9.vector的使用介绍和模拟实现
1.vector的介绍及使用
1.1 vector的介绍
vector的文档介绍
-
vector是表示可变大小数组的序列容器。 -
就像数组一样,
vector也采用的连续存储空间来存储元素。也就是意味着可以采用下标对vector的元素进行访问,和数组一样高效。但是又不像数组,它的大小是可以动态改变的,而且它的大小会被容器自动处理。 -
本质讲,
vector使用动态分配数组来存储它的元素。当新元素插入时候,这个数组需要被重新分配大小为了增加存储空间。其做法是,分配一个新的数组,然后将全部元素移到这个数组。就时间而言,这是一个相对代价高的任务,因为每当一个新的元素加入到容器的时候,vector并不会每次都重新分配大小。 -
vector分配空间策略:vector会分配一些额外的空间以适应可能的增长,因为存储空间比实际需要的存储空间更大。不同的库采用不同的策略权衡空间的使用和重新分配。但是无论如何,重新分配都应该是对数增长的间隔大小,以至于在末尾插入一个元素的时候是在常数时间的复杂度完成的。 -
因此,
vector占用了更多的存储空间,为了获得管理存储空间的能力,并且以一种有效的方式动态增长。 -
与其它动态序列容器相比(
deque, list and forward_list),vector在访问元素的时候更加高效,在末尾添加和删除元素相对高效。对于其它不在末尾的删除和插入操作,效率更低。比起list和forward_list统一的迭代器和引用更好。
1.2 vector的使用
push_back的用法
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;void test_vector1()
{// 使用int实例化一个vector对象vector<int> v;v.push_back(1);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(4);for (size_t i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i){cout << v[i] << " ";}cout << endl;// 使用迭代器打印容器中的数据vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin();while (it != v.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;// 使用for循环打印容器中的数据for (auto e : v){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;// 打印容器的最大存储容量cout << v.max_size() << endl;//vector<char> vstr; // vector并不可以替代string//string str;
}
reserve的用法
void test_vector2()
{vector<int> v;// 向容器中尾插数据// void push_back (const value_type& val);v.push_back(1);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(4);v.push_back(5);cout << v.capacity() << endl; // 打印结果为6// 调整容器的大小v.reserve(10);cout << v.capacity() << endl; // 打印结果为10// 比当前容量小时,不缩容v.reserve(4);cout << v.capacity() << endl; // 打印结果为10// 调整容器size的大小v.resize(8);v.resize(15, 1);v.resize(3);
}
// vector的扩容机制
void TestVectorExpand()
{size_t sz;vector<int> v;// 提前预留空间(在已知将要插入多少数据量)v.reserve(100);sz = v.capacity();cout << sz << endl;cout << "making v grow:\n";for (int i = 0; i < 100; ++i){v.push_back(i);if (sz != v.capacity()){sz = v.capacity();cout << "capacity changed: " << sz << '\n';}}
}
size和[]重载
// size只有一个接口,为const接口(size只需要提供读的功能)
// size_type size() const;// operator[]提供了两个接口(operator[]要有读和写的功能)
// reference operator[] (size_type n);
// const_reference operator[] (size_type n) const;
void Func(const vector<int>& v)
{v.size();v[0];// 错误演示, v被const修饰,因此调用的接口为const_reference operator[] (size_type n) const;// 因此v[0]是不可以被修改的// v[0]++; // Returns a reference to the element at position n in the vector.// 返回vector中n下标位置的元素的引用// reference 就是类型, value_type&// reference at (size_type n);// const_reference at (size_type n) const;v.at(0);
}
// 总结
// 1.只读接口函数。const; 如size()
// 2.只写接口函数。非const; 如push_back()
// 3.可读可写的接口函数。const+非const; 如operator[]void test_vector3()
{vector<int> v;v.push_back(1);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(3);v.size();v[0];v[0]++;v.at(0);Func(v);
}
operator[]和at()越界的区别
// operator[]和at()越界的区别就是:一个是assert,一个是抛异常
void test_vector4()
{vector<int> v;//v.reserve(10);v.resize(10);for (size_t i = 0; i < 10; ++i){v[i] = i; // assert // v.at(i) = i; // 抛异常// v.push_back(i);}
}
assign的用法
// assign()
// template <class InputIterator>
// void assign (InputIterator first, InputIterator last);
// 新内容是由范围内的每个元素构建的元素,顺序相同,从第一个元素到最后一个元素。// void assign (size_type n, const value_type& val);
// 这个版本的 assign() 函数接受一个整数参数 count 和一个值 value,它会用 count 个 value 值来替换容器中的元素
void test_vector5()
{vector<int> v;v.push_back(1);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(3);for (auto e : v){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;// 对应 void assign (size_type n, const value_type& val);v.assign(10, 1); for (auto e : v){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;vector<int> v1; v1.push_back(10);v1.push_back(20);v1.push_back(30);// 对应template <class InputIterator> // void assign (InputIterator first, InputIterator last);// 将v容器中的元素替换为,v1容器中(begin指针到end指针之间的元素)v.assign(v1.begin(), v1.end());for (auto e : v){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;string str("hello world");v.assign(str.begin(), str.end()); //有迭代器就可以使用for (auto e : v){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;v.assign(++str.begin(), --str.end());for (auto e : v){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;
}
find、insert、swap的用法
// std::find的源码
/*template <class InputIterator, class T>InputIterator find (InputIterator first, InputIterator last, const T& val);The behavior of this function template is equivalent to:
template<class InputIterator, class T>
InputIterator find (InputIterator first, InputIterator last, const T& val)
{while (first!=last) {if (*first==val) return first;++first;}return last;
}
*/void test_vector6()
{vector<int> v;v.push_back(1);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(3);v.insert(v.begin(), 4);v.insert(v.begin()+2, 4);//vector<int>::iterator it = v.find(3);vector<int>::iterator it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 3);if (it != v.end()){v.insert(it, 30);}for (auto e : v){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;vector<int> v1;v1.push_back(10);v1.push_back(20);v1.push_back(30);// 专门为vector写的非成员函数,就是为了防止调用算法库中的swap(),哪个需要将交换的对象实例化,代价太大
// std::swap (vector) // 使用这个swap就相当于调用 v1.swap(v);// template <class T, class Alloc>
// void swap (vector<T,Alloc>& x, vector<T,Alloc>& y);v1.swap(v); swap(v1, v); // std::swap (vector),对swap的重载
}
void test_vector7()
{vector<int> v;v.reserve(10);v.push_back(1);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(4);v.push_back(5);cout << v.size() << endl;cout << v.capacity() << endl;// 设计理念:不动空间,不去缩容 空间换时间v.reserve(5);cout << v.size() << endl;cout << v.capacity() << endl;v.resize(3);cout << v.size() << endl;cout << v.capacity() << endl;v.clear();cout << v.size() << endl;cout << v.capacity() << endl;// 设计理念:时间换空间,一般缩容都是异地,代价不小,一般不要轻易使用v.push_back(1);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(3);// 这个函数的功能就是v.shrink_to_fit();cout << v.size() << endl;cout << v.capacity() << endl;
}int main()
{try{test_vector4();}catch (const exception& e){cout << e.what() << endl;}//TestVectorExpand();return 0;
}// 增:push_back 不直接头插(需要挪动数据,效率低,建议少用) 偶尔头插,使用insert(v.begin(),val)
// 删:pop_back 不直接头删(需要挪动数据,效率低,建议少用) 偶尔头删,使用erase(v.begin())
// 查:算法库的find
// 改:迭代器 + []
习题
只出现一次的数字

- 分析
// &(按位与) 都为1则按位与为1,有0,则按位与为0// & (按位与)
//00000000000000000000000000000011 - 3的补码(正数的原码,补码,反码相同)
// //10000000000000000000000000000101 - -5的原码
// //11111111111111111111111111111010 - -5的反码(符号位不变,其他位按位取反)
//
// //11111111111111111111111111111011 - -5的补码
// //00000000000000000000000000000011 - 3的补码
// //00000000000000000000000000000011 - &后的补码(放到内存中的都是补码);// |(按位或) 有1则按位或为1,都为0则按位或为0
// 00000000000000000000000000000011 - 3的补码(正数的原码,补码,反码相同)
// 10000000000000000000000000000101 - -5的原码
// 11111111111111111111111111111010 - -5的反码(符号位不变,其他位按位取反)
//
// 11111111111111111111111111111011 - -5的补码
// 00000000000000000000000000000011 - 3的补码
// 11111111111111111111111111111011 - |(按位或) 后的补码(放到内存中的都是补码);// ^(按位异或) 相同,则按位异或为0,相反则按位异或为1
// 00000000000000000000000000000011 - 3的补码(正数的原码,补码,反码相同)
// 10000000000000000000000000000101 - -5的原码
// 11111111111111111111111111111010 - -5的反码(符号位不变,其他位按位取反)
//
// 11111111111111111111111111111011 - -5的补码
// 00000000000000000000000000000011 - 3的补码
// 11111111111111111111111111111000 - ^(按位异或)后的补码(放到内存中的都是补码);// 任何数按位异或0,都等于它本身; 如 a^0 = a
// 任何数按位异或其本身,都等于0, 如 a^a = 0
// 3^3^5 = 5
// 3^5^3 = 5
//由以上可得异或操作符支持交换律
class Solution {
public:int singleNumber(vector<int>& nums) {int ret = 0;// 范围forfor(auto e : nums){// 数组中只有一个数据是单个,其余数据都是两两一组,且相等// 又因为a^0 == a// a^a == 0// a^b^c == a^c^b 按位异或 的复合交换律ret ^= e;}return ret;}
};
杨辉三角
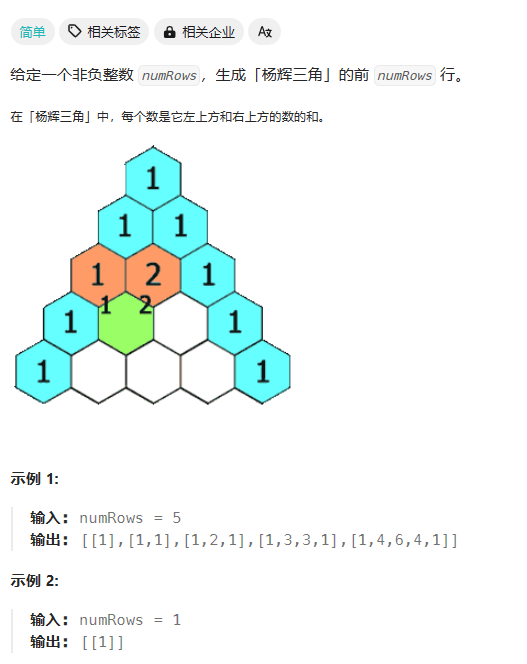
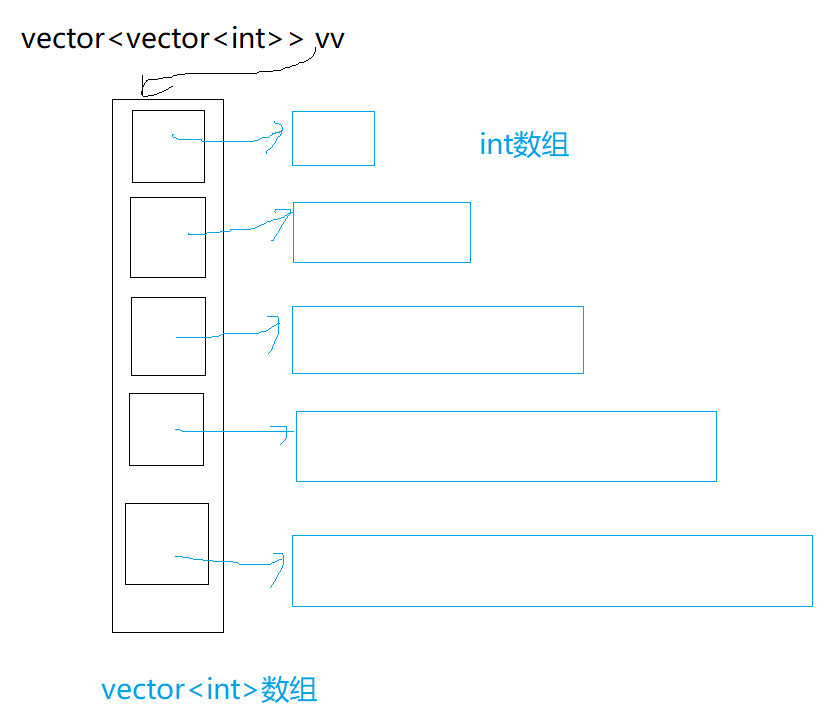
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> generate(int numRows){// 先创建一个二维数组的vector对象(存放的数据为int)vector<vector<int>> vv;// 确定vector的大小;// 使用resize可以对其初始化,如果不传参,会使用缺省参数vv.resize(numRows);// 像遍历二维数组一样,将相应的数值进行存储// vv.size()代表的就是二维数组的行数// 因为在vv中,一个元素的大小就是vector<int>的大小for(size_t i = 0; i < vv.size(); ++i){// 确定vector<int>的大小,并初始化// void resize (size_type n, value_type val = value_type());// 调整容器的大小,使其包含 n 个元素。 // 如果新的大小大于当前大小,则容器将增加到 n 个元素,并用可选的第二个参数 value 的值进行填充。vv[i].resize(i+1,0);// 边界的数值填充// 左边界就是vv[i][0]; 右边界是vv[i][vv[i].size() - 1]vv[i][0] = vv[i][vv[i].size() - 1] = 1;}// 杨辉三角一共有vv.size()行,每一行有vv[i].size()列for(size_t i = 0; i < vv.size(); ++i){for(size_t j = 0; j < vv[i].size(); ++j){// 如果值为1,为边界的值,不用处理// 如果值为0,这个值的大小等于左上方的值加上右上方的值if(vv[i][j] == 0){vv[i][j] = vv[i-1][j] + vv[i-1][j-1];}}}return vv;}
};
电话号码的字母组合
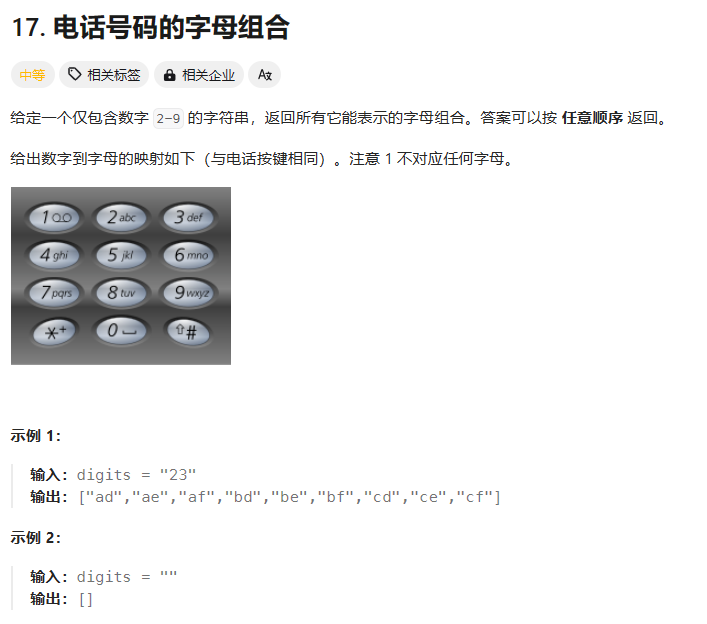
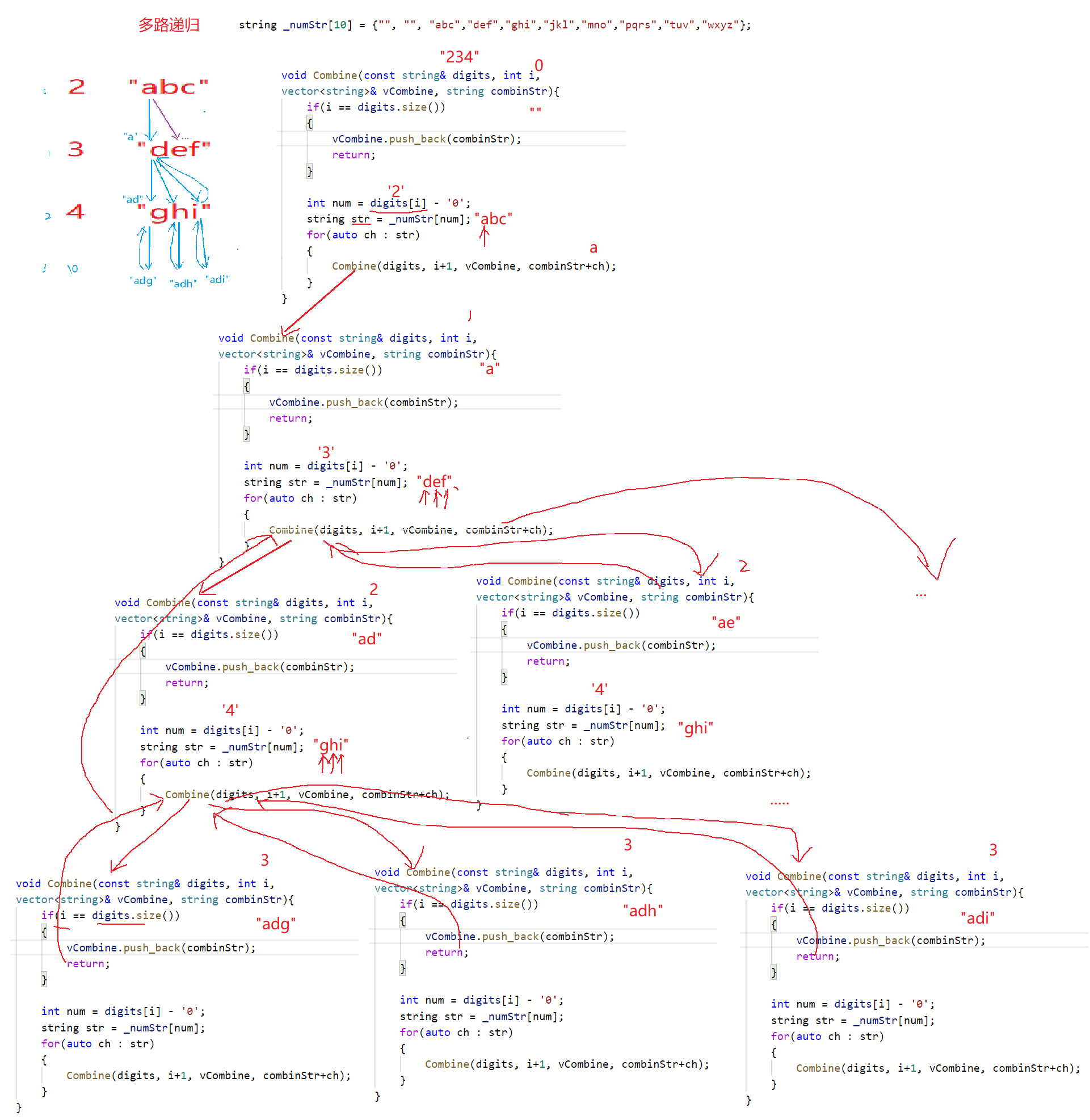
// 解题思路
class Solution {// 2~9所有数字对应的字符string _numStr[10] = {"", "", "abc", "def", "ghi", "jkl", "mno", "pqrs", "tuv", "wxyz"};public:void Combine(const string& digits, int i, vector<string>& vCombine, string combinestr) {// 当i等于digits.size()时,迭代完成// 将已经组合好的字符串combinestr尾插到vCombine中if(i == digits.size()) {vCombine.push_back(combinestr);return;}// 第一次迭代// digits[i]是字符的ASCLL值,因此需要减去字符'0'才可以拿到相应的数// num就是电话号码的第一个数字int num = digits[i] - '0'; // 将电话号码第一个数字对应的字符串存储到str中string str = _numStr[num]; // 遍历strfor(auto ch : str) {// 开始迭代// 经过for循环,会将str存储的所有字符串,都执行一次 Combine,层层递归,直到i == digits.size()为真结束Combine(digits, i+1, vCombine, combinestr + ch); } } // 题目给出的接口vector<string> letterCombinations(string digits){// 用来存储组合好的字符串vector<string> vCombine;// 如果没有输入字符,则返回一个空的vector<string>; // 特殊的,作单独处理if(digits.empty()){return vCombine;}// i为string digits的下标size_t i = 0;// str是用来存储组合起来的字符串的// 对应这个构造函数string(); 这个构造的对象为空串string str; // digit是题目给我们的数字,这些数字存放在字符串当中// i是字符串中,字符对应的下标Combine(digits, i, vCombine, str);return vCombine;}
};
2.vector深度剖析及模拟实现
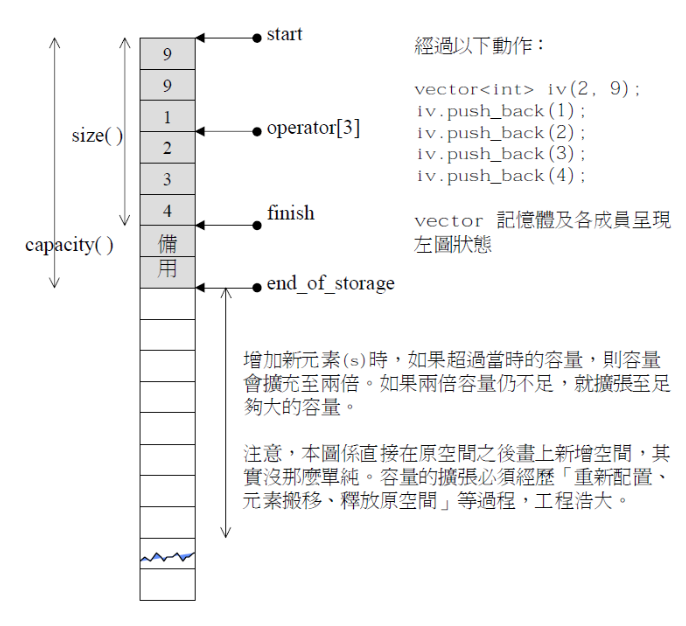
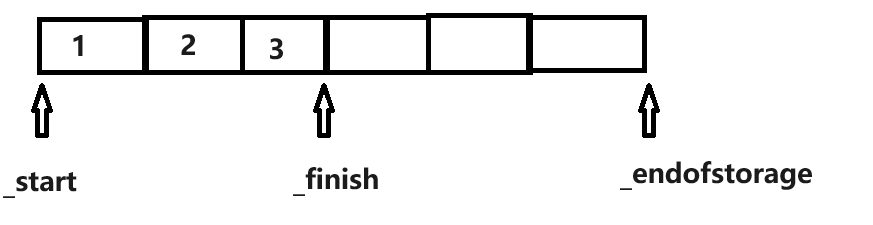
vector的私有成员变量
iterator _start; // 指向数组的起始位置
iterator _finish; // _finish == _start + size(); 指向数组的末尾(指向末尾元素的下一个元素)
iterator _endofstorage; // _endofstorage == _start + capacity(); 数组的容量,指向数组容量的末尾(末尾的下一个元素)
迭代器
typedef T* iterator;
typedef const T* const_iterator; // 普通迭代器
iterator begin()
{return _start;
}iterator end()
{return _finish;
}// const迭代器
const_iterator begin() const
{return _start;
}const_iterator end() const
{return _finish;
}
operator[]重载
// 普通重载operator[]
T& operator[](size_t pos)
{assert(pos < size());return _start[pos];
}// const重载operator[]
const T& operator[](size_t pos) const
{assert(pos < size());return _start[pos];
}
默认构造函数
// 默认构造函数
vector()
:_start(nullptr)
, _finish(nullptr)
, _endofstorage(nullptr)
{}// n可以为负数(这种方法不建议)
// vector<int> v1(10, 1); // 10为int类型,1为int类型
// vector<int> v1(10, 1) 匹配 vector(int n, const T& val = T())// size_t 不会有负数(建议使用这种构造方法)
// vector<char> v1(10, 'A'); // 10为int类型,'A'为char类型
// vector<char> v1(10, 'A') 匹配 vector(size_t n, const T& val = T())
// int会发生整型提升,提升为size_t类型
// 用n个val值来填充容器vector(int n, const T& val = T())
:_start(nullptr)
, _finish(nullptr)
, _endofstorage(nullptr)
{reserve(n);for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){push_back(val);}
}vector(size_t n, const T& val = T())
:_start(nullptr)
, _finish(nullptr)
, _endofstorage(nullptr)
{reserve(n);for (size_t i = 0; i < n; ++i){push_back(val);}
}
拷贝构造函数
// 传统的拷贝构造的写法
// v2(v1)
/*
vector(const vector<T>& v)
:_start(nullptr)
, _finish(nullptr)
, _endofstorage(nullptr)
{reserve(v.capacity());for (const auto& e : v){push_back(e);}
}*/// 现代写法的拷贝构造
// v1(v2)
template <class InputIterator>
vector(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
:_start(nullptr)
, _finish(nullptr)
, _endofstorage(nullptr)
{// 用迭代器的方法将v2的数据,一个一个插入到v1中while (first != last){push_back(*first);++first;}
}// v1(v2)
vector(const vector<T>& v)
:_start(nullptr)
, _finish(nullptr)
, _endofstorage(nullptr)
{// 使用上述的现代写法的拷贝构造函数将v2的数据拷贝给tmpvector<T> tmp(v.begin(), v.end()); // 将v的数据拷贝到tmp// 交换tmp和v1的成员变量swap(tmp);
}void swap(vector<T>& v)
{std::swap(_start, v._start);std::swap(_finish, v._finish);std::swap(_endofstorage, v._endofstorage);
}
operator=
// v1 = v2
// 这里的vector<T> v 是v2的拷贝
vector<T>& operator=(vector<T> v)
{// v出了作用域就会被销毁// 交换v和v1swap(v);return *this;
}
reserve, 扩容
// 扩容
void reserve(size_t n)
{// 如果将要扩容的容量n大于原有的容量capacity(),那么就要进行扩容;但是如果将要扩容的容量n小于原有的容量capacity(),那么不进行处理(不会进行缩容)if (n > capacity()){// 此处必须将size()的返回值进行存储// 如果_start被改变,则size()的返回值也会被改变;(size()的返回值就是_start与_finsh两个指针之间元素的个数)size_t oldSize = size();// tmp是扩容后,新空间的地址T* tmp = new T[n];if (_start){// 将旧空间的数据按字节拷贝到新空间memcpy(tmp, _start, sizeof(T)*oldSize); // 将原空间的数据拷贝到新空间delete[] _start; // 将原空间释放}// 更新成员变量_start = tmp; _finish = tmp + oldSize; // 指针+整型 = 指针 (指针+1 就会跳过 T* 个字节的地址)_endofstorage = _start + n;}
}
resize();调整数组的大小
// 设置数据个数的大小,并对扩容空间进行初始化初始化(使用val进行初始化)
void resize(size_t n, T val = T())
{// 如果n > capacity(),则需要先进行扩容if (n > capacity()) {reserve(n);}if (n > size()){// size()位置到n位置的数据进行初始化;也就是对n-size()个数据初始化// 即n-(_finish - _start) > 0while (_finish < _start + n) {*_finish = val;++_finish;}}else{// 当n <= size()时,令 n == size()即可,也就是 n == _finish - _start_finish = _start + n;}
}
尾插,尾删
void push_back(const T& x)
{// 如果数组的大小与数组的容量相等,那么要插入,就需要进行扩容if (_finish == _endofstorage){size_t newCapacity = capacity() == 0 ? 4 : capacity() * 2;reserve(newCapacity);}*_finish = x;++_finish;
}void pop_back()
{assert(!empty());--_finish;
}
insert;任意位置插入
// 迭代器失效 : 扩容引起,野指针问题
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& val)
{// pos只是形参; this->_start; this->_finishassert(pos >= _start);assert(pos < _finish);// 扩容(容量满了,需要进行扩容)if (_finish == _endofstorage){// 记录起始位置和pos位置之间的长度size_t len = pos - _start;size_t newCapacity = capacity() == 0 ? 4 : capacity() * 2;reserve(newCapacity);// 这里如果不更新pos就会导致野指针// 扩容之后,编译器可能会重新分配新的空间,pos还指向原来的空间(也就是野指针)// 扩容会导致pos迭代器失效,需要更新处理一下pos = _start + len;}// 挪动数据(将pos以及pos位置后的数据向后挪动一个位置)// _finish 指向数组最后一个元素的下一个位置// _finish - 1 指向数组的最后一个元素iterator end = _finish - 1;while (end >= pos) {*(end + 1) = *end;--end;}*pos = val;++_finish;// 返回更新之后的pos指针,这里的pos指针是主函数的形参,必须返回更新主函数的pos实参return pos;
}
erase任意位置删除
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{assert(pos >= _start);assert(pos < _finish);// 将pos位置后的所有数据向前挪动iterator begin = pos+1;while (begin < _finish){*(begin-1) = *(begin);++begin;}--_finish;// 返回更新之后的pos指针,这里的pos指针是主函数的形参,必须返回更新主函数的pos实参return pos;
}
3.vector的完整实现
// vector.h
#pragma once
namespace qwy
{template<class T>class vector{public:typedef T* iterator; typedef const T* const_iterator; // 普通迭代器iterator begin(){return _start;}iterator end(){return _finish;}// const迭代器const_iterator begin() const{return _start;}const_iterator end() const{return _finish;}// 普通重载operator[]T& operator[](size_t pos){assert(pos < size());return _start[pos];}// const重载operator[]const T& operator[](size_t pos) const{assert(pos < size());return _start[pos];}// 默认构造函数vector():_start(nullptr), _finish(nullptr), _endofstorage(nullptr){}// n可以为负数(这种方法不建议)// vector<int> v1(10, 1); // 10为int类型,1为int类型// vector<int> v1(10, 1) 匹配 vector(int n, const T& val = T())// size_t 不会有负数(建议使用这种构造方法)// vector<char> v1(10, 'A'); // 10为int类型,'A'为char类型// vector<char> v1(10, 'A') 匹配 vector(size_t n, const T& val = T())// int会发生整型提升,提升为size_t类型// 用n个val值来填充容器vector(int n, const T& val = T()):_start(nullptr), _finish(nullptr), _endofstorage(nullptr){reserve(n);for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){push_back(val);}}vector(size_t n, const T& val = T()):_start(nullptr), _finish(nullptr), _endofstorage(nullptr){reserve(n);for (size_t i = 0; i < n; ++i){push_back(val);}}// 传统的拷贝构造的写法// v2(v1)/*vector(const vector<T>& v):_start(nullptr), _finish(nullptr), _endofstorage(nullptr){reserve(v.capacity());for (const auto& e : v){push_back(e);}}*/// 现代写法的拷贝构造// v1(v2)template <class InputIterator>vector(InputIterator first, InputIterator last):_start(nullptr), _finish(nullptr), _endofstorage(nullptr){// 用迭代器的方法将v2的数据,一个一个插入到v1中while (first != last){push_back(*first);++first;}}vector(const vector<T>& v):_start(nullptr), _finish(nullptr), _endofstorage(nullptr){vector<T> tmp(v.begin(), v.end()); // 将v的数据拷贝到tmpswap(tmp);}// v1 = v2// v1 = v1; // 极少数情况,能保证正确性,所以这里就这样写没什么问题vector<T>& operator=(vector<T> v){swap(v);return *this;}// 析构函数~vector(){delete[] _start;_start = _finish = _endofstorage = nullptr;}// 扩容void reserve(size_t n){if (n > capacity()){// 此处必须将size()的返回值进行存储// 如果_start被改变,则size()的返回值也会被改变;(size()的返回值为_start与_finsh的差值)size_t oldSize = size();T* tmp = new T[n];if (_start){memcpy(tmp, _start, sizeof(T)*oldSize); // 将原空间的数据拷贝到新空间delete[] _start; // 将原空间释放}_start = tmp; _finish = tmp + oldSize;_endofstorage = _start + n;}}// 设置数据个数的大小,并对其初始化void resize(size_t n, T val = T()){if (n > capacity()) // 如果n > capacity(),则需要先进行扩容{reserve(n);}if (n > size()){// size()位置到n位置的数据进行初始化;也就是对n-size()个数据初始化// 即n-(_finish - _start) > 0while (_finish < _start + n) {*_finish = val;++_finish;}}else{// 当n <= size()时,令 n == size()即可,也就是 n == _finish - _start_finish = _start + n;}}bool empty() const{return _finish == _start;}size_t size() const{return _finish - _start;}size_t capacity() const{// 指针-指针 = 两个指针之间元素的个数return _endofstorage - _start;}void push_back(const T& x){if (_finish == _endofstorage){size_t newCapacity = capacity() == 0 ? 4 : capacity() * 2;reserve(newCapacity);}*_finish = x;++_finish;}void pop_back(){assert(!empty());--_finish;}// 迭代器失效 : 扩容引起,野指针问题iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& val){// pos只是形参; this->_start; this->_finishassert(pos >= _start);assert(pos < _finish);// 扩容if (_finish == _endofstorage){size_t len = pos - _start;size_t newCapacity = capacity() == 0 ? 4 : capacity() * 2;reserve(newCapacity);// 扩容之后,编译器可能会重新分配新的空间,pos还指向原来的空间(也就是野指针)// 扩容会导致pos迭代器失效,需要更新处理一下pos = _start + len;}// 挪动数据iterator end = _finish - 1;while (end >= pos) {*(end + 1) = *end;--end;}*pos = val;++_finish;return pos;}iterator erase(iterator pos){assert(pos >= _start);assert(pos < _finish);iterator begin = pos+1;while (begin < _finish){*(begin-1) = *(begin);++begin;}--_finish;return pos;}void swap(vector<T>& v){std::swap(_start, v._start);std::swap(_finish, v._finish);std::swap(_endofstorage, v._endofstorage);}void clear(){_finish = _start;}private:iterator _start; iterator _finish; // _finish == _start + size()iterator _endofstorage; // _endofstorage == _start + capacity()};void test_vector1(){vector<int> v;v.push_back(1);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(4);for (size_t i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i){cout << v[i] << " ";}cout << endl;vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin();while (it != v.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;for (auto e : v){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;v.pop_back();v.pop_back();v.pop_back();v.pop_back();v.pop_back();for (auto e : v){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;}void test_vector2(){vector<int> v;v.resize(10, -1);for (auto e : v){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;v.resize(5);for (auto e : v){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;}void test_vector3(){vector<int> v;//v.reserve(10);v.push_back(1);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(4);for (size_t i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i){cout << v[i] << " ";}cout << endl;v.insert(v.begin(), 0);for (auto e : v){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;// 算法库中的find// template <class InputIterator, class T>// InputIterator find (InputIterator first, InputIterator last, const T& val);vector<int>::iterator it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 3);if (it != v.end()){v.insert(it, 30);}for (auto e : v){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;}void test_vector4(){vector<int> v;v.push_back(1);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(4);// 算法库中的findvector<int>::iterator it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 3);if (it != v.end()){v.insert(it, 30);}// insert以后 it还能否继续使用 -- 不能,可能迭代器失效(野指针)// insert以后,实参it并不会发生改变,但是形参pos会发生改变;(形参改变并不会影响实参)// (*it)++;// *it *= 100;for (auto e : v){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;}// 算法库实现的测试--> 最后发现程序崩溃了// 这是由于v.erase(it)调用之后, it就失效了;因此我们需要去更新it(即it = v.erase(it))void test_vector5(){std::vector<int> v;v.push_back(1);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(4);// it失效还是不失效?(这里一定会失效,具体原因详细看erase的模拟实现)std::vector<int>::iterator it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 3);if (it != v.end()){v.erase(it);}// 读 (在vs下会失效)cout << *it << endl;// 写 (在vs下会失效)(*it)++;for (auto e : v){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;}// 算法库中实现的erase()的测试 //void test_vector6()//{// // 要求删除所有偶数// std::vector<int> v;// v.push_back(1);// v.push_back(2);// v.push_back(2);// v.push_back(3);// v.push_back(4);// std::vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin();// while (it != v.end())// {// if (*it % 2 == 0)// {// it = v.erase(it);// }// else// {// ++it;// }// }// for (auto e : v)// {// cout << e << " ";// }// cout << endl;//}// 我们自己实现的erase()的测试void test_vector6(){// 要求删除所有偶数vector<int> v;v.push_back(1);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(4);//v.push_back(5);vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin();while (it != v.end()){if (*it % 2 == 0){// 这里更新it指针,那么pos就不会失效// erase(iterator pos)it = v.erase(it);}else{++it;} }for (auto e : v){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;}// 测试拷贝构造void test_vector7(){vector<int> v;v.push_back(1);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(4);vector<int> v1(v);for (auto e : v1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;vector<int> v2;v2.push_back(10);v2.push_back(20);v1 = v2;for (auto e : v1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;v1 = v1;for (auto e : v1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;}void test_vector8(){std::string str("hello");vector<int> v(str.begin(), str.end());for (auto e : v){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;//vector<int> v1(v.begin(), v.end());vector<int> v1(10, 1);//vector<char> v1(10, 'A');for (auto e : v1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;}// 测试杨辉三角// 杨辉三角的实现程序class Solution {public:vector<vector<int>> generate(int numRows) {vector<vector<int>> vv;vv.resize(numRows);for (size_t i = 0; i < vv.size(); ++i){vv[i].resize(i + 1, 0);vv[i][0] = vv[i][vv[i].size() - 1] = 1;}for (size_t i = 0; i < vv.size(); ++i){for (size_t j = 0; j < vv[i].size(); ++j){if (vv[i][j] == 0){vv[i][j] = vv[i - 1][j] + vv[i - 1][j - 1];}}}return vv;}};// 需要注意的问题如:void test_vector9()void test_vector10(){vector<string> v;v.push_back("1111111111111111111111111111");v.push_back("1111111111111111111111111111");v.push_back("1111111111111111111111111111");v.push_back("1111111111111111111111111111");v.push_back("1111111111111111111111111111");for (auto& e : v){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;}// 测试杨辉三角void test_vector9(){// 内部运行原理// vv的类型是vector<vector<int>> 给vv中插入5个v,v的类型是vector<int>// v中开辟5个空间,每个空间初始化为1// 根据我们写的底层原理,插入第5个数据的时候,程序会进行扩容// 扩容时会调用reserve()函数,如果reserve()函数中使用memcopy()来拷贝原空间的数据到扩容的新空间,但是这个新空间是vv的新空间,vv中的v指向的还是原来的空间,并没有给v开辟新空间,并将v的数据拷贝到新空间(v的指针:_start,_finish,_endofstorage是在vv中)// 拷贝数据之后,就会将v指向的原空间释放,但是没有给v开辟新空间,并将将数据拷贝// 解决方案:// 将memcopy()函数拷贝,替换为// for (size_t i = 0; i < oldSize; ++i)// {// tmp[i] = _start[i]; // 对应 vector<T>& operator=(vector<T> v)// }// 这样就可以将v的数据拷贝到新空间,原空间被释放,并不会对现在的v指向的空间有影响vector<vector<int>> vv;vector<int> v(5, 1);vv.push_back(v);vv.push_back(v);vv.push_back(v);vv.push_back(v);vv.push_back(v);for (size_t i = 0; i < vv.size(); ++i){for (size_t j = 0; j < vv[i].size(); ++j){cout << vv[i][j] << " ";}cout << endl;}cout << endl;}
}// test.cpp
int main()
{try{bit::test_vector9();}catch (const exception& e){cout << e.what() << endl;}return 0;
}
测试杨辉三角(使用自己的vector)
// 测试杨辉三角(下面的代码,使用我自己的vector容器会报错,具体原因如下,改进方式如下)void test_vector9(){// 内部运行原理// vv的类型是vector<vector<int>> 给vv中插入5个v,v的类型是vector<int>// v中开辟5个空间,每个空间初始化为1// 根据我们写的底层原理,插入第5个数据的时候,程序会进行扩容// 扩容时会调用reserve()函数,如果reserve()函数中使用memcopy()来拷贝原空间的数据到扩容的新空间,但是这个新空间是vv的新空间,vv中的v指向的还是原来的空间,并没有给v开辟新空间,并将v的数据拷贝到新空间(v的指针:_start,_finish,_endofstorage是在vv中)// 拷贝数据之后,就会将v指向的原空间释放,但是没有给v开辟新空间,并将将数据拷贝// 解决方案:// 将memcopy()函数拷贝,替换为// for (size_t i = 0; i < oldSize; ++i)// {// tmp[i] = _start[i]; // 对应 vector<T>& operator=(vector<T> v)// }// 这样就可以将v的数据拷贝到新空间,原空间被释放,并不会对现在的v指向的空间有影响vector<vector<int>> vv;vector<int> v(5, 1);vv.push_back(v);vv.push_back(v);vv.push_back(v);vv.push_back(v);vv.push_back(v);for (size_t i = 0; i < vv.size(); ++i){for (size_t j = 0; j < vv[i].size(); ++j){cout << vv[i][j] << " ";}cout << endl;}cout << endl;}
相关文章:

9.vector的使用介绍和模拟实现
1.vector的介绍及使用 1.1 vector的介绍 vector的文档介绍 vector是表示可变大小数组的序列容器。 就像数组一样,vector也采用的连续存储空间来存储元素。也就是意味着可以采用下标对vector的元素进行访问,和数组一样高效。但是又不像数组,…...

探索设计模式的魅力:MVVM模式在AI大模型领域的创新应用-打破传统,迎接智能未来
🌈 个人主页:danci_ 🔥 系列专栏:《设计模式》 💪🏻 制定明确可量化的目标,坚持默默的做事。 MVVM模式在AI大模型领域的创新应用-打破传统迎接智能未来 🚀 “在人工智能的领域里&a…...
Docker使用— Docker部署安装Nginx
Nginx简介 Nginx 是一款高性能的 web 服务器、反向代理服务器以及电子邮件(IMAP/POP3/SMTP)代理服务器,由俄罗斯开发者伊戈尔塞索耶夫(Igor Sysoev)编写,并在2004年10月4日发布了首个公开版本0.1.0。Nginx…...
C/C++基础----运算符
算数运算符 运算符 描述 例子 两个数字相加 两个变量a b得到两个变量之和 - 两个数字相减 - * 两个数字相乘 - / 两个数字相除 - % 两个数字相除后取余数 8 % 3 2 -- 一个数字递减 变量a:a-- 、--a 一个数字递增 变量a: a 、 a 其中递…...

YOLOv9:下一代目标检测的革新
目标检测作为计算机视觉领域的一个重要分支,一直是研究的热点。YOLO系列作为目标检测算法的佼佼者,自YOLO1发布以来,就在速度和精度上取得了很好的平衡,深受业界和学术界的喜爱。 YOLOv9作为该系列的最新版本,不仅在性…...
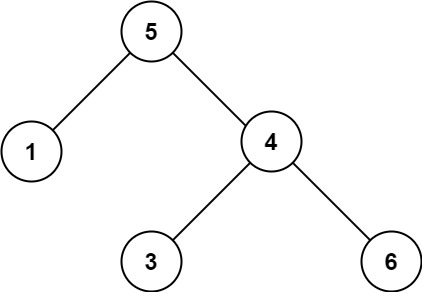
Leetcode算法训练日记 | day20
一、合并二叉树 1.题目 Leetcode:第 617 题 给你两棵二叉树: root1 和 root2 。 想象一下,当你将其中一棵覆盖到另一棵之上时,两棵树上的一些节点将会重叠(而另一些不会)。你需要将这两棵树合并成一棵新…...
conda创建虚拟环境太慢,Collecting package metadata (current_repodata.json): failed
(省流版:只看加粗红色,末尾也有哦) 平时不怎么用conda,在前公司用服务器的时候用的是公司的conda源,在自己电脑上直接用python创建虚拟环境完事儿,所以对conda的配置并不熟悉~~【狗头】。但是python虚拟环境的最大缺点…...
Tensorflow(GPU版本配置)一步到位!!!
Tensorflow(GPU版本配置)一步到位!!! CUDA安装CUDA配置Tensorflow配置常见的包 CUDA安装 配置了N次的Tensorflow–Gpu版本,完成了踩坑,这里以配置Tensorflow_gpu 2.6.0为例子进行安装 以下为ten…...

STL之map
CSTL之map 1.介绍 map是映射的意思,即每个x对应一个y,我们这里说成key和value 举例子说明:运动->篮球 (运动是key,篮球是value)用电脑->写代码 (用电脑是key,写代码是value)…...
)
闲谈2024(一)
时光飞逝,一转眼24年的第一个季度已经过去了,回望这3个多月,感触颇多。首先,24年从一个一心只读圣贤书,全身心投入在技术上的研发工程师,转变为一个团队的小leader。从我个人对自己的定位来说,我…...
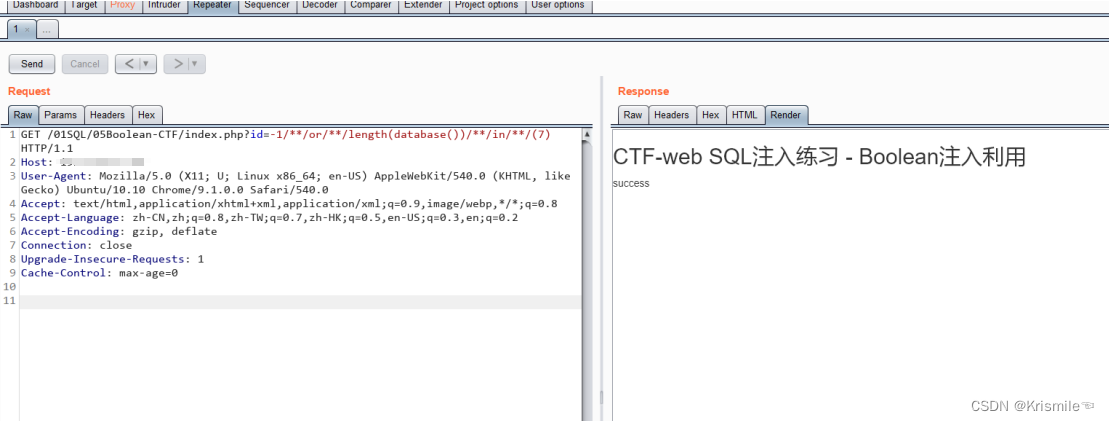
SQL注入利用 学习- 布尔盲注
布尔盲注适用场景: 1、WAF或者过滤函数完全过滤掉union关键字 2、页面中不再回显具体数据,但是在SQL语句执行成功或失败返回不同的内容 代码分析:过滤关键字 union if(preg_match(/union/i, $id)) { echo "fail"; exit; } 代码…...

前端项目部署教程——有域名有证书
一、拉取nginx镜像 docker pull nginx //先拉取nginx镜像二、打包前端项目 1、将Vue打包项目传输到/usr/local/vue/下blog和admin文件夹下 重点: 每一个子域名都要申请证书,在阿里云每年可以免费申请20个证书, 免费证书申请教程在 免费证书申请教程 …...

《看漫画学C++》第12章 可大可小的“容器”——向量
在C编程的世界里,数组是一种基础且广泛使用的数据结构。然而,传统的静态数组在大小固定、管理不便等方面的局限性,常常让开发者感到束手束脚。幸运的是,C标准库中的vector类为我们提供了一种更加灵活、高效的动态数组解决方案。 …...

OpenAI推出GPTBot网络爬虫:提升AI模型同时引发道德法律争议
文章目录 一、GPTBot 简介二、功能特点三、技术细节3.1、用户代理标识3.2、数据采集规则3.3、数据使用目的3.4、网站屏蔽方法3.5、数据过滤 四、GPTBot 的道德和法律问题五、GPTBot 的使用方法和限制六、总结 一、GPTBot 简介 OpenAI 推出的网络爬虫GPTBot旨在通过从互联网上收…...

Claude使用教程
claude 3 opus面世后,网上盛传吊打了GPT-4。网上这几天也已经有了许多应用,但竟然还有很多小伙伴不知道国内怎么用gpt,也不知道怎么去用这个据说已经吊打了gpt-4的claude3。 今天我们想要进行的一项尝试就是—— 用claude3和gpt4,…...
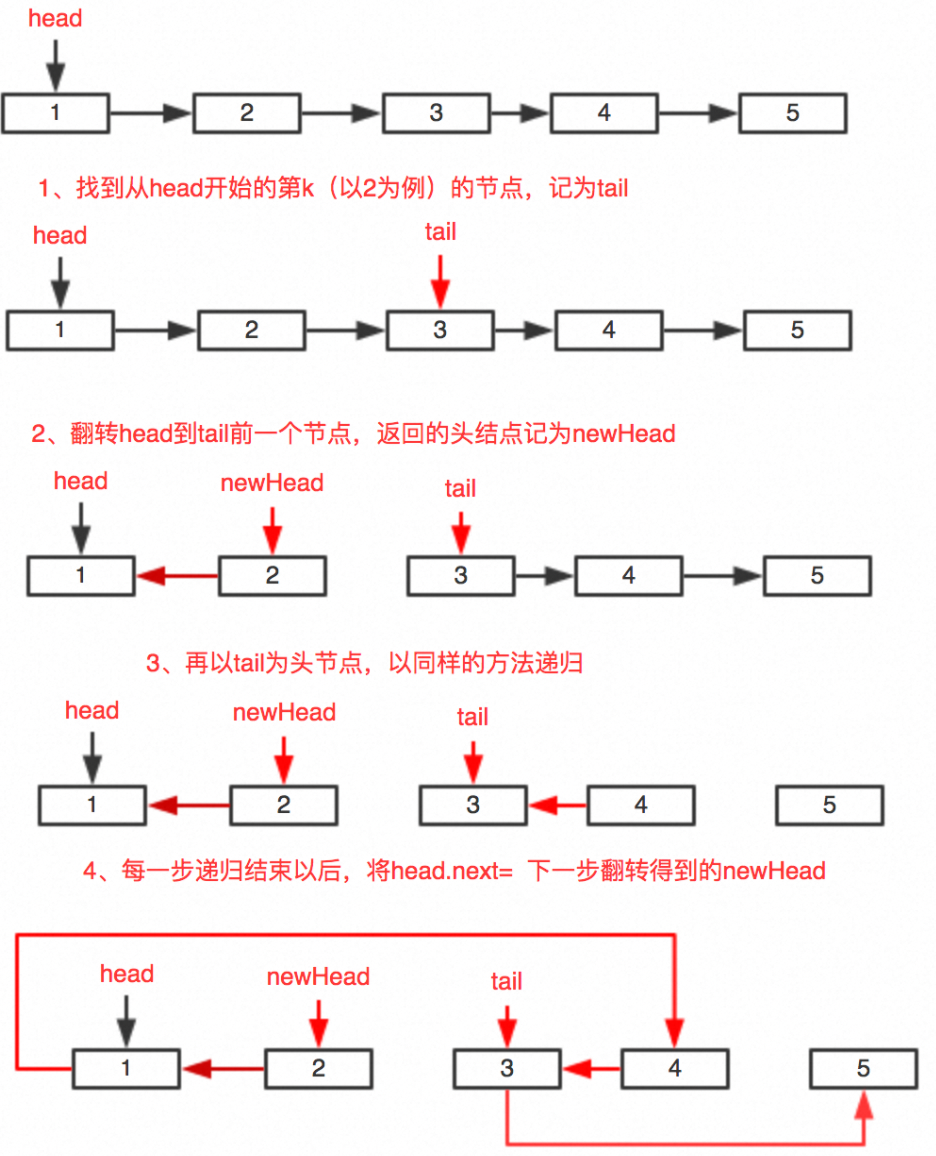
【经典算法】LeetCode25:K 个一组翻转链表(Java/C/Python3,Hard)
#算法 目录 题目描述思路及实现方式一:递归思路代码实现Java 版本C 语言版本Python3 版本 复杂度分析 方式二:迭代和原地反转思路代码实现Java 版本C 语言版本Python3 版本 复杂度分析 总结相似题目 标签:链表、递归 题目描述 给你链表的头…...
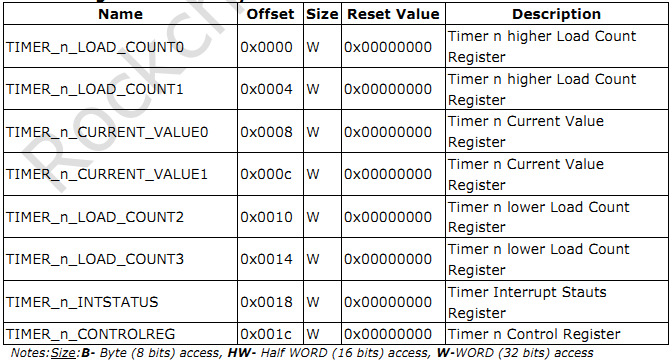
6.11物联网RK3399项目开发实录-驱动开发之定时器的使用(wulianjishu666)
嵌入式实战开发例程【珍贵收藏,开发必备】: 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1tkDBNH9R3iAaHOG1Zj9q1Q?pwdt41u 定时器使用 前言 RK3399有 12 个 Timers (timer0-timer11),有 12 个 Secure Timers(stimer0~stimer11) 和 2 个 …...
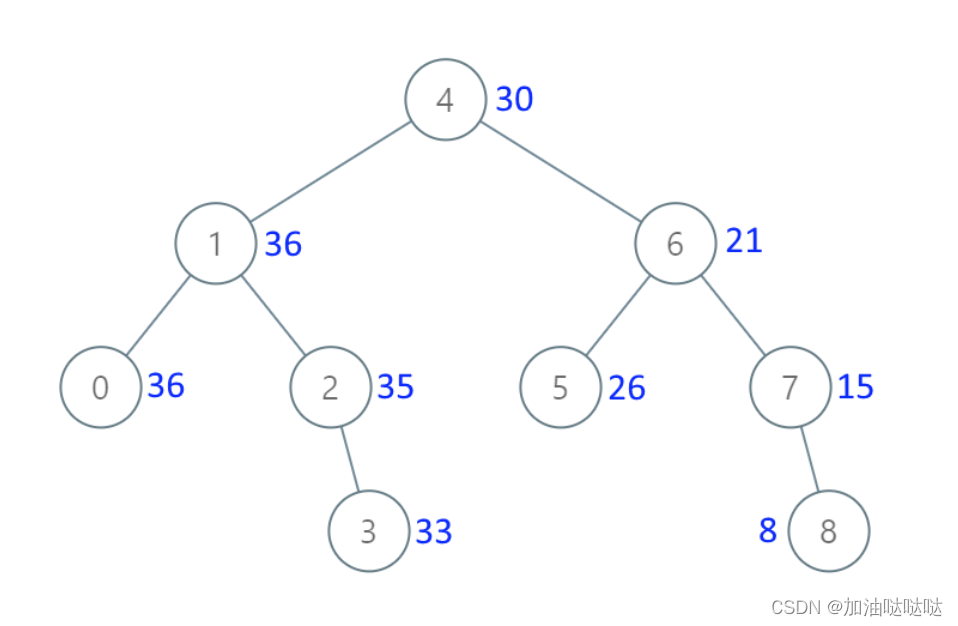
算法训练营第二十三天(二叉树完结)
算法训练营第二十三天(二叉树完结) 669. 修剪二叉搜索树 力扣题目链接(opens new window) 题目 给定一个二叉搜索树,同时给定最小边界L 和最大边界 R。通过修剪二叉搜索树,使得所有节点的值在[L, R]中 (R>L) 。你可能需要改…...
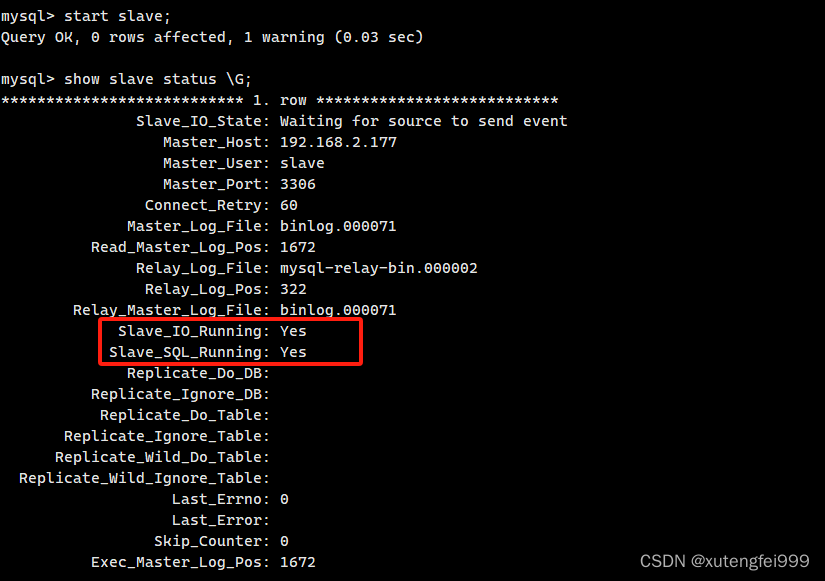
mysql主从复制Slave_SQL_Running: No
1、SHOW SLAVE STATUS \G; Slave_SQL_Running: No 解决方案: 重新同步主库和从库的数据 1、从库先停掉slave stop slave; 2、在主库查看此时的日志文件和位置 show master status; 3、在从库中执行 change master to master_host192.168.2.177,master_userslave…...
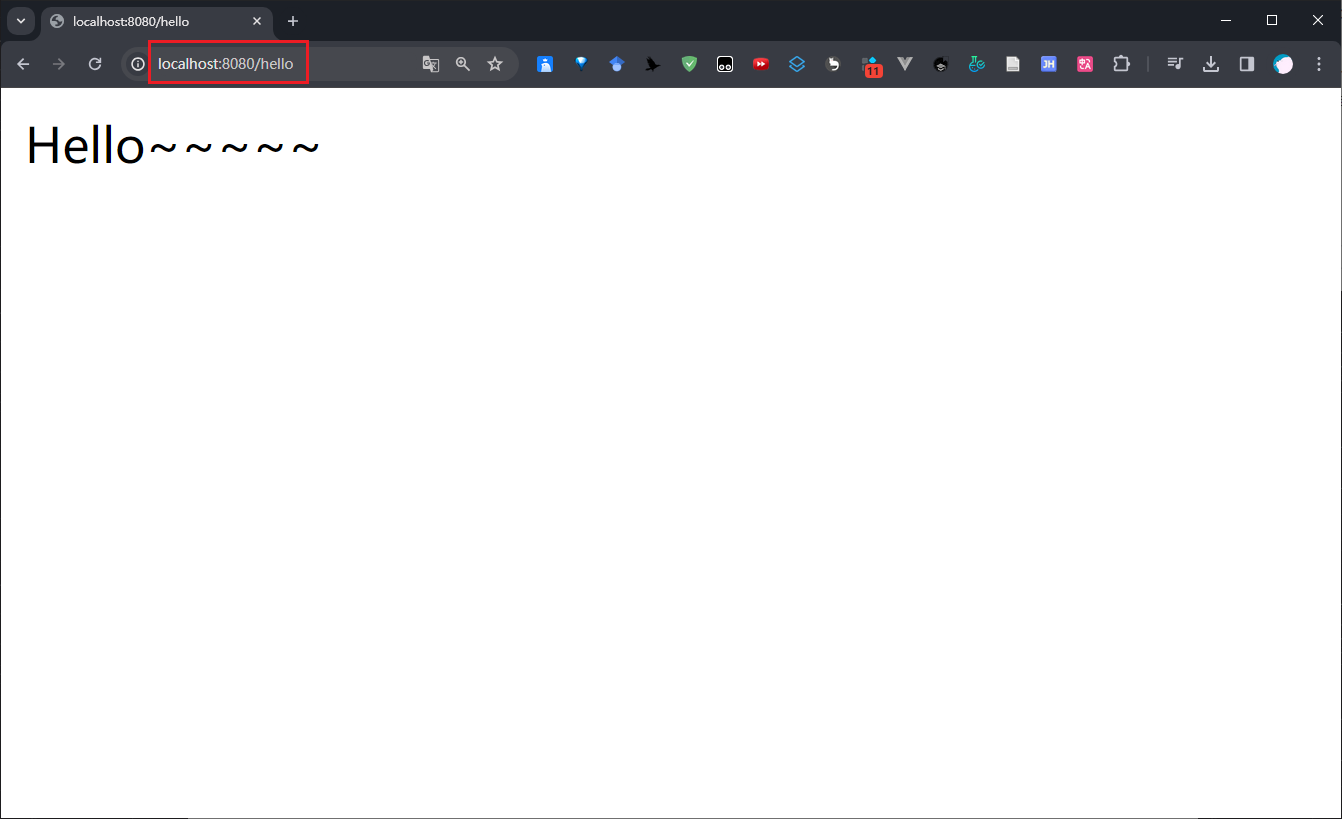
【SpringBoot】SpringBoot项目快速搭建
本文将介绍Springboot项目的快速搭建 快速创建SpringBoot项目 打开IDEA在File->New->Project中新建项目 点击左侧的Spring Initializr 输入以下信息: Name 项目名称Group 根据公司域名来,或者默认com.example【倒序域名】Package Name 包名&am…...

调用支付宝接口响应40004 SYSTEM_ERROR问题排查
在对接支付宝API的时候,遇到了一些问题,记录一下排查过程。 Body:{"datadigital_fincloud_generalsaas_face_certify_initialize_response":{"msg":"Business Failed","code":"40004","sub_msg…...
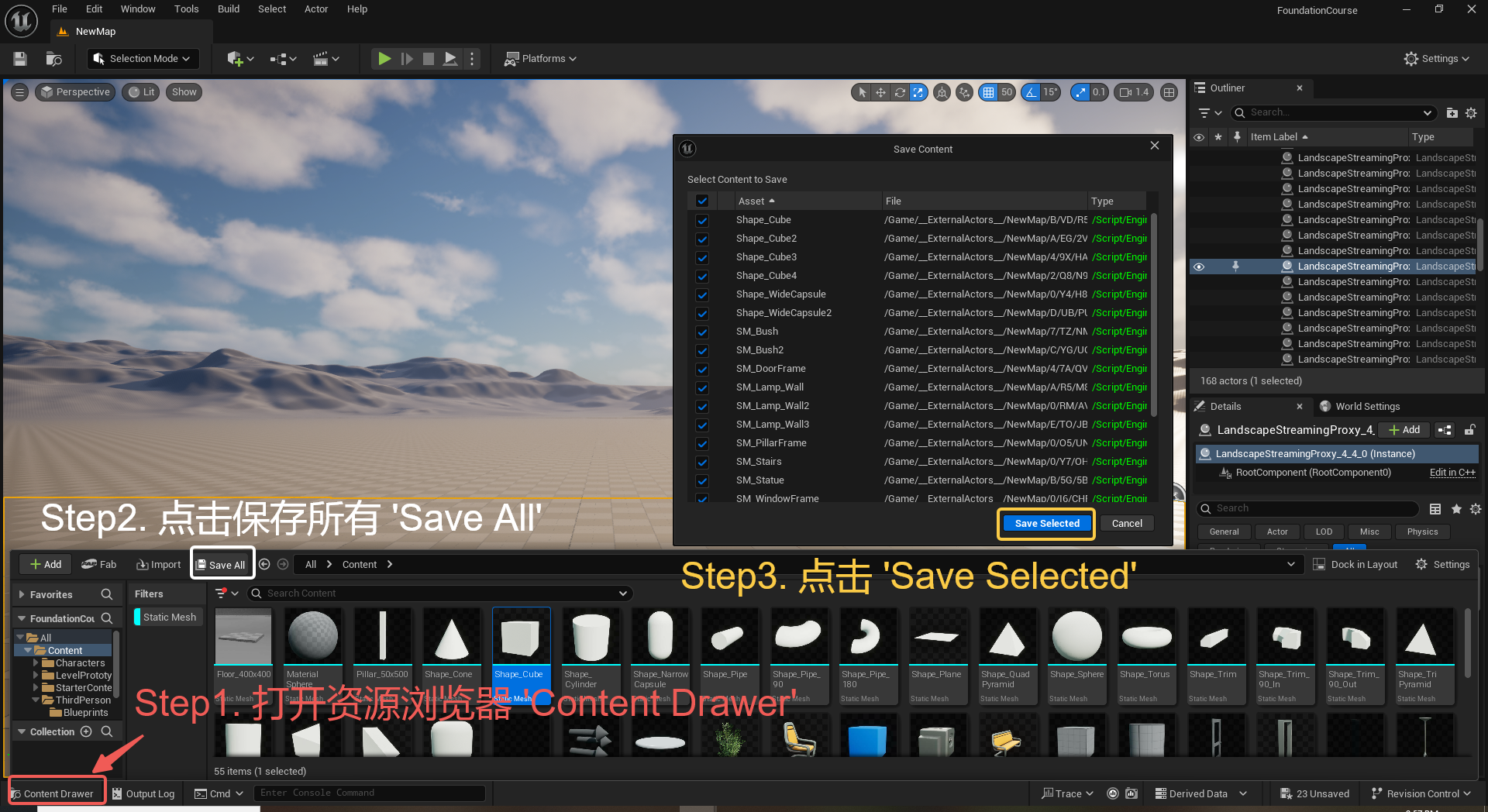
UE5 学习系列(三)创建和移动物体
这篇博客是该系列的第三篇,是在之前两篇博客的基础上展开,主要介绍如何在操作界面中创建和拖动物体,这篇博客跟随的视频链接如下: B 站视频:s03-创建和移动物体 如果你不打算开之前的博客并且对UE5 比较熟的话按照以…...

python报错No module named ‘tensorflow.keras‘
是由于不同版本的tensorflow下的keras所在的路径不同,结合所安装的tensorflow的目录结构修改from语句即可。 原语句: from tensorflow.keras.layers import Conv1D, MaxPooling1D, LSTM, Dense 修改后: from tensorflow.python.keras.lay…...
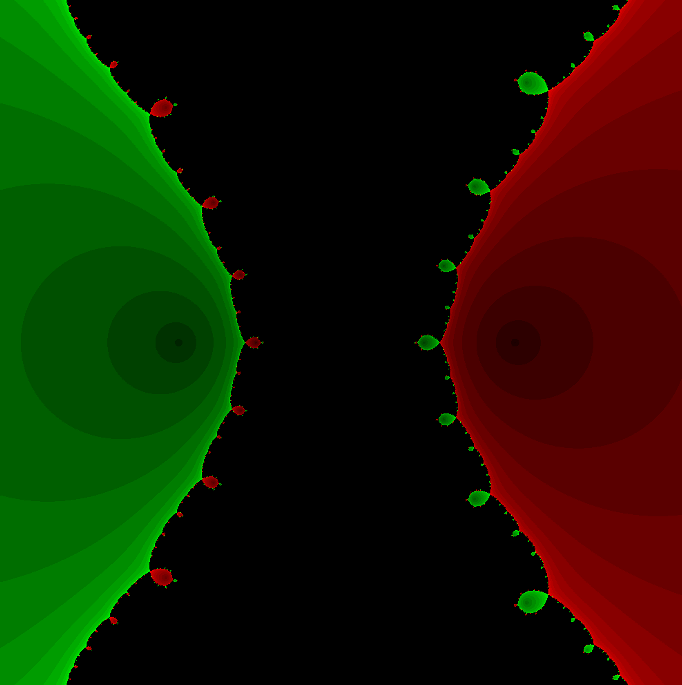
在Mathematica中实现Newton-Raphson迭代的收敛时间算法(一般三次多项式)
考察一般的三次多项式,以r为参数: p[z_, r_] : z^3 (r - 1) z - r; roots[r_] : z /. Solve[p[z, r] 0, z]; 此多项式的根为: 尽管看起来这个多项式是特殊的,其实一般的三次多项式都是可以通过线性变换化为这个形式…...

es6+和css3新增的特性有哪些
一:ECMAScript 新特性(ES6) ES6 (2015) - 革命性更新 1,记住的方法,从一个方法里面用到了哪些技术 1,let /const块级作用域声明2,**默认参数**:函数参数可以设置默认值。3&#x…...
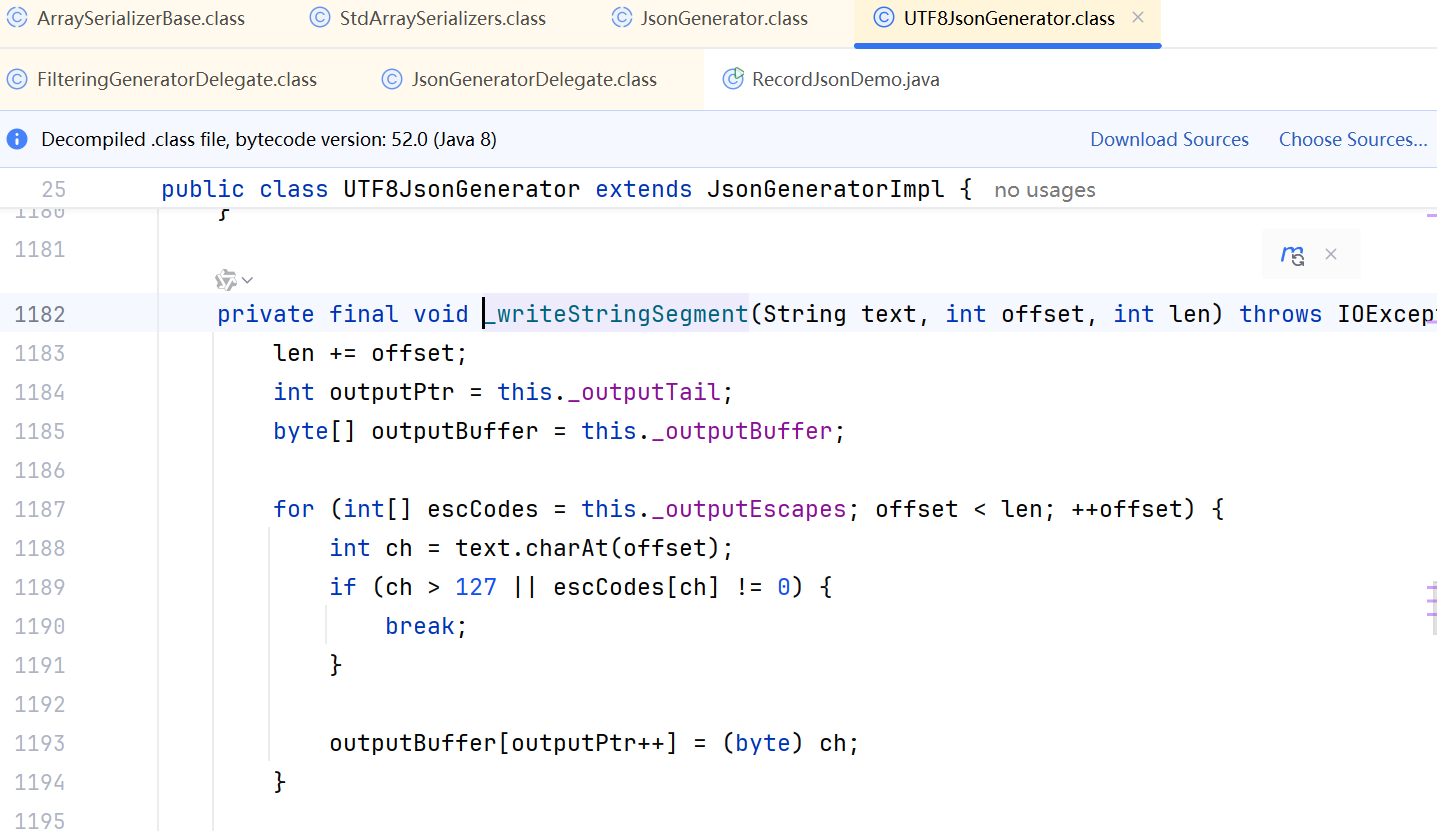
JDK 17 序列化是怎么回事
如何序列化?其实很简单,就是根据每个类型,用工厂类调用。逐个完成。 没什么漂亮的代码,只有有效、稳定的代码。 代码中调用toJson toJson 代码 mapper.writeValueAsString ObjectMapper DefaultSerializerProvider 一堆实…...
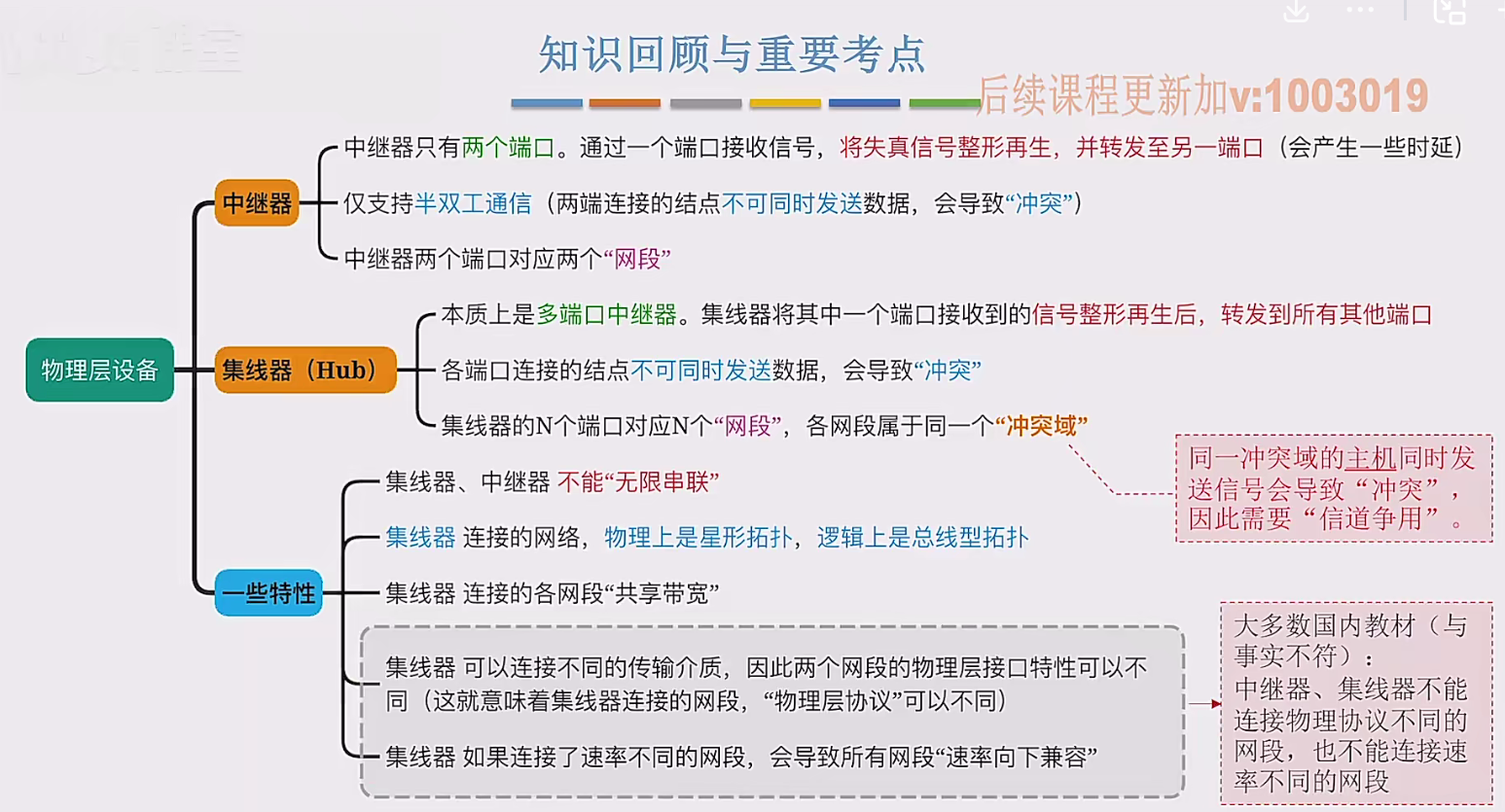
2.3 物理层设备
在这个视频中,我们要学习工作在物理层的两种网络设备,分别是中继器和集线器。首先来看中继器。在计算机网络中两个节点之间,需要通过物理传输媒体或者说物理传输介质进行连接。像同轴电缆、双绞线就是典型的传输介质,假设A节点要给…...

用神经网络读懂你的“心情”:揭秘情绪识别系统背后的AI魔法
用神经网络读懂你的“心情”:揭秘情绪识别系统背后的AI魔法 大家好,我是Echo_Wish。最近刷短视频、看直播,有没有发现,越来越多的应用都开始“懂你”了——它们能感知你的情绪,推荐更合适的内容,甚至帮客服识别用户情绪,提升服务体验。这背后,神经网络在悄悄发力,撑起…...

【java面试】微服务篇
【java面试】微服务篇 一、总体框架二、Springcloud(一)Springcloud五大组件(二)服务注册和发现1、Eureka2、Nacos (三)负载均衡1、Ribbon负载均衡流程2、Ribbon负载均衡策略3、自定义负载均衡策略4、总结 …...

深入理解 React 样式方案
React 的样式方案较多,在应用开发初期,开发者需要根据项目业务具体情况选择对应样式方案。React 样式方案主要有: 1. 内联样式 2. module css 3. css in js 4. tailwind css 这些方案中,均有各自的优势和缺点。 1. 方案优劣势 1. 内联样式: 简单直观,适合动态样式和…...
