Golang语法、技巧和窍门

Golang简介
- 命令式语言
- 静态类型
- 语法标记类似于C(但括号较少且没有分号),结构类似Oberon-2
- 编译为本机代码(没有JVM)
- 没有类,但有带有方法的结构
- 接口
- 没有实现继承。不过有type嵌入。
- 函数是一等公民
- 函数可以返回多个值
- 支持闭包
- 指针,但没有指针算术
- 内置并发原语:Goroutines和Channels
基本语法
你好,世界
文件 hello.go:
package mainimport "fmt"func main() {fmt.Println("Hello Go")
}
$ go run hello.go
运算符
算术运算符
| 运算符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
+ | 加法 |
- | 减法 |
* | 乘法 |
/ | 除法 |
% | 取余 |
& | 位与 |
| ` | ` |
^ | 位异或 |
&^ | 位清除(非) |
<< | 左移 |
>> | 右移 |
比较运算符
| 运算符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
== | 等于 |
!= | 不等于 |
< | 小于 |
<= | 小于等于 |
> | 大于 |
>= | 大于等于 |
逻辑运算符
| 运算符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
&& | 逻辑与 |
| ` | |
! | 逻辑非 |
其他
| 运算符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
& | 取地址 / 创建指针 |
* | 解引用指针 |
<- | 发送 / 接收操作符(见下面的‘通道’部分) |
声明
类型在标识符之后!
var foo int // declaration without initialization
var foo int = 42 // declaration with initialization
var foo, bar int = 42, 1302 // declare and init multiple vars at once
var foo = 42 // type omitted, will be inferred
foo := 42 // shorthand, only in func bodies, omit var keyword, type is always implicit
const constant = "This is a constant"// iota can be used for incrementing numbers, starting from 0
const (_ = iotaabc = 1 << iotad
)fmt.Println(a, b) // 1 2 (0 is skipped)fmt.Println(c, d) // 8 16 (2^3, 2^4)
函数
// a simple function
func functionName() {}// function with parameters (again, types go after identifiers)
func functionName(param1 string, param2 int) {}// multiple parameters of the same type
func functionName(param1, param2 int) {}// return type declaration
func functionName() int {return 42
}// Can return multiple values at once
func returnMulti() (int, string) {return 42, "foobar"
}
var x, str = returnMulti()// Return multiple named results simply by return
func returnMulti2() (n int, s string) {n = 42s = "foobar"// n and s will be returnedreturn
}
var x, str = returnMulti2()
函数作为值和闭包
func main() {// assign a function to a nameadd := func(a, b int) int {return a + b}// use the name to call the functionfmt.Println(add(3, 4))
}// Closures, lexically scoped: Functions can access values that were
// in scope when defining the function
func scope() func() int{outer_var := 2foo := func() int { return outer_var}return foo
}func another_scope() func() int{// won't compile because outer_var and foo not defined in this scopeouter_var = 444return foo
}// Closures
func outer() (func() int, int) {outer_var := 2inner := func() int {outer_var += 99 // outer_var from outer scope is mutated.return outer_var}inner()return inner, outer_var // return inner func and mutated outer_var 101
}
可变参数函数
func main() {fmt.Println(adder(1, 2, 3)) // 6fmt.Println(adder(9, 9)) // 18nums := []int{10, 20, 30}fmt.Println(adder(nums...)) // 60
}// By using ... before the type name of the last parameter you can indicate that it takes zero or more of those parameters.
// The function is invoked like any other function except we can pass as many arguments as we want.
func adder(args ...int) int {total := 0for _, v := range args { // Iterates over the arguments whatever the number.total += v}return total
}
内置类型
boolstringint int8 int16 int32 int64
uint uint8 uint16 uint32 uint64 uintptrbyte // alias for uint8rune // alias for int32 ~= a character (Unicode code point) - very Vikingfloat32 float64complex64 complex128
所有Go的预声明标识符都定义在builtin包中。
类型转换
var i int = 42
var f float64 = float64(i)
var u uint = uint(f)// alternative syntax
i := 42
f := float64(i)
u := uint(f)
包
- 在每个源文件的顶部声明包
- 可执行文件位于
main包中 - 约定:包的名称等于导入路径的最后一个部分(导入路径
math/rand=> 包rand) - 大写标识符:导出的(可以从其他包中访问)
- 小写标识符:私有的(不能从其他包中访问)
控制结构
判断
func main() {// Basic oneif x > 10 {return x} else if x == 10 {return 10} else {return -x}// You can put one statement before the conditionif a := b + c; a < 42 {return a} else {return a - 42}// Type assertion inside ifvar val interface{} = "foo"if str, ok := val.(string); ok {fmt.Println(str)}
}
循环
// There's only `for`, no `while`, no `until`for i := 1; i < 10; i++ {}for ; i < 10; { // while - loop}for i < 10 { // you can omit semicolons if there is only a condition}for { // you can omit the condition ~ while (true)}// use break/continue on current loop// use break/continue with label on outer loop
here:for i := 0; i < 2; i++ {for j := i + 1; j < 3; j++ {if i == 0 {continue here}fmt.Println(j)if j == 2 {break}}}there:for i := 0; i < 2; i++ {for j := i + 1; j < 3; j++ {if j == 1 {continue}fmt.Println(j)if j == 2 {break there}}}
条件
// switch statementswitch operatingSystem {case "darwin":fmt.Println("Mac OS Hipster")// cases break automatically, no fallthrough by defaultcase "linux":fmt.Println("Linux Geek")default:// Windows, BSD, ...fmt.Println("Other")}// as with for and if, you can have an assignment statement before the switch valueswitch os := runtime.GOOS; os {case "darwin": ...}// you can also make comparisons in switch casesnumber := 42switch {case number < 42:fmt.Println("Smaller")case number == 42:fmt.Println("Equal")case number > 42:fmt.Println("Greater")}// cases can be presented in comma-separated listsvar char byte = '?'switch char {case ' ', '?', '&', '=', '#', '+', '%':fmt.Println("Should escape")}
数组, 切片, 遍历
数组
var a [10]int // declare an int array with length 10. Array length is part of the type!
a[3] = 42 // set elements
i := a[3] // read elements// declare and initialize
var a = [2]int{1, 2}
a := [2]int{1, 2} //shorthand
a := [...]int{1, 2} // elipsis -> Compiler figures out array length
切片
var a []int // declare a slice - similar to an array, but length is unspecified
var a = []int {1, 2, 3, 4} // declare and initialize a slice (backed by the array given implicitly)
a := []int{1, 2, 3, 4} // shorthand
chars := []string{0:"a", 2:"c", 1: "b"} // ["a", "b", "c"]var b = a[lo:hi] // creates a slice (view of the array) from index lo to hi-1
var b = a[1:4] // slice from index 1 to 3
var b = a[:3] // missing low index implies 0
var b = a[3:] // missing high index implies len(a)
a = append(a,17,3) // append items to slice a
c := append(a,b...) // concatenate slices a and b// create a slice with make
a = make([]byte, 5, 5) // first arg length, second capacity
a = make([]byte, 5) // capacity is optional// create a slice from an array
x := [3]string{"Лайка", "Белка", "Стрелка"}
s := x[:] // a slice referencing the storage of x
数组和切片的操作
len(a) 返回数组/切片的长度。这是一个内置函数,而不是数组的属性/方法。
// loop over an array/a slice
for i, e := range a {// i is the index, e the element
}// if you only need e:
for _, e := range a {// e is the element
}// ...and if you only need the index
for i := range a {
}// In Go pre-1.4, you'll get a compiler error if you're not using i and e.
// Go 1.4 introduced a variable-free form, so that you can do this
for range time.Tick(time.Second) {// do it once a sec
}
哈希表
m := make(map[string]int)
m["key"] = 42
fmt.Println(m["key"])delete(m, "key")elem, ok := m["key"] // test if key "key" is present and retrieve it, if so// map literal
var m = map[string]Vertex{"Bell Labs": {40.68433, -74.39967},"Google": {37.42202, -122.08408},
}// iterate over map content
for key, value := range m {
}
结构体
Go中没有类,只有结构体。结构体可以拥有方法。
// A struct is a type. It's also a collection of fields// Declaration
type Vertex struct {X, Y float64
}// Creating
var v = Vertex{1, 2}
var v = Vertex{X: 1, Y: 2} // Creates a struct by defining values with keys
var v = []Vertex{{1,2},{5,2},{5,5}} // Initialize a slice of structs// Accessing members
v.X = 4// You can declare methods on structs. The struct you want to declare the
// method on (the receiving type) comes between the the func keyword and
// the method name. The struct is copied on each method call(!)
func (v Vertex) Abs() float64 {return math.Sqrt(v.X*v.X + v.Y*v.Y)
}// Call method
v.Abs()// For mutating methods, you need to use a pointer (see below) to the Struct
// as the type. With this, the struct value is not copied for the method call.
func (v *Vertex) add(n float64) {v.X += nv.Y += n
}
匿名结构体: 比使用 map[string]interface{} 更经济和更安全。
point := struct {X, Y int
}{1, 2}
指针
p := Vertex{1, 2} // p is a Vertex
q := &p // q is a pointer to a Vertex
r := &Vertex{1, 2} // r is also a pointer to a Vertex// The type of a pointer to a Vertex is *Vertexvar s *Vertex = new(Vertex) // new creates a pointer to a new struct instance
接口
// interface declaration
type Awesomizer interface {Awesomize() string
}// types do *not* declare to implement interfaces
type Foo struct {}// instead, types implicitly satisfy an interface if they implement all required methods
func (foo Foo) Awesomize() string {return "Awesome!"
}
嵌入
Go中没有子类化。相反,有接口和结构体嵌入。
// ReadWriter implementations must satisfy both Reader and Writer
type ReadWriter interface {ReaderWriter
}// Server exposes all the methods that Logger has
type Server struct {Host stringPort int*log.Logger
}// initialize the embedded type the usual way
server := &Server{"localhost", 80, log.New(...)}// methods implemented on the embedded struct are passed through
server.Log(...) // calls server.Logger.Log(...)// the field name of the embedded type is its type name (in this case Logger)
var logger *log.Logger = server.Logger
错误
Go中没有异常处理。相反,可能产生错误的函数只是声明了一个额外的返回值,类型为error。这是error接口:
// The error built-in interface type is the conventional interface for representing an error condition,
// with the nil value representing no error.
type error interface {Error() string
}
这是一个示例:
func sqrt(x float64) (float64, error) {if x < 0 {return 0, errors.New("negative value")}return math.Sqrt(x), nil
}func main() {val, err := sqrt(-1)if err != nil {// handle errorfmt.Println(err) // negative valuereturn}// All is good, use `val`.fmt.Println(val)
}
并发
协程
Goroutines是轻量级线程(由Go管理,而不是操作系统线程)。go f(a, b)启动一个新的goroutine来运行f(假设f是一个函数)。
// just a function (which can be later started as a goroutine)
func doStuff(s string) {
}func main() {// using a named function in a goroutinego doStuff("foobar")// using an anonymous inner function in a goroutinego func (x int) {// function body goes here}(42)
}
通道
ch := make(chan int) // create a channel of type int
ch <- 42 // Send a value to the channel ch.
v := <-ch // Receive a value from ch// Non-buffered channels block. Read blocks when no value is available, write blocks until there is a read.// Create a buffered channel. Writing to a buffered channels does not block if less than <buffer size> unread values have been written.
ch := make(chan int, 100)close(ch) // closes the channel (only sender should close)// read from channel and test if it has been closed
v, ok := <-ch// if ok is false, channel has been closed// Read from channel until it is closed
for i := range ch {fmt.Println(i)
}// select blocks on multiple channel operations, if one unblocks, the corresponding case is executed
func doStuff(channelOut, channelIn chan int) {select {case channelOut <- 42:fmt.Println("We could write to channelOut!")case x := <- channelIn:fmt.Println("We could read from channelIn")case <-time.After(time.Second * 1):fmt.Println("timeout")}
}
通道原理
-
向空通道发送会永远阻塞
var c chan string c <- "Hello, World!" // fatal error: all goroutines are asleep - deadlock! -
从空通道接收会永远阻塞。
var c chan string fmt.Println(<-c) // fatal error: all goroutines are asleep - deadlock! -
向已关闭的通道发送会引发恐慌。
var c = make(chan string, 1) c <- "Hello, World!" close(c) c <- "Hello, Panic!" // panic: send on closed channel -
从已关闭的通道接收会立即返回零值。
var c = make(chan int, 2) c <- 1 c <- 2 close(c) for i := 0; i < 3; i++ {fmt.Printf("%d ", <-c) } // 1 2 0
打印
fmt.Println("Hello, 你好, नमस्ते, Привет, ᎣᏏᏲ") // basic print, plus newline
p := struct { X, Y int }{ 17, 2 }
fmt.Println( "My point:", p, "x coord=", p.X ) // print structs, ints, etc
s := fmt.Sprintln( "My point:", p, "x coord=", p.X ) // print to string variablefmt.Printf("%d hex:%x bin:%b fp:%f sci:%e",17,17,17,17.0,17.0) // c-ish format
s2 := fmt.Sprintf( "%d %f", 17, 17.0 ) // formatted print to string variablehellomsg := `"Hello" in Chinese is 你好 ('Ni Hao')"Hello" in Hindi is नमस्ते ('Namaste')
` // multi-line string literal, using back-tick at beginning and end
反射
类型切换
类型切换类似于常规的switch语句,但类型切换中的情况指定要与给定接口值持有的值的类型进行比较的类型,而不是值。
func do(i interface{}) {switch v := i.(type) {case int:fmt.Printf("Twice %v is %v\n", v, v*2)case string:fmt.Printf("%q is %v bytes long\n", v, len(v))default:fmt.Printf("I don't know about type %T!\n", v)}
}func main() {do(21)do("hello")do(true)
}
片段
文件嵌入
Go程序可以使用"embed"包嵌入静态文件,如下所示:
package mainimport ("embed""log""net/http"
)// content holds the static content (2 files) for the web server.
//go:embed a.txt b.txt
var content embed.FSfunc main() {http.Handle("/", http.FileServer(http.FS(content)))log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil))
}
完整的Playground示例
HTTP服务器
package mainimport ("fmt""net/http"
)// define a type for the response
type Hello struct{}// let that type implement the ServeHTTP method (defined in interface http.Handler)
func (h Hello) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {fmt.Fprint(w, "Hello!")
}func main() {var h Hellohttp.ListenAndServe("localhost:4000", h)
}// Here's the method signature of http.ServeHTTP:
// type Handler interface {
// ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request)
// }
相关文章:

Golang语法、技巧和窍门
Golang简介 命令式语言静态类型语法标记类似于C(但括号较少且没有分号),结构类似Oberon-2编译为本机代码(没有JVM)没有类,但有带有方法的结构接口没有实现继承。不过有type嵌入。函数是一等公民函数可以返…...
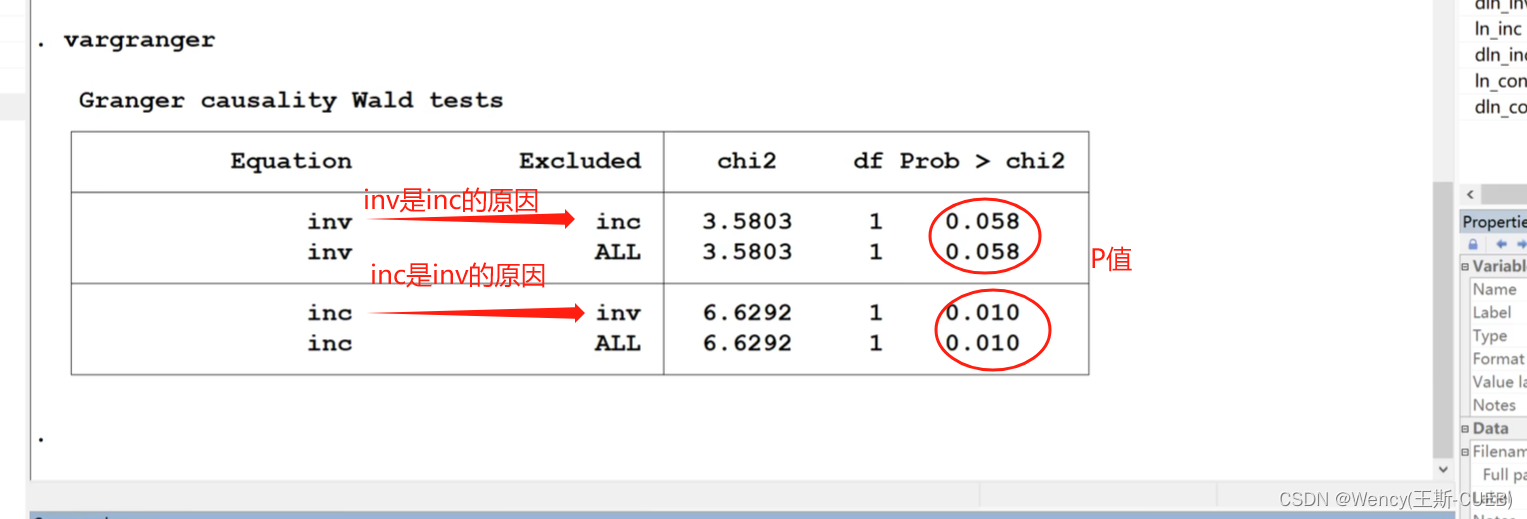
Grander因果检验(格兰杰)原理+操作+解释
笔记来源: 1.【传送门】 2.【传送门】 前沿原理介绍 Grander因果检验是一种分析时间序列数据因果关系的方法。 基本思想在于,在控制Y的滞后项 (过去值) 的情况下,如果X的滞后项仍然有助于解释Y的当期值的变动,则认为 X对 Y产生…...
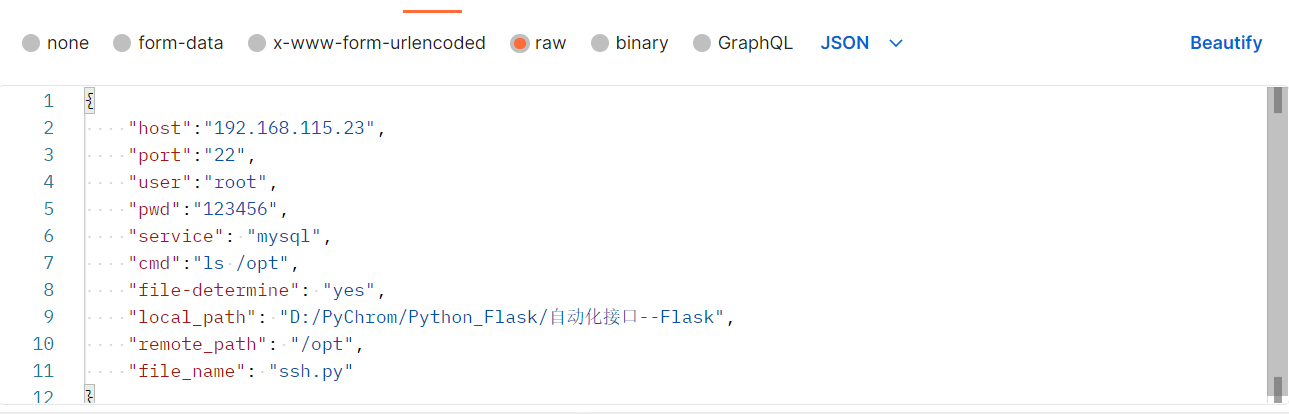
Python-Flask:编写自动化连接demo脚本:v1.0.0
主函数: # _*_ Coding : UTF-8 _*_ # Time : 13:14 # Author : YYZ # File : Flask # Project : Python_Project_爬虫 import jsonfrom flask import Flask,request,jsonify import sshapi Flask(__name__)# methods: 指定请求方式 接口解析参数host host_info[…...
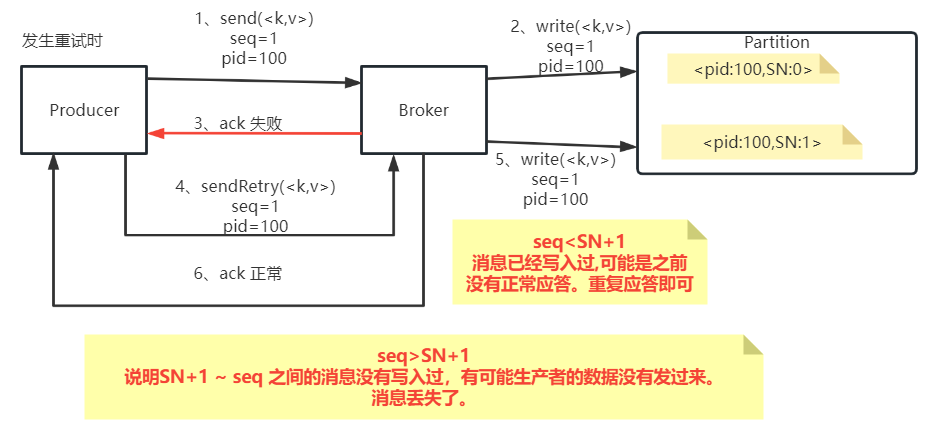
kafka客户端应用参数详解
一、基本客户端收发消息 Kafka提供了非常简单的客户端API。只需要引入一个Maven依赖即可: <dependency><groupId>org.apache.kafka</groupId><artifactId>kafka_2.13</artifactId><version>3.4.0</version></depend…...

Apache Doris 行列转换可以这样玩
行列转换在做报表分析时还是经常会遇到的,今天就说一下如何实现行列转换吧。 行列转换就是如下图所示两种展示形式的互相转换 1. 行转列 我们来看一个简单的例子,我们要把下面这个表的数据,转换成图二的样式 image-20230914151818953.png …...
及键盘事件、右键事件)
【Qt图形视图框架】自定义QGraphicsItem和QGraphicsView,实现鼠标(移动、缩放)及键盘事件、右键事件
自定义QGraphicsItem和QGraphicsView 说明示例myitem.hmyitem.cppmyview.hmyview.cpp调用main.cpp 效果 说明 在使用Qt的图形视图框架实现功能时,一般会在其基础上进行自定义功能实现。 如:滚轮对场景的缩放,鼠标拖动场景中的项,…...
C语言结构体指针学习
结构体变量存放内存中,也有起始地址,定义一个变量来存放这个地址,那这个变量就是结构体指针; typedef struct mydata{int a1;int a2;int a3; }mydata;void CJgtzzView::OnDraw(CDC* pDC) {CJgtzzDoc* pDoc GetDocument();ASSERT…...
华为云云耀云服务器L实例评测|部署在线轻量级备忘录 memos
华为云云耀云服务器L实例评测|部署在线轻量级备忘录 memos 一、云耀云服务器L实例介绍1.1 云服务器介绍1.2 产品优势1.3 应用场景1.4 支持镜像 二、云耀云服务器L实例配置2.1 重置密码2.2 服务器连接2.3 安全组配置 三、部署 memos3.1 memos介绍3.2 Docker 环境搭建…...
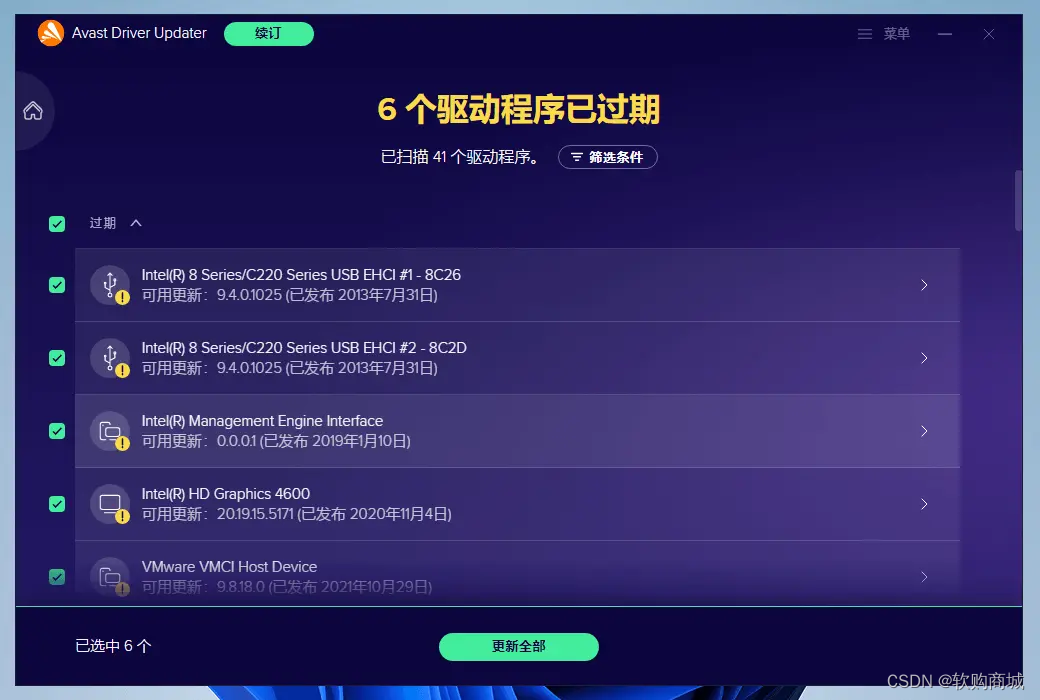
详解Avast Driver Updater:电脑驱动更新工具的利器还是多余的软件?
亲爱的读者朋友们,你是不是经常为电脑的驱动问题而烦恼?如果是的话,你可能会对这款软件——Avast Driver Updater 电脑驱动更新工具感兴趣。但在你决定尝试之前,不妨先和我一起深入探讨一下它的优点、缺点以及它适用的使用场景。 …...

大数据Flink(九十五):DML:Window TopN
文章目录 DML:Window TopN DML:Window TopN Window TopN 定义(支持 Streaming):Window TopN 是一种特殊的 TopN,它的返回结果是每一个窗口内的 N 个最小值或者最大值。 应用场景...

使用OKHttpClient访问网络
使用OKHttpClient前要引入依赖: 在build.gradle(Moduel :app)中添加 implementation com.squareup.okhttp3:okhttp:3.14.1 implementation com.squareup.okhttp3:logging-interceptor:3.14.1 implementation com.squareup.okio:okio:1.6.0 1. GET(同步…...

maui 开发AMD CPU踩的坑。
刚换的 amd R7735HS 笔记本,8核16线程,32GB内存。性能得实强悍 。 当需要发布iOS版本时发现,我没有macos ,那就安装个vmware 吧。看了一下Apple 要求以后的发布的APP需要以xcode14.3或以后版本开发的版本,但xcode14.3…...
宝塔反代openai官方API接口详细教程,502 Bad Gateway问题解决
一、前言 宝塔反代openai官方API接口详细教程,实现国内使用ChatGPT502 Bad Gateway问题解决, 此方法最简单快捷,没有复杂步骤,不容易出错,即最简单,零代码、零部署的方法。 二、实现前提 一台海外VPS服务…...

【leetocde】128. 最长连续序列
给定一个未排序的整数数组 nums ,找出数字连续的最长序列(不要求序列元素在原数组中连续)的长度。 请你设计并实现时间复杂度为 O(n) 的算法解决此问题。 示例 1: 输入:nums [100,4,200,1,3,2] 输出:4 …...

【Vue3】动态 class 类
如果你想在 Vue.js 中动态设置元素的 class 类名,你可以使用以下两种主要方式: 绑定一个动态的 class 对象:你可以使用 v-bind 或简写的 : 来绑定一个包含类名的对象,其中类名的键是类名字符串,值是一个布尔值或计算属…...
【Redis】redis基本数据类型详解(String、List、Hash、Set、ZSet)
目录 RedisString(字符串)List(列表)Hash(字典)Set(集合)ZSet(有序集合) Redis Redis有5种基本的数据结构,分别为:string(字符串)、list(列表)、set(集合)、hash(哈希&a…...

ubuntu源码安装aria2
github:GitHub - aria2/aria2: aria2 is a lightweight multi-protocol & multi-source, cross platform download utility operated in command-line. It supports HTTP/HTTPS, FTP, SFTP, BitTorrent and Metalink. 发行说明:GitHub - aria2/aria2 at releas…...
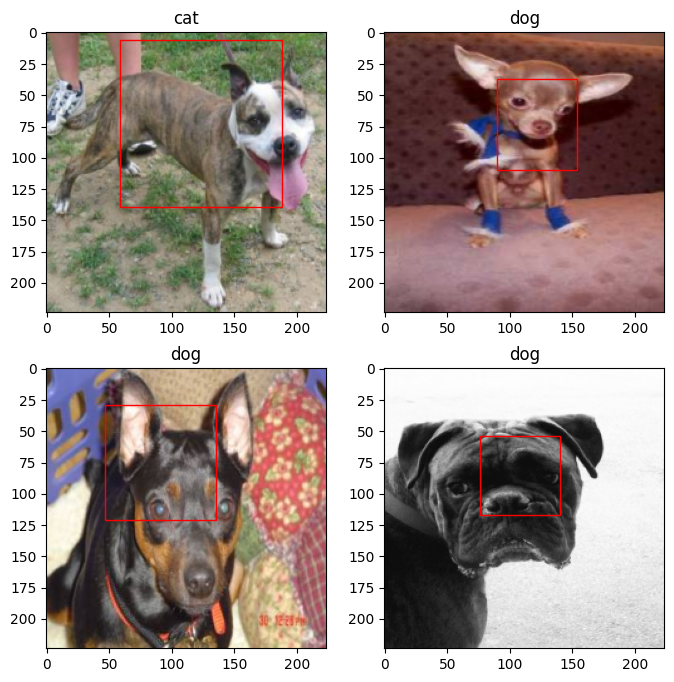

【多任务案例:猫狗脸部定位与分类】
【猫狗脸部定位与识别】 1 引言2 损失函数3 The Oxford-IIIT Pet Dataset数据集4 数据预处理4 创建模型输入5 自定义数据集加载方式6 显示一批次数据7 创建定位模型8 模型训练9 绘制损失曲线10 模型保存与预测 1 引言 猫狗脸部定位与识别分为定位和识别,即定位猫狗…...

.Net 锁的介绍
在.NET中,有多种锁机制可用于多线程编程,用来确保线程安全和共享资源的同步。以下是.NET中常见的锁机制: 1. **Monitor(互斥锁):** `Monitor` 是.NET中最基本的锁机制之一。它使用 `lock` 关键字实现,可以确保在同一时刻只有一个线程能够访问被锁定的代码块。`Monitor`…...

Office 2021 小型企业版商用办公软件评测:提升工作效率与协作能力的专业利器
作为一名软件评测人员,我将为您带来一篇关于 Office 2021 小型企业版商用办公软件的评测文章。在这篇评测中,我将从实用性、使用场景、优点和缺点等多个方面对该软件进行客观分析,在专业角度为您揭示它的真正实力和潜力。 一、实用性…...
eNSP-Cloud(实现本地电脑与eNSP内设备之间通信)
说明: 想象一下,你正在用eNSP搭建一个虚拟的网络世界,里面有虚拟的路由器、交换机、电脑(PC)等等。这些设备都在你的电脑里面“运行”,它们之间可以互相通信,就像一个封闭的小王国。 但是&#…...

CTF show Web 红包题第六弹
提示 1.不是SQL注入 2.需要找关键源码 思路 进入页面发现是一个登录框,很难让人不联想到SQL注入,但提示都说了不是SQL注入,所以就不往这方面想了 先查看一下网页源码,发现一段JavaScript代码,有一个关键类ctfs…...

2024年赣州旅游投资集团社会招聘笔试真
2024年赣州旅游投资集团社会招聘笔试真 题 ( 满 分 1 0 0 分 时 间 1 2 0 分 钟 ) 一、单选题(每题只有一个正确答案,答错、不答或多答均不得分) 1.纪要的特点不包括()。 A.概括重点 B.指导传达 C. 客观纪实 D.有言必录 【答案】: D 2.1864年,()预言了电磁波的存在,并指出…...

Spring Boot面试题精选汇总
🤟致敬读者 🟩感谢阅读🟦笑口常开🟪生日快乐⬛早点睡觉 📘博主相关 🟧博主信息🟨博客首页🟫专栏推荐🟥活动信息 文章目录 Spring Boot面试题精选汇总⚙️ **一、核心概…...
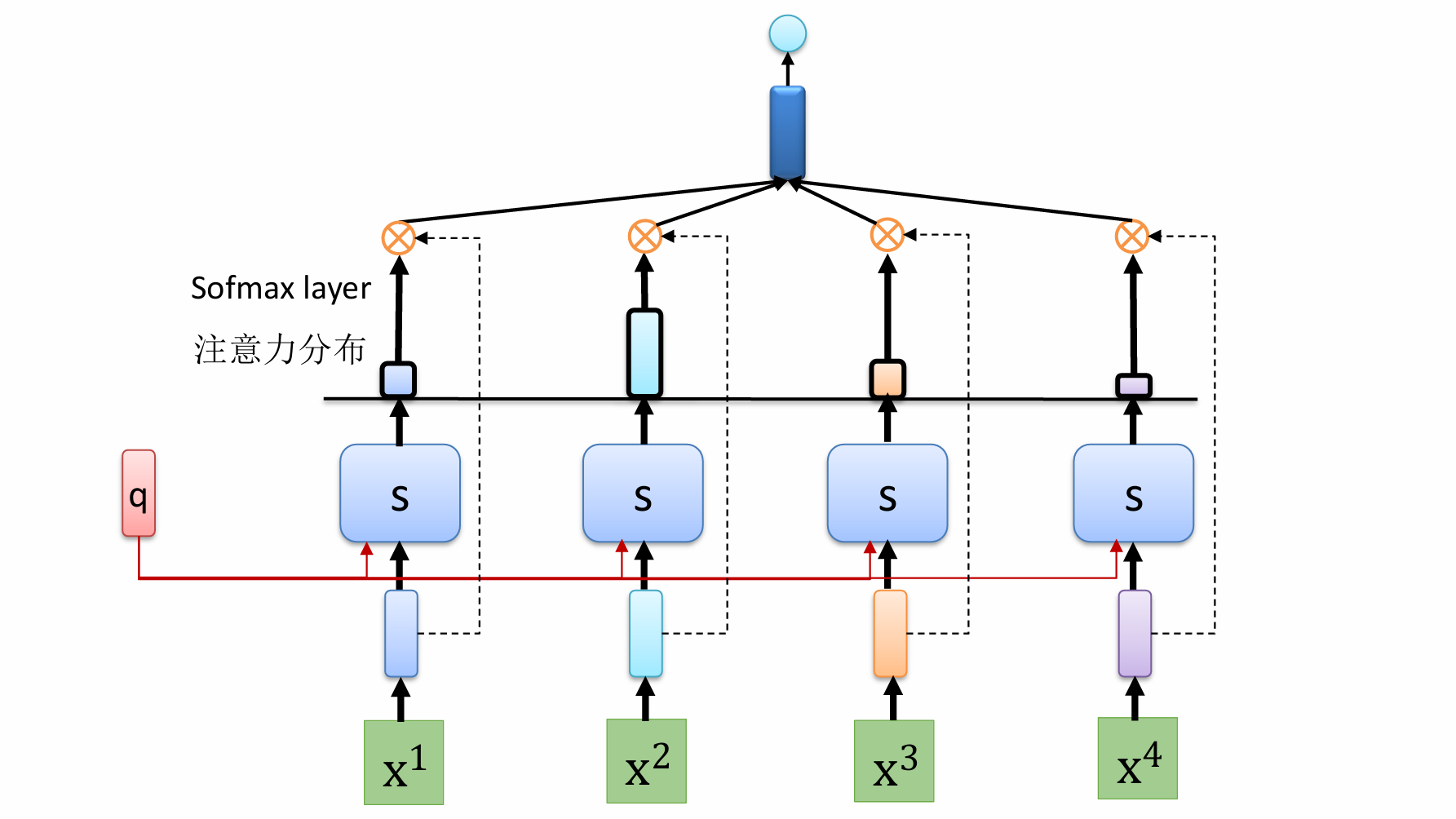
自然语言处理——循环神经网络
自然语言处理——循环神经网络 循环神经网络应用到基于机器学习的自然语言处理任务序列到类别同步的序列到序列模式异步的序列到序列模式 参数学习和长程依赖问题基于门控的循环神经网络门控循环单元(GRU)长短期记忆神经网络(LSTM)…...
集成 Mybatis-Plus 和 Mybatis-Plus-Join)
纯 Java 项目(非 SpringBoot)集成 Mybatis-Plus 和 Mybatis-Plus-Join
纯 Java 项目(非 SpringBoot)集成 Mybatis-Plus 和 Mybatis-Plus-Join 1、依赖1.1、依赖版本1.2、pom.xml 2、代码2.1、SqlSession 构造器2.2、MybatisPlus代码生成器2.3、获取 config.yml 配置2.3.1、config.yml2.3.2、项目配置类 2.4、ftl 模板2.4.1、…...

跨平台商品数据接口的标准化与规范化发展路径:淘宝京东拼多多的最新实践
在电商行业蓬勃发展的当下,多平台运营已成为众多商家的必然选择。然而,不同电商平台在商品数据接口方面存在差异,导致商家在跨平台运营时面临诸多挑战,如数据对接困难、运营效率低下、用户体验不一致等。跨平台商品数据接口的标准…...

【版本控制】GitHub Desktop 入门教程与开源协作全流程解析
目录 0 引言1 GitHub Desktop 入门教程1.1 安装与基础配置1.2 核心功能使用指南仓库管理日常开发流程分支管理 2 GitHub 开源协作流程详解2.1 Fork & Pull Request 模型2.2 完整协作流程步骤步骤 1: Fork(创建个人副本)步骤 2: Clone(克隆…...
OPENCV图形计算面积、弧长API讲解(1)
一.OPENCV图形面积、弧长计算的API介绍 之前我们已经把图形轮廓的检测、画框等功能讲解了一遍。那今天我们主要结合轮廓检测的API去计算图形的面积,这些面积可以是矩形、圆形等等。图形面积计算和弧长计算常用于车辆识别、桥梁识别等重要功能,常用的API…...

linux设备重启后时间与网络时间不同步怎么解决?
linux设备重启后时间与网络时间不同步怎么解决? 设备只要一重启,时间又错了/偏了,明明刚刚对时还是对的! 这在物联网、嵌入式开发环境特别常见,尤其是开发板、树莓派、rk3588 这类设备。 解决方法: 加硬件…...
