal_threshold = 20; // Write every 20 normal timestampsbool in_jump_mode = false; // Flag indicating if currently in jump modesize_t jump_remaining = 0; // Number of jump-related timestamps remaining to writestd::vector<std::string> jump_buffer; // Buffer to store jump-related timestampswhile (running.load()) {// Wait for 1 second before processingstd::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(1));// Retrieve all timestamps from the queuestd::queue<std::string> tempQueue = timeQueue.popAll();while (!tempQueue.empty()) {std::string current_timestamp_str = tempQueue.front();tempQueue.pop();// Update recent_timestamps bufferrecent_timestamps.push_back(current_timestamp_str);if (recent_timestamps.size() > buffer_size) {recent_timestamps.pop_front();}uint64_t current_timestamp_us = parseTimestamp(current_timestamp_str);bool time_jump = false;if (selective_logging && last_timestamp_us != 0 && current_timestamp_us < last_timestamp_us) {time_jump = true;}if (selective_logging && time_jump && !in_jump_mode) {// Time jump detected, enter jump modein_jump_mode = true;jump_remaining = 10; // Number of timestamps to write after the jumpjump_buffer.clear();// Add the last 10 timestamps before the jumpfor (const auto& ts : recent_timestamps) {jump_buffer.push_back(ts);}// Add the current (jump) timestampjump_buffer.push_back(current_timestamp_str);last_timestamp_us = current_timestamp_us;}else if (selective_logging && in_jump_mode) {// In jump mode, collect the next 10 timestampsjump_buffer.push_back(current_timestamp_str);jump_remaining--;last_timestamp_us = current_timestamp_us;if (jump_remaining == 0) {// Write all collected jump timestamps to file with [TIME_JUMP] flagfor (size_t i = 0; i < jump_buffer.size(); ++i) {if (i == buffer_size) { // The jump timestampoutFile << jump_buffer[i] << " [TIME_JUMP]" << std::endl;}else {outFile << jump_buffer[i] << std::endl;}}outFile.flush();jump_buffer.clear();in_jump_mode = false;}}else {// Normal timestamp processingnormal_count++;if (normal_count >= normal_threshold) {outFile << current_timestamp_str << std::endl;outFile.flush();normal_count = 0;}last_timestamp_us = current_timestamp_us;}// Check if file size exceeds the maximum limitstd::size_t current_size = getFileSize(filename);if (current_size >= max_file_size) {outFile.close();// Generate a new filename with an indexstd::ostringstream new_filename;new_filename << filename << "." << file_index++;// Rename the current fileif (std::rename(filename.c_str(), new_filename.str().c_str()) != 0) {std::cerr << "Failed to rotate log file." << std::endl;} else {std::cout << "Rotated log file to " << new_filename.str() << std::endl;}// Open a new fileoutFile.open(filename, std::ios::out | std::ios::app);if (!outFile.is_open()) {std::cerr << "Unable to open new file for writing: " << filename << std::endl;running.store(false);return;}// Reset last_timestamp_us and buffers after rotationlast_timestamp_us = 0;recent_timestamps.clear();jump_buffer.clear();in_jump_mode = false;normal_count = 0;}}}// Handle any remaining timestamps before exitingstd::queue<std::string> remainingQueue = timeQueue.popAll();while (!remainingQueue.empty()) {std::string current_timestamp_str = remainingQueue.front();remainingQueue.pop();// Update recent_timestamps bufferrecent_timestamps.push_back(current_timestamp_str);if (recent_timestamps.size() > buffer_size) {recent_timestamps.pop_front();}uint64_t current_timestamp_us = parseTimestamp(current_timestamp_str);bool time_jump = false;if (selective_logging && last_timestamp_us != 0 && current_timestamp_us < last_timestamp_us) {time_jump = true;}if (selective_logging && time_jump && !in_jump_mode) {// Time jump detected, enter jump modein_jump_mode = true;jump_remaining = 10; // Number of timestamps to write after the jumpjump_buffer.clear();// Add the last 10 timestamps before the jumpfor (const auto& ts : recent_timestamps) {jump_buffer.push_back(ts);}// Add the current (jump) timestampjump_buffer.push_back(current_timestamp_str);last_timestamp_us = current_timestamp_us;}else if (selective_logging && in_jump_mode) {// In jump mode, collect the next 10 timestampsjump_buffer.push_back(current_timestamp_str);jump_remaining--;last_timestamp_us = current_timestamp_us;if (jump_remaining == 0) {// Write all collected jump timestamps to file with [TIME_JUMP] flagfor (size_t i = 0; i < jump_buffer.size(); ++i) {if (i == buffer_size) { // The jump timestampoutFile << jump_buffer[i] << " [TIME_JUMP]" << std::endl;}else {outFile << jump_buffer[i] << std::endl;}}outFile.flush();jump_buffer.clear();in_jump_mode = false;}}else {// Normal timestamp processingnormal_count++;if (normal_count >= normal_threshold) {outFile << current_timestamp_str << std::endl;outFile.flush();normal_count = 0;}last_timestamp_us = current_timestamp_us;}// Check if file size exceeds the maximum limitstd::size_t current_size = getFileSize(filename);if (current_size >= max_file_size) {outFile.close();// Generate a new filename with an indexstd::ostringstream new_filename;new_filename << filename << "." << file_index++;// Rename the current fileif (std::rename(filename.c_str(), new_filename.str().c_str()) != 0) {std::cerr << "Failed to rotate log file." << std::endl;} else {std::cout << "Rotated log file to " << new_filename.str() << std::endl;}// Open a new fileoutFile.open(filename, std::ios::out | std::ios::app);if (!outFile.is_open()) {std::cerr << "Unable to open new file for writing: " << filename << std::endl;running.store(false);return;}// Reset last_timestamp_us and buffers after rotationlast_timestamp_us = 0;recent_timestamps.clear();jump_buffer.clear();in_jump_mode = false;normal_count = 0;}}outFile.flush();outFile.close();});std::cout << "Program will run for " << run_time_seconds << " seconds and then exit." << std::endl;// Let the program run for the specified durationstd::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(run_time_seconds));running.store(false);// Wait for threads to finishproducer.join();consumer.join();std::cout << "Program has ended." << std::endl;return 0;
}相关文章:

C++编程:实现简单的高精度时间日志记录小程序
0. 概述 为了检查是否存在系统时间跳变,本文使用C实现了一个简单的高精度时间日志记录小程序。该程序能够每隔指定时间(默认40毫秒)记录一次系统时间到文件中,并具备以下功能: 自定义时间间隔和文件名:通…...

QQ机器人搭建
使用QQ官方机器人Python SDK和三方框架搭建QQ群聊机器人 文章目录 使用QQ官方机器人Python SDK和三方框架搭建QQ群聊机器人前言编写机器人代码机器人监听群聊进行文字回复机器人监听群聊进行图片回复机器人监听群聊进行文件发送机器人监听群聊进行视频发送机器人监听群聊进行语…...

flink设置保存点和恢复保存点
增加了hdfs package com.qyt;import org.apache.flink.api.java.functions.KeySelector; import org.apache.flink.api.java.tuple.Tuple2;import org.apache.flink.runtime.state.storage.FileSystemCheckpointStorage;import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.Dat…...

使用python获取百度一下,热搜TOP数据详情
一、查找对应链接 # 警告:以下代码仅供学习和交流使用,严禁用于任何违法活动。 # 本代码旨在帮助理解和学习编程概念,不得用于侵犯他人权益或违反法律法规的行为。 1、打开百度页面 百度一下,你就知道 2、点击F12 或 右键鼠标…...

Go conc库学习与使用
文章目录 主要功能和特点conc 的安装典型使用场景示例代码并行执行多个 Goroutines错误处理限制并发 Goroutines 数量使用 context.Context 进行任务控制 常见问题1. **任务中发生 panic**原因:解决方法: 2. **conc.Group 重复调用 Wait()**原因…...

大模型prompt先关
对于未出现的任务,prompt编写技巧: 1、假设你是资深的摘要生成专家,根据提供的内容,总结对应的摘要信息。请生成一个指令,指令中带有一个使用例子。直接提供给大型模型以执行此任务。 2、基于大模型提供的内容再进行二…...
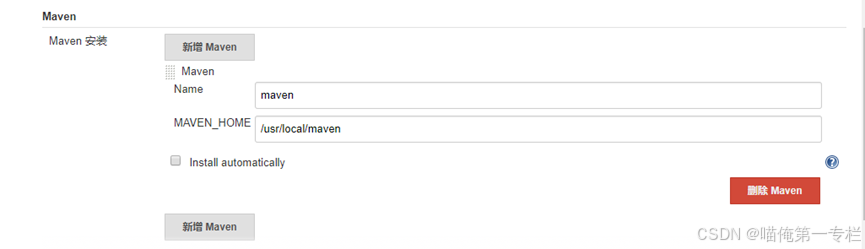
尚品汇-自动化部署-Jenkins的安装与环境配置(五十六)
目录: 自动化持续集成 (1)环境准备 (2)初始化 Jenkins 插件和管理员用户 (3)工作流程 (4)配置 Jenkins 构建工具 自动化持续集成 互联网软件的开发和发布…...

【尚跑】2024铜川红色照金半程马拉松赛,大爬坡152安全完赛
1、赛事背景 2024年9月22日8点,2024铜川红色照金半程马拉松赛于照金1933广场鸣枪起跑! 起跑仪式上,6000位选手们合唱《歌唱祖国》,熟悉的旋律响彻陕甘边革命根据地照金纪念馆前,激昂的歌声凝聚心中不变的热爱。随着国…...

WPS中让两列数据合并的方法
有这样一个需求,就是把A列数据和B列数据进行合并(空单元格略过)具体实现效果如图下: 该如何操作呢? 首先在新的一列第一个单元格中输入公式"A1&B1" 然后回车,就出现了两列单元格数据合并的效…...

使用yum为centos系统安装软件以及使用(包含阿里云yum源配置)
centos系统配置阿里云yum源 因为centos7官方停止维护,自带yum源用不了了,所以可以更换成阿里云yum源 方法: 使用root权限执行以下语句 curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo https://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo CentOS…...

《深度学习》【项目】OpenCV 发票识别 透视变换、轮廓检测解析及案例解析
目录 一、透视变换 1、什么是透视变换 2、操作步骤 1)选择透视变换的源图像和目标图像 2)确定透视变换所需的关键点 3)计算透视变换的变换矩阵 4)对源图像进行透视变换 5)对变换后的图像进行插值处理 二、轮廓检测…...

Linux 线程互斥
前言 对于初学线程的伙伴来讲,多线程并发访问导致的数据不一致问题,总是让人陷入怀疑,很多人只是给你说加锁!但没有人告诉你为什么?本篇博客将详解! 目录 前言 一、线程互斥 • 为什么票会出现负数的情…...

【Redis 源码】6AOF持久化
1 AOF功能说明 aof.c 文件是 Redis 中负责 AOF(Append-Only File)持久化的核心文件。AOF 持久化通过记录服务器接收到的每个写命令来实现数据的持久化。这样,在 Redis 重启时,可以通过重放这些命令来恢复数据。 2 AOF相关配置 a…...

6.MySQL基本查询
目录 表的增删查改Insert(插入)插入替换插入替换2 Retrieve(查找)SELECT 列全列查找指定列查询查询字段为表达式为查询结果指定别名结果去重 WHERE 条件order by子句筛选分页结果 Update(更新)delete&#…...

Linux字符设备驱动开发
Linux 字符设备驱动开发是内核模块开发中的一个重要部分,主要用于处理字节流数据设备(如串口、键盘、鼠标等)。字符设备驱动的核心任务是定义如何与用户空间程序交互,通常通过一组文件操作函数进行。这些函数会映射到 open、read、…...

HTML5+JavaScript绘制闪烁的网格错觉
HTML5JavaScript绘制闪烁的网格错觉 闪烁的网格错觉(scintillating grid illusion)是一种视觉错觉,通过简单的黑白方格网格和少量的精心设计,能够使人眼前出现动态变化的效果。 闪烁的栅格错觉,是一种经典的视觉错觉…...

每日OJ题_牛客_拼三角_枚举/DFS_C++_Java
目录 牛客_拼三角_枚举/DFS 题目解析 C代码1 C代码2 Java代码 牛客_拼三角_枚举/DFS 拼三角_枚举/DFS 题目解析 简单枚举,不过有很多种枚举方法,这里直接用简单粗暴的枚举方式。 C代码1 #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> …...
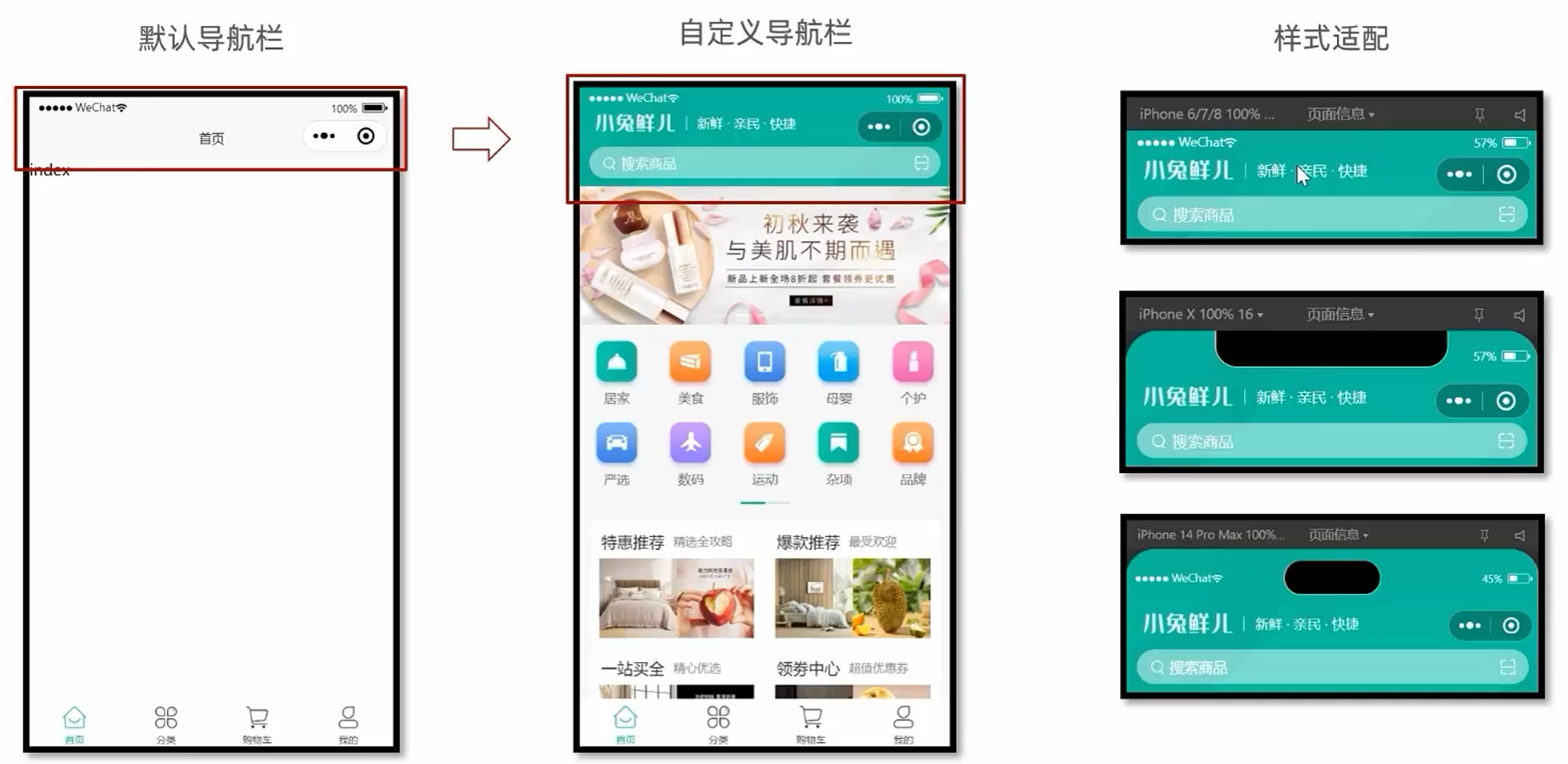
[uni-app]小兔鲜-01项目起步
项目介绍 效果演示 技术架构 创建项目 HBuilderX创建 下载HBuilderX编辑器 HBuilderX/创建项目: 选择模板/选择Vue版本/创建 安装插件: 工具/插件安装/uni-app(Vue3)编译器 vue代码不能直接运行在小程序环境, 编译插件帮助我们进行代码转换 绑定微信开发者工具: 指定微信开…...

安全的价值:构建现代企业的基础
物理安全对于组织来说并不是事后才考虑的问题:它是关键的基础设施。零售商、医疗保健提供商、市政当局、学校和所有其他类型的组织都依赖安全系统来保障其人员和场所的安全。 随着安全技术能力的不断发展,许多组织正在以更广泛的视角看待他们的投资&am…...
模式)
门面(外观)模式
简介 门面模式(Facade Pattern)又叫作外观模式,提供了一个统一的接口,用来访问子系统中的一群接口。其主要特征是定义了一个高层接口,让子系统更容易使用,属于结构型设计模式。 通用模板 创建子系统角色类…...
)
uniapp 对接腾讯云IM群组成员管理(增删改查)
UniApp 实战:腾讯云IM群组成员管理(增删改查) 一、前言 在社交类App开发中,群组成员管理是核心功能之一。本文将基于UniApp框架,结合腾讯云IM SDK,详细讲解如何实现群组成员的增删改查全流程。 权限校验…...
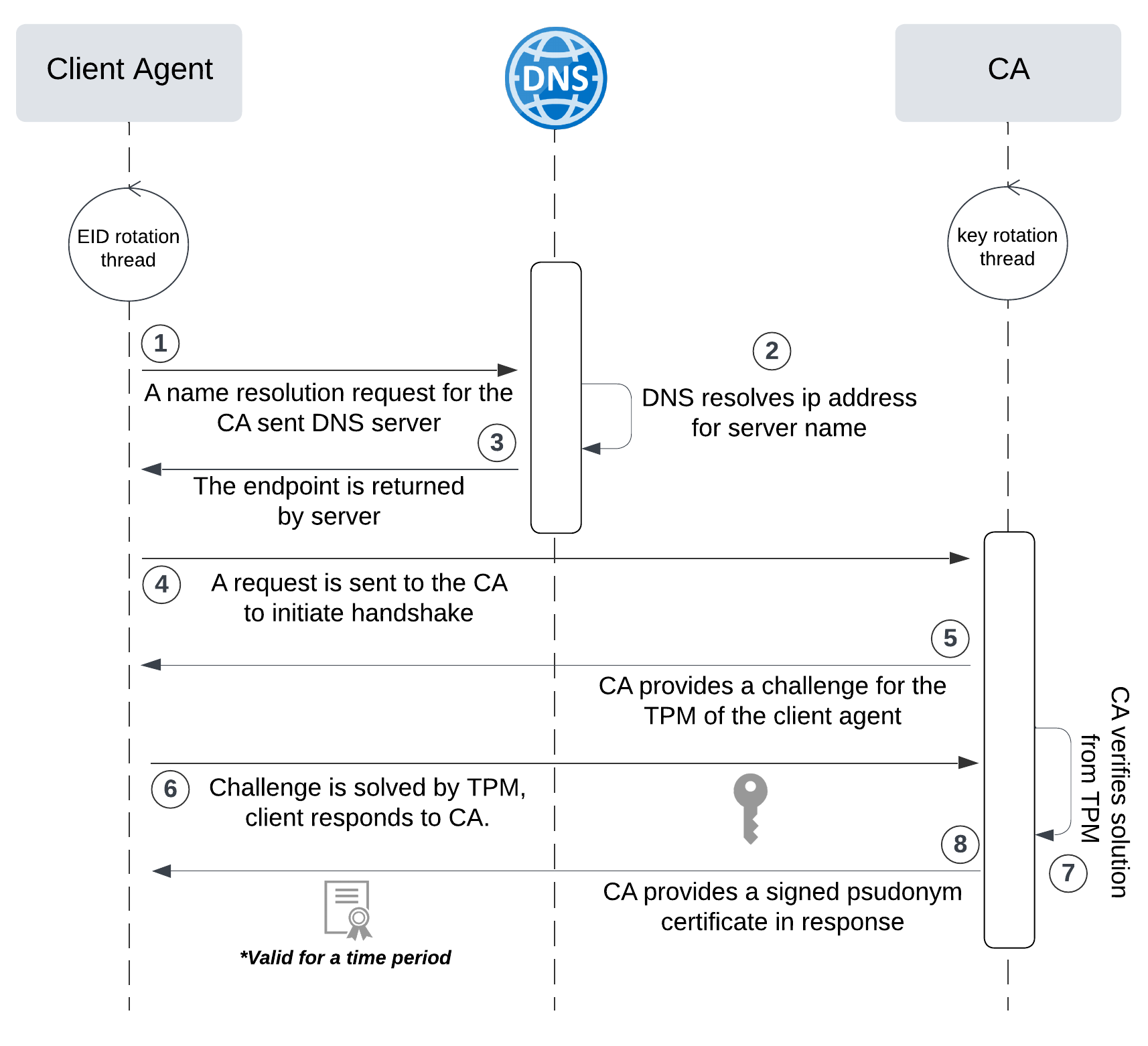
网络六边形受到攻击
大家读完觉得有帮助记得关注和点赞!!! 抽象 现代智能交通系统 (ITS) 的一个关键要求是能够以安全、可靠和匿名的方式从互联车辆和移动设备收集地理参考数据。Nexagon 协议建立在 IETF 定位器/ID 分离协议 (…...

挑战杯推荐项目
“人工智能”创意赛 - 智能艺术创作助手:借助大模型技术,开发能根据用户输入的主题、风格等要求,生成绘画、音乐、文学作品等多种形式艺术创作灵感或初稿的应用,帮助艺术家和创意爱好者激发创意、提高创作效率。 - 个性化梦境…...
)
云计算——弹性云计算器(ECS)
弹性云服务器:ECS 概述 云计算重构了ICT系统,云计算平台厂商推出使得厂家能够主要关注应用管理而非平台管理的云平台,包含如下主要概念。 ECS(Elastic Cloud Server):即弹性云服务器,是云计算…...

SciencePlots——绘制论文中的图片
文章目录 安装一、风格二、1 资源 安装 # 安装最新版 pip install githttps://github.com/garrettj403/SciencePlots.git# 安装稳定版 pip install SciencePlots一、风格 简单好用的深度学习论文绘图专用工具包–Science Plot 二、 1 资源 论文绘图神器来了:一行…...

2021-03-15 iview一些问题
1.iview 在使用tree组件时,发现没有set类的方法,只有get,那么要改变tree值,只能遍历treeData,递归修改treeData的checked,发现无法更改,原因在于check模式下,子元素的勾选状态跟父节…...

NFT模式:数字资产确权与链游经济系统构建
NFT模式:数字资产确权与链游经济系统构建 ——从技术架构到可持续生态的范式革命 一、确权技术革新:构建可信数字资产基石 1. 区块链底层架构的进化 跨链互操作协议:基于LayerZero协议实现以太坊、Solana等公链资产互通,通过零知…...
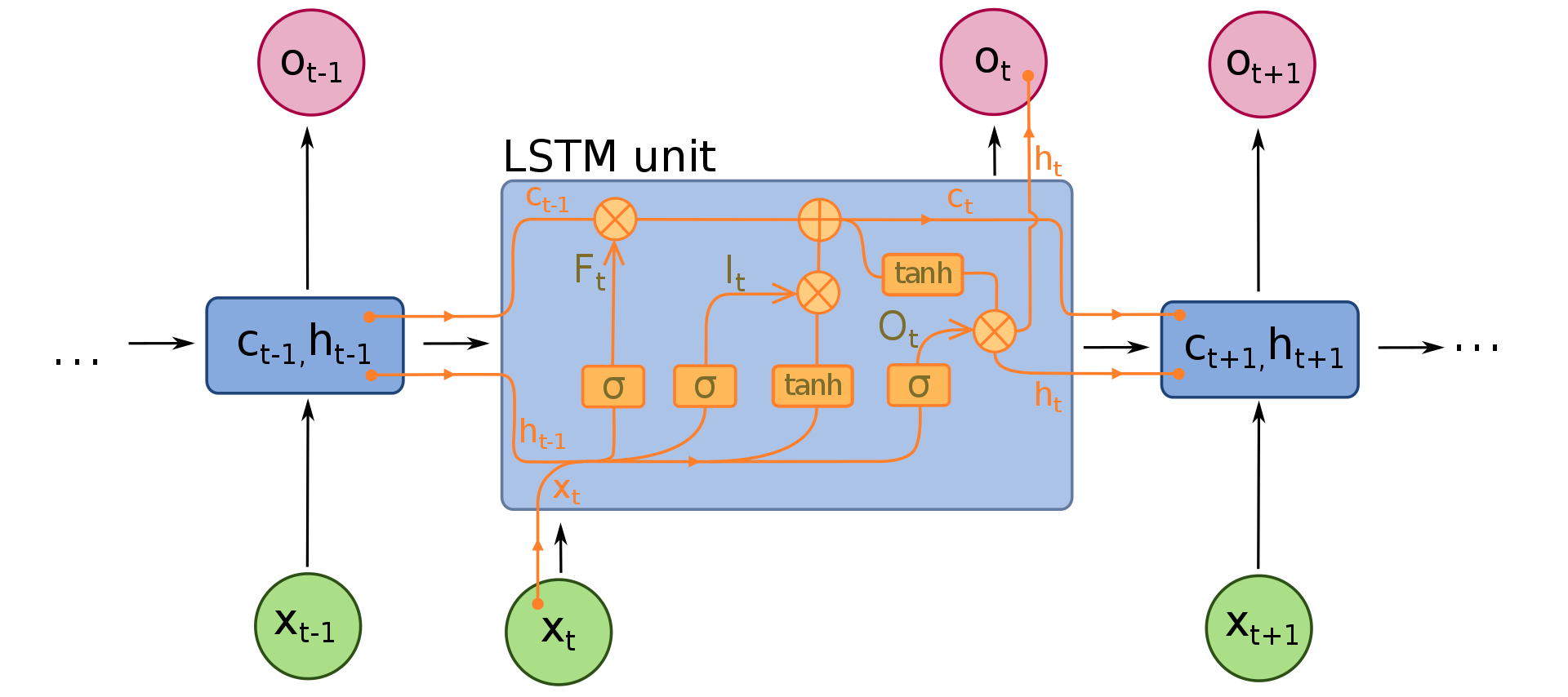
NLP学习路线图(二十三):长短期记忆网络(LSTM)
在自然语言处理(NLP)领域,我们时刻面临着处理序列数据的核心挑战。无论是理解句子的结构、分析文本的情感,还是实现语言的翻译,都需要模型能够捕捉词语之间依时序产生的复杂依赖关系。传统的神经网络结构在处理这种序列依赖时显得力不从心,而循环神经网络(RNN) 曾被视为…...

Linux C语言网络编程详细入门教程:如何一步步实现TCP服务端与客户端通信
文章目录 Linux C语言网络编程详细入门教程:如何一步步实现TCP服务端与客户端通信前言一、网络通信基础概念二、服务端与客户端的完整流程图解三、每一步的详细讲解和代码示例1. 创建Socket(服务端和客户端都要)2. 绑定本地地址和端口&#x…...
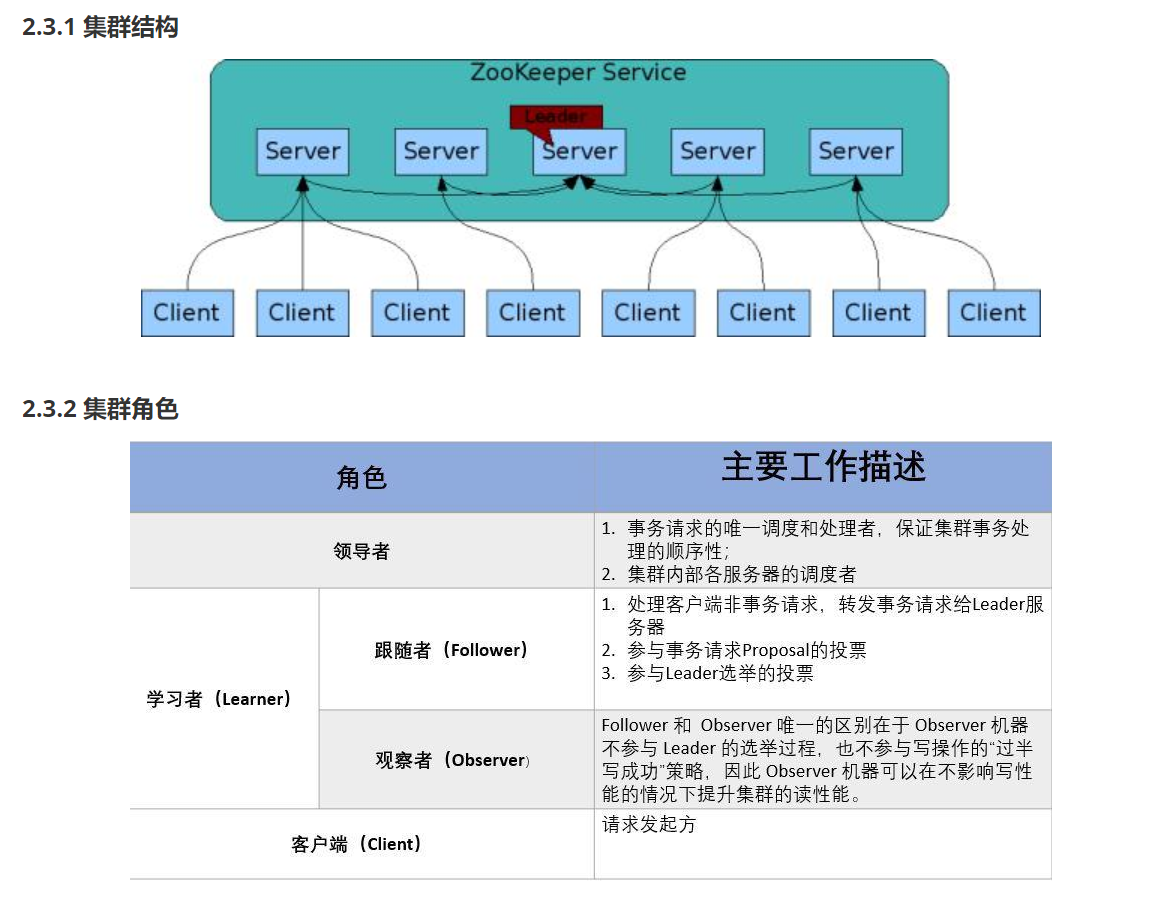
HDFS分布式存储 zookeeper
hadoop介绍 狭义上hadoop是指apache的一款开源软件 用java语言实现开源框架,允许使用简单的变成模型跨计算机对大型集群进行分布式处理(1.海量的数据存储 2.海量数据的计算)Hadoop核心组件 hdfs(分布式文件存储系统)&a…...
