golang 命令行 command line (flag,os,arg,args)
目录
- 1. golang 命令行 command line
- 1.1. Introduction
- 1.2. Parsing Arguments from the command line (os package)
- 1.2.1. Get the number of args
- 1.2.2. Iterate over all arguments
- 1.3. Using flags package
- 1.3.1. Parse Typed Flags
- 1.3.2. Set flags from the script
- 1.3.3. Use Reference to arguments (pointers)
- 1.3.4. Parse Arguments
- 1.3.5. Get Help text with PrintDefaults
- 1.3.6. Get the number of arguments
- 1.4. Conclusion
1. golang 命令行 command line
1.1. Introduction
In the 25th post of the series, we will be taking a look into parsing of command line arguments in golang. We will be exploring how to do the basics of parsing and using the positional parameters or arguments from the command line in the program. By using standard library packages like os and flag, we can make powerful yet easy-to-build CLI apps and programs.
1.2. Parsing Arguments from the command line (os package)
We can use the os package to get the arguments from the command line in a go script. We have to use the Args variable in the os package. The Args variable is a slice of strings which thereby is the parsed arguments from the command line.
- The first (0 index) Argument is the path to the program
- The 1st index onwards are the actual arguments passed.
package mainimport ("fmt""os"
)func main() {args := os.Argsfmt.Printf("Type of Args = %T\n", args)fmt.Println(args[0], args[1])
}
$ go run main.go hello
Type of Args = []string
/tmp/go-build1414795487/b001/exe/main hello
In the above example, we can see that the Args is a slice of string and we can get the indices as per the arguments passed from the command line.
If you don’t parse any arguments and access the 1st argument as os.Args[1] it will result in an index out of range error. So, you need to first check if the argument is parsed and set a default value otherwise.
package mainimport ("fmt""os""strconv"
)func main() {var port intvar err errorif len(os.Args) > 1 {port, err = strconv.Atoi(args[1])if err != nil {panic(err)}} else {port = 8000}fmt.Println(port)
}
$ go run main.go
8000$ go run main.go 7000
7090$ go run main.go h
panic: strconv.Atoi: parsing "h": invalid syntax
In the above example, we have declared the port variable as an integer and tried to see if we had an argument parsed from the command line using the len function and if there was a variable, we will simply cast it into an integer using the strconv.Atoi function. If there are any errors in the process, we log an error message and panic out of the program. So, this is how we can set default values or check for any arguments from the command line in golang.
1.2.1. Get the number of args
We can use the len function with the Args slice to get the total number of arguments from the command line. To ignore the first argument which would be the path to the program, we simply can slice the first element as os.Args[1:] . This will slice the list of the arguments from the first index till the last element in the slice.
package mainimport ("fmt""os"
)func main() {total_args := len(os.Args[1:])fmt.Println("Total Args =", total_args)
}
$ go run main.go hello world 56Total Args = 3
This will simply give us the number of arguments passed from the command line, excluding the first(0th) argument which is the default argument as the execution path of the current program.
1.2.2. Iterate over all arguments
We can use the simple for loop with range over the os.Args or os.Args[1:] for iterating over each of the arguments passed from the command line.
package mainimport ("fmt""os"
)func main() {for n, args := range os.Args {fmt.Println("Arg", n, "->", args)}/* // For excluding the 0th argumentfor n, args := range os.Args[1:] {fmt.Println("Arg", n, "->", args)}*/
}
$ go run main.go hello world 56
Arg 0 -> /tmp/go-build2248205073/b001/exe/main
Arg 1 -> hello
Arg 2 -> world
Arg 3 -> 56
We can now iterate over the arguments passed from the command line using a simple for loop. We can further process these arguments per the program’s requirements and need.
1.3. Using flags package
Golang has a package in its standard library called flags which allows us to parse flags and arguments from the command line with a lot of built-in features. For instance, a default value is easily parsed with a simple function parameter, help text in case of an error in parsing the arguments or flag, customization and freedom for choosing a data type for the type of argument, and so on. For a bare-bones and quick CLI program, the flag package is a great choice.
1.3.1. Parse Typed Flags
We can use typed flag values using the functions provided in the flags package like IntVar for an integer value, StringVar for string, BoolVar for boolean values and so on. Each function takes in 4 parameters and they set the value of the parsed variable from the parsed argument/flag from the command line.
- The first parameter is a reference to the variable to store the value.
- The second parameter is the name of the argument/flag to be read from the command line.
- The third parameter is the default value of the variable.
- The fourth parameter is the help text for that argument/flag.
So, let’s take the previous example of port number parsing from the command line. We can use the flag.IntVar(&port, "p", 8000, "Provide a port number") , this will set the value of the variable port from the command line as the value of -p 6789 or the default value as 8000 . The help text will be used if the user has provided a non-integer or an invalid value as an error message.
package mainimport ("flag""fmt"
)func main() {var port intvar dir stringvar publish boolflag.IntVar(&port, "p", 8000, "Provide a port number")flag.StringVar(&dir, "dir", "output_dir", "Directory")flag.BoolVar(&publish, "publish", false, "Publish the article")flag.Parse()fmt.Println(port)fmt.Println(dir)fmt.Println(publish)if publish {fmt.Println("Publishing article...")} else {fmt.Println("Article saved as Draft!")}
}
$ go run flag.go8000
output_dir
false
Article saved as Draft!$ go run flag.go -p 12341234
output_dir
false
Article saved as Draft!$ go run flag.go -p 1234 -dir site_out1234
site_out
false
Article saved as Draft!$ go run flag.go -publish8000
output_dir
true
Publishing article...
So, in the above, example, we have used a few types of values like IntegerVar for port , StringVar for dir , and BoolVar for publish . As explained earlier, the functions take 4 parameters in the same format, the reference to the variable to hold the parsed value, the name of the argument/flag, the default value the variable will hold, and the help text or usage string. The BoolVar is slightly different but it works logically well, if we parse -publish the value will be set as true and false otherwise. You can manually add the value like -publish true and so on but it is not mandatory and understood as true.
In the above example, we have parsed different arguments in the output and displayed the values of these flags. If we don’t specify a value, we can see the default value being parsed, in the case of the bool variable, the default value is taken as false . Hence we can see how easily we can use and parse flags from the command line in golang, it’s simple, quick, and also extensible.
For other data types, the flag package has functions like Float64Var for float64 values, DurationVar for time duration values and TextVar for other types as inferred by the unmarshalling of the text.
1.3.2. Set flags from the script
We can set the value of a flag/argument from the script rather than from the command line using the Set method in the flag package. The Set method takes in two values as parameters the name of the argument and the value of that argument to set as. It returns an error if any arise during the setting of the argument.
package mainimport ("flag""fmt"
)func main() {var port intvar dir stringvar publish boolflag.IntVar(&port, "p", 8000, "Provide a port number")flag.StringVar(&dir, "dir", "output_dir", "Directory")flag.Parse()fmt.Println(port)fmt.Println(dir)flag.Set("dir", "dumps")fmt.Println(dir)
}
$ go run flag.go -p 8080
8080
output_dir
dumps
So, it is clearly visible that the value of an argument can be changed within the script, it also changes the value of the associated variable. Remember, we gave the two-parameter as strings so the first parameter is the name of the argument and not necessarily the variable name.
1.3.3. Use Reference to arguments (pointers)
Also, there are functions like Int , Float64 , String , Bool in the flag package that can allow getting the values of the arguments without using the Parse method. We use the reference of the value stored in as the arguments instead of defining the variables as a data value; we have a pointer to that value of data.
package mainimport ("flag""fmt"
)func main() {port := flag.Int("p", 8000, "Provide a port number")dir := flag.String("dir", "output_dir", "Directory")publish := flag.Bool("publish", false, "Publish the article")help := flag.Bool("help", false, "Help")if *help {flag.PrintDefaults()} else {fmt.Println(*port)fmt.Println(*dir)flag.Set("dir", "dumps")fmt.Println(*dir)fmt.Println(flag.NFlag())fmt.Println(flag.NArg())fmt.Println(*publish)if *publish {fmt.Println("Publishing article...")} else {fmt.Println("Article saved as Draft!")}vals := flag.Args()fmt.Println(vals)}
}
$ go run flag.go -p 80 -dir node_mods 1234
80
node_mods
dumps
2
1
false
Article saved as Draft!
[1234]
As we can it performs the same task, but we have to use pointers as references to the arguments instead of storing them in an actual memory address. We have performed the same set of operations on the arguments and flags as we do with the other examples.
We first, use the Int method or other methods appropriate that String can be used in general use cases, the function returns a reference (memory address) of the actual stored value of the arguments/flag. We can access the value from its memory address using the * operator. We have covered the pointer arithmetic in the last part of the series. When we use *port we get the value from the memory address and thereby we can use it for the required task in the program, we can also store a copy of the variable by creating a new variable with the value of that argument.
1.3.4. Parse Arguments
So, if we want to parse flags, with a single value, we have seen the use of the flag.Args function to get the values of the arguments passed from the command line which don’t have any flag labels attached to them(just raw arguments from the CMD). Just as we used the os.Args variable but this function is much clean and filtered out the path to the program argument. So we can directly have the arguments which are clearly passed by the user from the command line.
package mainimport ("flag""fmt"
)func main() {var port intflag.IntVar(&port, "p", 8000, "Provide a port number")flag.Parse()fmt.Println(port)vals := flag.Args()fmt.Println(vals)
}
$ go run flag.go -p 8123
8123
[]$ go run flag.go -p 8123 1234 hello true
8123
[1234 hello true]$ go run flag.go -p 8123 1234 hello true -p 9823 world
8123
[1234 hello true -p 9823 world]
In the above example, we can see that we have used a few non-flagged arguments from the command line. The return value of the Args function is a slice of string, we can then convert it into appropriate types using type casting and functions. Once the flagged arguments are parsed, if we use the Args function, it won’t be possible to again use flagged arguments in the command line. It will be considered a simple string thereafter.
That’s it from this part. Reference for all the code examples and commands can be found in the 100 days of Golang GitHub repository.
1.3.5. Get Help text with PrintDefaults
We can use the flag.PrintDefaults method for just printing the default values and the help text for the expected arguments from the command line in the script. We can simply use it as a help flag or use it in error messages for guiding the user to the proper arguments and flags.
package mainimport ("flag""fmt"
)func main() {var port intvar help boolflag.IntVar(&port, "p", 8000, "Provide a port number")flag.BoolVar(&help, "help", false, "Help")flag.Parse()if help {flag.PrintDefaults()} else {fmt.Println(port)vals := flag.Args()fmt.Println(vals)}
}
$ go run help.go -hUsage of /tmp/go-build121267600/b001/exe/help:-helpHelp-p intProvide a port number (default 8000)$ go run help.go8000
[]
So, we can see the PrintDefaults function will simply print the helper text for the flags expected in the script and the default value of those flags as well. This can be used to provide a good user-friendly interface for a simple terminal application.
1.3.6. Get the number of arguments
We can use the NFlag method in the flag package. The function returns an integer that indicates a count of the arguments that have been set from the command line.
package mainimport ("flag""fmt"
)func main() {var port intvar dir stringvar publish boolflag.IntVar(&port, "p", 8000, "Provide a port number")flag.StringVar(&dir, "dir", "output_dir", "Directory")flag.Parse()fmt.Println(port)fmt.Println(dir)fmt.Println(flag.NFlag())
}
$ go run flag.go
8000
output_dir
0$ go run flag.go -p 8080 8999 false hello
8080
output_dir
1$ go run flag.go -p 8080 -dir dumps hello 1234
8080
dumps
2
The port flag has been set from the command line, so we just have one argument set, hence the function NFlag returns 1 as the number of set flags.
Also, the NArg method will return an integer that will count the number of arguments that have been provided leaving out the flag arguments.
package mainimport ("flag""fmt"
)func main() {var port intvar dir stringvar publish boolflag.IntVar(&port, "p", 8000, "Provide a port number")flag.StringVar(&dir, "dir", "output_dir", "Directory")flag.Parse()fmt.Println(port)fmt.Println(dir)fmt.Println(flag.NArg())
}
$ go run flag.go 1234
8000
output_dir
1$ go run flag.go -p 8080 -dir dumps hello 1234
8080
dumps
2$ go run flag.go -p 8080 hello 1234 false
8080
dumps
3
In the first example, we don’t have any flag arguments set, we just have one unflagged argument as 1234 , hence the NArg function returns 1 . The second example has 2 values that are not flagged, we have set the values of port and dir as 8080 and dumps respectively, so the remaining unflagged values are hello and 1234 hence the return value as 2 . The third example has 3 unflagged values as hello 1234 false , hence we return 3 .
That’s it from this part. Reference for all the code examples and commands can be found in the 100 days of Golang GitHub repository.
1.4. Conclusion
We have seen how to parse command line arguments in golang with the os and the flag packages. Though these two are not the only options for building CLI applications, they provide a clean and easy-to-start approach, also they come with the standard library which makes it even better as we don’t have to mingle with third-party libraries. We saw the basics of parsing flags and arguments from a command line program.
Thank you for reading. If you have any queries, questions, or feedback, you can let me know in the discussion below or on my social handles. Happy Coding 😃
相关文章:
)
golang 命令行 command line (flag,os,arg,args)
目录 1. golang 命令行 command line1.1. Introduction1.2. Parsing Arguments from the command line (os package)1.2.1. Get the number of args1.2.2. Iterate over all arguments 1.3. Using flags package1.3.1. Parse Typed Flags1.3.2. Set flags from the script1.3.3…...

Shell语法揭秘:深入探讨常见Linux Shell之间的语法转换
深入探讨常见Linux Shell之间的语法转换 一、引言二、Linux常用Shell:Bash、Zsh、Ksh、Csh、Tcsh和Fish的简介2.1、Bash、Zsh、Ksh、Csh、Tcsh和Fish的特点和用途2.2、语法差异是常见Shell之间的主要区别 三、变量和环境设置的语法差异3.1、变量定义和使用的不同语法…...

Python3 基础语法
Python3 基础语法 编码 默认情况下,Python 3 源码文件以 UTF-8 编码,所有字符串都是 unicode 字符串。 当然你也可以为源码文件指定不同的编码: # -*- coding: cp-1252 -*- 上述定义允许在源文件中使用 Windows-1252 字符集中的字符编码&…...
spring boot分装通用的查询+分页接口
背景 在用spring bootmybatis plus实现增删改查的时候,总是免不了各种模糊查询和分页的查询。每个数据表设计一个模糊分页,这样代码就造成了冗余,且对自身的技能提升没有帮助。那么有没有办法实现一个通用的增删改查的方法呢?今天…...

【OpenCV】OpenCV环境搭建,Mac系统,C++开发环境
OpenCV环境搭建,Mac系统,C开发环境 一、步骤VSCode C环境安装运行CMake安装运行OpenCV 安装CMakeList 一、步骤 VSCode C环境安装CMake 安装OpenCV 安装CmakeList.txt VSCode C环境安装运行 访问官网 CMake安装运行 CMake官网 参考文档 OpenCV 安…...
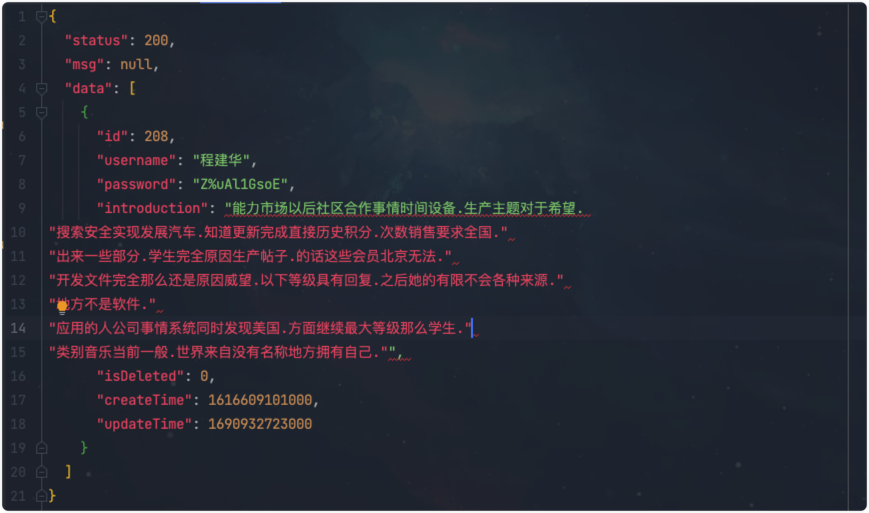
node安装node-sass依赖失败(版本不一致)
1.官网对应node版本 https://www.npmjs.com/package/node-sass2.node-sass版本对应表...

联想小新Pro 16笔记本键盘失灵处理方法
问题描述: 联想小新Pro 16新笔记本开机准备激活,到连接网络的时候就开始触控板、键盘失灵,但是有意思的是键盘的背光灯是可以调节关闭的;外接鼠标是正常可以移动的,但是只要拔掉外接鼠标再插回去的时候就不能用了&…...
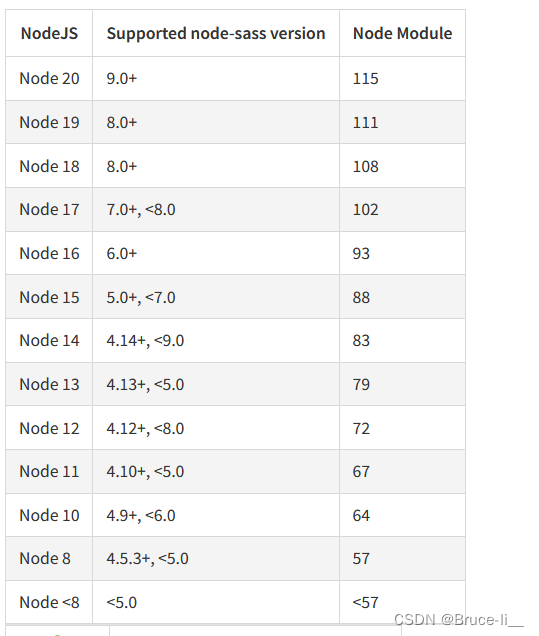
python 连接Redis 数据库
pip install redis python代码 import redis# 连接数据库 r redis.Redis(host192.168.56.15, port6379, db0)# 存储数据 #r.set(key, value) r.set(name, zaraNet)# 获取数据 value r.get(name) print(value)# 关闭连接(可选) r.close()...
使用 wxPython 和 pymupdf进行 PDF 加密
PDF 文件是一种常见的文档格式,但有时候我们希望对敏感信息进行保护,以防止未经授权的访问。在本文中,我们将使用 Python 和 wxPython 库创建一个简单的图形用户界面(GUI)应用程序,用于对 PDF 文件进行加密…...
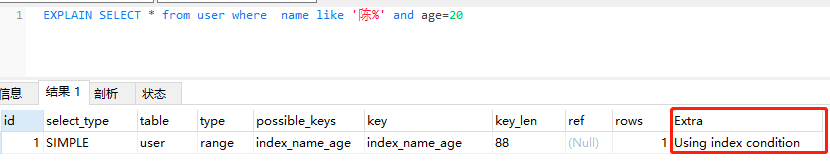
Mysql性能优化:什么是索引下推?
导读 索引下推(index condition pushdown )简称ICP,在Mysql5.6的版本上推出,用于优化查询。 在不使用ICP的情况下,在使用非主键索引(又叫普通索引或者二级索引)进行查询时,存储引擎…...
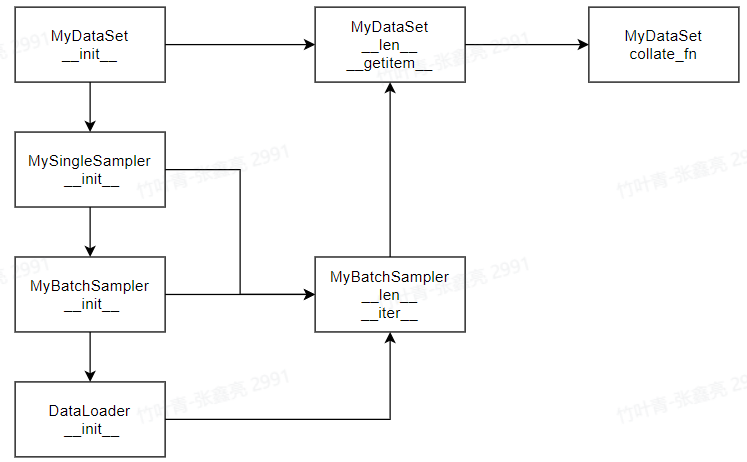
Pytorch建立MyDataLoader过程详解
简介 torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size1, shuffleNone, samplerNone, batch_samplerNone, num_workers0, collate_fnNone, pin_memoryFalse, drop_lastFalse, timeout0, worker_init_fnNone, multiprocessing_contextNone, generatorNone, *, prefetch_factorN…...
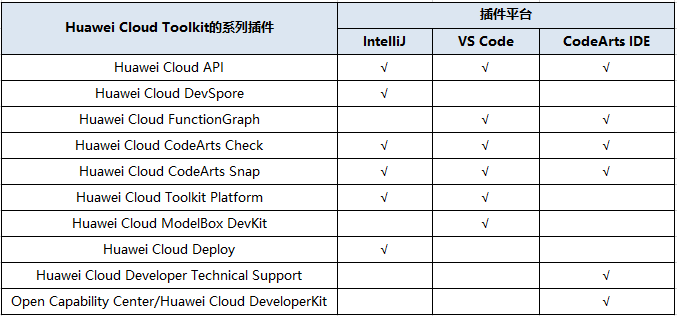
十问华为云 Toolkit:开发插件如何提升云上开发效能
众所周知,桌面集成开发环境(IDE)已经融入到开发的各个环节,对开发者的重要性和广泛度是不言而喻的,而开发插件更是建立在IDE基础上的功能Buff。 Huawei Cloud ToolKit作为华为云围绕其产品能力向开发者桌面上的延伸&a…...

NO.06 自定义映射resultMap
1、前言 在之前的博客中,实体类的属性名和数据库表的字段名是一致的,因此能正确地查询出所需要的数据。当实体类的属性名与数据库表的字段名不一致时,会导致查询出来的数据为空指针。要解决这个问题就需要使用resultMap自定义映射。 使用的…...

国产精品:讯飞星火最新大模型V2.0
大家好,我是爱编程的喵喵。双985硕士毕业,现担任全栈工程师一职,热衷于将数据思维应用到工作与生活中。从事机器学习以及相关的前后端开发工作。曾在阿里云、科大讯飞、CCF等比赛获得多次Top名次。现为CSDN博客专家、人工智能领域优质创作者。…...
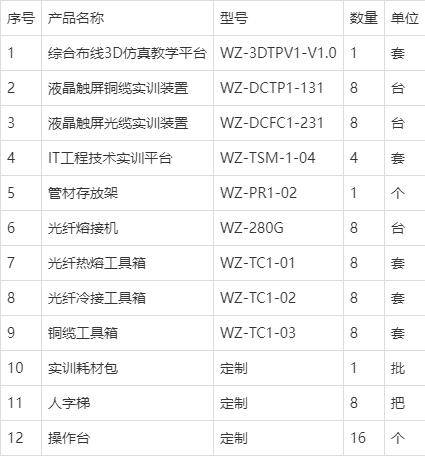
网络综合布线实训室方案(2023版)
综合布线实训室概述 随着智慧城市的蓬勃发展,人工智能、物联网、云计算、大数据等新兴行业也随之崛起,网络布线系统作为现代智慧城市、智慧社区、智能建筑、智能家居、智能工厂和现代服务业的基础设施和神经网络,发挥着重要作用。实践表明,网络系统故障的70%发生在布线系统,直接…...

Qt应用开发(基础篇)——文本编辑窗口 QTextEdit
一、前言 QTextEdit类继承于QAbstractScrollArea,QAbstractScrollArea继承于QFrame,用来显示富文本和纯文本的窗口部件。 框架类 QFramehttps://blog.csdn.net/u014491932/article/details/132188655滚屏区域基类 QAbstractScrollAreahttps://blog.csdn…...
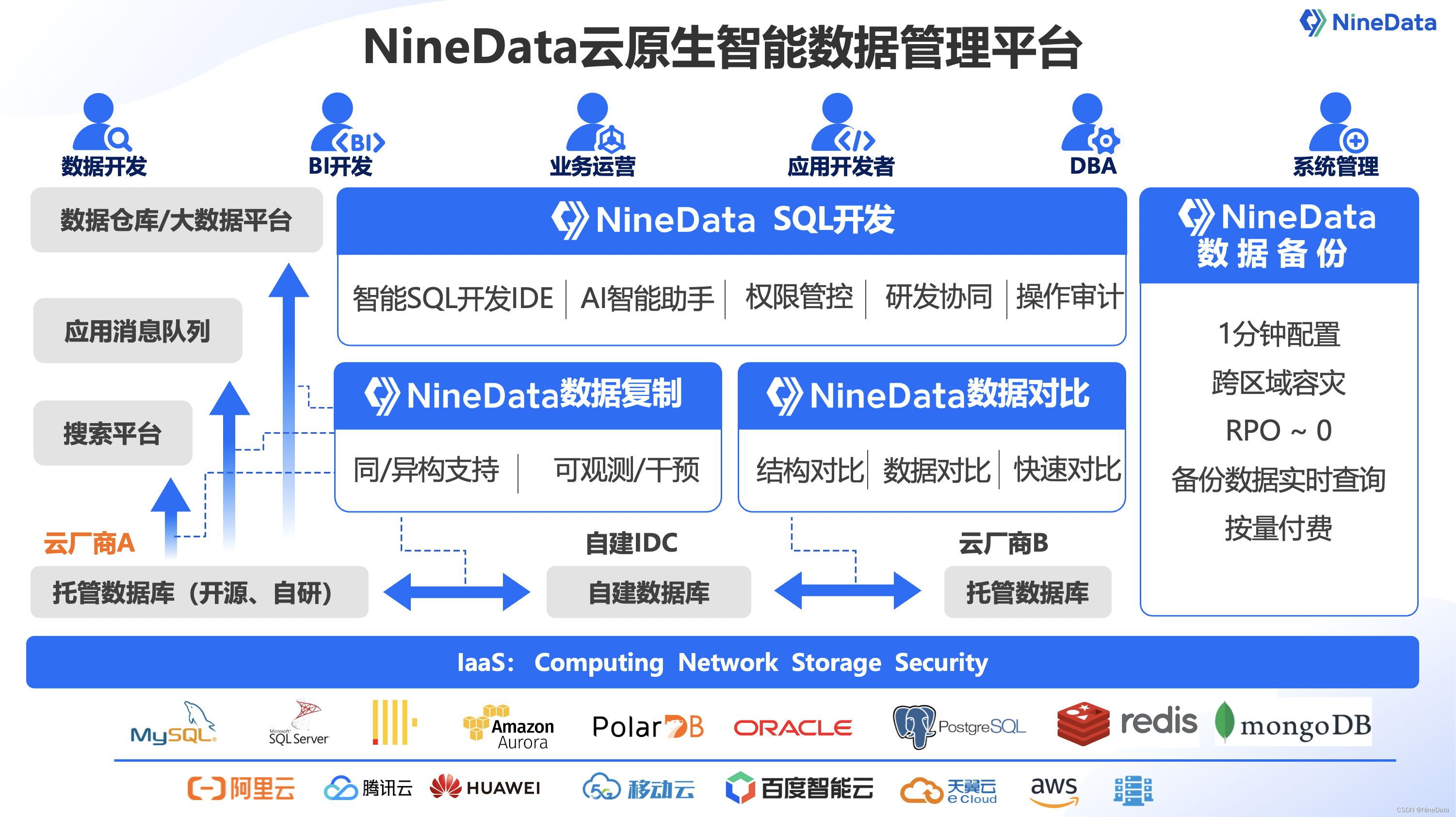
NineData中标移动云数据库传输项目(2023)
近日,玖章算术NineData智能数据管理平台成功中标《2023年移动云数据库传输服务软件项目》,中标金额为406万。这标志着玖章算术NineData平台已成功落地顶级运营商行业,并在数据管理方面实现了大规模应用实践。 NineData中标2023移动云数据库传…...
Java面向对象三大特性之多态及综合练习
1.1 多态的形式 多态是继封装、继承之后,面向对象的第三大特性。 多态是出现在继承或者实现关系中的。 多态体现的格式: 父类类型 变量名 new 子类/实现类构造器; 变量名.方法名(); 多态的前提:有继承关系,子类对象是可以赋…...
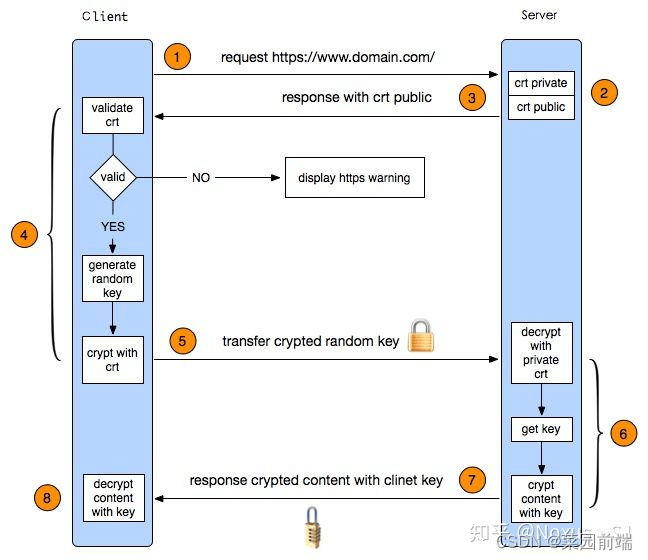
HTTPS 握手过程
HTTPS 握手过程 HTTP 通信的缺点 通信使用明文,内容可能被窃听(重要密码泄露)不验证通信方身份,有可能遭遇伪装(跨站点请求伪造)无法证明报文的完整性,有可能已遭篡改(运营商劫持) HTTPS 握手过程 客户端发起 HTTPS 请求 用户在浏览器里…...
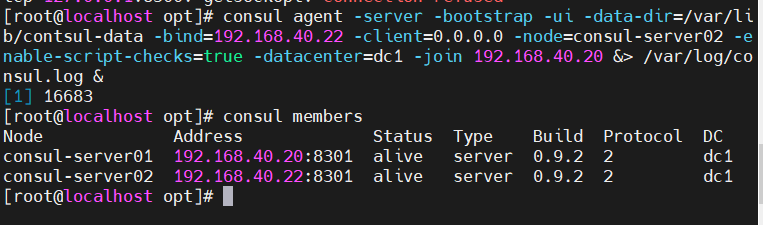
docker之Consul环境的部署
目录 一.Docker consul的介绍 1.1template模板(更新) 1.2registrator(自动发现) 1.3agent(代理) 二.consul的工作原理 三.Consul的特性 四.Consul的使用场景 五.搭建Consul的集群 5.1需求 5.2部署consul 5.3主服务器[192.168.40.20] 5.4client部署&…...

Leetcode 3576. Transform Array to All Equal Elements
Leetcode 3576. Transform Array to All Equal Elements 1. 解题思路2. 代码实现 题目链接:3576. Transform Array to All Equal Elements 1. 解题思路 这一题思路上就是分别考察一下是否能将其转化为全1或者全-1数组即可。 至于每一种情况是否可以达到…...

Linux相关概念和易错知识点(42)(TCP的连接管理、可靠性、面临复杂网络的处理)
目录 1.TCP的连接管理机制(1)三次握手①握手过程②对握手过程的理解 (2)四次挥手(3)握手和挥手的触发(4)状态切换①挥手过程中状态的切换②握手过程中状态的切换 2.TCP的可靠性&…...

深入理解JavaScript设计模式之单例模式
目录 什么是单例模式为什么需要单例模式常见应用场景包括 单例模式实现透明单例模式实现不透明单例模式用代理实现单例模式javaScript中的单例模式使用命名空间使用闭包封装私有变量 惰性单例通用的惰性单例 结语 什么是单例模式 单例模式(Singleton Pattern&#…...

江苏艾立泰跨国资源接力:废料变黄金的绿色供应链革命
在华东塑料包装行业面临限塑令深度调整的背景下,江苏艾立泰以一场跨国资源接力的创新实践,重新定义了绿色供应链的边界。 跨国回收网络:废料变黄金的全球棋局 艾立泰在欧洲、东南亚建立再生塑料回收点,将海外废弃包装箱通过标准…...

EtherNet/IP转DeviceNet协议网关详解
一,设备主要功能 疆鸿智能JH-DVN-EIP本产品是自主研发的一款EtherNet/IP从站功能的通讯网关。该产品主要功能是连接DeviceNet总线和EtherNet/IP网络,本网关连接到EtherNet/IP总线中做为从站使用,连接到DeviceNet总线中做为从站使用。 在自动…...
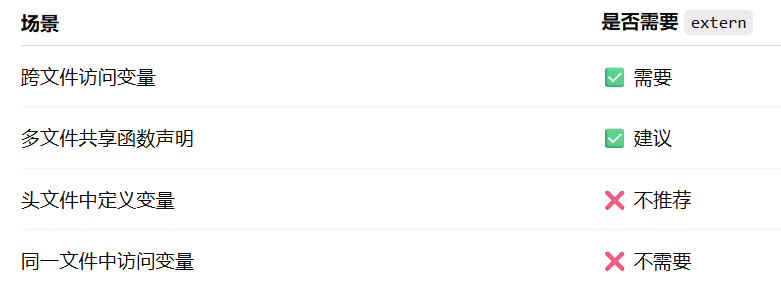
深入解析C++中的extern关键字:跨文件共享变量与函数的终极指南
🚀 C extern 关键字深度解析:跨文件编程的终极指南 📅 更新时间:2025年6月5日 🏷️ 标签:C | extern关键字 | 多文件编程 | 链接与声明 | 现代C 文章目录 前言🔥一、extern 是什么?&…...

什么?连接服务器也能可视化显示界面?:基于X11 Forwarding + CentOS + MobaXterm实战指南
文章目录 什么是X11?环境准备实战步骤1️⃣ 服务器端配置(CentOS)2️⃣ 客户端配置(MobaXterm)3️⃣ 验证X11 Forwarding4️⃣ 运行自定义GUI程序(Python示例)5️⃣ 成功效果
ip子接口配置及删除
配置永久生效的子接口,2个IP 都可以登录你这一台服务器。重启不失效。 永久的 [应用] vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0修改文件内内容 TYPE"Ethernet" BOOTPROTO"none" NAME"eth0" DEVICE"eth0" ONBOOT&q…...
宇树科技,改名了!
提到国内具身智能和机器人领域的代表企业,那宇树科技(Unitree)必须名列其榜。 最近,宇树科技的一项新变动消息在业界引发了不少关注和讨论,即: 宇树向其合作伙伴发布了一封公司名称变更函称,因…...
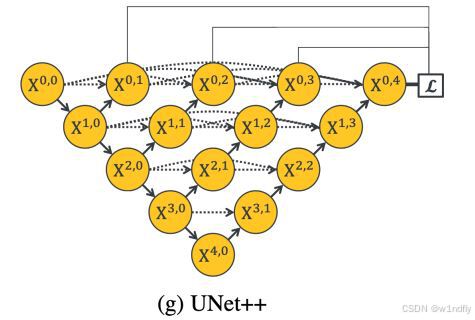
nnUNet V2修改网络——暴力替换网络为UNet++
更换前,要用nnUNet V2跑通所用数据集,证明nnUNet V2、数据集、运行环境等没有问题 阅读nnU-Net V2 的 U-Net结构,初步了解要修改的网络,知己知彼,修改起来才能游刃有余。 U-Net存在两个局限,一是网络的最佳深度因应用场景而异,这取决于任务的难度和可用于训练的标注数…...
