你知道这20个数组方法是怎么实现的吗?
前言
你们一定对JavaScript中的数组很熟悉,我们每天都会用到它的各种方法,比如push、pop、forEach、map……等等。
但是仅仅使用它就足够了吗?如此出色,您一定不想停在这里。我想和你一起挑战实现20+数组方法的功能。
1、forEach
forEach 是我们工作中非常常用的数组方法,实现起来也比较简单。这是我们需要完成的第一个功能。
代码
Array.prototype.forEach2 = function (callback, thisCtx) {if (typeof callback !== 'function') {throw`${callback} is not a function` }const length = this.lengthlet i = 0while (i < length) {// Deleted, the newly added element index i is not in the array, so it will not be accessedif (this.hasOwnProperty(i)) { callback.call(thisCtx, this[ i ], i, this) } i++ }}测试一下
let demoArr = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, , 5 ]demoArr.forEach2((it, i) => {if (i === 1) {// 5 will not be printed out demoArr.push(5) } elseif (i === 2) {// 4 will not be printed out, but "4-4" will be printed out demoArr.splice(3, 1, '4-4') }console.log(it)})/* 1 2 3 4-4 5*/哇,恭喜!我们已经实现了 forEach 的功能。
2、map
你一般用map做什么?大多数时候是将一个数组转换为另一个数组。
代码
Array.prototype.map2 = function (callback, thisCtx) {if (typeof callback !== 'function') {throw`${callback} is not a function` }const length = this.lengthlet i = 0// The return value of the map method is a new arraylet newArray = []while (i < length) {// Deleted and uninitialized values will not be accessedif (this.hasOwnProperty(i)) { newArray.push(callback.call(thisCtx, this[ i ], i, this)) } i++ }// Return new arrayreturn newArray}测试一下
let arr = [ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4,, 5 ]let arr2 = arr.map2(function (it, i, array) {console.log(it, i, array, this)return it * it}, { name: 'fatfish' })console.log(arr2) // [0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25]朋友们,你们觉得不难吗?那是因为你太厉害了。
3、every
every() 方法测试数组中的所有元素是否通过提供的函数实现的测试。它返回一个布尔值。
每种方法都有你以前可能没有注意到的三点,它们是什么?
在空数组上调用 every 方法将返回 true。
回调方法只会被已经赋值的索引调用。
如果值被删除,回调将不会被调用
let emptyArr = []// Calling every method on an empty array returns trueconsole.log(emptyArr.every((it) => it > 0)) // true// The `callback` method will only be called by an index that has already been assigned a value.let arr = [ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4,, 5, -1 ]// The `callback` method will not be called when an array value is deleted or an index that has never been assigned a value.delete arr[7]console.log(arr.every((it) => it >= 0)) // true代码
Array.prototype.every2 = function (callback, thisCtx) {if (typeof callback !== 'function') {throw`${callback} is not a function` }const length = this.lengthlet i = 0// If the length of the array is 0, the while loop will not be enteredwhile (i < length) {// False will be returned as long as a value does not conform to the judgment of callbackif (this.hasOwnProperty(i) && !callback.call(thisCtx, this[ i ], i, this)) {returnfalse } i++ }returntrue}测试一下
let emptyArr = []// Calling every method on an empty array returns trueconsole.log(emptyArr.every2((it) => it > 0)) // true// The `callback` method will only be called by an index that has already been assigned a value.let arr = [ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4,, 5, -1 ]// The `callback` method will not be called when an array value is deleted or an index that has never been assigned a value.delete arr[7]console.log(arr.every2((it) => it >= 0)) // true4、some
some() 方法测试数组中的至少一个元素是否通过了提供的函数实现的测试。
代码
Array.prototype.some2 = function (callback, thisCtx) {if (typeof callback !== 'function') {throw`${callback} is not a function` }const length = this.lengthlet i = 0while (i < length) {// Returns true if any element meets the callback conditionif (this.hasOwnProperty(i) && callback.call(thisCtx, this[ i ], i, this)) {returntrue } i++ }returnfalse}测试一下
let emptyArr = []// An empty array will return falseconsole.log(emptyArr.some2((it) => it > 0)) // falselet arr = [ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4,, 5, -1 ]delete arr[7]console.log(arr.some2((it) => it < 0)) // falseconsole.log(arr.some2((it) => it > 0)) // true5、filter
filter() 方法创建一个新数组,其中包含所有通过所提供函数实现的测试的元素。
Array.prototype.filter2 = function (callback, thisCtx) {if (typeof callback !== 'function') {throw`${callback} is not a function` }const length = this.length// The return value will be a new arraylet newArray = []let i = 0while (i < length) {if (this.hasOwnProperty(i) && callback.call(thisCtx, this[ i ], i, this)) { newArray.push(this[ i ]) } i++ }return newArray}测试一下
// The position with index 5 will not be traversed because it has no initialization valuelet arr = [ 0, 1, 2, -3, 4,, 5 ]// we try to remove the last elementdelete arr[6]// filter out values greater than 0let filterArr = arr.filter2((it) => it > 0)console.log(filterArr) // [ 1, 2, 4 ]6、reduce
这个函数稍微复杂一些。让我们用一个例子来看看它是如何使用的。
const sum = [1, 2, 3, 4].reduce((prev, cur) => {return prev + cur;})console.log(sum) // 10// initializationprev = initialValue = 1, cur = 2// step 1prev = (1 + 2) = 3, cur = 3// step 2prev = (3 + 3) = 6, cur = 4// step 3prev = (6 + 4) = 10, cur = undefined (quit)代码
Array.prototype.reduce2 = function (callback, initValue) {if (typeof callback !== 'function') {throw`${callback} is not a function` }let pre = initValuelet i = 0const length = this.length// When the initial value is not passed, use the first value of the array as the initial value if (typeof pre === 'undefined') { pre = this[0] i = 1 }while (i < length) {if (this.hasOwnProperty(i)) { pre = callback(pre, this[ i ], i, this) } i++ }return pre}测试一下
const sum = [1, 2, 3, 4].reduce2((prev, cur) => {return prev + cur;})console.log(sum) // 107、reduceRight
reduceRight() 方法对累加器和数组的每个值(从右到左)应用一个函数,以将其减少为单个值。
它与 reduce 非常相似,只是 reduceRight 从右到左遍历。
const sum = [1, 2, 3, 4].reduce((prev, cur) => {console.log(prev, cur)return prev + cur;})// 1 2// 3 3// 6 4console.log(sum) // 10const sum2 = [1, 2, 3, 4].reduceRight((prev, cur) => {console.log(cur)return prev + cur;})// 4 3// 7 2// 9 1console.log(sum2) // 10代码
Array.prototype.reduceRight2 = function (callback, initValue) {if (typeof callback !== 'function') {throw`${callback} is not a function` }let pre = initValueconst length = this.length// Start with the last elementlet i = length - 1// If no initial value is passed, the last element is taken as the initial valueif (typeof pre === 'undefined') { pre = this[i] i-- }while (i >= 0) {if (this.hasOwnProperty(i)) { pre = callback(pre, this[ i ], i, this) } i-- }return pre}测试一下
const sum = [1, 2, 3, 4].reduceRight2((prev, cur) => {console.log(cur)return prev + cur;})// 4 3// 7 2// 9 1console.log(sum) // 108、find
find() 方法返回提供的数组中满足提供的测试功能的第一个元素。如果没有值满足测试函数,则返回 undefined。
代码
Array.prototype.find2 = function (callback, thisCtx) {if (typeof callback !== 'function') {throw`${callback} is not a function` }const length = this.lengthlet i = 0while (i < length) {const value = this[ i ]// As long as there is an element that matches the logic of the callback function, the element value is returnedif (callback.call(thisCtx, value, i, this)) {return value } i++ }// otherwise return undefined returnundefined}测试一下
let arr = [ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4,, 5 ]let ele = arr.find2(function (it, i, array) {console.log(it, i, array, this)return it > 3}, { name: 'fatfish' })console.log(ele) // 49、findIndex
findIndex() 方法返回数组中满足提供的测试函数的第一个元素的索引。否则,它返回 -1,表示没有元素通过测试。
let arr = [ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4,, 5 ]let index = arr.findIndex((it, i, array) => {return it > 2})console.log(index) // 3代码
Array.prototype.findIndex2 = function (callback, thisCtx) {if (typeof callback !== 'function') {throw`${callback} is not a function` }const length = this.lengthlet i = 0while (i < length) {// Return index i that conforms to callback logicif (callback.call(thisCtx, this[ i ], i, this)) {return i } i++ }return-1}测试一下
let arr = [ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4,, 5 ]let index = arr.findIndex2(function (it, i, array) {console.log(it, i, array, this)return it > 2}, { name: 'fatfish' })console.log(index) // 310、indexOf
indexOf() 方法返回可以在数组中找到给定元素的第一个索引,如果不存在,则返回 -1。
笔记:
如果开始搜索的索引值大于等于数组的长度,则表示不会在数组中进行搜索,返回-1。
如果fromIndex为负数,则按照-1表示从最后一个元素开始查找,-2表示从倒数第二个元素开始查找的规则进行查找,以此类推。
如果 fromIndex 为负数,则仍然从前向后搜索数组。
constarray = [2, 5, 9]console.log(array.indexOf(2)) // 0console.log(array.indexOf(7)) // -1console.log(array.indexOf(9, 2)) // 2console.log(array.indexOf(2, -1)) // -1console.log(array.indexOf(2, -3)) // 0console.log(array.indexOf(2, -4)) // 0代码
Array.prototype.indexOf2 = function (targetEle, fromIndex) {const length = this.length fromIndex = +fromIndex || 0// If the array is empty or the search starts from a place greater than or equal to the length of the array, it will directly return -1if (length === 0 || fromIndex >= length) {return-1 }/* 1. Search elements from fromIndex 2. Use it directly when fromindex is greater than 0 3. If it is less than 0, first subtract the absolute value of fromIndex from the length. If it is still less than 0, take 0 directly */let i = Math.max(fromIndex >= 0 ? fromIndex : length - Math.abs(fromIndex), 0)while (i < length) {// element in the array and equal to targetEleif (this.hasOwnProperty(i) && targetEle === this[ i ]) {return i } i++ }return-1}测试一下
const array = [2, 5, 9]console.log(array.indexOf2(2)) // 0console.log(array.indexOf2(7)) // -1console.log(array.indexOf2(9, 2)) // 2console.log(array.indexOf2(2, -1)) // -1console.log(array.indexOf2(2, -3)) // 0console.log(array.indexOf2(2, -4)) // 011、lastIndexOf
lastIndexOf() 方法返回可以在数组中找到给定元素的最后一个索引,如果不存在,则返回 -1。从 fromIndex 开始向后搜索数组。
它与 indexOf 非常相似,只是 lastIndexOf 从右到左遍历。
let array = [2, 5, 9, 2]console.log(array.lastIndexOf(2)) // 3console.log(array.lastIndexOf(7)) // -1console.log(array.lastIndexOf(2, 3)) // 3console.log(array.lastIndexOf(2, 2)) // 0console.log(array.lastIndexOf(2, -2)) // 0console.log(array.lastIndexOf(2, -1)) // 3代码
Array.prototype.lastIndexOf2 = function (targetEle, fromIndex) {const length = this.length fromIndex = typeof fromIndex === 'undefined' ? length - 1 : fromIndex// // Empty array, when fromIndex is negative and the absolute value is greater than the length of the array, the method returns -1, that is, the array will not be searched.if (length === 0 || fromIndex < 0 && Math.abs(fromIndex) >= length) {return-1 }let iif (fromIndex >= 0) {// If `fromIndex` is greater than or equal to the length of the array, the entire array is searched. i = Math.min(fromIndex, length - 1) } else { i = length - Math.abs(fromIndex) }while (i >= 0) {// Returns the index when it is equal to targetEleif (i inthis && targetEle === this[ i ]) {return i } i-- }// Returns -1 when the current value is not foundreturn-1}测试一下
let array = [2, 5, 9, 2]console.log(array.lastIndexOf2(2)) // 3console.log(array.lastIndexOf2(7)) // -1console.log(array.lastIndexOf2(2, 3)) // 3console.log(array.lastIndexOf2(2, 2)) // 0console.log(array.lastIndexOf2(2, -2)) // 0console.log(array.lastIndexOf2(2, -1)) // 312、includes
includes() 方法确定数组是否在其条目中包含某个值,根据需要返回 true 或 false。
arr.includes(valueToFind[, fromIndex])笔记
include 方法将从 fromIndex 索引开始搜索 valueToFind。
如果 fromIndex 为负数,则开始搜索 array.length + fromIndex 的索引。
如果数组中存在 NaN,则 [..., NaN] Includes (NaN) 为真。
console.log([1, 2, 3].includes(2)) // trueconsole.log([1, 2, 3].includes(4)) // falseconsole.log([1, 2, 3].includes(3, 3)) // falseconsole.log([1, 2, 3].includes(3, -1)) // trueconsole.log([1, 2, NaN].includes(NaN)) // true代码
Array.prototype.includes2 = function (targetEle, fromIndex) {const length = this.length fromIndex = +fromIndex || 0if (length === 0 || fromIndex >= length) {returnfalse }// Search for elements from the position of fromIndexlet i = Math.max(fromIndex >= 0 ? fromIndex : length - Math.abs(fromIndex), 0)while (i < length) {const value = this[ i ]// Please note NaNif (targetEle === value || typeof targetEle === 'number' && typeof value === 'number' && isNaN(targetEle) && isNaN(value)) {returntrue } i++ }returnfalse}测试一下
console.log([1, 2, 3].includes2(2)) // trueconsole.log([1, 2, 3].includes2(4)) // falseconsole.log([1, 2, 3].includes2(3, 3)) // falseconsole.log([1, 2, 3].includes2(3, -1)) // trueconsole.log([1, 2, NaN].includes2(NaN)) // true13、push
push() 方法将一个或多个元素添加到数组的末尾,并返回数组的新长度。
const animals = ['pigs', 'goats', 'sheep']animals.push('cows')console.log(animals, animals.length) // ["pigs", "goats", "sheep", "cows"], 4animals.push('chickens', 'cats', 'dogs')console.log(animals, animals.length) // ["pigs", "goats", "sheep", "cows", "chickens", "cats", "dogs"], 7代码
Array.prototype.push2 = function (...pushEles) {const pushEleLength = pushEles.lengthconst length = this.lengthlet i = 0while (i < pushEleLength) {this[ length + i ] = pushEles[ i ] i++ }returnthis.length}测试一下
const animals = ['pigs', 'goats', 'sheep']animals.push2('cows')console.log(animals, animals.length) // ["pigs", "goats", "sheep", "cows"], 4animals.push2('chickens', 'cats', 'dogs')console.log(animals, animals.length) // ["pigs", "goats", "sheep", "cows", "chickens", "cats", "dogs"], 714、pop
pop() 方法从数组中删除最后一个元素并返回该元素,此方法更改数组的长度。
let arr = [ 1, 2 ]let arr2 = []console.log(arr.pop(), arr) // 2 [1]console.log(arr2.pop(), arr2) // undefined []代码
Array.prototype.pop2 = function () {const length = this.length// If it is an empty array, return undefinedif (length === 0) {returnundefined }const delEle = this[ length - 1 ]this.length = length - 1return delEle}测试一下
let arr = [ 1, 2 ]let arr2 = []console.log(arr.pop2(), arr) // 2 [1]console.log(arr2.pop2(), arr2) // undefined []15、unshift
unshift() 方法将一个或多个元素添加到数组的开头并返回数组的新长度。
笔记
如果传入多个参数调用 unshift 一次,与传入一个参数调用 unshift 多次(例如循环调用)会得到不同的结果。
let arr = [4,5,6]// Insert multiple elements at oncearr.unshift(1,2,3)console.log(arr) // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]let arr2 = [4,5,6]// Insert multiple timesarr2.unshift(1)arr2.unshift(2)arr2.unshift(3)console.log(arr2); // [3, 2, 1, 4, 5, 6]代码
Array.prototype.unshift2 = function (...unshiftEles) {// With "...", Insert the element to be added in front of the arraylet newArray = [ ...unshiftEles, ...this ]let length = newArray.lengthlet i = 0if (unshiftEles.length === 0) {return length }// Recopy to arraywhile (i < length) {this[ i ] = newArray[ i ] i++ }returnthis.length}测试一下
let arr = [4,5,6]// Insert multiple elements at oncearr.unshift2(1,2,3)console.log(arr) // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]let arr2 = [4,5,6]// Insert multiple timesarr2.unshift2(1)arr2.unshift2(2)arr2.unshift2(3)console.log(arr2); // [3, 2, 1, 4, 5, 6]16、 shift
shift() 方法从数组中删除第一个元素并返回该删除的元素。此方法更改数组的长度。
let arr = [ 1, 2 ]console.log(arr.shift(), arr) // 1 [2]console.log(arr.shift(), arr) // 2 []代码
Array.prototype.shift2 = function () {const length = this.lengthconst delValue = this[ 0 ] let i = 1while (i < length) {// Starting from the first element, the following elements move forward one bitthis[ i - 1 ] = this[ i ] i++ }// Set the length of the arraythis.length = length - 1// Return deleted valuereturn delValue}测试一下
let arr = [ 1, 2 ]console.log(arr.shift2(), arr) // 1 [2]console.log(arr.shift2(), arr) // 2 []17、reverse
(来自 MDN) reverse() 方法将数组反转到位。第一个数组元素成为最后一个,最后一个数组元素成为第一个。
const arr = [1, 2, 3]console.log(arr) // [1, 2, 3]arr.reverse()console.log(arr) // [3, 2, 1]代码
Array.prototype.reverse2 = function () { let i = 0 let j = this.length - 1while (i < j) { [ this[ i ], this[ j ] ] = [ this[ j ], this[ i ] ] i++ j-- }returnthis}测试一下
const arr = [1, 2, 3]console.log(arr) // [1, 2, 3]arr.reverse2()console.log(arr) // [3, 2, 1]18、fill
fill() 方法将数组中的所有元素更改为静态值,从开始索引(默认 0)到结束索引(默认 array.length),它返回修改后的数组。
const array1 = [1, 2, 3, 4];console.log(array1.fill(0, 2, 4)) // [1, 2, 0, 0]console.log(array1.fill(5, 1)) // [1, 5, 5, 5]console.log(array1.fill(6)) // [6, 6, 6, 6]代码
Array.prototype.fill2 = function (value, start, end) { const length = this.lengthstart = start >> 0 // The defaultvalueofendislengthend = typeof end === 'undefined' ? length : end >> 0 // The minimumvalueofstartis0and the maximum valueislengthstart = start >= 0 ? Math.min(start, length) : Math.max(start + length, 0) // The minimumvalueofendis0and the maximum valueislengthend = end >= 0 ? Math.min(end, length) : Math.max(end + length, 0) // The element that fills the specified rangeisvaluewhile (start < end) { this[ start ] = valuestart++ }return this}测试一下
const array1 = [1, 2, 3, 4];console.log(array1.fill2(0, 2, 4)) // [1, 2, 0, 0]console.log(array1.fill2(5, 1)) // [1, 5, 5, 5]console.log(array1.fill2(6)) // [6, 6, 6, 6]19、concat
concat() 方法用于合并两个或多个数组。此方法不会更改现有数组,而是返回一个新数组。
let num1 = [[1]]let num2 = [2, [3]]let num3=[5,[6]]let nums = num1.concat(num2) // [[1], 2, [3]]let nums2 = num1.concat(4, num3) // [[1], 4, 5,[6]]代码
Array.prototype.concat2 = function (...concatEles) {const length = concatEles.length// The array itself needs to be expanded one layerlet newArray = [ ...this ]let i = 0while (i < length) {const value = concatEles[ i ]Array.isArray(value) ? newArray.push(...value) : newArray.push(value) i++ }return newArray}测试一下
let num1 = [[1]]let num2 = [2, [3]]let num3=[5,[6]]let nums = num1.concat2(num2) // [[1], 2, [3]]let nums2 = num1.concat2(4, num3) // [[1], 4, 5,[6]]20、join
join() 方法通过连接数组(或类似数组的对象)中的所有元素创建并返回一个新字符串,用逗号或指定的分隔符字符串分隔。如果数组只有一个项目,则将返回该项目而不使用分隔符。
const elements = ['Fire', 'Air', 'Water']const elements2 = ['Fire']console.log(elements.join()) // Fire,Air,Waterconsole.log(elements.join('')) // FireAirWaterconsole.log(elements.join('-')) // Fire-Air-Waterconsole.log(elements2.join('-')) // Fire代码
Array.prototype.join2 = function (format = ',') {const length = this.length// Save the last element because it does not participate in the connection of formatlet lastEle = this[ length - 1 ]letstring = ''if (length === 0) {returnstring }for (i = 0; i < length - 1; i++) {string += this[ i ] + format }returnstring + lastEle}测试一下
const elements = ['Fire', 'Air', 'Water']const elements2 = ['Fire']console.log(elements.join2()) // Fire,Air,Waterconsole.log(elements.join2('')) // FireAirWaterconsole.log(elements.join2('-')) // Fire-Air-Waterconsole.log(elements2.join2('-')) // Fire最后
以上就是我今天跟你分享的20个数组方法的实现,希望对你有用,如果你觉得有帮助的话,请记得点赞我,关注我,并将他分享给你身边做开发的朋友。
相关文章:

你知道这20个数组方法是怎么实现的吗?
前言你们一定对JavaScript中的数组很熟悉,我们每天都会用到它的各种方法,比如push、pop、forEach、map……等等。但是仅仅使用它就足够了吗?如此出色,您一定不想停在这里。我想和你一起挑战实现20数组方法的功能。1、forEachforEa…...

《系统架构设计》-01-架构和架构师概述
文章目录1. 架构的基本定义1.1 架构组成理论1.1.1 系统元素1)概念2)静态结构和动态结构1.1.2 基本系统属性1.1.3 设计和发展原则1.2 架构的决策理论1.2.1 统一软件过程(Rational Unified Process,统一软件过程)1.2.2 决…...
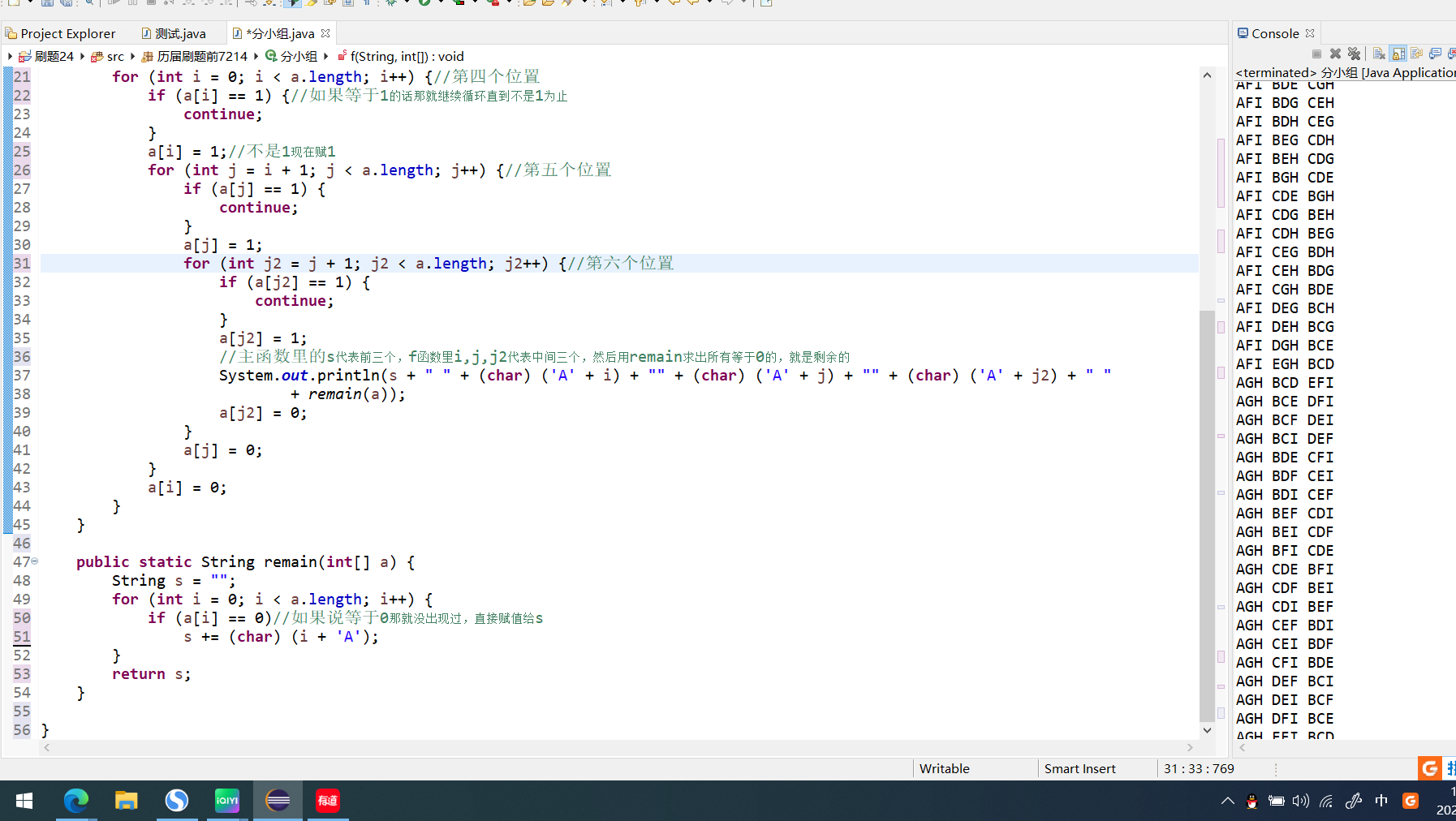
第七届蓝桥杯省赛——5分小组
题目:9名运动员参加比赛,需要分3组进行预赛。有哪些分组的方案呢?我们标记运动员为 A,B,C,... I下面的程序列出了所有的分组方法。该程序的正常输出为:ABC DEF GHIABC DEG FHIABC DEH FGIABC DEI FGHABC DFG EHIABC DFH EGIABC DF…...

中国专科医院行业市场规模及未来发展趋势
中国专科医院行业市场规模及未来发展趋势中国专科医院行业在过去几年中取得了跨越式发展,市场规模不断扩大,未来的发展前景也远比过去更加乐观。根据市场调研在线网发布的2023-2029年中国专科医院行业运营现状及发展前景预测报告分析,截至2018年…...
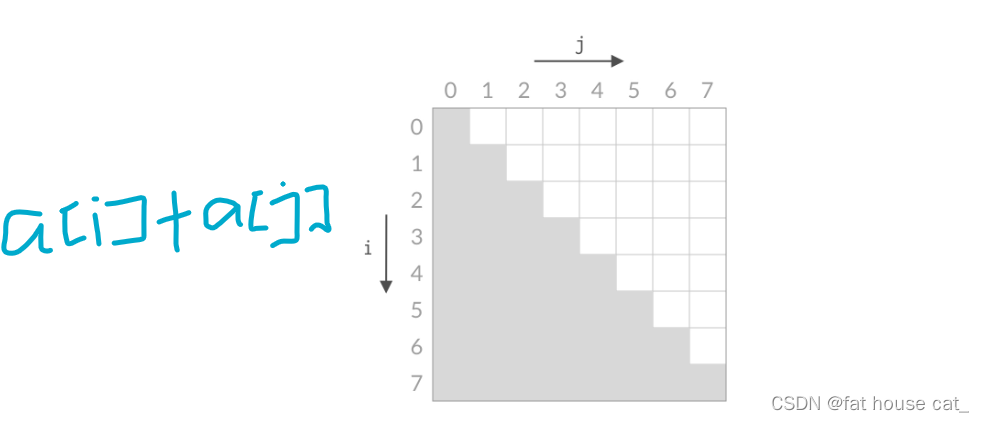
【刷题笔记】--两数之和Ⅳ,从二叉树中找出两数之和
法一:深度搜索中序遍历双指针 思路:通过中序遍历二叉树得到一个递增的数列,再在这个递增的二叉树中找到这两数。 主要学到双指针这个方法。 对于一般数列,我们要找到两数满足其之和等于目标数,我们一般会进行暴力&a…...

浏览器渲染原理JavaScript V8引擎
浏览器渲染原理 前言 在我们面试过程中,面试官经常会问到这么一个问题,那就是从在浏览器地址栏中输入URL到页面显示,浏览器到底发生了什么? 浏览器内有哪些进程,这些进程都有些什么作用;浏览器地址输入U…...

在TheSandbox 的「BOYS PLANET」元宇宙中与你的男孩们见面吧!
世界各的男孩们成为 K-Pop 男团的旅程。 Mnet 的全球项目 BOYS PLANET 终于在 2 月 2 日首次亮相! The Sandbox 与 CJ ENM 合作,于 2 月 6 日晚上 10 点开始举办两个基于 BOYS PLANET 生存节目的虚拟体验:BOYS PLANET:BOYS LAND 和…...

数据结构与算法:java对象的比较
1.基本类型的比较 在Java中,基本类型的对象可以直接比较大小。 public class TestCompare {public static void main(String[] args) {int a 10;int b 20;System.out.println(a > b);System.out.println(a < b);System.out.println(a b);char c1 A;char…...

python(16)--类
一、类的基本操作1.定义一个类格式:class Classname( ):内容💎鄙人目前还是一名学生,最熟悉的也就是学校了,所以就以学校为例子来建立一个类吧class School():headline"帝国理工大学"def schoolmotto(self):…...
Calico 介绍与原理(二))
CNI 网络流量分析(七)Calico 介绍与原理(二)
文章目录CNI 网络流量分析(七)Calico 介绍与原理(二)CNIIPAM指定 IP指定非 IPAM IPCNI 网络流量分析(七)Calico 介绍与原理(二) CNI 支持多种 datapath,默认是 linuxDa…...

API安全的最大威胁:三体攻击
最近《三体》火的一塌糊涂,动画片、电视剧和书都受到了大家的喜爱。在API安全上,最近也发现了三体攻击。 当然了,肯定是不来自于三体人的攻击,这里的三体攻击指的是(trinity,也称三位一体攻击),是一个新的攻击手法。具体的情况老李也找到了相关的介绍,下面就分享给大…...

分布式事务解决方案——TCC
TCC是Try、Confirm、Cancel三个词语的缩写,TCC要求每个分支事务实现三个操作:预处理Try、确认Confirm、撤销Cancel。1、Try 阶段是做业务检查(一致性)及资源预留(隔离),此阶段仅是一个初步操作,它和后续的Confirm一起才能真正构成…...

ITSS认证分为几个级别,哪个级别最高
一、什么是ITSS ITSS( 信息技术服务标准,简称ITSS)是国内第一套成体系和综合配套的信息技术服务标准库,全面规范了IT服务产品及其组成要素,用于指导实施标准化和可信赖的IT服务。 ITSS是在工业和信息化部、国家标准化管理委员会的联合指导下…...

ZigBee案例笔记 - USART
文章目录1.串行通信接口简述2.串行通信接口寄存器U0CSR (0x86) -USART 0 控制和状态U0UCR (0xC4)–USART 0 UART 控制U0GCR (0xC5)–USART 0 通用控制U0BUF (0xC1) – USART 0 接收/传送数据缓存U0BAUD (0xC2) – USART 0 波特率控制3.设置串行通信接口比特率控制寄存器4.外设I…...

java | 基于Redis的分布式锁实现①
前言 首先,为了确保分布式锁可用,我们至少要确保锁的实现同时满足以下四个条件: 互斥性。在任意时刻,只有一个客户端能持有锁。不会发生死锁。即使有一个客户端在持有锁的期间崩溃而没有主动解锁,也能保证后续其他客户…...

十六、基于FPGA的CRC校验设计实现
1,CRC校验循环冗余校验(Cyclic Redundancy Check, CRC)是一种根据网络数据包或计算机文件等数据产生简短固定位数校验码的一种信道编码技术,主要用来检测或校验数据传输或者保存后可能出现的错误。它是利用除法及余数的…...

2022爱分析 · DataOps厂商全景报告 | 爱分析报告
报告编委 李喆 爱分析合伙人&首席分析师 廖耘加 爱分析分析师 目录 1. 研究范围定义 2. 市场洞察 3. 厂商全景地图 4. 市场分析与厂商评估 5. 入选厂商列表 1. 研究范围定义 研究范围 在后疫情时代,以数据分析为代表的数据消费场景日益丰富&…...

京东前端react面试题及答案
useEffect 与 useLayoutEffect 的区别 (1)共同点 运用效果: useEffect 与 useLayoutEffect 两者都是用于处理副作用,这些副作用包括改变 DOM、设置订阅、操作定时器等。在函数组件内部操作副作用是不被允许的,所以需…...
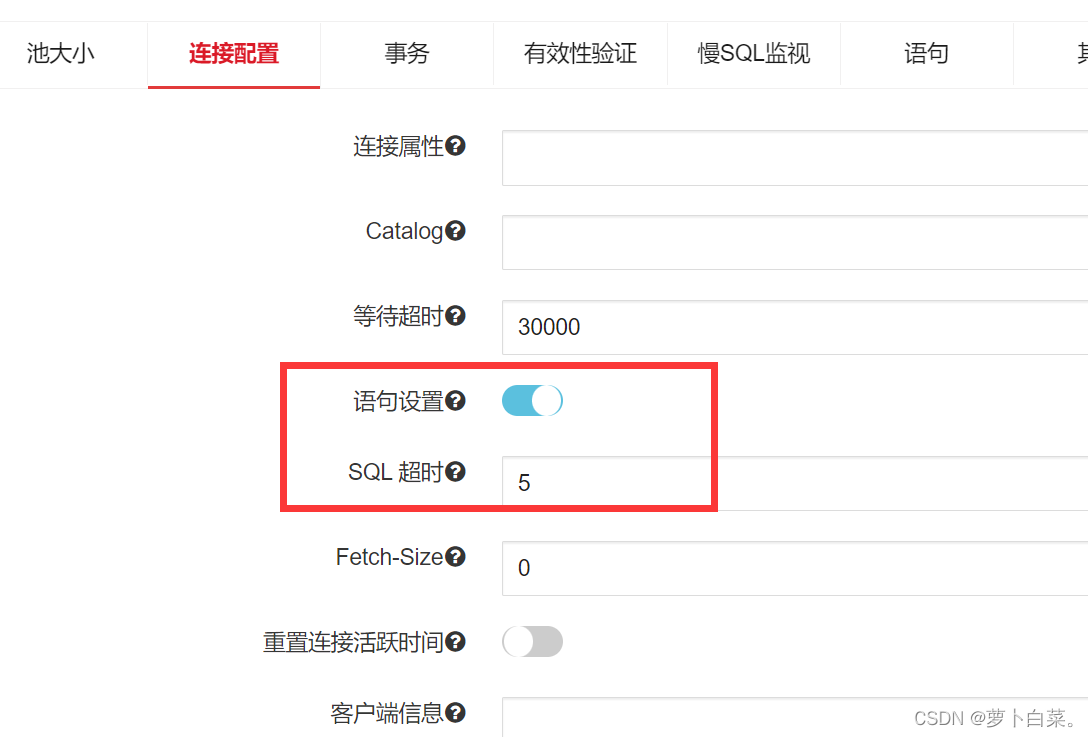
TongWeb8数据源相关问题
问题一:数据源连接不足当TongWeb数据源连接用完时,除了监控中看到连接占用高以外,日志中会有如下提示信息。2023-02-14 10:24:43 [WARN] - com.tongweb.web.jdbc.pool.PoolExhaustedException: [TW-0.0.0.0-8088-3] Timeout: Pool empty. Una…...
关于最近大热的AI,你怎么看?
AI人工智能,相信大家都不陌生,也都接触过不少。但是最近小编在网上冲浪的时候发现各大媒体又掀起了一阵AI热潮,AI不是很常见了吗?是又有什么新的发展吗? 带着强烈的好奇心,我在地铁上读完了一篇关于Chatgp…...

【大模型RAG】拍照搜题技术架构速览:三层管道、两级检索、兜底大模型
摘要 拍照搜题系统采用“三层管道(多模态 OCR → 语义检索 → 答案渲染)、两级检索(倒排 BM25 向量 HNSW)并以大语言模型兜底”的整体框架: 多模态 OCR 层 将题目图片经过超分、去噪、倾斜校正后,分别用…...
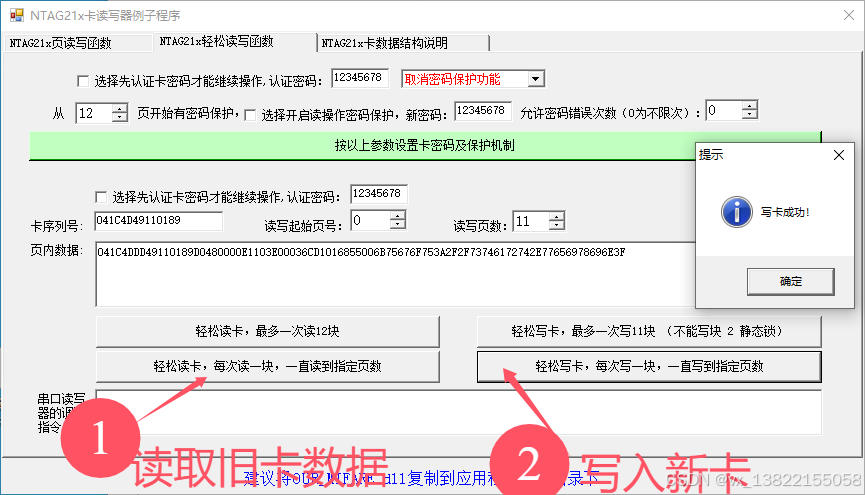
VB.net复制Ntag213卡写入UID
本示例使用的发卡器:https://item.taobao.com/item.htm?ftt&id615391857885 一、读取旧Ntag卡的UID和数据 Private Sub Button15_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button15.Click轻松读卡技术支持:网站:Dim i, j As IntegerDim cardidhex, …...

Linux相关概念和易错知识点(42)(TCP的连接管理、可靠性、面临复杂网络的处理)
目录 1.TCP的连接管理机制(1)三次握手①握手过程②对握手过程的理解 (2)四次挥手(3)握手和挥手的触发(4)状态切换①挥手过程中状态的切换②握手过程中状态的切换 2.TCP的可靠性&…...

在四层代理中还原真实客户端ngx_stream_realip_module
一、模块原理与价值 PROXY Protocol 回溯 第三方负载均衡(如 HAProxy、AWS NLB、阿里 SLB)发起上游连接时,将真实客户端 IP/Port 写入 PROXY Protocol v1/v2 头。Stream 层接收到头部后,ngx_stream_realip_module 从中提取原始信息…...

Java多线程实现之Callable接口深度解析
Java多线程实现之Callable接口深度解析 一、Callable接口概述1.1 接口定义1.2 与Runnable接口的对比1.3 Future接口与FutureTask类 二、Callable接口的基本使用方法2.1 传统方式实现Callable接口2.2 使用Lambda表达式简化Callable实现2.3 使用FutureTask类执行Callable任务 三、…...

【JavaSE】绘图与事件入门学习笔记
-Java绘图坐标体系 坐标体系-介绍 坐标原点位于左上角,以像素为单位。 在Java坐标系中,第一个是x坐标,表示当前位置为水平方向,距离坐标原点x个像素;第二个是y坐标,表示当前位置为垂直方向,距离坐标原点y个像素。 坐标体系-像素 …...

图表类系列各种样式PPT模版分享
图标图表系列PPT模版,柱状图PPT模版,线状图PPT模版,折线图PPT模版,饼状图PPT模版,雷达图PPT模版,树状图PPT模版 图表类系列各种样式PPT模版分享:图表系列PPT模板https://pan.quark.cn/s/20d40aa…...

高效线程安全的单例模式:Python 中的懒加载与自定义初始化参数
高效线程安全的单例模式:Python 中的懒加载与自定义初始化参数 在软件开发中,单例模式(Singleton Pattern)是一种常见的设计模式,确保一个类仅有一个实例,并提供一个全局访问点。在多线程环境下,实现单例模式时需要注意线程安全问题,以防止多个线程同时创建实例,导致…...

智能AI电话机器人系统的识别能力现状与发展水平
一、引言 随着人工智能技术的飞速发展,AI电话机器人系统已经从简单的自动应答工具演变为具备复杂交互能力的智能助手。这类系统结合了语音识别、自然语言处理、情感计算和机器学习等多项前沿技术,在客户服务、营销推广、信息查询等领域发挥着越来越重要…...
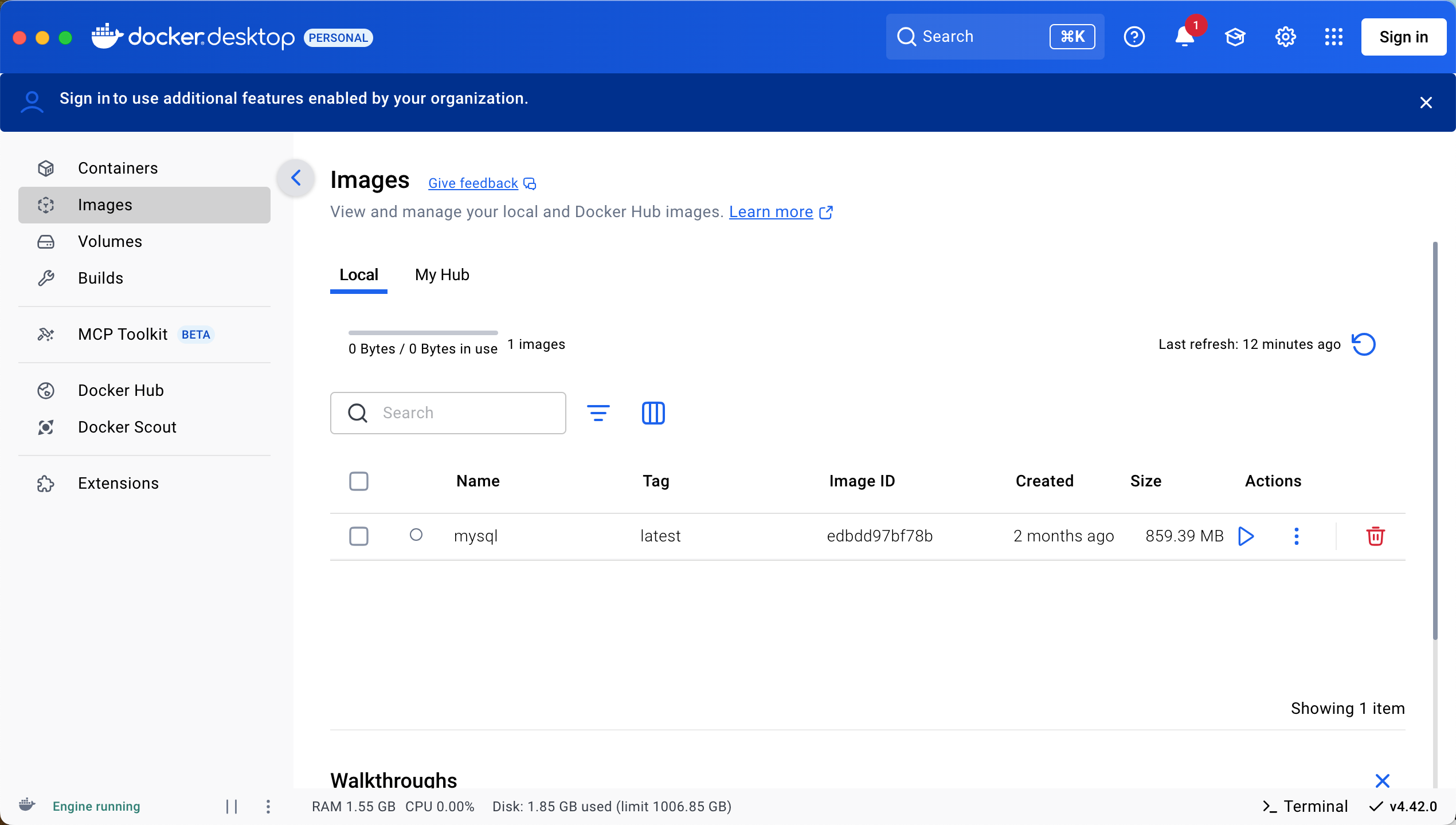
Docker 本地安装 mysql 数据库
Docker: Accelerated Container Application Development 下载对应操作系统版本的 docker ;并安装。 基础操作不再赘述。 打开 macOS 终端,开始 docker 安装mysql之旅 第一步 docker search mysql 》〉docker search mysql NAME DE…...
