数据结构严蔚敏版精简版-线性表以及c语言代码实现
线性表、栈、队列、串和数组都属于线性结构。线性结构的基本特点是除第一个元素无直接前驱,最后一个元素无直接后继之外,其他每个数据元素都有一个前驱和后继。
1 线性表的定义和特点
如此类由n(n大于等于0)个数据特性相同的元素构成的有限序列称为线性表。 线性表中元素的个数n定义为线性表的长度,n=0时称为空表。
对千非空的线性表或线性结构,其特点是:
(1)存在唯一的一个被称作“第一个"的数据元素;
(2)存在唯一的一个被称作“最后一个"的数据元素;
(3)除第一个之外,结构中的每个数据元素均只有一个前驱;
(4)除最后一个之外,结构中的每个数据元素均只有一个后继。
2 线性表的顺序存储表示
线性表的顺序表示指的是用一组地址连续的存储单元依次存储线性表的数据元素,这种表示 也称作线性表的顺序存储结构或顺序映像。通常,称这种存储结构的线性表为顺序表(Sequential List)。其特点是,逻辑上相邻的数据元素,其物理次序也是相邻的。
2.1顺序表的操作

代码实现:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#define LONG 8//最大容量
#define inc 3typedef int Elemtype;
typedef struct Seqlist{Elemtype *base;//基地址 int capacity;//最大容量 int size;//所含元素的多少
}Seqlist; bool INC(Seqlist *L){Elemtype *newbase=(Elemtype*)realloc(L->base,sizeof(Elemtype)*(L->capacity+inc));if(newbase==NULL){printf("满了,不能开辟空间");return false;}L->base=newbase;L->capacity+=inc;return true;}
void InitSeqlist(Seqlist *L)//初始化
{L->base=(Elemtype*)malloc(sizeof(Elemtype)*LONG);assert(L->base !=NULL);L->size=0;L->capacity=LONG;}
void Push_back(Seqlist *L,Elemtype x)//尾插
{if(L->size>=L->capacity&&!INC(L)){printf("满了");return;}L->base[L->size]=x;L->size++;
}
void show_list(Seqlist *L)//展示
{for(int i ;i< L->size;i++){printf("%d ",L->base[i]);}printf("\n");
}
void Push_front(Seqlist *L,Elemtype x)//头插
{if(L->size>=L->capacity&&!INC(L)){printf("满了,不能头插");return;}for(int i=L->size;i>0;i--){L->base[i]=L->base[i-1];}L->base[0]=x;L->size++;
}
void pop_back(Seqlist *L)//尾部删除
{if(L->size==0){printf("空表不能尾部删除"); }L->size--;} void pop_front(Seqlist *L)//头部删除 {if(L->size==0){printf("空表不能头部删除"); }for(int i=1;i<L->size;i++) {L->base[i-1]=L->base[i];}L->size--;}
void insert_pos(Seqlist *L,int pos,Elemtype itim)
{if(L->size>=L->capacity){printf("满了,不能按位置插");return;}if(pos<0 || pos>L->size ){printf("位置不和合法"); }for(int i=L->size;i>pos;i--) {L->base[i]=L->base[i-1];}L->base[pos]=itim;L->size++;
}
int find(Seqlist *L,Elemtype x)
{if(L->size==0){printf("空表");return -1;}for(int i=0;i<L->size;i++){if(L->base[i]==x)return i;}return -1;
}
int length(Seqlist *L)
{printf("长度为%d,容量为%d",L->size,L->capacity);return L->size;
}
void delete_pos(Seqlist *L,int pos)
{if(pos<0||pos>L->size){printf("位置非法");return;}for(int i=pos;i<L->size;i++){L->base[i]=L->base[i+1];}L->size--;
}
void delete_val(Seqlist *L,int x)
{int pos=find(L,x);if(pos==-1){printf("数据不存在");return;}delete_pos(L,pos);
}void sort(Seqlist *L)
{for(int i=0;i<L->size-1;i++){for(int j=0;j<L->size-i-1;j++){if(L->base[j]>L->base[j+1]){Elemtype tmp=L->base[j];L->base[j]=L->base[j+1];L->base[j+1]=tmp; }}}
}void resver(Seqlist *L)
{int head=0;int rear=L->size-1;while(1){int tmp=L->base[head];L->base[head]=L->base[rear];L->base[rear]=tmp;head++;rear--;if(head>rear)break;}}void clear(Seqlist *L)
{L->size=0;
}void destory(Seqlist *L)
{free(L->base);L->size=NULL;L->capacity=0;L->size=0;}int main1()
{ Seqlist L;InitSeqlist(&L);int setlect=1while(select){printf("************************************\n");printf("* [1]push_back [2]push_front *\n");printf("* [3]show_list [4]pop_back *\n");printf("* [5]pop_front [6]insert_pos *\n");printf("* [7]find [8]length *\n");printf("* [9]delete_pos [10]delete_va *\n");printf("* [11]sort [12]resver *\n");printf("* [13]clear [14]destroy [0]quit_system *\n");printf("************************************\n");printf("请选择"); scanf("%d",&select); if(select==0)break;switch(select){case 1:printf("输入插的数据-1结束");while(scanf("%d",&itim),itim !=-1){Push_back(&L,itim);}break;case 2:printf("请输入数据头插");scanf("%d",&itim);Push_front(&L,itim);break;case 3:show_list(&L); break;case 4:pop_back(&L);break;case 5:pop_front(&L);break;case 6:printf("请输入插入数据");scanf("%d",&itim) ;printf("请输入位置");scanf("%d",&pos);insert_pos(&L,pos,itim);break;case 7:printf("输入查找数据");scanf("%d",&itim);pos=find(&L,itim);if(pos>=0) printf("查找成功%d的位置在%d\n",itim,pos);else printf("查找%d失败,没有找到\n",itim) ;break;case 8:printf("表的长度为%d\n",length(&L));break;case 9:printf("请输入要删除的位置:");scanf("%d",&pos);delete_pos(&L,pos);break; case 10:printf("请输入要删除的数据:");scanf("%d",&itim);delete_val(&L,itim);break;case 11:sort(&L);break;case 12:resver(&L);break;case 13:clear(&L);break;case 14:destory(&L);break;} }destory(&L);
}2.2顺序表的优缺点
顺序表可以随机存取表中任一元素,其存储位置可用一个简单、直观的公式来表示。然而, 从另一方面来看,这个特点也造成了这种存储结构的缺点:在做插入或删除操作时,需移动大量元素。另外由千数组有长度相对固定的静态特性,当表中数据元素个数较多且变化较大时, 操作过程相对复杂,必然导致存储空间的浪费。所有这些问题,都可以通过线性表的另一种表 示方法�式存储结构来解决。
3 线性表的链式表示
用单链表表示线性表时,数据元素之间的逻辑关系是由结点中的指针指示的。换句话说,指 针为数据元素之间的逻辑关系的映像,则逻辑上相邻的两个数据元素其存储的物理位置不要求紧 邻,由此,这种存储结构为非顺序映像或链式映像。
链表增加头结点的作用:
(1)便于首元结点的处理增加了头结点后,首元结点的地址保存在头结点(即其“前驱”结点)的指针域中,则对链表 的第一个数据元素的操作与其他数据元素相同,无需进行特殊处理。
(2)便于空表和非空表的统一处理 当链表不设头结点时,假设L为单链表的头指针,它应该指向首元结点,则当单链表为长度 n为0的空表时,L指针为空。
3.1单链表的操作
包含链表的头插头删,尾差尾删,逆置,排序等操作。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#include<assert.h>
#define Elemtype int
typedef struct Node
{Elemtype data;struct Node *next;
}Node,*PNode;typedef struct List
{PNode first;//头指针 PNode last;//尾指针 size_t size;
}List;
void Initlist(List *L)//初始化
{L->first=L->last=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));L->first->next=NULL; L->last->next=NULL; L->size=0;
}
void push_back(List *L,Elemtype x)//尾插
{Node *s=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));assert(s!=NULL);s->data=x;s->next=NULL;L->last->next=s;L->last=s;L->size++;
}
void push_front(List *L,Elemtype x)//头插
{Node *s=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));assert(s!=NULL);s->data=x;s->next=L->first->next;L->first->next=s;if(L->size==0){L->last=s;}L->size++;
}
void show_list(List *L)//打印链表
{if(L->size==0){printf("为空表");return; }Node *p=L->first->next;while(p!=NULL){printf("%d-->",p->data);p=p->next;}printf("NULL\n");
}void pop_back(List *L)//尾删
{if(L->size==0){printf("空表");return;}Node *p=L->first;while(p->next !=L->last)p=p->next;free(p->next);L->last=p;L->size--;p->next=NULL;//或L->last->next=NULL; }
void pop_front(List *L)//头删
{if(L->size==0){printf("空表");return;}Node *p=L->first->next;L->first->next=p->next;free(p);L->size--; if(L->size==1){L->last=L->first;}}
void insert_val(List *L,Elemtype x)//在排序的链表中插入数据,并使其不变
{ Node *s=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));s->data=x;s->next=NULL;Node *p=L->first;while(p->next!=NULL && p->next->data<x){p=p->next;}/*printf("%d",p->data);*/if(p->next==NULL){printf("到头了");printf("%d",p->next) ;L->last=s;}s->next=p->next;p->next=s;L->size++;
}
Node* find(List *L,Elemtype key)//查找节点
{Node *p=L->first->next;while(p!=NULL&&p->data!=key){p=p->next;}return p;
}
int length(List *L)
{return L->size;
}void delete_val(List *L,Elemtype x)//删除指定元素
{
Node *p=find(L,x);if(L->size==0)return;else if(p==NULL){printf("不存在");return;}else if(p==L->last){ pop_back(L);}else{Node *q=p->next;p->data=q->data;p->next=q->next;free(q);L->size--;}}
void sort(List *L)//链表排序
{if(L->size==0||L->size==1){return ;}Node *s=L->first->next;Node *q=s->next;L->last=s;L->last->next=NULL;while(q!=NULL)//q为第二段 {int data;data=q->data;printf("%d",data); insert_val(L,data);q=q->next;}
}
void resver(List *L)//链表逆置
{if(L->size==1||L->size==0)return;Node *s=L->first;Node *q=s->next;L->last=s;L->last->next=NULL;while(q!=NULL)//q为第二段 {int data;data=q->data;//printf("%d",data); push_front(L,data);q=q->next;}
}
void clear(List *L)//清空
{if(L->size==0)return;Node *p=L->first->next;Node *s=p->next;while(p!=NULL){L->first->next=p->next;free(p);p=L->first->next;}L->last=L->first;L->size=0;
}void destory(List *L)//销毁
{clear(L);free(L->first);L->first=L->last=NULL;}
int main()
{List L;Elemtype itim;int pos;Initlist(&L);int select=1;while(select){printf("************************************\n");printf("* [1]push_back [2]push_front *\n");printf("* [3]show_list [4]pop_back *\n");printf("* [5]pop_front [6]insert_val *\n");printf("* [7]find [8]length *\n");printf("* [9]delete_val [10]sort *\n");printf("* [11]resver [12]clear *\n");printf("* [13]destroy [0]quit_system *\n");printf("************************************\n");printf("请选择");scanf("%d",&select);if(select==0)break;switch(select){case 1:printf("请输入要出入的数据(-1结束)");while(scanf("%d",&itim),itim!=-1){push_back(&L,itim);}break;case 2:printf("请输入数据头插(-1结束)");while(scanf("%d",&itim),itim!=-1){push_front(&L,itim);}break;case 3:show_list(&L);break;case 4:pop_back(&L);break;case 5:pop_front(&L);break;case 6:printf("请输入数据:");scanf("%d",&itim);insert_val(&L,itim);break;case 7:printf("请输入要查找的数据:");scanf("%d",&itim);if(find(&L,itim)==NULL){printf("不存在"); } else{printf("存在");}break;case 8:printf("大小为%d",length(&L));break;case 9:printf("请输入要删除的数据:");scanf("%d",&itim);delete_val(&L,itim);break;case 10:sort(&L); break;case 11:resver(&L);break; case 12:clear(&L);break;//case 13:// // break;default:printf("数据不合法");break; }} destory(&L);
} 3.2单循环链表的操作与实现
包含单循环链表的头插头删,尾差尾删,逆置,排序等操作。
#define Elemtype int
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
typedef struct Node
{Elemtype data;struct Node *next;
}Node,*PNode;typedef struct List
{PNode first;PNode last;int size;} List;void initlist(List *L)//初始化 {Node *s=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));L->first=L->last=s;L->last->next=L->first;L->size=0;}Node *_buynode(Elemtype x)//创建节点 {Node *s=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));s->data=x;s->next=NULL;return s;}void show_list(List *L)//打印链表 {Node *p=L->first->next;while(p!=L->first){printf("%d-->",p->data);p=p->next;}}void push_back(List *L,Elemtype x)//尾插 {Node *s=_buynode(x);L->last->next=s;L->last=s;L->last->next=L->first;L->size++; }void push_front(List *L,Elemtype x)//头插 {Node *s=_buynode(x);s->next=L->first->next;L->first->next=s;if(L->size==0){L->last=s;}L->size++;}void pop_front(List *L)//头删 {if(L->size==0)return;Node *s=L->first->next;Node *p=s->next;L->first->next=p;free(s);if(L->size==1){L->last=L->first;}L->size--;}void pop_back(List *L)//尾删 {if(L->size==0){return;}Node *p=L->first;while(p->next!=L->last){p=p->next;}free(p->next);p->next=L->first;L->last=p;L->size--;}
void insert_val(List *L,Elemtype x)//插入表,使其保持顺序不变
{Node *p=L->first;while(p->next!=L->last&&p->next->data<x){p=p->next;}if(p->next->next==L->first&&p->next->data<x)//p->next==L->last; 因为L->last->next=L->first; {push_back(L,x);}else{ Node *s=_buynode(x);s->next=p->next;p->next=s;L->size++;}
}
Node* find(List *L,Elemtype x)//查找
{if(L->size==0)return NULL;Node *p=L->first->next;while(p!=L->first&&p->data!=x){p=p->next;}if(p==L->first){return NULL;}return p;} int length(List *L){return L->size;} void delete_val(List *L,Elemtype x)//指定值删除 {if(L->size==0)return;Node *p=find(L,x);if(p==NULL){printf("不存在");return;} if(p==L->last){pop_back(L);}else{Node *s=p->next;p->data=s->data;p->next=s->next;free(s);L->size--;}}void sort(List *L)//排序
{ if(L->size==0||L->size==1)return;Node *p=L->first->next;Node *s=p->next;//第二段 L->last->next=NULL;L->last=p;L->last->next=L->first;while(s!=NULL){ Node *z=s->next;;int x=s->data;// printf("%d",x); insert_val(L,x);L->size--;free(s); s=z;}}
void resver(List *L)//逆置
{if(L->size==0||L->size==1)return;Node *p=L->first->next;Node *s=p->next;//第二段 L->last->next=NULL;L->last=p;L->last->next=L->first;while(s!=NULL){ Node *z=s->next;;int x=s->data;// printf("%d",x); push_front(L,x);free(s);L->size--;s=z;}
}
void clear(List *L)//清空
{Node *p=L->first->next;while(p!=L->first){L->first->next=p->next;free(p);p=L->first->next;}L->size=0;L->last=L->first;L->last->next=L->first;
}
void destory(List *L)//销毁
{clear(L);free(L->first);free(L->last);L->first=L->last=NULL;
}
int main()
{List L;Elemtype itim;int pos;initlist(&L);int select=1;while(select){printf("************************************\n");printf("* [1]push_back [2]push_front *\n");printf("* [3]show_list [4]pop_back *\n");printf("* [5]pop_front [6]insert_val *\n");printf("* [7]find [8]length *\n");printf("* [9]delete_val [10]sort *\n");printf("* [11]resver [12]clear *\n");printf("* [13]destroy [0]quit_system *\n");printf("************************************\n");printf("请选择");scanf("%d",&select);if(select==0)break;switch(select){case 1:printf("请输入要出入的数据(-1结束)");while(scanf("%d",&itim),itim!=-1){push_back(&L,itim);}break;case 2:printf("请输入数据头插(-1结束)");while(scanf("%d",&itim),itim!=-1){push_front(&L,itim);}break;case 3:show_list(&L);break;case 4:pop_back(&L);break;case 5:pop_front(&L);break;case 6:printf("请输入数据:");scanf("%d",&itim);insert_val(&L,itim);break;case 7:printf("请输入要查找的数据:");scanf("%d",&itim);if(find(&L,itim)==NULL){printf("不存在"); } else{printf("存在");}break;case 8:printf("大小为%d",length(&L));break;case 9:printf("请输入要删除的数据:");scanf("%d",&itim);delete_val(&L,itim);break;case 10:sort(&L); break;case 11:resver(&L);break; case 12:clear(&L);break;//case 13:// // break;*/default:printf("数据不合法");break; }} destory(&L);
} 3.3双循环链表的实现
包含双循环链表的头插头删,尾差尾删,逆置,排序等操作。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#include<assert.h>
#define Elemtype int
typedef struct Node{Elemtype data;struct Node *next;struct Node *prio;
}Node;typedef struct List{Node *first;//前驱 Node *last;//后继 int size;
}List;Node* _buynode(Elemtype x)//创建节点
{Node *p=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));p->data=x;p->next=p->prio=NULL;return p;
}
void InitList(List *L)//初始化
{Node *s=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));L->first=s;L->first->next=NULL;L->last=s;L->first->prio=L->last;L->last->next=L->first;
}
void show_list(List *L)//打印链表
{ if(L->size==0){printf("空表");return;}Node *p=L->first->next;while(p!=L->first){printf("%d-->",p->data);p=p->next;}
}void push_back(List *L,Elemtype x)//尾插
{Node *p=_buynode(x);p->next=L->last->next;p->next->prio=p;p->prio=L->last;L->last->next=p;L->last=p;L->size++;
}
void push_front(List *L,Elemtype x)//头插
{Node *p=_buynode(x);p->next=L->first->next;p->next->prio=p;L->first->next=p;p->prio=L->first; if(L->size==0){L->last=p;p->next=L->first;L->first->prio=L->last;}L->size++;
}void pop_back(List *L)//尾删
{if(L->size==0){return;}Node *p=L->last;L->last=p->prio;p->next->prio=p->prio;p->prio->next=p->next;free(p);L->size--;
}
void pop_front(List *L)//头删
{if(L->size==0)return;Node *p=L->first->next;p->next->prio=p->prio;p->prio->next=p->next;free(p);if(L->size==1){L->last=L->first;}L->size--;
}void insert_val(List *L,Elemtype x )//有序的链表,插入x后保持有序
{Node *p=L->first;while(p->next!=L->first&&p->next->data<x)p=p->next;if(p->next==L->first){push_back(L,x);} else{Node *s=_buynode(x);s->next=p->next;s->next->prio=s;s->prio=p;p->next=s;L->size++;}}Node* find(List *L,Elemtype x)//查找
{Node *p=L->first->next;while(p->next!=L->first&&p->data!=x){p=p->next;}if(p->next==L->first&&p->data!=x)return NULL;return p;
}int length(List *L)
{return L->size;
}void delete_val(List *L,Elemtype x)//删除指定值
{Node *p=find(L,x);if(p==NULL){return;}else{p->prio->next=p->next;p->next->prio=p->prio;free(p);}L->size--;} void sort(List *L)//排序 {if(L->size==0||L->size==1){return;}Node *s=L->first->next;Node *q=s->next;L->last->next=NULL;L->last=s;L->last->next=L->first;L->first->prio=L->last;while(q!=NULL){s=q;q=q->next;Node *p=L->first->next;while(p->next!=L->last&&p->next->data<s->data)p=p->next;if(p->next==L->last&&p->next->data<s->data){s->next=L->last->next;s->next->prio=s;s->prio=L->last;L->last->next=s;L->last=s;} else{s->next=p->next;s->next->prio=s;s->prio=p;p->next=s;}}}void resver(List *L)//逆置 {if(L->size==0||L->size==1){return;}Node *s=L->first->next;Node *q=s->next;L->last->next=NULL;L->last=s;L->last->next=L->first;L->first->prio=L->last;while(q!=NULL){s=q;q=q->next;s->next=L->first->next;s->next->prio=s;L->first->next=s;s->prio=L->first;}}
void clear(List *L)//清空
{ if(L->size==0)return;Node *p=L->first->next;while(p!=L->first){p->next->prio=L->first;L->first->next=p->next;free(p);p=L->first->next;L->size--;
}
L->last=L->first ;
}
void destory(List *L)
{clear(L);free(L->first);L->first=L->last=NULL;
}
int main()
{List L;Elemtype itim;int pos;InitList(&L);int select=1;while(select){printf("************************************\n");printf("* [1]push_back [2]push_front *\n");printf("* [3]show_list [4]pop_back *\n");printf("* [5]pop_front [6]insert_val *\n");printf("* [7]find [8]length *\n");printf("* [9]delete_val [10]sort *\n");printf("* [11]resver [12]clear *\n");printf("* [13]destroy [0]quit_system *\n");printf("************************************\n");printf("请选择");scanf("%d",&select);if(select==0)break;switch(select){case 1:printf("请输入要出入的数据(-1结束)");while(scanf("%d",&itim),itim!=-1){push_back(&L,itim);}break;case 2:printf("请输入数据头插(-1结束)");while(scanf("%d",&itim),itim!=-1){push_front(&L,itim);}break;case 3:show_list(&L);break;case 4:pop_back(&L);break;case 5:pop_front(&L);break;case 6:printf("请输入数据:");scanf("%d",&itim);insert_val(&L,itim);break;case 7:printf("请输入要查找的数据:");scanf("%d",&itim);if(find(&L,itim)==NULL){printf("不存在"); } else{printf("存在");}break;case 8:printf("大小为%d",length(&L));break;case 9:printf("请输入要删除的数据:");scanf("%d",&itim);delete_val(&L,itim);break;case 10:sort(&L); break;case 11:resver(&L);break; case 12:clear(&L);break;/*case 13:destory(&L);break;*/default:printf("数据不合法");break; }} //destory(&L);
} 4 顺序表和链表的比较
4.1空问性能的比较
(1)存储空间的分配 顺序表的存储空间必须预先分配,元素个数扩充受一定限制,易造成存储空间浪费或空间溢出现象;而链表不需要为其预先分配空间,只要内存空间允许,链表中的元素个数就没有限制。 基于此,当线性表的长度变化较大,难以预估存储规模时,宜采用链表作为存储结构。
(2)存储密度的大小 链表的每个结点除了设置数据域用来存储数据元素外,还要额外设置指针域,用来存储指示 元素之间逻辑关系的指针,从存储密度上来讲,这是不经济的。所谓存储密度是指数据元素本身 所占用的存储量和整个结点结构所占用的存储量之比,

存储密度越大,存储空间的利用率就越高。显然,顺序表的存储密度为1,而链表的存储密度小于1。
4.2 时间性能的比较
(l)存取元素的效率 顺序表是由数组实现的,它是一种随机存取结构,指定任意一个位置序号都可以在0(1) 时间内直接存取该位置上的元素,即取值操作的效率高;而链表是一种顺序存取结构,按位置访问链表中元素时,只能从表头开始依次向后遍历链表,直到找到第i个位置上的元素,时间复杂度为O(n), 即取值操作的效率低。
(2)插入和删除操作的效率对比
链表在确定插入或删除的位置后,插入或删除操作无需移动数据,只需要修改指针, 时间复杂度为0(1)。顺序表进行插入或删除时,平均要移动表中近一半的结点,时间复杂度为O(n)。
相关文章:

数据结构严蔚敏版精简版-线性表以及c语言代码实现
线性表、栈、队列、串和数组都属于线性结构。线性结构的基本特点是除第一个元素无直接前驱,最后一个元素无直接后继之外,其他每个数据元素都有一个前驱和后继。 1 线性表的定义和特点 如此类由n(n大于等于0)个数据特性相同的元素…...
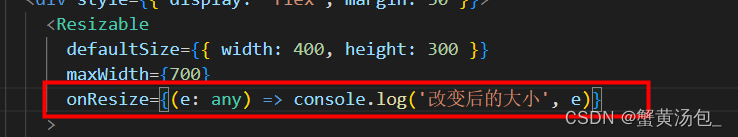
【react】react项目支持鼠标拖拽的边框改变元素宽度的组件
目录 安装使用方法示例Props 属性方法示例代码调整兄弟div的宽度 re-resizable github地址 安装 $ npm install --save re-resizable这将安装re-resizable库并将其保存为项目的依赖项。 使用方法 re-resizable 提供了一个 <Resizable> 组件,它可以包裹任何…...
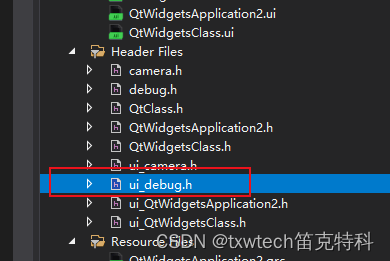
QT 创建文件 Ui 不允许使用不完整类型,可以尝试添加一下任何头文件
#include "debug.h" #include "qmessagebox.h" #pragma execution_character_set("utf-8") //QT 创建文件 Ui 不允许使用不完整类型,尝试添加一下任何头文件,或者添加ui_xx.h头文件 debug::debug(QWidget *parent) : QDialog(p…...

Python:深入探索其生态系统与应用领域
Python:深入探索其生态系统与应用领域 Python,作为一种广泛应用的编程语言,其生态系统之丰富、应用领域之广泛,常常令人叹为观止。那么,Python究竟涉及哪些系统?本文将从四个方面、五个方面、六个方面和七…...
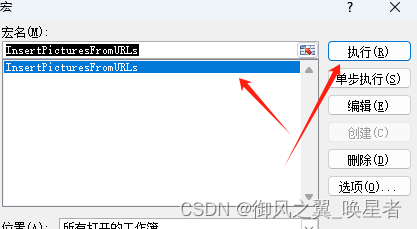
EXCEL从图片链接获取图片
step1: 选中图片地址列 step2:开发工具→Visual Basic 文件→导入 导入我制作的脚本(代码见文章末尾) 点击excel的小图标回到表格界面。 点击【宏】 选中刚才导入的脚本,点执行,等待完成。 代码本体: Sub InsertPict…...
)
Docker迁移默认存储目录(GPT-4o)
Docker在Ubuntu的默认存储目录是/var/lib/docker,要将 Docker 的默认存储目录迁移到指定目录(譬如大存储磁盘),可以通过修改 Docker 守护进程的配置文件来实现。 1.创建新的存储目录: 选择你想要存储 Docker 分层存储…...
植物大战僵尸杂交版2.0.88最新版安装包
游戏简介 游戏中独特的杂交植物更是为游戏增添了不少亮点。这些杂交植物不仅外观独特,而且拥有更强大的能力,能够帮助玩家更好地应对游戏中的挑战。玩家可以通过一定的条件和方式,解锁并培养这些杂交植物,从而不断提升自己的战斗…...
)
MQ基础(RabbitMQ)
通信 同步通信:就相当于打电话,双方交互是实时的。同一时刻,只能与一人交互。 异步通信:就相当于发短信,双方交互不是实时的。不需要立刻回应对方,可以多线程操作,跟不同人同时聊天。 RabbitM…...
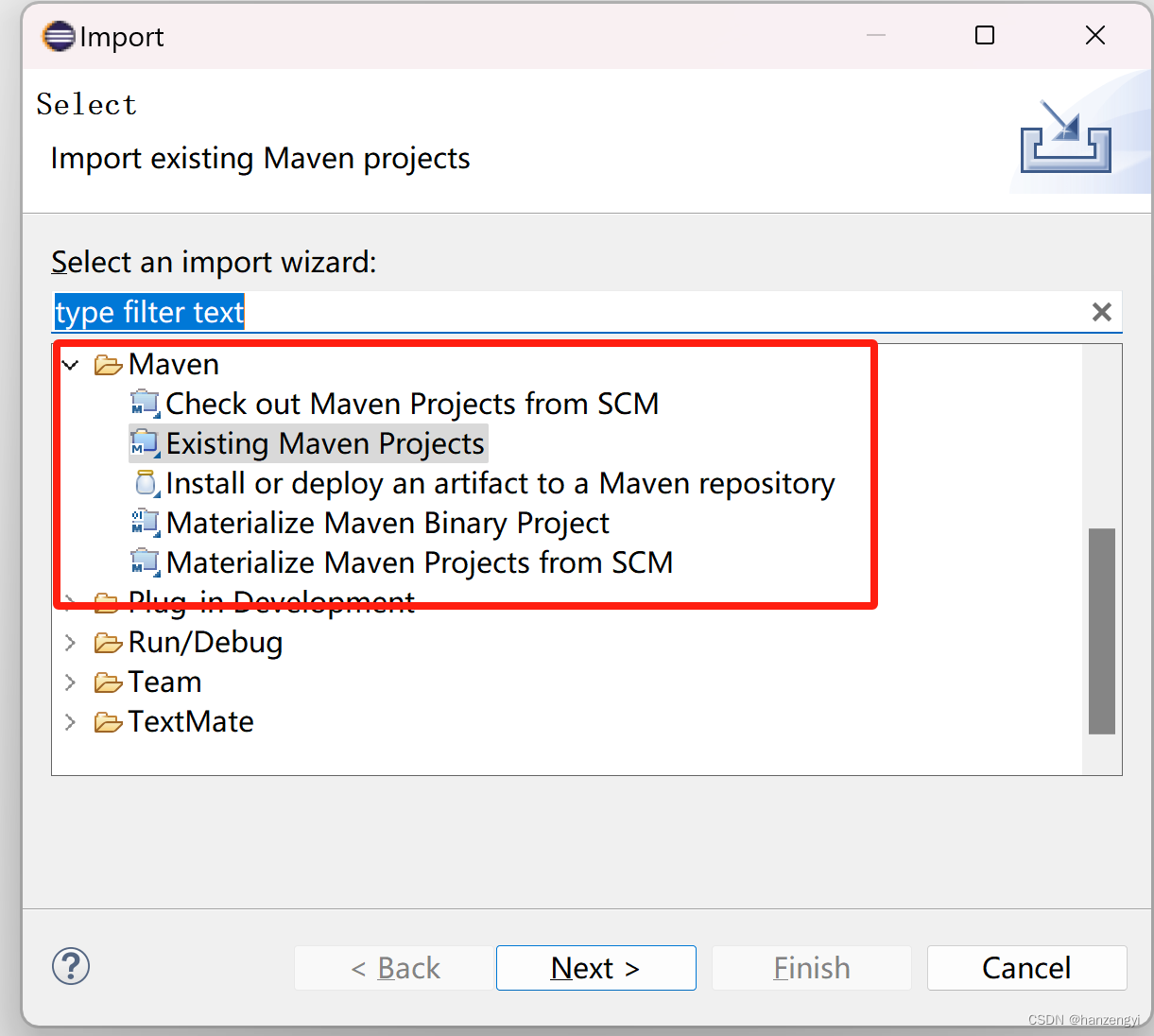
eclipse添加maven插件
打开eclipse菜单 Help/Install New SoftwareWork with下拉菜单选择 2022-03 - https://download.eclipse.org/releases/2022-03‘type filter text’搜索框中输入 maven选择 M2E - Maven Integration for Eclipse一路next安装,重启eclipseImport项目时,就…...

知识库系统:从认识到搭建
在这个信息过载的时代,企业越来越需要一个集中的知识库系统来促进员工协作和解决问题。本文跟着LookLook同学一起来探讨搭建高效知识库系统的所有注意事项和知识库系统的最佳推荐。 | 什么是知识库系统 知识库系统是一种软件或工具,旨在填补组织内的知识…...

JVM双亲委派模型
在之前的JVM类加载器篇中说过,各个类加载器都有自己加载的范围,比如引导类加载器只加载Java核心库中的class如String,那如果用户自己建一个包名和类名与String相同的类,会不会被引导类加载器加载。可以通过如下代码测试࿰…...

Python语言与算法:深度探索与实战应用
Python语言与算法:深度探索与实战应用 在数字化浪潮汹涌的时代,Python语言以其简洁、易读和强大的功能库成为了编程界的翘楚。而算法,作为计算机科学的核心,是解决问题、优化性能的关键。本文将围绕Python语言与算法的结合&#…...

Python实现连连看7
3.3 根据地图显示图片 在获取了图片地图之后,就可以根据该图片地图显示图片了。显示图片的功能在自定义函数drawMap()中实现。 3.3.1 清除画布中的内容 在画布上显示图片之前,需要将画布中图1的启动界面内容清除,代码如下所示。 canvas.delete(all) 其中,delete()方法…...

C#中的as和is
在 C# 中,as 和 is 是用于类型转换和类型检查的操作符。 as 操作符: as 操作符用于尝试将一个对象转换为指定的引用类型或可空类型,如果转换失败,将返回 null。语法:expression as type示例: object obj &…...

示波器眼图怎么看
目录 什么是眼图? 怎么看? 眼图的电压幅度(Y轴) 眼睛幅度和高度 信噪比 抖动 上升时间和下降时间 眼宽 什么是眼图? 眼图(Eye Diagram)是一种用于分析高速数字信号传输质量的重要工具。通…...
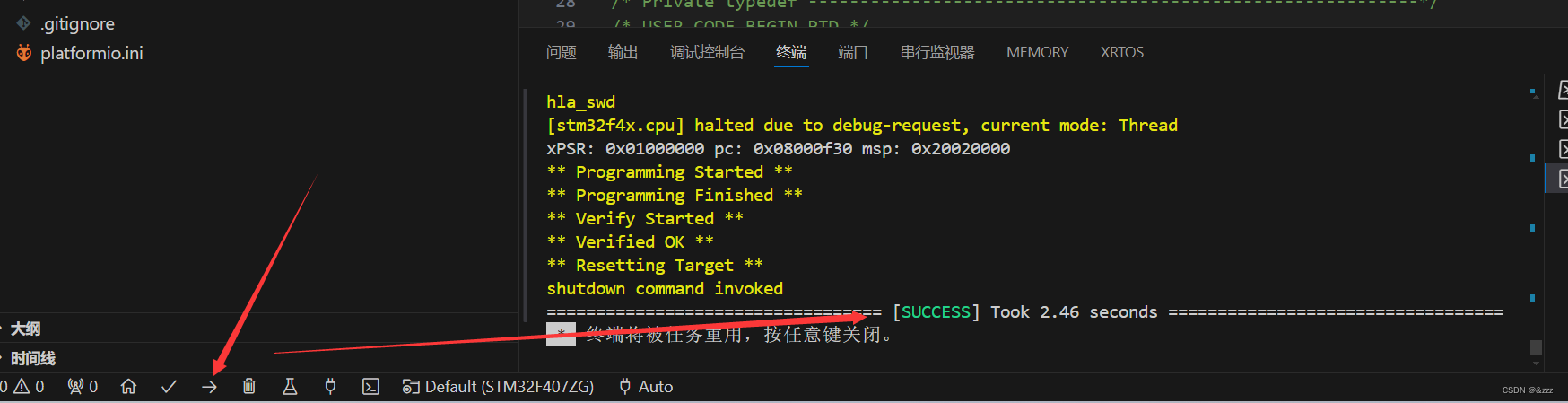
Visual Studio Code编辑STM32CubeMX已生成的文件
在这里插入图片描述...

【读脑仪game】
读脑仪(Brain-Computer Interface,BCI)游戏是一种利用脑电信号来控制游戏的新型交互方式。这类游戏通常需要专业的硬件设备来读取用户的脑电信号,并将这些信号转化为游戏中的控制信号。编写这样的游戏代码涉及到多个方面ÿ…...

基于STM32的毕业设计示例
**基于STM32的毕业设计示例** 一、引言 在当前的电子工程领域,STM32微控制器因其高性能、低功耗和丰富的外设接口而备受青睐。本次毕业设计旨在展示基于STM32微控制器的系统设计与实现能力,通过构建一个具有实际应用价值的系统,体现对嵌入式…...

图片格式怎么转成pdf,简单的方法
在现代数字化时代,图片格式转换成PDF已经成为许多人的日常需求。无论是为了存档、分享还是打印,将图片转换为PDF都是一项非常实用的技能。本文将详细介绍如何将图片格式转换成PDF的方法。 用浏览器打开 "轻云处理pdf官网,上传图片。 图…...

在 Debian 上使用和配置 SSH 的指南
SSH(Secure Shell)是用于在不安全网络上安全登录远程计算机和执行命令的协议。本文将详细介绍如何在 Debian 系统上安装、配置和使用 SSH。 1. 安装 SSH 首先,您需要安装 OpenSSH 服务器和客户端(也可直接安装服务器端ÿ…...
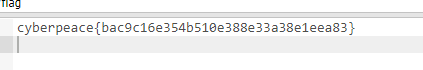
XCTF-web-easyupload
试了试php,php7,pht,phtml等,都没有用 尝试.user.ini 抓包修改将.user.ini修改为jpg图片 在上传一个123.jpg 用蚁剑连接,得到flag...
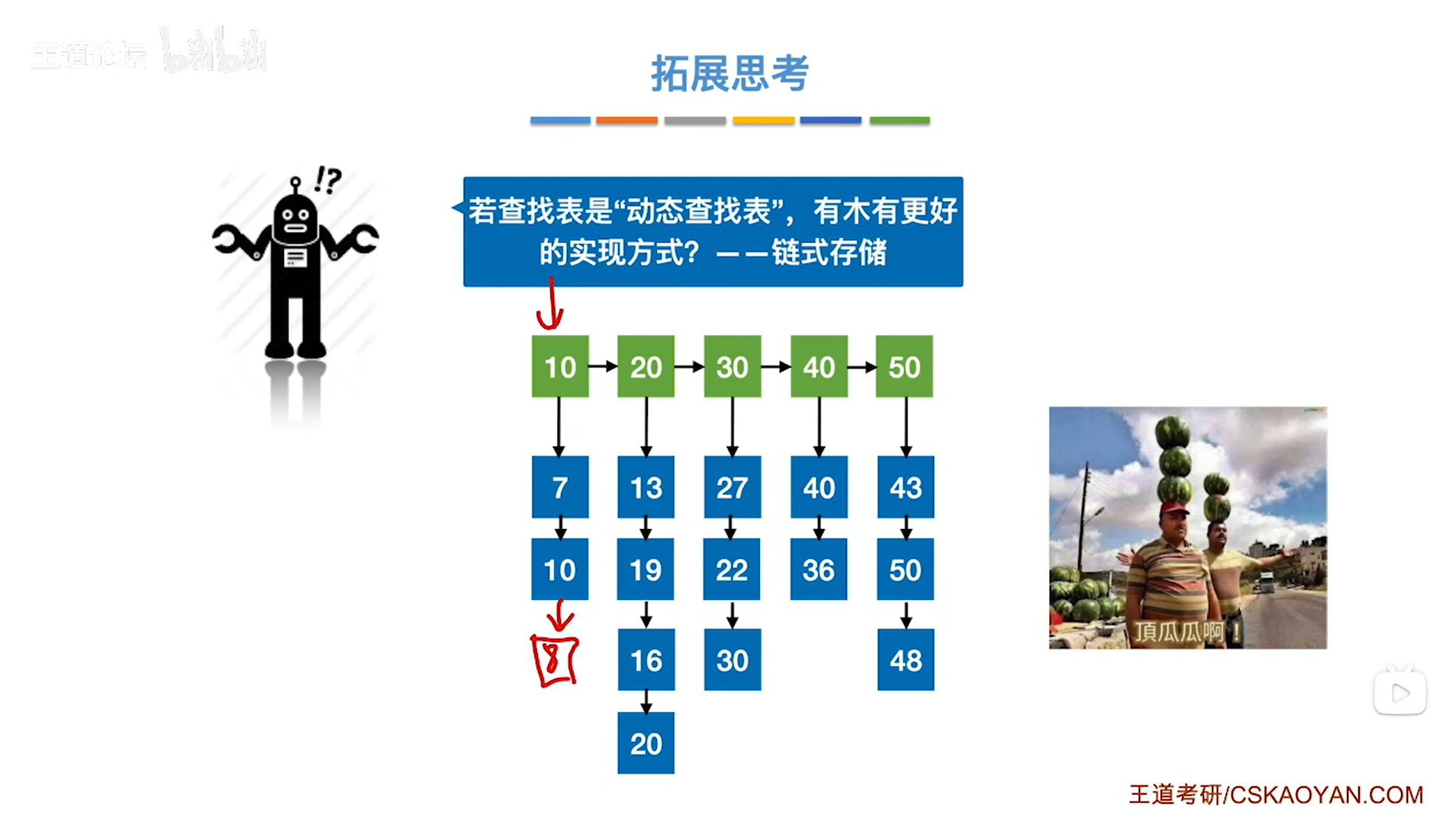
7.4.分块查找
一.分块查找的算法思想: 1.实例: 以上述图片的顺序表为例, 该顺序表的数据元素从整体来看是乱序的,但如果把这些数据元素分成一块一块的小区间, 第一个区间[0,1]索引上的数据元素都是小于等于10的, 第二…...
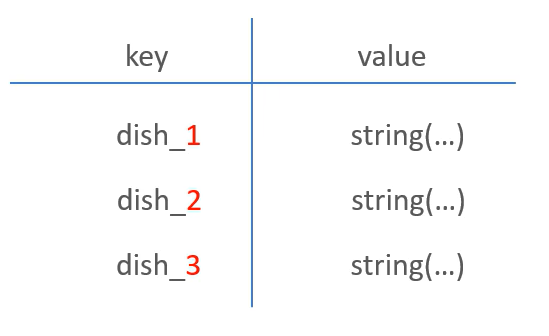
苍穹外卖--缓存菜品
1.问题说明 用户端小程序展示的菜品数据都是通过查询数据库获得,如果用户端访问量比较大,数据库访问压力随之增大 2.实现思路 通过Redis来缓存菜品数据,减少数据库查询操作。 缓存逻辑分析: ①每个分类下的菜品保持一份缓存数据…...

Linux云原生安全:零信任架构与机密计算
Linux云原生安全:零信任架构与机密计算 构建坚不可摧的云原生防御体系 引言:云原生安全的范式革命 随着云原生技术的普及,安全边界正在从传统的网络边界向工作负载内部转移。Gartner预测,到2025年,零信任架构将成为超…...

管理学院权限管理系统开发总结
文章目录 🎓 管理学院权限管理系统开发总结 - 现代化Web应用实践之路📝 项目概述🏗️ 技术架构设计后端技术栈前端技术栈 💡 核心功能特性1. 用户管理模块2. 权限管理系统3. 统计报表功能4. 用户体验优化 🗄️ 数据库设…...
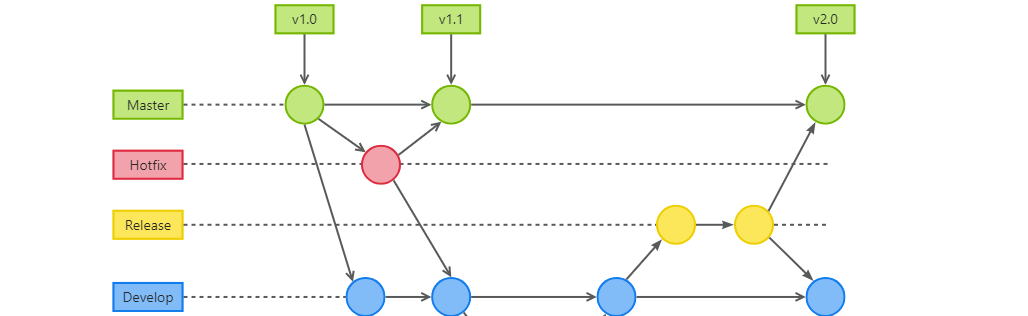
GitFlow 工作模式(详解)
今天再学项目的过程中遇到使用gitflow模式管理代码,因此进行学习并且发布关于gitflow的一些思考 Git与GitFlow模式 我们在写代码的时候通常会进行网上保存,无论是github还是gittee,都是一种基于git去保存代码的形式,这样保存代码…...

三分算法与DeepSeek辅助证明是单峰函数
前置 单峰函数有唯一的最大值,最大值左侧的数值严格单调递增,最大值右侧的数值严格单调递减。 单谷函数有唯一的最小值,最小值左侧的数值严格单调递减,最小值右侧的数值严格单调递增。 三分的本质 三分和二分一样都是通过不断缩…...

Oracle11g安装包
Oracle 11g安装包 适用于windows系统,64位 下载路径 oracle 11g 安装包...

pycharm 设置环境出错
pycharm 设置环境出错 pycharm 新建项目,设置虚拟环境,出错 pycharm 出错 Cannot open Local Failed to start [powershell.exe, -NoExit, -ExecutionPolicy, Bypass, -File, C:\Program Files\JetBrains\PyCharm 2024.1.3\plugins\terminal\shell-int…...

前端开发者常用网站
Can I use网站:一个查询网页技术兼容性的网站 一个查询网页技术兼容性的网站Can I use:Can I use... Support tables for HTML5, CSS3, etc (查询浏览器对HTML5的支持情况) 权威网站:MDN JavaScript权威网站:JavaScript | MDN...
