transformers 阅读:Llama 模型
正文
学习一下 transformers 库中,Llama 模型的代码,学习过程中写下这篇笔记,一来加深印象,二来可以多次回顾。
笔者小白,里面错误之处请不吝指出。
层归一化 LlamaRMSNorm
transformers 中对于 LlamaRMSNorm 类的定义如下:
class LlamaRMSNorm(nn.Module): def __init__(self, hidden_size, eps=1e-6): """ LlamaRMSNorm is equivalent to T5LayerNorm """ super().__init__() self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(hidden_size)) self.variance_epsilon = eps def forward(self, hidden_states): input_dtype = hidden_states.dtype hidden_states = hidden_states.to(torch.float32) variance = hidden_states.pow(2).mean(-1, keepdim=True) hidden_states = hidden_states * torch.rsqrt(variance + self.variance_epsilon) return self.weight * hidden_states.to(input_dtype)这里采用了 RMS(Root Mean Square) 归一化,其中 RMS 计算公式为:
RMS(x)=1n∑xi2RMS(x)=\sqrt{\frac{1}{n}\sum{x_i^2}}RMS(x)=n1∑xi2
则 RMSNorm 归一化的计算公式为:
RMS(x)=xRMS(x)+ϵ∗WRMS(x)=\frac{x}{\sqrt{RMS(x)+\epsilon}} * WRMS(x)=RMS(x)+ϵx∗W
加上一个小常数,确保分母不为零,保持数据稳定性。
旋转位置编码 LlamaRotaryEmbedding
- 绝对位置编码:计算高效,效果欠佳
- 相对位置编码:满足 NLP 领域在序列长度方向上具有平移不变性,计算效率低。
- 旋转位置编码:采用绝对位置编码达到相位置编码的效果
transformers 中对于 LlamaRotaryEmbedding 类的定义如下,它用于实现旋转位置嵌入:
class LlamaRotaryEmbedding(nn.Module): def __init__(self, dim, max_position_embeddings=2048, base=10000, device=None): super().__init__() self.dim = dim self.max_position_embeddings = max_position_embeddings self.base = base inv_freq = 1.0 / (self.base ** (torch.arange(0, self.dim, 2).float().to(device) / self.dim)) self.register_buffer("inv_freq", inv_freq, persistent=False) # Build here to make `torch.jit.trace` work. self._set_cos_sin_cache( seq_len=max_position_embeddings, device=self.inv_freq.device, dtype=torch.get_default_dtype() ) def _set_cos_sin_cache(self, seq_len, device, dtype): self.max_seq_len_cached = seq_len t = torch.arange(self.max_seq_len_cached, device=device, dtype=self.inv_freq.dtype) freqs = torch.einsum("i,j->ij", t, self.inv_freq) # Different from paper, but it uses a different permutation in order to obtain the same calculation emb = torch.cat((freqs, freqs), dim=-1) self.register_buffer("cos_cached", emb.cos().to(dtype), persistent=False) self.register_buffer("sin_cached", emb.sin().to(dtype), persistent=False) def forward(self, x, seq_len=None): # x: [bs, num_attention_heads, seq_len, head_size] if seq_len > self.max_seq_len_cached: self._set_cos_sin_cache(seq_len=seq_len, device=x.device, dtype=x.dtype) return ( self.cos_cached[:seq_len].to(dtype=x.dtype), self.sin_cached[:seq_len].to(dtype=x.dtype), )其中定义的变量意义如下:
- dim:表示模型输出维度
- max_position_embeddings:最大编码长度,默认为2048
- base:基数,默认为10000
inv_freq = 1.0 / (self.base ** (torch.arange(0, self.dim, 2).float().to(device) / self.dim)) 实现公式为:
inv_freq=1base2i/diminv\_freq=\frac{1}{base^{2i/dim}}inv_freq=base2i/dim1
在上面代码中,t 的维度为[max_position_embeddings], inv_freq 的维度为[dim/2]。
经过 torch.einsum("i,j->ij", t, self.inv_freq) 之后维度为 [max_position_embeddings, dim/2]。
然后经过 emb = torch.cat((freqs, freqs), dim=-1) 操作,维度变为 [max_position_embeddings, dim]。
二维情况下旋转矩阵如下:
R(k)=(coskθ−sinkθsinkθcoskθ)R(k)=\begin{pmatrix} cosk\theta & -sink\theta \\ sink\theta & cosk\theta \\ \end{pmatrix}R(k)=(coskθsinkθ−sinkθcoskθ)
旋转位置编码计算公式如下:
R(k)x=(coskθ0coskθ0coskθ1coskθ1…coskθd/2−1coskθd/2−1)∘(x0x1x2x3…xd−2xd−1)+(sinkθ0sinkθ0sinkθ1sinkθ1…sinkθd/2−1sinkθd/2−1)∘(−x1x0−x3x2…−xd−1xd−2)R(k)x= \begin{pmatrix} cos{k\theta_0} \\ cos{k\theta_0} \\ cos{k\theta_1} \\ cos{k\theta_1} \\ … \\ cos{k\theta_{d/2-1}} \\ cos{k\theta_{d/2-1}} \end{pmatrix} \circ \begin{pmatrix} x_0 \\ x_1 \\ x_2 \\ x_3 \\ … \\ x_{d-2} \\ x_{d-1} \end{pmatrix} + \begin{pmatrix} sin{k\theta_0} \\ sin{k\theta_0} \\ sin{k\theta_1} \\ sin{k\theta_1} \\ … \\ sin{k\theta_{d/2-1}} \\ sin{k\theta_{d/2-1}} \end{pmatrix} \circ \begin{pmatrix} -x_1 \\ x_0 \\ -x_3 \\ x_2 \\ … \\ -x_{d-1} \\ x_{d-2} \end{pmatrix} R(k)x=⎝⎛coskθ0coskθ0coskθ1coskθ1…coskθd/2−1coskθd/2−1⎠⎞∘⎝⎛x0x1x2x3…xd−2xd−1⎠⎞+⎝⎛sinkθ0sinkθ0sinkθ1sinkθ1…sinkθd/2−1sinkθd/2−1⎠⎞∘⎝⎛−x1x0−x3x2…−xd−1xd−2⎠⎞
在使用 LLM 时,我们希望对上下文长度进行拓展,以便能进行多轮对话,由此有下面几种方法:
外推法:直接沿用当前公式计算计算更长位置的编码。
这种方法比较简单,但是存在相关性衰减问题,如果模型训练语料在 2k 长度左右,模型能够学习到 2k 长度左右的 token 之间相关性关系的规律。
如果直接将此规律沿用到 5k 上下文,可能导致在中间某个位置相关性衰减到零,从而无法捕捉两个 token 之间的相关性。
线性内插:线性内插会改变编码公式,将 token 之间的距离等比例缩小。
例如在 2k 上下文情况下,两个 token 之间距离为 16,那么在 32k 上下文下,这两个 token 之间距离缩短到 1。
对于短距离的衰减规律,可能造成非常大的变化,但是线性内插没有改变模型学习到的衰减规律的应用范围,不考虑微调的话,其效果一般好于直接外推方案。
transformers 中对于线性内插的实现如下:
class LlamaLinearScalingRotaryEmbedding(LlamaRotaryEmbedding): """LlamaRotaryEmbedding extended with linear scaling. Credits to the Reddit user /u/kaiokendev""" def __init__(self, dim, max_position_embeddings=2048, base=10000, device=None, scaling_factor=1.0): self.scaling_factor = scaling_factor super().__init__(dim, max_position_embeddings, base, device) def _set_cos_sin_cache(self, seq_len, device, dtype): self.max_seq_len_cached = seq_len t = torch.arange(self.max_seq_len_cached, device=device, dtype=self.inv_freq.dtype) t = t / self.scaling_factor freqs = torch.einsum("i,j->ij", t, self.inv_freq) # Different from paper, but it uses a different permutation in order to obtain the same calculation emb = torch.cat((freqs, freqs), dim=-1) self.register_buffer("cos_cached", emb.cos().to(dtype), persistent=False) self.register_buffer("sin_cached", emb.sin().to(dtype), persistent=False)可以看到,在 t = t / self.scaling_factor 这行代码中,除以一个缩放因子,从而达到线性缩放的效果。
动态 NTK 扩展:外推法对于长距离的 token 不能很好计算相关性,线性内插对于短距离 token 计算相关性会产生很大变化,因此可以综合两者进行扩展。
为了在短距离情况下具有外推特性,长距离情况下具有内插特性,可以设置一个与位置序号有关频率因子,动态调整。
transformers 中对于动态 NTK 扩展的实现如下:
class LlamaDynamicNTKScalingRotaryEmbedding(LlamaRotaryEmbedding): """LlamaRotaryEmbedding extended with Dynamic NTK scaling. Credits to the Reddit users /u/bloc97 and /u/emozilla""" def __init__(self, dim, max_position_embeddings=2048, base=10000, device=None, scaling_factor=1.0): self.scaling_factor = scaling_factor super().__init__(dim, max_position_embeddings, base, device) def _set_cos_sin_cache(self, seq_len, device, dtype): self.max_seq_len_cached = seq_len if seq_len > self.max_position_embeddings: base = self.base * ( (self.scaling_factor * seq_len / self.max_position_embeddings) - (self.scaling_factor - 1) ) ** (self.dim / (self.dim - 2)) inv_freq = 1.0 / (base ** (torch.arange(0, self.dim, 2).float().to(device) / self.dim)) self.register_buffer("inv_freq", inv_freq, persistent=False) t = torch.arange(self.max_seq_len_cached, device=device, dtype=self.inv_freq.dtype) freqs = torch.einsum("i,j->ij", t, self.inv_freq) # Different from paper, but it uses a different permutation in order to obtain the same calculation emb = torch.cat((freqs, freqs), dim=-1) self.register_buffer("cos_cached", emb.cos().to(dtype), persistent=False) self.register_buffer("sin_cached", emb.sin().to(dtype), persistent=False)可以看到,如果长度超过 max_position_embeddings,对于 base 做出了如下公式操作:
base=base∗(factor∗seq_lenmax_len−(factor−1))dimdim−2base=base*(factor*\frac{seq\_len}{max\_len}-(factor-1))^{\frac{dim}{dim-2}}base=base∗(factor∗max_lenseq_len−(factor−1))dim−2dim
如果 seq_len > max_position_embeddings,在 factor = 1 的情况下,base 变大。
显然 base > 1,则 inv_freq 值变小,这样将短距离的规律扩展到了长距离。
具体计算位置编码的代码如下:
def rotate_half(x): """Rotates half the hidden dims of the input.""" x1 = x[..., : x.shape[-1] // 2] x2 = x[..., x.shape[-1] // 2 :] return torch.cat((-x2, x1), dim=-1) # Copied from transformers.models.gpt_neox.modeling_gpt_neox.apply_rotary_pos_emb
def apply_rotary_pos_emb(q, k, cos, sin, position_ids): cos = cos[position_ids].unsqueeze(1) # [seq_len, dim] -> [batch_size, 1, seq_len, head_dim] sin = sin[position_ids].unsqueeze(1) q_embed = (q * cos) + (rotate_half(q) * sin) k_embed = (k * cos) + (rotate_half(k) * sin) return q_embed, k_embed在 rotate_half() 中,将输入 x 沿着最后一维分隔成两部分,然后进行拼接。
Llama 中对 Q 的旋转位置编码按照如下方式计算:
R(k)Q=(coskθ0coskθ1…coskθd/2−1coskθ0coskθ1…coskθd/2−1)∘(q0q1…qd/2−1qd/2qd/2+1…qd−1)+(sinkθ0sinkθ1…sinkθd/2−1sinkθ0sinkθ1…sinkθd/2−1)∘(−qd/2−qd/2+1…−qd−1q0q1…qd−1)R(k)Q= \begin{pmatrix} cos{k\theta_0} \\ cos{k\theta_1} \\ … \\ cos{k\theta_{d/2-1}} \\ cos{k\theta_0} \\ cos{k\theta_1} \\ … \\ cos{k\theta_{d/2-1}} \end{pmatrix} \circ \begin{pmatrix} q_0 \\ q_1 \\ … \\ q_{d/2-1} \\ q_{d/2} \\ q_{d/2+1} \\ … \\ q_{d-1} \end{pmatrix} + \begin{pmatrix} sin{k\theta_0} \\ sin{k\theta_1} \\ … \\ sin{k\theta_{d/2-1}} \\ sin{k\theta_0} \\ sin{k\theta_1} \\ … \\ sin{k\theta_{d/2-1}} \end{pmatrix} \circ \begin{pmatrix} -q_{d/2} \\ -q_{d/2+1} \\ … \\ -q_{d-1} \\ q_0 \\ q_1 \\ … \\ q_{d-1} \end{pmatrix} R(k)Q=⎝⎛coskθ0coskθ1…coskθd/2−1coskθ0coskθ1…coskθd/2−1⎠⎞∘⎝⎛q0q1…qd/2−1qd/2qd/2+1…qd−1⎠⎞+⎝⎛sinkθ0sinkθ1…sinkθd/2−1sinkθ0sinkθ1…sinkθd/2−1⎠⎞∘⎝⎛−qd/2−qd/2+1…−qd−1q0q1…qd−1⎠⎞
这里只对 Q 和 K 加入位置编码信息。
前馈网络 LlamaMLP
transformers 中对于前馈网络的定义如下:
class LlamaMLP(nn.Module): def __init__(self, config): super().__init__() self.config = config self.hidden_size = config.hidden_size self.intermediate_size = config.intermediate_size self.gate_proj = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, self.intermediate_size, bias=False) self.up_proj = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, self.intermediate_size, bias=False) self.down_proj = nn.Linear(self.intermediate_size, self.hidden_size, bias=False) self.act_fn = ACT2FN[config.hidden_act] def forward(self, x): if self.config.pretraining_tp > 1: slice = self.intermediate_size // self.config.pretraining_tp gate_proj_slices = self.gate_proj.weight.split(slice, dim=0) up_proj_slices = self.up_proj.weight.split(slice, dim=0) down_proj_slices = self.down_proj.weight.split(slice, dim=1) gate_proj = torch.cat( [F.linear(x, gate_proj_slices[i]) for i in range(self.config.pretraining_tp)], dim=-1 ) up_proj = torch.cat([F.linear(x, up_proj_slices[i]) for i in range(self.config.pretraining_tp)], dim=-1) intermediate_states = (self.act_fn(gate_proj) * up_proj).split(slice, dim=2) down_proj = [ F.linear(intermediate_states[i], down_proj_slices[i]) for i in range(self.config.pretraining_tp) ] down_proj = sum(down_proj) else: down_proj = self.down_proj(self.act_fn(self.gate_proj(x)) * self.up_proj(x)) return down_proj在 __init__() 函数中,定义了 hidden_size 和 intermediate_size 控制模型尺寸。
同时定义了三个全连接层:
gate_proj:将 hidden_size 投影到 intermediate_sizeup_proj:将 hidden_size 投影到 intermediate_sizedown_proj:将 intermediate_size 投影到 hidden_size
这里会将输入通过 up_proj 先从 hidden_size 维度转换到 intermediate_size 维度,然后通过 down_proj 从 intermediate_size 维度转换到 hidden_size 维度。
同时里面采用 gate_proj 配合激活函数,实现了一个门控作用。
在 forward() 函数中会根据 config.pretraining_tp 选择不同的执行策略。这里是将三个全连接层切分为若干块,分别与输入 x 进行映射操作,得到多个子投影,然后将多个子投影拼接起来。
多头注意力 LlamaAttention
transformers 中对于多头注意力的定义如下:
class LlamaAttention(nn.Module): """Multi-headed attention from 'Attention Is All You Need' paper""" def __init__(self, config: LlamaConfig): super().__init__() self.config = config self.hidden_size = config.hidden_size self.num_heads = config.num_attention_heads self.head_dim = self.hidden_size // self.num_heads self.num_key_value_heads = config.num_key_value_heads self.num_key_value_groups = self.num_heads // self.num_key_value_heads self.max_position_embeddings = config.max_position_embeddings self.rope_theta = config.rope_theta if (self.head_dim * self.num_heads) != self.hidden_size: raise ValueError( f"hidden_size must be divisible by num_heads (got `hidden_size`: {self.hidden_size}" f" and `num_heads`: {self.num_heads})." ) self.q_proj = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, self.num_heads * self.head_dim, bias=config.attention_bias) self.k_proj = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, self.num_key_value_heads * self.head_dim, bias=config.attention_bias) self.v_proj = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, self.num_key_value_heads * self.head_dim, bias=config.attention_bias) self.o_proj = nn.Linear(self.num_heads * self.head_dim, self.hidden_size, bias=config.attention_bias) self._init_rope() def _init_rope(self): if self.config.rope_scaling is None: self.rotary_emb = LlamaRotaryEmbedding( self.head_dim, max_position_embeddings=self.max_position_embeddings, base=self.rope_theta, ) else: scaling_type = self.config.rope_scaling["type"] scaling_factor = self.config.rope_scaling["factor"] if scaling_type == "linear": self.rotary_emb = LlamaLinearScalingRotaryEmbedding( self.head_dim, max_position_embeddings=self.max_position_embeddings, scaling_factor=scaling_factor, base=self.rope_theta, ) elif scaling_type == "dynamic": self.rotary_emb = LlamaDynamicNTKScalingRotaryEmbedding( self.head_dim, max_position_embeddings=self.max_position_embeddings, scaling_factor=scaling_factor, base=self.rope_theta, ) else: raise ValueError(f"Unknown RoPE scaling type {scaling_type}")这里主要定义了下面几种属性:
- hidden_size:隐藏层的大小
- num_heads:注意力头的数量
- head_dim:每个注意力头的维度,它通过 hidden_size // num_heads 得到
- num_key_value_heads:键值注意力头的数量
- num_key_value_groups:键值注意力头分组数量,它通过 num_heads // num_key_value_heads 得到
- rope_theta:即前面 RoPE 的 base
此外还定义了四个线性变换的全连接层,分别用于计算查询(Q)、键(K)、值(V)和输出(O)。
注意到键值注意力头的数量与查询注意力头的数量不同。
键值注意力头数量可以是查询注意力头数量的几分之一,这样可以减少参数规模。
多头注意力的计算代码如下:
def forward( self, hidden_states: torch.Tensor, attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None, position_ids: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None, past_key_value: Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor]] = None, output_attentions: bool = False, use_cache: bool = False, padding_mask: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, Optional[torch.Tensor], Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor]]]: bsz, q_len, _ = hidden_states.size() if self.config.pretraining_tp > 1: key_value_slicing = (self.num_key_value_heads * self.head_dim) // self.config.pretraining_tp query_slices = self.q_proj.weight.split( (self.num_heads * self.head_dim) // self.config.pretraining_tp, dim=0 ) key_slices = self.k_proj.weight.split(key_value_slicing, dim=0) value_slices = self.v_proj.weight.split(key_value_slicing, dim=0) query_states = [F.linear(hidden_states, query_slices[i]) for i in range(self.config.pretraining_tp)] query_states = torch.cat(query_states, dim=-1) key_states = [F.linear(hidden_states, key_slices[i]) for i in range(self.config.pretraining_tp)] key_states = torch.cat(key_states, dim=-1) value_states = [F.linear(hidden_states, value_slices[i]) for i in range(self.config.pretraining_tp)] value_states = torch.cat(value_states, dim=-1) else: query_states = self.q_proj(hidden_states) key_states = self.k_proj(hidden_states) value_states = self.v_proj(hidden_states) query_states = query_states.view(bsz, q_len, self.num_heads, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2) key_states = key_states.view(bsz, q_len, self.num_key_value_heads, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2) value_states = value_states.view(bsz, q_len, self.num_key_value_heads, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2) kv_seq_len = key_states.shape[-2] if past_key_value is not None: kv_seq_len += past_key_value[0].shape[-2] cos, sin = self.rotary_emb(value_states, seq_len=kv_seq_len) query_states, key_states = apply_rotary_pos_emb(query_states, key_states, cos, sin, position_ids) if past_key_value is not None: # reuse k, v, self_attention key_states = torch.cat([past_key_value[0], key_states], dim=2) value_states = torch.cat([past_key_value[1], value_states], dim=2) past_key_value = (key_states, value_states) if use_cache else None key_states = repeat_kv(key_states, self.num_key_value_groups) value_states = repeat_kv(value_states, self.num_key_value_groups) attn_weights = torch.matmul(query_states, key_states.transpose(2, 3)) / math.sqrt(self.head_dim) if attn_weights.size() != (bsz, self.num_heads, q_len, kv_seq_len): raise ValueError( f"Attention weights should be of size {(bsz, self.num_heads, q_len, kv_seq_len)}, but is" f" {attn_weights.size()}" ) if attention_mask is not None: if attention_mask.size() != (bsz, 1, q_len, kv_seq_len): raise ValueError( f"Attention mask should be of size {(bsz, 1, q_len, kv_seq_len)}, but is {attention_mask.size()}" ) attn_weights = attn_weights + attention_mask # upcast attention to fp32 attn_weights = nn.functional.softmax(attn_weights, dim=-1, dtype=torch.float32).to(query_states.dtype) attn_output = torch.matmul(attn_weights, value_states) if attn_output.size() != (bsz, self.num_heads, q_len, self.head_dim): raise ValueError( f"`attn_output` should be of size {(bsz, self.num_heads, q_len, self.head_dim)}, but is" f" {attn_output.size()}" ) attn_output = attn_output.transpose(1, 2).contiguous() attn_output = attn_output.reshape(bsz, q_len, self.hidden_size) if self.config.pretraining_tp > 1: attn_output = attn_output.split(self.hidden_size // self.config.pretraining_tp, dim=2) o_proj_slices = self.o_proj.weight.split(self.hidden_size // self.config.pretraining_tp, dim=1) attn_output = sum([F.linear(attn_output[i], o_proj_slices[i]) for i in range(self.config.pretraining_tp)]) else: attn_output = self.o_proj(attn_output) if not output_attentions: attn_weights = None return attn_output, attn_weights, past_key_value多头注意力基本与《Attention Is All You Need》中一致,计算公式如下:
Attention(Q,K,V)=softmax(QKTdk)VAttention(Q,K,V)=softmax(\frac{QK^T}{\sqrt{d_k}})VAttention(Q,K,V)=softmax(dkQKT)V
在 llama 中每进行一次注意力计算,都会对 Q 和 K 计算一次位置编码(RoPE)。
因为 K 和 V 注意力头数是 Q 的几分之一,所以在计算前首先进行 repeat 操作,对应代码如下:
key_states = repeat_kv(key_states, self.num_key_value_groups)
value_states = repeat_kv(value_states, self.num_key_value_groups)计算注意力的代码如下:
attn_weights = torch.matmul(query_states, key_states.transpose(2, 3)) / math.sqrt(self.head_dim)attn_weights = attn_weights + attention_mask # 可选操作attn_weights = nn.functional.softmax(attn_weights, dim=-1, dtype=torch.float32).to(query_states.dtype)
attn_output = torch.matmul(attn_weights, value_states)最终 attn_output 经过 o_proj 的线性变换之后输出。
与前馈网络类似,如果 config 中设置 pretraining_tp,会对输入进行切片后分块操作。
解码层 LlamaDecoderLayer
transfromers 中对解码层的定义如下:
class LlamaDecoderLayer(nn.Module): def __init__(self, config: LlamaConfig): super().__init__() self.hidden_size = config.hidden_size self.self_attn = ( LlamaAttention(config=config) if not getattr(config, "_flash_attn_2_enabled", False) else LlamaFlashAttention2(config=config) ) self.mlp = LlamaMLP(config) self.input_layernorm = LlamaRMSNorm(config.hidden_size, eps=config.rms_norm_eps) self.post_attention_layernorm = LlamaRMSNorm(config.hidden_size, eps=config.rms_norm_eps)解码层由 AttentionLayer、MLP 和两个 LayerNorm 组成。
前向计算代码如下:
def forward( self, hidden_states: torch.Tensor, attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None, position_ids: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None, past_key_value: Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor]] = None, output_attentions: Optional[bool] = False, use_cache: Optional[bool] = False, padding_mask: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
) -> Tuple[torch.FloatTensor, Optional[Tuple[torch.FloatTensor, torch.FloatTensor]]]: """ Args: hidden_states (`torch.FloatTensor`): input to the layer of shape `(batch, seq_len, embed_dim)` attention_mask (`torch.FloatTensor`, *optional*): attention mask of size `(batch, 1, tgt_len, src_len)` where padding elements are indicated by very large negative values. output_attentions (`bool`, *optional*): Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. See `attentions` under returned tensors for more detail. use_cache (`bool`, *optional*): If set to `True`, `past_key_values` key value states are returned and can be used to speed up decoding (see `past_key_values`). past_key_value (`Tuple(torch.FloatTensor)`, *optional*): cached past key and value projection states """ residual = hidden_states hidden_states = self.input_layernorm(hidden_states) # Self Attention hidden_states, self_attn_weights, present_key_value = self.self_attn( hidden_states=hidden_states, attention_mask=attention_mask, position_ids=position_ids, past_key_value=past_key_value, output_attentions=output_attentions, use_cache=use_cache, padding_mask=padding_mask, ) hidden_states = residual + hidden_states # Fully Connected residual = hidden_states hidden_states = self.post_attention_layernorm(hidden_states) hidden_states = self.mlp(hidden_states) hidden_states = residual + hidden_states outputs = (hidden_states,) if output_attentions: outputs += (self_attn_weights,) if use_cache: outputs += (present_key_value,) return outputs在解码器层中,输入 hidden_states 依次经历如下计算:
- 经过 input_layernorm 进行层归一化。
- 计算一次自注意力。
- 做一次残差连接。
- 经过 post_attention_layernorm 进行层归一化。
- 经过 mlp,并将结果与步骤3结果做一次残差连接。
模型 LlamaModel
transformers 中对模型定义如下:
class LlamaModel(LlamaPreTrainedModel): """ Transformer decoder consisting of *config.num_hidden_layers* layers. Each layer is a [`LlamaDecoderLayer`] Args: config: LlamaConfig """ def __init__(self, config: LlamaConfig): super().__init__(config) self.padding_idx = config.pad_token_id self.vocab_size = config.vocab_size self.embed_tokens = nn.Embedding(config.vocab_size, config.hidden_size, self.padding_idx) self.layers = nn.ModuleList([LlamaDecoderLayer(config) for _ in range(config.num_hidden_layers)]) self.norm = LlamaRMSNorm(config.hidden_size, eps=config.rms_norm_eps) self.gradient_checkpointing = False # Initialize weights and apply final processing self.post_init()Llama 模型是由若干个解码层堆叠而成。
在前向传播时设置 gradient_checkpointing=True 可以节约显存。
但是这个参数不能和 use_cache=True 同时设置,这两个参数不兼容。
if self.gradient_checkpointing and self.training: if use_cache: logger.warning_once( "`use_cache=True` is incompatible with gradient checkpointing. Setting `use_cache=False`..." ) use_cache = False在前向传播中自定义了前向传播函数:
def create_custom_forward(module): def custom_forward(*inputs): # None for past_key_value return module(*inputs, past_key_value, output_attentions, padding_mask=padding_mask) return custom_forward使用 torch.utils.checkpoint.checkpoint() 函数,它允许将前向传播的一部分分成小块以减小内存占用,并且可以在反向传播时实现显存优化。前提是设置 gradient_checkpointing=True。
layer_outputs = torch.utils.checkpoint.checkpoint( create_custom_forward(decoder_layer), hidden_states, attention_mask, position_ids
)代码中的 decode_layer 为前文中提到的解码器层。
经过多层解码器层后,将输出经过 RMSNorm 层,得到最终结果。
语言模型 LlamaForCausalLM
transformers 中对语言模型的定义如下:
class LlamaForCausalLM(LlamaPreTrainedModel): _tied_weights_keys = ["lm_head.weight"] def __init__(self, config): super().__init__(config) self.model = LlamaModel(config) self.vocab_size = config.vocab_size self.lm_head = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.vocab_size, bias=False) # Initialize weights and apply final processing self.post_init()实质是在前文提到的 LlamaModel 基础上加入一个 llm_head 来生成结果。
前向传播核心计算代码如下:
# decoder outputs consists of (dec_features, layer_state, dec_hidden, dec_attn)
outputs = self.model( input_ids=input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask, position_ids=position_ids, past_key_values=past_key_values, inputs_embeds=inputs_embeds, use_cache=use_cache, output_attentions=output_attentions, output_hidden_states=output_hidden_states, return_dict=return_dict,
) hidden_states = outputs[0]
if self.config.pretraining_tp > 1: lm_head_slices = self.lm_head.weight.split(self.vocab_size // self.config.pretraining_tp, dim=0) logits = [F.linear(hidden_states, lm_head_slices[i]) for i in range(self.config.pretraining_tp)] logits = torch.cat(logits, dim=-1)
else: logits = self.lm_head(hidden_states)
logits = logits.float()如果输入 labels 会自动计算交叉熵损失。
分类模型 LlamaForSequenceClassification
分类模型也是由 LlamaModel 加上一个 score 的线性层构成。
在计算损失的时候,会根据不同的类型,选择不同的损失函数:
if self.config.problem_type == "regression": loss_fct = MSELoss() if self.num_labels == 1: loss = loss_fct(pooled_logits.squeeze(), labels.squeeze()) else: loss = loss_fct(pooled_logits, labels)
elif self.config.problem_type == "single_label_classification": loss_fct = CrossEntropyLoss() loss = loss_fct(pooled_logits.view(-1, self.num_labels), labels.view(-1))
elif self.config.problem_type == "multi_label_classification": loss_fct = BCEWithLogitsLoss() loss = loss_fct(pooled_logits, labels)总结
以 LlamaModel 为例总结数据流向:
- 输入的如果是 input_ids,会首先计算 inputs_embeds,然后作为 hidden_states,经过若干个 LlamaDecoderLayer、LlamaRMSNorm 组合后输出。
- 在 LlamaDecoderLayer 中,经历如下步骤:
- 先记录原始输入,然后对于输入的 hidden_states 先做一次 LlamaRMSNorm。
- 对步骤1的结果做一次 LlamaAttention。
- 将步骤2的结果与原始输入做一次残差连接,并记录这次结果。
- 将步骤3的结果做一次 LlamaRMSNorm。
- 将步骤4的结果做一次 LlamaMLP。
- 将步骤5的结果与步骤3的结果做一次残差连接,将结果输出。
- 在 LlamaAttention 中,经历如下步骤:
- 将输入的 hidden_states 做 Q、K、V 变换。
- 计算 Q、K 的旋转位置编码。
- 根据公式计算自注意力。
- 注意力经过线性变换后输出。
- 在 LlamaMLP 中,经历如下步骤:
- 原始输入经过线性变换,得到上投影。
- 原始输入经过门函数和激活函数,得到门控投影。
- 将步骤1的上投影和步骤2的门控投影对应元素相乘。
- 将步骤3的结果经过线性变换,得到下投影,输出这个结果。
那么,我们该如何学习大模型?
作为一名热心肠的互联网老兵,我决定把宝贵的AI知识分享给大家。 至于能学习到多少就看你的学习毅力和能力了 。我已将重要的AI大模型资料包括AI大模型入门学习思维导图、精品AI大模型学习书籍手册、视频教程、实战学习等录播视频免费分享出来。
一、大模型全套的学习路线
学习大型人工智能模型,如GPT-3、BERT或任何其他先进的神经网络模型,需要系统的方法和持续的努力。既然要系统的学习大模型,那么学习路线是必不可少的,下面的这份路线能帮助你快速梳理知识,形成自己的体系。
L1级别:AI大模型时代的华丽登场
L2级别:AI大模型API应用开发工程
L3级别:大模型应用架构进阶实践

L4级别:大模型微调与私有化部署

一般掌握到第四个级别,市场上大多数岗位都是可以胜任,但要还不是天花板,天花板级别要求更加严格,对于算法和实战是非常苛刻的。建议普通人掌握到L4级别即可。
以上的AI大模型学习路线,不知道为什么发出来就有点糊,高清版可以微信扫描下方CSDN官方认证二维码免费领取【保证100%免费】

二、640套AI大模型报告合集
这套包含640份报告的合集,涵盖了AI大模型的理论研究、技术实现、行业应用等多个方面。无论您是科研人员、工程师,还是对AI大模型感兴趣的爱好者,这套报告合集都将为您提供宝贵的信息和启示。

三、大模型经典PDF籍
随着人工智能技术的飞速发展,AI大模型已经成为了当今科技领域的一大热点。这些大型预训练模型,如GPT-3、BERT、XLNet等,以其强大的语言理解和生成能力,正在改变我们对人工智能的认识。 那以下这些PDF籍就是非常不错的学习资源。
四、AI大模型商业化落地方案

作为普通人,入局大模型时代需要持续学习和实践,不断提高自己的技能和认知水平,同时也需要有责任感和伦理意识,为人工智能的健康发展贡献力量。
相关文章:

transformers 阅读:Llama 模型
正文 学习一下 transformers 库中,Llama 模型的代码,学习过程中写下这篇笔记,一来加深印象,二来可以多次回顾。 笔者小白,里面错误之处请不吝指出。 层归一化 LlamaRMSNorm transformers 中对于 LlamaRMSNorm 类的…...

python绘制piper三线图
piper三线图 Piper三线图是一种常用于水化学分析的图表,它能够帮助我们理解和比较水样的化学成分。该图表由三个部分组成:两个三角形和一个菱形。两个三角形分别用于显示阳离子和阴离子的相对比例,而菱形部分则综合显示了这些离子比例在水样…...

咖啡机器人如何精准控制液位流量
在如今快节奏的生活中,精确控制液位流量的需求愈发迫切,特别是在咖啡机器人等精密设备中。为了满足这一需求,工程师们不断研发出各种先进的技术,以确保液体流量的精准控制。其中,霍尔式流量计和光电式流量计就是两种常…...

Go go-redis应用
go-redis 是 Go 语言的一个流行的 Redis 客户端库,它提供了丰富的功能来与 Redis 数据库进行交互。 1、简单应用 package mainimport ("context""fmt""log""github.com/redis/go-redis/v9" )func main() {ctx : context…...

从混乱到有序:PDM系统如何优化物料编码
在现代制造业中,物料管理是企业运营的核心。物料编码作为物料管理的基础,对于确保物料的准确性、唯一性和高效性至关重要。随着产品种类的不断增加和产品变型的多样化,传统的物料编码管理方式已经不能满足企业的需求。本文将探讨产品数据管理…...

npm发布自己的插件包
要发布自己的插件包到npm,可以按照以下步骤进行操作: 1.创建一个新项目 首先确保你已经安装了Node.js和npm。然后,在你的项目目录中初始化一个新的npm项目:npm init命令会引导你创建一个package.json文件,其中包含你插件包的基本…...

Pygame:新手指南与入门教程
在游戏开发领域,pygame 是一个广受欢迎的 Python 库,它提供了开发二维游戏的丰富工具和方法。这个库让开发者可以较少地关注底层图形处理细节,更多地专注于游戏逻辑和玩法的实现。本文将详细介绍 pygame,包括其安装过程、基本概念、主要功能和一个简单游戏的开发流程。 一…...

动态IP与静态IP的优缺点
在网络连接中,使用动态和静态 IP 地址取决于连接的性质和要求。静态 IP 地址通常更适合企业相关服务,而动态 IP 地址更适合家庭网络。让我们来看看动态 IP 与静态 IP 的优缺点。 1.静态IP的优点: 更好的 DNS 支持:静态 IP 地址在…...

上海市计算机学会竞赛平台2024年1月月赛丙组最大的和
题目描述 给定两个序列 𝑎1,𝑎2,…,𝑎𝑛a1,a2,…,an 与 𝑏1,𝑏2,…,𝑏𝑛b1,b2,…,bn,请从这两个序列中分别各找一个数,要求这两个数的差不超过给…...

C++三大特性之继承,详细介绍
阿尼亚全程陪伴大家学习~ 前言 每个程序员在开发新系统时,都希望能够利用已有的软件资源,以缩短开发周期,提高开发效率。 为了提高软件的可重用性(reusability),C提供了类的继承机制。 1.继承的概念 继承: 指在现有…...

Python推导式详解
引言 推导式(Comprehensions)是Python中一种简洁且强大的语法结构,可以用来生成列表、字典和集合。推导式使得代码更加简洁、易读,同时也更具Pythonic风格。今天我将将详细介绍列表推导式、字典推导式和集合推导式…...

stm32中如何实现EXTI线 0 ~ 15与对应IO口的配置呢?
STM32的EXTI控制器支持19 个外部中断/ 事件请求。每个中断设有状态位,每个中断/ 事件都有独立的触发和屏蔽设置。 STM32的19个外部中断对应着19路中断线,分别是EXTI_Line0-EXTI_Line18: 线0~15:对应外部 IO口的输入中断。 线16&…...
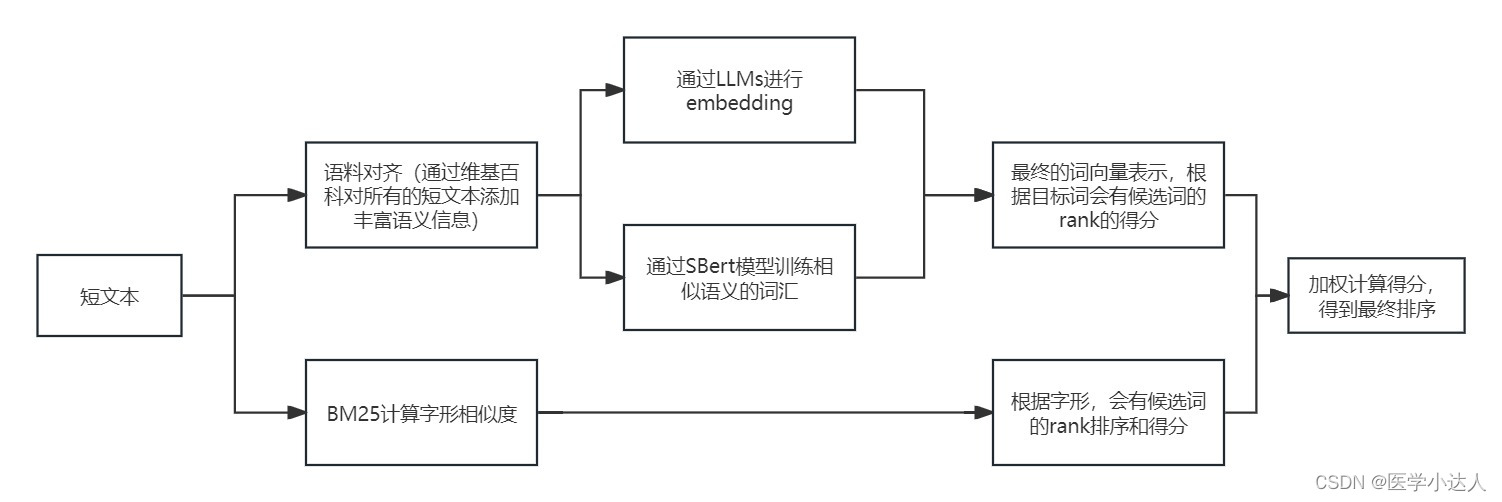
Python 短文本匹配,短文本语义相似度,基于大模型的短文本匹配,基于LLMs的短文本语义相似度识别,短文本语义扩充和匹配
1.任务描述 之前在做疾病相似度匹配的时候,堪称史诗级难题,虽然最后加上规则以及一些nlp模型,取得了差强人意的效果,但是短文本的语义相似度匹配一直属于比较难以攻克的难题 2.思路 随着近年大模型的飞速发展,就之前…...

提升接口性能方式汇总
1,sql 2,缓存,尤其面向用户,如app数据。可用redis咖啡,二级缓存。 充分利用redis,redis数据类型很多,平时场景中结合实际情况,找一下对应的redis实现方案 比如Zset可以排序&#…...

C++中的常见语法糖汇总
C中的语法糖是指使代码更简洁、可读性更高的语言特性和简化的语法。以下是一些常见的C语法糖: 1. 自动类型推导(auto) 使用 auto 关键字可以让编译器自动推导变量的类型,简化变量的声明。 auto x 10; // 编译器推导 x…...

TensorFlow Playground神经网络演示工具使用方法详解
在现代机器学习领域,神经网络无疑是一个重要的研究方向。然而,对于许多初学者来说,神经网络的概念和实际操作可能显得相当复杂。幸运的是,TensorFlow Playground 提供了一个交互式的在线工具,使得我们可以直观地理解和实验神经网络的基本原理。在这篇博客中,我们将详细介…...
【git】subtree 简单教程
git subtree使用案例 😄生命不息,写作不止 🔥 继续踏上学习之路,学之分享笔记 👊 总有一天我也能像各位大佬一样 🏆 博客首页 怒放吧德德 To记录领地 🌝分享学习心得,欢迎指正&am…...

C语言基础:字符串函数使用与剖析
strtok(分割字符串) char * strtok ( char * str, const char * sep ); sep参数是个字符串,定义了用作分隔符的字符集合 第一个参数指定一个字符串,它包含了0个或者多个由sep字符串中一个或者多个分隔符分割的标 记。strtok函数找…...

搭建Vulnhub靶机网络问题(获取不到IP)
搭建好靶场后,在攻击机运行arp-scan -l无法发现靶机IP。 这时候去看下靶机网络有没有问题。 重新启动客户机,一直按e进入安全模式(要是直接开机了就先按shift进入grub界面,再按e)找到ro,将ro改为rw signie…...

Prompt 提示词强大方法论和框架2
自从ChatGPT Chat Generative Pre-trained Transformer于2022年11月30日发布以来,一个新兴的行业突然兴起, 那就是提示工程Prompt engineering,可谓如日冲天。 从简单的文章扩写到RAG,ChatGPT展现了前所未有的惊人能力。 在上一…...

调用支付宝接口响应40004 SYSTEM_ERROR问题排查
在对接支付宝API的时候,遇到了一些问题,记录一下排查过程。 Body:{"datadigital_fincloud_generalsaas_face_certify_initialize_response":{"msg":"Business Failed","code":"40004","sub_msg…...

生成 Git SSH 证书
🔑 1. 生成 SSH 密钥对 在终端(Windows 使用 Git Bash,Mac/Linux 使用 Terminal)执行命令: ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "your_emailexample.com" 参数说明: -t rsa&#x…...

论文浅尝 | 基于判别指令微调生成式大语言模型的知识图谱补全方法(ISWC2024)
笔记整理:刘治强,浙江大学硕士生,研究方向为知识图谱表示学习,大语言模型 论文链接:http://arxiv.org/abs/2407.16127 发表会议:ISWC 2024 1. 动机 传统的知识图谱补全(KGC)模型通过…...
与常用工具深度洞察App瓶颈)
iOS性能调优实战:借助克魔(KeyMob)与常用工具深度洞察App瓶颈
在日常iOS开发过程中,性能问题往往是最令人头疼的一类Bug。尤其是在App上线前的压测阶段或是处理用户反馈的高发期,开发者往往需要面对卡顿、崩溃、能耗异常、日志混乱等一系列问题。这些问题表面上看似偶发,但背后往往隐藏着系统资源调度不当…...

return this;返回的是谁
一个审批系统的示例来演示责任链模式的实现。假设公司需要处理不同金额的采购申请,不同级别的经理有不同的审批权限: // 抽象处理者:审批者 abstract class Approver {protected Approver successor; // 下一个处理者// 设置下一个处理者pub…...

C#中的CLR属性、依赖属性与附加属性
CLR属性的主要特征 封装性: 隐藏字段的实现细节 提供对字段的受控访问 访问控制: 可单独设置get/set访问器的可见性 可创建只读或只写属性 计算属性: 可以在getter中执行计算逻辑 不需要直接对应一个字段 验证逻辑: 可以…...
mac 安装homebrew (nvm 及git)
mac 安装nvm 及git 万恶之源 mac 安装这些东西离不开Xcode。及homebrew 一、先说安装git步骤 通用: 方法一:使用 Homebrew 安装 Git(推荐) 步骤如下:打开终端(Terminal.app) 1.安装 Homebrew…...
免费数学几何作图web平台
光锐软件免费数学工具,maths,数学制图,数学作图,几何作图,几何,AR开发,AR教育,增强现实,软件公司,XR,MR,VR,虚拟仿真,虚拟现实,混合现实,教育科技产品,职业模拟培训,高保真VR场景,结构互动课件,元宇宙http://xaglare.c…...

【Android】Android 开发 ADB 常用指令
查看当前连接的设备 adb devices 连接设备 adb connect 设备IP 断开已连接的设备 adb disconnect 设备IP 安装应用 adb install 安装包的路径 卸载应用 adb uninstall 应用包名 查看已安装的应用包名 adb shell pm list packages 查看已安装的第三方应用包名 adb shell pm list…...
PHP 8.5 即将发布:管道操作符、强力调试
前不久,PHP宣布了即将在 2025 年 11 月 20 日 正式发布的 PHP 8.5!作为 PHP 语言的又一次重要迭代,PHP 8.5 承诺带来一系列旨在提升代码可读性、健壮性以及开发者效率的改进。而更令人兴奋的是,借助强大的本地开发环境 ServBay&am…...
