3.类与对象(中篇)介绍了类的6个默认构造函数,列举了相关案例,实现了一个日期类
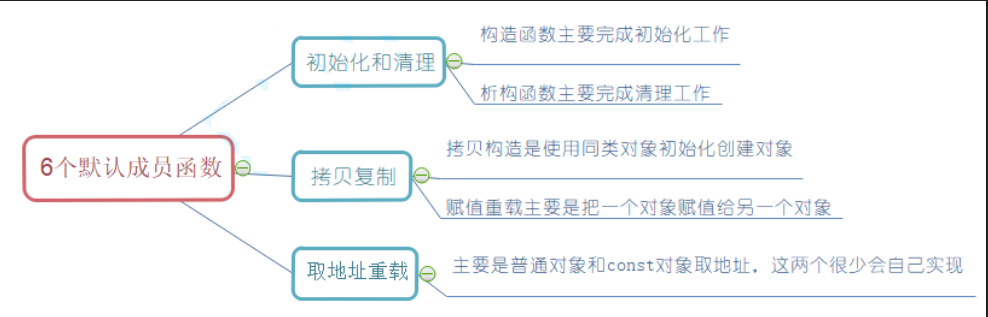
1.类的6个默认成员函数
-
如果一个类中什么成员都没有,简称为空类。
-
空类中真的什么都没有吗?并不是,任何类在什么都不写时,编译器会自动生成以下6个默认成员函数。
-
默认成员函数:用户没有显式实现,编译器会生成的成员函数称为默认成员函数。
默认成员函数是一种特殊成员函数:
1**.我们不写,编译器会自己生成一个;我们写了,编译器就不会生成。(例如构造函数,析构函数)**
2.隐含意思:对于有些类,需要我们自己写;对于另一些类,编译器默认生成就可以用。
class Date {};
2. 构造函数
2.1 概念
对于下面的Date类:
class Date
{
public:/*void Init(int year, int month, int day) // 普通的初始化函数{_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}*/// 初始化(构造函数)// 1.带参构造函数// 可以使用缺省;使用缺省参数就可以不用传参Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1) {_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}/*// 构造函数可以重载,但是对于这两个构造函数,如果不传参数,会造成二义性(因为两个构造函数,都可以不用进行传参,但是语法上这么写是正确的,但是函数调用时,会有二义性)// 2.无参构造函数Date() {_year = 1;_month = 1;_day = 1;}*/void Print(){cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;}private:int _year; // 年int _month; // 月int _day; // 日
};int main()
{Date d1(2022, 9, 21); // 给构造函数传参,在创建的对象后写需要传递的参数Date d2(2022, 9, 21);Date d3; // 不传参的形式// 无参的不要像下面这样写// Date d4();// Date func(); // 编译器无法判断func()是函数还是对象d1.Print();d2.Print();d3.Print();return 0;
}
-
对于
Date类,可以通过Init公有方法给对象设置日期,但如果每次创建对象时都调用该方法设置信息,未免有点麻烦,那能否在对象创建时,就将信息设置进去呢? -
构造函数是一个特殊的成员函数,名字与类名相同,创建类类型对象时由编译器自动调用,以保证每个数据成员都有 一个合适的初始值,并且在对象整个生命周期内只调用一次。
2.2 特性
构造函数是特殊的成员函数,需要注意的是,构造函数虽然名称叫构造,但是构造函数的主要任务并不是开空间创建对象,而是初始化对象。
其特征如下:
-
函数名与类名相同。
-
无返回值。
-
对象实例化时编译器自动调用对应的构造函数。
-
构造函数可以重载。
class Date
{
public:// 1.无参构造函数Date(){}// 2.带参构造函数Date(int year, int month, int day){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};void TestDate()
{// 调用无参构造函数Date d1; // 调用带参的构造函数Date d2(2015, 1, 1); // 注意:如果通过无参构造函数创建对象时,对象后面不用跟括号,否则就成了函数声明// 以下代码的函数:声明了d3函数(并不是d3对象),该函数无参,返回一个日期类型的对象// warning C4930: “Date d3(void)”: 未调用原型函数(是否是有意用变量定义的?)Date d3(); // 错误演示
}int main()
{TestDate();return 0;
}
// case1:class Stack
{
public:// 构造函数Stack(int capacity = 4) {_a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*capacity);if (_a == nullptr){perror("malloc fail");exit(-1);}_top = 0;_capacity = capacity;}~Stack() // 析构函数{free(_a);_a = nullptr;_top = _capacity = 0;}void Push(int x){// ....// 扩容_a[_top++] = x;}private:int* _a;int _top;int _capacity;
};int main()
{// 有了构造函数和析构函数,我们不在需要主动对创建的对象进行初始化; 而对象在销毁时会自动调用析构函数,完成对象中资源的清理工作(和Destory的功能类似)。Stack st; st.Push(1);st.Push(2);st.Push(3);return 0;
}
- 如果类中没有显式定义构造函数,则C++编译器会自动生成一个无参的默认构造函数,一旦用户显式定义编译器将不再生成。
class Date
{
public:/*// 如果用户显式定义了构造函数,编译器将不再生成Date(int year, int month, int day){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}*/void Print(){cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;}private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};int main()
{// 将Date类中我们自己定义的构造函数屏蔽后,代码可以通过编译,因为编译器生成了一个无参的默认构造函数// 将Date类中我们自己定义构造函数放开(则不会生成默认构造函数),代码编译失败(由于自己写的构造函数需要传参,但Date d1并没有传参,因此匹配不到合适的构造函数),因为一旦显式定义任何构造函数,编译器将不再生成// 无参构造函数,放开后报错:error C2512: “Date”: 没有合适的默认构造函数可用Date d1;return 0;
}
-
关于编译器生成的默认成员函数,很多人会有疑惑:不实现构造函数的情况下,编译器会生成默认的构造函数。但是看起来默认构造函数又没什么用?d对象调用了编译器生成的默认构造函数,但是d对象
year/_month/_day,依旧是随机值。也就说在这里编译器生成的默认构造函数并没有什么用??解答:C++把类型分成内置类型(基本类型)和自定义类型。内置类型就是语言提供的数据类型,如:
int/char...,自定义类型就是我们使用class/struct/union等自己定义的类型,看看下面的程序,就会发现编译器生成默认的构造函数会对自定类型成员_t调用的它的默认构造函数。
// case1:编译器生成默认的构造函数会对自定类型成员 _t 调用的它的默认构造函数class Time
{
public:// 内置类型,需要自己定义构造函数Time(){cout << "Time()" << endl;_hour = 0;_minute = 0;_second = 0;}// 内置类型 (默认构造函数对其不进行处理,因此需要我们自己来写构造函数)
private:int _hour;int _minute;int _second;
};class Date
{
private:// 基本类型(内置类型)int _year;int _month;int _day;// 自定义类型(类名为Time的自定义类型,不需要我们来写构造函数,编译器会直接调用默认构造函数)// 但是内置类型又无法处理// 因此,需要用到初始化列表 ==> 类和对象下篇再解释初始化列表Time _t;
};int main()
{Date d;return 0;
}
// case2:编译器生成默认的构造函数会对自定类型成员_pushST,_popST调用的它的默认构造函数class Stack
{
public:// 自己创建的默认构造函数Stack(int capacity = 4) {cout << "Stack(int capacity = 4)" << endl;_a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*capacity);if (_a == nullptr){perror("malloc fail");exit(-1);}_top = 0;_capacity = capacity;}~Stack() // 自己创建的析构函数{cout << "~Stack()" << endl;free(_a);_a = nullptr;_top = _capacity = 0;}void Push(int x){// ....// 扩容_a[_top++] = x;}private:int* _a;int _top;int _capacity;
};class MyQueue
{
public:void push(int x){_pushST.Push(x);}Stack _pushST;Stack _popST;//size_t _size; 如果myQueue还存在一个内置类型,又该怎么办呢?
};// 面向需求:编译器默认生成就可以满足,就不用自己写,不满足就需要自己写// Stack的构造函数需要自己写// MyQueue构造函数就不需要自己写,默认生成就可以用// Stack的析构函数,需要我们自己写// MyQueue 就不需要自己写析构函数,默认生成就可以用int main()
{MyQueue mq;mq.push(1);mq.push(2);return 0;
}
注意:C++11 中针对内置类型成员不初始化的缺陷,又打了补丁,即:内置类型成员变量在类中声明时可以给默认值。
class Time
{
public:Time(){cout << "Time()" << endl;_hour = 0;_minute = 0;_second = 0;}private:int _hour;int _minute;int _second;
};class Date
{
private:// 基本类型(内置类型) //此处,为内置类型:内置类型成员变量在类中声明时可以给默认值(则默认构造函数,可以不用考虑内置类型)int _year = 1970;int _month = 1;int _day = 1;// 自定义类型 (内置类型已经给了缺省值,因此,默认构造函数不用考虑内置类型)Time _t;
};int main()
{Date d;return 0;
}再例如:
class Stack
{
public:/*// 如果构造函数的参数不是全缺省值,则不是默认构造函数,编译器会报错// 在class MyQueue中,会调用Stack初始化Stack _pushST;Stack _popST, 但是Stack的构造函数不是全缺省值,所以会报错Stack(int capacity) {cout << "Stack(int capacity = 4)" << endl;_a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*capacity);if (_a == nullptr){perror("malloc fail");exit(-1);}_top = 0;_capacity = capacity;}*/// 析构函数~Stack(){cout << "~Stack()" << endl;free(_a);_a = nullptr;_top = _capacity = 0;}// 再声明内置类型时,给到缺省值,则相当于默认构造
private:int* _a = nullptr;int _top = 0;int _capacity = 0;/*// 只有创建对象之后,才会调用默认构造函数,才会malloc空间// 下面这种方法无法检测malloc是否成功开辟空间int* _a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*4); int _top = 0;int _capacity = 4;*/
};// 用两个栈来实现一个队列
class MyQueue {
public:/*// 初始化列表 -- 类和对象下篇再讲MyQueue(size_t capacity = 8):_popST(8), _pushST(8), _size(0){_size = 0;}*/void push(int x){//_pushST.Push(x);}private:// 调用Stack的默认构造函数来初始化Stack _pushST;Stack _popST;// 下面这种在定义时给缺省值的方式,不建议(建议使用初始化列表,后续讲解)// 这里不是初始化,给的缺省值,但并不会开辟空间(则默认构造函数不用考虑这个内置类型,默认构造函数就会使用其进行初始化)size_t _size = 0;
}; int main()
{MyQueue q;return 0;
}
7.无参的构造函数和全缺省的构造函数都称为默认构造函数,并且默认构造函数只能有一个。
注意:无参构造函数、全缺省构造函数、我们没写编译器默认生成的构造函数,都可以认为是默认构造函数。(也就是不需要传参数,就可以调用的构造函数,就叫默认构造函数)
class Date
{
public:// 无参构造函数(可以将其看做是默认构造函数)Date() {_year = 1900;_month = 1;_day = 1;}// 全缺省构造函数(可以将其看做是默认构造函数)Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1) {_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};// 以下测试函数能通过编译吗?
void Test()
{Date d1;
}// 答:不能够通过测试,因为无参构造函数和全缺省构造函数都可以接收参数,因此,由于d1对象,没有传参,导致二义性(也就是没有默认构造函数)
3.析构函数
3.1 概念
通过前面构造函数的学习,我们知道一个对象是怎么来的,那一个对象又是怎么没呢的?
- 析构函数:与构造函数功能相反,析构函数不是完成对对象本身的销毁,局部对象销毁工作是由编译器完成的。而对象在销毁时会自动调用析构函数,完成对象中资源的清理工作。
3.2 特性
-
析构函数名是在类名前加上字符 ~。
-
无参数无返回值类型。
-
一个类只能有一个析构函数。若未显式定义,系统会自动生成默认的析构函数。注意:析构函数不能重载
-
对象生命周期结束时,C++编译系统系统自动调用析构函数。
typedef int DataType;
class Stack
{
public:// 自己写的默认构造函数(全缺省)Stack(size_t capacity = 3) {_array = (DataType*)malloc(sizeof(DataType) * capacity);if (NULL == _array){perror("malloc申请空间失败!!!");return;}_capacity = capacity;_size = 0;}void Push(DataType data){// CheckCapacity();_array[_size] = data;_size++;}// 其他方法...// 自己写的析构函数~Stack() {if (_array){free(_array);_array = NULL;_capacity = 0;_size = 0;}}// 内置类型(默认析构函数对其不进行处理,因此需要我们自己来写析构函数)// 内置类型(默认构造函数对其不进行处理,因此需要我们自己来写构造函数)
private:DataType* _array;int _capacity;int _size;
};void TestStack()
{Stack s;s.Push(1);s.Push(2);}int main()
{TestStack();return 0;
}
5.关于编译器自动生成的析构函数,是否会完成一些事情呢?下面的程序我们会看到,编译器生成的默认析构函数,对自定类型成员调用它的析构函数。
#include<iostream>
#include <assert.h>
using namespace std;// 栈的类
class Stack
{
public:// 默认构造函数Stack(int capacity = 4){cout << "Stack(int capacity = 4)" << endl;_a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*capacity);if (_a == nullptr){perror("malloc fail");exit(-1);}_top = 0;_capacity = capacity;}~Stack(){cout << "~Stack()" << endl;free(_a);_a = nullptr;_top = _capacity = 0;}// 内置类型
private:int* _a;int _top;int _capacity;
};// 队列的类
class MyQueue
{
public:void push(int x){//_pushST.Push(x);}// 自定义类型
private:Stack _pushST;Stack _popST;
};// 面向需求:编译器默认生成就可以满足,就不用自己写,不满足就需要自己写// 用两个栈来实现一个队列
// Stack的构造函数需要自己写 (都是内置类型)
// MyQueue构造函数就不需要自己写,默认生成就可以用(都是自定义类型)// Stack的析构函数,需要我们自己写 (都是内置类型)
// MyQueue 就不需要自己写析构函数,默认生成就可以用 都是自定义类型)int main()
{Date d1;MyQueue q;return 0;
}
两个栈实现一个队列
实现上述oj题,深刻体会编译器生成析构函数的作用。
- 如果类中没有申请资源时,析构函数可以不写,直接使用编译器生成的默认析构函数,比如Date类;有资源申请时,一定要写,否则会造成资源泄漏,比如Stack类。
4. 拷贝构造函数
4.1 概念
在现实生活中,可能存在一个与你一样的自己,我们称其为双胞胎

那在创建对象时,可否创建一个与已存在对象一某一样的新对象呢?
拷贝构造函数:只有单个形参,该形参是对本类类型对象的引用(一般常用const修饰),在用已存在的类类型对象创建新对象时由编译器自动调用。
4.2 特性
拷贝构造函数也是特殊的成员函数,其特征如下:
-
拷贝构造函数是构造函数的一个重载形式。
-
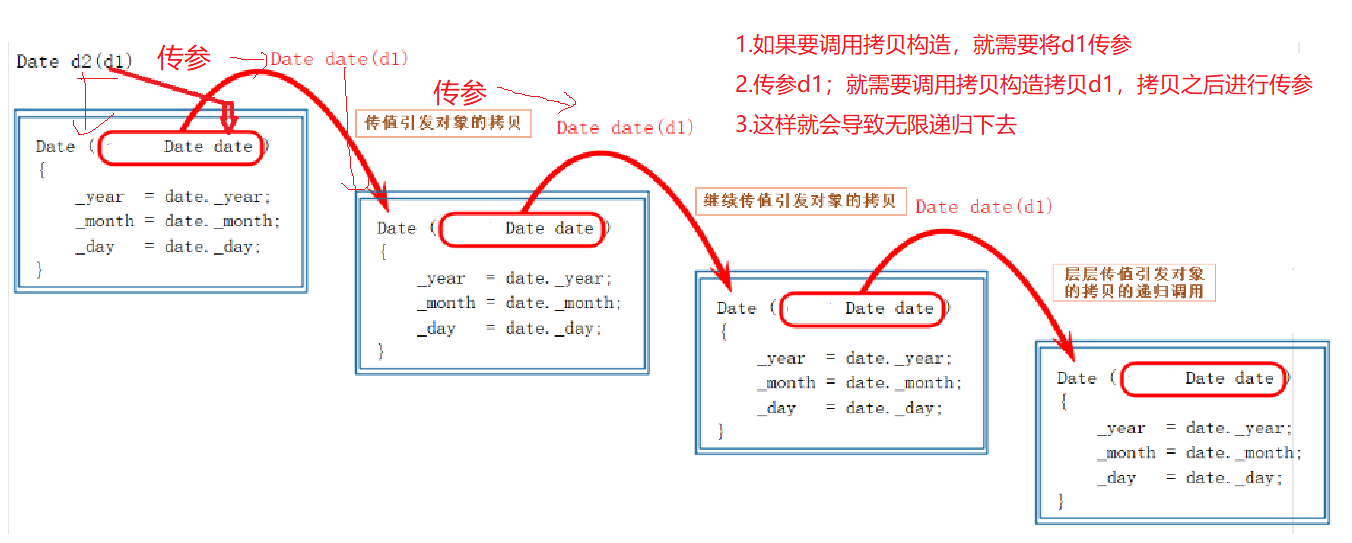
拷贝构造函数的参数只有一个且必须是类类型对象的引用,使用传值方式编译器直接报错,因为这会引发无穷递归调用。
#include<iostream>using namespace std;class Date
{
public:// 自己写的默认构造函数Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}// 拷贝构造函数Date(const Date& d) {cout << "Date 拷贝构造" << endl;_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;// 形参加const,防止写反了,下面问题就可以检查出来(因为d被const修饰,所以d是无法被修改的)//d._day = _day;}private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};void Func1(Date d)
{cout << "Func1()" << endl;
}void Func2(Date& d)
{cout << "Func2()" << endl;
}int main()
{// 构造 - 初始化Date d1(2022, 9, 22); // 为传值传参,因此传参,需要先调用拷贝函数拷贝d1,再将拷贝的值传参给void Func1(Date d)Func1(d1); // 为引用,因此不需要调用拷贝函数Func2(d1); // 拷贝一份d1// 拷贝构造 -- 拷贝初始化// Date d2(d1); return 0;
}// 打印结果
// Date 拷贝构造
// Func1()
// Func2()
思考:为什么调用func1时,会先调用拷贝函数?
答:由下图可知,将d1传参,需要先调用拷贝函数 拷贝d1,再将其传参给Func1(Date d),而Date& d,不需要拷贝传参,d为d1的别名,不需要拷贝d1,也就不需要调用拷贝函数
- 若未显式定义,编译器会生成默认的拷贝构造函数。 默认的拷贝构造函数对象按内存存储按字节序完成拷贝,这种拷贝叫做浅拷贝,或者值拷贝。
class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}// 我们不写拷贝函数,则编译器会默认生成拷贝函数 private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};int main()
{// 构造 - 初始化Date d1(2022, 9, 22); // 拷贝一份d1// 拷贝构造 -- 拷贝初始化Date d2(d1); return 0;
}
注意:在编译器生成的默认拷贝构造函数中,内置类型是按照字节方式直接拷贝的,而自定义类型是调用其拷贝构造函数完成拷贝的。
4.编译器生成的默认拷贝构造函数已经可以完成字节序的值拷贝了,还需要自己显式实现吗?当然像日期类这样的类是没必要的。那么下面的类呢?验证一下试试?
class Stack
{
public:// 默认构造函数Stack(int capacity = 4) {cout << "Stack(int capacity = 4)" << endl;_a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*capacity);if (_a == nullptr){perror("malloc fail");exit(-1);}_top = 0;_capacity = capacity;}/*// 我们不写拷贝函数,则默认生成拷贝函数//默认生成的函数,就是类似于这样的实现Stack(const Stack& st) {_a = st._a;_top = st._top;_capacity = st._capacity;}*/// 析构函数~Stack() {cout << "~Stack()" << endl;free(_a);_a = nullptr;_top = _capacity = 0;}void Push(int x){// ....// 扩容_a[_top++] = x;}private:int* _a;int _top;int _capacity;
};int main()
{ Stack st1;st1.Push(1);st1.Push(2);//浅拷贝,st1和st2在堆上会共用一块空间;两个对象,因此会调用两次析构函数,所以会报错Stack st2(st1); return 0;
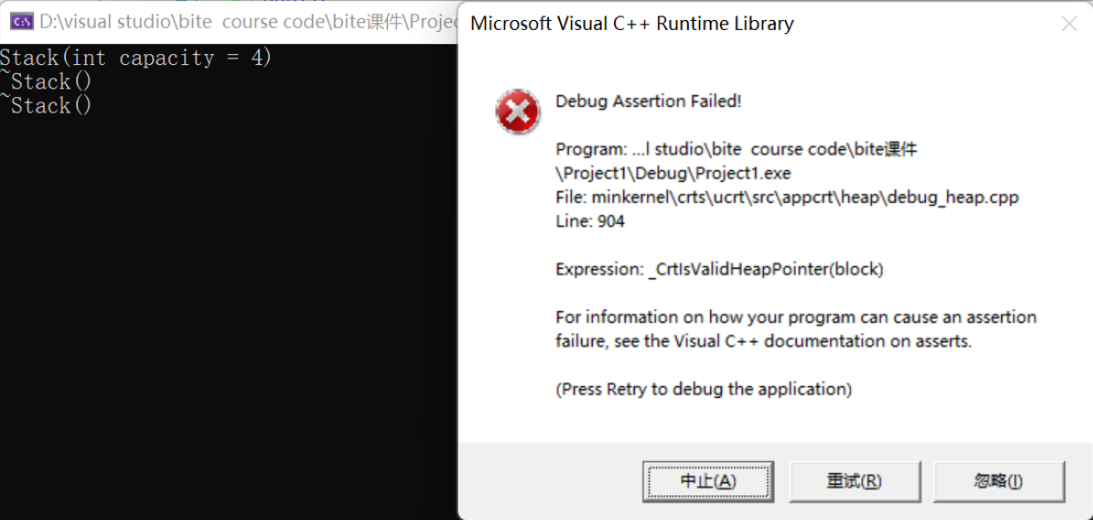
}
运行之后我们会发现程序崩溃了
思考:
由下图可以得出:st1和st2共用一块空间,被调用两次析构函数,同一块空间被释放两次,因此会发生报错。
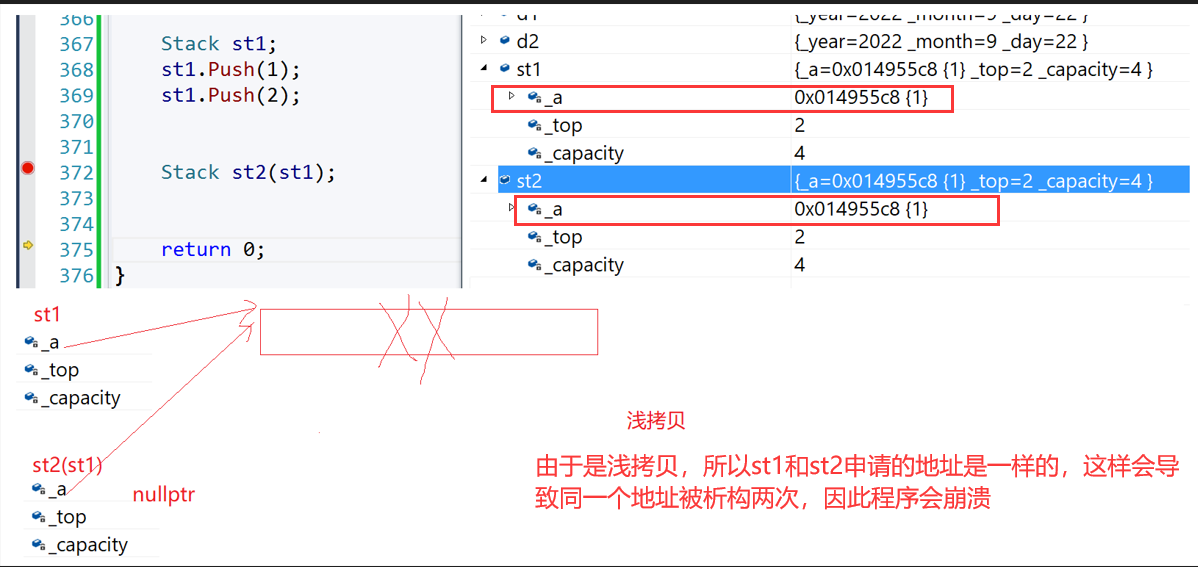
注意:类中如果没有涉及资源申请时,拷贝构造函数是否写都可以;一旦涉及到资源申请时,则拷贝构造函数是一定要写的,否则就是浅拷贝。
-
我们应该如何解决浅拷贝的问题呢?
-
为了解决浅拷贝,一旦涉及到资源申请时,则拷贝构造函数我们自己需要写,这也就是深拷贝
class Stack
{
public:Stack(int capacity = 4){cout << "Stack(int capacity = 4)" << endl;_a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*capacity);if (_a == nullptr){perror("malloc fail");exit(-1);}_top = 0;_capacity = capacity;}// 我们自己写的拷贝构造函数(这样拷贝时才是深拷贝,不会出现浅拷贝的问题)Stack(const Stack& st){cout << "Stack(const Stack& st)" << endl;// 申请一块空间,这块空间是给拷贝的新的栈对象用的// 这样就不会出现,两个站对象用一块空间的问题了_a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*st._capacity);if (_a == nullptr){perror("malloc fail");exit(-1);}memcpy(_a, st._a, sizeof(int)*st._top);_top = st._top;_capacity = st._capacity;}~Stack(){cout << "~Stack()" << endl;free(_a);_a = nullptr;_top = _capacity = 0;}void Push(int x){// ....// 扩容_a[_top++] = x;}private:int* _a;int _top;int _capacity;
};// 需要写析构函数的类,都需要写深拷贝的拷贝构造 Stack
// 不需要写析构函数的类,默认生成的浅拷贝的拷贝构造就可以用 Date/MyQueueclass MyQueue {
public:void push(int x){_pushST.Push(x);}
private:Stack _pushST;Stack _popST;size_t _size = 0;
};int main()
{Stack st1; // 调用默认构造函数st1.Push(1);st1.Push(2);Stack st2(st1); // 调用拷贝函数st2.Push(10);// MyQueue为自定义类型,调用默认的拷贝构造函数(如果默认拷贝构造函数,满足需求,则我们不用自己写)// 调用两次默认构造函数(因为队列,是由两个栈来实现的,所以会调用两次栈的默认构造函数)MyQueue q1; // 调用两次拷贝函数(因为队列,是由两个栈来实现的,所以会调用两次栈的默认拷贝函数)MyQueue q2(q1); return 0; // 调用6次析构函数
}// 打印结果如下:
/*
Stack(int capacity = 4)
Stack(const Stack& st)
Stack(int capacity = 4)
Stack(int capacity = 4)
Stack(const Stack& st)
Stack(const Stack& st)
~Stack()
~Stack()
~Stack()
~Stack()
~Stack()
~Stack()
*/**5.**赋值运算符重载
5.1 运算符重载
C++为了增强代码的可读性引入了运算符重载,运算符重载是具有特殊函数名的函数,也具有其返回值类型,函数名字以及参数列表,其返回值类型与参数列表与普通的函数类似。
函数名字为:关键字operator后面接需要重载的运算符符号。
函数原型:返回值类型 operator操作符(参数列表);如:bool operator==(const Date& d1, const Date& d2)
注意:
-
不能通过连接其他符号来创建新的操作符:比如operator@
-
重载操作符必须有一个类类型参数
-
用于内置类型的运算符,其含义不能改变,例如:内置的整型+,不能改变其含义
-
作为类成员函数重载时,其形参看起来比操作数数目少1,因为成员函数的第一个参数为隐藏的this指针
-
.* :: sizeof ?: . 注意这5个运算符不能重载。
// 全局的operator== ;判断两个日期类是否相等class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}//private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};// 这里会发现运算符重载成全局的,就需要成员变量是公有的,那么问题来了,封装性如何保证?
bool operator==(const Date& d1, const Date& d2)
{return d1._year == d2._year&& d1._month == d2._month&& d1._day == d2._day;
}int main()
{Date d1(2022, 9, 22);Date d2(2023, 1, 1);//d1 > d2;cout << (d1 == d2) << endl; // 程序运行时会转换成operator == (d1, d2);// 也可以显示调用,一般不这样operator==(d1, d2);return 0;
}
// 将operator== 定义在类里面#include<iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}// bool operator==(Date* this, const Date& d2)// 这里需要注意的是,左操作数是this,指向调用函数的对象(==操作符应该刚好是两个操作数)// 成员函数都是放在公共代码区bool operator==(const Date& d) {return _year == d._year&& _month == d._month&& _day == d._day;}private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};int main()
{Date d1(2022, 9, 22);Date d2(2023, 1, 1);//d1 > d2;// (d1 == d2) 一定要加括号,因为<< 的优先级比+高// 运行时会转换成 d1.operator==(d2)cout << (d1 == d2) << endl; // 也可以显示调用,一般不这样cout << (d1.operator == (d2)) << endl;return 0;
}
5.2 赋值运算符重载
1.赋值运算符重载格式
参数类型:
const T&,传递引用可以提高传参效率返回值类型:
T&,返回引用可以提高返回的效率,有返回值目的是为了支持连续赋值检测是否自己给自己赋值
返回*this :要复合连续赋值得含义
我们自己写的运算符重载(日期类)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
public:int GetMonthDay(int year, int month) // 得到对应月份的天数{// 将数组定义在静态区,这样每次创建对象时,都不需要重新创建一个数组static int monthDayArray[13] = { 0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };if (month == 2 && ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0))){return 29;}else{return monthDayArray[month];}}Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1) // 默认构造函数{_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;// 检查日期是否合法if (!(year >= 1&& (month >= 1 && month <= 12)&& (day >= 1 && day <= GetMonthDay(year, month)))){cout << "非法日期" << endl;}}// cout << (d1 == d2) << endl; // 转换成d1.operator==(d2)// 判断两个日期类是否相等bool operator==(const Date& d) {return _year == d._year&& _month == d._month&& _day == d._day;}// d1 > d2bool operator>(const Date& d) {if (_year > d._year){return true;}else if (_year == d._year && _month > d._month){return true;}else if (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day){return true;}return false;}// d1 >= d2bool operator >= (const Date& d){return *this > d || *this == d; // *this 也就是d1}// .... < <= != 都可以按照如上的方式来实现// d1 += 100// 使用传引用返回,则不会拷贝*this来返回,栈帧销毁后d1还存在Date& operator += (int day) {_day += day;while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)) {_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month); _month++;if (_month == 13){++_year;_month = 1;}}return *this;}// d1 + 100 不会改变d1的值// 由于栈帧销毁后,对ret没有访问权限,所以不能够使用传引用返回// ret是一个临时创建的日期类对象,只在当前运算符重载函数中存活Date operator+(int day) {// 调用拷贝构造函数来创建ret这个日期类对象Date ret(*this); ret += day;return ret;}void print(){cout << _year << endl;cout << _month << endl;cout << _day << endl;}// d1 = d2;(赋值重载)Date& operator=(const Date& d){if (this != &d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}return *this;}private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};void TestDate1()
{Date d1;Date d2(2022, 10, 8);// 初始化时,可以检测出来为非法日期Date d3(2022, 2, 40); // 初始化时,可以检测出来为非法日期Date d4(2022, 2, 29); d3.Print(); d4.Print();
}void TestDate2()
{Date d0;Date d1;Date d2(2022, 10, 8);// 拷贝构造(初始化) 将d2拷贝来初始化d3Date d3(d2); // 拷贝构造(将d2拷贝给d4)Date d4 = d2; d1.Print();// 赋值重载(复制拷贝) 已经存在两个对象之间拷贝d0 = d1 = d2; d1.Print();int i, j;(i = j = 10)++;cout << i << " " << j << endl; // 打印结果为 11 10
}int main()
{TestDate1();Date d1(2022, 9, 22);Date d2(2022, 9, 22);d1 += 8;d2 += 100;Date d3 = d1 + 9;d1.print();d3.print();/*d1 - d2;*/return 0;
}
系统默认生成的运算符重载(栈)
class Stack
{
public:// 默认构造函数Stack(int capacity = 4) {cout << "Stack(int capacity = )" <<capacity<<endl;_a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*capacity);if (_a == nullptr){perror("malloc fail");exit(-1);}_top = 0;_capacity = capacity;}// 拷贝构造函数// st2(st1);Stack(const Stack& st) {cout << "Stack(const Stack& st)" << endl;_a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*st._capacity);if (_a == nullptr){perror("malloc fail");exit(-1);}memcpy(_a, st._a, sizeof(int)*st._top);_top = st._top;_capacity = st._capacity;}// st1 = st2// 此处我们不自己写运算符重载的函数,使用系统默认生成的运算符重载函数~Stack(){cout << "~Stack()" << endl;free(_a);_a = nullptr;_top = _capacity = 0;}void Push(int x){// ....// 扩容_a[_top++] = x;}private:int* _a;int _top;int _capacity;
};void TestSatck()
{Stack st1;st1.Push(1);st1.Push(2);Stack st2(10);st2.Push(10);st2.Push(20);st2.Push(30);st2.Push(40);st1 = st2;
}int main()
{TestSatck();return 0;
}运行之后我们会发现使用默认生成的运算符重载,系统崩溃了
系统为什么会崩溃呢,出现了那些问题?
1.通过下图可知,赋值重载之后,st1和st2中_a的地址是相同的
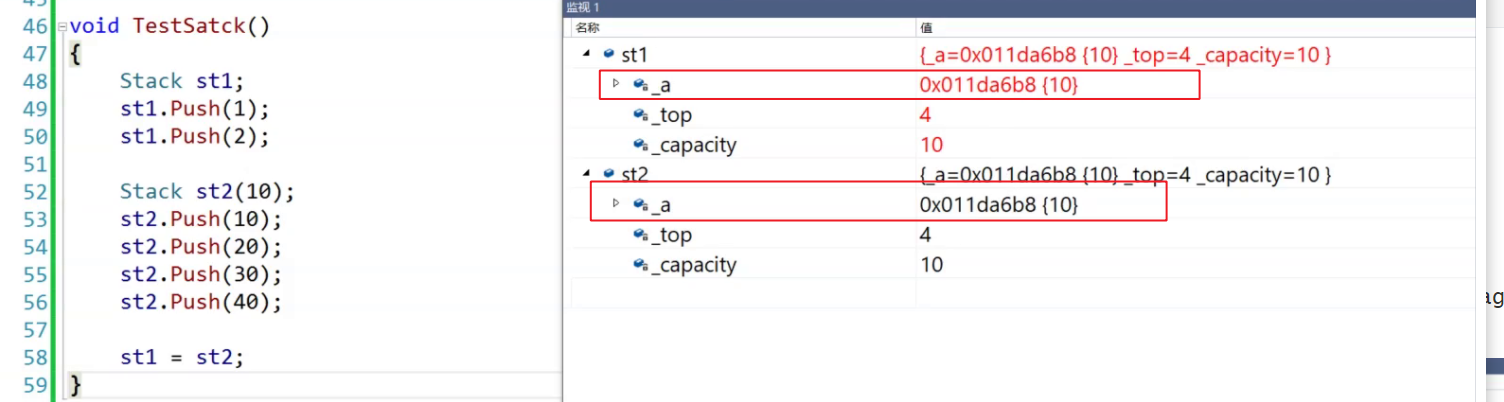
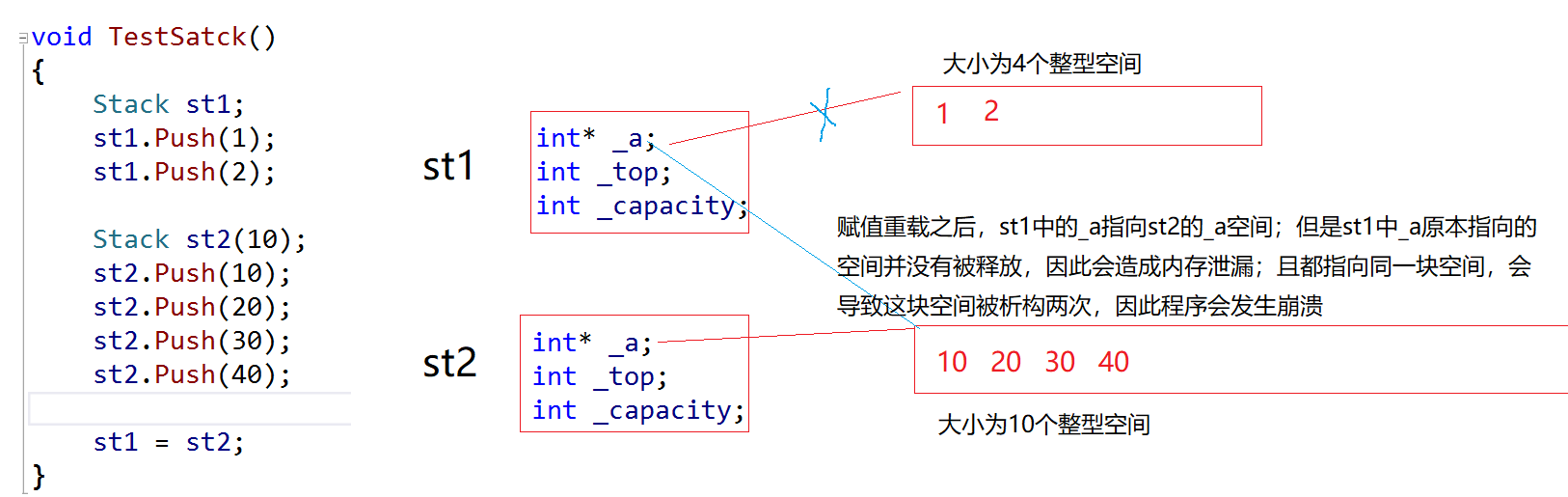
2.通过详细的分析得出下面的结论
我们自己写的运算符重载(栈)
/*
1.怎样才可以保证不发生如上所说的内存泄漏,且对同一块空间多次析构?
第一步:首先释放st1的空间
第二步:为st1申请一块和st2同样大小的空间
第三步:将st2的数据拷贝到st1中
*/// st1 = st2;
Stack& operator=(const Stack& st)
{cout << " Stack& operator=(const Stack& st)" << endl;// 考虑到会有本身给本身赋值的情况,所以在赋值前,要确保this != &st为真if (this != &st) {// 1.首先释放st1的空间free(_a);// 2.为st1申请一块和st2同样大小的空间_a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*st._capacity);if (_a == nullptr){perror("malloc fail");exit(-1);}// 3.将st2的数据拷贝到st1中memcpy(_a, st._a, sizeof(int)*st._top);_top = st._top;_capacity = st._capacity;}// 将st1对象返回return *this;
}
- 使用我们自己写的运算符重载,再来运行一下
class Stack
{
public:Stack(int capacity = 4){cout << "Stack(int capacity = )" <<capacity<<endl;_a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*capacity);if (_a == nullptr){perror("malloc fail");exit(-1);}_top = 0;_capacity = capacity;}// st2(st1)Stack(const Stack& st){cout << "Stack(const Stack& st)" << endl;_a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*st._capacity);if (_a == nullptr){perror("malloc fail");exit(-1);}memcpy(_a, st._a, sizeof(int)*st._top);_top = st._top;_capacity = st._capacity;}// st1 = st2;// st1 = st1;Stack& operator=(const Stack& st) // 我们自己写的运算符赋值重载{cout << " Stack& operator=(const Stack& st)" << endl;if (this != &st){free(_a);_a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*st._capacity);if (_a == nullptr){perror("malloc fail");exit(-1);}memcpy(_a, st._a, sizeof(int)*st._top);_top = st._top;_capacity = st._capacity;}return *this;}~Stack(){cout << "~Stack()" << endl;free(_a);_a = nullptr;_top = _capacity = 0;}void Push(int x){// ....// 扩容_a[_top++] = x;}private:int* _a;int _top;int _capacity;
};class MyQueue
{public:void push(int x){_pushST.Push(x);}private:Stack _pushST;Stack _popST;size_t _size = 0;
};void TestSatck()
{//Stack st1(10000);// 运行结果证明,自己写的运算符重载,不会再导致程序崩溃// 默认生成operator= 不行 需要自己实现Stack st1;st1.Push(1);st1.Push(2);Stack st2(10);st2.Push(10);st2.Push(20);st2.Push(30);st2.Push(40);st1 = st2;st1 = st1;// MyQueue 默认生成operator= 是可以的,我们不需要自己去写MyQueue q1;q1.push(1);q1.push(2);q1.push(3);MyQueue q2;q2.push(10);q2.push(20);q2.push(30);q1 = q2;
}int main()
{TestSatck();return 0;
}
6.日期类的实现(完善日期类,并将它的声明与定义分离)
Date.h
// Date.h
class Date
{ // 友元声明(这个声明可以写在类的任意位置)// 有了这个友元声明,那么这两个运算符重载函数就可以访问类内的成员变量和成员函数friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d); // 流输出friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d); // 流输入public:// 这个函数可以得到,年份月份对应的天数,如2024-4,就有30天int GetMonthDay(int year, int month){static int monthDayArray[13] = { 0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };if (month == 2 && ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0))){return 29;}else{return monthDayArray[month];}}// 默认构造函数Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;// 检查日期是否合法if (!(year >= 1&& (month >= 1 && month <= 12)&& (day >= 1 && day <= GetMonthDay(year, month)))){cout << "非法日期" << endl;}}// d1 == d2bool operator==(const Date& d) const;// d1 > d2bool operator>(const Date& d) const;// d1 >= d2bool operator>=(const Date& d) const;// d1 <= d2bool operator<=(const Date& d) const;// d1 < d2bool operator<(const Date& d) const;// d1 != d2bool operator!=(const Date& d) const;// d1 += 100Date& operator+=(int day);// d1 + 100Date operator+(int day) const; // d1是不改变的// d1 -= 100Date& operator-=(int day);// d1 - 100Date operator-(int day) const;// 前置++Date& operator++();// 后置++Date operator++(int);// 前置--Date& operator--();// 后置--Date operator--(int);// d1 - d2int operator-(const Date& d) const;/*// 错误演示// d1.operator<<(cout); // d1 << cout// << 和 >> 重载一般不写为成员函数,因为this默认抢了第一个参数的位置,Date对象就是左操作数,不符合使用习惯和可读性; 因此我们可以考虑将其定义为全局变量// 如果operator<<不是成员函数的话,那么第一个参数就不是this指针,就不需要写为d1 << cout// 错误演示// ostream 为流插入的类类型 // 不可以作为成员函数void operator<<(ostream& out) {out << _year << "年" << _month << "月" << _day << "日" << endl;}*/// 取类对象地址的重载// 要求这个类的对象不让取地址(需要自己写取地址及const取地址操作符重载的一种情况)Date* operator&(){// 自己写的重载,使用&,取类对象的地址,拿到的就是空指针return nullptr;//return this; // 只是取类的对象的地址,则不需要自己写,系统默认生成的就可以}// 取类对象地址的重载(这个是被const修饰的)const Date* operator&() const{return nullptr;//return this;}private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};// 流插入的声明
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d);
// 此处operator运算符重载必须声明与定义分离;因为其是全局的,不是类的成员函数// 错误演示;如果都定义到Date.h中,由于Date.cpp和test.cpp都包含了Date.h那么他们生成的.o文件中都会包含这个函数,则在编译链接时,就会报错/*
// 不可以直接定义到Date.h
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d)
{out << d._year << "年" << d._month << "月" << d._day << "日" << endl;return out;
}
*/// 解决方法
// 1.声明与定义分离
// 2.用static来修饰 operator
// 3.定义为内联函数 这样可以放到Date.h
// 注意:将函数定义为全局变量,那么想要访问类里面的私有成员变量,则需要在类里面添加友元声明/*
// static修饰(则链接时,函数不进入符号表)
static ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d)
{out << d._year << "年" << d._month << "月" << d._day << "日" << endl;return out;
}
*/// 内联函数(则链接时,函数不进入符号表)
// 流插入
inline ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d)
{out << d._year << "年" << d._month << "月" << d._day << "日" << endl;return out;
}// 流提取
// cin >> d1 operator(cin, d1)
inline istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d)
{in >> d._year >> d._month >> d._day;return in;
}
Date.cpp
// Date.cpp
#include "Date.h"// 运算符重载
bool Date::operator==(const Date& d)
{return _year == d._year&& _month == d._month&& _day == d._day;
}// d1 > d2(被const修饰的运算符重载)
// 这种被const修饰的函数,是专门给被const修饰的对象调用的,普通对象也可以调用,只是不可以进行修改
// 注:最右侧的const是修饰隐藏的this指针的
bool Date::operator>(const Date& d) const
{if (_year > d._year){return true;}else if (_year == d._year && _month > d._month){return true;}else if (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day){return true;}return false;
}// d1 >= d2
bool Date::operator>=(const Date& d) const
{// 大于 或上 等于,也就是大于等于,直接复用,不用自己重新写// 编译器会自行调用 bool Date::operator>(const Date& d) const// bool Date::operator==(const Date& d)进行重载return *this > d || *this == d;
}// d1 <= d2
bool Date::operator<=(const Date& d) const
{return !(*this > d); // 大于取反,也就是小于等于
}// d1 < d2
bool Date::operator<(const Date& d) const
{return !(*this >= d); // 大于等于取反也就是小于
}// d1 != d2
bool Date::operator!=(const Date& d) const
{return !(*this == d);
}Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{if (day < 0){//return *this -= -day;return *this -= abs(day);}_day += day;while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);_month++;if (_month == 13){++_year;_month = 1;}}return *this;
}// d1 + 100
Date Date::operator+(int day) const
{Date ret(*this);ret += day;return ret;
}// d1 -= 100
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{if (day < 0){//return *this -= -day;return *this += abs(day);}_day -= day;while (_day <= 0){--_month;if (_month == 0){--_year;_month = 12;}_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);}return *this;
}// d1 - 100
Date Date::operator-(int day) const
{Date ret(*this);ret -= day;return ret;
}// 前置
Date& Date::operator++()
{*this += 1;return *this; // 前置++返回加加之后的值
}// 后置++ 括号中多一个int参数主要是为了和前置++ 进行区分
// 构成函数重载
Date Date::operator++(int)
{Date tmp(*this);*this += 1;return tmp; // 后置++:返回++之前的值
}// 前置--
Date& Date::operator--()
{*this -= 1;return *this;
}// 后置--
Date Date::operator--(int)
{Date tmp = *this;*this -= 1;return tmp;
}// d1 - d2
int Date::operator-(const Date& d) const
{Date max = *this;Date min = d;int flag = 1;// 针对于if (d > *this) // 如果 bool operator>(const Date& d) const; 没有加const修饰*this,则程序会报错// 因为d被const修饰,但是传参过去之后的*this并没有并const修饰,是一种权限放大,因此会报错// 加上const修饰*this之后;if (d > *this) 和 if (*this < d) 都是可行的if (*this < d) //if (d > *this) {max = d;min = *this;flag = -1;}int n = 0;while (min != max){++n;++min;}return n*flag;
}// 重载流插入
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d)
{out << d._year << "年" << d._month << "月" << d._day << "日" << endl;return out;
}test.cpp
// test.cpp#include "Date.h"void TestDate1()
{Date d1(2022, 10, 8);Date d3(d1);Date d4(d1);d1 -= 10000;d1.Print();Date d2(d1);/*// 打印 d2 - 10000 的两种方法Date d3 = d2 - 10000; d3.Print();*/(d2 - 10000).Print();d2.Print();d3 -= -10000;d3.Print();d4 += -10000;d4.Print();
}void TestDate2()
{Date d1(2022, 10, 8);Date d2(d1);Date d3(d1);Date d4(d1);(++d1).Print(); // d1.operator++()d1.Print();// 后置++,会存在一个占位符(d2++).Print(); // d2.operator++(1)d2.Print();(--d1).Print(); // d1.operator--()d1.Print();(d2--).Print(); // d2.operator--(1)d2.Print();
}void TestDate3()
{Date d1(2022, 10, 10);Date d2(2023, 7, 1);cout << d2 - d1 << endl;cout << d1 - d2 << endl;
}void TestDate4()
{Date d1, d2;//cin >> d1; // 流提取//cout << d1; // 流插入//d1 << cout; // d1.operator<<(cout);cin >> d1 >> d2;cout << d1 << d2 << endl; // operator<<(cout, d1); // 根据优先级,会先运行cout << d1; 因此operator<<的返回值类型应为ostream&;这样才可以支持d2进行插入cout << d1 - d2 << endl;
}void TestDate5()
{Date d1(2022, 10, 10);d1.Print();// 此处详解看下图(被const修饰的类类型对象)const Date d2(2022, 10, 10); d2.Print(); //d2 += 10;cout << d2 + 1000 << endl;cout << &d1 << endl; // 取地址及const取地址操作符重载cout << &d2 << endl;
}int main()
{TestDate2();return 0;
}
- 下图是对d2.Print() 的详解
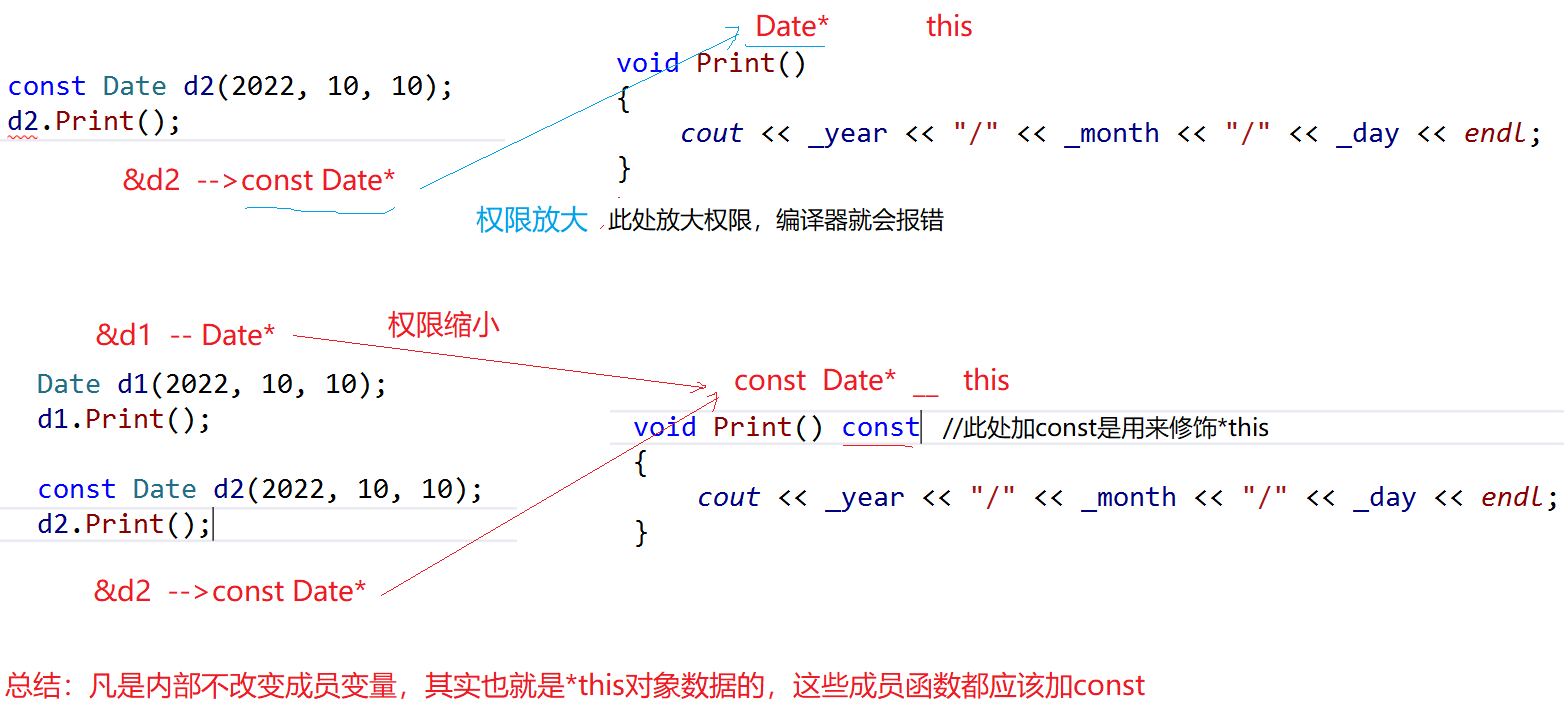
7.const
-
将const修饰的“成员函数"称之为const成员函数,
-
const修饰类成员函数,实际修饰该成员函数隐含的
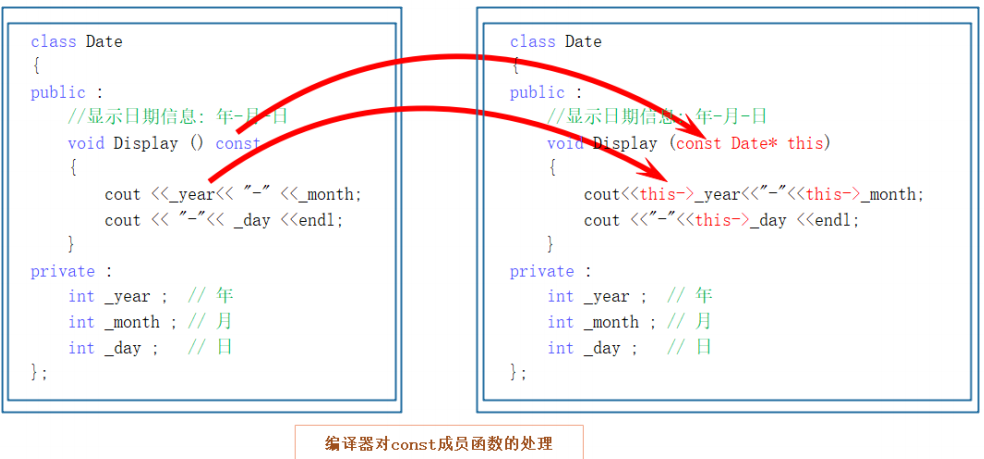
this指针(也就是const Date* this),表明在该成员函数中不能对类的任何成员变量进行修改。
// const 在*的左侧是修饰 *this; (*this就是this指针指向的对象)
// const Date* this; Date const* this// const 在*的右侧修饰 this;
// Date* const this
我们来看看下面的代码:
class Date
{
public:Date(int year, int month, int day){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}void Print(){cout << "Print()" << endl;cout << "year:" << _year << endl;cout << "month:" << _month << endl;cout << "day:" << _day << endl << endl;}void Print() const{cout << "Print()const" << endl;cout << "year:" << _year << endl;cout << "month:" << _month << endl;cout << "day:" << _day << endl << endl;}
private:int _year; // 年int _month; // 月int _day; // 日
};void Test()
{//调用 void Print()Date d1(2022, 1, 13);d1.Print(); //调用 void Print() constconst Date d2(2022, 1, 13);d2.Print();
}
请思考下面的几个问题:
-
const对象可以调用非const成员函数吗?
不可以。const 对象被视为只读对象,它们不允许修改对象的状态。因此,对 const 对象调用非 const 成员函数将违反 const-correctness 规则,因此编译器会报错。 -
非const对象可以调用const成员函数吗?
是的。非 const 对象可以调用 const 成员函数。const 成员函数被设计用于不修改对象状态的情况,因此它们可以安全地被非 const 对象调用。 -
const成员函数内可以调用其它的非const成员函数吗?
不可以。const 成员函数被视为只读函数,它们保证不会修改对象的状态。因此,在 const 成员函数内部调用非 const 成员函数将破坏这一保证,编译器会报错。 -
非const成员函数内可以调用其它的const成员函数吗?
是的。非 const 成员函数可以调用 const 成员函数。const 成员函数不会修改对象的状态,因此它们可以安全地被非 const 成员函数调用。
总结:
- const 成员函数可以访问对象的成员变量,但不能修改它们。
- 非 const 成员函数可以访问并修改对象的成员变量。
- const 成员函数之间可以互相调用,但不能调用非 const 成员函数。
- 非 const 成员函数之间可以互相调用,也可以调用 const 成员函数。
8.取地址及const取地址操作符重载
class Date
{
public:Date* operator&(){return this;}const Date* operator&() const{return this;}private:int _year; // 年int _month; // 月int _day; // 日
};//这两个运算符一般不需要重载,使用编译器生成的默认取地址的重载即可,只有特殊情况,才需要重载,比如想让别人获取到指定的内容!
相关文章:

3.类与对象(中篇)介绍了类的6个默认构造函数,列举了相关案例,实现了一个日期类
1.类的6个默认成员函数 如果一个类中什么成员都没有,简称为空类。 空类中真的什么都没有吗?并不是,任何类在什么都不写时,编译器会自动生成以下6个默认成员函数。 默认成员函数:用户没有显式实现,编译器会…...

Vue实现手机APP页面的切换,如何使用Vue Router进行路由管理呢?
在Vue中,实现手机APP页面的切换,通常会使用Vue Router进行路由管理。Vue Router是Vue.js官方的路由管理器,它和Vue.js深度集成,使构建单页面应用变得易如反掌。 以下是一个简单的步骤说明,展示如何使用Vue Router实现…...
软考--软件设计师(软件工程总结2)
目录 1.测试方法 2.软件项目管理 3.软件容错技术 4.软件复杂性度量 5.结构化分析方法(一种面向数据流的开发方法) 6.数据流图 1.测试方法 软件测试:静态测试(被测程序采用人工检测,计算机辅助静态分析的手段&…...

渗透测试之SSRF漏洞
一、SSRF介绍 SSRF(Cross-site Scripting,简称XSS)是一种安全漏洞,它允许攻击者通过构造特定的请求,使服务器发起对外网无法访问的内部系统请求。这种漏洞通常发生在服务端提供了从其他服务器应用获取数据的功能&#…...
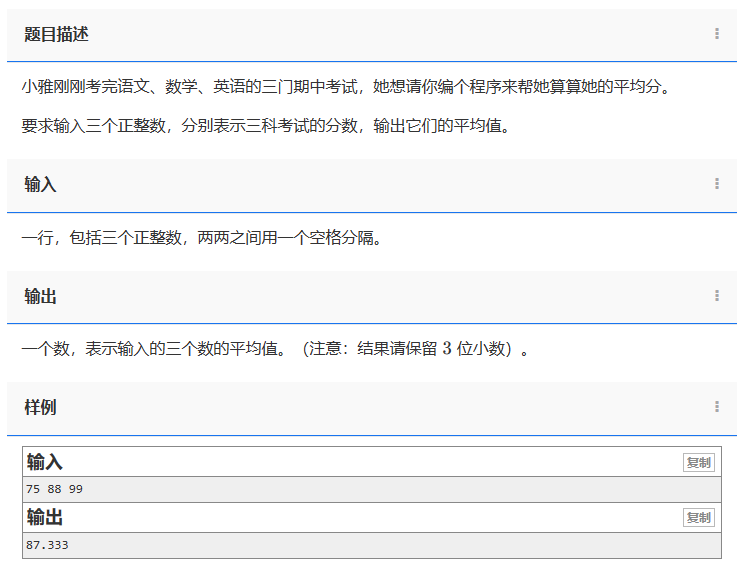
【C++】1957. 求三个数的平均数
问题:1957. 求三个数的平均数 类型:基本运算、小数运算 题目描述: 小雅刚刚考完语文、数学、英语的三门期中考试,她想请你编个程序来帮她算算她的平均分。 要求输入三个正整数,分别表示三科考试的分数,输…...
GPU部署ChatGLM3
首先,检查一下自己的电脑有没有CUDA环境,没有的话,去安装一个。我的电脑是4060显卡,买回来就自带这些环境了。没有显卡的话,也不要紧,这个懒人安装包支持CPU运行,会自动识别没有GPU,…...
Windows远程执行
Windows远程执行 前言 1、在办公环境中,利用系统本身的远程服务进行远程代码执行甚至内网穿透横向移动的安全事件是非常可怕的,因此系统本身的一些远程服务在没有必要的情况下建议关闭,防止意外发生; 2、作为安全人员࿰…...
AJAX —— 学习(一)
目录 一、原生 AJAX (一)AJAX 介绍 1.理解 2.作用 3.最大的优势 4.应用例子 (二)XML 介绍 1.理解 2.作用 (三)AJAX 的特点 1.优点 2.缺点 二、HTTP 协议 (一)HTTP 介…...
Activity——idea(2020以后)配置actiBPM
文章目录 前言jar下载idea 安装本地扩展插件 前言 2020及之后版本的idea中,未维护对应的actiBPM扩展插件。如果需要安装该插件,则需要使用本地导入 jar的方式。 jar下载 访问官方网站,搜索对应的actiBPM扩展插件。 https://plugins.jetbra…...

MyBatis——配置优化和分页插件
MyBatis配置优化 MyBatis配置文件的元素结构如下: configuration(配置) properties(属性) settings(设置) typeAliases(类型别名) plugins(插件)…...

[蓝桥杯 2013 省 B] 翻硬币
[蓝桥杯 2013 省 B] 翻硬币 题目背景 小明正在玩一个“翻硬币”的游戏。 题目描述 桌上放着排成一排的若干硬币。我们用 * 表示正面,用 o 表示反面(是小写字母,不是零),比如可能情形是 **oo***oooo,如果…...
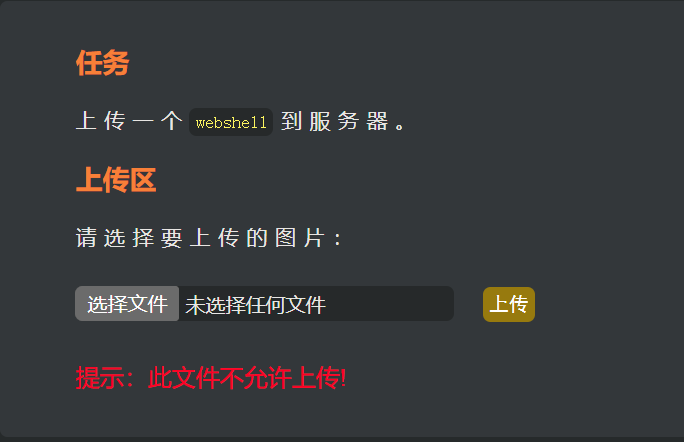
[BT]BUUCTF刷题第13天(4.1)
第13天 Upload-Labs-Linux (Basic) Pass-01 根据题目提示,该题为绕过js验证。 一句话木马: <?php eval(system($_POST["cmd"]));?> // 符号 表示后面的语句即使执行错误,也不报错。 // eval() 把括号内的字符串全部…...

特别详细的Spring Cloud 系列教程1:服务注册中心Eureka的启动
Eureka已经被Spring Cloud继承在其子项目spring-cloud-netflix中,搭建Eureka Server的方式还是非常简单的。只需要通过一个独立的maven工程即可搭建Eureka Server。 我们引入spring cloud的依赖和eureka的依赖。 <dependencyManagement><!-- spring clo…...
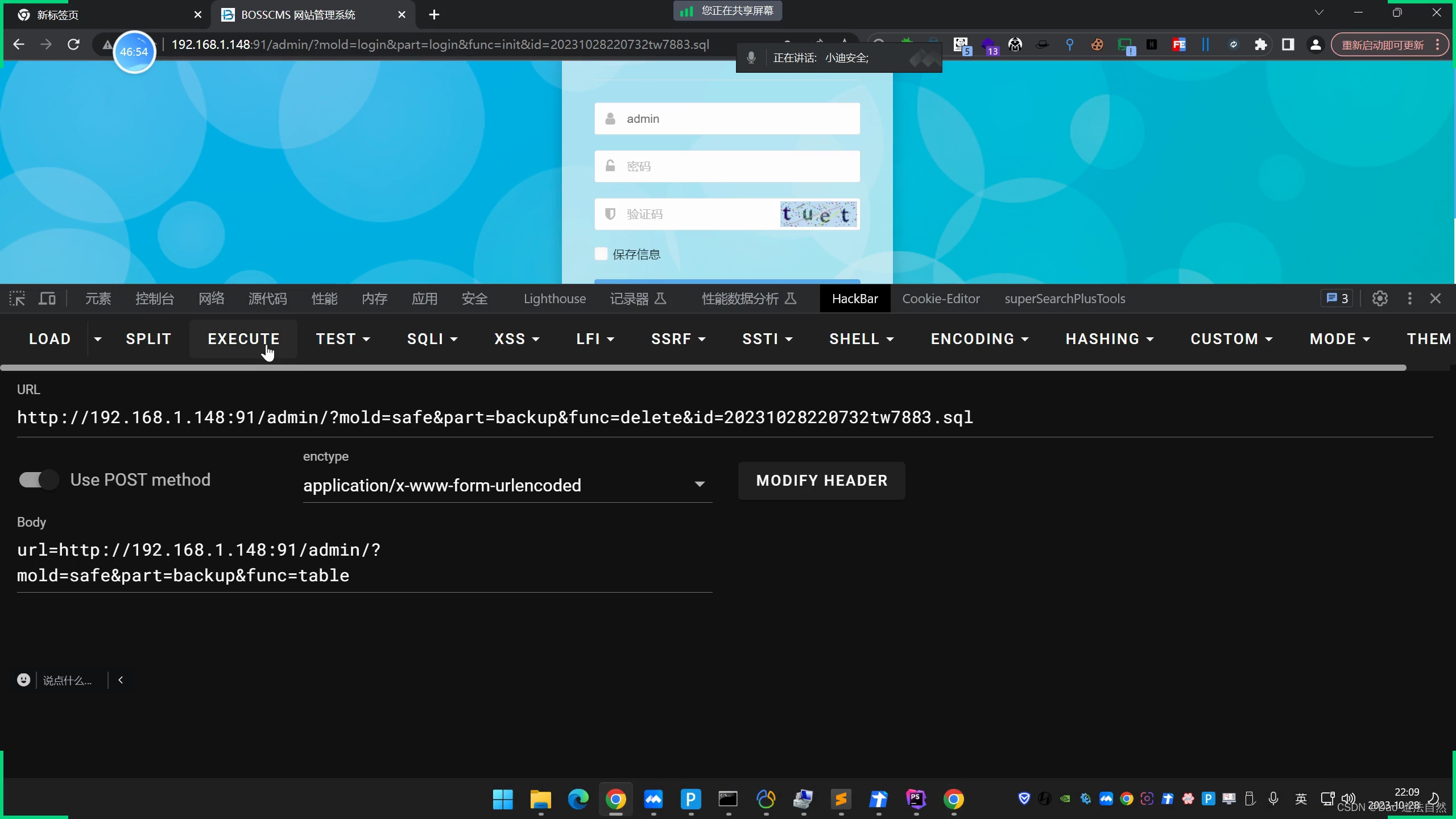
Day108:代码审计-PHP模型开发篇MVC层动态调试未授权脆弱鉴权未引用错误逻辑
目录 案例1-Xhcms-动态调试-脆弱的鉴权逻辑 案例2-Cwcms-动态调试-未引用鉴权逻辑 案例3-Bosscms-动态调试-不严谨的鉴权逻辑 知识点: 1、PHP审计-动态调试-未授权安全 2、PHP审计-文件对比-未授权安全 3、PHP审计-未授权访问-三种形态 动态调试优点: 环境配置&…...
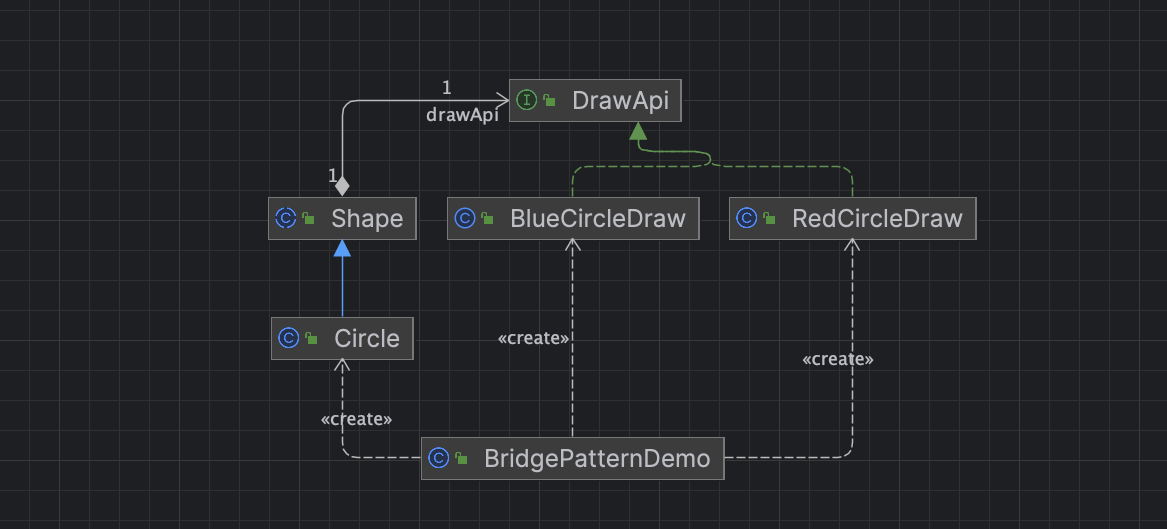
重读Java设计模式: 桥接模式详解
引言 在软件开发中,经常会遇到需要在抽象与实现之间建立连接的情况。当系统需要支持多个维度的变化时,使用传统的继承方式往往会导致类爆炸和耦合度增加的问题。为了解决这一问题,我们可以使用桥接模式。桥接模式是一种结构型设计模式&#…...

新规解读 | 被网信办豁免数据出境申报义务的企业,还需要做什么?
为了促进数据依法有序自由流动,激发数据要素价值,扩大高水平对外开放,《促进和规范数据跨境流动规定》(以下简称《规定》)对数据出境安全评估、个人信息出境标准合同、个人信息保护认证等数据出境制度作出优化调整。 …...
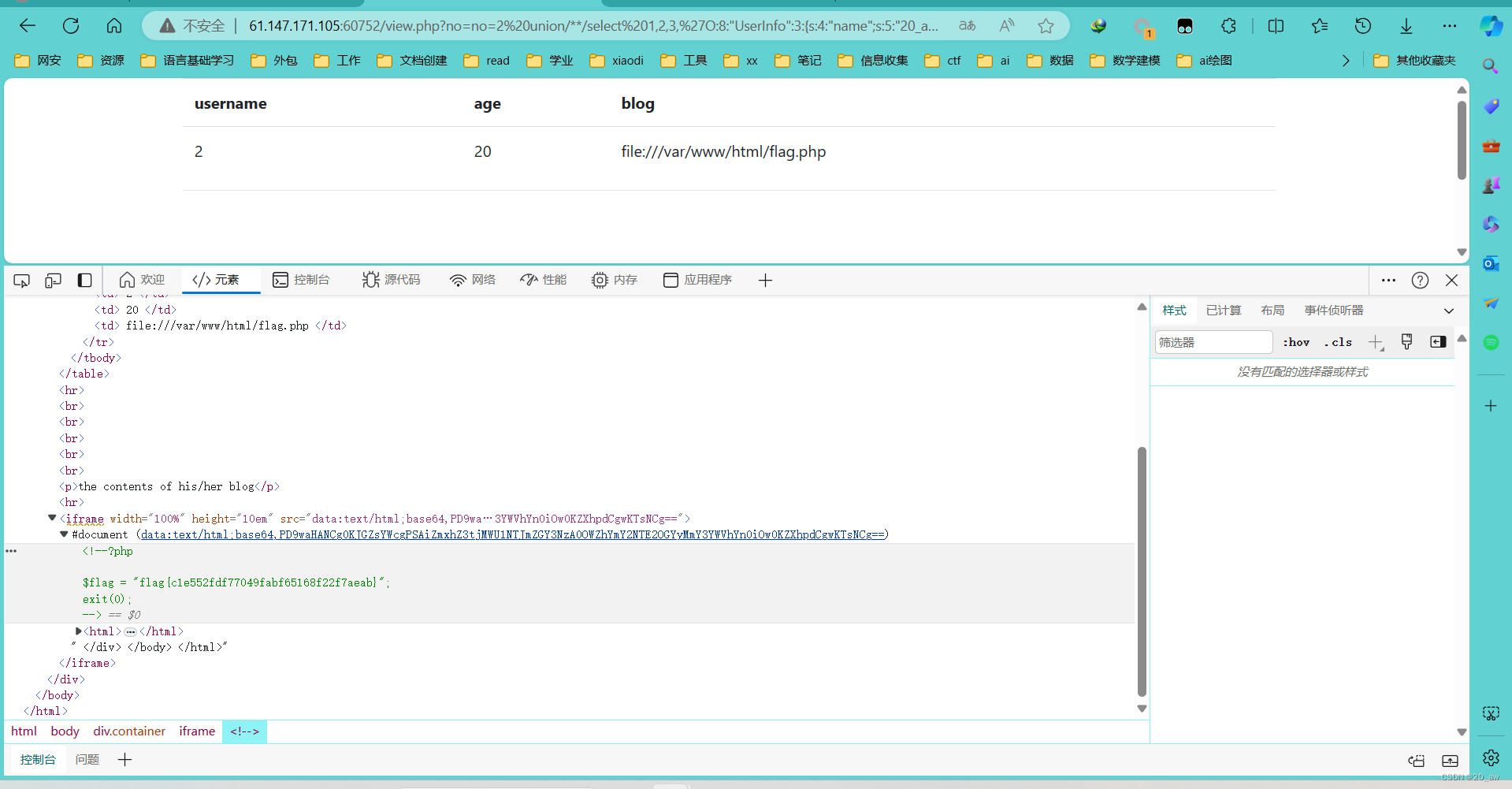
fakebook-攻防世界
题目 先目录扫描一下 dirseach 打开flag.php是空白的 访问robots.txt,访问user.php.bak <?php class UserInfo { public $name ""; public $age 0; public $blog ""; public function __construct($name, $age, $blog) { …...
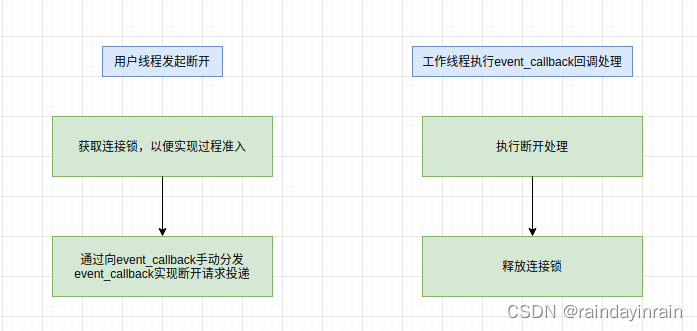
mynet开源库
1.介绍 个人实现的c开源网络库. 2.软件架构 1.结构图 2.基于event的自动分发机制 3.多优先级分发队列,延迟分发队列 内部event服务于通知机制的优先级为0,外部event优先级为1. 当集中处理分发的event_callback时,…...
深度挖掘商品信息,jd.item_get API助您呈现商品全面规格参数
深度挖掘商品信息,特别是在电商平台上,对于商家、开发者和用户来说都至关重要。jd.item_get API作为京东开放平台提供的一个强大工具,能够帮助用户轻松获取商品的全面规格参数,进而为商品分析、推荐、比较等提供有力的数据支撑。 …...

A Random Walk Based Anonymous Peer-to-Peer
一、 背景 匿名性一直是P2P系统等自组织环境中最具挑战性的问题之一。在本文中,我们提出了一个匿名协议,称为基于随机漫步的匿名协议(RWAP),在分散的P2P系统。我们通过全面的轨迹驱动模拟来评估RWAP。结果表明,与现有方法相比,RWAP显著降低了流量成本和加密开销。 二、 …...

在鸿蒙HarmonyOS 5中实现抖音风格的点赞功能
下面我将详细介绍如何使用HarmonyOS SDK在HarmonyOS 5中实现类似抖音的点赞功能,包括动画效果、数据同步和交互优化。 1. 基础点赞功能实现 1.1 创建数据模型 // VideoModel.ets export class VideoModel {id: string "";title: string ""…...

全球首个30米分辨率湿地数据集(2000—2022)
数据简介 今天我们分享的数据是全球30米分辨率湿地数据集,包含8种湿地亚类,该数据以0.5X0.5的瓦片存储,我们整理了所有属于中国的瓦片名称与其对应省份,方便大家研究使用。 该数据集作为全球首个30米分辨率、覆盖2000–2022年时间…...

2021-03-15 iview一些问题
1.iview 在使用tree组件时,发现没有set类的方法,只有get,那么要改变tree值,只能遍历treeData,递归修改treeData的checked,发现无法更改,原因在于check模式下,子元素的勾选状态跟父节…...

三体问题详解
从物理学角度,三体问题之所以不稳定,是因为三个天体在万有引力作用下相互作用,形成一个非线性耦合系统。我们可以从牛顿经典力学出发,列出具体的运动方程,并说明为何这个系统本质上是混沌的,无法得到一般解…...

在QWebEngineView上实现鼠标、触摸等事件捕获的解决方案
这个问题我看其他博主也写了,要么要会员、要么写的乱七八糟。这里我整理一下,把问题说清楚并且给出代码,拿去用就行,照着葫芦画瓢。 问题 在继承QWebEngineView后,重写mousePressEvent或event函数无法捕获鼠标按下事…...

【无标题】路径问题的革命性重构:基于二维拓扑收缩色动力学模型的零点隧穿理论
路径问题的革命性重构:基于二维拓扑收缩色动力学模型的零点隧穿理论 一、传统路径模型的根本缺陷 在经典正方形路径问题中(图1): mermaid graph LR A((A)) --- B((B)) B --- C((C)) C --- D((D)) D --- A A -.- C[无直接路径] B -…...

wpf在image控件上快速显示内存图像
wpf在image控件上快速显示内存图像https://www.cnblogs.com/haodafeng/p/10431387.html 如果你在寻找能够快速在image控件刷新大图像(比如分辨率3000*3000的图像)的办法,尤其是想把内存中的裸数据(只有图像的数据,不包…...

认识CMake并使用CMake构建自己的第一个项目
1.CMake的作用和优势 跨平台支持:CMake支持多种操作系统和编译器,使用同一份构建配置可以在不同的环境中使用 简化配置:通过CMakeLists.txt文件,用户可以定义项目结构、依赖项、编译选项等,无需手动编写复杂的构建脚本…...

Python 高效图像帧提取与视频编码:实战指南
Python 高效图像帧提取与视频编码:实战指南 在音视频处理领域,图像帧提取与视频编码是基础但极具挑战性的任务。Python 结合强大的第三方库(如 OpenCV、FFmpeg、PyAV),可以高效处理视频流,实现快速帧提取、压缩编码等关键功能。本文将深入介绍如何优化这些流程,提高处理…...
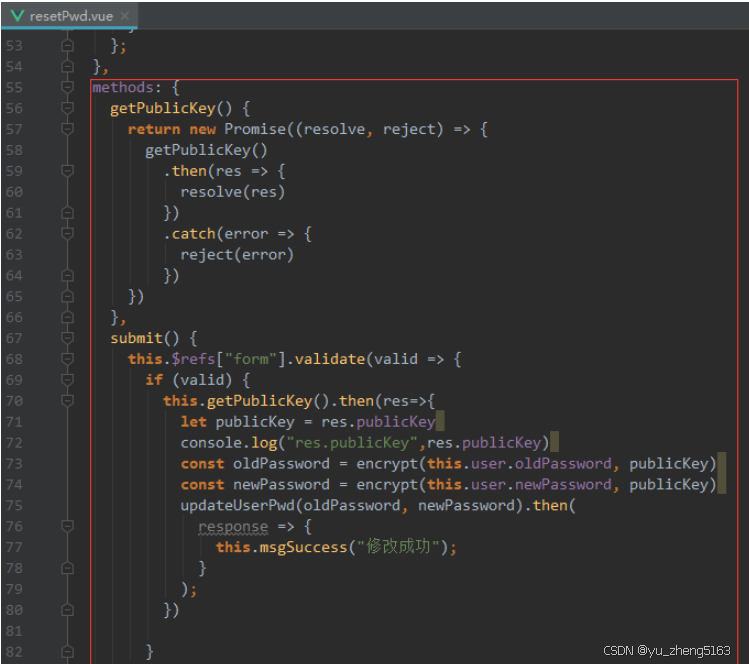
若依登录用户名和密码加密
/*** 获取公钥:前端用来密码加密* return*/GetMapping("/getPublicKey")public RSAUtil.RSAKeyPair getPublicKey() {return RSAUtil.rsaKeyPair();}新建RSAUti.Java package com.ruoyi.common.utils;import org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Base64; im…...
