File类及IO流说明
目录
1.File类说明
(1)构造方法创建文件
(2)创建功能
(3)File类的判断和获取功能
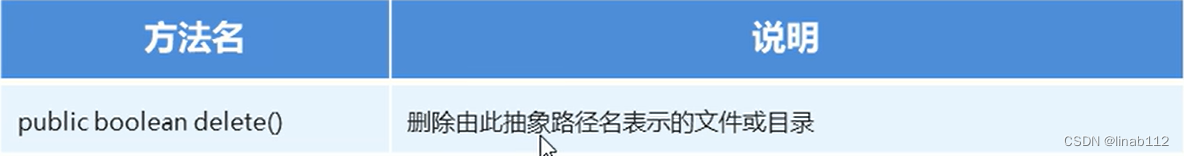
(4)文件删除功能
2.I/O流说明
(1).分类
3.字节流写数据
(1)说明
(2)字节流写数据的三种方式
(3)写入时实现换行和追加写入
(4)异常处理中加入finally实现资源的释放
4.字节流读数据
(1)说明
5.字节缓冲流
6.字符流
(1)说明
(2)字符流写数据的5种方式
(3)字符流读数据的两种方式
(4)FileReader及FileWriter
(5)字符缓冲流
(6)字符缓冲流的特有功能
1.File类说明
File:它是文件和目录路径名的抽象表示。
(1)构造方法创建文件
文件和目录是可以通过File封装成对象的。
对于File而言,其封装的并不是一个真正存在的文件,仅仅是一个路径名而已。它可以是存在的,也可以是不存在的.将来是要通过具体的操作把这个路径的内容转换为具体存在的。

示例:
package com.example.demo.file;import java.io.File;
import java.io.InputStream;/*** @Author linaibo* @Date 2023/2/19 9:03* @PackageName:com.example.demo.file* @ClassName: FileDemo1* @Version 1.0*/
public class FileDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) {File file1 = new File("D:\\13-Notepad3-代替记事本\\Readme.txt");System.out.println(file1);File file2 = new File("D:\\13-Notepad3-代替记事本", "Readme.txt");System.out.println(file2);File file = new File("D:\\13-Notepad3-代替记事本");File file3 = new File(file, "Readme.txt");System.out.println(file3);}
}
(2)创建功能
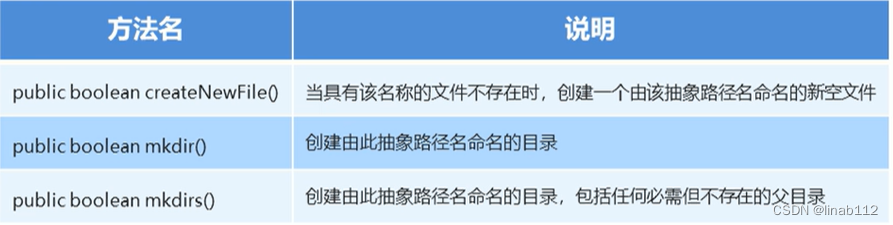
File类创建功能:
public boolean createNewFile():当具有该名称的文件不存在时,创建一个由该抽象路径名命名的新空文件;如果文件不存在,就创建文件,并返回true;如果文件存在,就不创建文件,并返回false。
public boolean mkdir(): 创建由此抽象路径名命名的目录如果目录不存在,就创建目录,并返回true;如果目录存在,就不创建文件,并返回false。
public boolean mkdirs():创建由此抽象路径名命名的目录如果目录不存在,就创建目录,并返回true;如果目录存在,就不创建文件,并返回false。
示例:
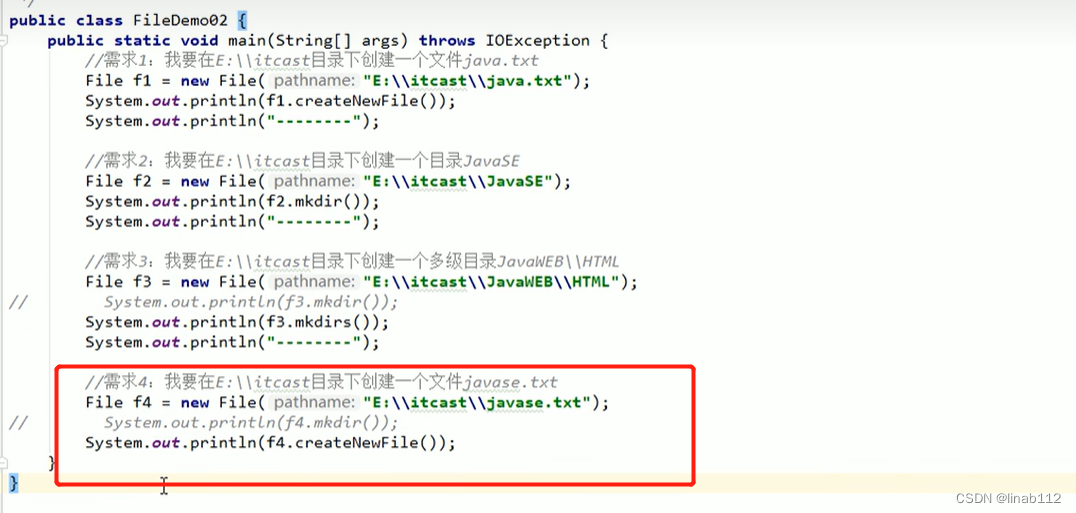
注意:如果要创建文件,但是调用创建目录的方法,会创建出来目录,如果不删除此目录,再执行创建文件的方法会报错,只有将文件删除掉才能创建文件,这点需要注意。
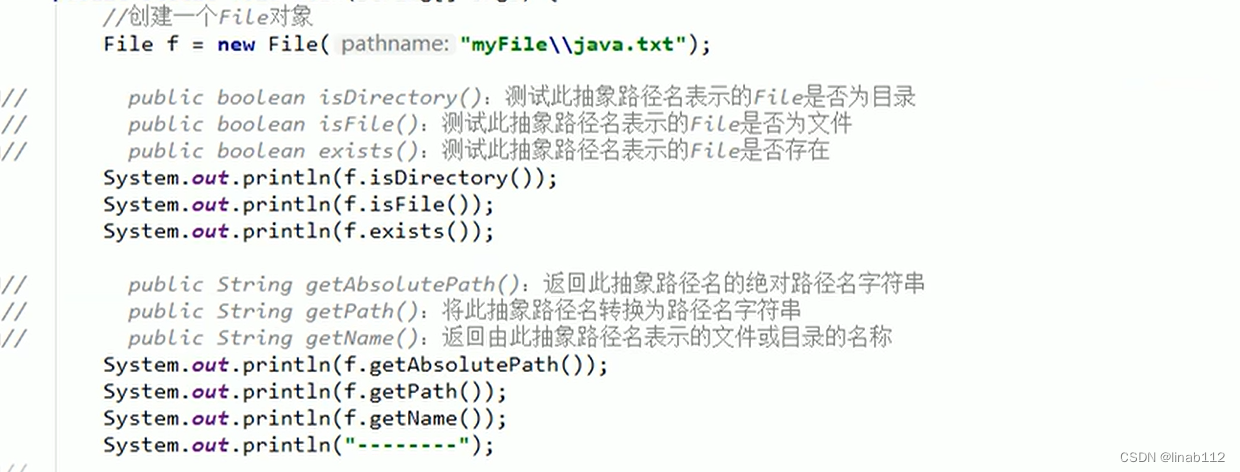
(3)File类的判断和获取功能

示例1:
示例2:
package com.example.demo.file;import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;/*** @Author linaibo* @Date 2023/2/21 11:53* @PackageName:com.example.demo.file* @ClassName: FileDemo2* @Version 1.0*/
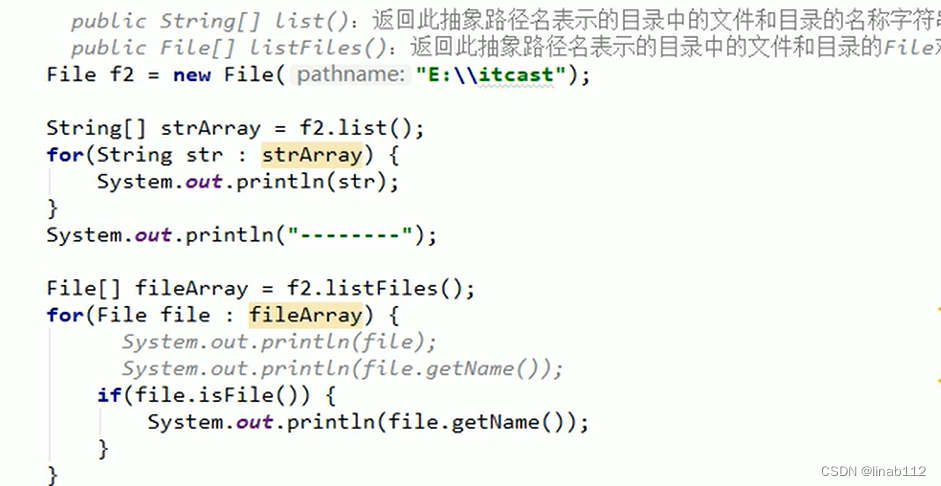
public class FileDemo2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {File file1 = new File("D:\\13-Notepad3-代替记事本");System.out.println(file1);boolean directory = file1.isDirectory();System.out.println("isDirectory:" + directory);boolean file = file1.isFile();System.out.println("isFile:" + file);boolean exists = file1.exists();System.out.println("exists:" + exists);String absolutePath = file1.getAbsolutePath();System.out.println("getAbsolutePath:" + absolutePath);String path = file1.getPath();System.out.println("getPath:" + path);String name = file1.getName();System.out.println("getName:" + name);System.out.println("list" + "------");String[] list1 = file1.list();for (String str : list1) {System.out.println(str);}System.out.println("listFiles" + "*******");File[] files = file1.listFiles();for (File fi : files) {System.out.println(fi);}}
}
结果:
D:\13-Notepad3-代替记事本
isDirectory:true
isFile:false
exists:true
getAbsolutePath:D:\13-Notepad3-代替记事本
getPath:D:\13-Notepad3-代替记事本
getName:13-Notepad3-代替记事本
list------
Docs
Favorites
grepWinLicense.txt
grepWinNP3.exe
License.txt
lng
minipath.exe
minipath.ini
Notepad3.exe
Notepad3.ini
Readme.txt
Themes
listFiles*******
D:\13-Notepad3-代替记事本\Docs
D:\13-Notepad3-代替记事本\Favorites
D:\13-Notepad3-代替记事本\grepWinLicense.txt
D:\13-Notepad3-代替记事本\grepWinNP3.exe
D:\13-Notepad3-代替记事本\License.txt
D:\13-Notepad3-代替记事本\lng
D:\13-Notepad3-代替记事本\minipath.exe
D:\13-Notepad3-代替记事本\minipath.ini
D:\13-Notepad3-代替记事本\Notepad3.exe
D:\13-Notepad3-代替记事本\Notepad3.ini
D:\13-Notepad3-代替记事本\Readme.txt
D:\13-Notepad3-代替记事本\Themes(4)文件删除功能
2.I/O流说明
(1).分类
按照数据的流向
- 输入流:读数据
- 输出流:写数据
按照数据类型来分
- 字节流:字节输入流,字节输出流
- 字符流:字符输入流,字符输出流
一般来说,我们说IO流的分类是按照数据类型来分的那么这两种流都在什么情况下使用呢?
如果数据通过Window自带的记事本软件打开,我们还可以读懂里面的内容,就使用字符流。否则使用字节流。如果你不知道该使用哪种类型的流,就使用字节流。
3.字节流写数据
(1)说明
OutputStream:这个抽象类是表示输出字节流的所有类的超类。
它的子类都是以outputStream结尾的。
FileOutputStream: 文件输出流用于将数据写入File。FileOutputStream(String name): 创建文件输出流以指定的名称写入文件
使用字节输出流写数据的步骤:
创建字节输出流对象(调用系统功能创建了文件,创建字节输出流对象,让字节输出流对象指向文件)。
调用字节输出流对象的写数据方法。
释放资源(关闭此文件输出流并释放与此流相关联的任何系统资源)。
write方法:
/*** Writes <code>b.length</code> bytes from the specified byte array* to this file output stream.** @param b the data.* @exception IOException if an I/O error occurs.*/public void write(byte b[]) throws IOException {writeBytes(b, 0, b.length, append);}/*** Writes <code>b.length</code> bytes from the specified byte array* to this file output stream.** @param b the data.* @exception IOException if an I/O error occurs.*/public void write(byte b[]) throws IOException {writeBytes(b, 0, b.length, append);}/*** Writes <code>len</code> bytes from the specified byte array* starting at offset <code>off</code> to this file output stream.** @param b the data.* @param off the start offset in the data.* @param len the number of bytes to write.* @exception IOException if an I/O error occurs.*/public void write(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {writeBytes(b, off, len, append);}第一种方式参数为ASCII码,例如当值为97时,文件中显示的a。
第二种方式参数为byte数组,可以使用String.getBytes()方法将字符串转换成byte数组。
第三种方式可以实现对数组的部分内容进行写出的,off为其实位置,设置为0,len为长度,代表读取几位。
示例:
package com.example.demo.file;import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;/*** @Author linaibo* @Date 2023/2/21 12:00* @PackageName:com.example.demo.file* @ClassName: FileOutputStreamDemo1* @Version 1.0*/
public class FileOutputStreamDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {String path = "F:\\output";File file = new File(path);if (!file.exists()) {file.mkdir();}File file1 = new File(file, "out.txt");if (!file1.exists()) {file1.createNewFile();}FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("F:\\output\\out.txt", true);try {fileOutputStream.write("你好".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));fileOutputStream.write("\r\n".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));fileOutputStream.write("世界".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));fileOutputStream.write("\r\n".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));} finally {if (fileOutputStream != null) {fileOutputStream.close();}}}
}
(2)字节流写数据的三种方式

(3)写入时实现换行和追加写入
换行:window:\r\n linux:\n mac:\r
追加写入:
public FileOutputStream(String name,boolean append)
创建文件输出流以指定的名称写入文件。如果第二个参数为true,则字节将写入文件的末尾而不是开头。
示例:

(4)异常处理中加入finally实现资源的释放
 释放之前要判断一下流是否为null,为null时不用关闭,避免空指针异常。
释放之前要判断一下流是否为null,为null时不用关闭,避免空指针异常。
4.字节流读数据
(1)说明
InputStream:这个抽象类是表示输入字节流的所有类的超类。
它的子类都是以inputStream结尾的。
FilelnputStream:从文件系统中的文件获取输入字节。
FilelnputStream(String name):通过打开与实际文件的连接来创建一个FilelnputStream,该文件由文件系统中的路径名name命名。
使用字节输入流读数据的步骤:
- 创建字节输入流对象。
- 用字节输入流对象的读数据方法。
- 释放资源。
read方法:
/*** Reads a byte of data from this input stream. This method blocks* if no input is yet available.** @return the next byte of data, or <code>-1</code> if the end of the* file is reached.* @exception IOException if an I/O error occurs.*/public int read() throws IOException {return read0();}/*** Reads up to <code>b.length</code> bytes of data from this input* stream into an array of bytes. This method blocks until some input* is available.** @param b the buffer into which the data is read.* @return the total number of bytes read into the buffer, or* <code>-1</code> if there is no more data because the end of* the file has been reached.* @exception IOException if an I/O error occurs.*/public int read(byte b[]) throws IOException {return readBytes(b, 0, b.length);}/*** Reads up to <code>len</code> bytes of data from this input stream* into an array of bytes. If <code>len</code> is not zero, the method* blocks until some input is available; otherwise, no* bytes are read and <code>0</code> is returned.** @param b the buffer into which the data is read.* @param off the start offset in the destination array <code>b</code>* @param len the maximum number of bytes read.* @return the total number of bytes read into the buffer, or* <code>-1</code> if there is no more data because the end of* the file has been reached.* @exception NullPointerException If <code>b</code> is <code>null</code>.* @exception IndexOutOfBoundsException If <code>off</code> is negative,* <code>len</code> is negative, or <code>len</code> is greater than* <code>b.length - off</code>* @exception IOException if an I/O error occurs.*/public int read(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {return readBytes(b, off, len);}说明:
第一种方法用来一个个读取。
第二种方法是读取到一个byte数组中。
第三种方法是读取到数组的某个部分。
一次读取一个字节数据的示例:
package com.example.demo.file;import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;/*** @Author linaibo* @Date 2023/2/21 12:21* @PackageName:com.example.demo.file* @ClassName: FileInputStreamDemo1* @Version 1.0*/
public class FileInputStreamDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {FileInputStream fi = new FileInputStream("F:\\output\\out.txt");int read;while ((read = fi.read()) != -1) {System.out.print(read);}fi.close();}
}
结果:
228189160229165189131022818415023114914013102281891602291651891310228184150231149140131022818916022916518913102281841502311491401310如果读取的值为-1,则意味着文件已经读完了。
一次读取一个字节数组的示例:
package com.example.demo.file;import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;/*** @Author linaibo* @Date 2023/2/21 12:33* @PackageName:com.example.demo.file* @ClassName: FileInputStreamDemo2* @Version 1.0*/
public class FileInputStreamDemo2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {FileInputStream fi = new FileInputStream("F:\\output\\out.txt");int read;byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];while ((read = fi.read(bytes)) != -1) {System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,read));}fi.close();}
}
结果:
你好
世界
你好
世界
你好
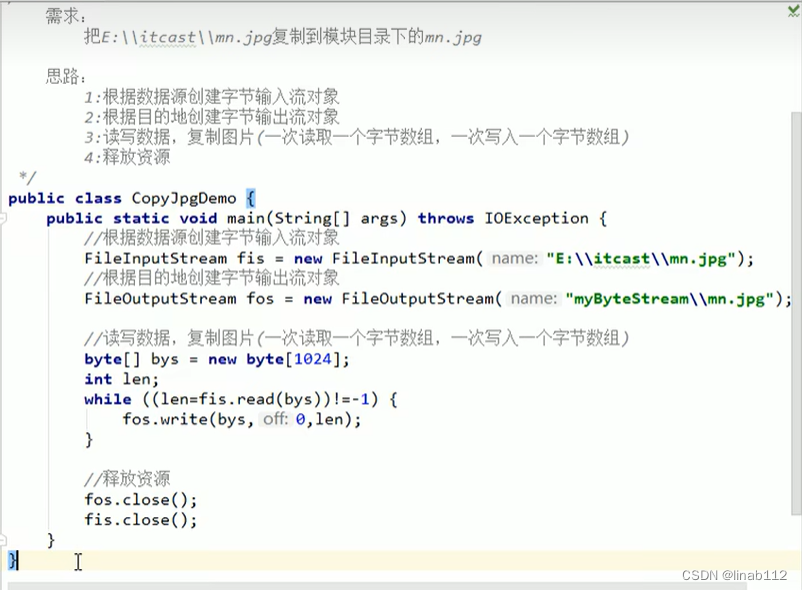
世界字节流复制图片,文档,视频,音乐的示例:
package com.example.demo.file;import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;/*** @Author linaibo* @Date 2023/2/21 21:47* @PackageName:com.example.demo.file* @ClassName: CopyJpgDemo* @Version 1.0*/
public class CopyJpgDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {FileInputStream fi = new FileInputStream("D:\\Backup\\Documents\\My Pictures\\Saved Pictures\\图片1.png");FileOutputStream fo = new FileOutputStream("F:\\output\\图片1.png");int read;byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];while ((read = fi.read(bytes)) != -1) {fo.write(bytes, 0, read);}fi.close();fo.close();FileInputStream fi1 = new FileInputStream("D:\\Backup\\Documents\\My Music\\测试音乐.mp3");FileOutputStream fo1 = new FileOutputStream("F:\\output\\测试音乐.mp3");int num;byte[] bytes1 = new byte[1024];while ((num = fi1.read(bytes1)) != -1) {fo1.write(bytes1, 0, num);}fi1.close();fo1.close();FileInputStream fi2 = new FileInputStream("D:\\Backup\\Documents\\MuMu共享文件夹\\123.xlsx");FileOutputStream fo2 = new FileOutputStream("F:\\output\\123.xlsx");int num2;byte[] bytes2 = new byte[1024];while ((num2 = fi2.read(bytes2)) != -1) {fo2.write(bytes2, 0, num2);}fi2.close();fo2.close();FileInputStream fi3 = new FileInputStream("D:\\Backup\\Documents\\My Videos\\bilibili\\234.mp4");FileOutputStream fo3 = new FileOutputStream("F:\\output\\234.mp4");int num3;byte[] bytes3 = new byte[1024];while ((num3 = fi3.read(bytes3)) != -1) {fo3.write(bytes3,0,num3);}fi3.close();fo3.close();}}
5.字节缓冲流
字节缓冲流:
BufferOutputStream:该类实现缓冲输出流。通过设置这样的输出流,应用程序可以向底层输出流写入字节,而不必为写入的每个字节导致底层系统的调用。
BuferedInputStream:建BufferedInputStream将创建一个内部缓冲区数组,当从流中读取或跳过字节时,内部缓冲区将根据需要从所包含的输入流中重新填充,一次很多字节。
构造方法:
字节缓冲输出流: BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out)
字节缓冲输入流:BufferedInputStream(lnputStreamin)
为什么构造方法需要的是字节流,而不是具体的文件或者路径呢?
字节缓冲流仅仅提供缓冲区而真正的读写数据还得依靠基本的字节流对象进行操作。
package com.example.demo.file;import java.io.*;/*** @Author linaibo* @Date 2023/2/21 21:47* @PackageName:com.example.demo.file* @ClassName: CopyJpgDemo* @Version 1.0*/
public class CopyJpgDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {long start = System.currentTimeMillis();FileInputStream fi3 = new FileInputStream("D:\\Backup\\Documents\\My Videos\\bilibili\\234.mp4");FileOutputStream fo3 = new FileOutputStream("F:\\output\\234.mp4");int num3;byte[] bytes3 = new byte[1024];while ((num3 = fi3.read(bytes3)) != -1) {fo3.write(bytes3, 0, num3);}fi3.close();fo3.close();long end = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("共耗时" + (end - start) + "毫秒");long start1 = System.currentTimeMillis();BufferedInputStream bi = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:\\Backup\\Documents\\My Videos\\bilibili\\234.mp4"));BufferedOutputStream bo = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("F:\\output\\2344.mp4"));int num4;byte[] bytes4 = new byte[1024];while ((num4 = bi.read(bytes4)) != -1) {bo.write(bytes4, 0, num4);}bi.close();bo.close();long end1 = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("共耗时" + (end1 - start1) + "毫秒");}}
结果:
共耗时47毫秒
共耗时18毫秒使用缓冲流可以提高性能。
6.字符流
(1)说明
字符流抽象基类:
Reader:字符输入流的抽象类
Writer: 字符输出流的抽象类
字符流中和编码解码问题相关的两个类:
InputStreamReader
OutputStreamWriter
InputstreamReader: 是从字节流到字符流的桥梁。它读取字节,并使用指定的编码将其解码为字符它使用的字符集可以由名称指定,也可以被明确指定,或者可以接受平台的默认字符集。
OutputStreamWriter: 是从字符流到字节流的桥梁。使用指定的编码将写入的字符编码为字节。它使用的字符集可以由名称指定,也可以被明确指定,或者可以接受平台的默认字符集。
字符输出流的构造方法

字符输入流的构造方法

示例:

(2)字符流写数据的5种方式

示例:
package com.example.demo.file;import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;/*** @Author linaibo* @Date 2023/2/25 9:53* @PackageName:com.example.demo.file* @ClassName: FileReaderDemo1* @Version 1.0*/
public class FileReaderDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//一次写入一个字符OutputStreamWriter writer = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("F:\\output\\test.xlsx"));writer.write(97);writer.flush();writer.write("你好");writer.flush();writer.close();//一次写入一个字符数组OutputStreamWriter writer1 = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("F:\\output\\test2.xlsx"));char[] chars = {'1','2','3'};writer1.write(chars);writer1.flush();writer1.write(chars,1,2);writer1.close();}}
flush():刷新流,还可以继续写数据。
close():关闭流,释放资源 ,但是在关闭之前会先刷新流,一旦关闭就不能继续写入数据。
(3)字符流读数据的两种方式
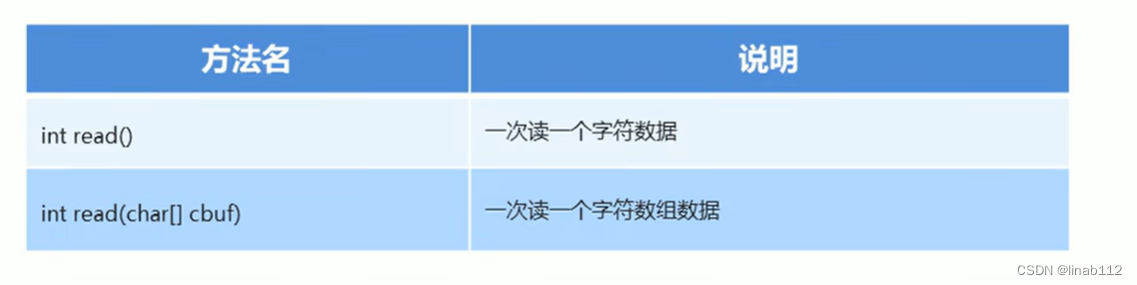
示例:
package com.example.demo.file;import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;/*** @Author linaibo* @Date 2023/2/25 10:19* @PackageName:com.example.demo.file* @ClassName: FileWriterDemo1* @Version 1.0*/
public class FileWriterDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//一次读取一个字符InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("F:\\output\\out.txt"));int num;while((num = reader.read()) != -1){System.out.print(num);}reader.close();//一次读取一个字符数组InputStreamReader reader2 = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("F:\\output\\out.txt"));char[] chars = new char[1024];int num2;while((num2 = reader2.read(chars)) != -1){System.out.print(new String(chars,0, chars.length));}reader2.close();}
}
复制文件的示例:
package com.example.demo.file;import java.io.*;/*** @Author linaibo* @Date 2023/2/25 10:31* @PackageName:com.example.demo.file* @ClassName: CopyFileDemo1* @Version 1.0*/
public class CopyFileDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 创建流InputStreamReader in = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("F:\\output\\test.txt"));OutputStreamWriter out = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("F:\\output\\test1.txt"));// 读取数据int num;char[] chars = new char[1024];while((num = in.read(chars)) != -1){out.write(chars,0, chars.length);}// 关闭流in.close();out.close();}
}
(4)FileReader及FileWriter
转换流的名字比较长,而我们常见的操作都是按照本地默认编码实现的,所以,为了简化书写,转换流提供了对应的子类,如果要指定其他编码,则不能使用此类。
FileReader:用于读取字符文件的便捷类。构造方法如下:
FileWriter:用于写入字符文件的便捷类。构造方法如下:
 示例:
示例:
(5)字符缓冲流
BufferedWriter: 将文本写入字符输出流,缓冲字符,以提供单个字符,数组和字符串的高效写入,可以指定缓冲区大小,或者可以接受默认大小。默认值足够大,可用于大多数用途。
BufferedReader: 从字符输入流读取文本,缓冲字符,以提供字符,数组和行的高效读取,可以指定缓冲区大小,或者可以使用默认大小。默认值足够大,可用于大多数用途。
构造方法:
BufferedWriter(Writer out)
BufferedReader(Readerin)
字符缓冲输出流示例:
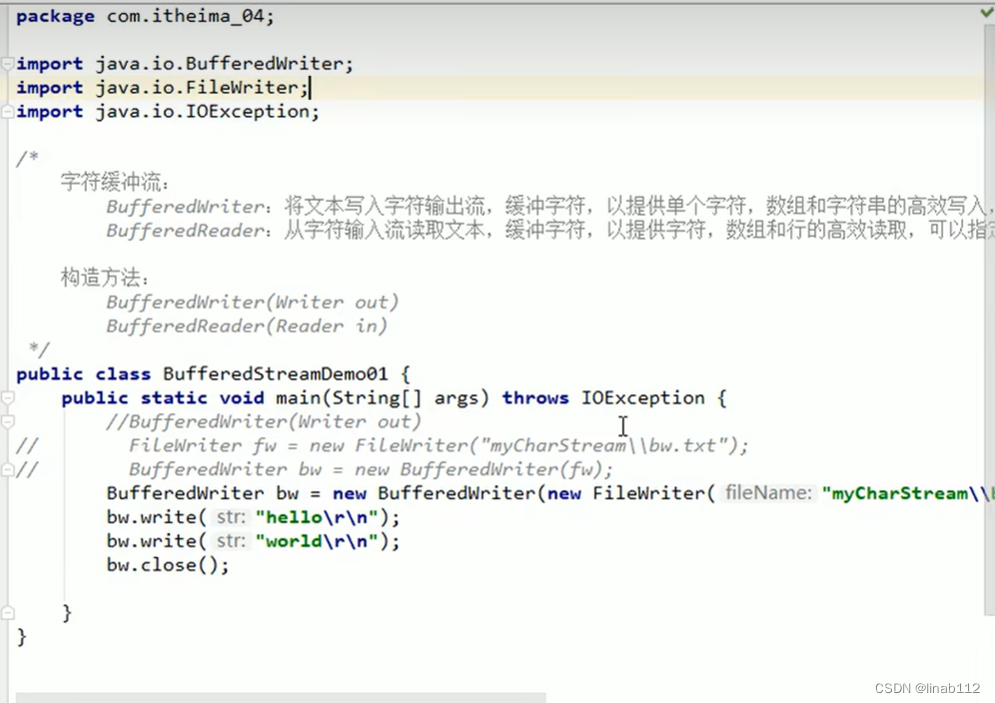
字符缓冲输入流示例:
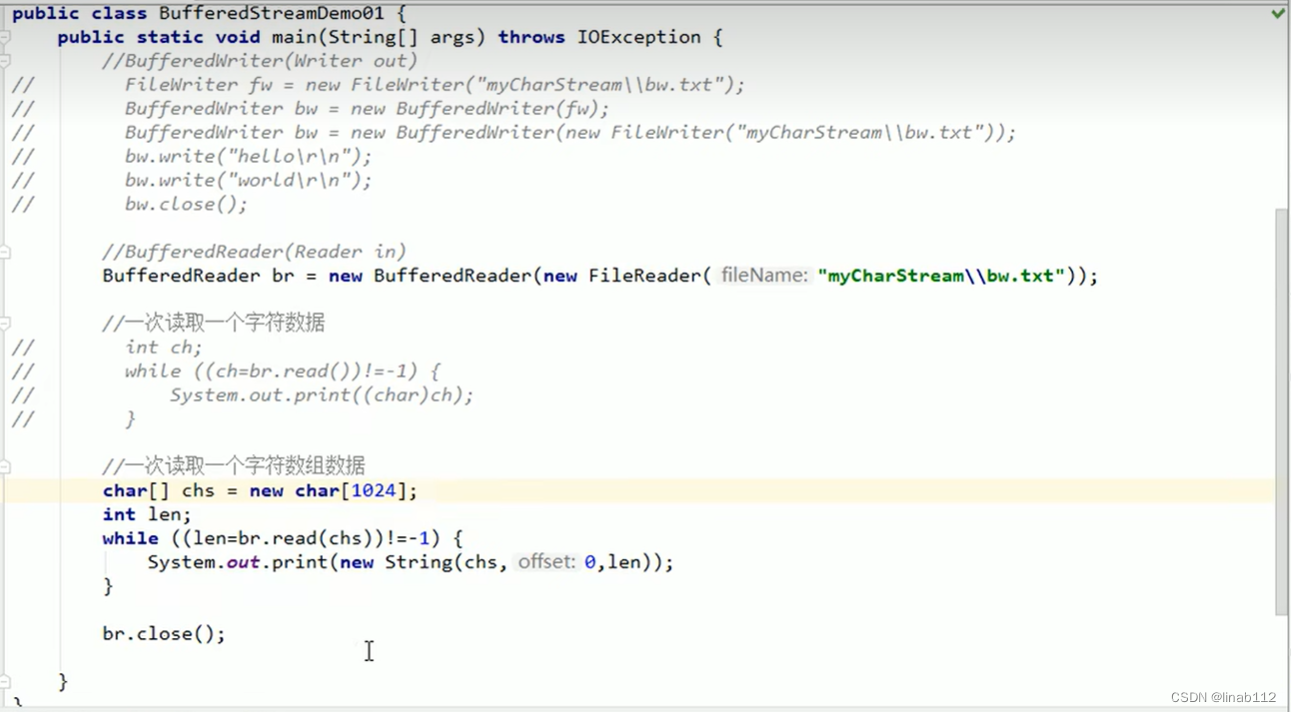
字符缓冲流复制文件案例:

(6)字符缓冲流的特有功能
BufferedWriter:
void newLine0:写一行行分隔符,行分隔符字符串由系统属性定义。
BufferedReader:
public String readLine(): 读一行文字。结果包含行的内容的字符串,不包括任何行终止字符,如果流的结尾已经到达,则为null。
示例1:
package com.example.demo.file;import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;/*** @Author linaibo* @Date 2023/2/25 10:57* @PackageName:com.example.demo.file* @ClassName: BufferWriterDemo1* @Version 1.0*/
public class BufferWriterDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("F:\\output\\test.txt"));for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {// 写入bw.write("abc");// 换行bw.newLine();// 刷新bw.flush();}// 关闭bw.close();}
}
示例2:
package com.example.demo.file;import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;/*** @Author linaibo* @Date 2023/2/25 11:02* @PackageName:com.example.demo.file* @ClassName: BufferReaderDemo* @Version 1.0*/
public class BufferReaderDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("F:\\output\\test.txt"));String line;while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {System.out.println(line);}br.close();}
}
示例3(复制文件):
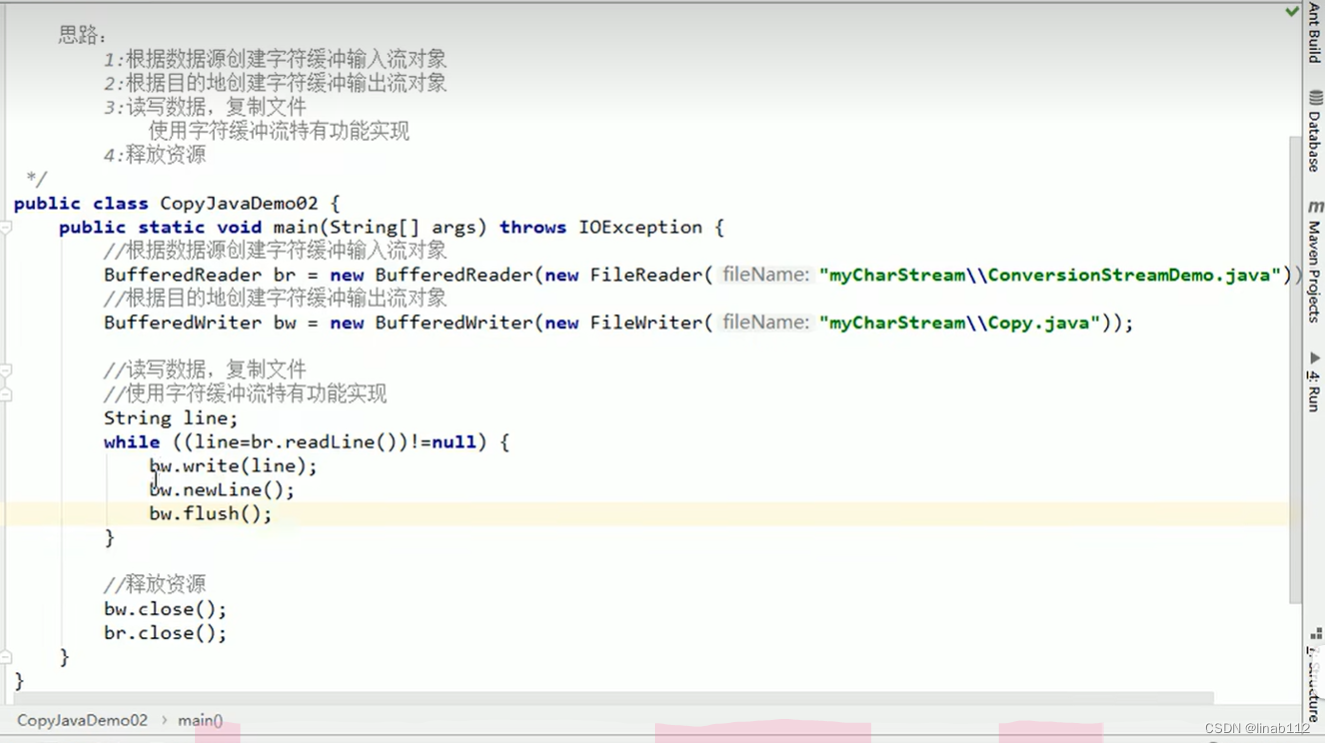
相关文章:

File类及IO流说明
目录 1.File类说明 (1)构造方法创建文件 (2)创建功能 (3)File类的判断和获取功能 (4)文件删除功能 2.I/O流说明 (1).分类 3.字节流写数据 (1)说明 (2)字节流写数据的三种方式 (3)写入时实现换行和追加写入 (4)异常处理中加入finally实现资源的释放 4.字节流读数据 …...
优秀的网络安全工程师应该有哪些能力?
网络安全工程师是一个各行各业都需要的职业,工作内容属性决定了它不会只在某一方面专精,需要掌握网络维护、设计、部署、运维、网络安全等技能。目前稍有经验的薪资在10K-30K之间,全国的网络安全工程师还处于一个供不应求的状态,因…...

[C++11] auto初始值类型推导
背景:旧标准的auto 在旧标准中,auto代表“具有自动存储期的 局部变量” auto int i 0; //具有自动存储期的局部变量 //C98/03,可以默认写成int i0; static int j 0; //静态类型的定义方法实际上,我们很少使用auto,…...

【Java】List集合去重的方式
List集合去重的方式方式一:利用TreeSet集合特性排序去重(有序)方式二:利用HashSet的特性去重(无序)方式三:利用LinkedHashSet去重(有序)方式四:迭代器去重&am…...
每个人都应该知道的5个NLP代码库
在本文中,将详细介绍目前常用的Python NLP库。内容译自网络。这些软件包可处理多种NLP任务,例如词性(POS)标注,依存分析,文档分类,主题建模等等。NLP库的基本目标是简化文本预处理。目前有许多工…...
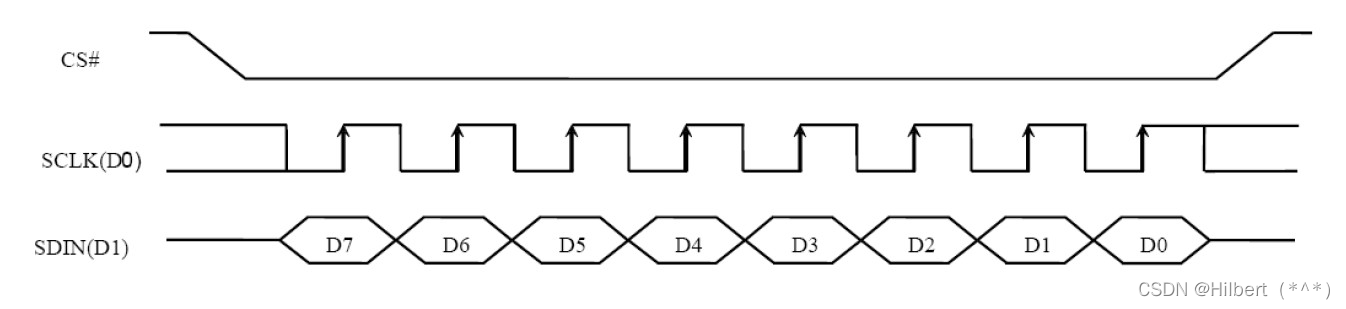
SPI协议介绍
SPI协议介绍 文章目录SPI协议介绍一、 SPI硬件知识1.1 硬件连线1.2 SPI控制器内部结构二、 SPI协议2.1 传输示例2.2 SPI模式致谢一、 SPI硬件知识 1.1 硬件连线 引脚含义如下: 引脚含义DO(MOSI)Master Output, Slave Input,SPI主控用来发出数据&#x…...

MySQL数据库中索引的优点及缺点
一、索引的优点 1)创建索引可以大幅提高系统性能,帮助用户提高查询的速度; 2)通过索引的唯一性,可以保证数据库表中的每一行数据的唯一性; 3)可以加速表与表之间的链接; 4&#…...
sort函数总结(基础篇))
(q)sort函数总结(基础篇)
1.sort函数 介绍:这是一个C的函数,包含于algorithm头文件中。 基本格式: sort(起始地址(常为变量名),排序终止的地址(变量名加上排序长度),自定义的比较函数) 重点&a…...

【数据库】MongoDB数据库详解
目录 一,数据库管理系统 1, 什么是数据库 2,什么是数据库管理系统 二, NoSQL 是什么 1,NoSQL 简介 2,NoSQL数据库 3,NoSQL 与 RDBMS 对比 三,MongoDB简介 1, MongoDB 是什…...
【linux】进程间通信——system V
system V一、system V介绍二 、共享内存2.1 共享内存的原理2.2 共享内存接口2.2.1 创建共享内存shmget2.2.2 查看IPC资源2.2.3 共享内存的控制shmctl2.2.4 共享内存的关联shmat2.2.5 共享内存的去关联shmdt2.3 进程间通信2.4 共享内存的特性2.5 共享内存的大小三、消息队列3.1 …...

计算机网络的基本组成
计算机网络是由多个计算机、服务器、网络设备(如路由器、交换机、集线器等)通过各种通信线路(如有线、无线、光纤等)和协议(如TCP/IP、HTTP、FTP等)互相连接组成的复杂系统,它们能够在物理层、数…...
【数据结构趣味多】Map和Set
1.概念及场景 Map和set是一种专门用来进行搜索的容器或者数据结构,其搜索的效率与其具体的实例化子类有关。 在此之前,我还接触过直接查询O(N)和二分查询O(logN),这两个查询有很多不足之出,直接查询的速率太低,而二分查…...

Redis 之企业级解决方案
文章目录一、缓存预热二、缓存雪崩三、缓存击穿四、缓存穿透五、性能指标监控5.1 监控指标5.2 监控方式🍌benchmark🍌monitor🍌slowlog提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容,Redis系列学习将会持续更新 一、缓存预热 1.1 现象…...
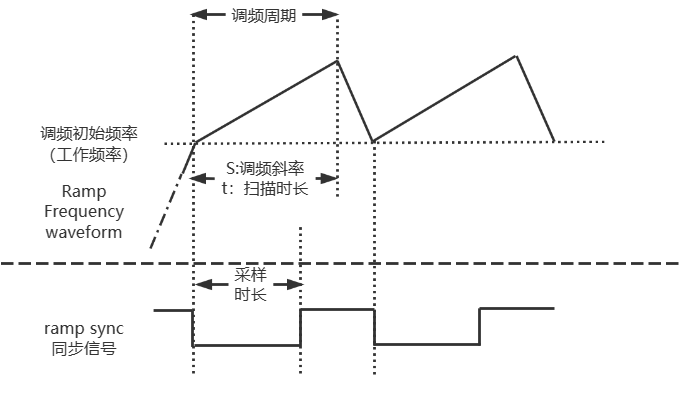
雷达实战之射频前端配置说明
在无线通信领域,射频系统主要分为射频前端,以及基带。从发射通路来看,基带完成语音等原始信息通过AD转化等手段转化成基带信号,然后经过调制生成包含跟多有效信息,且适合信道传输的信号,最后通过射频前端将信号发射出去…...

Android SDK删除内置的触宝输入法
问题 Android 8.1.0, 展锐平台。 过CTA认证,内置的触宝输入法会连接网络,且默认就获取到访问网络的权限,没有弹请求窗口访问用户,会导致过不了认证。 预置应用触宝输入法Go版连网未明示(开启后࿰…...

[202002][Spring 实战][第5版][张卫滨][译]
[202002][Spring 实战][第5版][张卫滨][译] habuma/spring-in-action-5-samples: Home for example code from Spring in Action 5. https://github.com/habuma/spring-in-action-5-samples 第 1 部分 Spring 基础 第 1 章 Spring 起步 1.1 什么是 Spring 1.2 初始化 Spr…...

H5视频上传与播放
背景 需求场景: 后台管理系统: (1)配置中支持上传视频、上传成功后封面缩略图展示,点击后自动播放视频; (2)配置中支持上传多个文件; 前台系统: &#…...
通过OpenAI来做机械智能故障诊断-测试(1)
通过OpenAI来做机械智能故障诊断 1. 注册使用2. 使用案例1-介绍故障诊断流程2.1 对话内容2.2 对话小结3. 使用案例2-写一段轴承故障诊断的代码3.1 对话内容3.2 对话小结4. 对话加载Paderborn轴承故障数据集并划分4.1 加载轴承故障数据集并划分第一次测试4.2 第二次加载数据集自…...
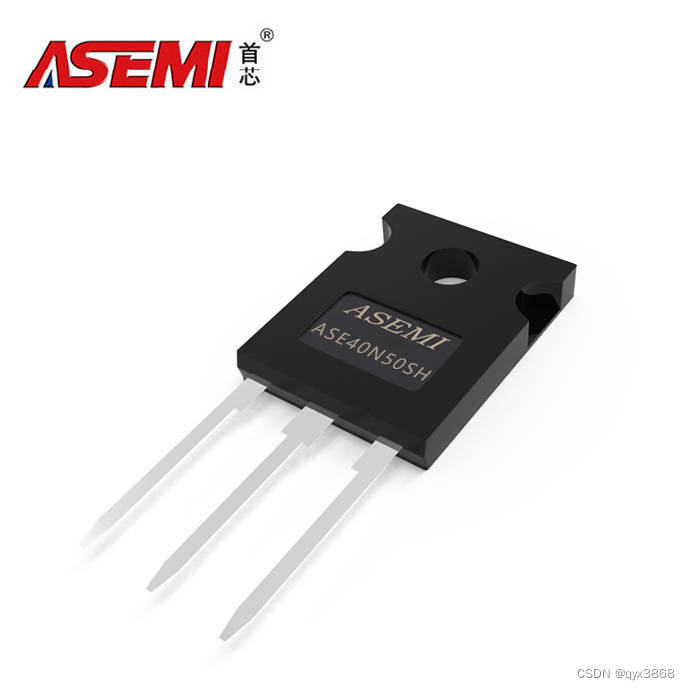

ASE40N50SH-ASEMI高压MOS管ASE40N50SH
编辑-Z ASE40N50SH在TO-247封装里的静态漏极源导通电阻(RDS(ON))为100mΩ,是一款N沟道高压MOS管。ASE40N50SH的最大脉冲正向电流ISM为160A,零栅极电压漏极电流(IDSS)为1uA,其工作时耐温度范围为-55~150摄氏度。ASE40N…...

MySQL基础命令大全——新手必看
Mysql 是一个流行的开源关系型数据库管理系统,广泛用于各种 Web 应用程序和服务器环境中。Mysql 有很多命令可以使用,以下是 Mysql 基础命令: 1、连接到Mysql服务器: mysql -h hostname -u username -p 其中,"ho…...

在鸿蒙HarmonyOS 5中实现抖音风格的点赞功能
下面我将详细介绍如何使用HarmonyOS SDK在HarmonyOS 5中实现类似抖音的点赞功能,包括动画效果、数据同步和交互优化。 1. 基础点赞功能实现 1.1 创建数据模型 // VideoModel.ets export class VideoModel {id: string "";title: string ""…...

蓝桥杯 2024 15届国赛 A组 儿童节快乐
P10576 [蓝桥杯 2024 国 A] 儿童节快乐 题目描述 五彩斑斓的气球在蓝天下悠然飘荡,轻快的音乐在耳边持续回荡,小朋友们手牵着手一同畅快欢笑。在这样一片安乐祥和的氛围下,六一来了。 今天是六一儿童节,小蓝老师为了让大家在节…...

Cilium动手实验室: 精通之旅---20.Isovalent Enterprise for Cilium: Zero Trust Visibility
Cilium动手实验室: 精通之旅---20.Isovalent Enterprise for Cilium: Zero Trust Visibility 1. 实验室环境1.1 实验室环境1.2 小测试 2. The Endor System2.1 部署应用2.2 检查现有策略 3. Cilium 策略实体3.1 创建 allow-all 网络策略3.2 在 Hubble CLI 中验证网络策略源3.3 …...

土地利用/土地覆盖遥感解译与基于CLUE模型未来变化情景预测;从基础到高级,涵盖ArcGIS数据处理、ENVI遥感解译与CLUE模型情景模拟等
🔍 土地利用/土地覆盖数据是生态、环境和气象等诸多领域模型的关键输入参数。通过遥感影像解译技术,可以精准获取历史或当前任何一个区域的土地利用/土地覆盖情况。这些数据不仅能够用于评估区域生态环境的变化趋势,还能有效评价重大生态工程…...
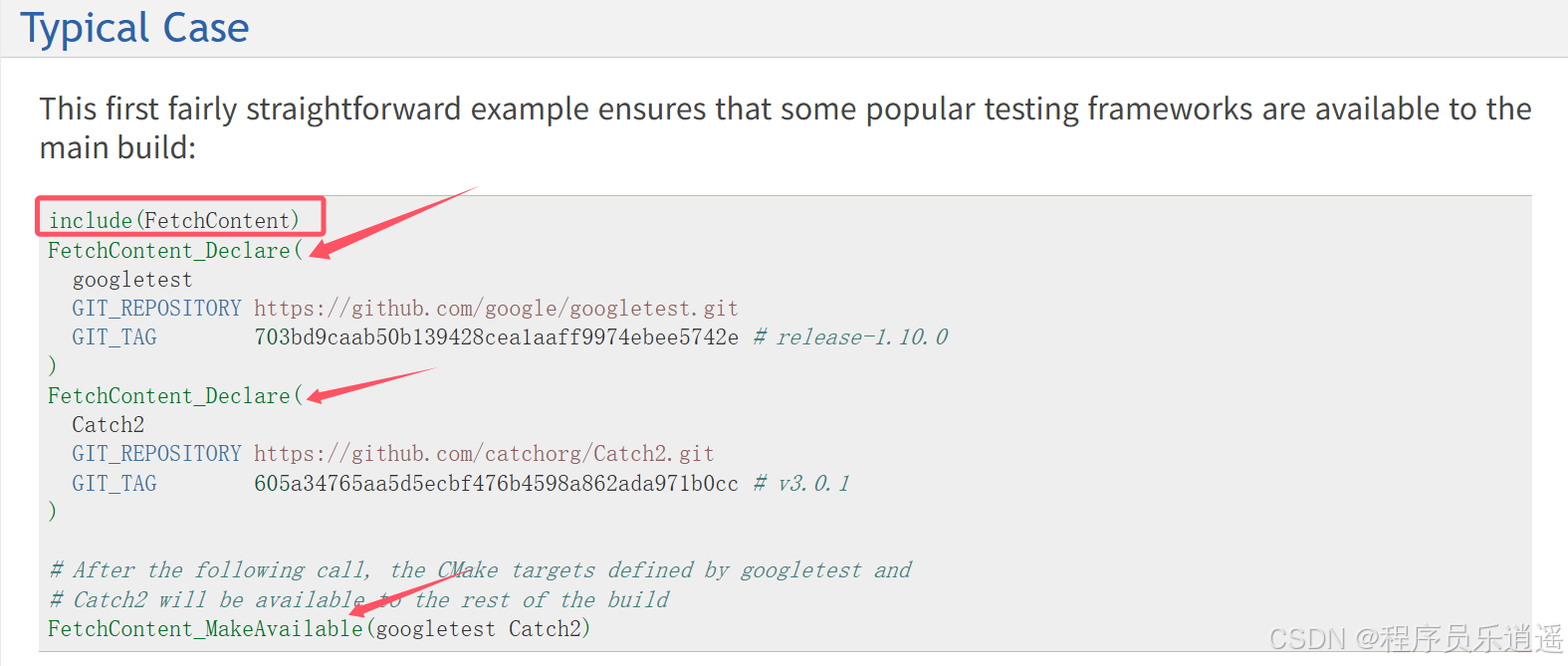
CMake 从 GitHub 下载第三方库并使用
有时我们希望直接使用 GitHub 上的开源库,而不想手动下载、编译和安装。 可以利用 CMake 提供的 FetchContent 模块来实现自动下载、构建和链接第三方库。 FetchContent 命令官方文档✅ 示例代码 我们将以 fmt 这个流行的格式化库为例,演示如何: 使用 FetchContent 从 GitH…...
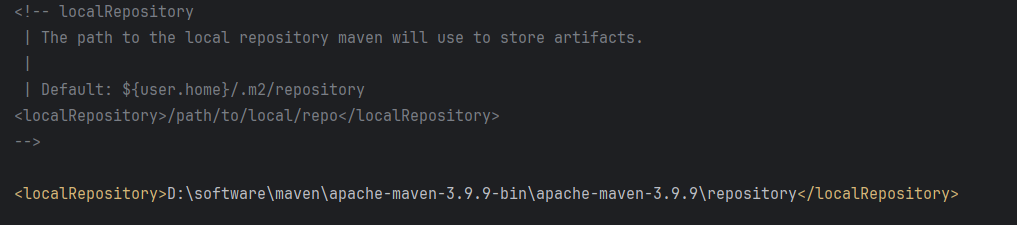
Maven 概述、安装、配置、仓库、私服详解
目录 1、Maven 概述 1.1 Maven 的定义 1.2 Maven 解决的问题 1.3 Maven 的核心特性与优势 2、Maven 安装 2.1 下载 Maven 2.2 安装配置 Maven 2.3 测试安装 2.4 修改 Maven 本地仓库的默认路径 3、Maven 配置 3.1 配置本地仓库 3.2 配置 JDK 3.3 IDEA 配置本地 Ma…...
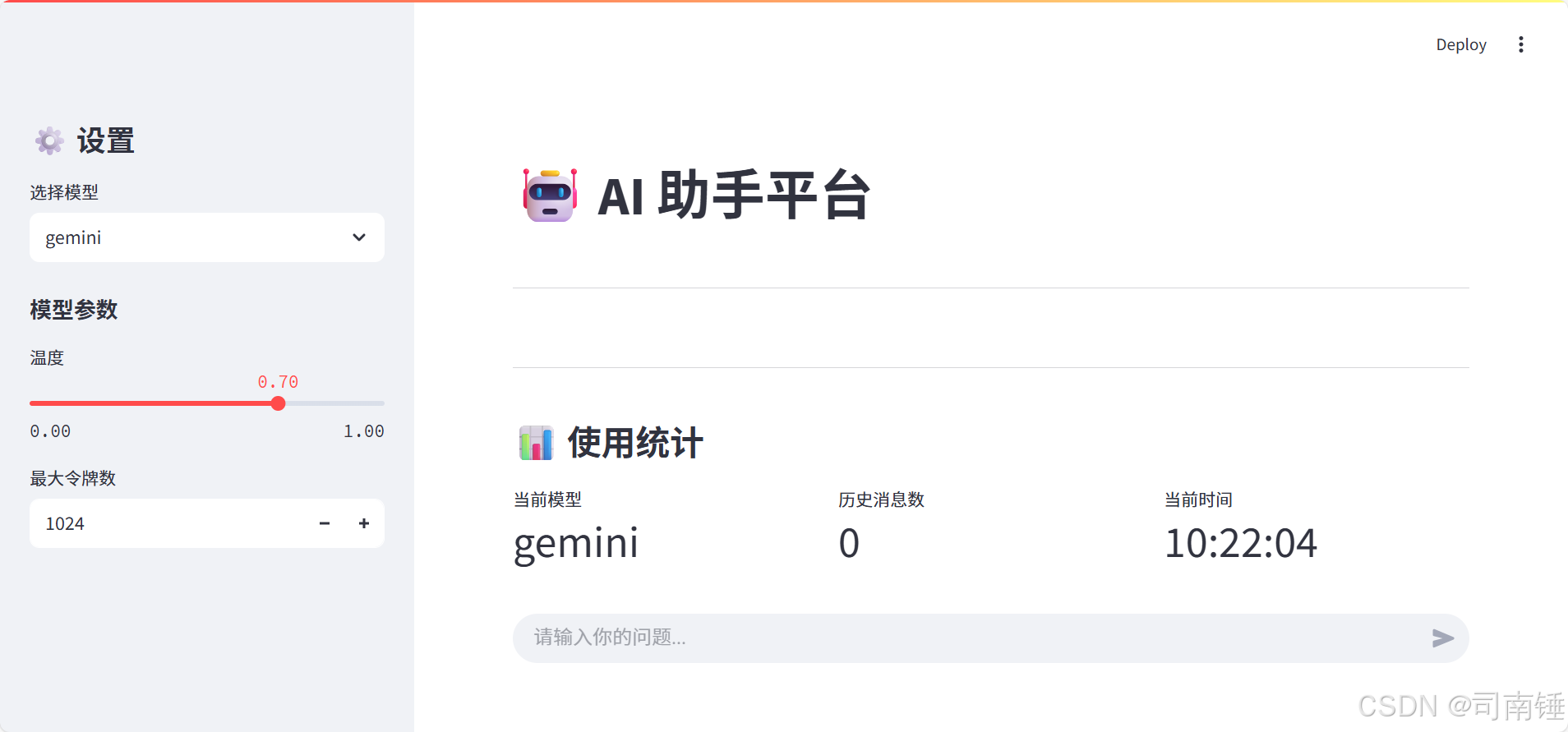
使用 Streamlit 构建支持主流大模型与 Ollama 的轻量级统一平台
🎯 使用 Streamlit 构建支持主流大模型与 Ollama 的轻量级统一平台 📌 项目背景 随着大语言模型(LLM)的广泛应用,开发者常面临多个挑战: 各大模型(OpenAI、Claude、Gemini、Ollama)接口风格不统一;缺乏一个统一平台进行模型调用与测试;本地模型 Ollama 的集成与前…...

CSS设置元素的宽度根据其内容自动调整
width: fit-content 是 CSS 中的一个属性值,用于设置元素的宽度根据其内容自动调整,确保宽度刚好容纳内容而不会超出。 效果对比 默认情况(width: auto): 块级元素(如 <div>)会占满父容器…...

JS手写代码篇----使用Promise封装AJAX请求
15、使用Promise封装AJAX请求 promise就有reject和resolve了,就不必写成功和失败的回调函数了 const BASEURL ./手写ajax/test.jsonfunction promiseAjax() {return new Promise((resolve, reject) > {const xhr new XMLHttpRequest();xhr.open("get&quo…...

LCTF液晶可调谐滤波器在多光谱相机捕捉无人机目标检测中的作用
中达瑞和自2005年成立以来,一直在光谱成像领域深度钻研和发展,始终致力于研发高性能、高可靠性的光谱成像相机,为科研院校提供更优的产品和服务。在《低空背景下无人机目标的光谱特征研究及目标检测应用》这篇论文中提到中达瑞和 LCTF 作为多…...
