LeetCode刷题记(一):1~30题
1. 两数之和
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出 和为目标值 target 的那 两个 整数,并返回它们的数组下标。
你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,数组中同一个元素在答案里不能重复出现。
你可以按任意顺序返回答案。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9 输出:[0,1] 解释:因为 nums[0] + nums[1] == 9 ,返回 [0, 1] 。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [3,2,4], target = 6 输出:[1,2]
示例 3:
输入:nums = [3,3], target = 6 输出:[0,1]
提示:
2 <= nums.length <= 10^4-10^9 <= nums[i] <= 10^9-10^9 <= target <= 10^9- 只会存在一个有效答案
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
using namespace std;vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {map<int, int> map;vector<int> result;for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {int complement = target - nums[i]; // 差值if (map.find(complement) != map.end()) {result.push_back(map[complement]);result.push_back(i);return result;}map[nums[i]] = i;}return result;
}int main() {vector<int> nums;int target;int temp;while(cin>>temp){nums.push_back(temp);if(cin.get() == '\n')break;}cin>>target;vector<int> result = twoSum(nums, target);for (int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {cout << result[i] << " ";}return 0;
}
2. 两数相加
给你两个 非空 的链表,表示两个非负的整数。它们每位数字都是按照 逆序 的方式存储的,并且每个节点只能存储 一位 数字。
请你将两个数相加,并以相同形式返回一个表示和的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数都不会以 0 开头。
示例 1:

输入:l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4] 输出:[7,0,8] 解释:342 + 465 = 807.
示例 2:
输入:l1 = [0], l2 = [0] 输出:[0]
示例 3:
输入:l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9] 输出:[8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]
提示:
- 每个链表中的节点数在范围
[1, 100]内 0 <= Node.val <= 9- 题目数据保证列表表示的数字不含前导零
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;struct ListNode {int val;ListNode *next;ListNode() : val(0), next(NULL) {}ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};class Solution {public:ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0);ListNode* curr = dummy;int carry = 0; // 进位while(l1 != NULL || l2 != NULL) {int x = (l1 != NULL) ? l1->val : 0; int y = (l2 != NULL) ? l2->val : 0;int sum = x + y + carry;carry = sum / 10;curr->next = new ListNode(sum % 10);curr = curr->next;if(l1 != NULL) l1 = l1->next;if(l2 != NULL) l2 = l2->next;} // 增添1位 if(carry > 0) {curr->next = new ListNode(carry);}return dummy->next;}
};ListNode* createList() {ListNode* head = NULL;ListNode* current = NULL;int val;while(cin >> val) {ListNode* newNode = new ListNode(val);if(head == NULL) {head = newNode;current = newNode;} else {current->next = newNode;current = current->next;}if(cin.get() == '\n')break;}return head;
}void printList(ListNode* head) {ListNode* current = head;while(current != NULL) {cout << current->val << " ";current = current->next;}
}int main() {Solution solution;ListNode* list1 = createList();ListNode* list2 = createList();ListNode* result = solution.addTwoNumbers(list1, list2);printList(result);return 0;
}3. 无重复字符的最长子串
给定一个字符串 s ,请你找出其中不含有重复字符的 最长子串 的长度。
示例 1:
输入: s = "abcabcbb" 输出: 3 解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 "abc",所以其长度为 3。
示例 2:
输入: s = "bbbbb" 输出: 1 解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 "b",所以其长度为 1。
示例 3:
输入: s = "pwwkew" 输出: 3 解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 "wke",所以其长度为 3。请注意,你的答案必须是子串的长度,"pwke"是一个子序列,不是子串。
提示:
0 <= s.length <= 5 * 10^4s由英文字母、数字、符号和空格组成
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {// 使用滑动窗口来找出最长的不含重复字符的子串 int n = s.length();int res = 0; // 记录最长子串的长度 vector<int> index(128, -1); // 记录每个字符在字符串s中最近出现的位置 for(int i = 0, j = 0; j < n; j++) {i = max(i, index[s[j]] + 1); // 当遇到重复的字符时,将左边界i移动到该重复字符的下一个位置,确保窗口内没有重复字符 res = max(res, j - i + 1); // 每次更新窗口长度并与res比较,取较大者 index[s[j]] = j; // 更新字符在index数组中的位置为当前位置 }return res;}
};int main() {Solution solution;string s;cin >> s;cout << solution.lengthOfLongestSubstring(s);return 0;
}4. 寻找两个正序数组的中位数
给定两个大小分别为 m 和 n 的正序(从小到大)数组 nums1 和 nums2。请你找出并返回这两个正序数组的 中位数 。
算法的时间复杂度应该为 O(log (m+n)) 。
示例 1:
输入:nums1 = [1,3], nums2 = [2] 输出:2.00000 解释:合并数组 = [1,2,3] ,中位数 2
示例 2:
输入:nums1 = [1,2], nums2 = [3,4] 输出:2.50000 解释:合并数组 = [1,2,3,4] ,中位数 (2 + 3) / 2 = 2.5 ^
提示:
nums1.length == mnums2.length == n0 <= m <= 10000 <= n <= 10001 <= m + n <= 2000-10^6 <= nums1[i], nums2[i] <= 10^6
解法一:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:double findMedianSortedArrays(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {vector<int> curr;int m = nums1.size();int n = nums2.size();for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {curr.push_back(nums1[i]);}for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {curr.push_back(nums2[i]);}sort(curr.begin(), curr.end());if((m + n) % 2 == 0) {return (curr[(m + n) / 2] + curr[(m + n) / 2 - 1] ) / 2.0; } else {return curr[(m + n) / 2];}}
};int main() {Solution solution;vector<int> nums1, nums2;int tmp;cout << "请输入nums1数组的元素:" << endl;while(cin >> tmp) {nums1.push_back(tmp);if(cin.get() == '\n')break;}cout << "请输入nums2数组的元素:" << endl;while(cin >> tmp) {nums2.push_back(tmp);if(cin.get() == '\n')break;}cout << solution.findMedianSortedArrays(nums1, nums2);return 0;
}解法二:
class Solution {public:double findMedianSortedArrays(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {vector<int> curr;int m = nums1.size();int n = nums2.size();int i = 0, j = 0;while(i < m && j < n) {if(nums1[i] < nums2[j]) {curr.push_back(nums1[i]);i++;}else {curr.push_back(nums2[j]);j++;}}while(i < m) {curr.push_back(nums1[i]);i++;}while(j < n) {curr.push_back(nums2[j]);j++;}if((m + n) % 2 == 0) {return (curr[(m + n) / 2] + curr[(m + n) / 2 - 1] ) / 2.0; } else {return curr[(m + n) / 2];}}
};5. 最长回文子串
给你一个字符串 s,找到 s 中最长的回文子串。
如果字符串的反序与原始字符串相同,则该字符串称为回文字符串。
示例 1:
输入:s = "babad" 输出:"bab" 解释:"aba" 同样是符合题意的答案。
示例 2:
输入:s = "cbbd" 输出:"bb"
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 1000s仅由数字和英文字母组成
// C++
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:string longestPalindrome(string s) {int n = s.size();if(n < 2) {return s;}int maxLen = 1;int begin = 0;//dp[i][j]表示s[i··j]是否为回文串vector<vector <int> > dp(n,vector<int>(n, true));//递归开始//先枚举子串长度for(int L = 2; L <= n; L++) {//枚举左边界,左边界的上限设置可以宽松一些for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {int j = L + i - 1;//如果右边界越界,就可以退出当前循环if(j >= n) {break;}if(s[i] != s[j]) {dp[i][j] = false;} else {if(j-i < 3) {dp[i][j] = true;} else {dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1][j - 1];}}// 只要dp[i][j] == true成立,就表示子串s[i···L]是回文,此时记录回文长度和起始位置。if(dp[i][j] && j - i + 1 > maxLen) {maxLen = j - i + 1;begin = i;}}}return s.substr(begin,maxLen);}
};int main() {string s = "";cin>>s;Solution solution;cout<<solution.longestPalindrome(s)<<endl;return 0;
}解法二:
// C++
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:string longestPalindrome(string s) {if(s.empty()) {return "";}int start = 0, end = 0;for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {int len1 = expandAroundCenter(s, i, i);int len2 = expandAroundCenter(s, i, i + 1);int len = max(len1, len2);if(len > end - start) {start = i - (len - 1) / 2;end = i + len / 2;}}return s.substr(start, end - start + 1);}int expandAroundCenter(string s, int left, int right) {while(left >= 0 && right < s.size() && s[left] == s[right]) {left--;right++;}return right - left - 1;}
};int main() {string s = "";cin>>s;Solution solution;cout<<solution.longestPalindrome(s)<<endl;return 0;
}6. Z字型变换
将一个给定字符串 s 根据给定的行数 numRows ,以从上往下、从左到右进行 Z 字形排列。
比如输入字符串为 "PAYPALISHIRING" 行数为 3 时,排列如下:
P A H N A P L S I I G Y I R
之后,你的输出需要从左往右逐行读取,产生出一个新的字符串,比如:"PAHNAPLSIIGYIR"。
请你实现这个将字符串进行指定行数变换的函数:
string convert(string s, int numRows);
示例 1:
输入:s = "PAYPALISHIRING", numRows = 3 输出:"PAHNAPLSIIGYIR"
示例 2:
输入:s = "PAYPALISHIRING", numRows = 4 输出:"PINALSIGYAHRPI" 解释: P I N A L S I G Y A H R P I
示例 3:
输入:s = "A", numRows = 1 输出:"A"
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 1000s由英文字母(小写和大写)、','和'.'组成1 <= numRows <= 1000
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:string covert(string s, int numRows) {if(numRows == 1) return s;int n = s.size();int k = 2 * numRows - 2; // 计算 Z 字形的周期长度,即每个完整的 Z 字形有多少个字符vector<string> a(numRows);// 创建一个长度为 numRows 的字符串数组 a,用于存储 Z 字形排列后的每一行字符串for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {a[min(k - i % k, i % k)] += s[i];// k - i % k 和 i % k 分别表示当前字符在 Z 字形周期中的上半部分和下半部分的位置}return accumulate(a.begin(), a.end(), string("")); // 拼接}
};int main() {string s;cin >> s;int numRows;cin >> numRows; Solution solution;cout << solution.covert(s, numRows);return 0;
}
7. 整数反转
给你一个 32 位的有符号整数 x ,返回将 x 中的数字部分反转后的结果。
如果反转后整数超过 32 位的有符号整数的范围 [−2^31, 2^31 − 1] ,就返回 0。
假设环境不允许存储 64 位整数(有符号或无符号)。
示例 1:
输入:x = 123 输出:321
示例 2:
输入:x = -123 输出:-321
示例 3:
输入:x = 120 输出:21
示例 4:
输入:x = 0 输出:0
提示:
-2^31 <= x <= 2^31 - 1
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:int reverse(int x) {
// if(x == 0) return 0;int res = 0;while(x != 0) {if(res < INT_MIN / 10 || res > INT_MAX / 10) {return 0;}res = res * 10 + x % 10;x /= 10;}return res;}
};int main() {int x;cin >> x;Solution solution;cout << solution.reverse(x) << endl;return 0;
}8. 字符串转换正数(atoi)
请你来实现一个 myAtoi(string s) 函数,使其能将字符串转换成一个 32 位有符号整数(类似 C/C++ 中的 atoi 函数)。
函数 myAtoi(string s) 的算法如下:
- 读入字符串并丢弃无用的前导空格
- 检查下一个字符(假设还未到字符末尾)为正还是负号,读取该字符(如果有)。 确定最终结果是负数还是正数。 如果两者都不存在,则假定结果为正。
- 读入下一个字符,直到到达下一个非数字字符或到达输入的结尾。字符串的其余部分将被忽略。
- 将前面步骤读入的这些数字转换为整数(即,"123" -> 123, "0032" -> 32)。如果没有读入数字,则整数为
0。必要时更改符号(从步骤 2 开始)。 - 如果整数数超过 32 位有符号整数范围
[−231, 231 − 1],需要截断这个整数,使其保持在这个范围内。具体来说,小于−231的整数应该被固定为−231,大于231 − 1的整数应该被固定为231 − 1。 - 返回整数作为最终结果。
注意:
- 本题中的空白字符只包括空格字符
' '。 - 除前导空格或数字后的其余字符串外,请勿忽略 任何其他字符。
示例 1:
输入:s = "42" 输出:42 解释:加粗的字符串为已经读入的字符,插入符号是当前读取的字符。 第 1 步:"42"(当前没有读入字符,因为没有前导空格)^ 第 2 步:"42"(当前没有读入字符,因为这里不存在 '-' 或者 '+')^ 第 3 步:"42"(读入 "42")^ 解析得到整数 42 。 由于 "42" 在范围 [-231, 231 - 1] 内,最终结果为 42 。
示例 2:
输入:s = " -42" 输出:-42 解释: 第 1 步:" -42"(读入前导空格,但忽视掉)^ 第 2 步:" -42"(读入 '-' 字符,所以结果应该是负数)^ 第 3 步:" -42"(读入 "42")^ 解析得到整数 -42 。 由于 "-42" 在范围 [-231, 231 - 1] 内,最终结果为 -42 。
示例 3:
输入:s = "4193 with words" 输出:4193 解释: 第 1 步:"4193 with words"(当前没有读入字符,因为没有前导空格)^ 第 2 步:"4193 with words"(当前没有读入字符,因为这里不存在 '-' 或者 '+')^ 第 3 步:"4193 with words"(读入 "4193";由于下一个字符不是一个数字,所以读入停止)^ 解析得到整数 4193 。 由于 "4193" 在范围 [-231, 231 - 1] 内,最终结果为 4193 。
提示:
0 <= s.length <= 200s由英文字母(大写和小写)、数字(0-9)、' '、'+'、'-'和'.'组成
#include<iostream>
#include<ctype.h>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:int myAtoi(string s) {int i = 0; // 索引 int sign = 1; // 符号位long long result = 0;// 跳过前面的空格字符while(i < s.size() && s[i] == ' ') {i++;} // 检查最终结果为正数还是负数if(i < s.size() && (s[i] == '+' || s[i] == '-')) {sign = (s[i++] == '-' ? -1 : 1);} // 把字符串转换成数字 while(i < s.size() && isdigit(s[i])) {result = result * 10 + (s[i++] - '0');if(result * sign > INT_MAX) {return INT_MAX;} if(result * sign < INT_MIN) {return INT_MIN;}} return result * sign;}
};int main() {string s;cin >> s;Solution solution;cout << solution.myAtoi(s);return 0;
}9. 回文数
给你一个整数 x ,如果 x 是一个回文整数,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
回文数是指正序(从左向右)和倒序(从右向左)读都是一样的整数。
- 例如,
121是回文,而123不是。
示例 1:
输入:x = 121 输出:true
示例 2:
输入:x = -121 输出:false 解释:从左向右读, 为 -121 。 从右向左读, 为 121- 。因此它不是一个回文数。
示例 3:
输入:x = 10 输出:false 解释:从右向左读, 为 01 。因此它不是一个回文数。
提示:
-2^31 <= x <= 2^31 - 1
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;bool isPalindrome(int num){if(num < 0){ return false;} int original = num;long long reversed = 0;while(num > 0) {reversed = reversed * 10 + num % 10;num /= 10;}return original == reversed;
}int main()
{int num;cin>>num;cout<<boolalpha<<isPalindrome(num)<<endl;return 0;
}10. 正则表达式匹配
给你一个字符串 s 和一个字符规律 p,请你来实现一个支持 '.' 和 '*' 的正则表达式匹配。
'.'匹配任意单个字符'*'匹配零个或多个前面的那一个元素
所谓匹配,是要涵盖 整个 字符串 s的,而不是部分字符串。
示例 1:
输入:s = "aa", p = "a" 输出:false 解释:"a" 无法匹配 "aa" 整个字符串。
示例 2:
输入:s = "aa", p = "a*" 输出:true 解释:因为 '*' 代表可以匹配零个或多个前面的那一个元素, 在这里前面的元素就是 'a'。因此,字符串 "aa" 可被视为 'a' 重复了一次。
示例 3:
输入:s = "ab", p = ".*" 输出:true 解释:".*" 表示可匹配零个或多个('*')任意字符('.')。
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 201 <= p.length <= 20s只包含从a-z的小写字母。p只包含从a-z的小写字母,以及字符.和*。- 保证每次出现字符
*时,前面都匹配到有效的字符
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {
public:bool isMatch(string s, string p) {int m = s.size();int n = p.size();vector<vector<bool>> dp(m + 1, vector<bool>(n + 1, false));dp[0][0] = true;/*使用两层循环遍历dp数组,其中i表示s的长度,j表示p的长度。在内层循环中,分情况讨论:如果p[j-1]为'',则dp[i][j]为dp[i][j-2](''匹配0次)或者(s的第i个字符和p的第j-1个字符匹配,并且dp[i-1][j]为true)。如果p[j-1]不为'*',则dp[i][j]为dp[i-1][j-1](s的第i个字符和p的第j个字符匹配)。*/for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++) {for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {if (p[j - 1] == '*') {dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 2] || (i > 0 && (s[i - 1] == p[j - 2] || p[j - 2] == '.') && dp[i - 1][j]);} else {dp[i][j] = i > 0 && dp[i - 1][j - 1] && (s[i - 1] == p[j - 1] || p[j - 1] == '.');}}}return dp[m][n];}
};int main() {string s, p;cin >> s >> p;Solution solution;cout << boolalpha << solution.isMatch(s, p);return 0;
}11. 盛最多的水
给定一个长度为 n 的整数数组 height 。有 n 条垂线,第 i 条线的两个端点是 (i, 0) 和 (i, height[i]) 。
找出其中的两条线,使得它们与 x 轴共同构成的容器可以容纳最多的水。
返回容器可以储存的最大水量。
说明:你不能倾斜容器。
示例 1:
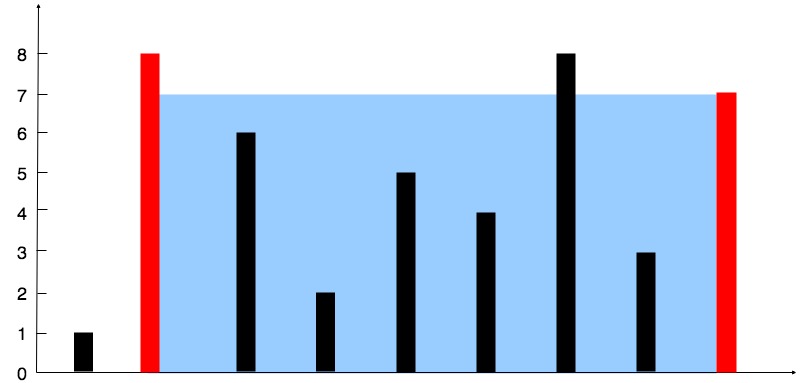
输入:[1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7] 输出:49 解释:图中垂直线代表输入数组 [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]。在此情况下,容器能够容纳水(表示为蓝色部分)的最大值为 49。
示例 2:
输入:height = [1,1] 输出:1
提示:
n == height.length2 <= n <= 10^50 <= height[i] <= 10^4
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:int maxArea(vector<int>& height) {int n = height.size();int left = 0;int right = n - 1;int result = 0;while(left < right) {result = max(result, (right - left) * min(height[left], height[right]));if(height[left] > height[right]) {--right;} else {++left;}}return result;}
}; int main() {Solution solution;vector<int> height;int tmp;while(cin >> tmp) {height.push_back(tmp);if(cin.get() == '\n')break;}cout << solution.maxArea(height);return 0;
}12. 整数转罗马数字
罗马数字包含以下七种字符: I, V, X, L,C,D 和 M。
字符 数值 I 1 V 5 X 10 L 50 C 100 D 500 M 1000
例如, 罗马数字 2 写做 II ,即为两个并列的 1。12 写做 XII ,即为 X + II 。 27 写做 XXVII, 即为 XX + V + II 。
通常情况下,罗马数字中小的数字在大的数字的右边。但也存在特例,例如 4 不写做 IIII,而是 IV。数字 1 在数字 5 的左边,所表示的数等于大数 5 减小数 1 得到的数值 4 。同样地,数字 9 表示为 IX。这个特殊的规则只适用于以下六种情况:
I可以放在V(5) 和X(10) 的左边,来表示 4 和 9。X可以放在L(50) 和C(100) 的左边,来表示 40 和 90。C可以放在D(500) 和M(1000) 的左边,来表示 400 和 900。
给你一个整数,将其转为罗马数字。
示例 1:
输入: num = 3 输出: "III"
示例 2:
输入: num = 4 输出: "IV"
示例 3:
输入: num = 9 输出: "IX"
示例 4:
输入: num = 58 输出: "LVIII" 解释: L = 50, V = 5, III = 3.
示例 5:
输入: num = 1994 输出: "MCMXCIV" 解释: M = 1000, CM = 900, XC = 90, IV = 4.
提示:
1 <= num <= 3999
解法一:
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:string intToRoman(int num) {vector<int> values = {1000, 900, 500, 400, 100, 90, 50, 40, 10, 9, 5, 4, 1};vector<string> symbols = {"M", "CM", "D", "CD", "C", "XC", "L", "XL", "X", "IX", "V", "IV", "I"};string result = "";for(int i = 0; i < values.size(); i++) {while(num >= values[i]) {num -= values[i];result += symbols[i];}}return result;}
};int main() {Solution solution;int num;cin >> num;cout << solution.intToRoman(num);return 0;
}解法二:
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:string intToRoman(int num) {map<int, string> romanMap;romanMap[1] = "I";romanMap[4] = "IV";romanMap[5] = "V";romanMap[9] = "IX";romanMap[10] = "X";romanMap[40] = "XL";romanMap[50] = "L";romanMap[90] = "XC";romanMap[100] = "C";romanMap[400] = "CD";romanMap[500] = "D";romanMap[900] = "CM";romanMap[1000] = "M";string result = "";for(auto it = romanMap.rbegin(); it != romanMap.rend(); ++it) {while(num >= it->first) {result += it->second;num -= it->first;}}return result;}
};int main() {Solution solution;int num;cin >> num;cout << solution.intToRoman(num);return 0;
}13. 罗马数字转整数
罗马数字包含以下七种字符: I, V, X, L,C,D 和 M。
字符 数值 I 1 V 5 X 10 L 50 C 100 D 500 M 1000
例如, 罗马数字 2 写做 II ,即为两个并列的 1 。12 写做 XII ,即为 X + II 。 27 写做 XXVII, 即为 XX + V + II 。
通常情况下,罗马数字中小的数字在大的数字的右边。但也存在特例,例如 4 不写做 IIII,而是 IV。数字 1 在数字 5 的左边,所表示的数等于大数 5 减小数 1 得到的数值 4 。同样地,数字 9 表示为 IX。这个特殊的规则只适用于以下六种情况:
I可以放在V(5) 和X(10) 的左边,来表示 4 和 9。X可以放在L(50) 和C(100) 的左边,来表示 40 和 90。C可以放在D(500) 和M(1000) 的左边,来表示 400 和 900。
给定一个罗马数字,将其转换成整数。
示例 1:
输入: s = "III" 输出: 3
示例 2:
输入: s = "IV" 输出: 4
示例 3:
输入: s = "IX" 输出: 9
示例 4:
输入: s = "LVIII" 输出: 58 解释: L = 50, V= 5, III = 3.
示例 5:
输入: s = "MCMXCIV" 输出: 1994 解释: M = 1000, CM = 900, XC = 90, IV = 4.
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 15s仅含字符('I', 'V', 'X', 'L', 'C', 'D', 'M')- 题目数据保证
s是一个有效的罗马数字,且表示整数在范围[1, 3999]内 - 题目所给测试用例皆符合罗马数字书写规则,不会出现跨位等情况。
- IL 和 IM 这样的例子并不符合题目要求,49 应该写作 XLIX,999 应该写作 CMXCIX 。
- 关于罗马数字的详尽书写规则,可以参考 罗马数字 - Mathematics 。
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
using namespace std;int romanToInt(string s){map<char, int> romanMap;romanMap['I'] = 1;romanMap['V'] = 5;romanMap['X'] = 10;romanMap['L'] = 50;romanMap['C'] = 100;romanMap['D'] = 500;romanMap['M'] = 1000;int result = 0;for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {if(i < s.length() - 1 && romanMap[s[i]] < romanMap[s[i + 1]]) {result -= romanMap[s[i]];} else {result += romanMap[s[i]];}}return result;
} int main(){string romanNum;cin>>romanNum;cout<<romanToInt(romanNum);return 0;
} 14. 最长公共前缀
编写一个函数来查找字符串数组中的最长公共前缀。
如果不存在公共前缀,返回空字符串 ""。
示例 1:
输入:strs = ["flower","flow","flight"] 输出:"fl"
示例 2:
输入:strs = ["dog","racecar","car"] 输出:"" 解释:输入不存在公共前缀。
提示:
1 <= strs.length <= 2000 <= strs[i].length <= 200strs[i]仅由小写英文字母组成
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;string longestCommonPrefix(vector<string>& strs) {if(strs.empty()) {return "";} string ans = strs[0];for(int i = 1; i < strs.size(); i++) {int j = 0;for(; j < ans.length() && j < strs[i].length(); j++) {if(ans[j] != strs[i][j])break;}ans = ans.substr(0, j);if(ans == "")return ans;} return ans;
}int main() {vector<string> strs;string tmp;while(cin>>tmp) {strs.push_back(tmp);if(cin.get() == '\n') break;}cout<<longestCommonPrefix(strs)<<endl;return 0;
} 15. 三数之和
给你一个整数数组 nums ,判断是否存在三元组 [nums[i], nums[j], nums[k]] 满足 i != j、i != k 且 j != k ,同时还满足 nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] == 0 。请
你返回所有和为 0 且不重复的三元组。
注意:答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [-1,0,1,2,-1,-4] 输出:[[-1,-1,2],[-1,0,1]] 解释: nums[0] + nums[1] + nums[2] = (-1) + 0 + 1 = 0 。 nums[1] + nums[2] + nums[4] = 0 + 1 + (-1) = 0 。 nums[0] + nums[3] + nums[4] = (-1) + 2 + (-1) = 0 。 不同的三元组是 [-1,0,1] 和 [-1,-1,2] 。 注意,输出的顺序和三元组的顺序并不重要。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0,1,1] 输出:[] 解释:唯一可能的三元组和不为 0 。
示例 3:
输入:nums = [0,0,0] 输出:[[0,0,0]] 解释:唯一可能的三元组和为 0 。
提示:
3 <= nums.length <= 3000-10^5 <= nums[i] <= 10^5
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:vector<vector<int> > threeSum(vector<int>& nums) {vector<vector<int> > result;sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {if(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) {continue; // 重复 }int target = -nums[i];int left = i + 1;int right = nums.size() - 1;while(left < right) {int sum = nums[left] + nums[right];if(sum < target) { // 小于0 left++;} else if(sum > target) { // 大于0 right--;} else { // 等于0 result.push_back({nums[i], nums[left], nums[right]});while(left < right && nums[left] == nums[left + 2]) {left++;}while(left < right &&nums[right] == nums[right - 1]) {right--;}left++;right--;}}}return result;}
};int main() {int tmp;vector<int> nums;while(cin >> tmp) {nums.push_back(tmp);if(cin.get() == '\n')break;}Solution solution;vector<vector<int>> result = solution.threeSum(nums);
// for(const auto& triplet : result) {
// cout << "[";
// for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
// cout << triplet[i];
// if(i < 2) {
// cout << ", ";
// }
// }
// cout << "] ";
// }cout << "[";for(vector<vector<int> >::iterator it = result.begin(); it != result.end(); ++it) {cout << "[";for(int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) {cout << (*it)[i];if(i < 2) {cout << ",";}}if(it == result.end() - 1) {cout << "]";} else {cout << "], ";}}cout << "]";return 0;
} 16. 最接近的三数之和
给你一个长度为 n 的整数数组 nums 和 一个目标值 target。请你从 nums 中选出三个整数,使它们的和与 target 最接近。
返回这三个数的和。
假定每组输入只存在恰好一个解。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [-1,2,1,-4], target = 1 输出:2 解释:与 target 最接近的和是 2 (-1 + 2 + 1 = 2) 。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0,0,0], target = 1 输出:0
提示:
3 <= nums.length <= 1000-1000 <= nums[i] <= 1000-10^4 <= target <= 10^4
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<climits>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:int threeSumClosest(vector<int>& nums, int target) {sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());int closestSum = INT_MAX;int minDiff = INT_MAX;for(int i = 0; i < nums.size() - 2; i++) {int left = i + 1;int right = nums.size() - 1;while(left < right) {int sum = nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right];int diff = abs(sum - target);if(diff < minDiff) { // 更新最小差值 minDiff = diff;closestSum = sum;}if(sum < target) {++left; // 偏小 } else if(sum > target) {--right; // 偏大 } else {return sum; // 相等 }}}return closestSum;}
};int main() {int target;vector<int> nums;while(cin >> target) {nums.push_back(target);if(cin.get() == '\n')break;}cin >> target;Solution solution;cout << solution.threeSumClosest(nums, target);return 0;
}17. 电话号码的字母组合
给定一个仅包含数字 2-9 的字符串,返回所有它能表示的字母组合。答案可以按 任意顺序 返回。
给出数字到字母的映射如下(与电话按键相同)。注意 1 不对应任何字母。

示例 1:
输入:digits = "23" 输出:["ad","ae","af","bd","be","bf","cd","ce","cf"]
示例 2:
输入:digits = "" 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:digits = "2" 输出:["a","b","c"]
提示:
0 <= digits.length <= 4digits[i]是范围['2', '9']的一个数字。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_map>using namespace std;class Solution {
public:vector<string> letterCombinations(string digits) {vector<string> result;if (digits.empty()) {return result;}unordered_map<char, string> digitToLetters = {{'2', "abc"},{'3', "def"},{'4', "ghi"},{'5', "jkl"},{'6', "mno"},{'7', "pqrs"},{'8', "tuv"},{'9', "wxyz"}};string current;backtrack(digits, 0, current, result, digitToLetters);return result;}void backtrack(string& digits, int index, string& current, vector<string>& result, unordered_map<char, string>& digitToLetters) {if (index == digits.length()) {result.push_back(current);return;}char digit = digits[index];string letters = digitToLetters[digit];for (char letter : letters) {current.push_back(letter);backtrack(digits, index + 1, current, result, digitToLetters);current.pop_back();}}
};int main() {string digits;cin >> digits;Solution solution;vector<string> result = solution.letterCombinations(digits);for (string& combination : result) {cout << combination << " ";}return 0;
}
18. 四数之和
给你一个由 n 个整数组成的数组 nums ,和一个目标值 target 。请你找出并返回满足下述全部条件且不重复的四元组 [nums[a], nums[b], nums[c], nums[d]] (若两个四元组元素一一对应,则认为两个四元组重复):
0 <= a, b, c, d < na、b、c和d互不相同nums[a] + nums[b] + nums[c] + nums[d] == target
你可以按 任意顺序 返回答案 。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,0,-1,0,-2,2], target = 0 输出:[[-2,-1,1,2],[-2,0,0,2],[-1,0,0,1]]
示例 2:
输入:nums = [2,2,2,2,2], target = 8 输出:[[2,2,2,2]]
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 200-10^9 <= nums[i] <= 10^9-10^9 <= target <= 10^9
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:vector<vector<int>> fourSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {vector<vector<int>> result;int n = nums.size();if(n < 4) {return result;}sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());for(int i = 0; i < n - 3; i++) {if(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) {continue;}for(int j = i + 1; j < n - 2; j++) {if(j > i + 1 && nums[j] == nums[j - 1]) {continue;}int left = j + 1;int right = n - 1;while(left < right) {long sum = static_cast<long>(nums[i]) + nums[j] + nums[left] + nums[right];if(sum < target) {++left;} else if(sum > target) {--right;} else {result.push_back({nums[i], nums[j], nums[left], nums[right]});while(left < right && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]) {++left;}while(left < right && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]) {--right;}++left;--right;}}}}return result;}
};int main() {int target;vector<int> nums;while(cin >> target) {nums.push_back(target);if(cin.get() == '\n')break;}cin >> target;Solution solution;vector<vector<int>> result = solution.fourSum(nums, target);for(vector<int>& quadruplet : result) {cout << "[";for(int num : quadruplet) {cout << num << " ";}cout << "] ";}return 0;}19. 删除链表的倒数第N个结点
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2 输出:[1,2,3,5]
示例 2:
输入:head = [1], n = 1 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:head = [1,2], n = 1 输出:[1]
提示:
- 链表中结点的数目为
sz 1 <= sz <= 300 <= Node.val <= 1001 <= n <= sz
进阶:你能尝试使用一趟扫描实现吗?
解题思路:要删除链表的倒数第n个结点,可以使用双指针技巧。首先定义两个指针,分别为快指针和慢指针,初始时均指向头节点。然后让快指针先向后移动n + 1步,这样快指针和慢指针之间就会相隔n个节点。接着同时移动快指针和慢指针,直到快指针指向链表末尾。此时慢指针指向的节点就是要删除的节点的前一个结点。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;// Definition for single-linked list
struct ListNode {int val;ListNode *next;ListNode() : val(0), next(NULL) {}ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};class Solution {public:ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0);dummy->next = head;ListNode* fast = dummy;ListNode* slow = dummy;// 向后移动n + 1步 for(int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) {fast = fast->next;}while(fast != NULL) {fast = fast->next;slow = slow->next;}// 删除结点 ListNode * q = slow->next;slow->next = slow->next->next;delete q;return dummy->next;}
};ListNode* createList() {ListNode* head = NULL;ListNode* current = NULL;int val;while(cin >> val) {ListNode* newNode = new ListNode(val);if(head == NULL) {head = newNode;current = newNode;} else {current->next = newNode;current = newNode;}if(cin.get() == '\n')break;}return head;
}void printList(ListNode* head) {ListNode* current = head;while(current != NULL) {cout << current->val << " ";current = current->next;}
}int main() {ListNode* head = createList();int n;cin >> n;Solution solution;ListNode* result = solution.removeNthFromEnd(head, n);printList(result);return 0;
}20. 有效的括号
给定一个只包括 '(',')','{','}','[',']' 的字符串 s ,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
- 左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
- 左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
- 每个右括号都有一个对应的相同类型的左括号。
示例 1:
输入:s = "()" 输出:true
示例 2:
输入:s = "()[]{}"
输出:true
示例 3:
输入:s = "(]" 输出:false
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 104s仅由括号'()[]{}'组成
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
#include<map>
using namespace std;bool isValid(string s) {stack<char> stk;map<char, char> brackets;brackets.insert(make_pair(')', '('));brackets.insert(make_pair('}', '{'));brackets.insert(make_pair(']', '['));for(string::iterator it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); ++it) {char c = *it;// 如果是右括号if(brackets.find(c) != brackets.end()) {// 栈为空或者栈顶元素与当前右括号不匹配,返回falseif(stk.empty() || stk.top() != brackets[c]) {return false;}stk.pop(); } else {stk.push(c); // 左括号 }}return stk.empty();
}int main() {string s;cin>>s;cout<<boolalpha<<isValid(s)<<endl;return 0;
}21. 合并两个有序链表
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例 1:
输入:l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4] 输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]
示例 2:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = [] 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = [0] 输出:[0]
提示:
- 两个链表的节点数目范围是
[0, 50] -100 <= Node.val <= 100l1和l2均按 非递减顺序 排列
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;struct ListNode {int val;ListNode *next;ListNode() : val(0), next(NULL) {}ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};class Solution {public:ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) { // 递归if(list1 == NULL) return list2;if(list2 == NULL)return list1;if(list1->val < list2->val) {list1->next = mergeTwoLists(list1->next, list2);return list1;}else {list2->next = mergeTwoLists(list1, list2->next);return list2;}}
};int main() {ListNode* list1 = NULL;ListNode* list2 = NULL;cout << "Enter elements for list1 (enter -1 to stop): ";int val;while (cin >> val && val != -1) {ListNode* node = new ListNode(val);if (list1 == NULL) {list1 = node;} else {ListNode* temp = list1;while (temp->next != NULL) {temp = temp->next;}temp->next = node;}}cout << "Enter elements for list2 (enter -1 to stop): ";while (cin >> val && val != -1) {ListNode* node = new ListNode(val);if (list2 == NULL) {list2 = node;} else {ListNode* temp = list2;while (temp->next != NULL) {temp = temp->next;}temp->next = node;}}Solution solution;ListNode* mergedList = solution.mergeTwoLists(list1, list2);// Print the merged listListNode* temp = mergedList;cout << "Merged list: ";while (temp != NULL) {cout << temp->val << " ";temp = temp->next;}cout << endl;return 0;
}
22. 括号生成
数字 n 代表生成括号的对数,请你设计一个函数,用于能够生成所有可能的并且 有效的 括号组合。
示例 1:
输入:n = 3 输出:["((()))","(()())","(())()","()(())","()()()"]
示例 2:
输入:n = 1 输出:["()"]
提示:
1 <= n <= 8
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:void helper(vector<string>& result, string current, int open, int close, int n) {if(current.size() == 2 * n) {result.push_back(current);return; // 递归结束 }if(open < n) {helper(result, current + "(", open + 1, close, n);}if(close < open) {helper(result, current + ")", open, close + 1, n);}}vector<string> generateParenthesis(int n) {vector<string> result;helper(result, "", 0, 0, n);return result;}
}; int main() {int n;cin >> n;Solution solution;vector<string> result = solution.generateParenthesis(n);cout << "[";for(auto it = result.begin(); it != result.end(); ++it) {if(it == result.end() - 1) {cout << *it;} else {cout << *it <<", ";}}cout << "]";return 0;
}23. 合并K个升序链表
给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。
请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
示例 1:
输入:lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]] 输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6] 解释:链表数组如下: [1->4->5,1->3->4,2->6 ] 将它们合并到一个有序链表中得到。 1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
示例 2:
输入:lists = [] 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:lists = [[]] 输出:[]
提示:
k == lists.length0 <= k <= 10^40 <= lists[i].length <= 500-10^4 <= lists[i][j] <= 10^4lists[i]按 升序 排列lists[i].length的总和不超过10^4
解题思路:要合并K个升序链表,可以使用优先队列(最小堆)来实现。首先将每个链表的头节点加入到优先队列中,然后不断从优先队列中取出最小的节点,将其加入到结果链表中,并将该节点的下一个节点加入到优先队列中。重复这个过程直到优先队列为空。
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;// Definition for singly-linked list
struct ListNode {int val;ListNode *next;ListNode() : val(0), next(NULL) {}ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};struct compare {bool operator()(ListNode* a, ListNode* b) {return a->val > b->val;}
};class Solution {public:ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {priority_queue<ListNode*, vector<ListNode*>, compare> pq;for(ListNode* list : lists) { // 添加各个链表的头节点 if(list) {pq.push(list);}}ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0);ListNode* tail = dummy;while(!pq.empty()) {ListNode* node = pq.top(); // 获取堆顶元素pq.pop();tail->next = node;tail = tail->next;if(node->next) {// 把堆顶元素所在链表的下一个节点入队 pq.push(node->next);} }return dummy->next; }
};ListNode* createList() {ListNode* head = NULL;ListNode* current = NULL;int val;while(cin >> val) {ListNode* newNode = new ListNode(val);if(head == NULL) {head = newNode;current = newNode;} else {current->next = newNode;current = newNode;}if(cin.get() == '\n')break;}return head;
}void printList(ListNode* head) {ListNode* current = head;while(current != NULL) {cout << current->val << " ";current = current->next;}
}int main() {vector<ListNode*> lists;int flag = 0;while(true) {cout << "请输入链表元素:";ListNode* head = createList();lists.push_back(head);cout << "是否需要继续创建链表数组:0(继续), 1(结束):"; cin >> flag;if(flag == 1) { // flag = 1时,结束创建链表数组 break;}}cout << "Merged List: ";Solution solution;ListNode* mergedList = solution.mergeKLists(lists);printList(mergedList);return 0;
}24. 两两交换链表中的节点
给你一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后链表的头节点。你必须在不修改节点内部的值的情况下完成本题(即,只能进行节点交换)。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4] 输出:[2,1,4,3]
示例 2:
输入:head = [] 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:head = [1] 输出:[1]
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目在范围
[0, 100]内 0 <= Node.val <= 100
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;// Definition for singly-linked list
struct ListNode {int val;ListNode *next;ListNode() : val(0), next(NULL) {}ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};class Solution {public:ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {if(!head || !head->next) {return head;}ListNode *dummy = new ListNode(0);dummy->next = head;ListNode *prev = dummy;while(prev->next && prev->next->next) {ListNode *first = prev->next;ListNode *second = prev->next->next;prev->next = second;first->next = second->next;second->next = first;prev = first;}return dummy->next;}
};ListNode* createList() {ListNode *head = NULL;ListNode *current = NULL;int val;while(cin >> val) {ListNode *newNode = new ListNode(val);if(head == NULL) {head = newNode;current = newNode;} else {current->next = newNode;current = current->next;}if(cin.get() == '\n') {break;}}return head;
}void printList(ListNode *head) {ListNode *current = head;while(current != NULL) {cout << current->val << " ";current = current->next;}
}int main() {Solution solution;ListNode *head = createList();ListNode *result = solution.swapPairs(head);printList(result);return 0;}25. K个一组翻转链表
给你链表的头节点 head ,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回修改后的链表。
k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。如果节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际进行节点交换。
示例 1:

输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2 输出:[2,1,4,3,5]
示例 2:
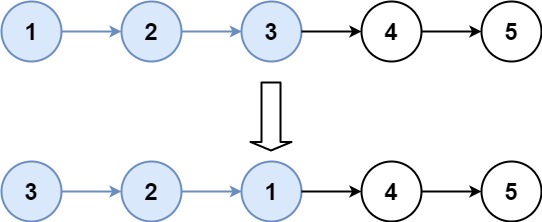
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 3 输出:[3,2,1,4,5]
提示:
- 链表中的节点数目为
n 1 <= k <= n <= 50000 <= Node.val <= 1000
进阶:你可以设计一个只用 O(1) 额外内存空间的算法解决此问题吗?
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;// Definition for singly-linked list
struct ListNode {int val;ListNode *next;ListNode() : val(0), next(NULL) {}ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
}; class Solution {public:ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {if(!head || k == 1) {return head;}ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0);dummy->next = head;ListNode* pre = dummy;int count = 0;ListNode* cur = head;while(cur) {count++;ListNode* nextNode = cur->next;if(count == k) {pre = reverse(pre, nextNode); // 翻转 count = 0;}cur = nextNode;}return dummy->next;}ListNode* reverse(ListNode* pre, ListNode* end) {if(!pre || !pre->next || !pre->next->next) {return pre->next;}ListNode* head = pre->next;ListNode* cur = head->next;while(cur != end) {head->next = cur->next;cur->next = pre->next;pre->next = cur;cur = head->next;}return head;}
};ListNode* createList() {ListNode *head = NULL;ListNode *current = NULL;int val;while(cin >> val) {ListNode *newNode = new ListNode(val);if(head == NULL) {head = newNode;current = newNode;} else {current->next = newNode;current = current->next;}if(cin.get() == '\n') {break;}}return head;
}void printList(ListNode *head) {ListNode *current = head;while(current != NULL) {cout << current->val << " ";current = current->next;}
}int main() {Solution solution;ListNode *head = createList();int k;cin >> k;ListNode *result = solution.reverseKGroup(head, k);printList(result);return 0;
}26. 删除有序数组中的重复项
给你一个 非严格递增排列 的数组 nums ,请你 原地 删除重复出现的元素,使每个元素 只出现一次 ,返回删除后数组的新长度。元素的 相对顺序 应该保持 一致 。然后返回 nums 中唯一元素的个数。
考虑 nums 的唯一元素的数量为 k ,你需要做以下事情确保你的题解可以被通过:
- 更改数组
nums,使nums的前k个元素包含唯一元素,并按照它们最初在nums中出现的顺序排列。nums的其余元素与nums的大小不重要。 - 返回
k。
判题标准:
系统会用下面的代码来测试你的题解:
int[] nums = [...]; // 输入数组
int[] expectedNums = [...]; // 长度正确的期望答案int k = removeDuplicates(nums); // 调用assert k == expectedNums.length;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {assert nums[i] == expectedNums[i];
}
如果所有断言都通过,那么您的题解将被 通过。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,1,2] 输出:2, nums = [1,2,_] 解释:函数应该返回新的长度 2,并且原数组 nums 的前两个元素被修改为 1, 2 。不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0,0,1,1,1,2,2,3,3,4] 输出:5, nums = [0,1,2,3,4] 解释:函数应该返回新的长度 5, 并且原数组 nums 的前五个元素被修改为 0, 1, 2, 3, 4。不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 3 * 10^4-10^4 <= nums[i] <= 10^4nums已按 非严格递增 排列
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:int removeDuplicates(vector<int>& nums) {int size = nums.size();int left = 0, right = 1;while(--size) {if(nums[left] == nums[right]) {right++;} else {nums[left + 1] = nums[right];right++;left++;}}return left + 1;}
};int main() {vector<int> nums;int temp;while(cin >> temp) {nums.push_back(temp);if(cin.get() == '\n')break;}Solution solution;cout<<solution.removeDuplicates(nums);return 0;
}解法2:使用STL中的unique函数进行优化。unique函数可以将重复的元素移动到数组的末尾,并返回指向不重复部分的尾后迭代器。我们可以利用这个特性来简化代码。只需要调用unique函数,并返回结果与数组起始位置之间的距离,即为不重复元素的个数。
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:int removeDuplicates(vector<int>& nums) {return distance(nums.begin(), unique(nums.begin(), nums.end()));}
};int main() {vector<int> nums;int temp;while(cin >> temp) {nums.push_back(temp);if(cin.get() == '\n')break;}Solution solution;cout<<solution.removeDuplicates(nums);return 0;
}解法3:在这个优化后的代码中,我们使用了两个指针left和right,其中left指针指向不重复部分的最后一个元素,right指针用于遍历数组。当遇到一个与left指针指向的元素不相同的元素时,将该元素移动到left指针的下一个位置,并将left指针后移一位。遍历完成后,left指针的位置加1即为不重复元素的个数。
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:int removeDuplicates(vector<int>& nums) {int n = nums.size();if(n < 2) {return n;}int left = 0;for(int right = 1; right < n; right++) {if(nums[left] != nums[right]) {left++;nums[left] = nums[right];}}return left + 1;}
};int main() {vector<int> nums;int temp;while(cin >> temp) {nums.push_back(temp);if(cin.get() == '\n')break;}Solution solution;cout<<solution.removeDuplicates(nums);return 0;
}27. 移除元素
给你一个数组 nums 和一个值 val,你需要 原地 移除所有数值等于 val 的元素,并返回移除后数组的新长度。
不要使用额外的数组空间,你必须仅使用 O(1) 额外空间并 原地 修改输入数组。
元素的顺序可以改变。你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
说明:
为什么返回数值是整数,但输出的答案是数组呢?
请注意,输入数组是以「引用」方式传递的,这意味着在函数里修改输入数组对于调用者是可见的。
你可以想象内部操作如下:
// nums 是以“引用”方式传递的。也就是说,不对实参作任何拷贝
int len = removeElement(nums, val);// 在函数里修改输入数组对于调用者是可见的。
// 根据你的函数返回的长度, 它会打印出数组中 该长度范围内 的所有元素。
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {print(nums[i]);
}
示例 1:
输入:nums = [3,2,2,3], val = 3 输出:2, nums = [2,2] 解释:函数应该返回新的长度 2, 并且 nums 中的前两个元素均为 2。你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。例如,函数返回的新长度为 2 ,而 nums = [2,2,3,3] 或 nums = [2,2,0,0],也会被视作正确答案。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0,1,2,2,3,0,4,2], val = 2 输出:5, nums = [0,1,3,0,4] 解释:函数应该返回新的长度 5, 并且 nums 中的前五个元素为 0, 1, 3, 0, 4。注意这五个元素可为任意顺序。你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
提示:
0 <= nums.length <= 1000 <= nums[i] <= 500 <= val <= 100
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:int removeElement(vector<int>& nums, int val) {int j = 0;for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {if(nums[i] != val) {nums[j++] = nums[i]; // 不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素}}return j;}
};int main() {int val;int temp;vector<int> nums;while(cin >> temp) {nums.push_back(temp);if(cin.get() == '\n') {break;}}cin>>val;Solution solution;int len = solution.removeElement(nums, val);cout << len;return 0;
} 28.找出字符串中第一个匹配项的下标
给你两个字符串 haystack 和 needle ,请你在 haystack 字符串中找出 needle 字符串的第一个匹配项的下标(下标从 0 开始)。如果 needle 不是 haystack 的一部分,则返回 -1 。
示例 1:
输入:haystack = "sadbutsad", needle = "sad" 输出:0 解释:"sad" 在下标 0 和 6 处匹配。 第一个匹配项的下标是 0 ,所以返回 0 。
示例 2:
输入:haystack = "leetcode", needle = "leeto" 输出:-1 解释:"leeto" 没有在 "leetcode" 中出现,所以返回 -1 。
提示:
1 <= haystack.length, needle.length <= 10^4haystack和needle仅由小写英文字符组成
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:int strStr(string haystack, string needle) {return haystack.find(needle);}
};int main() {string haystack, needle;cin >> haystack >> needle;Solution solution;cout<<solution.strStr(haystack, needle);return 0;
}注:在C++中,string类的find()函数用于在一个字符串中查找子字符串,并返回第一次出现的位置。find()函数有多种重载形式,常用的形式包括:
size_t find(const string& str, size_t pos = 0) const: 在当前字符串中从指定位置pos开始查找子字符串str,返回第一次出现的位置。如果未找到则返回string::npos。size_t find(const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const: 在当前字符串中从指定位置pos开始查找C风格字符串s,返回第一次出现的位置。如果未找到则返回string::npos。size_t find(char c, size_t pos = 0) const: 在当前字符串中从指定位置pos开始查找字符c,返回第一次出现的位置。如果未找到则返回string::npos。
示例用法:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main() {string str = "Hello, World!";// 查找子字符串size_t found = str.find("World");if (found != string::npos) {cout << "Found at position: " << found << endl;} else {cout << "Not found" << endl;}// 查找字符size_t foundChar = str.find(',');if (foundChar != string::npos) {cout << "Found character at position: " << foundChar << endl;} else {cout << "Character not found" << endl;}return 0;
}
29. 两数相除
给你两个整数,被除数 dividend 和除数 divisor。将两数相除,要求 不使用 乘法、除法和取余运算。
整数除法应该向零截断,也就是截去(truncate)其小数部分。例如,8.345 将被截断为 8 ,-2.7335 将被截断至 -2 。
返回被除数 dividend 除以除数 divisor 得到的 商 。
注意:假设我们的环境只能存储 32 位 有符号整数,其数值范围是 [−231, 231 − 1] 。本题中,如果商 严格大于 231 − 1 ,则返回 231 − 1 ;如果商 严格小于 -231 ,则返回 -231 。
示例 1:
输入: dividend = 10, divisor = 3 输出: 3 解释: 10/3 = 3.33333.. ,向零截断后得到 3 。
示例 2:
输入: dividend = 7, divisor = -3 输出: -2 解释: 7/-3 = -2.33333.. ,向零截断后得到 -2 。
提示:
-2^31 <= dividend, divisor <= 2^31 - 1divisor != 0
#include<iostream>
#include<climits>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:int divide(int dividend, int divisor) {if(dividend == INT_MIN && divisor == -1) {return INT_MAX;}long dvd = labs(dividend);long dvs = labs(divisor);int sign = (dividend > 0) ^ (divisor > 0) ? -1 : 1;long res = 0;while(dvd >= dvs) {long temp = dvs, m = 1;while(temp<<1 <= dvd) {temp <<= 1;m <<= 1; // 左移一位 }dvd = -= temp;res += m;}return sign * res;}
}; int main() {int dividend, divisor;cin >> dividend >> divisor;Solution solution;cout << solution.divide(dividend, divisor);return 0;
}30. 串联所有单词的子串
给定一个字符串 s 和一个字符串数组 words。 words 中所有字符串 长度相同。
s 中的 串联子串 是指一个包含 words 中所有字符串以任意顺序排列连接起来的子串。
- 例如,如果
words = ["ab","cd","ef"], 那么"abcdef","abefcd","cdabef","cdefab","efabcd", 和"efcdab"都是串联子串。"acdbef"不是串联子串,因为他不是任何words排列的连接。
返回所有串联子串在 s 中的开始索引。你可以以 任意顺序 返回答案。
示例 1:
输入:s = "barfoothefoobarman", words = ["foo","bar"] 输出:[0,9]解释:因为 words.length == 2 同时 words[i].length == 3,连接的子字符串的长度必须为 6。 子串 "barfoo" 开始位置是 0。它是 words 中以 ["bar","foo"] 顺序排列的连接。 子串 "foobar" 开始位置是 9。它是 words 中以 ["foo","bar"] 顺序排列的连接。 输出顺序无关紧要。返回 [9,0] 也是可以的。
示例 2:
输入:s = "wordgoodgoodgoodbestword", words = ["word","good","best","word"] 输出:[] 解释:因为 words.length == 4 并且 words[i].length == 4,所以串联子串的长度必须为 16。 s 中没有子串长度为 16 并且等于 words 的任何顺序排列的连接。 所以我们返回一个空数组。
示例 3:
输入:s = "barfoofoobarthefoobarman", words = ["bar","foo","the"] 输出:[6,9,12] 解释:因为 words.length == 3 并且 words[i].length == 3,所以串联子串的长度必须为 9。 子串 "foobarthe" 开始位置是 6。它是 words 中以 ["foo","bar","the"] 顺序排列的连接。 子串 "barthefoo" 开始位置是 9。它是 words 中以 ["bar","the","foo"] 顺序排列的连接。 子串 "thefoobar" 开始位置是 12。它是 words 中以 ["the","foo","bar"] 顺序排列的连接。
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 1041 <= words.length <= 50001 <= words[i].length <= 30words[i]和s由小写英文字母组成
解法一:超时版
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<unordered_map>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:vector<int> findSubstring(string s, vector<string>& words) {vector<int> result;if(s.empty() || words.empty()) {return result;}int wordLen = words[0].length();int wordCount = words.size();int totalLen = wordLen * wordCount;unordered_map<string, int> wordFreq;for(const string& word : words) {wordFreq[word]++;}for(int i = 0; i <= (int)s.length() - totalLen; ++i) {unordered_map<string, int> seen;int j = 0;for(; j < wordCount; ++j) {string word = s.substr(i + j * wordLen, wordLen);if(wordFreq.find(word) == wordFreq.end()) {break;}seen[word]++;if(seen[word] > wordFreq[word]) {break;}}if(j == wordCount) {result.push_back(i);}}return result;}
};int main() {string s;vector<string> words;string tmp;cin >> s;while(cin >> tmp) {words.push_back(tmp);if(cin.get() == '\n')break;} Solution solution;vector<int> result = solution.findSubstring(s, words);for(auto num : result) {cout << num << " ";}return 0;
}解法二:在每个可能的位置只遍历一次,使用滑动窗口来优化时间复杂度。
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<unordered_map>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:vector<int> findSubstring(string s, vector<string>& words) {vector<int> result;if(s.empty() || words.empty()) {return result;}int wordLen = words[0].length();int wordCount = words.size();int totalLen = wordLen * wordCount;unordered_map<string, int> wordFreq;for(const string& word : words) {wordFreq[word]++;}for(int i = 0; i < wordLen; i++) {int left = i, count = 0;unordered_map<string, int> seen;for(int j = i; j <= (int)s.length() - totalLen; j += wordLen) {string word = s.substr(j, wordLen);if(wordFreq.find(word) != wordFreq.end()) {seen[word]++;count++;while(seen[word] > wordFreq[word]) {string temp = s.substr(left, wordLen);seen[temp]--;count--;left += wordLen;}if(count == wordCount) {result.push_back(left);string temp = s.substr(left, wordLen);seen[temp]--;count--;left += wordLen;}} else {seen.clear();count = 0;left = j + wordLen;}}}return result;}
};int main() {string s;vector<string> words;string tmp;cin >> s;while(cin >> tmp) {words.push_back(tmp);if(cin.get() == '\n')break;} Solution solution;vector<int> result = solution.findSubstring(s, words);for(auto num : result) {cout << num << " ";}return 0;
}原题链接:题库 - 力扣 (LeetCode) 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
相关文章:

LeetCode刷题记(一):1~30题
1. 两数之和 给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出 和为目标值 target 的那 两个 整数,并返回它们的数组下标。 你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,数组中同一个元素在答案里不能重复出现。 你可以…...
芒果YOLOv5改进89:卷积SPConv篇,即插即用,去除特征图中的冗余,FLOPs 和参数急剧下降,提升小目标检测
芒果专栏 基于 SPConv 的改进结构,改进源码教程 | 详情如下🥇 👉1. SPConv 结构、👉2. CfSPConv 结构 💡本博客 改进源代码改进 适用于 YOLOv5 按步骤操作运行改进后的代码即可 即插即用 结构。博客 包括改进所需的 核心结构代码 文件 YOLOv5改进专栏完整目录链接:…...
Linux:详解TCP报头类型
文章目录 温习序号的意义序号和确认序号报文的类型 TCP报头类型详解ACK: 确认号是否有效SYN: 请求建立连接; 我们把携带SYN标识的称为同步报文段FIN: 通知对方, 本端要关闭了PSH: 提示接收端应用程序立刻从TCP缓冲区把数据读走RST: 对方要求重新建立连接; 我们把携带RST标识的称…...
【Leetcode】top 100 二分查找
35 搜索插入位置 给定一个排序数组和一个目标值,在数组中找到目标值,并返回其索引。如果目标值不存在于数组中,返回它将会被按顺序插入的位置。请必须使用时间复杂度为 O(log n) 的算法。 基础写法!!!牢记…...
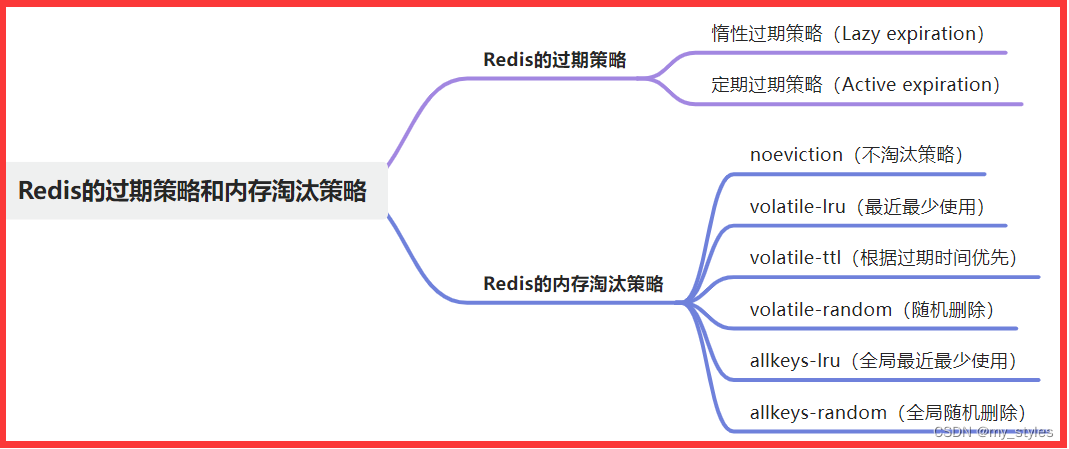
Redis高级面试题-2024
说说你对Redis的理解 Redis是一个基于Key-Value存储结构的开源内存数据库,也是一种NoSQL数据库。 它支持多种数据类型,包括String、Map、Set、ZSet和List,以满足不同应用场景的需求。 Redis以内存存储和优化的数据结构为基础,提…...

HarmonyOS 应用开发之FA模型与Stage模型应用组件
应用配置文件概述(FA模型) 每个应用项目必须在项目的代码目录下加入配置文件,这些配置文件会向编译工具、操作系统和应用市场提供描述应用的基本信息。 应用配置文件需申明以下内容: 应用的软件Bundle名称,应用的开发…...

6个黑科技网站,永久免费
1、http://mfsc123.com https://www.mfsc123.com 一个非常赞的免费商用素材导航网站。 收集了各种免费、免版权的图片、插画、视频、视频模板、音乐、音效、字体、图标网站。 再也不用担心版权问题,都能免费商用,自媒体作者必备。 而且还在每个网站…...

Linux 内核优化简笔 - 高并发的系统
简介 Linux 服务器在高并发场景下,默认的内核参数无法利用现有硬件,造成软件崩溃、卡顿、性能瓶颈。 当然,修改参数只是让Linux更好软件的去利用已有的硬件资源,如果硬件资源不够也无法解决问题的。而且当硬件资源不足的时候&am…...
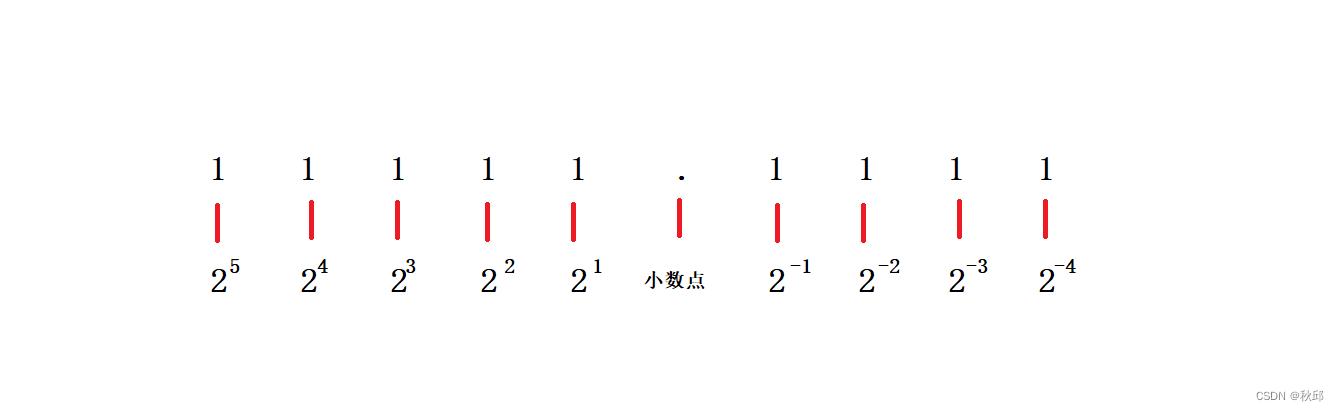
整型之韵,数之舞:大小端与浮点数的内存之旅
✨✨欢迎👍👍点赞☕️☕️收藏✍✍评论 个人主页:秋邱’博客 所属栏目:人工智能 (感谢您的光临,您的光临蓬荜生辉) 1.0 整形提升 我们先来看看代码。 int main() {char a 3;char b 127;char …...

变量作用域
变量作用域 标识符的作用域是定义为其声明在程序里的可应用范围, 或者即是我们所说的变量可见性。换句话说,就好像在问你自己,你可以在程序里的哪些部分去访问一个制定的标识符。变量可以是局部域或者全局域。 全局变量与局部变量 定义在函数内的变量有局部作用域,在一个…...
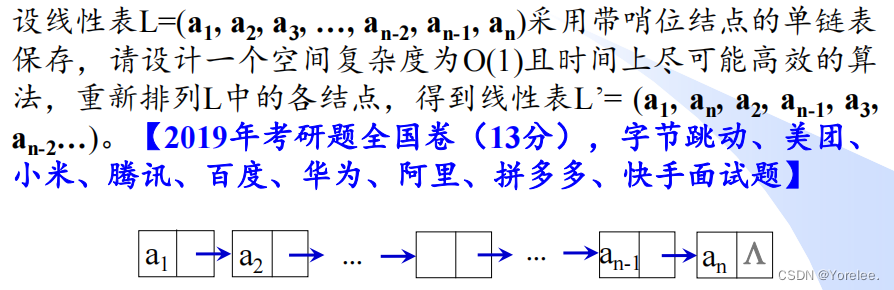
数据结构:链表的双指针技巧
文章目录 一、链表相交问题二、单链表判环问题三、回文链表四、重排链表结点 初学双指针的同学,请先弄懂删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点。 并且在学习这一节时,不要将思维固化,认为只能这样做,这里的做法只是技巧。 一、链表相交问题 …...

用WHERE命令可以在命令行搜索文件
文章目录 用WHERE命令可以在命令行搜索文件概述笔记没用的小程序END 用WHERE命令可以在命令行搜索文件 概述 想确认PATH变量中是否存在某个指定的程序(具体是在PATH环境变量中给出的哪个路径底下?). 开始不知道windows有where这个命令, 还自己花了2个小时写了一个小程序. 后…...

持续交付/持续部署流水线介绍(CD)
目录 一、概述 二、典型操作流程 2.1 CI/CD典型操作流 2.2 CI/CD操作流程说明 2.3 总结 三、基于GitHubDocker的持续交付/持续部署流水线(公有云) 3.1 基于GitHubDocker的持续交付/持续部署操作流程示意图 3.2 GitHubDocker持续交付/持续部署流水…...

第四百三十八回
文章目录 1. 概念介绍2. 思路与方法2.1 实现思路2.2 实现方法 3. 示例代码4. 内容总结 们在上一章回中介绍了"不同平台上换行的问题"相关的内容,本章回中将介绍如何在页面上显示蒙板层.闲话休提,让我们一起Talk Flutter吧。 1. 概念介绍 我们…...

Python学习:面相对象
面向对象 面向对象技术简介 类(Class): 用来描述具有相同的属性和方法的对象的集合。它定义了该集合中每个对象所共有的属性和方法。对象是类的实例。方法:类中定义的函数。类变量:类变量在整个实例化的对象中是公用的。类变量定义在类中且在函数体之外。类变量通常不作为实…...
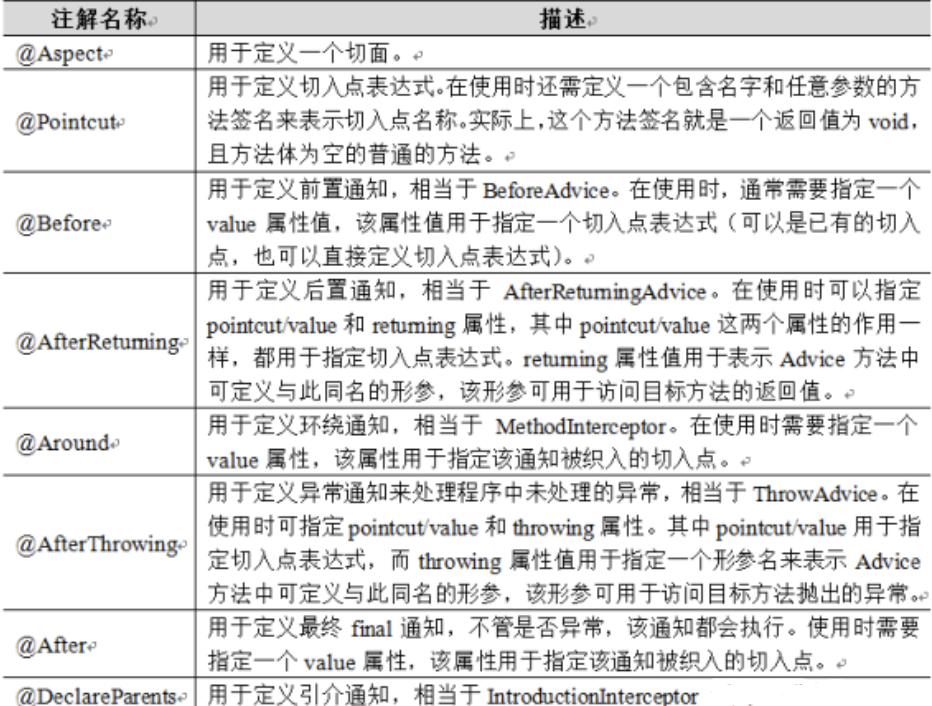
SSM学习——Spring AOP与AspectJ
Spring AOP与AspectJ 概念 AOP的全称为Aspect-Oriented Programming,即面向切面编程。 想象你是汉堡店的厨师,每一份汉堡都有好几层,这每一层都可以视作一个切面。现在有一位顾客想要品尝到不同风味肉馅的汉堡,如果按照传统的方…...

Android 使用LeakCanary检测内存泄漏,分析原因
内存泄漏是指无用对象(不再使用的对象)持续占有内存或无用对象的内存得不到及时释放,从而造成内存空间的浪费称为内存泄漏。 平时我们在使用app时,少量的内存泄漏我们是发现不了的,但是当内存泄漏达到一定数量时&…...
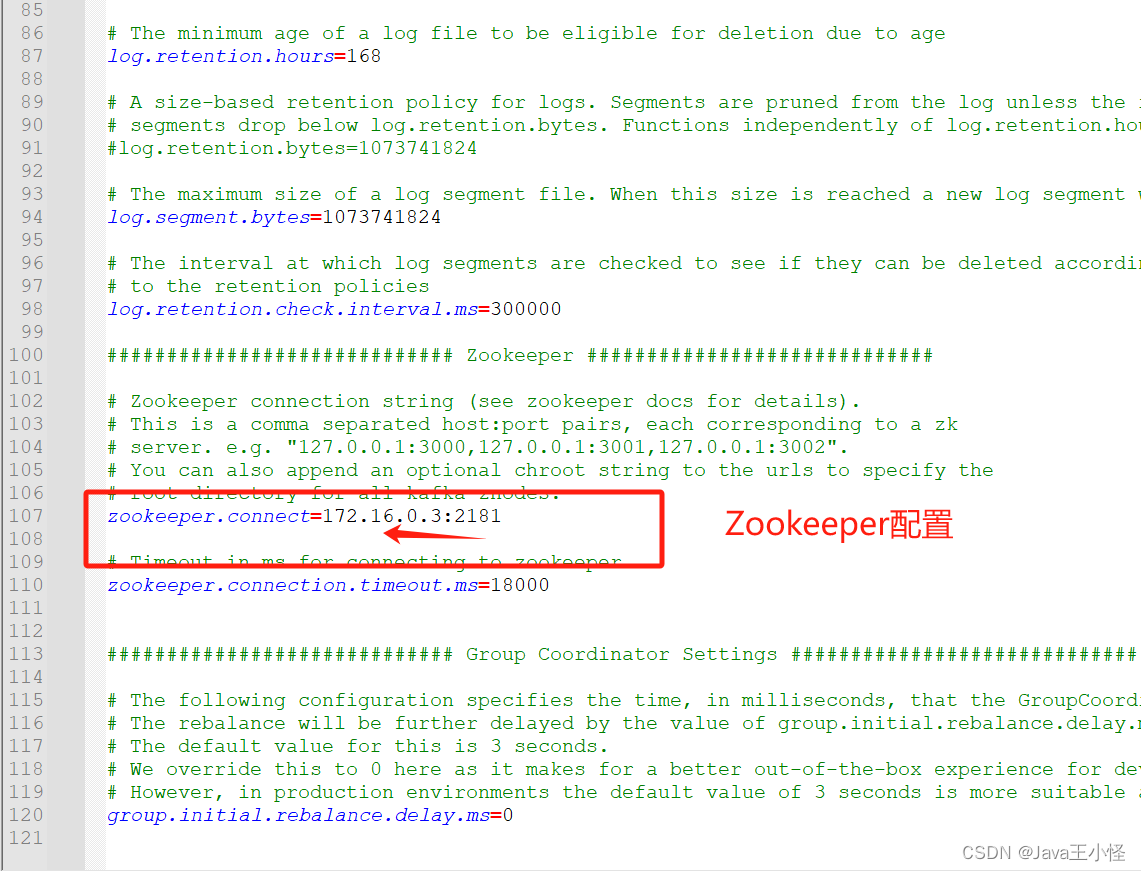
Linux部署Kafka2.8.1
安装Jdk 首先确保你的机器上安装了Jdk,Kafka需要Java运行环境,低版本的Kafka还需要Zookeeper,我此次要安装的Kafka版本为2.8.1,已经内置了一个Zookeeper环境,所以我们可以不部署Zookeeper直接使用。 1、解压Jdk包 t…...
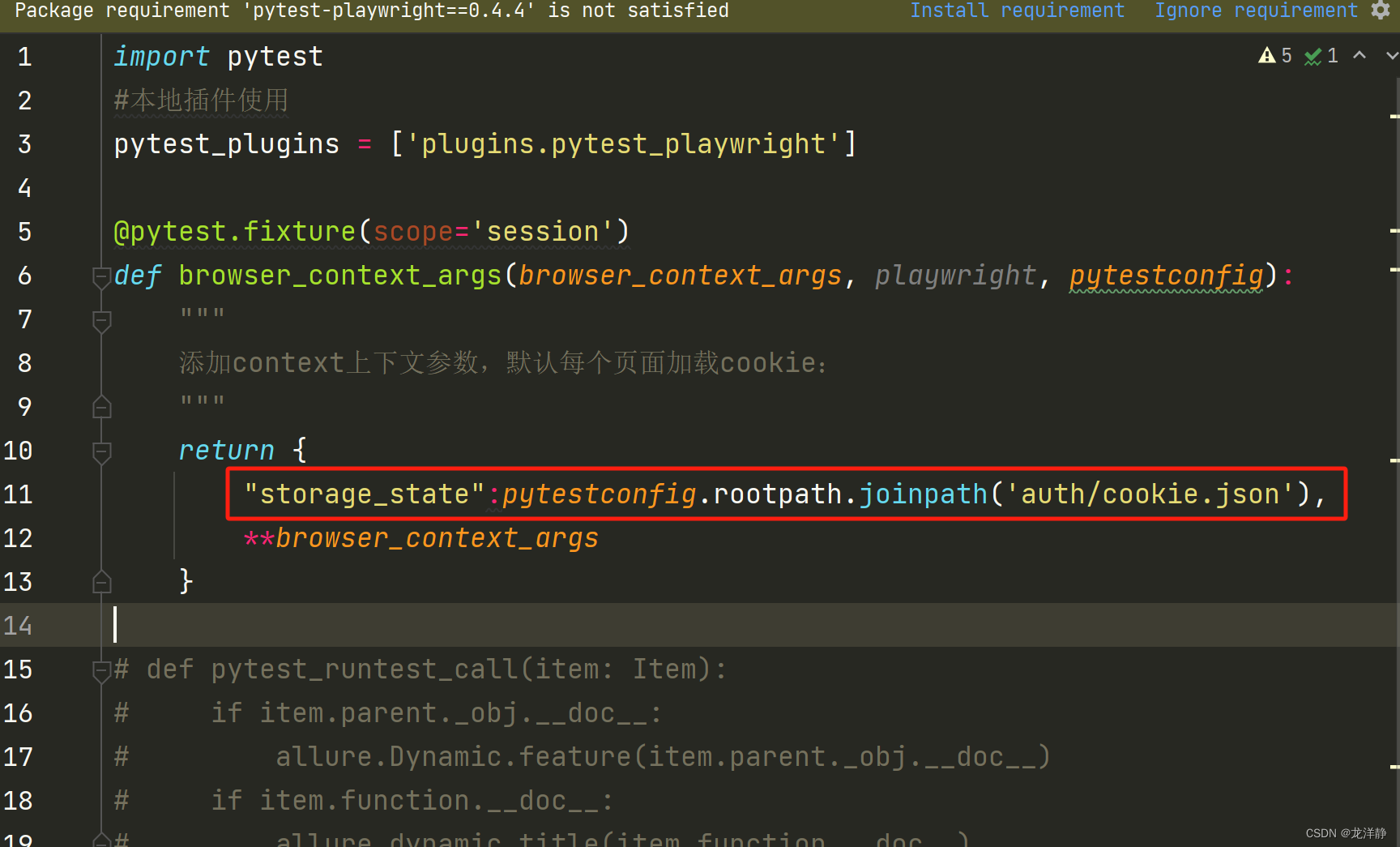
【pytest、playwright】allure报告生成视频和图片
目录 1、修改插件pytest_playwright 2、conftest.py配置 3、修改pytest.ini文件 4、运行case 5、注意事项 1、修改插件pytest_playwright pytest_playwright.py内容如下: # Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. # # Licensed under the Apache License, Ver…...
浅谈iOS开发中的自动引用计数ARC
1.ARC是什么 我们知道,在C语言中,创建对象时必须手动分配和释放适量的内存。然而,在 Swift 中,当不再需要类实例时,ARC 会自动释放这些实例的内存。 Swift 使用 ARC 来跟踪和管理应用程序的内存,其主要是由…...
)
rknn优化教程(二)
文章目录 1. 前述2. 三方库的封装2.1 xrepo中的库2.2 xrepo之外的库2.2.1 opencv2.2.2 rknnrt2.2.3 spdlog 3. rknn_engine库 1. 前述 OK,开始写第二篇的内容了。这篇博客主要能写一下: 如何给一些三方库按照xmake方式进行封装,供调用如何按…...
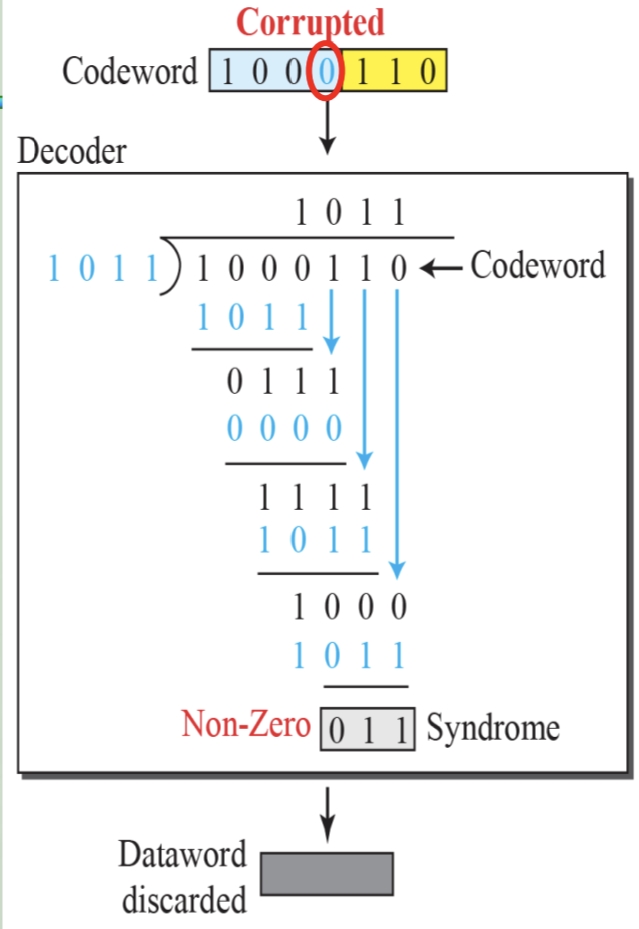
循环冗余码校验CRC码 算法步骤+详细实例计算
通信过程:(白话解释) 我们将原始待发送的消息称为 M M M,依据发送接收消息双方约定的生成多项式 G ( x ) G(x) G(x)(意思就是 G ( x ) G(x) G(x) 是已知的)࿰…...

Leetcode 3577. Count the Number of Computer Unlocking Permutations
Leetcode 3577. Count the Number of Computer Unlocking Permutations 1. 解题思路2. 代码实现 题目链接:3577. Count the Number of Computer Unlocking Permutations 1. 解题思路 这一题其实就是一个脑筋急转弯,要想要能够将所有的电脑解锁&#x…...

ETLCloud可能遇到的问题有哪些?常见坑位解析
数据集成平台ETLCloud,主要用于支持数据的抽取(Extract)、转换(Transform)和加载(Load)过程。提供了一个简洁直观的界面,以便用户可以在不同的数据源之间轻松地进行数据迁移和转换。…...
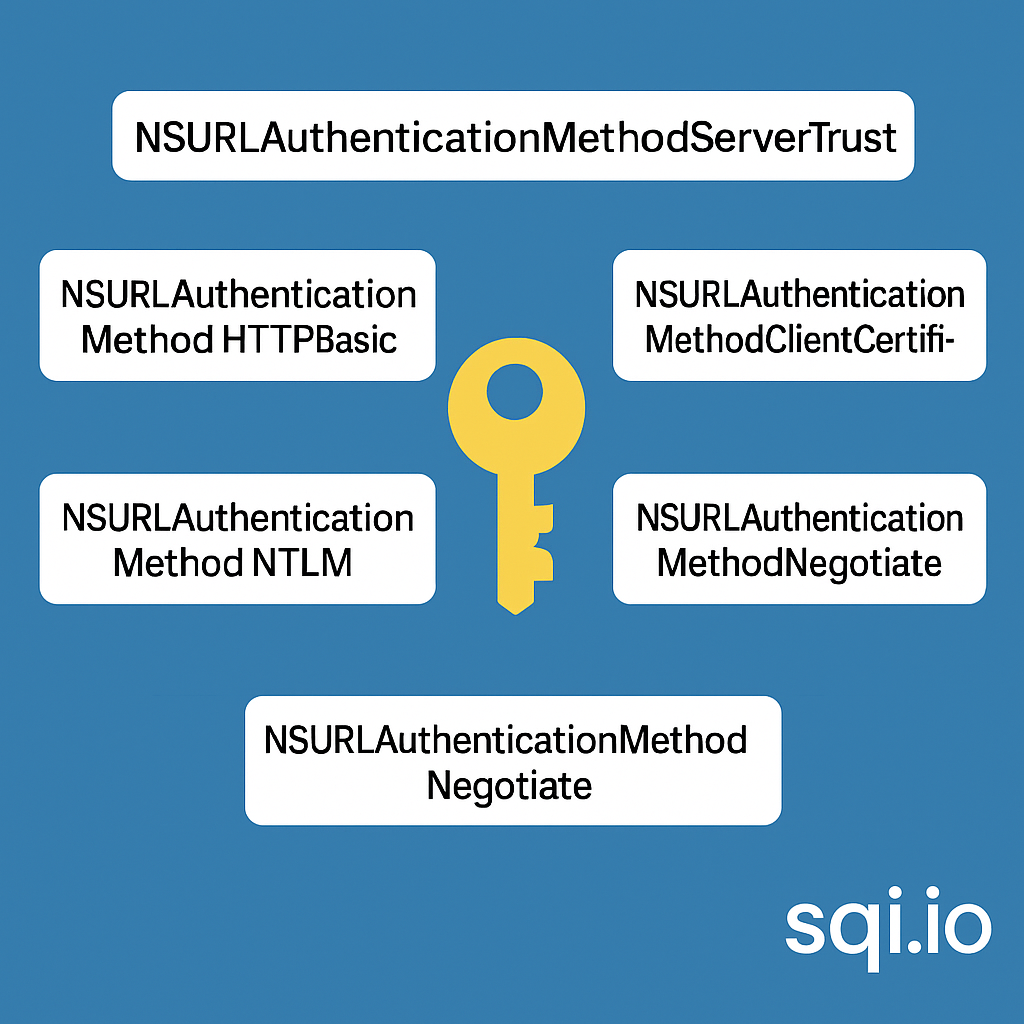
ServerTrust 并非唯一
NSURLAuthenticationMethodServerTrust 只是 authenticationMethod 的冰山一角 要理解 NSURLAuthenticationMethodServerTrust, 首先要明白它只是 authenticationMethod 的选项之一, 并非唯一 1 先厘清概念 点说明authenticationMethodURLAuthenticationChallenge.protectionS…...
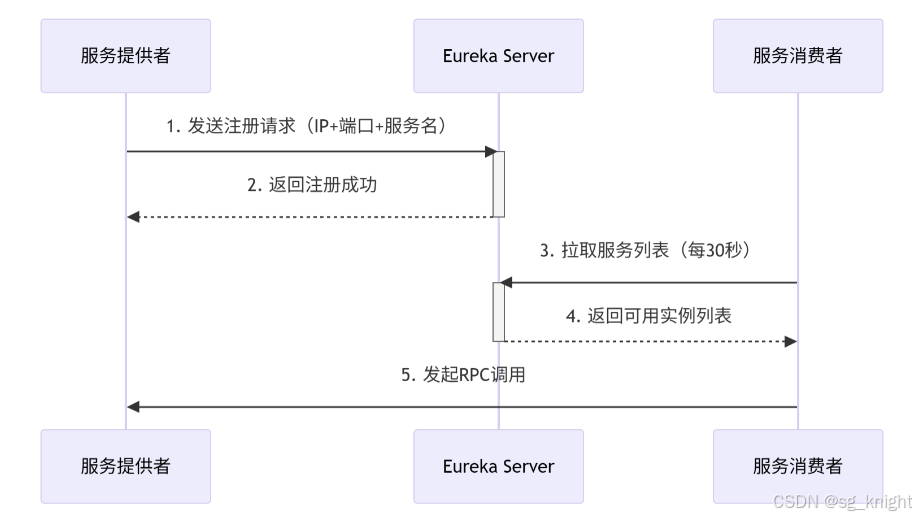
Springcloud:Eureka 高可用集群搭建实战(服务注册与发现的底层原理与避坑指南)
引言:为什么 Eureka 依然是存量系统的核心? 尽管 Nacos 等新注册中心崛起,但金融、电力等保守行业仍有大量系统运行在 Eureka 上。理解其高可用设计与自我保护机制,是保障分布式系统稳定的必修课。本文将手把手带你搭建生产级 Eur…...

linux 下常用变更-8
1、删除普通用户 查询用户初始UID和GIDls -l /home/ ###家目录中查看UID cat /etc/group ###此文件查看GID删除用户1.编辑文件 /etc/passwd 找到对应的行,YW343:x:0:0::/home/YW343:/bin/bash 2.将标红的位置修改为用户对应初始UID和GID: YW3…...

vue3 定时器-定义全局方法 vue+ts
1.创建ts文件 路径:src/utils/timer.ts 完整代码: import { onUnmounted } from vuetype TimerCallback (...args: any[]) > voidexport function useGlobalTimer() {const timers: Map<number, NodeJS.Timeout> new Map()// 创建定时器con…...
【Java_EE】Spring MVC
目录 Spring Web MVC 编辑注解 RestController RequestMapping RequestParam RequestParam RequestBody PathVariable RequestPart 参数传递 注意事项 编辑参数重命名 RequestParam 编辑编辑传递集合 RequestParam 传递JSON数据 编辑RequestBody …...

《C++ 模板》
目录 函数模板 类模板 非类型模板参数 模板特化 函数模板特化 类模板的特化 模板,就像一个模具,里面可以将不同类型的材料做成一个形状,其分为函数模板和类模板。 函数模板 函数模板可以简化函数重载的代码。格式:templa…...
