Python/C API - 模組,型別,Tuple,例外和引用計數
Python/C API - 模組,型別,Tuple,例外和引用計數
- 前言
- Python/C API - Common Object Structures
- PyObject
- PyMethodDef
- PyGetSetDef
- Python/C API - Module Objects
- PyModuleDef
- PyModule_Create
- PyModule_AddObject
- PyModule_AddObjectRef
- Initialization, Finalization, and Threads
- Py_Initialize
- Importing Modules
- PyImport_AppendInittab
- PyImport_ImportModule
- Python/C API - Type Objects
- PyTypeObject
- tp_getset
- tp_methods
- Python/C API - Tuple Objects
- PyTuple_New
- PyTuple_SetItem
- PyTuple_SET_ITEM
- Useful macros
- PyDoc_STRVAR
- Exception
- PyErr_NewException
- PyErr_SetString
- Reference Counting
- Py_INCREF
- Py_XINCREF
- Py_DECREF
- Py_XDECREF
- Py_CLEAR
前言
本文介紹在寫Python的C擴展時常用到的Python/C API中關於模組,型別,Tuple,例外和引用計數的函數。
Python/C API - Common Object Structures
PyObject
PyObject
type PyObject
Part of the Limited API. (Only some members are part of the stable ABI.)
All object types are extensions of this type. This is a type which contains the information Python needs to treat a pointer to an object as an object. In a normal “release” build, it contains only the object’s reference count and a pointer to the corresponding type object. Nothing is actually declared to be a PyObject, but every pointer to a Python object can be cast to a PyObject*. Access to the members must be done by using the macros Py_REFCNT and Py_TYPE.
所有的物件都沿伸自PyObject。
PyMethodDef
PyMethodDef
type PyMethodDef
Part of the Stable ABI (including all members).
Structure used to describe a method of an extension type. This structure has four fields:const char *ml_name¶
name of the methodPyCFunction ml_meth
pointer to the C implementationint ml_flags
flags bits indicating how the call should be constructedconst char *ml_doc
points to the contents of the docstring
由以下四個欄位定義:
ml_name:函數在Python中的名字ml_meth:實作的C函數的地址ml_flags:用於指示方法如何被呼叫。- 使用
METH_VARARGS表示Python函數將接受positional argument。 - 如果希望函數能接受keyword(named) argument,可以改為
METH_VARARGS | METH_KEYWORDS。
- 使用
ml_doc:函數的說明文檔
Extending and Embedding the Python Interpreter中的例子:
// method table
static PyMethodDef SpamMethods[] = {{"system", // namespam_system, // addressMETH_VARARGS, // or "METH_VARARGS | METH_KEYWORDS"// METH_VARARGS: expect the Python-level parameters to be passed in as a tuple acceptable for parsing via PyArg_ParseTuple()// METH_KEYWORDS: the C function should accept a third PyObject * parameter which will be a dictionary of keywords. Use PyArg_ParseTupleAndKeywords() to parse"Execute a shell command."},{NULL, NULL, 0, NULL} // sentinel
};
PyGetSetDef
PyGetSetDef
An optional pointer to a static NULL-terminated array of PyGetSetDef structures, declaring computed attributes of instances of this type.
計算過後的屬性,所以可以理解為函數。
| Field | C Type | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| name | const char * | attribute name |
| get | getter | C function to get the attribute |
| set | setter | optional C function to set or delete the attribute, if omitted the attribute is readonly |
| doc | const char * | optional docstring |
| closure | void * | optional function pointer, providing additional data for getter and setter |
PyGetSetDef由以上五個欄位定義:名字name,取值函數get,設值函數set,函數說明doc以及提供給getter和setter的額外資訊closure。
Python/C API - Module Objects
PyModuleDef
PyModuleDef
type PyModuleDef
Part of the Stable ABI (including all members).
The module definition struct, which holds all information needed to create a module object. There is usually only one statically initialized variable of this type for each module.PyModuleDef_Base m_base
Always initialize this member to PyModuleDef_HEAD_INIT.const char *m_name
Name for the new module.const char *m_doc
Docstring for the module; usually a docstring variable created with PyDoc_STRVAR is used.Py_ssize_t m_size
Module state may be kept in a per-module memory area that can be retrieved with PyModule_GetState(), rather than in static globals. This makes modules safe for use in multiple sub-interpreters.This memory area is allocated based on m_size on module creation, and freed when the module object is deallocated, after the m_free function has been called, if present.Setting m_size to -1 means that the module does not support sub-interpreters, because it has global state.Setting it to a non-negative value means that the module can be re-initialized and specifies the additional amount of memory it requires for its state. Non-negative m_size is required for multi-phase initialization.See PEP 3121 for more details.PyMethodDef *m_methods
A pointer to a table of module-level functions, described by PyMethodDef values. Can be NULL if no functions are present.PyModuleDef_Slot *m_slots
An array of slot definitions for multi-phase initialization, terminated by a {0, NULL} entry. When using single-phase initialization, m_slots must be NULL.Changed in version 3.5: Prior to version 3.5, this member was always set to NULL, and was defined as:inquiry m_reload
traverseproc m_traverse
A traversal function to call during GC traversal of the module object, or NULL if not needed.This function is not called if the module state was requested but is not allocated yet. This is the case immediately after the module is created and before the module is executed (Py_mod_exec function). More precisely, this function is not called if m_size is greater than 0 and the module state (as returned by PyModule_GetState()) is NULL.Changed in version 3.9: No longer called before the module state is allocated.inquiry m_clear
A clear function to call during GC clearing of the module object, or NULL if not needed.This function is not called if the module state was requested but is not allocated yet. This is the case immediately after the module is created and before the module is executed (Py_mod_exec function). More precisely, this function is not called if m_size is greater than 0 and the module state (as returned by PyModule_GetState()) is NULL.Like PyTypeObject.tp_clear, this function is not always called before a module is deallocated. For example, when reference counting is enough to determine that an object is no longer used, the cyclic garbage collector is not involved and m_free is called directly.Changed in version 3.9: No longer called before the module state is allocated.freefunc m_free
A function to call during deallocation of the module object, or NULL if not needed.This function is not called if the module state was requested but is not allocated yet. This is the case immediately after the module is created and before the module is executed (Py_mod_exec function). More precisely, this function is not called if m_size is greater than 0 and the module state (as returned by PyModule_GetState()) is NULL.Changed in version 3.9: No longer called before the module state is allocated.
-
第一個參數
PyModuleDef_Base m_base固定為PyModuleDef_HEAD_INIT。 -
第二個參數
const char *m_name為module的名字 -
第三個參數
const char *m_doc為module的描述文檔 -
第四個參數
Py_ssize_t m_size為module的大小,在多數情況下會被設為-1,表示該module會在全域變數裡維護狀態,不支援sub-interpreters -
第五個參數
PyMethodDef *m_methods是一個指標,指向module-level函數的表格(method table)
Extending and Embedding the Python Interpreter給出的用法示例如下:
static struct PyModuleDef spammodule = {PyModuleDef_HEAD_INIT,"spam", // name of modulespam_doc, // module documentation, may be NULL-1, // size of per-interpreter state of the module, or -1 if the module keeps state in global variables.SpamMethods // the method table
};
PyModule_Create
PyModule_Create
PyObject *PyModule_Create(PyModuleDef *def)
Return value: New reference.
Create a new module object, given the definition in def. This behaves like PyModule_Create2() with module_api_version set to PYTHON_API_VERSION.
根據傳入的PyModuleDef指標生成Python模組物件。
並且根據Extending and Embedding the Python Interpreter例子中的注釋,它還會將稍早與模組物件關聯的method table插入新建的模組物件中:
// module definition structure
static struct PyModuleDef spammodule = {PyModuleDef_HEAD_INIT,"spam", // name of modulespam_doc, // module documentation, may be NULL // Docstring for the module; usually a docstring variable created with PyDoc_STRVAR is used.-1, // size of per-interpreter state of the module, or -1 if the module keeps state in global variables.SpamMethods // the method table
};
PyObject* m;// returns a module object, and inserts built-in function objects into the newly created module based upon the table (an array of PyMethodDef structures) found in the module definition// The init function must return the module object to its caller, so that it then gets inserted into sys.modulesm = PyModule_Create(&spammodule);
PyModule_AddObject
PyModule_AddObject
int PyModule_AddObject(PyObject *module, const char *name, PyObject *value)
Part of the Stable ABI.
Similar to PyModule_AddObjectRef(), but steals a reference to value on success (if it returns 0).The new PyModule_AddObjectRef() function is recommended, since it is easy to introduce reference leaks by misusing the PyModule_AddObject() function.
功能與PyModule_AddObjectRef類似,PyModule_AddObjectRef是比較被建議使用的版本。
Extending and Embedding the Python Interpreter中給出的例子:
// PyInit_spam is module’s initialization function
// must be named PyInit_name
// it will be called when python program imports module spam for the first time
// should be the only non-static item defined in the module file!
// if adding "static", variables and functions can only be used in the specific file, can't be linked through "extern"
// PyMODINIT_FUNC declares the function as PyObject * return type, declares any special linkage declarations required by the platform, and for C++ declares the function as extern "C"
PyMODINIT_FUNC
PyInit_spam(void){PyObject* m;// returns a module object, and inserts built-in function objects into the newly created module based upon the table (an array of PyMethodDef structures) found in the module definition// The init function must return the module object to its caller, so that it then gets inserted into sys.modulesm = PyModule_Create(&spammodule);if(m == NULL)return NULL;// if the last 2 arguments are NULL, then it creates a class who base class is Excetion// exception type, exception instance, and a traceback objectSpamError = PyErr_NewException("spam.error", NULL, NULL);// retains a reference to the newly created exception class// Since the exception could be removed from the module by external code, an owned reference to the class is needed to ensure that it will not be discarded, causing SpamError to become a dangling pointer// Should it become a dangling pointer, C code which raises the exception could cause a core dump or other unintended side effectsPy_XINCREF(SpamError);if(PyModule_AddObject(m, "error", SpamError) < 0){// clean up garbage (by making Py_XDECREF() or Py_DECREF() calls for objects you have already created) when you return an error indicator// Decrement the reference count for object o. The object may be NULL, in which case the macro has no effect; otherwise the effect is the same as for Py_DECREF(), and the same warning applies.Py_XDECREF(SpamError);// Decrement the reference count for object o. The object may be NULL, in which case the macro has no effect; otherwise the effect is the same as for Py_DECREF(), except that the argument is also set to NULL.Py_CLEAR(SpamError);// Decrement the reference count for object o.// If the reference count reaches zero, the object’s type’s deallocation function (which must not be NULL) is invoked.Py_DECREF(m);return NULL;}return m;
}
PyModule_AddObjectRef
PyModule_AddObjectRef
int PyModule_AddObjectRef(PyObject *module, const char *name, PyObject *value)
Part of the Stable ABI since version 3.10.
Add an object to module as name. This is a convenience function which can be used from the module’s initialization function.On success, return 0. On error, raise an exception and return -1.Return NULL if value is NULL. It must be called with an exception raised in this case.
將value這個PyObject(物件)加到module裡,之後在Python裡就可以透過module.name的方式存取這個物件。
成功時回傳0,否則回傳-1。
Initialization, Finalization, and Threads
Py_Initialize
void Py_Initialize()
Part of the Stable ABI.
Initialize the Python interpreter. In an application embedding Python, this should be called before using any other Python/C API functions; see Before Python Initialization for the few exceptions.This initializes the table of loaded modules (sys.modules), and creates the fundamental modules builtins, __main__ and sys. It also initializes the module search path (sys.path). It does not set sys.argv; use PySys_SetArgvEx() for that. This is a no-op when called for a second time (without calling Py_FinalizeEx() first). There is no return value; it is a fatal error if the initialization fails.Note On Windows, changes the console mode from O_TEXT to O_BINARY, which will also affect non-Python uses of the console using the C Runtime.
初始化Python直譯器。如果有程式想用任何其它的Python/C API函數,必須事先調用本函數。
Importing Modules
PyImport_AppendInittab
PyImport_AppendInittab
int PyImport_AppendInittab(const char *name, PyObject *(*initfunc)(void))
Part of the Stable ABI.
Add a single module to the existing table of built-in modules. This is a convenience wrapper around PyImport_ExtendInittab(), returning -1 if the table could not be extended. The new module can be imported by the name name, and uses the function initfunc as the initialization function called on the first attempted import. This should be called before Py_Initialize().
將模組加入內建模組的表格(PyImport_Inittab)中。
name:之後使用這個名字來import這個新模組initfunc:初次導入模組時所用的初始化函數
本函數應在Py_Initialize前使用,這樣子名為name的模組的初始化函數initfunc才會自動被調用。
Extending and Embedding the Python Interpreter中給出的例子:
//add a built-in module, before Py_Initialize//When embedding Python, the PyInit_spam() function is not called automatically unless there’s an entry in the PyImport_Inittab table. To add the module to the initialization table, use PyImport_AppendInittab(), optionally followed by an import of the moduleif(PyImport_AppendInittab("spam", PyInit_spam) == -1){fprintf(stderr, "Error: could not extend in-built modules table\n");exit(1);}
PyImport_ImportModule
PyImport_ImportModule
PyObject *PyImport_ImportModule(const char *name)
Return value: New reference. Part of the Stable ABI.
This is a simplified interface to PyImport_ImportModuleEx() below, leaving the globals and locals arguments set to NULL and level set to 0. When the name argument contains a dot (when it specifies a submodule of a package), the fromlist argument is set to the list ['*'] so that the return value is the named module rather than the top-level package containing it as would otherwise be the case. (Unfortunately, this has an additional side effect when name in fact specifies a subpackage instead of a submodule: the submodules specified in the package’s __all__ variable are loaded.) Return a new reference to the imported module, or NULL with an exception set on failure. A failing import of a module doesn’t leave the module in sys.modules.This function always uses absolute imports.
import一個名為name的模組並回傳,如果有拋出例外或是失敗的話則會回傳NULL。
Extending and Embedding the Python Interpreter中給出的例子:
// Optionally import the module; alternatively,// import can be deferred until the embedded script imports it.PyObject* pmodule = PyImport_ImportModule("spam");if(!pmodule){PyErr_Print();fprintf(stderr, "Error: could not import module 'spam'\n");}
Python/C API - Type Objects
PyTypeObject
Type Objects
type PyTypeObject
Part of the Limited API (as an opaque struct).
The C structure of the objects used to describe built-in types.
PyTypeObject是一個用來描述Python內建型別的C的結構體。
tp_getset
PyTypeObject.tp_getset
struct PyGetSetDef *PyTypeObject.tp_getset
An optional pointer to a static NULL-terminated array of PyGetSetDef structures, declaring computed attributes of instances of this type.For each entry in the array, an entry is added to the type’s dictionary (see tp_dict below) containing a getset descriptor.
為PyTypeObject的屬性之一。是一個可選的指標,指向PyGetSetDef陣列,代表本型別計算過後的屬性。
tp_methods
PyTypeObject.tp_methods
struct PyMethodDef *PyTypeObject.tp_methods
An optional pointer to a static NULL-terminated array of PyMethodDef structures, declaring regular methods of this type.For each entry in the array, an entry is added to the type’s dictionary (see tp_dict below) containing a method descriptor.
為PyTypeObject的屬性之一。是一個可選的指標,指向PyMethodDef陣列,代表本型別一般的方法。
Python/C API - Tuple Objects
Python/C API - Tuple Objects
PyTuple_New
PyObject *PyTuple_New(Py_ssize_t len)
Return value: New reference. Part of the Stable ABI.
Return a new tuple object of size len, or NULL on failure.
新建一個長度為len的tuple並回傳。
PyTuple_SetItem
int PyTuple_SetItem(PyObject *p, Py_ssize_t pos, PyObject *o)
Part of the Stable ABI.
Insert a reference to object o at position pos of the tuple pointed to by p. Return 0 on success. If pos is out of bounds, return -1 and set an IndexError exception.Note This function “steals” a reference to o and discards a reference to an item already in the tuple at the affected position.
在p這個指標所指向的tuple的第pos個位置插入物件o。成功時回傳0,如果pos超過邊界,則回傳-1。
PyTuple_SET_ITEM
void PyTuple_SET_ITEM(PyObject *p, Py_ssize_t pos, PyObject *o)
Like PyTuple_SetItem(), but does no error checking, and should only be used to fill in brand new tuples.Note This macro “steals” a reference to o, and, unlike PyTuple_SetItem(), does not discard a reference to any item that is being replaced; any reference in the tuple at position pos will be leaked.
跟PyTuple_SetItem的功能一樣,但不做錯誤檢查,並且只適用於填充新的tuple。
Useful macros
PyDoc_STRVAR
PyDoc_STRVAR
PyDoc_STRVAR(name, str)Creates a variable with name `name` that can be used in docstrings. If Python is built without docstrings, the value will be empty.Use [`PyDoc_STRVAR`](https://docs.python.org/3/c-api/intro.html#c.PyDoc_STRVAR) for docstrings to support building Python without docstrings, as specified in [**PEP 7**](https://peps.python.org/pep-0007/).
創造一個名為name的變數,它可以被當作文檔字串來使用。如:
PyDoc_STRVAR(pop_doc, "Remove and return the rightmost element.");static PyMethodDef deque_methods[] = {// ...{"pop", (PyCFunction)deque_pop, METH_NOARGS, pop_doc},// ...
}
Extending and Embedding the Python Interpreter中給出的例子,首先創建一個名為spam_doc的變數:
// Creates a variable with name name that can be used in docstrings. If Python is built without docstrings, the value will be empty.
PyDoc_STRVAR(spam_doc, "Spam module that call system function.");
這個spam_doc便可以作為PyModuleDef的m_doc欄位使用:
// module definition structure
static struct PyModuleDef spammodule = {PyModuleDef_HEAD_INIT,"spam", // name of modulespam_doc, // module documentation, may be NULL // Docstring for the module; usually a docstring variable created with PyDoc_STRVAR is used.-1, // size of per-interpreter state of the module, or -1 if the module keeps state in global variables.SpamMethods // the method table
};
Exception
PyErr_NewException
PyErr_NewException
PyObject *PyErr_NewException(const char *name, PyObject *base, PyObject *dict)
Return value: New reference. Part of the Stable ABI.
This utility function creates and returns a new exception class. The name argument must be the name of the new exception, a C string of the form module.classname. The base and dict arguments are normally NULL. This creates a class object derived from Exception (accessible in C as PyExc_Exception).The __module__ attribute of the new class is set to the first part (up to the last dot) of the name argument, and the class name is set to the last part (after the last dot). The base argument can be used to specify alternate base classes; it can either be only one class or a tuple of classes. The dict argument can be used to specify a dictionary of class variables and methods.
創造並返回一個新的exception類別,這個新exception類別繼承自Python的Exception(即C中的PyExc_Exception)。
參數:
name:新例外的名字,型式為module.classnamebase:替代的基礎類別,通常是NULL。dict:類別變數和方法的字典,通常是NULL。
Extending and Embedding the Python Interpreter中給出的例子:
// define your own new exception
static PyObject* SpamError;
SpamError = PyErr_NewException("spam.error", NULL, NULL);
PyErr_SetString
PyErr_SetString
void **PyErr_SetString**([PyObject](https://docs.python.org/3/c-api/structures.html#c.PyObject) *type, const char *message)*Part of the [Stable ABI](https://docs.python.org/3/c-api/stable.html#stable).*This is the most common way to set the error indicator. The first argument specifies the exception type; it is normally one of the standard exceptions, e.g. `PyExc_RuntimeError`. You need not increment its reference count. The second argument is an error message; it is decoded from `'utf-8'`.
英文說set the error indicator,其實就是raise exception,發起例外,表示程序在這裡出錯的意思。
其參數有二:
type:例外的型別,不需要手動增加其引用計數message:錯誤訊息
Extending and Embedding the Python Interpreter中給出的例子:
PyErr_SetString(SpamError, "System command failed");
Reference Counting
Py_INCREF
Py_INCREF
void Py_INCREF(PyObject *o)
Indicate taking a new strong reference to object o, indicating it is in use and should not be destroyed.This function is usually used to convert a borrowed reference to a strong reference in-place. The Py_NewRef() function can be used to create a new strong reference.When done using the object, release it by calling Py_DECREF().The object must not be NULL; if you aren’t sure that it isn’t NULL, use Py_XINCREF().Do not expect this function to actually modify o in any way.
將o標記為正在使用且不可被銷毀。如果用完了o,可以透過Py_DECREF將它釋放掉。
o不可為NULL。
Extending and Embedding the Python Interpreter中給出的例子:
SpamError = PyErr_NewException("spam.error", NULL, NULL);// retains a reference to the newly created exception class// Since the exception could be removed from the module by external code, an owned reference to the class is needed to ensure that it will not be discarded, causing SpamError to become a dangling pointer// Should it become a dangling pointer, C code which raises the exception could cause a core dump or other unintended side effectsPy_XINCREF(SpamError);if(PyModule_AddObject(m, "error", SpamError) < 0){// clean up garbage (by making Py_XDECREF() or Py_DECREF() calls for objects you have already created) when you return an error indicator// Decrement the reference count for object o. The object may be NULL, in which case the macro has no effect; otherwise the effect is the same as for Py_DECREF(), and the same warning applies.Py_XDECREF(SpamError);// Decrement the reference count for object o. The object may be NULL, in which case the macro has no effect; otherwise the effect is the same as for Py_DECREF(), except that the argument is also set to NULL.Py_CLEAR(SpamError);// Decrement the reference count for object o.// If the reference count reaches zero, the object’s type’s deallocation function (which must not be NULL) is invoked.Py_DECREF(m);return NULL;}
Py_XINCREF
Py_XINCREF
void Py_XINCREF(PyObject *o)
Similar to Py_INCREF(), but the object o can be NULL, in which case this has no effect.See also Py_XNewRef().
跟Py_INCREF類似,但是o可以為NULL,o為NULL時函數沒有作用。
Py_DECREF
Py_DECREF
void Py_DECREF(PyObject *o)
Release a strong reference to object o, indicating the reference is no longer used.Once the last strong reference is released (i.e. the object’s reference count reaches 0), the object’s type’s deallocation function (which must not be NULL) is invoked.This function is usually used to delete a strong reference before exiting its scope.The object must not be NULL; if you aren’t sure that it isn’t NULL, use Py_XDECREF().Do not expect this function to actually modify o in any way.Warning The deallocation function can cause arbitrary Python code to be invoked (e.g. when a class instance with a __del__() method is deallocated). While exceptions in such code are not propagated, the executed code has free access to all Python global variables. This means that any object that is reachable from a global variable should be in a consistent state before Py_DECREF() is invoked. For example, code to delete an object from a list should copy a reference to the deleted object in a temporary variable, update the list data structure, and then call Py_DECREF() for the temporary variable.
釋放o的strong reference,將它標記為不再被使用。
當物件的最後一個strong reference被釋放,也就是其reference count達到0後,該物體的deallocation function會自動被調用。
Py_XDECREF
Py_XDECREF
void Py_XDECREF(PyObject *o)
Similar to Py_DECREF(), but the object o can be NULL, in which case this has no effect. The same warning from Py_DECREF() applies here as well.
跟Py_DECREF類似,但是o可以為NULL,o為NULL時函數沒有作用。
Py_CLEAR
Py_CLEAR
void Py_CLEAR(PyObject *o)¶
Release a strong reference for object o. The object may be NULL, in which case the macro has no effect; otherwise the effect is the same as for Py_DECREF(), except that the argument is also set to NULL. The warning for Py_DECREF() does not apply with respect to the object passed because the macro carefully uses a temporary variable and sets the argument to NULL before releasing the reference.It is a good idea to use this macro whenever releasing a reference to an object that might be traversed during garbage collection.
釋放o的strong reference,作用與Py_DECREF相同。
o可以為NULL,o為NULL時函數沒有作用。
相关文章:

Python/C API - 模組,型別,Tuple,例外和引用計數
Python/C API - 模組,型別,Tuple,例外和引用計數 前言Python/C API - Common Object StructuresPyObjectPyMethodDefPyGetSetDef Python/C API - Module ObjectsPyModuleDefPyModule_CreatePyModule_AddObjectPyModule_AddObjectRef Initiali…...

人工智能轨道交通行业周刊-第59期(2023.9.4-9.10)
本期关键词:无锡智慧地铁、无人车站、钢轨打磨、混元大模型、开源大模型 1 整理涉及公众号名单 1.1 行业类 RT轨道交通人民铁道世界轨道交通资讯网铁路信号技术交流北京铁路轨道交通网上榜铁路视点ITS World轨道交通联盟VSTR铁路与城市轨道交通RailMetro轨道世界…...

ASP.NET Core 中的 MVC架构
MVC 架构 MVC架构把 App 按照逻辑分成三层: Controllers,接收 http request,配合 model,通过http response 返回 view,尽量不做别的事Models, 负责业务逻辑,App 的状态,以及数据处理Views&…...
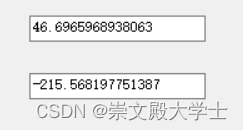
C# PSO 粒子群优化算法 遗传算法 随机算法 求解复杂方程的最大、最小值
复杂方程可以自己定义,以下是看别人的题目,然后自己来做 以下是计算结果 private void GetMinResult(out double resultX1, out double min){double x1, result;Random random1 new Random(DateTime.Now.Millisecond* DateTime.Now.Second);min 99999…...
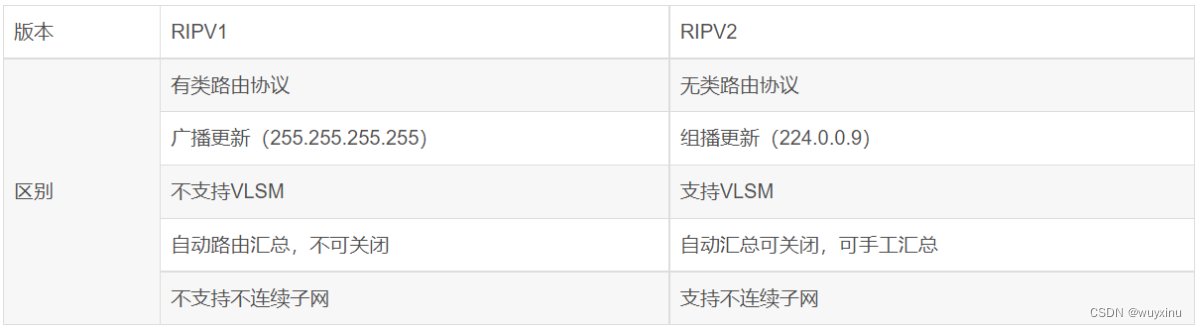
网络协议从入门到底层原理学习(三)—— 路由
网络协议从入门到底层原理学习(三)—— 路由 1、简介 路由(routing)是指分组从源到目的地时,决定端到端路径的网络范围的进程 在不同网段之间转发数据,需要有路由器的支持 默认情况下,路由器…...

2023/9/6 -- C++/QT
一、输出流对象cout 1> 该对象是来自于ostream的类对象,功能上类似于printf函数 2> 该类对象本质上调用成员函数插入运算符重载函数 3> 输出数据时,无需使用格式控制符:%d、%c、%s。。。,直接输出即可 4> 换行使用…...

python爬虫,多线程与生产者消费者模式
使用队列完成生产者消费者模式使用类创建多线程提高爬虫速度 https://sc.chinaz.com/tupian/index.html https://sc.chinaz.com/tupian/index_2.html https://sc.chinaz.com/tupian/index_3.html from threading import Thread from queue import Queue import requests from b…...

WordPress 提示“此站点遇到了致命错误”的解决方法
WordPress 提示“此站点遇到了致命错误”的解决方法 WordPress 网站博客提示“此站点遇到了致命错误。”如何解决?今天老唐不幸遇到了这个问题,搜了一下解决方法,发现致命错误原因有很多,所以需要先打开 WordPress 的 WP_DEBUG 功…...
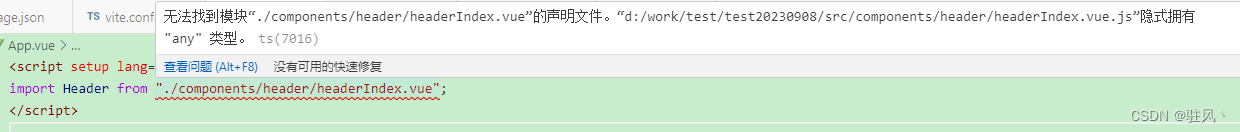
Vue3,Typescript中引用组件路径无法找到模块报错
是这么个事,我在vue3新创建的项目里,写了个组件叫headerIndex.vue,放到app.vue中import就会报错 路径肯定没写错,找到了解决方法,但是也没想明白为什么 解决方法如下 在vite-env.d.ts文件中加入 declare module &qu…...

科技成果鉴定之鉴定测试报告
鉴定测试 由于软件类科技成果的复杂、内部结构难以鉴别等特点,我们提供了软件类科技成果鉴定测试服务。软件类科技成果鉴定测试是依据其科研项目计划任务书或技术合同书,参照相应的国家标准对要申请鉴定的软件类科技成果进行的一种符合性测试࿰…...
NFTScan 浏览器正式版上线 2 周年!
NFTScan 成立于 2021 年 4 月份,总部位于香港。在 2021 年的 7 月份,NFTScan 团队对外发布了 NFTScan 浏览器公测版,并在同年的 9 月 4 号,对外发布了 NFTScan 浏览器正式版,同步启用了全球品牌域名:NFTSCA…...
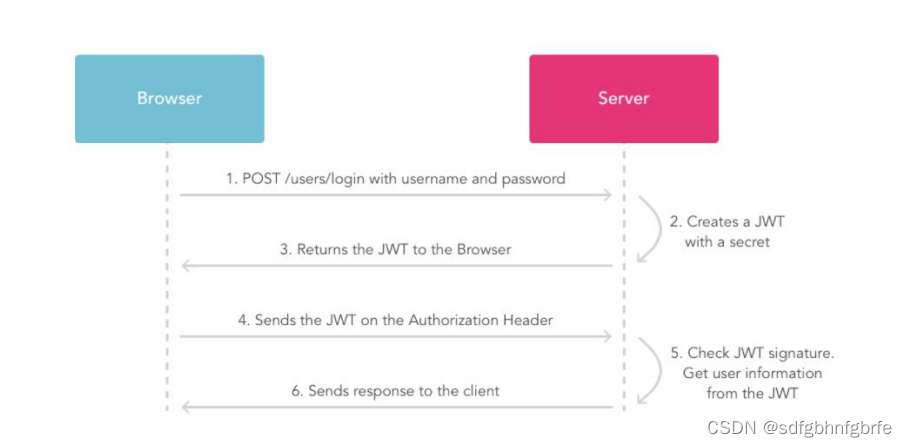
为什么要使用Token
传统的session认证 我们知道,http协议是一种无状态的协议,这就意味着当用户向我们的应用提供了用户名和密码进行用户认证,那么在下一次登录的时候,用户还要再进行验证,因为根据http协议,浏览器并不知道是谁…...
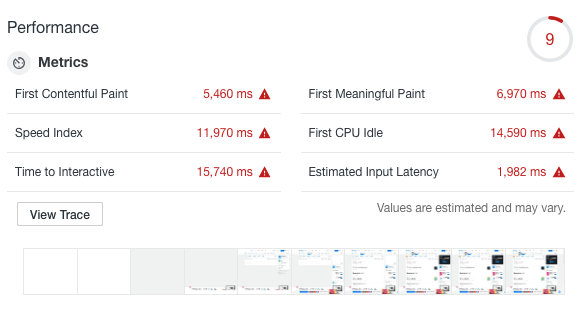
前端面试的话术集锦第 8 篇:高频考点(JS性能优化 性能优化琐碎事)
这是记录前端面试的话术集锦第八篇博文——高频考点(JS性能优化 & 性能优化琐碎事),我会不断更新该博文。❗❗❗ 1. 从V8中看JS性能优化 注意:该知识点属于性能优化领域。 1.1 测试性能⼯具 Chrome已经提供了⼀个⼤⽽全的性能测试⼯具Audits。 点我们点击Audits后,可…...

【数据分析】Python:处理缺失值的常见方法
在数据分析和机器学习中,缺失值是一种常见的现象。在实际数据集中,某些变量的某些条目可能没有可用的值。处理缺失值是一个重要的数据预处理步骤。在本文中,我们将介绍如何在 Pandas 中处理缺失值。 我们将探讨以下内容: 什么是缺…...
“批量随机字母命名文件,轻松管理你的文件库“
你是否曾经遇到过文件命名混乱,难以管理的问题?为了解决这个问题,我们推出了一款全新的文件改名工具,它可以帮助你批量给文件名添加一个随机字母,让你的文件库更加有序、易于管理。 首先第一步,我们要进入…...
elasticsearch的数据聚合
聚合可以让我们极其方便的实现对数据的统计、分析、运算。例如: 什么品牌的手机最受欢迎? 这些手机的平均价格、最高价格、最低价格? 这些手机每月的销售情况如何? 实现这些统计功能的比数据库的sql要方便的多,而且…...

【网络编程·数据链路层】MAC帧/以太网协议/ARP协议/RARP协议
需要云服务器等云产品来学习Linux的同学可以移步/-->腾讯云<--/-->阿里云<--/-->华为云<--/官网,轻量型云服务器低至112元/年,新用户首次下单享超低折扣。 目录 一、MAC帧 1、IP地址和MAC地址的区别 2、MAC帧协议 3、MTU对IP协议的…...

算法:移除数组中的val的所有元素---双指针[2]
文章来源: https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45630258/article/details/132689237 欢迎各位大佬指点、三连 1、题目: 给你一个数组 nums和一个值 val,你需要原地移除所有数值等于 val 的元素,并返回移除后数组的新长度。 不要使用…...

Python小知识 - Python爬虫进阶:如何克服反爬虫技术
Python爬虫进阶:如何克服反爬虫技术 爬虫是一种按照一定的规则,自动抓取网页信息的程序。爬虫也叫网页蜘蛛、蚂蚁、小水滴,是一种基于特定算法的自动化程序,能够按照一定的规则自动的抓取网页中的信息。爬虫程序的主要作用就是从一…...
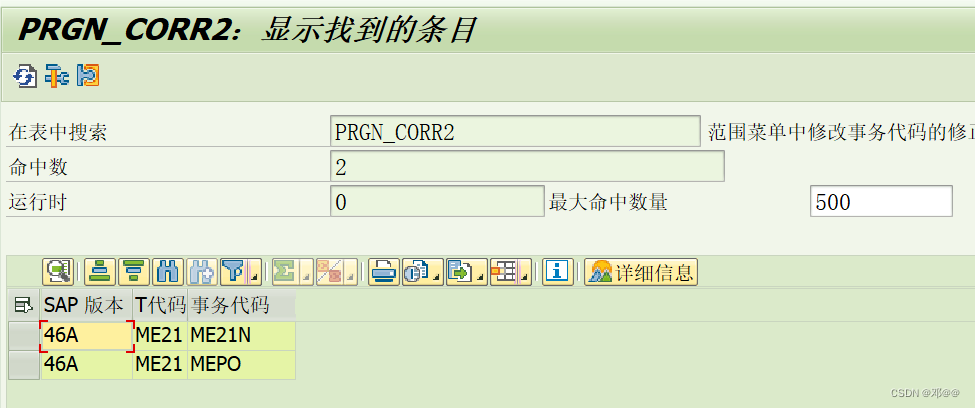
SAP中的新旧事务码
SAP中的新旧事务码 SAP随着新版本的发布,我们知道sap已经更新了很多的程序和TCODE。sap提供了很多新的TCODE来替换旧的TCODE,新TCODE有很多的新特性和新功能。在这个这种情况下,很多旧TCODE就会被废弃。我们如何查找这个替换呢? …...

未来机器人的大脑:如何用神经网络模拟器实现更智能的决策?
编辑:陈萍萍的公主一点人工一点智能 未来机器人的大脑:如何用神经网络模拟器实现更智能的决策?RWM通过双自回归机制有效解决了复合误差、部分可观测性和随机动力学等关键挑战,在不依赖领域特定归纳偏见的条件下实现了卓越的预测准…...
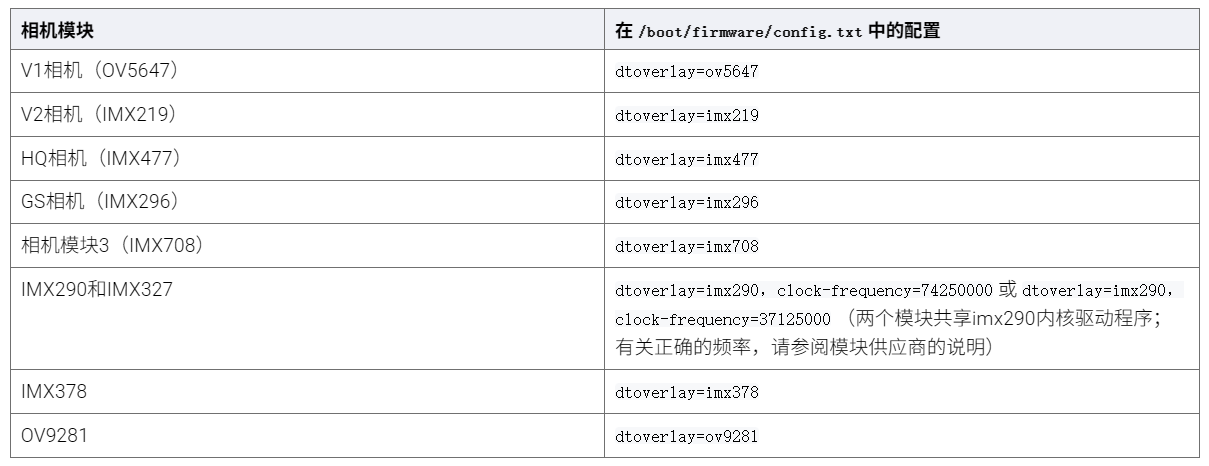
树莓派超全系列教程文档--(61)树莓派摄像头高级使用方法
树莓派摄像头高级使用方法 配置通过调谐文件来调整相机行为 使用多个摄像头安装 libcam 和 rpicam-apps依赖关系开发包 文章来源: http://raspberry.dns8844.cn/documentation 原文网址 配置 大多数用例自动工作,无需更改相机配置。但是,一…...
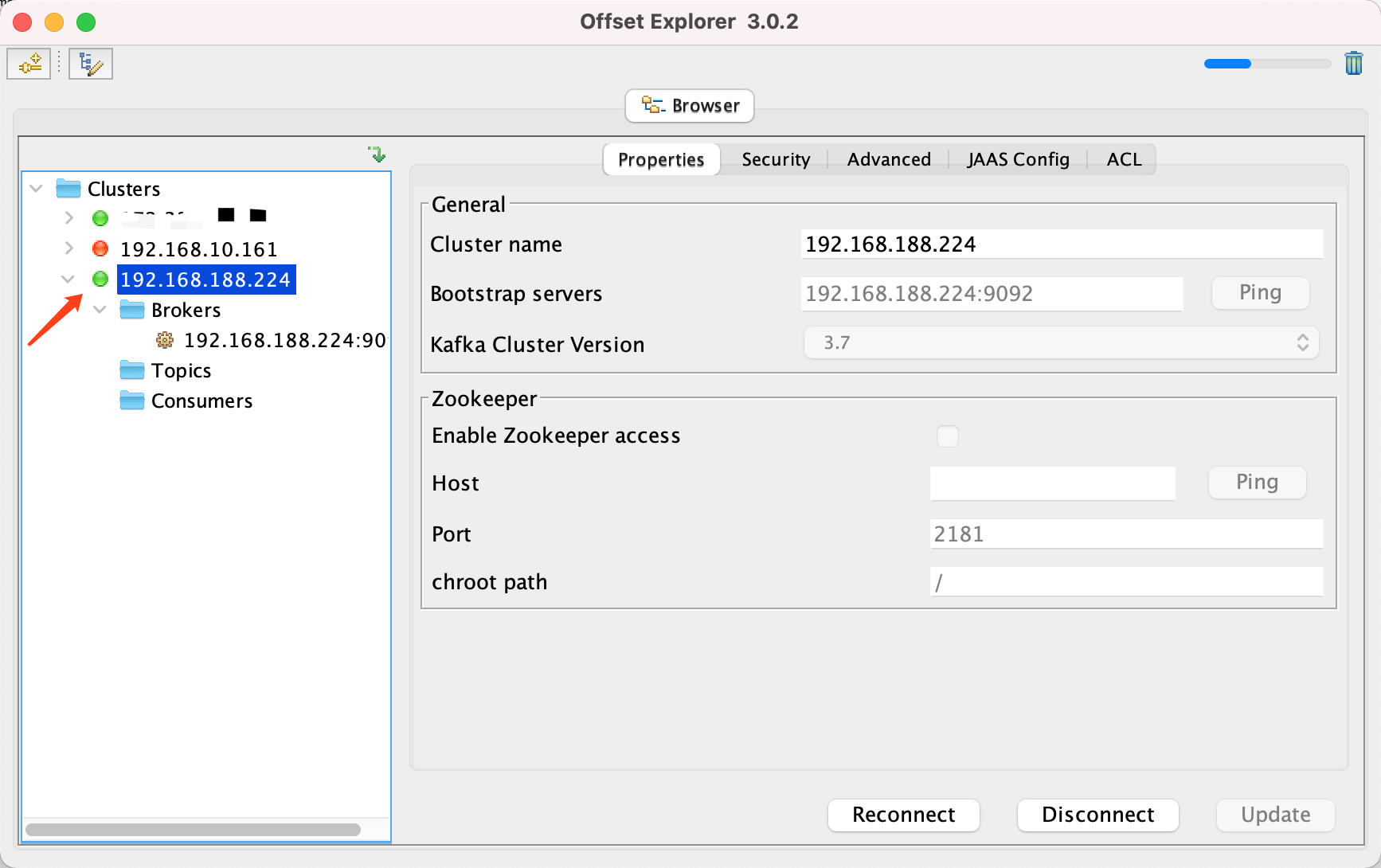
Docker 运行 Kafka 带 SASL 认证教程
Docker 运行 Kafka 带 SASL 认证教程 Docker 运行 Kafka 带 SASL 认证教程一、说明二、环境准备三、编写 Docker Compose 和 jaas文件docker-compose.yml代码说明:server_jaas.conf 四、启动服务五、验证服务六、连接kafka服务七、总结 Docker 运行 Kafka 带 SASL 认…...

Qt Http Server模块功能及架构
Qt Http Server 是 Qt 6.0 中引入的一个新模块,它提供了一个轻量级的 HTTP 服务器实现,主要用于构建基于 HTTP 的应用程序和服务。 功能介绍: 主要功能 HTTP服务器功能: 支持 HTTP/1.1 协议 简单的请求/响应处理模型 支持 GET…...
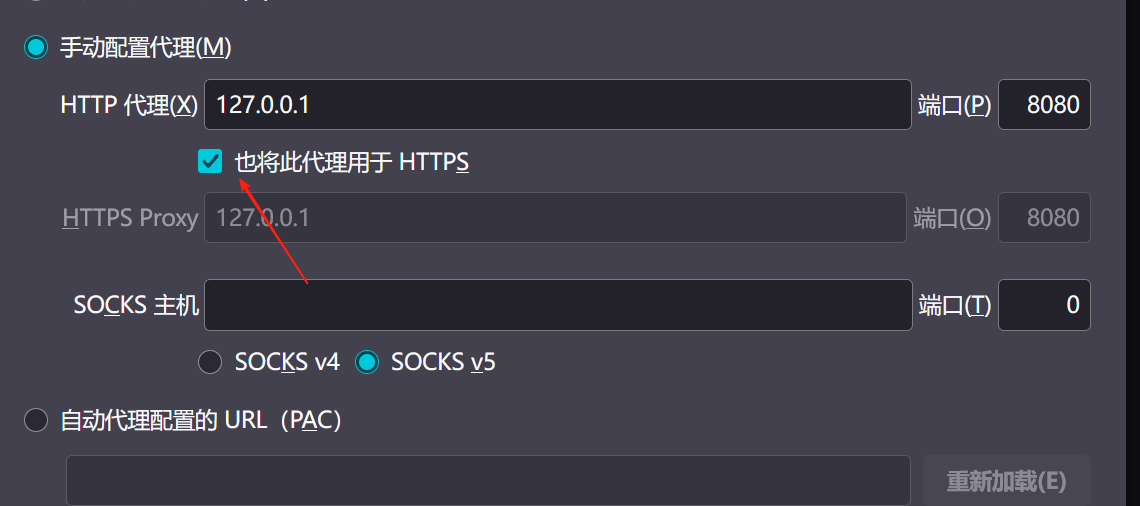
【2025年】解决Burpsuite抓不到https包的问题
环境:windows11 burpsuite:2025.5 在抓取https网站时,burpsuite抓取不到https数据包,只显示: 解决该问题只需如下三个步骤: 1、浏览器中访问 http://burp 2、下载 CA certificate 证书 3、在设置--隐私与安全--…...
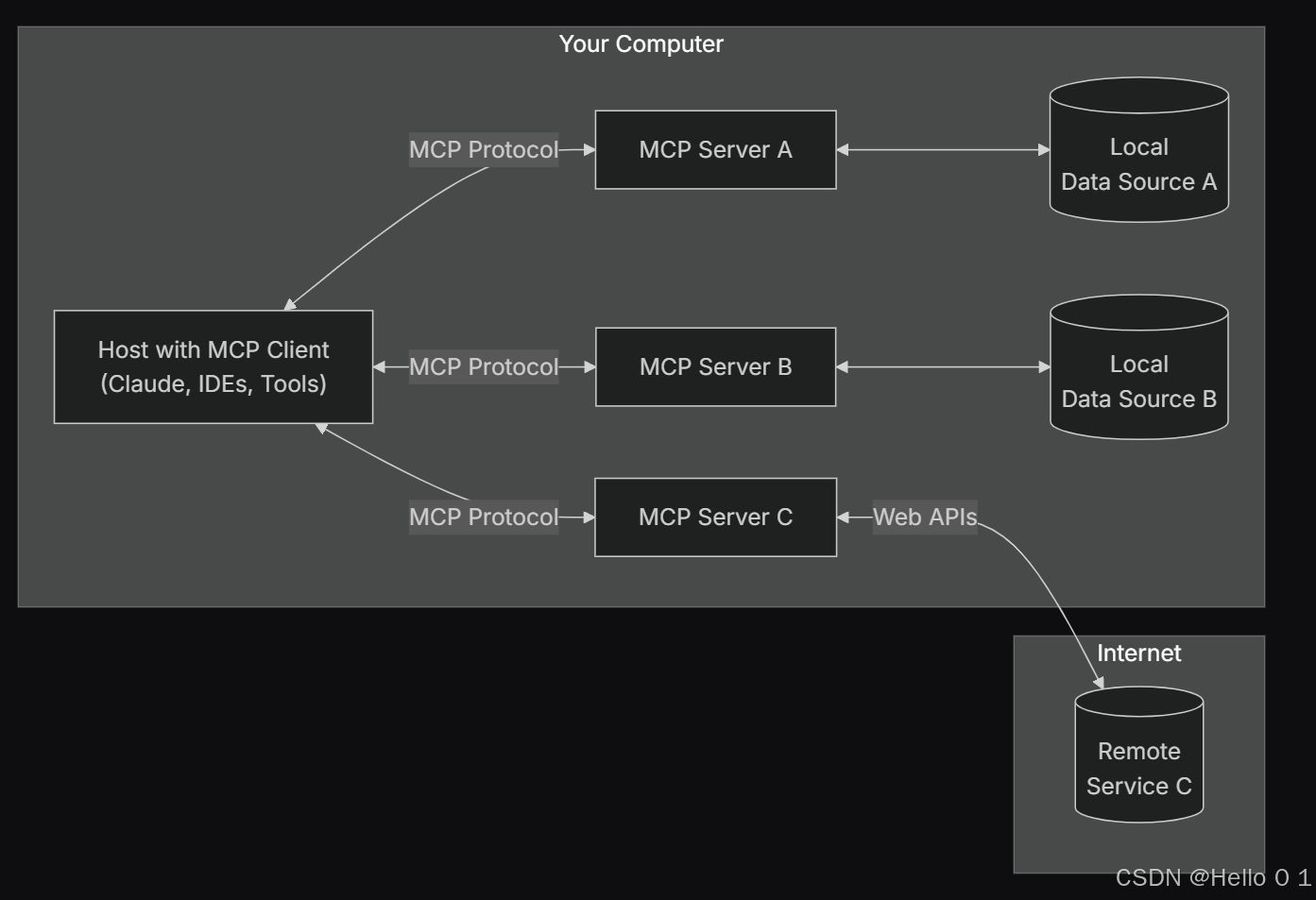
让AI看见世界:MCP协议与服务器的工作原理
让AI看见世界:MCP协议与服务器的工作原理 MCP(Model Context Protocol)是一种创新的通信协议,旨在让大型语言模型能够安全、高效地与外部资源进行交互。在AI技术快速发展的今天,MCP正成为连接AI与现实世界的重要桥梁。…...

Spring Cloud Gateway 中自定义验证码接口返回 404 的排查与解决
Spring Cloud Gateway 中自定义验证码接口返回 404 的排查与解决 问题背景 在一个基于 Spring Cloud Gateway WebFlux 构建的微服务项目中,新增了一个本地验证码接口 /code,使用函数式路由(RouterFunction)和 Hutool 的 Circle…...
Reasoning over Uncertain Text by Generative Large Language Models
https://ojs.aaai.org/index.php/AAAI/article/view/34674/36829https://ojs.aaai.org/index.php/AAAI/article/view/34674/36829 1. 概述 文本中的不确定性在许多语境中传达,从日常对话到特定领域的文档(例如医学文档)(Heritage 2013;Landmark、Gulbrandsen 和 Svenevei…...
基于 TAPD 进行项目管理
起因 自己写了个小工具,仓库用的Github。之前在用markdown进行需求管理,现在随着功能的增加,感觉有点难以管理了,所以用TAPD这个工具进行需求、Bug管理。 操作流程 注册 TAPD,需要提供一个企业名新建一个项目&#…...
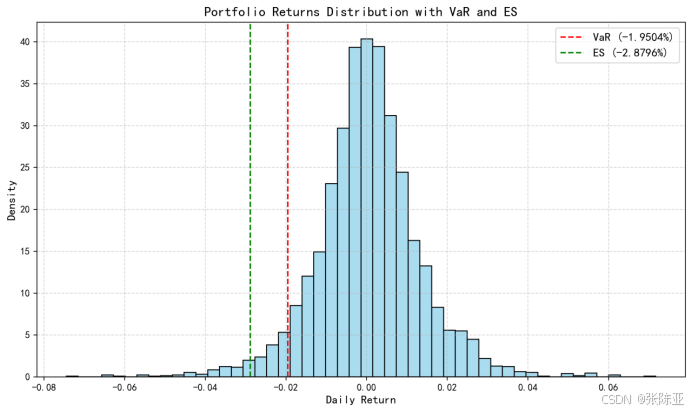
Python基于历史模拟方法实现投资组合风险管理的VaR与ES模型项目实战
说明:这是一个机器学习实战项目(附带数据代码文档),如需数据代码文档可以直接到文章最后关注获取。 1.项目背景 在金融市场日益复杂和波动加剧的背景下,风险管理成为金融机构和个人投资者关注的核心议题之一。VaR&…...
