CS 144 Lab Four 收尾 -- 网络交互全流程解析
CS 144 Lab Four 收尾 -- 网络交互全流程解析
- 引言
- Tun/Tap简介
- tcp_ipv4.cc文件
- 配置信息初始化
- cs144实现的fd家族体系
- 基于自定义fd体系进行数据读写的adapter适配器体系
- 自定义socket体系
- 自定义事件循环EventLoop
- 模板类TCPSpongeSocket详解
- listen_and_accept方法
- _tcp_main方法
- _initialize_TCP初始化Tcp连接和事件循环
- _tcp_loop函数启动tcp事件循环
- connect 方法
- bidirectional_stream_copy方法
- TCPSpongeSocket的wait_until_closed方法
- 通道串联起子主线程
- 小结
对应课程视频: 【计算机网络】 斯坦福大学CS144课程
本节作为Lab Four的收尾,主要带领各位来看看网络交互的整体流程是怎样的。
引言
这里以tcp_ipv4.cc文件为起点,来探究一下cs144是如何实现整个协议栈的。
首先,项目根路径中的 tun.sh 会使用 ip tuntap 技术创建虚拟 Tun/Tap 网络设备。这类接口仅能工作在内核中。不同于普通的网络接口,没有物理硬件。这样做的目的应该是为了模拟真实网络环境下的网络环境。
Tun/Tap简介
关于Tun/Tap的介绍可以参考:
- 虚拟设备之TUN和TAP
- Linux官方内核文档: Tun/Tap驱动程序说明
TUN/TAP提供了用户空间程序的数据包接收和传输功能。
它可以被视为一个简单的点对点或以太网设备,不是从物理媒体接收数据包,而是从用户空间程序接收数据包,并且不是通过物理媒体发送数据包,而是将数据包写入用户空间程序。
为了使用驱动程序,程序必须打开/dev/net/tun,并发出相应的ioctl()来向内核注册一个网络设备。网络设备将显示为tunXX或tapXX,这取决于所选择的选项。当程序关闭文件描述符时,网络设备和所有相应的路由都将消失。
根据所选择的设备类型,用户空间程序必须读取/写入IP数据包(对于tun)或以太网帧(对于tap),使用哪种取决于ioctl()给定的标志。
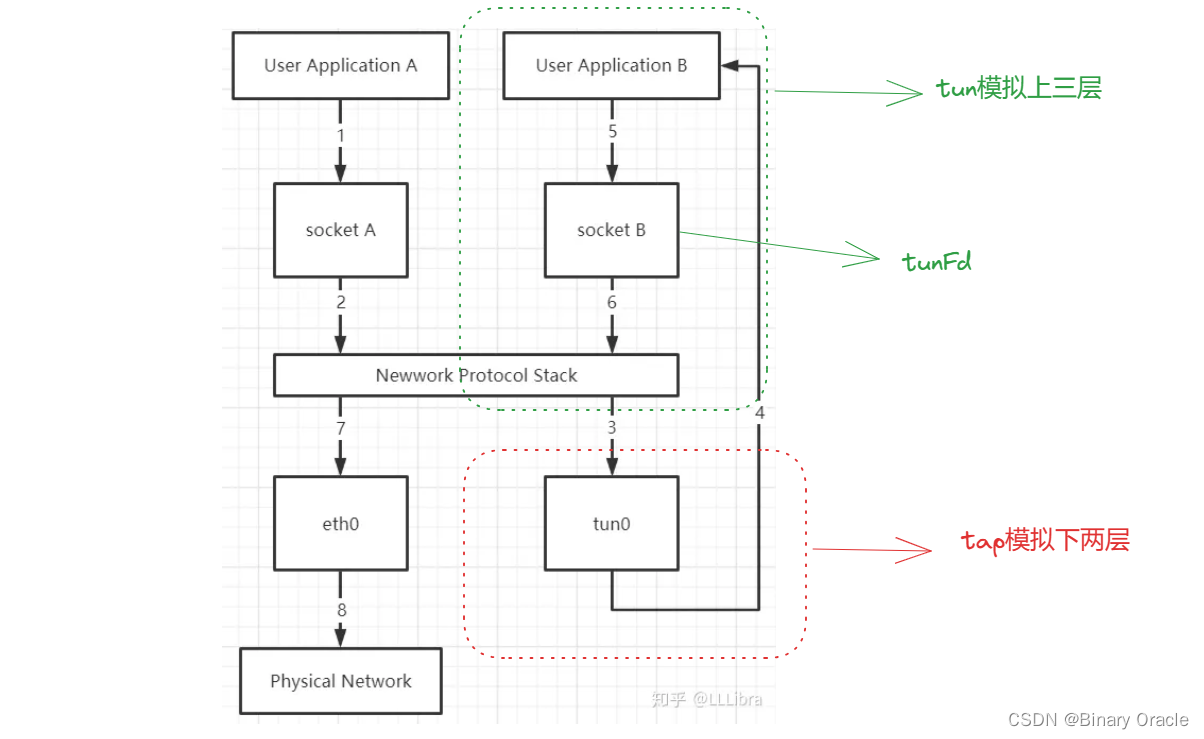
- TUN 是一个虚拟网络设备,它模拟的是一个三层设备,通过它可以处理来自网络层的数据包,也就是 IP 数据包。由于它只模拟到了 IP 层,所以它无法与物理网卡做 bridge,也没有 MAC 地址,但是可以通过三层交换的方式来与物理网卡相互通信。
- TAP 模拟的是一个二层设备,它比 TUN 更加深入,它可以处理数据链路层的数据包,拥有 MAC 地址,可以与物理网卡做 bridge,支持 MAC 层广播,也可以给它设置 IP 地址。
tcp_ipv4.cc文件
当 Tun/Tap 网络设备建立好后,接下来我们进入到 tcp_ipv4.cc 的main函数中:
int main(int argc, char **argv) {try {// 参数个数检查: 第一个参数是编译器传入的程序名,然后是我们需要传入的host和portif (argc < 3) {show_usage(argv[0], "ERROR: required arguments are missing.");return EXIT_FAILURE;}// 解析参数,获取TCPConfig,FdAdapterConfig,当前启动的模式(server or client) 和 选择哪个网卡auto [c_fsm, c_filt, listen, tun_dev_name] = get_config(argc, argv);// 借助Tun/Tap实现一个虚拟网卡,该虚拟网络设备实现到了IP层// TunFD是tun设备的文件描述符// TCPOverIPv4OverTunFdAdapter封装从tun设备读取和写入IPV4数据报的操作// LossyTCPOverIPv4OverTunFdAdapter采用装饰器模式在前者基础上,增加写入时根据先前设置的丢包率随机丢包的功能// LossyTCPOverIPv4SpongeSocket 对上层提供一个标准Socket接口,进行调用LossyTCPOverIPv4SpongeSocket tcp_socket(LossyTCPOverIPv4OverTunFdAdapter(TCPOverIPv4OverTunFdAdapter(TunFD(tun_dev_name == nullptr ? TUN_DFLT : tun_dev_name))));// 如果启动的是server mode,那么在监听指定端口上的消息 if (listen) {tcp_socket.listen_and_accept(c_fsm, c_filt);} else {// 如果启动的是client mode,那么主动与对应server建立连接tcp_socket.connect(c_fsm, c_filt);}// 键盘输入的数据会写入socket,socket有可读的数据会输出到屏幕上bidirectional_stream_copy(tcp_socket);// 同步等待直到_tcp_thread线程结束tcp_socket.wait_until_closed();} catch (const exception &e) {cerr << "Exception: " << e.what() << endl;return EXIT_FAILURE;}return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
配置信息初始化
下面给出get_config方法源码解析,感兴趣可以瞅两眼:
//! Config for TCP sender and receiver
class TCPConfig {public:// 发送器和接收器缓冲区的默认容量。缓冲区容量指的是在给定时间内可以存储的最大数据量static constexpr size_t DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 64000; //!< Default capacity// tcp数据报中payload部分最大容量限制static constexpr size_t MAX_PAYLOAD_SIZE = 1000; //!< Conservative max payload size for real Internet// 默认的重传超时时间,以毫秒为单位。// 当TCP发送器向接收器传输数据时,它期望在规定的超时时间内收到一个确认(ACK)。如果发送器在超时时间内没有收到确认,它会重新传输数据static constexpr uint16_t TIMEOUT_DFLT = 1000; //!< Default re-transmit timeout is 1 second// 数据包在放弃之前允许的最大重传次数。如果发送器在经过指定的重传尝试次数后仍未收到确认,它会认为连接不可靠并采取适当的措施static constexpr unsigned MAX_RETX_ATTEMPTS = 8; //!< Maximum re-transmit attempts before giving up// 用于保存重传超时的初始值,以毫秒为单位。它指定发送器在重新传输数据之前应等待ACK的时间// 由于重传超时时间会在网络拥塞的时候动态增加,因此当重置超时重传计数器时,需要将重传超时时间恢复为初始值 uint16_t rt_timeout = TIMEOUT_DFLT; //!< Initial value of the retransmission timeout, in milliseconds// 接收和发送缓冲区默认大小size_t recv_capacity = DEFAULT_CAPACITY; //!< Receive capacity, in bytessize_t send_capacity = DEFAULT_CAPACITY; //!< Sender capacity, in bytes// 初始序列号,如果没有设置,那么会采用随机值策略std::optional<WrappingInt32> fixed_isn{};
};//! Config for classes derived from FdAdapter
class FdAdapterConfig {public:// 源ip地址和端口号Address source{"0", 0}; //!< Source address and port// 目的ip地址和端口号Address destination{"0", 0}; //!< Destination address and port// 下行丢包率,即从服务器发往客户端的数据包丢失的概率uint16_t loss_rate_dn = 0; //!< Downlink loss rate (for LossyFdAdapter)// 上行丢包率,即从客户端发往服务器的数据包丢失的概率uint16_t loss_rate_up = 0; //!< Uplink loss rate (for LossyFdAdapter)
};static tuple<TCPConfig, FdAdapterConfig, bool, char *> get_config(int argc, char **argv) {TCPConfig c_fsm{};FdAdapterConfig c_filt{};char *tundev = nullptr;int curr = 1;bool listen = false;// 如果我们不指定Host和Port,那么使用默认提供的ip地址和随机端口号string source_address = LOCAL_ADDRESS_DFLT;string source_port = to_string(uint16_t(random_device()()));// 判断是否传入了相关参数,保留最后两个host和port值while (argc - curr > 2) {// 打开server端的Listen模式if (strncmp("-l", argv[curr], 3) == 0) {listen = true;curr += 1;} else if (strncmp("-a", argv[curr], 3) == 0) {// -a 用来指定自己的ip地址check_argc(argc, argv, curr, "ERROR: -a requires one argument.");source_address = argv[curr + 1];curr += 2;} else if (strncmp("-s", argv[curr], 3) == 0) {// -s 用来指定自己的端口号check_argc(argc, argv, curr, "ERROR: -s requires one argument.");source_port = argv[curr + 1];curr += 2;} else if (strncmp("-w", argv[curr], 3) == 0) {// -w 用来指定自己接收窗口大小check_argc(argc, argv, curr, "ERROR: -w requires one argument.");c_fsm.recv_capacity = strtol(argv[curr + 1], nullptr, 0);curr += 2;} else if (strncmp("-t", argv[curr], 3) == 0) {// -t 指定RTO超时时间check_argc(argc, argv, curr, "ERROR: -t requires one argument.");c_fsm.rt_timeout = strtol(argv[curr + 1], nullptr, 0);curr += 2;} else if (strncmp("-d", argv[curr], 3) == 0) {// -d 指定要连接的tundev也就是网卡check_argc(argc, argv, curr, "ERROR: -t requires one argument.");tundev = argv[curr + 1];curr += 2;} else if (strncmp("-Lu", argv[curr], 3) == 0) {// -Lu 此选项设置上行丢包率,即从客户端发往服务器的数据包丢失的概率check_argc(argc, argv, curr, "ERROR: -Lu requires one argument.");float lossrate = strtof(argv[curr + 1], nullptr);using LossRateUpT = decltype(c_filt.loss_rate_up);c_filt.loss_rate_up =static_cast<LossRateUpT>(static_cast<float>(numeric_limits<LossRateUpT>::max()) * lossrate);curr += 2;} else if (strncmp("-Ld", argv[curr], 3) == 0) {// -Ld 此选项设置下行丢包率,即从服务器发往客户端的数据包丢失的概率check_argc(argc, argv, curr, "ERROR: -Lu requires one argument.");float lossrate = strtof(argv[curr + 1], nullptr);using LossRateDnT = decltype(c_filt.loss_rate_dn);c_filt.loss_rate_dn =static_cast<LossRateDnT>(static_cast<float>(numeric_limits<LossRateDnT>::max()) * lossrate);curr += 2;} else if (strncmp("-h", argv[curr], 3) == 0) {// -h 显示提示信息show_usage(argv[0], nullptr);exit(0);} else {show_usage(argv[0], string("ERROR: unrecognized option " + string(argv[curr])).c_str());exit(1);}}// parse positional command-line arguments// 是否打开了server端LISTEN模式if (listen) {// 说明当前启动的是server端 --> 从参数中获取监听端口号// 将过滤器的源地址配置为 "0"(表示监听所有本地网络接口的地址)c_filt.source = {"0", argv[curr + 1]};if (c_filt.source.port() == 0) {show_usage(argv[0], "ERROR: listen port cannot be zero in server mode.");exit(1);}} else {// 说明当前启动的是client端 -- 目的ip地址和端口号从最后两个参数获取c_filt.destination = {argv[curr], argv[curr + 1]};// 我们可以通过-a或者-s参数指定启动的客户端监听的ip地址和端口c_filt.source = {source_address, source_port};}return make_tuple(c_fsm, c_filt, listen, tundev);
}
cs144实现的fd家族体系
main函数中会建立一个 TCPOverIPv4OverTunFdAdapter。TunFd指的是连接进 Tun 设备上的 socket :
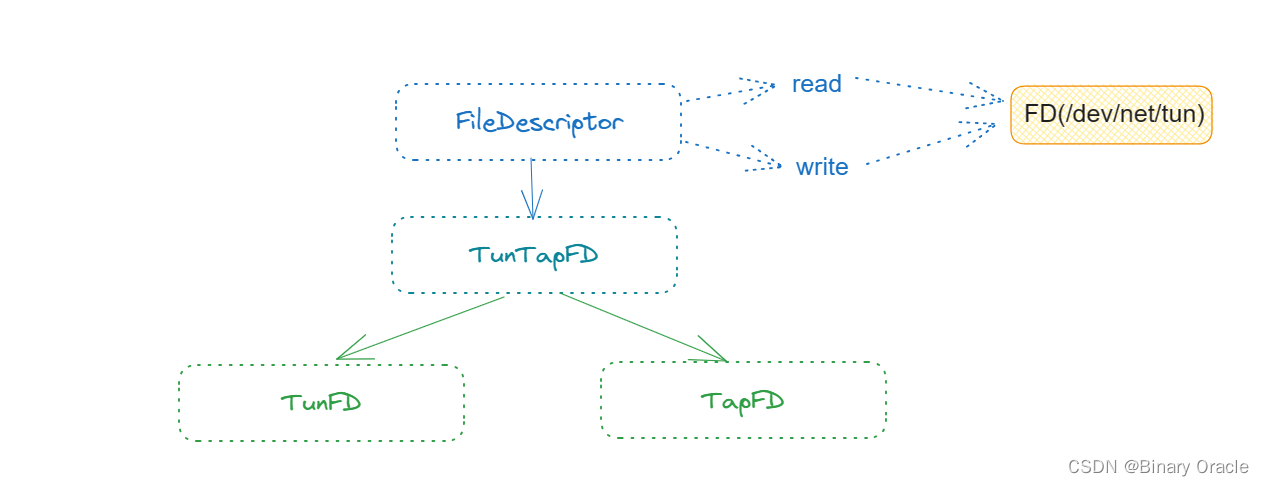
TunFD具体应用可以看app/tun.cc :
int main() {try {TunFD tun("tun144");while (true) {auto buffer = tun.read();cout << "\n\n***\n*** Got packet:\n***\n";hexdump(buffer.data(), buffer.size());IPv4Datagram ip_dgram;cout << "attempting to parse as ipv4 datagram... ";if (ip_dgram.parse(move(buffer)) != ParseResult::NoError) {cout << "failed.\n";continue;}cout << "success! totlen=" << ip_dgram.header().len << ", IPv4 header contents:\n";cout << ip_dgram.header().to_string();if (ip_dgram.header().proto != IPv4Header::PROTO_TCP) {cout << "\nNot TCP, skipping.\n";continue;}cout << "\nAttempting to parse as a TCP segment... ";TCPSegment tcp_seg;if (tcp_seg.parse(ip_dgram.payload(), ip_dgram.header().pseudo_cksum()) != ParseResult::NoError) {cout << "failed.\n";continue;}cout << "success! payload len=" << tcp_seg.payload().size() << ", TCP header contents:\n";cout << tcp_seg.header().to_string() << endl;}} catch (const exception &e) {cout << "Exception: " << e.what() << endl;return EXIT_FAILURE;}return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
基于自定义fd体系进行数据读写的adapter适配器体系
TCPOverIPv4OverTunFdAdapter是一个 IP 层面的封装接口。当调用 adapter 向其写入 TCP 报文段时,它会自动 wrap 上 IP 段并传输进网络设备中;读取也是亦然,会自动解除 IP 段并返回其内部封装的 TCP报文段:
// A FD adapter for IPv4 datagrams read from and written to a TUN device
class TCPOverIPv4OverTunFdAdapter : public TCPOverIPv4Adapter {private:TunFD _tun;public://! Construct from a TunFDexplicit TCPOverIPv4OverTunFdAdapter(TunFD &&tun) : _tun(std::move(tun)) {}//! Attempts to read and parse an IPv4 datagram containing a TCP segment related to the current connection// 从tun设备返回的以太网帧中解析得到ip数据报std::optional<TCPSegment> read() {InternetDatagram ip_dgram;if (ip_dgram.parse(_tun.read()) != ParseResult::NoError) {return {};}// 去除ip头,返回tcp报文段return unwrap_tcp_in_ip(ip_dgram);}//! Creates an IPv4 datagram from a TCP segment and writes it to the TUN device// 将写入的tcp报文段添加上ip头后写入tun设备void write(TCPSegment &seg) { _tun.write(wrap_tcp_in_ip(seg).serialize()); }//! Access the underlying TUN deviceoperator TunFD &() { return _tun; }//! Access the underlying TUN deviceoperator const TunFD &() const { return _tun; }
};
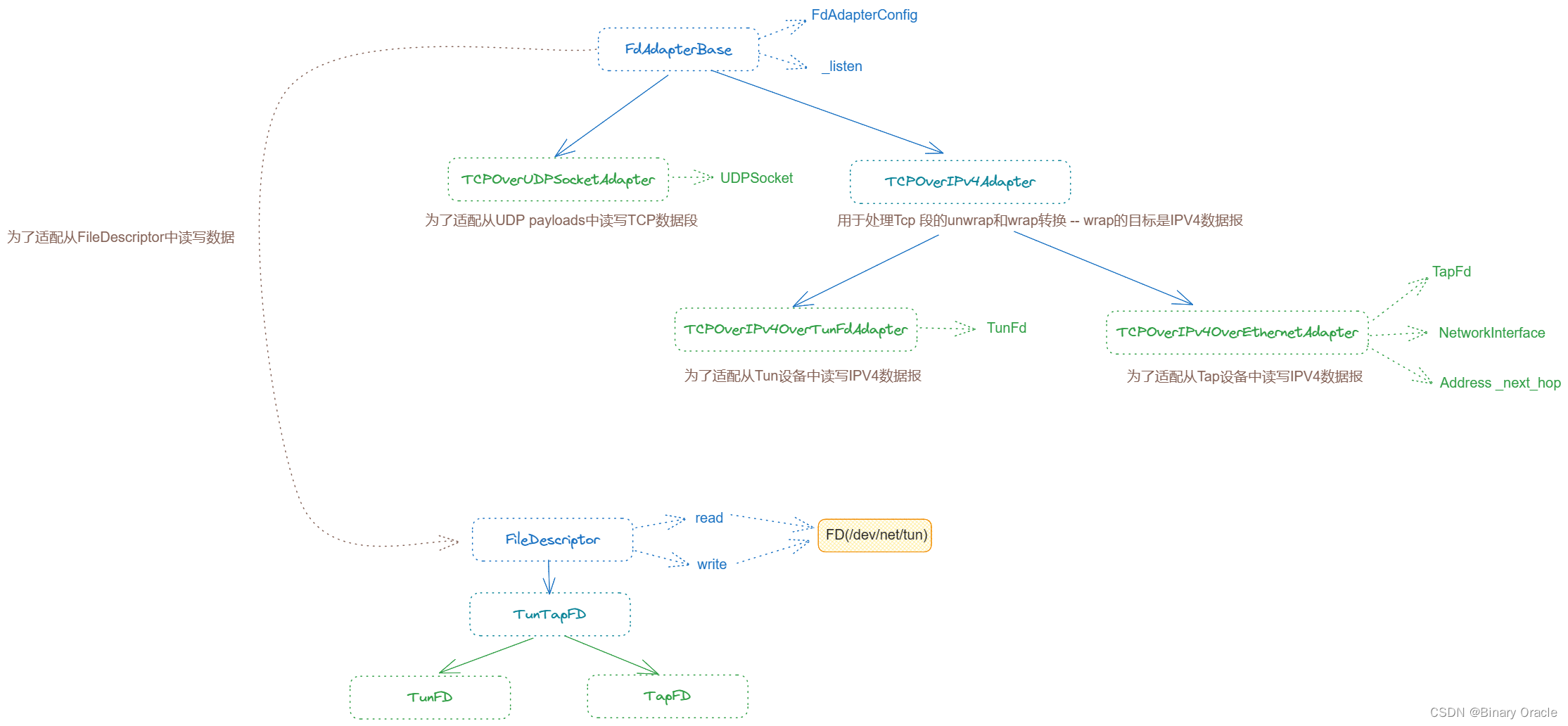
LossyTCPOverIPv4OverTunFdAdapter本身由模板类LossyFdAdapter实例化而来,该模板类通过装饰器模式对内部持有的Adapter进行功能增强,主要增加在读写数据时,根据先前设置丢包率来判断是否丢弃此次的数据报:
template <typename AdapterT>
class LossyFdAdapter {private://! Fast RNG used by _should_drop()std::mt19937 _rand{get_random_generator()};//! The underlying FD adapterAdapterT _adapter;...bool _should_drop(bool uplink) {const auto &cfg = _adapter.config();const uint16_t loss = uplink ? cfg.loss_rate_up : cfg.loss_rate_dn;return loss != 0 && uint16_t(_rand()) < loss;}//! \brief Read from the underlying AdapterT instance, potentially dropping the read datagram//! \returns std::optional<TCPSegment> that is empty if the segment was dropped or if//! the underlying AdapterT returned an empty valuestd::optional<TCPSegment> read() {auto ret = _adapter.read();if (_should_drop(false)) {return {};}return ret;}//! \brief Write to the underlying AdapterT instance, potentially dropping the datagram to be written//! \param[in] seg is the packet to either write or dropvoid write(TCPSegment &seg) {if (_should_drop(true)) {return;}return _adapter.write(seg);}...
};
自定义socket体系
cs144中封装的Socket继承体系如下所示:
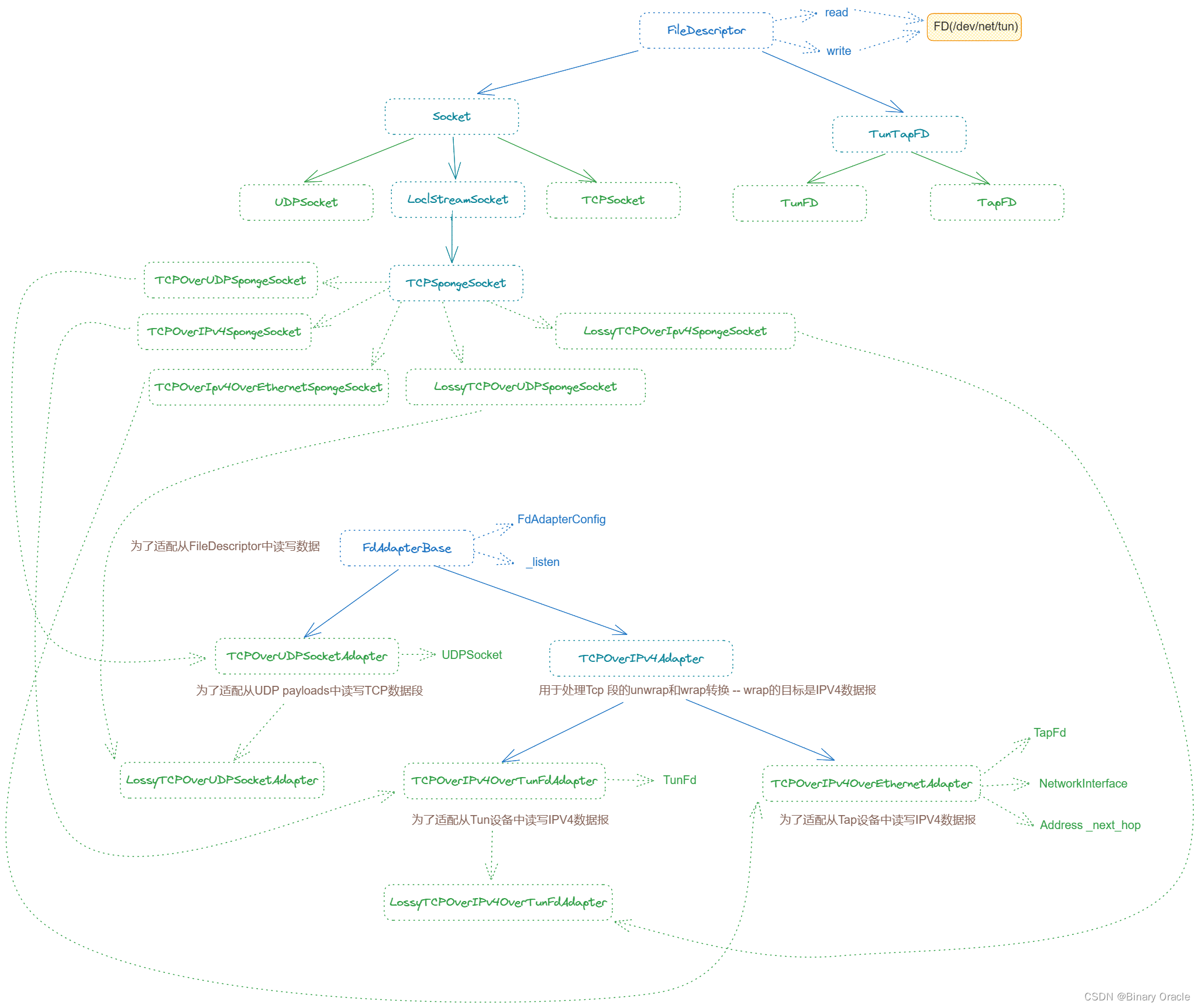
socket的read/write接口都位于顶层FileDescriptor父类中:
//! \param[in] limit is the maximum number of bytes to read; fewer bytes may be returned
//! \param[out] str is the string to be read
// 通过系统调用read从fd对应的设备或者文件中读取数据
void FileDescriptor::read(std::string &str, const size_t limit) {constexpr size_t BUFFER_SIZE = 1024 * 1024; // maximum size of a readconst size_t size_to_read = min(BUFFER_SIZE, limit);str.resize(size_to_read);ssize_t bytes_read = SystemCall("read", ::read(fd_num(), str.data(), size_to_read));if (limit > 0 && bytes_read == 0) {_internal_fd->_eof = true;}if (bytes_read > static_cast<ssize_t>(size_to_read)) {throw runtime_error("read() read more than requested");}str.resize(bytes_read);register_read();
}// 通过write系统调用向fd对应的设备或者文件中写入数据
size_t FileDescriptor::write(BufferViewList buffer, const bool write_all) {size_t total_bytes_written = 0;do {auto iovecs = buffer.as_iovecs();const ssize_t bytes_written = SystemCall("writev", ::writev(fd_num(), iovecs.data(), iovecs.size()));if (bytes_written == 0 and buffer.size() != 0) {throw runtime_error("write returned 0 given non-empty input buffer");}if (bytes_written > ssize_t(buffer.size())) {throw runtime_error("write wrote more than length of input buffer");}register_write();buffer.remove_prefix(bytes_written);total_bytes_written += bytes_written;} while (write_all and buffer.size());return total_bytes_written;
}
自定义事件循环EventLoop
cs144在Linux提供的多路复用模型Poll基础上进行封装,造出了一个简易版本的事件循环机制EventLoop:
//! Waits for events on file descriptors and executes corresponding callbacks.
class EventLoop {public:// 对fd的读事件还是写事件感兴趣enum class Direction : short {In = POLLIN, Out = POLLOUT};private:using CallbackT = std::function<void(void)>;using InterestT = std::function<bool(void)>;// 内部类Rule,说白了就是持有用户对哪个fd的那些事件感兴趣的信息载体// 同时持有对应事件发生和取消时的回调接口class Rule {public:FileDescriptor fd;Direction direction;// 发生感兴趣事件的时候回调该接口CallbackT callback;// 返回值决定当前fd是否需要被监听InterestT interest;// 当对应fd关闭,出错时,回调该接口CallbackT cancel;// 根据direction的不同返回当前fd已经被读取或者写入了多少次unsigned int service_count() const;};// 用户注册的感兴趣的事件集合std::list<Rule> _rules{};public:// 事件监听的返回结果enum class Result {Success, // At least one Rule was triggered.Timeout, // No rules were triggered before timeout.Exit // All rules have been canceled or were uninterested; make no further calls to EventLoop::wait_next_event.};// 用户添加感兴趣的事件void add_rule(const FileDescriptor &fd,const Direction direction,const CallbackT &callback,const InterestT &interest = [] { return true; },const CallbackT &cancel = [] {});// 等待下一个感兴趣的事件发生 --- 参数是等待超时时间Result wait_next_event(const int timeout_ms);
};
- add_rule函数: 注册感兴趣的事件
void EventLoop::add_rule(const FileDescriptor &fd,const Direction direction,const CallbackT &callback,const InterestT &interest,const CallbackT &cancel) {_rules.push_back({fd.duplicate(), direction, callback, interest, cancel});
}
- service_count函数: 当前fd已经被读取或者写入了多少次
unsigned int EventLoop::Rule::service_count() const {return direction == Direction::In ? fd.read_count() : fd.write_count();
}
- wait_next_event函数: 等待获取下一个发生的感兴趣的事件
EventLoop::Result EventLoop::wait_next_event(const int timeout_ms) {vector<pollfd> pollfds{};pollfds.reserve(_rules.size());bool something_to_poll = false;// set up the pollfd for each rule// 遍历所有Rulefor (auto it = _rules.cbegin(); it != _rules.cend();) { // NOTE: it gets erased or incremented in loop bodyconst auto &this_rule = *it;// 如果当前rule期望从fd中读取数据,并且此时fd已经没有数据可以读取了,那么回调当前rule的cacel回调接口// 并且将当前rule从已有的rule集合中移除if (this_rule.direction == Direction::In && this_rule.fd.eof()) {// no more reading on this rule, it's reached eofthis_rule.cancel();it = _rules.erase(it);continue;}// 如果当前fd关闭了,同上处理if (this_rule.fd.closed()) {this_rule.cancel();it = _rules.erase(it);continue;}// 判断是否对当前rule感兴趣,如果感兴趣则加入pollfds进入下面事件轮询阶段if (this_rule.interest()) {// pollfd由三个属性: 需要轮询的fd,是对fd的可读还是可写事件感兴趣,实际发生了什么事件pollfds.push_back({this_rule.fd.fd_num(), static_cast<short>(this_rule.direction), 0});something_to_poll = true;} else {// 为了保持 pollfds 数组和规则列表 _rules 中的规则一一对应,仍然需要将一个 pollfd 结构体添加到 pollfds 数组中// 但是对应的事件设置为 0,表示不关注任何事件,相当于占位符pollfds.push_back({this_rule.fd.fd_num(), 0, 0}); // placeholder --- we still want errors}++it;}// quit if there is nothing left to poll --- 没有任何rule需要轮询if (not something_to_poll) {return Result::Exit;}// call poll -- wait until one of the fds satisfies one of the rules (writeable/readable)try {// 通过调用poll对pollfds集合中所有pollfd开启事件轮询// 最后一个参数: 如果没有感兴趣事件发生,最多轮询等待多久if (0 == SystemCall("poll", ::poll(pollfds.data(), pollfds.size(), timeout_ms))) {return Result::Timeout;}} catch (unix_error const &e) {if (e.code().value() == EINTR) {return Result::Exit;}}// go through the poll results// 遍历poll结果 -- rules和pollfds集合索引是一一对应的for (auto [it, idx] = make_pair(_rules.begin(), size_t(0)); it != _rules.end(); ++idx) {const auto &this_pollfd = pollfds[idx];// revents保存着实际发生的事件 -- 是否发生错误const auto poll_error = static_cast<bool>(this_pollfd.revents & (POLLERR | POLLNVAL));if (poll_error) {throw runtime_error("EventLoop: error on polled file descriptor");}const auto &this_rule = *it;// 获取发生了哪些感兴趣的事件 const auto poll_ready = static_cast<bool>(this_pollfd.revents & this_pollfd.events);// 当描述符关闭时或者对端连接关闭时,会设置描述符挂起事件const auto poll_hup = static_cast<bool>(this_pollfd.revents & POLLHUP);// 如果当前描述符被挂起了,那么将当前rule移除if (poll_hup && this_pollfd.events && !poll_ready) {// if we asked for the status, and the _only_ condition was a hangup, this FD is defunct:// - if it was POLLIN and nothing is readable, no more will ever be readable// - if it was POLLOUT, it will not be writable againthis_rule.cancel();it = _rules.erase(it);continue;}// 如果存在感兴趣的事件发生if (poll_ready) {// we only want to call callback if revents includes the event we asked forconst auto count_before = this_rule.service_count();// 回调Rule对应的接口this_rule.callback();// only check for busy wait if we're not canceling or exitingif (count_before == this_rule.service_count() and this_rule.interest()) {throw runtime_error("EventLoop: busy wait detected: callback did not read/write fd and is still interested");}}++it; // if we got here, it means we didn't call _rules.erase()}return Result::Success;
}
模板类TCPSpongeSocket详解
TCPSpongeSocket本身是一个模板类,再该模板类基础上衍生出大量实例化类型:
using TCPOverUDPSpongeSocket = TCPSpongeSocket<TCPOverUDPSocketAdapter>;
using TCPOverIPv4SpongeSocket = TCPSpongeSocket<TCPOverIPv4OverTunFdAdapter>;
using TCPOverIPv4OverEthernetSpongeSocket = TCPSpongeSocket<TCPOverIPv4OverEthernetAdapter>;using LossyTCPOverUDPSpongeSocket = TCPSpongeSocket<LossyTCPOverUDPSocketAdapter>;
using LossyTCPOverIPv4SpongeSocket = TCPSpongeSocket<LossyTCPOverIPv4OverTunFdAdapter>;
TCPSpongeSocket类中重要的属性如下所示:
//! Multithreaded wrapper around TCPConnection that approximates the Unix sockets API
template <typename AdaptT>
class TCPSpongeSocket : public LocalStreamSocket {private://! Stream socket for reads and writes between owner and TCP threadLocalStreamSocket _thread_data;protected://! Adapter to underlying datagram socket (e.g., UDP or IP)AdaptT _datagram_adapter;private://! Set up the TCPConnection and the event loopvoid _initialize_TCP(const TCPConfig &config);//! TCP state machine -- Lab Four实现的std::optional<TCPConnection> _tcp{};//! eventloop that handles all the events (new inbound datagram, new outbound bytes, new inbound bytes)// 事件循环机制 -- 参考Select和Epoll模型EventLoop _eventloop{};//! Process events while specified condition is truevoid _tcp_loop(const std::function<bool()> &condition);//! Main loop of TCPConnection threadvoid _tcp_main();//! Handle to the TCPConnection thread; owner thread calls join() in the destructorstd::thread _tcp_thread{};//! Construct LocalStreamSocket fds from socket pair, initialize eventloopTCPSpongeSocket(std::pair<FileDescriptor, FileDescriptor> data_socket_pair, AdaptT &&datagram_interface);std::atomic_bool _abort{false}; //!< Flag used by the owner to force the TCPConnection thread to shut downbool _inbound_shutdown{false}; //!< Has TCPSpongeSocket shut down the incoming data to the owner?bool _outbound_shutdown{false}; //!< Has the owner shut down the outbound data to the TCP connection?bool _fully_acked{false}; //!< Has the outbound data been fully acknowledged by the peer?...
listen_and_accept方法
我们先来看一下TCPSpongeSocket类的listen_and_accept方法实现,服务端会调用该方法进行端口监听:
//! \param[in] c_tcp is the TCPConfig for the TCPConnection
//! \param[in] c_ad is the FdAdapterConfig for the FdAdapter
template <typename AdaptT>
void TCPSpongeSocket<AdaptT>::listen_and_accept(const TCPConfig &c_tcp, const FdAdapterConfig &c_ad) {if (_tcp) {throw runtime_error("listen_and_accept() with TCPConnection already initialized");}// 初始化TCP连接和事件循环_initialize_TCP(c_tcp);_datagram_adapter.config_mut() = c_ad;_datagram_adapter.set_listening(true);cerr << "DEBUG: Listening for incoming connection...\n";// 启动tcp事件循环,传入的函数为condition,其返回值决定事件循环是否继续// 该事件循环只负责将连接建立起来,三次握手结束后,退出事件循环 -- 事务循环函数解析下面会给出_tcp_loop([&] {const auto s = _tcp->state();return (s == TCPState::State::LISTEN or s == TCPState::State::SYN_RCVD or s == TCPState::State::SYN_SENT);});cerr << "New connection from " << _datagram_adapter.config().destination.to_string() << ".\n";// _tcp_thread线程负责完成当前TCP连接后续数据传输,此时线程已经启动 _tcp_thread = thread(&TCPSpongeSocket::_tcp_main, this);
}
_tcp_main方法
template <typename AdaptT>
void TCPSpongeSocket<AdaptT>::_tcp_main() {try {if (not _tcp.has_value()) {throw runtime_error("no TCP");}// 开启tcp事件循环,不断运行,直到TCP连接断开_tcp_loop([] { return true; });// 关闭当前Socketshutdown(SHUT_RDWR);if (not _tcp.value().active()) {cerr << "DEBUG: TCP connection finished "<< (_tcp.value().state() == TCPState::State::RESET ? "uncleanly" : "cleanly.\n");}// 将optional里面保存的TCPConnection清空_tcp.reset();} catch (const exception &e) {cerr << "Exception in TCPConnection runner thread: " << e.what() << "\n";throw e;}
}
_initialize_TCP初始化Tcp连接和事件循环
_initialize_TCP负责初始化tcp连接和事件循环:
template <typename AdaptT>
void TCPSpongeSocket<AdaptT>::_initialize_TCP(const TCPConfig &config) {// 将tcpConfig设置到TCPConnection中_tcp.emplace(config);// Set up the event loop// There are four possible events to handle://// 1) Incoming datagram received (needs to be given to// TCPConnection::segment_received method)//// 2) Outbound bytes received from local application via a write()// call (needs to be read from the local stream socket and// given to TCPConnection::data_written method)//// 3) Incoming bytes reassembled by the TCPConnection// (needs to be read from the inbound_stream and written// to the local stream socket back to the application)//// 4) Outbound segment generated by TCP (needs to be// given to underlying datagram socket)// rule 1: read from filtered packet stream and dump into TCPConnection// 监听网络是否有数据报到达_eventloop.add_rule(// 监听的fd本质是tun设备_datagram_adapter,Direction::In,// 当感兴趣事件发生时,会回调该接口[&] {// 从tun设备读取数据auto seg = _datagram_adapter.read();// 交给TcpConnection进行处理if (seg) {_tcp->segment_received(move(seg.value()));}// debugging output:if (_thread_data.eof() and _tcp.value().bytes_in_flight() == 0 and not _fully_acked) {cerr << "DEBUG: Outbound stream to " << _datagram_adapter.config().destination.to_string()<< " has been fully acknowledged.\n";_fully_acked = true;}},// 只要tcp连接还活跃,那么就继续轮询当前rule[&] { return _tcp->active(); });// rule 2: read from pipe into outbound buffer// 监听应用程序是否有数据需要传输_eventloop.add_rule(// 监听_thread_data -- 竖立在应用程序和协议栈直接的数据传输通道_thread_data,Direction::In,[&] {// 应用程序向_thread_data中写入数据,然后通知协议栈有数据需要发送// 根据tcp写入窗口剩余空闲大小读取指定的需要写出的数据量const auto data = _thread_data.read(_tcp->remaining_outbound_capacity());const auto len = data.size();// 调用TCPConnection的write方法进行写出const auto amount_written = _tcp->write(move(data));if (amount_written != len) {throw runtime_error("TCPConnection::write() accepted less than advertised length");}// 如果应用程序主动调用close关闭了_thread_data通道,那么tcp写入通道也可以关闭了 if (_thread_data.eof()) {_tcp->end_input_stream();// 输出通道关闭_outbound_shutdown = true;// debugging output:cerr << "DEBUG: Outbound stream to " << _datagram_adapter.config().destination.to_string()<< " finished (" << _tcp.value().bytes_in_flight() << " byte"<< (_tcp.value().bytes_in_flight() == 1 ? "" : "s") << " still in flight).\n";}},// 只要当前tcp连接还活跃并且输出通道还没有关闭并且当前tcp写入窗口大小不为0,就继续轮询当前rule[&] { return (_tcp->active()) and (not _outbound_shutdown) and (_tcp->remaining_outbound_capacity() > 0); },// fd发生错误时,回调该接口[&] {_tcp->end_input_stream();_outbound_shutdown = true;});// rule 3: read from inbound buffer into pipe// 监听是否有按序到达的字节流还未写入,同时_thread_data通道还未关闭,如果有则写入_thread_data通道_eventloop.add_rule(// 监听thread_data_thread_data,// 关注可写事件Direction::Out,[&] {// 获取tcp接收器的读取流ByteStream &inbound = _tcp->inbound_stream();// Write from the inbound_stream into// the pipe, handling the possibility of a partial// write (i.e., only pop what was actually written).// 一口气把所有已经按序达到的字节流全部读取出来const size_t amount_to_write = min(size_t(65536), inbound.buffer_size());const std::string buffer = inbound.peek_output(amount_to_write);// 将读取出来的数据全部写入_thread_data管道中const auto bytes_written = _thread_data.write(move(buffer), false);// 已经成功被应用程序接收的字节流可以丢掉了inbound.pop_output(bytes_written);// 如果tcp进入四次挥手阶段或者断开连接了,那么关闭_thread_data管道if (inbound.eof() or inbound.error()) {_thread_data.shutdown(SHUT_WR);_inbound_shutdown = true;// debugging output:cerr << "DEBUG: Inbound stream from " << _datagram_adapter.config().destination.to_string()<< " finished " << (inbound.error() ? "with an error/reset.\n" : "cleanly.\n");// 满足下面这个条件说明目前此端为客户端,并且进入了四次挥手的TIME_WAIT阶段if (_tcp.value().state() == TCPState::State::TIME_WAIT) {cerr << "DEBUG: Waiting for lingering segments (e.g. retransmissions of FIN) from peer...\n";}}},// 如果tcp接收器还存在按序到达的字节流没有读取,或者tcp_receiver还没有接收到FIN包,那么就继续轮询当前rule[&] {return (not _tcp->inbound_stream().buffer_empty()) or((_tcp->inbound_stream().eof() or _tcp->inbound_stream().error()) and not _inbound_shutdown);});// rule 4: read outbound segments from TCPConnection and send as datagrams// 监听TCPConnection是否有数据需要发送,如果有则发送,前提是_datagram_adapter可写_eventloop.add_rule(_datagram_adapter,Direction::Out,[&] {// 如果TCPConnection的segments_out等待队列不为空,说明存在待传输的数据包while (not _tcp->segments_out().empty()) {// 写入segments_out,进行数据包的实际传输_datagram_adapter.write(_tcp->segments_out().front());_tcp->segments_out().pop();}},// 只要segments_out不为空,就继续轮询当前rule[&] { return not _tcp->segments_out().empty(); });
}
_tcp_loop函数启动tcp事件循环
_tcp_loop函数启动tcp事件循环:
//! \param[in] condition is a function returning true if loop should continue
template <typename AdaptT>
void TCPSpongeSocket<AdaptT>::_tcp_loop(const function<bool()> &condition) {auto base_time = timestamp_ms();// 什么时候停止事件循环取决于condition函数返回值while (condition()) {// 等待获取下一个待发生的rule,超时则返回 -- 超时时间为10毫秒auto ret = _eventloop.wait_next_event(TCP_TICK_MS);// 没有事件发生,说明TCP断开了连接if (ret == EventLoop::Result::Exit or _abort) {break;}// 如果tcp连接仍然活跃if (_tcp.value().active()) {// 每隔10毫秒,调用一次TCPConnection的tick方法const auto next_time = timestamp_ms();// 传入参数: 距离上次调用该方法过了多久_tcp.value().tick(next_time - base_time);// 只有TCPOverIPv4OverEthernetAdapter的tick函数才有意义 -- lab five会讲解// 其他adapter均为空实现_datagram_adapter.tick(next_time - base_time);base_time = next_time;}}
}
connect 方法
//! \param[in] c_tcp is the TCPConfig for the TCPConnection
//! \param[in] c_ad is the FdAdapterConfig for the FdAdapter
template <typename AdaptT>
void TCPSpongeSocket<AdaptT>::connect(const TCPConfig &c_tcp, const FdAdapterConfig &c_ad) {if (_tcp) {throw runtime_error("connect() with TCPConnection already initialized");}// 初始化TCP连接和事件循环_initialize_TCP(c_tcp);_datagram_adapter.config_mut() = c_ad;cerr << "DEBUG: Connecting to " << c_ad.destination.to_string() << "...\n";// 开始三次握手,首先由Client发出一个SYN包_tcp->connect();const TCPState expected_state = TCPState::State::SYN_SENT;if (_tcp->state() != expected_state) {throw runtime_error("After TCPConnection::connect(), state was " + _tcp->state().name() + " but expected " +expected_state.name());}// 使用事件循环,等待三次连接建立完毕_tcp_loop([&] { return _tcp->state() == TCPState::State::SYN_SENT; });cerr << "Successfully connected to " << c_ad.destination.to_string() << ".\n";// 单独开启一个线程用于后续数据传输 _tcp_thread = thread(&TCPSpongeSocket::_tcp_main, this);
}
bidirectional_stream_copy方法
无论对于 Server 还是 Client,在三次握手之后,都会建立一个新的线程,来专门执行 LossyTCPOverIPv4SpongeSocket 中的 eventloop。而主线程会另起一个 eventloop 以及另外开辟两个缓冲区,用于存放用户写入的数据与即将输出至屏幕的数据。当用户通过 stdin 输入数据时, eventloop 中所注册的 poll 事件被检测到,则数据将会被写入进本地输入缓冲区中。当 TCPOverIPv4OverTunFdAdapter 可写时,它会将本地输入缓冲区中的数据全部写入至 TCPOverIPv4OverTunFdAdapter ,并最终传输至远程。
而 webget 与真实服务器通信的原理,也是通过将 IP 报文写入 tun 虚拟网络设备,将其注入进 OS 协议栈中,模拟实际的发包情况。
// 在标准输入(stdin)和标准输出(stdout)之间以及一个自定义的 socket 对象之间进行双向数据复制
// 标准输入 --> socket --> 标准输出
// 键盘输入的数据会写入socket,socket有可读的数据会输出到屏幕上
void bidirectional_stream_copy(Socket &socket) {constexpr size_t max_copy_length = 65536;constexpr size_t buffer_size = 1048576;EventLoop _eventloop{};FileDescriptor _input{STDIN_FILENO};FileDescriptor _output{STDOUT_FILENO};ByteStream _outbound{buffer_size};ByteStream _inbound{buffer_size};bool _outbound_shutdown{false};bool _inbound_shutdown{false};socket.set_blocking(false);_input.set_blocking(false);_output.set_blocking(false);// rule 1: read from stdin into outbound byte stream// 标准输入有数据可读则写入_outbound通道_eventloop.add_rule(_input,Direction::In,[&] {_outbound.write(_input.read(_outbound.remaining_capacity()));if (_input.eof()) {_outbound.end_input();}},[&] { return (not _outbound.error()) and (_outbound.remaining_capacity() > 0) and (not _inbound.error()); },[&] { _outbound.end_input(); });// rule 2: read from outbound byte stream into socket// socket可写,则将_outbound通道中数据写入socket_eventloop.add_rule(socket,Direction::Out,[&] {const size_t bytes_to_write = min(max_copy_length, _outbound.buffer_size());const size_t bytes_written = socket.write(_outbound.peek_output(bytes_to_write), false);_outbound.pop_output(bytes_written);if (_outbound.eof()) {socket.shutdown(SHUT_WR);_outbound_shutdown = true;}},[&] { return (not _outbound.buffer_empty()) or (_outbound.eof() and not _outbound_shutdown); },[&] { _outbound.end_input(); });// rule 3: read from socket into inbound byte stream// socket有可读数据,则读取数据并写入_inbound通道_eventloop.add_rule(socket,Direction::In,[&] {_inbound.write(socket.read(_inbound.remaining_capacity()));if (socket.eof()) {_inbound.end_input();}},[&] { return (not _inbound.error()) and (_inbound.remaining_capacity() > 0) and (not _outbound.error()); },[&] { _inbound.end_input(); });// rule 4: read from inbound byte stream into stdout// 如果标准输出可写,则将数据从_inbound中读取出来,然后写入标准输出_eventloop.add_rule(_output,Direction::Out,[&] {const size_t bytes_to_write = min(max_copy_length, _inbound.buffer_size());const size_t bytes_written = _output.write(_inbound.peek_output(bytes_to_write), false);_inbound.pop_output(bytes_written);if (_inbound.eof()) {_output.close();_inbound_shutdown = true;}},[&] { return (not _inbound.buffer_empty()) or (_inbound.eof() and not _inbound_shutdown); },[&] { _inbound.end_input(); });// loop until completion -- 死循环,每次都阻塞到下一次事件发生while (true) {if (EventLoop::Result::Exit == _eventloop.wait_next_event(-1)) {return;}}
}
TCPSpongeSocket的wait_until_closed方法
wait_until_closed方法负责同步等待直到_tcp_thread线程结束:
template <typename AdaptT>
void TCPSpongeSocket<AdaptT>::wait_until_closed() {// 关闭当前socketshutdown(SHUT_RDWR);// 同步等待直到_tcp_thread线程结束if (_tcp_thread.joinable()) {cerr << "DEBUG: Waiting for clean shutdown... ";_tcp_thread.join();cerr << "done.\n";}
}
通道串联起子主线程
首先,我们来看一下TCPSpongeSocket的构造函数和析构函数:
// socketpair系统调用的作用是在本地进程间创建一对已连接的套接字(sockets)。
// 这对套接字可用于本地通信,类似于网络套接字的用法,但是不需要通过网络协议栈进行通信,而是直接在内核中完成通信,因此效率更高。
static inline pair<FileDescriptor, FileDescriptor> socket_pair_helper(const int type) {int fds[2];// 具体来说,socketpair创建了两个相关联的套接字,一个作为读取套接字(reading socket),另一个作为写入套接字(writing socket)。// 这两个套接字之间形成了一条双向的通信通道,任何通过写入套接字发送的数据都可以通过读取套接字接收,并且反之亦然。 SystemCall("socketpair", ::socketpair(AF_UNIX, type, 0, static_cast<int *>(fds)));return {FileDescriptor(fds[0]), FileDescriptor(fds[1])};
}//! \param[in] datagram_interface is the underlying interface (e.g. to UDP, IP, or Ethernet)
template <typename AdaptT>
TCPSpongeSocket<AdaptT>::TCPSpongeSocket(AdaptT &&datagram_interface): TCPSpongeSocket(socket_pair_helper(SOCK_STREAM), move(datagram_interface)) {}template <typename AdaptT>
TCPSpongeSocket<AdaptT>::TCPSpongeSocket(pair<FileDescriptor, FileDescriptor> data_socket_pair,AdaptT &&datagram_interface)// 主线程拿着通道一端 : LocalStreamSocket(move(data_socket_pair.first))// 子线程拿着通道的另一端, _thread_data(move(data_socket_pair.second)), _datagram_adapter(move(datagram_interface)) {_thread_data.set_blocking(false);
}template <typename AdaptT>
TCPSpongeSocket<AdaptT>::~TCPSpongeSocket() {try {if (_tcp_thread.joinable()) {cerr << "Warning: unclean shutdown of TCPSpongeSocket\n";// force the other side to exit_abort.store(true);_tcp_thread.join();}} catch (const exception &e) {cerr << "Exception destructing TCPSpongeSocket: " << e.what() << endl;}
}
主线程和子线程通过socketpair系统调用创建的一对已连接的套接字(sockets)进行本地通信。
- 主线程中发生键盘输入事件,到输入的内容通过socktpair创建的双向通道传输到子线程,然后由子线程将数据最终通过tun设备发送出去,这中间结合了两个eventloop共同协作完成
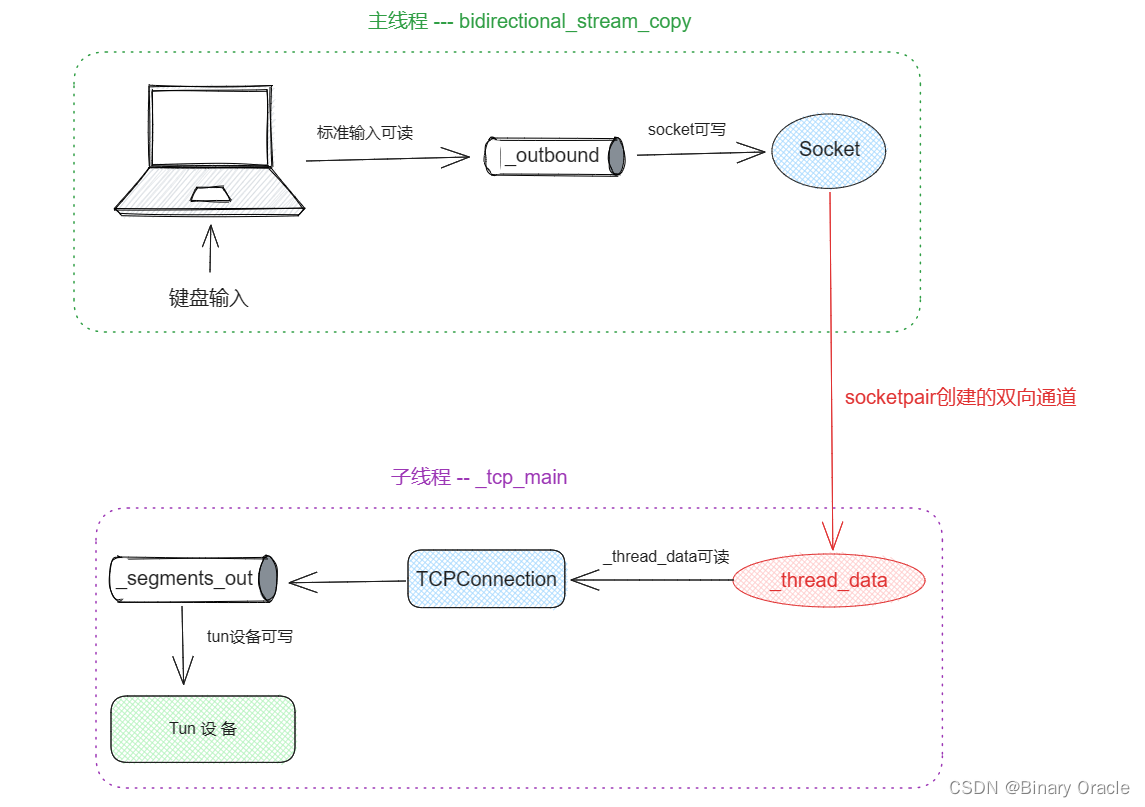
- 当tun设备接收到网络数据包的时候,会将数据包传输给TCP协议栈进行处理,TCP协议栈处理完后,如果发现_thread_data双向通道可写,则将处理完毕的数据包丢到通道中,主线程中的Socket发现来数据了,将数据写入_inbound通道中,此时发现标准输出可写,最终将接收到的数据包输出到屏幕上
- 这中间同样结合了两个eventloop共同协作工作,大家可以好好理解一下
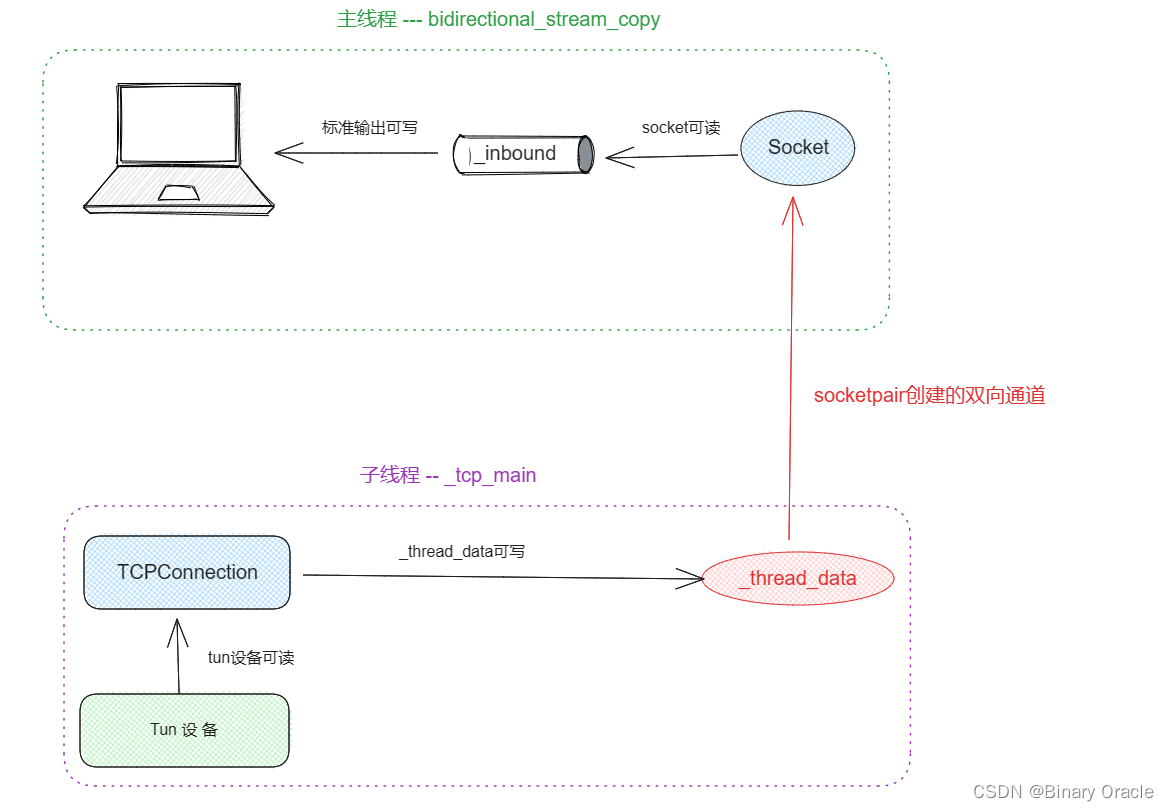
- 这中间同样结合了两个eventloop共同协作工作,大家可以好好理解一下
小结
以上就是我个人对cs144 Lab Four测试文件tcp_ipv4.cc文件大体流程的理解,可能会存在错误,欢迎各位大佬评论区指出,同时由于篇幅有限,不能将所有源码一一贴出讲解,所以阅读过程中大家可以对照cs144 lab four相关源码进行学习
相关文章:

CS 144 Lab Four 收尾 -- 网络交互全流程解析
CS 144 Lab Four 收尾 -- 网络交互全流程解析 引言Tun/Tap简介tcp_ipv4.cc文件配置信息初始化cs144实现的fd家族体系基于自定义fd体系进行数据读写的adapter适配器体系自定义socket体系自定义事件循环EventLoop模板类TCPSpongeSocket详解listen_and_accept方法_tcp_main方法_in…...

Linux面试专题
Linux面试专题 1 Linux中主要有哪几种内核锁?2 Linux 中的用户模式和内核模式是什么含意?3 怎样申请大块内核内存?4用户进程间通信主要哪几种方式?5通过伙伴系统申请内核内存的函数有哪些?6) Linux 虚拟文件系统的关键数据结构有哪些?(至少写出四个)7) 对文件或设备的操作…...
详解)
MySQL错误日志(Error Log)详解
错误日志(Error Log)是 MySQL 中最常用的一种日志,主要记录 MySQL 服务器启动和停止过程中的信息、服务器在运行过程中发生的故障和异常情况等。 作为初学者,要学会利用错误日志来定位问题。下面介绍如何操作查看错误日志。 启动…...
Qt应用开发(基础篇)——LCD数值类 QLCDNumber
一、前言 QLCDNumber类继承于QFrame,QFrame继承于QWidget,是Qt的一个基础小部件。 QLCDNumber用来显示一个带有类似lcd数字的数字,适用于信号灯、跑步机、体温计、时钟、电表、水表、血压计等仪器类产品的数值显示。 QLCDNumber可以显示十进制…...
新版百度、百家号旋转验证码识别
昨天突然发现,百度旋转验证码发生了变化,导致使用老版本验证码训练出来的识别模型效果不佳。所有昨天花了一天时间完成了新版模型的训练。 老版本验证码 新版本验证码 新版的验证码感觉像是AI绘画随机生成的,还有随机阴影出现。 验证码识别…...
)
PMP考试每日一练(8月8日)
1、项目经理正在领导一个正在努力协作的多元文化团队。项目经理一开始将此视为团队建设的典型震荡阶段,但团队未能成功通过该阶段。结果,项目开始落后于进度。 项目经理在第一次发现这个问题时应该做哪两项工作?(选两个࿰…...
机器学习实战1-kNN最近邻算法
文章目录 机器学习基础机器学习的关键术语 k-近邻算法(KNN)准备:使用python导入数据实施kNN分类算法示例:使用kNN改进约会网站的配对效果准备数据:从文本文件中解析数据分析数据准备数据:归一化数值测试算法…...
【eNSP】静态路由
【eNSP】静态路由 原理网关路由表 实验根据图片连接模块配置路由器设备R1R2R3R4 配置PC的IP地址、掩码、网关PC1PC2PC3 配置静态路由查看路由表R1R2R3R4测试能否通信 原理 网关 网关与路由器地址相同,一般路由地址为.1或.254。 网关是当电脑发送的数据的目标IP不在…...

算法训练Day42|1049. 最后一块石头的重量 II ● 494. 目标和 ● 474.一和零
背包类别 01背包:有n种物品,每种物品只有一个. 完全背包:有n种物品,每种物品有无限个. 多重背包:有n种物品,每种物品个数各不相同. 区别:仅仅体现在物品个数上的不同而已。 确定dp[i][j]数组的…...

HBase-组成
client 读写请求HMaster 管理元数据监控region是否需要进行负载均衡,故障转移和region的拆分RegionServer 负责数据cell的处理,例如写入数据put,查询数据get等 拆分合并Region的实际执行者,由Master监控,由regionServ…...

第一部分:领域中的基本概念
目录 一、什么是模型 二、什么是领域 三、什么是领域模型 四、什么是领域建模 一、什么是模型 模型是一种简化、它是对现实的解释,它与解决问题密切相关的方面抽象出来,而忽略无关细节。 二、什么是领域 领域是指某一专业或事物方面范围的涵盖。比如…...

react使用ref调用子组件的方法
Class类组件 import React, { useRef } from react;const MyComponent () > {const myComponentRef useRef(null);const handleClick () > {// 调用MyComponent组件的方法myComponentRef.current.myMethod();};return (<div><MyComponent ref{myComponentRe…...
JVM面试突击班2
JVM面试突击班2 对象被判定为不可达对象之后就“死”了吗 对象的生命周期 创建阶段 (1)为对象分配存储空间 (2)开始构造对象 (3)从超类到子类对static成员进行初始化 (4)超类成…...

【80天学习完《深入理解计算机系统》】第二天 2.2 整数的表示【有符号数,无符号数,符号数的扩展,有无符号数的转变】
专注 效率 记忆 预习 笔记 复习 做题 欢迎观看我的博客,如有问题交流,欢迎评论区留言,一定尽快回复!(大家可以去看我的专栏,是所有文章的目录) 文章字体风格: 红色文字表示&#…...

基于 CentOS 7 构建 LVS-DR 群集以及配置nginx负载均衡
目录 一、基于 CentOS 7 构建 LVS-DR 群集 1、前期准备 1、关闭防火墙 2、安装ifconfig 3、准备四台虚拟机 2、在DS上 2.1、配置LVS虚拟IP 2.2、手工执行配置添加LVS服务并增加两台RS 2.3、查看配置 3、在RS端(第三台、第四台) 上 3.1、配置W…...
golang trace view 视图详解
大家好,我是蓝胖子,在golang中可以使用go pprof的工具对golang程序进行性能分析,其中通过go trace 命令生成的trace view视图对于我们分析系统延迟十分有帮助,鉴于当前对trace view视图的介绍还是很少,在粗略的看过tra…...

zju代码题:4-6
一 分段函数算水费 #include <stdio.h>int main() {/*** 定义两个* 定义浮点型变量* y:水费* x:用水的吨数* */double x, y;printf("Enter x(x>=0):\n"...

数据链路层概述
数据传输过程如下: 数据包按上述过程传输,详见(计算机网络概述三)。在分析数据链路层时可以假象成其沿着水平传播。 这三段链路层的传播方式可能会有所不同。 基本概念: 链路:指一个节点到相邻节点的一段物…...

Python代码使用技巧汇总:提升你的编程技能
各位程序员朋友们,今天我要跟大家分享一些关于Python代码的最佳使用技巧,这些技巧可以帮助你们成为更专业且高效的程序员。不管你是刚刚入门还是已经有一些经验,这些技巧都能够为你提供实际操作价值。 一、合理使用Python的数据结构和算法&am…...

Ae 效果:CC Spotlight
透视/CC Spotlight Perspective/CC Spotlight CC Spotlight(CC 聚光灯) 主要用途是创建和控制逼真的聚光灯效果。通过调整这些属性,可以模拟出各种不同的照明环境和效果,比如舞台照明、日出日落、特定的颜色照明等。 ◆ ◆ ◆ 效…...

未来机器人的大脑:如何用神经网络模拟器实现更智能的决策?
编辑:陈萍萍的公主一点人工一点智能 未来机器人的大脑:如何用神经网络模拟器实现更智能的决策?RWM通过双自回归机制有效解决了复合误差、部分可观测性和随机动力学等关键挑战,在不依赖领域特定归纳偏见的条件下实现了卓越的预测准…...
label-studio的使用教程(导入本地路径)
文章目录 1. 准备环境2. 脚本启动2.1 Windows2.2 Linux 3. 安装label-studio机器学习后端3.1 pip安装(推荐)3.2 GitHub仓库安装 4. 后端配置4.1 yolo环境4.2 引入后端模型4.3 修改脚本4.4 启动后端 5. 标注工程5.1 创建工程5.2 配置图片路径5.3 配置工程类型标签5.4 配置模型5.…...
-----深度优先搜索(DFS)实现)
c++ 面试题(1)-----深度优先搜索(DFS)实现
操作系统:ubuntu22.04 IDE:Visual Studio Code 编程语言:C11 题目描述 地上有一个 m 行 n 列的方格,从坐标 [0,0] 起始。一个机器人可以从某一格移动到上下左右四个格子,但不能进入行坐标和列坐标的数位之和大于 k 的格子。 例…...
:爬虫完整流程)
Python爬虫(二):爬虫完整流程
爬虫完整流程详解(7大核心步骤实战技巧) 一、爬虫完整工作流程 以下是爬虫开发的完整流程,我将结合具体技术点和实战经验展开说明: 1. 目标分析与前期准备 网站技术分析: 使用浏览器开发者工具(F12&…...

【配置 YOLOX 用于按目录分类的图片数据集】
现在的图标点选越来越多,如何一步解决,采用 YOLOX 目标检测模式则可以轻松解决 要在 YOLOX 中使用按目录分类的图片数据集(每个目录代表一个类别,目录下是该类别的所有图片),你需要进行以下配置步骤&#x…...
)
Java入门学习详细版(一)
大家好,Java 学习是一个系统学习的过程,核心原则就是“理论 实践 坚持”,并且需循序渐进,不可过于着急,本篇文章推出的这份详细入门学习资料将带大家从零基础开始,逐步掌握 Java 的核心概念和编程技能。 …...
AI书签管理工具开发全记录(十九):嵌入资源处理
1.前言 📝 在上一篇文章中,我们完成了书签的导入导出功能。本篇文章我们研究如何处理嵌入资源,方便后续将资源打包到一个可执行文件中。 2.embed介绍 🎯 Go 1.16 引入了革命性的 embed 包,彻底改变了静态资源管理的…...
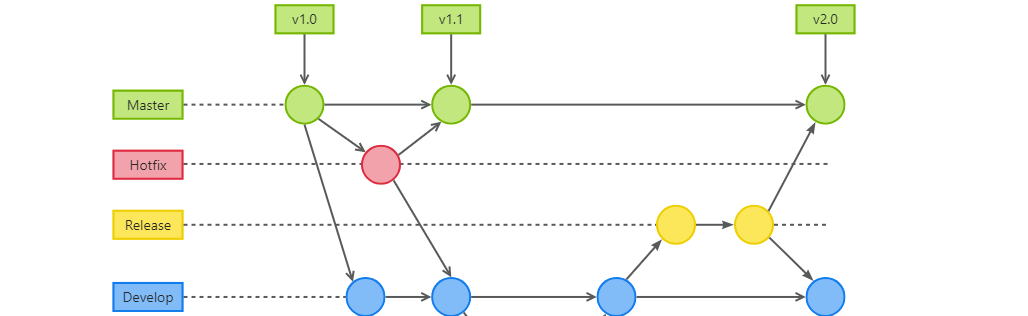
GitFlow 工作模式(详解)
今天再学项目的过程中遇到使用gitflow模式管理代码,因此进行学习并且发布关于gitflow的一些思考 Git与GitFlow模式 我们在写代码的时候通常会进行网上保存,无论是github还是gittee,都是一种基于git去保存代码的形式,这样保存代码…...
 Module Federation:Webpack.config.js文件中每个属性的含义解释)
MFE(微前端) Module Federation:Webpack.config.js文件中每个属性的含义解释
以Module Federation 插件详为例,Webpack.config.js它可能的配置和含义如下: 前言 Module Federation 的Webpack.config.js核心配置包括: name filename(定义应用标识) remotes(引用远程模块࿰…...
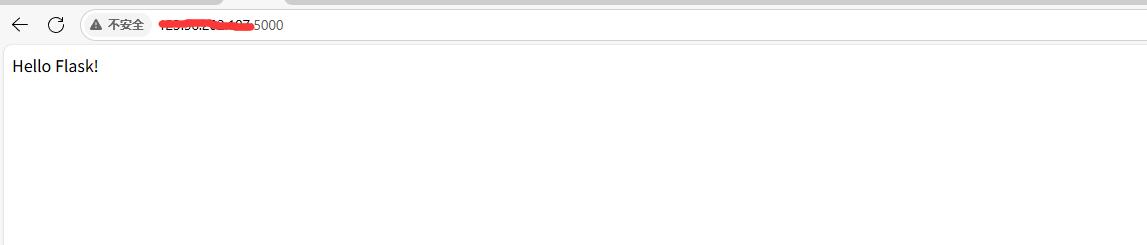
阿里云Ubuntu 22.04 64位搭建Flask流程(亲测)
cd /home 进入home盘 安装虚拟环境: 1、安装virtualenv pip install virtualenv 2.创建新的虚拟环境: virtualenv myenv 3、激活虚拟环境(激活环境可以在当前环境下安装包) source myenv/bin/activate 此时,终端…...
