Python “贪吃蛇”游戏,在不断改进中学习pygame编程
目录
前言
改进过程一
增加提示信息
原版帮助摘要
pygame.draw
pygame.font
class Rect
class Surface
改进过程二
增加显示得分
改进过程三
增加背景景乐
增加提示音效
音乐切换
静音切换
mixer.music.play 注意事项
原版帮助摘要
pygame.mixer
pygame.mixer.Sound
小结
pygame编程框架
前言
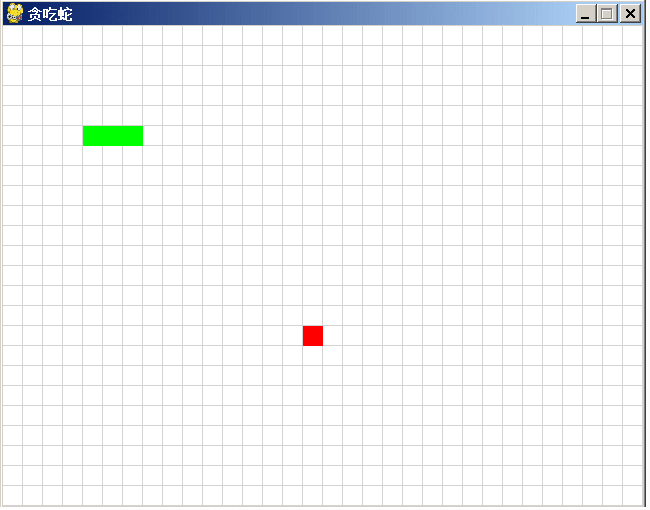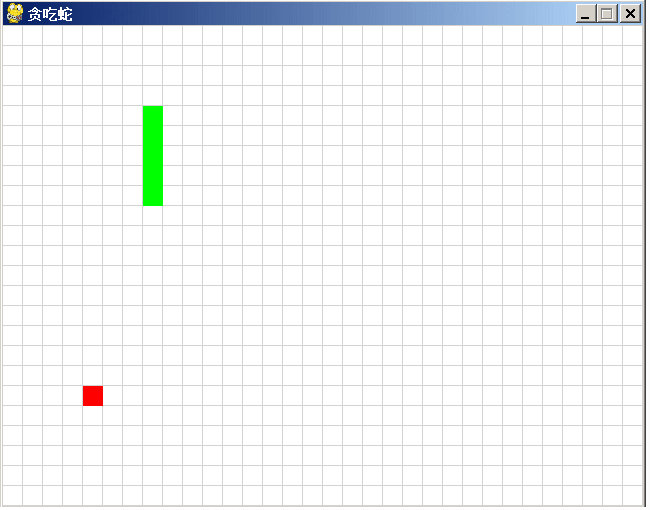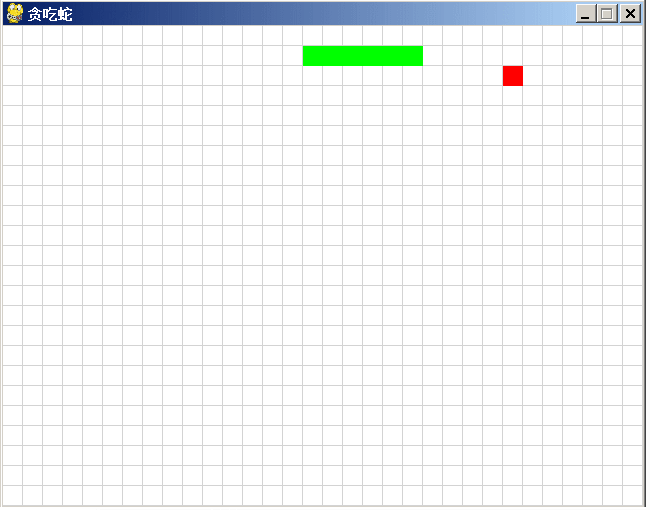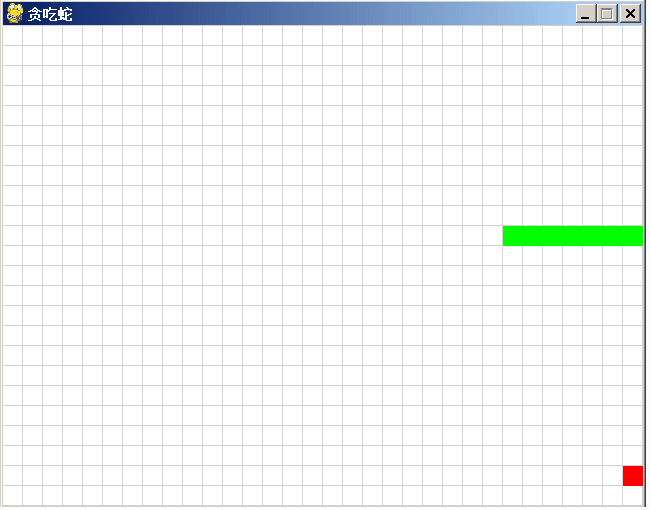
在上一篇博文里,从讯飞星火中获取到游戏“贪吃蛇”的代码,运行效果如上图。代码并不完整,当蛇死了就退出游戏,不能多次玩这个游戏。
前文链接:
讯飞星火、文心一言和通义千问同时编“贪吃蛇”游戏,谁会胜出?
代码如下:
import pygame
import sys
import random# 定义颜色
WHITE = (255, 255, 255)
GREEN = (0, 255, 0)
RED = (255, 0, 0)
GREY = (211, 211, 211) # 淡灰色def init():global screen, screen_sizeglobal snake_pos, food_pos, snake_speed# 初始化pygamepygame.init()# 设置屏幕大小screen_size = (640, 480)screen = pygame.display.set_mode(screen_size)# 设置游戏标题pygame.display.set_caption("贪吃蛇")# 蛇的初始位置snake_pos = [[100, 100], [80, 100], [60, 100]]# 食物的初始位置food_pos = [300, 300]# 蛇的初始速度snake_speed = [20, 0]def repaint():# 绘制游戏界面screen.fill(WHITE)# 定义线段的端点坐标x,y = (-1,640,640,-1)*16, []for i in range(36):for _ in range(2):y.append(19+i*20)# 使用pygame.draw.lines()函数绘制线段points = list(zip(x,y))pygame.draw.lines(screen, GREY, False, points, 1) # 线宽为1points = list(zip(y,x))pygame.draw.lines(screen, GREY, False, points, 1) # 重画蛇和食物for pos in snake_pos:pygame.draw.rect(screen, GREEN, pygame.Rect(pos[0], pos[1], 20, 20))pygame.draw.rect(screen, RED, pygame.Rect(food_pos[0], food_pos[1], 20, 20))pygame.display.flip()def game_quit():pygame.quit()sys.exit()def main():global screen, screen_sizeglobal snake_pos, food_pos, snake_speed# 主循环while True:# 处理游戏事件for event in pygame.event.get():if event.type == pygame.QUIT:game_quit()elif event.type == pygame.KEYDOWN:if event.key == pygame.K_UP:snake_speed = [0, -20]elif event.key == pygame.K_DOWN:snake_speed = [0, 20]elif event.key == pygame.K_LEFT:snake_speed = [-20, 0]elif event.key == pygame.K_RIGHT:snake_speed = [20, 0]# 更新蛇的位置snake_pos.insert(0, [snake_pos[0][0] + snake_speed[0], snake_pos[0][1] + snake_speed[1]])# 检查蛇头是否碰到食物if snake_pos[0] == food_pos:food_pos = [random.randrange(1, screen_size[0] // 20) * 20, random.randrange(1, screen_size[1] // 20) * 20]else:snake_pos.pop()# 检查蛇头是否碰到墙壁或者蛇身if snake_pos[0][0] < 0 or snake_pos[0][0] >= screen_size[0] or snake_pos[0][1] < 0 or snake_pos[0][1] >= screen_size[1] or snake_pos[0] in snake_pos[1:]:game_quit()'''此处可增加与用户的交互,如:if askyesno('title','again?'):init() # Yes to Play againelse:game_quit() # No to Exit'''# 重画界面及蛇和食物repaint()# 控制游戏速度pygame.time.Clock().tick(10)if __name__ == "__main__":init()main()改进过程一
增加提示信息
之前没有仔细学过pygame的编程,刚好拿这例程练练手,在不断改进中学习pygame编程。
原代码一执行,蛇就开始游动了,就从这里入手。开始前,增加显示“按任意键开始...”的提示。
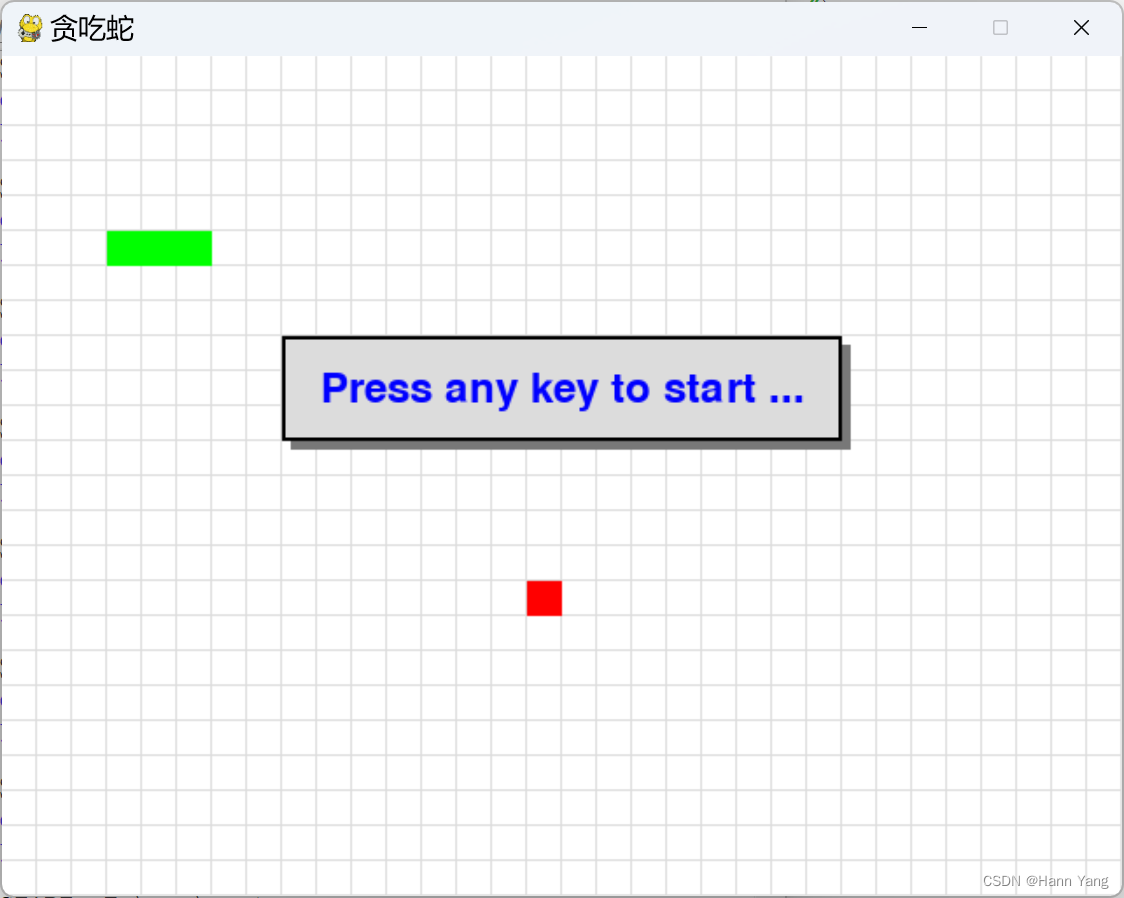
蛇死后,提醒是否重来?Yes to play again, No to quit game.

同时,在游戏中允许按ESC键暂停游戏,再按一次继续。
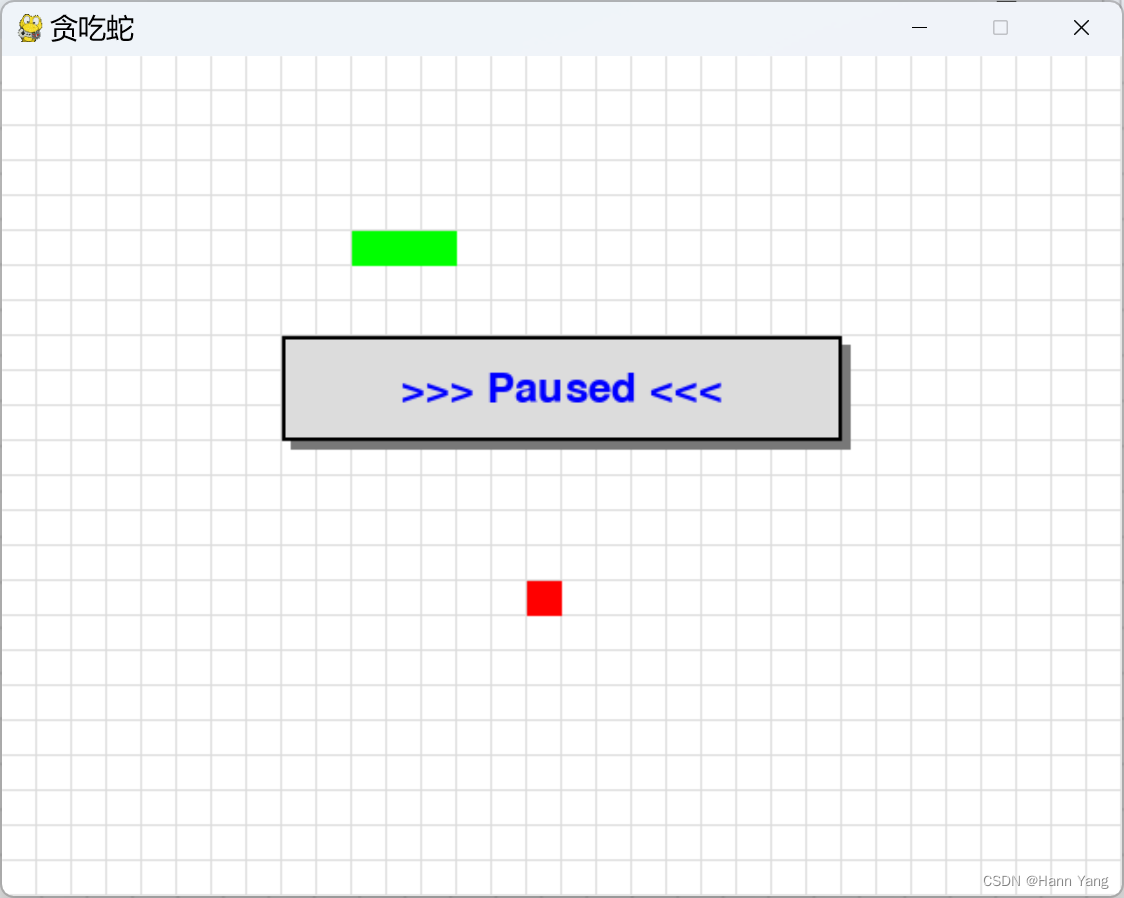
由于没查到 pygame 有弹出信息窗口的方法(函数),于是用了DOS时代显示信息窗口的办法,画多个矩形窗口来模拟窗口,最后在矩形框上写上提示文字。代码如下:
def show_msg(msg, color = BLUE):
x = screen.get_rect().centerx
y = screen.get_rect().centery - 50
font = pygame.font.Font(None, 36)
text = font.render(msg, True, color)
text_rect = text.get_rect()
text_rect.centerx = x
text_rect.centery = y
rectangle1 = pygame.Rect(x-155, y-25, 320, 60)
rectangle2 = pygame.Rect(x-160, y-30, 320, 60)
pygame.draw.rect(screen, DARK, rectangle1)
pygame.draw.rect(screen, GREY, rectangle2)
pygame.draw.rect(screen, BLACK, rectangle2, 2) # 边框宽为2
screen.blit(text, text_rect)
pygame.display.flip()
原版帮助摘要
pygame.draw
NAME
pygame.draw - pygame module for drawing shapes
FUNCTIONS
aaline(...)
aaline(surface, color, start_pos, end_pos) -> Rect
aaline(surface, color, start_pos, end_pos, blend=1) -> Rect
draw a straight antialiased line
aalines(...)
aalines(surface, color, closed, points) -> Rect
aalines(surface, color, closed, points, blend=1) -> Rect
draw multiple contiguous straight antialiased line segments
arc(...)
arc(surface, color, rect, start_angle, stop_angle) -> Rect
arc(surface, color, rect, start_angle, stop_angle, width=1) -> Rect
draw an elliptical arc
circle(...)
circle(surface, color, center, radius) -> Rect
circle(surface, color, center, radius, width=0, draw_top_right=None, draw_top_left=None, draw_bottom_left=None, draw_bottom_right=None) -> Rect
draw a circle
ellipse(...)
ellipse(surface, color, rect) -> Rect
ellipse(surface, color, rect, width=0) -> Rect
draw an ellipse
line(...)
line(surface, color, start_pos, end_pos) -> Rect
line(surface, color, start_pos, end_pos, width=1) -> Rect
draw a straight line
lines(...)
lines(surface, color, closed, points) -> Rect
lines(surface, color, closed, points, width=1) -> Rect
draw multiple contiguous straight line segments
polygon(...)
polygon(surface, color, points) -> Rect
polygon(surface, color, points, width=0) -> Rect
draw a polygon
rect(...)
rect(surface, color, rect) -> Rect
rect(surface, color, rect, width=0, border_radius=0, border_top_left_radius=-1, border_top_right_radius=-1, border_bottom_left_radius=-1, border_bottom_right_radius=-1) -> Rect
draw a rectangle
pygame.font
NAME
pygame.font - pygame module for loading and rendering fonts
CLASSES
builtins.object
Font
class Font(builtins.object)
| Font(file_path=None, size=12) -> Font
| Font(file_path, size) -> Font
| Font(pathlib.Path, size) -> Font
| Font(object, size) -> Font
| create a new Font object from a file
|
| Methods defined here:
|
| __init__(self, /, *args, **kwargs)
| Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.
|
| get_ascent(...)
| get_ascent() -> int
| get the ascent of the font
|
| get_bold(...)
| get_bold() -> bool
| check if text will be rendered bold
|
| get_descent(...)
| get_descent() -> int
| get the descent of the font
|
| get_height(...)
| get_height() -> int
| get the height of the font
|
| get_italic(...)
| get_italic() -> bool
| check if the text will be rendered italic
|
| get_linesize(...)
| get_linesize() -> int
| get the line space of the font text
|
| get_strikethrough(...)
| get_strikethrough() -> bool
| check if text will be rendered with a strikethrough
|
| get_underline(...)
| get_underline() -> bool
| check if text will be rendered with an underline
|
| metrics(...)
| metrics(text) -> list
| gets the metrics for each character in the passed string
|
| render(...)
| render(text, antialias, color, background=None) -> Surface
| draw text on a new Surface
|
| set_bold(...)
| set_bold(bool) -> None
| enable fake rendering of bold text
|
| set_italic(...)
| set_italic(bool) -> None
| enable fake rendering of italic text
|
| set_script(...)
| set_script(str) -> None
| set the script code for text shaping
|
| set_strikethrough(...)
| set_strikethrough(bool) -> None
| control if text is rendered with a strikethrough
|
| set_underline(...)
| set_underline(bool) -> None
| control if text is rendered with an underline
|
| size(...)
| size(text) -> (width, height)
| determine the amount of space needed to render text
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Data descriptors defined here:
|
| bold
| bold -> bool
| Gets or sets whether the font should be rendered in (faked) bold.
|
| italic
| italic -> bool
| Gets or sets whether the font should be rendered in (faked) italics.
|
| strikethrough
| strikethrough -> bool
| Gets or sets whether the font should be rendered with a strikethrough.
|
| underline
| underline -> bool
| Gets or sets whether the font should be rendered with an underline.
class Rect
Help on class Rect in module pygame.rect:
class Rect(builtins.object)
| Rect(left, top, width, height) -> Rect
| Rect((left, top), (width, height)) -> Rect
| Rect(object) -> Rect
| pygame object for storing rectangular coordinates
|
| Methods defined here:
|
| clamp(...)
| clamp(Rect) -> Rect
| moves the rectangle inside another
|
| clamp_ip(...)
| clamp_ip(Rect) -> None
| moves the rectangle inside another, in place
|
| clip(...)
| clip(Rect) -> Rect
| crops a rectangle inside another
|
| clipline(...)
| clipline(x1, y1, x2, y2) -> ((cx1, cy1), (cx2, cy2))
| clipline(x1, y1, x2, y2) -> ()
| clipline((x1, y1), (x2, y2)) -> ((cx1, cy1), (cx2, cy2))
| clipline((x1, y1), (x2, y2)) -> ()
| clipline((x1, y1, x2, y2)) -> ((cx1, cy1), (cx2, cy2))
| clipline((x1, y1, x2, y2)) -> ()
| clipline(((x1, y1), (x2, y2))) -> ((cx1, cy1), (cx2, cy2))
| clipline(((x1, y1), (x2, y2))) -> ()
| crops a line inside a rectangle
|
| collidedict(...)
| collidedict(dict) -> (key, value)
| collidedict(dict) -> None
| collidedict(dict, use_values=0) -> (key, value)
| collidedict(dict, use_values=0) -> None
| test if one rectangle in a dictionary intersects
|
| collidedictall(...)
| collidedictall(dict) -> [(key, value), ...]
| collidedictall(dict, use_values=0) -> [(key, value), ...]
| test if all rectangles in a dictionary intersect
|
| collidelist(...)
| collidelist(list) -> index
| test if one rectangle in a list intersects
|
| collidelistall(...)
| collidelistall(list) -> indices
| test if all rectangles in a list intersect
|
| collideobjects(...)
| collideobjects(rect_list) -> object
| collideobjects(obj_list, key=func) -> object
| test if any object in a list intersects
|
| collideobjectsall(...)
| collideobjectsall(rect_list) -> objects
| collideobjectsall(obj_list, key=func) -> objects
| test if all objects in a list intersect
|
| collidepoint(...)
| collidepoint(x, y) -> bool
| collidepoint((x,y)) -> bool
| test if a point is inside a rectangle
|
| colliderect(...)
| colliderect(Rect) -> bool
| test if two rectangles overlap
|
| contains(...)
| contains(Rect) -> bool
| test if one rectangle is inside another
|
| copy(...)
| copy() -> Rect
| copy the rectangle
|
| fit(...)
| fit(Rect) -> Rect
| resize and move a rectangle with aspect ratio
|
| inflate(...)
| inflate(x, y) -> Rect
| grow or shrink the rectangle size
|
| inflate_ip(...)
| inflate_ip(x, y) -> None
| grow or shrink the rectangle size, in place
|
| move(...)
| move(x, y) -> Rect
| moves the rectangle
|
| move_ip(...)
| move_ip(x, y) -> None
| moves the rectangle, in place
|
| normalize(...)
| normalize() -> None
| correct negative sizes
|
| scale_by(...)
| scale_by(scalar) -> Rect
| scale_by(scalex, scaley) -> Rect
| scale the rectangle by given a multiplier
|
| scale_by_ip(...)
| scale_by_ip(scalar) -> None
| scale_by_ip(scalex, scaley) -> None
| grow or shrink the rectangle size, in place
|
| union(...)
| union(Rect) -> Rect
| joins two rectangles into one
|
| union_ip(...)
| union_ip(Rect) -> None
| joins two rectangles into one, in place
|
| unionall(...)
| unionall(Rect_sequence) -> Rect
| the union of many rectangles
|
| unionall_ip(...)
| unionall_ip(Rect_sequence) -> None
| the union of many rectangles, in place
|
| update(...)
| update(left, top, width, height) -> None
| update((left, top), (width, height)) -> None
| update(object) -> None
| sets the position and size of the rectangle
class Surface
class Surface(builtins.object)
| Surface((width, height), flags=0, depth=0, masks=None) -> Surface
| Surface((width, height), flags=0, Surface) -> Surface
| pygame object for representing images
|
| Methods defined here:
|
| blit(...)
| blit(source, dest, area=None, special_flags=0) -> Rect
| draw one image onto another
|
| blits(...)
| blits(blit_sequence=((source, dest), ...), doreturn=1) -> [Rect, ...] or None
| blits(((source, dest, area), ...)) -> [Rect, ...]
| blits(((source, dest, area, special_flags), ...)) -> [Rect, ...]
| draw many images onto another
|
| convert(...)
| convert(Surface=None) -> Surface
| convert(depth, flags=0) -> Surface
| convert(masks, flags=0) -> Surface
| change the pixel format of an image
|
| convert_alpha(...)
| convert_alpha(Surface) -> Surface
| convert_alpha() -> Surface
| change the pixel format of an image including per pixel alphas
|
| copy(...)
| copy() -> Surface
| create a new copy of a Surface
|
| fill(...)
| fill(color, rect=None, special_flags=0) -> Rect
| fill Surface with a solid color
|
| get_abs_offset(...)
| get_abs_offset() -> (x, y)
| find the absolute position of a child subsurface inside its top level parent
|
| get_abs_parent(...)
| get_abs_parent() -> Surface
| find the top level parent of a subsurface
|
| get_alpha(...)
| get_alpha() -> int_value
| get the current Surface transparency value
|
| get_at(...)
| get_at((x, y)) -> Color
| get the color value at a single pixel
|
| get_at_mapped(...)
| get_at_mapped((x, y)) -> Color
| get the mapped color value at a single pixel
|
| get_bitsize(...)
| get_bitsize() -> int
| get the bit depth of the Surface pixel format
|
| get_blendmode(...)
| Return the surface's SDL 2 blend mode
|
| get_bounding_rect(...)
| get_bounding_rect(min_alpha = 1) -> Rect
| find the smallest rect containing data
|
| get_buffer(...)
| get_buffer() -> BufferProxy
| acquires a buffer object for the pixels of the Surface.
|
| get_bytesize(...)
| get_bytesize() -> int
| get the bytes used per Surface pixel
|
| get_clip(...)
| get_clip() -> Rect
| get the current clipping area of the Surface
|
| get_colorkey(...)
| get_colorkey() -> RGB or None
| Get the current transparent colorkey
|
| get_flags(...)
| get_flags() -> int
| get the additional flags used for the Surface
|
| get_height(...)
| get_height() -> height
| get the height of the Surface
|
| get_locked(...)
| get_locked() -> bool
| test if the Surface is current locked
|
| get_locks(...)
| get_locks() -> tuple
| Gets the locks for the Surface
|
| get_losses(...)
| get_losses() -> (R, G, B, A)
| the significant bits used to convert between a color and a mapped integer
|
| get_masks(...)
| get_masks() -> (R, G, B, A)
| the bitmasks needed to convert between a color and a mapped integer
|
| get_offset(...)
| get_offset() -> (x, y)
| find the position of a child subsurface inside a parent
|
| get_palette(...)
| get_palette() -> [RGB, RGB, RGB, ...]
| get the color index palette for an 8-bit Surface
|
| get_palette_at(...)
| get_palette_at(index) -> RGB
| get the color for a single entry in a palette
|
| get_parent(...)
| get_parent() -> Surface
| find the parent of a subsurface
|
| get_pitch(...)
| get_pitch() -> int
| get the number of bytes used per Surface row
|
| get_rect(...)
| get_rect(**kwargs) -> Rect
| get the rectangular area of the Surface
|
| get_shifts(...)
| get_shifts() -> (R, G, B, A)
| the bit shifts needed to convert between a color and a mapped integer
|
| get_size(...)
| get_size() -> (width, height)
| get the dimensions of the Surface
|
| get_view(...)
| get_view(<kind>='2') -> BufferProxy
| return a buffer view of the Surface's pixels.
|
| get_width(...)
| get_width() -> width
| get the width of the Surface
|
| lock(...)
| lock() -> None
| lock the Surface memory for pixel access
|
| map_rgb(...)
| map_rgb(Color) -> mapped_int
| convert a color into a mapped color value
|
| mustlock(...)
| mustlock() -> bool
| test if the Surface requires locking
|
| premul_alpha(...)
| premul_alpha() -> Surface
| returns a copy of the surface with the RGB channels pre-multiplied by the alpha channel.
|
| scroll(...)
| scroll(dx=0, dy=0) -> None
| Shift the surface image in place
|
| set_alpha(...)
| set_alpha(value, flags=0) -> None
| set_alpha(None) -> None
| set the alpha value for the full Surface image
|
| set_at(...)
| set_at((x, y), Color) -> None
| set the color value for a single pixel
|
| set_clip(...)
| set_clip(rect) -> None
| set_clip(None) -> None
| set the current clipping area of the Surface
|
| set_colorkey(...)
| set_colorkey(Color, flags=0) -> None
| set_colorkey(None) -> None
| Set the transparent colorkey
|
| set_masks(...)
| set_masks((r,g,b,a)) -> None
| set the bitmasks needed to convert between a color and a mapped integer
|
| set_palette(...)
| set_palette([RGB, RGB, RGB, ...]) -> None
| set the color palette for an 8-bit Surface
|
| set_palette_at(...)
| set_palette_at(index, RGB) -> None
| set the color for a single index in an 8-bit Surface palette
|
| set_shifts(...)
| set_shifts((r,g,b,a)) -> None
| sets the bit shifts needed to convert between a color and a mapped integer
|
| subsurface(...)
| subsurface(Rect) -> Surface
| create a new surface that references its parent
|
| unlock(...)
| unlock() -> None
| unlock the Surface memory from pixel access
|
| unmap_rgb(...)
| unmap_rgb(mapped_int) -> Color
| convert a mapped integer color value into a Color
另外增加了3个状态变量,初始状态为:
is_running = False
is_paused = False
is_dead = False
增加了4个按键判别:
is_dead时,判断重新开始还是退出游戏
pygame.K_y: 字母Y/y
pygame.K_n: 字母N/n
暂停和恢复
pygame.K_ESCAPE: Esc键
pygame.K_SPACE: 空格键
完整代码如下:
import pygame
import sys
import random# 定义颜色
BLACK = (0, 0, 0)
WHITE = (255, 255, 255)
RED = (255, 0, 0)
GREEN = (0, 255, 0)
BLUE = (0, 0, 255)
GREY = (220, 220, 220) # 淡灰色
DARK = (120, 120, 120) # 深灰色def init():global screen, screen_sizeglobal snake_pos, food_pos, snake_speed# 初始化pygamepygame.init()# 设置屏幕大小screen_size = (640, 480)screen = pygame.display.set_mode(screen_size)# 设置游戏标题pygame.display.set_caption("贪吃蛇")# 蛇的初始位置snake_pos = [[100, 100], [80, 100], [60, 100]]# 食物的初始位置food_pos = [300, 300]# 蛇的初始速度snake_speed = [20, 0]def show_msg(msg, color = BLUE):x = screen.get_rect().centerxy = screen.get_rect().centery - 50font = pygame.font.Font(None, 36)text = font.render(msg, True, color)text_rect = text.get_rect()text_rect.centerx = xtext_rect.centery = yrectangle1 = pygame.Rect(x-155, y-25, 320, 60)rectangle2 = pygame.Rect(x-160, y-30, 320, 60)pygame.draw.rect(screen, DARK, rectangle1)pygame.draw.rect(screen, GREY, rectangle2)pygame.draw.rect(screen, BLACK, rectangle2, 2) # 边框宽为2screen.blit(text, text_rect)pygame.display.flip()def repaint():# 绘制游戏界面screen.fill(WHITE)# 定义线段的端点坐标x,y = (-1,640,640,-1)*16, []for i in range(36):for _ in range(2):y.append(19+i*20)# 使用pygame.draw.lines()函数绘制线段points = list(zip(x,y))pygame.draw.lines(screen, GREY, False, points, 1) # 线宽为1points = list(zip(y,x))pygame.draw.lines(screen, GREY, False, points, 1) # 重画蛇和食物for pos in snake_pos:pygame.draw.rect(screen, GREEN, pygame.Rect(pos[0], pos[1], 20, 20))pygame.draw.rect(screen, RED, pygame.Rect(food_pos[0], food_pos[1], 20, 20))pygame.display.flip()def game_quit():pygame.quit()sys.exit()def main():global screen, screen_sizeglobal snake_pos, food_pos, snake_speedis_running = Falseis_paused = Falseis_dead = Falserepaint()show_msg("Press any key to start ...")# 主循环while True:# 处理游戏事件for event in pygame.event.get():if event.type == pygame.QUIT:game_quit()elif event.type == pygame.KEYDOWN:if event.key == pygame.K_UP:snake_speed = [0, -20]elif event.key == pygame.K_DOWN:snake_speed = [0, 20]elif event.key == pygame.K_LEFT:snake_speed = [-20, 0]elif event.key == pygame.K_RIGHT:snake_speed = [20, 0]elif event.key == pygame.K_y:if is_dead:init()is_dead = Falseis_running = Trueelif event.key == pygame.K_n:if is_dead: game_quit()else: is_running = Trueelif event.key == pygame.K_ESCAPE:if is_running:show_msg(">>> Paused <<<")is_paused = not is_pausedelse: # 任意键进入开始状态is_running = Trueif not is_running: continueif is_paused and is_running: continue# 更新蛇的位置snake_pos.insert(0, [snake_pos[0][0] + snake_speed[0], snake_pos[0][1] + snake_speed[1]])# 检查蛇头是否碰到食物if snake_pos[0] == food_pos:food_pos = [random.randrange(1, screen_size[0] // 20) * 20, random.randrange(1, screen_size[1] // 20) * 20]else:snake_pos.pop()# 检查蛇头是否碰到墙壁或者蛇身if snake_pos[0][0] < 0 or snake_pos[0][0] >= screen_size[0] or snake_pos[0][1] < 0 or snake_pos[0][1] >= screen_size[1] or snake_pos[0] in snake_pos[1:]:show_msg("Dead! Again? (Y or N)")is_running = Falseis_dead = Truecontinue# 重画界面及蛇和食物repaint()# 控制游戏速度pygame.time.Clock().tick(10)if __name__ == "__main__":init()main()改进过程二
增加显示得分
每吃到一个食物+10分,蛇长和食物靠近边界会有额外加分;顺带显示出蛇的坐标位置。
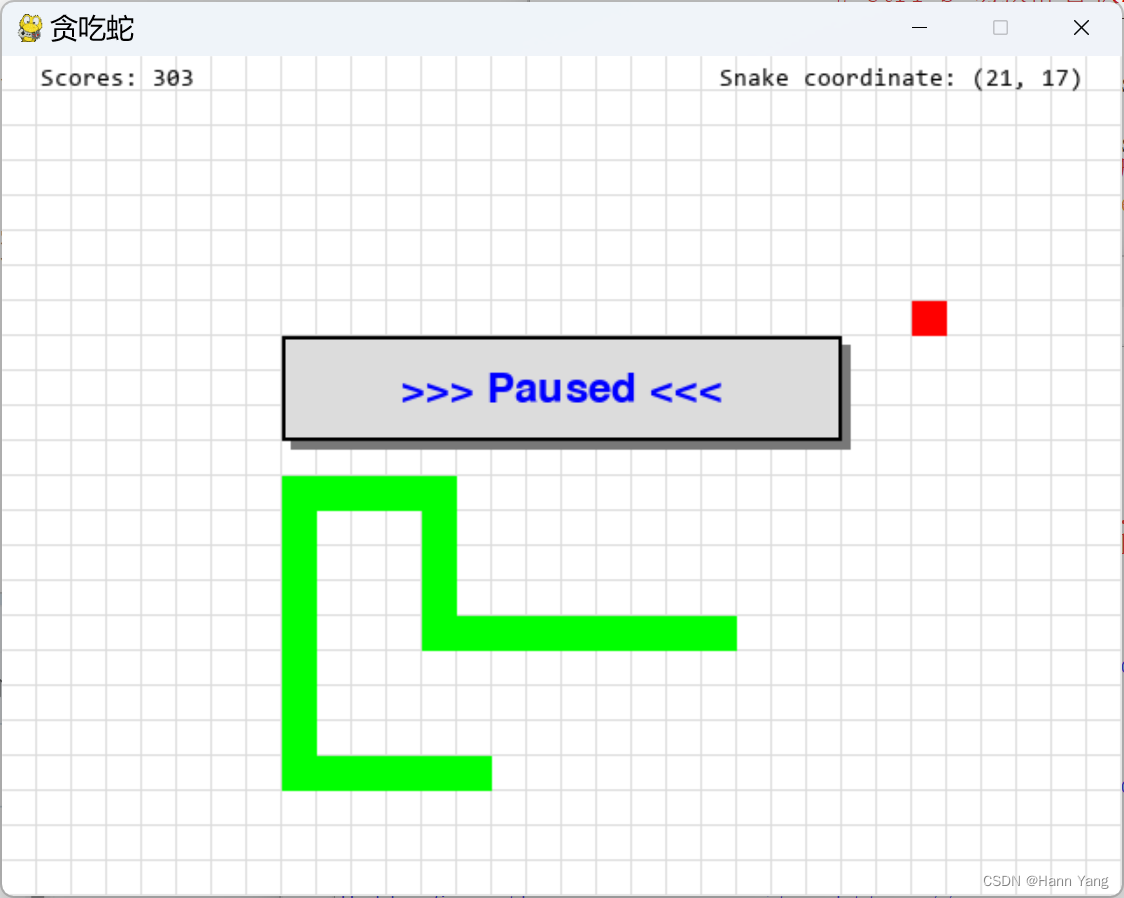
函数show_msg_at(),比show_msg增加x,y坐标,把信息显示到指定的位置:
def show_msg_at(x, y, msg):
font = pygame.font.SysFont('Consolas', 14) # 使用系统字库
text = font.render(msg, True, BLACK)
text_rect = text.get_rect()
text_rect.x, text_rect.y = x, y
screen.blit(text, text_rect)
pygame.display.flip()
另外新增一个全局变量 scores,当碰到食物时加10分,蛇长超过5以及食物靠近边界的距离小3会有额外加分,规则可以自己定,例如:
if snake_pos[0] == food_pos:
scores += 10 + len(snake_pos) // 5
if not 1 < snake_pos[0][0]//20 < 30 or not 1 < snake_pos[0][1]//20 < 22:
scores += 5
完整代码如下:
import pygame
import sys
import random# 定义颜色
BLACK = (0, 0, 0)
WHITE = (255, 255, 255)
RED = (255, 0, 0)
GREEN = (0, 255, 0)
BLUE = (0, 0, 255)
GREY = (220, 220, 220) # 淡灰色
DARK = (120, 120, 120) # 深灰色def init():global screen, screen_size, scoresglobal snake_pos, food_pos, snake_speed# 初始化pygamescores = 0pygame.init()# 设置屏幕大小screen_size = (640, 480)screen = pygame.display.set_mode(screen_size)# 设置游戏标题pygame.display.set_caption("贪吃蛇")# 蛇的初始位置snake_pos = [[100, 100], [80, 100], [60, 100]]# 食物的初始位置food_pos = [300, 300]# 蛇的初始速度snake_speed = [20, 0]def show_msg(msg, color = BLUE):x = screen.get_rect().centerxy = screen.get_rect().centery - 50font = pygame.font.Font(None, 36)text = font.render(msg, True, color)text_rect = text.get_rect()text_rect.centerx = xtext_rect.centery = yrectangle1 = pygame.Rect(x-155, y-25, 320, 60)rectangle2 = pygame.Rect(x-160, y-30, 320, 60)pygame.draw.rect(screen, DARK, rectangle1)pygame.draw.rect(screen, GREY, rectangle2)pygame.draw.rect(screen, BLACK, rectangle2, 2) # 边框宽为2screen.blit(text, text_rect)pygame.display.flip()def repaint():# 绘制游戏界面screen.fill(WHITE)# 定义线段的端点坐标x,y = (-1,640,640,-1)*16, []for i in range(36):for _ in range(2):y.append(19+i*20)# 使用pygame.draw.lines()函数绘制线段points = list(zip(x,y))pygame.draw.lines(screen, GREY, False, points, 1) # 线宽为1points = list(zip(y,x))pygame.draw.lines(screen, GREY, False, points, 1) # 重画蛇和食物for pos in snake_pos:pygame.draw.rect(screen, GREEN, pygame.Rect(pos[0], pos[1], 20, 20))pygame.draw.rect(screen, RED, pygame.Rect(food_pos[0], food_pos[1], 20, 20))pygame.display.flip()show_msg_at(22, 6, f'Scores: {scores}')show_msg_at(410, 6, f'Snake coordinate: ({1+snake_pos[0][0]//20:2}, {1+snake_pos[0][1]//20:2})')def show_msg_at(x, y, msg):font = pygame.font.SysFont('Consolas', 14)text = font.render(msg, True, BLACK)text_rect = text.get_rect()text_rect.x, text_rect.y = x, yscreen.blit(text, text_rect)pygame.display.flip()def game_quit():pygame.quit()sys.exit()def main():global screen, screen_size, scoresglobal snake_pos, food_pos, snake_speedis_running = Falseis_paused = Falseis_dead = Falserepaint()show_msg("Press any key to start ...")# 主循环while True:# 处理游戏事件for event in pygame.event.get():if event.type == pygame.QUIT:game_quit()elif event.type == pygame.KEYDOWN:if event.key == pygame.K_UP:snake_speed = [0, -20]elif event.key == pygame.K_DOWN:snake_speed = [0, 20]elif event.key == pygame.K_LEFT:snake_speed = [-20, 0]elif event.key == pygame.K_RIGHT:snake_speed = [20, 0]elif event.key == pygame.K_y:if is_dead:init()is_dead = Falseis_running = Trueelif event.key == pygame.K_n:if is_dead: game_quit()else: is_running = Trueelif event.key == pygame.K_SPACE:if is_dead: continueif is_paused: is_paused = Falseis_running = Trueelif event.key == pygame.K_ESCAPE:if is_running:show_msg(">>> Paused <<<")is_paused = not is_pausedelse: # 任意键进入开始状态if is_dead: continueis_running = Trueif not is_running: continueif is_paused and is_running: continue# 更新蛇的位置snake_pos.insert(0, [snake_pos[0][0] + snake_speed[0], snake_pos[0][1] + snake_speed[1]])# 检查蛇头是否碰到食物if snake_pos[0] == food_pos:scores += 10 + len(snake_pos) // 5if not 1 < snake_pos[0][0]//20 < 30 or not 1 < snake_pos[0][1]//20 < 22:scores += 5 food_pos = [random.randrange(1, screen_size[0] // 20) * 20, random.randrange(1, screen_size[1] // 20) * 20]else:snake_pos.pop()# 检查蛇头是否碰到墙壁或者蛇身if snake_pos[0][0] < 0 or snake_pos[0][0] >= screen_size[0] or snake_pos[0][1] < 0 or snake_pos[0][1] >= screen_size[1] or snake_pos[0] in snake_pos[1:]:show_msg("Dead! Again? (Y or N)")is_running = Falseis_dead = Truecontinue# 重画界面及蛇和食物repaint()# 控制游戏速度pygame.time.Clock().tick(10)if __name__ == "__main__":init()main()改进过程三
增加背景景乐
def play_music(mp3, volume = 1, loops = -1):
# 初始化pygame的mixer模块
pygame.mixer.init()
# 加载音乐文件
pygame.mixer.music.load(mp3)
# 控制音量 volume = 0~1,1为最高音量
pygame.mixer.music.set_volume(volume)
# 播放音乐 loops = -1 为循环播放
pygame.mixer.music.play(loops)
增加提示音效
def play_sound(wav_no):
sound_fn = f'sound{wav_no}.wav'
if os.path.exists(sound_fn):
alert_sound = pygame.mixer.Sound(sound_fn)
alert_sound.play()
音乐切换
快捷键 Ctrl+M
elif event.key == pygame.K_m and event.mod & pygame.KMOD_CTRL:
# Ctrl+M 切换背景音乐
is_mute = False
music_no = 1 if music_no == 3 else music_no + 1
music_fn = f"voice{music_no}.mp3"
if os.path.exists(music_fn):
t = threading.Thread(target=play_music, args=(music_fn,0.8,))
t.start()
静音切换
快捷键 Ctrl+S
elif event.key == pygame.K_s and event.mod & pygame.KMOD_CTRL:
# Ctrl+S 切换静音状态
is_mute = not is_mute
if is_mute:
pygame.mixer.music.pause()
else:
pygame.mixer.music.unpause()
mixer.music.play 注意事项
1. pygame.mixer.music.play() 只能播放pygame支持的音频格式,包括WAV, MP3等。
2. 如果音频文件未找到或无法读取,pygame.mixer.music.play( ) 会抛出一个异常。使用需要确保音频文件的路径正确,且文件存在。导入os库,用os.path.exists(music_file) 判断文件是否存在。
3. pygame.mixer.music.play() 是一个阻塞函数,在音频播放期间程序将不会执行其他操作。如果需要在播放同时执行其他操作,需要在一个单独的线程中调用pygame.mixer.music.play()。
4. 多线程需要导入threading库,例如:
t = threading.Thread(target=play_music, args=(music_fn,0.8,))
t.start()
原版帮助摘要
pygame.mixer
NAME
pygame.mixer_music - pygame module for controlling streamed audio
FUNCTIONS
fadeout(...)
fadeout(time) -> None
stop music playback after fading out
get_busy(...)
get_busy() -> bool
check if the music stream is playing
get_endevent(...)
get_endevent() -> type
get the event a channel sends when playback stops
get_pos(...)
get_pos() -> time
get the music play time
get_volume(...)
get_volume() -> value
get the music volume
load(...)
load(filename) -> None
load(fileobj, namehint=) -> None
Load a music file for playback
pause(...)
pause() -> None
temporarily stop music playback
play(...)
play(loops=0, start=0.0, fade_ms=0) -> None
Start the playback of the music stream
queue(...)
queue(filename) -> None
queue(fileobj, namehint=, loops=0) -> None
queue a sound file to follow the current
rewind(...)
rewind() -> None
restart music
set_endevent(...)
set_endevent() -> None
set_endevent(type) -> None
have the music send an event when playback stops
set_pos(...)
set_pos(pos) -> None
set position to play from
set_volume(...)
set_volume(volume) -> None
set the music volume
stop(...)
stop() -> None
stop the music playback
unload(...)
unload() -> None
Unload the currently loaded music to free up resources
unpause(...)
unpause() -> None
resume paused music
pygame.mixer.Sound
class Sound(builtins.object)
| Sound(filename) -> Sound
| Sound(file=filename) -> Sound
| Sound(file=pathlib_path) -> Sound
| Sound(buffer) -> Sound
| Sound(buffer=buffer) -> Sound
| Sound(object) -> Sound
| Sound(file=object) -> Sound
| Sound(array=object) -> Sound
| Create a new Sound object from a file or buffer object
|
| Methods defined here:
|
| __init__(self, /, *args, **kwargs)
| Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.
|
| fadeout(...)
| fadeout(time) -> None
| stop sound playback after fading out
|
| get_length(...)
| get_length() -> seconds
| get the length of the Sound
|
| get_num_channels(...)
| get_num_channels() -> count
| count how many times this Sound is playing
|
| get_raw(...)
| get_raw() -> bytes
| return a bytestring copy of the Sound samples.
|
| get_volume(...)
| get_volume() -> value
| get the playback volume
|
| play(...)
| play(loops=0, maxtime=0, fade_ms=0) -> Channel
| begin sound playback
|
| set_volume(...)
| set_volume(value) -> None
| set the playback volume for this Sound
|
| stop(...)
| stop() -> None
| stop sound playback
完整代码:
import pygame
import sys, os
import random
import threading# 定义颜色
BLACK = (0, 0, 0)
WHITE = (255, 255, 255)
RED = (255, 0, 0)
GREEN = (0, 255, 0)
BLUE = (0, 0, 255)
GREY = (220, 220, 220) # 淡灰色
DARK = (120, 120, 120) # 深灰色def init():global screen, screen_size, scoresglobal snake_pos, food_pos, snake_speed# 初始化pygamescores = 0pygame.init()# 设置屏幕大小screen_size = (640, 480)screen = pygame.display.set_mode(screen_size)# 设置游戏标题pygame.display.set_caption("贪吃蛇")# 蛇的初始位置snake_pos = [[100, 100], [80, 100], [60, 100]]# 食物的初始位置food_pos = [300, 300]# 蛇的初始速度snake_speed = [20, 0]def play_music(mp3, volume = 1, loops = -1):# 初始化pygame的mixer模块pygame.mixer.init()# 加载音乐文件pygame.mixer.music.load(mp3)# 控制音量pygame.mixer.music.set_volume(volume)# 播放音乐pygame.mixer.music.play(loops)def play_sound(wav_no):sound_fn = f'sound{wav_no}.wav'if os.path.exists(sound_fn):alert_sound = pygame.mixer.Sound(sound_fn)alert_sound.play()def show_msg(msg, color = BLUE):x = screen.get_rect().centerxy = screen.get_rect().centery - 50font = pygame.font.Font(None, 36)text = font.render(msg, True, color)text_rect = text.get_rect()text_rect.centerx = xtext_rect.centery = yrectangle1 = pygame.Rect(x-155, y-25, 320, 60)rectangle2 = pygame.Rect(x-160, y-30, 320, 60)pygame.draw.rect(screen, DARK, rectangle1)pygame.draw.rect(screen, GREY, rectangle2)pygame.draw.rect(screen, BLACK, rectangle2, 2) # 边框宽为2screen.blit(text, text_rect)pygame.display.flip()def repaint():# 绘制游戏界面screen.fill(WHITE)# 定义线段的端点坐标x,y = (-1,640,640,-1)*16, []for i in range(36):for _ in range(2):y.append(19+i*20)# 使用pygame.draw.lines()函数绘制线段points = list(zip(x,y))pygame.draw.lines(screen, GREY, False, points, 1) # 线宽为1points = list(zip(y,x))pygame.draw.lines(screen, GREY, False, points, 1) # 重画蛇和食物for pos in snake_pos:pygame.draw.rect(screen, GREEN, pygame.Rect(pos[0], pos[1], 20, 20))pygame.draw.rect(screen, RED, pygame.Rect(food_pos[0], food_pos[1], 20, 20))pygame.display.flip()show_msg_at(22, 6, f'Scores: {scores}')show_msg_at(410, 6, f'Snake coordinate: ({1+snake_pos[0][0]//20:2}, {1+snake_pos[0][1]//20:2})')def show_msg_at(x, y, msg):font = pygame.font.SysFont('Consolas', 14)text = font.render(msg, True, BLACK)text_rect = text.get_rect()text_rect.x, text_rect.y = x, yscreen.blit(text, text_rect)pygame.display.flip()def game_quit():pygame.quit()sys.exit()def main():global screen, screen_size, scoresglobal snake_pos, food_pos, snake_speedis_running = Falseis_paused = Falseis_dead = Falseis_mute = Falserepaint()show_msg("Press any key to start ...")# 创建一个线程来播放音乐music_no = 1music_fn = "voice1.mp3"if os.path.exists(music_fn):t = threading.Thread(target=play_music, args=(music_fn,0.8,))t.start()# 主循环while True:# 处理游戏事件for event in pygame.event.get():if event.type == pygame.QUIT:game_quit()elif event.type == pygame.KEYDOWN:if event.key == pygame.K_UP:snake_speed = [0, -20]elif event.key == pygame.K_DOWN:snake_speed = [0, 20]elif event.key == pygame.K_LEFT:snake_speed = [-20, 0]elif event.key == pygame.K_RIGHT:snake_speed = [20, 0]elif event.key == pygame.K_y:if is_dead:init()is_dead = Falseis_running = Trueelif event.key == pygame.K_n:if is_dead: game_quit()else: is_running = Trueelif event.key == pygame.K_SPACE:if is_dead: continueif is_paused: is_paused = Falseis_running = Trueelif event.key == pygame.K_ESCAPE:if is_running:show_msg(">>> Paused <<<")is_paused = not is_pausedif not is_mute and is_paused: play_sound(1)elif event.key == pygame.K_m and event.mod & pygame.KMOD_CTRL:# Ctrl+M 切换背景音乐is_mute = Falsemusic_no = 1 if music_no == 3 else music_no + 1music_fn = f"voice{music_no}.mp3"if os.path.exists(music_fn):t = threading.Thread(target=play_music, args=(music_fn,0.8,))t.start()elif event.key == pygame.K_s and event.mod & pygame.KMOD_CTRL:# Ctrl+S 切换静音状态is_mute = not is_muteif is_mute:pygame.mixer.music.pause()else:pygame.mixer.music.unpause()is_running = Trueelse: # 任意键进入开始状态if is_dead: continueis_running = Trueif not is_running: continueif is_paused and is_running: continue# 更新蛇的位置snake_pos.insert(0, [snake_pos[0][0] + snake_speed[0], snake_pos[0][1] + snake_speed[1]])# 检查蛇头是否碰到食物if snake_pos[0] == food_pos:scores += 10 + len(snake_pos) // 5if not 1 < snake_pos[0][0]//20 < 30 or not 1 < snake_pos[0][1]//20 < 22:scores += 5if not is_mute: play_sound(2)food_pos = [random.randrange(1, screen_size[0] // 20) * 20, random.randrange(1, screen_size[1] // 20) * 20]else:snake_pos.pop()# 检查蛇头是否碰到墙壁或者蛇身if snake_pos[0][0] < 0 or snake_pos[0][0] >= screen_size[0] or snake_pos[0][1] < 0 or snake_pos[0][1] >= screen_size[1] or snake_pos[0] in snake_pos[1:]:show_msg("Dead! Again? (Y or N)")is_running = Falseis_dead = Trueif not is_mute: play_sound(3)continue# 重画界面及蛇和食物repaint()# 控制游戏速度pygame.time.Clock().tick(10)if __name__ == "__main__":init()main()小结
本文以贪吃蛇游戏为例,对pygame编程的一个简单框架进行了深入的学习,包括对画图、字体、音乐等各个方面操作的各种方法和函数,学习后在pygame这方面的编程能力有所长进提高。
pygame编程框架
import pygame
import sys# 初始化Pygame
pygame.init()# 设置窗口大小
screen_size = (800, 600)# 创建窗口
screen = pygame.display.set_mode(screen_size)# 设置窗口标题
pygame.display.set_caption("Pygame Example")# 主循环
while True:# 处理事件for event in pygame.event.get():if event.type == pygame.QUIT:pygame.quit()sys.exit()elif event.type == ...... // 处理按键事件# 填充背景色screen.fill((255, 255, 255))# 绘制矩形pygame.draw.rect(screen, (0, 0, 255), (400, 300, 100, 50))# 更新显示pygame.display.flip()最终版的源代码及音乐文件列表如下:
下载地址:
https://download.csdn.net/download/boysoft2002/88231961
相关文章:

Python “贪吃蛇”游戏,在不断改进中学习pygame编程
目录 前言 改进过程一 增加提示信息 原版帮助摘要 pygame.draw pygame.font class Rect class Surface 改进过程二 增加显示得分 改进过程三 增加背景景乐 增加提示音效 音乐切换 静音切换 mixer.music.play 注意事项 原版帮助摘要 pygame.mixer pygame.mix…...

Linux网络编程_Ubuntu环境配置安装
文章目录: 一:基于vmware虚拟机安装Ubuntu系统(虚拟机) 1.vmware下载 2.Ubuntu系统下载 3.配置 3.1 无法连网:这里很容易出现问题 3.2 更换国内源 3.3 无法屏幕适配全屏 3.4 汉化 二:直接安装Ubun…...

gradle java插件
gradle java插件 1. 由来 Gradle是一种现代化的构建工具,Java插件是Gradle官方提供的插件,用于支持和管理Java项目的构建过程。 2. 常见五种示例和说明 示例1:配置源代码目录和编译选项 plugins {id java }sourceSets {main {java {srcD…...

神经网络基础-神经网络补充概念-48-rmsprop
概念## 标题 RMSProp(Root Mean Square Propagation)是一种优化算法,用于在训练神经网络等机器学习模型时自适应地调整学习率,以加速收敛并提高性能。RMSProp可以有效地处理不同特征尺度和梯度变化,对于处理稀疏数据和…...
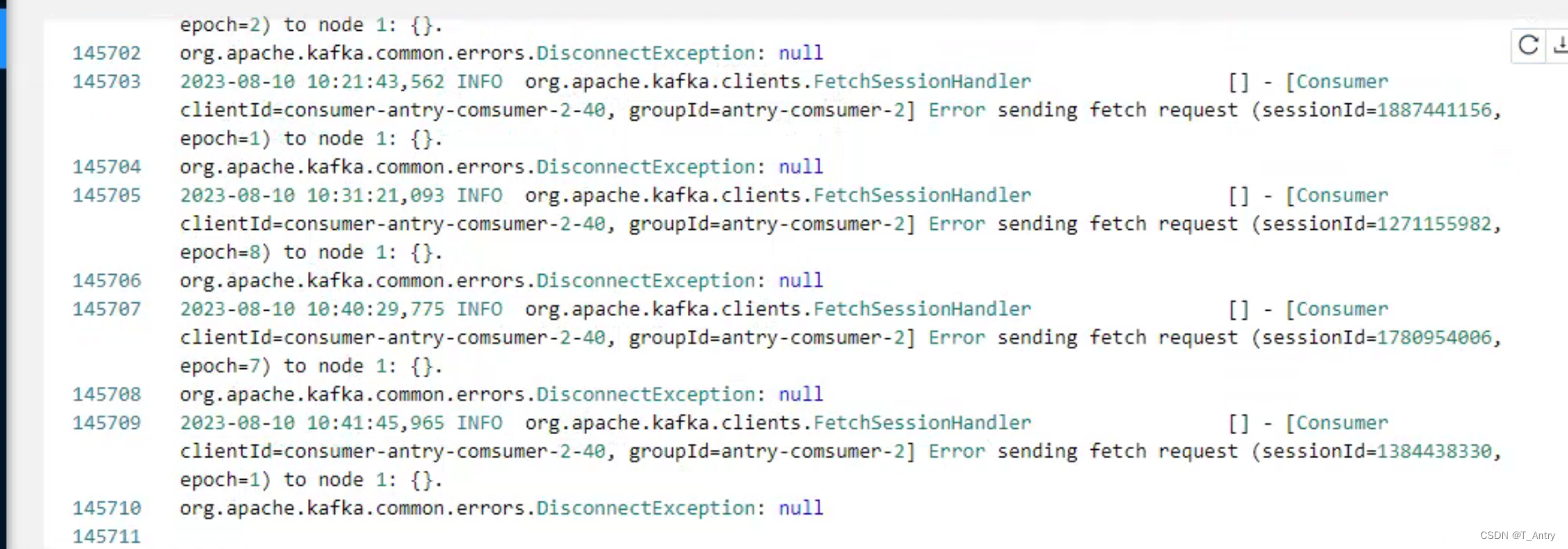
分析Flink,源和算子并行度不一致时,运行一段时间后,看似不再继续消费的问题,提供解决思路。
文章目录 背景分析 问题来了比较一开始的情况解决方式 背景 之前有分析过一次类似问题,最终结论是在keyby之后,其中有一个key数量特别庞大,导致对应的subtask压力过大,进而使得整个job不再继续运作。在这个问题解决之后ÿ…...
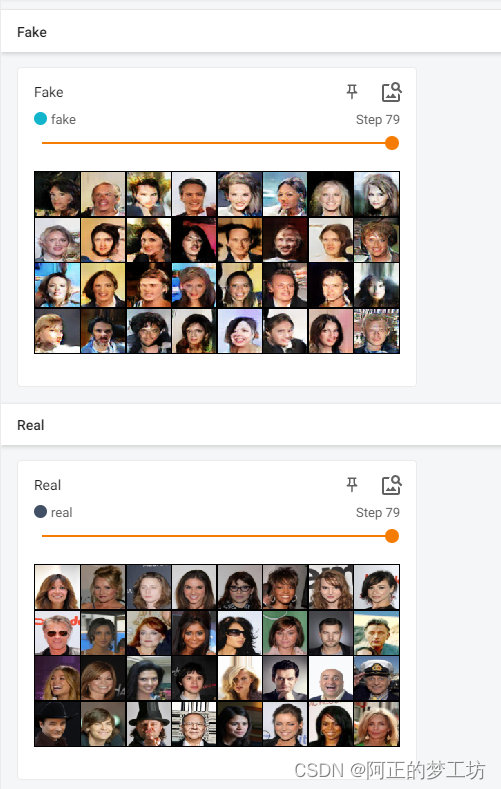
PyTorch训练深度卷积生成对抗网络DCGAN
文章目录 DCGAN介绍代码结果参考 DCGAN介绍 将CNN和GAN结合起来,把监督学习和无监督学习结合起来。具体解释可以参见 深度卷积对抗生成网络(DCGAN) DCGAN的生成器结构: 图片来源:https://arxiv.org/abs/1511.06434 代码 model.py impor…...

Spring-4-掌握Spring事务传播机制
今日目标 能够掌握Spring事务配置 Spring事务管理 1 Spring事务简介【重点】 1.1 Spring事务作用 事务作用:在数据层保障一系列的数据库操作同成功同失败 Spring事务作用:在数据层或业务层保障一系列的数据库操作同成功同失败 1.2 案例分析Spring…...
[PyTorch][chapter 49][创建自己的数据集 1]
前言: 后面几章主要利用DataSet 创建自己的数据集,实现建模, 训练,迁移等功能。 目录: pokemon 数据集深度学习工程步骤 一 pokemon 数据集介绍 1.1 pokemon: 数据集地址: 百度网盘路径: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1…...
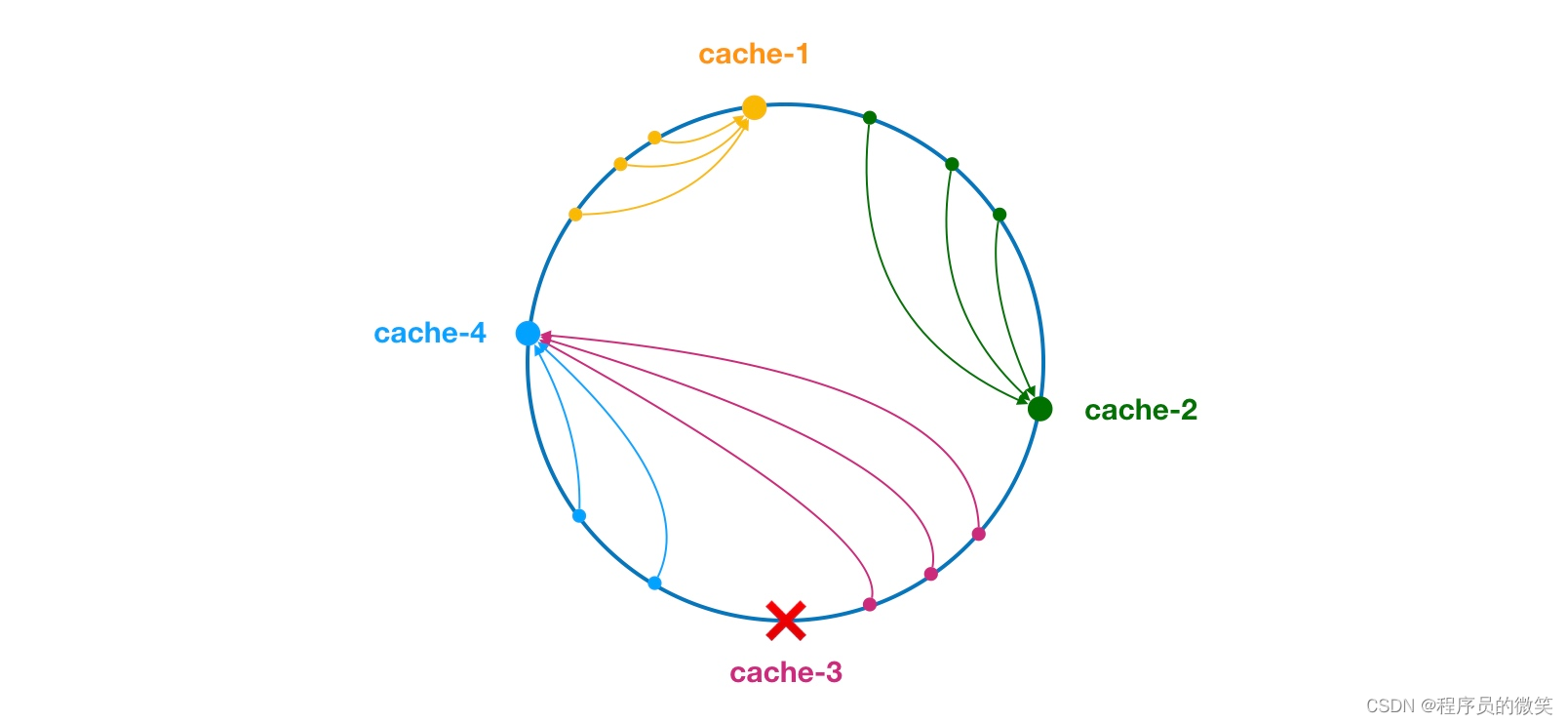
中间件(二)dubbo负载均衡介绍
一、负载均衡概述 支持轮询、随机、一致性hash和最小活跃数等。 1、轮询 ① sequences:内部的序列计数器 ② 服务器接口方法权重一样:(sequences1)%服务器的数量(决定调用)哪个服务器的服务。 ③ 服务器…...
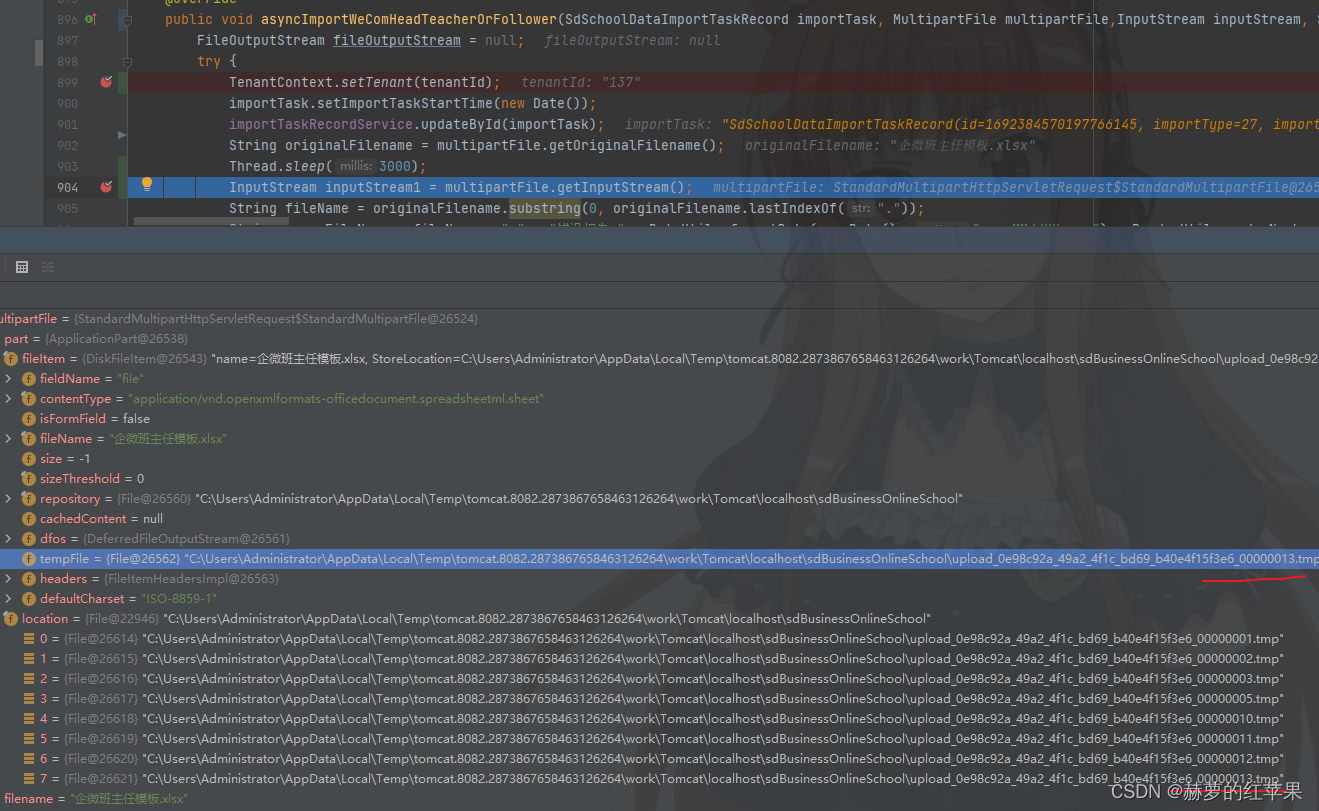
springboot异步文件上传获取输入流提示找不到文件java.io.FileNotFoundException
springboot上传文件,使用异步操作处理上传的文件数据,出现异常如下: 这个是在异步之后使用传过来的MultipartFile对象尝试调用getInputStream方法发生的异常。 java.io.FileNotFoundException: C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Temp\to…...

安装jenkins-cli
1、要在 Linux 操作系统上安装 jcli curl -L https://github.com/jenkins-zh/jenkins-cli/releases/latest/download/jcli-linux-amd64.tar.gz|tar xzv sudo mv jcli /usr/local/bin/ 在用户根目录下,增加 jcli 的配置文件: jcli config gen -ifalse …...

linux通过NC工具启动临时端口监听
1.安装nc工具 yum install nc -y2. 启动监听指定端口 #例如监听8080端口 nc -lk 8080#后台监听 nc -lk 8080 &3. 验证 #通过另外一台网络能通的机器,telnet 该机器ip 监听端口能通,并且能接手数据 telnet 192.xxx.xxx.xx 8080...

开源语音聊天软件Mumble
网友 大气 告诉我,Openblocks在国内还有个版本叫 码匠,更贴合国内软件开发的需求,如接入了国内常用的身份认证,接入了国内的数据库和云服务,也对小程序、企微 sdk 等场景做了适配。 在 https://majiang.co/docs/docke…...

JDK 1.6与JDK 1.8的区别
ArrayList使用默认的构造方式实例 jdk1.6默认初始值为10jdk1.8为0,第一次放入值才初始化,属于懒加载 Hashmap底层 jdk1.6与jdk1.8都是数组链表 jdk1.8是链表超过8时,自动转为红黑树 静态方式不同 jdk1.6是先初始化static后执行main方法。 jdk1.8是懒加…...

单片机实训报告
这周我们进行了单片机实训,一周中我们通过七个项目1:P1 口输入/输出 2:继电器控制 3 音频控制 4:子程序设计 5:字符碰头程序设计 6:外部中断 7: 急救车与交通信号灯,练习编写了子程…...

【编织时空四:探究顺序表与链表的数据之旅】
本章重点 链表的分类 带头双向循环链表接口实现 顺序表和链表的区别 缓存利用率参考存储体系结构 以及 局部原理性。 一、链表的分类 实际中链表的结构非常多样,以下情况组合起来就有8种链表结构: 1. 单向或者双向 2. 带头或者不带头 3. 循环或者非…...

PHP8的字符串操作1-PHP8知识详解
字符串是php中最重要的数据之一,字符串的操作在PHP编程占有重要的地位。在使用PHP语言开发web项目的过程中,为了实现某些功能,经常需要对某些字符串进行特殊的处理,比如字符串的格式化、字符串的连接与分割、字符串的比较、查找等…...
电脑提示msvcp140.dll丢失的解决方法,dll组件怎么处理
Windows系统有时在打开游戏或者软件时, 系统会弹窗提示缺少“msvcp140.dll.dll”文件 或者类似错误提示怎么办? 错误背景: msvcp140.dll是Microsoft Visual C Redistributable Package中的一个动态链接库文件,它在运行软件时提…...

stable diffusion基础
整合包下载:秋叶大佬 【AI绘画8月最新】Stable Diffusion整合包v4.2发布! 参照:基础04】目前全网最贴心的Lora基础知识教程! VAE 作用:滤镜微调 VAE下载地址:C站(https://civitai.com/models…...

Greiner–Hormann裁剪算法深度探索:C++实现与应用案例
介绍 在计算几何中,裁剪是一个核心的主题。特别是,多边形裁剪已经被广泛地应用于计算机图形学,地理信息系统和许多其他领域。Greiner-Hormann裁剪算法是其中之一,提供了一个高效的方式来计算两个多边形的交集、并集等。在本文中&…...

关于iview组件中使用 table , 绑定序号分页后序号从1开始的解决方案
问题描述:iview使用table 中type: "index",分页之后 ,索引还是从1开始,试过绑定后台返回数据的id, 这种方法可行,就是后台返回数据的每个页面id都不完全是按照从1开始的升序,因此百度了下,找到了…...

【解密LSTM、GRU如何解决传统RNN梯度消失问题】
解密LSTM与GRU:如何让RNN变得更聪明? 在深度学习的世界里,循环神经网络(RNN)以其卓越的序列数据处理能力广泛应用于自然语言处理、时间序列预测等领域。然而,传统RNN存在的一个严重问题——梯度消失&#…...

学习STC51单片机31(芯片为STC89C52RCRC)OLED显示屏1
每日一言 生活的美好,总是藏在那些你咬牙坚持的日子里。 硬件:OLED 以后要用到OLED的时候找到这个文件 OLED的设备地址 SSD1306"SSD" 是品牌缩写,"1306" 是产品编号。 驱动 OLED 屏幕的 IIC 总线数据传输格式 示意图 …...
指令的指南)
在Ubuntu中设置开机自动运行(sudo)指令的指南
在Ubuntu系统中,有时需要在系统启动时自动执行某些命令,特别是需要 sudo权限的指令。为了实现这一功能,可以使用多种方法,包括编写Systemd服务、配置 rc.local文件或使用 cron任务计划。本文将详细介绍这些方法,并提供…...
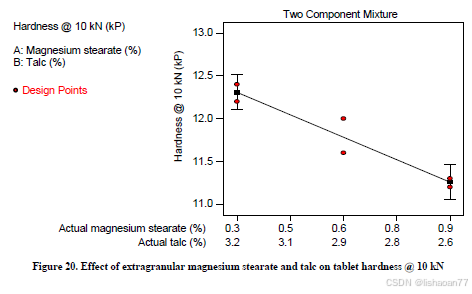
R语言速释制剂QBD解决方案之三
本文是《Quality by Design for ANDAs: An Example for Immediate-Release Dosage Forms》第一个处方的R语言解决方案。 第一个处方研究评估原料药粒径分布、MCC/Lactose比例、崩解剂用量对制剂CQAs的影响。 第二处方研究用于理解颗粒外加硬脂酸镁和滑石粉对片剂质量和可生产…...

【Go语言基础【12】】指针:声明、取地址、解引用
文章目录 零、概述:指针 vs. 引用(类比其他语言)一、指针基础概念二、指针声明与初始化三、指针操作符1. &:取地址(拿到内存地址)2. *:解引用(拿到值) 四、空指针&am…...

MySQL JOIN 表过多的优化思路
当 MySQL 查询涉及大量表 JOIN 时,性能会显著下降。以下是优化思路和简易实现方法: 一、核心优化思路 减少 JOIN 数量 数据冗余:添加必要的冗余字段(如订单表直接存储用户名)合并表:将频繁关联的小表合并成…...

4. TypeScript 类型推断与类型组合
一、类型推断 (一) 什么是类型推断 TypeScript 的类型推断会根据变量、函数返回值、对象和数组的赋值和使用方式,自动确定它们的类型。 这一特性减少了显式类型注解的需要,在保持类型安全的同时简化了代码。通过分析上下文和初始值,TypeSc…...

tomcat指定使用的jdk版本
说明 有时候需要对tomcat配置指定的jdk版本号,此时,我们可以通过以下方式进行配置 设置方式 找到tomcat的bin目录中的setclasspath.bat。如果是linux系统则是setclasspath.sh set JAVA_HOMEC:\Program Files\Java\jdk8 set JRE_HOMEC:\Program Files…...

Python 训练营打卡 Day 47
注意力热力图可视化 在day 46代码的基础上,对比不同卷积层热力图可视化的结果 import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.optim as optim from torchvision import datasets, transforms from torch.utils.data import DataLoader import matplotlib.pypl…...
