浅谈密码相关原理及代码实现
本代码仅供学习、研究、教育或合法用途。开发者明确声明其无意将该代码用于任何违法、犯罪或违反道德规范的行为。任何个人或组织在使用本代码时,需自行确保其行为符合所在国家或地区的法律法规。
开发者对任何因直接或间接使用该代码而导致的法律责任、经济损失或其他后果概不负责。使用者需自行承担因使用本代码产生的全部风险和责任。请勿将本代码用于任何违反法律、侵犯他人权益或破坏公共秩序的活动。
本文是作者对密码学浅薄学习后的一些总结,分为古典密码学和现代密码学和本人学习后对加密的新的认知。
一·传统密码学:
方法 1:凯撒密码
代码实例
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;// 凯撒加密函数
string caesarEncrypt(string text, int shift) {string result = "";for (char c : text) {if (isalpha(c)) {char base = islower(c) ? 'a' : 'A';result += (c - base + shift) % 26 + base;} else {result += c; // 非字母不加密}}return result;
}int main() {ifstream inputFile("1.txt");ofstream outputFile("1_encrypted.txt");if (!inputFile) {cerr << "无法打开文件 1.txt" << endl;return 1;}string content((istreambuf_iterator<char>(inputFile)), istreambuf_iterator<char>());int shift = 3; // 偏移量string encrypted = caesarEncrypt(content, shift);outputFile << encrypted;cout << "加密完成,结果保存在 1_encrypted.txt 中" << endl;inputFile.close();outputFile.close();return 0;
}加密过程和原理
- 将字母按字母表顺序移动指定偏移量(如 3)。
- 非字母字符保持不变。
- 偏移量可调整,用于创建不同的密钥。
- 解密时只需反向移动同样偏移量。
方法 2:维吉尼亚密码
代码实例
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;// 维吉尼亚加密函数
string vigenereEncrypt(string text, string key) {string result = "";int keyIndex = 0;for (char c : text) {if (isalpha(c)) {char base = islower(c) ? 'a' : 'A';int shift = key[keyIndex % key.size()] - base;result += (c - base + shift) % 26 + base;keyIndex++;} else {result += c;}}return result;
}int main() {ifstream inputFile("1.txt");ofstream outputFile("1_encrypted.txt");if (!inputFile) {cerr << "无法打开文件 1.txt" << endl;return 1;}string content((istreambuf_iterator<char>(inputFile)), istreambuf_iterator<char>());string key = "KEYWORD"; // 密钥string encrypted = vigenereEncrypt(content, key);outputFile << encrypted;cout << "加密完成,结果保存在 1_encrypted.txt 中" << endl;inputFile.close();outputFile.close();return 0;
}加密过程和原理
- 使用关键字中每个字母的偏移量加密文本。
- 根据字母表的字母序列循环使用关键字。
- 每个字母偏移量由关键字决定,增加加密强度。
方法 3:栅栏密码
代码实例
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;// 栅栏加密函数
string railFenceEncrypt(string text, int key) {vector<string> rail(key, "");int direction = 1; // 1 表示向下,-1 表示向上int row = 0;for (char c : text) {rail[row] += c;row += direction;if (row == 0 || row == key - 1) direction = -direction;}string result = "";for (string line : rail) result += line;return result;
}int main() {ifstream inputFile("1.txt");ofstream outputFile("1_encrypted.txt");if (!inputFile) {cerr << "无法打开文件 1.txt" << endl;return 1;}string content((istreambuf_iterator<char>(inputFile)), istreambuf_iterator<char>());int key = 3; // 栅栏的行数string encrypted = railFenceEncrypt(content, key);outputFile << encrypted;cout << "加密完成,结果保存在 1_encrypted.txt 中" << endl;inputFile.close();outputFile.close();return 0;
}加密过程和原理
- 将文本分布在多个行(栅栏)中。
- 按从上到下、再从下到上的顺序排列字符。
- 最后按行拼接成加密后的字符串。
方法 4:单表替代密码(Simple Substitution Cipher)
代码实例
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;// 单表替代加密函数
string substitutionEncrypt(string text, unordered_map<char, char> substitutionTable) {string result = "";for (char c : text) {if (isalpha(c)) {result += substitutionTable[c];} else {result += c; // 非字母不加密}}return result;
}int main() {ifstream inputFile("1.txt");ofstream outputFile("1_encrypted.txt");if (!inputFile) {cerr << "无法打开文件 1.txt" << endl;return 1;}string content((istreambuf_iterator<char>(inputFile)), istreambuf_iterator<char>());// 替代表unordered_map<char, char> substitutionTable = {{'a', 'q'}, {'b', 'w'}, {'c', 'e'}, {'d', 'r'}, {'e', 't'},{'f', 'y'}, {'g', 'u'}, {'h', 'i'}, {'i', 'o'}, {'j', 'p'},{'k', 'a'}, {'l', 's'}, {'m', 'd'}, {'n', 'f'}, {'o', 'g'},{'p', 'h'}, {'q', 'j'}, {'r', 'k'}, {'s', 'l'}, {'t', 'z'},{'u', 'x'}, {'v', 'c'}, {'w', 'v'}, {'x', 'b'}, {'y', 'n'},{'z', 'm'}};string encrypted = substitutionEncrypt(content, substitutionTable);outputFile << encrypted;cout << "加密完成,结果保存在 1_encrypted.txt 中" << endl;inputFile.close();outputFile.close();return 0;
}加密过程和原理
- 为每个字母定义唯一的替换字母。
- 使用替代表逐字替换文本中的字母。
- 非字母字符保持不变。
方法 5:逆序加密(Reverse Cipher)
代码实例
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;// 逆序加密函数
string reverseEncrypt(string text) {reverse(text.begin(), text.end());return text;
}int main() {ifstream inputFile("1.txt");ofstream outputFile("1_encrypted.txt");if (!inputFile) {cerr << "无法打开文件 1.txt" << endl;return 1;}string content((istreambuf_iterator<char>(inputFile)), istreambuf_iterator<char>());string encrypted = reverseEncrypt(content);outputFile << encrypted;cout << "加密完成,结果保存在 1_encrypted.txt 中" << endl;inputFile.close();outputFile.close();return 0;
}加密过程和原理
- 将文本字符顺序反转。
方法 6:Playfair 密码
代码实例
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;// 创建 Playfair 密钥矩阵
vector<vector<char>> createPlayfairMatrix(string key) {vector<vector<char>> matrix(5, vector<char>(5));string alphabet = "ABCDEFGHIKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"; // 'J' 被合并到 'I'string adjustedKey = "";vector<bool> used(26, false);for (char c : key) {if (c == 'J') c = 'I';if (!used[c - 'A'] && isalpha(c)) {adjustedKey += c;used[c - 'A'] = true;}}for (char c : alphabet) {if (!used[c - 'A']) {adjustedKey += c;used[c - 'A'] = true;}}int k = 0;for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i)for (int j = 0; j < 5; ++j)matrix[i][j] = adjustedKey[k++];return matrix;
}// 加密一个双字母对
string encryptPair(char a, char b, const vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {int row1, col1, row2, col2;for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {for (int j = 0; j < 5; ++j) {if (matrix[i][j] == a) row1 = i, col1 = j;if (matrix[i][j] == b) row2 = i, col2 = j;}}if (row1 == row2) {return string(1, matrix[row1][(col1 + 1) % 5]) + matrix[row2][(col2 + 1) % 5];} else if (col1 == col2) {return string(1, matrix[(row1 + 1) % 5][col1]) + matrix[(row2 + 1) % 5][col2];} else {return string(1, matrix[row1][col2]) + matrix[row2][col1];}
}// Playfair 加密函数
string playfairEncrypt(string text, string key) {vector<vector<char>> matrix = createPlayfairMatrix(key);string adjustedText = "";for (char c : text) {if (c == 'J') c = 'I';if (isalpha(c)) adjustedText += toupper(c);}if (adjustedText.size() % 2 != 0) adjustedText += 'X';string result = "";for (int i = 0; i < adjustedText.size(); i += 2) {char a = adjustedText[i];char b = (i + 1 < adjustedText.size() && adjustedText[i + 1] != a) ? adjustedText[i + 1] : 'X';result += encryptPair(a, b, matrix);}return result;
}int main() {ifstream inputFile("1.txt");ofstream outputFile("1_encrypted.txt");if (!inputFile) {cerr << "无法打开文件 1.txt" << endl;return 1;}string content((istreambuf_iterator<char>(inputFile)), istreambuf_iterator<char>());string key = "KEYWORD";string encrypted = playfairEncrypt(content, key);outputFile << encrypted;cout << "加密完成,结果保存在 1_encrypted.txt 中" << endl;inputFile.close();outputFile.close();return 0;
}加密过程和原理
- 构造 5x5 的字母矩阵,关键字中的字母优先填充。
- 按规则将字母对替换为矩阵中的对应字母。
- 解密时反向执行相同规则。
方法 7:摩斯密码(Morse Code Cipher)
代码实例
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;map<char, string> morseCode = {{'A', ".-"}, {'B', "-..."}, {'C', "-.-."}, {'D', "-.."}, {'E', "."},{'F', "..-."}, {'G', "--."}, {'H', "...."}, {'I', ".."}, {'J', ".---"},{'K', "-.-"}, {'L', ".-.."}, {'M', "--"}, {'N', "-."}, {'O', "---"},{'P', ".--."}, {'Q', "--.-"}, {'R', ".-."}, {'S', "..."}, {'T', "-"},{'U', "..-"}, {'V', "...-"}, {'W', ".--"}, {'X', "-..-"}, {'Y', "-.--"},{'Z', "--.."}, {'0', "-----"}, {'1', ".----"}, {'2', "..---"}, {'3', "...--"},{'4', "....-"}, {'5', "....."}, {'6', "-...."}, {'7', "--..."}, {'8', "---.."},{'9', "----."}, {' ', "/"}
};string morseEncrypt(string text) {string result = "";for (char c : text) {c = toupper(c);if (morseCode.count(c)) result += morseCode[c] + " ";}return result;
}int main() {ifstream inputFile("1.txt");ofstream outputFile("1_encrypted.txt");if (!inputFile) {cerr << "无法打开文件 1.txt" << endl;return 1;}string content((istreambuf_iterator<char>(inputFile)), istreambuf_iterator<char>());string encrypted = morseEncrypt(content);outputFile << encrypted;cout << "加密完成,结果保存在 1_encrypted.txt 中" << endl;inputFile.close();outputFile.close();return 0;
}加密过程和原理
- 将每个字符替换为摩斯电码表示(点和横线组合)。
- 空格用“/”表示。
- 解密时根据摩斯电码反查字母。
方法 8:希尔密码(Hill Cipher)
代码实例
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;vector<vector<int>> keyMatrix = {{6, 24}, {1, 13}};string hillEncrypt(string text) {string result = "";for (int i = 0; i < text.size(); i += 2) {int x = text[i] - 'A';int y = text[i + 1] - 'A';result += (keyMatrix[0][0] * x + keyMatrix[0][1] * y) % 26 + 'A';result += (keyMatrix[1][0] * x + keyMatrix[1][1] * y) % 26 + 'A';}return result;
}int main() {ifstream inputFile("1.txt");ofstream outputFile("1_encrypted.txt");if (!inputFile) {cerr << "无法打开文件 1.txt" << endl;return 1;}string content((istreambuf_iterator<char>(inputFile)), istreambuf_iterator<char>());for (char& c : content) if (islower(c)) c = toupper(c);if (content.size() % 2 != 0) content += 'X';string encrypted = hillEncrypt(content);outputFile << encrypted;cout << "加密完成,结果保存在 1_encrypted.txt 中" << endl;inputFile.close();outputFile.close();return 0;
}加密过程和原理
- 使用矩阵乘法对字母对进行加密。
- 每对字母转换为向量,与密钥矩阵相乘。
- 结果向量再映射回字母。
方法 9:书本密码(Book Cipher)
代码实例
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;vector<pair<int, int>> key = {{1, 1}, {1, 5}, {2, 3}}; // 示例关键字string bookEncrypt(string text, string book) {string result = "";stringstream bookStream(book);vector<string> lines;string line;while (getline(bookStream, line)) lines.push_back(line);for (auto [lineIdx, wordIdx] : key) {stringstream lineStream(lines[lineIdx - 1]);string word;for (int i = 0; i < wordIdx; ++i) lineStream >> word;result += word + " ";}return result;
}int main() {ifstream inputFile("1.txt"), bookFile("book.txt");ofstream outputFile("1_encrypted.txt");if (!inputFile || !bookFile) {cerr << "无法打开文件" << endl;return 1;}string content((istreambuf_iterator<char>(inputFile)), istreambuf_iterator<char>());string bookContent((istreambuf_iterator<char>(bookFile)), istreambuf_iterator<char>());string encrypted = bookEncrypt(content, bookContent);outputFile << encrypted;cout << "加密完成,结果保存在 1_encrypted.txt 中" << endl;inputFile.close();bookFile.close();outputFile.close();return 0;
}加密过程和原理
- 使用书中的位置(行号和单词号)指代加密文本。
- 密钥是行号和单词号的组合。
- 解密时需参考相同书本和密钥。
方法 10:换位密码(Transposition Cipher)
代码实例
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;string transpositionEncrypt(string text, int key) {vector<string> grid(key, "");int direction = 1, row = 0;for (char c : text) {grid[row] += c;row += direction;if (row == 0 || row == key - 1) direction = -direction;}string result = "";for (string line : grid) result += line;return result;
}int main() {ifstream inputFile("1.txt");ofstream outputFile("1_encrypted.txt");if (!inputFile) {cerr << "无法打开文件 1.txt" << endl;return 1;}string content((istreambuf_iterator<char>(inputFile)), istreambuf_iterator<char>());string encrypted = transpositionEncrypt(content, 3);outputFile << encrypted;cout << "加密完成,结果保存在 1_encrypted.txt 中" << endl;inputFile.close();outputFile.close();return 0;
}加密过程和原理
- 将文本重新排列为行和列的形式。
- 按列顺序提取字符重新组成密文。
- 解密需恢复原排列顺序。
接下来分享几种各位同行们经常用来加密对抗的小玩意:
二·现代密码学
方法 11:高级加密标准(AES,Advanced Encryption Standard)
代码实例
cpp复制代码
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <openssl/aes.h>
using namespace std;// AES 加密函数
string aesEncrypt(const string& text, const unsigned char* key) {AES_KEY encryptKey;AES_set_encrypt_key(key, 128, &encryptKey); // 128 位密钥unsigned char encrypted[AES_BLOCK_SIZE];AES_encrypt((unsigned char*)text.c_str(), encrypted, &encryptKey);return string((char*)encrypted, AES_BLOCK_SIZE);
}int main() {ifstream inputFile("1.txt");ofstream outputFile("1_encrypted.txt");if (!inputFile) {cerr << "无法打开文件 1.txt" << endl;return 1;}string content((istreambuf_iterator<char>(inputFile)), istreambuf_iterator<char>());unsigned char key[16] = "examplekey123456"; // 示例密钥string encrypted = aesEncrypt(content, key);outputFile << encrypted;cout << "加密完成,结果保存在 1_encrypted.txt 中" << endl;inputFile.close();outputFile.close();return 0;
}加密过程和原理
- 块加密:AES 使用固定大小的块(128 位)。
- 密钥长度:支持 128、192 和 256 位密钥。
- 多轮替代和排列:使用 S 盒替代、行移位、列混合、轮密钥添加等操作。
- 安全性强:广泛用于文件、网络通信的加密。
方法 12:RSA 加密
代码实例
cpp复制代码
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <openssl/rsa.h>
#include <openssl/pem.h>
using namespace std;// RSA 加密函数
string rsaEncrypt(const string& text, const string& publicKeyFile) {FILE* pubKeyFile = fopen(publicKeyFile.c_str(), "r");if (!pubKeyFile) {cerr << "无法打开公钥文件" << endl;return "";}RSA* rsa = PEM_read_RSA_PUBKEY(pubKeyFile, NULL, NULL, NULL);fclose(pubKeyFile);unsigned char encrypted[256];int encryptedLen = RSA_public_encrypt(text.size(), (unsigned char*)text.c_str(),encrypted, rsa, RSA_PKCS1_PADDING);RSA_free(rsa);return string((char*)encrypted, encryptedLen);
}int main() {ifstream inputFile("1.txt");ofstream outputFile("1_encrypted.txt");if (!inputFile) {cerr << "无法打开文件 1.txt" << endl;return 1;}string content((istreambuf_iterator<char>(inputFile)), istreambuf_iterator<char>());string encrypted = rsaEncrypt(content, "public.pem");outputFile << encrypted;cout << "加密完成,结果保存在 1_encrypted.txt 中" << endl;inputFile.close();outputFile.close();return 0;
}加密过程和原理
- 非对称加密:使用公钥加密,私钥解密。
- 数学基础:基于大整数分解的难题。
- 常见用途:用于密钥交换、数字签名和认证。
- 高安全性:广泛用于 HTTPS 和 VPN。
方法 13:哈希函数(SHA-256)
代码实例
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <openssl/sha.h>
using namespace std;// SHA-256 哈希函数
string sha256(const string& text) {unsigned char hash[SHA256_DIGEST_LENGTH];SHA256((unsigned char*)text.c_str(), text.size(), hash);char outputBuffer[65];for (int i = 0; i < SHA256_DIGEST_LENGTH; i++) {sprintf(outputBuffer + (i * 2), "%02x", hash[i]);}outputBuffer[64] = 0;return string(outputBuffer);
}int main() {ifstream inputFile("1.txt");ofstream outputFile("1_hashed.txt");if (!inputFile) {cerr << "无法打开文件 1.txt" << endl;return 1;}string content((istreambuf_iterator<char>(inputFile)), istreambuf_iterator<char>());string hashed = sha256(content);outputFile << hashed;cout << "哈希计算完成,结果保存在 1_hashed.txt 中" << endl;inputFile.close();outputFile.close();return 0;
}加密过程和原理
- 单向函数:无法从结果反推输入。
- 固定输出长度:无论输入大小,输出都是 256 位。
- 用途:广泛用于数字签名、数据完整性校验。
方法 14:消息认证码(HMAC,Hash-based Message Authentication Code)
代码实例
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <openssl/hmac.h>
using namespace std;// HMAC 计算函数
string hmacSha256(const string& text, const string& key) {unsigned char* result;unsigned int len = 32;result = HMAC(EVP_sha256(), key.c_str(), key.size(), (unsigned char*)text.c_str(), text.size(), NULL, NULL);char outputBuffer[65];for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {sprintf(outputBuffer + (i * 2), "%02x", result[i]);}outputBuffer[64] = 0;return string(outputBuffer);
}int main() {ifstream inputFile("1.txt");ofstream outputFile("1_hmac.txt");if (!inputFile) {cerr << "无法打开文件 1.txt" << endl;return 1;}string content((istreambuf_iterator<char>(inputFile)), istreambuf_iterator<char>());string key = "examplekey";string hmac = hmacSha256(content, key);outputFile << hmac;cout << "HMAC 计算完成,结果保存在 1_hmac.txt 中" << endl;inputFile.close();outputFile.close();return 0;
}加密过程和原理
- 哈希函数结合密钥:用密钥增强哈希的安全性。
- 防篡改:确保数据完整性和来源认证。
- 应用场景:用于网络安全协议(如 TLS 和 JWT)。
如果需要进一步的加密技术或更详细的安全分析,请告诉我!好的,下面是几种适合信息技术加密对抗和网络安全的加密方法,包括加密名称、代码实例、以及加密过程和原理的简要概括。
方法 15:AES(高级加密标准)
代码实例
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <openssl/aes.h>
#include <openssl/rand.h>void AES_encrypt(const std::vector<unsigned char>& input, std::vector<unsigned char>& output, const std::vector<unsigned char>& key) {AES_KEY encryptKey;AES_set_encrypt_key(key.data(), 128, &encryptKey);AES_encrypt(input.data(), output.data(), &encryptKey);
}int main() {std::vector<unsigned char> key(AES_BLOCK_SIZE);RAND_bytes(key.data(), key.size()); // 生成随机密钥std::vector<unsigned char> input(AES_BLOCK_SIZE, 'A'); // 明文std::vector<unsigned char> output(AES_BLOCK_SIZE);AES_encrypt(input, output, key);std::ofstream outputFile("1_encrypted.bin", std::ios::binary);outputFile.write((const char*)output.data(), output.size());std::cout << "加密完成,结果保存在 1_encrypted.bin 中" << std::endl;return 0;
}加密过程和原理
- 使用 128 位密钥对数据进行分组加密。
- 数据被分为 16 字节(128 位)块。
- 采用多轮加密过程,确保安全性;解密过程相似。
- AES 是对称密钥加密,传输时需安全交换密钥。
方法 16:RSA(Rivest-Shamir-Adleman)
代码实例
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <openssl/rsa.h>
#include <openssl/pem.h>void RSA_encrypt(const std::string& plaintext, std::ofstream &outputFile, RSA * publicKey) {int size = RSA_size(publicKey);std::vector<unsigned char> encrypted(size);RSA_public_encrypt(plaintext.size(), (unsigned char*)plaintext.c_str(), encrypted.data(), publicKey, RSA_PKCS1_OAEP_PADDING);outputFile.write((const char*)encrypted.data(), encrypted.size());
}int main() {int bits = 2048;RSA* rsaKey = RSA_generate_key(bits, RSA_F4, nullptr, nullptr);std::ofstream outputFile("1_encrypted.bin", std::ios::binary);std::string plaintext = "Hello, RSA!"; // 要加密的明文RSA_encrypt(plaintext, outputFile, rsaKey);outputFile.close();RSA_free(rsaKey);std::cout << "加密完成,结果保存在 1_encrypted.bin 中" << std::endl;return 0;
}加密过程和原理
- 采用一对公钥和私钥,其中公钥用于加密,私钥用于解密。
- RSA 基于大整数的分解困难性,提供较高的安全性。
- 通常用于小块数据,加密消息摘要或对称密钥。
- 易于实现数字签名,确保数据完整性。
方法 17:SHA-256(安全哈希算法)
代码实例
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <openssl/sha.h>
#include <iomanip>void SHA256_hash(const std::string& input, std::ofstream &outputFile) {unsigned char hash[SHA256_DIGEST_LENGTH];SHA256((unsigned char*)input.c_str(), input.length(), hash);for (int i = 0; i < SHA256_DIGEST_LENGTH; i++) {outputFile << std::hex << std::setw(2) << std::setfill('0') << (int)hash[i];}
}int main() {std::ofstream outputFile("1_hashed.txt");std::string input = "Hello, SHA-256!"; //要哈希的明文SHA256_hash(input, outputFile);outputFile.close();std::cout << "哈希完成,结果保存在 1_hashed.txt 中" << std::endl;return 0;
}加密过程和原理
- SHA-256 将任意长度的数据映射为 256 位(32 字节)的哈希值。
- 不可逆,加密后的数据不能被解析回原始数据。
- 用于数据完整性验证、数字签名等。
- 强大的抗碰撞能力,确保不同输入不会生成相同的哈希值。
方法 18:双重加密(Double Encryption)
代码实例
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <openssl/aes.h>
#include <openssl/rand.h>void AES_encrypt(const std::vector<unsigned char>& input, std::vector<unsigned char>& output, const std::vector<unsigned char>& key) {AES_KEY encryptKey;AES_set_encrypt_key(key.data(), 128, &encryptKey);AES_encrypt(input.data(), output.data(), &encryptKey);
}int main() {std::vector<unsigned char> key1(AES_BLOCK_SIZE);std::vector<unsigned char> key2(AES_BLOCK_SIZE);RAND_bytes(key1.data(), key1.size());RAND_bytes(key2.data(), key2.size());std::vector<unsigned char> input(AES_BLOCK_SIZE, 'A');std::vector<unsigned char> output1(AES_BLOCK_SIZE), output2(AES_BLOCK_SIZE);AES_encrypt(input, output1, key1); // 第一次加密AES_encrypt(output1, output2, key2); // 第二次加密std::ofstream outputFile("1_double_encrypted.bin", std::ios::binary);outputFile.write((const char*)output2.data(), output2.size());std::cout << "双重加密完成,结果保存在 1_double_encrypted.bin 中" << std::endl;return 0;
}加密过程和原理
- 对相同明文进行两次AES加密,使用两个不同密钥。
三·理解
通过上文的学习,我对密码学有了初步的认知,想出了基于打表加密的一种方法,与中文字符相对:
代码实现(C++)
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <string>// 定义英文字母与中文汉字的映射表
std::unordered_map<char, std::string> englishToChinese = {{'a', "阿"}, {'b', "博"}, {'c', "成"}, {'d', "东"}, {'e', "恩"},{'f', "风"}, {'g', "光"}, {'h', "海"}, {'i', "爱"}, {'j', "杰"},{'k', "康"}, {'l', "兰"}, {'m', "明"}, {'n', "宁"}, {'o', "欧"},{'p', "鹏"}, {'q', "强"}, {'r', "荣"}, {'s', "山"}, {'t', "天"},{'u', "宇"}, {'v', "维"}, {'w', "威"}, {'x', "夏"}, {'y', "阳"},{'z', "志"}, {'A', "安"}, {'B', "北"}, {'C', "川"}, {'D', "达"},{'E', "儿"}, {'F', "飞"}, {'G', "国"}, {'H', "和"}, {'I', "伊"},{'J', "健"}, {'K', "凯"}, {'L', "力"}, {'M', "美"}, {'N', "娜"},{'O', "欧"}, {'P', "平"}, {'Q', "清"}, {'R', "瑞"}, {'S', "顺"},{'T', "涛"}, {'U', "优"}, {'V', "文"}, {'W', "王"}, {'X', "霞"},{'Y', "雅"}, {'Z', "卓"}, {' ', " "}, // 空格直接对应空格
};// 打表加密函数
std::string encryptToChinese(const std::string& input) {std::string encryptedText = "";for (char c : input) {if (englishToChinese.find(c) != englishToChinese.end()) {encryptedText += englishToChinese[c]; // 查表加密} else {encryptedText += c; // 直接保留未定义字符}}return encryptedText;
}// 打表解密函数(反向映射)
std::string decryptToEnglish(const std::string& input) {// 反向映射表std::unordered_map<std::string, char> chineseToEnglish;for (const auto& pair : englishToChinese) {chineseToEnglish[pair.second] = pair.first;}std::string decryptedText = "";std::string buffer = ""; // 用于存储汉字缓冲for (char c : input) {if ((unsigned char)c >= 0x80) { // 判断是否为汉字(中文多字节编码)buffer += c;// 汉字通常是 3 字节,完成一个汉字if (buffer.size() == 3) {if (chineseToEnglish.find(buffer) != chineseToEnglish.end()) {decryptedText += chineseToEnglish[buffer]; // 查表解密} else {decryptedText += buffer; // 如果未定义,直接保留}buffer.clear();}} else {decryptedText += c; // 非汉字字符直接追加}}return decryptedText;
}int main() {std::string plaintext = "Hello World! This is a test.";// 加密std::string encrypted = encryptToChinese(plaintext);std::cout << "加密后的文本: " << encrypted << std::endl;// 解密std::string decrypted = decryptToEnglish(encrypted);std::cout << "解密后的文本: " << decrypted << std::endl;return 0;
}运行结果
输入文本为:
Hello World! This is a test.
加密后输出:
海恩兰兰欧 威欧荣兰达! 天海爱山 爱山 阿 天恩山天.
解密后输出:
Hello World! This is a test.
代码说明
- 映射表:
englishToChinese是用来映射英文字母到中文汉字的表。- 字母大小写区分,空格直接映射为空格。
- 未在映射表中的字符(如标点符号)会直接保留。
- 加密逻辑:
- 遍历输入字符串中的每个字符。
- 如果字符在映射表中,查表并加密为对应的汉字;否则,保留原字符。
- 解密逻辑:
- 创建反向映射表,将汉字映射回字母。
- 使用缓冲区处理汉字(汉字是多字节编码,需要逐字解析)。
- 非汉字字符直接保留。
- 扩展性:
- 可以随意修改或扩展
englishToChinese映射表,比如加入更多字符的映射。
- 可以随意修改或扩展
优点与局限性
优点:
- 简单易实现,方便理解。
- 加密和解密是双向的,可轻松实现反向转换。
局限性:
- 安全性较低,打表加密本质上属于“单表替换密码”,容易被破解。
- 只适合简单的加密需求,无法满足高强度安全需求。
四·结合
这种加密本质上是换汤不换药的,我们需要有所创新,下面是我的想法(key{A}和key{B}表示的是A和B独有的秘钥):
假设现在有服务器192.168.1.1,本机扮演角色A,服务器扮演角色B,进行如下逻辑:A拥有A的专属秘钥(汉字秘钥)进行一次加密发送给B,B接受到后再用B的专属秘钥再次加密发送给A,然后A接受到有两次加密的内容后用A的秘钥解开一次内容再发给B,B接收到后用B的秘钥解开查看内容,以helloword为内容,代码如下:
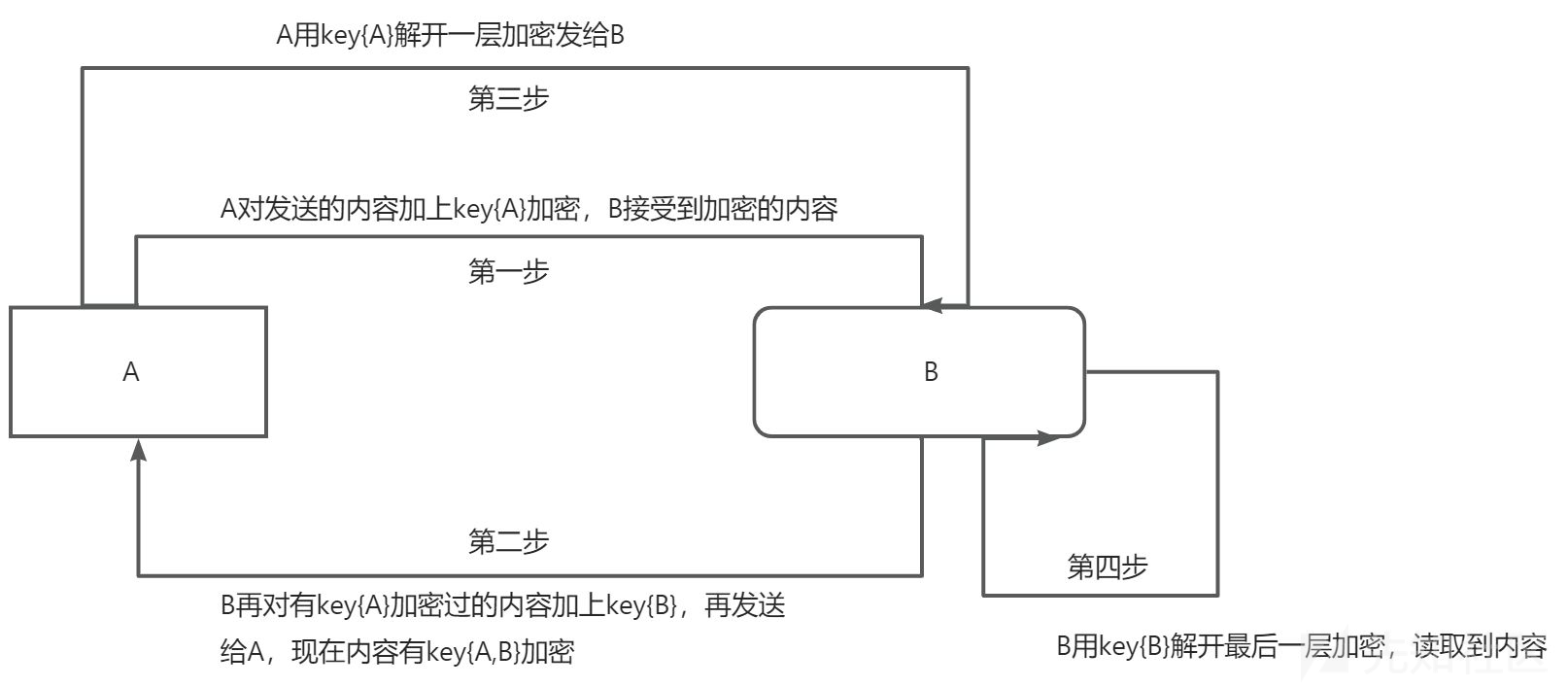
加密解密函数模块**
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <string>// 定义角色 A 和 B 的专属秘钥
std::unordered_map<char, std::string> AKey = {{'h', "海"}, {'e', "恩"}, {'l', "兰"}, {'o', "欧"}, {'w', "威"},{'r', "荣"}, {'d', "达"}, {'H', "汉"}, {'E', "尔"}, {'L', "理"},{'O', "奥"}, {'W', "王"}, {'R', "日"}, {'D', "德"}, {' ', " "},
};std::unordered_map<char, std::string> BKey = {{'h', "鸿"}, {'e', "艺"}, {'l', "雷"}, {'o', "欧"}, {'w', "文"},{'r', "仁"}, {'d', "东"}, {'H', "和"}, {'E', "恩"}, {'L', "流"},{'O', "奥"}, {'W', "沃"}, {'R', "瑞"}, {'D', "大"}, {' ', " "},
};// 打表加密函数
std::string encrypt(const std::string& input, const std::unordered_map<char, std::string>& key) {std::string encryptedText = "";for (char c : input) {if (key.find(c) != key.end()) {encryptedText += key.at(c); // 查表加密} else {encryptedText += c; // 未定义字符直接保留}}return encryptedText;
}// 打表解密函数(反向映射)
std::string decrypt(const std::string& input, const std::unordered_map<char, std::string>& key) {// 构造反向映射表std::unordered_map<std::string, char> reverseKey;for (const auto& pair : key) {reverseKey[pair.second] = pair.first;}std::string decryptedText = "";std::string buffer = ""; // 用于存储汉字缓冲for (char c : input) {if ((unsigned char)c >= 0x80) { // 判断是否为汉字(中文多字节编码)buffer += c;// 完成一个汉字if (buffer.size() == 3) {if (reverseKey.find(buffer) != reverseKey.end()) {decryptedText += reverseKey[buffer]; // 查表解密} else {decryptedText += buffer; // 未定义字符直接保留}buffer.clear();}} else {decryptedText += c; // 非汉字字符直接追加}}return decryptedText;
}角色 A 的代码
角色 A 扮演客户端,连接到服务器 B,发送和接收数据。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include "encryption_module.h" // 包含加密解密逻辑#define SERVER_IP "127.0.0.1" // 或者替换为 "192.168.1.1"
#define SERVER_PORT 8080int main() {// 创建 Socketint clientSocket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);if (clientSocket < 0) {std::cerr << "Socket creation failed!" << std::endl;return -1;}// 设置服务器地址sockaddr_in serverAddr;serverAddr.sin_family = AF_INET;serverAddr.sin_port = htons(SERVER_PORT);inet_pton(AF_INET, SERVER_IP, &serverAddr.sin_addr);// 连接服务器if (connect(clientSocket, (sockaddr*)&serverAddr, sizeof(serverAddr)) < 0) {std::cerr << "Connection to server failed!" << std::endl;close(clientSocket);return -1;}// 原始消息std::string message = "helloworld";std::cout << "原始消息: " << message << std::endl;// A 使用 AKey 加密std::string encryptedByA = encrypt(message, AKey);send(clientSocket, encryptedByA.c_str(), encryptedByA.size(), 0);std::cout << "A 加密后发送: " << encryptedByA << std::endl;// 接收 B 的加密消息char buffer[1024] = {0};int bytesReceived = recv(clientSocket, buffer, sizeof(buffer) - 1, 0);std::string encryptedByB(buffer, bytesReceived);std::cout << "A 收到双重加密消息: " << encryptedByB << std::endl;// A 解密一次std::string decryptedByA = decrypt(encryptedByB, AKey);std::cout << "A 解密后发送给 B: " << decryptedByA << std::endl;send(clientSocket, decryptedByA.c_str(), decryptedByA.size(), 0);// 关闭连接close(clientSocket);return 0;
}角色 B 的代码
角色 B 扮演服务器,接收来自 A 的消息,加密后再发送回去。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include "encryption_module.h" // 包含加密解密逻辑#define SERVER_PORT 8080int main() {// 创建 Socketint serverSocket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);if (serverSocket < 0) {std::cerr << "Socket creation failed!" << std::endl;return -1;}// 绑定地址和端口sockaddr_in serverAddr;serverAddr.sin_family = AF_INET;serverAddr.sin_port = htons(SERVER_PORT);serverAddr.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY;if (bind(serverSocket, (sockaddr*)&serverAddr, sizeof(serverAddr)) < 0) {std::cerr << "Bind failed!" << std::endl;close(serverSocket);return -1;}// 监听连接if (listen(serverSocket, 1) < 0) {std::cerr << "Listen failed!" << std::endl;close(serverSocket);return -1;}std::cout << "等待客户端连接..." << std::endl;// 接受连接sockaddr_in clientAddr;socklen_t clientLen = sizeof(clientAddr);int clientSocket = accept(serverSocket, (sockaddr*)&clientAddr, &clientLen);if (clientSocket < 0) {std::cerr << "Accept failed!" << std::endl;close(serverSocket);return -1;}std::cout << "客户端已连接!" << std::endl;// 接收 A 的加密消息char buffer[1024] = {0};int bytesReceived = recv(clientSocket, buffer, sizeof(buffer) - 1, 0);std::string encryptedByA(buffer, bytesReceived);std::cout << "B 收到 A 的消息: " << encryptedByA << std::endl;// B 使用 BKey 加密std::string encryptedByB = encrypt(encryptedByA, BKey);send(clientSocket, encryptedByB.c_str(), encryptedByB.size(), 0);std::cout << "B 加密后发送: " << encryptedByB << std::endl;// 接收 A 解密后的消息bytesReceived = recv(clientSocket, buffer, sizeof(buffer) - 1, 0);std::string decryptedByA(buffer, bytesReceived);std::cout << "B 收到 A 解密后的消息: " << decryptedByA << std::endl;// B 解密std::string finalMessage = decrypt(decryptedByA, BKey);std::cout << "B 解密后的消息: " << finalMessage << std::endl;// 关闭连接close(clientSocket);close(serverSocket);return 0;
}运行说明
- 先启动角色 B(服务器)。
- 再启动角色 A(客户端)。
- 角色 A 和角色 B 会进行多轮消息加密、解密和传输,最终在角色 B 的终端上看到解密后的原始消息
helloworld。
结果示例
- A 发送加密消息:
海恩兰兰欧威欧荣兰达 - B 接收到后再次加密:
鸿艺雷雷欧文欧仁雷东 - A 解密后发送给 B:
海恩兰兰欧威欧荣兰达 - B 最终解密得到原文:
helloworld
五·小结
密码学通过加密和解密技术,确保数据的机密性、完整性、真实性和不可否认性。它不仅可以防止未经授权的访问,还能验证通信双方的身份,保证数据在传输中的可靠性。例如,现代网络中的 HTTPS 协议、电子邮件加密、数字签名和区块链技术,都依赖于密码学提供的安全保障。
同时,随着量子计算等新兴技术的发展,传统的加密算法可能面临破解的风险,这也推动了后量子密码学的研究和应用。因此,密码学不仅是信息安全的基石,更是技术发展的前沿领域,对构建可信赖的数字社会具有不可替代的作用。在未来,密码学的创新将继续为网络安全提供坚实屏障。
相关文章:

浅谈密码相关原理及代码实现
本代码仅供学习、研究、教育或合法用途。开发者明确声明其无意将该代码用于任何违法、犯罪或违反道德规范的行为。任何个人或组织在使用本代码时,需自行确保其行为符合所在国家或地区的法律法规。 开发者对任何因直接或间接使用该代码而导致的法律责任、经济损失或…...
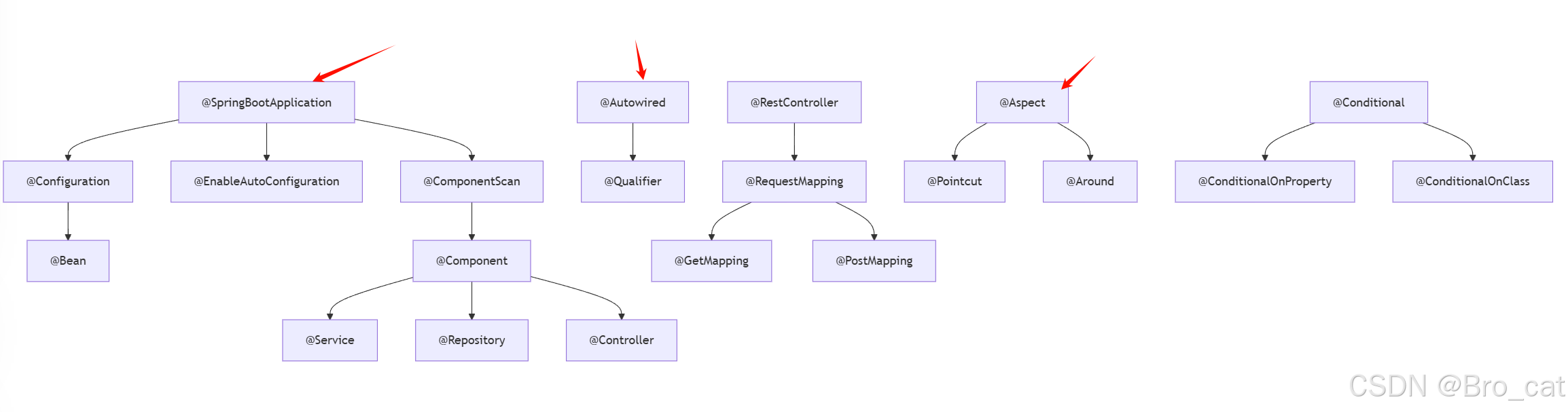
Spring Boot常用注解深度解析:从入门到精通
今天,这篇文章带你将深入理解Spring Boot中30常用注解,通过代码示例和关系图,帮助你彻底掌握Spring核心注解的使用场景和内在联系。 一、启动类与核心注解 1.1 SpringBootApplication 组合注解: SpringBootApplication Confi…...
can not add outlook new accounts on the outlook
link : Reference url...
私有化部署 DeepSeek + Dify,构建你的专属私人 AI 助手
私有化部署 DeepSeek Dify,构建你的专属私人 AI 助手 概述 DeepSeek 是一款开创性的开源大语言模型,凭借其先进的算法架构和反思链能力,为 AI 对话交互带来了革新性的体验。通过私有化部署,你可以充分掌控数据安全和使用安全。…...
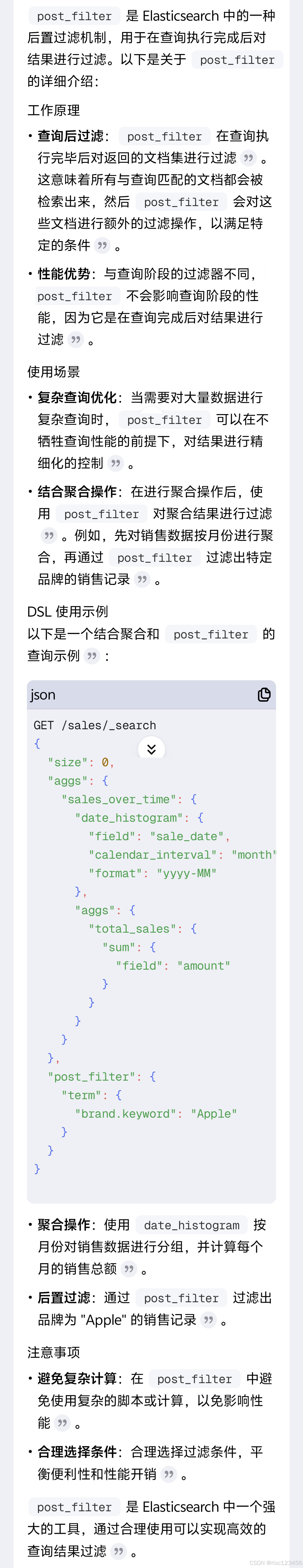
【Elasticsearch】post_filter
post_filter是 Elasticsearch 中的一种后置过滤机制,用于在查询执行完成后对结果进行过滤。以下是关于post_filter的详细介绍: 工作原理 • 查询后过滤:post_filter在查询执行完毕后对返回的文档集进行过滤。这意味着所有与查询匹配的文档都…...

验证工具:GVIM和VIM
一、定义与关系 gVim:gVim是Vim的图形界面版本,提供了更多的图形化功能,如菜单栏、工具栏和鼠标支持。它使得Vim的使用更加直观和方便,尤其对于不习惯命令行界面的用户来说。Vim:Vim是一个在命令行界面下运行的文本编…...
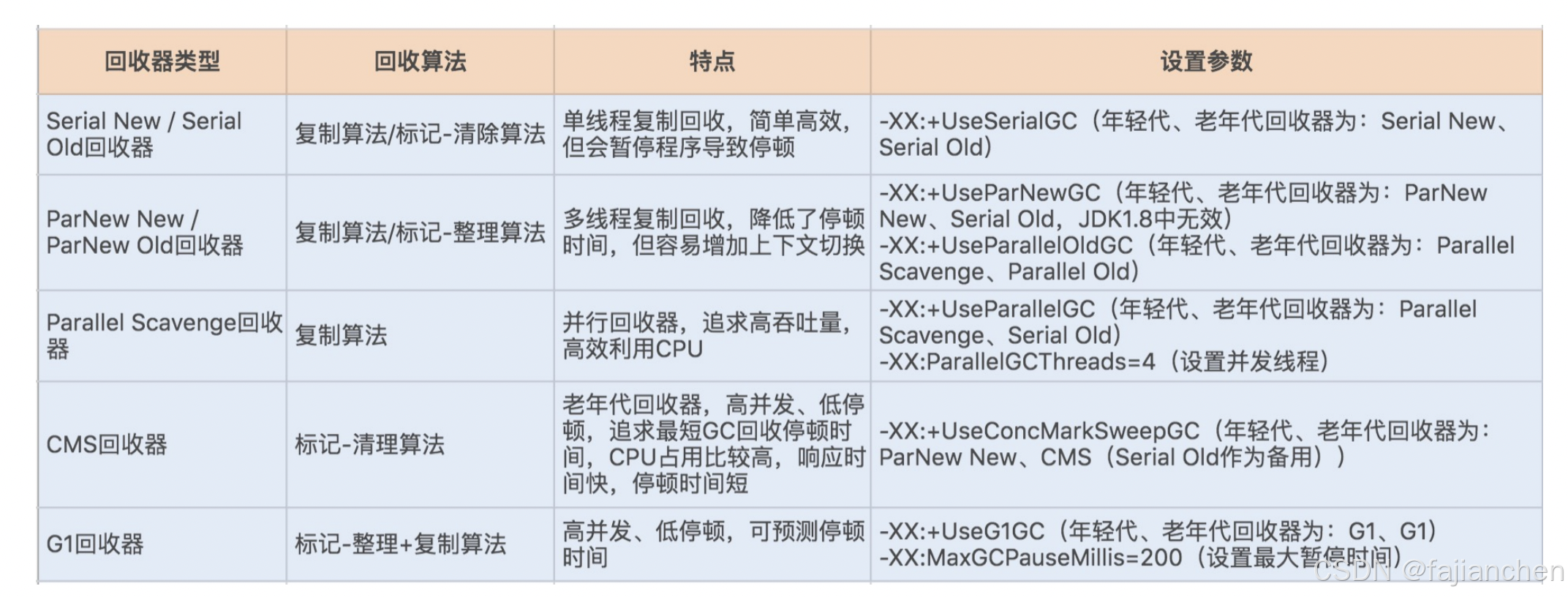
如何优化垃圾回收机制?
垃圾回收机制 掌握 GC 算法之前,我们需要先弄清楚 3 个问题。第一,回收发生在哪里?第二,对象在 什么时候可以被回收?第三,如何回收这些对象? 回收发生在哪里? JVM 的内存区域中&…...

beyond the ‘PHYSICAL‘ memory limit.问题处理
Container [pid5616,containerIDcontainer_e50_1734408743176_3027740_01_000006] is running 507887616B beyond the ‘PHYSICAL’ memory limit. Current usage: 4.5 GB of 4 GB physical memory used; 6.6 GB of 8.4 GB virtual memory used. Killing container. 1.增大map…...

Day36【AI思考】-表达式知识体系总览
文章目录 **表达式知识体系总览**回答1:**表达式知识体系****一、三种表达式形式对比****二、表达式转换核心方法****1. 中缀转后缀(重点)****2. 中缀转前缀** **三、表达式计算方法****1. 后缀表达式计算(栈实现)****…...
调试)
段错误(Segmentation Fault)调试
1. 使用 GDB(GNU Debugger) GDB 是一个强大的调试工具,可以帮助你逐步执行程序并检查变量状态。 编译时添加调试信息: gcc -g your_program.c -o your_program启动 GDB: gdb ./your_program运行程序: …...
每日Attention学习19——Convolutional Multi-Focal Attention
每日Attention学习19——Convolutional Multi-Focal Attention 模块出处 [ICLR 25 Submission] [link] UltraLightUNet: Rethinking U-shaped Network with Multi-kernel Lightweight Convolutions for Medical Image Segmentation 模块名称 Convolutional Multi-Focal Atte…...

LeetCode题练习与总结:三个数的最大乘积--628
一、题目描述 给你一个整型数组 nums ,在数组中找出由三个数组成的最大乘积,并输出这个乘积。 示例 1: 输入:nums [1,2,3] 输出:6示例 2: 输入:nums [1,2,3,4] 输出:24示例 3&a…...

Colorful/七彩虹 隐星P15 TA 24 原厂Win11 家庭版系统 带F9 Colorful一键恢复功能
Colorful/七彩虹 隐星P15 TA 24 原厂Win11 家庭中文版系统 带F9 Colorful一键恢复功能 自动重建COLORFUL RECOVERY功能 带所有随机软件和机型专用驱动 支持机型:隐星P15 TA 24 文件下载:asusoem.cn/745.html 文件格式:ISO 系统版本&…...

第二篇:多模态技术突破——DeepSeek如何重构AI的感知与认知边界
——从跨模态对齐到因果推理的工程化实践 在AI技术从单一模态向多模态跃迁的关键阶段,DeepSeek通过自研的多模态融合框架,在视觉-语言-语音的联合理解与生成领域实现系统性突破。本文将从技术实现层面,解构其跨模态表征学习、动态融合机制与…...

CTreeCtrl 设置图标
mfc界面修改真难受 使用CTreeCtrl 进行设置导航视图时,有时候需要设置图标,一般使用如下代码 m_TreeViewImages.DeleteImageList();UINT uiBmpId IDB_ICONLIST_TREE;CBitmap bmp; if (!bmp.LoadBitmap(uiBmpId)) return;BITMAP bmpObj; bmp.GetBitmap…...

在JAX-RS中获取请求头信息的方法
在JAX-RS中获取请求头信息的方法 HeaderParam注解,可以直接将请求头中的特定值注入到方法参数中,代码示例: import javax.ws.rs.GET; import javax.ws.rs.HeaderParam; import javax.ws.rs.Path; import javax.ws.rs.core.Response;Path(&q…...

Java 面试之结束问答
技术优化 线程池优化 设置最大线程数设置最小核心线程数设置额外线程存活时间选择线程池队列选择合适的线程池选择合适的饱和策略 锁优化 尽量不要锁住方法缩小同步代码块,只锁数据锁中尽量不要再包含锁将锁私有化,在内部管理锁进行适当的锁分解 HT…...
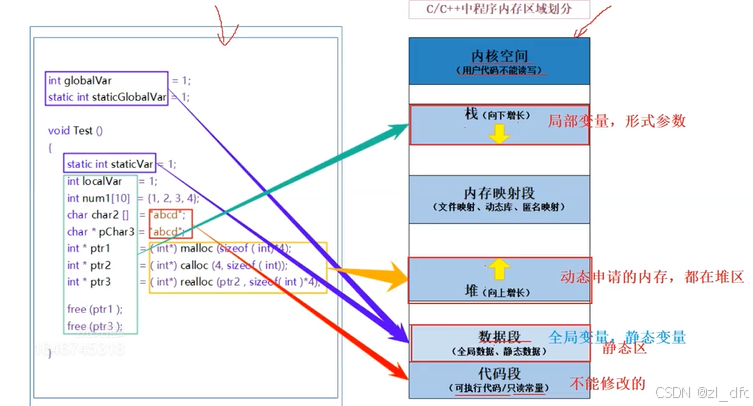
柔性数组与c/c++程序中内存区域的划分
1.柔性数组 1.1柔性数组的定义 柔性数组是指在结构体中定义的,其大小在编译时未确定,而在运行时动态分配的数组。这种数组允许结构体的大小根据需要动态变化。语法如下: struct D {int a;int arry1[0]; };struct F {int a;int arry2[]; };…...

mini-lsm通关笔记Week2Day7
项目地址:https://github.com/skyzh/mini-lsm 个人实现地址:https://gitee.com/cnyuyang/mini-lsm 在上一章中,您已经构建了一个完整的基于LSM的存储引擎。在本周末,我们将实现存储引擎的一些简单但重要的优化。欢迎来到Mini-LSM的…...
Typora免费使用
一.下载地址 https://typoraio.cn/ 二.修改配置文件 1.找到安装路径下的LicenseIndex.180dd4c7.4da8909c.chunk.js文件 文件路径为:安装路径\resources\page-dist\static\js\LicenseIndex.180dd4c7.4da8909c.chunk.js 将js中的 e.hasActivated"true"e.hasActiva…...
)
rknn优化教程(二)
文章目录 1. 前述2. 三方库的封装2.1 xrepo中的库2.2 xrepo之外的库2.2.1 opencv2.2.2 rknnrt2.2.3 spdlog 3. rknn_engine库 1. 前述 OK,开始写第二篇的内容了。这篇博客主要能写一下: 如何给一些三方库按照xmake方式进行封装,供调用如何按…...
` 方法)
深入浅出:JavaScript 中的 `window.crypto.getRandomValues()` 方法
深入浅出:JavaScript 中的 window.crypto.getRandomValues() 方法 在现代 Web 开发中,随机数的生成看似简单,却隐藏着许多玄机。无论是生成密码、加密密钥,还是创建安全令牌,随机数的质量直接关系到系统的安全性。Jav…...

线程与协程
1. 线程与协程 1.1. “函数调用级别”的切换、上下文切换 1. 函数调用级别的切换 “函数调用级别的切换”是指:像函数调用/返回一样轻量地完成任务切换。 举例说明: 当你在程序中写一个函数调用: funcA() 然后 funcA 执行完后返回&…...

服务器硬防的应用场景都有哪些?
服务器硬防是指一种通过硬件设备层面的安全措施来防御服务器系统受到网络攻击的方式,避免服务器受到各种恶意攻击和网络威胁,那么,服务器硬防通常都会应用在哪些场景当中呢? 硬防服务器中一般会配备入侵检测系统和预防系统&#x…...

质量体系的重要
质量体系是为确保产品、服务或过程质量满足规定要求,由相互关联的要素构成的有机整体。其核心内容可归纳为以下五个方面: 🏛️ 一、组织架构与职责 质量体系明确组织内各部门、岗位的职责与权限,形成层级清晰的管理网络…...

vue3 字体颜色设置的多种方式
在Vue 3中设置字体颜色可以通过多种方式实现,这取决于你是想在组件内部直接设置,还是在CSS/SCSS/LESS等样式文件中定义。以下是几种常见的方法: 1. 内联样式 你可以直接在模板中使用style绑定来设置字体颜色。 <template><div :s…...

大学生职业发展与就业创业指导教学评价
这里是引用 作为软工2203/2204班的学生,我们非常感谢您在《大学生职业发展与就业创业指导》课程中的悉心教导。这门课程对我们即将面临实习和就业的工科学生来说至关重要,而您认真负责的教学态度,让课程的每一部分都充满了实用价值。 尤其让我…...
Springboot社区养老保险系统小程序
一、前言 随着我国经济迅速发展,人们对手机的需求越来越大,各种手机软件也都在被广泛应用,但是对于手机进行数据信息管理,对于手机的各种软件也是备受用户的喜爱,社区养老保险系统小程序被用户普遍使用,为方…...

服务器--宝塔命令
一、宝塔面板安装命令 ⚠️ 必须使用 root 用户 或 sudo 权限执行! sudo su - 1. CentOS 系统: yum install -y wget && wget -O install.sh http://download.bt.cn/install/install_6.0.sh && sh install.sh2. Ubuntu / Debian 系统…...

【无标题】路径问题的革命性重构:基于二维拓扑收缩色动力学模型的零点隧穿理论
路径问题的革命性重构:基于二维拓扑收缩色动力学模型的零点隧穿理论 一、传统路径模型的根本缺陷 在经典正方形路径问题中(图1): mermaid graph LR A((A)) --- B((B)) B --- C((C)) C --- D((D)) D --- A A -.- C[无直接路径] B -…...
