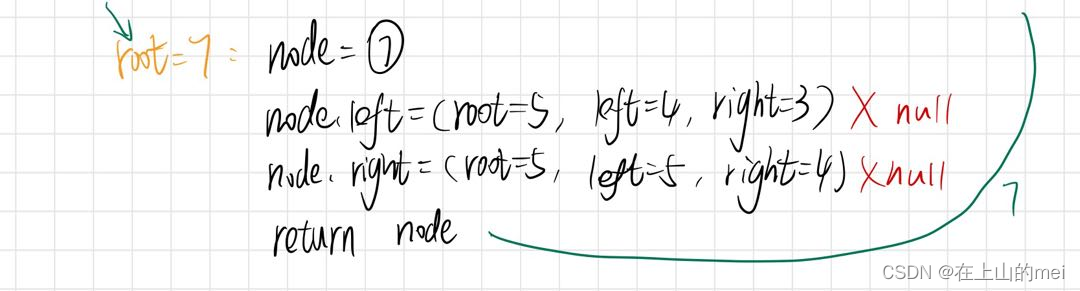剑指offer(中等)
目录
二维数组中的查找
重建二叉树
矩阵中的路径
剪绳子
剪绳子②
数值的整数次方
表示数值的字符串
树的子结构
栈的压入、弹出序列
从上到下打印二叉树①
从上到下打印二叉树③
二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
二叉树中和为某一值的路径
复杂链表的复制
二叉搜索树与双向链表
字符串的排列
数字序列中某一位的数字
把数字翻译成字符串
礼物的最大价值
最长不含重复字符的子字符串
丑数
数组中数字出现的次数
数组中数字出现的次数②
n个骰子的点数
股票的最大利润
求1+2+...+n
构建乘积数组
只出现一次的数字
单词长度的最大乘积
数组中和为0的三个数
和大于等于target的最短子数组
乘积小于K的子数组
和为k的子数组
0和1个数相同的子数组
二维子矩阵的和
字符串中的变位词
字符串中的所有变位词
不含重复字符的最长子字符串
回文子字符串的个数
删除链表的倒数第n个结点
链表中环的入口节点
链表中的两数相加
重排链表
展平多级双向链表
排序的循环链表
插入、删除和随机访问都是O(1)的容器
最近最少使用缓存
变位词组
最小时间差
后缀表达式
小行星碰撞
每日温度
往完全二叉树添加节点
二叉树最底层最左边的值
二叉树的右侧视图
二叉树剪枝
从根节点到叶节点的路径数字之和
向下的路径节点之和
二叉搜索树中的中序后继
所有大于等于节点的值之和
二叉搜索树迭代器
值和下标之差都在给定的范围内
日程表
出现频率最高的k个数字
和最小的k个数对
先到这里吧,后面就好多是没学过的知识(比如前缀树),有时间精力再做吧
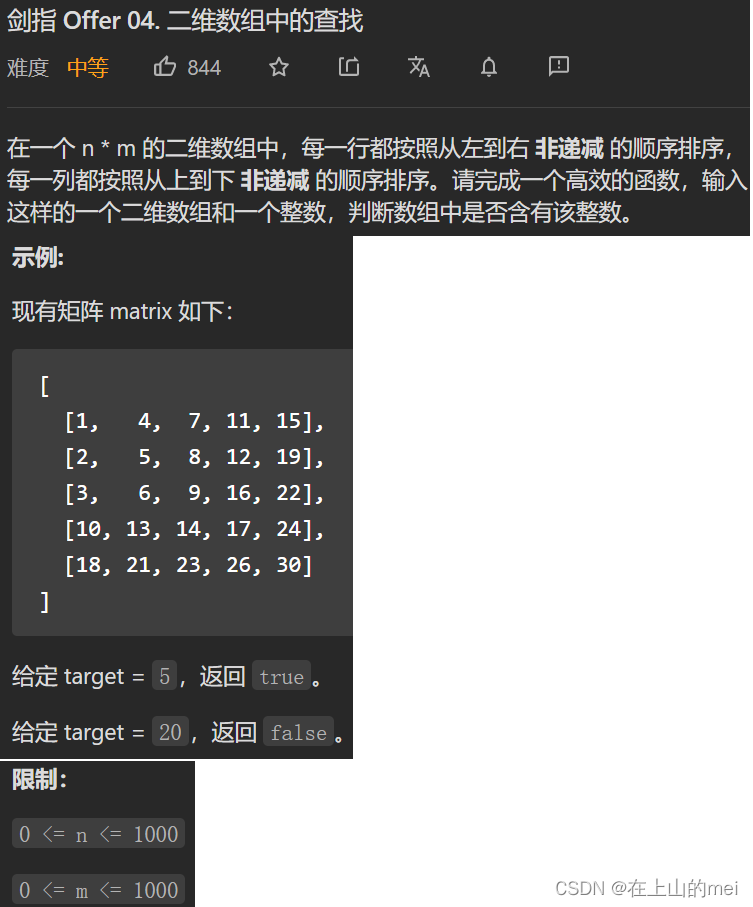
二维数组中的查找
剑指 Offer 04. 二维数组中的查找
- 方法1:Z字形查找
class Solution {public boolean findNumberIn2DArray(int[][] matrix, int target) {if(matrix.length==0 || matrix[0].length==0)return false;int n=0;int m=matrix[0].length-1;while(n<matrix.length && m>=0){if(target>matrix[n][m]){n++;}else if(target<matrix[n][m]){m--;}else{return true;}}return false;} }
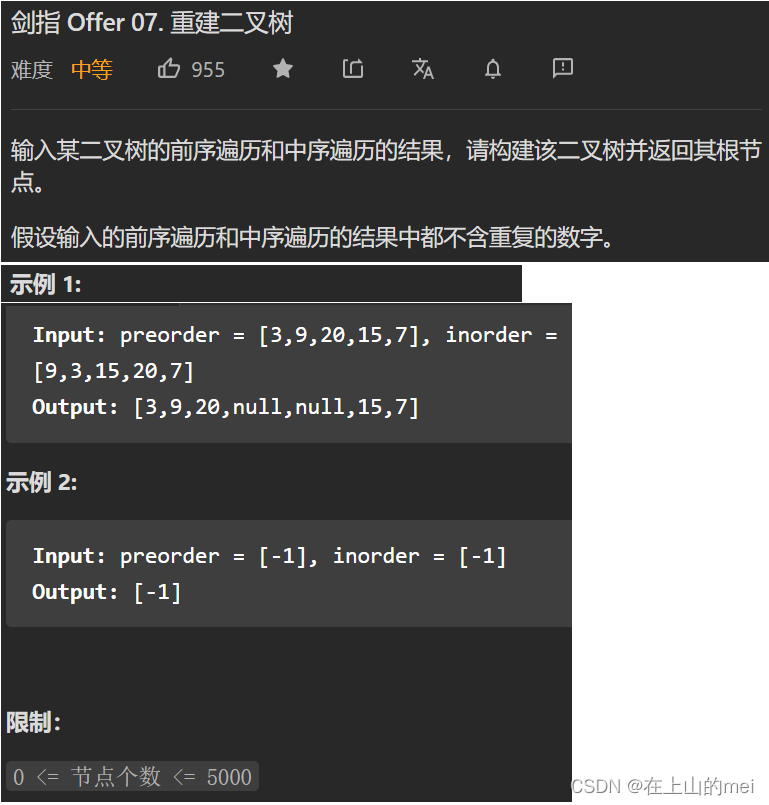
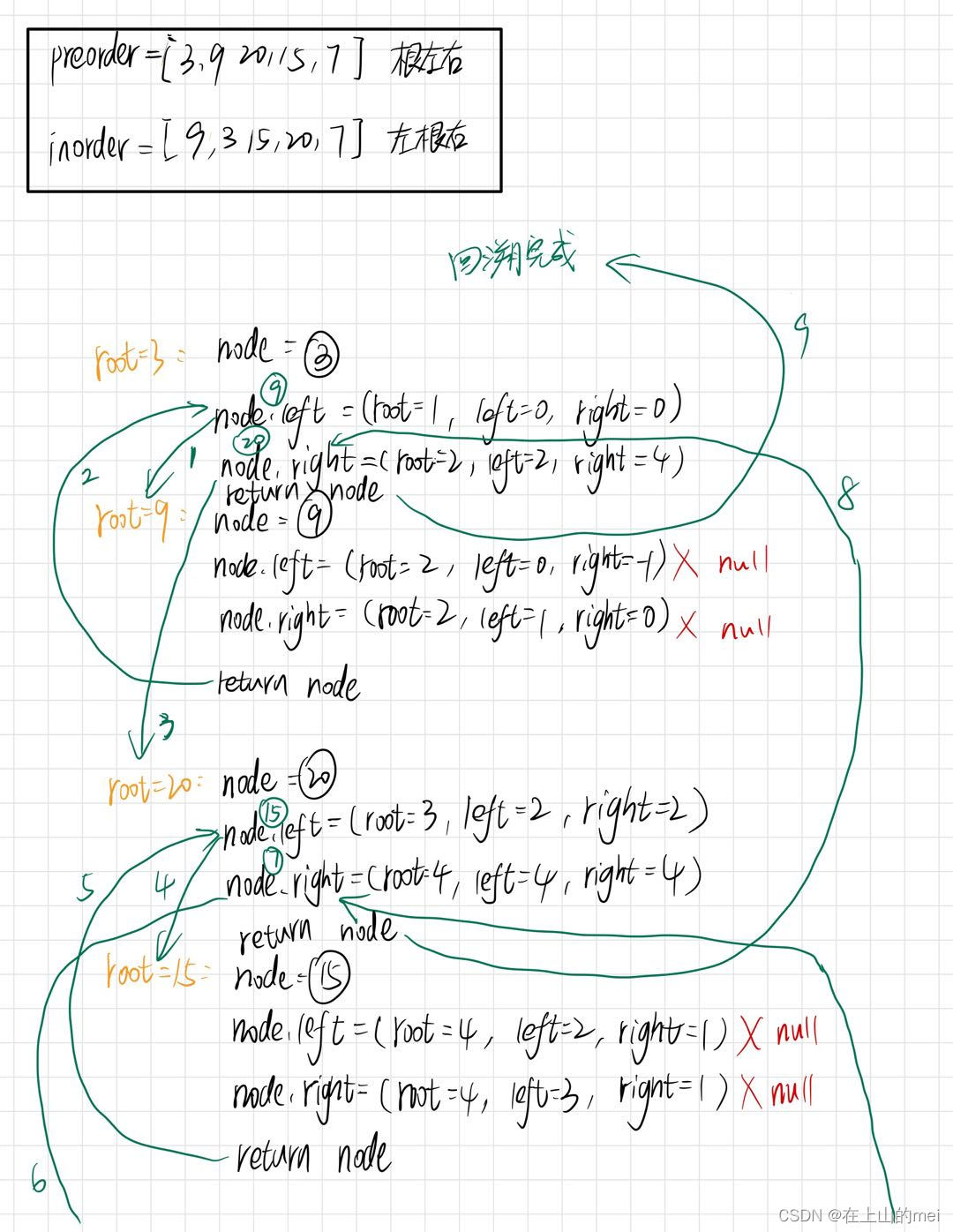
重建二叉树
剑指 Offer 07. 重建二叉树
- 方法1:分治算法
大佬讲的很清楚
我的代码过程展示:
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }* }*/ class Solution {int[] preorder;HashMap<Integer,Integer> map=new HashMap<>();public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {this.preorder=preorder;if(preorder.length==0)return null;for(int i=0;i<inorder.length;i++){map.put(inorder[i],i);}return buildTree2(0,0,inorder.length-1);}public TreeNode buildTree2(int root,int left,int right){if(left>right)return null;TreeNode node=new TreeNode(preorder[root]);int i=map.get(preorder[root]);node.left=buildTree2(root+1,left,i-1);node.right=buildTree2(i-left+root+1,i+1,right);return node;} }
矩阵中的路径
剑指 Offer 12. 矩阵中的路径
- 方法1:深度优先搜索(DFS)+剪枝
思路
class Solution {public boolean exist(char[][] board, String word) {char[] words=word.toCharArray();for(int i=0;i<board.length;i++){for(int j=0;j<board[0].length;j++){if(dfs(board,words,i,j,0))return true;}}return false;}public boolean dfs(char[][]board,char[] words,int i,int j,int k){//这个是终止条件(边界)if(i<0 || i>=board.length || j<0 || j>=board[0].length || board[i][j]!=words[k])return false;//如果k已经是单词的长度,那么说明单词存在于网格中if(k==words.length-1)return true;//给他做上标记,此坐标中的字母已经使用过了board[i][j]='0';//找下一个字母boolean res=dfs(board,words,i-1,j,k+1)||dfs(board,words,i+1,j,k+1)||dfs(board,words,i,j-1,k+1)||dfs(board,words,i,j+1,k+1);//到这一步就已经是递归完成了,因此我们需要把网格中的字母还原,以备后面查找使用board[i][j]=words[k];return res;} }
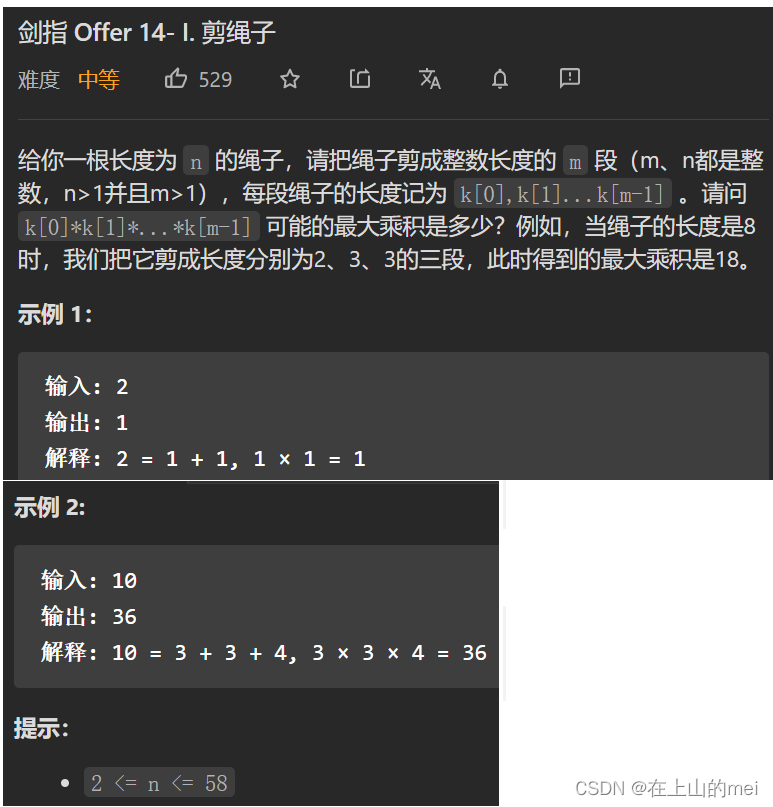
剪绳子
剑指 Offer 14- I. 剪绳子
方法1:动态规划
思路
class Solution {public int cuttingRope(int n) {int[] dp=new int[n+1];dp[2]=1;for(int i=3;i<n+1;i++){for(int j=2;j<i;j++){dp[i]=Math.max(dp[i],Math.max(j*(i-j),j*dp[i-j]));}}return dp[n];} }方法2:贪心算法
class Solution {public int cuttingRope(int n) {if(n < 4){return n - 1;}int res = 1;while(n > 4){res *= 3;n -= 3;}return res * n;} }
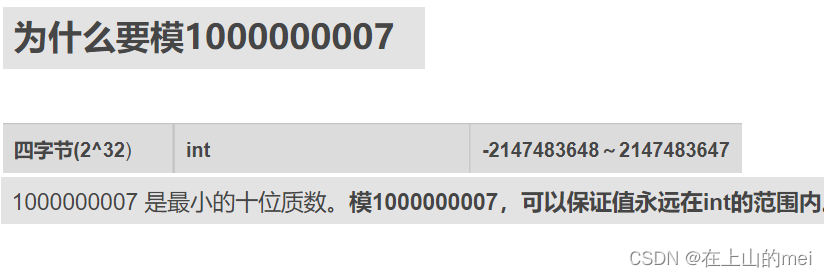
剪绳子②
剑指 Offer 14- II. 剪绳子 II
- 方法1:贪心算法
思路
class Solution {public int cuttingRope(int n) {if(n<4){return n-1;}long res=1;while(n>4){res=res*3%1000000007;n-=3;}return (int)(res*n%1000000007);} }
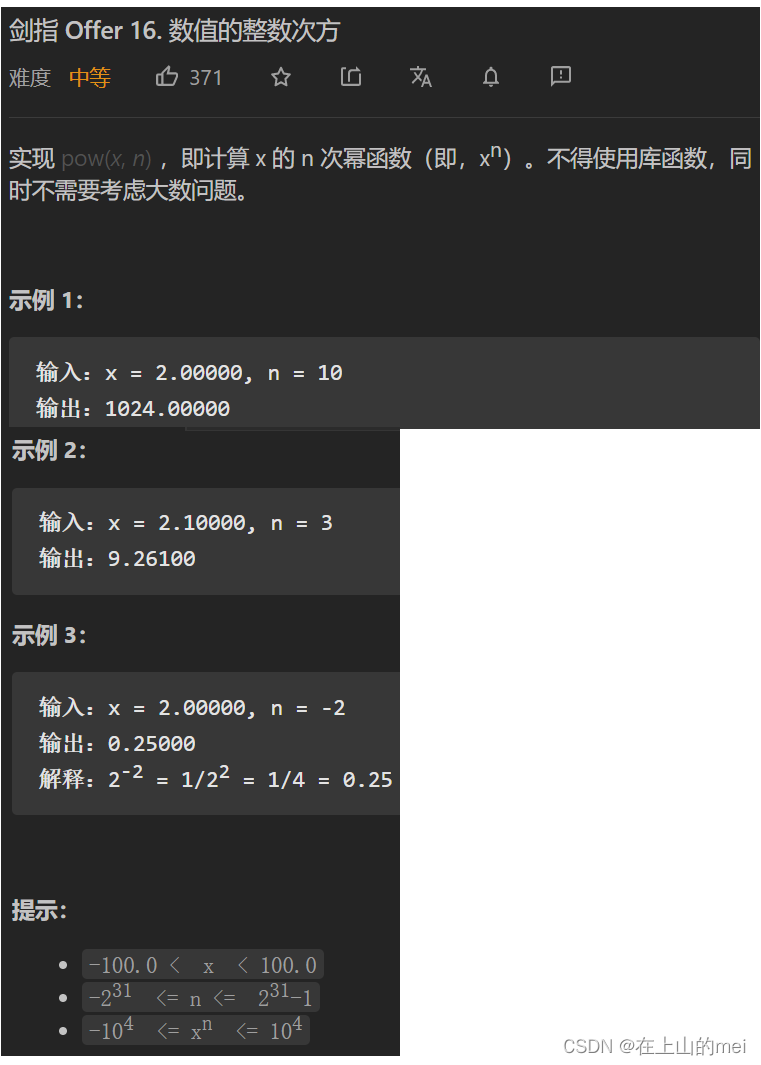
数值的整数次方
剑指 Offer 16. 数值的整数次方
- 方法1:快速幂(使用二分法+二进制方法实现)
思路
class Solution {public double myPow(double x, int n) {if(x==0)return 0;if(n==0)return 1;long b=n;double res=1.0;int zhengfu=1;if(b<0){zhengfu*=-1;b=-b;}while(b>0){if((b&1)==1){res*=x;}x*=x;b>>=1;}if(zhengfu==-1){res=1/res;}return res;} }
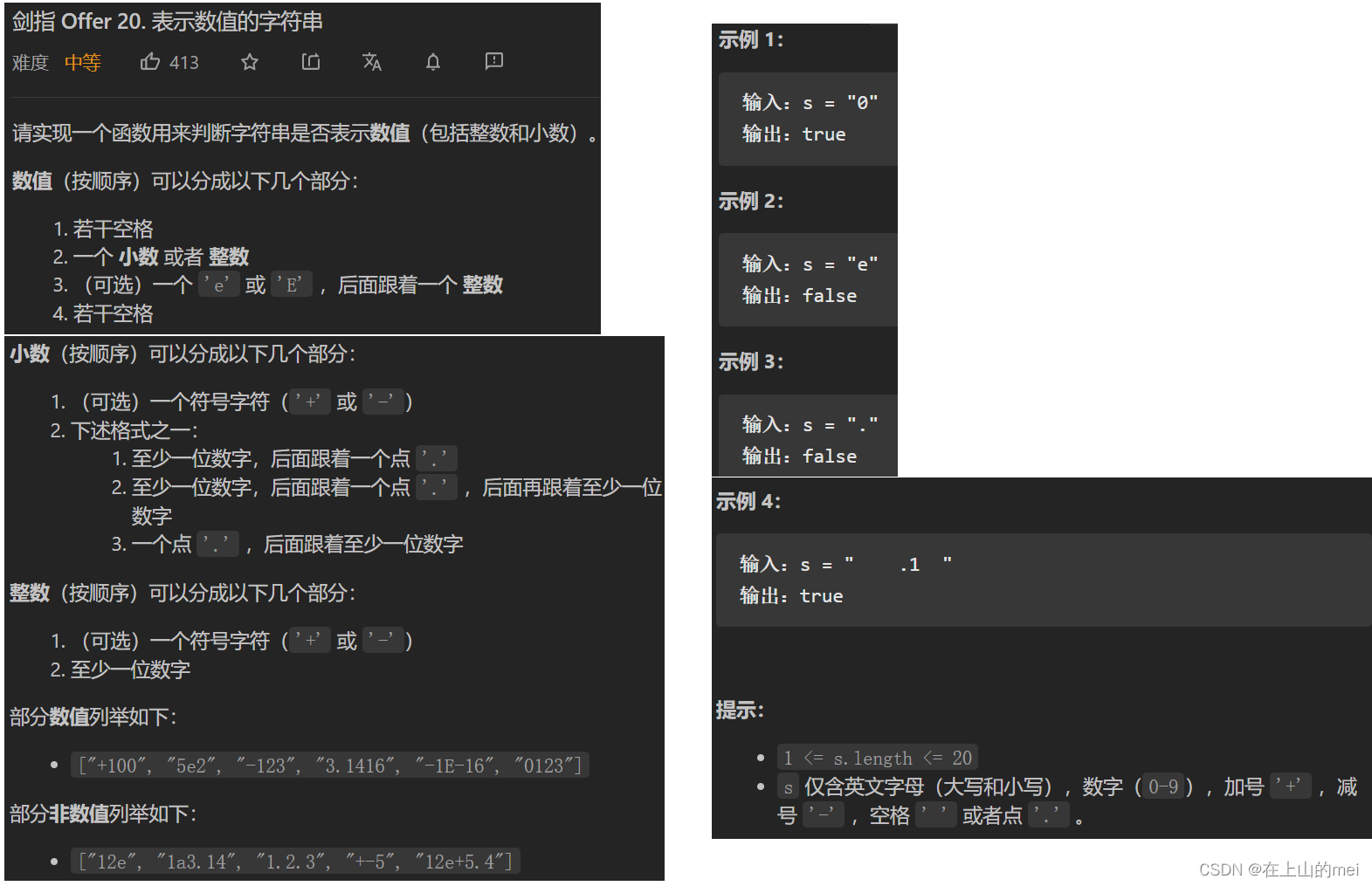
表示数值的字符串
剑指 Offer 20. 表示数值的字符串
思路
class Solution {public boolean isNumber(String s) {//去掉首位空格s = s.trim();//是否出现数字boolean numFlag = false;//是否出现小数点boolean dotFlag = false;boolean eFlag = false;for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {//判定为数字,则标记numFlagif (s.charAt(i) >= '0' && s.charAt(i) <= '9') {numFlag = true;//小数点只可以出现再e之前,且只能出现一次.num num.num num.都是被允许的} else if (s.charAt(i) == '.' && !dotFlag && !eFlag) {dotFlag = true;//判定为e,需要没出现过e,并且出过数字了} else if ((s.charAt(i) == 'e' || s.charAt(i) == 'E') && !eFlag && numFlag) {eFlag = true;//避免e以后没有出现数字numFlag = false;//判定为+-符号,只能出现在第一位或者紧接e后面} else if ((s.charAt(i) == '+' || s.charAt(i) == '-') && (i == 0 || s.charAt(i - 1) == 'e' || s.charAt(i - 1) == 'E')) {//其他情况,都是非法的} else {return false;}}//是否出现了数字 return numFlag;} }
树的子结构
剑指 Offer 26. 树的子结构
- 方法1:先序遍历
思路
class Solution {public boolean isSubStructure(TreeNode A, TreeNode B) {return (A != null && B != null) && (recur(A, B) || isSubStructure(A.left, B) || isSubStructure(A.right, B));}boolean recur(TreeNode A, TreeNode B) {if(B == null) return true;if(A == null || A.val != B.val) return false;return recur(A.left, B.left) && recur(A.right, B.right);} }
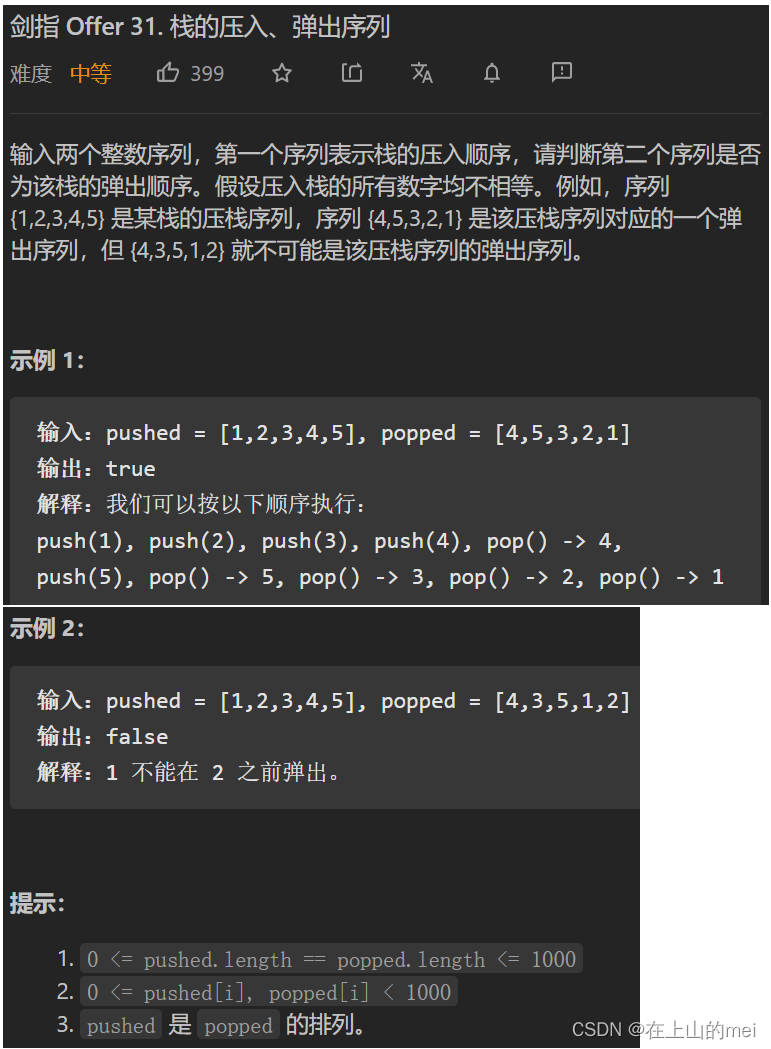
栈的压入、弹出序列
剑指 Offer 31. 栈的压入、弹出序列
- 方法1:模拟栈
思路
class Solution {public boolean validateStackSequences(int[] pushed, int[] popped) {Stack<Integer> stack=new Stack<>();int i=0;for(int num:pushed){stack.push(num);while(!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek()==popped[i]){stack.pop();i++;}}return stack.isEmpty();} }
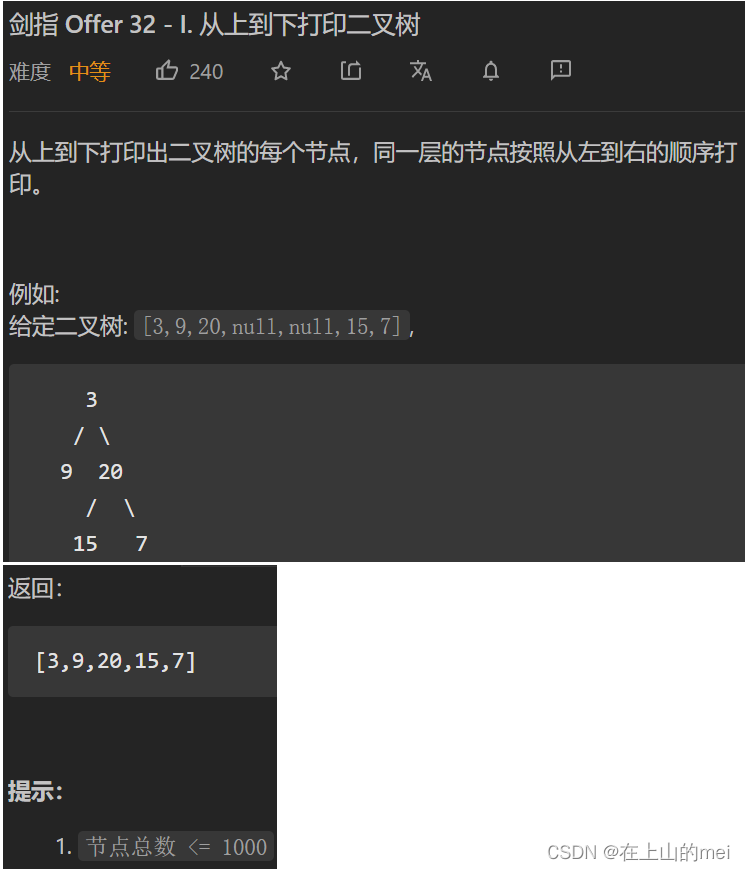
从上到下打印二叉树①
剑指 Offer 32 - I. 从上到下打印二叉树
- 方法1:借助队列实现
思路
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }* }*/ class Solution {public int[] levelOrder(TreeNode root) {if(root==null)return new int[0];Queue<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);List<Integer> res=new ArrayList<>();while(!queue.isEmpty()){TreeNode tmp=queue.poll();res.add(tmp.val);if(tmp.left!=null){queue.offer(tmp.left);}if(tmp.right!=null){queue.offer(tmp.right);}}int[] arr=new int[res.size()];for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){arr[i]=res.get(i);}return arr;} }
从上到下打印二叉树③
剑指 Offer 32 - III. 从上到下打印二叉树 III
- 方法1:借助双端队列实现
思路
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }* }*/ class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>();Deque<TreeNode> de=new LinkedList<>();if(root!=null)de.offer(root);while(!de.isEmpty()){List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();for(int i=de.size();i>0;i--){TreeNode tmp=de.pollFirst();list.add(tmp.val);if(tmp.left!=null)de.offerLast(tmp.left);if(tmp.right!=null)de.offerLast(tmp.right);}res.add(list);if(de.isEmpty())break;list=new ArrayList<>();for(int i=de.size();i>0;i--){TreeNode tmp=de.pollLast();list.add(tmp.val);if(tmp.right!=null)de.offerFirst(tmp.right);if(tmp.left!=null)de.offerFirst(tmp.left);}res.add(list);}return res;} }
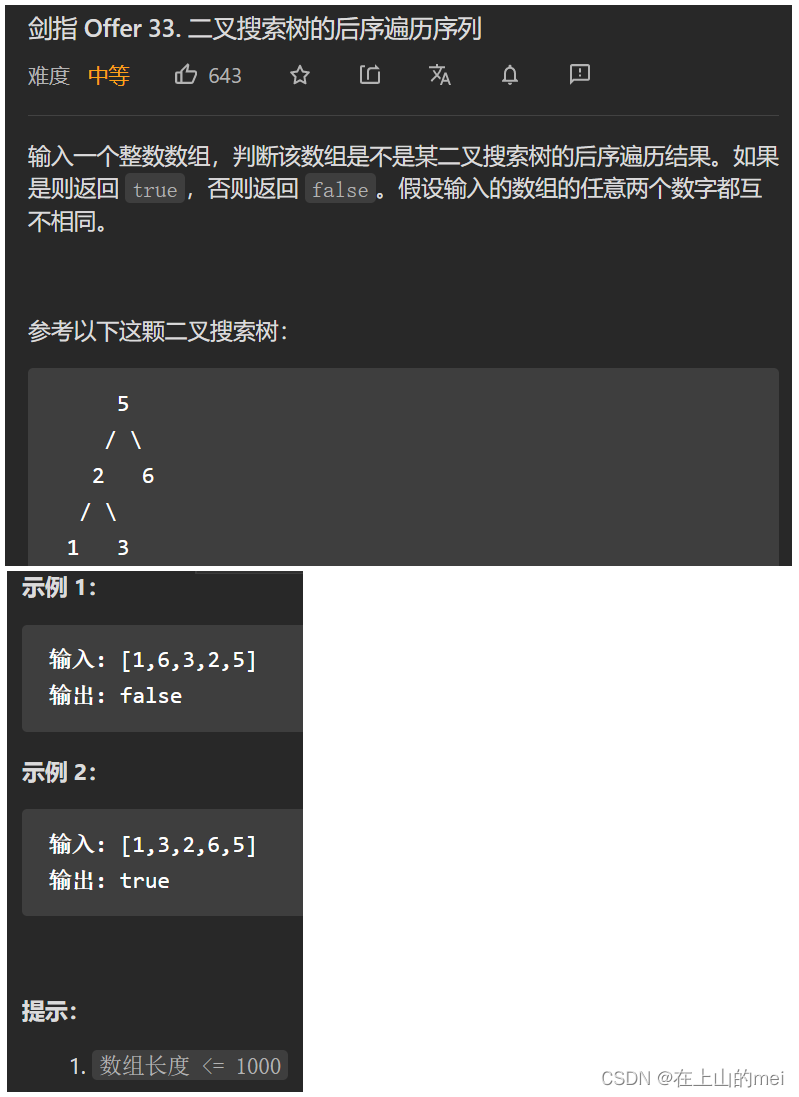
二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
剑指 Offer 33. 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
- 方法1:递归分治
class Solution {public boolean verifyPostorder(int[] postorder) {if(postorder.length==0)return true;return postOrder(postorder,0,postorder.length-1);}public boolean postOrder(int[] postorder,int start,int end){if(start>=end)return true;int i=start;for(;i<end;i++){if(postorder[i]>postorder[end]){break;}}for(int j=i;j<end;j++){if(postorder[j]<postorder[end]){return false;}}return postOrder(postorder,start,i-1) && postOrder(postorder,i,end-1);} }
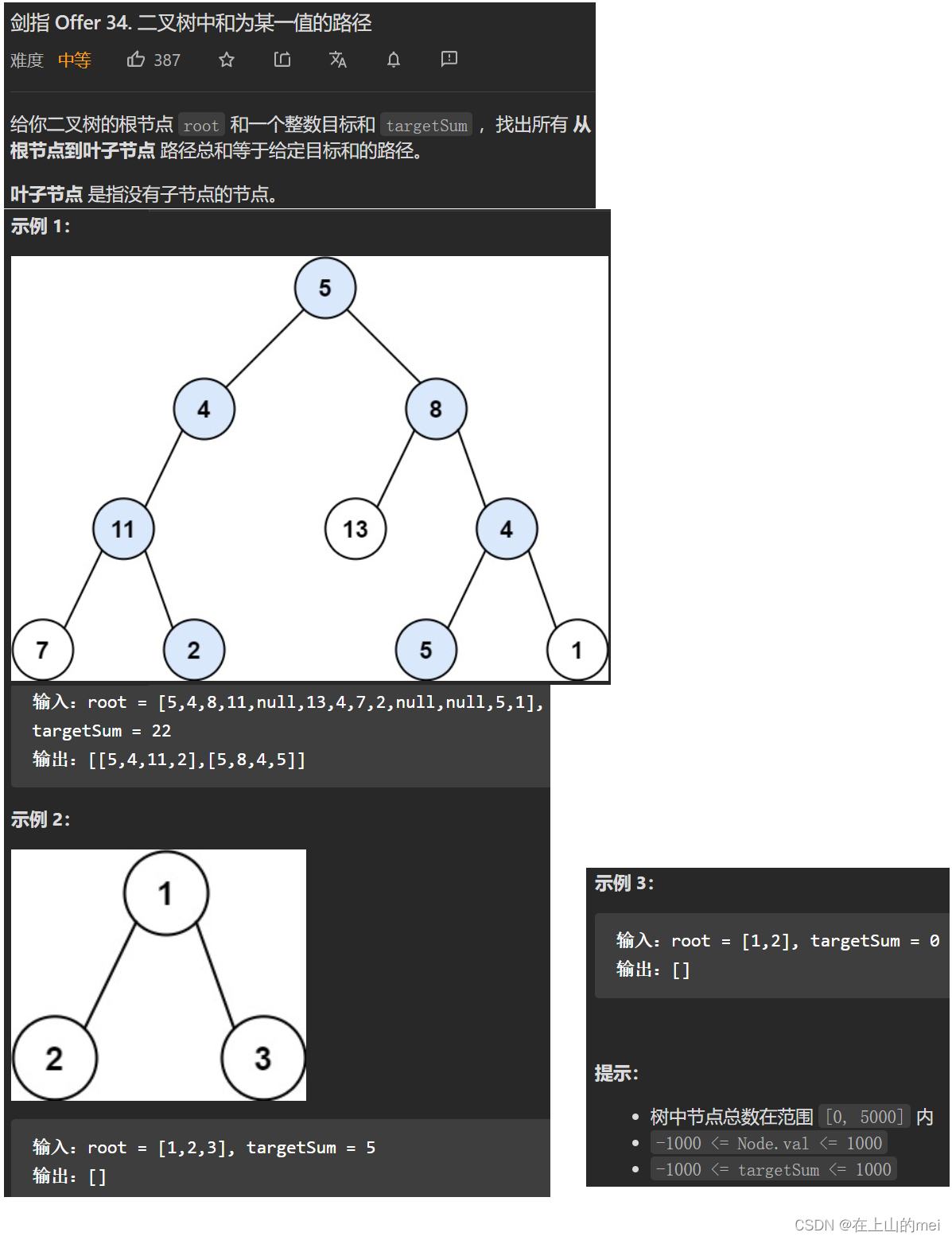
二叉树中和为某一值的路径
剑指 Offer 34. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径
- 方法1:深度优先搜索
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode() {}* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {* this.val = val;* this.left = left;* this.right = right;* }* }*/ class Solution {List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>();List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int target) {return dfs(root,target);}public void dfs(TreeNode root,int target){if(root==null)return;target-=root.val;list.add(root.val);if(target==0 && root.left==null && root.right==null){res.add(list);}dfs(root.left,target);dfs(root.right,target);list.remove(list.size()-1);} }
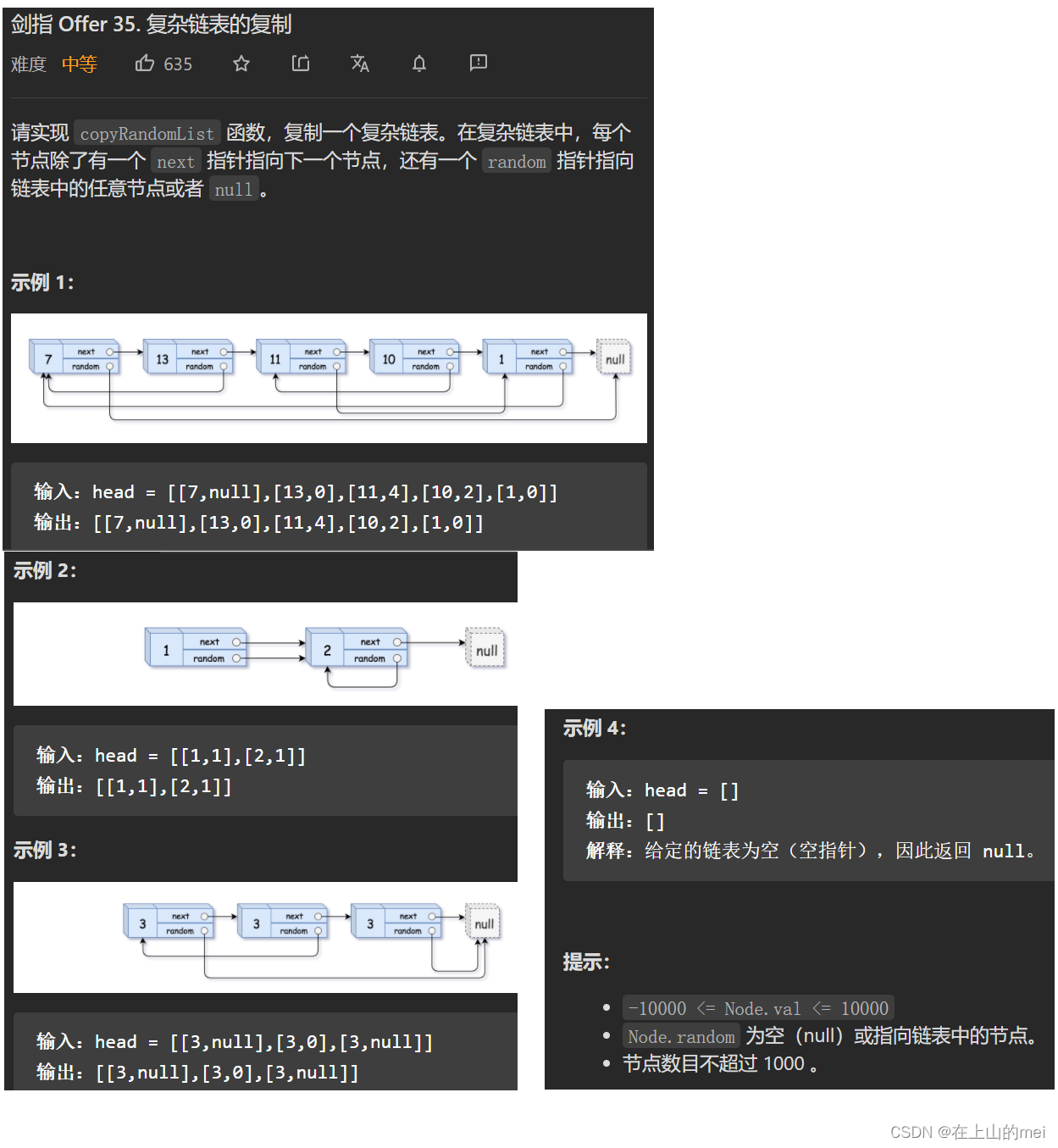
复杂链表的复制
剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制
- 方法1:哈希表
/* // Definition for a Node. class Node {int val;Node next;Node random;public Node(int val) {this.val = val;this.next = null;this.random = null;} } */ class Solution {public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {if(head==null)return null;Map<Node,Node> map=new HashMap<>();Node cur=head;while(cur!=null){map.put(cur,new Node(cur.val));cur=cur.next;}cur=head;while(cur!=null){map.get(cur).next=map.get(cur.next);map.get(cur).random=map.get(cur.random);cur=cur.next;}return map.get(head);} }
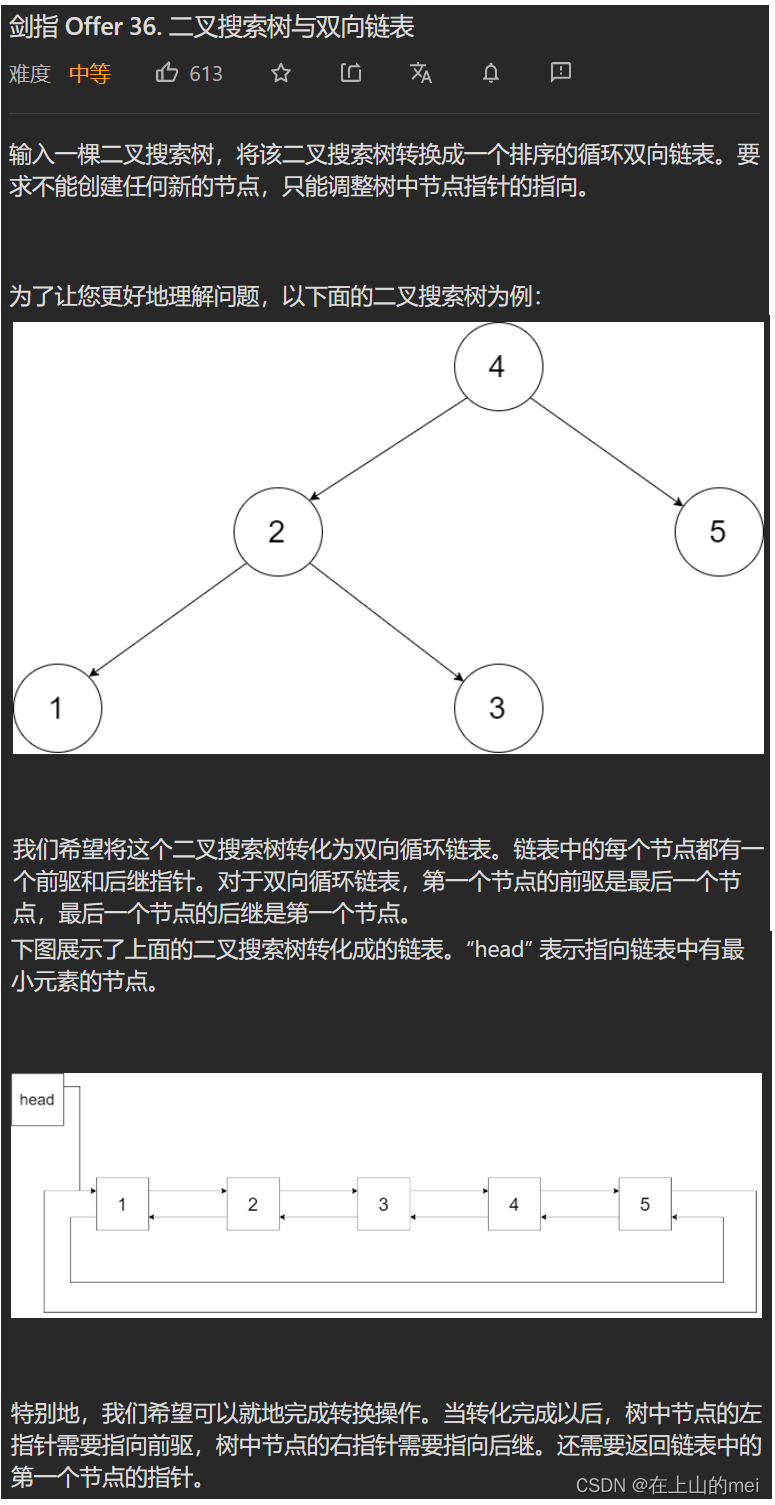
二叉搜索树与双向链表
剑指 Offer 36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表
- 方法1:中序遍历
自己写出来的!!!
/* // Definition for a Node. class Node {public int val;public Node left;public Node right;public Node() {}public Node(int _val) {val = _val;}public Node(int _val,Node _left,Node _right) {val = _val;left = _left;right = _right;} }; */ class Solution {Node tmp=new Node(-1);Node pre=tmp;public Node treeToDoublyList(Node root) {if(root==null)return null;Node cur=root;inOrder(cur);tmp.right.left=pre;pre.right=tmp.right;return tmp.right;}public void inOrder(Node cur){if(cur==null)return;inOrder(cur.left);pre.right=cur;cur.left=pre;pre=cur;inOrder(cur.right);} }
字符串的排列
剑指 Offer 38. 字符串的排列
- 方法1:深度优先搜索(dfs)
思路
class Solution {List<String> res=new ArrayList<>();char[] c;public String[] permutation(String s) {c=s.toCharArray();dfs(0);return res.toArray(new String[res.size()]);}public void dfs(int x){if(x==c.length-1){res.add(String.valueOf(c));}Set<Character> set=new HashSet<>();for(int i=x;i<c.length;i++){if(set.contains(c[i]))continue;set.add(c[i]);swap(i,x);dfs(x+1);swap(i,x);}}public void swap(int i,int x){char tmp=c[i];c[i]=c[x];c[x]=tmp;} }
数字序列中某一位的数字
剑指 Offer 44. 数字序列中某一位的数字
- 方法1:思路
目前做过可能两遍了,但是靠自己想只能想出一半,还有不懂的地方,下次做的时候看看能不能想通:
1.题目说从下标0开始计数,这个条件在代码的哪里应用了?
2.关于算num和算最终返回值的思路
class Solution {public int findNthDigit(int n) {int weishu=1;long start=1;long count=9;while(n>count){n-=count;weishu+=1;start*=10;count=weishu*start*9;}long num=start+(n-1)/weishu;return Long.toString(num).charAt((n-1)%weishu)-'0';} }
把数字翻译成字符串
剑指 Offer 46. 把数字翻译成字符串
- 方法1:动归(通过字符串遍历的方式实现动归)
class Solution {public int translateNum(int num) {String s=String.valueOf(num);int a=1;int b=1;for(int i=2;i<=s.length();i++){String tmp=s.substring(i-2,i);int c=tmp.compareTo("10")>=0 && tmp.compareTo("25")<=0?a+b:a;b=a;a=c;}return a;} }
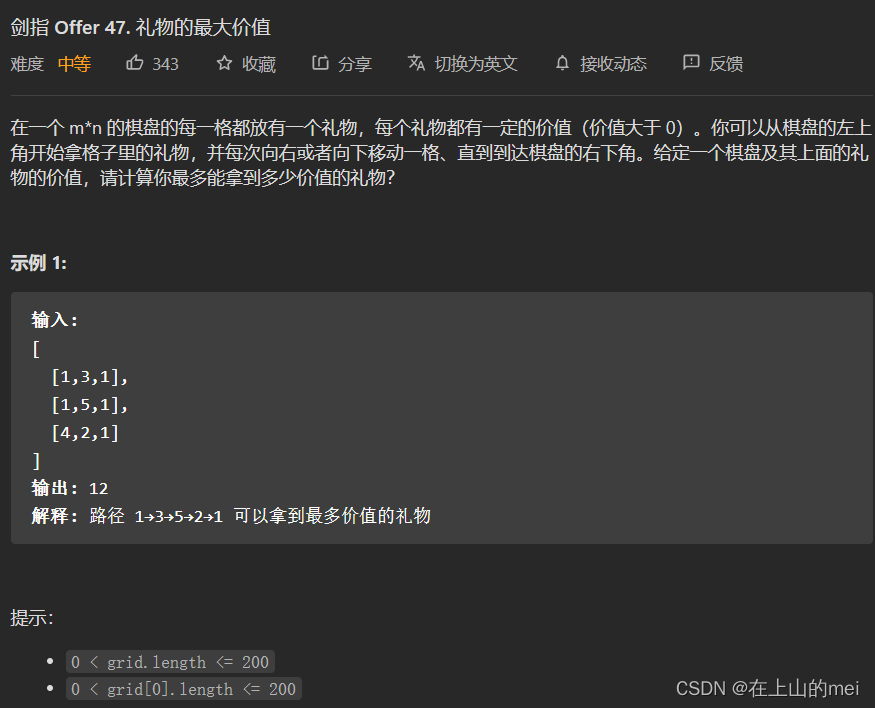
礼物的最大价值
剑指 Offer 47. 礼物的最大价值
- 方法1:动态规划
思路
class Solution {public int maxValue(int[][] grid) {int[][] dp=new int[grid.length][grid[0].length];dp[0][0]=grid[0][0];for(int i=1;i<grid.length;i++){dp[i][0]=dp[i-1][0]+grid[i][0];}for(int j=1;j<grid[0].length;j++){dp[0][j]=dp[0][j-1]+grid[0][j];}for(int i=1;i<grid.length;i++){for(int j=1;j<grid[0].length;j++){dp[i][j]=Math.max(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-1])+grid[i][j];}}return dp[grid.length-1][grid[0].length-1];} }
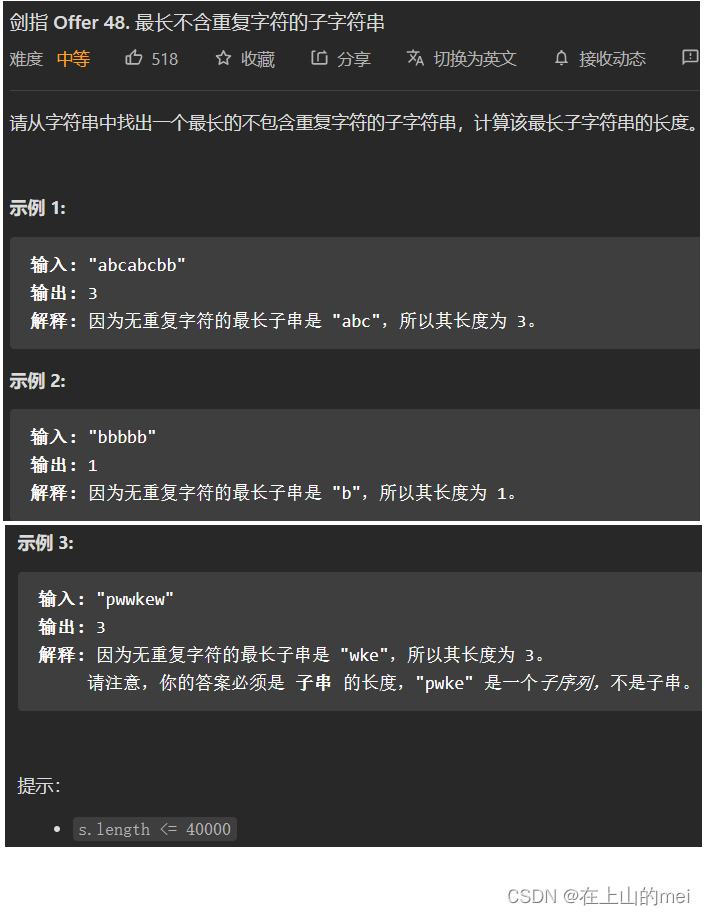
最长不含重复字符的子字符串
剑指 Offer 48. 最长不含重复字符的子字符串
- 方法1:动态规划+哈希表
思路
这道题下次还得再做啊
class Solution {public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {int tmp=0;int res=0;Map<Character,Integer> map=new HashMap<>();for(int j=0;j<s.length();j++){int i=map.getOrDefault(s.charAt(j),-1);map.put(s.charAt(j),j);tmp=tmp<j-i?tmp+1:j-i;res=Math.max(res,tmp);}return res;} }
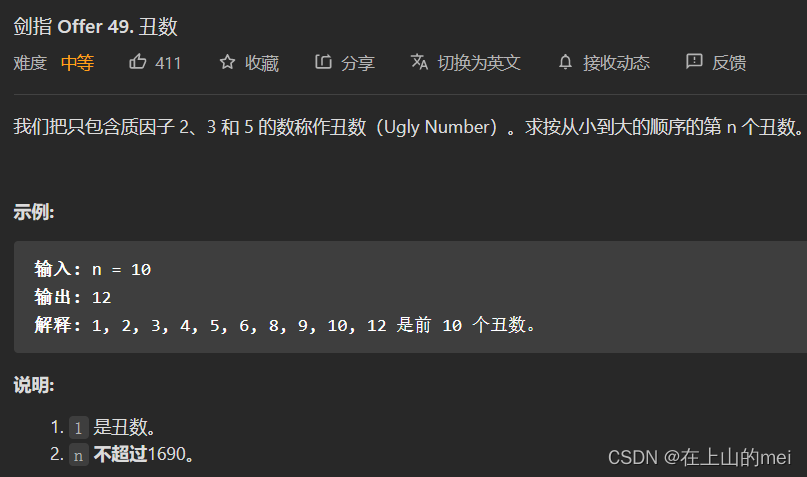
丑数
剑指 Offer 49. 丑数
- 方法1:动态规划
思路
class Solution {public int nthUglyNumber(int n) {int[] dp=new int[n];dp[0]=1;int a=0;int b=0;int c=0;for(int i=1;i<dp.length;i++){dp[i]=Math.min(Math.min(dp[a]*2,dp[b]*3),dp[c]*5);if(dp[a]*2==dp[i])a++;if(dp[b]*3==dp[i])b++;if(dp[c]*5==dp[i])c++;}return dp[dp.length-1];} }
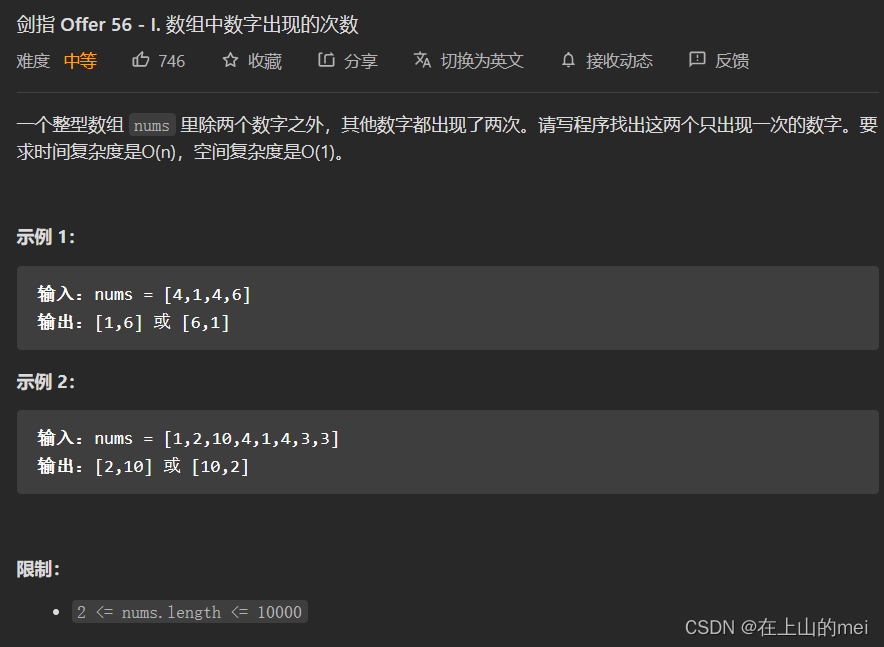
数组中数字出现的次数
剑指 Offer 56 - I. 数组中数字出现的次数
一开始我想的是用HashMap,虽然能通过,但是题目要求时间复杂度是O(n),空间复杂度是O(1),如果使用HashMap空间复杂度就超了
所以看了大佬的思路,用下面这种方法做的
- 方法1:位运算
思路
class Solution {public int[] singleNumbers(int[] nums) {int x=0;//x为其中一个只出现一次的数字int y=0;//y为另外一个只出现一次的数字int n=0;//n为遍历数组各数字异或运算的结果int m=1;//m为x^y二进制位首位出现1时的对应的数字for(int num:nums){n^=num;}while((n & m)==0){m<<=1;}for(int num:nums){if((num & m)==0){x^=num;}}return new int[]{x,x^n};} }
数组中数字出现的次数②
剑指 Offer 56 - II. 数组中数字出现的次数 II
- 方法1:位运算(利用遍历统计法实现)
思路
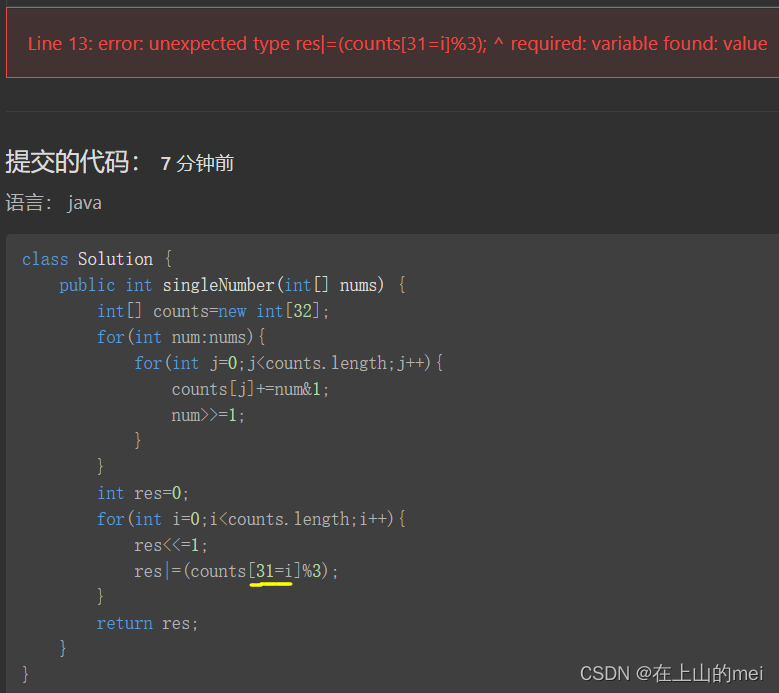
class Solution {public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {int[] counts=new int[32];for(int num:nums){for(int j=0;j<counts.length;j++){counts[j]+=num&1;num>>=1;}}int res=0; for(int i=0;i<counts.length;i++){res<<=1;res|=counts[31-i]%3;}return res;} }写的过程中这里大意写错了,报了这样的错误,就去了解下这个错误啥意思
required variable found value_qq_44842466的博客-CSDN博客
n个骰子的点数
剑指 Offer 60. n个骰子的点数
- 方法1:动态规划
思路
这道题我真的还是没看懂,也就是刚看完题解自己依旧做不出来的程度,所以这里不放代码提醒自己这道题相当于还没做,大家可以直接看上面的思路,思路里有大佬写的代码哦
股票的最大利润
剑指 Offer 63. 股票的最大利润
- 方法1:动态规划
思路
class Solution {public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {int cost=Integer.MAX_VALUE;//cost将来用来存放当前股票的最小价格int profit=0;//profit将来用来存放当前最大利润for(int price:prices){cost=Math.min(cost,price);profit=Math.max(profit,price-cost);}return profit;} }
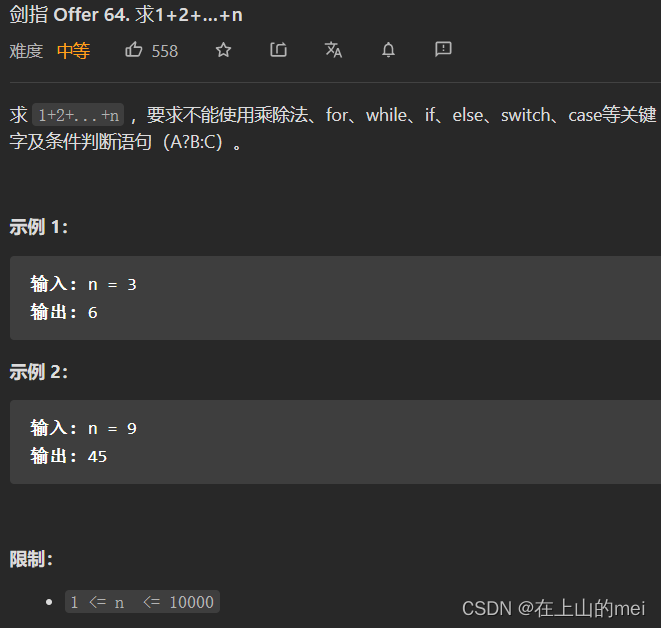
求1+2+...+n
剑指 Offer 64. 求1+2+…+n
- 方法1:逻辑符短路
思路
class Solution {public int sumNums(int n) {boolean x=n>1 && (n+=sumNums(n-1))>0;return n;} }我一开始想的是二分法+位运算,但是失败了,然后去看题解看有没有和自己想法一样的,位运算解法之类的,官方题解里到时有位运算(快速乘)的,但是...emmmm,算了还是先放弃位运算的方法吧
构建乘积数组
剑指 Offer 66. 构建乘积数组
- 方法1:动态规划
我先看的这个思路,但代码没有按这个大佬的写,而是看的下面评论区的另一位大佬用动态规划的思路写的
class Solution {public int[] constructArr(int[] a) {if(a==null || a.length==0)return new int[0];int len=a.length;int[] leftOfI=new int[len];int[] rightOfI=new int[len];leftOfI[0]=1;rightOfI[len-1]=1;for(int i=1;i<len;i++){leftOfI[i]=leftOfI[i-1]*a[i-1];}for(int i=len-2;i>=0;i--){rightOfI[i]=rightOfI[i+1]*a[i+1];}int[] res=new int[len];for(int i=0;i<len;i++){res[i]=leftOfI[i]*rightOfI[i];}return res;} }
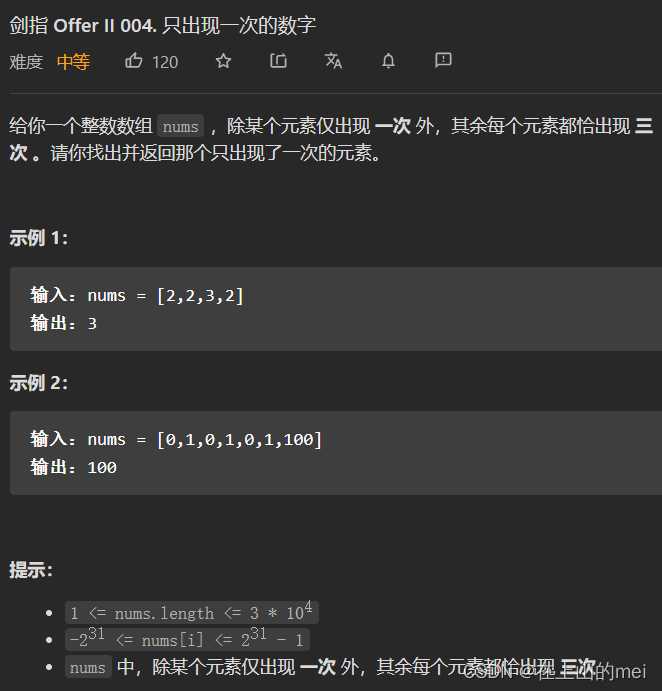
只出现一次的数字
剑指 Offer II 004. 只出现一次的数字
这道题和之前做的这道题
题目不一样,提示不一样,但做法代码一模一样,你会数组中数字出现的次数②这道题,那么此题你也就会,不过我把这道题还是贴在这儿了,大家可以找找不同,同时要建立一个警报系统,对于做过的题要有条件反射,拥有这种意识和能力,这对未来大家面试做没做过或相似的题的时候有帮助~大家想看此题代码,去数组中数字出现的次数②这道题中看代码就行(就在这篇博客里),我这里就不放了
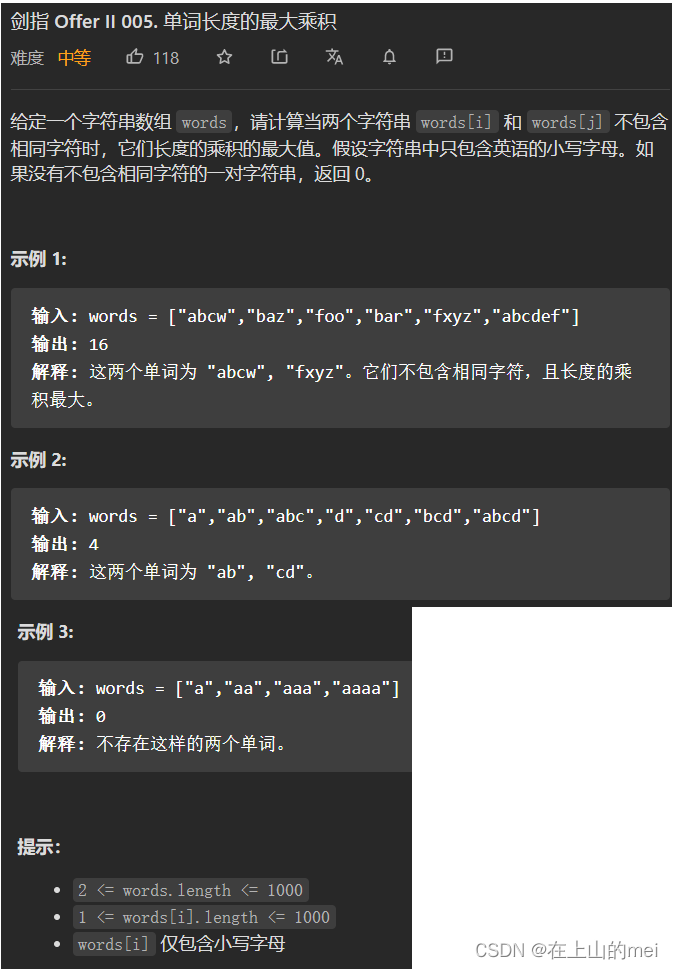
单词长度的最大乘积
剑指 Offer II 005. 单词长度的最大乘积
- 方法1:位运算模拟
这道题我最终搞懂是靠的这三位大佬
首先我先看的大佬1思路,然后对于或运算和左移那一行代码不是很明白,因此我就又看了大佬2的图以及大佬3的视频讲解
最终明白了或运算和左移那一行代码的意思,最终自己了一遍代码(思路还是大佬1的)
class Solution {public int maxProduct(String[] words) {int[] word=new int[words.length];int index=0;for(String w:words){int res=0;for(int i=0;i<w.length();i++){int tmp=w.charAt(i)-'a';res|=(1<<tmp);}word[index++]=res;}int max=0;for(int i=0;i<word.length;i++){for(int j=0;j<i;j++){if((word[i]&word[j])==0){max=Math.max(max,words[i].length()*words[j].length());}}}return max;} }
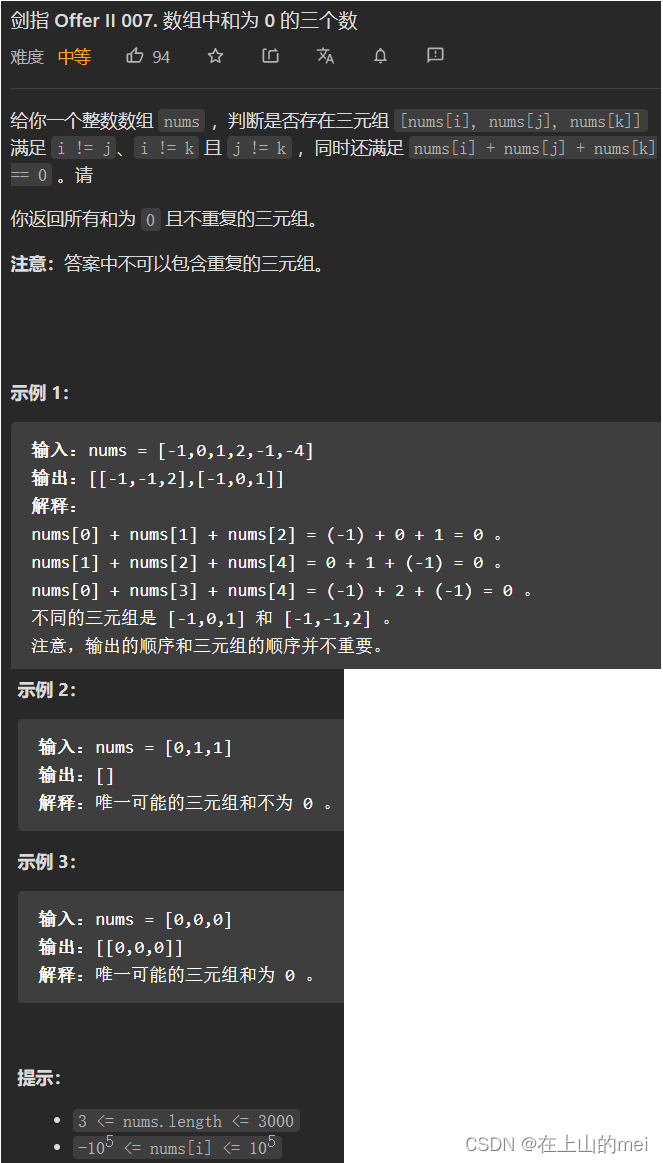
数组中和为0的三个数
剑指 Offer II 007. 数组中和为 0 的三个数
方法1:排序+双指针
思路
使用HashSet进行去重
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {Arrays.sort(nums);Set<List<Integer>> set=new HashSet<>();for(int i=0;i<nums.length-2;i++){if(i>0 && nums[i]==nums[i-1])continue;int target=-nums[i];int left=i+1;int right=nums.length-1;while(left<right){int sum=nums[left]+nums[right];if(sum==target){set.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i],nums[left],nums[right]));left++;right--;}else if(sum>target){right--;}else{left++;}}}return new ArrayList<>(set);} }优化:(是上面思路里面评论区赵四儿大佬的优化思路)
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {Arrays.sort(nums);List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>();for(int i=0;i<nums.length-2;i++){if(nums[i]>0)break;if(i>0 && nums[i]==nums[i-1])continue;int target=-nums[i];int left=i+1;int right=nums.length-1;while(left<right){int sum=nums[left]+nums[right];if(sum==target){res.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i],nums[left],nums[right]));left++;right--;while(left<right && nums[left]==nums[left-1]){left++;}while(left<right && nums[right]==nums[right+1]){right--;}}else if(sum<target){left++;}else{right--;}}}return res;} }
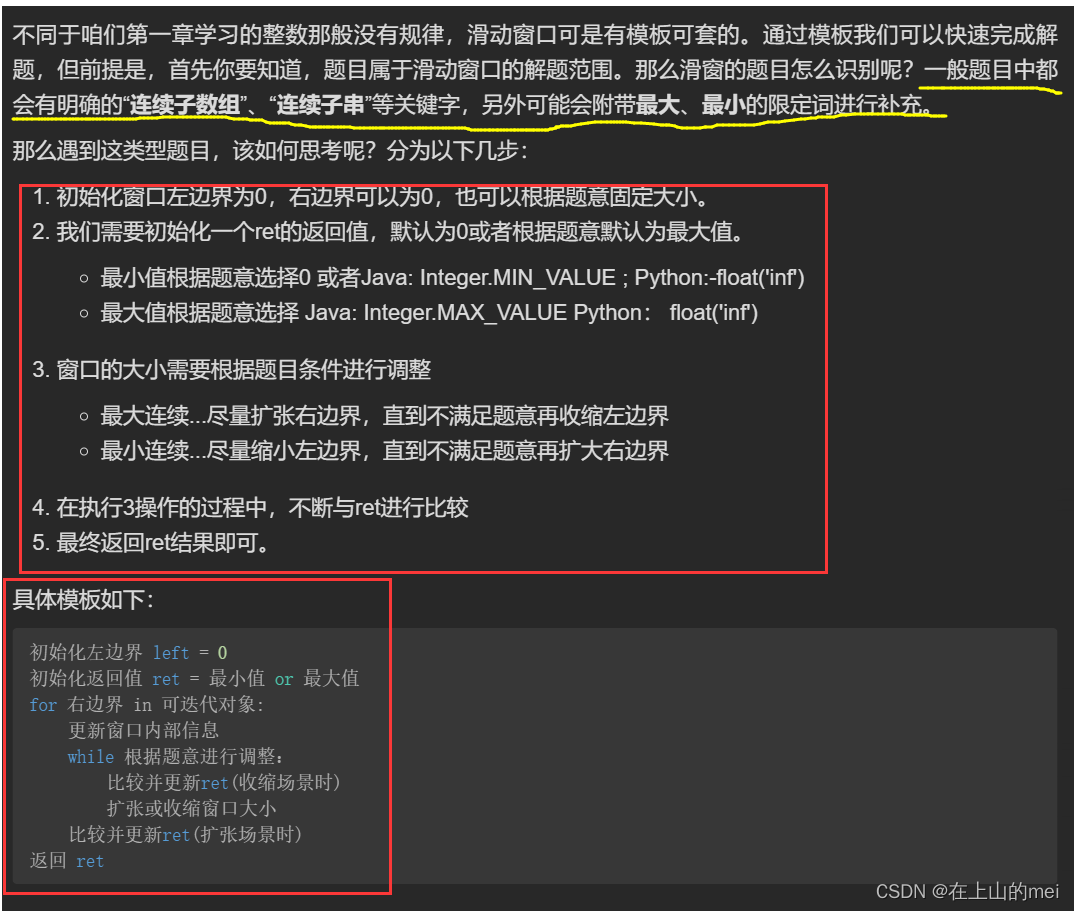
和大于等于target的最短子数组
剑指 Offer II 008. 和大于等于 target 的最短子数组
- 方法1:滑动窗口
思路
class Solution {public int minSubArrayLen(int target, int[] nums) {int left=0;int sum=0;int res=Integer.MAX_VALUE;for(int right=0;right<nums.length;right++){sum+=nums[right];while(sum>=target){res=Math.min(res,right-left+1);sum-=nums[left];left++;}}return res>target?0:res;} }
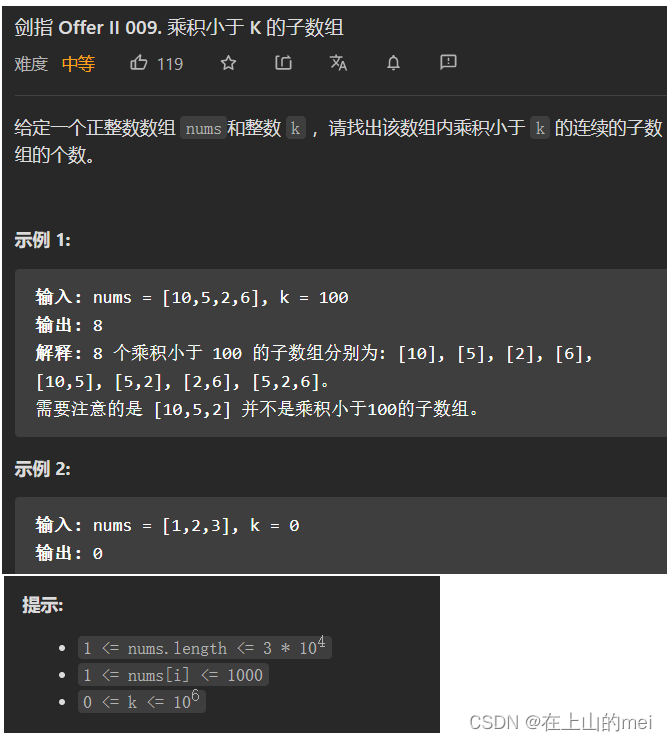
乘积小于K的子数组
剑指 Offer II 009. 乘积小于 K 的子数组
- 方法1:滑动窗口
思路
class Solution {public int numSubarrayProductLessThanK(int[] nums, int k) {int left=0;int sum=1;int count=0;for(int right=0;right<nums.length;right++){sum*=nums[right];while(left<=right && sum>=k){sum/=nums[left++];}if(left<=right){count+=right-left+1;}}return count;} }
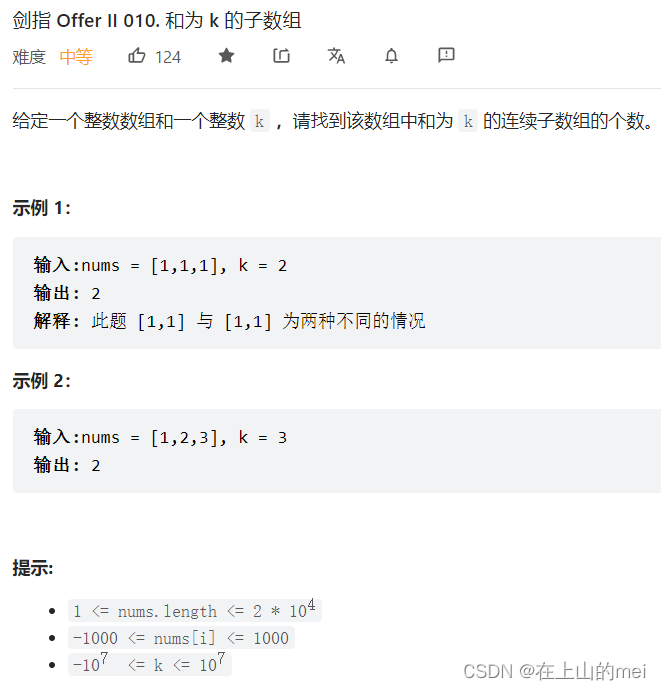
和为k的子数组
剑指 Offer II 010. 和为 k 的子数组
这题还得再看再做!!!
- 方法1:前缀和+哈希表
这道题如果nums[i]的取值范围不包括负数的话,那么就可以用滑动窗口
但是这样看来,这道题不能用滑动窗口
因此我们要找一个其他的方法——前缀和
这个大佬的思路 加上 这个大佬的图
看完相信你应该懂得差不多了
class Solution {public int subarraySum(int[] nums, int k) {int sum=0;//记录前缀和int count=0;//记录个数Map<Integer,Integer> map=new HashMap<>();map.put(0,1);for(int i:nums){sum+=i;count+=map.getOrDefault(sum-k,0);map.put(sum,map.getOrDefault(sum,0)+1);}return count;} }
0和1个数相同的子数组
剑指 Offer II 011. 0 和 1 个数相同的子数组
这题还得再看再做!!!
- 方法1:前缀和+哈希表
思路
class Solution {public int findMaxLength(int[] nums) {int sum=0;//记录前缀和int count=0;//记录个数Map<Integer,Integer> map=new HashMap<>();map.put(0,-1);for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){sum+=nums[i]==0?-1:1;if(map.containsKey(sum)){count=Math.max(count,i-map.get(sum));}else{map.put(sum,i);}}return count;} }
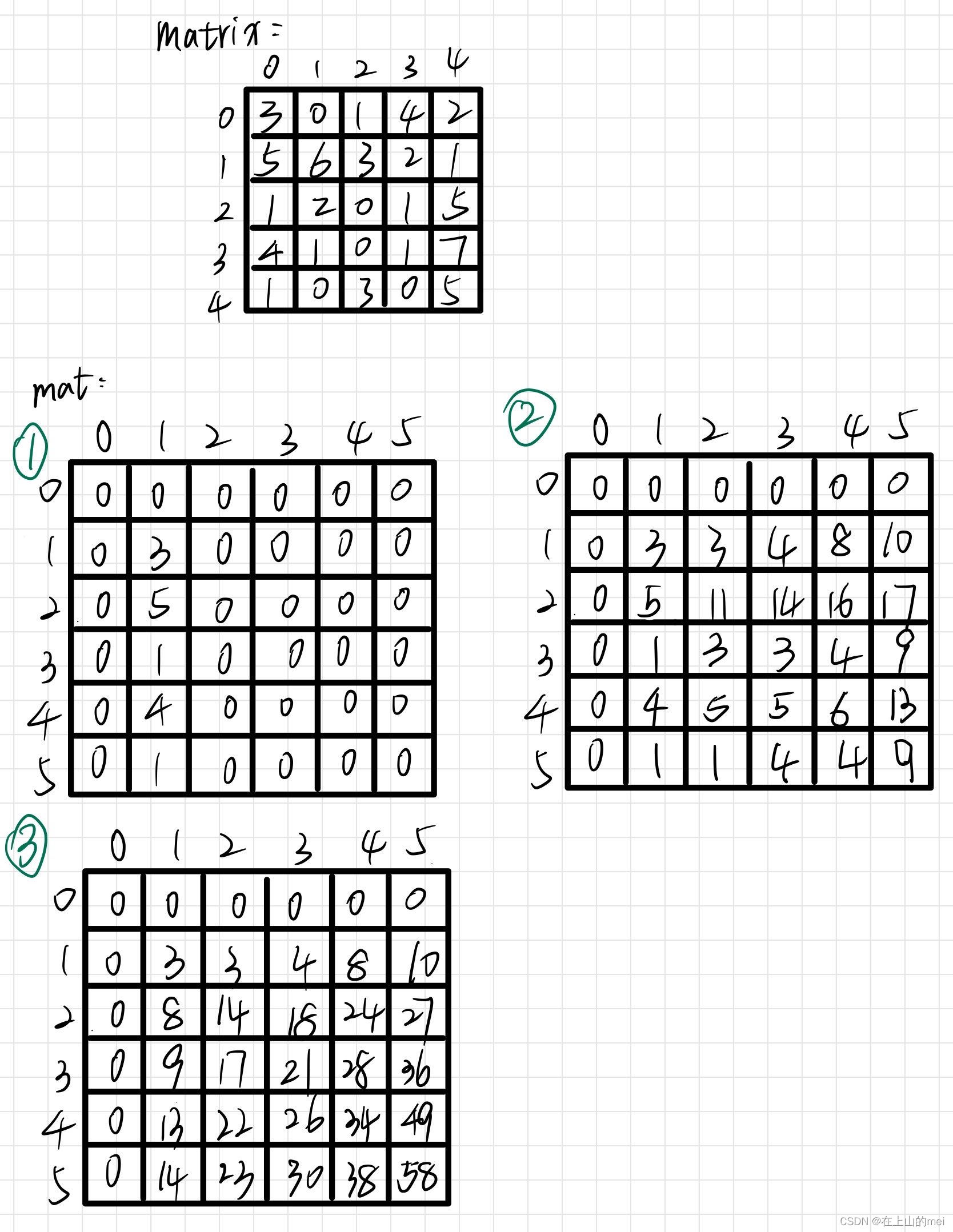
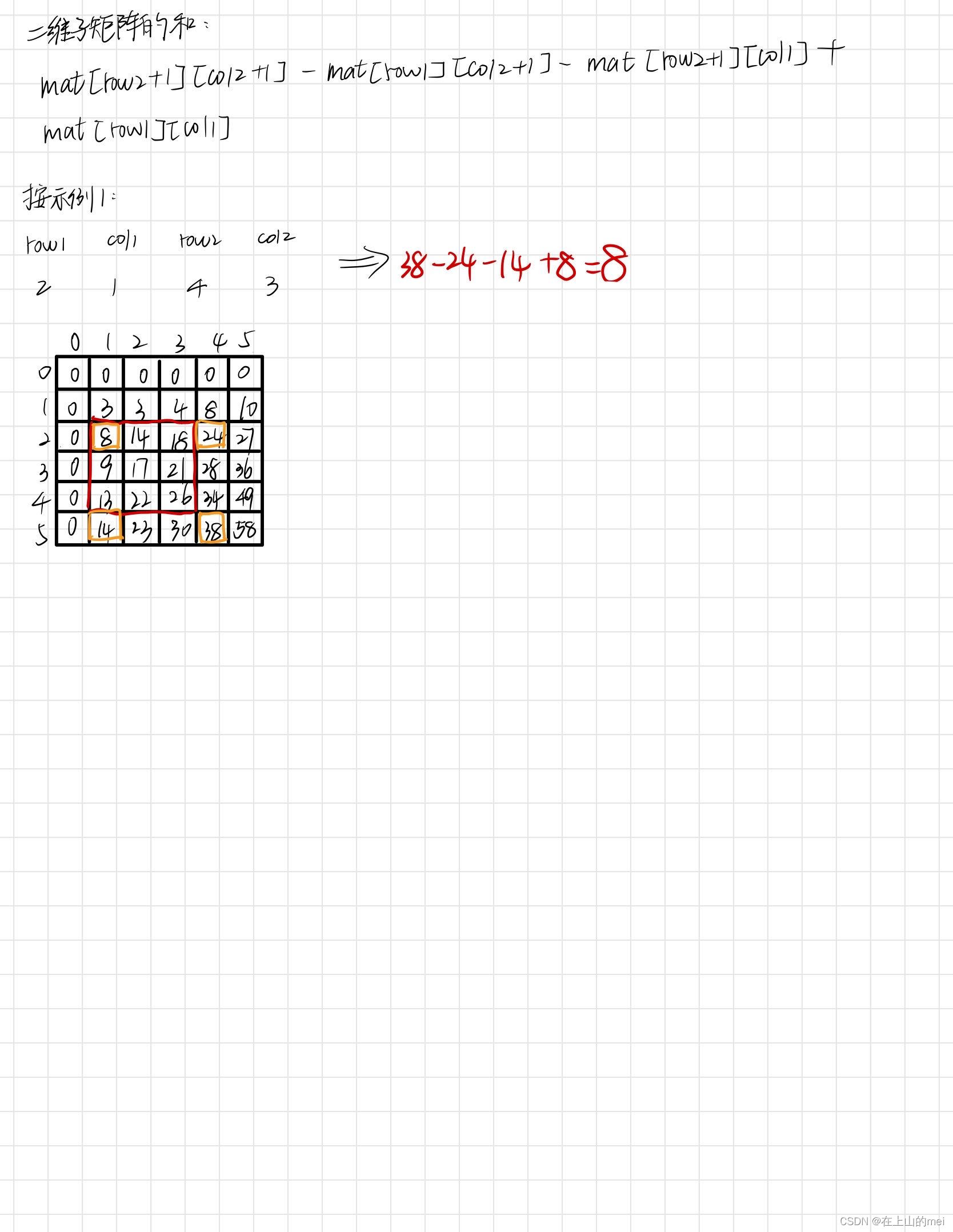
二维子矩阵的和
剑指 Offer II 013. 二维子矩阵的和

没懂没懂没懂!!!
- 方法1:前缀和
思路
class NumMatrix {int[][] mat;public NumMatrix(int[][] matrix) {int m = matrix.length;int n = matrix[0].length;mat = new int[m + 1][n + 1];for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {mat[i][1] = matrix[i-1][0];}for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {mat[i][j] = mat[i][j-1] + matrix[i-1][j-1];}}for (int i = 2; i <= m; i++) {for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {mat[i][j] += mat[i-1][j];}}}public int sumRegion(int row1, int col1, int row2, int col2) {return mat[row2 + 1][col2 + 1] - mat[row1][col2 + 1] - mat[row2 + 1][col1] + mat[row1][col1];} }
字符串中的变位词
剑指 Offer II 014. 字符串中的变位词
- 方法1:滑动窗口
思路
class Solution {public boolean checkInclusion(String s1, String s2) {if(s1.length()>s2.length())return false;int[] arr1=new int[26];int[] arr2=new int[26];for(int i=0;i<s1.length();i++){arr1[s1.charAt(i)-'a']++;arr2[s2.charAt(i)-'a']++;}for(int i=s1.length();i<s2.length();i++){if(Arrays.equals(arr1,arr2)){return true;}arr2[s2.charAt(i-s1.length())-'a']--;arr2[s2.charAt(i)-'a']++;}return Arrays.equals(arr1,arr2);} }
字符串中的所有变位词
剑指 Offer II 015. 字符串中的所有变位词

- 方法1:滑动窗口
思路:有了这道题上面的题——字符串中的变位词的基础
这道题不是手到擒来嘛哇哈哈哈哈哈哈
class Solution {public List<Integer> findAnagrams(String s, String p) {List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();if(p.length()>s.length())return list;int[] arrs=new int[26];int[] arrp=new int[26];for(int i=0;i<p.length();i++){arrs[s.charAt(i)-'a']++;arrp[p.charAt(i)-'a']++;}for(int i=p.length();i<s.length();i++){if(Arrays.equals(arrs,arrp)){list.add(i-p.length());}arrs[s.charAt(i-p.length())-'a']--;arrs[s.charAt(i)-'a']++;}if(Arrays.equals(arrs,arrp)){list.add(s.length()-p.length());}return list;} }
不含重复字符的最长子字符串
剑指 Offer II 016. 不含重复字符的最长子字符串
还得再做!!!
- 方法1:滑动窗口
思路
class Solution {public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {int left=0;int count=0;if(s.length()<=1)return s.length();Map<Character,Integer> map=new HashMap<>();int right=0;for(;right<s.length();right++){if(map.containsKey(s.charAt(right))){count=Math.max(count,right-left);left=Math.max(left,map.get(s.charAt(right))+1);}map.put(s.charAt(right),right);}count=Math.max(count,right-left);return count;} }
回文子字符串的个数
剑指 Offer II 020. 回文子字符串的个数
还得再做!!!
- 方法1:中心扩展
class Solution {public int countSubstrings(String s) {int count = 0;//字符串的每个字符都作为回文中心进行判断,中心是一个字符或两个字符for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); ++i) {count += countPalindrome(s, i, i);count += countPalindrome(s, i, i+1);}return count;}//从字符串的第start位置向左,end位置向右,比较是否为回文并计数private int countPalindrome(String s, int start, int end) {int count = 0;while (start >= 0 && end < s.length() && s.charAt(start) == s.charAt(end)) {count++;start--;end++;}return count;} }
删除链表的倒数第n个结点
剑指 Offer II 021. 删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点
- 方法1:双指针+傀儡节点
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/ class Solution {public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {ListNode pre=new ListNode(-1);pre.next=head;ListNode fast=pre;ListNode slow=pre;while(n!=0){fast=fast.next;n--;}while(fast.next!=null){fast=fast.next;slow=slow.next;}slow.next=slow.next.next;return pre.next;}}
链表中环的入口节点
剑指 Offer II 022. 链表中环的入口节点
- 方法1:快慢指针
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode(int x) {* val = x;* next = null;* }* }*/ public class Solution {public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {ListNode fast=head;ListNode slow=head;while(fast!=null && fast.next!=null){fast=fast.next.next;slow=slow.next;if(fast==slow)break;}if(fast==null || fast.next==null)return null;slow=head;while(fast!=slow){fast=fast.next;slow=slow.next;}return slow;} }
链表中的两数相加
剑指 Offer II 025. 链表中的两数相加
- 方法1:反转链表
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/ class Solution {public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {l1=reserveList(l1);l2=reserveList(l2);ListNode pre=new ListNode(-1);int sum=0;int jinwei=0;int num1=0,num2=0;while(l1!=null || l2!=null || jinwei!=0){if(l1!=null){num1=l1.val;l1=l1.next;}else{num1=0;}if(l2!=null){num2=l2.val;l2=l2.next;}else{num2=0;}sum=num1+num2+jinwei;jinwei=sum/10;ListNode node=new ListNode(sum%10);node.next=pre.next;pre.next=node;}return pre.next;}public ListNode reserveList(ListNode head){ListNode pre=null;while(head!=null){ListNode headN=head.next;head.next=pre;pre=head;head=headN;}return pre;} }
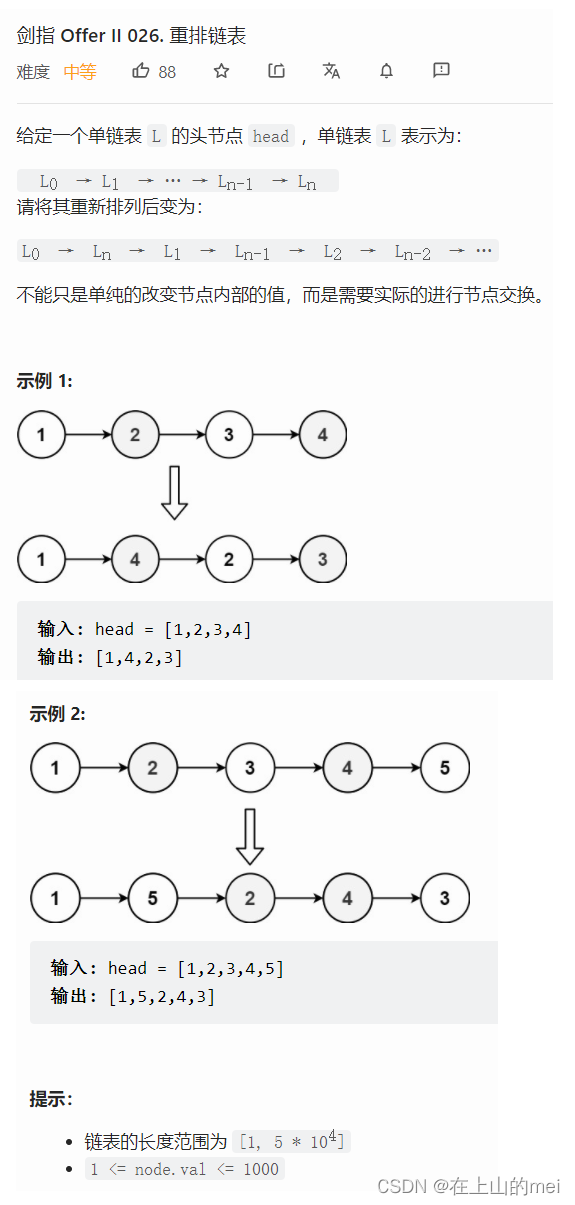
重排链表
剑指 Offer II 026. 重排链表
- 方法1:快慢指针+反转链表+链表合并
class Solution {public void reorderList(ListNode head) {// 找到中间节点ListNode mid = findMid(head);// 通过中间节点,将链表分为两部分,左边一部分不动,将右边一部分翻转ListNode curA = head;ListNode curB = reverse(mid.next);// 中间节点划分到左边部分mid.next = null;// 将链表一分为二// 将两个链表合并merge(curA, curB);}private ListNode findMid(ListNode head){// 创建一个辅助头节点ListNode tmp = new ListNode(0);tmp.next = head;// 从辅助头节点开始,快指针一次走2个单位,慢指针一次走1个单位// 当快指针.next == null 或者 快指针 == null 则表明,slow 指向了中间节点。ListNode slow = tmp, fast = tmp;while (fast != null && fast.next != null){slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next.next;}return slow;}private ListNode reverse(ListNode head){ListNode reversedList = null;while (head != null){ListNode next = head.next;head.next = reversedList;reversedList = head;head = next;}return reversedList;}private ListNode merge(ListNode l1, ListNode l2){int flag = 1;// 设定一个标记,辅助交叉遍历两个链表// flag 为奇数则插入 l1 的节点, flag 为偶数则插入 l2 的节点ListNode head = new ListNode(0);ListNode cur=head;while (l1 != null || l2 != null){if (flag % 2 == 0){cur.next = l2;l2 = l2.next;}else{cur.next = l1;l1 = l1.next;}flag++;cur = cur.next;}return head.next;} }
展平多级双向链表
剑指 Offer II 028. 展平多级双向链表
- 方法1:深度优先搜索
/* // Definition for a Node. class Node {public int val;public Node prev;public Node next;public Node child; }; */class Solution {public Node flatten(Node head) {Node last=dfs(head);return head; }public Node dfs(Node node){Node cur=node;Node last=null;// 记录链表的最后一个节点while(cur!=null){Node next=cur.next;if(cur.child!=null){Node childLast=dfs(cur.child);cur.next=cur.child;cur.child.prev=cur;// 如果 next 不为空,就将 last 与 next 相连if(next!=null){childLast.next=next;next.prev=childLast;}cur.child=null;// 将 child 置为空last=childLast;//这一步也很重要,想想为什么}else{last=cur;}cur=next;}return last;} }
排序的循环链表
剑指 Offer II 029. 排序的循环链表

还得再写!!!
- 方法1:链表模拟
思路
我是先看的上面这个思路然后自己写的代码,我感觉写的没问题,但是可能有很多代码的冗余,因此导致运行超时
这时回头去看思路当中的代码,发现大佬写的代码很妙~
class Solution {public Node insert(Node he, int x) {Node t = new Node(x);t.next = t;if (he == null) return t;Node ans = he;int min = he.val, max = he.val;while (he.next != ans) {he = he.next;min = Math.min(min, he.val);max = Math.max(max, he.val);}if (min == max) {t.next = ans.next;ans.next = t;} else {while (!(he.val == max && he.next.val == min)) he = he.next;while (!(x <= min || x >= max) && !(he.val <= x && x <= he.next.val)) he = he.next;t.next = he.next;he.next = t;}return ans;} }
插入、删除和随机访问都是O(1)的容器
剑指 Offer II 030. 插入、删除和随机访问都是 O(1) 的容器
还需要再练练!!!
- 方法1:变长数组+哈希表
思路
class RandomizedSet {List<Integer> list;Map<Integer,Integer> map;Random random;/** Initialize your data structure here. */public RandomizedSet() {list=new ArrayList<>();map=new HashMap<>();random=new Random();}/** Inserts a value to the set. Returns true if the set did not already contain the specified element. */public boolean insert(int val) {if(!map.containsKey(val)){int listIndex=list.size();list.add(val);map.put(val,listIndex);return true;}return false;}/** Removes a value from the set. Returns true if the set contained the specified element. */public boolean remove(int val) {if(map.containsKey(val)){int mapIndex=map.get(val);int last=list.get(list.size()-1);list.set(mapIndex,last);map.put(last,mapIndex);list.remove(list.size()-1);map.remove(val);return true;}return false;}/** Get a random element from the set. */public int getRandom() {int rr=random.nextInt(list.size());return list.get(rr);} }/*** Your RandomizedSet object will be instantiated and called as such:* RandomizedSet obj = new RandomizedSet();* boolean param_1 = obj.insert(val);* boolean param_2 = obj.remove(val);* int param_3 = obj.getRandom();*/
最近最少使用缓存
剑指 Offer II 031. 最近最少使用缓存

还要再做!!!
- 方法1:哈希表+双向链表
思路
class LRUCache {class DLinkedNode {int key; //初始化keyint value; //初始化value//初始化双向链表前后联系指针DLinkedNode prev;DLinkedNode next;//初始化双向链表public DLinkedNode() {}public DLinkedNode(int _key, int _value) {key = _key;value = _value;}}//创建哈希表HashMap<Integer, DLinkedNode> map = new HashMap<>();//链表当前大小int size;//链表当前容量int capacity;//链表头部尾部节点DLinkedNode head;DLinkedNode tail;public LRUCache(int capacity) {//大小初始化this.size = 0;//容量初始化this.capacity = capacity;//使用伪头部和伪尾部节点head = new DLinkedNode();tail = new DLinkedNode();head.next = tail;tail.prev = head;}public int get(int key) {//在哈希表中找到key所对应的节点DLinkedNode node = map.get(key);//如果这个节点不存在则返回-1if (node == null) {return -1;}//将这个节点移到头部,再返回这个节点所对应的值movetohead(node);return node.value;}public void put(int key, int value) {//在哈希表中找到key所对应的节点DLinkedNode node = map.get(key);//如果这个节点不存在,则创建一个新的节点进行添加if (node == null) {//创建新节点DLinkedNode newnode = new DLinkedNode(key, value);//将节点加入哈希表map.put(key, newnode);//将这个节点添加到双向链表头部addtohead(newnode);//双向链表容量+1size++;//如果容量超过最大容量,则需将双向链表尾部的节点移除if (size > capacity) {//在链表中删去尾部节点,同时哈希表中也移除掉这个节点,并且双向链表容量-1DLinkedNode tail = removetail();map.remove(tail.key);size--;}} else {//如果这个节点存在,则直接修改valuenode.value = value;//将这个节点在双向链表中移到头部movetohead(node);}}//在头部添加节点的方法public void addtohead(DLinkedNode node) {//head为虚拟头结点,由于是双向链表,添加一个节点需要建立四个连接关系node.prev = head;node.next = head.next;head.next.prev = node;head.next = node;}//移除节点方法public void removenode(DLinkedNode node) {//跳过这个节点重新建立双向连接关系node.prev.next = node.next;node.next.prev = node.prev;}//将节点移到头部的方法public void movetohead(DLinkedNode node) {removenode(node);addtohead(node);}//将节点从尾部移除的方法public DLinkedNode removetail() {//尾部的待删除节点即为虚拟尾结点的前一个节点DLinkedNode res = tail.prev;//将这个节点删除removenode(res);return res;} }
变位词组
剑指 Offer II 033. 变位词组
方法1:哈希表+排序
思路,看的是方法1排序,方法2计数有时间可以看看
class Solution {public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) {Map<String,List<String>> map=new HashMap<>();for(String str:strs){char[] cc=str.toCharArray();Arrays.sort(cc);String key=new String(cc);List<String> list=map.getOrDefault(key,new ArrayList<String>());//妙啊妙啊这思路list.add(str);map.put(key,list);}return new ArrayList<>(map.values());} }
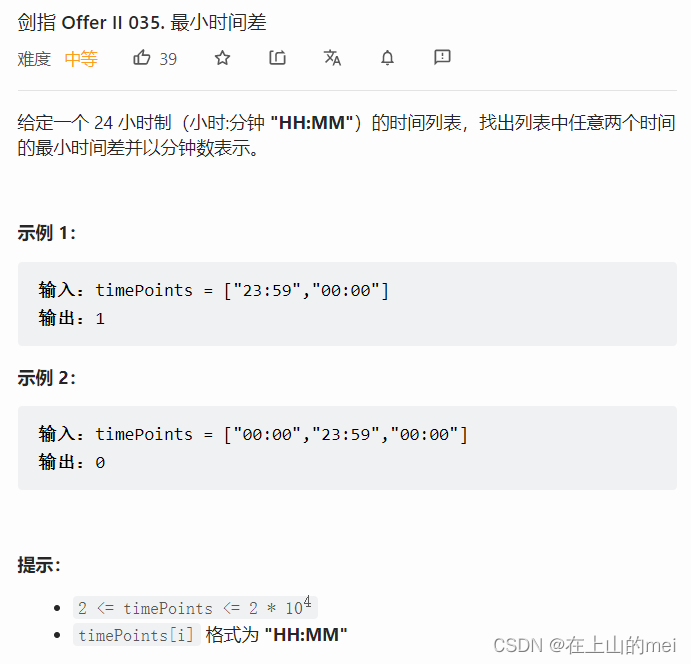
最小时间差
剑指 Offer II 035. 最小时间差
这道题代码看懂了,但自己没有单独写一遍,有时间自己要写一遍!!!
- 方法1:排序
思路,看的方法1哦
解释下1440怎么来的
class Solution {public int findMinDifference(List<String> timePoints) {Collections.sort(timePoints);int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;int t0Minutes = getMinutes(timePoints.get(0));int preMinutes = t0Minutes;for (int i = 1; i < timePoints.size(); ++i) {int minutes = getMinutes(timePoints.get(i));ans = Math.min(ans, minutes - preMinutes); // 相邻时间的时间差preMinutes = minutes;}ans = Math.min(ans, t0Minutes + 1440 - preMinutes); // 首尾时间的时间差return ans;}public int getMinutes(String t) {return ((t.charAt(0) - '0') * 10 + (t.charAt(1) - '0')) * 60 + (t.charAt(3) - '0') * 10 + (t.charAt(4) - '0');} }
后缀表达式
剑指 Offer II 036. 后缀表达式
- 方法1:栈
class Solution {public int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<Integer>();int n = tokens.length;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {String token = tokens[i];if (isNumber(token)) {stack.push(Integer.parseInt(token));} else {int num2 = stack.pop();int num1 = stack.pop();switch (token) {case "+":stack.push(num1 + num2);break;case "-":stack.push(num1 - num2);break;case "*":stack.push(num1 * num2);break;case "/":stack.push(num1 / num2);break;default:}}}return stack.pop();}public boolean isNumber(String token) {return !("+".equals(token) || "-".equals(token) || "*".equals(token) || "/".equals(token));} }
小行星碰撞
剑指 Offer II 037. 小行星碰撞

- 方法1:栈
思路
class Solution {public int[] asteroidCollision(int[] asteroids) {Stack<Integer> s=new Stack<>();int p=0;while(p<asteroids.length){if(s.empty() || s.peek()<0 || asteroids[p]>0){s.push(asteroids[p]);}else if(s.peek()<=-asteroids[p]){if(s.pop()<-asteroids[p]){continue;}}p++;}int[] arr=new int[s.size()];for(int i=arr.length-1;i>=0;i--){arr[i]=s.pop();}return arr;} }
每日温度
剑指 Offer II 038. 每日温度
- 方法1:栈
思路
class Solution {public int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] temperatures) {Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();int[] ret = new int[temperatures.length];for (int i = 0; i < temperatures.length; i++) {while (!stack.empty() && temperatures[stack.peek()] < temperatures[i]) {int index = stack.pop();ret[index] = i - index;}stack.push(i);}return ret;} }
往完全二叉树添加节点
剑指 Offer II 043. 往完全二叉树添加节点
- 方法1:层序遍历+队列
思路
class CBTInserter { private Queue<TreeNode> queue;private TreeNode root;public CBTInserter(TreeNode root) {this.root = root;queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);//在初始化树时就层序遍历到第一个没有左或右子树的节点,即为待插入位置的父节点,在队列头部while (queue.peek().left != null && queue.peek().right != null) {TreeNode node = queue.poll();queue.offer(node.left);queue.offer(node.right);}}public int insert(int v) {//队列头部节点即为待插入位置的父节点TreeNode parent = queue.peek();TreeNode node = new TreeNode(v);//插入左子树,父节点仍无右子树,父节点不变//插入右子树,左右子树入列,并将该父节点出列,待插入位置更改为下一个if (parent.left == null) {parent.left = node;} else {parent.right = node;queue.poll();queue.offer(parent.left);queue.offer(parent.right);}return parent.val;}public TreeNode get_root() {return root;} }
二叉树每层的最大值
剑指 Offer II 044. 二叉树每层的最大值
这道题完完全全是自己写出来的!!呱唧呱唧!当然也是因为自己之前做题思路的积累,在这基础上结合题目进行匹配~
- 方法1:队列
下面这个未通过的例子帮助我修改代码,最终AC
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode() {}* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {* this.val = val;* this.left = left;* this.right = right;* }* }*/ class Solution {public List<Integer> largestValues(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();if(root==null)return list;Queue<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);list.add(root.val);while(!queue.isEmpty()){int curSize=queue.size();int ss=curSize;int curCengMax=Integer.MIN_VALUE;int flag=0;while(curSize!=0){TreeNode tmp=queue.poll();if(tmp.left!=null && tmp.right!=null){curCengMax=Math.max(curCengMax,Math.max(tmp.left.val,tmp.right.val));queue.offer(tmp.left);queue.offer(tmp.right);flag+=0;}else{if(tmp.left!=null){curCengMax=Math.max(curCengMax,tmp.left.val);queue.offer(tmp.left);flag+=0;}else if(tmp.right!=null){curCengMax=Math.max(curCengMax,tmp.right.val);queue.offer(tmp.right);flag+=0;}else{flag+=1;}}curSize--;}if(flag<ss){list.add(curCengMax);}}return list;} }
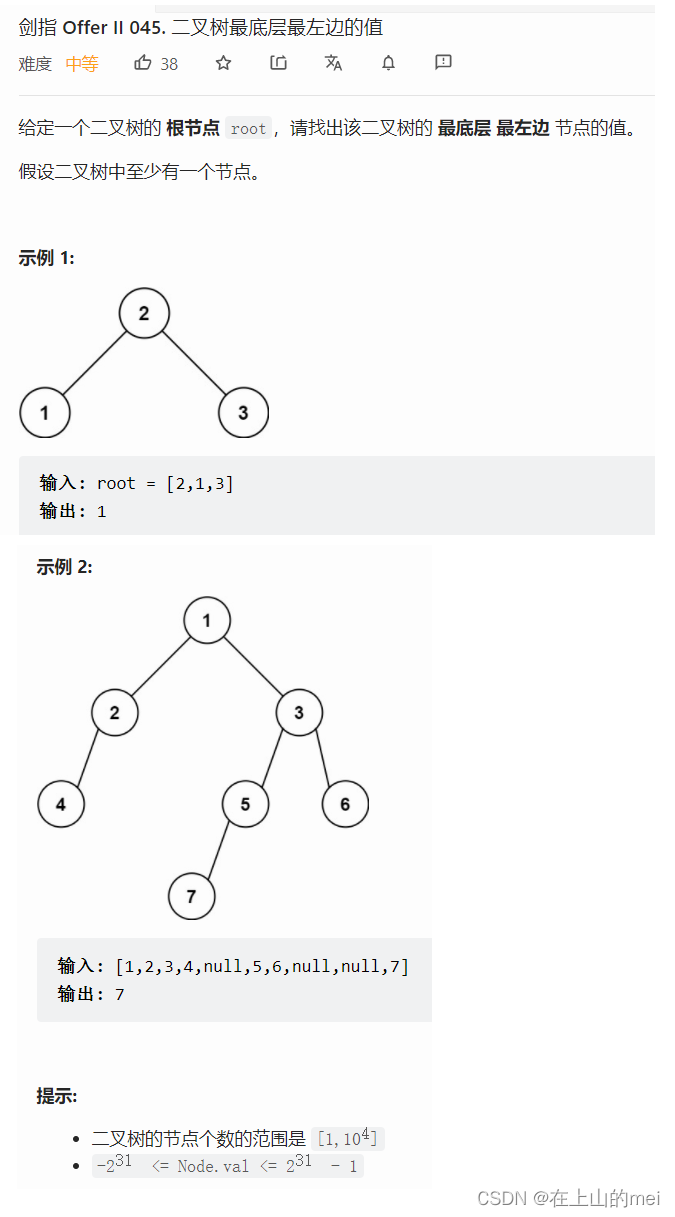
二叉树最底层最左边的值
剑指 Offer II 045. 二叉树最底层最左边的值
- 方法1:层序遍历+队列
原来这道题也是用这样的思路啊,有点没想到哈哈哈还是经验优先啊举一反三能力还差点,再加油!
思路
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode() {}* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {* this.val = val;* this.left = left;* this.right = right;* }* }*/ class Solution {public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {Queue<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);int res=0;while(!queue.isEmpty()){int curSize=queue.size();for(int i=0;i<curSize;i++){TreeNode curRoot=queue.poll();if(i==0){res=curRoot.val;}if(curRoot.left!=null){queue.offer(curRoot.left);}if(curRoot.right!=null){queue.offer(curRoot.right);}}}return res;} }
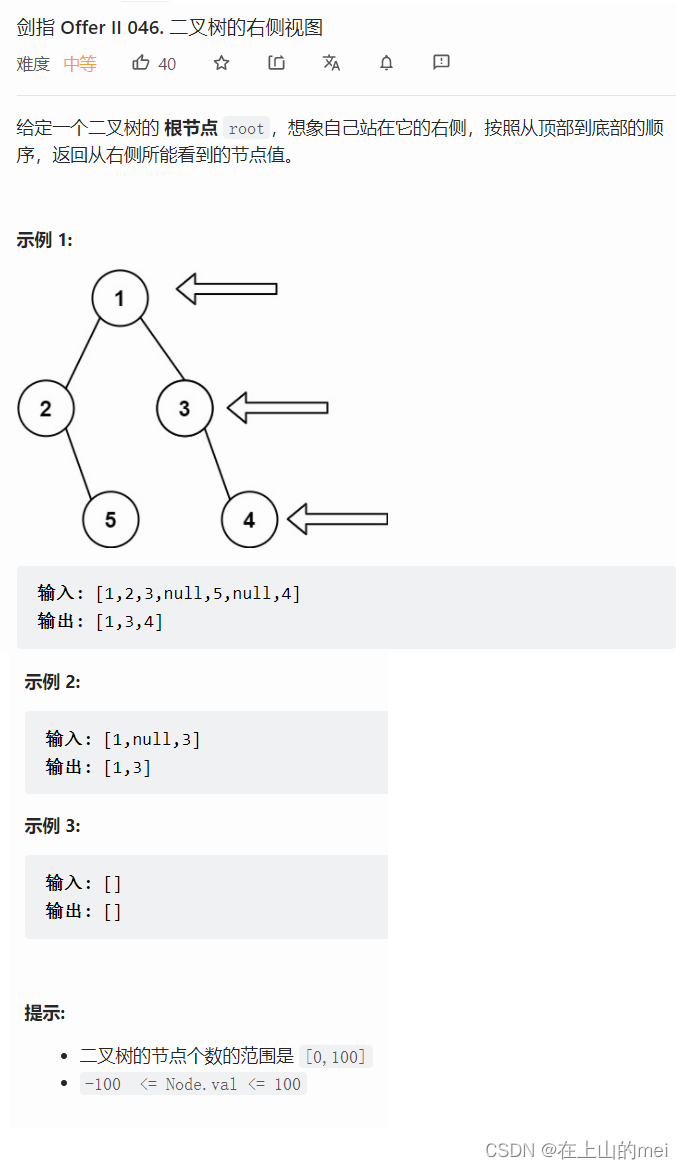
二叉树的右侧视图
剑指 Offer II 046. 二叉树的右侧视图
- 方法1:层序遍历+队列
这道题导致我没做出来我觉得还是没有把层序遍历+队列的思路融会贯通,导致遇到套用这个思路的题,他变了一些就还是会卡壳。
另外这道题也因为有侧视图如果右子树比左子树短,会不会能看到左子树那边在纠结这个问题。。。就比如下面这个
思路
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode() {}* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {* this.val = val;* this.left = left;* this.right = right;* }* }*/ class Solution {public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {Queue<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList<>();List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();if(root!=null){queue.offer(root);}while(!queue.isEmpty()){int curSize=queue.size();for(int i=0;i<curSize;i++){TreeNode curRoot=queue.poll();if(i==curSize-1){list.add(curRoot.val);}if(curRoot.left!=null){queue.offer(curRoot.left);}if(curRoot.right!=null){queue.offer(curRoot.right);}}}return list;} }
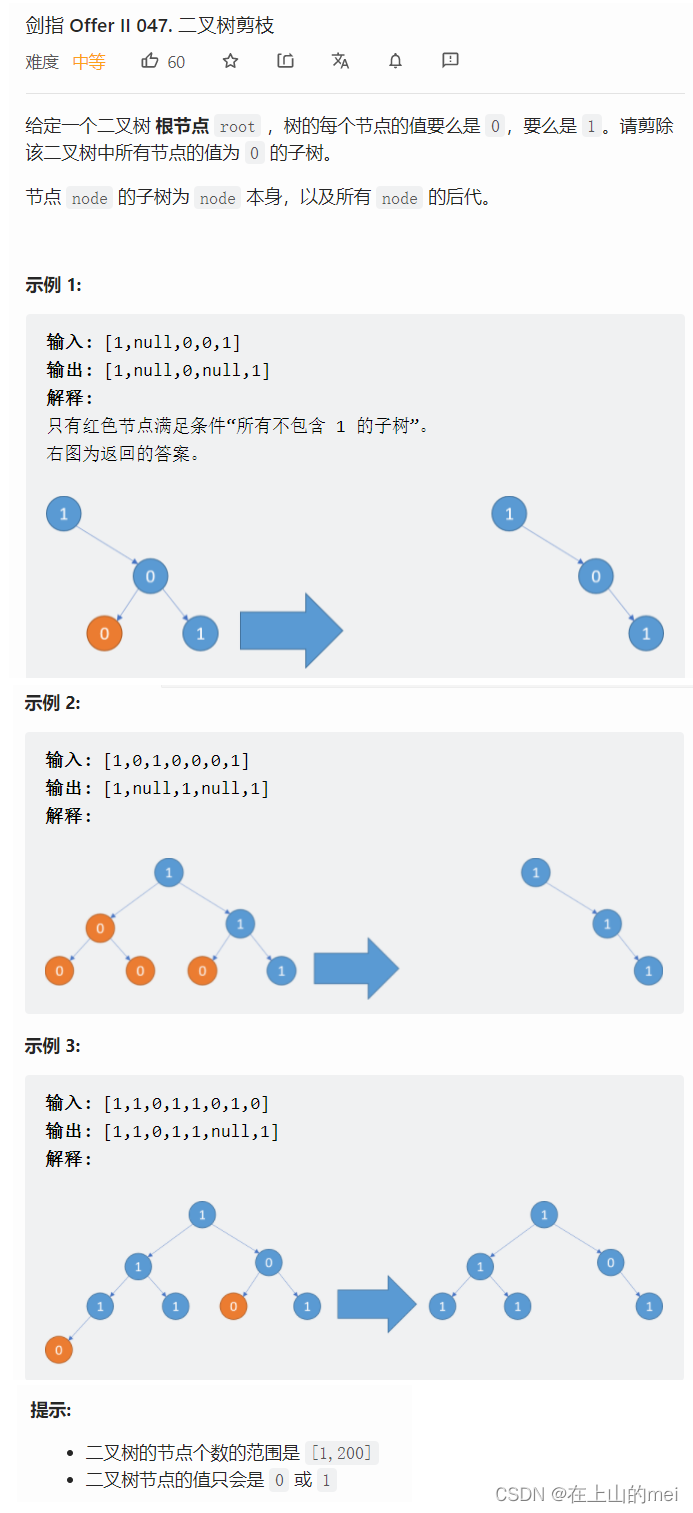
二叉树剪枝
剑指 Offer II 047. 二叉树剪枝
有时间可以再做做,这个思路需要自己看到就能想到才算真的成功
- 方法1:深度优先搜索
思路
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode() {}* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {* this.val = val;* this.left = left;* this.right = right;* }* }*/ class Solution {public TreeNode pruneTree(TreeNode root) {if(root==null)return null;root.left=pruneTree(root.left);root.right=pruneTree(root.right);if(root.val==0 && root.left==null && root.right==null){root=null;}return root;} }
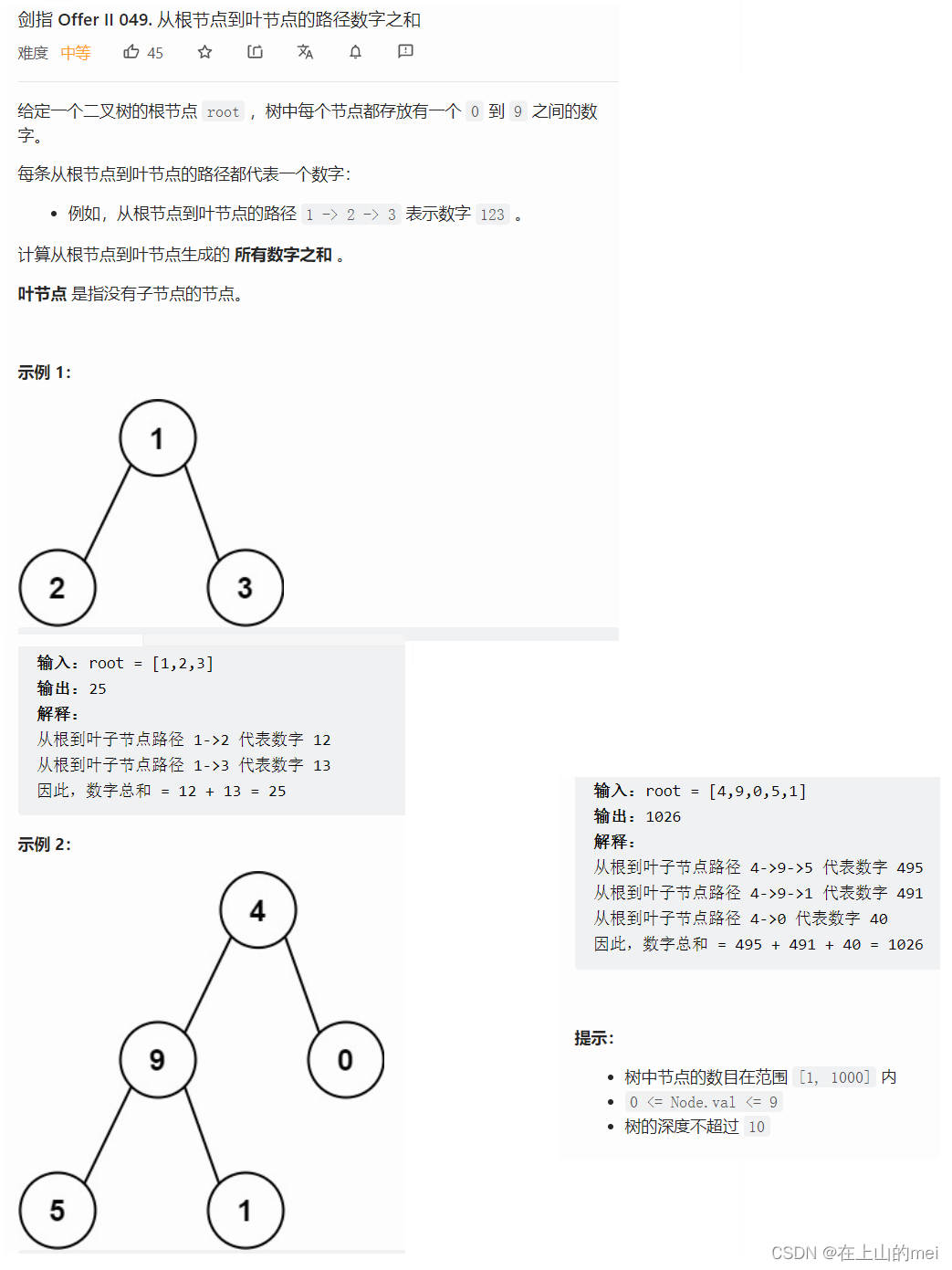
从根节点到叶节点的路径数字之和
剑指 Offer II 049. 从根节点到叶节点的路径数字之和
这道题还得再写,思路还得自己想出来才行啊啊啊啊啊
- 方法1:深度优先搜索
思路
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode() {}* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {* this.val = val;* this.left = left;* this.right = right;* }* }*/ class Solution {public int sumNumbers(TreeNode root) {return dfs(root,0);}public int dfs(TreeNode node,int val){if(node==null)return 0;val=val*10+node.val;if(node.left==null && node.right==null){return val;}return dfs(node.left,val)+dfs(node.right,val);} }
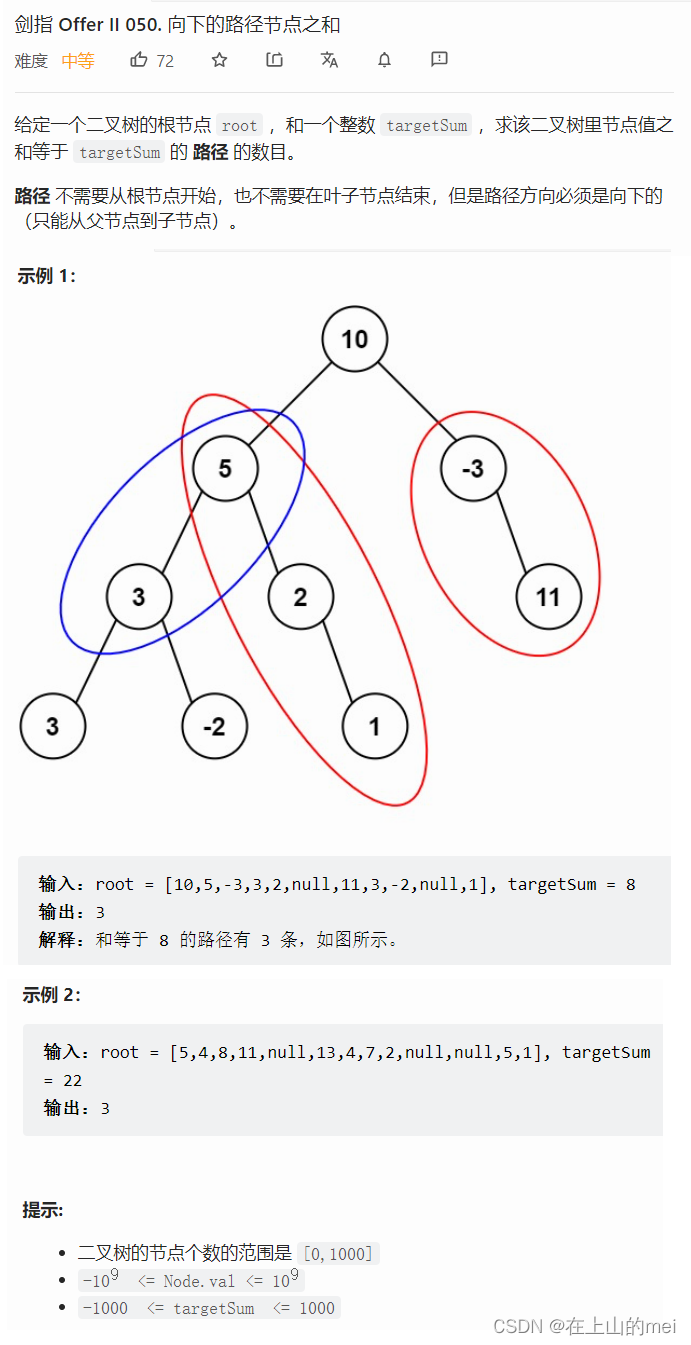
向下的路径节点之和
剑指 Offer II 050. 向下的路径节点之和
两个思路的代码都是直接拿过来的,自己没写呢,还得再看这道题!!这种题怎么这么难啊对我来说...
两个方法的思路
- 方法1:深度优先搜索
class Solution {public int pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {if (root == null) {return 0;}int ret = rootSum(root, targetSum);ret += pathSum(root.left, targetSum);ret += pathSum(root.right, targetSum);return ret;}public int rootSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {int ret = 0;if (root == null) {return 0;}int val = root.val;if (val == targetSum) {ret++;} ret += rootSum(root.left, targetSum - val);ret += rootSum(root.right, targetSum - val);return ret;} }
- 方法2:前缀和
class Solution {public int pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {HashMap<Long, Integer> prefix = new HashMap<>();prefix.put(0L, 1);return dfs(root, prefix, 0, targetSum);}public int dfs(TreeNode root, Map<Long, Integer> prefix, long curr, int targetSum) {if (root == null) {return 0;}int ret = 0;curr += root.val;ret = prefix.getOrDefault(curr - targetSum, 0);prefix.put(curr, prefix.getOrDefault(curr, 0) + 1);ret += dfs(root.left, prefix, curr, targetSum);ret += dfs(root.right, prefix, curr, targetSum);prefix.put(curr, prefix.getOrDefault(curr, 0) - 1);return ret;} }
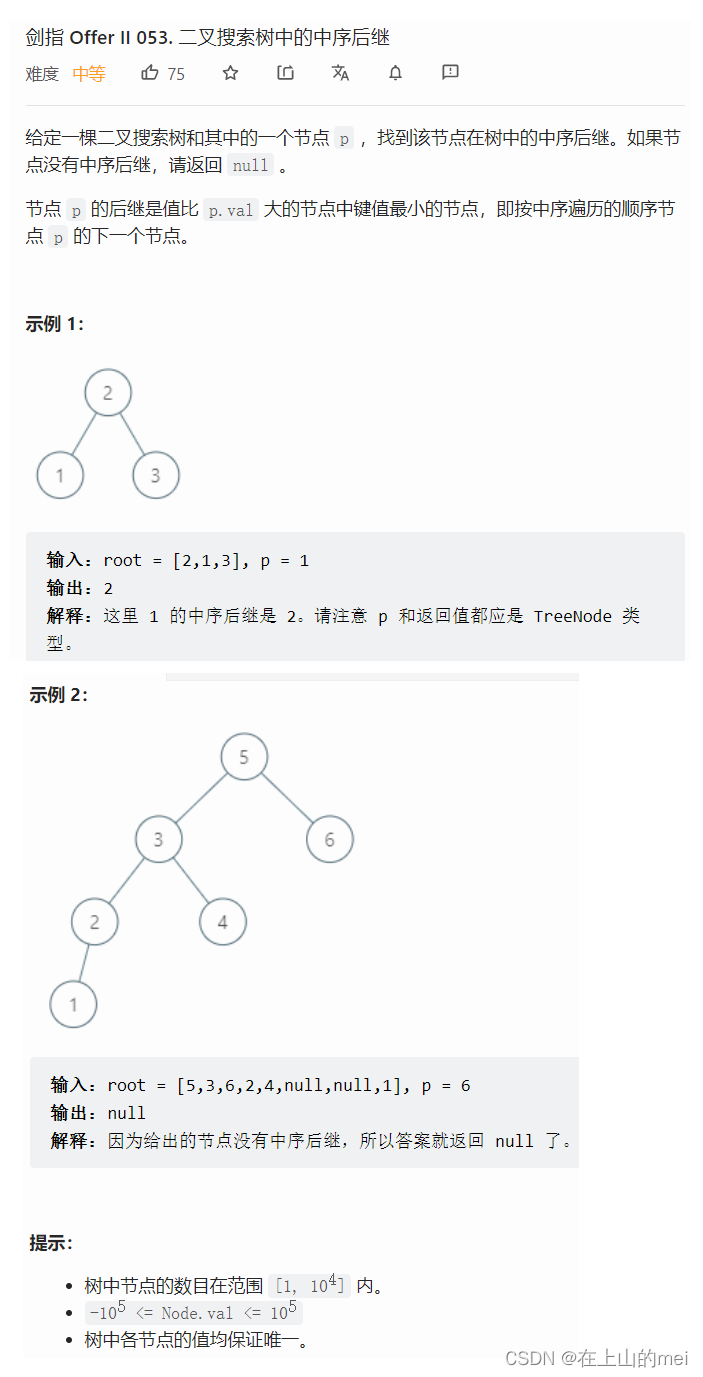
二叉搜索树中的中序后继
剑指 Offer II 053. 二叉搜索树中的中序后继
还得再做!!思路得是自己想出来的才行!!
以下两种方法思路
- 方法1:中序遍历迭代解法(使用栈)
class Solution {public TreeNode inorderSuccessor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p) {Deque<TreeNode> stack = new ArrayDeque<TreeNode>();TreeNode prev = null, curr = root;while (!stack.isEmpty() || curr != null) {while (curr != null) {stack.push(curr);curr = curr.left;}curr = stack.pop();if (prev == p) {return curr;}prev = curr;curr = curr.right;}return null;} }
- 方法2:利用二叉搜索树特点
class Solution {public TreeNode inorderSuccessor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p) {TreeNode successor = null;if (p.right != null) {successor = p.right;while (successor.left != null) {successor = successor.left;}return successor;}TreeNode node = root;while (node != null) {if (node.val > p.val) {successor = node;node = node.left;} else {node = node.right;}}return successor;} }
所有大于等于节点的值之和
剑指 Offer II 054. 所有大于等于节点的值之和

还得再做
- 方法1:反序中序遍历
思路
class Solution {int sum = 0;public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {if (root != null) {convertBST(root.right);sum += root.val;root.val = sum;convertBST(root.left);}return root;} }
二叉搜索树迭代器
剑指 Offer II 055. 二叉搜索树迭代器
两个方法都看懂了,会做了,但是自己没有写,只是把代码贴上来了,下次自己写
以下两个方法的思路
- 方法1:递归
class BSTIterator {private int idx;private List<Integer> arr;public BSTIterator(TreeNode root) {idx = 0;arr = new ArrayList<Integer>();inorderTraversal(root, arr);}public int next() {return arr.get(idx++);}public boolean hasNext() {return idx < arr.size();}private void inorderTraversal(TreeNode root, List<Integer> arr) {if (root == null) {return;}inorderTraversal(root.left, arr);arr.add(root.val);inorderTraversal(root.right, arr);} }
- 方法2:迭代
class BSTIterator {private TreeNode cur;private Deque<TreeNode> stack;public BSTIterator(TreeNode root) {cur = root;stack = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();}public int next() {while (cur != null) {stack.push(cur);cur = cur.left;}cur = stack.pop();int ret = cur.val;cur = cur.right;return ret;}public boolean hasNext() {return cur != null || !stack.isEmpty();} }
值和下标之差都在给定的范围内
剑指 Offer II 057. 值和下标之差都在给定的范围内
没看懂,所以还没写
思路
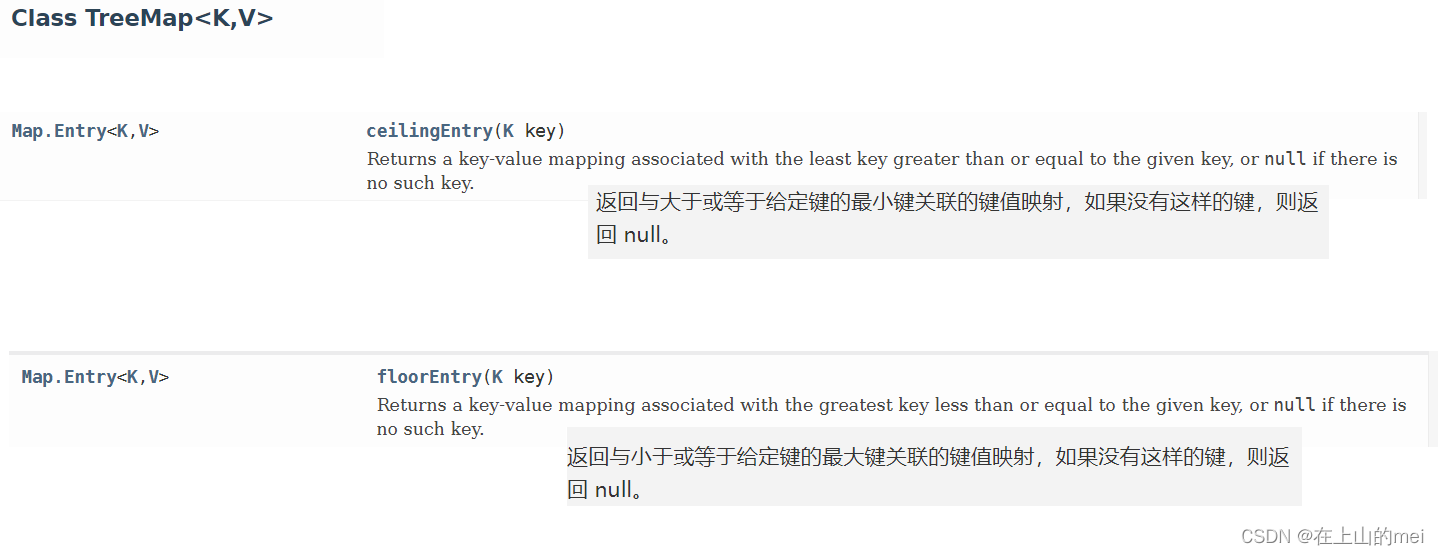
日程表
剑指 Offer II 058. 日程表
- 方法1:直接遍历
思路
class MyCalendar {List<int[]> booked;public MyCalendar() {booked = new ArrayList<int[]>();}public boolean book(int start, int end) {for (int[] arr : booked) {int l = arr[0], r = arr[1];if (l < end && start < r) {return false;}}booked.add(new int[]{start, end});return true;} }
- 方法2:平衡二叉树
思路
class MyCalendar {private TreeMap<Integer, Integer> map;public MyCalendar() {this.map = new TreeMap<>();}public boolean book(int start, int end) {Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry1 = map.floorEntry(start);Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry2 = map.ceilingEntry(start);if (entry1 != null && entry1.getValue() > start) {return false;}if (entry2 != null && entry2.getKey() < end) {return false;}map.put(start, end);return true;} }/*** Your MyCalendar object will be instantiated and called as such:* MyCalendar obj = new MyCalendar();* boolean param_1 = obj.book(start,end);*/
出现频率最高的k个数字
剑指 Offer II 060. 出现频率最高的 k 个数字
- 方法1:堆(优先级队列)
思路
class Solution {public int[] topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) {Map<Integer,Integer> map=new HashMap<>();for(int n: nums){map.put(n,map.getOrDefault(n,0)+1);}PriorityQueue<int[]> pq=new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<int[]>(){public int compare(int[] m,int[] n){return m[1]-n[1];}});for(Map.Entry<Integer,Integer> entry:map.entrySet()){int kk=entry.getKey();int vv=entry.getValue();if(pq.size()==k){if(pq.peek()[1]<vv){pq.poll();pq.offer(new int[]{kk,vv});}}else{pq.offer(new int[]{kk,vv});}}int[] res=new int[k];for(int i=0;i<k;i++){res[i]=pq.poll()[0];}return res;} }
和最小的k个数对
剑指 Offer II 061. 和最小的 k 个数对
代码自己没写,但差不多看懂了,还得自己写出来才行
- 方法1:优先级队列
代码来自这里
思路来自这里
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> kSmallestPairs(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int k) {PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> {return (nums1[o1[0]] + nums2[o1[1]]) - (nums1[o2[0]] + nums2[o2[1]]);});// Math.min(nums1.length, k)加快处理速度for(int i = 0; i < Math.min(nums1.length, k); i ++) {pq.offer(new int[] {i, 0});}List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();while(k -- > 0 && !pq.isEmpty()) {int[] arr = pq.poll();list.add(Arrays.asList(nums1[arr[0]], nums2[arr[1]]));// 上一个循环已经考虑完所有nums1的数,这个循环考虑nums2中的数if(++arr[1] < nums2.length) {pq.offer(new int[] {arr[0], arr[1]});}}return list;} }
先到这里吧,后面就好多是没学过的知识(比如前缀树),有时间精力再做吧
相关文章:

剑指offer(中等)
目录 二维数组中的查找 重建二叉树 矩阵中的路径 剪绳子 剪绳子② 数值的整数次方 表示数值的字符串 树的子结构 栈的压入、弹出序列 从上到下打印二叉树① 从上到下打印二叉树③ 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列 二叉树中和为某一值的路径 复杂链表的复制 二叉搜索树与…...
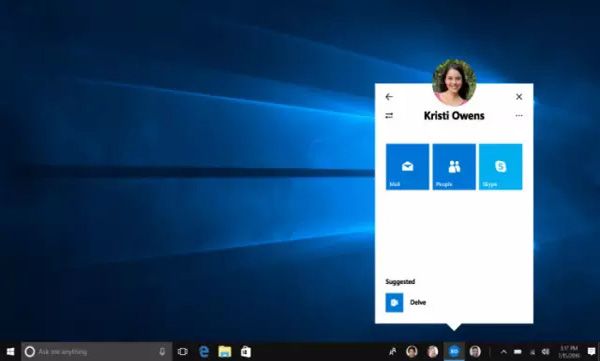
微软发布会精华回顾:“台式电脑”抢了风头
Lightbot北京时间2016年10月26日晚10点,微软在纽约发布了名为 Surface Studio 的一体机、名为 Surface Dial 的配件以及外观未变的顶配版 Surface Book。同时,微软宣布了 Windows 10 下一个重要版本——“Creators Update”的数项新功能,包括…...

CF1561C Deep Down Below 题解
CF1561C Deep Down Below 题解题目链接字面描述Deep Down Below题面翻译题目描述输入格式输出格式样例 #1样例输入 #1样例输出 #1提示思路TLE算法具体思想TLE特例AC思想代码实现备注题目 链接 https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/CF1561C 字面描述 Deep Down Below 题面翻译…...

秒杀项目之服务调用分布式session
目录 nginx动静分离 服务调用 创建配置zmall-cart购物车模块 创建配置zmall-order订单模块 服务调用 spring session实战 什么是Spring Session 为什么要使用Spring Session 错误案例展示 配置spring-session 二级域名问题 用户登录 nginx动静分离 第1步ÿ…...
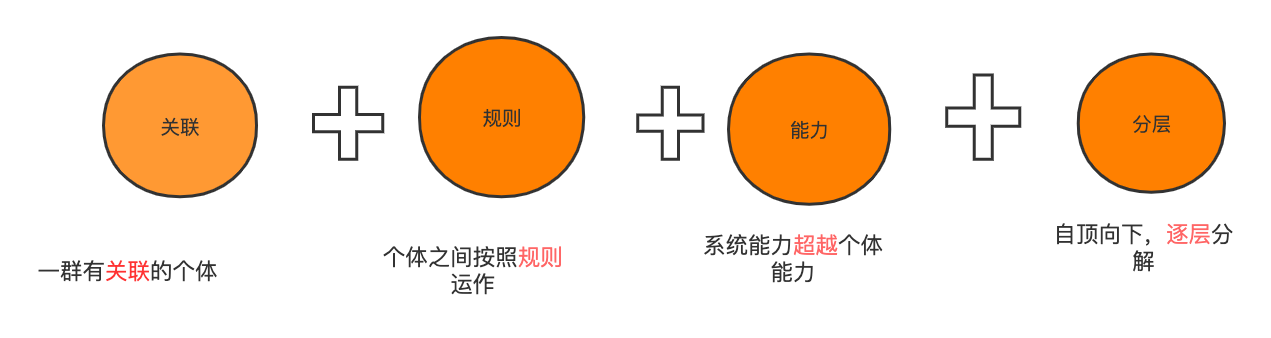
聊聊什么是架构,你理解对了吗?
什么是架构?软件有架构?建筑也有架构?它们有什么相同点和不同点? 下面咱们就介绍一下,容易混淆的几个概念 一、系统与子系统 系统 泛指由一群有关联的个体组成,根据某种规则运作,能完成个别元件不能单独完成的工作的群体。它的意思是 “总体”、“整体”或“联盟” 子系…...
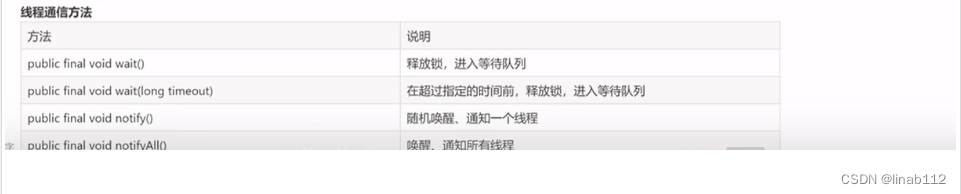
java多线程开发
1.并发和并行 并发:同一时间段内多个任务同时进行。 并行:同一时间点多个任务同时进行。 2.进程线程 进程(Process):进程是程序的一次动态执行过程,它经历了从代码加载、执行、到执行完毕的一个完整过程…...

杂记7--opencv的ar码模块学习
背景:项目需要用到marker知识,所以到官网上临时补一些知识。 概要:主要介绍marker一些接口的含义,纯属个人理解,有误则希望大佬不吝赐教 1、 涉及ar码操作学习,其头文件为: #include <op…...
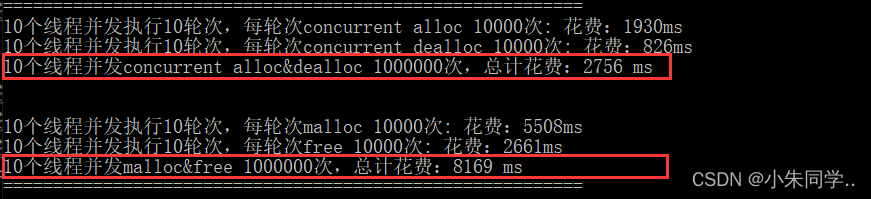
[项目设计]高并发内存池
目录 1、项目介绍 2、高并发内存池整体框架设计 3、thread cache <1>thread cache 哈希桶对齐规则 <2>Thread Cache类设计 4、Central Cache <1>Central Cache类设计 5、page cache <1>Page Cache类设计 6、性能分析 <1>定长内存池实现…...
28岁才转行软件测试,目前32了,我的一些经历跟感受
我是92年的,算是最早的90后,现在跟你介绍的时候还恬不知耻的说我是90后,哈哈,计算机专业普通本科毕业。在一个二线城市,毕业后因为自身能力问题、认知水平问题,再加上运气不好,换过多份工作&…...
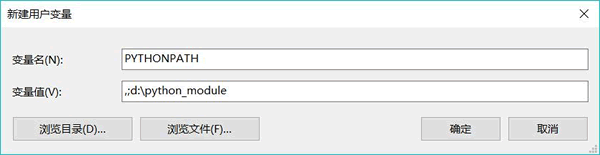
Python导入模块的3种方式
很多初学者经常遇到这样的问题,即自定义 Python 模板后,在其它文件中用 import(或 from...import) 语句引入该文件时,Python 解释器同时如下错误:ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 模块名意思是 Pytho…...
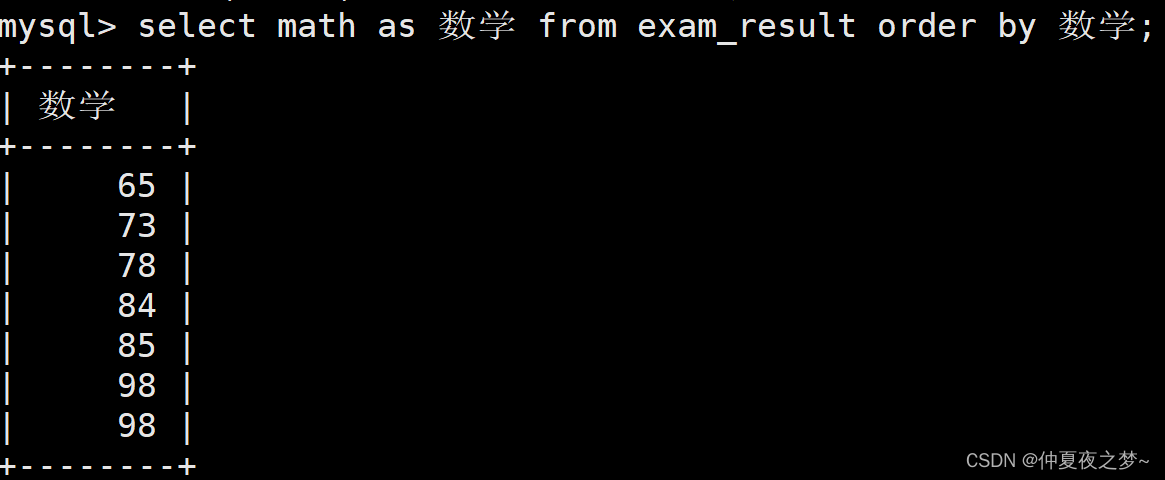
select 与 where、order by、limit 子句执行优先级比较
当 select 和 其他三种语句的一者或者多者同时出现时,他们之间是存在执行先后顺序的。 他们的优先级顺序是:where > select > order by > limit 目录 1、select 与 where 2、select 与 order by 3、order by 与 limit 4、优先级证明 1、s…...
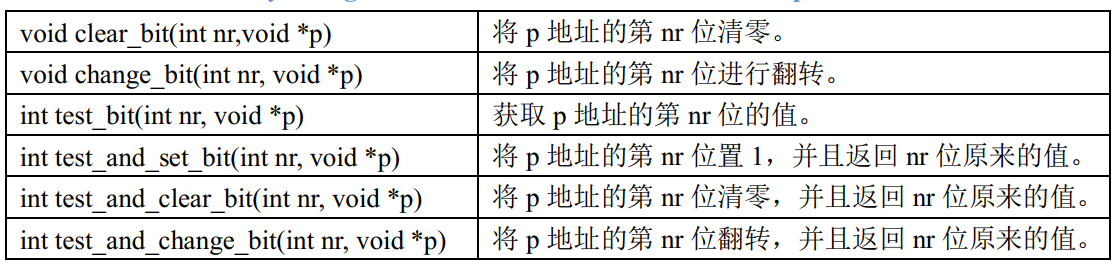
Linux内核并发与竞争-原子操作
一.原子操作的概念首先看一下原子操作,原子操作就是指不能再进一步分割的操作,一般原子操作用于变量或者位操作。假如现在要对无符号整形变量 a 赋值,值为 3,对于 C 语言来讲很简单,直接就是: a3但是 C 语言…...
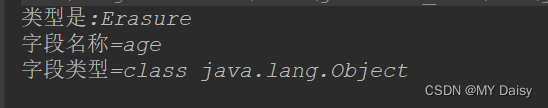
Java笔记-泛型的使用
参考: Java 泛型,你了解类型擦除吗? 泛型的使用 1、泛型的定义 可以广泛使用的类型,一种较为准确的说法就是为了参数化类型,或者说可以将类型当作参数传递给一个类或者是方法。 2、泛型的使用 2.1泛型类 public c…...
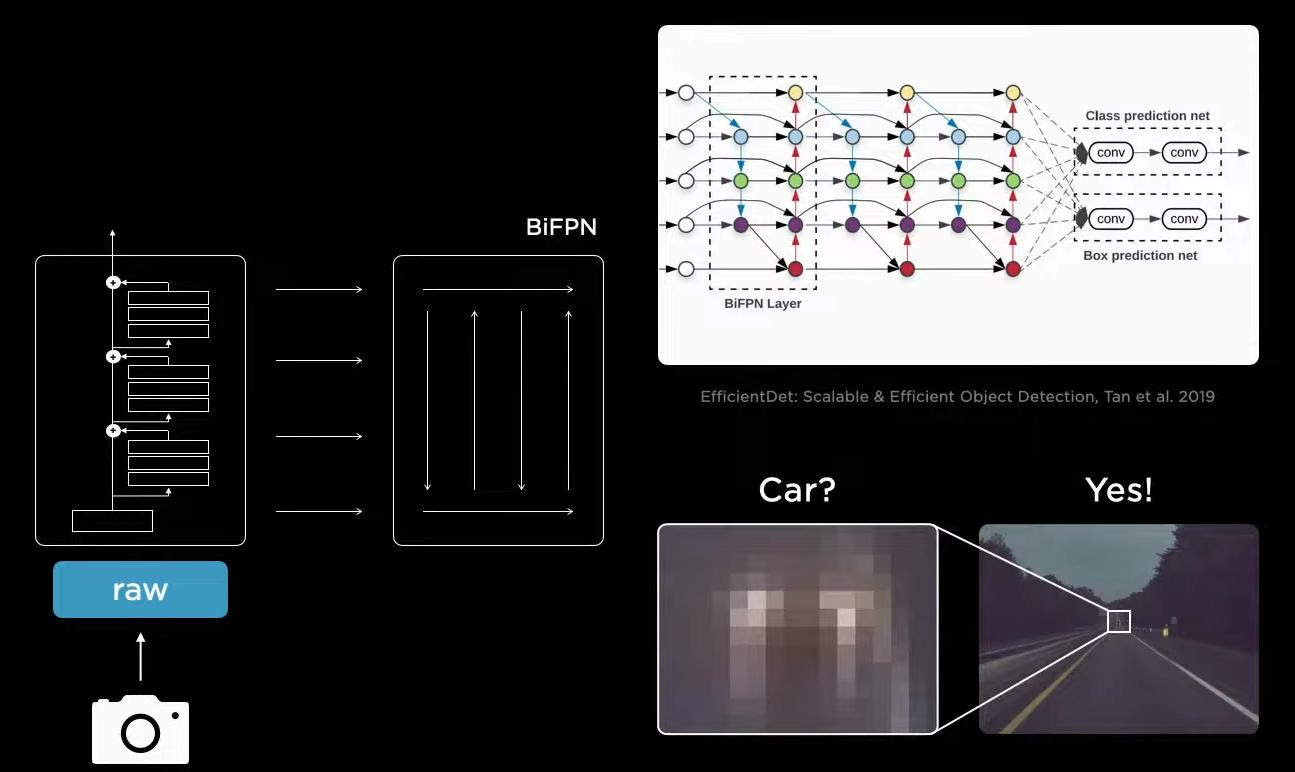
特斯拉无人驾驶解读
来源于Tesla AI Day Tesla无人驾驶算法的核心任务就是如何理解我们所看到的一切呢?也就是说,不使用高端的设备,比如激光雷达,仅仅使用摄像头就能够将任务做得很好。Tesla使用环绕型的8个摄像头获得输入。 第一步是特征提取模块Backbone,无论什么任务都离不开特征…...
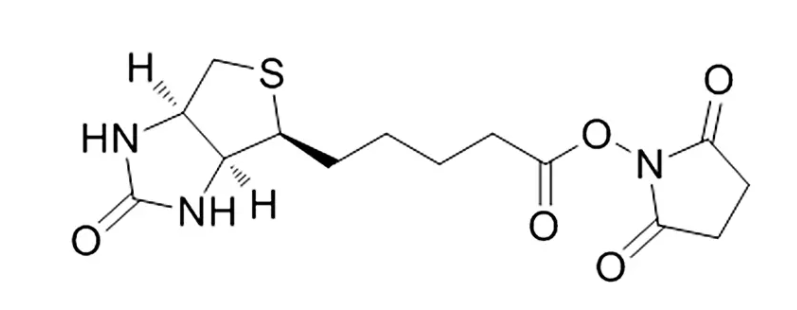
生物素-琥珀酰亚胺酯Biotin-NHS;CAS号:35013-72-0;可对溶液中的抗体,蛋白质和任何其他含伯胺的大分子进行简单有效的生物素标记。
结构式: 生物素-琥珀酰亚胺酯Biotin NHS CAS号:35013-72-0 英文名称:Biotin-NHS 中文名称:D-生物素 N-羟基琥珀酰亚胺酯;生物素-琥珀酰亚胺酯 CAS号:35013-72-0 密度:1.50.1 …...
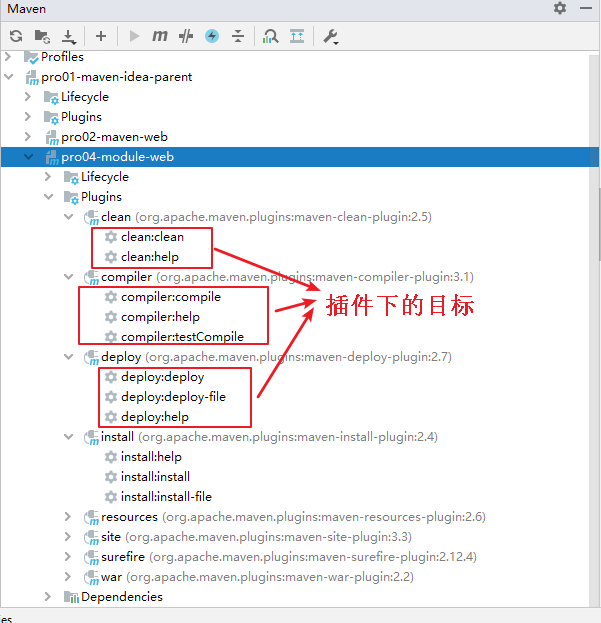
Maven_第五章 核心概念
目录第五章 其他核心概念1、生命周期①作用②三个生命周期③特点2、插件和目标①插件②目标3、仓库第五章 其他核心概念 1、生命周期 ①作用 为了让构建过程自动化完成,Maven 设定了三个生命周期,生命周期中的每一个环节对应构建过程中的一个操作。 …...

【深度学习】人脸识别工程化落地
文章目录前言1、facenet2、使用2.1.其它blog2.2 实践总结前言 老早以前就希望能写一篇关于人脸识别的工程化落地的案例,一年前做疲劳驾驶时使用的dlib插件,它封装好了,人脸检测、对齐、相似度计算三个部分,就是插件比较难装,但同时也少了很多…...
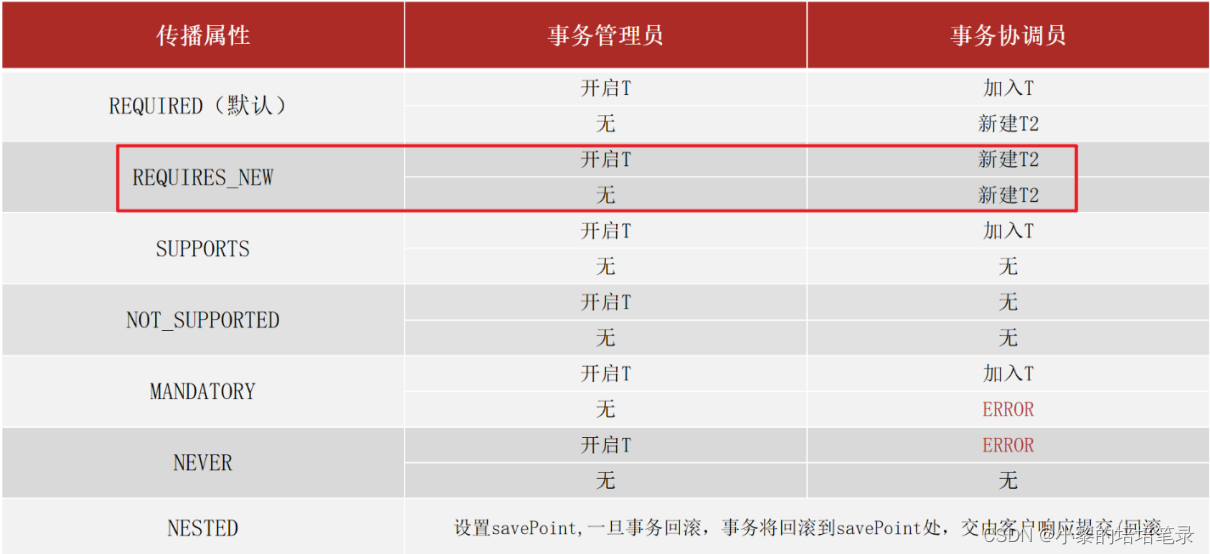
AOP面向切面编程思想。
目录 一、AOP工作流程 1、基本概念 2、AOP工作流程 二、AOP核心配置 1、AOP切入点表达式 2、AOP通知类型 三、AOP通知获取数据 1、获取参数 2、获取返回值 3、获取异常 四、AOP事务管理 1、Spring事务简介 2、Spring事务角色 3、事务属性 一、AOP工作流程 1、…...

实验7-变治技术及动态规划初步
目录 1.统计个数 2.数塔dp -A 3.Horspool算法 4.计数排序 5.找零问题1-最少硬币 1.统计个数 【问题描述】有n个数、每个元素取值在1到9之间,试统计每个数的个数 【输入形式】第一行,n的值;第二行...
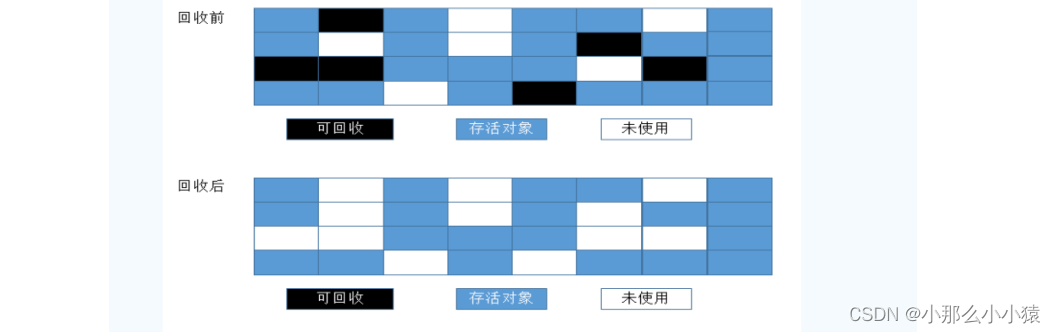
JVM垃圾回收机制GC理解
目录JVM垃圾回收分代收集如何识别垃圾引用计数法可达性分析法引用关系四种类型: 强、软、弱、虚强引用软引用 SoftReference弱引用 WeakReferenceWeakHashMap软引用与虚引用的使用场景虚引用与引用队列引用队列虚引用 PhantomReference垃圾回收算法引用计数复制 Cop…...
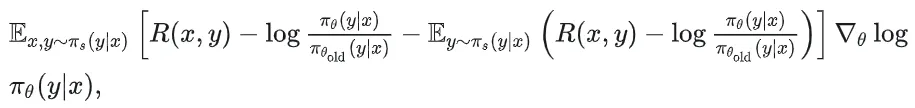
51c自动驾驶~合集58
我自己的原文哦~ https://blog.51cto.com/whaosoft/13967107 #CCA-Attention 全局池化局部保留,CCA-Attention为LLM长文本建模带来突破性进展 琶洲实验室、华南理工大学联合推出关键上下文感知注意力机制(CCA-Attention),…...
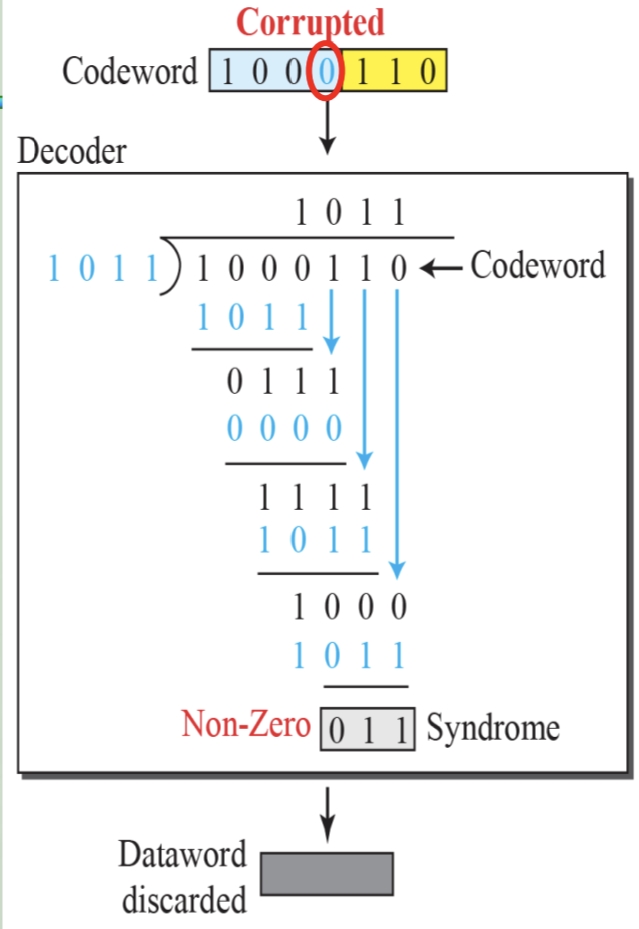
循环冗余码校验CRC码 算法步骤+详细实例计算
通信过程:(白话解释) 我们将原始待发送的消息称为 M M M,依据发送接收消息双方约定的生成多项式 G ( x ) G(x) G(x)(意思就是 G ( x ) G(x) G(x) 是已知的)࿰…...

pam_env.so模块配置解析
在PAM(Pluggable Authentication Modules)配置中, /etc/pam.d/su 文件相关配置含义如下: 配置解析 auth required pam_env.so1. 字段分解 字段值说明模块类型auth认证类模块,负责验证用户身份&am…...
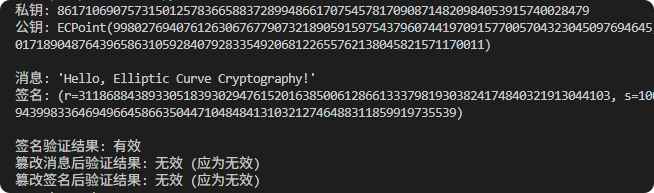
现代密码学 | 椭圆曲线密码学—附py代码
Elliptic Curve Cryptography 椭圆曲线密码学(ECC)是一种基于有限域上椭圆曲线数学特性的公钥加密技术。其核心原理涉及椭圆曲线的代数性质、离散对数问题以及有限域上的运算。 椭圆曲线密码学是多种数字签名算法的基础,例如椭圆曲线数字签…...
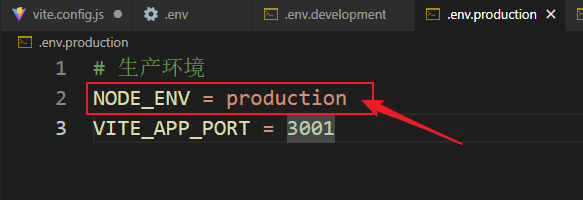
vue3+vite项目中使用.env文件环境变量方法
vue3vite项目中使用.env文件环境变量方法 .env文件作用命名规则常用的配置项示例使用方法注意事项在vite.config.js文件中读取环境变量方法 .env文件作用 .env 文件用于定义环境变量,这些变量可以在项目中通过 import.meta.env 进行访问。Vite 会自动加载这些环境变…...

【Oracle】分区表
个人主页:Guiat 归属专栏:Oracle 文章目录 1. 分区表基础概述1.1 分区表的概念与优势1.2 分区类型概览1.3 分区表的工作原理 2. 范围分区 (RANGE Partitioning)2.1 基础范围分区2.1.1 按日期范围分区2.1.2 按数值范围分区 2.2 间隔分区 (INTERVAL Partit…...

学习STC51单片机32(芯片为STC89C52RCRC)OLED显示屏2
每日一言 今天的每一份坚持,都是在为未来积攒底气。 案例:OLED显示一个A 这边观察到一个点,怎么雪花了就是都是乱七八糟的占满了屏幕。。 解释 : 如果代码里信号切换太快(比如 SDA 刚变,SCL 立刻变&#…...
什么是Ansible Jinja2
理解 Ansible Jinja2 模板 Ansible 是一款功能强大的开源自动化工具,可让您无缝地管理和配置系统。Ansible 的一大亮点是它使用 Jinja2 模板,允许您根据变量数据动态生成文件、配置设置和脚本。本文将向您介绍 Ansible 中的 Jinja2 模板,并通…...

在web-view 加载的本地及远程HTML中调用uniapp的API及网页和vue页面是如何通讯的?
uni-app 中 Web-view 与 Vue 页面的通讯机制详解 一、Web-view 简介 Web-view 是 uni-app 提供的一个重要组件,用于在原生应用中加载 HTML 页面: 支持加载本地 HTML 文件支持加载远程 HTML 页面实现 Web 与原生的双向通讯可用于嵌入第三方网页或 H5 应…...
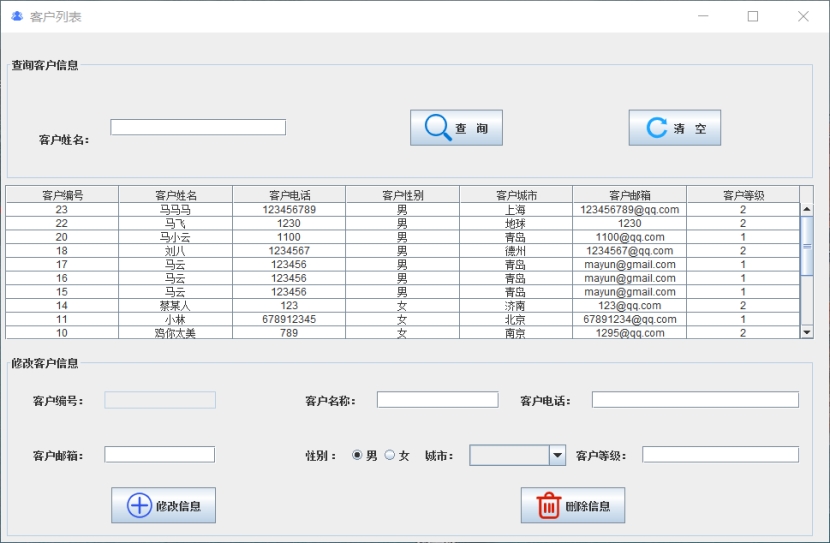
基于Java+MySQL实现(GUI)客户管理系统
客户资料管理系统的设计与实现 第一章 需求分析 1.1 需求总体介绍 本项目为了方便维护客户信息为了方便维护客户信息,对客户进行统一管理,可以把所有客户信息录入系统,进行维护和统计功能。可通过文件的方式保存相关录入数据,对…...