ONNX版本YOLOV5-DeepSort (rknn版本已经Ready)
目录
1. 前言
2. 储备知识
3. 准备工作
4. 代码修改的地方
5.结果展示
1. 前言
之前一直在忙着写文档,之前一直做分类,检测和分割,现在看到跟踪算法,花了几天时间找代码调试,看了看,展示效果比单纯的检测要更加的炸裂一点。
2. 储备知识
DeepSORT(Deep Learning to Track Multi-Object in SORT)是一种基于深度学习的多目标跟踪算法,它结合了深度学习的目标检测和传统的轨迹跟踪方法,旨在实现在复杂场景中准确和稳定地跟踪多个移动目标。以下是关于DeepSORT的检测思想、特点和应用方面的介绍:
检测思想: DeepSORT的核心思想是结合深度学习目标检测和轨迹跟踪方法,以实现多目标跟踪。首先,利用深度学习目标检测模型(如YOLO、Faster R-CNN等)检测出每一帧图像中的所有目标物体,并提取其特征。然后,通过应用传统的轨迹跟踪算法(如卡尔曼滤波器和轨迹关联等),将目标在连续帧之间进行关联,从而生成每个目标的运动轨迹。
特点:
- 多目标跟踪: DeepSORT专注于同时跟踪多个目标,适用于需要同时监测和追踪多个物体的场景,如交通监控、人群管理等。
- 深度特征: 通过使用深度学习模型提取目标的特征,DeepSORT可以更准确地表示目标,从而提高跟踪的精度和鲁棒性。
- 轨迹关联: DeepSORT使用传统的轨迹关联技术来连接不同帧之间的目标,确保在物体出现、消失、重叠等情况下仍能准确跟踪。
- 实时性能: DeepSORT设计用于实时应用,可以在视频流中高效地进行目标跟踪,适用于要求实时性能的应用场景。
需要了解的算法内容:详细介绍
- 目前主流的目标跟踪算法都是基于Tracking-by-Detecton策略,即基于目标检测的结果来进行目标跟踪。DeepSORT运用的就是这个策略,上面的视频是DeepSORT对人群进行跟踪的结果,每个bbox左上角的数字是用来标识某个人的唯一ID号。
-
这里就有个问题,视频中不同时刻的同一个人,位置发生了变化,那么是如何关联上的呢?答案就是匈牙利算法和卡尔曼滤波。
匈牙利算法可以告诉我们当前帧的某个目标,是否与前一帧的某个目标相同。卡尔曼滤波可以基于目标前一时刻的位置,来预测当前时刻的位置,并且可以比传感器(在目标跟踪中即目标检测器,比如Yolo等)更准确的估计目标的位置。
3. 准备工作
基础代码:黄老师的github,参考的是这位博主的,我做了相应的修改
4. 代码修改的地方
具体需要修改的有两个py文件
(1) main.py文件,里面的检测器yolo用onnx做推理,onnx模型参考我的博文yolov5转rknn(聪明的你应该会的)
import cv2
import torch
import numpy as np
import onnxruntime as rtdef sigmoid(x):return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))def nms_boxes(boxes, scores):"""Suppress non-maximal boxes.# Argumentsboxes: ndarray, boxes of objects.scores: ndarray, scores of objects.# Returnskeep: ndarray, index of effective boxes."""x = boxes[:, 0]y = boxes[:, 1]w = boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0]h = boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1]areas = w * horder = scores.argsort()[::-1]keep = []while order.size > 0:i = order[0]keep.append(i)xx1 = np.maximum(x[i], x[order[1:]])yy1 = np.maximum(y[i], y[order[1:]])xx2 = np.minimum(x[i] + w[i], x[order[1:]] + w[order[1:]])yy2 = np.minimum(y[i] + h[i], y[order[1:]] + h[order[1:]])w1 = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 0.00001)h1 = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 0.00001)inter = w1 * h1ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter)inds = np.where(ovr <= 0.45)[0]order = order[inds + 1]keep = np.array(keep)return keepdef process(input, mask, anchors):anchors = [anchors[i] for i in mask]grid_h, grid_w = map(int, input.shape[0:2])box_confidence = sigmoid(input[..., 4])box_confidence = np.expand_dims(box_confidence, axis=-1)box_class_probs = sigmoid(input[..., 5:])box_xy = sigmoid(input[..., :2])*2 - 0.5col = np.tile(np.arange(0, grid_w), grid_w).reshape(-1, grid_w)row = np.tile(np.arange(0, grid_h).reshape(-1, 1), grid_h)col = col.reshape(grid_h, grid_w, 1, 1).repeat(3, axis=-2)row = row.reshape(grid_h, grid_w, 1, 1).repeat(3, axis=-2)grid = np.concatenate((col, row), axis=-1)box_xy += gridbox_xy *= int(img_size/grid_h)box_wh = pow(sigmoid(input[..., 2:4])*2, 2)box_wh = box_wh * anchorsbox = np.concatenate((box_xy, box_wh), axis=-1)return box, box_confidence, box_class_probsdef filter_boxes(boxes, box_confidences, box_class_probs):"""Filter boxes with box threshold. It's a bit different with origin yolov5 post process!# Argumentsboxes: ndarray, boxes of objects.box_confidences: ndarray, confidences of objects.box_class_probs: ndarray, class_probs of objects.# Returnsboxes: ndarray, filtered boxes.classes: ndarray, classes for boxes.scores: ndarray, scores for boxes."""box_classes = np.argmax(box_class_probs, axis=-1)box_class_scores = np.max(box_class_probs, axis=-1)pos = np.where(box_confidences[..., 0] >= 0.5)boxes = boxes[pos]classes = box_classes[pos]scores = box_class_scores[pos]return boxes, classes, scoresdef yolov5_post_process(input_data):masks = [[0, 1, 2], [3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8]]anchors = [[10, 13], [16, 30], [33, 23], [30, 61], [62, 45],[59, 119], [116, 90], [156, 198], [373, 326]]boxes, classes, scores = [], [], []for input,mask in zip(input_data, masks):b, c, s = process(input, mask, anchors)b, c, s = filter_boxes(b, c, s)boxes.append(b)classes.append(c)scores.append(s)boxes = np.concatenate(boxes)boxes = xywh2xyxy(boxes)classes = np.concatenate(classes)scores = np.concatenate(scores)nboxes, nclasses, nscores = [], [], []for c in set(classes):inds = np.where(classes == c)b = boxes[inds]c = classes[inds]s = scores[inds]keep = nms_boxes(b, s)nboxes.append(b[keep])nclasses.append(c[keep])nscores.append(s[keep])if not nclasses and not nscores:return None, None, Noneboxes = np.concatenate(nboxes)classes = np.concatenate(nclasses)scores = np.concatenate(nscores)return boxes, classes, scoresdef letterbox(img, new_shape=(640, 640), color=(114, 114, 114), auto=True, scaleFill=False, scaleup=True, stride=32):# Resize and pad image while meeting stride-multiple constraintsshape = img.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]if isinstance(new_shape, int):new_shape = (new_shape, new_shape)# Scale ratio (new / old)r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])if not scaleup: # only scale down, do not scale up (for better test mAP)r = min(r, 1.0)# Compute paddingratio = r, r # width, height ratiosnew_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))dw, dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1] # wh paddingif auto: # minimum rectangledw, dh = np.mod(dw, stride), np.mod(dh, stride) # wh paddingelif scaleFill: # stretchdw, dh = 0.0, 0.0new_unpad = (new_shape[1], new_shape[0])ratio = new_shape[1] / shape[1], new_shape[0] / shape[0] # width, height ratiosdw /= 2 # divide padding into 2 sidesdh /= 2if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resizeimg = cv2.resize(img, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))img = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color) # add borderreturn img, ratio, (dw, dh)def clip_coords(boxes, img_shape):# Clip bounding xyxy bounding boxes to image shape (height, width)boxes[:, 0].clamp_(0, img_shape[1]) # x1boxes[:, 1].clamp_(0, img_shape[0]) # y1boxes[:, 2].clamp_(0, img_shape[1]) # x2boxes[:, 3].clamp_(0, img_shape[0]) # y2def xywh2xyxy(x):# Convert nx4 boxes from [x, y, w, h] to [x1, y1, x2, y2] where xy1=top-left, xy2=bottom-righty = x.clone() if isinstance(x, torch.Tensor) else np.copy(x)y[:, 0] = x[:, 0] - x[:, 2] / 2 # top left xy[:, 1] = x[:, 1] - x[:, 3] / 2 # top left yy[:, 2] = x[:, 0] + x[:, 2] / 2 # bottom right xy[:, 3] = x[:, 1] + x[:, 3] / 2 # bottom right yreturn yCLASSES = ['person', 'bicycle', 'car', 'motorcycle', 'airplane', 'bus', 'train', 'truck', 'boat', 'traffic light','fire hydrant', 'stop sign', 'parking meter', 'bench', 'bird', 'cat', 'dog', 'horse', 'sheep', 'cow','elephant', 'bear', 'zebra', 'giraffe', 'backpack', 'umbrella', 'handbag', 'tie', 'suitcase', 'frisbee','skis', 'snowboard', 'sports ball', 'kite', 'baseball bat', 'baseball glove', 'skateboard', 'surfboard','tennis racket', 'bottle', 'wine glass', 'cup', 'fork', 'knife', 'spoon', 'bowl', 'banana', 'apple', 'sandwich','orange', 'broccoli', 'carrot', 'hot dog', 'pizza', 'donut', 'cake', 'chair', 'couch', 'potted plant', 'bed','dining table', 'toilet', 'tv', 'laptop', 'mouse', 'remote', 'keyboard', 'cell phone', 'microwave', 'oven', 'toaster', 'sink','refrigerator', 'book', 'clock', 'vase', 'scissors', 'teddy bear', 'hair drier', 'toothbrush']def preprocess(img, img_size):img0 = img.copy()img = letterbox(img, new_shape=img_size)[0]img = img[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1)img = np.ascontiguousarray(img).astype(np.float32)img = torch.from_numpy(img)img /= 255.0if img.ndimension() == 3:img = img.unsqueeze(0)return img0, imgdef draw(image, boxes, scores, classes):"""Draw the boxes on the image.# Argument:image: original image.boxes: ndarray, boxes of objects.classes: ndarray, classes of objects.scores: ndarray, scores of objects.all_classes: all classes name."""for box, score, cl in zip(boxes, scores, classes):top, left, right, bottom = box# print('class: {}, score: {}'.format(CLASSES[cl], score))# print('box coordinate left,top,right,down: [{}, {}, {}, {}]'.format(top, left, right, bottom))top = int(top)left = int(left)right = int(right)bottom = int(bottom)cv2.rectangle(image, (top, left), (right, bottom), (255, 0, 0), 2)cv2.putText(image, '{0} {1:.2f}'.format(CLASSES[cl], score),(top, left - 6),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,0.6, (0, 0, 255), 2)def detect(im, img_size, sess, input_name, outputs_name):im0, img = preprocess(im, img_size)input_data = onnx_inference(img.numpy(), sess, input_name, outputs_name)boxes, classes, scores = yolov5_post_process(input_data)if boxes is not None:draw(im, boxes, scores, classes)cv2.imshow('demo', im)cv2.waitKey(1)def onnx_inference(img, sess, input_name, outputs_name):# 模型推理:模型输出节点名,模型输入节点名,输入数据(注意节点名的格式!!!!!)outputs = sess.run(outputs_name, {input_name: img})input0_data = outputs[0]input1_data = outputs[1]input2_data = outputs[2]input0_data = input0_data.reshape([3, 80, 80, 85])input1_data = input1_data.reshape([3, 40, 40, 85])input2_data = input2_data.reshape([3, 20, 20, 85])input_data = list()input_data.append(np.transpose(input0_data, (1, 2, 0, 3)))input_data.append(np.transpose(input1_data, (1, 2, 0, 3)))input_data.append(np.transpose(input2_data, (1, 2, 0, 3)))return input_datadef load_onnx_model():# onnx模型前向推理sess = rt.InferenceSession('./weights/modified_yolov5s.onnx')# 模型的输入和输出节点名,可以通过netron查看input_name = 'images'outputs_name = ['396', '440', '484']return sess, input_name, outputs_nameif __name__ == '__main__':# create onnx_modelsess, input_name, outputs_name = load_onnx_model()# input_model_sizeimg_size = 640# read videovideo = cv2.VideoCapture('./video/cut3.avi')print("Loaded video ...")frame_interval = 2 # 间隔帧数,例如每隔10帧获取一次frame_count = 0while True:# 读取每帧图片_, im = video.read()if frame_count % frame_interval == 0:if im is None:break# 缩小尺寸,1920x1080->960x540im = cv2.resize(im, (640, 640))list_bboxs = []# det_objectdetect(im, img_size, sess, input_name, outputs_name)frame_count += 1video.release()cv2.destroyAllWindows()(2) feature_extractor.py的修改:
这里有4种推理情况:ckpt.t7是ReID( Re-identification利用算法),在图像库中找到要搜索的目标的技术,所以它是属于图像检索的一个子问题。
(1) 动态的batch_size推理:由于检测到的目标是多个object,在本项目的代码REID推理中,会将目标通过torch.cat连接起来,变成(n, 64, 128)的形状,所以需要用动态的onnx模型
(2)那我就想要静态的怎么办,安排!!!,思路就是将cat的拆分开就行了,shape变成(1, 64 , 128),单个推理后将结果cat起来就行了,easy的。
重要!!!!ckpt文件转onnx的代码
import os
import cv2
import time
import argparse
import torch
import numpy as np
from deep_sort import build_tracker
from utils.draw import draw_boxes
from utils.parser import get_config
from tqdm import tqdmif __name__ == '__main__':parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()parser.add_argument("--config_deepsort", type=str, default="./configs/deep_sort.yaml", help='Configure tracker')parser.add_argument("--cpu", dest="use_cuda", action="store_false", default=True, help='Run in CPU')args = parser.parse_args()cfg = get_config()cfg.merge_from_file(args.config_deepsort)use_cuda = args.use_cuda and torch.cuda.is_available()torch.set_grad_enabled(False)model = build_tracker(cfg, use_cuda=False)model.reid = Truemodel.extractor.net.eval()device = 'cpu'output_onnx = 'deepsort.onnx'# ------------------------ export -----------------------------print("==> Exporting model to ONNX format at '{}'".format(output_onnx))input_names = ['input']output_names = ['output']input_tensor = torch.randn(1, 3, 128, 64, device=device)torch.onnx.export(model.extractor.net, input_tensor, output_onnx, export_params=True, verbose=False,input_names=input_names, output_names=output_names, opset_version=13,do_constant_folding=True)
(3)但是要转rknn怎么办,ckpt.t7转onnx后,有一个ReduceL2,不支持量化,我就转的fp16(在RK3588上是可以的,rk1808不知道行不行),不过我尝试了将最后两个节点删除,对结果好像没有什么影响(用的是cut后的onnx推理),有懂的朋友可以解释一下!!!
(4) 就是rknn的推理,这里就不展示了,需要的私聊我吧
import torch
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import numpy as np
import cv2
# import onnxruntime as rt
# from rknnlite.api import RKNNLiteclass Extractor(object):def __init__(self, model_path):self.model_path = model_pathself.device = "cpu"self.size = (64, 128)self.norm = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor(),transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]),])def _preprocess(self, im_crops):"""TODO:1. to float with scale from 0 to 12. resize to (64, 128) as Market1501 dataset did3. concatenate to a numpy array3. to torch Tensor4. normalize"""def _resize(im, size):return cv2.resize(im.astype(np.float32) / 255., size)im_batch = torch.cat([self.norm(_resize(im, self.size)).unsqueeze(0) for im in im_crops], dim=0).float()return im_batchdef __call__(self, im_crops):im_batch = self._preprocess(im_crops)# sess = rt.InferenceSession(self.model_path)# 模型的输入和输出节点名,可以通过netron查看# input_name = 'input'# outputs_name = ['output']# (1)动态输出# features = sess.run(outputs_name, {input_name: im_batch.numpy()})# print('features:', np.array(features)[0, :, :].shape)# return np.array(features)[0, :, :]# (2)静态态输出# sort_results = []# n = im_batch.numpy().shape[0]# for i in range(n):# img = im_batch.numpy()[i, :, :].reshape(1, 3, 128, 64)# feature = sess.run(outputs_name, {input_name: img})# feature = np.array(feature)# sort_results.append(feature)# features = np.concatenate(sort_results, axis=1)[0, :, :]# print(features.shape)# return np.array(features)# (3)去掉onnx的最后两个节点的静态模型输出# input_name = 'input'# outputs_name = ['204']# sort_results = []# n = im_batch.numpy().shape[0]# for i in range(n):# img = im_batch.numpy()[i, :, :].reshape(1, 3, 128, 64)# feature = sess.run(outputs_name, {input_name: img})# feature = np.array(feature)# sort_results.append(feature)# features = np.concatenate(sort_results, axis=1)[0, :, :]# print(features.shape)# return np.array(features)# (4 )rk模型修改# rknn_lite = RKNNLite()# rknn_lite.load_rknn('./weights/ckpt_fp16.rknn')# ret = rknn_lite.init_runtime(core_mask=RKNNLite.NPU_CORE_0_1_2)# if ret != 0:# print('Init runtime environment failed')# exit(ret)# print('done')# sort_results = []# n = im_batch.numpy().shape[0]# for i in range(n):# img = im_batch.numpy()[i, :, :].reshape(1, 3, 128, 64)# feature = self.model_path.inference(inputs=[img])# feature = np.array(feature)# sort_results.append(feature)# features = np.concatenate(sort_results, axis=1)[0, :, :]# print(features.shape)# return np.array(features)5.结果展示
onnx的转换结果(测试视频地址)
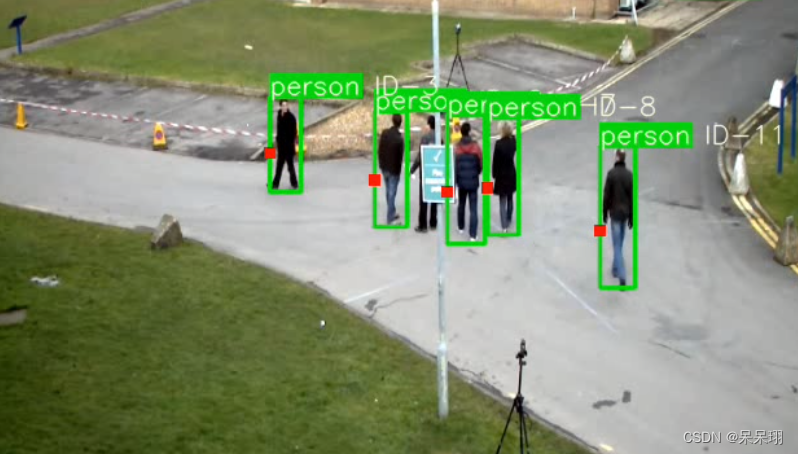


检测结果
相关文章:

ONNX版本YOLOV5-DeepSort (rknn版本已经Ready)
目录 1. 前言 2. 储备知识 3. 准备工作 4. 代码修改的地方 5.结果展示 1. 前言 之前一直在忙着写文档,之前一直做分类,检测和分割,现在看到跟踪算法,花了几天时间找代码调试,看了看,展示效果比单纯的检…...

MySQL的约束
文章目录 1、约束的概念2、约束的分类2.1 主键约束2.1.1 概念2.1.2 主键操作 2.2 自增约束2.2.1 概念2.2.2 自增操作 2.3 唯一约束2.3.1 概念2.3.2 唯一操作 2.4 非空约束2.4.1 概念2.4.2 非空操作 2.5 默认约束2.5.1 概念2.5.2 默认操作 2.6 外键约束2.6.1 概念2.6.2 外键操作…...

Lnton羚通关于【PyTorch】教程:torchvision 目标检测微调
torchvision 目标检测微调 本教程将使用Penn-Fudan Database for Pedestrian Detection and Segmentation 微调 预训练的Mask R-CNN 模型。 它包含 170 张图片,345 个行人实例。 定义数据集 用于训练目标检测、实例分割和人物关键点检测的参考脚本允许轻松支持添加…...

AMD fTPM RNG的BUG使得Linus Torvalds不满
导读因为在 Ryzen 系统上对内核造成了困扰,Linus Torvalds 最近在邮件列表中表达了对 AMD fTPM 硬件随机数生成器的不满,并提出了禁用该功能的建议。 因为在 Ryzen 系统上对内核造成了困扰,Linus Torvalds 最近在邮件列表中表达了对 AMD fTPM…...
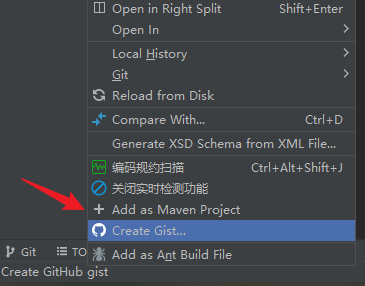
idea 转换为 Maven Project 的方法
选项: Add as Maven Project...

es1.7.2 按照_type先聚合,再按照时间二次聚合
// 设置查询条件if (this.query ! null) {this.searchbuilder.setQuery(this.query);}TermsBuilder typeAggregation AggregationBuilders.terms("agg_type").field("_type");DateHistogramBuilder dateTermsBuilder AggregationBuilders.dateHistogram(…...

pyqt5 如何修改QplainTextEdit 背景色和主窗口的一样颜色
如果您希望将 QPlainTextEdit 的背景颜色设置为与窗口背景相似的灰色,您可以使用窗口的背景颜色作为基准来设置 QPlainTextEdit 的背景颜色。以下是一个示例代码,展示如何实现这一点: from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindo…...

解决使用element ui时el-input的属性type=number,仍然可以输入e的问题。
使用element ui时el-input的属性typenumber,仍然可以输入e, 其他的中文特殊字符都不可以输入,但是只有e是可以输入的,原因是e也输入作为科学计数法的时候,e是可以被判定为数字的, 但是有些场景是需要把e这种…...
ShardingSphere 可观测 SQL 指标监控
ShardingSphere并不负责如何采集、存储以及展示应用性能监控的相关数据,而是将SQL解析与SQL执行这两块数据分片的最核心的相关信息发送至应用性能监控系统,并交由其处理。 换句话说,ShardingSphere仅负责产生具有价值的数据,并通过…...

Redisson实现分布式锁示例
一、引入依赖 <dependency><groupId>org.redisson</groupId><artifactId>redisson</artifactId><version>3.16.0</version></dependency>二、配置类 import org.redisson.Redisson; import org.redisson.api.RedissonClient;…...

使用Nginx作为一个普通代理服务器
使用Nginx作为一个普通代理服务器, 请不要用于违法用途哦 nginx作为一个反向代理工具,除了可以进行反向代理之外,还可以用来作为代理工具来使用,作为代理工具使用的步骤如下,这个配置目前支持80端口 Windows系统代理设置对应IP, …...
chatglm2-6b模型在9n-triton中部署并集成至langchain实践 | 京东云技术团队
一.前言 近期, ChatGLM-6B 的第二代版本ChatGLM2-6B已经正式发布,引入了如下新特性: ①. 基座模型升级,性能更强大,在中文C-Eval榜单中,以51.7分位列第6; ②. 支持8K-32k的上下文;…...

Shell编程之正则表达式(非常详细)
正则表达式 1.通配符和正则表达式的区别2.基本正则表达式2.1 元字符 (字符匹配)2.2 表示匹配次数2.4 位置锚定2.5 分组 和 或者 3.扩展正则表达式4.部分文本处理工具4.1 tr 命令4.2 cut命令4.3 sort命令4.4 uniq命令 1.通配符和正则表达式的区别 通配符一般用于文件…...
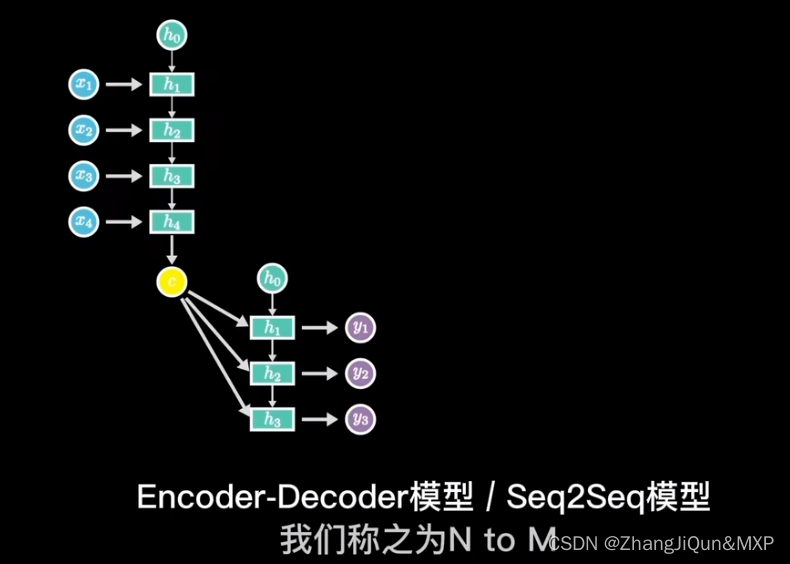
RNN模型简单理解和CNN区别
目录 神经网络:水平方向延伸,数据不具有关联性 RNN:在神经网络的基础上加上了时间顺序,语义理解 RNN: 训练中采用梯度下降,反向传播 长短期记忆模型 输出关系:1 toN,N to N 单入…...
【Axure高保真原型】JS日期选择器筛选中继器表格
今天和大家分享JS日期选择器筛选中继器表格的原型模板,通过调用浏览器的日期选择器,所以可以获取真实的日历效果,具体包括哪一年二月份有29天,几号对应星期几,都是真实的,获取日期值后,通过交互…...

android bp脚本
一。android大约从7.0开始引入 .bp文件代替以前的.mk文件,用于帮助android项目的编译配置文件。 二。mk文件转化为bp文件,可以使用下面命令转化,注意命令中>,这是写入文件。androidmk是android源码自带的工具,他可…...
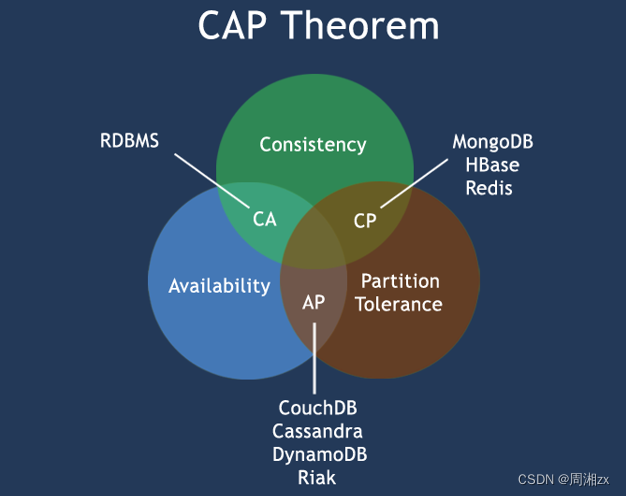
Redis 数据库 NoSQL
目录 一、NoSQL 二、为什么会出现NoSQL技术 三、NoSQL的类别 键值(Key-Value)存储数据库 列存储数据库 文档型数据库 图形(Graph)数据库 四、NoSQL适应场景 五、在分布式数据库中CAP原理 1、CAP 2、BASE 一、NoSQL NoS…...

RN 项目异常问题整理
常见问题 无法找到 CardStackStyleInterpolator StackViewStyleInterpolator 这个方法集来代替 CardStackStyleInterpolator的,这个方法集的路径也需要注意一下,在2.12.1版本之前, 该文件在react-navigation/src/views/StackView/中…...
STM8编程[TIM1多路PWM输出选项字节(Option Byte)操作和IO复用]
TIM1多路PWM输出选项字节(Option Byte)操作和IO复用 本文摘录于:https://blog.csdn.net/freeape/article/details/47008033只是做学习备份之用,绝无抄袭之意,有疑惑请联系本人! 代码上要使用TIME1输出3路PWM,代码如下: void tim…...
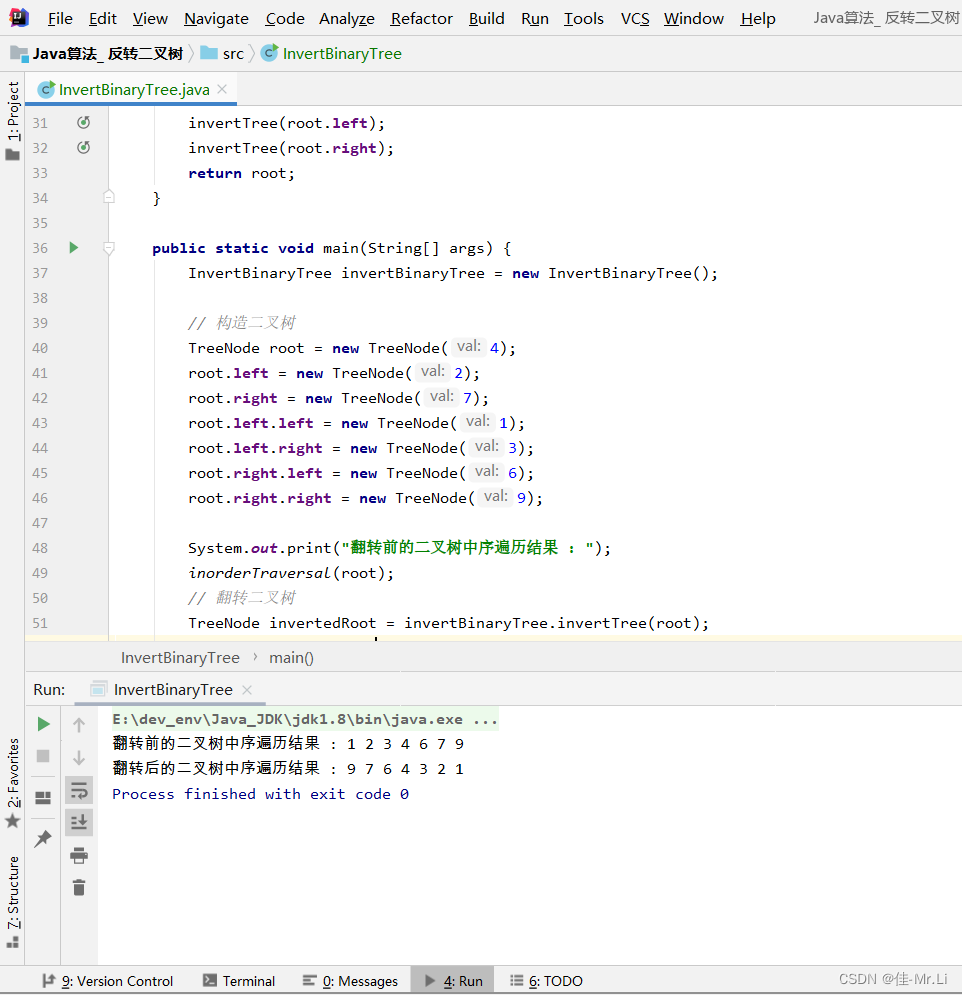
Java算法_ 反转二叉树(LeetCode_Hot100)
题目描述:给你一棵二叉树的根节点 ,翻转这棵二叉树,并返回其根节点。root。 获得更多?算法思路:代码文档,算法解析的私得。 运行效果 完整代码 /*** 2 * Author: LJJ* 3 * Date: 2023/8/16 13:18* 4*/public class In…...
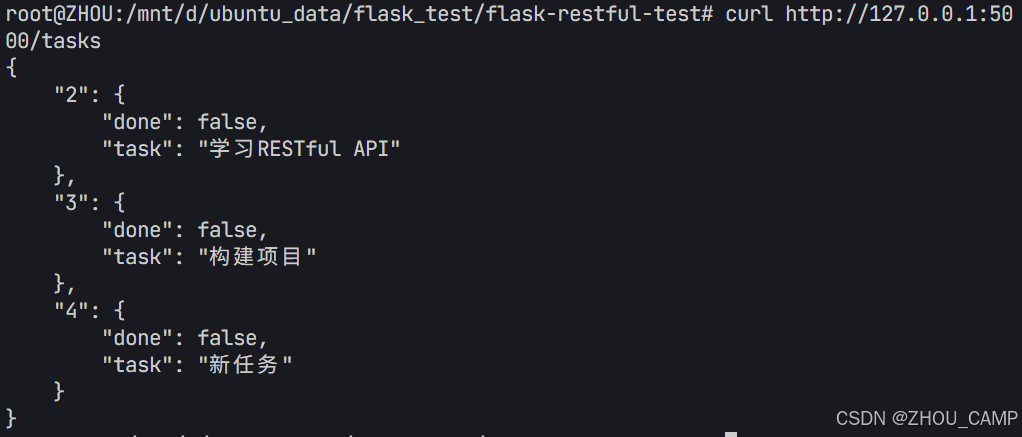
Flask RESTful 示例
目录 1. 环境准备2. 安装依赖3. 修改main.py4. 运行应用5. API使用示例获取所有任务获取单个任务创建新任务更新任务删除任务 中文乱码问题: 下面创建一个简单的Flask RESTful API示例。首先,我们需要创建环境,安装必要的依赖,然后…...
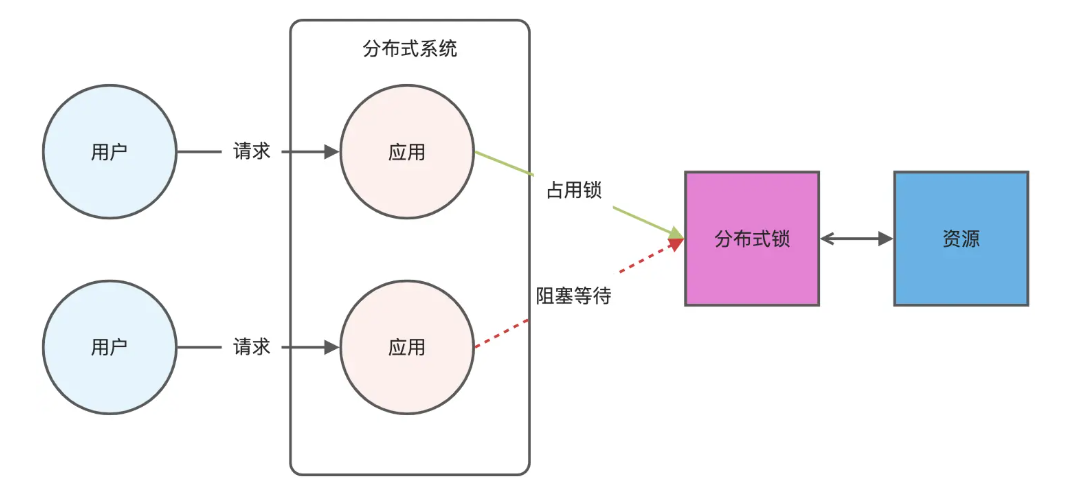
Redis相关知识总结(缓存雪崩,缓存穿透,缓存击穿,Redis实现分布式锁,如何保持数据库和缓存一致)
文章目录 1.什么是Redis?2.为什么要使用redis作为mysql的缓存?3.什么是缓存雪崩、缓存穿透、缓存击穿?3.1缓存雪崩3.1.1 大量缓存同时过期3.1.2 Redis宕机 3.2 缓存击穿3.3 缓存穿透3.4 总结 4. 数据库和缓存如何保持一致性5. Redis实现分布式…...

Linux相关概念和易错知识点(42)(TCP的连接管理、可靠性、面临复杂网络的处理)
目录 1.TCP的连接管理机制(1)三次握手①握手过程②对握手过程的理解 (2)四次挥手(3)握手和挥手的触发(4)状态切换①挥手过程中状态的切换②握手过程中状态的切换 2.TCP的可靠性&…...
华为OD机试-食堂供餐-二分法
import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Scanner;public class DemoTest3 {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner in new Scanner(System.in);// 注意 hasNext 和 hasNextLine 的区别while (in.hasNextLine()) { // 注意 while 处理多个 caseint a in.nextIn…...
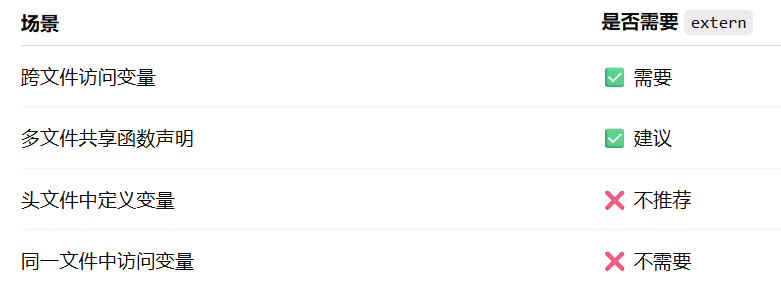
深入解析C++中的extern关键字:跨文件共享变量与函数的终极指南
🚀 C extern 关键字深度解析:跨文件编程的终极指南 📅 更新时间:2025年6月5日 🏷️ 标签:C | extern关键字 | 多文件编程 | 链接与声明 | 现代C 文章目录 前言🔥一、extern 是什么?&…...
相比,优缺点是什么?适用于哪些场景?)
Redis的发布订阅模式与专业的 MQ(如 Kafka, RabbitMQ)相比,优缺点是什么?适用于哪些场景?
Redis 的发布订阅(Pub/Sub)模式与专业的 MQ(Message Queue)如 Kafka、RabbitMQ 进行比较,核心的权衡点在于:简单与速度 vs. 可靠与功能。 下面我们详细展开对比。 Redis Pub/Sub 的核心特点 它是一个发后…...

【7色560页】职场可视化逻辑图高级数据分析PPT模版
7种色调职场工作汇报PPT,橙蓝、黑红、红蓝、蓝橙灰、浅蓝、浅绿、深蓝七种色调模版 【7色560页】职场可视化逻辑图高级数据分析PPT模版:职场可视化逻辑图分析PPT模版https://pan.quark.cn/s/78aeabbd92d1...
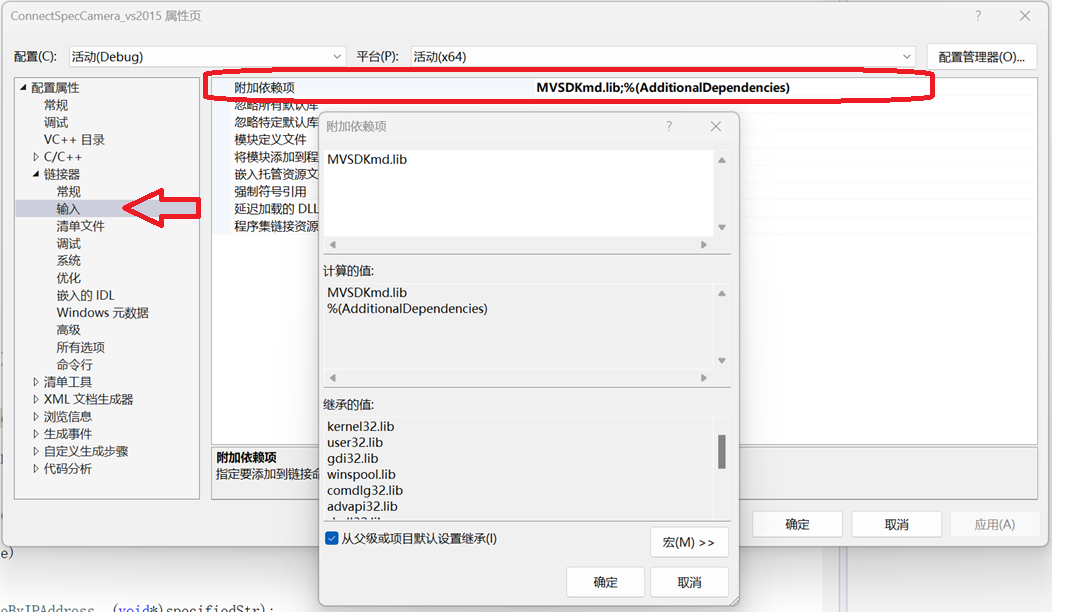
C/C++ 中附加包含目录、附加库目录与附加依赖项详解
在 C/C 编程的编译和链接过程中,附加包含目录、附加库目录和附加依赖项是三个至关重要的设置,它们相互配合,确保程序能够正确引用外部资源并顺利构建。虽然在学习过程中,这些概念容易让人混淆,但深入理解它们的作用和联…...

前端中slice和splic的区别
1. slice slice 用于从数组中提取一部分元素,返回一个新的数组。 特点: 不修改原数组:slice 不会改变原数组,而是返回一个新的数组。提取数组的部分:slice 会根据指定的开始索引和结束索引提取数组的一部分。不包含…...

【Elasticsearch】Elasticsearch 在大数据生态圈的地位 实践经验
Elasticsearch 在大数据生态圈的地位 & 实践经验 1.Elasticsearch 的优势1.1 Elasticsearch 解决的核心问题1.1.1 传统方案的短板1.1.2 Elasticsearch 的解决方案 1.2 与大数据组件的对比优势1.3 关键优势技术支撑1.4 Elasticsearch 的竞品1.4.1 全文搜索领域1.4.2 日志分析…...
