【Java8特性】——Stream API
一、概述
<1> 是什么
是数据渠道,用于操作数据源(集合、数组等)所生成的元素序列。
- Stream 不会存储数据
- Stream 不会改变数据源,相反,会返回一个持有结果的新Stream。
- Stream 操作是延迟执行的,这意味着会等到需要结果的时候才执行。
<2> Stream 和collection的区别
Connection是一种静态的内存数据结构,Stream是有关计算的,前者主要面向内存,存储在内存中,后者是面向CPU,通过CPU实现计算。
集合讲的是数据,Stream讲的是计算。
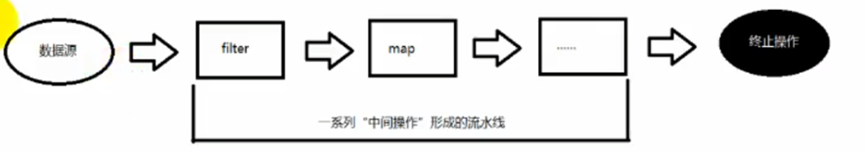
<3> 执行步骤
- 创建Stream
一个数据源,会获取一个流 - 中间操作
一个中间操作链,对数据源的数据进行处理。 - 终止操作(终端操作)
一旦执行终止操作,就执行中间操作链,并产生结果,之后,不会再被使用。
二、创建方式
<1> 通过集合
default Stream<E> stream() : 返回一个顺序流
default Stream<E> parallelStream() : 返回一个并行流
/*** 方式一: 通过集合创建流* default Stream<E> stream() ,返回一个顺序流* default Stream<E> parallelStream() ,返回一个并行流*/@Testpublic void test1() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();// default Stream<E> stream() ,返回一个顺序流Stream<Employee> stream = employees.stream();// default Stream<E> parallelStream() ,返回一个并行流Stream<Employee> parallelStream = employees.parallelStream();}
<2> 通过数组创建流
Java8 中的Arrays的静态方法stream()可以获取数据流。
static IntStream stream(int[] array)
/*** 方式二: 通过数组创建流* Java8 中的Arrays的静态方法stream()可以获取数据流。* <p>* static IntStream stream(int[] array)*/@Testpublic void test2() {int[] arr = new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5};// static IntStream stream(int[] array)IntStream stream = Arrays.stream(arr);Employee employee1 = new Employee(1002, "玛火腿", 34, 123);Employee employee2 = new Employee(1003, "tom", 23, 2222);Employee[] employees = new Employee[]{employee1, employee2};Stream<Employee> stream1 = Arrays.stream(employees);}<3> 通过Stream的of()
可以调用Stream类的静态方法of(),通过显示值创建一个流。他可以接受任意数量的参数
public static<T> Stream<T> of(T... values)
/*** 方式三: 通过Stream的of()* 可以调用Stream类的静态方法of(),通过显示值创建一个流。他可以接受任意数量的参数* public static<T> Stream<T> of(T... values)*/@Testpublic void test3() {Stream<Integer> integerStream = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);}
<4> 创建无限流
以使用静态方法Stream.iterate()和Stream.generate(),创建无限流
/*** 方式四: 创建无限流* 可以使用静态方法Stream.iterate()和Stream.generate(),创建无限流*/@Testpublic void test4() {//迭代// public static<T> Stream<T> iterate(final T seed, final UnaryOperator<T> f)Stream.iterate(0, t -> t + 2).limit(10).forEach(System.out::println);//出生//public static<T> Stream<T> generate(Supplier<T> s)Stream.generate(Math::random).limit(10).forEach(System.out::println);}三、中间操作
<1> 筛选&切片
多个中间操作可以连接起来形成一个流水线,除非流水线上触发种植操作,否则中间操作不会执行任何的处理,而在种植操作时一次性全部处理,称为“惰性求值”。
1. filter
从流中排除某些元素
Stream<T> filter(Predicate<? super T> predicate);
/*** 从流中排除某些元素* Stream<T> filter(Predicate<? super T> predicate);* filter 中 参数 通过Lambda表达式 实现 Predicate 函数式接口*/@Testpublic void test1() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();employees.stream().filter(e -> e.getAge() > 23).forEach(System.out::println);}
2. limit
截断流 ,使元素不超过给定数量
/*** 截断流 ,使元素不超过给定数量* Stream<T> limit(long maxSize);*/@Testpublic void test2() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();employees.stream().limit(5).forEach(System.out::println);}
3. skip
掉过元素,返回一个扔掉前n个元素的流,若流中元素不足n个,,则返回一个空流
/*** 掉过元素,返回一个扔掉前n个元素的流,若流中元素不足n个,,则返回一个空流* Stream<T> skip(long n);*/@Testpublic void test3() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();employees.stream().skip(5).forEach(System.out::println);}
4. distinct
筛选,通过流所生成的元素的hashcode()和equals()去除重复元素。
/*** 筛选, 通过流所生成的元素的hashcode()和equals()去除重复元素。* Stream<T> distinct();*/@Testpublic void test4() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();employees.stream().distinct().forEach(System.out::println);System.out.println("-----------------------------------------------------");employees.stream().forEach(System.out::println);}
<2> 映射
1. map
接受一个函数作为参数,将元素转换为其他形式或者提取信息,该函数会被应用到每个元素上,并将其映射成一个新的元素
/*** 映射* 接受一个函数作为参数,将元素转换为其他形式或者提取信息,该函数会被应用到每个元素上,并将其映射成一个新的元素* <R> Stream<R> map(Function<? super T, ? extends R> mapper);*/@Testpublic void test5() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();employees.stream().map(Employee::getName).filter(name -> name.length() > 3).forEach(System.out::println);}
2. flatMap
接收一个函数作为参数,将流中的每个值都换成另一个流,然后把所有流连接成一个流。
/*** 接收一个函数作为参数,将流中的每个值都换成另一个流,然后把所有流连接成一个流。* <R> Stream<R> flatMap(Function<? super T, ? extends Stream<? extends R>> mapper);*/@Testpublic void test6() {List<String> list = Arrays.asList("aa","bbbb");Stream<Stream<Character>> streamStream = list.stream().map(Stream_api_test2::formStringtoStream);streamStream.forEach(System.out::println);System.out.println("-----------------------------------------------------");list.stream().map(Stream_api_test2::formStringtoStream).forEach(e->{e.forEach(System.out::println);});System.out.println("-----------------------------------------------------");Stream<Character> characterStream = list.stream().flatMap(Stream_api_test2::formStringtoStream);characterStream.forEach(System.out::println);}/*** 将字符串中的多个字符构成的集合转换为对应Stream的实例* @param str 字符串* @return Stream实例*/public static Stream<Character> formStringtoStream(String str) {List<Character> arrayList = new ArrayList();for (Character s :str.toCharArray()) {arrayList.add(s);}Stream<Character> stream = arrayList.stream();return stream;}
<3> 排序
1. sorted-自然排序
自然排序 , 产生一个新的流,其中按自然顺序排序
/*** 自然排序 , 产生一个新的流,其中按自然顺序排序* Stream<T> sorted();*/@Testpublic void test7() {List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(23, 44, 34, 6, 1, 334, 546, 23, 1211, 453435, 2, 1, 3, 3);list.stream().sorted().forEach(System.out::println);}
2. sorted-定制排序
定制排序 ,产生一个新的流,其中按比较器顺序排序
/*** 定制排序 ,产生一个新的流,其中按比较器顺序排序* Stream<T> sorted(Comparator<? super T> comparator);*/@Testpublic void test8() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();employees.stream().sorted((e1, e2) -> Integer.compare(e1.getAge(), e2.getAge())).forEach(System.out::println);}
四、 终止操作
<1> 匹配 & 查找
1. allMatch
检查是否匹配所有元素,所有元素匹配就是ture ,否则为false
/*** 检查是否匹配所有元素,所有元素匹配就是ture ,否则为false* boolean allMatch(Predicate<? super T> predicate);*/@Testpublic void test1() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();//都大于18 则为ture,否则为falseboolean b = employees.stream().allMatch(e -> e.getAge() > 18);System.out.println(b);}
2. anyMatch
检查是否至少一个匹配的元素,有一个匹配就是ture ,否则为false
/*** 检查是否至少一个匹配的元素,有一个匹配就是ture ,否则为false* boolean anyMatch(Predicate<? super T> predicate);*/@Testpublic void test2() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();//有一个大于33 则为ture,否则为falseboolean b = employees.stream().anyMatch(e -> e.getAge() > 33);System.out.println(b);}
3. noneMatch
是否没有匹配的元素 ,有一个匹配就是false ,全都不匹配则为ture
/*** 是否没有匹配的元素 ,有一个匹配就是false ,全都不匹配则为ture* boolean noneMatch(Predicate<? super T> predicate);*/@Testpublic void test3() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();//有大于33的元素 则为false,否则为tureboolean b = employees.stream().noneMatch(e -> e.getAge() > 33);System.out.println(b);}
4. findFirst
返回第一个元素
/*** 返回第一个元素* Optional<T> findFirst();*/@Testpublic void test4() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();Optional<Employee> employee = employees.stream().findFirst();System.out.println(employee);}
5. findAny
返回任意一个元素
/*** 返回任意一个元素* Optional<T> findAny();*/@Testpublic void test5() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();Optional<Employee> employee = employees.stream().findAny();System.out.println(employee);}
6. count
返回流中元素的总个数
/*** 返回流中元素的总个数* long count();*/@Testpublic void test6() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();long count = employees.stream().filter(e->e.getAge()>30). count ();System.out.println(count);}
7. max
返回流最大值
/*** 返回流最大值*/@Testpublic void test7() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();Optional<Employee> maxEmployee = employees.stream().max((e1, e2) -> Integer.compare(e1.getAge(), e2.getAge()));System.out.println(maxEmployee);}
8. min
返回流中最小值
/*** 返回流中最小值*/@Testpublic void test8() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();Optional<Employee> maxEmployee = employees.stream().min((e1, e2) -> Integer.compare(e1.getAge(), e2.getAge()));System.out.println(maxEmployee);}
9. forEach
/*** 内部迭代*/@Testpublic void test9() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();employees.stream().forEach(System.out::println);}
<2> 规约
1. reduce-T
将流中的元素返回结合起来,得到一个值,返回 T
/*** 将流中的元素返回结合起来,得到一个值,返回 T* T reduce(T identity, BinaryOperator<T> accumulator);* T identity 为一个初始值*/@Testpublic void test1() {List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10);Integer reduce = list.stream().reduce(0, Integer::sum);System.out.println(reduce);}
2. reduce - Optional
将流中的元素返回结合起来,得到一个值,返回一个Optional
/*** 将流中的元素返回结合起来,得到一个值,返回一个Optional<T>* Optional<T> reduce(BinaryOperator<T> accumulator);*/@Testpublic void test2() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();Optional<Double> reduce = employees.stream().map(Employee::getSalary).reduce(Double::sum);System.out.println(reduce);System.out.println("-------------------------------------");employees.stream().map(Employee::getSalary).reduce((d1, d2) -> {System.out.println("d1 : "+d1);System.out.println("d2 : "+d2);System.out.println("d1 + d2 : "+(d1 + d2));System.out.println("-----------");return d1 + d2;});}
<3> 收集
将流转换为其他形式,接受一个Collector接口的实现,用于给Stream中元素做汇总的方法。Collector接口中发给发的实现决定了如何对流执行收集操作 , 如收集到 List,Set,Map。Collector实用类提供了很多静态方法,可以方便地创建收集器实例。如下:
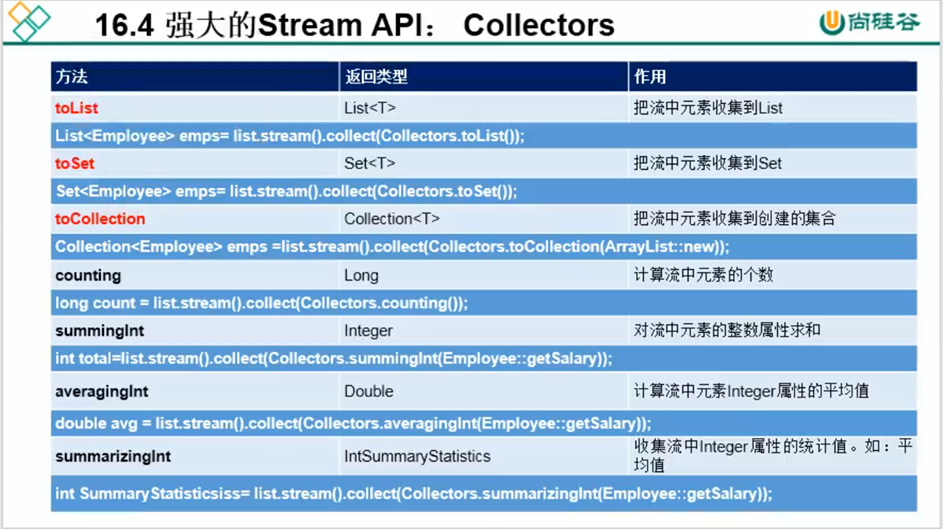
/*** 将流转换为其他形式,接受一个Collector接口的实现,用于给Stream中元素做汇总的方法* Collector接口中发给发的实现决定了如何对流执行收集操作 , 如收集到 List,Set,Map* Collector实用类提供了很多静态方法,可以方便地创建收集器实例。* <R, A> R collect(Collector<? super T, A, R> collector);*/@Testpublic void test3() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();List<String> collect = employees.stream().filter(e->e.getAge()>30).map(Employee::getName).collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println(collect);System.out.println("-------------------------------------");Set<String> collect1 = employees.stream().filter(e -> e.getAge() > 30).map(Employee::getName).collect(Collectors.toSet());System.out.println(collect1);}
相关文章:

【Java8特性】——Stream API
一、概述 <1> 是什么 是数据渠道,用于操作数据源(集合、数组等)所生成的元素序列。 Stream 不会存储数据Stream 不会改变数据源,相反,会返回一个持有结果的新Stream。Stream 操作是延迟执行的,这意…...

grep命令的用法
文章目录 前言一、使用说明二、应用举例 前言 grep 命令用于查找文件里符合条件的字符串。 一、使用说明 -r: 如果需要搜索目录中的文件内容, 需要进行递归操作, 必须指定该参数 -i: 对应要搜索的关键字, 忽略字符大小写的差别 -n: 在显示符合样式的那一行之前,标…...
【无标题】jenkins消息模板(飞书)
这里写目录标题 Jenkins 安装的插件 发送消息到飞书预览 1 (单Job)预览 2 (多Job,概览) Jenkins 安装的插件 插件名称作用Rebuilder Rebuilder。 官方地址:https://plugins.jenkins.io/rebuild 安装方式&a…...

2023年国赛 高教社杯数学建模思路 - 案例:随机森林
文章目录 1 什么是随机森林?2 随机深林构造流程3 随机森林的优缺点3.1 优点3.2 缺点 4 随机深林算法实现 建模资料 ## 0 赛题思路 (赛题出来以后第一时间在CSDN分享) https://blog.csdn.net/dc_sinor?typeblog 1 什么是随机森林ÿ…...

element Collapse 折叠面板 绑定事件
1. 点击面板触发事件 change <el-collapse accordion v-model"activeNames" change"handleChange"><el-collapse-item title"一致性 Consistency"><div>与现实生活一致:与现实生活的流程、逻辑保持一致,…...

CSS :mix-blend-mode、aspect-ratio
mix-blend-mode 元素的内容应该与元素的直系父元素的内容和元素的背景如何混合。 mix-blend-mode: normal; // 正常mix-blend-mode: multiply; // 正片叠底mix-blend-mode: screen; // 滤色mix-blend-mode: overlay; // 叠加mix-blend-mode: darken; // 变暗mix-blend-mode: …...
Module not found: Error: Can‘t resolve ‘less-loader‘解决办法
前言: 主要是在自我提升方面,感觉自己做后端还是需要继续努力,争取炮筒前后端,作为一个全栈软阿金开发人员,所以还是需要努力下,找个方面,目前是计划学会Vue,这样后端有java和pytho…...

量化QAT QLoRA GPTQ
模型量化的思路可以分为PTQ(Post-Training Quantization,训练后量化)和QAT(Quantization Aware Training,在量化过程中进行梯度反传更新权重,例如QLoRA),GPTQ是一种PTQ的思路。 QAT…...

CentOS下查看 ssd 寿命
SSD写入量达到设计极限,颗粒擦写寿命耗尽后会导致磁盘写入速度非常缓慢,读取正常。 使用smartctl及raid卡管理软件查看硬盘smart信息可以发现Media_Wearout_Indicator值降为1,表明寿命完全耗尽。 涉及范围 所有SSD处理方案 查看SSD smart信…...

Node基础--npm相关内容
下面,我们一起来看看Node中的至关重要的一个知识点-----npm 1.npm概述 npm(Node Package Manager),CommonJS包规范是理论,npm是其中一种实践。 对于Node而言,NPM帮助其完成了第三方模块的发布、安装和依赖等。借助npm,Node与第三方模块之间形成了很好的一个 生态系统。(类…...

Python图片爬虫工具
不废话了,直接上代码: import re import os import requests import tqdmheader{User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/66.0.3359.139 Safari/537.36}def getImg(url,idx,path):imgre…...

制造执行系统(MES)在汽车行业中的应用
汽车行业在不断发展中仍然面临一些挑战和痛点。以下是一些当前汽车行业可能面临的问题: 1.电动化和可持续性转型:汽车行业正逐渐向电动化和可持续性转型,但这需要投入大量资金和资源,包括电池技术、充电基础设施等,同时…...
Spring与Mybatis集成且Aop整合
目录 一、集成 1.1 集成的概述 1.2 集成的优点 1.3 代码示例 二、整合 2.1 整合概述 2.2 整合进行分页 一、集成 1.1 集成的概述 集成是指将不同的组件、部分或系统组合在一起,以形成一个整体功能完整的解决方案。它是通过连接、交互和协调组件之间的关系来实…...

【nonebot-plugin-mystool】快速安装使用nonebot-plugin-mystool
快速安装使用nonebot-plugin-mystool,以qq为主 前期准备:注册一个QQ号,python3.9以上的版本安装,go-cqhttp下载 用管理员模式打开powershell,并输入以下命令 #先排查是否有安装过的nonebot,若有则删除 pip uninstal…...
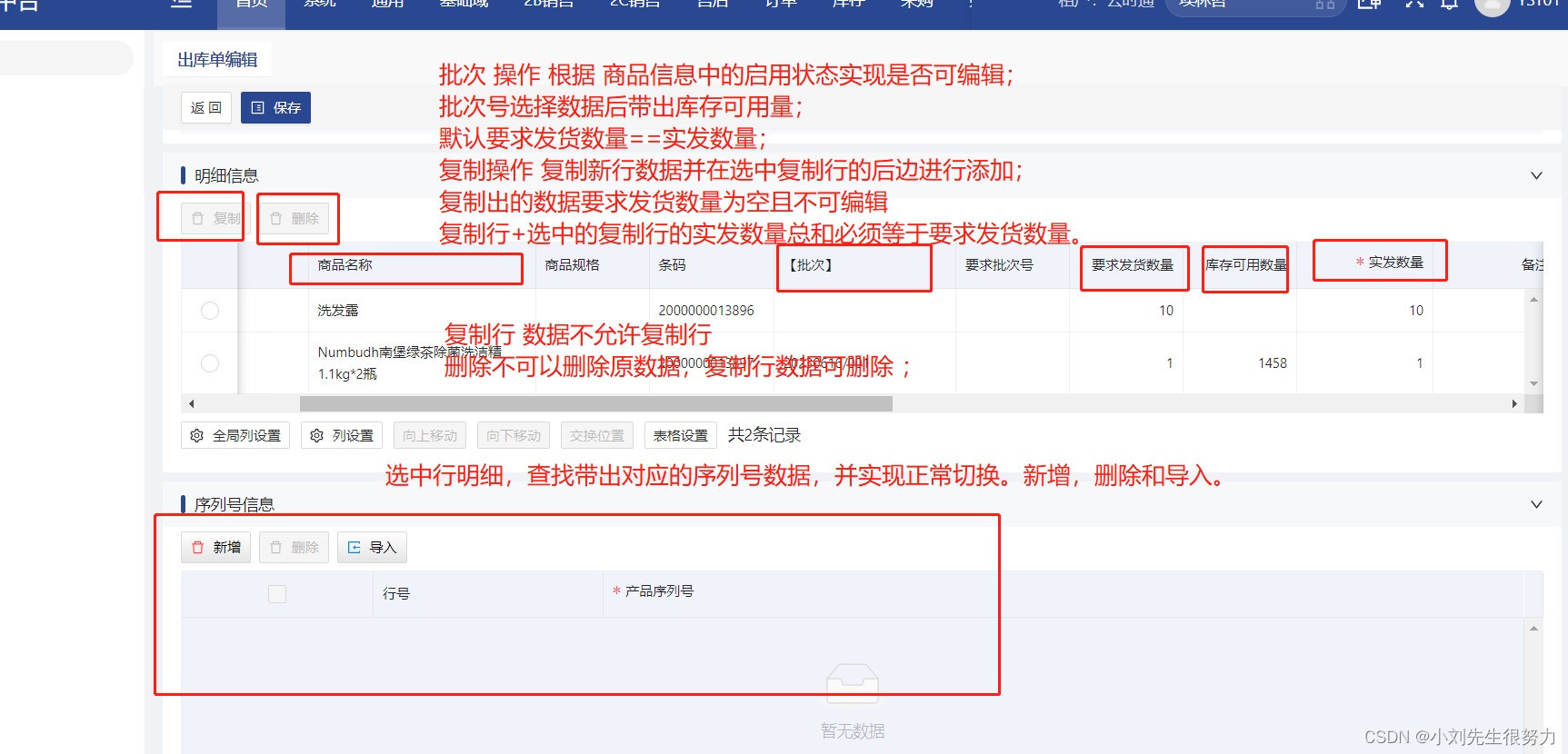
js实现数据关联查找更新。数据求和验证
为了实现这个功能我们和后端定义了数据结构 data:{id:‘’,formInfo:,formInfo2:,formInfo3:,formInfo4:, ......deailData:[ // 明细数据 // saleData 查询带出的对应明细序列号数据{ id:, ocopyId:, copyId:, odoId:, ......, saleData:[ { id:, oc…...

区块链上地址与银行账户有什么区别?
在区块链世界中,除了交易还有另一个基础要素:地址。在日前推出的Onchain AML合规技术方案,也有一个与区块链地址密切相关的概念:KYA(Know Your Address,了解你的地址)。 那问题来了,区块链地址究竟有什么用…...
)
CF 148 D Bag of mice(概率dp求概率)
CF 148 D. Bag of mice(概率dp求概率) Problem - 148D - Codeforces 大意:袋子里有 w 只白鼠和 b 只黑鼠 ,A和B轮流从袋子里抓,谁先抓到白色谁就赢。A每次随机抓一只,B每次随机抓完一只之后会有另一只随机老鼠跑出来。如果两个人…...

引入本地 jar 包教程
将本地 jar 包,放到 resource 目录下,在 pom.xml 文件中加入如下依赖: <dependency><groupId>com.hk</groupId><artifactId>examples</artifactId><version>1.0</version><scope>system<…...
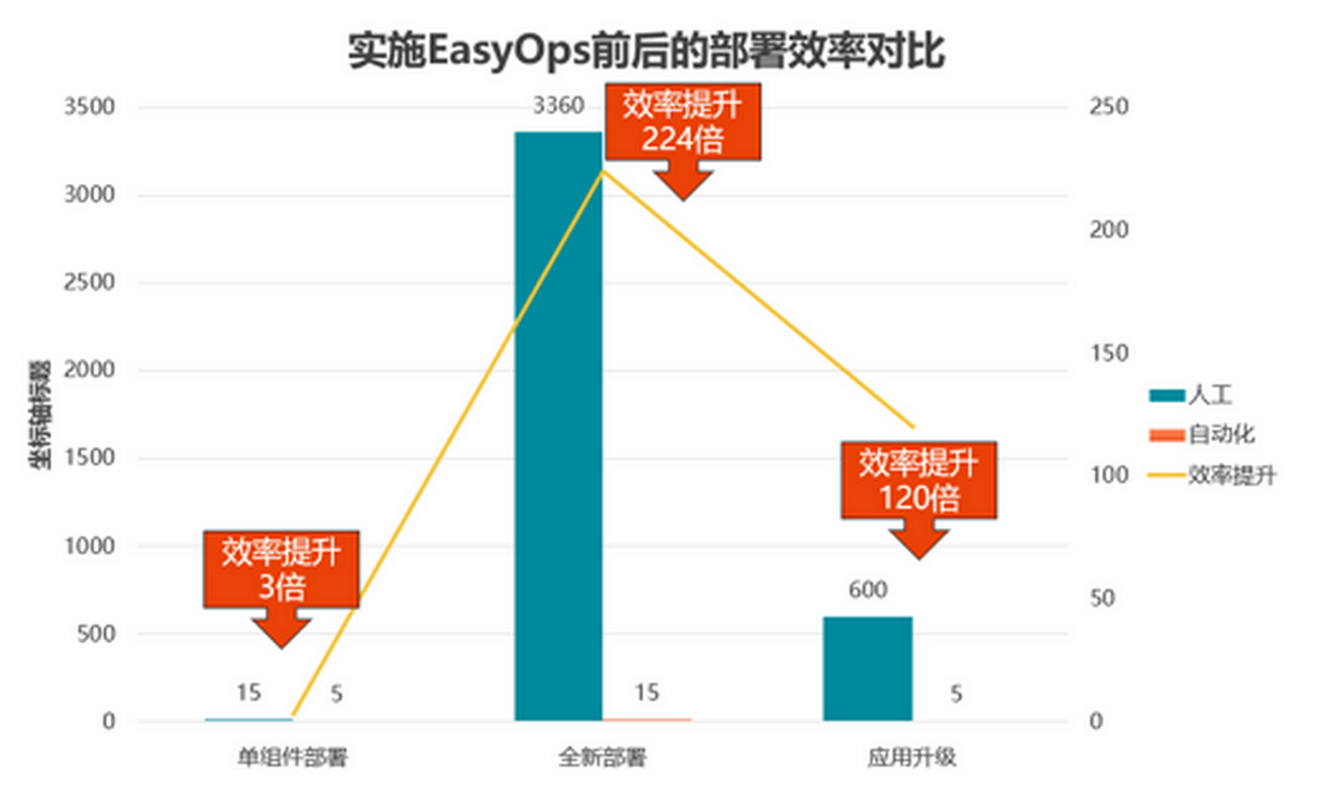
优维产品最佳实践第5期:什么是持续集成?
谈到到DevOps,持续交付流水线是绕不开的一个话题,相对于其他实践,通过流水线来实现快速高质量的交付价值是相对能快速见效的,特别对于开发测试人员,能够获得实实在在的收益。 本期EasyOps产品使用最佳实践,…...
空时自适应处理用于机载雷达——元素空间空时自适应处理(Matla代码实现)
💥💥💞💞欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️💥💥 🏆博主优势:🌞🌞🌞博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。 ⛳️座右铭&a…...
51c自动驾驶~合集58
我自己的原文哦~ https://blog.51cto.com/whaosoft/13967107 #CCA-Attention 全局池化局部保留,CCA-Attention为LLM长文本建模带来突破性进展 琶洲实验室、华南理工大学联合推出关键上下文感知注意力机制(CCA-Attention),…...
)
IGP(Interior Gateway Protocol,内部网关协议)
IGP(Interior Gateway Protocol,内部网关协议) 是一种用于在一个自治系统(AS)内部传递路由信息的路由协议,主要用于在一个组织或机构的内部网络中决定数据包的最佳路径。与用于自治系统之间通信的 EGP&…...
剑指offer20_链表中环的入口节点
链表中环的入口节点 给定一个链表,若其中包含环,则输出环的入口节点。 若其中不包含环,则输出null。 数据范围 节点 val 值取值范围 [ 1 , 1000 ] [1,1000] [1,1000]。 节点 val 值各不相同。 链表长度 [ 0 , 500 ] [0,500] [0,500]。 …...

[10-3]软件I2C读写MPU6050 江协科技学习笔记(16个知识点)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16...

Neo4j 集群管理:原理、技术与最佳实践深度解析
Neo4j 的集群技术是其企业级高可用性、可扩展性和容错能力的核心。通过深入分析官方文档,本文将系统阐述其集群管理的核心原理、关键技术、实用技巧和行业最佳实践。 Neo4j 的 Causal Clustering 架构提供了一个强大而灵活的基石,用于构建高可用、可扩展且一致的图数据库服务…...
初学 pytest 记录
安装 pip install pytest用例可以是函数也可以是类中的方法 def test_func():print()class TestAdd: # def __init__(self): 在 pytest 中不可以使用__init__方法 # self.cc 12345 pytest.mark.api def test_str(self):res add(1, 2)assert res 12def test_int(self):r…...
HDFS分布式存储 zookeeper
hadoop介绍 狭义上hadoop是指apache的一款开源软件 用java语言实现开源框架,允许使用简单的变成模型跨计算机对大型集群进行分布式处理(1.海量的数据存储 2.海量数据的计算)Hadoop核心组件 hdfs(分布式文件存储系统)&a…...

【生成模型】视频生成论文调研
工作清单 上游应用方向:控制、速度、时长、高动态、多主体驱动 类型工作基础模型WAN / WAN-VACE / HunyuanVideo控制条件轨迹控制ATI~镜头控制ReCamMaster~多主体驱动Phantom~音频驱动Let Them Talk: Audio-Driven Multi-Person Conversational Video Generation速…...
免费数学几何作图web平台
光锐软件免费数学工具,maths,数学制图,数学作图,几何作图,几何,AR开发,AR教育,增强现实,软件公司,XR,MR,VR,虚拟仿真,虚拟现实,混合现实,教育科技产品,职业模拟培训,高保真VR场景,结构互动课件,元宇宙http://xaglare.c…...
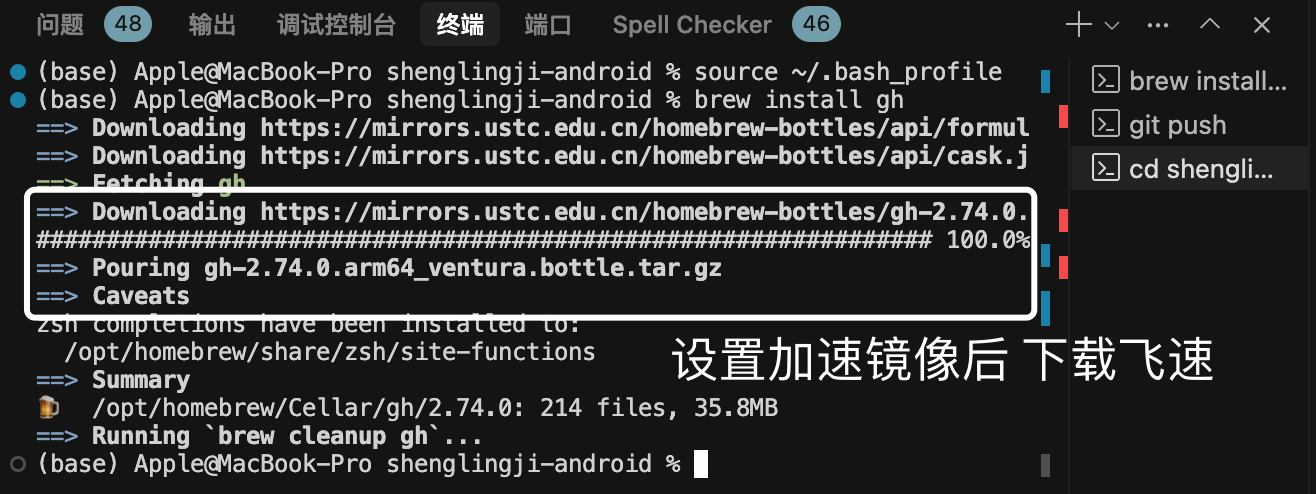
MacOS下Homebrew国内镜像加速指南(2025最新国内镜像加速)
macos brew国内镜像加速方法 brew install 加速formula.jws.json下载慢加速 🍺 最新版brew安装慢到怀疑人生?别怕,教你轻松起飞! 最近Homebrew更新至最新版,每次执行 brew 命令时都会自动从官方地址 https://formulae.…...
