【iOS】Category、Extension和关联对象
Category分类
Category 是 比继承更为简洁 的方法来对Class进行扩展,无需创建子类就可以为现有的类动态添加方法。
- 可以给项目内任何已经存在的类 添加
Category - 甚至可以是系统库/闭源库等只暴露了声明文件的类 添加
Category(看不到.m文件的类) - 通过
Category可以添加 实例方法、类方法、属性- 注意:通过
Category可以添加属性,会声明setter、getter方法 ,但需要 开发者 自己 实现setter、getter方法(使用关联对象实现属性) - 通过
Class添加属性,会默认生成并实现setter、getter方法
- 注意:通过
- 分类也可以把
framework私有方法公开化- 比如我们假如我有一个类里有一个私有方法A 外界是调用不到的 但是我给这个类写了个
category在里里面申明了一个方法(也叫A,只申明,不实现) 现在我import这个category调用 这个A 的情况是怎么样的呢?实际上这时候就会调用私有方法这个A,我们通过分类将私有方法公开化了
- 比如我们假如我有一个类里有一个私有方法A 外界是调用不到的 但是我给这个类写了个
- 通过
Category可以 重新实现 在Class中已存在的 方法 - 通过
Category可以 重新实现 在 其它Category中已存在/已实现 的方法
[ 在iOS中,实例对象/类对象方法调用顺序严格依赖 源码文件的编译顺序,编译顺序的查看可以通过Xcode>Build Phases>Compile Sources查看:
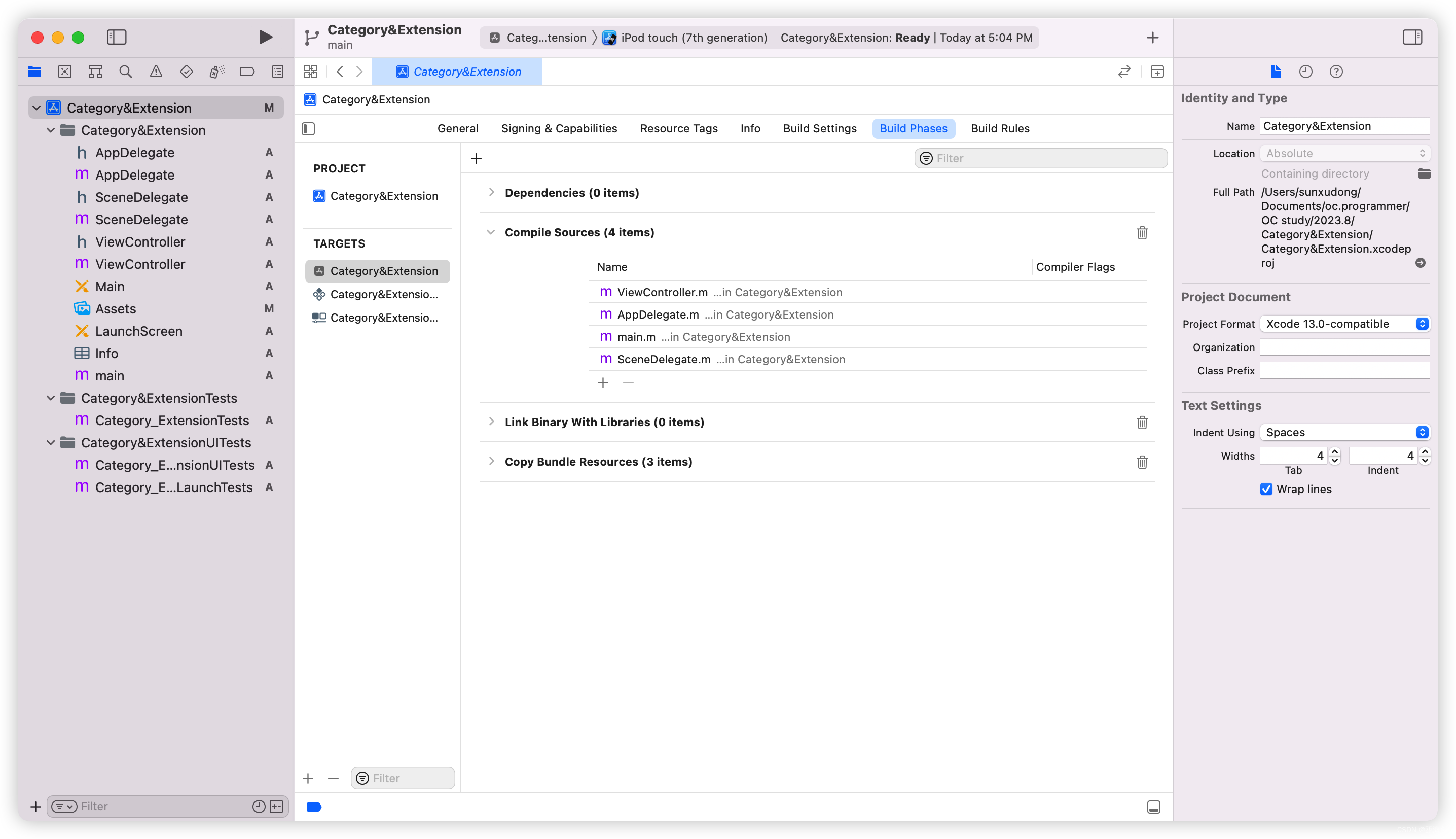
- 类与 各个分类 各自声明且实现各自的方法:没有方法的实现被覆盖,分类 只是扩展了 类的 功能
- 类与 各个分类 存在 声明 且实现 了同名的 方法: 存在 方法的实现被覆盖(实际上不是被覆盖,而是方法地址后挪,系统会找到同名方法在内存地址中位置较前的方法 实现 调用)
- 分类 方法实现 的优先级 > 原来的类
- 各个分类 中 被覆盖的情况严格 依赖 源码 文件的编译顺序:
- 先编译的 方法 会 先加入 方法列表「先入栈」
- 后编译的 方法 会 后加入 方法列表「后入栈」
- 系统在调用 方法 的实现的时候,通过 对象(实例对象、类对象等) 和 方法API 在底层发送消息,拿到方法 实现 的 实现 IMP指针 找到 方法的具体实现(实际上最终拿到的方法实现,是后编译的源码文件中的方法实现)
官方介绍的优点有两点:
- 可以把类的实现分开在几个不同的文件里面
- 可以减少分开文件的体积
- 可以把不同的功能组织到不同的category里
- 可以有多个开发者共同完成一个类
- 可以按需加载想要的类别等等
- 声明专有方法
Extension扩展
延展(Extension)可以理解成是匿名的Category
可以用来给类 添加 属性和方法 的声明,不作用在Subclass
可以 通过 在.m文件 给其它类 或者 当前 类 添加 Extension
给当前类添加 Extension 时,编译器会默认给 添加的属性 声明且实现 其setter&&getter方法
也可以 通过 .h文件 给类 添加 Extension
要对 Extension添加的 属性和方法进行实现
若 对 Extension的实现中 ,重新实现 原来 类或其它分类中已有的方法,不会对原来的方法执行产生影响(因为没有自身的.m文件,不存在源码实现文件的编译的情况)
Extension的作用更多在于拆分结构复杂的类,比较清晰的暴露声明
Category的实质
Category结构体
typedef struct category_t *Category;
struct category_t {const char *name;classref_t cls;struct method_list_t *instanceMethods; //实例方法struct method_list_t *classMethods; //类方法struct protocol_list_t *protocols; //协议struct property_list_t *instanceProperties; //实例属性// Fields below this point are not always present on disk.struct property_list_t *_classProperties; //类属性method_list_t *methodsForMeta(bool isMeta) {if (isMeta) return classMethods;else return instanceMethods;}property_list_t *propertiesForMeta(bool isMeta, struct header_info *hi);
};
分类的结构体中可以为类添加对象方法、类方法、协议、属性,但是并没有成员变量
将分类转成C++看起
接着我们将分类的.m文件转成C++文件来了解一下:
我们首先先创建一个分类:
#import "Car.h"
#import "protocolForCar.h"NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_BEGIN@interface Car (match)<CarProtocol>
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *carType;- (void)matchPrint;
+ (void)matchClass;@endNS_ASSUME_NONNULL_END
我们在其中声明了一个实例方法、一个类方法、一个属性
分类遵循一个协议,协议里面也是一个类方法和对象方法
#ifndef protocolForCar_h
#define protocolForCar_h@protocol CarProtocol <NSObject>- (void)protocolMethod;
+ (void)protocolClassMethod;@end
然后使用:xcrun -sdk iphoneos clang -arch arm64 -rewrite-objc Car+match.m -o test.cpp,将该分类的.m文件转为C++文件:
//category结构体
struct _category_t {const char *name;struct _class_t *cls;const struct _method_list_t *instance_methods;const struct _method_list_t *class_methods;const struct _protocol_list_t *protocols;const struct _prop_list_t *properties;
};//category结构体赋值
static struct _category_t _OBJC_$_CATEGORY_Car_$_match __attribute__ ((used, section ("__DATA,__objc_const"))) =
{"Car",0, // &OBJC_CLASS_$_Car,(const struct _method_list_t *)&_OBJC_$_CATEGORY_INSTANCE_METHODS_Car_$_match,(const struct _method_list_t *)&_OBJC_$_CATEGORY_CLASS_METHODS_Car_$_match,(const struct _protocol_list_t *)&_OBJC_CATEGORY_PROTOCOLS_$_Car_$_match,(const struct _prop_list_t *)&_OBJC_$_PROP_LIST_Car_$_match,
};//结构体数组
static struct _category_t *L_OBJC_LABEL_CATEGORY_$ [1] __attribute__((used, section ("__DATA, __objc_catlist,regular,no_dead_strip")))= {&_OBJC_$_CATEGORY_Car_$_match,
};
我们可以看到重点的三个元素
- category结构体
- category结构体的赋值语句
- category结构体数组
对象方法列表结构体
//本类对象方法的实现
static void _I_Car_match_matchPrint(Car * self, SEL _cmd) {NSLog((NSString *)&__NSConstantStringImpl__var_folders_6p_mn3hwpz14_7dg_gr79rtm4n80000gn_T_Car_match_633f34_mi_0);
}//协议中对象方法的实现
static void _I_Car_match_protocolMethod(Car * self, SEL _cmd) {NSLog((NSString *)&__NSConstantStringImpl__var_folders_6p_mn3hwpz14_7dg_gr79rtm4n80000gn_T_Car_match_633f34_mi_2);
}//对象方法列表结构体
static struct /*_method_list_t*/ {unsigned int entsize; // sizeof(struct _objc_method)unsigned int method_count;struct _objc_method method_list[2];
} _OBJC_$_CATEGORY_INSTANCE_METHODS_Car_$_match __attribute__ ((used, section ("__DATA,__objc_const"))) = {sizeof(_objc_method),2,{{(struct objc_selector *)"matchPrint", "v16@0:8", (void *)_I_Car_match_matchPrint},{(struct objc_selector *)"protocolMethod", "v16@0:8", (void *)_I_Car_match_protocolMethod}}
};
- (void)matchPrint和- (void)protocolMethod方法的实现- 对象方法结构体列表结构体
只要是在Category中实现了的对象方法(包括代理中的对象方法)。都会添加到对象方法列表结构体_OBJC_$_CATEGORY_INSTANCE_METHODS_Car_$_match中来,如果仅仅是定义,没有实现,不会加进来
类方法列表结构体
//本类类方法的实现
static void _C_Car_match_matchClass(Class self, SEL _cmd) {NSLog((NSString *)&__NSConstantStringImpl__var_folders_6p_mn3hwpz14_7dg_gr79rtm4n80000gn_T_Car_match_633f34_mi_1);
}//协议中的类方法
static void _C_Car_match_protocolClassMethod(Class self, SEL _cmd) {NSLog((NSString *)&__NSConstantStringImpl__var_folders_6p_mn3hwpz14_7dg_gr79rtm4n80000gn_T_Car_match_633f34_mi_3);
}//类方法列表结构体
static struct /*_method_list_t*/ {unsigned int entsize; // sizeof(struct _objc_method)unsigned int method_count;struct _objc_method method_list[2];
} _OBJC_$_CATEGORY_CLASS_METHODS_Car_$_match __attribute__ ((used, section ("__DATA,__objc_const"))) = {sizeof(_objc_method),2,{{(struct objc_selector *)"matchClass", "v16@0:8", (void *)_C_Car_match_matchClass},{(struct objc_selector *)"protocolClassMethod", "v16@0:8", (void *)_C_Car_match_protocolClassMethod}}
};
+ (void)matchClass和+ (void)protocolClassMethod类方法的实现- 类方法列表结构体
只要是Category中实现了的类方法(包括代理中的类方法)。都会添加到类方法列表结构体_OBJC_$_CATEGORY_CLASS_METHODS_Car_$_match中来
协议列表结构体
//协议结构体
struct _protocol_t {void * isa; // NULLconst char *protocol_name;const struct _protocol_list_t * protocol_list; // super protocolsconst struct method_list_t *instance_methods;const struct method_list_t *class_methods;const struct method_list_t *optionalInstanceMethods;const struct method_list_t *optionalClassMethods;const struct _prop_list_t * properties;const unsigned int size; // sizeof(struct _protocol_t)const unsigned int flags; // = 0const char ** extendedMethodTypes;
};//分类中添加的协议列表结构体
static struct /*_protocol_list_t*/ {long protocol_count; // Note, this is 32/64 bitstruct _protocol_t *super_protocols[1];
} _OBJC_PROTOCOL_REFS_CarProtocol __attribute__ ((used, section ("__DATA,__objc_const"))) = {1,&_OBJC_PROTOCOL_NSObject
};//协议列表 对象方法列表结构体
static struct /*_method_list_t*/ {unsigned int entsize; // sizeof(struct _objc_method)unsigned int method_count;struct _objc_method method_list[1];
} _OBJC_PROTOCOL_INSTANCE_METHODS_CarProtocol __attribute__ ((used, section ("__DATA,__objc_const"))) = {sizeof(_objc_method),1,{{(struct objc_selector *)"protocolMethod", "v16@0:8", 0}}
};//协议列表 类方法列表结构体
static struct /*_method_list_t*/ {unsigned int entsize; // sizeof(struct _objc_method)unsigned int method_count;struct _objc_method method_list[1];
} _OBJC_PROTOCOL_CLASS_METHODS_CarProtocol __attribute__ ((used, section ("__DATA,__objc_const"))) = {sizeof(_objc_method),1,{{(struct objc_selector *)"protocolClassMethod", "v16@0:8", 0}}
};//结构体赋值
struct _protocol_t _OBJC_PROTOCOL_CarProtocol __attribute__ ((used)) = {0,"CarProtocol",(const struct _protocol_list_t *)&_OBJC_PROTOCOL_REFS_CarProtocol,(const struct method_list_t *)&_OBJC_PROTOCOL_INSTANCE_METHODS_CarProtocol,(const struct method_list_t *)&_OBJC_PROTOCOL_CLASS_METHODS_CarProtocol,0,0,0,sizeof(_protocol_t),0,(const char **)&_OBJC_PROTOCOL_METHOD_TYPES_CarProtocol
};
struct _protocol_t *_OBJC_LABEL_PROTOCOL_$_CarProtocol = &_OBJC_PROTOCOL_CarProtocol;
属性列表结构体
//属性结构体
struct _prop_t {const char *name;const char *attributes;
};//属性列表结构体
static struct /*_prop_list_t*/ {unsigned int entsize; // sizeof(struct _prop_t)unsigned int count_of_properties;struct _prop_t prop_list[1];
} _OBJC_$_PROP_LIST_Car_$_match __attribute__ ((used, section ("__DATA,__objc_const"))) = {sizeof(_prop_t),1,{{"carType","T@\"NSString\",C,N"}}
};
从属性列表结构体源码中我们可以看到:只有person分类中添加的属性列表结构体_OBJC_$_PROP_LIST_NSObject_$_testCategory,没有成员变量结构体_ivar_list_t结构体。更没有对应的set/get方法相关的内容。
这也说明了Category中不能添加成员变量这一事实
category总结
主要包含下面几种部分内容:
_method_list_t类型的 对象方法列表结构体_method_list_t类型的 类方法列表结构体_protocol_list_t类型的 协议列表结构体_prop_list_t类型的 属性列表结构体_category_t结构体中并不包含_ivar_list_t类型,也就是不包含成员变量结构体
分类在运行期做了什么
(这部分内容比较臃肿,可以先去参考文章后面的分类加载的总结,然后结合总结看这里的源码分析会更有逻辑性)
要搞懂这个问题的话,我们就需要知道什么时候调用了分类的方法
_objc_init这个函数是runtime的初始化函数,我们就从_objc_init开始入手:
_objc_init
/***********************************************************************
* _objc_init
* Bootstrap initialization. Registers our image notifier with dyld.
* Called by libSystem BEFORE library initialization time
**********************************************************************/void _objc_init(void)
{static bool initialized = false;if (initialized) return;initialized = true;// fixme defer initialization until an objc-using image is found?//环境变量environ_init();//绑定线程析构函数tls_init();//静态构造函数static_init();//runtime准备,创建2张表runtime_init();//异常初始化exception_init();
#if __OBJC2__//缓存cache_t::init();
#endif//macos专有_imp_implementationWithBlock_init();_dyld_objc_notify_register(&map_images, load_images, unmap_image);#if __OBJC2__didCallDyldNotifyRegister = true;
#endif
}
其中我们发现了一些初始化创建过程,这里我们主要关注一下runtime_init:
void runtime_init(void)
{//分类加载表objc::unattachedCategories.init(32);//类的加载表objc::allocatedClasses.init();
}
可以看到其中有一张分类加载表。
接着我们在回到_objc_init中, map_images读取资源(images代表资源模块),来到map_images_nolock函数中找到_read_images函数,在_read_images函数中找到与分类相关的代码:
_read_images
// Discover categories. Only do this after the initial category// attachment has been done. For categories present at startup,// discovery is deferred until the first load_images call after// the call to _dyld_objc_notify_register completes. rdar://problem/53119145//发现类别。只有在初始类别之后才这样做//附件已完成。对于启动时出现的类别,//发现延迟到之后的第一个load_images调用//调用_dyld_objc_notify_register完成。rdar: / /问题/ 53119145//意思是非懒加载的分类走的是load_images//那么作为对应,懒加载的分类就走的是这里 _read_images中的操作//全局变量didInitialAttachCategories,执行load_images 的时候设置为YES//所以只有当执行过load_images的时候,这里才会遍历load_catagories_nolock去加载分类,而这里遍历的也是一些懒加载的类的分类。//这里的判断条件didInitialAttachCategories意思是是否进行完初始的分类添加(如果进行过的话,也就是非懒加载的分类以经添加了的话,就进去执行if分支中的内容)if (didInitialAttachCategories) {for (EACH_HEADER) {load_categories_nolock(hi);}}ts.log("IMAGE TIMES: discover categories");
load_images
void
load_images(const char *path __unused, const struct mach_header *mh)
{if (!didInitialAttachCategories && didCallDyldNotifyRegister) {didInitialAttachCategories = true;// 加载所有的分类loadAllCategories();}// Return without taking locks if there are no +load methods here.//有load方法的话直接返回,没有的话才执行后面找load方法和调用load方法的代码//如果这里没有+load方法,返回时不带锁。if (!hasLoadMethods((const headerType *)mh)) return;recursive_mutex_locker_t lock(loadMethodLock);// Discover load methods{// 找到load方法mutex_locker_t lock2(runtimeLock);prepare_load_methods((const headerType *)mh);}// Call +load methods (without runtimeLock - re-entrant)//调用load方法call_load_methods();
}
我们放上一张load_images的流程图,便于理解其中的整个过程。
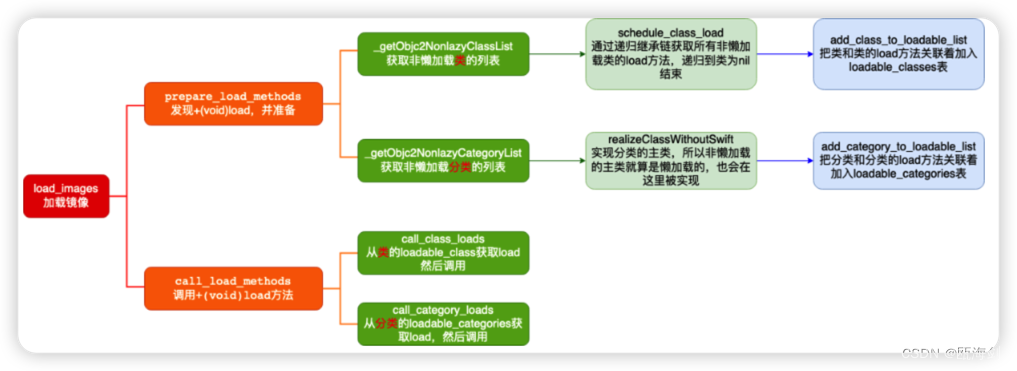
其中有一个重要的点,就是在获取分类的load方法的时候,我们是先获取了非懒加载分类的列表,然后调用realizeClassWithoutSwift对其分类的主类进行了实现,这点非常重要。后续整个流程总结时会提到,调用realizeClassWithoutSwift的源码如下:
//prepare_load_methods是load_images中获取主类和分类load方法时调用的函数
void prepare_load_methods(const headerType *mhdr)
{size_t count, i;runtimeLock.assertLocked();classref_t const *classlist = _getObjc2NonlazyClassList(mhdr, &count);for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {schedule_class_load(remapClass(classlist[i]));}category_t * const *categorylist = _getObjc2NonlazyCategoryList(mhdr, &count);for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {category_t *cat = categorylist[i];Class cls = remapClass(cat->cls);if (!cls) continue; // category for ignored weak-linked classif (cls->isSwiftStable()) {_objc_fatal("Swift class extensions and categories on Swift ""classes are not allowed to have +load methods");}//此处调用realizeClassWithoutSwift实现了分类对应的主类realizeClassWithoutSwift(cls, nil);ASSERT(cls->ISA()->isRealized());add_category_to_loadable_list(cat);}
}
用于实现主类的方法:realizeClassWithoutSwift的源码如下:
static Class realizeClassWithoutSwift(Class cls, Class previously)
{runtimeLock.assertLocked();class_rw_t *rw; // 读写数据Class supercls; // 父类Class metacls; // 元类if (!cls) return nil; // 如果为空,返回nilif (cls->isRealized()) return cls; // 如果已经实现,直接返回ASSERT(cls == remapClass(cls));// fixme verify class is not in an un-dlopened part of the shared cache?auto ro = (const class_ro_t *)cls->data(); // 读取类的数据auto isMeta = ro->flags & RO_META; // 是否是元类if (ro->flags & RO_FUTURE) { // rw已经有值的话走这里// This was a future class. rw data is already allocated.rw = cls->data();ro = cls->data()->ro();ASSERT(!isMeta);cls->changeInfo(RW_REALIZED|RW_REALIZING, RW_FUTURE);} else { // 正常的类走这里// Normal class. Allocate writeable class data.rw = objc::zalloc<class_rw_t>(); // 开辟rwrw->set_ro(ro); // 把cls的数据ro赋值给rwrw->flags = RW_REALIZED|RW_REALIZING|isMeta; // 更新flagscls->setData(rw); // 再把rw设置为cls的data数据}#if FAST_CACHE_METAif (isMeta) cls->cache.setBit(FAST_CACHE_META);
#endif// Choose an index for this class.// Sets cls->instancesRequireRawIsa if indexes no more indexes are availablecls->chooseClassArrayIndex();if (PrintConnecting) {_objc_inform("CLASS: realizing class '%s'%s %p %p #%u %s%s",cls->nameForLogging(), isMeta ? " (meta)" : "", (void*)cls, ro, cls->classArrayIndex(),cls->isSwiftStable() ? "(swift)" : "",cls->isSwiftLegacy() ? "(pre-stable swift)" : "");}// Realize superclass and metaclass, if they aren't already.//实现超类和元类(如果尚未实现)。// This needs to be done after RW_REALIZED is set above, for root classes.//对于根类,需要在上面设置了RW_REALIZED之后执行此操作。// This needs to be done after class index is chosen, for root metaclasses.//对于根元类,需要在选择类索引之后执行此操作。// This assumes that none of those classes have Swift contents,// or that Swift's initializers have already been called.// fixme that assumption will be wrong if we add support// for ObjC subclasses of Swift classes.// 递归调用 realizeClassWithoutSwift ,实现父类和元类supercls = realizeClassWithoutSwift(remapClass(cls->superclass), nil);metacls = realizeClassWithoutSwift(remapClass(cls->ISA()), nil);#if SUPPORT_NONPOINTER_ISAif (isMeta) { // 如果是元类,对isa处理// Metaclasses do not need any features from non pointer ISA// This allows for a faspath for classes in objc_retain/objc_release.cls->setInstancesRequireRawIsa();} else { // 不是元类,也是对isa处理// Disable non-pointer isa for some classes and/or platforms.// Set instancesRequireRawIsa.bool instancesRequireRawIsa = cls->instancesRequireRawIsa();bool rawIsaIsInherited = false;static bool hackedDispatch = false;if (DisableNonpointerIsa) {// Non-pointer isa disabled by environment or app SDK versioninstancesRequireRawIsa = true;}else if (!hackedDispatch && 0 == strcmp(ro->name, "OS_object")){// hack for libdispatch et al - isa also acts as vtable pointerhackedDispatch = true;instancesRequireRawIsa = true;}else if (supercls && supercls->superclass &&supercls->instancesRequireRawIsa()){// This is also propagated by addSubclass()// but nonpointer isa setup needs it earlier.// Special case: instancesRequireRawIsa does not propagate// from root class to root metaclassinstancesRequireRawIsa = true;rawIsaIsInherited = true;}if (instancesRequireRawIsa) {cls->setInstancesRequireRawIsaRecursively(rawIsaIsInherited);}}
// SUPPORT_NONPOINTER_ISA
#endif// Update superclass and metaclass in case of remapping// 确定继承链,赋值父类和元类cls->superclass = supercls;cls->initClassIsa(metacls);// Reconcile instance variable offsets / layout.// 协调实例变量的偏移量/布局。// This may reallocate class_ro_t, updating our ro variable.if (supercls && !isMeta) reconcileInstanceVariables(cls, supercls, ro);// Set fastInstanceSize if it wasn't set already.// 经过上一步,再次协调属性对齐后,设置实例大小cls->setInstanceSize(ro->instanceSize);// Copy some flags from ro to rw// 赋值一些 ro 中的 flags标识位 到 rwif (ro->flags & RO_HAS_CXX_STRUCTORS) {cls->setHasCxxDtor();if (! (ro->flags & RO_HAS_CXX_DTOR_ONLY)) {cls->setHasCxxCtor();}}// Propagate the associated objects forbidden flag from ro or from// the superclass.// 从ro或父类传播关联的对象禁止标志。if ((ro->flags & RO_FORBIDS_ASSOCIATED_OBJECTS) ||(supercls && supercls->forbidsAssociatedObjects())){rw->flags |= RW_FORBIDS_ASSOCIATED_OBJECTS;}// Connect this class to its superclass's subclass lists// 添加当前类到父类的子类列表中,如果没有父类,设置自己就是根类if (supercls) {addSubclass(supercls, cls);} else {addRootClass(cls);}// Attach categories// 附加分类methodizeClass(cls, previously);return cls;
}
可以看到最后也是执行了一个methodizeClass函数来向主类附加分类,methodizeClass源码如下:
//methodizeClass函数用于附加分类
static void methodizeClass(Class cls, Class previously)
{runtimeLock.assertLocked();bool isMeta = cls->isMetaClass();auto rw = cls->data();auto ro = rw->ro(); // 读取ro数据auto rwe = rw->ext(); // 读取ext,赋值给rwe// Methodizing for the first timeif (PrintConnecting) {_objc_inform("CLASS: methodizing class '%s' %s", cls->nameForLogging(), isMeta ? "(meta)" : "");}// Install methods and properties that the class implements itself.method_list_t *list = ro->baseMethods(); // 获取ro中的方法列表if (list) {// 对方法列表list重新排序prepareMethodLists(cls, &list, 1, YES, isBundleClass(cls));if (rwe) rwe->methods.attachLists(&list, 1); // 如果有rwe,添加方法列表list到rwe的methodsList}property_list_t *proplist = ro->baseProperties;if (rwe && proplist) {rwe->properties.attachLists(&proplist, 1);}protocol_list_t *protolist = ro->baseProtocols;if (rwe && protolist) {rwe->protocols.attachLists(&protolist, 1);}// Root classes get bonus method implementations if they don't have // them already. These apply before category replacements.if (cls->isRootMetaclass()) {// root metaclass 根元类添加initialize方法addMethod(cls, @selector(initialize), (IMP)&objc_noop_imp, "", NO);}// Attach categories. 附加分类if (previously) {if (isMeta) {objc::unattachedCategories.attachToClass(cls, previously,ATTACH_METACLASS);} else {// When a class relocates, categories with class methods// may be registered on the class itself rather than on// the metaclass. Tell attachToClass to look for those.objc::unattachedCategories.attachToClass(cls, previously,ATTACH_CLASS_AND_METACLASS);}}objc::unattachedCategories.attachToClass(cls, cls,isMeta ? ATTACH_METACLASS : ATTACH_CLASS);#if DEBUG// Debug: sanity-check all SELs; log method list contentsfor (const auto& meth : rw->methods()) {if (PrintConnecting) {_objc_inform("METHOD %c[%s %s]", isMeta ? '+' : '-', cls->nameForLogging(), sel_getName(meth.name));}ASSERT(sel_registerName(sel_getName(meth.name)) == meth.name); }
#endif
}
还有我们发现load_images里面的确调用了loadAllCategories函数,接着我们再来看一下loadAllCategories的实现:
loadAllCategories
static void loadAllCategories() {mutex_locker_t lock(runtimeLock);for (auto *hi = FirstHeader; hi != NULL; hi = hi->getNext()) {//调用load_categories_nolock来加载分类load_categories_nolock(hi);}
}
接着我们来看load_categories_nolock函数的实现(这个方法在load_images中和map_images两个流程中都会有调用到,其中执行的内容各稍有不同):
load_categories_nolock
static void load_categories_nolock(header_info *hi) {bool hasClassProperties = hi->info()->hasCategoryClassProperties();size_t count;auto processCatlist = [&](category_t * const *catlist) {for (unsigned i = 0; i < count; i++) {category_t *cat = catlist[i];Class cls = remapClass(cat->cls);locstamped_category_t lc{cat, hi};if (!cls) {// Category's target class is missing (probably weak-linked).// Ignore the category.if (PrintConnecting) {_objc_inform("CLASS: IGNORING category \?\?\?(%s) %p with ""missing weak-linked target class",cat->name, cat);}continue;}// Process this category.if (cls->isStubClass()) {// Stub classes are never realized. Stub classes// don't know their metaclass until they're// initialized, so we have to add categories with// class methods or properties to the stub itself.// methodizeClass() will find them and add them to// the metaclass as appropriate.if (cat->instanceMethods ||cat->protocols ||cat->instanceProperties ||cat->classMethods ||cat->protocols ||(hasClassProperties && cat->_classProperties)){objc::unattachedCategories.addForClass(lc, cls);}} else {// First, register the category with its target class.// Then, rebuild the class's method lists (etc) if// the class is realized.//首先,将类别注册到它的目标类。//如果那个类已经实现就重建它的方法列表if (cat->instanceMethods || cat->protocols|| cat->instanceProperties){if (cls->isRealized()) {//一般是map_images中调用load_categories_nolock函数时cls都会实现的,所以会走这个方法去将分类中的内容粘贴到主类中,但是现版本中map_images的注释中说到将分类添加主类的操作延迟到了第一次load_images执行时attachCategories(cls, &lc, 1, ATTACH_EXISTING);//而如果是load_images中调用的load_categories_nolock函数的话,一般cls都没实现,就会走下面的else里的方法,将分类添加到unattachedCategories(未向主类粘贴内容的分类表)表中} else {//这个表就是分类表objc::unattachedCategories.addForClass(lc, cls);}}if (cat->classMethods || cat->protocols|| (hasClassProperties && cat->_classProperties)){if (cls->ISA()->isRealized()) {//一般是map_images中调用load_categories_nolock函数时元类也都会实现的,所以会走这个方法去将分类中的内容粘贴到主元类中attachCategories(cls->ISA(), &lc, 1, ATTACH_EXISTING | ATTACH_METACLASS);//而如果是load_images中调用的load_categories_nolock函数的话,一般其元类都没实现,就会走下面的else里的方法,将分类添加到unattachedCategories(未向主元类类粘贴内容的分类表)表中} else {// runtime_init的时候创建,第一部分有讲到objc::unattachedCategories.addForClass(lc, cls->ISA());}}}}};processCatlist(hi->catlist(&count));processCatlist(hi->catlist2(&count));
}
- 获取
category列表list - 遍历
category list中的每一个category - 获取
category的对应的主类cls,如果没有cls就跳过(continue)这个继续获取下一个
(分类对应的主类是类对象时)如果其有对应的主类,并其有实例方法、协议、属性,则调用objc::unattachedCategories.addForClass(load_images中执行到这里时调用objc::unattachedCategories.addForClass来将分类注册到它对应的主类里面去,方便后续重建类的方法列表,如果是map_images中执行到这里时会调用attachCategories。这两种情况调用分支不同的原因就是在load_images中调用到的时候分类对应的主类并没有被实现,那些主类在load_images后续获取分类的load方法时才被实现,导致map_images执行到那里的时候分类对应的主类已经被实现了,所以if就走了不同的分支) - (分类对应的主类是元类对象时)如果其有对应的主类,并其有类方法、协议,则调用
objc::unattachedCategories.addForClass(load_images中执行到这里时调用objc::unattachedCategories.addForClass来将分类注册到它对应的主类里面去,方便后续重建类的方法列表,如果是map_images中执行到这里时会调用attachCategories)
这里肯定会疑惑为什么load_images中先将分类添加到unattachedCategories中,再将实现主类将分类内容添加到主类,map_images中最后调用的read_images中也是先将分类添加到unattachedCategories中,再将实现主类将分类内容添加到主类,其实从map_images处理分类那段代码的上方注释就可以理解,我们的load_images中走的添加分类到主类处理的都是非懒加载的分类,而read_images中走的添加分类到主类处理的都是懒加载的分类,而且都是清一色的先将分类添加到unattachedCategories中与主类产生关联并存放分类到内存中,然后再等到后面调用realizeClassWithoutSwift函数实现(初始化)主类的时候,再调用methodizeClass实现的具体的分类内容添加到主类
简言之就是加载分类有两个路径,一个是处理非懒加载分类的load_images中的路径,一个是处理懒加载分类的map_images中read_images处理的路径。
整个map_images的流程大致如下图:
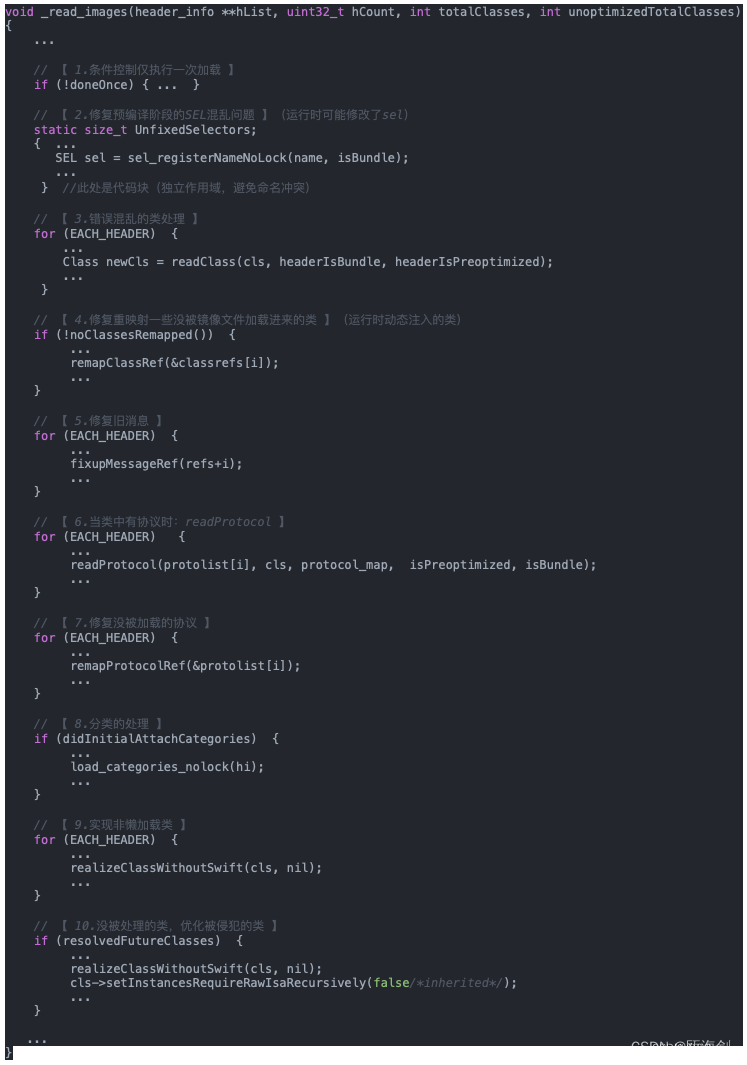
有趣的是,上面的第10步,初始化懒加载类,实际上也是调用我们上方说的realizeClassWithoutSwift进行的。
另外,对于懒加载类与非懒加载类的区别是:当前类是否实现 load 方法,实现了load方法就是非懒加载类,反之亦然,还有,懒加载类的数据加载推迟到第一次接收到消息的时候才开始加载,非懒加载类在map_images执行中就加载了所有类的数据
然后我们言归正传,回到load_categories_nolock函数上,其整个函数的流程其实是将所有分类添加到runtime_init中初始化的unattachedCategories表中或者调用attachCategories直接向主类中添加分类中的内容,注意这里的unattachedCategories表,意思是未将分类内容粘贴到主类的那些分类的表,说明后面就需要进行attachCategories操作来向主类粘贴。
然后我们来看一下unattachedCategories表:
class UnattachedCategories : public ExplicitInitDenseMap<Class, category_list>
{
public://将分类和主类关联起来void addForClass(locstamped_category_t lc, Class cls){runtimeLock.assertLocked();if (slowpath(PrintConnecting)) {_objc_inform("CLASS: found category %c%s(%s)",cls->isMetaClassMaybeUnrealized() ? '+' : '-',cls->nameForLogging(), lc.cat->name);}auto result = get().try_emplace(cls, lc);if (!result.second) {result.first->second.append(lc);}}//这个是向本类粘贴分类内容的方法void attachToClass(Class cls, Class previously, int flags){runtimeLock.assertLocked();ASSERT((flags & ATTACH_CLASS) ||(flags & ATTACH_METACLASS) ||(flags & ATTACH_CLASS_AND_METACLASS));auto &map = get();auto it = map.find(previously);if (it != map.end()) {category_list &list = it->second;if (flags & ATTACH_CLASS_AND_METACLASS) {int otherFlags = flags & ~ATTACH_CLASS_AND_METACLASS;//可以看到调用了attachCategories加载分类attachCategories(cls, list.array(), list.count(), otherFlags | ATTACH_CLASS);attachCategories(cls->ISA(), list.array(), list.count(), otherFlags | ATTACH_METACLASS);} else {attachCategories(cls, list.array(), list.count(), flags);}map.erase(it);}}void eraseCategoryForClass(category_t *cat, Class cls){runtimeLock.assertLocked();auto &map = get();auto it = map.find(cls);if (it != map.end()) {category_list &list = it->second;list.erase(cat);if (list.count() == 0) {map.erase(it);}}}void eraseClass(Class cls){runtimeLock.assertLocked();get().erase(cls);}
};
其中的addForClass其实就是将分类加载到内存的,里面我们发现有一个try_emplace方法,其代码如下:
template <typename... Ts>std::pair<iterator, bool> try_emplace(const KeyT &Key, Ts &&... Args) {BucketT *TheBucket;if (LookupBucketFor(Key, TheBucket))return std::make_pair(makeIterator(TheBucket, getBucketsEnd(), true),false); // Already in map.// Otherwise, insert the new element.TheBucket = InsertIntoBucket(TheBucket, Key, std::forward<Ts>(Args)...);return std::make_pair(makeIterator(TheBucket, getBucketsEnd(), true),true);}
这个创建一个存储桶的结构(这是一个键值对形式的结构),向里面存内容,结合上面的函数调用get().try_emplace(cls, lc)得知,以cls为key,lc为value进行存储。
接着我们来看一下向主类中添加分类中内容的attachCategories函数的源码:
// Attach method lists and properties and protocols from categories to a class.
// Assumes the categories in cats are all loaded and sorted by load order,
// oldest categories first.
//将方法列表、属性和协议从类别附加到一个类。
//假设猫的类别都是加载的,并按加载顺序排序,
//最古老的类别先开始。
static void
attachCategories(Class cls, const locstamped_category_t *cats_list, uint32_t cats_count,int flags)
{if (slowpath(PrintReplacedMethods)) {printReplacements(cls, cats_list, cats_count);}if (slowpath(PrintConnecting)) {_objc_inform("CLASS: attaching %d categories to%s class '%s'%s",cats_count, (flags & ATTACH_EXISTING) ? " existing" : "",cls->nameForLogging(), (flags & ATTACH_METACLASS) ? " (meta)" : "");}/** Only a few classes have more than 64 categories during launch.* This uses a little stack, and avoids malloc.** Categories must be added in the proper order, which is back* to front. To do that with the chunking, we iterate cats_list* from front to back, build up the local buffers backwards,* and call attachLists on the chunks. attachLists prepends the* lists, so the final result is in the expected order.*//**只有少数类在启动时拥有超过64个类别。*这使用了一个小堆栈,并避免了malloc。**类别必须以正确的顺序添加,这是回来*前面。为了使用分块实现这一点,我们需要迭代cats_list*从前面到后面,向后建立本地缓冲区,并在区块上调用attachLists。attachLists突出显示的*列表,因此最终结果按照预期的顺序。* ///创建方法列表、属性列表、协议列表,用来存储分类的方法、属性、协议constexpr uint32_t ATTACH_BUFSIZ = 64;method_list_t *mlists[ATTACH_BUFSIZ];property_list_t *proplists[ATTACH_BUFSIZ];protocol_list_t *protolists[ATTACH_BUFSIZ];uint32_t mcount = 0;// 记录方法的数量uint32_t propcount = 0;// 记录属性的数量uint32_t protocount = 0;// 记录协议的数量bool fromBundle = NO;// 记录是否是从 bundle 中取的bool isMeta = (flags & ATTACH_METACLASS);//取出当前类 cls 的 class_rwe_t 数据auto rwe = cls->data()->extAllocIfNeeded();//遍历分类for (uint32_t i = 0; i < cats_count; i++) {auto& entry = cats_list[i];// 取出分类中的方法列表。如果是元类,取得的是类方法列表;否则取得的是对象方法列表method_list_t *mlist = entry.cat->methodsForMeta(isMeta);if (mlist) {if (mcount == ATTACH_BUFSIZ) {prepareMethodLists(cls, mlists, mcount, NO, fromBundle, __func__);rwe->methods.attachLists(mlists, mcount);mcount = 0;}mlists[ATTACH_BUFSIZ - ++mcount] = mlist;// 将方法列表放入 mlists 方法列表数组中fromBundle |= entry.hi->isBundle();// 分类的头部信息中存储了是否是 bundle,将其记住}// 取出分类中的属性列表,如果是元类,取得的是 nilproperty_list_t *proplist =entry.cat->propertiesForMeta(isMeta, entry.hi);if (proplist) {if (propcount == ATTACH_BUFSIZ) {rwe->properties.attachLists(proplists, propcount);propcount = 0;}proplists[ATTACH_BUFSIZ - ++propcount] = proplist;}// 取出分类中遵循的协议列表protocol_list_t *protolist = entry.cat->protocolsForMeta(isMeta);if (protolist) {if (protocount == ATTACH_BUFSIZ) {rwe->protocols.attachLists(protolists, protocount);protocount = 0;}protolists[ATTACH_BUFSIZ - ++protocount] = protolist;}}if (mcount > 0) {// 存储方法、属性、协议数组到 rwe 中// 准备方法列表 mlists 中的方法【为什么需要准备方法列表这一步?】prepareMethodLists(cls, mlists + ATTACH_BUFSIZ - mcount, mcount,NO, fromBundle, __func__);// 将新方法列表添加到 rwe 中的方法列表中rwe->methods.attachLists(mlists + ATTACH_BUFSIZ - mcount, mcount);if (flags & ATTACH_EXISTING) {// 清除 cls 的缓存列表flushCaches(cls, __func__, [](Class c){// constant caches have been dealt with in prepareMethodLists// if the class still is constant here, it's fine to keepreturn !c->cache.isConstantOptimizedCache();});}}// 将新属性列表添加到 rwe 中的属性列表中rwe->properties.attachLists(proplists + ATTACH_BUFSIZ - propcount, propcount);// 将新协议列表添加到 rwe 中的协议列表中rwe->protocols.attachLists(protolists + ATTACH_BUFSIZ - protocount, protocount);
}
- 先创建方法列表、属性列表、协议列表的新列表并且给它们分配内存,然后存储该
cls所有的分类的方法、属性、协议,然后转交给了attachLists方法(就是后面的那几行代码)
为什么需要准备方法列表这一步呢?
方法的查找算法是通过二分查找算法,说明sel-imp是有排序的,那么是如何排序的呢?
perpareMethodLists中主要调用了fixup方法
在 fixupMethodList 方法中会遍历 mlist,把 sel 中的名字跟地址设置到 meth,然后根据地址对 mlist 进行重新排序
这也就意味着 remethodizeClass方法中实现类中方法(协议等)的序列化
attachLists方法保证其添加到列表的前面:
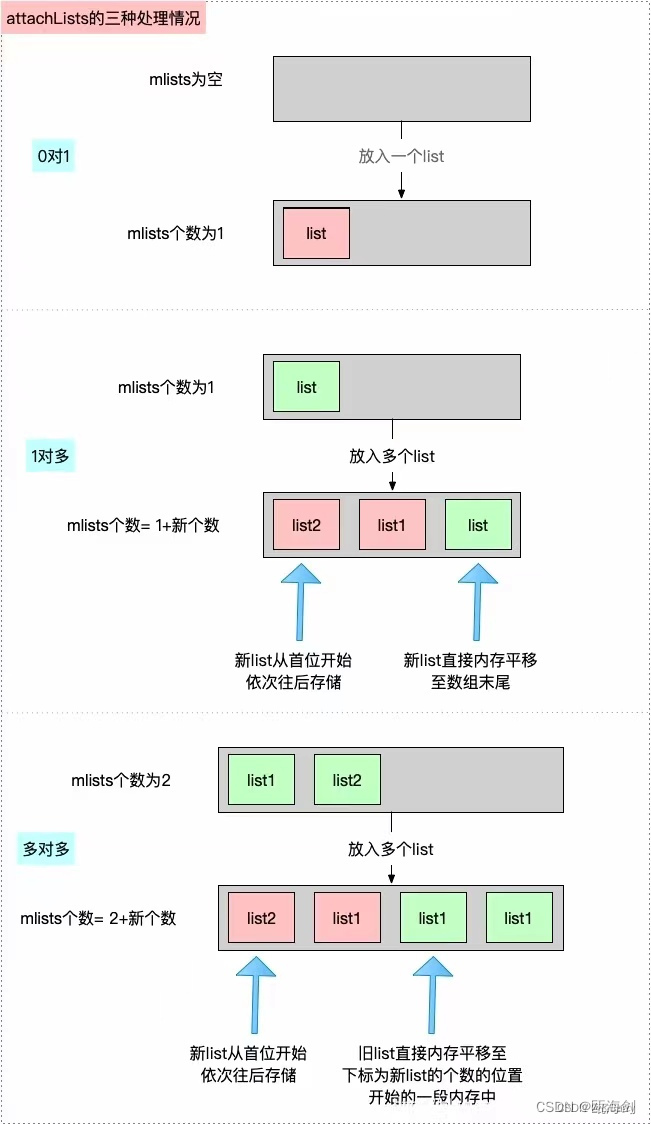
void attachLists(List* const * addedLists, uint32_t addedCount) {if (addedCount == 0) return;if (hasArray()) {// many lists -> many lists//大数组中原本有多个小数组,再到前面加多个小数组uint32_t oldCount = array()->count;uint32_t newCount = oldCount + addedCount;array_t *newArray = (array_t *)malloc(array_t::byteSize(newCount));newArray->count = newCount;array()->count = newCount;for (int i = oldCount - 1; i >= 0; i--)newArray->lists[i + addedCount] = array()->lists[i];for (unsigned i = 0; i < addedCount; i++)newArray->lists[i] = addedLists[i];free(array());setArray(newArray);validate();}//大数组中原本没有小数组,再到前面添加一个小数组else if (!list && addedCount == 1) {// 0 lists -> 1 listlist = addedLists[0];validate();} //大数组中原本有一个小数组,再到前面添加多个小数组else {// 1 list -> many listsPtr<List> oldList = list;uint32_t oldCount = oldList ? 1 : 0;uint32_t newCount = oldCount + addedCount;setArray((array_t *)malloc(array_t::byteSize(newCount)));array()->count = newCount;if (oldList) array()->lists[addedCount] = oldList;for (unsigned i = 0; i < addedCount; i++)array()->lists[i] = addedLists[i];validate();}}
具体的保证新添加的数组在大数组前面的实现上方代码已经体现地十分清晰了,就是对数组元素的简单插入,先将原来的元素后移我们需要新添加的元素的数量,然后将需要新添加的元素从下标0开始依次插入就实现了新添加的在前面。
下图很生动地表现了上述三种插入情况:
然后我们又回到load_images中,可以看到其中还调用了prepare_load_methods函数和call_load_methods函数,一个是用来 找到 所有非懒加载类和非懒加载分类的load方法的函数,一个是调用load方法进行最后 加载类和分类 的函数。
接下来我们先来看一下prepare_load_methods的实现:
调用load方法准备 (prepare_load_methods)
void prepare_load_methods(const headerType *mhdr)
{
size_t count, i;\
runtimeLock.assertLocked();//获取所有非懒加载类
classref_t const *classlist = _getObjc2NonlazyClassList(mhdr, &count);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {schedule_class_load(remapClass(classlist[i]));
}
//获取所有非懒加载分类
category_t * const *categorylist = _getObjc2NonlazyCategoryList(mhdr, &count);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {category_t *cat = categorylist[i];Class cls = remapClass(cat->cls);if (!cls) continue; // category for ignored weak-linked class//swift没有load方法if (cls->isSwiftStable()) {_objc_fatal("Swift class extensions and categories on Swift ""classes are not allowed to have +load methods");}//实现类realizeClassWithoutSwift(cls, nil);ASSERT(cls->ISA()->isRealized());add_category_to_loadable_list(cat);
}
调用load方法
void call_load_methods(void)
{static bool loading = NO;bool more_categories;//加锁:线程安全loadMethodLock.assertLocked();// Re-entrant calls do nothing; the outermost call will finish the job.if (loading) return;loading = YES;void *pool = objc_autoreleasePoolPush();do {// 1. Repeatedly call class +loads until there aren't any morewhile (loadable_classes_used > 0) {call_class_loads();}// 2. Call category +loads ONCE 加载分类more_categories = call_category_loads();// 3. Run more +loads if there are classes OR more untried categories} while (loadable_classes_used > 0 || more_categories);objc_autoreleasePoolPop(pool);loading = NO;
}
可以是调用了call_category_loads();函数里面调用了分类的load方法对其进行了最后分类的加载。
上面一大堆过程肯定看的迷迷糊糊,不妨按照下方总结的精简过程看上方的具体实现,会好看很多。
总结分类的加载
首先分类加载分为两种情况:非懒加载分类和懒加载分类,所以分类就有两条加载流程。
先讲非懒加载分类的加载流程:
- 进入
load_images,执行loadAllCategories,在loadAllCategories中调用了load_categories_nolock,再到load_categories_nolock中调用了addForClass
(流程就是:load_images–>loadAllCategories–>load_categories_nolock–>objc::unattachedCategories.addForClass)
此时的状态是: 分类对应的主类都还没有实现(没有被初始化),我们只是调用了load_categories_nolock中的objc::unattachedCategories.addForClass分支将分类和主类关联并将分类加载进了内存。
- 执行完
loadAllCategories之后,我们回到load_images中执行后面的内容,接着需要执行的是:prepare_load_methods方法获取类和分类的load方法,在其中调用了realizeClassWithoutSwift方法来实现(初始化)分类所对应的主类,在其中又调用了methodizeClass方法向主类中附加分类,在这之中又调用了objc::unattachedCategories.attachToClass,在这里面又调用了attachCategories来正式向主类中添加分类中的内容
(流程就是:prepare_load_methods –> realizeClassWithoutSwift –> methodizeClass –> objc::unattachedCategories.attachToClass –> attachCategories)
此时的状态是: 分类对应的主类已经实现,并已经将分类中的内容添加到了主类当中
- 执行完
prepare_load_methods之后,我们又回到load_images中执行后面的内容,接着需要执行的是:call_load_methods方法用来调用所有的类和分类的load方法,让这些非懒加载的类和分类正式加载到程序中去。
(最后的流程就是调用了:call_load_methods)
此时的状态是: 非懒加载类和其分类加载完毕
再讲懒加载分类的加载流程:
- 进入
map_images,执行map_images_nolock,再执行其中的_read_images,_read_images执行到与分类相关的部分是一个判断,判断是否执行过一次load_images,如果执行过load_images的话那个判断的参数didInitialAttachCategories的值就会是YES,然后就可以执行那个if中的代码,那些代码是循环调用load_categories_nolock,对于懒加载的分类,它们对应的懒加载主类还没有实现,所以又会调用load_categories_nolock中的objc::unattachedCategories.addForClass分支将分类和主类关联并将分类加载进了内存
(流程就是:map_images –> map_images_nolock –> _read_images –> load_categories_nolock –> objc::unattachedCategories.addForClass)
此时的状态: 懒加载分类对应的主类还没有实现(初始化),我们只是调用了load_categories_nolock中的objc::unattachedCategories.addForClass分支将分类和主类关联并将分类加载进了内存。
- 循环执行完
load_categories_nolock之后,我们又回到_read_images之中,接下来需要执行的是非懒加载类的实现(初始化),我们会调用到realizeClassWithoutSwift方法,不过由于我们在load_images当中已经调用过realizeClassWithoutSwift方法并实现了非懒加载类,所以这次刚刚进入realizeClassWithoutSwift就会返回nil而不执行任何操作。接着我们继续在_read_images中执行后续的代码,我们现在需要执行的是对懒加载类的实现(初始化),我们依然调用的是realizeClassWithoutSwift对懒加载类进行实现,并在其中调用了methodizeClass方法向主类中附加分类,在这之中又调用了objc::unattachedCategories.attachToClass,在这里面又调用了attachCategories来正式向主类中添加分类中的内容
(流程就是:realizeClassWithoutSwift –> realizeClassWithoutSwift –> methodizeClass –> objc::unattachedCategories.attachToClass –> attachCategories)
此时的状态: 懒加载分类的主类已经得到了实现(初始化),且懒加载分类中的内容已经添加到了懒加载主类之中。
以上就是本人对于整个分类的加载的总结叙述,如有问题望大家指正。
– 未完
相关文章:

【iOS】Category、Extension和关联对象
Category分类 Category 是 比继承更为简洁 的方法来对Class进行扩展,无需创建子类就可以为现有的类动态添加方法。 可以给项目内任何已经存在的类 添加 Category甚至可以是系统库/闭源库等只暴露了声明文件的类 添加 Category (看不到.m 文件的类)通过 Category 可以添加 实例…...
)
支持向量机(一)
文章目录 前言分析数据集线性可分情况下的支持向量机原始问题凸优化包解法对偶问题凸优化包解法 数据集线性不可分情况下的线性支持向量机与软间隔最大化 前言 在支持向量机中,理论逻辑很简单:最大化最小的几何间隔。但是实际编写代码过程中有一个小点需…...

MyBatis中至关重要的关系映射----全方面介绍
目录 一 对于映射的概念 1.1 三种关系映射 1.2 resultType与resultMap的区别 resultType: resultMap: 二,一对一关联查询 2.1 嵌套结果集编写 2.2 案例演示 三,一对多关联查询 3.1 嵌套结果集编写 3.3 案例演示 四&…...
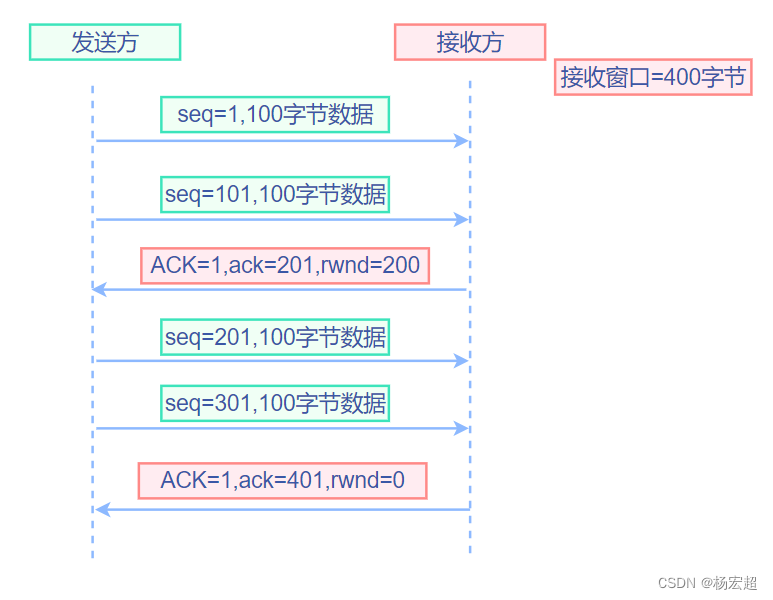
47、TCP的流量控制
从这一节开始,我们学习通信双方应用进程建立TCP连接之后,数据传输过程中,TCP有哪些机制保证传输可靠性的。本节先学习第一种机制:流量控制。 窗口与流量控制 首先,我们要知道的是:什么是流量控制ÿ…...
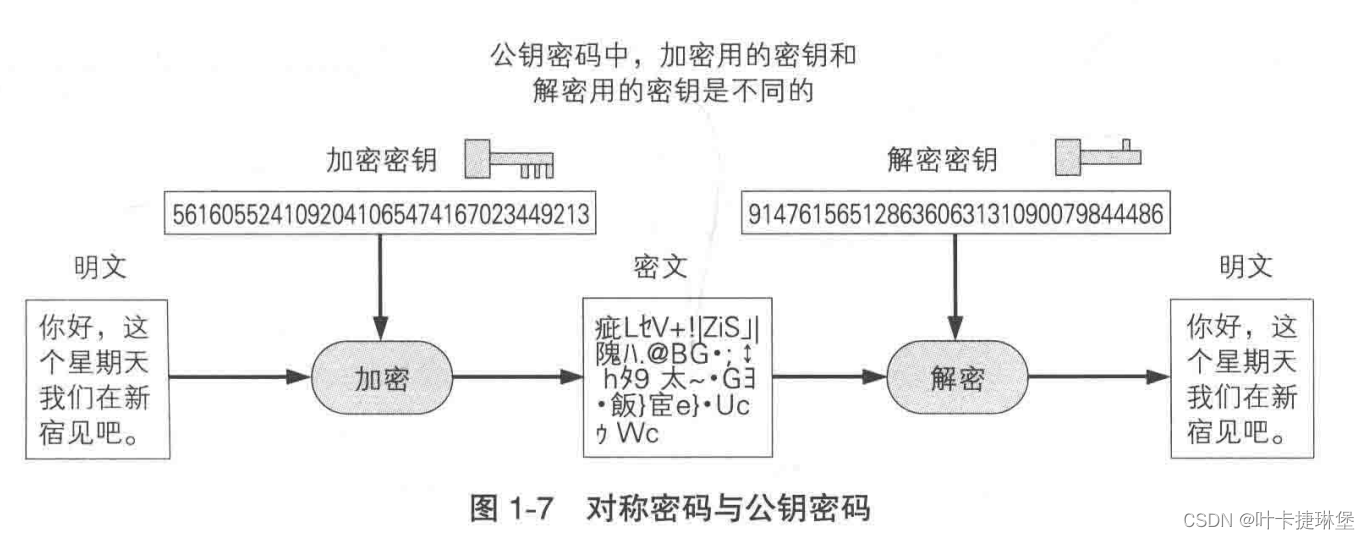
密码学入门——环游密码世界
文章目录 参考书目一、基本概念1.1 本书主要角色1.2 加密与解密 二、对称密码与公钥密码2.1 密钥2.2 对称密码和公钥密码2.3 混合密码技术 三、其他密码技术 参考书目 图解密码技术 第三版 一、基本概念 1.1 本书主要角色 1.2 加密与解密 加密 解密 密码破译 二、对称密…...
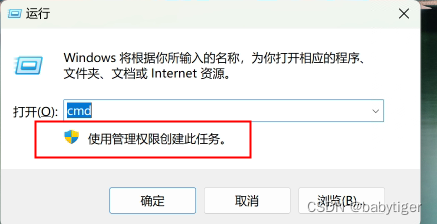
笔记本家庭版本win11上win+r,运行cmd默认没有管理员权限,如何调整为有管理员权限的
华为matebookeGo 笔记本之前有段时间不知怎么回事,打开运行框,没有了那一行“使用管理权限创建此任务”,而且cmd也不再是默认的管理员下的,这很不方便,虽然每次winr ,输入cmd后可以按ctrlshitenter以管理员权限运行&am…...

MavenCentral库发布记录
最近发布了 Android 路由库 URouter,支持 AGP8、ActivityResult启动等特性。 把提交到 Maven Central 过程记录一下。 一、注册 Sonatype 账号,新建项目 注册 https://issues.sonatype.org 登录后,新建项目: 相关选项&…...
的使用)
小程序进阶-env(safe-area-inset-bottom)的使用
一、简介 env(safe-area-inset-bottom)和env(safe-area-inset-top)是CSS中的变量,用于获取设备底部和顶部安全区域的大小。 所谓的安全区域就是指在iPhone X及以上的设备中,为避免被屏幕的“刘海”和“Home Indicator”所遮挡或者覆盖的有效区域区域&am…...
移动端App持续集成体系构建实战
这里写目录标题 一、目标1、前言2、优势:3、涉及技术点4、目标 二、测试app构建、打包过程1、安卓打包的环境要求 三、演示安卓源码打包四、演示安卓App部署1、前提条件2、命令控制apk安装与卸载 五、安卓UI自动化测试1、Appium app自动化测试-Python2、实现的验证点…...

Mybatis的关联关系配置一对一,一对多,多对多的映射关系
目录 关联关系映射 一对一关联: 一对多关联: 多对多关联: 导入数据库表 一对多 一对一 多对多 关联关系映射 关联关系映射在Mybatis中主要通过三种方式实现:一对一关联和一对多关联及多对多关联。 一对一关联:…...
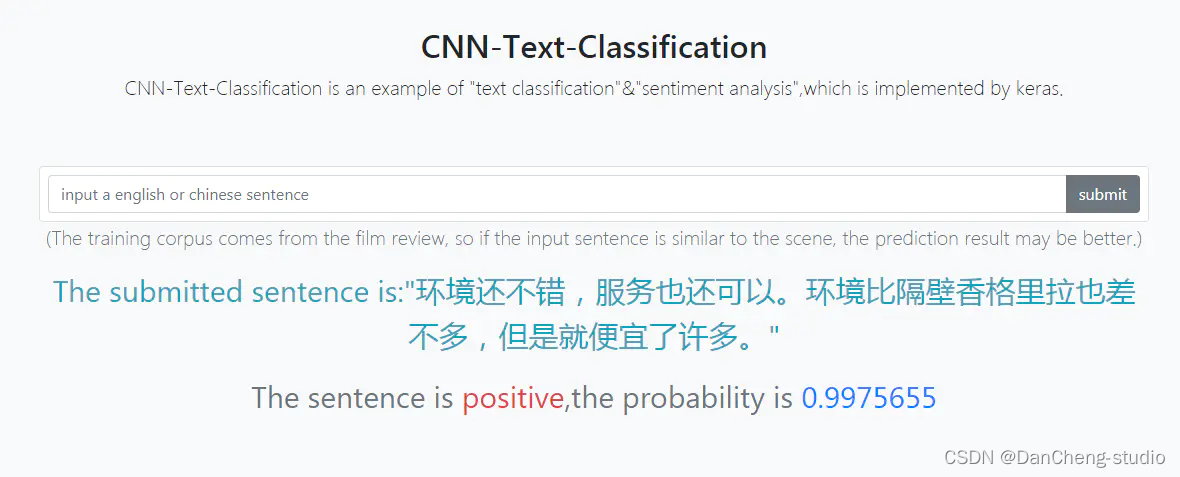
计算机竞赛 基于深度学习的中文情感分类 - 卷积神经网络 情感分类 情感分析 情感识别 评论情感分类
文章目录 1 前言2 情感文本分类2.1 参考论文2.2 输入层2.3 第一层卷积层:2.4 池化层:2.5 全连接softmax层:2.6 训练方案 3 实现3.1 sentence部分3.2 filters部分3.3 featuremaps部分3.4 1max部分3.5 concat1max部分3.6 关键代码 4 实现效果4.…...
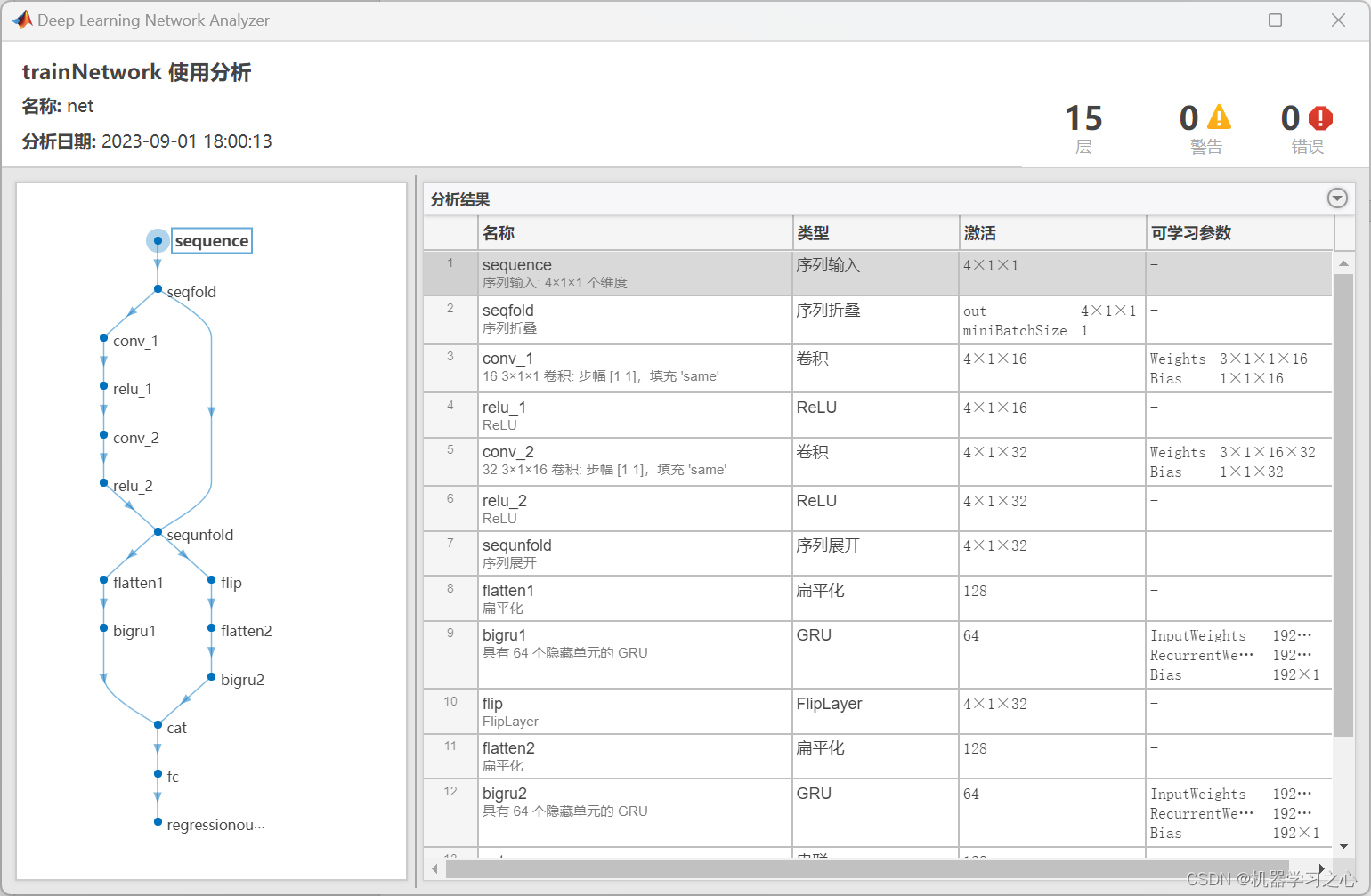
时序预测 | MATLAB实现CNN-BiGRU卷积双向门控循环单元时间序列预测
时序预测 | MATLAB实现CNN-BiGRU卷积双向门控循环单元时间序列预测 目录 时序预测 | MATLAB实现CNN-BiGRU卷积双向门控循环单元时间序列预测预测效果基本介绍程序设计参考资料 预测效果 基本介绍 1.MATLAB实现CNN-BiGRU卷积双向门控循环单元时间序列预测; 2.运行环境…...

[Rust GUI]0.10.0版本iced代码示例 - progress_bar
-1 字体支持 iced0.10.0 仅支持指定系统内置字体(iced默认字体中文会乱码) iced0.10.0 手动加载字体的功能已经砍了,想手动加载就用0.9.0版本,文档0.9.0版本 想显示中文则需要运行在一个自带字体的Windows系统上。而且这个字体最好不要钱。 (Windows闲着…...
使用vue-pdf出现的卡顿,空白,报错,浏览器崩溃解决办法
如果想直接知道解决办法,请翻到最下面 今天,接到了一个新的需求,我们公司的PDF展示卡住了,导致浏览器直接奔溃。我也刚来公司不久,就去看看是怎么发生的,公司前同事用的vue-pdf,刚开始以为是文…...
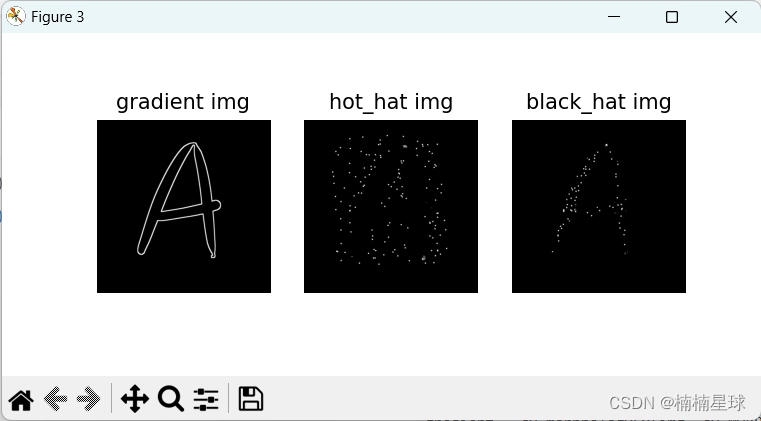
(笔记七)利用opencv进行形态学操作
(1)程序清单 形态学操作是一种图像处理技术,它基于数学形态学理论,用于改变图像的形状和结构。它主要通过结构元素的腐蚀和膨胀操作来实现。 #!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- """ author: LIFEI t…...

Spring是什么?
什么是Spring 我知道你现在可能迫不及待地想要开始编写Spring应用了。我向你保证,在本章结束之前,你肯定能够开发一个简单的Spring应用。但首先,我将使用Spring的一些基础概念为你搭建一个舞台,帮助你理解Spring是如何运转起来的…...

电梯SIP-IP五方对讲管理系统
电梯SIP-IP五方对讲管理系统 是深圳锐科达精心打磨的一款IP数字信号对讲设备,是在传统电梯对讲系统基础上的一次全新升级,突破了模拟、FM调频系统存在的技术障碍,实现联网;在模/数交替的过程中,继承了模拟、FM调频系统的优点&…...

leetcode283移动零
题目: 给定一个数组 nums,编写一个函数将所有 0 移动到数组的末尾,同时保持非零元素的相对顺序。 请注意 ,必须在不复制数组的情况下原地对数组进行操作。 示例 1: 输入: nums [0,1,0,3,12] 输出: [1,3,12,0,0]示例 2: 输入:…...

Docker 部署SpringBoot项目,使用外部配置文件启动项目
一、Springboot项目引入配置文件的方式: 第一种是在jar包的同一目录下建一个config文件夹,然后把配置文件放到这个文件夹下; 第二种是直接把配置文件放到jar包的同级目录; 第三种在classpath下建一个config文件夹,然后…...
电子半导体行业电能质量监测与治理系统解决方案 安科瑞 许敏
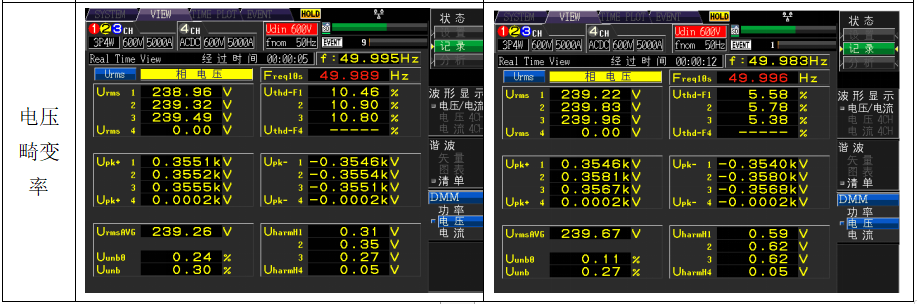
摘要:在国家鼓励半导体材料国产化的政策导向下,本土半导体材料厂商不断提升半导体产品技术水平和研发能力,逐渐打破了国外半导体厂商的垄断格局,推进中国半导体材料国产化进程,促进中国半导体行业的发展。半导体产品的…...
Linux 文件类型,目录与路径,文件与目录管理
文件类型 后面的字符表示文件类型标志 普通文件:-(纯文本文件,二进制文件,数据格式文件) 如文本文件、图片、程序文件等。 目录文件:d(directory) 用来存放其他文件或子目录。 设备…...
)
Spring Boot 实现流式响应(兼容 2.7.x)
在实际开发中,我们可能会遇到一些流式数据处理的场景,比如接收来自上游接口的 Server-Sent Events(SSE) 或 流式 JSON 内容,并将其原样中转给前端页面或客户端。这种情况下,传统的 RestTemplate 缓存机制会…...
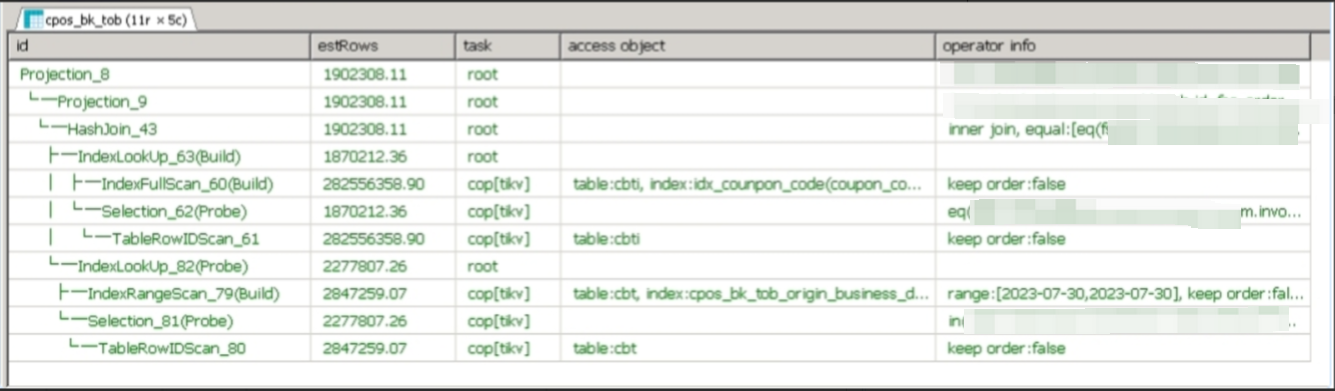
【入坑系列】TiDB 强制索引在不同库下不生效问题
文章目录 背景SQL 优化情况线上SQL运行情况分析怀疑1:执行计划绑定问题?尝试:SHOW WARNINGS 查看警告探索 TiDB 的 USE_INDEX 写法Hint 不生效问题排查解决参考背景 项目中使用 TiDB 数据库,并对 SQL 进行优化了,添加了强制索引。 UAT 环境已经生效,但 PROD 环境强制索…...
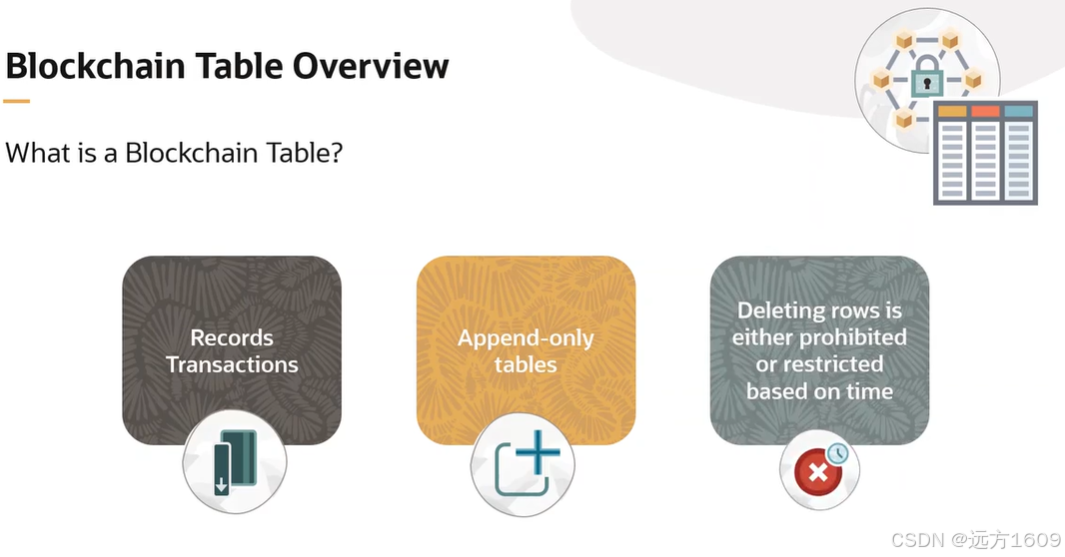
23-Oracle 23 ai 区块链表(Blockchain Table)
小伙伴有没有在金融强合规的领域中遇见,必须要保持数据不可变,管理员都无法修改和留痕的要求。比如医疗的电子病历中,影像检查检验结果不可篡改行的,药品追溯过程中数据只可插入无法删除的特性需求;登录日志、修改日志…...
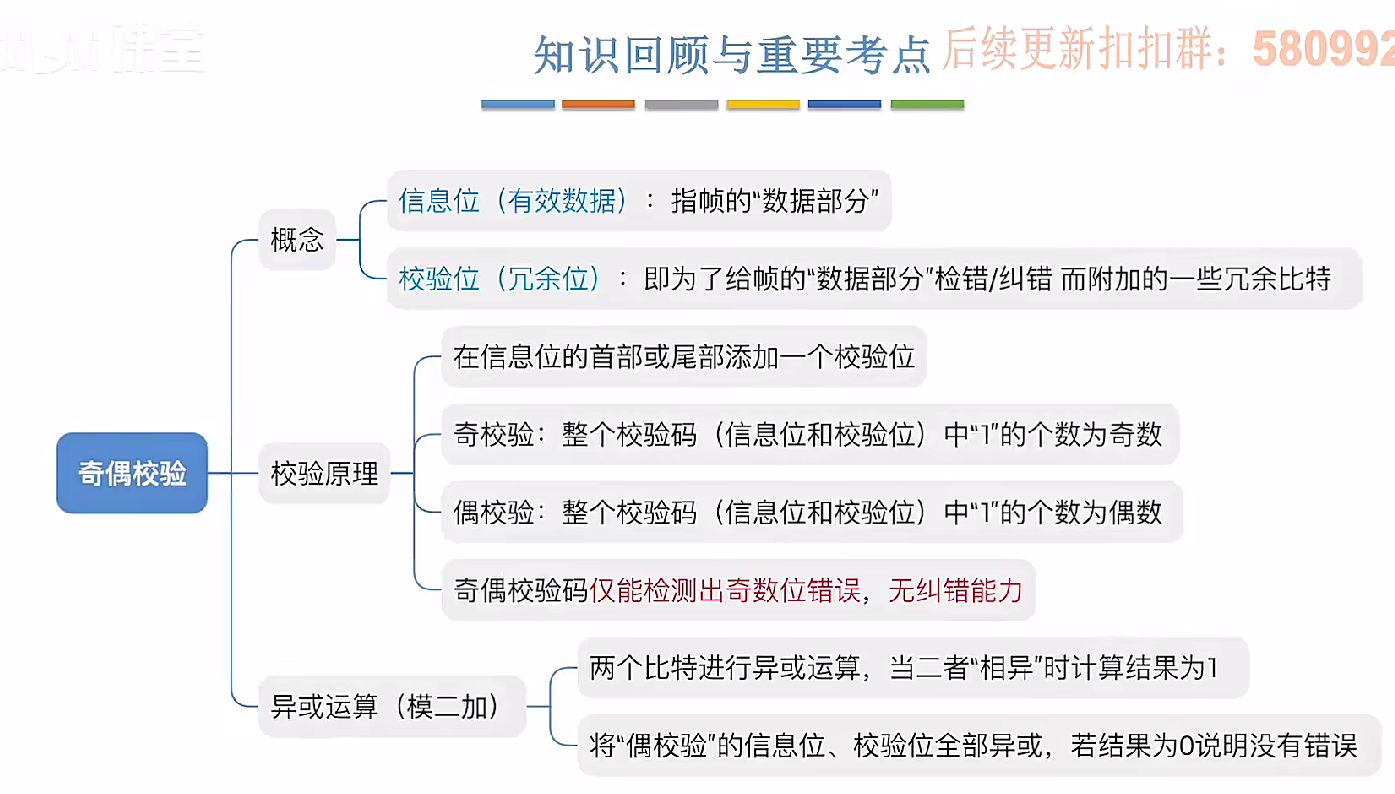
3.3.1_1 检错编码(奇偶校验码)
从这节课开始,我们会探讨数据链路层的差错控制功能,差错控制功能的主要目标是要发现并且解决一个帧内部的位错误,我们需要使用特殊的编码技术去发现帧内部的位错误,当我们发现位错误之后,通常来说有两种解决方案。第一…...
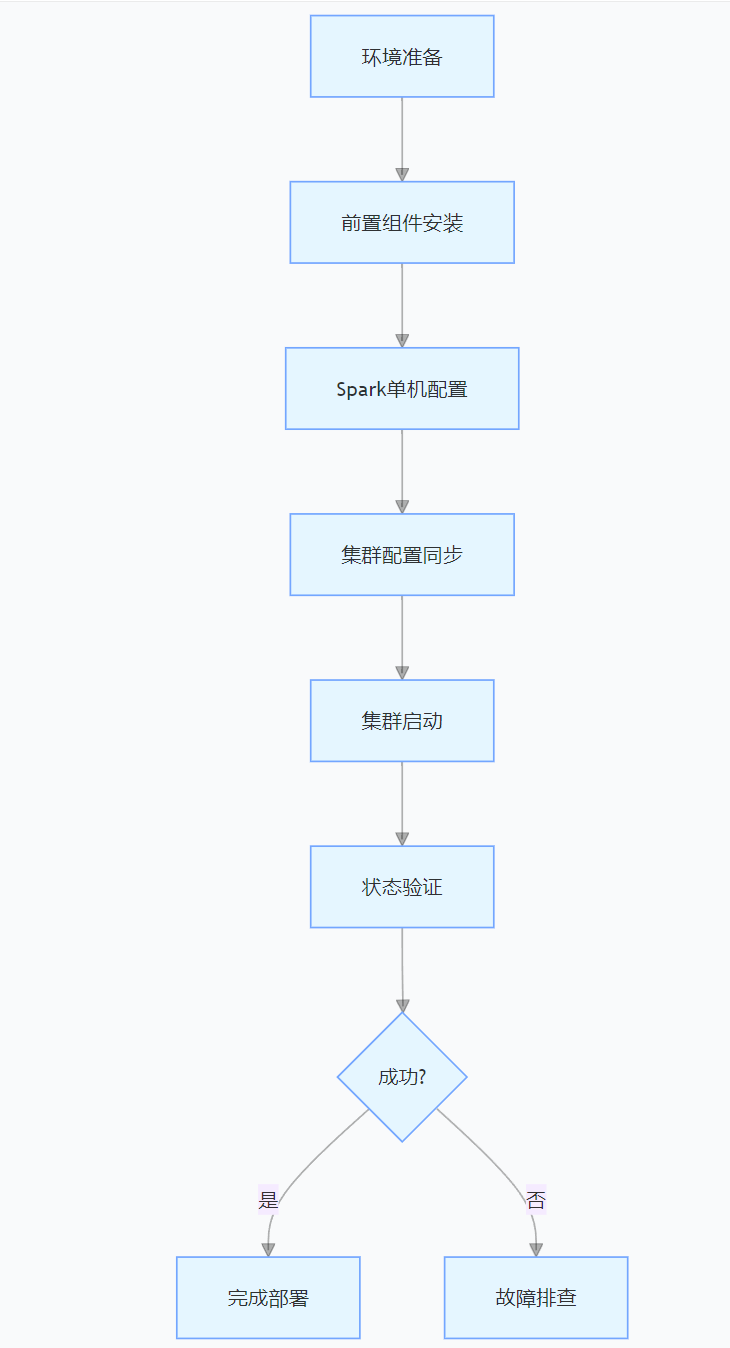
CentOS下的分布式内存计算Spark环境部署
一、Spark 核心架构与应用场景 1.1 分布式计算引擎的核心优势 Spark 是基于内存的分布式计算框架,相比 MapReduce 具有以下核心优势: 内存计算:数据可常驻内存,迭代计算性能提升 10-100 倍(文档段落:3-79…...

CMake控制VS2022项目文件分组
我们可以通过 CMake 控制源文件的组织结构,使它们在 VS 解决方案资源管理器中以“组”(Filter)的形式进行分类展示。 🎯 目标 通过 CMake 脚本将 .cpp、.h 等源文件分组显示在 Visual Studio 2022 的解决方案资源管理器中。 ✅ 支持的方法汇总(共4种) 方法描述是否推荐…...

高效线程安全的单例模式:Python 中的懒加载与自定义初始化参数
高效线程安全的单例模式:Python 中的懒加载与自定义初始化参数 在软件开发中,单例模式(Singleton Pattern)是一种常见的设计模式,确保一个类仅有一个实例,并提供一个全局访问点。在多线程环境下,实现单例模式时需要注意线程安全问题,以防止多个线程同时创建实例,导致…...

Java求职者面试指南:Spring、Spring Boot、MyBatis框架与计算机基础问题解析
Java求职者面试指南:Spring、Spring Boot、MyBatis框架与计算机基础问题解析 一、第一轮提问(基础概念问题) 1. 请解释Spring框架的核心容器是什么?它在Spring中起到什么作用? Spring框架的核心容器是IoC容器&#…...

08. C#入门系列【类的基本概念】:开启编程世界的奇妙冒险
C#入门系列【类的基本概念】:开启编程世界的奇妙冒险 嘿,各位编程小白探险家!欢迎来到 C# 的奇幻大陆!今天咱们要深入探索这片大陆上至关重要的 “建筑”—— 类!别害怕,跟着我,保准让你轻松搞…...
