Java Lock/AQS ReentrantLock 源码
前言
相关系列
- 《Java & Lock & 目录》(持续更新)
- 《Java & AQS & 目录》(持续更新)
- 《Java & Lock/AQS & ReentrantLock & 源码》(学习过程/多有漏误/仅作参考/不再更新)
- 《Java & Lock/AQS & ReentrantLock & 总结》(学习总结/最新最准/持续更新)
- 《Java & Lock/AQS & ReentrantLock & 问题》(学习解答/持续更新)
涉及内容
- 《Java & Lock & 总结》
- 《Java & AQS & 总结》
- 《Java & Condition & 总结》
- 《Java & Condition/AQS & ConditionObject & 总结》
- 《Java & synchronized & 总结》
源码
package juc.locks;import juc.TimeUnit;import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Collection;/*** A reentrant mutual exclusion {@link Lock} with the same basic behavior and semantics as the implicit monitor lock* accessed using {@code synchronized} methods and statements, but with extended capabilities.* 一个与使用synchronized方法和语句访问隐式监视锁一样的基本行为和语义的重入互斥锁,但是具有做拓展功能。* <p>* A {@code ReentrantLock} is <em>owned</em> by the thread last successfully locking, but not yet unlocking it. A* thread invoking {@code lock} will return, successfully acquiring the lock, when the lock is not owned by another* thread. The method will return immediately if the current thread already owns the lock. This can be checked using* methods {@link #isHeldByCurrentThread}, and {@link #getHoldCount}.* 重入锁通过最后成功加锁,但还没有解锁持有。当锁还没有被其它线程拥有时一个线程调用lock()方法将成功地获取锁并返* 回。如果当前线程已经拥有该锁则返回将立即返回。这可以使用isHeldByCurrentThread()方法或getHoldCount()方法检查。* <p>* The constructor for this class accepts an optional <em>fairness</em> parameter. When set {@code true}, under* contention, locks favor granting access to the longest-waiting thread. Otherwise this lock does not guarantee any* particular access order. Programs using fair locks accessed by many threads may display lower overall throughput* (i.e., are slower; often much slower) than those using the default setting, but have smaller variances in times to obtain* locks and guarantee lack of starvation. Note however, that fairness of locks does not guarantee fairness of thread* scheduling. Thus, one of many threads using a fair lock may obtain it multiple times in succession while other active* threads are not progressing and not currently holding the lock. Also note that the untimed {@link #tryLock()} method* does not honor the fairness setting. It will succeed if the lock is available even if other threads are waiting.* 该类的构造器接受一个可选公平性参数。当设置为true时,对于竞争,锁倾向于给予访问等待最长的线程。否则锁不保证任* 何特定的访问顺序。项目使用线程访问公平锁可能显示比它们使用默认设置更小(慢,总是慢)的总吞吐量,但是在获取锁* 的时间上有较小的差异,并保证不饥饿【即不会出现线程长时间等待而无法获取到锁的情况】。此外注意:锁的公平性不保* 证线程调度的公平性。因此,许多线程中的一个使用公平锁在其它活跃线程没有前进并当前没有持有锁期间可能多次获得锁。* 还有注意不定时的tryLock()方法不遵守公平性设置。如果锁可用即是其它线程正在等待它也将接替。* <p>* It is recommended practice to <em>always</em> immediately follow a call to {@code lock} with a {@code try} block,* most typically in a before/after construction such as:* 推建议在调用lock()方法之后立即使用try块,最典型的是在before/after构造中,例如:* <pre> {@code* class X {* private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();* // ...** public void m() {* // block until condition holds* // 阻塞直到条件持有* lock.lock();* try {* // ... method body* } finally {* lock.unlock()* }* }* }}</pre>** <p>* In addition to implementing the {@link Lock} interface, this class defines a number of {@code public} and* {@code protected} methods for inspecting the state of the lock. Some of these methods are only useful for* instrumentation and monitoring.* 除了实现所接口之外,该类还为检查锁的状态定义一些公共和受保护的方法。这些方法的其中一些在仪表化和监视时比较* 有用。* <p>* Serialization of this class behaves in the same way as built-in locks: a deserialized lock is in the unlocked state,* regardless of its state when serialized.* 该类的序列化与内置锁的行为方式相同:反序列化的锁处于解锁状态,无论其序列化时的状态如何。* <p>* This lock supports a maximum of 2147483647 recursive locks by the same thread. Attempts to exceed this limit result* in {@link Error} throws from locking methods.* 该锁支持一个线程最大2147483647【int类型的最大值】次递归加锁【即重入】。尝试超出这个线程会导致从加锁方法中* 抛出错误。** @author Doug Lea* @since 1.5*/
public class ReentrantLock implements Lock, Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = 7373984872572414699L;/*** Synchronizer providing all implementation mechanics* 同步器提供所有实现机制** @Description: ----------------------------------------------------------- 名称 -----------------------------------------------------------* 同步* @Description: ----------------------------------------------------------- 作用 -----------------------------------------------------------* 持有当前可重入锁底层AQS的引用* @Description: ----------------------------------------------------------- 逻辑 -----------------------------------------------------------* ~*/private final Sync sync;/*** Base of synchronization control for this lock. Subclassed into fair and nonfair versions below. Uses AQS state to* represent the number of holds on the lock.* 锁的基础同步控制。在下文子类分为公平和非公平版本。使用AQS状态代表所有的持有/重入数量。** @Description: ----------------------------------------------------------- 名称 -----------------------------------------------------------* 同步类* @Description: ----------------------------------------------------------- 作用 -----------------------------------------------------------* ---- 可重入锁类内部实现的AQS子类,同时也是公平/非公平AQS孙类父/超/基类,实现了两者间的共用逻辑。* @Description: ----------------------------------------------------------- 逻辑 -----------------------------------------------------------* ~*/abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {private static final long serialVersionUID = -5179523762034025860L;/*** Performs {@link Lock#lock}. The main reason for subclassing is to allow fast path for nonfair version.* 执行加锁。子类化的主要原因是为了允许非公平版本的快速通道** @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 名称 ---------------------------------------------------------* 加锁* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 作用 ---------------------------------------------------------* 令当前线程独占当前同步/AQS。* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 逻辑 ---------------------------------------------------------* ~*/abstract void lock();/*** Performs non-fair tryLock. tryAcquire is implemented in subclasses, but both need nonfair try for trylock method.* 执行非公平尝试加锁。尝试获取在子类中实现,但都需要trylock()方法的非公平尝试。** @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 名称 ---------------------------------------------------------* 非公平尝试获取* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 作用 ---------------------------------------------------------* 令当前线程以非公平的方式在独占模式下尝试获取当前同步/AQS指定数量的状态,成功则返回true;否则返回false。* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 逻辑 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 方法首先会获取当前线程及当前同步/AQS的[状态],随后判断[状态]是否为0。是则表示当前同步/AQS尚未被* 其它线程独占,当前线程可以尝试进行独占,即通过CAS操作将[状态]由0修改为指定获取。修改成功意味着独占成* 功,将自身设置进当前同步/AQS的[独占拥有者线程]中,表示当前线程为当前同步/AQS的独占线程,并直接返回* true;否则意味着有其它线程在并发执行相同操作而失败。* ---- 如果[状态]不为0,意味着当前线程已被独占,继续判断[独占拥有者线程]是否为当前线程,是则说明是当前线* 程独占了当前同步/AQS,执行重入,即直接通过相加操作增长[状态]。由于当前同步/AQS已被独占,因此不会出* 现其它线程的干扰,是线程安全的。我们先计算增长后的状态值,如果状态值小于0意味着线程重入的次数已经超* 出了Integer.MAX_VALUE,直接抛出错误;否则将状态值赋予[状态]中表示重入成功并返回true。* ---- 除了上述阐述的两种情况外,其它对独占失败和已被其它线程独占的情况都会直接返回false。*/final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {// ---- 方法首先会获取当前线程及当前同步/AQS的[状态],随后判断[状态]是否为0。是则表示当前同步/AQS尚未// 被其它线程独占,当前线程可以尝试进行独占,即通过CAS操作将[状态]由0修改为指定获取。修改成功意味着独// 占成功,将自身设置进当前同步/AQS的[独占拥有者线程]中,表示当前线程为当前同步/AQS的独占线程,并直// 接返回true;否则意味着有其它线程在并发执行相同操作而失败。final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();int c = getState();if (c == 0) {if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);return true;}} else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {// ---- 如果[状态]不为0,意味着当前线程已被独占,继续判断[独占拥有者线程]是否为当前线程,是则说明是当// 前线程独占了当前同步/AQS,执行重入,即直接通过相加操作增长[状态]。由于当前同步/AQS已被独占,因// 此不会出现其它线程的干扰,是线程安全的。我们先计算增长后的状态值,如果状态值小于0意味着线程重入// 的次数已经超出了Integer.MAX_VALUE,直接抛出错误;否则将状态值赋予[状态]中表示重入成功并返回true。int nextc = c + acquires;if (nextc < 0) {// overflowthrow new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");}setState(nextc);return true;}// ---- 除了上述阐述的两种情况外,其它对独占失败和已被其它线程独占的情况都会直接返回false。return false;}/*** @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 名称 ---------------------------------------------------------* 尝试释放* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 作用 ---------------------------------------------------------* 令当前线程在独占模式下释放指定数量的状态至当前同步/AQS中,如果其在独占模式下获取的所有状态都被释放则* 返回true;否则返回false。* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 逻辑 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 方法首先计算当前同步/AQS的[状态]减去指定数量状态后的值,随后判断当前线程是否是[独占拥有者线程]。* 该是为了保证[状态]不会被非法释放,因为按照可重入锁的规则只有独占同步/AQS的线程才可以释放[状态]。如果* 不是则抛出非法监视状态异常。* ---- 如果当前线程为[独占拥有者线程],则判断减去指定数量状态后的差是否等于0,是则说明当前线程已将其在独* 占模式下获取到的当前同步/AQS的状态全部释放,这意味着当前线程解除了基础对当前同步/AQS的独占,因此会* 将[独占拥有者线程]置null。而无论当前线程是否解除了对当前同步/AQS的独占,都需要将[状态]赋值为新值并返回* 返回释放结果。* ---- 上述流程中有一点比较奇怪的是并没有对[状态]少于指定数量的情况进行定义,即指定数量的状态大于[状态]的* 情况,这一点可能是因为在可重入锁的整体规则中并不会导致该情况的发生。*/@Overrideprotected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {// ---- 方法首先计算当前同步/AQS的[状态]减去指定数量状态后的值,随后判断当前线程是否是[独占拥有者线程]。// 该是为了保证[状态]不会被非法释放,因为按照可重入锁的规则只有独占同步/AQS的线程才可以释放[状态]。如// 果不是则抛出非法监视状态异常。int c = getState() - releases;if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();}// ---- 如果当前线程为[独占拥有者线程],则判断减去指定数量状态后的差是否等于0,是则说明当前线程已将其在// 独占模式下获取到的当前同步/AQS的状态全部释放,这意味着当前线程解除了基础对当前同步/AQS的独占,因// 此会将[独占拥有者线程]置null。而无论当前线程是否解除了对当前同步/AQS的独占,都需要将[状态]赋值为新值// 并返回返回释放结果。// ---- 上述流程中有一点比较奇怪的是并没有对[状态]少于指定数量的情况进行定义,即指定数量的状态大于[状态]// 的情况,这一点可能是因为在可重入锁的整体规则中并不会导致该情况的发生。boolean free = false;if (c == 0) {free = true;setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);}setState(c);return free;}/*** @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 名称 ---------------------------------------------------------* 是否独占持有* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 作用 ---------------------------------------------------------* 判断当前线程是否独占当前同步/AQS,是则返回true;否则返回false。* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 逻辑 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 方法会直接判断当前线程是否为[独占拥有者线程],是则返回true;否则返回false。*/@Overrideprotected final boolean isHeldExclusively() {// While we must in general read state before owner, we don't need to do so to check if current thread is owner// 虽然我们通常必须在所有者之前读取状态,但我们不需要这样做来检查当前线程是否是拥有者。(?啥意思?)// 方法会直接判断当前线程是否是[独占拥有者线程],是则返回true;否则返回false。return getExclusiveOwnerThread() == Thread.currentThread();}/*** @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 名称 ---------------------------------------------------------* 新条件* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 作用 ---------------------------------------------------------* 为当前同步/AQS创建一个新条件。* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 逻辑 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 方法会直接创建一个条件对象后返回。*/final ConditionObject newCondition() {// 实例化一个新的条件对象。return new ConditionObject();}// Methods relayed from outer class// 从外部类转发的方法/*** @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 名称 ---------------------------------------------------------* 获取拥有者* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 作用 ---------------------------------------------------------* 获取当前的同步/AQS的独占线程* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 逻辑 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 方法首先会判断[状态]是否为0,是则直接返回null;否则返回[独占拥有者线程]。之所以要判断[状态]是否为0* 是因为并发可能导致存在[状态]为0但[独占拥有者线程]存在的短暂中间状态,因此需要通过该判断确保在该情况下* 返回null。*/final Thread getOwner() {return getState() == 0 ? null : getExclusiveOwnerThread();}/*** @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 名称 ---------------------------------------------------------* 获取持有总数* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 作用 ---------------------------------------------------------* 获取当前AQS被当前线程在独占模式下获取的状态总数* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 逻辑 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 方法首先会判断当前当前同步/AQS是否是被当前线程独占,是则返回[状态],否则返回0。*/final int getHoldCount() {return isHeldExclusively() ? getState() : 0;}/*** @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 名称 ---------------------------------------------------------* 是否加锁* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 作用 ---------------------------------------------------------* 判断当前AQS是否已被独占,是则返回true;否则返回false。* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 逻辑 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 方法首先会判断当前当前同步/AQS是否是被当前线程独占,是则返回[状态],否则返回0。*/final boolean isLocked() {return getState() != 0;}/*** Reconstitutes the instance from a stream (that is, deserializes it).* 从流中重组实例(即反序列化)** @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 名称 ---------------------------------------------------------* 读取对象。* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 作用 ---------------------------------------------------------* 用于从流中序列化当前同步/AQS,而反序列化得到的当前同步/AQS会处于不被独占的状态。* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 逻辑 ---------------------------------------------------------* ----*/private void readObject(ObjectInputStream s) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {// 序列化方法,不用在意。s.defaultReadObject();setState(0); // reset to unlocked state}}/*** Sync object for non-fair locks* 非公平锁的同步对象** @Description: ----------------------------------------------------------- 名称 -----------------------------------------------------------* 非公平同步类* @Description: ----------------------------------------------------------- 作用 -----------------------------------------------------------* AQS的孙类,也是同步类的子类,用于实现可重入锁类的非公平模式。* @Description: ----------------------------------------------------------- 逻辑 -----------------------------------------------------------* ----*/static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {private static final long serialVersionUID = 7316153563782823691L;/*** Performs lock. Try immediate barge, backing up to normal acquire on failure.* 执行锁。尝试立刻冲撞,失败则回到正常获取。** @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 名称 ---------------------------------------------------------* 加锁* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 作用 ---------------------------------------------------------* 令当前线程独占当前非公平同步/AQS,如果当前非公平同步/AQS已被其它线程独占则无限等待至独占为止。* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 逻辑 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 方法首先会尝试通过AQS操作直接将[状态]由0修改为1,如果成功则将当前线程存入[独占拥有者线程]中;否则* 调用acquire(int arg)方法按正常的AQS流程独占当前非公平同步/AQS。*/@Overridefinal void lock() {// ---- 方法首先会尝试将当前非公平同步/AQS的[状态]由0CAS赋值为1,成功则意味当前线程已经成功独占当前非// 公平同步,遂将[独占拥有者线程]赋值为当前线程;否则意味着当前非公平同步/AQS已被其它线程独占,故而直// 接调用父类AQS的acquire(int arg)方法等待至成功独占当前非公平同步/AQS为止。if (compareAndSetState(0, 1)) {setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());} else {acquire(1);}}/*** Performs lock. Try immediate barge, backing up to normal acquire on failure.* 执行锁。尝试立刻冲撞,失败则回到正常获取。** @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 名称 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 尝试加锁* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 作用 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 尝试令当前线程持有当前非公平同步/AQS,成功则返回true;否则返回false。* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 逻辑 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 方法会直接通过nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires)方法尝试尝试令当前线程持有当前非公平同步/AQS,成功则返* 回true;否则返回false。*/@Overrideprotected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);}}/*** Sync object for fair locks* 公平锁的同步对象** @Description: ----------------------------------------------------------- 名称 -----------------------------------------------------------* ---- 公平同步类* @Description: ----------------------------------------------------------- 作用 -----------------------------------------------------------* ---- 作为实现公平可重入锁的底层实现* @Description: ----------------------------------------------------------- 逻辑 -----------------------------------------------------------* ----*/static final class FairSync extends Sync {private static final long serialVersionUID = -3000897897090466540L;/*** Performs lock. Try immediate barge, backing up to normal acquire on failure.* 执行锁。尝试立刻冲撞,失败则回到正常获取。** @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 名称 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 加锁* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 作用 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 令当前线程持有当前公平同步/AQS,如果当前非公平同步/AQS已被其它线程独占则无限等待至可被独占为止。* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 逻辑 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 方法直接通过调用acquire(int arg)方法按正常的AQS流程独占当前公平同步/AQS。即如果当前没有其它正在独* 占当前公平同步/AQS的线程,则当前线程不加入同步队列直接独占当前公平同步/AQS;否则需加入同步队列按顺* 序依次独占当前公平同步/AQS。*/@Overridefinal void lock() {acquire(1);}/*** Fair version of tryAcquire. Don't grant access unless recursive call or no waiters or is first.* 尝试获取的公平版本。不授予访问除非递归调用(即重入)或者没有等待者或者是首个访问线程。** @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 名称 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 尝试加锁* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 作用 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 令当前线程尝试独占当前公平同步/AQS* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 关键 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 在公平同步中,当前线程想要独占必须在[同步队列]不存在线程的条件下执行。*/@Overrideprotected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {// ---- 方法首先会获取当前线程,随后再从公平同步中获取[状态],并判断[状态]是否为0,以判断当前线程是否可// 以对公平同步进行独占。final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();int c = getState();if (c == 0) {// ---- 如果[状态]为0,意味公平同步未必独占,因此当前线程可以尝试进行独占。但由于公平性的原因,当前线// 程首先会判断[同步队列]中是否存在等待中的线程,如果存在则不允许获取,返回false。而在不存在的情况下// 如果竞争获取失败,则也返回false表示失败。而如果成功则将当前线程存入[独占拥有者线程]中。if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() && compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);return true;}} else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {// ---- 如果[状态]不为0,意味着公平同步已被独占。此时可以继续判断当前线程是否为[独占拥有者线程],是则// 可以直接增加指定数量的[状态]并返回true以表示重入。但需要注意的是[状态]并不支持无限大,因此当增加的// [状态]小于0时就说明[状态]发生了内存溢出,此时会抛出错误。int nextc = c + acquires;if (nextc < 0) {throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");}setState(nextc);return true;}// ---- 如果公平同步已被独占并且当前线程不为[独占拥有者线程],以及虽然公平同步未被独占但当前线程不具备获// 取资格或获取失败,则方法返回false。return false;}}/*** Creates an instance of {@code ReentrantLock}. This is equivalent to using {@code ReentrantLock(false)}.* 创建一个可重入锁实例。这等价于ReentrantLock(false)方法。** @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 名称 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 可重入锁* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 作用 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 创建非公平的可重入锁* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 关键 ---------------------------------------------------------*/public ReentrantLock() {// 可重入锁默认是非公平同步机制。sync = new NonfairSync();}/*** Creates an instance of {@code ReentrantLock} with the given fairness policy.* 随指定的公平策略创建可重入锁实例** @param fair {@code true} if this lock should use a fair ordering policy 如果锁应该使用公平顺序策略则为true* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 名称 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 可重入锁* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 作用 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 创建指定公平策略的可重入锁* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 关键 ---------------------------------------------------------*/public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) {// 设置可重入锁是是否公平。sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync();}/*** Acquires the lock.* 获取锁* <p>* Acquires the lock if it is not held by another thread and returns immediately, setting the lock hold count to one.* 如果锁未被其它线程持有则获取锁并立即返回,设置锁持有总数为1。* <p>* If the current thread already holds the lock then the hold count is incremented by one and the method returns* immediately.* 如果锁已被当前线程持有那么持有总数加1并且方法立即返回。* <p>* If the lock is held by another thread then the current thread becomes disabled for thread scheduling purposes* and lies dormant until the lock has been acquired, at which time the lock hold count is set to one.* 如果锁被其它线程持有那么出于线程调度目的当前线程将无效并休眠至成功获取锁,在该情况下锁持有总数将设置* 为1。** @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 名称 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 加锁* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 作用 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 令当前线程独占当前可重入锁。如果当前可重入锁未被独占则直接独占并立即返回;如果当前可重入锁已被当* 前线程独占则直接增加独占次数(重入)并立即返回;如果当前可重入锁已被其它线程独占则无限等待至成功独占* 后再返回。此外如果当前线程在进入方法/等待加锁时已/被中断不会抛出中断异常,但中断状态会被保留。* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 情况 ---------------------------------------------------------* ----*/@Overridepublic void lock() {sync.lock();}/*** Acquires the lock unless the current thread is {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupted}.* 获取锁除非当前线程已中断。* <p>* Acquires the lock if it is not held by another thread and returns immediately, setting the lock hold count to one.* 如果锁未被其它线程持有则持有锁并理解返回,设置锁持有总数为1.* <p>* If the current thread already holds this lock then the hold count is incremented by one and the method returns* immediately.* 如果当前锁已被当前线程持有则持有总数加1并且立即返回。* <p>* If the lock is held by another thread then the current thread becomes disabled for thread scheduling purposes* and lies dormant until one of two things happens:* 如果锁被其它线程持有那么出于线程调度目的当前线程将无效并休眠至两件事情发生:* 为1。* <ul>* <li>The lock is acquired by the current thread; or* 锁被当前线程成功持有;* <li>Some other thread {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupts} the current thread.* 某些其它线程中断当前线程。* </ul>* <p>* If the lock is acquired by the current thread then the lock hold count is set to one.* 如果锁被当前线程获取则所持有总数设置1.* <p>* If the current thread:* 如果当前线程:* <ul>* <li>has its interrupted status set on entry to this method; or* 进入当前方法时已被中断;或者* <li>is {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupted} while acquiring the lock,* 在获取锁期间被中断* </ul>* <p>* then {@link InterruptedException} is thrown and the current thread's interrupted status is cleared.* 那么将抛出中断异常并且当前线程中断状态将被清理。* <p>* In this implementation, as this method is an explicit interruption point, preference is given to responding to* the interrupt over normal or reentrant acquisition of the lock.* 在当前实现中,方法是一个显式中断点,偏向于相关正常中断或重入获取锁。** @throws InterruptedException if the current thread is interrupted* 中断异常:如果当前线程已被中断* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 名称 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 加锁(可中断)* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 作用 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 令当前线程独占当前可重入锁。如果当前可重入锁未被独占则直接独占并立即返回;如果当前可重入锁已被当* 前线程独占则直接增加独占次数(重入)并立即返回;如果当前可重入锁已被其它线程独占则无限等待至成功独占* 后再返回。此外如果当前线程在进入方法/等待加锁时已/被中断会抛出中断异常,且中断状态会被取消。* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 情况 ---------------------------------------------------------* ----*/@Overridepublic void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException {sync.acquireInterruptibly(1);}/*** Acquires the lock only if it is not held by another thread at the time of invocation.* 只当未被其它线程持有时获取一次锁。* <p>* Acquires the lock if it is not held by another thread and returns immediately with the value {@code true},* setting the lock hold count to one. Even when this lock has been set to use a fair ordering policy, a call to* {@code tryLock()} <em>will</em> immediately acquire the lock if it is available, whether or not other threads are* currently waiting for the lock. This "barging" behavior can be useful in certain circumstances, even* though it breaks fairness. If you want to honor the fairness setting for this lock, then use* {@link #tryLock(long, TimeUnit) tryLock(0, TimeUnit.SECONDS) } which is almost equivalent (it also detects* interruption).* 如果未被其它线程持有则获取锁并随着true值立即返回,设置所持有次数为1。即使当锁被设置为使用公平顺序策略,* 如果锁可用调用一次tryLock()也将立即获得锁,无论是否有其它线程正在等待锁。该冲撞行为有利于某些情况,虽然* 它破坏了公平性。如果你想要遵守锁的公平性设置,那么使用tryLock(long, TimeUnit)方法是几乎相同的(它也检查中* 断)* <p>* If the current thread already holds this lock then the hold count is incremented by one and the method returns* {@code true}.* 如果当前线程已经持有该锁则持有总数增加并且返回返回true。* <p>* If the lock is held by another thread then this method will return immediately with the value {@code false}.* 如果锁已被其它线程持有那么方法理解随着false返回。** @return {@code true} if the lock was free and was acquired by the current thread, or the lock was already held* by the current thread; and {@code false} otherwise* 如果锁是自由的并且被当前线程所获取,或者锁已经被当前线程所持有则返回true;否则返回false。* <p>* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 名称 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 尝试加锁* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 作用 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 令当前线程尝试独占当前可重入锁。如果当前可重入锁未被独占则直接独占并立即返回true;如果当前可重入锁* 已被当前线程独占则直接增加独占次数(重入)并立即返回true;如果当前可重入锁已被其它线程独占则立即返回* false。* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 情况 ---------------------------------------------------------* ----*/@Overridepublic boolean tryLock() {return sync.nonfairTryAcquire(1);}/*** Acquires the lock if it is not held by another thread within the given waiting time and the current thread has not* been {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupted}.* 如果锁未在指定等待时间内被其它线程持有并且当前线程没有被中断则获取锁。* <p>* Acquires the lock if it is not held by another thread and returns immediately with the value {@code true}, setting* the lock hold count to one. If this lock has been set to use a fair ordering policy then an available lock <em>will* not</em> be acquired if any other threads are waiting for the lock. This is in contrast to the {@link #tryLock()}* method. If you want a timed {@code tryLock} that does permit barging on a fair lock then combine the timed and* un-timed forms together:* 如果锁没有被其它线程持有则获取锁并立即返回true,设置锁的持有总数为1.如果锁已被设置为公平顺序策略那么如* 果有任意其它线程正在等待该锁那么一个可用的锁将无法被获取。这与tryLock()形成对比/相反。如果你想要一个允* 许闯入公平锁的定时tryLock,那么将定时和非定时表单组合在一起:* <pre> {@code* if (lock.tryLock() || lock.tryLock(timeout, unit)) {* ...* }}</pre>** <p>* If the current thread already holds this lock then the hold count is incremented by one and the method returns* {@code true}.* 如果当前线程已经持有锁那么持有总数增加1并立即返回true。* <p>* If the lock is held by another thread then the current thread becomes disabled for thread scheduling purposes and* lies dormant until one of three things happens:* 如果锁被其它线程持有那么当前线程出于线程调度目的将变得无效并将休眠至三种事情之一发生:* <ul>** <li>The lock is acquired by the current thread; or* 锁被当前线程获取;或者* <li>Some other thread {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupts} the current thread; or* 某些其它线程中断当前线程;或者* <li>The specified waiting time elapses* 指定等待时间到期* </ul>* <p>* If the lock is acquired then the value {@code true} is returned and the lock hold count is set to one.* 如果锁被获取那么返回true并且锁持有总数设置为1。* <p>* If the current thread:* 如果当前线程:* <ul>* <li>has its interrupted status set on entry to this method; or* 在进入当前方法时已被中断;或者* <li>is {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupted} while acquiring the lock,* 在获取锁期间被中断,* </ul>* then {@link InterruptedException} is thrown and the current thread's interrupted status is cleared.* 那么将抛出中断异常并且当前线程的中断状态将被清理。* <p>* If the specified waiting time elapses then the value {@code false} is returned. If the time is less than or equal* to zero, the method will not wait at all.* 如果指定等待时间到期那么返回false。如果时间小于或等于0,方法将完全不等待。* <p>* In this implementation, as this method is an explicit interruption point, preference is given to responding to the* interrupt over normal or reentrant acquisition of the lock, and over reporting the elapse of the waiting time.* 在当前实现中,例如当前方法是一个显式中断点,偏向沉溺于相关的正常中断或重入锁的获取,以及在等待时间消* 逝时报告。** @param timeout the time to wait for the lock 等待锁的时间* @param unit the time unit of the timeout argument 超时参数的时间单位* @return {@code true} if the lock was free and was acquired by the current thread, or the lock was already held* by the current thread; and {@code false} if the waiting time elapsed before the lock could be acquired* 如果锁是自由的并且被当前线程获取,或者锁已经被当前线程获取则返回true;以及如果在获取锁前等待时间消逝则* 返回false。* @throws InterruptedException if the current thread is interrupted* 中断异常:如果当前线程被中断。* @throws NullPointerException if the time unit is null* 空指针异常:如果时间单位为null* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 名称 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 尝试加锁* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 作用 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 令当前线程在指定等待时间内尝试独占当前可重入锁。如果当前可重入锁未被独占则直接独占并立即返回true;* 如果当前可重入锁已被当前线程独占则直接增加独占次数(重入)并立即返回true;如果当前可重入锁已被其它线程* 独占则在指定等待时间内等待至被独占并返回true;超出指定等待时间则返回false。此外如果当前线程在进入方法/* 等待加锁时已/被中断会抛出中断异常,且中断状态会被取消。* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 情况 ---------------------------------------------------------* ----*/@Overridepublic boolean tryLock(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {return sync.tryAcquireNanos(1, unit.toNanos(timeout));}/*** Attempts to release this lock.* 尝试释放当前锁。* <p>* If the current thread is the holder of this lock then the hold count is decremented. If the hold count is now zero* then the lock is released. If the current thread is not the holder of this lock then* {@link IllegalMonitorStateException} is thrown.* 如果当前线程持有当前锁那么持有总数减少。如果当前持有总数为0那么锁被释放。如果当前线程没有持有当前锁则* 抛出非法监视器异常。** @throws IllegalMonitorStateException if the current thread does not hold this lock* 非法监视器异常:如果当前线程没有持有当前锁* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 名称 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 解锁* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 作用 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 令当前线程解除对当前可重入锁的独占。如果当前可重入锁未被当前线程独占则抛出非法监视器异常;如果当前* 可重入锁已被当前线程独占则减少独占总数减一;如果独占总数减少后归零则彻底解除独占。* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 情况 ---------------------------------------------------------* ----*/@Overridepublic void unlock() {sync.release(1);}/*** Returns a {@link Condition} instance for use with this {@link Lock} instance.* 使用当前锁实例返回一个条件实例。* <p>* The returned {@link Condition} instance supports the same usages as do the {@link Object} monitor methods* ({@link Object#wait() wait}, {@link Object#notify notify}, and {@link Object#notifyAll notifyAll}) when used with* the built-in monitor lock.* 返回的条件实例当随构建的监视器锁使用时支持类似于对象监视器方法wait()/notify()/notifyAll()相同的作用。* <ul>** <li>* If this lock is not held when any of the {@link Condition} {@linkplain Condition#await() waiting} or {@linkplain* Condition#signal signalling} methods are called, then an {@link IllegalMonitorStateException} is thrown.* 如果任意条件的等待/信号方法被调用时如果锁未被持有,那么将抛出非法监视器异常。* <li>* When the condition {@linkplain Condition#await() waiting} methods are called the lock is released and, before* they return, the lock is reacquired and the lock hold count restored to what it was when the method was called.* 当条件等待方法被调用锁将被释放,而且在方法返回前锁将被重新获取,并且锁持有总数将恢复至方法调用时的样子。* <li>* If a thread is {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupted} while waiting then the wait will terminate, an* {@link InterruptedException} will be thrown, and the thread's interrupted status will be cleared.* 如果一个线程在等待期间被中断那么等待将终止,一个中断异常将被抛出,并且线程的中断状态将被清除。* <li> Waiting threads are signalled in FIFO order.* 等待中的线程将在FIFO的下顺序被信号。* <li>* The ordering of lock reacquisition for threads returning from waiting methods is the same as for threads initially* acquiring the lock, which is in the default case not specified, but for <em>fair</em> locks favors those threads* that have been waiting the longest.* 线程从等待的线程中返回获取锁的顺序与线程初始获取锁的顺序相同(即先等待的线程先获取锁),这在默认情况下* 不指定,但公平锁偏向于线程中已经等待最久的那一个。* </ul>** @return the Condition object 条件对象* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 名称 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 新条件* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 作用 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 基于当前可重入锁创建条件。* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 情况 ---------------------------------------------------------* ----*/@Overridepublic Condition newCondition() {return sync.newCondition();}/*** Queries the number of holds on this lock by the current thread.* 通过当前线程查询当前锁被持有的次数。* <p>* A thread has a hold on a lock for each lock action that is not matched by an unlock action.* 线程对每个锁动作都有一个锁的保持,而这个锁动作没有与解锁动作相匹配(即加锁的次数与解锁的次数不一定相同)。* <p>* The hold count information is typically only used for testing and debugging purposes. For example, if a certain* section of code should not be entered with the lock already held then we can assert that fact:* 持有总数信息通常是为了测试和调试目的使用。例如,如果代码的某部分不应该随已持有的锁进入那么可以断言事实:* <pre> {@code* class X {* ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();* // ...* public void m() {* assert lock.getHoldCount() == 0;* lock.lock();* try {* // ... method body* } finally {* lock.unlock();* }* }* }}</pre>** @return the number of holds on this lock by the current thread, or zero if this lock is not held by the current* thread* 锁被当前线程持有的数量,或者如果锁未被当前线程持有则为0。* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 名称 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 获取持有总数。* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 作用 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 获取当前线程持有当前可重入锁的总数。* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 情况 ---------------------------------------------------------* ----*/public int getHoldCount() {return sync.getHoldCount();}/*** Queries if this lock is held by the current thread.* 查询当前线程是否持有当前锁。* <p>* Analogous to the {@link Thread#holdsLock(Object)} method for built-in monitor locks, this method is typically* used for debugging and testing. For example, a method that should only be called while a lock is held can assert* that this is the case:* 类似于监视器锁的holdsLock(Object)方法,该方法常用用于调试和测试。例如,一个方法只应该在锁被持有时调用可* 以如此断言:* <pre> {@code* class X {* ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();* // ...** public void m() {* assert lock.isHeldByCurrentThread();* // ... method body* }* }}</pre>** <p>* It can also be used to ensure that a reentrant lock is used in a non-reentrant manner, for example:* 也可以确定一个可重入多在被非重入的使用,例如:* <pre> {@code* class X {* ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();* // ...** public void m() {* assert !lock.isHeldByCurrentThread();* lock.lock();* try {* // ... method body* } finally {* lock.unlock();* }* }* }}</pre>** @return {@code true} if current thread holds this lock and {@code false} otherwise* 如果当前线程持有当前锁返回true;否则返回false。* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 名称 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 是否被当前线程持有* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 作用 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 判断当前线程是否独占当前可重入锁,是则返回true;否则返回false。* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 情况 ---------------------------------------------------------* ----*/public boolean isHeldByCurrentThread() {return sync.isHeldExclusively();}/*** Queries if this lock is held by any thread. This method is designed for use in monitoring of the system state, not* for synchronization control.* 查询当前锁是否被任意线程持有。该方法被设计用于系统状态的监视,不是为了同步控制。** @return {@code true} if any thread holds this lock and {@code false} otherwise* 如果任意线程持有锁则返回true;否则返回false。* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 名称 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 是否锁* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 作用 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 判断当前可重入锁是否已被独占,是则返回true;否则返回false。* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 情况 ---------------------------------------------------------* ----*/public boolean isLocked() {// ---- 方法通过判断[状态]是否为0实现。return sync.isLocked();}/*** Returns {@code true} if this lock has fairness set true.* 如果当前锁已被设置为公平则返回true。** @return {@code true} if this lock has fairness set true 如果当前锁已被设置为公平则返回true* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 名称 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 是否公平* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 作用 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 判断当前可重入锁是否公平,是则返回true;否则返回false。* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 情况 ---------------------------------------------------------*/public final boolean isFair() {// ---- 方法通过判断[同步]是否为公平同步类实现。return sync instanceof FairSync;}/*** Returns the thread that currently owns this lock, or {@code null} if not owned. When this method is called by a* thread that is not the owner, the return value reflects a best-effort approximation of current lock status. For* example, the owner may be momentarily {@code null} even if there are threads trying to acquire the lock but* have not yet done so. This method is designed to facilitate construction of subclasses that provide more extensive* lock monitoring facilities.* 返回当前持有锁的线程,或者如果未持有则返回null。当当前方法通过一个不是拥有者的线程调用时,返回值代表当* 前锁状态的最佳效率的近似值。例如:拥有者可能短暂为null即使有现成尝试获取锁但尚未实现。该方法被设计促进* 提供更广阔的锁监视工具子类的构造。** @return the owner, or {@code null} if not owned 如果未被持有则返回null* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 名称 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 获取拥有者* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 作用 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 获取独占当前可重入锁的线程,由于独占线程记录的消除位于独占解除时候,因此如果发现独占被解除则独占线* 程一定为null。* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 情况 ---------------------------------------------------------*/protected Thread getOwner() {return sync.getOwner();}/*** Queries whether any threads are waiting to acquire this lock. Note that because cancellations may occur at any* time, a {@code true} return does not guarantee that any other thread will ever acquire this lock. This method is* designed primarily for use in monitoring of the system state.* 查询是否有线程在等待获取当前锁。注意由于取消可能在任意时间发生,因此返回true无法保证任意其它线程将永远* 获得锁。该方法主要被设计用于系统状态的监视。** @return {@code true} if there may be other threads waiting to acquire the lock* 如果有其它线程等待获取锁则返回true。* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 名称 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 有排队线程* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 作用 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 判断是否有线程在等待获取当前可重入锁,是则返回true;否则返回false。由于独占的获取/解除可能在任意时* 间发生,因此该方法的返回值无法作为准确的判断依据。* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 情况 ---------------------------------------------------------*/public final boolean hasQueuedThreads() {return sync.hasQueuedThreads();}/*** Queries whether the given thread is waiting to acquire this lock. Note that because cancellations may occur at* any time, a {@code true} return does not guarantee that this thread will ever acquire this lock. This method is* designed primarily for use in monitoring of the system state.* 查询指定线程是否正在等待获取当前锁。注意因为取消可能在任意时间发生,因此true无法保证当前线程将会获得锁。* 当前方法主要被设计用于系统状态的监视。** @param thread the thread 线程* @return {@code true} if the given thread is queued waiting for this lock 如果指定线程正在排队等待当前锁。* @throws NullPointerException if the thread is null* 空指针异常:如果线程为null* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 名称 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 有排队线程* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 作用 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 判断指定线程是否在等待获取当前可重入锁,是则返回true;否则返回false。由于独占的获取/解除可能在任意* 时间发生,因此该方法的返回值无法作为准确的判断依据。* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 情况 ---------------------------------------------------------*/public final boolean hasQueuedThread(Thread thread) {return sync.isQueued(thread);}/*** Returns an estimate of the number of threads waiting to acquire this lock. The value is only an estimate* because the number of threads may change dynamically while this method traverses internal data structures.* This method is designed for use in monitoring of the system state, not for synchronization control.* 返回正在等待获取当前锁的线程估计数量。该值只是估计值因为线程的数量在方法遍历内部数据结构期间可能动态* 的改变。当前方法被设置用于系统状态的监视,不为同步控制。** @return the estimated number of threads waiting for this lock 正在等待获取当前锁的线程估计数量* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 名称 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 获取队列长度* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 作用 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 获取等待独占当前可重入锁的线程总数的估计值。之所以是估计值是因为在查询期间总数可能发生变化。* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 情况 ---------------------------------------------------------*/public final int getQueueLength() {return sync.getQueueLength();}/*** Returns a collection containing threads that may be waiting to acquire this lock. Because the actual set of* threads may change dynamically while constructing this result, the returned collection is only a best-effort* estimate. The elements of the returned collection are in no particular order. This method is designed to* facilitate construction of subclasses that provide more extensive monitoring facilities.* 获取可能正在等待获取当前锁的线程集。因为线程的实际集可能在构造结果期间动态的改变,因此返回的集合只能* 是最尽最大可能的估计值。返回集中的元素并不按特定的顺序。该方法被设计用于促进提供更多衍生监视功能子类* 的构造。** @return the collection of threads 线程集* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 名称 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 获取排队线程集* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 作用 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 获取等待独占当前可重入锁的线程的估计集。之所以是估计集是因为在查询期间等待的线程可能发生变化。* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 情况 ---------------------------------------------------------*/protected Collection<Thread> getQueuedThreads() {return sync.getQueuedThreads();}/*** Queries whether any threads are waiting on the given condition associated with this lock. Note that because* timeouts and interrupts may occur at any time, a {@code true} return does not guarantee that a future* {@code signal} will awaken any threads. This method is designed primarily for use in monitoring of the system* state.* 查询是否有线程在当前锁关联的指定条件中等待。注意因为超时和中断可能在任意时间发生,因此返回true并不能* 保证一个未来的信号将唤醒任意线程。该方法主要设计用于系统状态的监视。** @param condition the condition 条件* @return {@code true} if there are any waiting threads 如果有任意等待中的线程则为true* @throws IllegalMonitorStateException if this lock is not held* 非法监视器异常:如果锁未被持有* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the given condition is not associated with this lock* 非法参数异常:日过指定条件不关联当前锁* @throws NullPointerException if the condition is null* 如果条件为null* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 名称 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 存在等待者* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 作用 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 判断指定与当前可重入锁关联的条件中是否存在等待线程,是则返回true;否则返回false。由于等待线程在查* 询期间可能发生变化,因此该方法的返回值无法作为准确的判断依据。* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 情况 ---------------------------------------------------------*/public boolean hasWaiters(Condition condition) {if (condition == null) {throw new NullPointerException();}if (!(condition instanceof AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject)) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("not owner");}return sync.hasWaiters((AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject) condition);}/*** Returns an estimate of the number of threads waiting on the given condition associated with this lock. Note that* because timeouts and interrupts may occur at any time, the estimate serves only as an upper bound on the* actual number of waiters. This method is designed for use in monitoring of the system state, not for* synchronization control.* 返回指定与当前可重入锁关联的条件中等待的线程的估计集。注意由于超时和中断可能在任意时间发生,因此该估计* 值只能作为等待者的实际数量的上限。该方法被设计用于对系统状态进行监视,不是你为了同步控制。** @param condition the condition 条件* @return the estimated number of waiting threads 等待线程的估计数量* @throws IllegalMonitorStateException if this lock is not held* 非法监视器状态异常:如果锁未被持有* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the given condition is not associated with this lock* 非法参数异常:如果指定条件不与当前锁关联* @throws NullPointerException if the condition is null* 空指针异常:如果条件为null* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 名称 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 存在等待队列长度* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 作用 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 获取在指定条件中等待获取当前可重入锁的线程总数估计值,由于在获取期间等待线程的总数可能因为取消(超* 时/中断)而发生变化,因此该方法的返回值不能作为准确的判断依据。* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 注意 ---------------------------------------------------------*/public int getWaitQueueLength(Condition condition) {// ---- 方法首先会判断指定条件是否为null,是则直接抛出中断异常。if (condition == null) {throw new NullPointerException();}// ---- 在条件不为null的情况下,方法会判断指定条件是否与当前可重入锁关联,是则抛出非法参数异常。if (!(condition instanceof AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject)) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("not owner");}// ---- 调用[同步]的getWaitQueueLength()方法获取在指定条件中等待的线程数量估计值。return sync.getWaitQueueLength((AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject) condition);}/*** Returns a collection containing those threads that may be waiting on the given condition associated with this lock.* Because the actual set of threads may change dynamically while constructing this result, the returned collection* is only a best-effort estimate. The elements of the returned collection are in no particular order. This method is* designed to facilitate construction of subclasses that provide more extensive condition monitoring facilities.* 返回包含在指定条件中等待获取当前锁的线程的集。因为在构造结果期间线程的实际集合可能发生变化,因为返回的* 集只是一个尽最大可能得估计值。返回集中的元素并不按特定的顺序。该方法被设计用于促进提供更多延伸条件监视* 工具子类的构建。** @param condition the condition 条件* @return the collection of threads 线程集* @throws IllegalMonitorStateException if this lock is not held* 非法监视器状态异常:如果锁未被持有* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the given condition is not associated with this lock* 非法参数异常:如果指定条件不与当前锁关联* @throws NullPointerException if the condition is null* 空指针一次航:如果条件不为null* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 名称 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 存在等待线程集* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 作用 ---------------------------------------------------------* ---- 获取在指定条件中等待获取当前可重入锁的线程估计集,由于在获取期间等待线程的总数可能因为取消(超时/* 中断)而发生变化,因此该方法的返回值不能作为准确的判断依据。* @Description: --------------------------------------------------------- 注意 ---------------------------------------------------------*/protected Collection<Thread> getWaitingThreads(Condition condition) {if (condition == null) {throw new NullPointerException();}if (!(condition instanceof AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject)) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("not owner");}return sync.getWaitingThreads((AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject) condition);}/*** Returns a string identifying this lock, as well as its lock state.* The state, in brackets, includes either the String {@code "Unlocked"}* or the String {@code "Locked by"} followed by the* {@linkplain Thread#getName name} of the owning thread.** @return a string identifying this lock, as well as its lock state*/@Overridepublic String toString() {Thread o = sync.getOwner();return super.toString() + ((o == null) ?"[Unlocked]" :"[Locked by thread " + o.getName() + "]");}
}相关文章:

Java Lock/AQS ReentrantLock 源码
前言 相关系列 《Java & Lock & 目录》(持续更新)《Java & AQS & 目录》(持续更新)《Java & Lock/AQS & ReentrantLock & 源码》(学习过程/多有漏误/仅作参考/不再更新)《Jav…...

魔法伤害--是谁偷走了我的0
起因:需要迁移数据进行数据更新,使用pandasorcal进行数据处理以及库迁移 首先把数据导出为xls格式数据文件,使用python import pandas as pdnew_obj pd.read_excel(ne,dtype{DAY: str, MONTH: str}) 原有导出数据格式为: 使用…...

【ArcGIS Pro实操第4期】绘制三维地图
【ArcGIS Pro实操第4期】绘制三维地图 ArcGIS Pro绘制三维地图-以DEM高程为例参考 如何使用ArcGIS Pro将栅格数据用三维的形式进行表达?在ArcGIS里可以使用ArcScene来实现,ArcGIS Pro实现原理跟ArcScene一致。由于Esri未来将不再对ArcGIS更新,…...

Vuestic 整理使用
简单示例 1. 条件渲染 2. 列表渲染 3. 组件插槽 4. 插值语法 5. 前后端路由的区别(还是转一下,可以减少代码量)SFC 构建 … … Okay,可以干活了,通顺 数据表的操作更加简化了 数据类别通过后端路由区别,但是还得由前端路由转一下 简单了许多呀,上脚手…...

学习伊圣雨老师的 epoll 编程
(1)书里提出了疑问,epoll 函数的工作方式,区分为水平触发与边缘触发 : (2) 谢谢...

详细了解C++11(1)
大家好呀,我是残念,希望在你看完之后,能对你有所帮助,有什么不足请指正!共同学习交流哦 本文由:残念ing原创CSDN首发,如需要转载请通知 个人主页:残念ing-CSDN博客,欢迎各…...

ITA的去锅盖处理流程
一、说明 锅盖是什么 锅盖的类型有哪些 二、去锅盖处理流程 去锅盖算法首先需要采集一份锅盖模板数据,该模板数据用户可以自定义保存,方便后面的开机重启直接导入使用。去锅盖处理包含两个历程:保存锅盖模板;去锅盖处理。 保存锅盖模板: ( 1 ) 打开采集锅盖模板开关。…...

日志管理系统的系统目标是什么?
在网络安全、数据管理、故障排查等领域,日志都被广泛使用并需要进行有效的管理与分析。因此,日志管理系统的系统目标显得尤为重要,如以下几方面。 1、确保数据的安全性及完整性 在企业和组织的日常运营中,各类信息数据都会通过系统…...

uniapp 底部导航栏tabBar设置后不显示的问题——已解决
uniapp 底部导航栏tabBar设置后不显示的问题——已解决 网上找了一堆解决办法,挨个对着试吧 解决办法一:tabBar里的list第一项和page中的第一项要相同,确实就能显示了。但是问题来了,page中的第一项是入口页,那就意味…...

JVM 类加载器
字节码的结构 魔数u4 cafe babe 版本u4 52 java8 常量池计数器u2 从1开始,0索引留给不需要的情况 常量池 表 #1 -> #计数器-1 类标识符 u2 public final abstrat class annotion interface 之类 类索引u2 名字 父类索引u2 父类名字 接口计数器 u2 接口数…...

《C++长时间运行程序:驯服内存膨胀的“怪兽”》
在 C编程的世界里,当我们编写长时间运行的程序时,内存膨胀问题就像一个隐藏在暗处的“怪兽”,随时可能吞噬我们程序的性能和稳定性。无论是服务器应用程序、大型模拟系统还是其他长时间运行的关键任务软件,有效地处理内存膨胀问题…...

ELK之路第二步——可视化界面Kibana
Kibana 1.安装2.解压3.修改配置4.启动 这部分内容就比较简单了,水一片文章。 1.安装 需要梯子 官网下载链接:https://www.elastic.co/cn/downloads/past-releases/kibana-7-3-0 如果你去官网下载页面,点击下载是404报错,记得切换…...
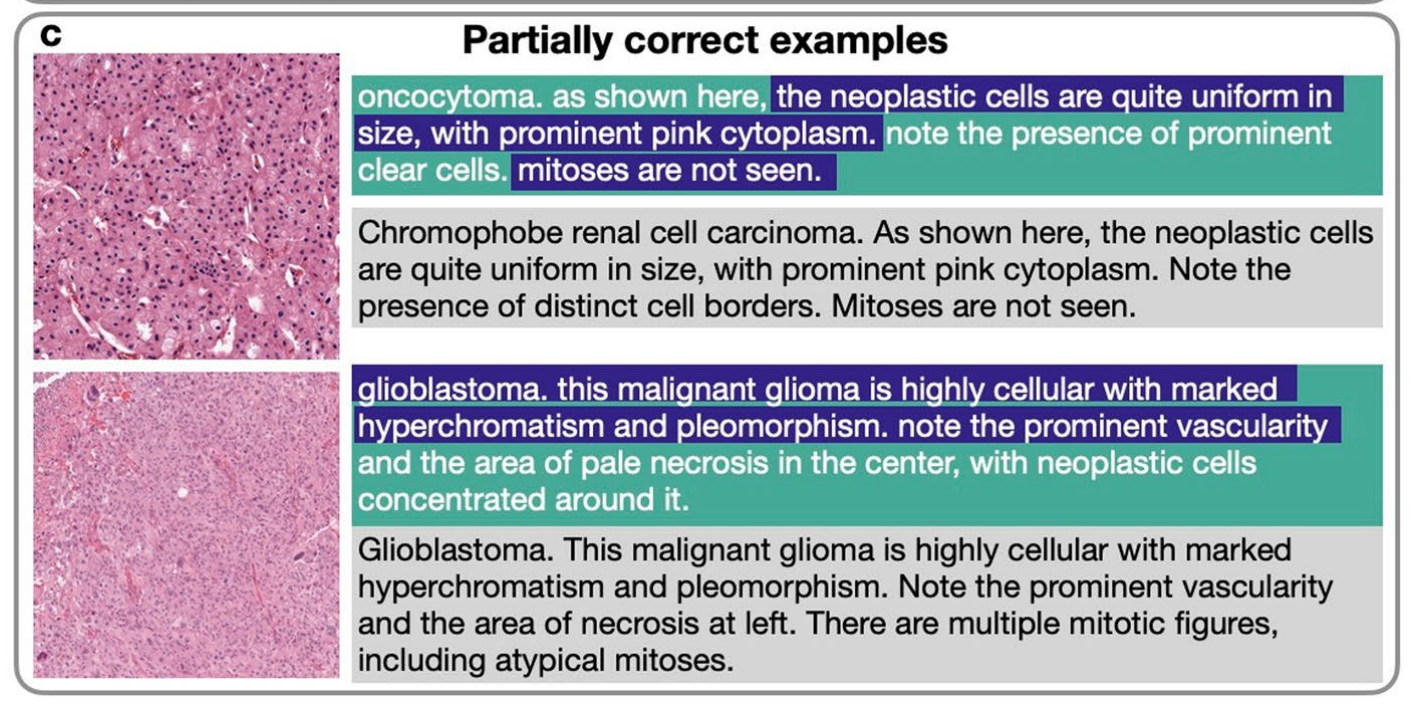
Nature Medicine病理AI汇总|CONCH:病理图像分析的零样本学习模型·顶刊精析·24-10-30
小罗碎碎念 最近在整理24年发表在Nature Medicine上的病理AI文章,简单列了一个表。 接下来我将按照先后顺序,系统的把这13篇文献分析完。其中底色做了填充的,代表商业公司在本论文中占据了一作或通讯。 本期推文介绍的模型是CONCH࿰…...

通过不当变更导致 PostgreSQL 翻车的案例分析与防范
在数据库管理领域,PostgreSQL 凭借其强大的功能和稳定性,赢得了广泛的认可。然而,即便是如此稳健的系统,在不当的变更操作下,也可能遭遇性能下降、数据丢失甚至系统崩溃的风险。本文将通过一个具体案例,分析…...

Windows高级技巧:轻松实现多进程窗口的连接与管理
在Windows操作系统中,管理多个进程窗口可能是一项复杂的任务,特别是在自动化测试或多任务处理时。本文将介绍一种高效的方法,通过Python编程和AirtestIDE工具,实现多进程窗口的便捷连接与管理。同时,将提供具体的代码示…...
洪水淹没制图
原文链接:洪水淹没制图https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__bizMzUzNTczMDMxMg&mid2247624956&idx2&sn2557e56396eed7568d27baf694dc86fe&chksmfa8da91bcdfa200d307ea12ab9f52394ca6ef0bea3111bd8a873b34c950bcd9441c377f13674&token1392391660&…...

PHP的 CSRF、XSS 攻击和防范
CSRF攻击 CSRF(Cross-Site Request Forgery)攻击,也称为跨站请求伪造,是一种常见的网络安全威胁。在这种攻击中,攻击者利用已认证的用户身份,在用户不知情的情况下伪造请求,冒充用户的操作向目…...
怎么在线制作活码?二维码活码的简单制作技巧
进入数字化时代,二维码已经成为主要的一种内容分享方式,将内容生成活码二维码,可以方便内容的传输与存储,在日常生活中的很多场景都有二维码的应用。通过生成二维码的方式可以更简单快速的分享内容给其他人,有效提高获…...

Lua中实现异步HTTP请求的方法
Lua,作为一种轻量级的脚本语言,因其简洁和高效,在游戏开发、嵌入式系统以及互联网应用中得到了广泛的应用。本文将介绍如何在Lua中实现异步HTTP请求,并提供相应的代码实现,包括如何通过代理服务器发送请求。 异步HTTP…...

拓展学习-golang的基础语法和常用开发工具
golang的基础语法 golang的基础语法和其他语言大部分都差别不大,如果我们有学习过其他语言,比如JavaScript,php,java,python等,有其他语言的语法基础,那么我们学习golang将更容易上手。那我们直…...

利用ngx_stream_return_module构建简易 TCP/UDP 响应网关
一、模块概述 ngx_stream_return_module 提供了一个极简的指令: return <value>;在收到客户端连接后,立即将 <value> 写回并关闭连接。<value> 支持内嵌文本和内置变量(如 $time_iso8601、$remote_addr 等)&a…...
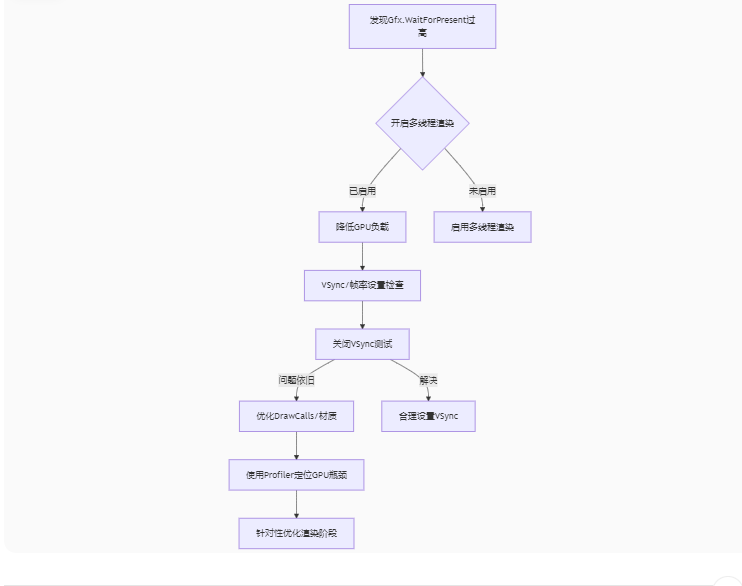
Unity3D中Gfx.WaitForPresent优化方案
前言 在Unity中,Gfx.WaitForPresent占用CPU过高通常表示主线程在等待GPU完成渲染(即CPU被阻塞),这表明存在GPU瓶颈或垂直同步/帧率设置问题。以下是系统的优化方案: 对惹,这里有一个游戏开发交流小组&…...
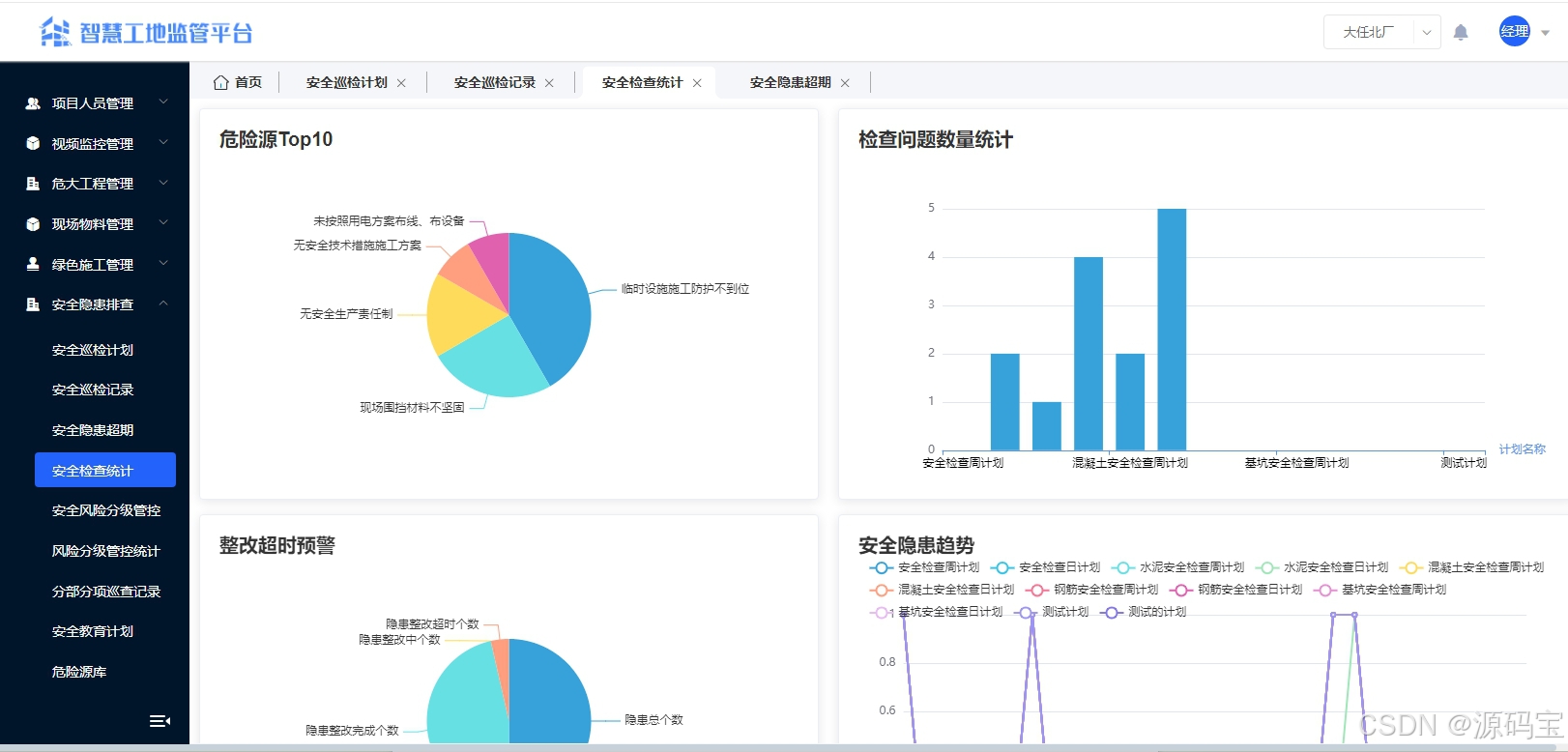
智慧工地云平台源码,基于微服务架构+Java+Spring Cloud +UniApp +MySql
智慧工地管理云平台系统,智慧工地全套源码,java版智慧工地源码,支持PC端、大屏端、移动端。 智慧工地聚焦建筑行业的市场需求,提供“平台网络终端”的整体解决方案,提供劳务管理、视频管理、智能监测、绿色施工、安全管…...
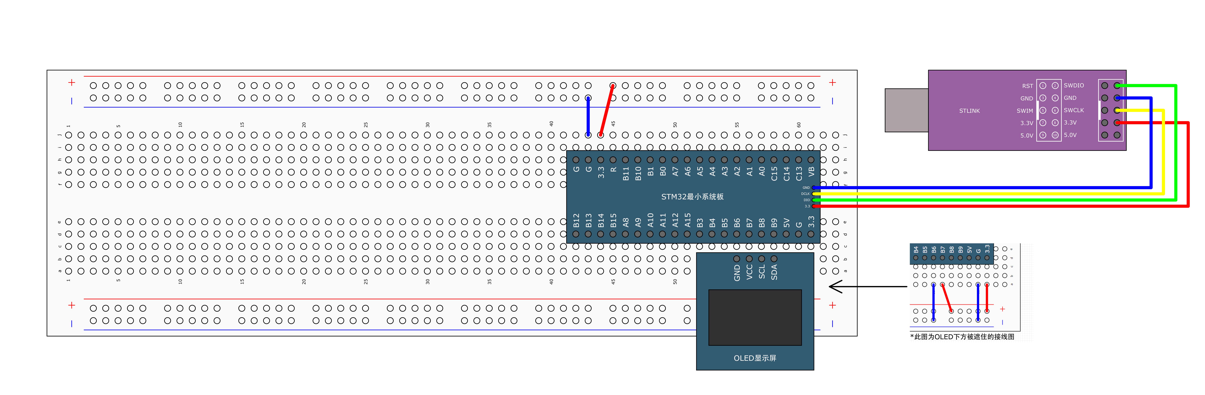
STM32标准库-DMA直接存储器存取
文章目录 一、DMA1.1简介1.2存储器映像1.3DMA框图1.4DMA基本结构1.5DMA请求1.6数据宽度与对齐1.7数据转运DMA1.8ADC扫描模式DMA 二、数据转运DMA2.1接线图2.2代码2.3相关API 一、DMA 1.1简介 DMA(Direct Memory Access)直接存储器存取 DMA可以提供外设…...

Qwen3-Embedding-0.6B深度解析:多语言语义检索的轻量级利器
第一章 引言:语义表示的新时代挑战与Qwen3的破局之路 1.1 文本嵌入的核心价值与技术演进 在人工智能领域,文本嵌入技术如同连接自然语言与机器理解的“神经突触”——它将人类语言转化为计算机可计算的语义向量,支撑着搜索引擎、推荐系统、…...
DIY|Mac 搭建 ESP-IDF 开发环境及编译小智 AI
前一阵子在百度 AI 开发者大会上,看到基于小智 AI DIY 玩具的演示,感觉有点意思,想着自己也来试试。 如果只是想烧录现成的固件,乐鑫官方除了提供了 Windows 版本的 Flash 下载工具 之外,还提供了基于网页版的 ESP LA…...

土地利用/土地覆盖遥感解译与基于CLUE模型未来变化情景预测;从基础到高级,涵盖ArcGIS数据处理、ENVI遥感解译与CLUE模型情景模拟等
🔍 土地利用/土地覆盖数据是生态、环境和气象等诸多领域模型的关键输入参数。通过遥感影像解译技术,可以精准获取历史或当前任何一个区域的土地利用/土地覆盖情况。这些数据不仅能够用于评估区域生态环境的变化趋势,还能有效评价重大生态工程…...
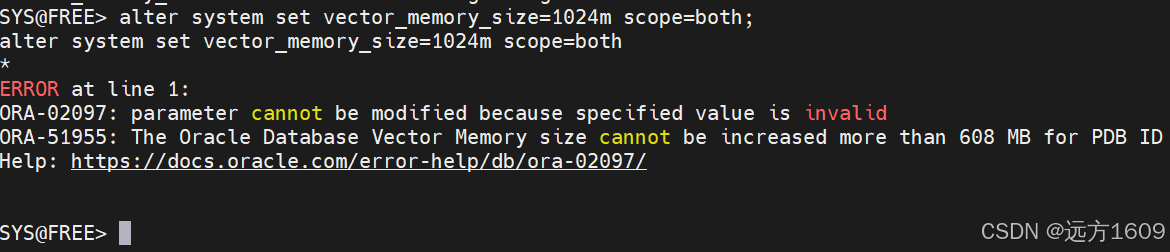
10-Oracle 23 ai Vector Search 概述和参数
一、Oracle AI Vector Search 概述 企业和个人都在尝试各种AI,使用客户端或是内部自己搭建集成大模型的终端,加速与大型语言模型(LLM)的结合,同时使用检索增强生成(Retrieval Augmented Generation &#…...
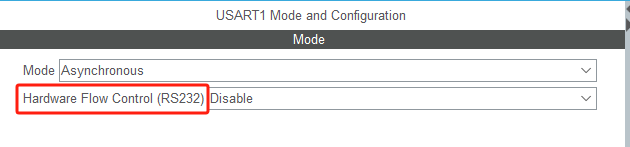
STM32HAL库USART源代码解析及应用
STM32HAL库USART源代码解析 前言STM32CubeIDE配置串口USART和UART的选择使用模式参数设置GPIO配置DMA配置中断配置硬件流控制使能生成代码解析和使用方法串口初始化__UART_HandleTypeDef结构体浅析HAL库代码实际使用方法使用轮询方式发送使用轮询方式接收使用中断方式发送使用中…...
Golang——7、包与接口详解
包与接口详解 1、Golang包详解1.1、Golang中包的定义和介绍1.2、Golang包管理工具go mod1.3、Golang中自定义包1.4、Golang中使用第三包1.5、init函数 2、接口详解2.1、接口的定义2.2、空接口2.3、类型断言2.4、结构体值接收者和指针接收者实现接口的区别2.5、一个结构体实现多…...
