C++(1) —— 基础语法入门
目录
一、C++初识
1.1 第一个C++程序
1.2 注释
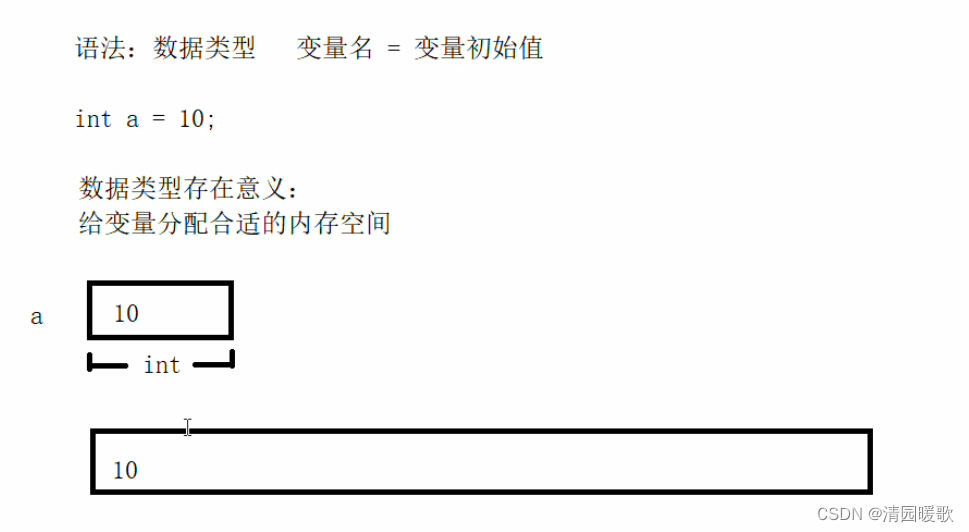
1.3 变量
1.4 常量
1.5 关键字
1.6 标识符命名规则
二、数据类型
2.1 整型
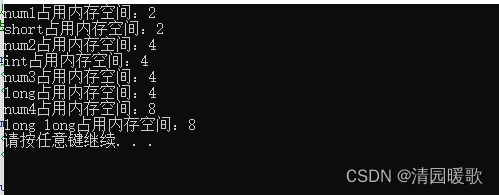
2.2 sizeof 关键字
2.3 实型(浮点型)
2.4 字符型
2.5 转义字符
2.6 字符串型
2.7 布尔类型 bool
2.8 数据的输入
三、运算符
3.1 算术运算符
3.1.1 加减乘除运算
3.1.2 取模运算(%)
3.1.3 递增递减(++、--)
3.2 赋值运算符
3.3 比较运算符
3.4 逻辑运算符
3.4.1 非(!)
3.4.2 与(&&)
3.4.3 或(||)
四、程序流程结构
4.1 选择结构
4.1.1 单行 if 语句
4.1.2 多行 if 语句
4.1.3 多条件 if 语句
4.1.4 嵌套 if 语句
4.1.5 练习:三只小猪称体重
4.1.6 三目运算符
4.1.7 switch 语句
4.2 循环结构
4.2.1 while 循环语句
4.2.2 while 循环练习案例:猜数字
4.2.3 do...while 循环语句
4.2.4 do...while 练习案例:水仙花数
4.2.5 for 循环
4.2.6 for 练习案例:敲桌子
4.2.7 嵌套循环
4.2.8 嵌套练习案例:乘法口诀表
4.3 跳转语句
4.3.1 break 语句
4.3.2 continue 语句
4.3.3 goto 语句
五、数组
5.1 概述
5.2 一维数组
5.2.1 一维数组定义方式
5.2.2 一维数组数组名
5.2.3 一维数组练习案例1:五只小猪称体重
5.2.4 一维数组练习案例2:数组元素逆置
5.2.5 冒泡排序
5.3 二维数组
5.3.1 二维数组定义方式
5.3.2 二维数组数组名
5.3.3 二维数组应用案例:考试成绩统计
六、函数
6.1 概述
6.2 函数的定义
6.3 函数的调用
6.4 值传递
6.5 函数的常见样式
6.6 函数的声明
6.7 函数的分文件编写
七、指针
7.1 指针的基本概念
7.2 指针变量的定义和使用
7.3 指针所占内存空间
7.4 空指针和野指针
7.5 const修饰指针
7.6 指针和数组
7.7 指针和函数
7.8 指针、数组、函数
八、结构体
8.1 结构体基本概念
8.2 结构体定义和使用
8.3 结构体数组
8.4 结构体指针
8.5 结构体嵌套结构体
8.6 结构体做函数参数
8.7 结构体中 const使用场景
8.8 结构体案例
8.8.1 案例1
8.8.2 案例2
视频:
01 课程安排_哔哩哔哩_bilibili

ctrl + k +c :多行注释
ctrl + k +u :解注释
一、C++初识
1.1 第一个C++程序

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{cout << "hello world" << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}
1.2 注释

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;// 1、单行注释/*2、多行注释
*/int main()
{// 输出 hello worldcout << "hello world" << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}1.3 变量

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{int a = 10;cout << "a = " << a << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}1.4 常量

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;// 常量的定义方式/*1、#define 宏常量2、const修饰的变量
*/// 1、define
#define Day 7int main()
{// Day = 14; // 会报错cout << "一周总共有:" << Day << "天" << endl;// 2、constconst int month = 12;// month = 24; // 错误,constx修饰的变量也成为常量cout << "一年总共有:" << month << "个月份" << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}1.5 关键字

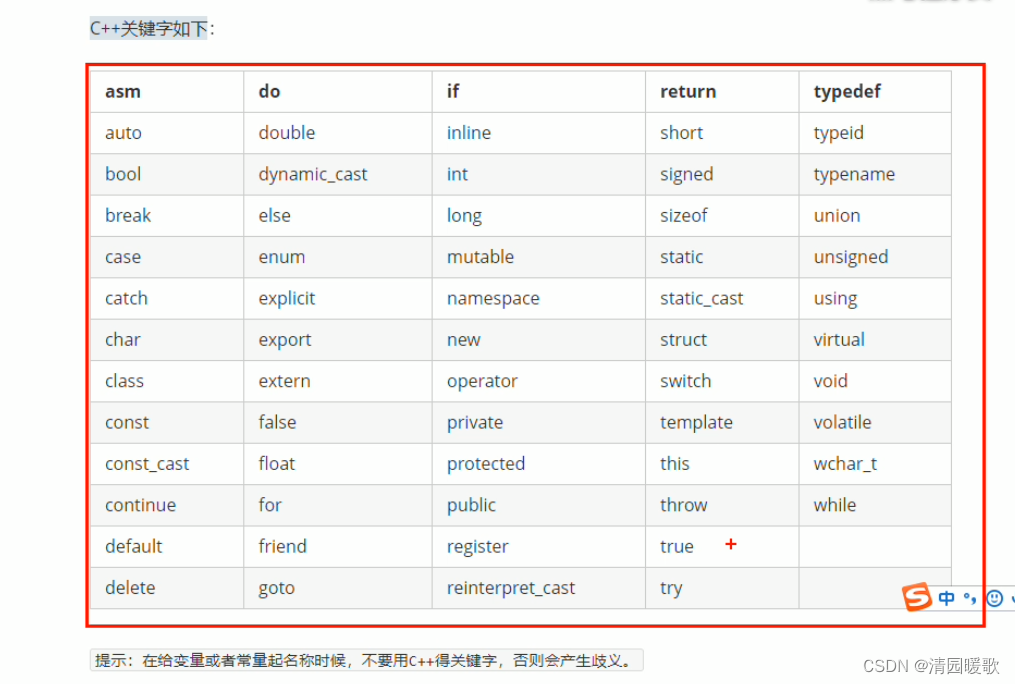
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{// 创建变量:数据类型 变量名称 = 变量初始值// 不要用关键子给变量或常量起名称int a = 10;cout << "hello world" << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}1.6 标识符命名规则

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;// 标识符命名规则
// 1、标识符b不可以是关键字
// 2、标识符是由字母、数字、下划线构成
// 3、标识符第一个字符只能是字符或下划线
// 4、标识符是区分大小写的int main()
{// 1、//int int = 10;// 2、int abc = 10;int _abc = 20;int _123abc = 30;// 3、// int 123abc = 40;// 4、int aaa = 100;cout << aaa << endl;// cout << AAA << endl; // aaa 和 AAA 不同 // 建议:给变量起名的时候,最好能够做到见名知意int num1 = 10;int num2 = 20;int sum = num1 + num2;cout << sum << endl;cout << "hello world" << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}二、数据类型
2.1 整型
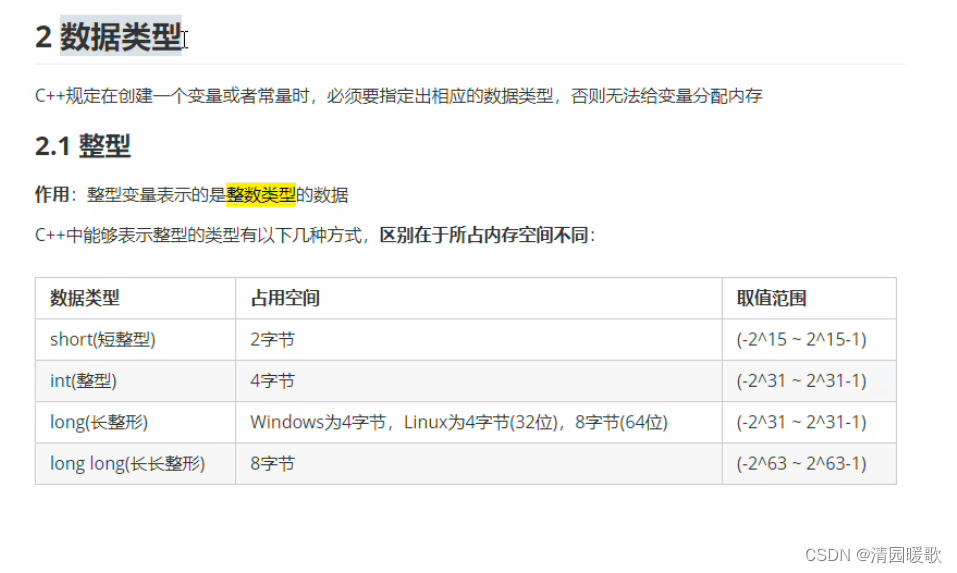
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{// 整型// 1、短整型(-32768 ~ 32767)short num1 = 10;// short num1 = 32768; // 输出是 -32768// 2、整型int num2 = 20;// 3、长整型long num3 = 30;// 4、长长整型long long num4 = 40;cout << "num1 = " << num1 << endl;cout << "num2 = " << num2 << endl;cout << "num3 = " << num3 << endl;cout << "num4 = " << num4 << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}
2.2 sizeof 关键字

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{// 整型:short (2) int (4) long (4) long long (8)// 可以利用sizeof求出数据类型占用内存大小// 语法: sizeof(数据类型/变量)short num1 = 10;cout << "num1占用内存空间:" << sizeof(num1) << endl;cout << "short占用内存空间:" << sizeof(short) << endl;int num2 = 10;cout << "num2占用内存空间:" << sizeof(num2) << endl;cout << "int占用内存空间:" << sizeof(int) << endl;long num3 = 10;cout << "num3占用内存空间:" << sizeof(num3) << endl;cout << "long占用内存空间:" << sizeof(long) << endl;long long num4 = 10;cout << "num4占用内存空间:" << sizeof(num4) << endl;cout << "long long占用内存空间:" << sizeof(long long) << endl;// 整型大小比较// short < int <= long <= long longsystem("pause");return 0;
}
2.3 实型(浮点型)

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{// 1、单精度 float// 2、双精度 double// 默认情况下 输出一个小数,会显示出6位有效数字float f1 = 3.1415926f; // float f1 = 3.14 的话3.14会默认当作 double,再转成 floatcout << "f1 = " << f1 << endl;double d1 = 3.1415926;cout << "d1 = " << d1 << endl;// 统计 float 和 double 占用内存空间cout << "float 占用内存空间为:" << sizeof(float) << endl; // 4字节cout << "double 占用内存空间为:" << sizeof(double) << endl; // 8字节// 科学计数法float f2 = 3e2; // 3*10^2cout << "f2 = " << f2 << endl;float f3 = 3e-2; // 3*0.1^2cout << "f3 = " << f3 << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}
2.4 字符型
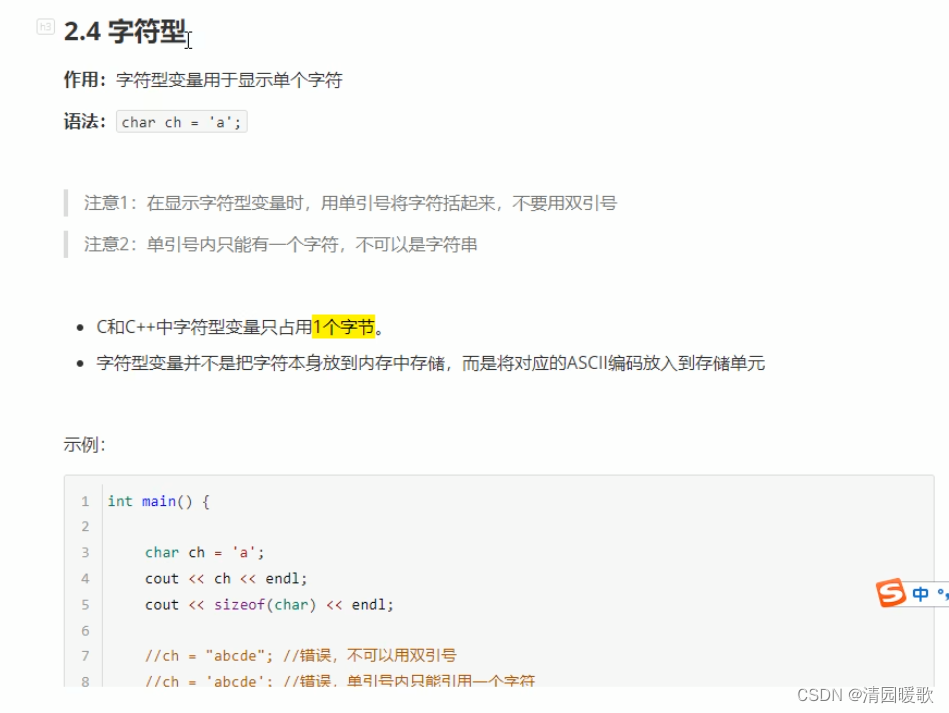
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
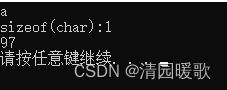
{// 1、字符型变量创建方式char ch = 'a';cout << ch << endl;// 2、字符型变量所占内存大小cout << "sizeof(char):" << sizeof(char) << endl;// 3、字符型变量常见错误// char ch2 = "b"; // 不能用双引号// char ch2 = 'abcdef' // 创建字符型变量单引号内只能有一个字符// 4、字符型变量对应 ASCII 编码// a - 97// A - 65cout << (int)ch << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}

2.5 转义字符
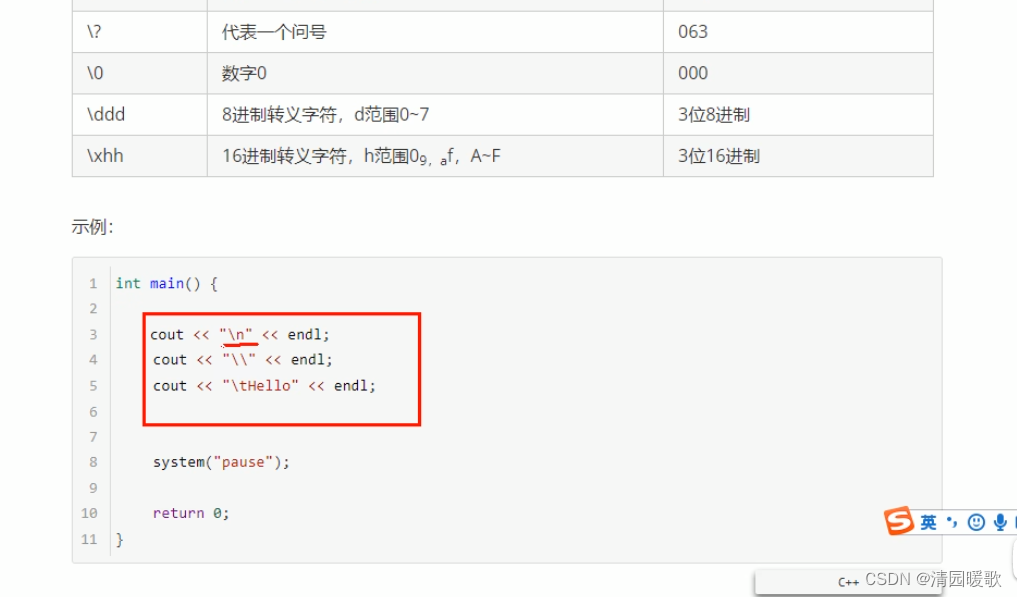
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{// 转义字符// 换行符 \ncout << "hello world\n" << endl;// 反斜杠 \\cout << "\\" << endl;// 水平制表符 \tcout << "aaa\thello world" << endl;cout << "a\thello world" << endl;cout << "aaaaa\thello world" << endl;// \t 占了4个位置,有3个a,后面就有5个空格// 最大用处:输出对齐system("pause");return 0;
}
2.6 字符串型
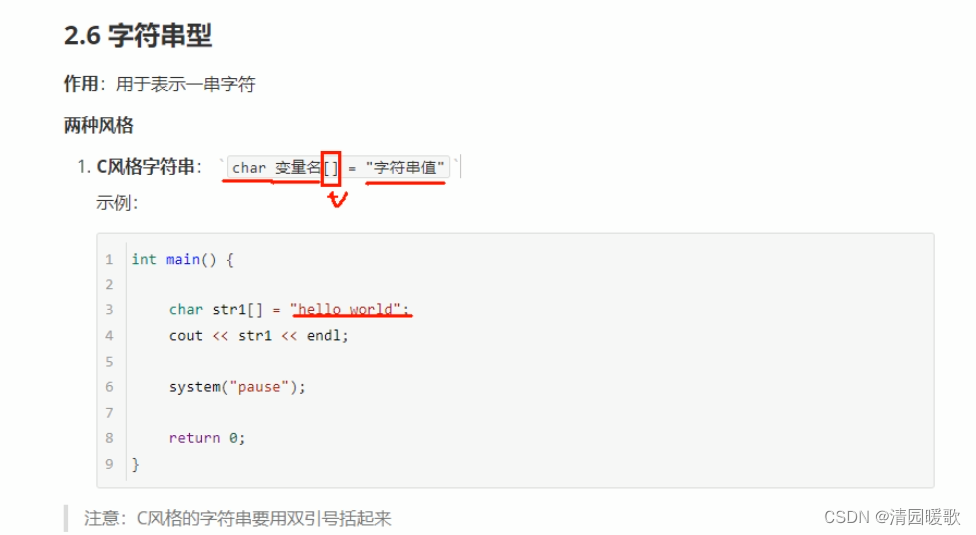
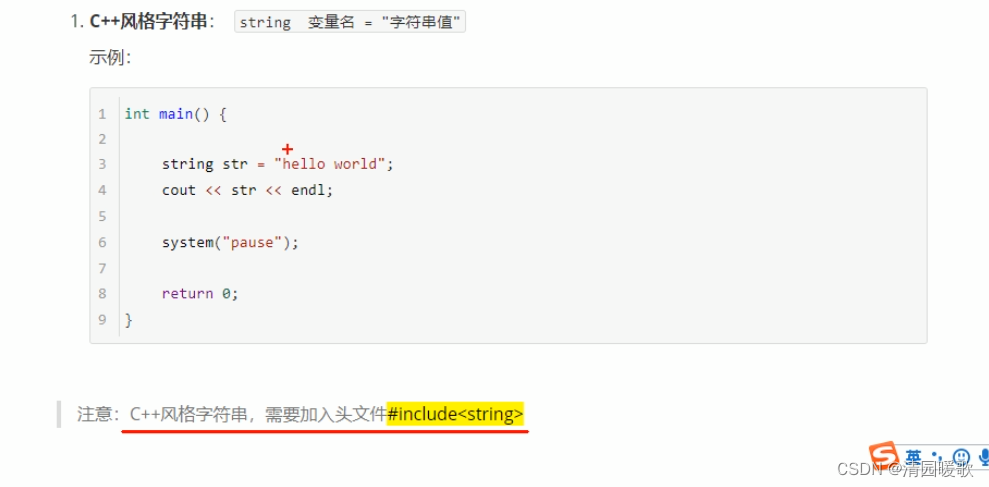
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <string> // 用C++风格字符串的时候,要包含这个头文件int main()
{// 1、C风格字符串// 注意事项 char 字符串名 []// 注意事项2 等号后面 要用双引号 包含起来字符串char str[] = "hello world";cout << str << endl;cout << "hello world" << endl;// 2、C++风格字符串// 包含一个头文件 #include <string>string str2 = "hello world";cout << str2 << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}
2.7 布尔类型 bool

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <string> // 用C++风格字符串的时候,要包含这个头文件int main()
{// 1、创建bool数据类型bool flag = true; // true代表真cout << flag << endl;flag = false; // false代表假cout << flag << endl;// 本质上 1代表真 0代表假// 2、查看bool类型所占内存空间cout << "bool类型所占内存空间:" << sizeof(bool) << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}
2.8 数据的输入

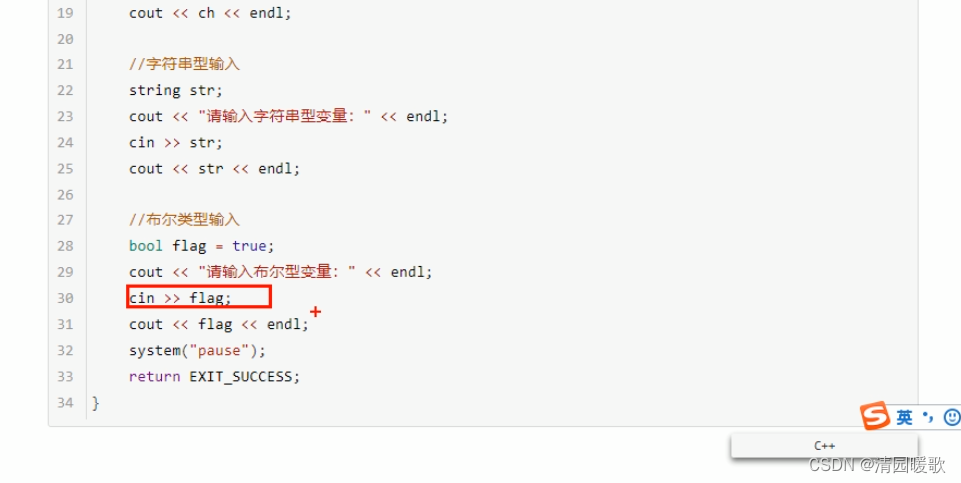
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <string> // 用C++风格字符串的时候,要包含这个头文件int main()
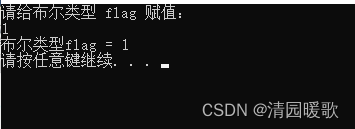
{// 1、整型/*int a = 0;cout << "请给整型变量a赋值:" << endl;cin >> a;cout << "整型变量a = " << a << endl;*/// 2、浮点型/*float f = 3.14f;cout << "请给浮点型变量f赋值:" << endl;cin >> f;cout << "浮点型变量 f= " << f << endl;*/// 3、字符型/*char ch = 'a';cout << "请给字符型变量ch赋值:" << endl;cin >> ch;cout << "字符型变量ch = " << ch << endl;*/// 4、字符串类型/*string str = "hello";cout << "请给字符串str赋值:" << endl;cin >> str;cout << "字符串str = " << str << endl;*/// 5、布尔类型bool flag = false;cout << "请给布尔类型 flag 赋值:" << endl;cin >> flag; // bool类型 只要是非0的值都代表真cout << "布尔类型flag = " << flag << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}
三、运算符

3.1 算术运算符

3.1.1 加减乘除运算
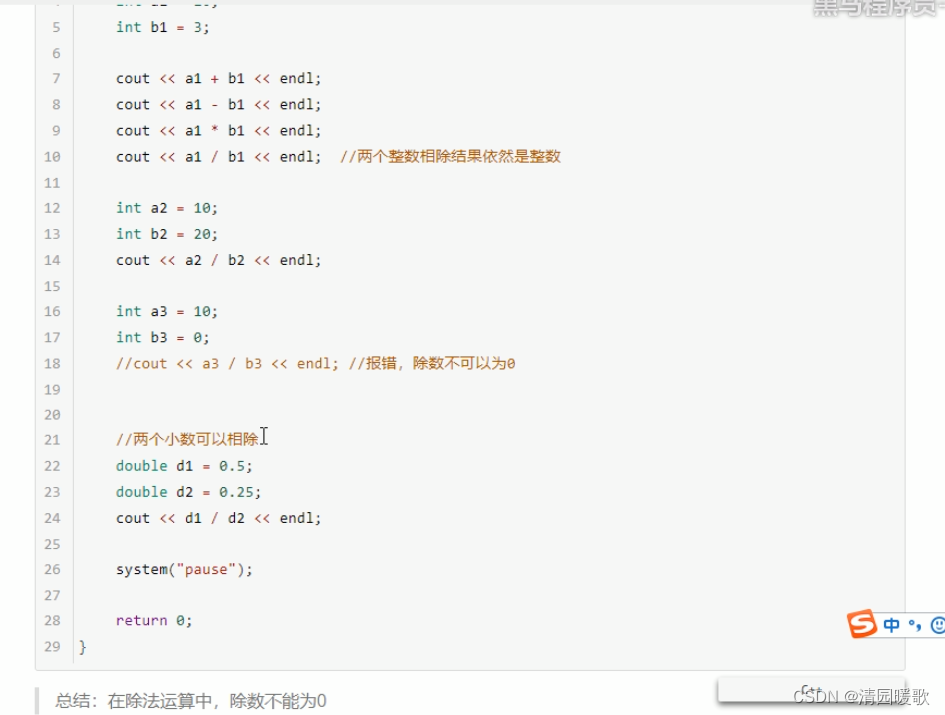
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{// 加减乘除int a1 = 10;int b1 = 3;cout << a1 + b1 << endl;cout << a1 - b1 << endl;cout << a1 * b1 << endl;cout << a1 / b1 << endl; // 两个整数相除 结果依然是整数,将小数部分去除int a2 = 10;int b2 = 20;cout << a2 / b2 << endl;int a3 = 19;int b3 = 0;// cout << a3 / b3 << endl; // 会报错,除数不能是0// 两个小数可以相除double d1 = 0.5;double d2 = 0.25;cout << d1 / d2 << endl;d1 = 0.5;d2 = 0.22;cout << d1 / d2 << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}
3.1.2 取模运算(%)

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{int a1 = 10;int b1 = 3;cout << a1 % b1 << endl;// 两个小数不可以做取模double d1 = 3.14;double d2 = 1.1;// cout << d1 % d2 << enld;system("pause");return 0;
}
3.1.3 递增递减(++、--)


#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{// 1、前置递增int a = 10;++a; // 让变量+1cout << "a:" << a << endl;// 2、后置递增int b = 10;b++;cout << "b:" << b << endl;// 3、前置和后置// 前置递增 先让+1,再进行表达式运算int a2 = 10;int b2 = ++a2 * 10;cout << "a2=" << a2 << endl;cout << "b2=" << b2 << endl;// 后置递增 先进行表达式运算,再+1int a3 = 10;int b3 = a3++ * 10;cout << "a3=" << a3 << endl;cout << "b3=" << b3 << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}
3.2 赋值运算符

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{// 赋值运算符// =int a = 10;a = 100;cout << "a = " << a << endl;// +=a = 10;a += 2; // a = a += 2cout << "a = " << a << endl;// -=a = 10;a -= 2;cout << "a = " << a << endl;// *=a = 10;a *= 2;cout << "a = " << a << endl;// /=a = 10;a /= 2;cout << "a = " << a << endl;// %=a = 10;a %= 2;cout << "a = " << a << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}
3.3 比较运算符
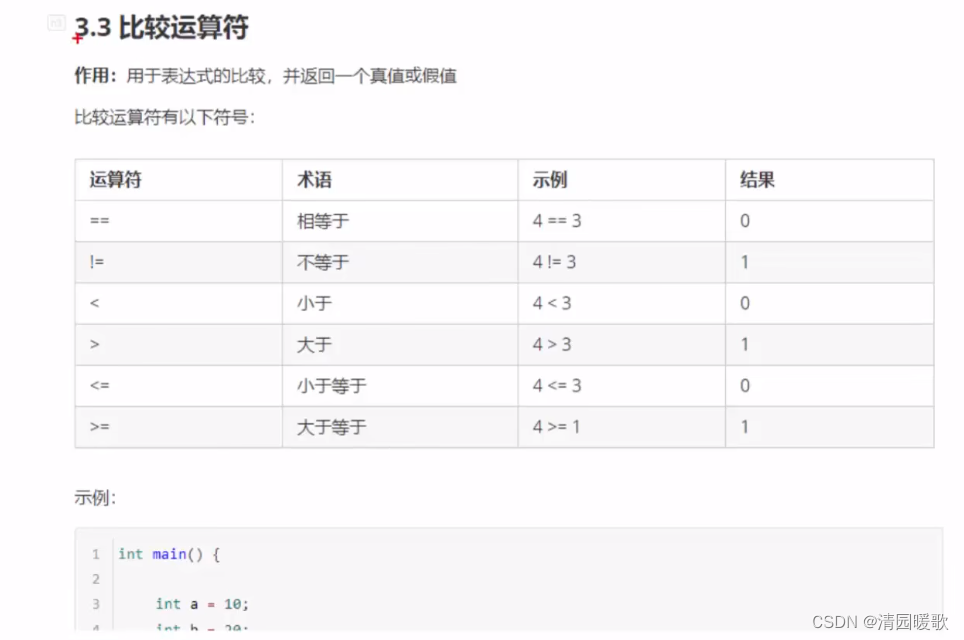
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{// 比较运算符// ==int a = 10;int b = 20;cout << (a == b) << endl;// !=cout << (a != b) << endl;// >cout << (a > b) << endl;// <cout << (a < b) << endl;// >=cout << (a >= b) << endl;// <=cout << (a <= b) << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}
3.4 逻辑运算符

3.4.1 非(!)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{// 逻辑运算符 非 !int a = 10;// 在C++中,除了0都是真cout << !a << endl;cout << !!a << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}
3.4.2 与(&&)

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{// 逻辑运算符 与 &&int a = 10;int b = 10;cout << (a && b) << endl;a = 0;b = 10;cout << (a && b) << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}
3.4.3 或(||)

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{// 逻辑运算符 与 &&int a = 10;int b = 10;cout << (a || b) << endl;a = 0;b = 10;cout << (a || b) << endl;a = 0;b = 0;cout << (a || b) << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}
四、程序流程结构

4.1 选择结构
4.1.1 单行 if 语句
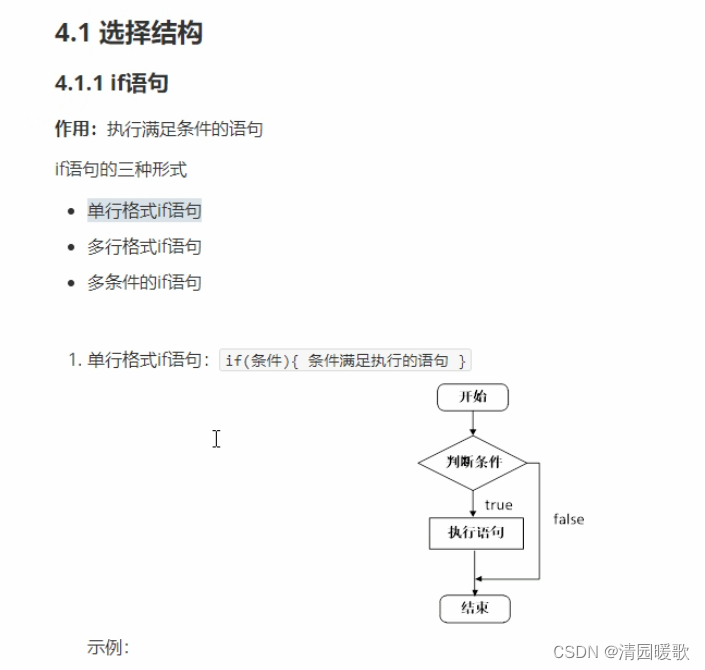
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{// 选择结构 单行if语句// 输入分数,大于600,就输出// 1、用户输入分数int score = 0;cout << "请输入您的分数:" << endl;cin >> score;// 2、打印用户输入的分数cout << "您输入的分数为:" << score << endl;// 3、判断分数是否大于600,大于就输出// 注意:if后面不要加分号if (score > 600){cout << "恭喜您考上一本大学" << endl;}system("pause");return 0;}
4.1.2 多行 if 语句
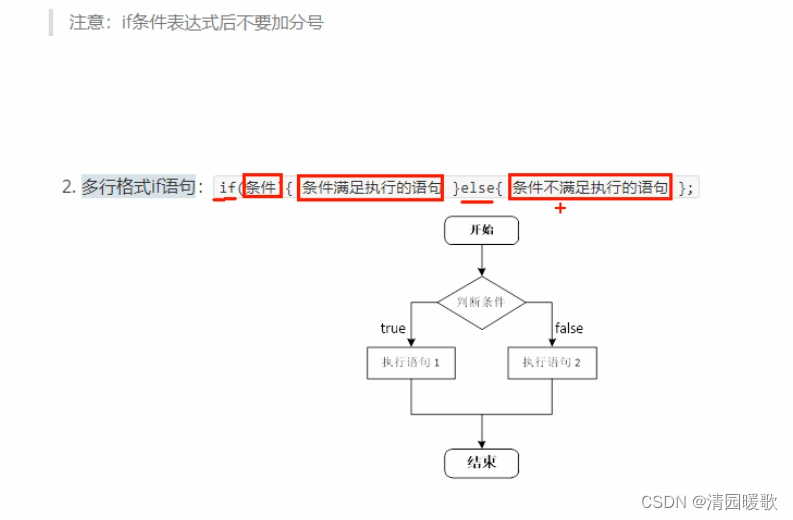
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{// 选择结构 单行if语句// 输入分数,大于600,就输出// 1、用户输入分数int score = 0;cout << "请输入您的分数:" << endl;cin >> score;// 2、打印用户输入的分数cout << "您输入的分数为:" << score << endl;// 3、判断分数是否大于600,大于就输出// 注意:if后面不要加分号if (score > 600){cout << "恭喜您考上一本大学" << endl;}else{cout << "未考上" << endl;}system("pause");return 0;}4.1.3 多条件 if 语句
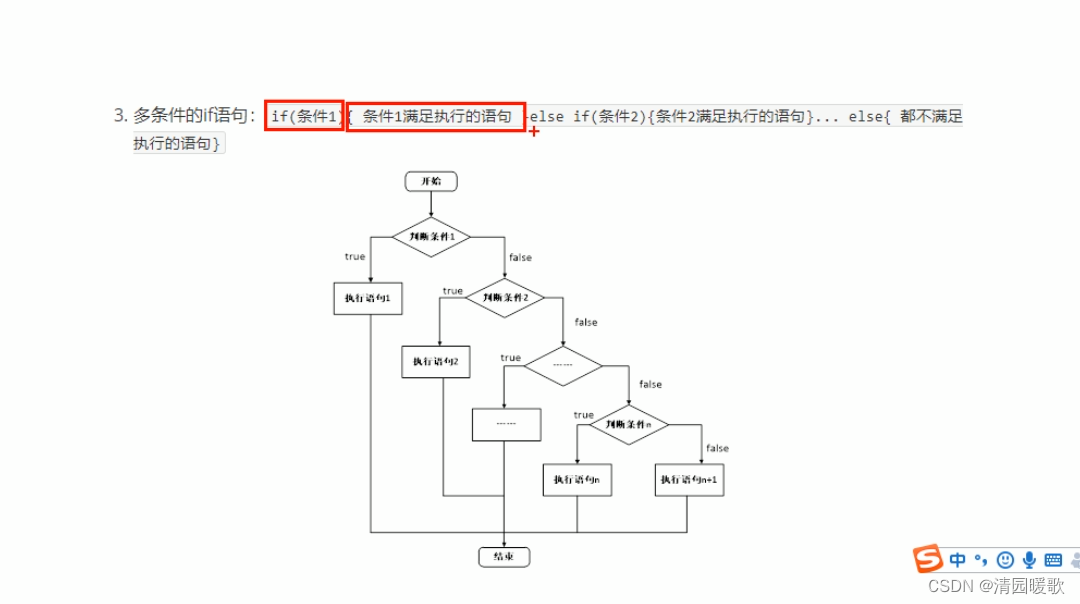
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{// 选择结构 多条件if语句// 输入分数,大于600,就输出考上,小于就打印未考上// 1、用户输入分数int score = 0;cout << "请输入您的分数:" << endl;cin >> score;// 2、打印用户输入的分数cout << "您输入的分数为:" << score << endl;// 3、判断分数是否大于600,大于就输出考上,否则未考上// 注意:if后面不要加分号if (score > 600){cout << "恭喜您考上一本大学" << endl;}else if (score > 500){cout << "恭喜您考上二本大学" << endl;}else{cout << "抱歉您未考上" << endl;}system("pause");return 0;}
4.1.4 嵌套 if 语句
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{/*提示用户输入一个高考考试分数,根据分数做如下判断分数如果大于600分视为考上一本,大于500分考上二本,大于400考上三本,其余视为未考上本科;在一本分数中,如果大于700分,考入北大,大于650分,考入清华,大于600考入人大。*/// 1、提示输入高考分数int score = 0;cout << "请输入你的分数:" << endl;cin >> score;// 2、显示高考分数cout << "你的分数是:" << score << endl;// 3、判断是否大于600,大于就是一本,大于500就是二本if (score > 600){cout << "恭喜考上一本" << endl;if (score > 700){cout << "恭喜考上清华" << endl;}else if (score > 650){cout << "恭喜考上北大" << endl;}else{cout << "恭喜考上人大" << endl;}}else if (score > 500){cout << "恭喜考上二本" << endl;}else if (score > 400){cout << "恭喜考上三本" << endl;}else{cout << "未考上" << endl;}system("pause");return 0;}4.1.5 练习:三只小猪称体重


#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{// 三只小猪称体重,判断哪只最重// 1、创建三只小猪的体重int num1 = 0;int num2 = 0;int num3 = 0;// 2、让用户输入三只小猪的体重cout << "请输入小猪A的体重:" << endl;cin >> num1;cout << "请输入小猪B的体重:" << endl;cin >> num2;cout << "请输入小猪C的体重:" << endl;cin >> num3;cout << "小猪A的体重是:" << num1 << endl;cout << "小猪B的体重是:" << num2 << endl;cout << "小猪C的体重是:" << num3 << endl;// 3、判断哪只最重if (num1 > num2){if (num1 > num3){cout << "小猪A最重" << endl;}else {cout << "小猪C最重" << endl;}}else{if (num2 > num3){cout << "小猪B最重" << endl;}else{cout << "小猪C最重" << endl;}}system("pause");return 0;}4.1.6 三目运算符

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{// 三目运算符// 创建三个变量 a,b,c// 将 a 和 b 做比较,把大的赋给 cint a = 10;int b = 20;int c = 0;c = (a > b ? a : b);cout << "c = " << c << endl;// 在C++中三目运算符返回的变量,可以继续赋值(a > b ? a : b) = 100;cout << "a = " << a << endl;cout << "b = " << b << endl;system("pause");return 0;}
4.1.7 switch 语句
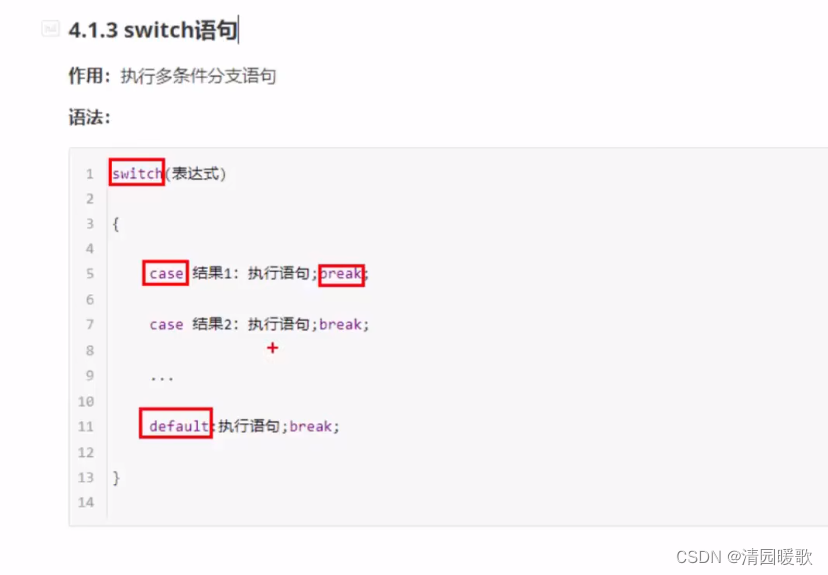
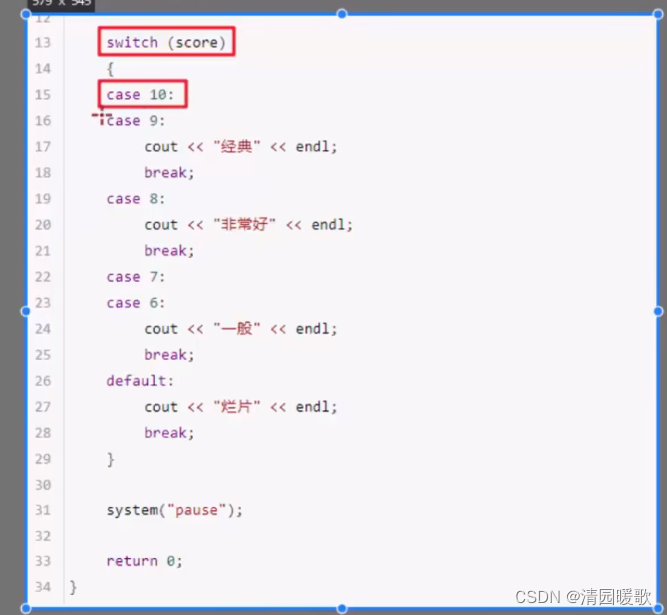
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{// swutch语句// 给电影打分// 10~9 经典// 8~7 非常好// 6~5 一般// 5以下 烂片// 1、提示用户评分cout << "请给电影打分:" << endl;// 2、用户打分int score = 0;cin >> score;cout << "您打的分数是:" << score << endl;// 3、根据打分提示结果switch (score){case 10:cout << "经典" << endl;break; // 退出,不往下执行case 9:cout << "经典" << endl;break;case 8:case 7:cout << "非常好" << endl;break;case 6:case 5:cout << "一般" << endl;break;default:cout << "您认为这是一个烂片" << endl;break;}// if 和 switch区别?// switch 缺点,判断的时候只能是整型huo字符型,不可以是一个区间// switch 优点,结构清晰,执行效率高system("pause");return 0;}
4.2 循环结构
4.2.1 while 循环语句
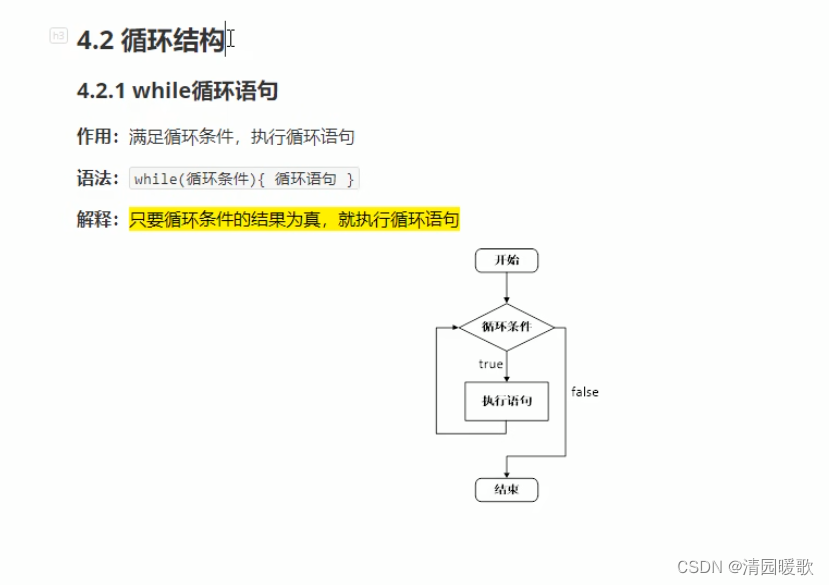
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{// while 循环// 在屏幕中打印 0 ~ 9 这十个数字int num = 0;// cout << num << endl;// 注意:循环中要注意出现死循环while (num < 10){cout << num << endl;num++;}system("pause");return 0;
}
4.2.2 while 循环练习案例:猜数字


#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// time系统时间头文件包含
#include<ctime>int main()
{// 添加随机数的种子 作用是利用当前系统的时间生成随机数,防止每次随机数都一样// 不添加的话每次生成的随机数都是一样的srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));// 1、系统生成随机数字int num = rand() % 100 + 1; // 生成 0+1~99+1 的随机数// cout << "num = " << num << endl;// 2、猜测int val = 0;while (1){cout << "请猜测:" << endl;cin >> val;cout << "你输入的数字是:" << val << endl;// 3、判断if (val > num){cout << "猜测过大" << endl;// 猜错 提示重猜}else if (val < num){cout << "猜测过小" << endl;// 猜错 提示重猜}else{cout << "恭喜猜对了" << endl;// 猜对 退出break; // 退出循环}}system("pause");return 0;
}
4.2.3 do...while 循环语句

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// time系统时间头文件包含
#include<ctime>int main()
{// do...while语句// 输出 0~9 十个数字int num = 0;do{cout << num << endl;num++;} while (num < 10);/*while (num){cout << num << endl;num++;}*/// do...while和while循环的区别在于 do...while会先执行一次循环语句system("pause");return 0;
}
4.2.4 do...while 练习案例:水仙花数


#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// time系统时间头文件包含
#include<ctime>int main()
{// 1、先打印所有三位数字int num = 100;do{// 2、找到水仙花数打印int ge = 0;int shi = 0;int bai = 0;ge = num % 10; // 个位shi = num / 10 % 10; // 十位bai = num / 100; // 百位if (ge*ge*ge + shi*shi*shi + bai*bai*bai == num){cout << num << "是水仙花数" << endl;}// cout << num << endl;num++;} while (num < 1000);system("pause");return 0;
}
4.2.5 for 循环


#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// time系统时间头文件包含
#include<ctime>int main()
{// for循环// 从数字0 打印到 数字9for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){cout << i << endl;}/*int i = 0;for (; ; ){if (i >= 10){break;}cout << i << endl;i++;}*/system("pause");return 0;
}
4.2.6 for 练习案例:敲桌子


#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// time系统时间头文件包含
#include<ctime>int main()
{// 敲桌子// 1、先输出100个数字for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++){// 2、找到特殊数字并打印// 7的倍数或个位、十位有7if (i % 7 == 0 || i % 10 == 7 || i / 10 == 7){cout << "敲桌子" << endl;}else{cout << i << endl;}}system("pause");return 0;
}
4.2.7 嵌套循环

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// time系统时间头文件包含
#include<ctime>int main()
{// 嵌套循环实现*图// 打印一行星图/*for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){cout << "* " ;}cout << endl;*/// 外层执行一次,内层执行一周// 外层循环for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){// 内层循环for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++){cout << "* ";}cout << endl;}system("pause");return 0;
}
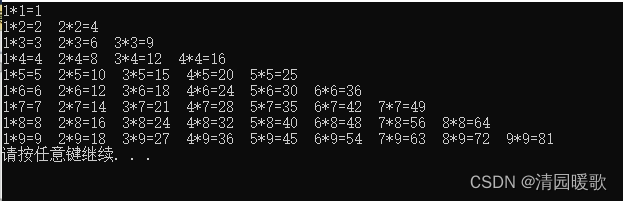
4.2.8 嵌套练习案例:乘法口诀表
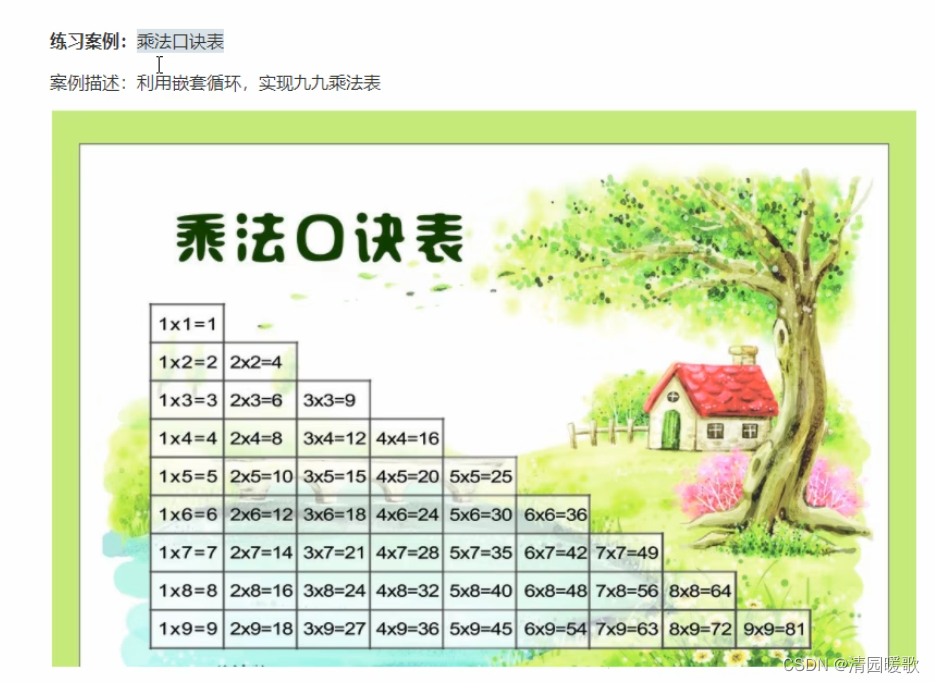
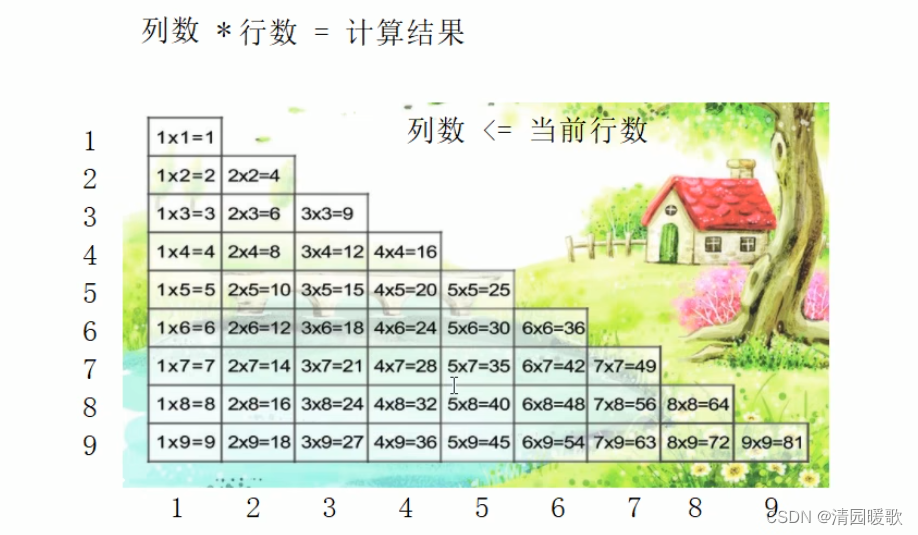
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// time系统时间头文件包含
#include<ctime>int main()
{// /*for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++){for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++){cout << " | " << j << " * " << i << " = " << j * i << " | ";}cout << endl;}*/// 乘法口诀表for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++){// cout << i << endl;for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++){cout << j << "*" << i << "=" << j * i << " ";}cout << endl;}system("pause");return 0;
}
4.3 跳转语句
4.3.1 break 语句
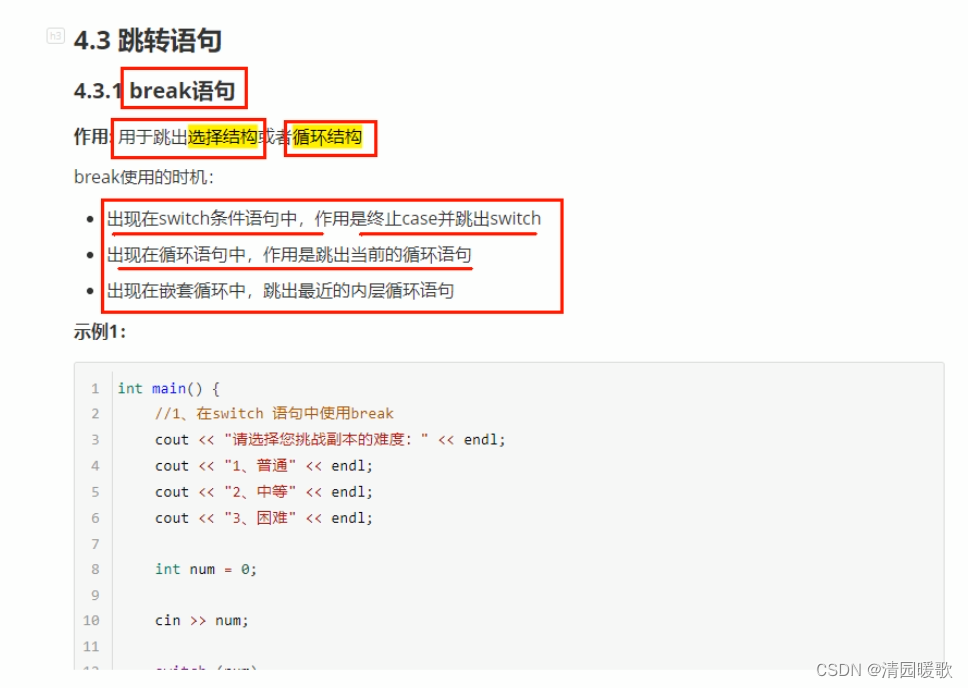
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{// break的使用时机// 1、出现在switch语句中//cout << "请选择副本的难度:" << endl;//cout << "1、普通" << endl;//cout << "2、中等" << endl;//cout << "3、困难" << endl;//int select = 0; // 创建选择结果的变量//cin >> select;//switch (select)//{//case 1:// cout << "您选择的是普通难度" << endl;// break;//case 2:// cout << "您选择的是中等难度" << endl;// break;//case 3:// cout << "您选择的是困难难度" << endl;// break;//default:// cout << "选择错误" << endl;// break;//}// 2、出现在循环语句中//for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)//{// if (i == 5)// {// break; // i=5 就退出循环// }// cout << i << endl;//}// 3、出现在嵌套循环语句中for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++){if (j == 5){break; // 退出内层循环}cout << "* ";}cout << endl;}system("pause");return 0;
}


4.3.2 continue 语句


#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{// continue 语句for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++){// 奇数就输出,偶数就不输出if (i % 2 == 0){continue; // 可以筛选条件,执行到此就不再向下执行,执行下一次循环// break 会退出,continue 不会}cout << i << endl;}system("pause");return 0;
}
4.3.3 goto 语句


#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{// goto 语句cout << "1、xxxx" << endl;cout << "2、xxxx" << endl;goto FLAG;cout << "3、xxxx" << endl;cout << "4、xxxx" << endl;FLAG:cout << "5、xxxx" << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}
五、数组
5.1 概述


5.2 一维数组
5.2.1 一维数组定义方式
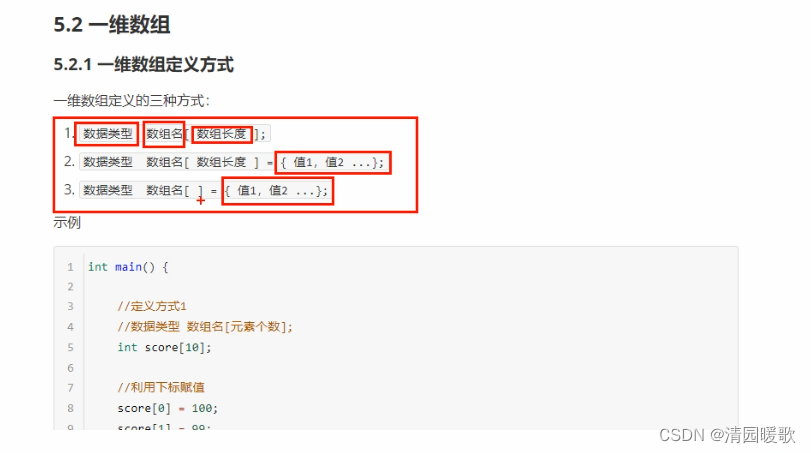
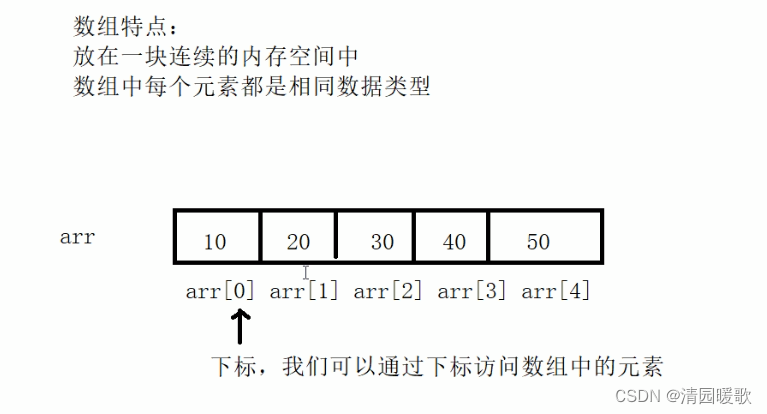

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{// 数组// 1.数据类型 数组名[ 数组长度 ];// 2.数据类型 数组名[ 数组长度 ] = { 值1,值2 ... }; // 3.数据类型 数组名[ ] = { 值1,值2 ... };// 1、数据类型 数组名[ 数组长度 ];int arr[5];// 给数组中的元素进行赋值// 数组元素的下标是从0开始索引的arr[0] = 10;arr[1] = 20;arr[2] = 30;arr[3] = 40;arr[4] = 50;// 访问数组元素for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){cout << arr[i] << endl;}// 2、数据类型 数组名[ 数组长度 ] = { 值1,值2 ... }; // 如果初始化数据的时候,没有全部填写完,会用0来填补剩余数据int arr2[5] = { 100, 200, 300};for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){cout << arr2[i] << endl;}// 3、数据类型 数组名[ ] = { 值1,值2 ... };// 定义数组的时候,必须有初始长度int arr3[] = { 90, 80, 70, 60, 50, 40, 30, 20, 10 };for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++){cout << arr3[i] << endl;}system("pause");return 0;
}
5.2.2 一维数组数组名



#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{// 数组名用途// 1、可以通过数组名统计整个数组占用内存大小int arr[10] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };cout << "整个数组占用内存空间为:" << sizeof(arr) << endl;cout << "sizeof(int) = " << sizeof(int) << endl;cout << "每个元素占用内存空间为:" << sizeof(arr[0]) << endl;cout << "数组中元素的个数为:" << sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]) << endl;// 2、可以通过数组名查看数组首地址cout << "数组首地址为(十六进制):" << arr << endl;cout << "数组首地址为(十进制):" << (int)arr << endl; // 强转成int十进制cout << "数组中第一个元素的地址为:" << (int)&arr[0] << endl;cout << "数组中第二个元素的地址为:" << (int)&arr[1] << endl;// 数组名是常量,不可以进行赋值操作// arr = 100;是不可以的system("pause");return 0;
}
5.2.3 一维数组练习案例1:五只小猪称体重


#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{// 1、创建5只小猪体重的数组int arr[5] = { 300, 350, 200, 400, 250 };// 2、从数组中找到最大值int max = 0;for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){// cout << arr[i] << endl;if (arr[i] > max){max = arr[i];}}// 3、打印最大值cout << "最重的小猪体重为:" << max << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}
5.2.4 一维数组练习案例2:数组元素逆置


#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{// 实现数组元素逆置// 1、创建数组int arr[5] = { 1, 3, 2, 5, 4 };cout << "数组逆置前:" << endl;for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){cout << arr[i] << endl;}// 2、实现逆置// 2.1 记录起始下标位置// 2.2 记录结束下标位置// 2.3 起始下标与结束下标的元素互换// 2.4 起始位置++, 结束位置--// 2.5 循环执行2.1操作,直到起始位置 >= 结束位置int start = 0; // 起始下标int end = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]) - 1; // 结束下标while (start <= end){// 实现元素互换int temp = arr[start];arr[start] = arr[end];arr[end] = temp;// 下标更新start++;end--;}// 3、打印逆置后的数组cout << "数组逆置后:" << endl;for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){cout << arr[i] << endl;}system("pause");return 0;
}
5.2.5 冒泡排序



#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{// 利用冒泡排序实现升序序列int arr[9] = { 4, 2, 8, 0, 5, 7, 1, 3, 9 };cout << "排序前:" << endl;for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++){cout << arr[i] << " ";}cout << endl;// 开始冒泡排序// 总共排序的轮数为 元素个数 - 1for (int i = 0; i < 9 - 1; i++){// 内层循环对比 次数 = 元素个数 - 当前轮数 - 1for (int j = 0; j < 9 - i - 1; j++){// 如果第一个数字,比第二个数字大,交换两个数字if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]){int temp = arr[j];arr[j] = arr[j + 1];arr[j + 1] = temp;}}}// 排序后结果cout << "排序后:" << endl;for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++){cout << arr[i] << " ";}cout << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}
5.3 二维数组

5.3.1 二维数组定义方式
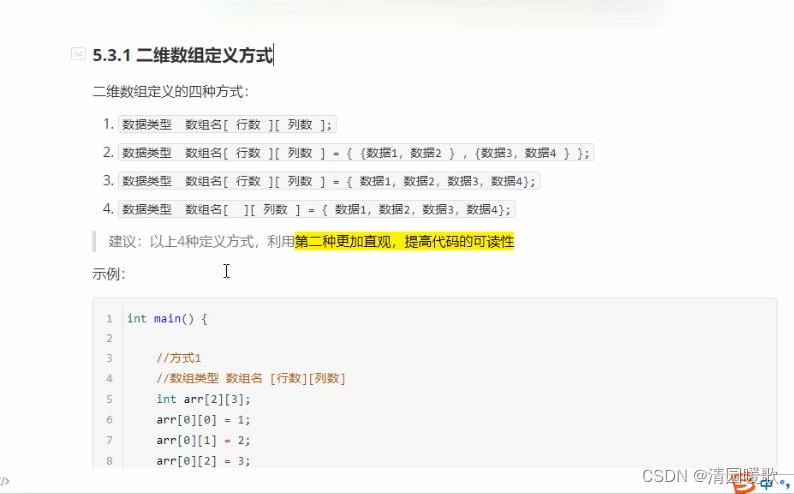

arr[2][3]
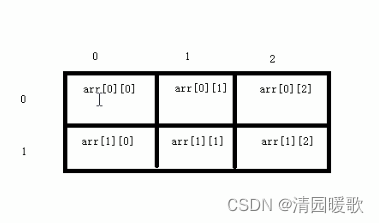
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{// 二维数组定义方式/*1. 数据类型数组名[行数][列数];2.数据类型数组名[行数][列数] = { {数据1,数据2},{数据3,数据4 } }; 3.数据类型数组名[行数][列数] = { 数据1,数据2,数据3,数据4 };4.数据类型数组名[][列数] = { 数据1,数据2,数据3,数据4 };*/// 1、数据类型数组名[行数][列数];int arr[2][3];arr[0][0] = 1;arr[0][1] = 2;arr[0][2] = 3;arr[1][0] = 4;arr[1][1] = 5;arr[1][2] = 6;for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++){for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++){cout << arr[i][j] << endl;}}// 2、数据类型数组名[行数][列数] = { {数据1,数据2},{数据3,数据4 } };int arr2[2][3] ={{1, 2, 3},{4, 5, 6}};for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++){for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++){cout << arr2[i][j] << " ";}cout << endl;}// 3、数据类型数组名[行数][列数] = { 数据1,数据2,数据3,数据4 };int arr3[2][3] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++){for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++){cout << arr3[i][j] << " ";}cout << endl;}// 4、数据类型数组名[][列数] = { 数据1,数据2,数据3,数据4 };int arr4[][3] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++){for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++){cout << arr4[i][j] << " ";}cout << endl;}system("pause");return 0;
}
5.3.2 二维数组数组名
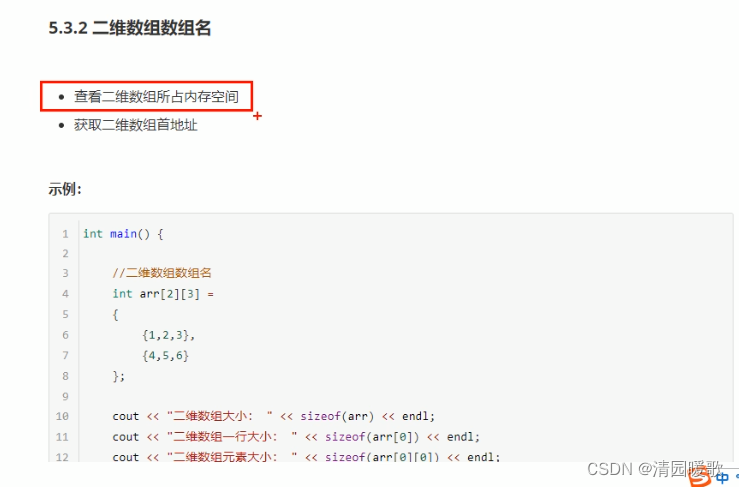
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
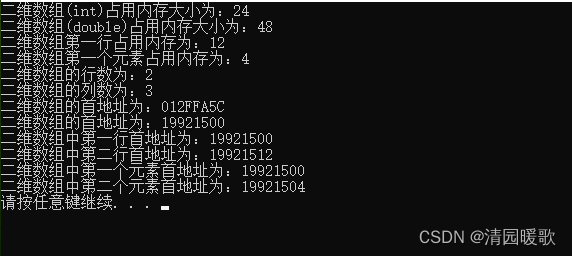
{// 二维数组名称用途// 1、可以查看占用内存大小int arr[2][3] ={{1, 2, 3},{4, 5, 6}};cout << "二维数组(int)占用内存大小为:" << sizeof(arr) << endl;double arr2[2][3] ={{1, 2, 3},{4, 5, 6}};cout << "二维数组(double)占用内存大小为:" << sizeof(arr2) << endl;cout << "二维数组第一行占用内存为:" << sizeof(arr[0]) << endl; cout << "二维数组第一个元素占用内存为:" << sizeof(arr[0][0]) << endl;cout << "二维数组的行数为:" << sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]) << endl;cout << "二维数组的列数为:" << sizeof(arr[0]) / sizeof(arr[0][0]) << endl;// 2、可以查看二维数组的首地址cout << "二维数组的首地址为:" << arr << endl;cout << "二维数组的首地址为:" << (int)arr << endl;cout << "二维数组中第一行首地址为:" << (int)arr[0] << endl;cout << "二维数组中第二行首地址为:" << (int)arr[1] << endl;cout << "二维数组中第一个元素首地址为:" << (int)&arr[0][0] << endl;cout << "二维数组中第二个元素首地址为:" << (int)&arr[0][1] << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}
5.3.3 二维数组应用案例:考试成绩统计

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>int main()
{// 二维数组案例-考试成绩统计// 1、创建二维数组int scores[3][3] ={{100, 100, 100},{90, 50, 100},{60, 70, 80}};string name[3] = { "张三", "李四", "王五" };// 2、统计每个人的总和分数for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++){int sum = 0;for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++){sum += scores[i][j];cout << scores[i][j] << " ";}cout << name[i] << "的总分为:" << sum << endl;}system("pause");return 0;
}
六、函数
6.1 概述

6.2 函数的定义


#include<iostream>
using namespace std;// 函数的定义
// 语法:
// 返回值类型 函数名 (参数列表) {函数体语句 return表达式}// 加法函数实现
int add(int num1, int num2)
{int sum = num1 + num2;return sum;
}int main()
{system("pause");return 0;
}6.3 函数的调用

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;// 函数的定义
// 语法:
// 返回值类型 函数名 (参数列表) {函数体语句 return表达式}// 加法函数实现
// 函数定义时,num1和num2没有实际数据
// 只是一个形式上的参数,简称形参
int add(int num1, int num2)
{int sum = num1 + num2;return sum;
}int main()
{int a = 10;int b = 20;// 函数调用// a和b称为 实际参数,简称实参// 调用时,实参的值会传递给形参int c = add(a, b);cout << "c = " << c << endl;a = 100;b = 500;c = add(a, b);cout << "c = " << c << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}
6.4 值传递

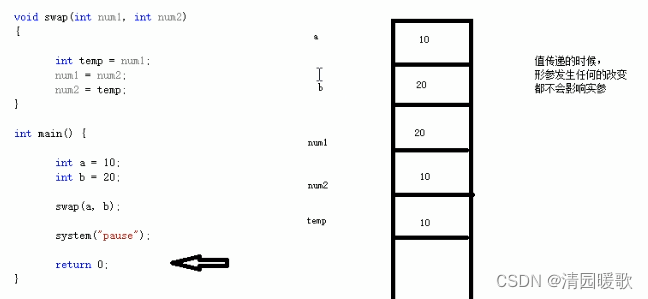
值传递时,形参发生改变,不会影响实参
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;// 值传递
// 定义函数,实现两个数字进行交换函数// 如果函数不需要返回值,声明的时候可以写 void
void swap(int num1, int num2)
{cout << "交换前:" << endl;cout << "num1 = " << num1 << endl;cout << "num2 = " << num2 << endl;int temp = num1;num1 = num2;num2 = temp;cout << "交换后:" << endl;cout << "num1 = " << num1 << endl;cout << "num2 = " << num2 << endl;// return; 返回值不需要的时候,可以不写return
}int main()
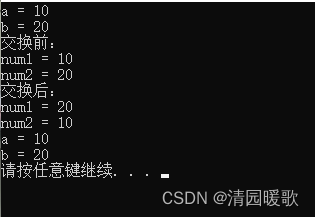
{int a = 10;int b = 20;cout << "a = " << a << endl;cout << "b = " << b << endl;// 当我们做值传递的时候,函数的形参发生改变,并不会影响实参swap(a, b);cout << "a = " << a << endl;cout << "b = " << b << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}
6.5 函数的常见样式
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;// 函数的常见样式
// 1、无参无返
void test01()
{cout << "this is test01" << endl;
}// 2、有参无返
void test02(int a)
{cout << "this is test02 a = " << a << endl;
}// 3、无参有返
int test03()
{cout << "this is test03" << endl;return 1000;
}// 4、有参有返
int test04(int a)
{cout << "this is test04 a = " << a << endl;return a;
}int main()
{// 1、无参无返test01();// 2、有参无返test02(100);// 3、无参有返int num1 = test03();cout << "num1 = " << num1 << endl;// 4、有参有返int num2 = test04(456);cout << "num2 = " << num2 << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}
6.6 函数的声明

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;// 函数的声明
// 比较函数,实现两个整型数字进行比较,返回较大的值// 定义,max函数必须卸载main的前面
// 所以可以提前告诉编译器函数的存在,可以利用函数的声明
// 声明可以写多次,但是定义只能有一次
int max(int a, int b);
int max(int a, int b);
int max(int a, int b);int main()
{int a = 10;int b = 20;cout << max(a, b) << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}int max(int a, int b)
{return a > b ? a : b;
}
6.7 函数的分文件编写
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include "swap.h" // 双引号表示自定义的头文件// 函数的分文件编写
// 实现两个数字进行交换的函数函数的声明
//void swap(int a, int b);函数的定义
//void swap(int a, int b)
//{
// int temp = a;
// a = b;
// b = temp;
// cout << "a = " << a << endl;
// cout << "b = " << b << endl;
//}// 1、创建.h后缀名的头文件
// 2、创建.cpp后缀名的源文件
// 3、在头文件写函数的声明
// 4、在源文件中先函数的定义int main()
{int a = 10;int b = 20;swap(a, b);system("pause");return 0;
}
swap.h
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;// 函数的声明
void swap(int a, int b);
swap.c
#include "swap.h" // 双引号表示自定义的头文件// 函数的定义
void swap(int a, int b)
{int temp = a;a = b;b = temp;cout << "a = " << a << endl;cout << "b = " << b << endl;
}七、指针
7.1 指针的基本概念

7.2 指针变量的定义和使用

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>int main()
{// 1、定义指针int a = 10;// 指针定义的语法:数据类型 * 指针变量名;int * p;// 让指针记录变量a的地址p = &a;cout << "a的地址为: " << &a << endl;cout << "a的地址为: " << (int)&a << endl;cout << "指针p为: " << p << endl;// 2、使用指针// 可以通过解引用的方式来找到指针指向的内存// 指针前加 * 代表解引用,找到指针指向的内存中的数据*p = 1000;cout << "a = " << a << endl;cout << "*p = " << *p << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}
7.3 指针所占内存空间
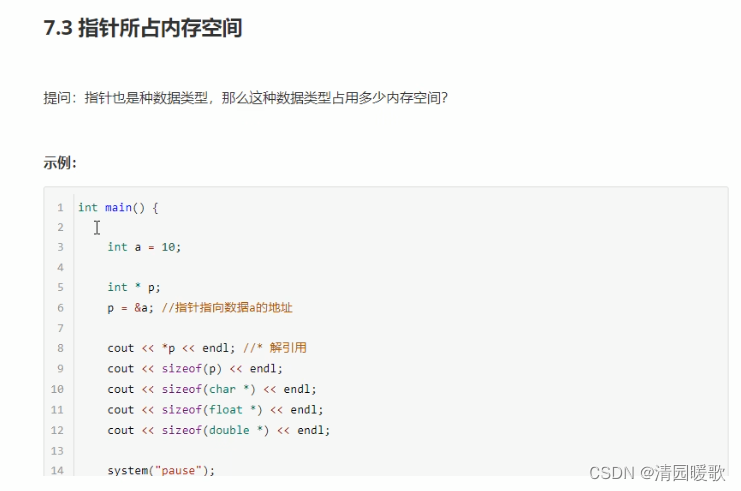
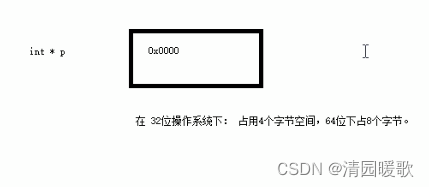
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>int main()
{// 指针所占内存空间int a = 10;// int * p;// p = &a;int * p = &a;// 32位操作系统下,指针是占4个字节空间大小,不管什么数据类型// 32位操作系统下,指针是占8个字节空间大小,不管什么数据类型cout << "sizeof(int *) = " << sizeof(int *) << endl;cout << "sizeof(float *) = " << sizeof(float *) << endl;cout << "sizeof(double *) = " << sizeof(double *) << endl;cout << "sizeof(char *) = " << sizeof(char *) << endl;cout << "sizeof(p) = " << sizeof(p) << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}
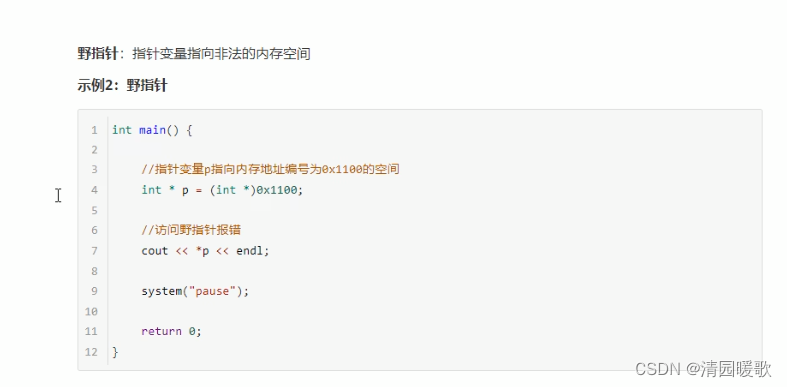
7.4 空指针和野指针

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>int main()
{// 空指针// 1、空指针用于给指针变量进行初始化int* p = NULL;// 2、空指针是不可以进行访问的// 0 ~ 255 之间的内存编号是系统占用的,因此不可以访问// *p = 100; 会报错system("pause");return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>int main()
{// 野指针// 在程序中,尽量避免出现野指针int* p = (int *)0x1100;// cout << *p << endl; 会报错system("pause");return 0;
}7.5 const修饰指针

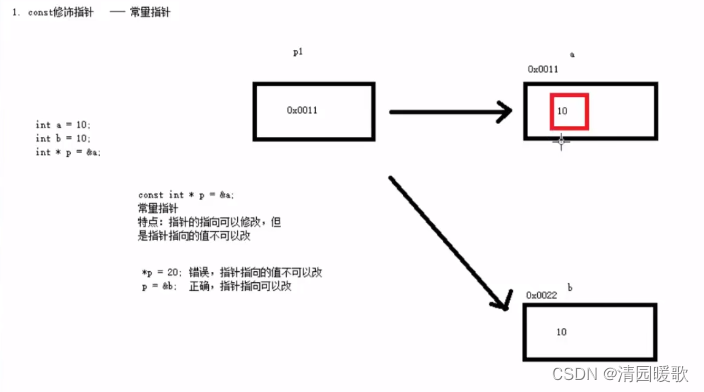
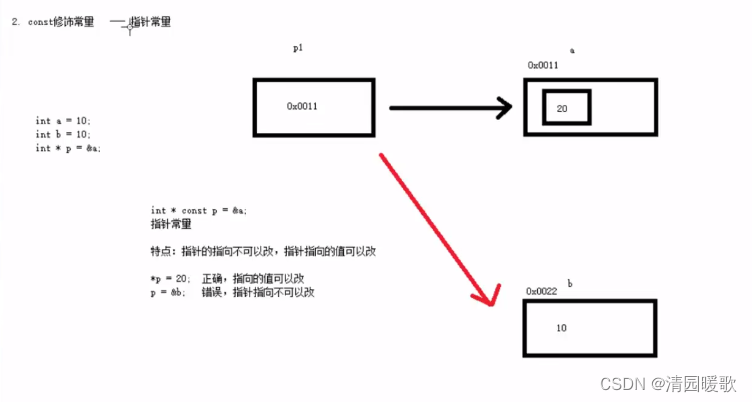

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>int main()
{// 1、const修饰指针(常量指针)int a = 10;int b = 20;const int * p = &a;// 指针指向的值不可以改,指针的指向可以改// *p = 20; 错误p = &b; // 正确// 2、const修饰常量(指针常量)// 指针的指向不可以改,指针指向的值可以改int* const p2 = &a;*p2 = 100; // 正确// p2 = &b; 错误,指针的指向不可以改// 3、const修饰指针和常量(既修饰指针也修饰常量)const int* const p3 = &a;// 指针的指向 和 指针指向的值 都不可以改// *p3 = 100; 错误// p3 = &b; 错误system("pause");return 0;
}7.6 指针和数组
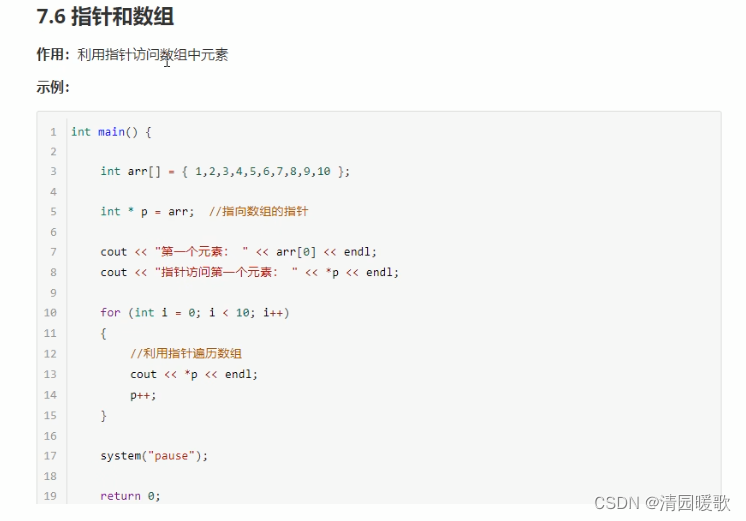
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>int main()
{// 指针和数组// 利用指针访问数组中的元素int arr[10] = { 1, 2, 6, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };cout << "第一个元素为:" << arr[0] << endl;int* p = arr; // arr就是数组首地址cout << "利用指针访问第一个元素:" << *p << endl;p++; // 让指针向后偏移4个字节cout << "利用指针访问第二个元素:" << *p << endl;cout << "利用指针访问第三个元素:" << *(p+1) << endl;cout << "利用指针遍历数组 " << endl;int* p2 = arr;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){// cout << arr[i] << endl;cout << *p2 << endl;p2++;}system("pause");return 0;
}
7.7 指针和函数
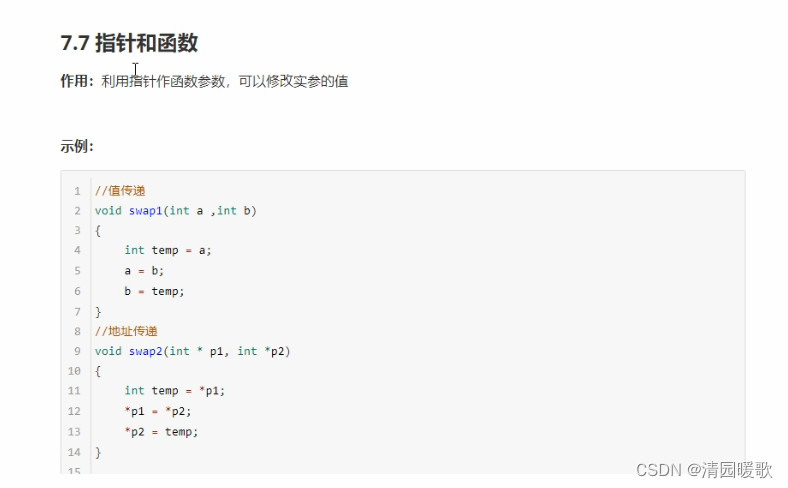
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>// 实现两个数字交换
void swap01(int a, int b)
{int temp = a;a = b;b = temp;
}void swap02(int* p1, int* p2)
{int temp = *p1;*p1 = *p2;*p2 = temp;
}int main()
{// 指针和函数// 1、值传递int a = 10;int b = 20;swap01(a, b);cout << "a = " << a << endl;cout << "b = " << b << endl;// 2、地址传递// 如果是地址传递,可以修饰实参swap02(&a, &b);cout << "a = " << a << endl;cout << "b = " << b << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}

7.8 指针、数组、函数

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>// 冒泡排序函数
void bubbleSort(int * arr, int len)
{for (int i = 0; i < len - 1; i++){for (int j = 0; j < len - i - 1; j++){// 如果 j > j+1 的值,就交换数字if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]){int temp = arr[j];arr[j] = arr[j + 1];arr[j + 1] = temp;}}}
}// 打印数组
void printArray(int* arr, int len)
{for (int i = 0; i < len; i++){cout << arr[i] << endl;}
}int main()
{// 1、先创建数组int arr[10] = { 4, 3, 6, 9, 1, 2, 10, 8, 7, 5 };// 数组长度int len = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);// 2、创建函数,实现冒泡排序bubbleSort(arr, len);// 3、 打印排序后的数组printArray(arr, len);system("pause");return 0;
}
八、结构体
8.1 结构体基本概念

8.2 结构体定义和使用

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>// 1、创建学生数据类型 :学生包括(姓名, 年龄, 分数)
// 自定义数据类型,一些类型集合组成的一个类型
// 语法 struct类型名称 { 成员列表 }
struct Student
{// 成员列表// 姓名string name;// 年龄int age;// 分数int score;
};// 2、通过学生类型创建具体学生int main()
{// 2.1 struct Student s1// struct 关键字可以省略struct Student s1;// Student s1;// 给s1属性赋值,通过.访问结构体变量中的属性s1.name = "张三";s1.age = 18;s1.score = 100;cout << "姓名: " << s1.name << " 年龄: " << s1.age << " 分数: " << s1.score << endl;// 2.2 struct Student s2 = { ... }struct Student s2 = {"李四", 19, 80};cout << "姓名: " << s2.name << " 年龄: " << s2.age << " 分数: " << s2.score << endl;// 2,3 在定义结构体时顺便创建结构体变量//struct Student//{// // 成员列表// // 姓名// string name;// // 年龄// int age;// // 分数// int score;//}s3; // 顺便创建结构体变量/*s3.name = "王五";s3.age = 20;s3.score = 60;cout << "姓名: " << s3.name << "年龄: " << s3.age << "分数: " << s3.score << endl;*/system("pause");return 0;
}
8.3 结构体数组
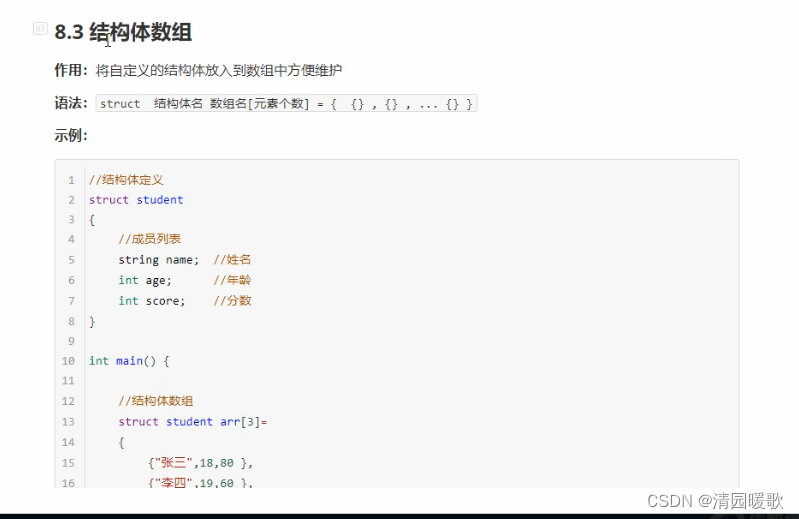
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>// 结构体数组
// 1、定义结构体
struct Student
{// 姓名string name;// 年龄int age;// 分数int score;
};int main()
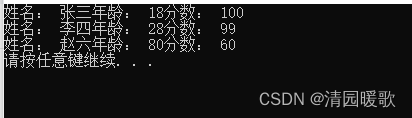
{// 2、创建结构体数组struct Student stuArray[3] ={{"张三", 18, 100},{"李四", 28, 99},{"王五", 38, 66}};// 3、给结构体数组中的元素赋值stuArray[2].name = "赵六";stuArray[2].age = 80;stuArray[2].score = 60;// 4、遍历结构体数组for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++){cout << "姓名: " << stuArray[i].name << "年龄: " << stuArray[i].age << "分数: " << stuArray[i].score << endl;}system("pause");return 0;
}
8.4 结构体指针
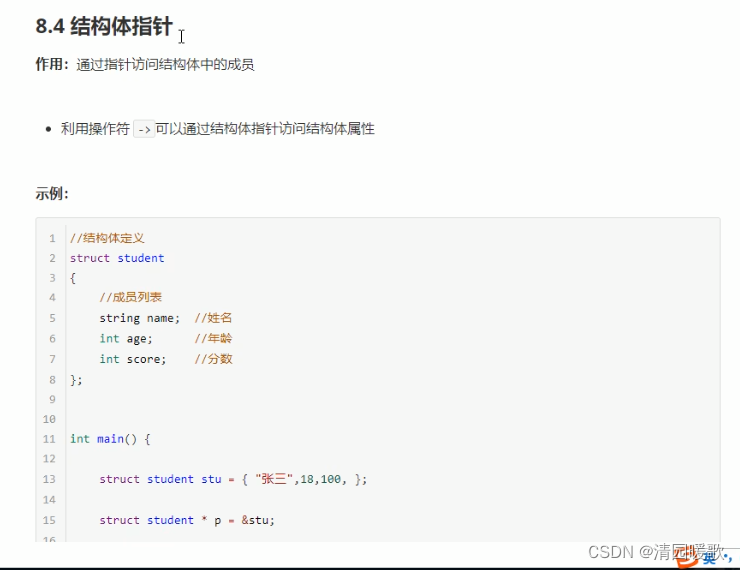
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>// 结构体指针
struct student
{// 姓名string name;// 年龄int age;// 分数int score;
};int main()
{// 1、创建学生的结构体变量struct student s = { "张三", 18, 100 };// 2、通过指针指向结构体变量struct student * p = &s; // struct可以省略// 3、通过指针访问结构体变量中的数据// 通过结构体指针 访问结构体中的属性,需要利用 '->'cout << "姓名: " << p->name << " 年龄: " << p->age << " 分数: " << p->score << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}
8.5 结构体嵌套结构体
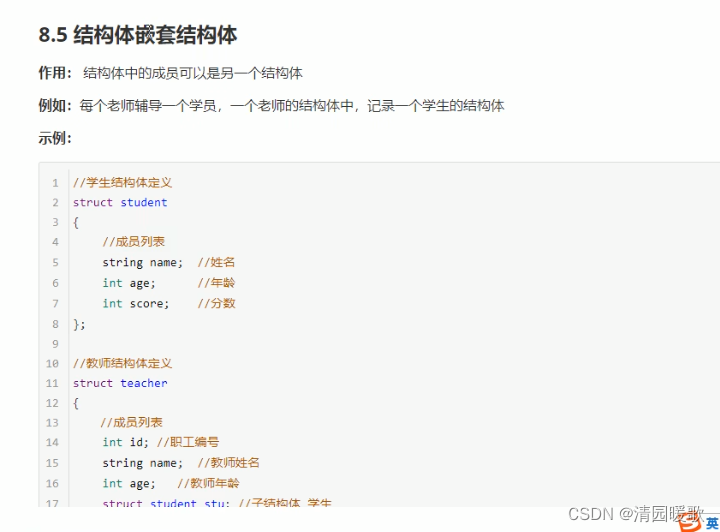

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>// 定义学生的结构体
struct student
{string name;int age;int score;
};// 定义老师结构体
struct teacher
{int id; // 编号string name; // 姓名int age; // 年龄struct student stu; // 学生的结构体
};int main()
{// 结构体嵌套结构体// 创建老师teacher t;t.id = 10000;t.name = "老王";t.age = 50;t.stu.name = "小王";t.stu.age = 20;t.stu.score = 60;cout << "老师姓名: " << t.name << " 老师编号: " << t.id << " 老师年龄: " << t.age<< " 老师辅导的学生姓名: " << t.stu.name << " 学生年龄: "<< t.stu.age<< " 学生考试分数为: " << t.stu.score << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}
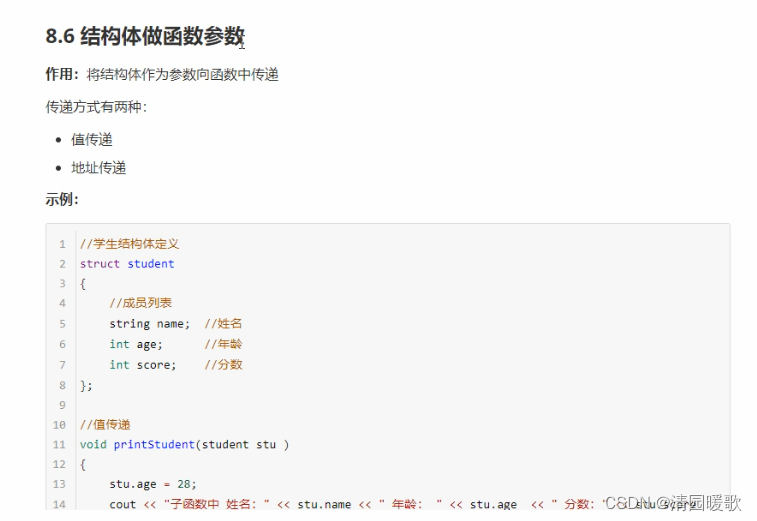
8.6 结构体做函数参数

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>// 定义学生的结构体
struct student
{string name;int age;int score;
};// 打印学生信息的函数
// 1、值传递
void printStudent1(struct student s)
{// 修改 s.age = 100; 不会改变实参s.age = 100;cout << "子函数1中 姓名: " << s.name << " 年龄: " << s.age << " 分数: " << s.score << endl;
}// 2、地址传递
void printStudent2(struct student * p)
{// 修改 s.age = 100; 会改变实参p->age = 200;cout << "子函数2中 姓名: " << p->name << " 年龄: " << p->age << " 分数: " << p->score << endl;
}int main()
{// 结构体做函数参数// 将学生传入到一个参数中,打印学生身上的所有信息// 创建结构体变量struct student s;s.name = "张三";s.age = 20;s.score = 85;cout << "main函数中初始打印 姓名: " << s.name << " 年龄: " << s.age << " 分数: " << s.score << endl;printStudent1(s);cout << "student1后打印 姓名: " << s.name << " 年龄: " << s.age << " 分数: " << s.score << endl;printStudent2(&s);cout << "student2后打印 姓名: " << s.name << " 年龄: " << s.age << " 分数: " << s.score << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}
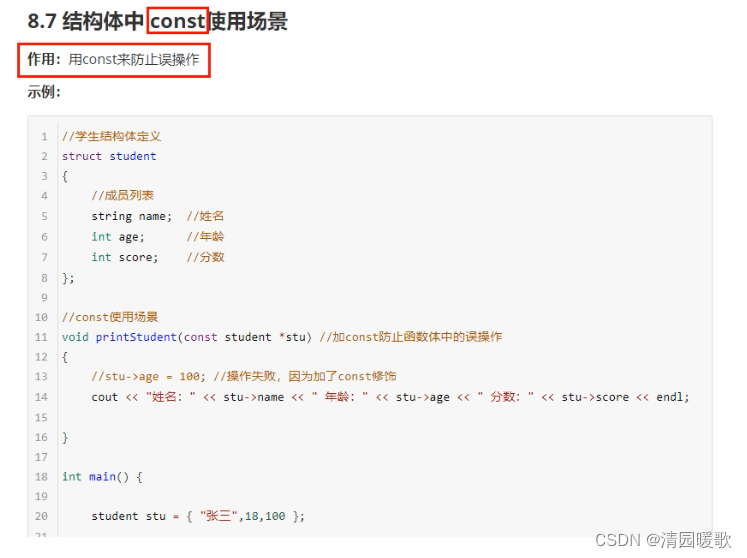
8.7 结构体中 const使用场景
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>// const的使用场景struct student
{string name;int age;int score;
};// 打印学生信息的函数
// 将函数中的形参改为指针,可以减少内存空间,而且不会复制新的副本出来
void printStudent1(const student *s)
{// s->age = 150; // 加入const之后,一旦有修改的操作就会报错,可以防止我们的误操作cout << "姓名: " << s->name << " 年龄: " << s->age << " 分数: " << s->score << endl;
}int main()
{// 创建结构体变量struct student s = { "张三", 15, 70 };// 通过函数打印结构体变量信息printStudent1(&s); // 一个指针只占4个字节cout << "姓名: " << s.name << " 年龄: " << s.age << " 分数: " << s.score << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}
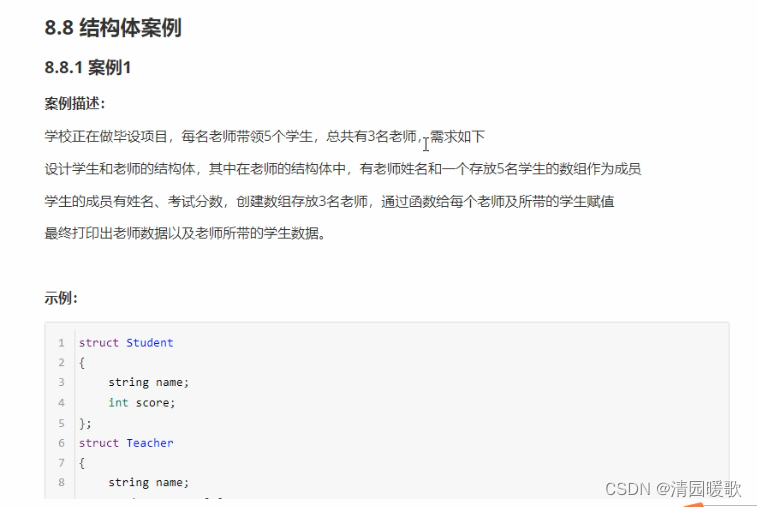
8.8 结构体案例
8.8.1 案例1

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<ctime>// 学生的结构体
struct Student
{string sName;int score;
};// 老师的结构体定义
struct Teacher
{// 姓名string tName;// 学生数组struct Student sArray[5];
};// 打印所有信息
void printInfo(struct Teacher tArray[], int len)
{for (int i = 0; i < len; i++){cout << "老师姓名: " << tArray[i].tName << endl;for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++){cout << "\t学生姓名: " << tArray[i].sArray[j].sName << " 考试分数: "<< tArray[i].sArray[j].score << endl;}}
}// 给老师和学生赋值的函数
void allocateSpace(Teacher tArray[], int len)
{string nameSeed = "ABCDE";for (int i = 0; i < len; i++){tArray[i].tName = "Teacher_";tArray[i].tName += nameSeed[i];// 通过循环给每名老师所带的学生赋值for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++){tArray[i].sArray[j].sName = "Student_";tArray[i].sArray[j].sName += nameSeed[j];int random = rand() % 61 + 40; // 40 ~ 100tArray[i].sArray[j].score = random;}}
}int main()
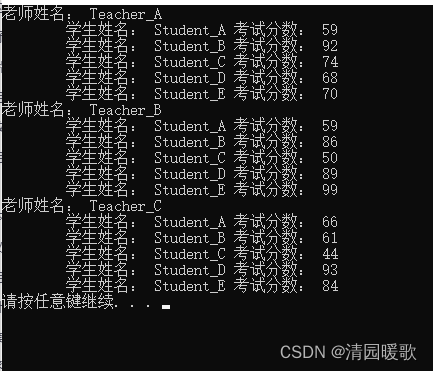
{// 随机数种子srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));// 1、创建3名老师的数组struct Teacher tArray[3];// 2、通过函数给3名老师的信息赋值,并给老师带的学生信息赋值int len = sizeof(tArray) / sizeof(tArray[0]);allocateSpace(tArray, len);// 3、打印所有老师及所带的学生信息printInfo(tArray, len);system("pause");return 0;
}
8.8.2 案例2

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<ctime>// 1、设计英雄结构体
// 英雄结构体
struct Hero
{// 姓名string name;// 年龄int age;// 性别string sex;
};// 冒泡排序 实现年龄的升序排序
void bubbleSort(struct Hero heroArray[], int len)
{for (int i = 0; i < len - 1; i++){for (int j = 0; j < len - 1; j++){// 如果j 下标的元素年龄 大于 j+1下标元素的年龄 , 交换两个元素if (heroArray[j].age > heroArray[j + 1].age){struct Hero temp = heroArray[j];heroArray[j] = heroArray[j + 1];heroArray[j + 1] = temp;}}}
}// 打印排序后数组中的信息
void printHero(struct Hero heroArray[], int len)
{for (int i = 0; i < len; i++){cout << "姓名: " << heroArray[i].name << " 年龄: " << heroArray[i].age<< " 性别: " << heroArray[i].sex << endl;}
}int main()
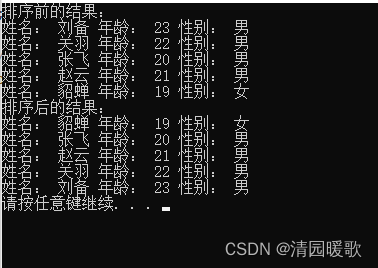
{// 随机数种子srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));// 2、创建数组存放5名英雄struct Hero heroArray[5] ={{"刘备", 23, "男"},{"关羽", 22, "男"},{"张飞", 20, "男"},{"赵云", 21, "男"},{"貂蝉", 19, "女"}};int len = sizeof(heroArray) / sizeof(heroArray[0]);cout << "排序前的结果:" << endl;for (int i = 0; i < len; i++){cout << "姓名: " << heroArray[i].name << " 年龄: " << heroArray[i].age<< " 性别: " << heroArray[i].sex << endl;}// 3、对数组进行排序,按照年龄进行升序排序bubbleSort(heroArray, len);cout << "排序后的结果:" << endl;// 4、将排序后结果输出printHero(heroArray, len);system("pause");return 0;
}
相关文章:

C++(1) —— 基础语法入门
目录 一、C初识 1.1 第一个C程序 1.2 注释 1.3 变量 1.4 常量 1.5 关键字 1.6 标识符命名规则 二、数据类型 2.1 整型 2.2 sizeof 关键字 2.3 实型(浮点型) 2.4 字符型 2.5 转义字符 2.6 字符串型 2.7 布尔类型 bool 2.8 数据的输入 三…...
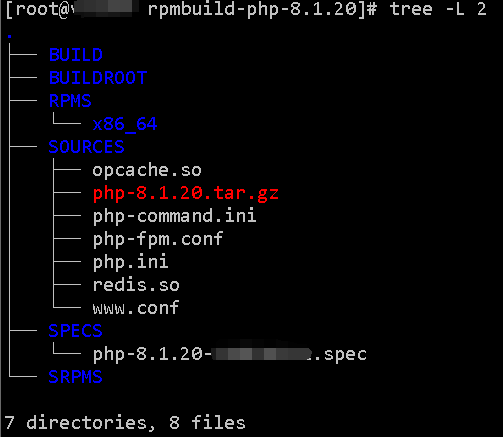
构建基于RHEL8系列(CentOS8,AlmaLinux8,RockyLinux8等)的支持63个常见模块的PHP8.1.20的RPM包
本文适用:rhel8系列,或同类系统(CentOS8,AlmaLinux8,RockyLinux8等) 文档形成时期:2023年 因系统版本不同,构建部署应略有差异,但本文未做细分,对稍有经验者应不存在明显障碍。 因软件世界之复杂和个人能力…...
)
Vue-插槽(Slots)
1. 介绍 在Vue.js中,插槽是一种强大的功能,它允许你创建可重用的模板,并在使用该模板的多个地方插入自定义内容。 插槽为你提供了一种方式,可以在父组件中定义一些“插槽”,然后在子组件中使用这些插槽,插…...

新火种AI|GPT-5前瞻!GPT-5将具备哪些新能力?
作者:小岩 编辑:彩云 Sam Altman在整个AI领域,乃至整个科技领域都被看作是极具影响力的存在,而2023年OpenAI无限反转的宫斗事件更是让Sam Altman刷足了存在感,他甚至被《时代》杂志评为“2023年度CEO”。 也正因此&…...
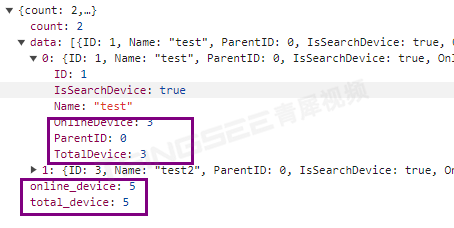
安防视频监控系统EasyCVR设备分组中在线/离线数量统计的开发与实现
安防视频监控EasyCVR系统具备较强的兼容性,它可以支持国标GB28181、RTSP/Onvif、RTMP,以及厂家的私有协议与SDK,如:海康ehome、海康sdk、大华sdk、宇视sdk、华为sdk、萤石云sdk、乐橙sdk等。EasyCVR平台可覆盖多类型的设备接入&am…...

spring cloud之集成sentinel
写在前面 源码 。 本文一起看下spring cloud的sentinel组件的使用。 1:准备 1.1:理论 对于一个系统来说,最重要的就是高可用,那么如何实现高可用呢?你可能会说,集群部署不就可以了,但事实并…...

让车辆做到“耳听八方”,毫米波雷达芯片与系统设计
摘要: 毫米波雷达,是指工作在毫米波波段(一般为30~300GHz频域,波长1~10mm)探测的雷达。毫米波雷达体积小、质量轻、空间分辨率高,穿透“雾烟灰”的能力强,还具备全天候全天时工作的优势。在智能网联汽车体系中,毫米波雷达是系统感知层不可或缺的重要硬件,能让智能驾…...

Python如何实现数据驱动的接口自动化测试
大家在接口测试的过程中,很多时候会用到对CSV的读取操作,本文主要说明Python3对CSV的写入和读取。下面话不多说了,来一起看看详细的介绍吧。 1、需求 某API,GET方法,token,mobile,email三个参数 token为必填项mobil…...

高级分布式系统-第15讲 分布式机器学习--联邦学习
高级分布式系统汇总:高级分布式系统目录汇总-CSDN博客 联邦学习 两种常见的架构:客户-服务器架构和对等网络架构 联邦学习在传统的分布式机器学习基础上的变化。 传统的分布式机器学习:在数据中心或计算集群中使用并行训练,因为…...

小程序基础学习(事件处理)
原理:组件内部设置点击事件,然后冒泡到页面捕获点击事件 在组件内部设置点击事件 处理点击事件,并告诉页面 页面捕获点击事件 页面处理点击事件 组件代码 <!--components/my-info/my-info.wxml--> <view class"title"…...
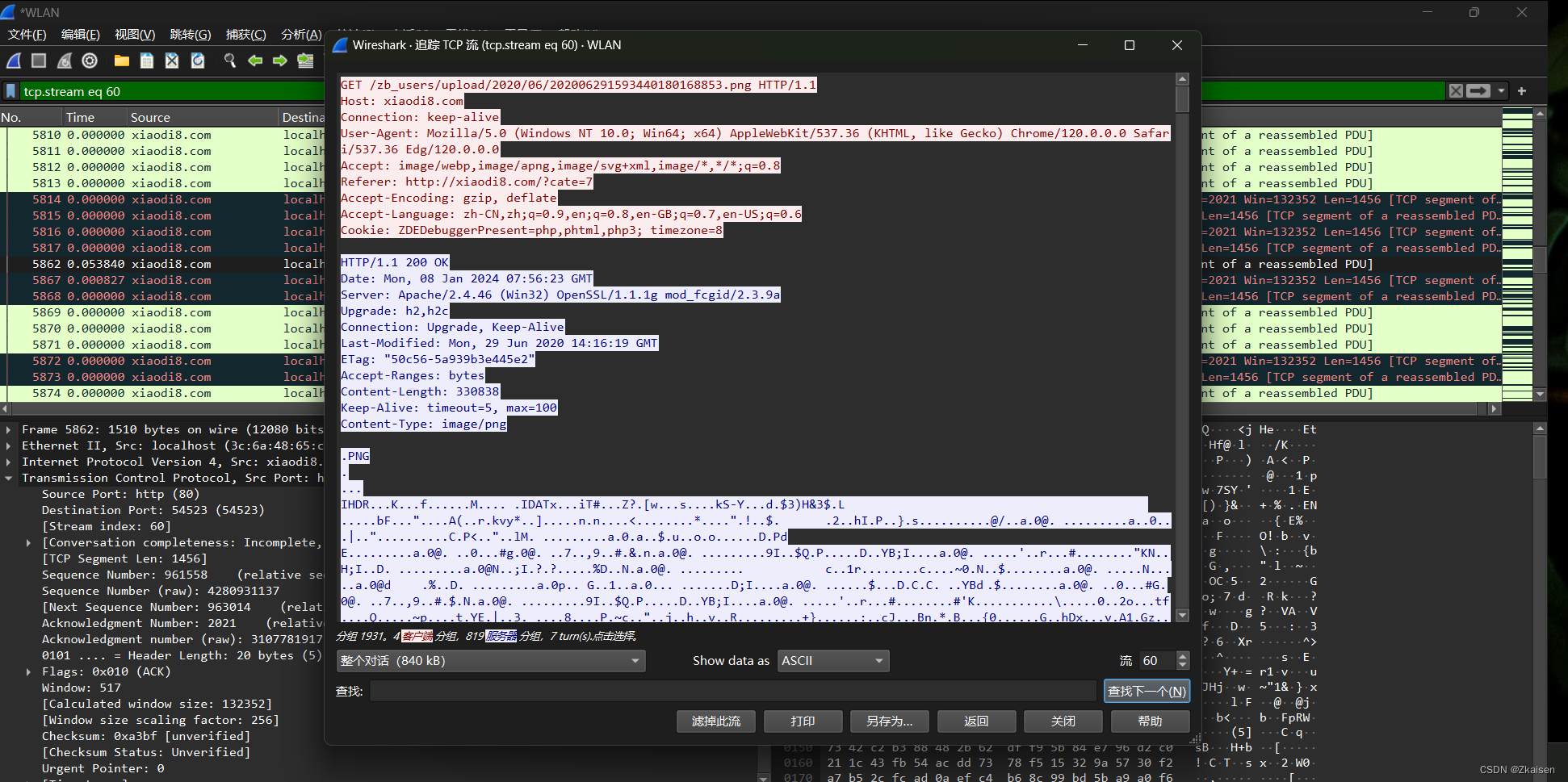
网络协议与攻击模拟_01winshark工具简介
一、TCP/IP协议簇 网络接口层(没有特定的协议) 物理层:PPPOE宽带拨号(应用场景:宽带拨号,运营商切网过来没有固定IP就需要拨号,家庭带宽一般都采用的是拨号方式)数据链路层网络层…...
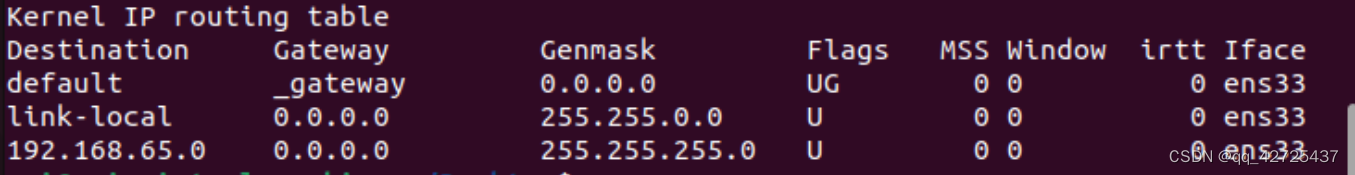
【linux学习笔记】网络
目录 【linux学习笔记】网络检查、监测网络ping-向网络主机发送特殊数据包traceroute-跟踪网络数据包的传输路径netstat-检查网络设置及相关统计数据 通过网络传输文件ftp 【linux学习笔记】网络 检查、监测网络 ping-向网络主机发送特殊数据包 最基本的网络连接命令就是pin…...

JUC-线程中断机制和LockSupport
线程中断机制 概念 java提供了一种用于停止线程的协商机制-中断。称为中断标识协商机制。 常用API public void interrupt() 仅仅让线程的中断标志位设置为true。不进行其他操作。public boolean isInterrupted() 获取中断标志位的状态。public static boolean interrupted…...
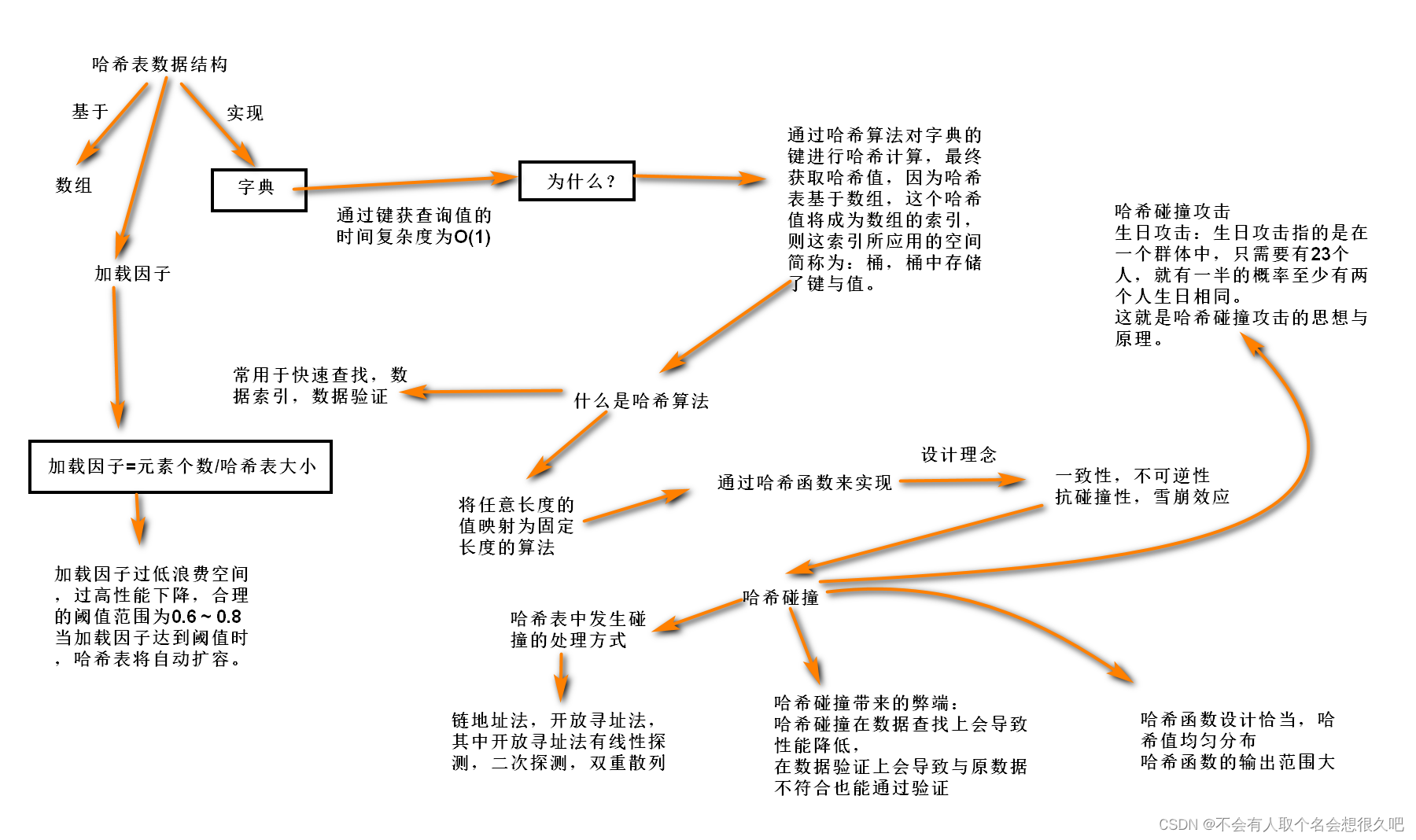
哈希表与哈希算法(Python系列30)
在讲哈希表数据结构和哈希算法之前,我想先刨析一下数组和python中的列表 首先来讲一下数组,我想在这提出一个疑问: 为什么数组通过索引查询数据的时间复杂度为O(1),也就是不管数组有多大,算法的执行时间都是不变的。…...

『 C++ 』AVL树详解 ( 万字 )
🦈STL容器类型 在STL的容器中,分为几种容器: 序列式容器(Sequence Containers): 这些容器以线性顺序存储元素,保留了元素的插入顺序。 支持随机访问,因此可以使用索引或迭代器快速访问任何位置的元素。 主要的序列式…...

Python下载安装pip方法与步骤_pip国内镜像
前提:下载安装好 python 打开命令提示符winR->cmd(不需要进入 python,直接在终端输入指令执行即可,也可以再 pycharm 终端执行命令)加入要安装ipython,需要执行以下命令: pip install **<…...
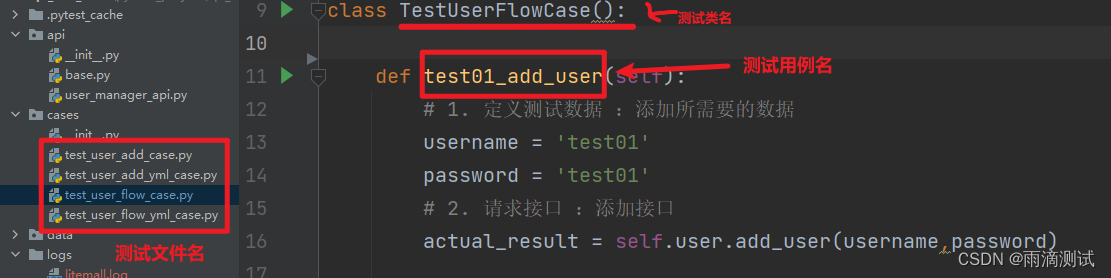
自动化测试框架pytest系列之基础概念介绍(一)
如果你要打算学习自动化测试 ,无论是web自动化、app自动化还是接口自动化 ,在学习的道路上,你几乎会遇到pytest这个测试框架,因为自动化编写没有测试框架,根本玩不了 。 如果你已经是一位自动化测试人员 ,…...

编码技巧:如何在Golang中高效解析和生成XML
编码技巧:如何在Golang中高效解析和生成XML 引言Golang中的XML基础解析XML文件生成XML文件错误处理和调试高级技巧和最佳实践总结 引言 在当今数据驱动的编程世界中,有效地处理各种数据格式是每个开发人员必备的技能之一。其中,XMLÿ…...

24校招,帆书测试开发工程师一面
前言 樊高读书是帆书的前身,我之前还看过他们的书,缘分闭环了 时间:25min 平台:飞书视频面试 过程 自我介绍为啥从后端转测试?通过实习经历,对测试有什么了解?讲一下游戏测试经历负责什么业…...

Java 方法以及在计算机内部的调用问题
修饰符 返回值类型 方法名( 形参列表 ){ 方法体代码(需要执行的功能代码) return 返回值; } 方法在内种没有先后顺序,但是不能把一个方法定义在另一个方法中。 方法的返回值类型写void(无返回申明)时,方法内不能使用return返回数…...
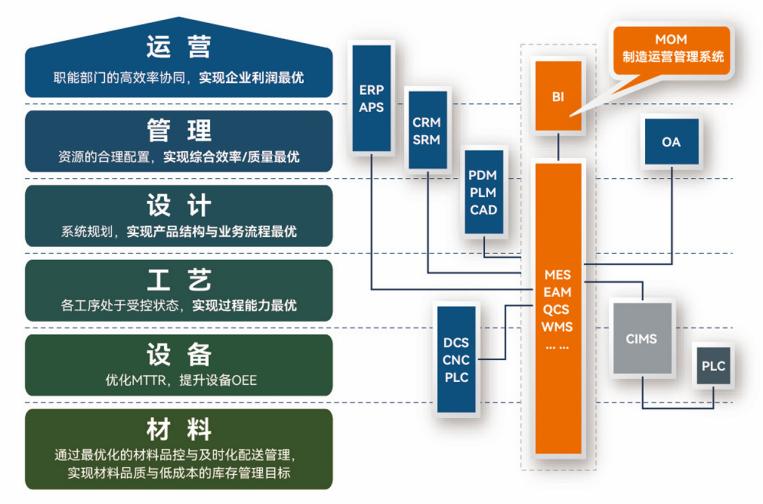
盘古信息PCB行业解决方案:以全域场景重构,激活智造新未来
一、破局:PCB行业的时代之问 在数字经济蓬勃发展的浪潮中,PCB(印制电路板)作为 “电子产品之母”,其重要性愈发凸显。随着 5G、人工智能等新兴技术的加速渗透,PCB行业面临着前所未有的挑战与机遇。产品迭代…...

STM32F4基本定时器使用和原理详解
STM32F4基本定时器使用和原理详解 前言如何确定定时器挂载在哪条时钟线上配置及使用方法参数配置PrescalerCounter ModeCounter Periodauto-reload preloadTrigger Event Selection 中断配置生成的代码及使用方法初始化代码基本定时器触发DCA或者ADC的代码讲解中断代码定时启动…...

Frozen-Flask :将 Flask 应用“冻结”为静态文件
Frozen-Flask 是一个用于将 Flask 应用“冻结”为静态文件的 Python 扩展。它的核心用途是:将一个 Flask Web 应用生成成纯静态 HTML 文件,从而可以部署到静态网站托管服务上,如 GitHub Pages、Netlify 或任何支持静态文件的网站服务器。 &am…...
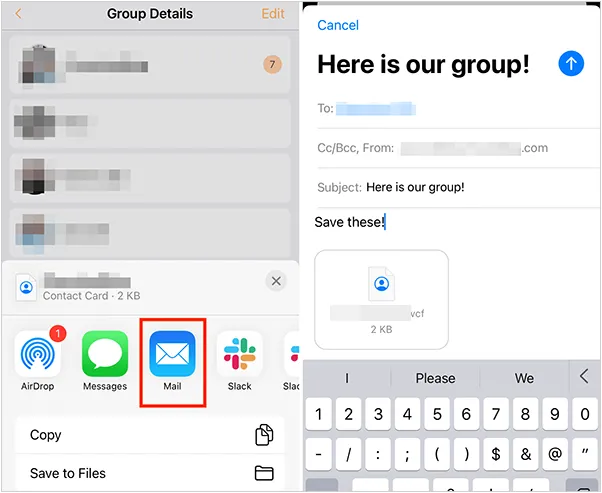
如何将联系人从 iPhone 转移到 Android
从 iPhone 换到 Android 手机时,你可能需要保留重要的数据,例如通讯录。好在,将通讯录从 iPhone 转移到 Android 手机非常简单,你可以从本文中学习 6 种可靠的方法,确保随时保持连接,不错过任何信息。 第 1…...

C++八股 —— 单例模式
文章目录 1. 基本概念2. 设计要点3. 实现方式4. 详解懒汉模式 1. 基本概念 线程安全(Thread Safety) 线程安全是指在多线程环境下,某个函数、类或代码片段能够被多个线程同时调用时,仍能保证数据的一致性和逻辑的正确性…...

Java线上CPU飙高问题排查全指南
一、引言 在Java应用的线上运行环境中,CPU飙高是一个常见且棘手的性能问题。当系统出现CPU飙高时,通常会导致应用响应缓慢,甚至服务不可用,严重影响用户体验和业务运行。因此,掌握一套科学有效的CPU飙高问题排查方法&…...

Spring是如何解决Bean的循环依赖:三级缓存机制
1、什么是 Bean 的循环依赖 在 Spring框架中,Bean 的循环依赖是指多个 Bean 之间互相持有对方引用,形成闭环依赖关系的现象。 多个 Bean 的依赖关系构成环形链路,例如: 双向依赖:Bean A 依赖 Bean B,同时 Bean B 也依赖 Bean A(A↔B)。链条循环: Bean A → Bean…...
:观察者模式)
JS设计模式(4):观察者模式
JS设计模式(4):观察者模式 一、引入 在开发中,我们经常会遇到这样的场景:一个对象的状态变化需要自动通知其他对象,比如: 电商平台中,商品库存变化时需要通知所有订阅该商品的用户;新闻网站中࿰…...
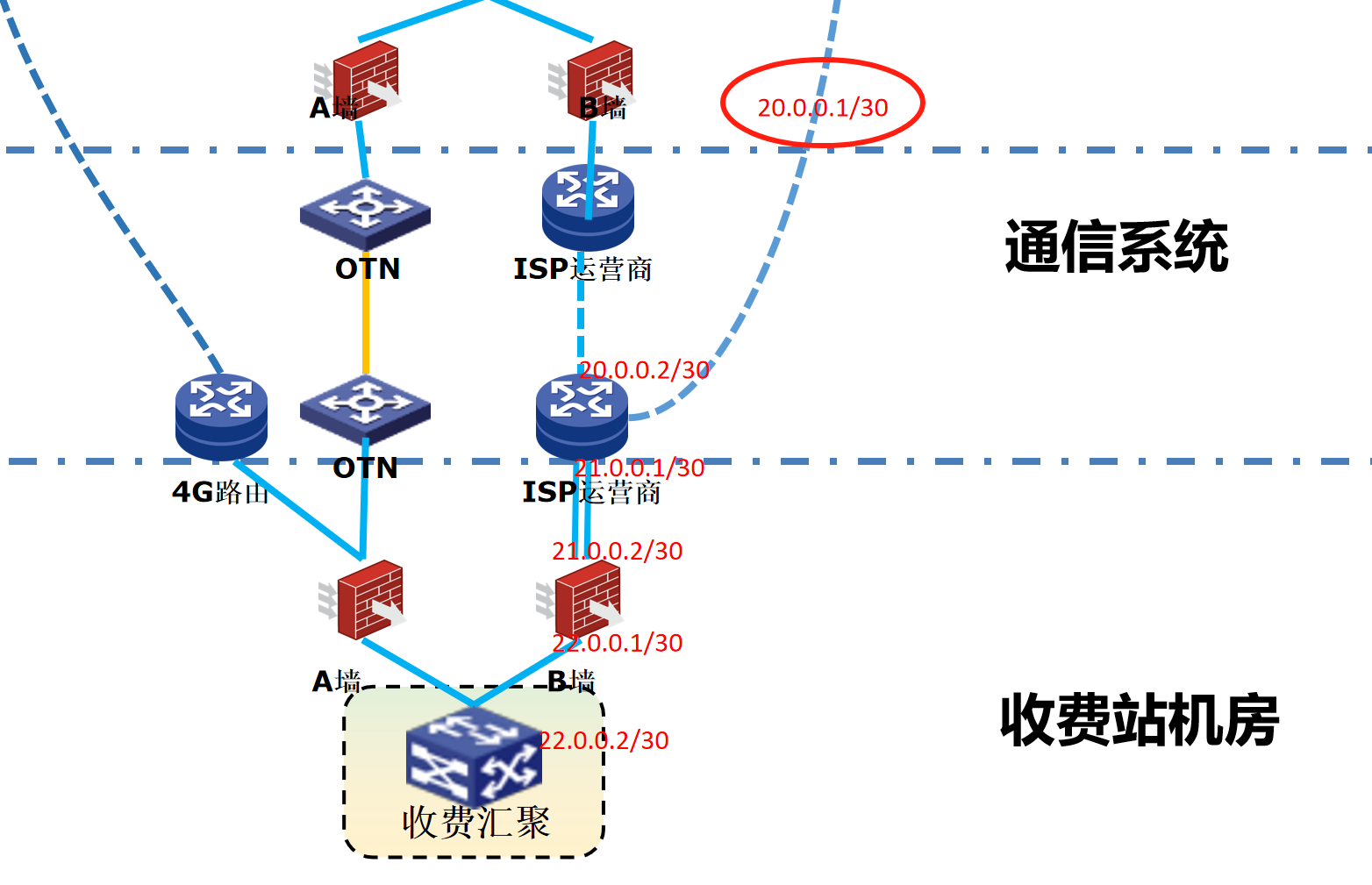
浪潮交换机配置track检测实现高速公路收费网络主备切换NQA
浪潮交换机track配置 项目背景高速网络拓扑网络情况分析通信线路收费网络路由 收费汇聚交换机相应配置收费汇聚track配置 项目背景 在实施省内一条高速公路时遇到的需求,本次涉及的主要是收费汇聚交换机的配置,浪潮网络设备在高速项目很少,通…...
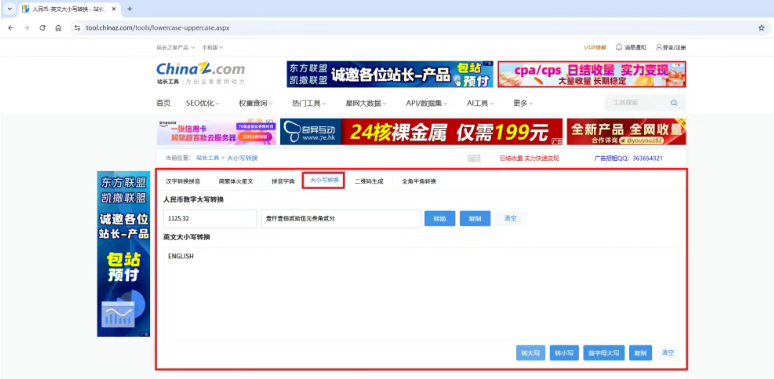
【分享】推荐一些办公小工具
1、PDF 在线转换 https://smallpdf.com/cn/pdf-tools 推荐理由:大部分的转换软件需要收费,要么功能不齐全,而开会员又用不了几次浪费钱,借用别人的又不安全。 这个网站它不需要登录或下载安装。而且提供的免费功能就能满足日常…...
