AlgoC++第八课:手写BP
目录
- 手写BP
- 前言
- 1. 数据加载
- 2. 前向传播
- 3. 反向传播
- 总结
手写BP
前言
手写AI推出的全新面向AI算法的C++课程 Algo C++,链接。记录下个人学习笔记,仅供自己参考。
本次课程主要是手写 BP 代码
课程大纲可看下面的思维导图

1. 数据加载
我们首先来实现下MNIST数据集的加载工作
#include <iostream>
#include <tuple>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include "matrix.hpp"using namespace std;namespace Application{namespace io{// 不要内存对齐struct __attribute__((packed)) mnist_labels_header_t{unsigned int magic_number;unsigned int number_of_items;}struct __attribute__((packed)) mnist_images_header_t{unsigned int magic_number;unsigned int number_of_images;unsigned int number_of_rows;unsigned int number_of_cols;}unsigned int inverse_byte(unsigned int v){unsigned char* p = (unsigned char*)&v;std::swap(p[0], p[3]);std::swap(p[1], p[2]);return v;}/* 加载mnist数据集 */tuple<Matrix, Matrix> load_data(const string& image_file, const string& label_file){// file, mode = rb/wb/a+Matrix images, labels;fstream fimage(image_file, ios::binary | ios::in);fstream flabel(label_file, ios::binary | ios::in)mnist_images_header_t images_header;mnist_labels_header_t labels_header;fimage.read((char *)&images_header, sizeof(images_header));flabel.read((char *)&labels_header, sizeof(labels_header));// 大小端转换images_header.number_of_images = inverse_byte(images_header.number_of_images);labels_header.number_of_items = inverse_byte(labels_header.number_of_items);images.resize(images_header.number_of_images, 28 * 28);// one hot, floatlabels.resize(labels_header.number_of_items, 10);// 中间存储作用, 它的大小等于文件中图像数据的大小std::vector<unsigned char> buffer(images.rows() * images.cols());fimage.read((char*)buffer.data(), buffer.size());// buffer 是unsigned char类型的图像数据,pixel// 现在需要转化到images矩阵中// 顺便把标准化给做了for(int i = 0; i < buffer.size() ++i)images.ptr()[i] = (buffer[i] / 255.0f - 0.1307f) / 0.3081f;// 开始处理label,ont-hot过程// labels是全零的矩阵buffer.resize(labels.rows());flabel.read((char*)buffer.data(), buffer.size());for(int i = 0; i < buffer.size(); ++i)labels.ptr(i)[buffer[i]] = 1; // one-hotreturn make_tuple(images, labels);}}int run(){// 验证Matrix images, labels;tie(images, labels) = io::load_data("mnist/train-images.idx3-ubyte","mnist/train-labels.idx1-ubyte");cout << labels;return 0;}
}int main(){return Application::run();
}
上面示例代码演示了 mnist 数据集加载的示例,其中
- 定义了两个用于 mnist 数据集的结构体,分别是
mnist_labels_header_t和mnist_images_header_t。这两个结构体表示 mnist 标签和图像的头信息 __attribute__((packed))是一个 GCC/Clang 的扩展,用于告诉编译器不要进行内存对齐,以便我们自己手动控制内存的布局和对齐。inverse_byte用于大小端转换。在 mnist 数据集中,头文件中存储的是大端模式,而读取数据时需要将其转换为小端模式。inverse_byte函数实现的方法是将 unsigned int 类型的变量按照字节顺序重新排列。load_data函数用于加载 mnist 数据集,需要传入图像和标签的文件名。在函数内部,使用 fstream 打开文件并读取头信息,对头信息进行大小端转换,然后根据图像和标签的大小创建矩阵。之后,读取图像和标签数据并进行归一化,最后返回归一化后的矩阵。
标签处理的代码有点看不懂,来分析下
buffer.resize(labels.rows());
flabel.read((char*)buffer.data(), buffer.size());
for(int i = 0; i < buffer.size(); ++i)labels.ptr(i)[buffer[i]] = 1;
在 MNIST 数据集中,标签是一个整数值,代表着手写数字的真实值。但是,在神经网络训练中,我们通常需要将标签转化为 one-hot 编码,以便于计算误差。例如,对于数字 5,它的 ont-hot 编码为[0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0],也就是在第 6 个位置上为 1,其余位置都为0
这段代码中,首先通过 resize 函数将 buffer 的大小设置为标签行数,也就是样本数。然后从 flabel 中读取 buffer.size() 个字节到 buffer 中。由于标签是一个字节大小的整数,所以 buffer 中存储的是一连串的整数值。接下来的 for 循环中,遍历 buffer 中的所有元素,将标签对应的位置设置为 1,其余位置设置为 0
labels.ptr(i) 返回 labels 中第i行的地址,然后用 [buffer[i]] 访问该行中第 buffer[i] 列的元素,将该元素的值设置为1。这样就完成了标签数据的转化,使其变为了适合神经网络训练的形式
2. 前向传播
来看下整个前向传播过程,包括初始化超参数和权重、偏置矩阵,矩阵相乘进行前传并求取 Loss
#include <iostream>
#include <tuple>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <random>
#include <cmath>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm> // shuffle
#include "matrix.hpp"using namespace std;namespace Application{namespace tools{vector<int> range(int end){vector<int> output(end);for(int i = 0; i < end; ++i)output[i] = i;return output;}// 通过指定索引数组,并且指定图像、索引的起点和终点。获取对应索引的对应图像,返回matrixMatrix slice(const Matrix& images, const vector<int>& indexs, int start, int size){Matrix output(size, images.cols());for(int i = 0; i < size; ++i){int image_row_index = indexs[start + i];// 把images[image_row_index]对应的一行,复制到output[i]行memcpy(output.ptr(i), images.ptr(image_row_index), sizeof(float) * images.cols());}return output;}};namespace random{// 对应的就是seedstatic default_random_engine global_random_engine;Matrix normal_distribution_matrix(int rows, int cols, float mean = 0.0f, float stddev = 0.0f){// seednormal_distribution<float> norm(mean, stddev);Matrix output(rows, cols);for(int i = 0; i < rows * cols; ++i)output.ptr()[i] = norm(global_random_engine);return output;}// inplace -> 现场修改void shuffle_array(vector<int>& indexs){std::shuffle(indexs.begin(), indexs.end(), global_random_engine);}};namespace nn{Matrix relu(cosnt Matrix& x){Matrix output = x;auto p = output.ptr();for(int i = 0; i < x.numel(); ++i, ++p){// max(float, int)*p = std::max(*p, 0.0f);}return output; }float sigmoid_cross_entropy_loss(const Matrix& output, const Matrix& y){static auto sigmoid = [](float x){return 1.0f / (1.0f + exp(-x));}// output => n x 10// y => n x 10auto po = output.ptr();auto py = y.ptr();float loss = 0;float eps = 1e-5;for(int i = 0; i < output.numnel(); ++i, ++po, ++py){float prob = sigmoid(*po);prob = max(min(prob, 1-eps), eps);// loss += -(y * log(p) + (1-y) * log(1-p));loss += (*py) * log(prob) + (1 - *py) * log(1 - prob);}return -loss / output.rows();}};int run(){Matrix trainimages, trainlabels;Matrix valimages, vallabels;tie(trainimages, trainlabels) = io::load_data("mnist/train-images.idx3-ubyte", "mnist/train-labels.idx1-ubyte");tie(valimage, vallabels) = io::load_data("mnist/t10k-images.idx3-ubyte", "mnist/t10k-labels.idx1-ubyte");// hidden = images @ w1 + b1// output = hidden @ w2 + b2// loss = lossfn(output, onehot_label)// loss.backward()int num_images = trainimages.rows(); // 60000int num_input = trainimages.cols(); // 784int num_hidden = 1024;int num_output = 10;int num_epoch = 10;float lr = 1e-1;int batch_size = 256;float momentum = 0.9f;// drop last -> pytorch dataloaderint num_batch_per_epoch = num_images / batch_size;// 训练流程// 1. 随机抓取一个batch,shuffle=True// 怎么实现随机呢?// 重点是,要求,每一个epoch,抓取的随机性不同// 按照索引抓取,index[0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7]// shuffle(indexs) ->[6,5,4,0,1,3,2,7] auto image_indexs = tools::range(num_images);// 确定矩阵的大小,并且对矩阵做初始化(凯明初始化fan_in,fan_out)float w1_gain = 2.0f / std::sqrt((float)num_input + num_hidden); // 对应激活函数 Matrix w1 = random::normal_distribution_matrix(num_input, num_hidden, 0, w1_gain);Matrix b1 = random::normal_distribution_matrix(1, num_hidden); float w2_gain = 1.0f / std::sqrt((float)num_hidden + num_output); // 对应激活函数 Matrix w2 = random::normal_distribution_matrix(num_hidden, num_output, 0, w1_gain);Matrix b2 = random::normal_distribution_matrix(1, num_output);for(int epoch = 0; epoch < num_epoch; ++epoch){random::shuffle_array(image_indexs);for(int ibatch = 0; ibatch < num_batch_per_epoch; ++ibatch){// image_indexs[ibatch * batch_size : (ibatch + 1) * batch_size]auto x = tools::slice(trainimages, image_indexs, ibatch * batch_size, batch_size);cout << x.rows() << ", " << x.cols() << endl;auto y = tools::slice(trainlabels, image_indexs, ibatch * batch_size, batch_size);// n x m + 1 x mauto hidden = x.gemm(w1) + b1;auto hidden_act = nn::relu(hidden);auto output = hidden_act.gemm(w2) + b2;float loss = nn::sigmoid_cross_entropy_loss(output, y);cout << "Loss: " << loss << endl;}}// 验证// Matrix t = random::normal_distribution_matrix(3, 3);// Matrix s = tools::slice(t, {0, 1, 2}, 1, 2);// cout << t;// cout << s;return 0;}
}int main(){return Application::run();
}
上面示例代码演示了前向传播的过程,包括初始化神经网络参数、进行前向传播计算、计算损失函数
- 首先,对神经网络的参数进行了初始化,包括输入层到隐藏层的权重矩阵 w1 和偏置向量 b1,隐藏层到输出层的权重矩阵 w2 和偏置向量 b2。这些参数都是通过调用
random::normal_distribution_matrix()函数生成的,该函数使用了高斯分布来初始化,而 w1 和 w2 的初始化还使用了凯明初始化 - 然后,代码进入了训练流程,首先进行了数据的随机抽取。随机抽取的方法是使用了
tools::range()函数生成一个索引数组,然后使用random::shuffle_array()函数对该索引数组进行打乱。打乱的目的是保证每个 epoch 中数据的随机性不同。 - 对于每个 batch,代码首先使用
tools::slice()函数从训练集抽取出 batch_size 个样本,然后进行前向传播计算。- hidden = images @ w1 + b1
- output = hidden @ w2 + b2
- 在得到输出层的数据后,代码计算了该 batch 的损失函数。其具体实现在
nn::sigmoid_cross_entropy_loss()函数中,采用交叉熵损失,它首先将 output 中的每个元素通过 sigmoid 函数,然后根据公式计算 loss 并返回。
3. 反向传播
我们先来回忆下反向传播的公式

根据上图来计算 L o s s Loss Loss 分别对 W 1 W_1 W1 B 1 B_1 B1 W 2 W_2 W2 B 2 B_2 B2 的梯度
-
1.隐藏层的输出为: H = r e l u ( X W 1 + B 1 ) H = relu(XW_1 + B_1) H=relu(XW1+B1)
-
2.输出层的预测概率为: P = s i g m o i d ( H W 2 + B 2 ) P = sigmoid(HW_2 + B_2) P=sigmoid(HW2+B2)
-
3.损失为: L = B i n a r y C r o s s E n t r o p y L o s s ( P , Y ) L = BinaryCrossEntropyLoss(P,Y) L=BinaryCrossEntropyLoss(P,Y)
-
4.计算 L L L 对 W 2 W_2 W2 和 B 2 B_2 B2 的梯度: ∂ L ∂ W 2 = H T ( P − Y ) \frac{\partial L}{\partial W_2}=H^{T}(P-Y) ∂W2∂L=HT(P−Y) ∂ L ∂ B 2 = r e d u c e _ s u m ( P − Y ) \frac{\partial L}{\partial B_{2}}= reduce\_sum(P-Y) ∂B2∂L=reduce_sum(P−Y)
-
5.计算 L L L 对 W 1 W_1 W1 和 B 1 B_1 B1 的梯度: ∂ L ∂ W 1 = X T ∂ L ∂ ( X W 1 + B 1 ) \frac{\partial L}{\partial W_{1}}=X^{T}\frac{\partial L}{\partial(X W_{1}+B_{1})} ∂W1∂L=XT∂(XW1+B1)∂L ∂ L ∂ B 1 = r e d u c e _ s u m ∂ L ∂ ( X W 1 + B 1 ) \frac{\partial L}{\partial B_{1}}=reduce\_sum\frac{\partial L}{\partial(X W_{1}+B_{1})} ∂B1∂L=reduce_sum∂(XW1+B1)∂L
-
6.拿到梯度后,对每一个参数应用优化器进行更新迭代
来看下整个反向传播的过程,根据 Loss 分别对 w1、b1、w2、b2 求取梯度,并更新参数
#include <iostream>
#include <tuple>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <random>
#include <cmath>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm> // shuffle
#include "matrix.hpp"using namespace std;namespace Application{namespace nn{Matrix drelu(const Matrix& g, cosnt Matrix& x){Matrix output = g;auto px = x.ptr();auto pg = output.ptr();for(int i = 0; i < x.numel(); ++i, ++px, ++pg){if(*px < 0)*pg = 0;}return output;}Matrix relu(cosnt Matrix& x){Matrix output = x;auto p = output.ptr();for(int i = 0; i < x.numel(); ++i, ++p){// max(float, int)*p = std::max(*p, 0.0f);}return output; }Matrix sigmoid(const Matrix& x){Matrix output = x;auto p = output.ptr();for(int i = 0; i < x.numel(); ++i, ++p){float t = *p;*p = 1.0f / (1.0f + exp(-t));}return output;}float sigmoid_cross_entropy_loss(const Matrix& prob, const Matrix& y){// static auto sigmoid = [](float x){return 1.0f / (1.0f + exp(-x));}auto prob = sigmoid(output);// output => n x 10// y => n x 10auto po = prob.ptr();auto py = y.ptr();float loss = 0;float eps = 1e-5;for(int i = 0; i < prob.numel(); ++i, ++po, ++py){float prob = *po;// prob = max(min(prob, 1-eps), eps);// loss += -(y * log(p) + (1-y) * log(1-p));loss += (*py) * log(p) + (1 - *py) * log(1 - p);}return -loss / prob.rows();}float eval_accuracy(const Matrix& testset, const Matrix& y,const Matrix& w1, const Matrix& b1, const Matrix& w2, const Matrix& b2){auto hidden = nn::relu(testset.gemm(w1) + b1);auto prob = nn::sigmoid(hidden.gemm(w2) + b2);int correct = 0;for(int i = 0; i < prob.rows(); ++i){// 为了拿到每一行预测的标签值,使用argmaxint predict_label = prob.argmax(i);// 因为y是one-hot,所以对应预测标签如果是1,则正确if(y(i, predict_label) == 1)correct++;}return correct / (float)prob.rows();}};int run(){Matrix trainimages, trainlabels;Matrix valimages, vallabels;tie(trainimages, trainlabels) = io::load_data("mnist/train-images.idx3-ubyte", "mnist/train-labels.idx1-ubyte");tie(valimages, vallabels) = io::load_data("mnist/t10k-images.idx3-ubyte", "mnist/t10k-labels.idx1-ubyte");// hidden = images @ w1 + b1// output = hidden @ w2 + b2// loss = lossfn(output, onehot_label)// loss.backward()int num_images = trainimages.rows(); // 60000int num_input = trainimages.cols(); // 784int num_hidden = 1024;int num_output = 10;int num_epoch = 10;float lr = 1e-1;int batch_size = 256;float momentum = 0.9f;// drop last -> pytorch dataloaderint num_batch_per_epoch = num_images / batch_size; // 60000 / 256 = 234(iter)// 训练流程// 1. 随机抓取一个batch,shuffle=True// 怎么实现随机呢?// 重点是,要求,每一个epoch,抓取的随机性不同// 按照索引抓取,index[0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7]// shuffle(indexs) ->[6,5,4,0,1,3,2,7] auto image_indexs = tools::range(num_images);// 确定矩阵的大小,并且对矩阵做初始化(凯明初始化fan_in,fan_out)float w1_gain = 2.0f / std::sqrt((float)num_input + num_hidden); // 对应激活函数 Matrix w1 = random::normal_distribution_matrix(num_input, num_hidden, 0, w1_gain);Matrix b1 = random::normal_distribution_matrix(1, num_hidden); float w2_gain = 1.0f / std::sqrt((float)num_hidden + num_output); // 对应激活函数 Matrix w2 = random::normal_distribution_matrix(num_hidden, num_output, 0, w1_gain);Matrix b2 = random::normal_distribution_matrix(1, num_output);for(int epoch = 0; epoch < num_epoch; ++epoch){random::shuffle_array(image_indexs);for(int ibatch = 0; ibatch < num_batch_per_epoch; ++ibatch){ // 一个epoch// image_indexs[ibatch * batch_size : (ibatch + 1) * batch_size]auto x = tools::slice(trainimages, image_indexs, ibatch * batch_size, batch_size);cout << x.rows() << ", " << x.cols() << endl;auto y = tools::slice(trainlabels, image_indexs, ibatch * batch_size, batch_size);// n x m + 1 x mauto hidden = x.gemm(w1) + b1;auto hidden_act = nn::relu(hidden);auto output = hidden_act.gemm(w2) + b2;auto probability = nn::sigmoid(output)float loss = nn::sigmoid_cross_entropy_loss(probability, y);cout << "Loss: " << loss << endl;// backward过程// dloss / doutput = (sigmoid(output) - y) / output.rows// C = AB// G = dloss / dC// dloss / dA = G @ B^T// dloss / dB = A^T @ G// output = hidden_act @ w2auto doutput = (probability - y) / (float)output.rows();auto db2 = doutput.reduce_sum_by_row();auto dhidden_act = doutput.gemm(w2, false, true);auto dw2 = hidden_act.gemm(doutput, true);// dloss / dhiddenauto dhidden = nn::drelu(dhidden_act, hidden);// x @ w1 + b1auto db1 = dhidden.reduce_sum_by_row();auto dw1 = x.gemm(dhidden, true);// 更新w1 = w1 - lr * dw1;b1 = b1 - lr * dw1;}float accuracy = nn::eval_accuracy(valimages, vallabels, w1, b1, w2, b2);printf("%d. accuracy: %.2f %%\n", epoch, accuracy * 100);}// 验证// Matrix t = random::normal_distribution_matrix(3, 3);// Matrix s = tools::slice(t, {0, 1, 2}, 1, 2);// cout << t;// cout << s;return 0;}
}int main(){return Application::run();
}
在上面的示例代码中,主要是求取梯度的过程比较繁琐,需要明确 L L L 分别对 W 1 W_1 W1 B 1 B_1 B1 W 2 W_2 W2 B 2 B_2 B2 的导数计算,后续就是利用 SGD 算法进行参数更新。最后在每个 epoch 结束后,计算测试集上的准确率并输出结果
总结
本次课程跟着杜老师手写了一遍 BP 反向传播算法,加深了对 BP 的认识,锻炼了自己的动手能力,提高了对 C++ 和神经网络的进一步理解。整个 BP 过程还是比较清晰的,无非是前传 => 计算Loss => 反传 => 更新,但还是要求对许多细节的把握,比如如何去优化代码提高性能,如何尽可能的减少矩阵相乘的次数等等,多想多写吧。期待下次手写 AutoGrad 课程😄
相关文章:

AlgoC++第八课:手写BP
目录 手写BP前言1. 数据加载2. 前向传播3. 反向传播总结 手写BP 前言 手写AI推出的全新面向AI算法的C课程 Algo C,链接。记录下个人学习笔记,仅供自己参考。 本次课程主要是手写 BP 代码 课程大纲可看下面的思维导图 1. 数据加载 我们首先来实现下MNIST…...

【Java笔试强训 27】
🎉🎉🎉点进来你就是我的人了博主主页:🙈🙈🙈戳一戳,欢迎大佬指点! 欢迎志同道合的朋友一起加油喔🤺🤺🤺 目录 一、选择题 二、编程题 🔥 不用加…...
java紫砂壶交易购物系统 mysql
网络紫砂壶可充通过色彩、图片、说明、设置动画加强了产品了宣传,大大达到了陶瓷业的“色型”要求。实现产品管理方便,起到立竿见影的效果,不用因为更改菜色而重新印刷。只要在后台鼠标轻轻一点,全线马上更新。采用B/S模式&#x…...

7-4 多态练习-计算面积
定义三个类,父类(抽象类)GeometricObject代表几何形状,子类Circle代表圆形,子类Rectangle代表矩形。具体属性和方法如下: 父类 (抽象类)GeometricObject 属性: private String color; private S…...

很佩服的一个Google大佬,离职了。。
这两天,科技圈又有一个突发的爆款新闻相信不少同学都已经看到了。 那就是75岁的计算机科学家Geoffrey Hinton从谷歌离职了,从而引起了科技界的广泛关注和讨论。 而Hinton自己也证实了这一消息。 提到Geoffrey Hinton这个名字,对于一些了解过…...
【Python习题集1】Python 语言基础知识
python习题 一、实验内容二、实验总结 一、实验内容 1、运用输入输出函数编写程序,将华氏温度转换成摄氏温度。换算公式:C(F-32)*5/9,其中C为摄氏温度,F为华氏温度。 (1)源代码: ffloat(input(输入华氏温…...

C语言进阶——数据在内存中的存储,你知道吗?
今天我们深度剖析数据在内存中的存储: 重点知识: 1、数据类型详细介绍 2、整形在内存中的存储:原码、反码、补码 3、大小端字节序介绍及判断 4、浮点型在内存中的存储解析 之前我们涉及关于这一部分的知识只是大致的进行讲解࿰…...

规则引擎----easy rules
一、规则引擎的作用 将复杂的if else判断剥离出来 二、使用 2.1、引入POM <!--easy rules核心库--><dependency><groupId>org.jeasy</groupId><artifactId>easy-rules-core</artifactId><version>3.3.0</version></depe…...

你手写过一把锁吗?你对轮询缓存怎么看?
当多个线程同时去操作一块内存的数据时如果不做一些限制,极其可能出现数据一致性问题。这时候,我们用一把锁锁住这块数据,持有钥匙者可以进入,不持有者等待钥匙用完再分配。所以在我看来啊,锁的本质就是一个标志位&…...
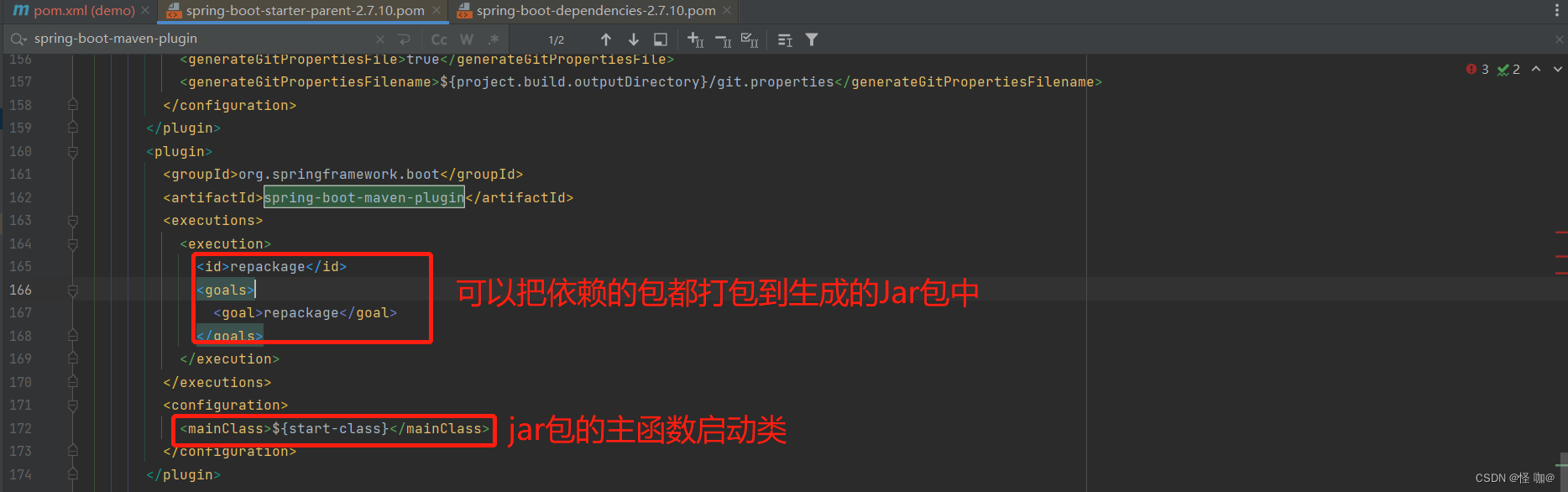
深入理解 spring-boot-starter-parent
目录 一、前言二、Maven继承三、分析spring-boot-starter-parent四、Maven单继承问题五、不继承spring-boot-starter-parent需要注意的 一、前言 在idea当中创建springboot项目的时候都会继承一个spring-boot-starter-parent作为父类,假如不继承我们的项目就不能使…...
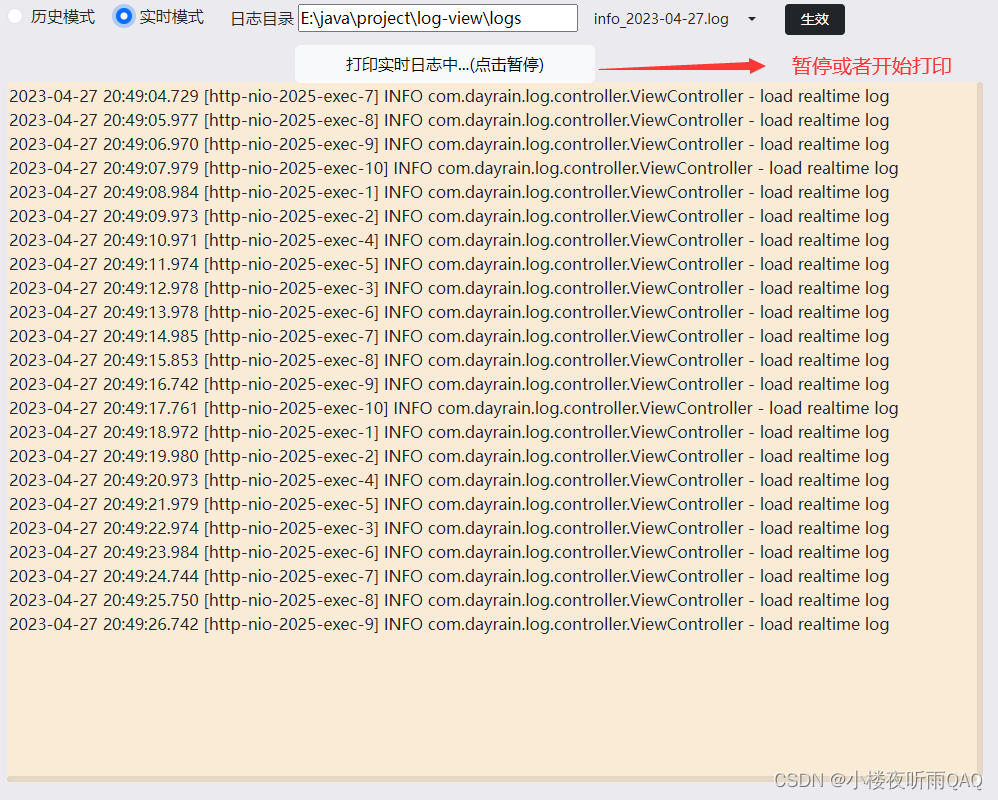
基于SpringBoot的线上日志阅读器
软件特点 部署后能通过浏览器查看线上日志。支持Linux、Windows服务器。采用随机读取的方式,支持大文件的读取。支持实时打印新增的日志(类终端)。支持日志搜索。 使用手册 基本页面 配置路径 配置日志所在的目录,配置后按回车…...
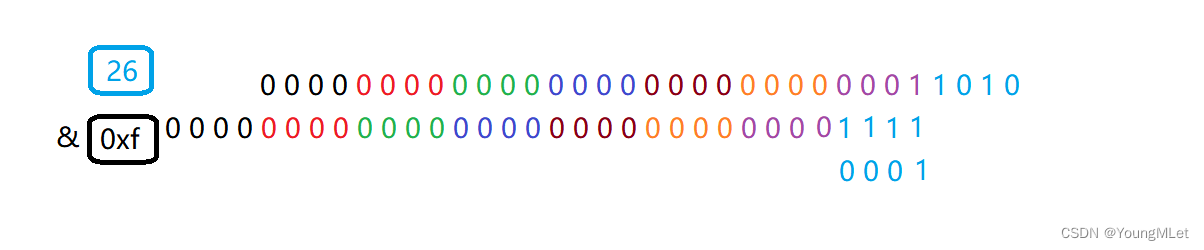
【Leetcode -405.数字转换为十六进制数 - 409.最长回文串】
Leetcode Leetcode -405.数字转换为十六进制数Leetcode - 409.最长回文串 Leetcode -405.数字转换为十六进制数 题目:给定一个整数,编写一个算法将这个数转换为十六进制数。对于负整数,我们通常使用 补码运算 方法。 注意 : 十六进制中所有…...

剑指 Offer:003 前 n 个数字二进制中 1 的个数
题目: 给定一个非负整数 n,请计算 0 到 n 之间的每个数字的二进制表示中 1 的个数,并输出一个数组 示例: 1、 输入: n 2 输出: [0,1,1] 解释: 0 --> 0 1 --> 1 2 --> 10 2、 输入: n 5 输出: [0,1,1,2,1,2] 解释: 0 …...
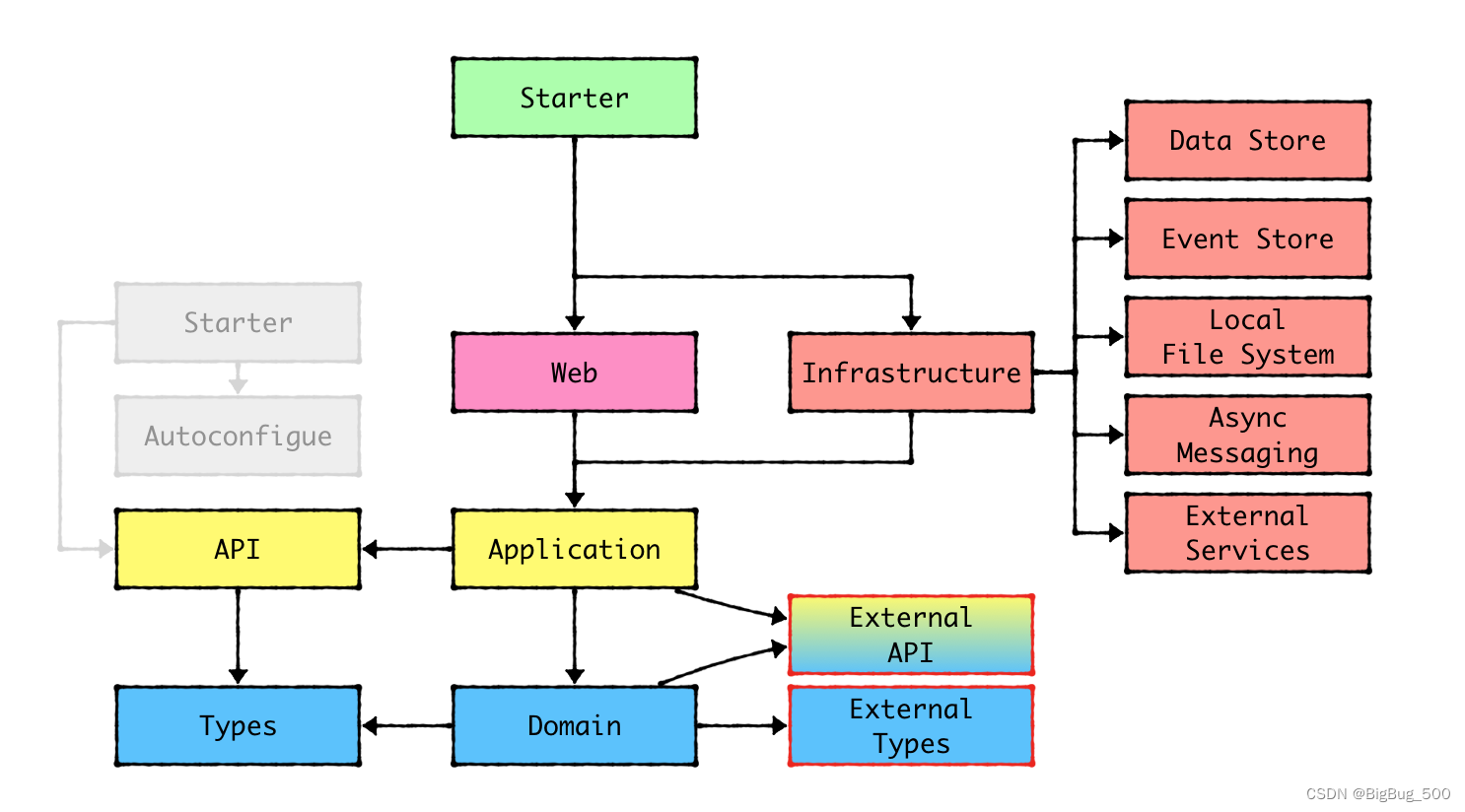
DDD系列:二、应用架构设计演变
作用: 通过规定一个固定的架构设计,可以让团队内有一个统一的开发规范,降低沟通成本,提升效率和代码质量。 目标: 在做架构设计时,一个好的架构应该需要实现以下几个目标: 独立于UI:前…...
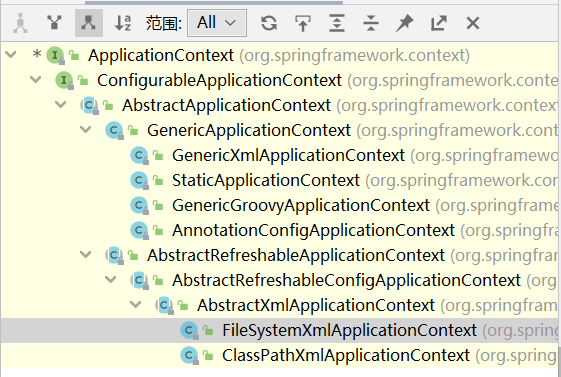
Spring-IOC
IOC概念和原理 什么是IOC 控制反转,为了将系统的耦合度降低,把对象的创建和对象直接的调用过程权限交给Spring进行管理。 IOC底层原理 XML解析 通过Java代码解析XML配置文件或者注解得到对应的类的全路径,获取对应的Class类 Class clazz …...
基于Java语言开发B/S架构实现的云HIS
一、云HIS系统框架简介 1、技术框架 (1)总体框架: SaaS应用,全浏览器访问 前后端分离,多服务协同 服务可拆分,功能易扩展 (2)技术细节: 前端:AngularNg…...

清洁赛道新势力,米博凭“减法”突围?
在五四青年节这个特殊的日子,方太旗下的高端智能清洁品牌“米博”发布了新一代无滚布洗地机7系列。 5月4日晚,米博以“减法生活,净请7代”为主题,举办了新品发布会。在发布会上,从小红书翻红的董洁作为方太集团米博产…...

代码随想录训练营Day6| 242、349、202、1
242. 有效的字母异位词 给定两个字符串 s 和 t ,编写一个函数来判断 t 是否是 s 的字母异位词。 注意:若 s 和 t 中每个字符出现的次数都相同,则称 s 和 t 互为字母异位词。 class Solution {public boolean isAnagram(String s, String t)…...
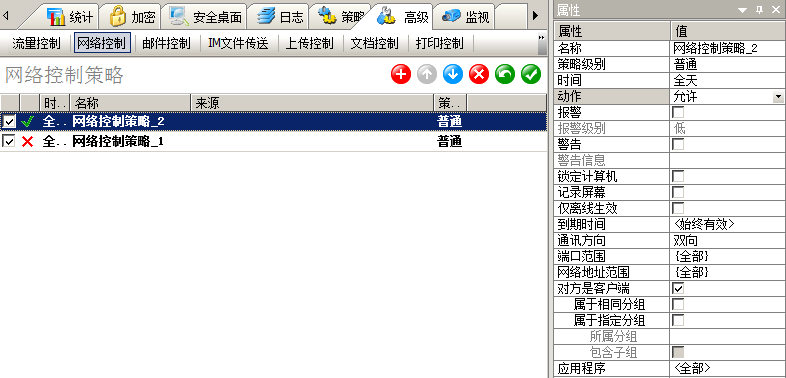
IP-GUARD如何通过网络控制策略禁止应用程序联网?
如何通过网络控制策略禁止应用程序联网? 可以在控制台-高级-网络控制中,添加以下策略: 动作:“禁止” 应用程序:填写要禁止的程序(以QQ示例) 如何禁止没有安装客户端的电脑访问客户端电脑? 可以给所有客户端设置只允许客户端电脑访问的网络控制策略; 在控制台左边的…...
Java RSA密钥转换,从RSAPrivateKey得到RSAPublicKey
概述: 在Java编程中,我们经常用到如下一段代码来生成RSA公私钥,分别拿到公私钥然后加解密计算: KeyPairGenerator keyPairGen; keyPairGen KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("RSA"); keyPairGen.initialize(2048, new S…...

Vue记事本应用实现教程
文章目录 1. 项目介绍2. 开发环境准备3. 设计应用界面4. 创建Vue实例和数据模型5. 实现记事本功能5.1 添加新记事项5.2 删除记事项5.3 清空所有记事 6. 添加样式7. 功能扩展:显示创建时间8. 功能扩展:记事项搜索9. 完整代码10. Vue知识点解析10.1 数据绑…...

TRS收益互换:跨境资本流动的金融创新工具与系统化解决方案
一、TRS收益互换的本质与业务逻辑 (一)概念解析 TRS(Total Return Swap)收益互换是一种金融衍生工具,指交易双方约定在未来一定期限内,基于特定资产或指数的表现进行现金流交换的协议。其核心特征包括&am…...
【开发技术】.Net使用FFmpeg视频特定帧上绘制内容
目录 一、目的 二、解决方案 2.1 什么是FFmpeg 2.2 FFmpeg主要功能 2.3 使用Xabe.FFmpeg调用FFmpeg功能 2.4 使用 FFmpeg 的 drawbox 滤镜来绘制 ROI 三、总结 一、目的 当前市场上有很多目标检测智能识别的相关算法,当前调用一个医疗行业的AI识别算法后返回…...

在QWebEngineView上实现鼠标、触摸等事件捕获的解决方案
这个问题我看其他博主也写了,要么要会员、要么写的乱七八糟。这里我整理一下,把问题说清楚并且给出代码,拿去用就行,照着葫芦画瓢。 问题 在继承QWebEngineView后,重写mousePressEvent或event函数无法捕获鼠标按下事…...
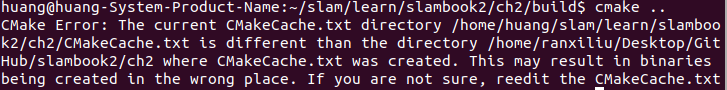
视觉slam十四讲实践部分记录——ch2、ch3
ch2 一、使用g++编译.cpp为可执行文件并运行(P30) g++ helloSLAM.cpp ./a.out运行 二、使用cmake编译 mkdir build cd build cmake .. makeCMakeCache.txt 文件仍然指向旧的目录。这表明在源代码目录中可能还存在旧的 CMakeCache.txt 文件,或者在构建过程中仍然引用了旧的路…...

JavaScript基础-API 和 Web API
在学习JavaScript的过程中,理解API(应用程序接口)和Web API的概念及其应用是非常重要的。这些工具极大地扩展了JavaScript的功能,使得开发者能够创建出功能丰富、交互性强的Web应用程序。本文将深入探讨JavaScript中的API与Web AP…...
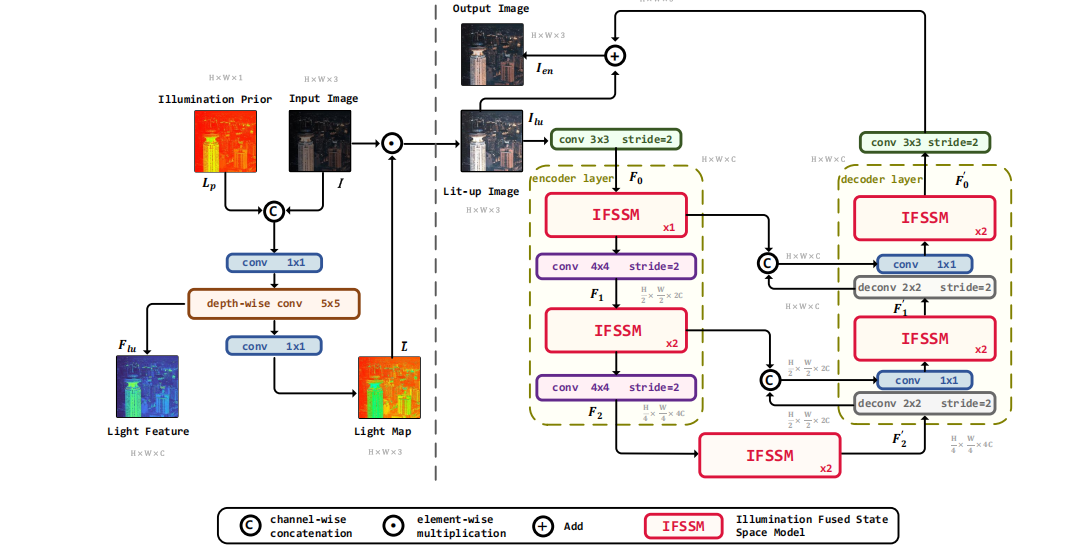
深度学习水论文:mamba+图像增强
🧀当前视觉领域对高效长序列建模需求激增,对Mamba图像增强这方向的研究自然也逐渐火热。原因在于其高效长程建模,以及动态计算优势,在图像质量提升和细节恢复方面有难以替代的作用。 🧀因此短时间内,就有不…...
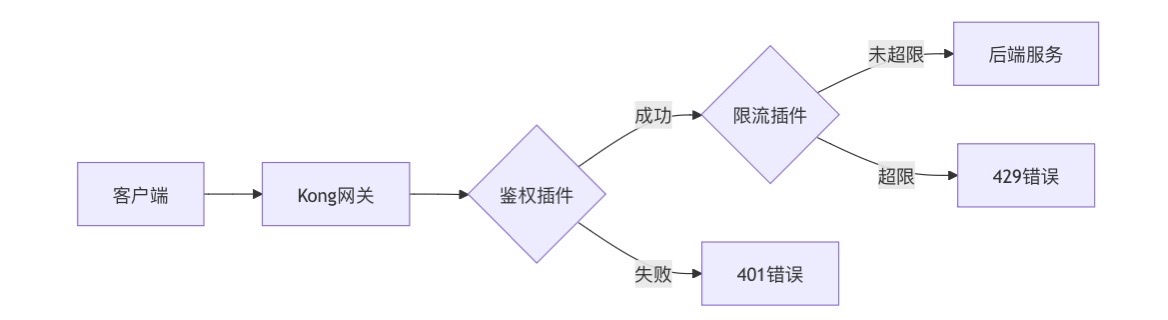
云原生安全实战:API网关Kong的鉴权与限流详解
🔥「炎码工坊」技术弹药已装填! 点击关注 → 解锁工业级干货【工具实测|项目避坑|源码燃烧指南】 一、基础概念 1. API网关(API Gateway) API网关是微服务架构中的核心组件,负责统一管理所有API的流量入口。它像一座…...

省略号和可变参数模板
本文主要介绍如何展开可变参数的参数包 1.C语言的va_list展开可变参数 #include <iostream> #include <cstdarg>void printNumbers(int count, ...) {// 声明va_list类型的变量va_list args;// 使用va_start将可变参数写入变量argsva_start(args, count);for (in…...

数学建模-滑翔伞伞翼面积的设计,运动状态计算和优化 !
我们考虑滑翔伞的伞翼面积设计问题以及运动状态描述。滑翔伞的性能主要取决于伞翼面积、气动特性以及飞行员的重量。我们的目标是建立数学模型来描述滑翔伞的运动状态,并优化伞翼面积的设计。 一、问题分析 滑翔伞在飞行过程中受到重力、升力和阻力的作用。升力和阻力与伞翼面…...
