用库造一个list的轮子 【C++】
文章目录
- list的模拟实现
- 默认成员函数
- 构造函数
- 拷贝构造函数
- 赋值运算符重载
- 析构函数
- 迭代器
- 迭代器为什么要存在?
- const_iterator
- begin和end
- insert
- erase
- push_back && pop_back
- push_front &&pop_front
- swap
- 完整代码
list的模拟实现
默认成员函数
构造函数
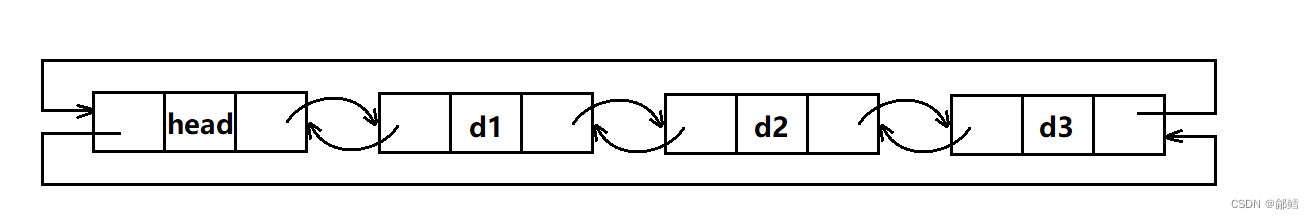
list是一个带头双向循环链表,在构造一个list对象时,new一个头结点,并让其prev和next都指向自己即可。
void empty_init(){_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;_size = 0;}//默认构造list(){empty_init();}
拷贝构造函数
//拷贝构造函数
list(const list<T>& lt)
{_head = new node; //申请一个头结点_head->_next = _head; //头结点的后继指针指向自己_head->_prev = _head; //头结点的前驱指针指向自己for (auto & e : lt) //两个 e都是同一个{push_back(e); //将容器lt当中的数据一个个尾插到新构造的容器后面}
}赋值运算符重载
版本一(推荐):
参数不使用引用,让编译器自动调用list的拷贝构造函数构造出来一个list对象,然后调用swap函数将原容器与该list对象进行交换
这样做相当于将应该用clear清理的数据,通过交换函数交给了容器lt,而当赋值运算符重载函数调用结束时,容器lt会自动销毁,并调用其析构函数进行清理。
list<T> & operator= (list<T> lt)//右值没有引用传参,间接调用拷贝构造//list<T>& operator= ( list<T> * this, list<T> lt)//右值没有引用传参,间接调用拷贝构造// lt1 = lt2{this->swap(lt);return *this; }
版本二:
先调用clear函数将原容器清空,然后将容器lt当中的数据,通过遍历的方式一个个尾插到清空后的容器当中即可。
list<T>& operator=(const list<T>& lt)
{if (this != <) //避免自己给自己赋值{clear(); //清空容器for (const auto& e : lt){push_back(e); //将容器lt当中的数据一个个尾插到链表后面}}return *this; //支持连续赋值
}析构函数
对对象进行析构时,首先调用clear函数清理容器当中的数据,然后将头结点释放,最后将头指针置空
void clear(){iterator it = begin();while (it!= end() ) {it = erase(it);}_size = 0;}~list(){clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}
迭代器
迭代器为什么要存在?
string 和vector的迭代器
string和vector将数据存储在一段连续的内存空间,那么可以通过指针进行自增、自减以及解引用等操作,就可以对相应位置的数据进行一系列操作,所以string和vector是天然的迭代器
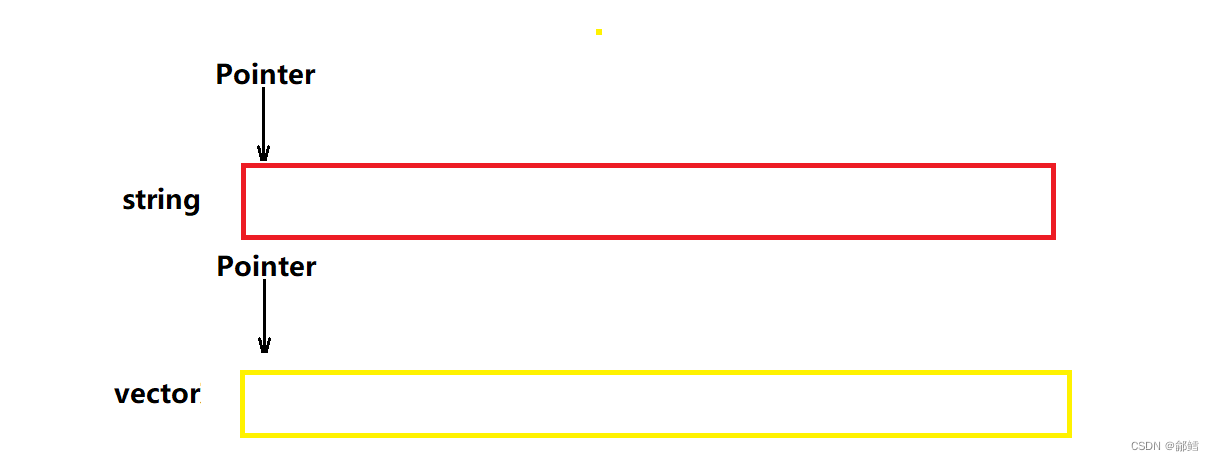

list的迭代器
list中各个结点在内存当中的位置是随机的,不一定是连续的,我们不能仅通过结点指针的自增、自减以及解引用等操作对相应结点的数据进行操作 ,采用类封装迭代器,在迭代器类的内部,重载 ++ 、 --、 *、 -> 、 !=、 == 这些迭代器会用到的运算符
const_iterator
在const迭代器中,const迭代器指向的内容不能被修改。也就是解引用返回的值不能被修改。迭代器本身是可以修改的,有两种解决方案 :
1 再封装一个const迭代器类
template< class T>//const 迭代器 ,让迭代器指向的内容不能修改, 迭代器本身可以修改struct __list_const_iterator{typedef list_node<T> Node;//构造函数__list_const_iterator(Node* node):_node(node){}const T& operator*()//出了作用域,节点的值还在,用引用//const: 返回节点的值,不能修改{return _node->_val;}//前置++,返回++之后的值__list_const_iterator& operator++()//__list_const_iterator& operator++(__list_const_iterator * this ){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}//后置++ ,返回++之前的值__list_const_iterator operator++(int){__list_const_iterator tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;// tmp出了作用域就被销毁 ,用传值返回 }bool operator==(const __list_iterator<T>& it){return *this == it._node;}bool operator!=(const __list_iterator<T>& it)//传值返回,返回的是拷贝,是一个临时对象,临时对象具有常性{return *this != it._node;}Node* _node;};
2 选择增加模板参数,复用代码(推荐)
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>

c++库就是用的这种解决方案
//template<class T> //list类存储的数据是任意类型,所以需要设置模板参数//普通迭代器//Ref是引用 ,Ptr是指针template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>struct __list_iterator{typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef __list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> self;//构造函数__list_iterator(Node* node):_node(node){}Ref operator*(){return _node->_val;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_val;}//前置++,返回++之后的值self & operator++()//__list_iterator<T> & operator++(__list_iterator<T> * this ){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}//后置++ ,返回++之前的值self operator++(int)// __list_iterator<T> operator++( __list_iterator<T> * this ,int){self tmp(*this);//拷贝构造_node = _node->_next;return tmp; // tmp出了作用域就被销毁 ,用传值返回 }bool operator!= (const self& it){return _node != it._node;}bool operator== (const self & it){return _node == it._node;}Node* _node;};template<class T>//list类存储的数据是任意类型,所以需要设置模板参数class list{typedef list_node<T> Node;public:typedef __list_iterator<T ,T&,T* > iterator;typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&, const T * > const_iterator;//迭代器 //能直接显示构造最好显式构造,不要把决定权给编译器进行单参数的隐式类型转换iterator end() //最后一个数据的下一个位置,即头节点{//return _head; // _head的类型是list_node<T>* ,iterator的类型是__list_iterator<T> ,类型不一致,涉及到单参数的构造函数支持隐式类型转换 //还可以写成 return iterator(_head);return iterator(_head);}iterator begin()//第一个数据的位置,即头节点的下一个位置{//return _head->_next;//单参数的构造函数支持隐式类型转换//还可以写成 return iterator(_head->_next)return iterator(_head->_next);}const_iterator begin() const{return const_iterator(_head->_next);}const_iterator end() const{return const_iterator(_head);}//默认构造list(){empty_init();}// lt2(lt1)//还没有实现const_iteratorlist(const list<T>& lt){empty_init();//拷贝数据for (auto & e :lt )//遍历lt{push_back(e);}}~list(){clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}void empty_init(){_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;_size = 0;}void swap(list<T> & lt){std:: swap(_head,lt._head );std::swap(_size, lt._size);}list<T> & operator= (list<T> lt)//右值没有引用传参,间接调用拷贝构造//list<T>& operator= ( list<T> * this, list<T> lt)//右值没有引用传参,间接调用拷贝构造// lt1 = lt2{this->swap(lt);return *this; }void clear(){iterator it = begin();while (it!= end() ) {it = erase(it);}_size = 0;}void push_back(const T& x){insert(end(), x);//在最后一个数据的下一个位置插入}//pos位置之前插入iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* newnode = new Node(x);// prev newnode cur 链接关系prev->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = prev;newnode->_next = cur;cur->_prev = newnode;++_size;return newnode;}iterator erase (iterator pos){assert(pos != end());Node* cur = pos._node;Node* next = cur->_next;Node* prev = cur->_prev;//prev next prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete cur;--_size;return next;}size_t size(){return _size;}void push_front( const T & x )//T可能是vector ,用引用,减少拷贝{insert(begin(),x);}void pop_back(){erase(--end());//end是最后一个数据的下一个位置,需要--,到达最后一个数据,这样才是尾删}void pop_front(){erase(begin());}private:Node* _head;size_t _size;};
当我们定义const对象时,会自动调用const修饰的迭代器。当调用const修饰的迭代器时,__list_iterator的模板参数就会实例化为const T&。实际上在实例化时,const和非const修饰的还是两个不同类,只不过是实例化的代码工作交给了编译器处理了。
begin和end
对于list,第一个有效数据的迭代器就是头结点后一个结点
begin函数返回的是第一个有效数据的迭代器,即头节点的下一个位置
end函数返回的是最后一个有效数据的下一个位置的迭代器,即头节点
iterator end() //最后一个数据的下一个位置,即头节点{return _head; // _head的类型是list_node<T>* ,iterator的类型是__list_iterator<T> ,类型不一致,涉及到单参数的构造函数支持隐式类型转换 //还可以写成 return iterator(_head);}iterator begin()//第一个数据的位置,即头节点的下一个位置{return _head->_next;//单参数的构造函数支持隐式类型转换//还可以写成 return iterator(_head->_next)}
const对象的begin函数和end函数
const_iterator begin() const{return const_iterator(_head->_next);//返回使用头结点后一个结点}const_iterator end() const{return const_iterator(_head);//返回使用头结点}insert
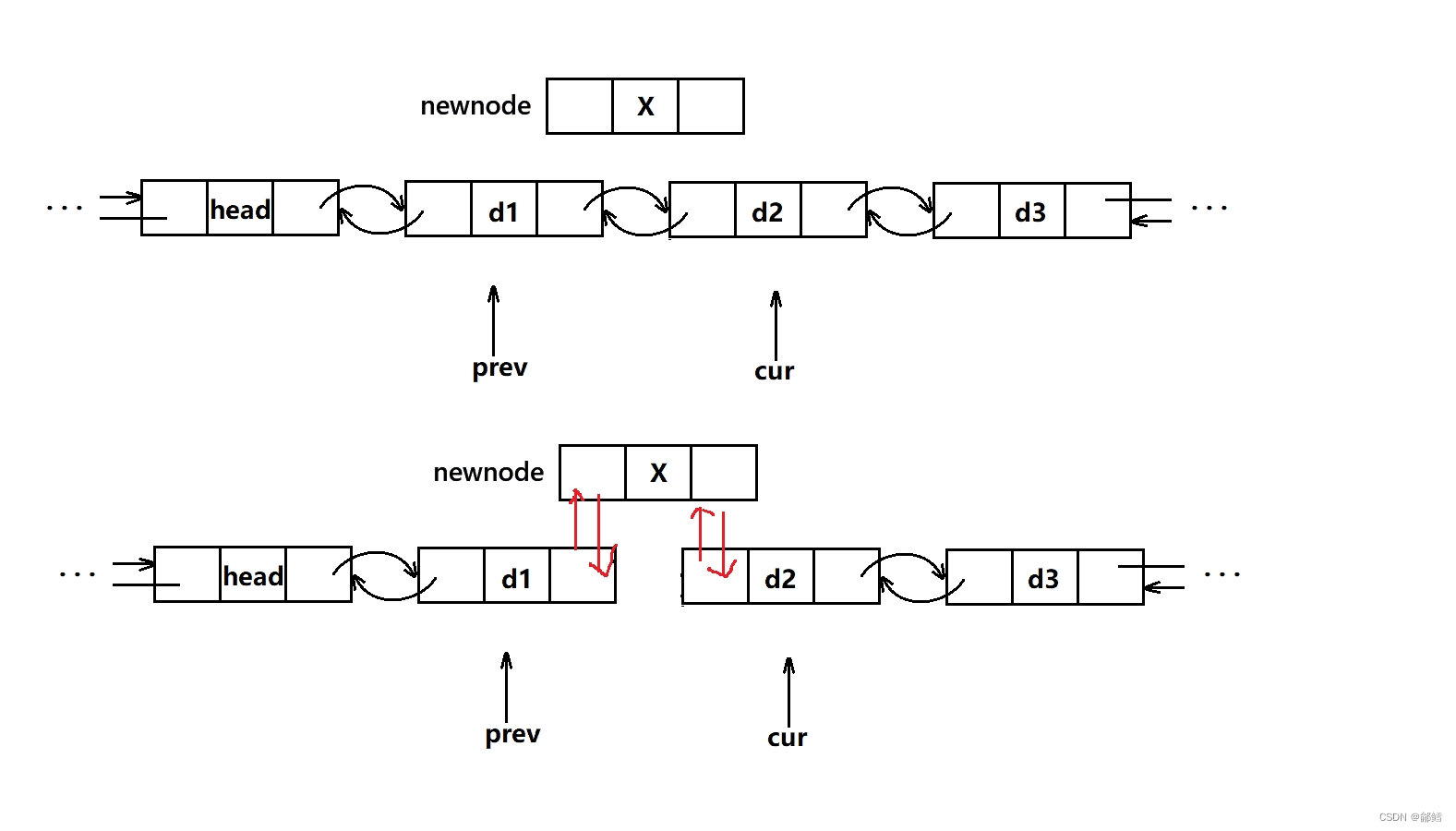
重新改变prev newnode cur 三者之间的链接关系
//pos位置之前插入iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* newnode = new Node(x);// prev newnode cur 链接关系prev->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = prev;newnode->_next = cur;cur->_prev = newnode;++_size;return newnode;}
erase
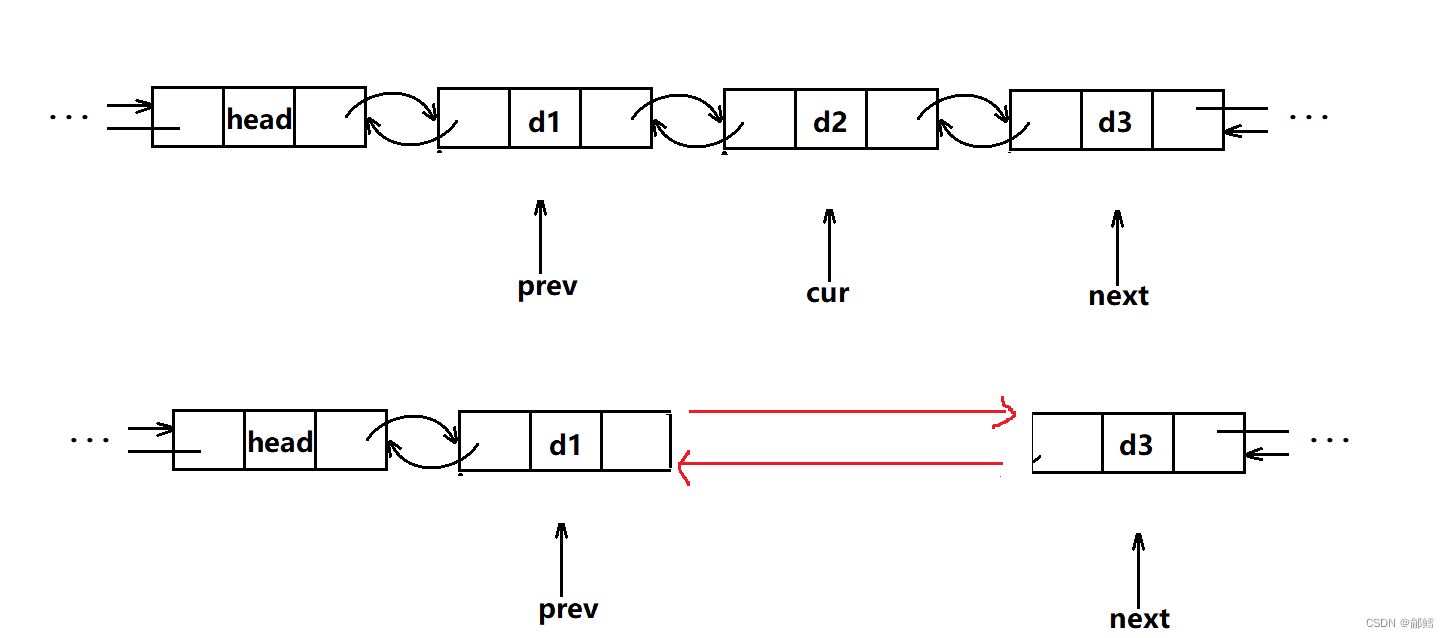
改变prev和next之间的链接关系,然后释放cur
iterator erase (iterator pos){assert(pos != end());Node* cur = pos._node;Node* next = cur->_next;Node* prev = cur->_prev;//prev next prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete cur ;--_size;return next;}
push_back && pop_back
void push_back(const T& x){insert(end(), x);//在最后一个数据的下一个位置插入}void pop_back(){erase(--end());//end是最后一个数据的下一个位置,需要--,到达最后一个数据,这样才是尾删}
push_front &&pop_front
void pop_front(){erase(begin());}void push_front( const T & x )//T可能是vector ,用引用,减少拷贝{insert(begin(),x);}
swap
swap函数用于交换两个容器,list容器当中存储的是链表的头指针和size,我们将这两个容器当中的头指针和size交换
void swap(list<T> & lt){std:: swap(_head,lt._head );std::swap(_size, lt._size);}
注意: 这里调用库里的swap模板函数,需要在swap函数之前加上“std::”,告诉编译器在c++标准库寻找swap函数,否则编译器编译时会认为你调用的是正在实现的swap函数(就近原则)
总结

完整代码
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
namespace cxq
{//list类存储的数据是任意类型,所以需要设置模板参数template<class T>//节点struct list_node{//构造函数list_node(const T& val = T()) //缺省值是匿名对象,c++对内置类型进行了升级:_prev(nullptr), _next(nullptr), _val(val){}list_node<T>* _prev;list_node<T>* _next;T _val;};//template<class T> //list类存储的数据是任意类型,所以需要设置模板参数//普通迭代器//Ref是引用 ,Ptr是指针template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>struct __list_iterator{typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef __list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> self;//构造函数__list_iterator(Node* node):_node(node){}Ref operator*(){return _node->_val;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_val;}//前置++,返回++之后的值self & operator++()//__list_iterator<T> & operator++(__list_iterator<T> * this ){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}//后置++ ,返回++之前的值self operator++(int)// __list_iterator<T> operator++( __list_iterator<T> * this ,int){self tmp(*this);//拷贝构造_node = _node->_next;return tmp; // tmp出了作用域就被销毁 ,用传值返回 }bool operator!= (const self& it){return _node != it._node;}bool operator== (const self & it){return _node == it._node;}Node* _node;};//template< class T>const 迭代器 ,让迭代器指向的内容不能修改, 迭代器本身可以修改//struct __list_const_iterator//{// typedef list_node<T> Node;// //构造函数// __list_const_iterator(Node* node)// :_node(node)// {// }// const T& operator*()//出了作用域,节点的值还在,用引用// //const: 返回节点的值,不能修改// {// return _node->_val;// }// //前置++,返回++之后的值// __list_const_iterator& operator++()// //__list_const_iterator& operator++(__list_const_iterator * this )// {// _node = _node->_next;// return *this;// }// //后置++ ,返回++之前的值// __list_const_iterator operator++(int)// {// __list_const_iterator tmp(*this);// _node = _node->_next;// return tmp;// tmp出了作用域就被销毁 ,用传值返回 // }// bool operator==(const __list_iterator<T>& it)// {// return *this == it._node;// }// bool operator!=(const __list_iterator<T>& it)//传值返回,返回的是拷贝,是一个临时对象,临时对象具有常性// {// return *this != it._node;// }// Node* _node;//};template<class T>//list类存储的数据是任意类型,所以需要设置模板参数class list{typedef list_node<T> Node;public:typedef __list_iterator<T ,T&,T* > iterator;//普通迭代器typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&, const T * > const_iterator;//const 迭代器//迭代器 //能直接显示构造最好显式构造,不要把决定权给编译器进行单参数的隐式类型转换iterator end() //最后一个数据的下一个位置,即头节点{//return _head; // _head的类型是list_node<T>* ,iterator的类型是__list_iterator<T> ,类型不一致,涉及到单参数的构造函数支持隐式类型转换 //还可以写成 return iterator(_head);return iterator(_head);}iterator begin()//第一个数据的位置,即头节点的下一个位置{//return _head->_next;//单参数的构造函数支持隐式类型转换//还可以写成 return iterator(_head->_next)return iterator(_head->_next);}const_iterator begin() const{return const_iterator(_head->_next);}const_iterator end() const{return const_iterator(_head);}//默认构造list(){empty_init();}// lt2(lt1)//还没有实现const_iteratorlist(const list<T>& lt){empty_init();//拷贝数据for (auto & e :lt )//遍历lt{push_back(e);}}~list(){clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}void empty_init(){_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;_size = 0;}void swap(list<T> & lt){std:: swap(_head,lt._head );std::swap(_size, lt._size);}list<T> & operator= (list<T> lt)//右值没有引用传参,间接调用拷贝构造//list<T>& operator= ( list<T> * this, list<T> lt)//右值没有引用传参,间接调用拷贝构造// lt1 = lt2{this->swap(lt);return *this; }void clear(){iterator it = begin();while (it!= end() ) {it = erase(it);}_size = 0;}void push_back(const T& x){找尾//Node* tail = _head->_prev;//Node* newnode = new Node(x);改变链接关系 ///*newnode = tail->next;*///tail->_next = newnode;//newnode->_prev = tail;//_head->_prev = newnode;//newnode->_next = _head;insert(end(), x);//在最后一个数据的下一个位置插入}//pos位置之前插入iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* newnode = new Node(x);// prev newnode cur 链接关系prev->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = prev;newnode->_next = cur;cur->_prev = newnode;++_size;return newnode;}iterator erase (iterator pos){assert(pos != end());Node* cur = pos._node;Node* next = cur->_next;Node* prev = cur->_prev;//prev next prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete cur;--_size;return next;}size_t size(){return _size;}void push_front( const T & x )//T可能是vector ,用引用,减少拷贝{insert(begin(),x);}void pop_back(){erase(--end());//end是最后一个数据的下一个位置,需要--,到达最后一个数据,这样才是尾删}void pop_front(){erase(begin());}private:Node* _head;size_t _size;};void test_list1(){list<int> lt1;lt1.push_back(1);lt1.push_back(2);list<int>::iterator it = lt1.begin();//拷贝构造while (it != lt1.end()){cout << *it << " ";it++;}cout << endl;}void test_list2(){list<int> lt1;lt1.push_back(1);lt1.push_back(2);list<int> lt2 (lt1);for (auto e : lt1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;}
}如果你觉得这篇文章对你有帮助,不妨动动手指给点赞收藏加转发,给鄃鳕一个大大的关注你们的每一次支持都将转化为我前进的动力!!!
相关文章:

用库造一个list的轮子 【C++】
文章目录 list的模拟实现默认成员函数构造函数拷贝构造函数赋值运算符重载析构函数 迭代器迭代器为什么要存在?const_iteratorbegin和end inserterasepush_back && pop_backpush_front &&pop_frontswap 完整代码 list的模拟实现 默认成员函数 构造…...

java中的,>>,<<位运算
目录 二进制 >>,<< & 二进制 计算机内部使用二进制计数 二进制:在数学和数字电路中指以2为基数的记数系统,以2为基数代表系统是二进位制的,这一系统中,通常用两个不同的符号0(代表零)和…...
成功解决Android设备adb连接后显示device unauthorized
一、提出问题 在电脑通过USB连接新的Android设备,想要通过adb来进行一些操作时,却发现命令提示符上在输入下面命令后显示设备未授权的信息也就是"unauthorized" adb devices二、不可行的解决方案 有人提出的解决方案是打开Android设备的开发…...

初识mysql数据库之引入mysql客户端库
目录 一、下载第三方库 1. 准备工作 1. 使用mysql官网提供的库 2. yum源安装 二、测试第三方库是否可用 三、mysql常用接口介绍 1. 查看官方文档 2. 初始化 3. 关闭mysql 4. 连接mysql 5. 下达sql指令 四、一个简单的C客户端库连接mysql程序 1. 头文件 2. 初始化…...
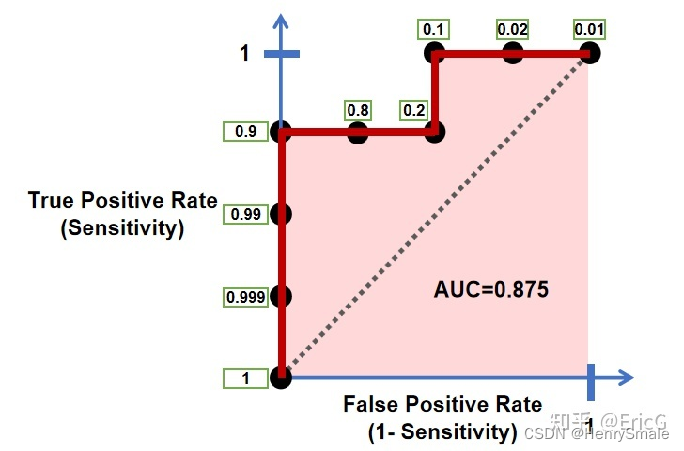
勘探开发人工智能技术:机器学习(1)
0 提纲 2.1 什么是机器学习 2.2 不确定性 2.3 数据类型 2.4 分类、回归、聚类 2.5 分类问题的训练与测试 2.6 性能评价指标 1 什么是机器学习 对于西瓜这个抽象类来说,它具有“色泽”,“根蒂”,“敲声”三个属性: 通过观察这个…...
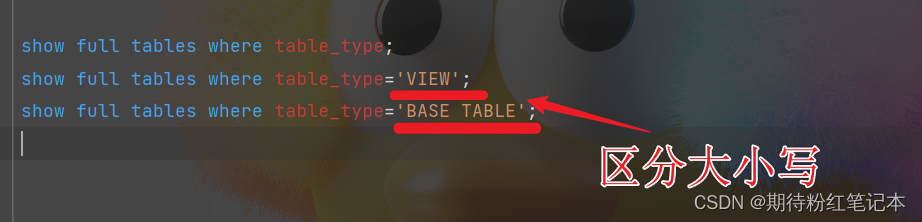
MySQL查看当前数据库视图-SQL语句
引言 查询语句为: show full tables where table_type 可查询当前数据库表 一,创建一个视图 # 创建视图 create view v_stu as # 视图内容(连接的一个表) select name from t_stu union all select tname from t_teach; 二&…...

Clickhouse 存储引擎
一、常用存储引擎分类 1.1 ReplacingMergeTree 这个引擎是在 MergeTree 的基础上,添加了”处理重复数据”的功能,该引擎和MergeTree的不同之处在于它会删除具有相同主键的重复项。 特点: 1使用ORDERBY排序键作为判断重复的唯一键 2.数据的去重只会在合并…...

基于golang多消息队列中间件的封装nsq,rabbitmq,kafka
基于golang多消息队列中间件的封装nsq,rabbitmq,kafka 场景 在创建个人的公共方法库中有这样一个需求,就是不同的项目会用到不同的消息队列中间件,我的思路把所有的消息队列中间件进行封装一个消息队列接口(MQer)有两个方法一个…...
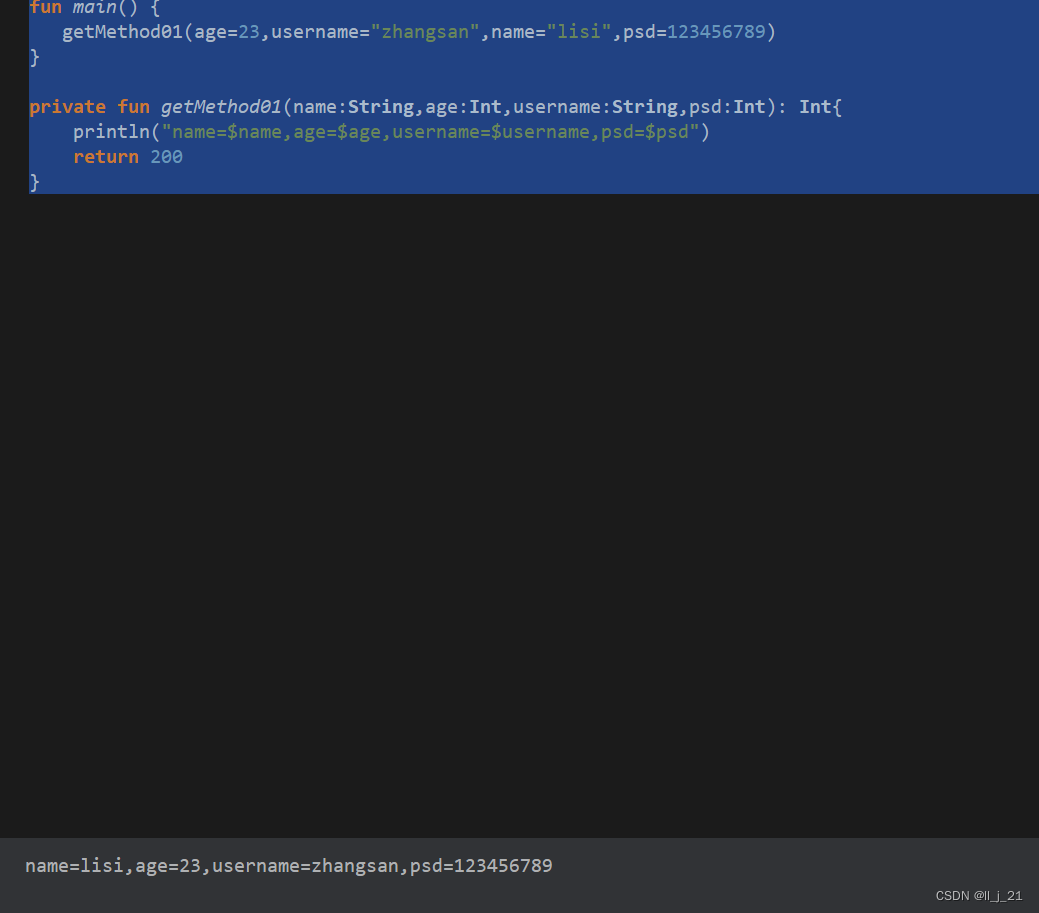
【第一阶段】kotlin的函数
函数头 fun main() {getMethod("zhangsan",22) }//kotlin语言默认是public,kotlin更规范,先有输入( getMethod(name:String,age:Int))再有输出(Int[返回值]) private fun getMethod(name:String,age:Int): Int{println("我叫…...

PAM安全配置-用户密码锁定策略
PAM是一个用于实现身份验证的模块化系统,可以在操作系统中的不同服务和应用程序中使用。 pam_faillock模块 pam_faillock模块用来实现账号锁定功能,它可以在一定的认证失败次数后锁定用户账号,防止暴力破解密码攻击。 常见选项 deny&…...

AndroidManifest.xml日常笔记
1 Bundle介绍 Bundle主要用于传递数据;它保存的数据,是以key-value(键值对)的形式存在的。 我们经常使用Bundle在Activity之间传递数据,传递的数据可以是boolean、byte、int、long、float、double、string等基本类型或它们对应的数组…...
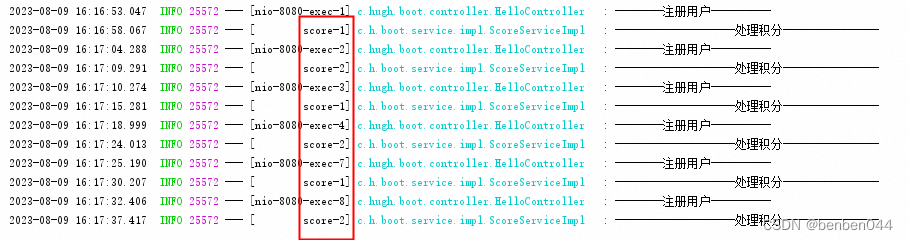
SpringBoot异步框架
参考:解剖SpringBoot异步线程池框架_哔哩哔哩_bilibili 1、 为什么要用异步框架,它解决什么问题? 在SpringBoot的日常开发中,一般都是同步调用的。但经常有特殊业务需要做异步来处理,例如:注册新用户&…...
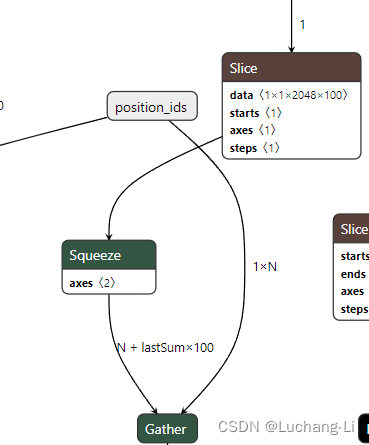
导出LLaMA ChatGlm2等LLM模型为onnx
通过onnx模型可以在支持onnx推理的推理引擎上进行推理,从而可以将LLM部署在更加广泛的平台上面。此外还可以具有避免pytorch依赖,获得更好的性能等优势。 这篇博客(大模型LLaMa及周边项目(二) - 知乎)进行…...

C++项目:在线五子棋对战网页版--匹配对战模块开发
玩家匹配是根据自己的天梯分数进行匹配的,而服务器中将玩家天梯分数分为三个档次: 1. 普通:天梯分数小于2000分 2. 高手:天梯分数介于2000~3000分之间 3. 大神:天梯分数大于3000分 当玩家进行对战匹配时,服…...
ssh 连接断开,正在执行的shell脚本也被中断了
背景 最近在训练chatGLM,一次训练经常要花掉近2个小时,但是由于网络不稳定,经常ssh莫名的断开,导致训练不得不重新开启,这就很浪费时间了 解决方案 下面教大家一种在后台执行命令的方案,即使你ssh连接断…...

UML 用例图,类图,时序图,活动图
UML之用例图,类图,时序图,活动图_用例图 时序图_siyan985的博客-CSDN博客 https://www.cnblogs.com/GumpYan/p/14734357.html 用例图与类图 - 简书...

Java 面试题2023
Java core JVM 1、JVM内存模型 2、JVM运行时内存分配 3、如何确定当前对象是个垃圾 4、GCrooot 包括哪些? 5、JVM对象头包含哪些部分 6、GC算法有哪些 7、JVM中类的加载机制 8、分代收集算法 9、JDK1.8 和 1.7做了哪些优化 10、内存泄漏和内存溢出有什么区别 11、J…...

【CSS3】CSS3 动画 ④ ( 使用动画制作地图热点图 )
文章目录 一、需求说明二、动画代码分析1、地图背景设置2、热点动画位置测量3、热点动画布局分析4、动画定义5、小圆点实现6、波纹效果盒子实现7、延迟动画设置 三、代码示例 一、需求说明 实现如下效果 , 在一张地图上 , 以某个位置为中心点 , 向四周发散 ; 核心 是实现 向四周…...
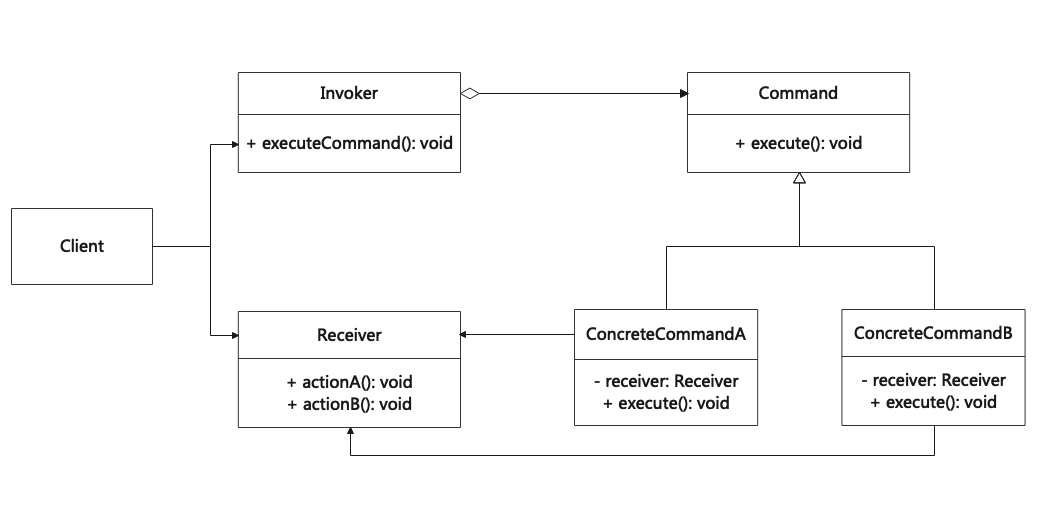
命令模式(Command)
命令模式是一种行为设计模式,可将一个请求封装为一个对象,用不同的请求将方法参数化,从而实现延迟请求执行或将其放入队列中或记录请求日志,以及支持可撤销操作。其别名为动作(Action)模式或事务(Transaction)模式。 Command is …...

Dapper 微型orm的光
介绍 Dapper是一个轻量级的ORM(对象关系映射)框架,它可以方便地将数据库查询结果映射到.NET对象上,同时也支持执行原生SQL查询。下面我将详细介绍Dapper的使用方法。 安装Dapper 首先,你需要通过NuGet包管理器将Dap…...
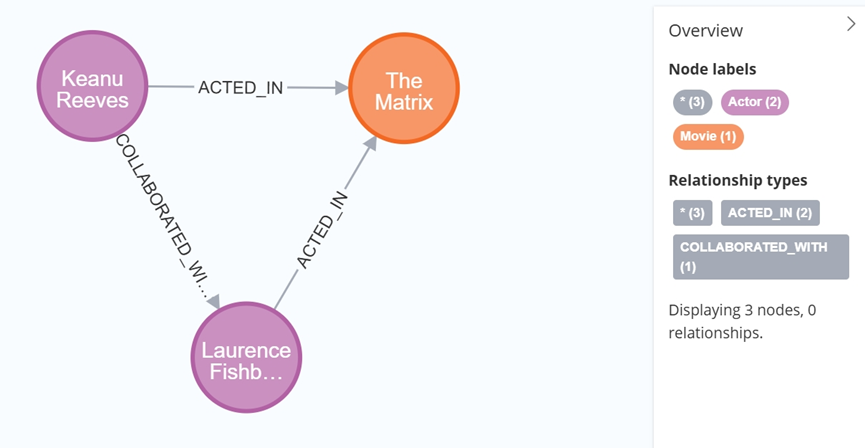
大数据学习栈记——Neo4j的安装与使用
本文介绍图数据库Neofj的安装与使用,操作系统:Ubuntu24.04,Neofj版本:2025.04.0。 Apt安装 Neofj可以进行官网安装:Neo4j Deployment Center - Graph Database & Analytics 我这里安装是添加软件源的方法 最新版…...

在鸿蒙HarmonyOS 5中实现抖音风格的点赞功能
下面我将详细介绍如何使用HarmonyOS SDK在HarmonyOS 5中实现类似抖音的点赞功能,包括动画效果、数据同步和交互优化。 1. 基础点赞功能实现 1.1 创建数据模型 // VideoModel.ets export class VideoModel {id: string "";title: string ""…...

在rocky linux 9.5上在线安装 docker
前面是指南,后面是日志 sudo dnf config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo sudo dnf install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io -y docker version sudo systemctl start docker sudo systemctl status docker …...

django filter 统计数量 按属性去重
在Django中,如果你想要根据某个属性对查询集进行去重并统计数量,你可以使用values()方法配合annotate()方法来实现。这里有两种常见的方法来完成这个需求: 方法1:使用annotate()和Count 假设你有一个模型Item,并且你想…...

【Oracle】分区表
个人主页:Guiat 归属专栏:Oracle 文章目录 1. 分区表基础概述1.1 分区表的概念与优势1.2 分区类型概览1.3 分区表的工作原理 2. 范围分区 (RANGE Partitioning)2.1 基础范围分区2.1.1 按日期范围分区2.1.2 按数值范围分区 2.2 间隔分区 (INTERVAL Partit…...

PAN/FPN
import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F import mathclass LowResQueryHighResKVAttention(nn.Module):"""方案 1: 低分辨率特征 (Query) 查询高分辨率特征 (Key, Value).输出分辨率与低分辨率输入相同。"""def __…...

处理vxe-table 表尾数据是单独一个接口,表格tableData数据更新后,需要点击两下,表尾才是正确的
修改bug思路: 分别把 tabledata 和 表尾相关数据 console.log() 发现 更新数据先后顺序不对 settimeout延迟查询表格接口 ——测试可行 升级↑:async await 等接口返回后再开始下一个接口查询 ________________________________________________________…...
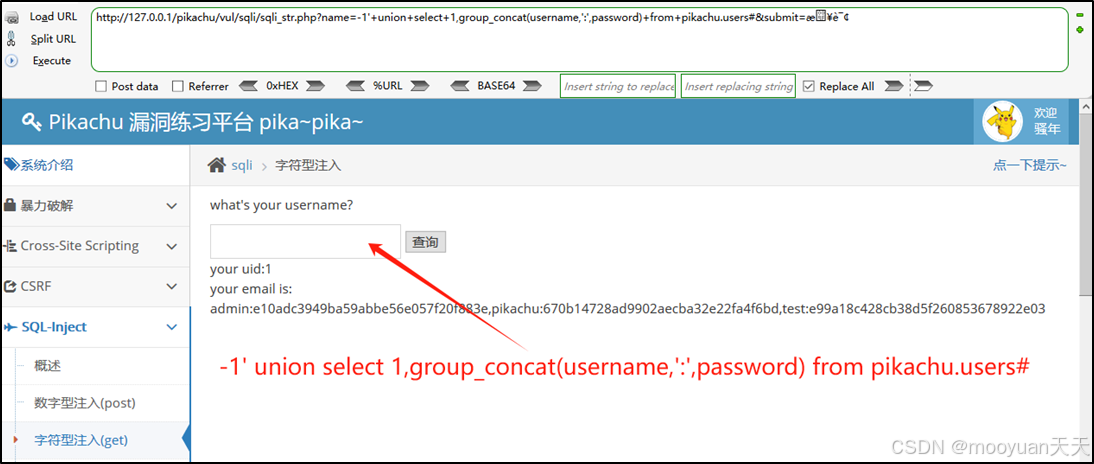
pikachu靶场通关笔记19 SQL注入02-字符型注入(GET)
目录 一、SQL注入 二、字符型SQL注入 三、字符型注入与数字型注入 四、源码分析 五、渗透实战 1、渗透准备 2、SQL注入探测 (1)输入单引号 (2)万能注入语句 3、获取回显列orderby 4、获取数据库名database 5、获取表名…...
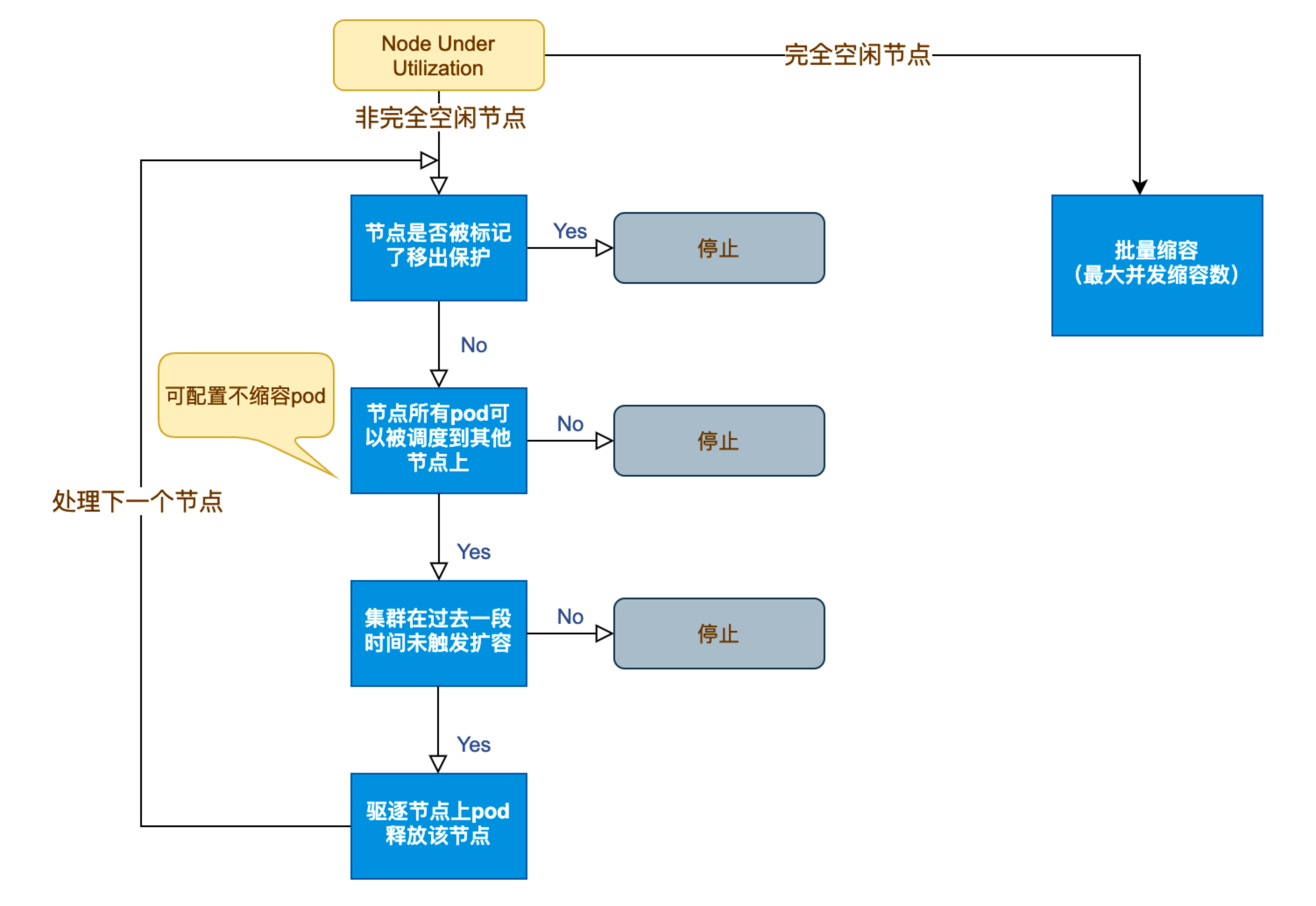
Kubernetes 节点自动伸缩(Cluster Autoscaler)原理与实践
在 Kubernetes 集群中,如何在保障应用高可用的同时有效地管理资源,一直是运维人员和开发者关注的重点。随着微服务架构的普及,集群内各个服务的负载波动日趋明显,传统的手动扩缩容方式已无法满足实时性和弹性需求。 Cluster Auto…...

flow_controllers
关键点: 流控制器类型: 同步(Sync):发布操作会阻塞,直到数据被确认发送。异步(Async):发布操作非阻塞,数据发送由后台线程处理。纯同步(PureSync…...
