专业学习|一文了解并实操自适应大邻域搜索(讲解代码)

一、自适应大邻域搜索概念介绍
自适应大邻域搜索(Adaptive Large Neighborhood Search,ALNS)是一种用于解决组合优化问题的元启发式算法。以下是关于它的详细介绍:
-自适应大领域搜索的核心思想是:破坏解、修复解、动态调整权重并选择(自适应)。
(一) 基本原理
(1)大邻域搜索(LNS)基础
传统的局部搜索算法通常在当前解的小邻域内进行搜索,容易陷入局部最优解。大邻域搜索则通过破坏(destroy)当前解的一部分,生成一个更大的邻域,然后再通过修复(repair)操作得到新的可行解,从而有可能跳出局部最优。
例如,在车辆路径规划问题中,破坏操作可以是移除一些客户节点,修复操作则是将这些移除的节点重新插入到路径中。
与同类算法相比:在邻域搜索算法中,有的算法可以只使用一种邻域,如模拟退火算法,因此它仅仅搜索了解空间的一小部分,找到全局最优的概率较小,它的优势之一是可以避免陷入局部最优;
邻域搜索算法以一个初始解 x xx 为输入,在 x xx 的邻域进行搜索,以寻找可能存在的更优解,每次找到一个更优解,就用它替换当前解,直到达到局部最优解(找不到任何更优解)。该算法被称为最佳改进算法,因为它总是选择邻域中的最佳解。
而有的算法可以使用多种算子,如变邻域搜索算法(VNS),它通过在当前解的多个邻域中寻找更满意的解,能够大大提高算法在解空间的搜索范围,但是它在使用算子时盲目地将每种算子形成的邻域结构都搜索一遍,缺少了一些启发式信息的指导;
而自适应大邻域搜索算法就弥补了这种不足,这种算法根据算子的历史表现与使用次数选择下一次迭代使用的算子,通过算子间的相互竞争来生成当前解的邻域结构,而在这种结构中有很大概率能够找到更好的解;
销毁方法通常包含随机元素,因此每次调用该方法时都会销毁解决方案的不同部分。然后,解 x xx 的邻域 N ( x ) N(x)N(x) 被定义为通过首先应用破坏方法然后应用修复方法可以达到的解集。
(2)自适应机制
ALNS在LNS的基础上引入了自适应机制。它会根据不同的破坏和修复操作在搜索过程中的表现,动态地调整这些操作被选择的概率。表现好的操作在后续搜索中被选择的概率会增加,反之则减少。
具体来说,算法会为每个破坏和修复操作维护一个分数,根据该分数更新操作的权重,进而影响操作被选择的概率。
(二) 主要步骤
 (1) 初始化
(1) 初始化
生成一个初始解。这个初始解可以是通过某种启发式方法得到的,也可以是随机生成的。
初始化各种破坏和修复操作的权重,通常初始权重可以设置为相等。
(2) 迭代搜索
选择操作:根据当前操作的权重,使用某种选择策略(如轮盘赌选择)选择一个破坏操作和一个修复操作。
破坏阶段:使用选择的破坏操作对当前解进行破坏,得到一个部分解。
修复阶段:使用选择的修复操作对部分解进行修复,得到一个新的可行解。
接受准则:根据一定的接受准则(如模拟退火中的Metropolis准则)决定是否接受这个新解。如果接受,则将新解作为当前解;否则,保持当前解不变。
更新操作分数和权重:根据新解的质量,更新所使用的破坏和修复操作的分数,然后根据分数更新操作的权重。
(3) 终止条件
当满足一定的终止条件(如达到最大迭代次数、运行时间超过限制等)时,算法停止,输出当前找到的最优解。
1. 生成初始解,当前解X0 = 初始解,最优解X1 = X02. 重复以下步骤进行迭代直到停止准则2.1 根据算子权重选择破坏与修复算子,并更新算子使用次数2.2 破坏算子和修复算子依次对当前解操作得到新解X22.3 更新当前解 - 如f(X2) < f(X0),则X0 = X2- 如f(X2) > f(X0),则以一定的概率接受该解作为当前解2.4 更新最优解 - 如f(X2) < f(X1),则X1 = X22.5 更新算子的分数2.6 更新算子的权重2.7 重置当前解3. 返回最优解X1
(4)关于破坏算子选择以及修复算子选择说明


(5)关于动态调整权重并选择(自适应过程)的说明


(三)算法评析
(1)优点
全局搜索能力强:通过大邻域搜索,能够跳出局部最优,有更大的机会找到全局最优解。
自适应特性:能够根据搜索过程中的反馈动态调整操作的选择概率,提高搜索效率。
灵活性高:可以应用于各种组合优化问题,只需要根据具体问题设计合适的破坏和修复操作。
(2) 缺点
参数调整复杂:算法中有多个参数需要调整,如初始权重、分数更新规则等,参数设置不当可能会影响算法的性能。
计算复杂度高:由于需要进行多次破坏和修复操作,计算量较大,对于大规模问题可能需要较长的运行时间。
(3) 应用领域
ALNS在许多组合优化问题中都有应用,例如:
车辆路径规划问题(VRP):包括带时间窗的VRP、多车辆VRP等。
调度问题:如作业车间调度、项目调度等。
资源分配问题:如护士排班、课程排课等。
二、算法实例
(一)ALNS算法实现34个城市的TSP问题
#以下是python实现的代码。 其中,destroy算子有3个:随机筛选N个城市、删除距离最大的N个城市和随机删#除连续的N个城市;repair算子有2个:随机插入和贪心插入,不过考虑到随机插入的效果大概率比较差,所以#代码中实际只使用了贪心插入。import copy
import time
import random
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import os
import math
import foliumclass ALNSSearch():# 计算TSP总距离# 计算TSP总距离@staticmethoddef dis_cal(path, dist_mat):distance = 0for i in range(len(path) - 1):distance += dist_mat[path[i]][path[i + 1]]distance += dist_mat[path[-1]][path[0]]return distance# 随机删除N个城市@staticmethoddef random_destroy(x, destroy_city_cnt):new_x = copy.deepcopy(x)removed_cities = []# 随机选择N个城市,并删除removed_index = random.sample(range(0, len(x)), destroy_city_cnt)for i in removed_index:removed_cities.append(new_x[i])x.remove(new_x[i])return removed_cities# 删除距离最大的N个城市@staticmethoddef max_n_destroy(x, destroy_city_cnt):new_x = copy.deepcopy(x)removed_cities = []# 计算顺序距离并排序dis = []for i in range(len(new_x) - 1):dis.append(dist_mat[new_x[i]][new_x[i + 1]])dis.append(dist_mat[new_x[-1]][new_x[0]])sorted_index = np.argsort(np.array(dis))# 删除最大的N个城市for i in range(destroy_city_cnt):removed_cities.append(new_x[sorted_index[-1 - i]])x.remove(new_x[sorted_index[-1 - i]])return removed_cities# 随机删除连续的N个城市@staticmethoddef continue_n_destroy(x, destroy_city_cnt):new_x = copy.deepcopy(x)removed_cities = []# 随机选择N个城市,并删除removed_index = random.sample(range(0, len(x) - destroy_city_cnt), 1)[0]for i in range(removed_index + destroy_city_cnt, removed_index, -1):removed_cities.append(new_x[i])x.remove(new_x[i])return removed_cities# destroy操作def destroy(self, flag, x, destroy_city_cnt):# 三个destroy算子,第一个是随机删除N个城市,第二个是删除距离最大的N个城市,第三个是随机删除连续的N个城市removed_cities = []if flag == 0:# 随机删除N个城市removed_cities = self.random_destroy(x, destroy_city_cnt)elif flag == 1:# 删除距离最大的N个城市removed_cities = self.max_n_destroy(x, destroy_city_cnt)elif flag == 2:# 随机删除连续的N个城市removed_cities = self.continue_n_destroy(x, destroy_city_cnt)return removed_cities# 随机插入def random_insert(x, removed_cities):insert_index = random.sample(range(0, len(x)), len(removed_cities))for i in range(len(insert_index)):x.insert(insert_index[i], removed_cities[i])# 贪心插入def greedy_insert(self, x, removed_cities):dis = float('inf')insert_index = -1for i in range(len(removed_cities)):# 寻找插入后的最小总距离for j in range(len(x) + 1):new_x = copy.deepcopy(x)new_x.insert(j, removed_cities[i])if self.dis_cal(new_x, dist_mat) < dis:dis = self.dis_cal(new_x, dist_mat)insert_index = j# 最小位置处插入x.insert(insert_index, removed_cities[i])dis = float('inf')# repair操作def repair(self, flag, x, removed_cities):# 两个repair算子,第一个是随机插入,第二个贪心插入if flag == 0:self.random_insert(x, removed_cities)elif flag == 1:self.greedy_insert(x, removed_cities)# 选择destroy算子def select_and_destroy(self, destroy_w, x, destroy_city_cnt):# 轮盘赌逻辑选择算子prob = destroy_w / np.array(destroy_w).sum()seq = [i for i in range(len(destroy_w))]destroy_operator = np.random.choice(seq, size=1, p=prob)[0]# destroy操作removed_cities = self.destroy(destroy_operator, x, destroy_city_cnt)return removed_cities, destroy_operator# 选择repair算子def select_and_repair(self, repair_w, x, removed_cities):# # 轮盘赌逻辑选择算子prob = repair_w / np.array(repair_w).sum()seq = [i for i in range(len(repair_w))]repair_operator = np.random.choice(seq, size=1, p=prob)[0]# repair操作:此处设定repair_operator=1,即只使用贪心策略self.repair(1, x, removed_cities)return repair_operator# ALNS主程序def calc_by_alns(self, dist_mat):# 模拟退火温度T = 100# 降温速度a = 0.97# destroy的城市数量destroy_city_cnt = int(len(dist_mat) * 0.1)# destroy算子的初始权重destroy_w = [1, 1, 1]# repair算子的初始权重repair_w = [1, 1]# destroy算子的使用次数destroy_cnt = [0, 0, 0]# repair算子的使用次数repair_cnt = [0, 0]# destroy算子的初始得分destroy_score = [1, 1, 1]# repair算子的初始得分repair_score = [1, 1]# destroy和repair的挥发系数lambda_rate = 0.5# 当前解,第一代,贪心策略生成removed_cities = [i for i in range(dist_mat.shape[0])]x = []self.repair(1, x, removed_cities)# 历史最优解,第一代和当前解相同,注意是深拷贝,此后有变化不影响x,也不会因x的变化而被影响history_best_x = copy.deepcopy(x)# 迭代cur_iter = 0max_iter = 100print('cur_iter: {}, best_f: {}, best_x: {}'.format(cur_iter, self.dis_cal(history_best_x, dist_mat),history_best_x))while cur_iter < max_iter:# 生成测试解,即伪代码中的x^ttest_x = copy.deepcopy(x)# destroy算子remove, destroy_operator_index = self.select_and_destroy(destroy_w, test_x, destroy_city_cnt)destroy_cnt[destroy_operator_index] += 1# repair算子repair_operator_index = self.select_and_repair(repair_w, test_x, remove)repair_cnt[repair_operator_index] += 1if self.dis_cal(test_x, dist_mat) <= self.dis_cal(x, dist_mat):# 测试解更优,更新当前解x = copy.deepcopy(test_x)if self.dis_cal(test_x, dist_mat) <= self.dis_cal(history_best_x, dist_mat):# 测试解为历史最优解,更新历史最优解,并设置最高的算子得分history_best_x = copy.deepcopy(test_x)destroy_score[destroy_operator_index] = 1.5repair_score[repair_operator_index] = 1.5else:# 测试解不是历史最优解,但优于当前解,设置第二高的算子得分destroy_score[destroy_operator_index] = 1.2repair_score[repair_operator_index] = 1.2else:if np.random.random() < np.exp((self.dis_cal(x, dist_mat) - self.dis_cal(test_x, dist_mat)) / T):# 当前解优于测试解,但满足模拟退火逻辑,依然更新当前解,设置第三高的算子得分x = copy.deepcopy(test_x)destroy_score[destroy_operator_index] = 0.8repair_score[repair_operator_index] = 0.8else:# 当前解优于测试解,也不满足模拟退火逻辑,不更新当前解,设置最低的算子得分destroy_score[destroy_operator_index] = 0.5repair_score[repair_operator_index] = 0.5# 更新destroy算子的权重destroy_w[destroy_operator_index] = \destroy_w[destroy_operator_index] * lambda_rate + \(1 - lambda_rate) * destroy_score[destroy_operator_index] / destroy_cnt[destroy_operator_index]# 更新repair算子的权重repair_w[repair_operator_index] = \repair_w[repair_operator_index] * lambda_rate + \(1 - lambda_rate) * repair_score[repair_operator_index] / repair_cnt[repair_operator_index]# 降低温度T = a * T# 结束一轮迭代,重置模拟退火初始温度cur_iter += 1print('cur_iter: {}, best_f: {}, best_x: {}'.format(cur_iter, self.dis_cal(history_best_x, dist_mat),history_best_x))# 打印ALNS得到的最优解print(history_best_x)print(self.dis_cal(history_best_x, dist_mat))return history_best_xif __name__ == '__main__':original_cities = [['西宁', 101.74, 36.56],['兰州', 103.73, 36.03],['银川', 106.27, 38.47],['西安', 108.95, 34.27],['郑州', 113.65, 34.76],['济南', 117, 36.65],['石家庄', 114.48, 38.03],['太原', 112.53, 37.87],['呼和浩特', 111.65, 40.82],['北京', 116.407526, 39.90403],['天津', 117.200983, 39.084158],['沈阳', 123.38, 41.8],['长春', 125.35, 43.88],['哈尔滨', 126.63, 45.75],['上海', 121.473701, 31.230416],['杭州', 120.19, 30.26],['南京', 118.78, 32.04],['合肥', 117.27, 31.86],['武汉', 114.31, 30.52],['长沙', 113, 28.21],['南昌', 115.89, 28.68],['福州', 119.3, 26.08],['台北', 121.3, 25.03],['香港', 114.173355, 22.320048],['澳门', 113.54909, 22.198951],['广州', 113.23, 23.16],['海口', 110.35, 20.02],['南宁', 108.33, 22.84],['贵阳', 106.71, 26.57],['重庆', 106.551556, 29.563009],['成都', 104.06, 30.67],['昆明', 102.73, 25.04],['拉萨', 91.11, 29.97],['乌鲁木齐', 87.68, 43.77]]original_cities = pd.DataFrame(original_cities, columns=['城市', '经度', '纬度'])D = original_cities[['经度', '纬度']].values * math.pi / 180city_cnt = len(original_cities)dist_mat = np.zeros((city_cnt, city_cnt))for i in range(city_cnt):for j in range(city_cnt):if i == j:# 相同城市不允许访问dist_mat[i][j] = 1000000else:# 单位:kmdist_mat[i][j] = 6378.14 * math.acos(math.cos(D[i][1]) * math.cos(D[j][1]) * math.cos(D[i][0] - D[j][0]) +math.sin(D[i][1]) * math.sin(D[j][1]))# ALNS求解TSPtime0 = time.time()alns = ALNSSearch()history_best_x = alns.calc_by_alns(dist_mat)print(city_cnt)print('使用ALNS求解TSP,耗时: {} s'.format(time.time() - time0))
#运行代码后可发现,经过不到4s的计算时间,ALNS便可以得到15662.59的解,和全局最优解15614.84之间的#gap仅约0.3%。(2) Robust Optimization for the Dual Sourcing Inventory Routing Problem in Disaster Relief
import numpy as np
import math
import re
import csv
import random
import copy
import time
import os
# --------------------------- Global Configuration ---------------------------------------removal_operators_list=['shaw','distance','worst','worst_replenishment_time','random']
insertion_operators_list=['greedy','2_regret','shaw']##################################################################################for root, dirs, files in os.walk('./Test_set'):for set_name in files:print(set_name)time_start = time.time()instance = set_nameproblem = base.generate_problem(instance)records = base.Record(removal_operators_list, insertion_operators_list)solution = base.generate_initial_solution(problem)removal_operators = base.Removal_operators(removal_operators_list)insertion_operators = base.Insertion_operators(insertion_operators_list)solution.obj = base.calculate_objective(solution, problem)current_solution = copy.deepcopy(solution)best_solution = copy.deepcopy(solution)time_end = time.time()time_cost = time_end - time_startrecords.initial_generator_time_cost = time_costtime_start = time.time()iteration_num = 0iteration_counter = 0segment_counter = 0while time_cost <= 3600:if problem.temperature <= 0.01:breakif iteration_counter >= problem.segments_capacity:segment_counter += 1iteration_counter = 0for i in removal_operators_list:records.removal_operator_score_record[i].append(removal_operators.removal_operator_score[i])records.removal_operator_weights_record[i].append(removal_operators.removal_operator_weight[i])records.removal_operator_times_record[i].append(removal_operators.removal_operator_times[i])for i in insertion_operators_list:records.insertion_operator_score_record[i].append(insertion_operators.insertion_operator_score[i])records.insertion_operator_weights_record[i].append(insertion_operators.insertion_operator_weight[i])records.insertion_operator_times_record[i].append(insertion_operators.insertion_operator_times[i])removal_operators.update_weight(removal_operators_list,problem)insertion_operators.update_weight(insertion_operators_list,problem)for i in removal_operators_list:removal_operators.removal_operator_score[i] = 0removal_operators.removal_operator_times[i] = 0for i in insertion_operators_list:insertion_operators.insertion_operator_score[i] = 0insertion_operators.insertion_operator_times[i] = 0best_solution, current_solution = base.do_2opt(best_solution, current_solution, problem)solution = copy.deepcopy(current_solution)selected_removal_operator = removal_operators.select(removal_operators_list)selected_insertion_operator = insertion_operators.select(insertion_operators_list)removal_operators.removal_operator_times[selected_removal_operator] +=1insertion_operators.insertion_operator_times[selected_insertion_operator] +=1sub_time_start = time.time()sub_time_cost = sub_time_start - time_endbase.do_remove(selected_removal_operator, solution, problem)sub_time_end = time.time()sub_time_cost = sub_time_end - sub_time_startsub_time_start = sub_time_endbase.do_insert(selected_insertion_operator, solution, problem)sub_time_end = time.time()sub_time_cost = sub_time_end - sub_time_startsub_time_start = sub_time_endrecords.best_solution_obj_record.append(best_solution.obj)if solution.obj < current_solution.obj:if solution.obj < best_solution.obj:removal_operators.removal_operator_score[selected_removal_operator] += problem.score_factor_1insertion_operators.insertion_operator_score[selected_insertion_operator] += problem.score_factor_1current_solution = copy.deepcopy(solution)best_solution = copy.deepcopy(solution)current_solution = copy.deepcopy(solution)records.best_solution_obj_record[iteration_num] = best_solution.objsegment_counter = 0print('get best solution= ', best_solution.obj)records.best_solution_update_iteration_num.append(iteration_num)else:removal_operators.removal_operator_score[selected_removal_operator] += problem.score_factor_2insertion_operators.insertion_operator_score[selected_insertion_operator] += problem.score_factor_2current_solution = copy.deepcopy(solution)elif random.random() < math.exp(-(solution.obj - current_solution.obj)/problem.temperature):removal_operators.removal_operator_score[selected_removal_operator] += problem.score_factor_3insertion_operators.insertion_operator_score[selected_insertion_operator] += problem.score_factor_3current_solution = copy.deepcopy(solution)iteration_num += 1iteration_counter += 1time_end = time.time()time_cost = time_end - time_startif time_cost >= 1200 and iteration_num <= 3000/3:problem.cooling_rate = (0.01/problem.temperature) ** (1/iteration_num)if time_cost >= 2400 and iteration_num <= 3000/2:problem.cooling_rate = (0.01/problem.temperature) ** (1/(iteration_num/2))problem.temperature = problem.temperature*problem.cooling_rateprint('iteration '+ str(iteration_num)+' finished!')print(problem.instance_name,' has finished!')with open('Data.csv', 'a', newline='', encoding="ANSI") as f_out:csv.writer(f_out, delimiter=',').writerow([set_name, best_solution.obj,time_cost])print(problem.instance_name, ' has finished!')
三、基础知识介绍
(一)轮盘赌是什么?


来源:Evolutionary Computing: 遗传算法_轮盘赌选择(转载) - 柠檬雨 - 博客园
参考引用(它山之石)
「1」https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/353562821
「2」元启发式算法详解:(自适应)大邻域搜索算法((A)LNS)-CSDN博客
「3」https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/102298240
相关文章:

专业学习|一文了解并实操自适应大邻域搜索(讲解代码)
一、自适应大邻域搜索概念介绍 自适应大邻域搜索(Adaptive Large Neighborhood Search,ALNS)是一种用于解决组合优化问题的元启发式算法。以下是关于它的详细介绍: -自适应大领域搜索的核心思想是:破坏解、修复解、动…...

9. k8s二进制集群之kube-controller-manager部署
同样在部署主机上创建证书请求文件(为之后的证书生成做准备)根据上面的证书文件创建证书(结果会在当前目录下产生kube-controller-manager证书)创建kube-controller-manager服务配置文件创建kube-controller-manager服务启动文件同步kube-controller-manager证书到对应mast…...

轮转数组-三次逆置
题目 给定一个整数数组 nums,将数组中的元素向右轮转 k 个位置,其中 k 是非负数。 void rotate(int* nums, int numsSize, int k){}示例: 输入: nums [1,2,3,4,5,6,7], k 3 输出: [5,6,7,1,2,3,4] 解释: 向右轮转 1 步: [7,1,2,3,4,5,6] …...

3 卷积神经网络CNN
1 Image Classification (Neuron Version) – 1.1 Observation 1 1.2 Observation 2 如果不同的receptive field需要相同功能的neuron,可以使这些neuron共享参数 1.3 Benefit of Convolutional Layer 2 Image Classification (Filter Version) 不用担心filter大小…...

穷举vs暴搜vs深搜vs回溯vs剪枝系列一>黄金矿工
目录 决策树:代码设计代码: 决策树: 代码设计 代码: class Solution {boolean[][] vis;int ret,m,n;public int getMaximumGold(int[][] grid) {m grid.length;n grid[0].length;vis new boolean[m][n]; for(int i 0; i <…...

java基础1(黑马)
一、初识Java 1.Java背景知识 1)Java是美国SUN公司在1995年推出的一门计算机高级编程语言。 2)Java早期名称为OAK,后来才改为Java。 3)Java之父:詹姆斯高斯林。 4)2009年,SUN公司被Oracle公…...

ES6 对象扩展:对象简写,对象属性 表达式,扩展运算符 ...,Object.assign,Object.is,用法和应用场景
1. 对象属性简写 1.1 基本语法 // 传统写法 const name John; const age 25; const user {name: name,age: age };// ES6 简写语法 const user {name,age };1.2 实际应用场景 // 1. 函数返回对象 function createUser(name, age, email) {return {name,age,email}; }// …...

2025 持续防范 GitHub 投毒,通过 Sharp4SuoExplorer 分析 Visual Studio 隐藏文件
在2024年底的网络安全事件中,某提权工具被发现植入后门,攻击者利用 .suo 文件作为隐蔽的攻击方式。由于 .suo 文件是 Visual Studio 项目的隐藏配置文件,通常不为安全研究人员所关注,因此为攻击者提供了潜在的攻击渠道。 初步调查…...

PCB走线宽度与过流能力参考
我们PCB走线,线宽与允许通过电流的大小是什么样的?几个因素 1、允许的温升:如果能够允许的铜线升高的温度越高,那么允许通过的电流自然也就越高 2、走线的线宽:线越宽 ,导线横截面积越大,电阻…...

电商项目-分布式事务(四)基于消息队列实现分布式事务
基于消息队列实现分布式事务,实现消息最终一致性 如何基于消息队列实现分布式事务? 通过消息队列实现分布式事务的话,可以保证当前数据的最终一致性。实现思路:将大的分布式事务,进行拆分,拆分成若干个小…...

g++ -> make -> cmake(草稿)
1 Windows上安装mingw 2 构建一个 c 项目 3 g 编译 4 make 编译 5 cmake 编译...

JSON常用的工具方法
前言: 在日常开发中,JSON 数据的处理是常见的需求。无论是数据转换、格式化还是与其他格式的互转,掌握一些常用的工具方法可以大大提高开发效率。本文将介绍一些实用的 JSON 操作方法,帮助你快速上手。 JSON常用的工具方法 1.json字符串转换…...

【Kubernetes Pod间通信-第2篇】使用BGP实现Pod到Pod的通信
Kubernetes中Pod间的通信 本系列文章共3篇: 【Kubernetes Pod间通信-第1篇】在单个子网中使用underlay网络实现Pod到Pod的通信【Kubernetes Pod间通信-第2篇】使用BGP实现Pod到Pod的通信(本文介绍)【Kubernetes Pod间通信-第3篇】Kubernetes中Pod与ClusterIP服务之间的通信…...

[权限提升] Windows 提权 维持 — 系统错误配置提权 - Trusted Service Paths 提权
关注这个专栏的其他相关笔记:[内网安全] 内网渗透 - 学习手册-CSDN博客 0x01:Trusted Service Paths 提权原理 Windows 的服务通常都是以 System 权限运行的,所以系统在解析服务的可执行文件路径中的空格的时候也会以 System 权限进行解析&a…...

8. k8s二进制集群之Kubectl部署
创建kubectl证书请求文件生成admin证书文件复制admin证书到指定目录生成kubeconfig配置文件接下来完成kubectl配置文件的角色绑定【扩展】kubectl命令补全操作继续上一篇文章《k8s二进制集群之Kube ApiServer部署》下面介绍一下k8s中的命令行管理工具kubectl。 通过kubectl可以…...

初学 Xvisor 之理解并跑通 Demo
官网:https://www.xhypervisor.org/ quick-start 文档:https://github.com/xvisor/xvisor/blob/master/docs/riscv/riscv64-qemu.txt 零、Xvisor 介绍 下面这部分是 Xvisor 官方的介绍 Xvisor 是一款开源的 Type-1 虚拟机管理程序,旨在提供一…...

深度内容运营与开源AI智能名片2+1链动模式S2B2C商城小程序在打造种草社区中的应用研究
摘要:移动互联网的迅猛发展极大地改变了消费者的购物行为和消费习惯,传统的购物体验已难以满足用户日益增长的个性化需求。在这种背景下,深度内容运营和实时互动成为提升用户购物体验、影响用户购物行为的重要手段。同时,开源AI智…...

RNN/LSTM/GRU 学习笔记
文章目录 RNN/LSTM/GRU一、RNN1、为何引入RNN?2、RNN的基本结构3、各种形式的RNN及其应用4、RNN的缺陷5、如何应对RNN的缺陷?6、BPTT和BP的区别 二、LSTM1、LSTM 简介2、LSTM如何缓解梯度消失与梯度爆炸? 三、GRU四、参考文献 RNN/LSTM/GRU …...

音频录制一般在什么情况下会选择保存为PCM?什么情况会选择保存为WAV?
在音频开发中,选择保存为 PCM 或 WAV 格式取决于具体的应用场景和需求。以下是两种格式的特点以及适用场景的分析: PCM 格式 特点: 原始音频数据: PCM 是未压缩的原始音频数据,没有任何文件头或元数据。数据直接以二进…...

C#常用744单词
1.visual 可见的 2.studio 工作室 3.dot 点 4.net 网 5.harp 尖端的,锋利的。 6.amework 骨架,构架,框架 7.beta 测试版,试用版 8.XML(全称:eXtensible Markup Language)…...

[2025CVPR]DeepVideo-R1:基于难度感知回归GRPO的视频强化微调框架详解
突破视频大语言模型推理瓶颈,在多个视频基准上实现SOTA性能 一、核心问题与创新亮点 1.1 GRPO在视频任务中的两大挑战 安全措施依赖问题 GRPO使用min和clip函数限制策略更新幅度,导致: 梯度抑制:当新旧策略差异过大时梯度消失收敛困难:策略无法充分优化# 传统GRPO的梯…...

【Go】3、Go语言进阶与依赖管理
前言 本系列文章参考自稀土掘金上的 【字节内部课】公开课,做自我学习总结整理。 Go语言并发编程 Go语言原生支持并发编程,它的核心机制是 Goroutine 协程、Channel 通道,并基于CSP(Communicating Sequential Processes࿰…...
)
【RockeMQ】第2节|RocketMQ快速实战以及核⼼概念详解(二)
升级Dledger高可用集群 一、主从架构的不足与Dledger的定位 主从架构缺陷 数据备份依赖Slave节点,但无自动故障转移能力,Master宕机后需人工切换,期间消息可能无法读取。Slave仅存储数据,无法主动升级为Master响应请求ÿ…...

Java面试专项一-准备篇
一、企业简历筛选规则 一般企业的简历筛选流程:首先由HR先筛选一部分简历后,在将简历给到对应的项目负责人后再进行下一步的操作。 HR如何筛选简历 例如:Boss直聘(招聘方平台) 直接按照条件进行筛选 例如:…...
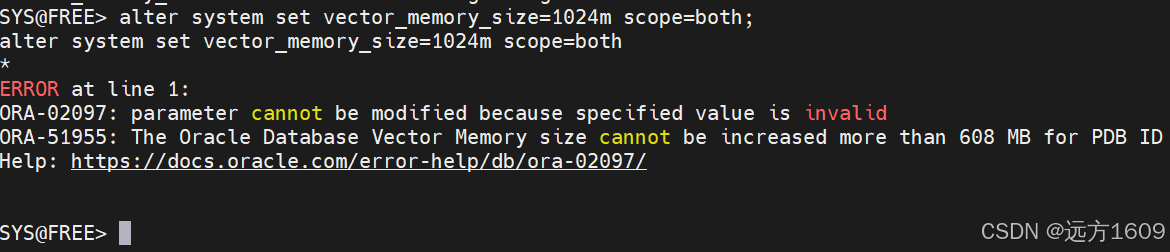
10-Oracle 23 ai Vector Search 概述和参数
一、Oracle AI Vector Search 概述 企业和个人都在尝试各种AI,使用客户端或是内部自己搭建集成大模型的终端,加速与大型语言模型(LLM)的结合,同时使用检索增强生成(Retrieval Augmented Generation &#…...

【JVM】Java虚拟机(二)——垃圾回收
目录 一、如何判断对象可以回收 (一)引用计数法 (二)可达性分析算法 二、垃圾回收算法 (一)标记清除 (二)标记整理 (三)复制 (四ÿ…...

Scrapy-Redis分布式爬虫架构的可扩展性与容错性增强:基于微服务与容器化的解决方案
在大数据时代,海量数据的采集与处理成为企业和研究机构获取信息的关键环节。Scrapy-Redis作为一种经典的分布式爬虫架构,在处理大规模数据抓取任务时展现出强大的能力。然而,随着业务规模的不断扩大和数据抓取需求的日益复杂,传统…...

十九、【用户管理与权限 - 篇一】后端基础:用户列表与角色模型的初步构建
【用户管理与权限 - 篇一】后端基础:用户列表与角色模型的初步构建 前言准备工作第一部分:回顾 Django 内置的 `User` 模型第二部分:设计并创建 `Role` 和 `UserProfile` 模型第三部分:创建 Serializers第四部分:创建 ViewSets第五部分:注册 API 路由第六部分:后端初步测…...
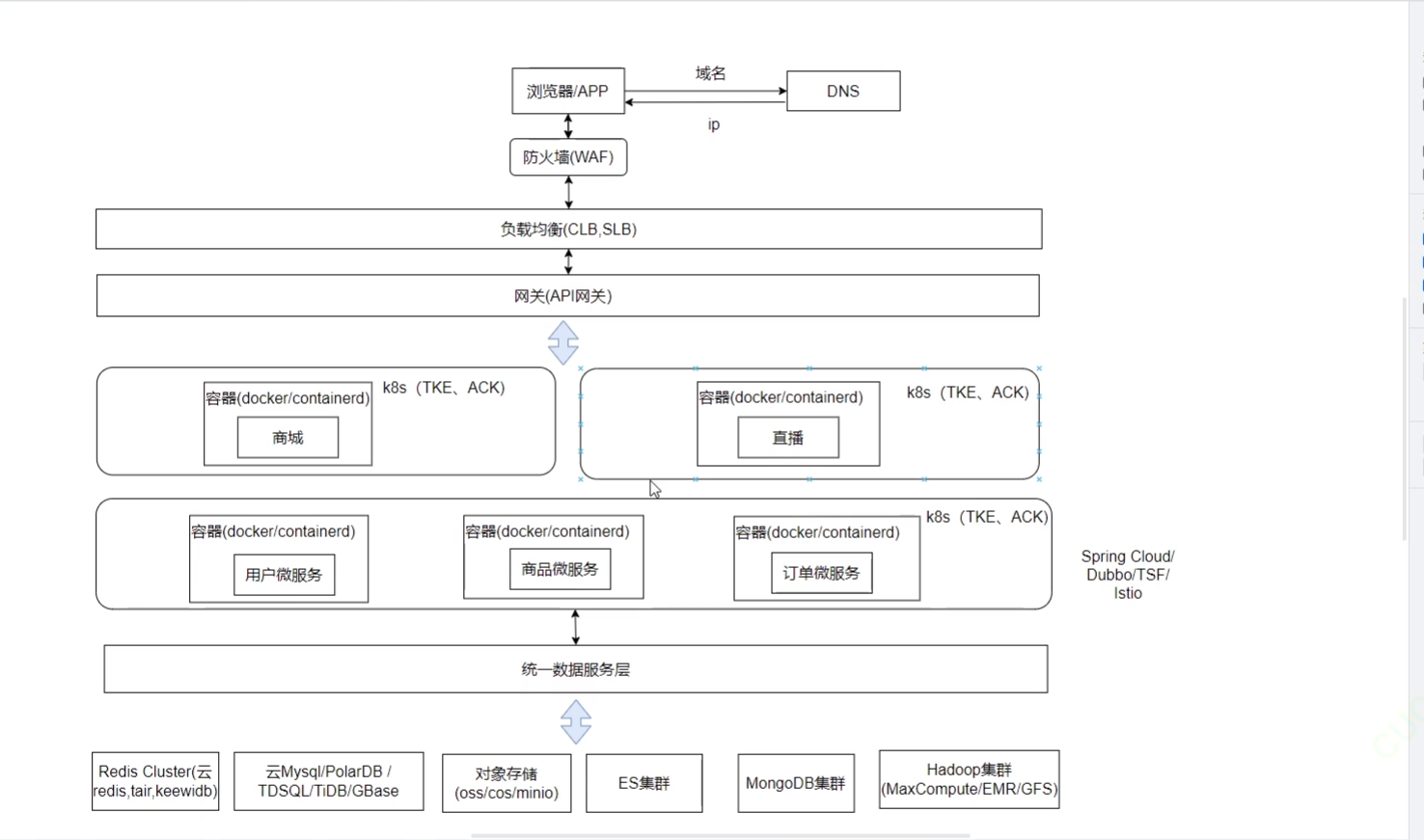
《Docker》架构
文章目录 架构模式单机架构应用数据分离架构应用服务器集群架构读写分离/主从分离架构冷热分离架构垂直分库架构微服务架构容器编排架构什么是容器,docker,镜像,k8s 架构模式 单机架构 单机架构其实就是应用服务器和单机服务器都部署在同一…...

Python实现简单音频数据压缩与解压算法
Python实现简单音频数据压缩与解压算法 引言 在音频数据处理中,压缩算法是降低存储成本和传输效率的关键技术。Python作为一门灵活且功能强大的编程语言,提供了丰富的库和工具来实现音频数据的压缩与解压。本文将通过一个简单的音频数据压缩与解压算法…...


