用Matlab 2015a svmtrain函数训练的SVM model在2021b无法使用的解决方法
背景
- 与r2015a版本的Matlab相比,r2021b版本中包含更多集成好的算法模块(尤其是深度学习的模块),想把原来r2015a版本的代码升级到r2021b
- 高版本的Matlab已经采用fitcsvm函数和predict函数替代了旧版本中svmtrain函数和svmclassify函数。在r2021b中运行原来的代码时提示
未定义与 'struct' 类型的输入参数相对应的函数 'svmclassify'
- 当直接把svmclassify换成predict函数时,提示
错误使用 predict (第 124 行)
No valid system or dataset was specified.
- 原先用于训练svm model的数据已经丢失,无法用新版本的fitcsvm函数重新训练svm model,想直接在r2021b中调用原先训练好的svm model
解决方法
把下面这4个函数保存到原来的代码文件夹中,再在Matlab r2021b中运行原来的代码即可,注意运行原来的代码前,把 svmclassify 改成 svmclassify_r2015a。(这4个函数是从matlab r2015a中复制过来并修改了函数名的)
function outclass = svmclassify_r2015a(svmStruct,sample, varargin)
%SVMCLASSIFY Classify data using a support vector machine
% SVMCLASSIFY will be removed in a future release. Use the PREDICT method of
% an object returned by FITCSVM instead.
%
% GROUP = SVMCLASSIFY(SVMSTRUCT, TEST) classifies each row in TEST using
% the support vector machine classifier structure SVMSTRUCT created
% using SVMTRAIN, and returns the predicted class level GROUP. TEST must
% have the same number of columns as the data used to train the
% classifier in SVMTRAIN. GROUP indicates the group to which each row of
% TEST is assigned.
%
% GROUP = SVMCLASSIFY(...,'SHOWPLOT',true) plots the test data TEST on
% the figure created using the SHOWPLOT option in SVMTRAIN.
%
% Example:
% % Load the data and select features for classification
% load fisheriris
% X = [meas(:,1), meas(:,2)];
% % Extract the Setosa class
% Y = nominal(ismember(species,'setosa'));
% % Randomly partitions observations into a training set and a test
% % set using stratified holdout
% P = cvpartition(Y,'Holdout',0.20);
% % Use a linear support vector machine classifier
% svmStruct = svmtrain(X(P.training,:),Y(P.training),'showplot',true);
% C = svmclassify(svmStruct,X(P.test,:),'showplot',true);
% err_rate = sum(Y(P.test)~= C)/P.TestSize % mis-classification rate
% conMat = confusionmat(Y(P.test),C) % the confusion matrix
%
% See also SVMTRAIN, CLASSIFY, TREEBAGGER, fitcsvm.% Copyright 2004-2014 The MathWorks, Inc.% References:
%
% [1] Cristianini, N., Shawe-Taylor, J An Introduction to Support
% Vector Machines, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 2000.
% http://www.support-vector.net
% [2] Kecman, V, Learning and Soft Computing,
% MIT Press, Cambridge, MA. 2001.
% [3] Suykens, J.A.K., Van Gestel, T., De Brabanter, J., De Moor, B.,
% Vandewalle, J., Least Squares Support Vector Machines,
% World Scientific, Singapore, 2002.% set defaults
plotflag = false;% check inputs
narginchk(2, Inf);% deal with struct input case
if ~isstruct(svmStruct)error(message('stats:svmclassify:TwoInputsNoStruct'));
endif ~isnumeric(sample) || ~ismatrix(sample)error(message('stats:svmclassify:BadSample'));
endif size(sample,2)~=size(svmStruct.SupportVectors,2)error(message('stats:svmclassify:TestSizeMismatch'));
end% deal with the various inputs
if nargin > 2if rem(nargin,2) == 1error(message('stats:svmclassify:IncorrectNumberOfArguments'));endokargs = {'showplot','-compilerhelper'};for j=1:2:nargin-2pname = varargin{j};pval = varargin{j+1};k = find(strncmpi(pname, okargs,numel(pname)));if isempty(k)error(message('stats:svmclassify:UnknownParameterName', pname));elseif length(k)>1error(message('stats:svmclassify:AmbiguousParameterName', pname));elseswitch(k)case 1 % plotflag ('SHOWPLOT')plotflag = opttf(pval,okargs{k}); case 2 % help the compiler find required function handles by including svmtrainsvmtrain_r2015a(eye(2),[1 0]);endendend
endgroupnames = svmStruct.GroupNames;% check group is a vector -- though char input is special...
if ~isvector(groupnames) && ~ischar(groupnames)error(message('stats:svmclassify:GroupNotVector'));
end% grp2idx sorts a numeric grouping var ascending, and a string grouping
% var by order of first occurrence
[~,groupString,glevels] = grp2idx(groupnames); % do the classification
if ~isempty(sample)% shift and scale the data if necessary:sampleOrig = sample;if ~isempty(svmStruct.ScaleData)for c = 1:size(sample, 2)sample(:,c) = svmStruct.ScaleData.scaleFactor(c) * ...(sample(:,c) + svmStruct.ScaleData.shift(c));endendtryoutclass = svmdecision_r2015a(sample,svmStruct);catch MEerror(message('stats:svmclassify:ClassifyFailed', ME.message));endif plotflagif isempty(svmStruct.FigureHandles)warning(message('stats:svmclassify:NoTrainingFigure'));elsetryhAxis = svmStruct.FigureHandles{1};hLines = svmStruct.FigureHandles{2};hSV = svmStruct.FigureHandles{3};% unscale the data for plotting purposes[~,hClassLines] = svmplotdata(sampleOrig,outclass,hAxis); trainingString = strcat(cellstr(groupString),' (training)');sampleString = strcat(cellstr(groupString),' (classified)');legendHandles = {hLines(1),hClassLines{1},...hLines(2),hClassLines{2},hSV};legendNames = {trainingString{1},sampleString{1},...trainingString{2},sampleString{2},'Support Vectors'};ok = ~cellfun(@isempty,legendHandles);legend([legendHandles{ok}],legendNames(ok));catch MEwarning(message('stats:svmclassify:DisplayFailed', ME.message));endendendoutclass(outclass == -1) = 2;unClassified = isnan(outclass);outclass = glevels(outclass(~unClassified),:);if any(unClassified)tryoutclass = statinsertnan(unClassified,outclass);catch MEif ~isequal(ME.identifier,'stats:statinsertnan:LogicalInput')rethrow(ME);elseerror(message('stats:svmclassify:logicalwithNaN'));endendendelseoutclass = [];
endfunction [svm_struct, svIndex] = svmtrain_r2015a(training, groupnames, varargin)
%SVMTRAIN Train a support vector machine classifier
% SVMTRAIN will be removed in a future release. Use FITCSVM instead.
%
% SVMSTRUCT = SVMTRAIN(TRAINING, Y) trains a support vector machine (SVM)
% classifier on data taken from two groups. TRAINING is a numeric matrix
% of predictor data. Rows of TRAINING correspond to observations; columns
% correspond to features. Y is a column vector that contains the known
% class labels for TRAINING. Y is a grouping variable, i.e., it can be a
% categorical, numeric, or logical vector; a cell vector of strings; or a
% character matrix with each row representing a class label (see help for
% groupingvariable). Each element of Y specifies the group the
% corresponding row of TRAINING belongs to. TRAINING and Y must have the
% same number of rows. SVMSTRUCT contains information about the trained
% classifier, including the support vectors, that is used by SVMCLASSIFY
% for classification. SVMTRAIN treats NaNs, empty strings or 'undefined'
% values as missing values and ignores the corresponding rows in
% TRAINING and Y.
%
% SVMSTRUCT = SVMTRAIN(TRAINING, Y, 'PARAM1',val1, 'PARAM2',val2, ...)
% specifies one or more of the following name/value pairs:
%
% Name Value
% 'kernel_function' A string or a function handle specifying the
% kernel function used to represent the dot
% product in a new space. The value can be one of
% the following:
% 'linear' - Linear kernel or dot product
% (default). In this case, SVMTRAIN
% finds the optimal separating plane
% in the original space.
% 'quadratic' - Quadratic kernel
% 'polynomial' - Polynomial kernel with default
% order 3. To specify another order,
% use the 'polyorder' argument.
% 'rbf' - Gaussian Radial Basis Function
% with default scaling factor 1. To
% specify another scaling factor,
% use the 'rbf_sigma' argument.
% 'mlp' - Multilayer Perceptron kernel (MLP)
% with default weight 1 and default
% bias -1. To specify another weight
% or bias, use the 'mlp_params'
% argument.
% function - A kernel function specified using
% @(for example @KFUN), or an
% anonymous function. A kernel
% function must be of the form
%
% function K = KFUN(U, V)
%
% The returned value, K, is a matrix
% of size M-by-N, where M and N are
% the number of rows in U and V
% respectively.
%
% 'rbf_sigma' A positive number specifying the scaling factor
% in the Gaussian radial basis function kernel.
% Default is 1.
%
% 'polyorder' A positive integer specifying the order of the
% polynomial kernel. Default is 3.
%
% 'mlp_params' A vector [P1 P2] specifying the parameters of MLP
% kernel. The MLP kernel takes the form:
% K = tanh(P1*U*V' + P2),
% where P1 > 0 and P2 < 0. Default is [1,-1].
%
% 'method' A string specifying the method used to find the
% separating hyperplane. Choices are:
% 'SMO' - Sequential Minimal Optimization (SMO)
% method (default). It implements the L1
% soft-margin SVM classifier.
% 'QP' - Quadratic programming (requires an
% Optimization Toolbox license). It
% implements the L2 soft-margin SVM
% classifier. Method 'QP' doesn't scale
% well for TRAINING with large number of
% observations.
% 'LS' - Least-squares method. It implements the
% L2 soft-margin SVM classifier.
%
% 'options' Options structure created using either STATSET or
% OPTIMSET.
% * When you set 'method' to 'SMO' (default),
% create the options structure using STATSET.
% Applicable options:
% 'Display' Level of display output. Choices
% are 'off' (the default), 'iter', and
% 'final'. Value 'iter' reports every
% 500 iterations.
% 'MaxIter' A positive integer specifying the
% maximum number of iterations allowed.
% Default is 15000 for method 'SMO'.
% * When you set method to 'QP', create the
% options structure using OPTIMSET. For details
% of applicable options choices, see QUADPROG
% options. SVM uses a convex quadratic program,
% so you can choose the 'interior-point-convex'
% algorithm in QUADPROG.
%
% 'tolkkt' A positive scalar that specifies the tolerance
% with which the Karush-Kuhn-Tucker (KKT) conditions
% are checked for method 'SMO'. Default is
% 1.0000e-003.
%
% 'kktviolationlevel' A scalar specifying the fraction of observations
% that are allowed to violate the KKT conditions for
% method 'SMO'. Setting this value to be positive
% helps the algorithm to converge faster if it is
% fluctuating near a good solution. Default is 0.
%
% 'kernelcachelimit' A positive scalar S specifying the size of the
% kernel matrix cache for method 'SMO'. The
% algorithm keeps a matrix with up to S * S
% double-precision numbers in memory. Default is
% 5000. When the number of points in TRAINING
% exceeds S, the SMO method slows down. It's
% recommended to set S as large as your system
% permits.
%
% 'boxconstraint' The box constraint C for the soft margin. C can be
% a positive numeric scalar or a vector of positive
% numbers with the number of elements equal to the
% number of rows in TRAINING.
% Default is 1.
% * If C is a scalar, it is automatically rescaled
% by N/(2*N1) for the observations of group one,
% and by N/(2*N2) for the observations of group
% two, where N1 is the number of observations in
% group one, N2 is the number of observations in
% group two. The rescaling is done to take into
% account unbalanced groups, i.e., when N1 and N2
% are different.
% * If C is a vector, then each element of C
% specifies the box constraint for the
% corresponding observation.
%
% 'autoscale' A logical value specifying whether or not to
% shift and scale the data points before training.
% When the value is true, the columns of TRAINING
% are shifted and scaled to have zero mean unit
% variance. Default is true.
%
% 'showplot' A logical value specifying whether or not to show
% a plot. When the value is true, SVMTRAIN creates a
% plot of the grouped data and the separating line
% for the classifier, when using data with 2
% features (columns). Default is false.
%
% SVMSTRUCT is a structure having the following properties:
%
% SupportVectors Matrix of data points with each row corresponding
% to a support vector.
% Note: when 'autoscale' is false, this field
% contains original support vectors in TRAINING.
% When 'autoscale' is true, this field contains
% shifted and scaled vectors from TRAINING.
% Alpha Vector of Lagrange multipliers for the support
% vectors. The sign is positive for support vectors
% belonging to the first group and negative for
% support vectors belonging to the second group.
% Bias Intercept of the hyperplane that separates
% the two groups.
% Note: when 'autoscale' is false, this field
% corresponds to the original data points in
% TRAINING. When 'autoscale' is true, this field
% corresponds to shifted and scaled data points.
% KernelFunction The function handle of kernel function used.
% KernelFunctionArgs Cell array containing the additional arguments
% for the kernel function.
% GroupNames A column vector that contains the known
% class labels for TRAINING. Y is a grouping
% variable (see help for groupingvariable).
% SupportVectorIndices A column vector indicating the indices of support
% vectors.
% ScaleData This field contains information about auto-scale.
% When 'autoscale' is false, it is empty. When
% 'autoscale' is set to true, it is a structure
% containing two fields:
% shift - A row vector containing the negative
% of the mean across all observations
% in TRAINING.
% scaleFactor - A row vector whose value is
% 1./STD(TRAINING).
% FigureHandles A vector of figure handles created by SVMTRAIN
% when 'showplot' argument is TRUE.
%
% Example:
% % Load the data and select features for classification
% load fisheriris
% X = [meas(:,1), meas(:,2)];
% % Extract the Setosa class
% Y = nominal(ismember(species,'setosa'));
% % Randomly partitions observations into a training set and a test
% % set using stratified holdout
% P = cvpartition(Y,'Holdout',0.20);
% % Use a linear support vector machine classifier
% svmStruct = svmtrain(X(P.training,:),Y(P.training),'showplot',true);
% C = svmclassify(svmStruct,X(P.test,:),'showplot',true);
% errRate = sum(Y(P.test)~= C)/P.TestSize %mis-classification rate
% conMat = confusionmat(Y(P.test),C) % the confusion matrix
%
% See also SVMCLASSIFY, CLASSIFY, TREEBAGGER, GROUPINGVARIABLE, fitcsvm.% Copyright 2004-2014 The MathWorks, Inc.% References:
%
% [1] Cristianini, N., Shawe-Taylor, J An Introduction to Support
% Vector Machines, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 2000.
% http://www.support-vector.net
% [2] Kecman, V, Learning and Soft Computing,
% MIT Press, Cambridge, MA. 2001.
% [3] Suykens, J.A.K., Van Gestel, T., De Brabanter, J., De Moor, B.,
% Vandewalle, J., Least Squares Support Vector Machines,
% World Scientific, Singapore, 2002.
% [4] J.C. Platt: A Fast Algorithm for Training Support Vector
% Machines, Advances in Kernel Methods - Support Vector Learning,
% MIT Press, 1998.
% [5] J.C. Platt: Fast Training of Support Vector Machines using
% Sequential Minimal Optimization Microsoft Research Technical
% Report MSR-TR-98-14, 1998.
% [6] http://www.kernel-machines.org/papers/tr-30-1998.ps.gz
%
% SVMTRAIN(...,'KFUNARGS',ARGS) allows you to pass additional
% arguments to kernel functions.narginchk(2, Inf);% check group is a vector or a char array
if ~isvector(groupnames) && ~ischar(groupnames)error(message('stats:svmtrain:GroupNotVector'));
end
% make sure that the data are correctly oriented.
if size(groupnames,1) == 1groupnames = groupnames';
endif ~isnumeric(training) || ~ismatrix(training) error(message('stats:svmtrain:TrainingBadType'));
end% grp2idx sorts a numeric grouping var ascending, and a string grouping
% var by order of first occurrence
[groupIndex, groupString] = grp2idx(groupnames);% make sure data is the right size
if size(training,1) ~= size(groupIndex,1)if size(training,2) == size(groupIndex,1)training = training';elseerror(message('stats:svmtrain:DataGroupSizeMismatch'))end
endif isempty(training)error(message('stats:svmtrain:NoData'))
endnans = isnan(groupIndex) | any(isnan(training),2);
if any(nans)training(nans,:) = [];groupIndex(nans) = [];
end
if isempty(training)error(message('stats:svmtrain:NoData'))
endngroups = length(unique(groupIndex));
nPoints = length(groupIndex);if ngroups > 2error(message('stats:svmtrain:TooManyGroups', ngroups))
end
if length(groupString) > ngroupswarning(message('stats:svmtrain:EmptyGroups'));end
% convert to groupIndex from 2 to -1.
groupIndex = 1 - (2* (groupIndex-1));pnames = {'kernel_function','method','showplot', 'polyorder','mlp_params',...'boxconstraint','rbf_sigma','autoscale', 'options',...'tolkkt','kktviolationlevel','kernelcachelimit'...'kfunargs', 'quadprog_opts','smo_opts'};
dflts = { 'linear', [], false, [], [], ....1, [], true , [] , ....[], [], [],...{} , [] , []};
[kfun,optimMethod, plotflag, polyOrder, mlpParams, boxC, rbf_sigma, ...autoScale, opts, tolkkt, kktvl,kerCL, kfunargs, qpOptsInput, ...smoOptsInput] = internal.stats.parseArgs(pnames, dflts, varargin{:});usePoly = false;
useMLP = false;
useSigma = false;
%parse kernel functions
if ischar(kfun)okfuns = {'linear','quadratic', 'radial','rbf','polynomial','mlp'};[~,i] = internal.stats.getParamVal(kfun,okfuns,'kernel_function');switch icase 1kfun = @linear_kernel;case 2kfun = @quadratic_kernel;case {3,4}kfun = @rbf_kernel;useSigma = true;case 5kfun = @poly_kernel;usePoly = true;case 6kfun = @mlp_kernel;useMLP = true;end
elseif ~isa(kfun, 'function_handle')error(message('stats:svmtrain:BadKernelFunction'));
end%parse optimization method
optimList ={'QP','SMO','LS'};
i = 2; % set to 'SMO'if ~isempty(optimMethod)[~,i] = internal.stats.getParamVal(optimMethod,optimList,'Method');if i==1 && ( ~license('test', 'optimization_toolbox') ...|| isempty(which('quadprog')))warning(message('stats:svmtrain:NoOptim'));i = 2;end
endif i == 2 && ngroups==1error(message('stats:svmtrain:InvalidY'));
end
optimMethod = optimList{i};% The large scale solver cannot handle this type of problem, so turn it off.
% qp_opts = optimset('LargeScale','Off','display','off');
% We can use the 'interior-point-convex' option
qp_opts = optimset('Algorithm','interior-point-convex','display','off');
smo_opts = statset('Display','off','MaxIter',15000);
%parse opts. opts will override 'quadprog_opt' and 'smo_opt' argument
if ~isempty(opts)qp_opts = optimset(qp_opts,opts);smo_opts = statset(smo_opts,opts);
else% only consider undocumented 'quadprog_opts' arguments% when 'opts' is empty; Otherwise, ignore 'quadprog_opts'if ~isempty(qpOptsInput)if isstruct(qpOptsInput)qp_opts = optimset(qp_opts,qpOptsInput);elseif iscell(qpOptsInput)qp_opts = optimset(qp_opts,qpOptsInput{:});elseerror(message('stats:svmtrain:BadQuadprogOpts'));endend
end% Turn off deprecation warning for svmsmoset
warning('off','stats:obsolete:ReplaceThisWith');
cleanupObj = onCleanup(@() warning('on','stats:obsolete:ReplaceThisWith'));if ~isempty(smoOptsInput) && isempty(tolkkt) && isempty(kktvl) ...&& isempty(kerCL) && isempty(opts)%back-compatibility.smo_opts = svmsmoset(smoOptsInput);
elseif isempty(tolkkt)tolkkt = 1e-3;endif isempty(kerCL)kerCL = 5000;endif isempty(kktvl)kktvl = 0;endsmo_opts = svmsmoset(smo_opts,'tolkkt',tolkkt,'KernelCacheLimit',kerCL,....'KKTViolationLevel',kktvl);
endif ~isscalar(smo_opts.TolKKT) || ~isnumeric(smo_opts.TolKKT) || smo_opts.TolKKT <= 0error(message('stats:svmtrain:badTolKKT'));
endif ~isscalar(smo_opts.KKTViolationLevel) || ~isnumeric(smo_opts.KKTViolationLevel)...|| smo_opts.KKTViolationLevel < 0 || smo_opts.KKTViolationLevel > 1error(message('stats:svmtrain:badKKTVL'));
endif ~isscalar(smo_opts.KernelCacheLimit) || ~isnumeric(smo_opts.KernelCacheLimit)...||smo_opts.KernelCacheLimit < 0error(message('stats:svmtrain:badKerCL'));
end%parse plot flag
plotflag = opttf(plotflag,'showplot');
if plotflag && size(training,2) ~=2plotflag = false;warning(message('stats:svmtrain:OnlyPlot2D'));
endif ~isempty(kfunargs) && ~iscell(kfunargs)kfunargs = {kfunargs};
end%polyOrder
if ~isempty(polyOrder)%setPoly = true;if ~usePolywarning(message('stats:svmtrain:PolyOrderNotPolyKernel'));elsekfunargs = {polyOrder};end
end% mlpparams
if ~isempty(mlpParams)if ~isnumeric(mlpParams) || numel(mlpParams)~=2error(message('stats:svmtrain:BadMLPParams'));endif mlpParams(1) <= 0error(message('stats:svmtrain:MLPWeightNotPositive'))endif mlpParams(2) >= 0warning(message('stats:svmtrain:MLPBiasNotNegative'))endif ~useMLPwarning(message('stats:svmtrain:MLPParamNotMLPKernel'));elsekfunargs = {mlpParams(1), mlpParams(2)};end
end%rbf_sigma
if ~isempty(rbf_sigma)if useSigmakfunargs = {rbf_sigma};elsewarning(message('stats:svmtrain:RBFParamNotRBFKernel'))end
end% box constraint: it can be a positive numeric scalar or a numeric vector
% of the same length as the number of data points
if isscalar(boxC) && isnumeric(boxC) && boxC > 0% scalar input: adjust to group size and transform into vector% set default value of box constraintboxconstraint = ones(nPoints, 1); n1 = length(find(groupIndex==1));n2 = length(find(groupIndex==-1));c1 = 0.5 * boxC * nPoints / n1;c2 = 0.5 * boxC * nPoints / n2;boxconstraint(groupIndex==1) = c1;boxconstraint(groupIndex==-1) = c2;
elseif isvector(boxC) && isnumeric(boxC) && all(boxC > 0) && (length(boxC) == nPoints)% vector inputboxconstraint = boxC;
elseerror(message('stats:svmtrain:InvalidBoxConstraint'));
end
% If boxconstraint == Inf then convergence will not
% happen so fix the value to 1/sqrt(eps).
boxconstraint = min(boxconstraint,repmat(1/sqrt(eps(class(boxconstraint))),...size(boxconstraint)));autoScale = opttf(autoScale,'autoscale');% plot the data if requested
if plotflag[hAxis,hLines] = svmplotdata(training,groupIndex);hLines = [hLines{1} hLines{2}];legend(hLines,cellstr(groupString));
end% autoscale data if required,
scaleData = [];
if autoScalescaleData.shift = - mean(training);stdVals = std(training);scaleData.scaleFactor = 1./stdVals;% leave zero-variance data unscaled:scaleData.scaleFactor(~isfinite(scaleData.scaleFactor)) = 1;% shift and scale columns of data matrix:for c = 1:size(training, 2)training(:,c) = scaleData.scaleFactor(c) * ...(training(:,c) + scaleData.shift(c));end
endif strcmpi(optimMethod, 'SMO')% if we have a kernel that takes extra arguments we must define a new% kernel function handle to be passed to seqminoptif ~isempty(kfunargs)tmp_kfun = @(x,y) feval(kfun, x,y, kfunargs{:});elsetmp_kfun = kfun;end[alpha, bias] = seqminopt(training, groupIndex, ...boxconstraint, tmp_kfun, smo_opts);svIndex = find(alpha > sqrt(eps));sv = training(svIndex,:);alphaHat = groupIndex(svIndex).*alpha(svIndex);else % QP and LS both need the kernel matrix:% calculate kernel function and add additional term required% for two-norm soft margintrykx = feval(kfun,training,training,kfunargs{:});% ensure function is symmetrickx = (kx+kx')/2 + diag(1./boxconstraint);catch MEm = message('stats:svmtrain:KernelFunctionError',func2str(kfun));throw(addCause(MException(m.Identifier,'%s',getString(m)),ME));end% create HessianH =((groupIndex * groupIndex').*kx);if strcmpi(optimMethod, 'QP')if strncmpi(qp_opts.Algorithm,'inte',4)X0 = [];elseX0= ones(nPoints,1);end[alpha, ~, exitflag, output] = quadprog(H,-ones(nPoints,1),[],[],...groupIndex',0,zeros(nPoints,1), Inf *ones(nPoints,1),...X0, qp_opts);if exitflag <= 0error(message('stats:svmtrain:UnsolvableOptimization', output.message));end% The support vectors are the non-zeros of alpha.% We could also use the zero values of the Lagrangian (fifth output of% quadprog) though the method below seems to be good enough.svIndex = find(alpha > sqrt(eps));sv = training(svIndex,:);% calculate the parameters of the separating line from the support% vectors.alphaHat = groupIndex(svIndex).*alpha(svIndex);% Calculate the bias by applying the indicator function to the support% vector with largest alpha.[~,maxPos] = max(alpha);bias = groupIndex(maxPos) - sum(alphaHat.*kx(svIndex,maxPos));% an alternative method is to average the values over all support vectors% bias = mean(groupIndex(sv)' - sum(alphaHat(:,ones(1,numSVs)).*kx(sv,sv)));% An alternative way to calculate support vectors is to look for zeros of% the Lagrangian (fifth output from QUADPROG).%% [alpha,fval,output,exitflag,t] = quadprog(H,-ones(nPoints,1),[],[],...% groupIndex',0,zeros(nPoints,1),inf *ones(nPoints,1),zeros(nPoints,1),opts);%% sv = t.lower < sqrt(eps) & t.upper < sqrt(eps);else % Least-Squares% now build up compound matrix for solverA = [0 groupIndex';groupIndex,H];b = [0;ones(size(groupIndex))];x = A\b;% calculate the parameters of the separating line from the support% vectors.sv = training;bias = x(1);alphaHat = groupIndex.*x(2:end);svIndex = (1:nPoints)';end
end
svm_struct.SupportVectors = sv;
svm_struct.Alpha = alphaHat;
svm_struct.Bias = bias;
svm_struct.KernelFunction = kfun;
svm_struct.KernelFunctionArgs = kfunargs;
svm_struct.GroupNames = groupnames;
svm_struct.SupportVectorIndices = svIndex;
svm_struct.ScaleData = scaleData;
svm_struct.FigureHandles = [];
if plotflaghSV = svmplotsvs(hAxis,hLines,groupString,svm_struct);svm_struct.FigureHandles = {hAxis,hLines,hSV};
endfunction [out,f] = svmdecision_r2015a(Xnew,svm_struct)
%SVMDECISION Evaluates the SVM decision function% Copyright 2004-2012 The MathWorks, Inc.sv = svm_struct.SupportVectors;
alphaHat = svm_struct.Alpha;
bias = svm_struct.Bias;
kfun = svm_struct.KernelFunction;
kfunargs = svm_struct.KernelFunctionArgs;f = (feval(kfun,sv,Xnew,kfunargs{:})'*alphaHat(:)) + bias;
out = sign(f);
% points on the boundary are assigned to class 1
out(out==0) = 1;
function options = svmsmoset_r2015a(varargin)
%SVMSMOSET Obsolete function.
% SVMSMOSET will be removed in a future release. Use FITCSVM instead.
%
% OPTIONS = SVMSMOSET('NAME1',VALUE1,'NAME2',VALUE2,...) creates an
% options structure OPTIONS in which the named properties have the
% specified values. Any unspecified properties have default values. It is
% sufficient to type only the leading characters that uniquely identify
% the property. Case is ignored for property names.
%
% OPTIONS = SVMSMOSET(OLDOPTS,'NAME1',VALUE1,...) alters an existing
% options structure OLDOPTS.
%
% OPTIONS = SVMSMOSET(OLDOPTS,NEWOPTS) combines an existing options
% structure OLDOPTS with a new options structure NEWOPTS. Any new
% properties overwrite corresponding old properties.
%
% SVMSMOSET with no input arguments displays all property names and their
% possible values.
%
% SVMSMOSET has the following properties:
%
% TolKKT
% Tolerance with which the Karush-Kuhn-Tucker (KKT) conditions are
% checked. Default value is 1e-3.
%
% MaxIter
% Maximum number of iterations of main loop. If this number is exceeded
% before the algorithm converges then the algorithm stops and gives an
% error. Default value is 15000.
%
% Display
% Controls the level of information about the optimization iterations
% that is displayed as the algorithm runs. The value can be 'off', which
% displays nothing, 'iter', which reports every 500 iterations, and
% 'final', which reports when the algorithm finishes. Default value is
% 'off'.
%
% KKTViolationLevel
% This number specifies the fraction of alphas that are allowed to
% violate the KKT conditions. Setting this to a value greater than 0 will
% help the algorithm to converge if it is fluctuating near a good
% solution. Default value is 0.
%
% KernelCacheLimit
% This number specifies the size of the kernel matrix cache. The
% algorithm keeps a matrix with up to KernelCacheLimit * KernelCacheLimit
% double numbers in memory. Default value is 5000.
%
% Examples:
%
% opts = svmsmoset('Display','final','MaxIter',20000,...
% 'KernelCacheLimit',1000);
% alt_opts = svmsmoset(opts,'Display','iter','KKTViolationLevel',.05);
%
% See also SVMCLASSIFY, SVMTRAIN, fitcsvm.% References:
%
% [1] Cristianini, N., Shawe-Taylor, J An Introduction to Support
% Vector Machines, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 2000.
% http://www.support-vector.net
% [2] J.C. Platt: A Fast Algorithm for Training Support Vector
% Machines, http://research.microsoft.com/users/jplatt/smo.html
% [3] R.-E. Fan, P.-H. Chen, and C.-J. Lin. Working Set Selection Using
% Second Order Information for Training SVM. Journal of Machine
% Learning Research, 6(2005), 1889-1918.
% [4] L. Bottou and C.-J. Lin. Support Vector Machine Solvers. 2006,
% available from http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/papers.html% Copyright 2006-2014 The MathWorks, Inc.%
% MaxNonBoundsIter -- may get added at a later date. Currently hardcoded
% Maximum number of iterations of the loop which tries to make the set of
% non-bound alphas (true support vectors) consistent. If this number is
% exceeded the algorithm continues with loop over the full set of alphas.
% Tuning this number can speed up the algorithm. Default value is 25.warning(message('stats:obsolete:ReplaceThisWith','svmsmoset','fitcsvm'));% Print out possible values of properties.
if (nargin == 0) && (nargout == 0)fprintf(' Display: [ off | iter | final ]\n');fprintf(' TolKKT: [ positive scalar ]\n');fprintf(' MaxIter: [ positive scalar ]\n');fprintf(' KernelCacheLimit: [ positive scalar ]\n');fprintf(' KKTViolationLevel: [ positive scalar]\n');fprintf('\n');return;
end% Create a struct of all the fields with all values set to
Options = {...'Display', 'off';'TolKKT', 1e-3;'MaxIter', 15000;'KKTViolationLevel', 0;'KernelCacheLimit', 5000;};Names = Options(:,1);
Defaults = Options(:,2);m = size(Names,1);% Combine all leading options structures o1, o2, ... in odeset(o1,o2,...).
for j = 1:moptions.(Names{j}) = Defaults{j};
end
% work through the inputs until we find a parameter name. Handle options
% structures as we go.
i = 1;
while i <= narginarg = varargin{i};if ischar(arg) % arg is an option namebreak;endif ~isempty(arg) % [] is a valid options argumentif ~isa(arg,'struct')error(message('stats:svmtrain:NoPropNameOrStruct', i));endfor j = 1:mif any(strcmp(fieldnames(arg),Names{j}))val = arg.(Names{j});elseval = [];endif ~isempty(val)options.(Names{j}) = val;endendendi = i + 1;
end% A finite state machine to parse name-value pairs.
if rem(nargin-i+1,2) ~= 0error(message('stats:svmtrain:ArgNameValueMismatch'));
end
expectval = 0; % start expecting a name, not a value
while i <= narginarg = varargin{i};if ~expectvalif ~ischar(arg)error(message('stats:svmtrain:NoPropName', i));endk = find(strncmpi(arg, Names,numel(arg)));if isempty(k)error(message('stats:svmtrain:UnknownParameterName', arg));elseif length(k)>1error(message('stats:svmtrain:AmbiguousParameterName', arg));endexpectval = 1; % we expect a value nextelseoptions.(Names{k}) = arg;expectval = 0;endi = i + 1;
endif expectvalerror(message('stats:svmtrain:NoValueForProp', arg));
end%check tolkkt其他
刚开始在网上搜索到 下载libsvm包并将其添加到Matlab toolbox中,可以继续使用svmtrain和svmclassify/svmpredict函数,尝试之后发现还是无法直接调用原来训练好的svm model,只能重新训练model
参考:
- 关于matlab2018a版本错误使用 svmclassify 分类器
- Matlab代码提示“svmtrain已删除 请改用fitcsvm”,以及svmpredict没有返回结果label和精度accuracy的解决办法
- LIBSVM – A Library for Support Vector Machines
- Old Version of LIBSVM
相关文章:

用Matlab 2015a svmtrain函数训练的SVM model在2021b无法使用的解决方法
背景 与r2015a版本的Matlab相比,r2021b版本中包含更多集成好的算法模块(尤其是深度学习的模块),想把原来r2015a版本的代码升级到r2021b高版本的Matlab已经采用fitcsvm函数和predict函数替代了旧版本中svmtrain函数和svmclassify函…...

umount:/home/tuners/windows files:目标忙。
您提到的错误信息 "umount: /home/tuners/windows files: 目标忙。" 是在尝试卸载(umount)一个文件系统时常见的错误。这个错误表明有一些进程仍然在使用挂载点(/home/tuners/windows files)下的文件或目录,…...
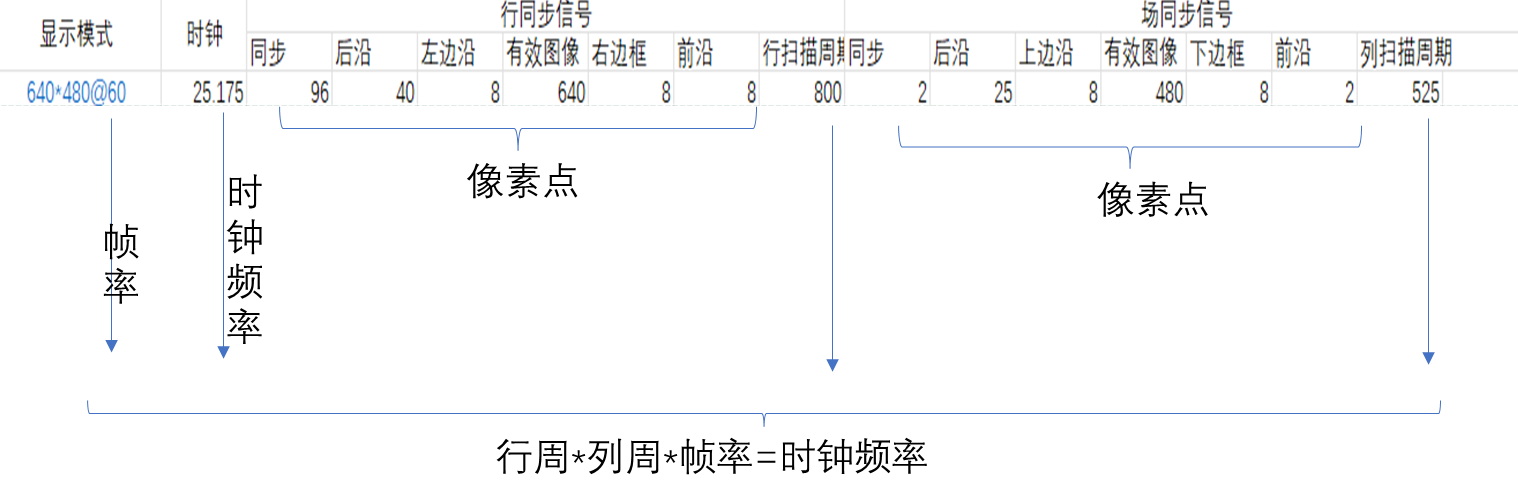
FPGA_vga显示
一 VGA 1.1 VGA VGA是视频图像阵列,是一种使用模拟信号进行视频传输的标准协议。 1.2 VGA接引脚定义 VGA分公母两种,RGB显示标准。 1.3 VGA显示器 VGA显示器采用图像扫描的方式进行图像显示,将构成图像的像素点,在行同步信号…...

sklearn模型指标和特征贡献度查看
文章目录 算法介绍r2_scoretrain_test_splitDecisionTreeRegressor参考文献支持快速查看traget和特征之间的关系 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import pandas as pd pd.set_option(display.max_columns, None) pd.set_option...
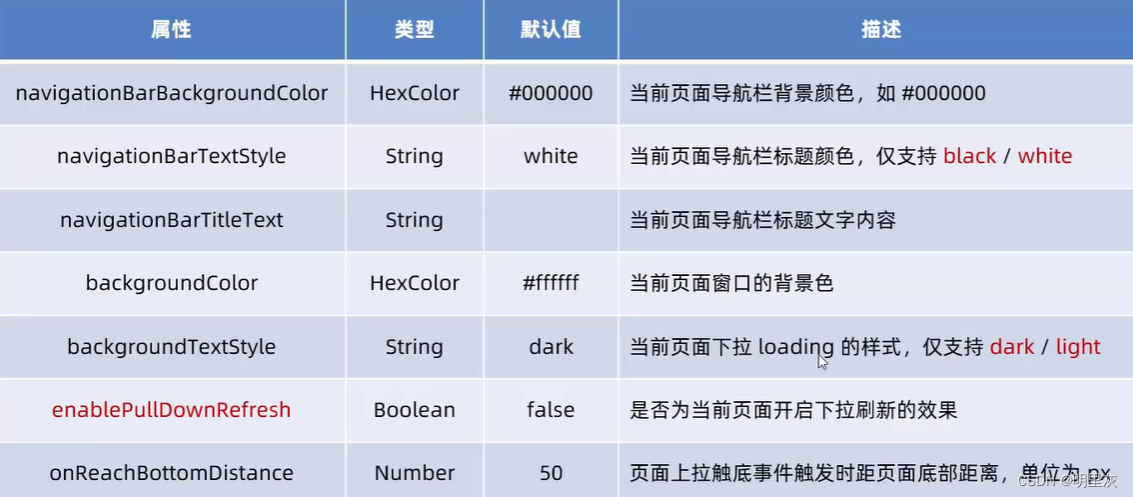
2024.2.6日总结(小程序开发3)
页面配置 页面配置和全局配置的关系: 小程序中,app.json中的window节点,可以全局配置小程序中每个页面的窗口表现 如果某些小程序想要有特殊的窗口表现,可以用页面级别的.json配置文件实现这个需求 页面配置和全局配置冲突时&…...

相机图像质量研究(10)常见问题总结:光学结构对成像的影响--光圈
系列文章目录 相机图像质量研究(1)Camera成像流程介绍 相机图像质量研究(2)ISP专用平台调优介绍 相机图像质量研究(3)图像质量测试介绍 相机图像质量研究(4)常见问题总结:光学结构对成像的影响--焦距 相机图像质量研究(5)常见问题总结:光学结构对成…...
(3)——3.HTTP基于TCP还是UDP?)
TCP和UDP相关问题(重点)(3)——3.HTTP基于TCP还是UDP?
HTTP/3.0 之前是基于 TCP 协议的,而 HTTP/3.0 将弃用 TCP,改用 基于 UDP 的 QUIC 协议 。具体见HTTP相关问题-CSDN博客...
基于modbus rtu协议操作PLC的EPICS示例
硬件设备 本实验中使用到的设备如下: 1、S7-200 Smart SR20 PLC 作为受控设备,执行机构。 S7-200 Smart是西门子的一款小型PLC产品(以下简称Smart系列)。 Smart系列PLC是西门子公司经过大量调研,为中国小型自动化…...
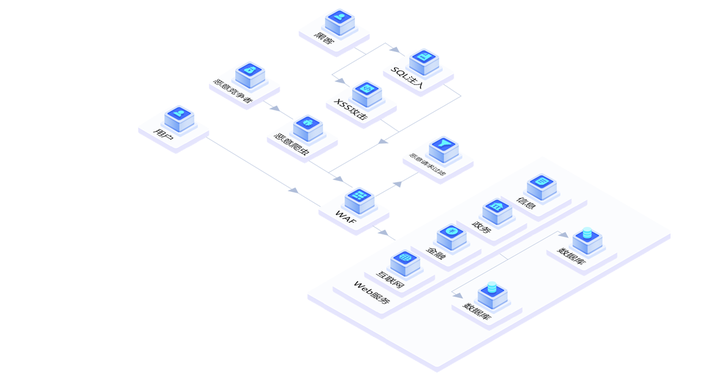
网站被攻击有什么办法呢?
最近,德迅云安全遇到不少网站用户遇到攻击问题,来咨询安全解决方案。目前在所有的网络攻击方式中,DDoS是最常见,也是最高频的攻击方式之一。不少用户网站上线后,经常会遭受到攻击的困扰。有些攻击持续时间比较短影响较…...

VoIP之主备注册服务器机制
在IP话机的实际使用中,不可避免的会出现服务器离线运维、服务宕机、IP话机和服务器连接中断等情况。为了保证电话服务的连续性,在VoIP部署服环境中必须有冗余机制。常见的冗余机制以主备服务器的形式实现。 一、主备机制原理 话机正常情况下注册在主服…...

【数据分享】1929-2023年全球站点的逐年平均降水量(Shp\Excel\免费获取)
气象数据是在各项研究中都经常使用的数据,气象指标包括气温、风速、降水、湿度等指标,说到常用的降水数据,最详细的降水数据是具体到气象监测站点的降水数据! 有关气象指标的监测站点数据,之前我们分享过1929-2023年全…...
uniapp /微信小程序 使用map组件实现手绘地图方案
获取地图范围 点图拾取坐标-地图开放平台|腾讯位置服务 获取需要手绘地图左下角和右上角GPS坐标 以北京故宫为例: 截取需要手绘地图进行手绘地图制作 素材处理 由于地图素材文件比较大,小程序又限制包大小<2M,无…...

react+antd+CheckableTag实现Tag标签单选或多选功能
1、效果如下图 实现tag标签单选或多选功能 2、环境准备 1、react18 2、antd 4 3、功能实现 原理: 封装一个受控组件,接受父组件的参数,数据发现变化后,回传给父组件 1、首先,引入CheckableTag组件和useEffect, useMemo, use…...

UUID和雪花(Snowflake)算法该如何选择?
UUID和雪花(Snowflake)算法该如何选择? UUID 和 Snowflake 都可以生成唯一标识,在分布式系统中可以说是必备利器,那么我们该如何对不同的场景进行不同算法的选择呢,UUID 简单无序十分适合生成 requestID, Snowflake 里…...

Jetpack Compose之进度条介绍(ProgressIndicator)
JetPack Compose系列(12)—进度条介绍 Compose自带进度条控件有两个,分别是:CircularProgressIndicator(圆形进度条)和LinearProgressIndicator(线性进度条)。 CircularProgressIn…...
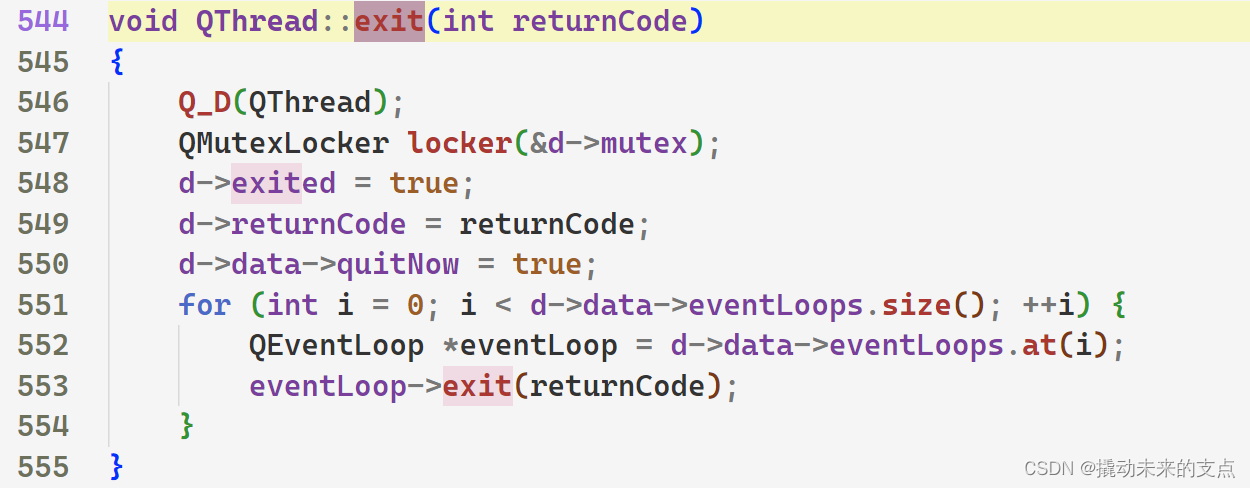
【Qt基本功修炼】Qt线程的两种运行模式
1. 前言 QThread是Qt中的线程类,用于实现多线程运行。 QThread有两种工作模式,即 消息循环模式无消息循环模式 两种模式分别适用于不同的场景。下面我们将从多个方面,讲解QThread两种工作模式的区别。 2. 消息循环模式 2.1 实现原理 Q…...
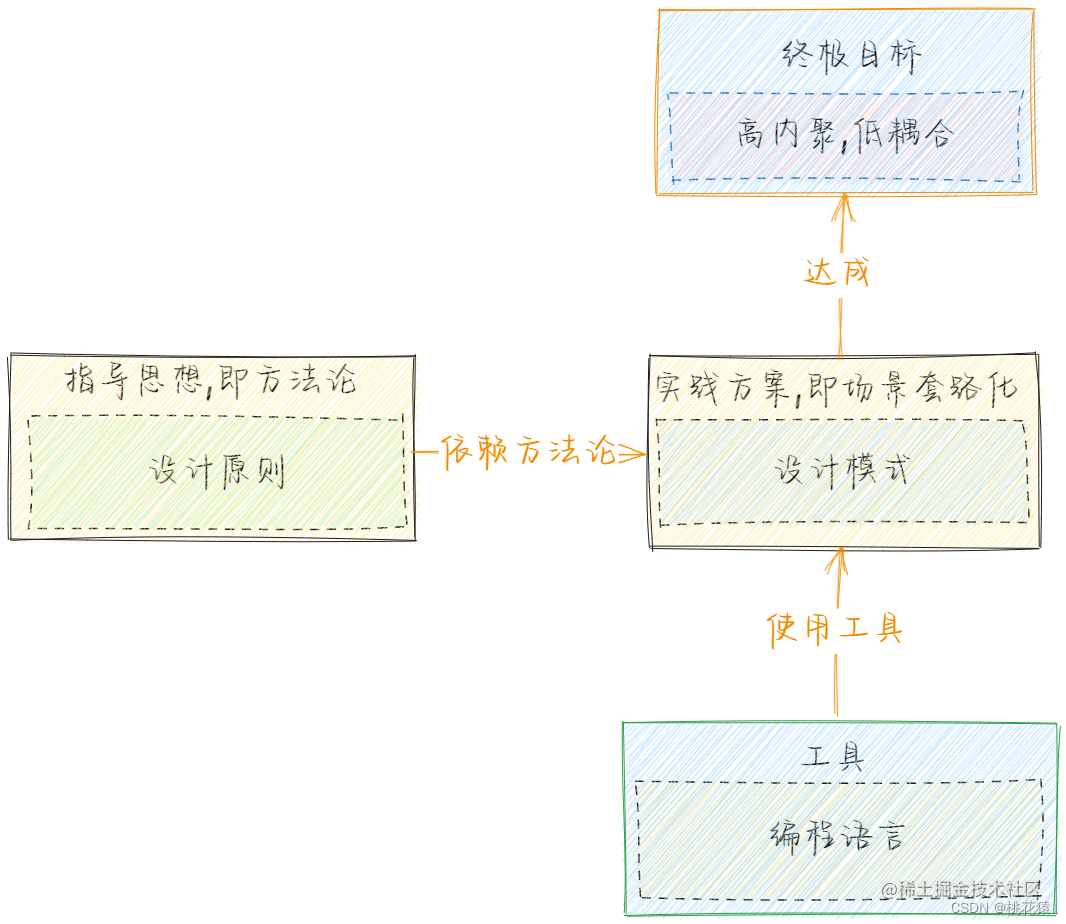
三、设计模式相关理论总结
一、面向对象编程 1.1 概述 简称Object Oriented Program(OOP),指以类或对象作为基础组织单元,遵循封装、继承、多态以及抽象等特性,进行编程。其中面向对象不一定遵循封装、继承、封装和多态等特性,只是前人总结的套路规范&…...

鸿蒙 WiFi 连接 流程
那当界面上显示扫描到的所有Ap时,我们选择其中的一个Ap发起连接,看下代码流程是怎样的。 // applications/standard/settings/product/phone/src/main/ets/model/wifiImpl/WifiModel.tsconnectWiFi(password: string) {let apInfo this.userSelectedAp…...

golang 创建unix socket http服务端
服务端 package mainimport ("fmt""net""net/http""os" )func main() {http.HandleFunc("/", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {w.Write([]byte("hello"))})http.HandleFunc("/world", …...

annaconda如何切换当前python环境
annaconda默认的python环境是base: 把各种项目的依赖都安装到base环境中不是一个好的习惯,比如说我们做爬虫项目和做自动化测试项目等所需要的依赖是不一样的,我们可以将为每个项目创建自己的环境,在各自的环境中安装自己的依赖&…...

利用ngx_stream_return_module构建简易 TCP/UDP 响应网关
一、模块概述 ngx_stream_return_module 提供了一个极简的指令: return <value>;在收到客户端连接后,立即将 <value> 写回并关闭连接。<value> 支持内嵌文本和内置变量(如 $time_iso8601、$remote_addr 等)&a…...
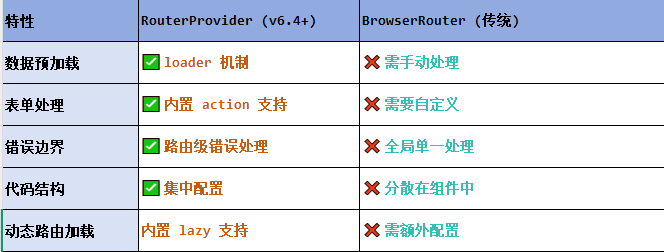
React第五十七节 Router中RouterProvider使用详解及注意事项
前言 在 React Router v6.4 中,RouterProvider 是一个核心组件,用于提供基于数据路由(data routers)的新型路由方案。 它替代了传统的 <BrowserRouter>,支持更强大的数据加载和操作功能(如 loader 和…...

FFmpeg 低延迟同屏方案
引言 在实时互动需求激增的当下,无论是在线教育中的师生同屏演示、远程办公的屏幕共享协作,还是游戏直播的画面实时传输,低延迟同屏已成为保障用户体验的核心指标。FFmpeg 作为一款功能强大的多媒体框架,凭借其灵活的编解码、数据…...

解决本地部署 SmolVLM2 大语言模型运行 flash-attn 报错
出现的问题 安装 flash-attn 会一直卡在 build 那一步或者运行报错 解决办法 是因为你安装的 flash-attn 版本没有对应上,所以报错,到 https://github.com/Dao-AILab/flash-attention/releases 下载对应版本,cu、torch、cp 的版本一定要对…...

Linux --进程控制
本文从以下五个方面来初步认识进程控制: 目录 进程创建 进程终止 进程等待 进程替换 模拟实现一个微型shell 进程创建 在Linux系统中我们可以在一个进程使用系统调用fork()来创建子进程,创建出来的进程就是子进程,原来的进程为父进程。…...
使用 SymPy 进行向量和矩阵的高级操作
在科学计算和工程领域,向量和矩阵操作是解决问题的核心技能之一。Python 的 SymPy 库提供了强大的符号计算功能,能够高效地处理向量和矩阵的各种操作。本文将深入探讨如何使用 SymPy 进行向量和矩阵的创建、合并以及维度拓展等操作,并通过具体…...

JS手写代码篇----使用Promise封装AJAX请求
15、使用Promise封装AJAX请求 promise就有reject和resolve了,就不必写成功和失败的回调函数了 const BASEURL ./手写ajax/test.jsonfunction promiseAjax() {return new Promise((resolve, reject) > {const xhr new XMLHttpRequest();xhr.open("get&quo…...
FFmpeg:Windows系统小白安装及其使用
一、安装 1.访问官网 Download FFmpeg 2.点击版本目录 3.选择版本点击安装 注意这里选择的是【release buids】,注意左上角标题 例如我安装在目录 F:\FFmpeg 4.解压 5.添加环境变量 把你解压后的bin目录(即exe所在文件夹)加入系统变量…...
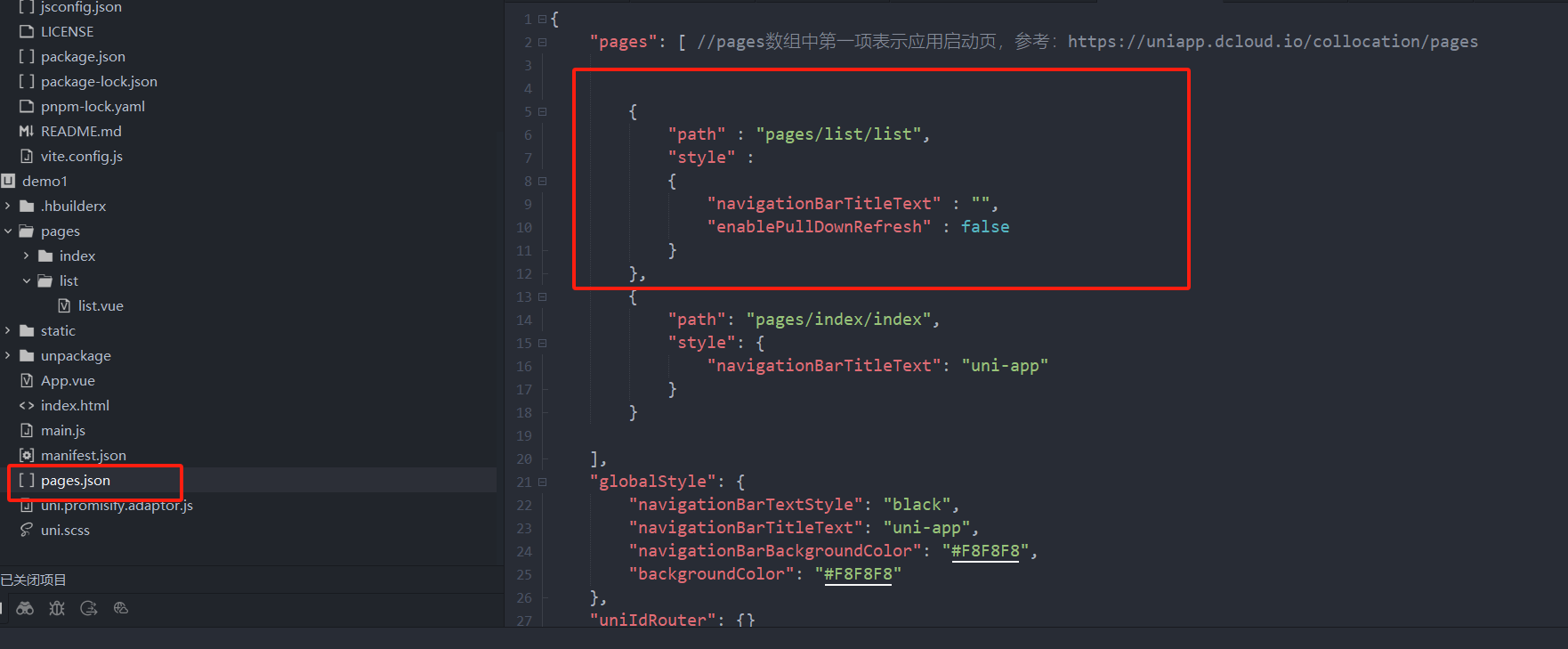
uniapp 小程序 学习(一)
利用Hbuilder 创建项目 运行到内置浏览器看效果 下载微信小程序 安装到Hbuilder 下载地址 :开发者工具默认安装 设置服务端口号 在Hbuilder中设置微信小程序 配置 找到运行设置,将微信开发者工具放入到Hbuilder中, 打开后出现 如下 bug 解…...

【HarmonyOS 5】鸿蒙中Stage模型与FA模型详解
一、前言 在HarmonyOS 5的应用开发模型中,featureAbility是旧版FA模型(Feature Ability)的用法,Stage模型已采用全新的应用架构,推荐使用组件化的上下文获取方式,而非依赖featureAbility。 FA大概是API7之…...
