torch一些操作
Pytorch文档
- Pytorch 官方文档
https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/index.html
- pytorch 里的一些基础tensor操作讲的不错
https://blog.csdn.net/abc13526222160/category_8614343.html
- 关于pytorch的Broadcast,合并与分割,数学运算,属性统计以及高阶操作
https://blog.csdn.net/abc13526222160/article/details/103520465
broadcast机制
对于涉及计算的两个tensor, 对于数量不匹配的dim, 可以进行自动重复拷贝,使得dim进行批评
Broadcast它能维度扩展和expand一样,它是自动扩展,并且不需要拷贝数据,能够节省内存。关键思想:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-WMOpueEB-1692628397278)(attachment:image.png)]
import sys, osimport torch, torchvision
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from mpl_toolkits import mplot3d
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
1. Pytorch索引与切片以及维度变换
TODO: https://zhangkaifang.blog.csdn.net/article/details/103517970
index, view, reshape, squeeze, unsqueeze, transpose/t, permute , expand/repeat
transpose()函数表示矩阵的维度交换,接受的参数为要交换的哪两个维度。
permute: transpose()函数一次只能两两交换。【b, c, h, w】=> 【b, w, h, c】,比如原来一个人的图片,交换过后图片可能不是人了,我们还希望变成原来的样子,可以看成多维度交换,其中参数为新的维度顺序。同样的道理permute函数也会把内存的顺序给打乱,因此要是涉及contious这个错误的时候,需要额外添加.contiguous()函数,来把内存的顺序变得连续。
2.1 合并与分割 cat, stack, split, chunk repeat
stack一般叠加在新的维度,concatenate在已有的dim上进行扩展,vstack,dstack,hstack分别是在dim = [0, 1, 2]上进行叠加
a = torch.rand([5, 5, 3])print('-'*10 + 'stack' + '-'*10)
t1 = torch.stack([a, a], dim = 0)
print('pre', a.shape, 'post',t1.shape)t1 = torch.stack([a, a], dim = 1)
print('pre', a.shape, 'post',t1.shape)t1 = torch.stack([a, a], dim = 2)
print('pre', a.shape, 'post',t1.shape)t1 = torch.stack([a, a], dim = 3)
print('pre', a.shape, 'post',t1.shape)print('-'*10 + 'concatenate' + '-'*10)
t1 = torch.cat([a, a], dim = 0)
print('pre', a.shape, 'post',t1.shape)t1 = torch.cat([a, a], dim = 1)
print('pre', a.shape, 'post',t1.shape)t1 = torch.cat([a, a], dim = 2)
print('pre', a.shape, 'post',t1.shape)print('-'*10 + 'v-h-d stack' + '-'*10)t1 = torch.vstack([a, a])
print('pre', a.shape, 'post',t1.shape)t1 = torch.hstack([a, a])
print('pre', a.shape, 'post',t1.shape)t1 = torch.dstack([a, a])
print('pre', a.shape, 'post',t1.shape)----------stack----------
pre torch.Size([5, 5, 3]) post torch.Size([2, 5, 5, 3])
pre torch.Size([5, 5, 3]) post torch.Size([5, 2, 5, 3])
pre torch.Size([5, 5, 3]) post torch.Size([5, 5, 2, 3])
pre torch.Size([5, 5, 3]) post torch.Size([5, 5, 3, 2])
----------concatenate----------
pre torch.Size([5, 5, 3]) post torch.Size([10, 5, 3])
pre torch.Size([5, 5, 3]) post torch.Size([5, 10, 3])
pre torch.Size([5, 5, 3]) post torch.Size([5, 5, 6])
----------v-h-d stack----------
pre torch.Size([5, 5, 3]) post torch.Size([10, 5, 3])
pre torch.Size([5, 5, 3]) post torch.Size([5, 10, 3])
pre torch.Size([5, 5, 3]) post torch.Size([5, 5, 6])
torch.split函数 按照长度进行切分
torch.split(tensor, split_size_or_sections, dim=0)
split_size_or_sections:需要切分的大小(int or list )
dim:切分维度
torch.chunk函数 按照数量进行切分
a = torch.rand([6, 256, 10, 10 ])
print('a', a.shape)t1 = torch.split(a, [3,3], dim = 0)
print('dim %d'%(0))
for ti in t1:print(ti.shape)print('dim %d'%(1))
t1 = torch.split(a, [128,128], dim = 1)
for ti in t1:print(ti.shape)print('dim %d'%(2))
t1 = torch.split(a, [5,5], dim = 2)
for ti in t1:print(ti.shape)
a torch.Size([6, 256, 10, 10])
dim 0
torch.Size([3, 256, 10, 10])
torch.Size([3, 256, 10, 10])
dim 1
torch.Size([6, 128, 10, 10])
torch.Size([6, 128, 10, 10])
dim 2
torch.Size([6, 256, 5, 10])
torch.Size([6, 256, 5, 10])
a = torch.rand([6, 256, 10, 10 ])
print('a', a.shape)t1 = torch.chunk(a, 2, dim = 0)
print('dim %d'%(0))
for ti in t1:print(ti.shape)print('dim %d'%(1))
t1 = torch.chunk(a, 2, dim = 1)
for ti in t1:print(ti.shape)print('dim %d'%(2))
t1 = torch.chunk(a, 2, dim = 2)
for ti in t1:print(ti.shape)
a torch.Size([6, 256, 10, 10])
dim 0
torch.Size([3, 256, 10, 10])
torch.Size([3, 256, 10, 10])
dim 1
torch.Size([6, 128, 10, 10])
torch.Size([6, 128, 10, 10])
dim 2
torch.Size([6, 256, 5, 10])
torch.Size([6, 256, 5, 10])
torch.repeat()&np.tile()
参数为沿着不同维度的扩展, 对于一个给定的tensor 给出其dims以及repeat的次数,类似于np.tile
由后往前进行匹配, 若超出当前的dims, 则新建一个dim, 进行repeat
当超出tensor 本身的 dims时,第一个dim 新起一个dim, 即沿着batch方向进行扩展
参考资料见
https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.Tensor.repeat.html?highlight=repeat#torch.Tensor.repeat
a = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3])
print(a.shape)
t1 = a.repeat(5, 2)
print('-'*10);print(t1.shape, a.shape); print(a,'\n', t1)t1 = a.repeat(2, 3, 2)
print('-'*10);print(t1.shape, a.shape); print(a,'\n', t1)a = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
print(a.shape)t1 = a.repeat([1, 1])
print('-'*10);print(t1.shape, a.shape); print(a,'\n', t1)t1 = a.repeat([2, 1]) # dim0 repeat 2
print('-'*10);print(t1.shape, a.shape); print(a,'\n', t1)t1 = a.repeat([1, 2]) # dim1 repeat 2
print('-'*10);print(t1.shape, a.shape); print(a,'\n', t1)t1 = a.repeat([2, 1, 1])
print('-'*10);print(t1.shape, a.shape); print(a,'\n', t1)torch.Size([3])
----------
torch.Size([5, 6]) torch.Size([3])
tensor([1, 2, 3]) tensor([[1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3],[1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3],[1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3],[1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3],[1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3]])
----------
torch.Size([2, 3, 6]) torch.Size([3])
tensor([1, 2, 3]) tensor([[[1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3],[1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3],[1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3]],[[1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3],[1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3],[1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3]]])
torch.Size([2, 3])
----------
torch.Size([2, 3]) torch.Size([2, 3])
tensor([[1, 2, 3],[4, 5, 6]]) tensor([[1, 2, 3],[4, 5, 6]])
----------
torch.Size([4, 3]) torch.Size([2, 3])
tensor([[1, 2, 3],[4, 5, 6]]) tensor([[1, 2, 3],[4, 5, 6],[1, 2, 3],[4, 5, 6]])
----------
torch.Size([2, 6]) torch.Size([2, 3])
tensor([[1, 2, 3],[4, 5, 6]]) tensor([[1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3],[4, 5, 6, 4, 5, 6]])
----------
torch.Size([2, 2, 3]) torch.Size([2, 3])
tensor([[1, 2, 3],[4, 5, 6]]) tensor([[[1, 2, 3],[4, 5, 6]],[[1, 2, 3],[4, 5, 6]]])
2.2 torch生成grid函数
-
torch.arange类似于np.arange[left, right), not include right. -
torch.linspace包括left, right, 且分割为若干个点 -
torch.meshgrid叠加后生成 x 和 y (opencv坐标系)下两个h*w的tensor。为了组装为后期可以用的点,所以需要先翻转后使用。
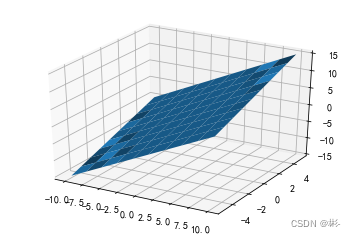
xs = torch.linspace(-10, 10, 10)
ys = torch.linspace(-5, 5, 10)x, y = torch.meshgrid(xs, ys, indexing='ij')
z = x + yax = plt.axes(projection= '3d')
ax.plot_surface(x.numpy(), y.numpy(), z.numpy())
plt.show()
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-m1idlV1z-1692628397282)(output_15_0.png)]
def coords_grid(batch, ht, wd, device, ifReverse = True):#ht,wd 55, 128coords = torch.meshgrid(torch.arange(ht, device=device), torch.arange(wd, device=device))if ifReverse:#NOTE, coords 为 x, y (opencv 坐标系下), y, x (numpy 坐标系)coords = torch.stack(coords[::-1], dim=0).float() # coords shape [ 2, ht, wd]else:#NOTE coords 为 x, y (numpy 坐标系下)coords = torch.stack(coords, dim=0).float()# 通过[::-1]转变为 y, x(numpy 坐标系)#coords = torch.reshape(coords, [1, 2, ht, wd])coords = coords.repeat(batch, 1, 1, 1)return coordsDEVICE = 'cuda'
grid_opencv = coords_grid(2, 12, 5, DEVICE, ifReverse=True)
grid_numpy = coords_grid(2, 12, 5, DEVICE, ifReverse= False)print(grid_numpy.shape, grid_opencv.shape)def visualize_grid(grid):# sample 1, x & yplot_x = grid[0, 0, :, :].reshape([-1]).cpu().numpy()plot_y = grid[0, 1, :, :].reshape([-1]).cpu().numpy()return plot_x, plot_yplt.figure(figsize=(8,6))
for pici, grid in enumerate([grid_opencv, grid_numpy]):plt.subplot(2, 1, pici + 1)plt.title(['opencv', 'numpy'][pici])plot_x, plot_y = visualize_grid(grid)for i in range(len(plot_x)):plt.scatter([plot_x[i]], [plot_y[i]], c = 'grey', marker = 'o')plt.annotate(xy = (plot_x[i], plot_y[i]), s= str(i))plt.show()/home/chwei/.local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/torch/functional.py:445: UserWarning: torch.meshgrid: in an upcoming release, it will be required to pass the indexing argument. (Triggered internally at ../aten/src/ATen/native/TensorShape.cpp:2157.)return _VF.meshgrid(tensors, **kwargs) # type: ignore[attr-defined]torch.Size([2, 2, 12, 5]) torch.Size([2, 2, 12, 5])
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-4XGp96GA-1692628397283)(output_17_2.png)]

3.1 数学运算
add/sub/mul/div加减乘除
a = torch.rand(3, 4)
b = torch.rand(4) # 这里基于pytorch 的broadcasting进行了dim 0的 broadcastc = a + bprint(a.shape, b.shape, c.shape)
#print(a+b)
#print(torch.add(a, b))print(torch.all(torch.eq(a-b, torch.sub(a, b))))
print(torch.all(torch.eq(a*b, torch.mul(a, b))))
print(torch.all(torch.eq(a/b, torch.div(a, b))))torch.Size([3, 4]) torch.Size([4]) torch.Size([3, 4])
tensor(True)
tensor(True)
tensor(True)
3.2 torch.matmul函数
-
基础case 1: 两个tensor 都是1 dim, If both tensors are 1-dimensional, the dot product (scalar) is returned.
-
基础case 2: 两个tensor 都是2 dims, If both arguments are 2-dimensional, the matrix-matrix product is returned.
-
基础case 3: 一个tensor 是1 dim, 另外一个 2dim. tensor with 1 dim进行扩展到2dim, 以适应 matrix-product
If the first argument is 1-dimensional and the second argument is 2-dimensional, a 1 is prepended to its dimension for the purpose of the matrix multiply. After the matrix multiply, the prepended dimension is removed.
If the first argument is 2-dimensional and the second argument is 1-dimensional, the matrix-vector product is returned. -
基础case 4: Batch Brocasted & batch matrix-product
思路: 把 first dim (batch dim) 排除, 每个sample 进行 matrix-product or vector product
若 有一个tensor 其维度不匹配, 沿着batch dim进行扩展broadcast之后计算
If both arguments are at least 1-dimensional and at least one argument is N-dimensional (where N > 2), then a batched matrix multiply is returned.
If the first argument is 1-dimensional, a 1 is prepended to its dimension for the purpose of the batched matrix multiply and removed after.
If the second argument is 1-dimensional, a 1 is appended to its dimension for the purpose of the batched matrix multiple and removed after.
The non-matrix (i.e. batch) dimensions are broadcasted (and thus must be broadcastable).
For example, if input is a ( j × 1 × n × n ) ( j × 1 × n × n ) (j \times 1 \times n \times n)(j×1×n×n) (j×1×n×n)(j×1×n×n) tensor and other is a ( k × n × n ) ( k × n × n ) (k \times n \times n)(k×n×n) (k×n×n)(k×n×n) tensor, out will be a ( j × k × n × n ) ( j × k × n × n ) (j \times k \times n \times n)(j×k×n×n) (j×k×n×n)(j×k×n×n) tensor.
这里 j j j 是 batch dim, 而 matrix product 执行的位置在于$ (1 \times n \times n) \times (k \times n \times n) $
Note that the broadcasting logic only looks at the batch dimensions when determining if the inputs are broadcastable, and not the matrix dimensions.
For example, if input is a ( j × 1 × n × m ) ( j × 1 × n × m ) (j \times 1 \times n \times m)(j×1×n×m) (j×1×n×m)(j×1×n×m) tensor and other is a ( k × m × p ) ( k × m × p ) (k \times m \times p)(k×m×p) (k×m×p)(k×m×p) tensor, these inputs are valid for broadcasting even though the final two dimensions (i.e. the matrix dimensions) are different. out will be a ( j × k × n × p ) ( j × k × n × p ) (j \times k \times n \times p)(j×k×n×p) (j×k×n×p)(j×k×n×p) tensor.
# vector x vector case 1
tensor1 = torch.randn(3)
tensor2 = torch.randn(3)
out = torch.matmul(tensor1, tensor2)
print('input', tensor1.shape, tensor2.shape, 'output',out.shape)
# matrix x matrix case 2
tensor1 = torch.randn(3, 1)
tensor2 = torch.randn(1, 3)
out = torch.matmul(tensor1, tensor2)
print('input', tensor1.shape, tensor2.shape, 'output',out.shape)# matrix x vector case 3
tensor1 = torch.randn(3, 4)
tensor2 = torch.randn(4)
out = torch.matmul(tensor1, tensor2)
print('input', tensor1.shape, tensor2.shape, 'output',out.shape)# batched matrix x broadcasted vector
tensor1 = torch.randn(10, 3, 4) # first dim is batch dim
tensor2 = torch.randn(4)
out = torch.matmul(tensor1, tensor2)
print('input', tensor1.shape, tensor2.shape, 'output',out.shape)# batched matrix x batched matrix
tensor1 = torch.randn(10, 3, 4) # first dim is batch dim
tensor2 = torch.randn(10, 4, 5) # first dim is batch dim
out = torch.matmul(tensor1, tensor2)
# matrix product (3 * 4 ) * (4 * 5) -> 3 * 5
print('input', tensor1.shape, tensor2.shape, 'output',out.shape) # batched matrix x broadcasted matrix
tensor1 = torch.randn(10, 3, 4) # first dim is batch dim
tensor2 = torch.randn(4, 5)
out = torch.matmul(tensor1, tensor2)
# matrix product (3 * 4 ) * (4 * 5) -> 3 * 5
print('input', tensor1.shape, tensor2.shape, 'output',out.shape)
input torch.Size([3]) torch.Size([3]) output torch.Size([])
input torch.Size([3, 1]) torch.Size([1, 3]) output torch.Size([3, 3])
input torch.Size([3, 4]) torch.Size([4]) output torch.Size([3])
input torch.Size([10, 3, 4]) torch.Size([4]) output torch.Size([10, 3])
input torch.Size([10, 3, 4]) torch.Size([10, 4, 5]) output torch.Size([10, 3, 5])
input torch.Size([10, 3, 4]) torch.Size([4, 5]) output torch.Size([10, 3, 5])
3.3 pow矩阵的次方以及sqrt/rsqrt/exp/log
a =torch.full([2, 2], 3) # 使用torch.full函数创建一个shape[2, 2],元素全部为3的张量
print(a.pow(2))
print(torch.pow(a, 2))
print(a**2)b = a**2
print(b.sqrt())
print(b.rsqrt()) # 平方根的导数print('=============================')
a = torch.exp(torch.ones(2, 2))
print(a)
print(torch.log(a)) # 默认以e为底,使用2为底或者其他的,自己设置.tensor([[9, 9],[9, 9]])
tensor([[9, 9],[9, 9]])
tensor([[9, 9],[9, 9]])
tensor([[3., 3.],[3., 3.]])
tensor([[0.3333, 0.3333],[0.3333, 0.3333]])
=============================
tensor([[2.7183, 2.7183],[2.7183, 2.7183]])
tensor([[1., 1.],[1., 1.]])
3.4 round矩阵近似运算
.floor()向下取整,.ceil()向上取整,.trunc()截取整数,.frac截取小数。
a = torch.tensor(3.14)
# .floor()向下取整,.ceil()向上取整,.trunc()截取整数,.frac截取小数。
print(a.floor(), a.ceil(), a.trunc(), a.frac())print(a.round())
b = torch.tensor(3.5)
print(b.round())
tensor(3.) tensor(4.) tensor(3.) tensor(0.1400)
tensor(3.)
tensor(4.)
3.6. clamp(裁剪)用的多
主要用在梯度裁剪里面,梯度离散(不需要从网络层面解决,因为梯度非常小,接近0)和梯度爆炸(梯度非常大,100已经算是大的了)。因此在网络训练不稳定的时候,可以打印一下梯度的模看看,w.grad.norm(2)表示梯度的二范数(一般100,1000已经算是大的了,一般10以内算是合适的)。
a.clamp(min):表示tensor a中小于10的都赋值为10,表示最小值为10;
grad = torch.rand(2, 3)*15
print(grad)
print(grad.max(), grad.median(), grad.min())
print('============================================')
print(grad.clamp(10)) # 最小值限定为10,小于10的都变为10;print(grad.clamp(8, 15))
print(torch.clamp(grad, 8, 15))tensor([[ 3.7078, 11.4988, 7.9875],[ 0.6747, 0.6269, 12.3761]])
tensor(12.3761) tensor(3.7078) tensor(0.6269)
============================================
tensor([[10.0000, 11.4988, 10.0000],[10.0000, 10.0000, 12.3761]])
tensor([[ 8.0000, 11.4988, 8.0000],[ 8.0000, 8.0000, 12.3761]])
tensor([[ 8.0000, 11.4988, 8.0000],[ 8.0000, 8.0000, 12.3761]])
4. 统计属性相关操作 TODO
4.1. norm范数,prod张量元素累乘(阶乘)
4.2. mean/sum/max/min/argmin/argmax
4.3. kthvalue()和topk()
这里: topk(3, dim=1)(最大的3个)返回结果如下图所示,如果把largest设置为False就是默认最小的几个。
这里: kthvalue(k,dim=1)表示第k小的(默认表示小的)。下面图中的一共10中可能,第8小就是表示第3大。
4.4. 比较运算符号>,>=,<,<=,!=,==
greater than表示大于等于。equal表示等于eq。
5. batch检索
torch.where, gather, index_select, masked_select, nonzero函数
TODO: https://www.cnblogs.com/liangjianli/p/13754817.html#3-gather%E5%87%BD%E6%95%B0
5.1 torch.where
高阶操作where和gather
5.2 torch.gather
TODO 依旧不是很理解,没有完全理解
gather 收集输入的特定维度指定位置的数值
注意,torch.gather里的index tensor必须是longtensor类型
- 官方解释
https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.gather.html?highlight=gather#torch.gather
out[i][j][k] = input[index[i][j][k]][j][k] # if dim == 0
out[i][j][k] = input[i][index[i][j][k]][k] # if dim == 1
out[i][j][k] = input[i][j][index[i][j][k]] # if dim == 2
a = torch.rand([4, 5])
indexes = torch.LongTensor([[4, 2],[3, 1],[2, 4],[1,2]])# 这个在q-learning中的batch actions中常见,注意一下
a_ = torch.gather(a, dim = 1, index = indexes)print(a.shape, a_.shape, '\n', a, '\n', a_)indexes = torch.LongTensor([[ 0, 2, 2], [1, 2, 3]])
a_ = torch.gather(a, dim = 0, index = indexes)
print(a.shape, a_.shape, '\n', a, '\n', a_)
torch.Size([4, 5]) torch.Size([4, 2]) tensor([[0.1330, 0.2177, 0.2177, 0.3287, 0.0809],[0.1803, 0.4438, 0.9827, 0.6353, 0.3548],[0.4980, 0.6792, 0.3885, 0.6338, 0.4985],[0.8367, 0.4682, 0.0805, 0.6161, 0.4861]]) tensor([[0.0809, 0.2177],[0.6353, 0.4438],[0.3885, 0.4985],[0.4682, 0.0805]])
torch.Size([4, 5]) torch.Size([2, 3]) tensor([[0.1330, 0.2177, 0.2177, 0.3287, 0.0809],[0.1803, 0.4438, 0.9827, 0.6353, 0.3548],[0.4980, 0.6792, 0.3885, 0.6338, 0.4985],[0.8367, 0.4682, 0.0805, 0.6161, 0.4861]]) tensor([[0.1330, 0.6792, 0.3885],[0.1803, 0.6792, 0.0805]])
10. torch vision下的一些操作
10.1 F.grid_sample
根据位置 对 batch 里的 feature flow 进行采样,可以理解为index, 但本函数允许index里为float类型(采用bilinear插值实现)
函数
torch.nn.functional.grid_sample(input, grid, mode='bilinear', padding_mode='zeros', align_corners=None)
iven an input and a flow-field grid, computes the output using input values and pixel locations from grid.
input: (N, C, Hin, Win)
grid: (N, Hout, Wout, 2) , 其中最后一维为opencv 坐标系下的x & y,
output: (N, C, Hout, Wout)
NOTE,输入的grid,需根据 input 的Hin, Win进行归一化到 -1 ~ 1,
grid specifies the sampling pixel locations normalized by the input spatial dimensions.
Therefore, it should have most values in the range of [-1, 1]. For example, values x = -1, y = -1 is the left-top pixel of input, and values x = 1, y = 1 is the right-bottom pixel of input.
参考资料:https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.functional.grid_sample.html?highlight=grid_sample#torch.nn.functional.grid_sample
以下通过图片展示如何使用:
DEVICE = 'cuda'def load_image(imfile):img = np.array(Image.open(imfile)).astype(np.uint8)img = torch.from_numpy(img).permute(2, 0, 1).float() # h, w, dim -> dim, h, wreturn img.to(DEVICE)def visualize(img):#input imgshape: 3, w, h# NOTE, dims convert, device convert, numpy convert, and dtype convertreturn img.permute(1, 2, 0).cpu().numpy().astype(np.uint8)def coords_grid(batch, ht, wd, device, ifReverse = True):#ht,wd 55, 128coords = torch.meshgrid(torch.arange(ht, device=device), torch.arange(wd, device=device))if ifReverse:#NOTE, coords 为 x, y (opencv 坐标系下), y, x (numpy 坐标系)coords = torch.stack(coords[::-1], dim=0).float() # coords shape [ 2, ht, wd]else:#NOTE coords 为 x, y (numpy 坐标系下)coords = torch.stack(coords, dim=0).float()# 通过[::-1]转变为 y, x(numpy 坐标系)#coords = torch.reshape(coords, [1, 2, ht, wd])coords = coords.repeat(batch, 1, 1, 1)return coords# 载入图片并显示
img1, img2 = load_image('demo-frames/frame_0016.png'), load_image('demo-frames/frame_0017.png')inputImg = torch.cat([img1.unsqueeze(0), img2.unsqueeze(0)], 0)
print(img1.shape, img2.shape, inputImg.shape)#------ visualize -----------
img1_, img2_ = visualize(img1), visualize(img2)plt.subplot(2, 1, 1)
plt.imshow(img1_)plt.subplot(2, 1, 2)
plt.imshow(img2_)
plt.show()
torch.Size([3, 436, 1024]) torch.Size([3, 436, 1024]) torch.Size([2, 3, 436, 1024])
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-zA8xwrlK-1692628397284)(output_36_1.png)]

# 生成grid
hImg, wImg = img1.shape[-2:]grid = coords_grid(batch = 2, ht = 100, wd = 100, device = 'cuda', ifReverse = True)
print(grid.shape) # dim 1: y & x(numpy 坐标系), x & y (opencv坐标系)torch.Size([2, 2, 100, 100])
# grid归一化操作
grid = grid.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
ygrid, xgrid = grid.split([1, 1], dim = -1) # 这里的xgrid, ygrid指的是 numpy 坐标系
print(grid.shape, xgrid.shape, ygrid.shape)ygrid = 2 * ygrid/(wImg - 1) -1
xgrid = 2 * xgrid/(hImg - 1) -1grid = torch.cat([ygrid, xgrid], dim=-1)
grid = grid.to(DEVICE)
# 输入的grid 最后一维为 opencv坐标系下的x & yinputImg_ = F.grid_sample(inputImg, grid, align_corners=True) # size 7040, 1, 9,9torch.Size([2, 100, 100, 2]) torch.Size([2, 100, 100, 1]) torch.Size([2, 100, 100, 1])
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
img_i = visualize(inputImg[0, :, :, :])
plt.imshow(img_i)
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)img_o = visualize(inputImg_[0, :, :, :])
plt.imshow(img_o)
plt.show()print(inputImg.shape, img_i.shape, img_o.shape)
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-l9dvPqBJ-1692628397285)(output_39_0.png)]

torch.Size([2, 3, 436, 1024]) (436, 1024, 3) (100, 100, 3)
上/下采样 方法1
F.interpolate
功能:利用插值方法,对输入的张量数组进行上\下采样操作,换句话说就是科学合理地改变数组的尺寸大小,尽量保持数据完整。
官方文档: https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.functional.interpolate.html?highlight=f%20interpolate#torch.nn.functional.interpolate
img1, img2 = load_image('demo-frames/frame_0016.png'), load_image('demo-frames/frame_0017.png')
inputImg = torch.cat([img1.unsqueeze(0), img2.unsqueeze(0)], 0)
print(img1.shape, img2.shape, inputImg.shape)torch.Size([3, 436, 1024]) torch.Size([3, 436, 1024]) torch.Size([2, 3, 436, 1024])
new_size = (2* inputImg.shape[2], 2 * inputImg.shape[3])
mode = 'bilinear'
inputImg_ = F.interpolate(inputImg, size=new_size, mode=mode, align_corners=True)
plt.subplot(2, 1, 1)
img_i = visualize(inputImg[0, :, :, :])
plt.imshow(img_i)
plt.subplot(2, 1, 2)
img_o = visualize(inputImg_[0, :, :, :])
plt.imshow(img_o)
plt.show()print(inputImg.shape, img_i.shape, img_o.shape)
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-CNtrY6FN-1692628397286)(output_43_0.png)]

torch.Size([2, 3, 436, 1024]) (436, 1024, 3) (872, 2048, 3)
相关文章:

torch一些操作
Pytorch文档 Pytorch 官方文档 https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/index.html pytorch 里的一些基础tensor操作讲的不错 https://blog.csdn.net/abc13526222160/category_8614343.html 关于pytorch的Broadcast,合并与分割,数学运算,属性统计以及高阶操作 https://blog.csd…...
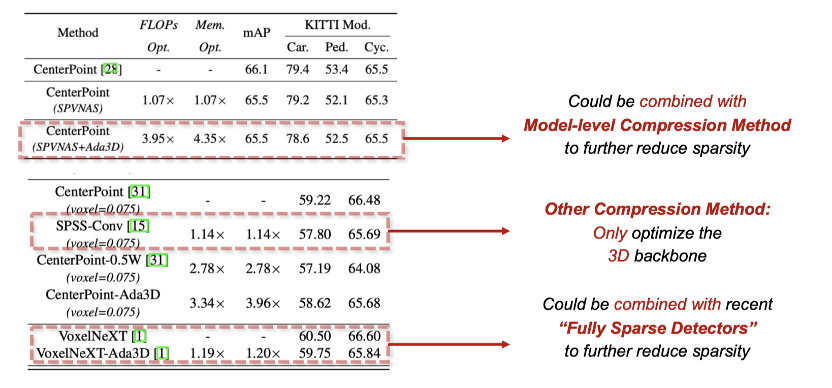
ICCV23 | Ada3D:利用动态推理挖掘3D感知任务中数据冗余性
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.08209 项目主页:https://a-suozhang.xyz/ada3d.github.io/ 01. 背景与动因 3D检测(3D Detection)任务是自动驾驶任务中的重要任务。由于自动驾驶任务的安全性至关重要(safety-critic),对感知算法的延…...

软件工程模型-架构师之路(四)
软件工程模型 敏捷开发: 个体和交互 胜过 过程和工具、可以工作的软件 胜过 面面俱到的文件、客户合作胜过合同谈判、响应变化 胜过 循序计划。(适应需求变化,积极响应) 敏捷开发与其他结构化方法区别特点:面向人的…...
ubuntu20.04共享文件夹—— /mnt/hgfs里没有共享文件夹
参考文章:https://blog.csdn.net/Edwinwzy/article/details/129580636 虚拟机启用共享文件夹后,/mnt/hgfs下面为空,使用 vmware-hgfsclient 查看设置的共享文件夹名字也是为空。 解决方法: 1. 重新安装vmware tools. 在菜单…...
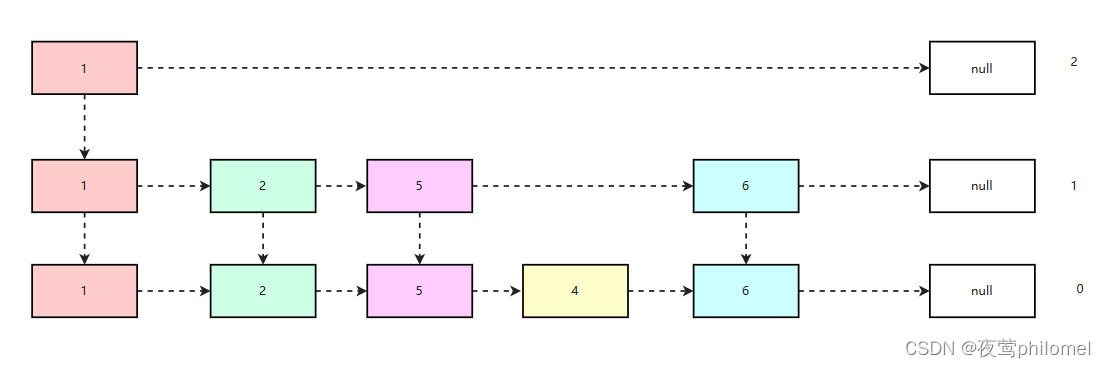
Redis中的有序集合及其底层跳表
前言 本文着重介绍Redis中的有序集合的底层实现中的跳表 有序集合 Sorted Set Redis中的Sorted Set 是一个有序的无重复值的集合,他底层是使用压缩列表和跳表实现的,和Java中的HashMap底层数据结构(1.8)链表红黑树异曲同工之妙…...
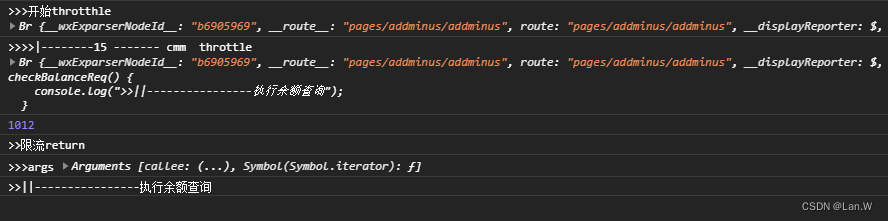
js 小程序限流函数 return闭包函数执行不了
问题: 调用限流 ,没走闭包的函数: checkBalanceReq() loadsh.js // 限流 const throttle (fn, context, interval) > {console.log(">>>>cmm throttle", context, interval)let canRun…...
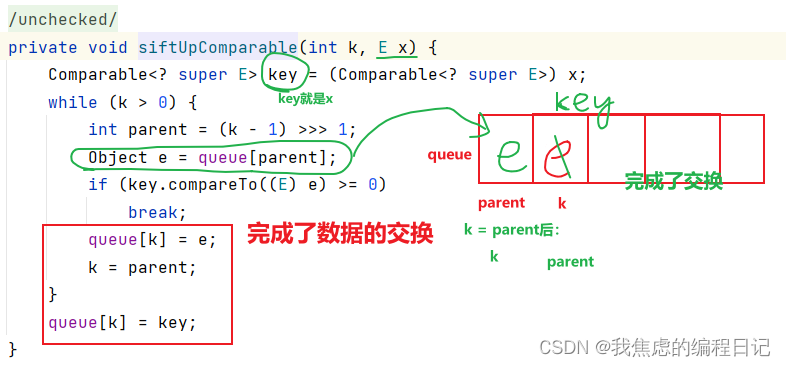
【数据结构】堆的初始化——如何初始化一个大根堆?
文章目录 源码是如何插入的?扩容向上调整实现大根堆代码: 源码是如何插入的? 扩容 在扩容的时候,如果容量小于64,那就2倍多2的扩容;如果大于64,那就1.5倍扩容。 还会进行溢出的判断,…...

【韩顺平 零基础30天学会Java】程序流程控制(2days)
day1 程序流程控制:顺序控制、分支控制、循环控制 顺序控制:从上到下逐行地执行,中间没有任何判断和跳转。 Java中定义变量时要采用合法的前向引用。 分支控制if-else:单分支、双分支和多分支。 单分支 import java.util.Scann…...

从入门到精通Python隧道代理的使用与优化
哈喽,Python爬虫小伙伴们!今天我们来聊聊如何从入门到精通地使用和优化Python隧道代理,让我们的爬虫程序更加稳定、高效!今天我们将对使用和优化进行一个简单的梳理,并且会提供相应的代码示例。 1. 什么是隧道代理&…...

19万字智慧城市总体规划与设计方案WORD
导读:原文《19万字智慧城市总体规划与设计方案WORD》(获取来源见文尾),本文精选其中精华及架构部分,逻辑清晰、内容完整,为快速形成售前方案提供参考。 感知基础设施 感知基础设施架构由感知范围、感知手…...
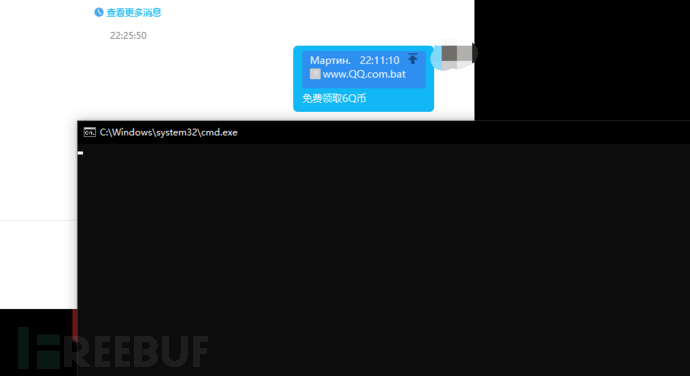
[赛博昆仑] 腾讯QQ_PC端,逻辑漏洞导致RCE漏洞
简介 !! 内容仅供学习,请不要进行非法网络活动,网络不是法外之地!! 赛博昆仑是国内一家较为知名的网络安全公司,该公司今日报告称 Windows 版腾讯 QQ 桌面客户端出现高危安全漏洞,据称“黑客利用难度极低、危害较大”,腾讯刚刚已经紧急发布…...
python Requests
Requests概述 官方文档:http://cn.python-requests.org/zh_CN/latest/,Requests是python的HTTP的库,我们可以安全的使用 Requests安装 pip install Requests -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple Requests的使用 Respose的属性 属性说明url响…...

【深入解析:数据结构栈的魅力与应用】
本章重点 栈的概念及结构 栈的实现方式 数组实现栈接口 栈面试题目 概念选择题 一、栈的概念及结构 栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端 称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数…...
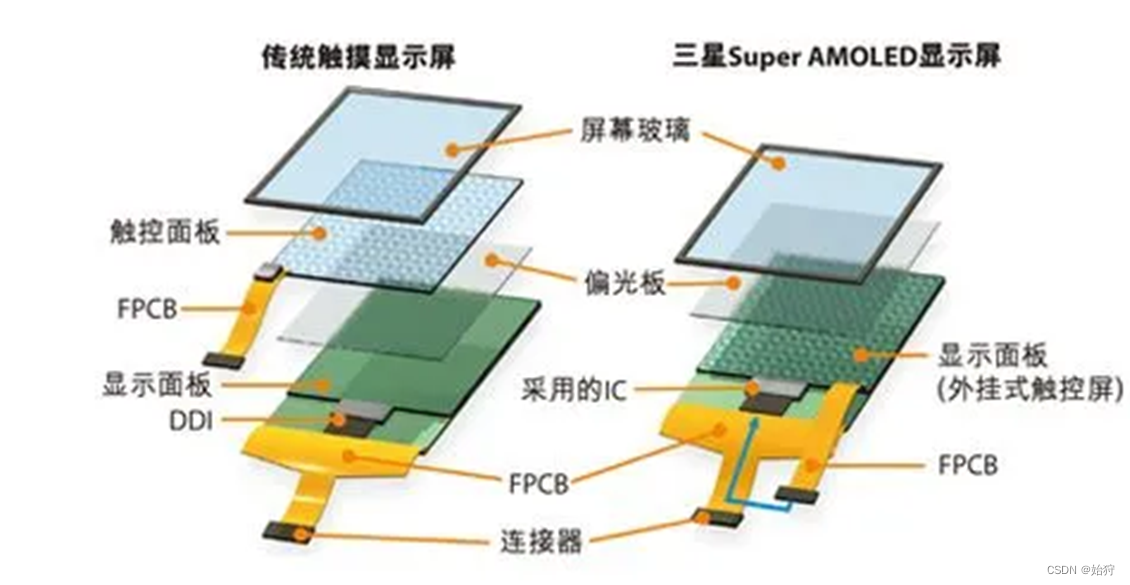
安卓机显示屏的硬件结构
显示屏的硬件结构 显示屏的硬件结构主要由背光源、液晶面板和驱动电路构成。可以将液晶面板看成一个三明治的结构,即在两片偏振方向互相垂直的偏光片系统中夹着一层液晶层。自然光源通过起偏器(偏光片之一)后,变成了垂直方向的偏…...
基于swing的超市管理系统java仓库库存进销存jsp源代码mysql
本项目为前几天收费帮学妹做的一个项目,Java EE JSP项目,在工作环境中基本使用不到,但是很多学校把这个当作编程入门的项目来做,故分享出本项目供初学者参考。 一、项目描述 基于swing的超市管理系统 系统有3权限:管…...
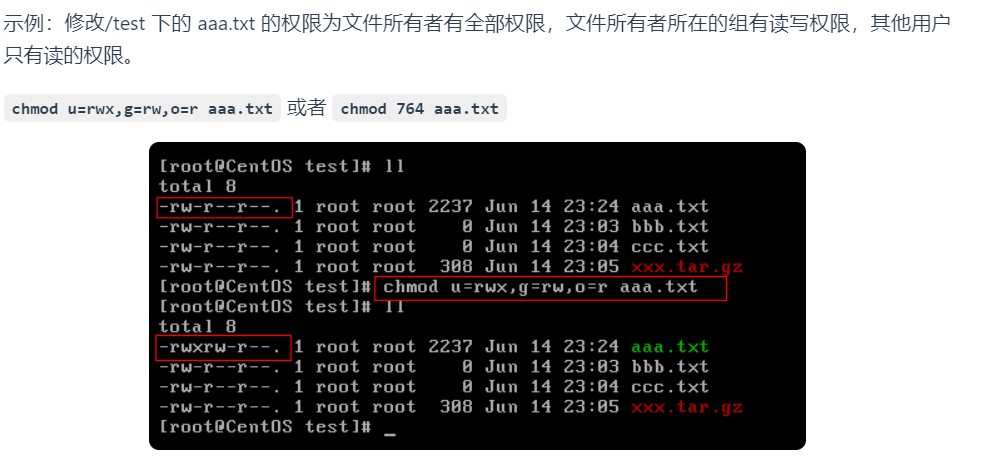
常用系统命令
重定向 cat aa.txt > bbb.txt 将输出定向到bbb.txt cat aaa.txt >> bbb.txt 输出并追加查看进程 ps ps -ef 显示所有进程 例⼦:ps -ef | grep mysql |:管道符 kill pid 结束进程, 如 kill 3732;根据进程名结束进程可以先…...
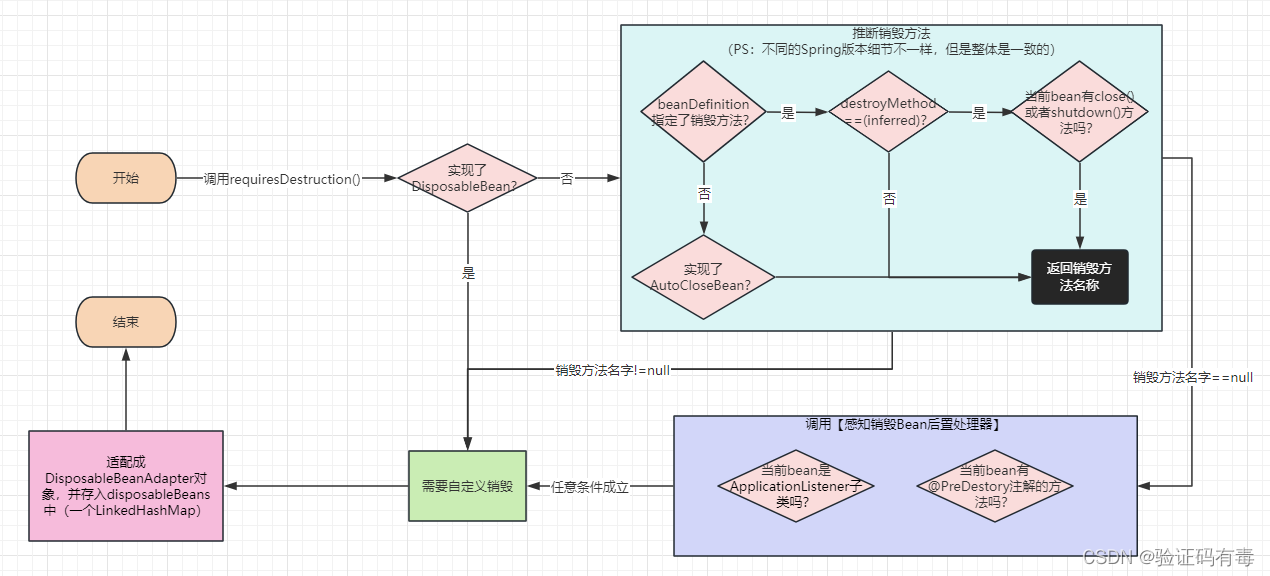
【Spring专题】Spring之Bean生命周期源码解析——阶段四(Bean销毁)(拓展,了解就好)
目录 前言阅读建议 课程内容一、Bean什么时候销毁二、实现自定义的Bean销毁逻辑2.1 实现DisposableBean或者AutoCloseable接口2.2 使用PreDestroy注解2.3 其他方式(手动指定销毁方法名字) 三、注册销毁Bean过程及方法详解3.1 AbstractBeanFactory#requir…...

配置Docker,漏洞复现
目录 配置Docker 漏洞复现 配置Docker Docker的配置在Linux系统中相对简单,以下是详细步骤: 1.安装Docker:打开终端,运行以下命令以安装Docker。 sudo apt update sudo apt install docker.io 2.启动Docker服务:运…...
微信小程序 游戏水平评估系统的设计与实现_pzbe0
近年来,随着互联网的蓬勃发展,游戏公司对信息的管理提出了更高的要求。传统的管理方式已无法满足现代人们的需求。为了迎合时代需求,优化管理效率,各种各样的管理系统应运而生,随着各行业的不断发展,使命召…...

moba登录不进去提示修改问题问题解决方式
问题: 安装moba后,运行时运行不起来,提示输入密码,安装、卸载多个版本都不行 方法: 使用ResetMasterPassword工具进行重置主密码 官网下载地址: MobaXterm Xserver and tabbed SSH client - resetmaster…...
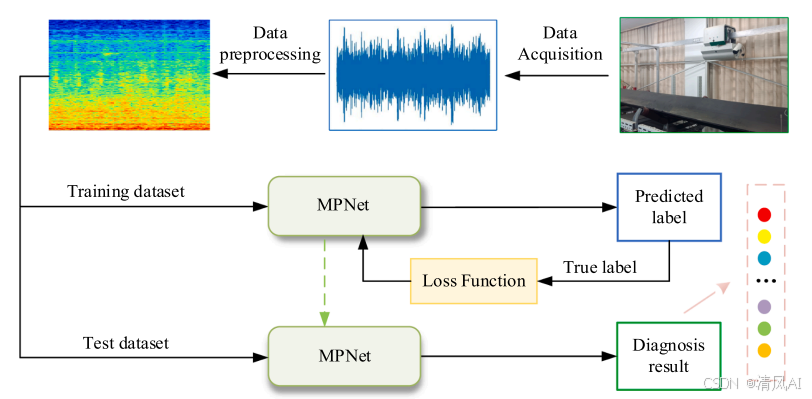
MPNet:旋转机械轻量化故障诊断模型详解python代码复现
目录 一、问题背景与挑战 二、MPNet核心架构 2.1 多分支特征融合模块(MBFM) 2.2 残差注意力金字塔模块(RAPM) 2.2.1 空间金字塔注意力(SPA) 2.2.2 金字塔残差块(PRBlock) 2.3 分类器设计 三、关键技术突破 3.1 多尺度特征融合 3.2 轻量化设计策略 3.3 抗噪声…...

java_网络服务相关_gateway_nacos_feign区别联系
1. spring-cloud-starter-gateway 作用:作为微服务架构的网关,统一入口,处理所有外部请求。 核心能力: 路由转发(基于路径、服务名等)过滤器(鉴权、限流、日志、Header 处理)支持负…...

golang循环变量捕获问题
在 Go 语言中,当在循环中启动协程(goroutine)时,如果在协程闭包中直接引用循环变量,可能会遇到一个常见的陷阱 - 循环变量捕获问题。让我详细解释一下: 问题背景 看这个代码片段: fo…...
Appium+python自动化(十六)- ADB命令
简介 Android 调试桥(adb)是多种用途的工具,该工具可以帮助你你管理设备或模拟器 的状态。 adb ( Android Debug Bridge)是一个通用命令行工具,其允许您与模拟器实例或连接的 Android 设备进行通信。它可为各种设备操作提供便利,如安装和调试…...

Go 语言接口详解
Go 语言接口详解 核心概念 接口定义 在 Go 语言中,接口是一种抽象类型,它定义了一组方法的集合: // 定义接口 type Shape interface {Area() float64Perimeter() float64 } 接口实现 Go 接口的实现是隐式的: // 矩形结构体…...

测试markdown--肇兴
day1: 1、去程:7:04 --11:32高铁 高铁右转上售票大厅2楼,穿过候车厅下一楼,上大巴车 ¥10/人 **2、到达:**12点多到达寨子,买门票,美团/抖音:¥78人 3、中饭&a…...
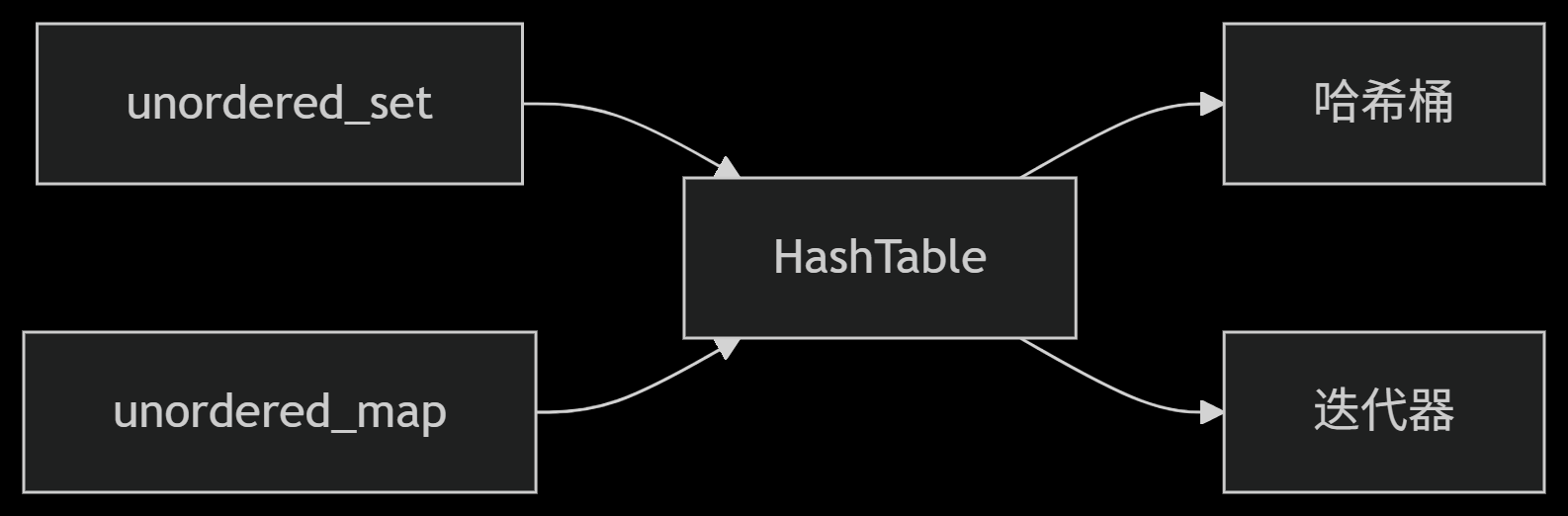
从零实现STL哈希容器:unordered_map/unordered_set封装详解
本篇文章是对C学习的STL哈希容器自主实现部分的学习分享 希望也能为你带来些帮助~ 那咱们废话不多说,直接开始吧! 一、源码结构分析 1. SGISTL30实现剖析 // hash_set核心结构 template <class Value, class HashFcn, ...> class hash_set {ty…...

laravel8+vue3.0+element-plus搭建方法
创建 laravel8 项目 composer create-project --prefer-dist laravel/laravel laravel8 8.* 安装 laravel/ui composer require laravel/ui 修改 package.json 文件 "devDependencies": {"vue/compiler-sfc": "^3.0.7","axios": …...

CSS | transition 和 transform的用处和区别
省流总结: transform用于变换/变形,transition是动画控制器 transform 用来对元素进行变形,常见的操作如下,它是立即生效的样式变形属性。 旋转 rotate(角度deg)、平移 translateX(像素px)、缩放 scale(倍数)、倾斜 skewX(角度…...
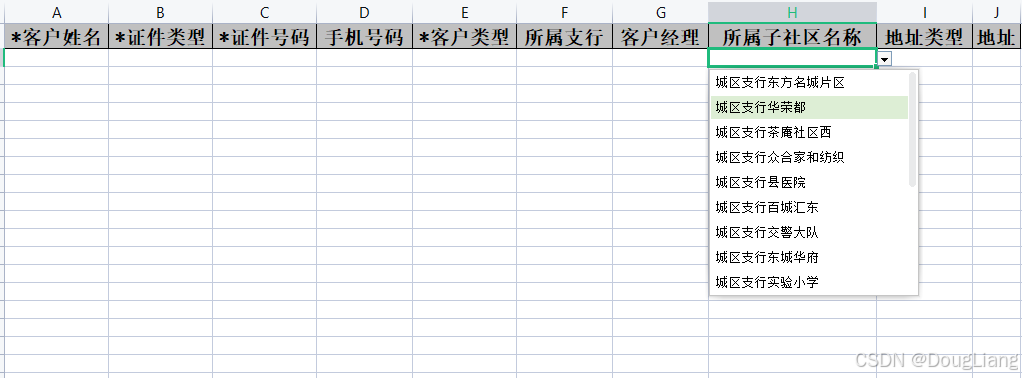
关于easyexcel动态下拉选问题处理
前些日子突然碰到一个问题,说是客户的导入文件模版想支持部分导入内容的下拉选,于是我就找了easyexcel官网寻找解决方案,并没有找到合适的方案,没办法只能自己动手并分享出来,针对Java生成Excel下拉菜单时因选项过多导…...
