[足式机器人]Part4 南科大高等机器人控制课 CH12 Robotic Motion Control
本文仅供学习使用
本文参考:
B站:CLEAR_LAB
笔者带更新-运动学
课程主讲教师:
Prof. Wei Zhang
课程链接 :
https://www.wzhanglab.site/teaching/mee-5114-advanced-control-for-robotics/
南科大高等机器人控制课 Ch12 Robotic Motion Control
- 1. Basic Linear Control Design
- 1.1 Error Response
- 1.2 Standard Second-Order Systems
- 1.3 Second-Order Response Characteristics
- 1.4 State-Space Controller Design
- 2. Motion Control Problems
- 2.1 Robotic Motion Control Problem
- 2.2 Variations in Robot Motion Control
- 3. Motion Control with Velocity/Acceleration as Input
- 3.1 Velocity-Resolved Control
- 3.2.1 Velocity-Resolved Joint Space Control
- 3.2.2 Velocity-Resolved Task Space Control
- 3.2 Acceleration-Resolved Control
- 3.2.1 Acceleration-Resolved Control in Joint Space
- 3.2.2 Acceleration-Resolved Control in Task Space
- 4. Motion Control with Torque as Input and Task Space Inverse Dynamics
- 4.1 Recall Properties of Robot Dynamics
- 4.2 Computed Torque Control
- 4.3 Inverse Dynamics Control
机器人——运动能力、计算能力、感知决策能力 的机电系统
1. Basic Linear Control Design
1.1 Error Response

Steady-state error : e s s = lim t → ∞ θ e ( t ) e_{\mathrm{ss}}=\underset{t\rightarrow \infty}{\lim}\theta _{\mathrm{e}}\left( t \right) ess=t→∞limθe(t)
Precent overshoot : P.O.
Rise time / Peak time :
Settling time : T s T_{\mathrm{s}} Ts
1.2 Standard Second-Order Systems
详细推导见 : (待补充)

1.3 Second-Order Response Characteristics
详细推导见 : (待补充)

1.4 State-Space Controller Design

- Eigenvalue assignment : Find control gain K K K such that e i g ( A − B K ) = e i g d e s i r e d eig\left( A-BK \right) =eig_{\mathrm{desired}} eig(A−BK)=eigdesired
- Solvability : We can always find such K K K if ( A , B ) \left( A,B \right) (A,B) is controllable ( r a n k ( m c ) = n rank\left( m_{\mathrm{c}} \right) =n rank(mc)=n)
- How to choose desired eigs? —— refer to 2nd-order system
specification (P.O. T s T_{\mathrm{s}} Ts T p T_{\mathrm{p}} Tp) ⇒ a r t \overset{art}{\Rightarrow} ⇒art dominant poles + other poles ⇒ \Rightarrow ⇒ e i g d e s i r e d eig_{\mathrm{desired}} eigdesired ⇒ s c i e n c e \overset{science}{\Rightarrow} ⇒science K K K
2. Motion Control Problems
2.1 Robotic Motion Control Problem
Dynamic equation of fully-acuated robot (with external force) : { τ = M ( q ) q ¨ + c ( q , q ˙ ) q ˙ + g ( q ) + J T ( q ) F e x t y = h ( q ) \begin{cases} \tau =M\left( q \right) \ddot{q}+c\left( q,\dot{q} \right) \dot{q}+g\left( q \right) +J^{\mathrm{T}}\left( q \right) \mathcal{F} _{\mathrm{ext}}\\ y=h\left( q \right)\\ \end{cases} {τ=M(q)q¨+c(q,q˙)q˙+g(q)+JT(q)Fexty=h(q)
q ∈ R n q\in \mathbb{R} ^n q∈Rn : joint positions (generalized coordinate)
τ ∈ R n \tau \in \mathbb{R} ^n τ∈Rn : joint torque (generalized input)
y y y : output (variable to be controlled) —— can be any func of q q q , e.g. y = q , y = [ T ( q ) ] ∈ S E ( 3 ) y=q,y=\left[ T\left( q \right) \right] \in SE\left( 3 \right) y=q,y=[T(q)]∈SE(3)
- Motion Control Problems : Let y y y track given reference y d y_{\mathrm{d}} yd
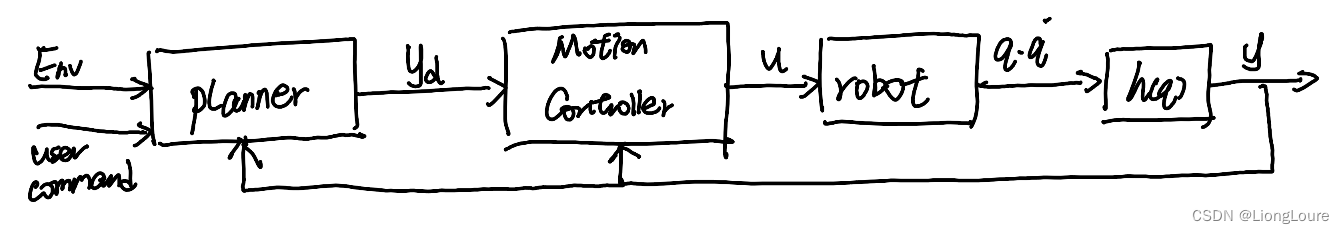
often times q d q_{\mathrm{d}} qd is given by planner represented by polynomials , so that q ˙ d , q ¨ d \dot{q}_{\mathrm{d}},\ddot{q}_{\mathrm{d}} q˙d,q¨d can be easily obtained
2.2 Variations in Robot Motion Control
-
Joint-space vs. Task-space control
Joint-space : y ( t ) = q ( t ) y\left( t \right) =q\left( t \right) y(t)=q(t) , i.e. , want q ( t ) q\left( t \right) q(t) to track a given q d ( t ) q_{\mathrm{d}}\left( t \right) qd(t) joint reference
Task-space : y ( t ) = [ T ( q ( t ) ) ] ∈ S E ( 3 ) y\left( t \right) =\left[ T\left( q\left( t \right) \right) \right] \in SE\left( 3 \right) y(t)=[T(q(t))]∈SE(3) denotes end-effector pose/configuration, we want y ( t ) y\left( t \right) y(t) to track y d ( t ) y_{\mathrm{d}}\left( t \right) yd(t) -
Actuation models:
Velocity source : u = q ˙ u=\dot{q} u=q˙ —— directly control velocity
Acceleration sources : u = q ¨ u=\ddot{q} u=q¨ —— directly control acceleration
Torque sources : u = τ u=\tau u=τ —— directly control torque

Acutation model make sense if for ant given u u u , the joint velocity q ˙ \dot{q} q˙ can immediatly reach u u u
Motion Control Problem
Design u u u to set y y y track desired reference y d y_{\mathrm{d}} yd
- Depending on our assumption on u / y u/y u/y
output y y y —— 6大基本问题
y ↔ q ∈ R n y\leftrightarrow q\in \mathbb{R} ^n y↔q∈Rn - joint variable : Joint space motion control (Velocity-resolved Joint-space control ; Acceleration-resolved Joint-space control ; Torque-resolved Joint-space control ; )
y ↔ [ T ( q ) ] ∈ S E ( 3 ) y\leftrightarrow \left[ T\left( q \right) \right] \in SE\left( 3 \right) y↔[T(q)]∈SE(3) or y = f ( q ) y=f\left( q \right) y=f(q) - task space variable - e.g. origin of end-effector frame : Task space motion control (Velocity-resolved Task-space ; Acceleration-resolved Task-space ; Torque-resolved Task-space ; )
Linear control / feedback lineariazation
3. Motion Control with Velocity/Acceleration as Input
3.1 Velocity-Resolved Control
Each joints’ velocity q ˙ i \dot{q}_{\mathrm{i}} q˙i can be directly controlled
Good approximation for hydraulic actuators
Common approxiamtion of the outer-loop control for the Inner / outer loop control setup

3.2.1 Velocity-Resolved Joint Space Control
Joint-space ‘dynamics’ : single integrator q ˙ = u \dot{q}=u q˙=u
Joint-space tracking becomes standard linear tracking control problem : u = q ˙ d + K 0 q ¨ ⇒ q ~ ˙ + K 0 q ¨ = 0 u=\dot{q}_{\mathrm{d}}+K_0\ddot{q}\Rightarrow \dot{\tilde{q}}+K_0\ddot{q}=0 u=q˙d+K0q¨⇒q~˙+K0q¨=0 , where q ~ = q d − q \tilde{q}=q_{\mathrm{d}}-q q~=qd−q is the joint position error. —— stable if e i g ( − K 0 ) ∈ O L H P eig\left( -K_0 \right) \in OLHP eig(−K0)∈OLHP
The error dynamic is stable if − K 0 -K_0 −K0 is Hurwitz
3.2.2 Velocity-Resolved Task Space Control
For task space control , y = [ T ( q ) ] y=\left[ T\left( q \right) \right] y=[T(q)] needs to track y d y_{\mathrm{d}} yd , y y y can be ant function of q q q, in particular , it can represents position and/or the end-effector frame
Taking derivatives of y y y , and letting u = q ˙ u=\dot{q} u=q˙ , we have : y ˙ = J a ( q ) u \dot{y}=J_{\mathrm{a}}\left( q \right) u y˙=Ja(q)u
Note that q q q is function of y y y through inverse kinematics ( q = I K ( y ) q=IK\left( y \right) q=IK(y))
So the above dynamics can be written in terms of y y y and u u u only. The detailed form can be quite complex in general y ˙ = J a ( I K ( y ) ) u \dot{y}=J_{\mathrm{a}}\left( IK\left( y \right) \right) u y˙=Ja(IK(y))u
- Let v y v_{\mathrm{y}} vy be virtual control y ˙ = v y \dot{y}=v_{\mathrm{y}} y˙=vy design v y v_{\mathrm{y}} vy to track y d y_{\mathrm{d}} yd (same as above)
- Find actual control u u u such that J a ( I K ( y ) ) u ≈ v y J_{\mathrm{a}}\left( IK\left( y \right) \right) u\approx v_{\mathrm{y}} Ja(IK(y))u≈vy


We can design outer-loop controller as if we can directly control y ˙ \dot{y} y˙
y ˙ = v y = y ˙ d + K ( y d − y ) ⟹ p l u g i n y ˙ = v y y ~ ˙ = − K y ~ \dot{y}=v_{\mathrm{y}}=\dot{y}_{\mathrm{d}}+K\left( y_{\mathrm{d}}-y \right) \overset{plug\,\,in\,\,\dot{y}=v_{\mathrm{y}}\,\,}{\Longrightarrow}\dot{\tilde{y}}=-K\tilde{y} y˙=vy=y˙d+K(yd−y)⟹pluginy˙=vyy~˙=−Ky~
We can select K K K such that − K -K −K is Hurtwiz , object of inner loop : determine u = q ˙ u=\dot{q} u=q˙ such that y ˙ ≈ v y \dot{y}\approx v_{\mathrm{y}} y˙≈vy
System(2) is nonlinear system , a commeon way is to break it into inner-outer loop , where the outer loop directly control velocity of y y y, and the inner loop tries to find u u u to generate desired task space velocity
Outer loop : y ˙ = v y \dot{y}=v_{\mathrm{y}} y˙=vy , where control v y = y ˙ d + K 0 y ~ v_{\mathrm{y}}=\dot{y}_{\mathrm{d}}+K_0\tilde{y} vy=y˙d+K0y~ , resulting in task-space closed-loop error dynamics: y ~ ˙ + K 0 y ~ = 0 \dot{\tilde{y}}+K_0\tilde{y}=0 y~˙+K0y~=0
Above task space tracking relies on a fictitious control v y v_{\mathrm{y}} vy , i.e. , it assumes y ˙ \dot{y} y˙ can be arbitrarily controlled by selecting appropriate u = q ˙ u=\dot{q} u=q˙ , which is true if J a J_{\mathrm{a}} Ja is full-row rank
Inner loop : Given v y v_{\mathrm{y}} vy from the outer loop, find the joint velocity control by solving
{ min u ∥ v y − J a ( q ) u ∥ 2 + r e g u l a r i z a t i o n t e r m s u b j . t o : C o n s t r a i n t s o n u , e . g . { q ˙ min ⩽ u ⩽ q ˙ max q min ⩽ q + u Δ t ⩽ q max \begin{cases} \min _{\mathrm{u}}\left\| v_{\mathrm{y}}-J_{\mathrm{a}}\left( q \right) u \right\| ^2+regularization\,\,term\\ subj.to\,\,: Constraints\,\,on\,\,u\,\,, e.g.\begin{cases} \dot{q}_{\min}\leqslant u\leqslant \dot{q}_{\max}\\ q_{\min}\leqslant q+u\varDelta t\leqslant q_{\max}\\ \end{cases}\\ \end{cases} ⎩ ⎨ ⎧minu∥vy−Ja(q)u∥2+regularizationtermsubj.to:Constraintsonu,e.g.{q˙min⩽u⩽q˙maxqmin⩽q+uΔt⩽qmax
Inner-loop is essentially a differential IK controller
One can also use the pseudo-inverse control u = J a † v y u={J_{\mathrm{a}}}^{\dagger}v_{\mathrm{y}} u=Ja†vy
3.2 Acceleration-Resolved Control
3.2.1 Acceleration-Resolved Control in Joint Space
Joint acceleration cna be directly controlled , resulting in double-integrator dynamics q ¨ = u \ddot{q}=u q¨=u . Given q d q_{\mathrm{d}} qd reference , we want q → q d q\rightarrow q_{\mathrm{d}} q→qd (double integartor)
Joint-space tracking becomes standard linear tracking control problem for double-integrator system:
u = q ¨ d + K 1 q ~ ˙ + K 0 q ~ = 0 , q ~ ∈ R n u=\ddot{q}_{\mathrm{d}}+K_1\dot{\tilde{q}}+K_0\tilde{q}=0,\tilde{q}\in \mathbb{R} ^n u=q¨d+K1q~˙+K0q~=0,q~∈Rn
—— PD control , closed-loop system , where q ~ = q d − q \tilde{q}=q_{\mathrm{d}}-q q~=qd−q is the joint position error.
Stablility condition : Let x = [ q ~ q ~ ˙ ] ∈ R 2 n x=\left[ \begin{array}{c} \tilde{q}\\ \dot{\tilde{q}}\\ \end{array} \right] \in \mathbb{R} ^{2n} x=[q~q~˙]∈R2n , [ 0 E − K 0 − K 1 ] [ q ~ q ~ ˙ ] , x ˙ = A x \left[ \begin{matrix} 0& E\\ -K_0& -K_1\\ \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{array}{c} \tilde{q}\\ \dot{\tilde{q}}\\ \end{array} \right] ,\dot{x}=Ax [0−K0E−K1][q~q~˙],x˙=Ax
closed-loop system is stable . if e i g ( A ) ∈ O L H P eig\left( A \right) \in OLHP eig(A)∈OLHP or A A A is Hurwitz
3.2.2 Acceleration-Resolved Control in Task Space
For task space control , y = [ T ( q ) ] ∈ S E ( 3 ) y=\left[ T\left( q \right) \right] \in SE\left( 3 \right) y=[T(q)]∈SE(3) needs to track y d y_{\mathrm{d}} yd

Note : For y = f ( q ) y=f\left( q \right) y=f(q) y ˙ = J a ( q ) q ˙ \dot{y}=J_{\mathrm{a}}\left( q \right) \dot{q} y˙=Ja(q)q˙ and y ¨ = J ˙ a ( q ) q ˙ + J a ( q ) q ¨ ⇒ y ¨ = J ˙ a ( q ) q ˙ + J a ( q ) u ⇐ \ddot{y}=\dot{J}_{\mathrm{a}}\left( q \right) \dot{q}+J_{\mathrm{a}}\left( q \right) \ddot{q}\Rightarrow \ddot{y}=\dot{J}_{\mathrm{a}}\left( q \right) \dot{q}+J_{\mathrm{a}}\left( q \right) u\Leftarrow y¨=J˙a(q)q˙+Ja(q)q¨⇒y¨=J˙a(q)q˙+Ja(q)u⇐ nonlinear dynamics
Following the same inner-outer loop strategy deiscussed before . Introduce virtual control , a y a_{\mathrm{y}} ay such that y ¨ = a y \ddot{y}=a_{\mathrm{y}} y¨=ay , we can design controller for a y a_{\mathrm{y}} ay to let y → y d y\rightarrow y_{\mathrm{d}} y→yd
Outer-loop dynamics : y ¨ = a y \ddot{y}=a_{\mathrm{y}} y¨=ay , with a y a_{\mathrm{y}} ay being the outer-loop control input a y = y ¨ d + K 1 y ~ ˙ + K 0 y ~ ⇒ y ~ ¨ + K 1 y ~ ˙ + K 0 y ~ = 0 a_{\mathrm{y}}=\ddot{y}_{\mathrm{d}}+K_1\dot{\tilde{y}}+K_0\tilde{y}\Rightarrow \ddot{\tilde{y}}+K_1\dot{\tilde{y}}+K_0\tilde{y}=0 ay=y¨d+K1y~˙+K0y~⇒y~¨+K1y~˙+K0y~=0
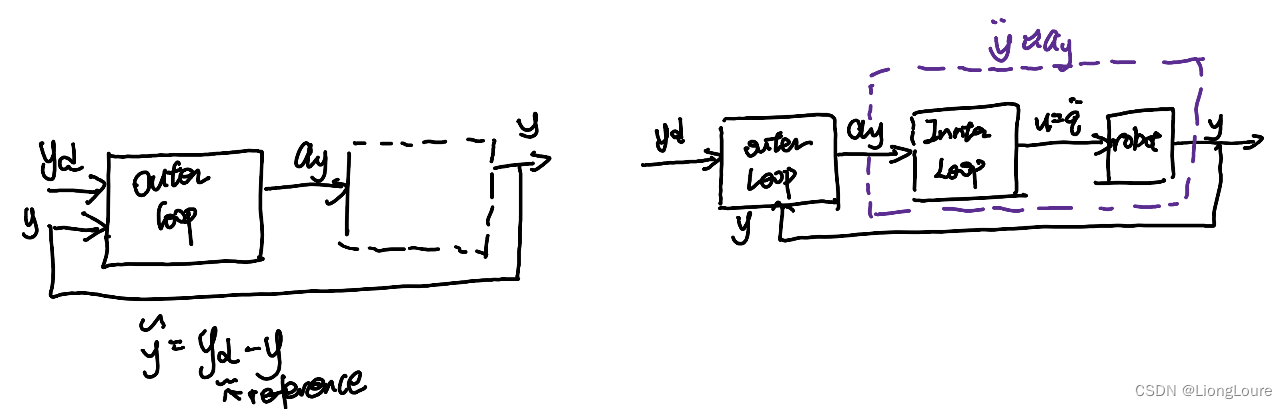
—— PD control , stable if [ 0 E − K 0 − K 1 ] \left[ \begin{matrix} 0& E\\ -K_0& -K_1\\ \end{matrix} \right] [0−K0E−K1] Hurwitz
Inner-loop : given a y a_{\mathrm{y}} ay from outer loop , find the “best” joint acceleration:
{ min u ∥ a y − J ˙ a ( q ) q ˙ − J a ( q ) u ∥ 2 + r e g u l a r i z a t i o n t e r m s u b j . t o : C o n s t r a i n t s o n u \begin{cases} \min _{\mathrm{u}}\left\| a_{\mathrm{y}}-\dot{J}_{\mathrm{a}}\left( q \right) \dot{q}-J_{\mathrm{a}}\left( q \right) u \right\| ^2+regularization\,\,term\\ subj.to\,\,: Constraints\,\,on\,\,u\,\,\\ \end{cases} ⎩ ⎨ ⎧minu ay−J˙a(q)q˙−Ja(q)u 2+regularizationtermsubj.to:Constraintsonu
—— u u u : optimization variable , J ˙ a ( q ) , q ˙ , q \dot{J}_{\mathrm{a}}\left( q \right) ,\dot{q},q J˙a(q),q˙,q - known
{ A c c : q ¨ min ⩽ u ⩽ q ¨ max V e l : q ˙ min ⩽ q + u Δ t ⩽ q ˙ max \begin{cases} Acc\,\,: \ddot{q}_{\min}\leqslant u\leqslant \ddot{q}_{\max}\\ Vel\,\,: \dot{q}_{\min}\leqslant q+u\varDelta t\leqslant \dot{q}_{\max}\\ \end{cases} {Acc:q¨min⩽u⩽q¨maxVel:q˙min⩽q+uΔt⩽q˙max
Mathematically , the above problem is the same as the Differential IK problem
At any given time , q ˙ , q \dot{q},q q˙,q can be measured , and then y , y ˙ y,\dot{y} y,y˙ can be computed, which allows us to compute outer loop control a y a_{\mathrm{y}} ay and inner loop control u u u
4. Motion Control with Torque as Input and Task Space Inverse Dynamics
4.1 Recall Properties of Robot Dynamics
For fully actuated robot :
τ = M ( q ) q ¨ + C ( q , q ˙ ) q ˙ + g ( q ) \tau =M\left( q \right) \ddot{q}+C\left( q,\dot{q} \right) \dot{q}+g\left( q \right) τ=M(q)q¨+C(q,q˙)q˙+g(q)
M ( q ) = ∑ J i T [ I i ] 6 × 6 J i ∈ R n × n M\left( q \right) =\sum{{J_{\mathrm{i}}}^{\mathrm{T}}\left[ \mathcal{I} _{\mathrm{i}} \right] _{6\times 6}J_{\mathrm{i}}}\in \mathbb{R} ^{n\times n} M(q)=∑JiT[Ii]6×6Ji∈Rn×n
There are many valid difinitions of C ( q , q ˙ ) C\left( q,\dot{q} \right) C(q,q˙) , typical choice for C C C include:
C i j = ∑ k 1 2 ( ∂ M i j ∂ q k + ∂ M i k ∂ q j − ∂ M j k ∂ q i ) C_{\mathrm{ij}}=\sum_k^{}{\frac{1}{2}\left( \frac{\partial M_{\mathrm{ij}}}{\partial q_{\mathrm{k}}}+\frac{\partial M_{\mathrm{ik}}}{\partial q_{\mathrm{j}}}-\frac{\partial M_{\mathrm{jk}}}{\partial q_{\mathrm{i}}} \right)} Cij=∑k21(∂qk∂Mij+∂qj∂Mik−∂qi∂Mjk)
For the above defined C C C , we have M ˙ − 2 C \dot{M}-2C M˙−2C is skew symmetric
For all valid C C C, we have q ˙ T [ M ˙ − 2 C ] q ˙ = 0 \dot{q}^{\mathrm{T}}\left[ \dot{M}-2C \right] \dot{q}=0 q˙T[M˙−2C]q˙=0
These properties play improtant role in designing motion controller
4.2 Computed Torque Control
For fully-actuated robot, we have M ( q ) ≻ 0 M\left( q \right) \succ 0 M(q)≻0 and q ¨ \ddot{q} q¨ can be arbitrarily specified through torque control u = τ u=\tau u=τ
q ¨ = M − 1 ( q ) [ u − C ( q , q ˙ ) q ˙ − g ( q ) ] \ddot{q}=M^{-1}\left( q \right) \left[ u-C\left( q,\dot{q} \right) \dot{q}-g\left( q \right) \right] q¨=M−1(q)[u−C(q,q˙)q˙−g(q)]
we know how to design controller if u = q ¨ u=\ddot{q} u=q¨

Thus , for fully-acuated robot, torque controlled case can be reduced to the acceleration-resolved case
Outer loop: q ¨ = a q \ddot{q}=a_{\mathrm{q}} q¨=aq with joint acceleration as control input
a q = q ¨ + K 1 y ~ ˙ + K 0 y ~ ⇒ q ~ ¨ + K 1 q ~ ˙ + K 0 q ~ = 0 a_{\mathrm{q}}=\ddot{q}+K_1\dot{\tilde{y}}+K_0\tilde{y}\Rightarrow \ddot{\tilde{q}}+K_1\dot{\tilde{q}}+K_0\tilde{q}=0 aq=q¨+K1y~˙+K0y~⇒q~¨+K1q~˙+K0q~=0
Inner loop : since M ( q ) M\left( q \right) M(q) is square and nonsingular , inner loop control u u u can be found analytically:
u = M ( q ) ( q ¨ d + K 1 q ~ ˙ + K 0 q ~ ) + C ( q , q ˙ ) q ˙ + g ( q ) u=M\left( q \right) \left( \ddot{q}_{\mathrm{d}}+K_1\dot{\tilde{q}}+K_0\tilde{q} \right) +C\left( q,\dot{q} \right) \dot{q}+g\left( q \right) u=M(q)(q¨d+K1q~˙+K0q~)+C(q,q˙)q˙+g(q)

The control law is a function of q , q ˙ q,\dot{q} q,q˙ and the reference q d q_{\mathrm{d}} qd. It is called computed-torque control.
The control law also relies on system model M , C , g M,C,g M,C,g if these model information are not accurate, the control will not perform well.
y = f ( q ) , y ¨ = J ˙ a ( q ) q ˙ + J a ( q ) M − 1 ( u − C − g ) y=f\left( q \right) ,\ddot{y}=\dot{J}_{\mathrm{a}}\left( q \right) \dot{q}+J_{\mathrm{a}}\left( q \right) M^{-1}\left( u-C-g \right) y=f(q),y¨=J˙a(q)q˙+Ja(q)M−1(u−C−g)
Idea easily extends to task space : y ˙ = J a ( q ) q ˙ \dot{y}=J_{\mathrm{a}}\left( q \right) \dot{q} y˙=Ja(q)q˙ and y ¨ = J ˙ a ( q ) q ˙ + J a ( q ) q ¨ \ddot{y}=\dot{J}_{\mathrm{a}}\left( q \right) \dot{q}+J_{\mathrm{a}}\left( q \right) \ddot{q} y¨=J˙a(q)q˙+Ja(q)q¨ —— τ = u = τ , q ¨ = M − 1 [ u − C − g ] \tau =u=\tau ,\ddot{q}=M^{-1}\left[ u-C-g \right] τ=u=τ,q¨=M−1[u−C−g]
Outer loop : y ¨ = a y \ddot{y}=a_{\mathrm{y}} y¨=ay and a y = y ¨ d + K 1 y ~ ˙ + K 0 y ~ a_{\mathrm{y}}=\ddot{y}_{\mathrm{d}}+K_1\dot{\tilde{y}}+K_0\tilde{y} ay=y¨d+K1y~˙+K0y~
Inner loop : sekect torque control u = τ u=\tau u=τ by
{ min u ∥ a y − J ˙ a ( q ) q ˙ − J a ( q ) M − 1 ( u − C q ˙ − g ) ∥ 2 s u b j . t o : C o n s t r a i n t s \begin{cases} \min _{\mathrm{u}}\left\| a_{\mathrm{y}}-\dot{J}_{\mathrm{a}}\left( q \right) \dot{q}-J_{\mathrm{a}}\left( q \right) M^{-1}\left( u-C\dot{q}-g \right) \right\| ^2\\ subj.to\,\,: Constraints\,\,\\ \end{cases} ⎩ ⎨ ⎧minu ay−J˙a(q)q˙−Ja(q)M−1(u−Cq˙−g) 2subj.to:Constraints
If J a J_{\mathrm{a}} Jais invertible and we don’t impose additional torque constraints, analytical control law can be easily obtained —— u = ( J a ( q ) M − 1 ) − 1 ( a y − J ˙ a ( q ) q ˙ . . . ) u=\left( J_{\mathrm{a}}\left( q \right) M^{-1} \right) ^{-1}\left( a_{\mathrm{y}}-\dot{J}_{\mathrm{a}}\left( q \right) \dot{q}... \right) u=(Ja(q)M−1)−1(ay−J˙a(q)q˙...)
4.3 Inverse Dynamics Control
The computed-torque controller above is also canned inverse dynamics control
Forward dynamics : given τ \tau τ to compute q ¨ \ddot{q} q¨ —— from torque to motion
Inverse dynamics : given desired acceleration a q a_{\mathrm{q}} aq, we inverted it to find the required control by u = M a q + C q ˙ + g u=Ma_{\mathrm{q}}+C\dot{q}+g u=Maq+Cq˙+g
Task space case can be viewed as inverting the task space dynamics —— Given a y a_{\mathrm{y}} ay ( y y y task space) , find τ \tau τ such that y ¨ = a y \ddot{y}=a_{\mathrm{y}} y¨=ay
With recent advances in optimization , it is often preferred to do ID with quedratic program

For example, above equation can be viewed as task-space ID. We can incorporate torque contraints explicitly as follows:
{ min u ∥ a y − J ˙ a ( q ) q ˙ − J a M − 1 ( u − C q ˙ − g ) ∥ 2 s u b j . t o : u − ⩽ u ⩽ u + \begin{cases} \min _{\mathrm{u}}\left\| a_{\mathrm{y}}-\dot{J}_{\mathrm{a}}\left( q \right) \dot{q}-J_{\mathrm{a}}M^{-1}\left( u-C\dot{q}-g \right) \right\| ^2\\ subj.to\,\,: u_-\leqslant u\,\,\leqslant u_+\,\,\\ \end{cases} ⎩ ⎨ ⎧minu ay−J˙a(q)q˙−JaM−1(u−Cq˙−g) 2subj.to:u−⩽u⩽u+
optimization variable u ∈ R n u\in \mathbb{R} ^n u∈Rn
This is equivalent to the following more popular form:
{ min u , q ¨ ∥ a y − J ˙ a q ˙ − J a q ¨ ∥ 2 s u b j . t o : M q ¨ + C q ˙ + g = u u − ⩽ u ∈ R n ⩽ u + \begin{cases} \underset{u,\ddot{q}}{\min}\left\| a_{\mathrm{y}}-\dot{J}_{\mathrm{a}}\dot{q}-J_{\mathrm{a}}\ddot{q} \right\| ^2\\ subj.to\,\,: \begin{array}{c} M\ddot{q}+C\dot{q}+g=u\\ u_-\leqslant u\in \mathbb{R} ^n\,\,\leqslant u_+\,\,\\ \end{array}\\ \end{cases} ⎩ ⎨ ⎧u,q¨min ay−J˙aq˙−Jaq¨ 2subj.to:Mq¨+Cq˙+g=uu−⩽u∈Rn⩽u+
optimization variable u , q ¨ ∈ R n u,\ddot{q}\in \mathbb{R} ^n u,q¨∈Rn
相关文章:

[足式机器人]Part4 南科大高等机器人控制课 CH12 Robotic Motion Control
本文仅供学习使用 本文参考: B站:CLEAR_LAB 笔者带更新-运动学 课程主讲教师: Prof. Wei Zhang 课程链接 : https://www.wzhanglab.site/teaching/mee-5114-advanced-control-for-robotics/ 南科大高等机器人控制课 Ch12 Robotic …...
)
【C++】知识点汇总(上)
C知识点复习上 一、C 概述1. 基本数据类型2. 变量定义和访问3. 常量与约束访问 二、程序控制结构详解与示例1. 表达式2. 选择控制2.1 if 语句2.2 switch 语句 3. 循环控制3.1 for 循环3.2 while 循环3.3 do-while 循环 4. goto 语句5. 控制语句的嵌套 三、函数1. 函数的定义和调…...

解决docker容器内无法连接宿主redis
背景 小程序的发短信服务挂了,随查看日志,该报错日志如下 Error 111 connecting to 127.0.0.1:6379. Connection refused. 6379是监听redis服务的端口,那大概是redis出错了。 首先查看了redis是否正常启动,检查出服务正常。 由于小…...
43 tmpfs/devtmpfs 文件系统
前言 在 linux 中常见的文件系统 有很多, 如下 基于磁盘的文件系统, ext2, ext3, ext4, xfs, btrfs, jfs, ntfs 内存文件系统, procfs, sysfs, tmpfs, squashfs, debugfs 闪存文件系统, ubifs, jffs2, yaffs 文件系统这一套体系在 linux 有一层 vfs 抽象, 用户程序不用…...
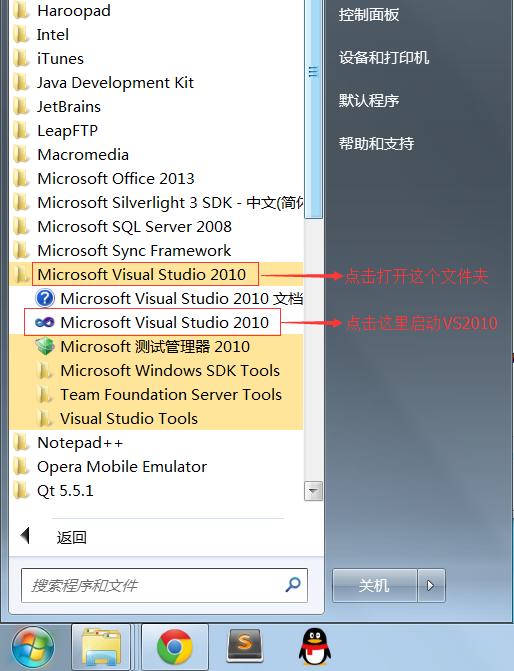
C语言编译器(C语言编程软件)完全攻略(第十二部分:VS2010下载地址和安装教程(图解))
介绍常用C语言编译器的安装、配置和使用。 十二、VS2010下载地址和安装教程(图解) 为了更好地支持 Win7 程序的开发,微软于2010年4月12日发布了 VS2010,它的界面被重新设计,变得更加简洁。需要注意的是,V…...

【VRTK】【VR开发】【Unity】18-VRTK与Unity UI控制的融合使用
课程配套学习项目源码资源下载 https://download.csdn.net/download/weixin_41697242/88485426?spm=1001.2014.3001.5503 【背景】 VRTK和Unity自身的UI控制包可以配合使用发挥效果。本篇就讨论这方面的实战内容。 之前可以互动的立体UI并不是传统的2D UI对象,在实际使用中…...
BERT(从理论到实践): Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers【3】
这是本系列文章中的第3弹,请确保你已经读过并了解之前文章所讲的内容,因为对于已经解释过的概念或API,本文不会再赘述。 本文要利用BERT实现一个“垃圾邮件分类”的任务,这也是NLP中一个很常见的任务:Text Classification。我们的实验环境仍然是Python3+Tensorflow/Keras…...
静态网页设计——校园官网(HTML+CSS+JavaScript)
前言 声明:该文章只是做技术分享,若侵权请联系我删除。!! 使用技术:HTMLCSSJS 主要内容:对学校官网的结构进行模仿,对布局进行模仿。 主要内容 1、首页 首页以多个div对页面进行分割和布局…...
phpstudy_pro 关于多版本php的问题
我在phpstudy中安装了多个PHP版本 我希望不同的网站可以对应不同的PHP版本,则在nginx配置文件中需要知道不同的PHP版本的监听端口是多少,如下图所示 然而找遍了php.ini配置,并未对listen进行设置,好奇是怎么实现不同的PHP监听不同…...
TemporalKit的纯手动安装
最近在用本地SD安装temporalkit插件 本地安装插件最常见的问题就是,GitCommandError:… 原因就是,没有科学上网,而且即使搭了ladder,在SD的“从网址上安装”或是“插件安装”都不行,都不行!!&am…...

人生重开模拟器
前言: 人生重开模拟器是前段时间非常火的一个小游戏,接下来我们将一起学习使用c语言写一个简易版的人生重开模拟器。 网页版游戏: 人生重开模拟器 (ytecn.com) 1.实现一个简化版的人生重开模拟器 (1) 游戏开始的时…...

优化算法3D可视化
编程实现优化算法,并3D可视化 1. 函数3D可视化 分别画出 和 的3D图 import numpy as np from matplotlib import pyplot as plt import torch# 画出x**2 class Op(object):def __init__(self):passdef __call__(self, inputs):return self.forward(inputs)def for…...
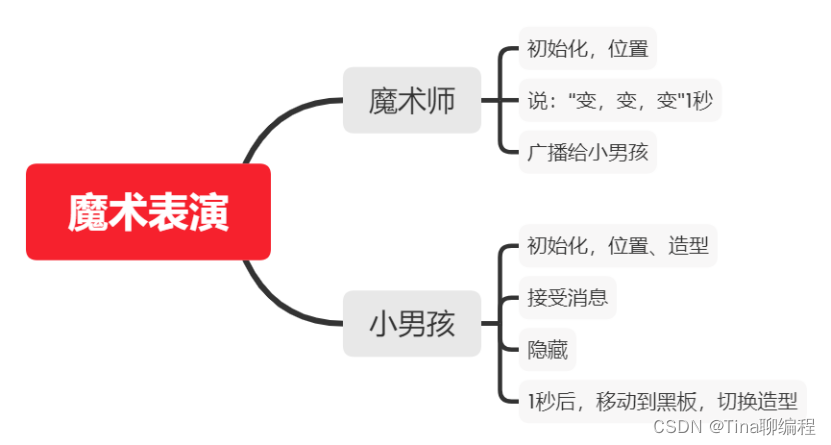
魔术表演Scratch-第14届蓝桥杯Scratch省赛真题第1题
1.魔术表演(20分) 评判标准: 4分:满足"具体要求"中的1); 8分:满足"具体要求"中的2); 8分,满足"具体要求"中的3)…...
LLM 中的长文本问题
近期,随着大模型技术的发展,长文本问题逐渐成为热门且关键的问题,不妨简单梳理一下近期出现的典型的长文本模型: 10 月上旬,Moonshot AI 的 Kimi Chat 问世,这是首个支持 20 万汉字输入的智能助手产品; 10 月下旬,百川智能发布 Baichuan2-192K 长窗口大模型,相当于一次…...

深入了解Swagger注解:@ApiModel和@ApiModelProperty实用指南
在现代软件开发中,提供清晰全面的 API 文档 至关重要。ApiModel 和 ApiModelProperty 这样的代码注解在此方面表现出色,通过增强模型及其属性的元数据来丰富文档内容。它们的主要功能是为这些元素命名和描述,使生成的 API 文档更加明确。 Api…...

Linux学习第48天:Linux USB驱动试验:保持热情,保持节奏,持续学习是作为一个技术人员应有的基本素质和要求
Linux版本号4.1.15 芯片I.MX6ULL 大叔学Linux 品人间百味 思文短情长 最近更新的速度和频率大不如以前,主要原因还是自己有些懈怠了。学习是一个持续努力的过程,一旦中断,再想保持以往的状态可能要…...

数据库索引简析
文章目录 前言一、索引是什么二、索引的有什么用三、索引的分类四、索引的数据结构总结 前言 在我们使用数据库的过程中,往往会碰到一个叫做索引的东西,不管是表的设计,还是数据库性能的优化往往都会涉及到索引。那么他是个什么东西ÿ…...
leetcode贪心(单调递增的数字、监控二叉树)
738.单调递增的数字 给定一个非负整数 N,找出小于或等于 N 的最大的整数,同时这个整数需要满足其各个位数上的数字是单调递增。 (当且仅当每个相邻位数上的数字 x 和 y 满足 x < y 时,我们称这个整数是单调递增的。ÿ…...

如何在win7同样支持Webview2 在 WPF 中使用本地 Webview2 ,如何不依赖系统 Runtime
项目运行环境: .Net Framework 4.5.2 Windows 7 x64 Service Pack 1 WebView2 Microsoft.WebView2.FixedVersionRuntime.120.0.2210.91.x64 考虑到很多老项目,本项目使用的是.Net Framework 4.5.2,.Net 更高版本的其实也是可以支持的。 …...

【docker】网络模式管理
目录 一、Docker网络实现原理 二、Docker的网络模式 1、host模式 1.1 host模式原理 1.2 host模式实操 2、Container模式 2.2 container模式实操 3、none模式 4、bridger模式 4.1 bridge模式的原理 4.2 bridge实操 5、overlay模式 6、自定义网络模式 6.1 为什么需要…...
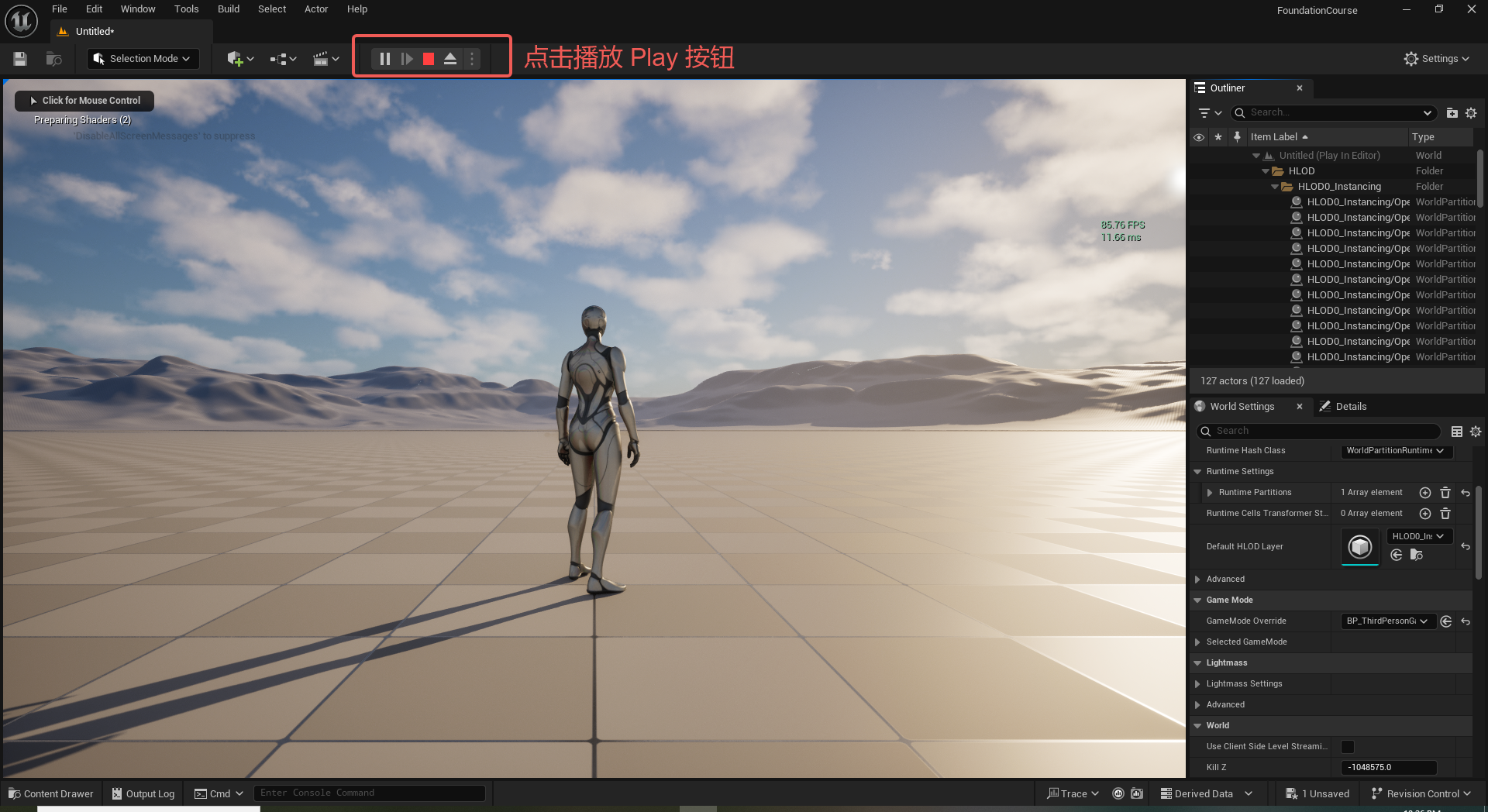
UE5 学习系列(二)用户操作界面及介绍
这篇博客是 UE5 学习系列博客的第二篇,在第一篇的基础上展开这篇内容。博客参考的 B 站视频资料和第一篇的链接如下: 【Note】:如果你已经完成安装等操作,可以只执行第一篇博客中 2. 新建一个空白游戏项目 章节操作,重…...

日语AI面试高效通关秘籍:专业解读与青柚面试智能助攻
在如今就业市场竞争日益激烈的背景下,越来越多的求职者将目光投向了日本及中日双语岗位。但是,一场日语面试往往让许多人感到步履维艰。你是否也曾因为面试官抛出的“刁钻问题”而心生畏惧?面对生疏的日语交流环境,即便提前恶补了…...
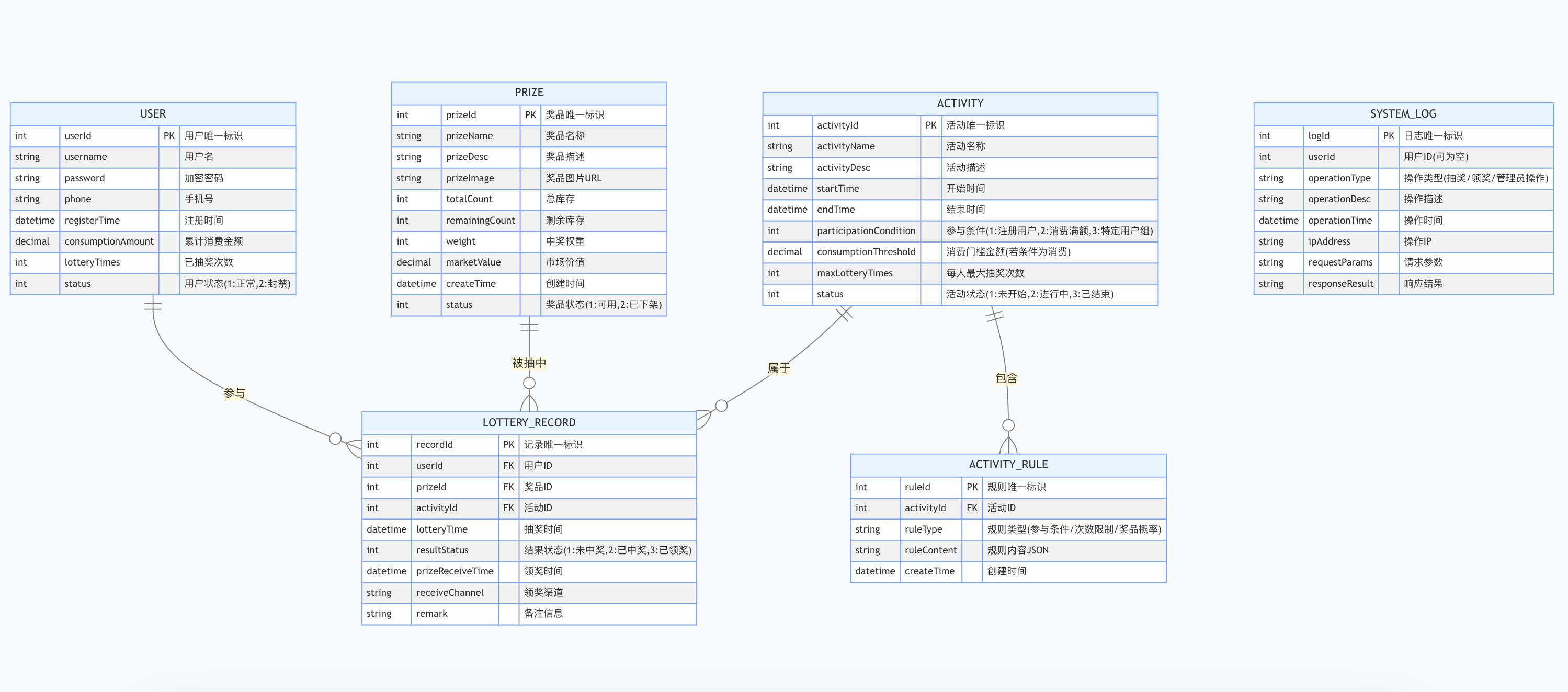
简易版抽奖活动的设计技术方案
1.前言 本技术方案旨在设计一套完整且可靠的抽奖活动逻辑,确保抽奖活动能够公平、公正、公开地进行,同时满足高并发访问、数据安全存储与高效处理等需求,为用户提供流畅的抽奖体验,助力业务顺利开展。本方案将涵盖抽奖活动的整体架构设计、核心流程逻辑、关键功能实现以及…...

在鸿蒙HarmonyOS 5中实现抖音风格的点赞功能
下面我将详细介绍如何使用HarmonyOS SDK在HarmonyOS 5中实现类似抖音的点赞功能,包括动画效果、数据同步和交互优化。 1. 基础点赞功能实现 1.1 创建数据模型 // VideoModel.ets export class VideoModel {id: string "";title: string ""…...

2024年赣州旅游投资集团社会招聘笔试真
2024年赣州旅游投资集团社会招聘笔试真 题 ( 满 分 1 0 0 分 时 间 1 2 0 分 钟 ) 一、单选题(每题只有一个正确答案,答错、不答或多答均不得分) 1.纪要的特点不包括()。 A.概括重点 B.指导传达 C. 客观纪实 D.有言必录 【答案】: D 2.1864年,()预言了电磁波的存在,并指出…...

多模态商品数据接口:融合图像、语音与文字的下一代商品详情体验
一、多模态商品数据接口的技术架构 (一)多模态数据融合引擎 跨模态语义对齐 通过Transformer架构实现图像、语音、文字的语义关联。例如,当用户上传一张“蓝色连衣裙”的图片时,接口可自动提取图像中的颜色(RGB值&…...
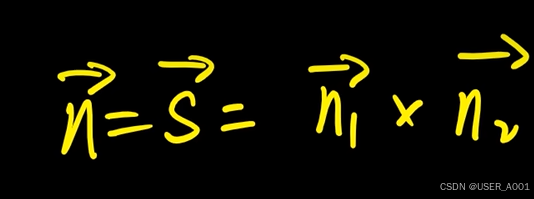
高等数学(下)题型笔记(八)空间解析几何与向量代数
目录 0 前言 1 向量的点乘 1.1 基本公式 1.2 例题 2 向量的叉乘 2.1 基础知识 2.2 例题 3 空间平面方程 3.1 基础知识 3.2 例题 4 空间直线方程 4.1 基础知识 4.2 例题 5 旋转曲面及其方程 5.1 基础知识 5.2 例题 6 空间曲面的法线与切平面 6.1 基础知识 6.2…...
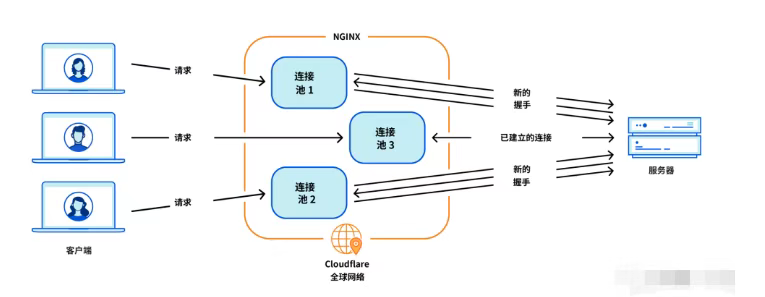
Cloudflare 从 Nginx 到 Pingora:性能、效率与安全的全面升级
在互联网的快速发展中,高性能、高效率和高安全性的网络服务成为了各大互联网基础设施提供商的核心追求。Cloudflare 作为全球领先的互联网安全和基础设施公司,近期做出了一个重大技术决策:弃用长期使用的 Nginx,转而采用其内部开发…...

鱼香ros docker配置镜像报错:https://registry-1.docker.io/v2/
使用鱼香ros一件安装docker时的https://registry-1.docker.io/v2/问题 一键安装指令 wget http://fishros.com/install -O fishros && . fishros出现问题:docker pull 失败 网络不同,需要使用镜像源 按照如下步骤操作 sudo vi /etc/docker/dae…...

Python 包管理器 uv 介绍
Python 包管理器 uv 全面介绍 uv 是由 Astral(热门工具 Ruff 的开发者)推出的下一代高性能 Python 包管理器和构建工具,用 Rust 编写。它旨在解决传统工具(如 pip、virtualenv、pip-tools)的性能瓶颈,同时…...
