live555 rtsp服务器实战之doGetNextFrame
live555关于RTSP协议交互流程
live555的核心数据结构值之闭环双向链表
live555 rtsp服务器实战之createNewStreamSource
live555 rtsp服务器实战之doGetNextFrame
live555搭建实时播放rtsp服务器
注意:该篇文章可能有些绕,最好跟着文章追踪下源码,不了解源码可能就是天书;
概要
live555用于实际项目开发时,createNewStreamSource和doGetNextFrame是必须要实现的两个虚函数,一般会创建两个类来实现这两个函数:假如这两个类为H264LiveVideoServerMediaSubssion和H264FramedLiveSource;H264LiveVideoServerMediaSubssion为实时视频会话类,用于实现createNewStreamSource虚函数;
H264FramedLiveSource为实时视频帧资源类,用户实现doGetNextFrame函数;
那么这两个函数是什么时候被调用以及他们的作用是什么呢?本节将详细介绍;
声明:该文章基于H264视频源为基础分析,其他源类似;
由于这两个类主要是自定义虚函数,所以存在一定的继承关系,首先需要明确这两个类的继承关系(本章只介绍H264FramedLiveSource):
H264FramedLiveSource:FramedSource:MediaSource:Medium
doGetNextFrame调用流程
doGetNextFrame函数声明于FrameSource类:
virtual void doGetNextFrame() = 0;该声明为纯虚函数,所以必须有子类对该函数进行实现,H264FramedLiveSource类就是用于实现该函数;doGetNextFrame函数只有一个功能:获取视频帧;
void H264FramedLiveSource::doGetNextFrame()
{uint8_t *frame = new uint8_t[1024*1024];int len = 0;//获取一帧视频帧get_frame(&frame, len);//将帧长度赋值给父类的成员变量fFrameSizefFrameSize = len;//将帧数据赋值给父类的成员变量fTomemcpy(fTo, frame, len);delete [] frame;// nextTask() = envir().taskScheduler().scheduleDelayedTask(0,(TaskFunc*)FramedSource::afterGetting, this);//表示延迟0秒后再执行 afterGetting 函数afterGetting(this);return;
}fFrameSize和fTo的两个父类变量在流传输时会用到;那么问题来了:doGetNextFrame函数在整个流程中在哪里被调用?什么时候调用?
首先doGetNextFrame函数是在PLAY信令交互的时候被调用;调用流程为:
handleCmd_PLAY->startStream->startPlaying(OnDemandServerMediaSubsession)->startPlaying(MediaSink)->continuePlaying(虚函数,子类H264or5VideoRTPSink实现)->continuePlaying(虚函数,子类MultiFramedRTPSink实现)->buildAndSendPacket->packFrame(MultiFramedRTPSink)->getNextFrame->doGetNextFrame下面详解介绍下这个流程,看过我的另一篇文章:"live555 rtsp服务器实战之createNewStreamSource" 的都知道handleRequestBytes函数调用了handleCmd_SETUP;同样handleCmd_PLAY函数也是在这里被调用的;handleRequestBytes函数就是用来处理各种客户端信令交互信息的;handleRequestBytes函数如下:
void RTSPServer::RTSPClientConnection::handleRequestBytes(int newBytesRead)
{...if (urlIsRTSPS != fOurRTSPServer.fOurConnectionsUseTLS){
#ifdef DEBUGfprintf(stderr, "Calling handleCmd_redirect()\n");
#endifhandleCmd_redirect(urlSuffix);}else if (strcmp(cmdName, "OPTIONS") == 0){// If the "OPTIONS" command included a "Session:" id for a session that doesn't exist,// then treat this as an error:if (requestIncludedSessionId && clientSession == NULL){
#ifdef DEBUGfprintf(stderr, "Calling handleCmd_sessionNotFound() (case 1)\n");
#endifhandleCmd_sessionNotFound();}else{// Normal case:handleCmd_OPTIONS();}}else if (urlPreSuffix[0] == '\0' && urlSuffix[0] == '*' && urlSuffix[1] == '\0'){// The special "*" URL means: an operation on the entire server. This works only for GET_PARAMETER and SET_PARAMETER:if (strcmp(cmdName, "GET_PARAMETER") == 0){handleCmd_GET_PARAMETER((char const *)fRequestBuffer);}else if (strcmp(cmdName, "SET_PARAMETER") == 0){handleCmd_SET_PARAMETER((char const *)fRequestBuffer);}else{handleCmd_notSupported();}}else if (strcmp(cmdName, "DESCRIBE") == 0){handleCmd_DESCRIBE(urlPreSuffix, urlSuffix, (char const *)fRequestBuffer);}else if (strcmp(cmdName, "SETUP") == 0){Boolean areAuthenticated = True;if (!requestIncludedSessionId){// No session id was present in the request.// So create a new "RTSPClientSession" object for this request.// But first, make sure that we're authenticated to perform this command:char urlTotalSuffix[2 * RTSP_PARAM_STRING_MAX];// enough space for urlPreSuffix/urlSuffix'\0'urlTotalSuffix[0] = '\0';if (urlPreSuffix[0] != '\0'){strcat(urlTotalSuffix, urlPreSuffix);strcat(urlTotalSuffix, "/");}strcat(urlTotalSuffix, urlSuffix);if (authenticationOK("SETUP", urlTotalSuffix, (char const *)fRequestBuffer)){clientSession = (RTSPServer::RTSPClientSession *)fOurRTSPServer.createNewClientSessionWithId();}else{areAuthenticated = False;}}if (clientSession != NULL){clientSession->handleCmd_SETUP(this, urlPreSuffix, urlSuffix, (char const *)fRequestBuffer);playAfterSetup = clientSession->fStreamAfterSETUP;}else if (areAuthenticated){
#ifdef DEBUGfprintf(stderr, "Calling handleCmd_sessionNotFound() (case 2)\n");
#endifhandleCmd_sessionNotFound();}}else if (strcmp(cmdName, "TEARDOWN") == 0 || strcmp(cmdName, "PLAY") == 0 || strcmp(cmdName, "PAUSE") == 0 || strcmp(cmdName, "GET_PARAMETER") == 0 || strcmp(cmdName, "SET_PARAMETER") == 0){if (clientSession != NULL){clientSession->handleCmd_withinSession(this, cmdName, urlPreSuffix, urlSuffix, (char const *)fRequestBuffer);}else{
#ifdef DEBUGfprintf(stderr, "Calling handleCmd_sessionNotFound() (case 3)\n");
#endifhandleCmd_sessionNotFound();}}else if (strcmp(cmdName, "REGISTER") == 0 || strcmp(cmdName, "DEREGISTER") == 0){// Because - unlike other commands - an implementation of this command needs// the entire URL, we re-parse the command to get it:char *url = strDupSize((char *)fRequestBuffer);if (sscanf((char *)fRequestBuffer, "%*s %s", url) == 1){// Check for special command-specific parameters in a "Transport:" header:Boolean reuseConnection, deliverViaTCP;char *proxyURLSuffix;parseTransportHeaderForREGISTER((const char *)fRequestBuffer, reuseConnection, deliverViaTCP, proxyURLSuffix);handleCmd_REGISTER(cmdName, url, urlSuffix, (char const *)fRequestBuffer, reuseConnection, deliverViaTCP, proxyURLSuffix);delete[] proxyURLSuffix;}else{handleCmd_bad();}delete[] url;}else{// The command is one that we don't handle:handleCmd_notSupported();}...
}handleCmd_withinSession函数内部就调用了handleCmd_PLAY函数;仅整理流程,调用途中的函数这里不做解释;直接跳到packFrame(MultiFramedRTPSink)函数:
void MultiFramedRTPSink::packFrame()
{// Get the next frame.// First, skip over the space we'll use for any frame-specific header:fCurFrameSpecificHeaderPosition = fOutBuf->curPacketSize();fCurFrameSpecificHeaderSize = frameSpecificHeaderSize();fOutBuf->skipBytes(fCurFrameSpecificHeaderSize);fTotalFrameSpecificHeaderSizes += fCurFrameSpecificHeaderSize;// See if we have an overflow frame that was too big for the last pktif (fOutBuf->haveOverflowData()){// Use this frame before reading a new one from the sourceunsigned frameSize = fOutBuf->overflowDataSize();struct timeval presentationTime = fOutBuf->overflowPresentationTime();unsigned durationInMicroseconds = fOutBuf->overflowDurationInMicroseconds();fOutBuf->useOverflowData();afterGettingFrame1(frameSize, 0, presentationTime, durationInMicroseconds);}else{// Normal case: we need to read a new frame from the sourceif (fSource == NULL)return;fSource->getNextFrame(fOutBuf->curPtr(), fOutBuf->totalBytesAvailable(),afterGettingFrame, this, ourHandleClosure, this);}
}这里调用了getNextFrame函数,来看下getNextFrame函数的实现:
void FramedSource::getNextFrame(unsigned char* to, unsigned maxSize,afterGettingFunc* afterGettingFunc,void* afterGettingClientData,onCloseFunc* onCloseFunc,void* onCloseClientData) {// Make sure we're not already being read:if (fIsCurrentlyAwaitingData) {envir() << "FramedSource[" << this << "]::getNextFrame(): attempting to read more than once at the same time!\n";envir().internalError();}fTo = to;fMaxSize = maxSize;fNumTruncatedBytes = 0; // by default; could be changed by doGetNextFrame()fDurationInMicroseconds = 0; // by default; could be changed by doGetNextFrame()fAfterGettingFunc = afterGettingFunc;fAfterGettingClientData = afterGettingClientData;fOnCloseFunc = onCloseFunc;fOnCloseClientData = onCloseClientData;fIsCurrentlyAwaitingData = True;doGetNextFrame();
}发现啦!发现doGetNextFrame函数啦!所以doGetNextFrame函数就是在getNextFrame内被调用的;但是问题来了:搜索可以发现在live555中doGetNextFrame函数很多;怎么就确定这里的doGetNextFrame和我们自定义的doGetNextFrame有关呢?
问的好!那这的关键点就在于fSource->getNextFrame的fSource变量到底是什么类的对象;才能确定doGetNextFrame到底调用的是哪个类的函数;fSource属于MediaSink类的成员变量:
FramedSource* fSource;但是FrameSource子类很多;所以需要确定fSource到底指向的是哪个子类;
既然fSource是MediaSink类的成员,那么fSource肯定是在MediaSink或其子类中被赋值;因此查找下这些类;首先明确下MediaSink的继承关系,从fSource调用的类开始查找:
//父类
MultiFramedRTPSink:RTPSink:MediaSink:Medium
//子类
H264VideoRTPSink:H264or5VideoRTPSink:VideoRTPSink:MultiFramedRTPSink因此在这些类中查找即可;根据调用流程可知startPlaying最先赋值,值是startPlaying的第一个参数;
Boolean MediaSink::startPlaying(MediaSource& source,afterPlayingFunc* afterFunc,void* afterClientData) {// Make sure we're not already being played:if (fSource != NULL) {envir().setResultMsg("This sink is already being played");return False;}// Make sure our source is compatible:if (!sourceIsCompatibleWithUs(source)) {envir().setResultMsg("MediaSink::startPlaying(): source is not compatible!");return False;}fSource = (FramedSource*)&source;fAfterFunc = afterFunc;fAfterClientData = afterClientData;return continuePlaying();
}而该函数是在StreamState类中的startPlaying函数中调用;
void StreamState ::startPlaying(Destinations *dests, unsigned clientSessionId,TaskFunc *rtcpRRHandler, void *rtcpRRHandlerClientData,ServerRequestAlternativeByteHandler *serverRequestAlternativeByteHandler,void *serverRequestAlternativeByteHandlerClientData)
{...if (!fAreCurrentlyPlaying && fMediaSource != NULL){if (fRTPSink != NULL){fRTPSink->startPlaying(*fMediaSource, afterPlayingStreamState, this);fAreCurrentlyPlaying = True;}else if (fUDPSink != NULL){fUDPSink->startPlaying(*fMediaSource, afterPlayingStreamState, this);fAreCurrentlyPlaying = True;}}
}startPlaying的第一个参数是fMediaSource;而fMediaSource是在StreamState类的构造函数中被赋值的:
StreamState::StreamState(OnDemandServerMediaSubsession &master,Port const &serverRTPPort, Port const &serverRTCPPort,RTPSink *rtpSink, BasicUDPSink *udpSink,unsigned totalBW, FramedSource *mediaSource,Groupsock *rtpGS, Groupsock *rtcpGS): fMaster(master), fAreCurrentlyPlaying(False), fReferenceCount(1),fServerRTPPort(serverRTPPort), fServerRTCPPort(serverRTCPPort),fRTPSink(rtpSink), fUDPSink(udpSink), fStreamDuration(master.duration()),fTotalBW(totalBW), fRTCPInstance(NULL) /* created later */,fMediaSource(mediaSource), fStartNPT(0.0), fRTPgs(rtpGS), fRTCPgs(rtcpGS)
{
}StreamState是在OnDemandServerMediaSubsession类的getStreamParameters函数中被调用:
void OnDemandServerMediaSubsession ::getStreamParameters(unsigned clientSessionId,struct sockaddr_storage const &clientAddress,Port const &clientRTPPort,Port const &clientRTCPPort,int tcpSocketNum,unsigned char rtpChannelId,unsigned char rtcpChannelId,TLSState *tlsState,struct sockaddr_storage &destinationAddress,u_int8_t & /*destinationTTL*/,Boolean &isMulticast,Port &serverRTPPort,Port &serverRTCPPort,void *&streamToken)
{if (addressIsNull(destinationAddress)){// normal case - use the client address as the destination address:destinationAddress = clientAddress;}isMulticast = False;if (fLastStreamToken != NULL && fReuseFirstSource){// Special case: Rather than creating a new 'StreamState',// we reuse the one that we've already created:serverRTPPort = ((StreamState *)fLastStreamToken)->serverRTPPort();serverRTCPPort = ((StreamState *)fLastStreamToken)->serverRTCPPort();++((StreamState *)fLastStreamToken)->referenceCount();streamToken = fLastStreamToken;}else{// Normal case: Create a new media source:unsigned streamBitrate;FramedSource *mediaSource = createNewStreamSource(clientSessionId, streamBitrate);...streamToken = fLastStreamToken = new StreamState(*this, serverRTPPort, serverRTCPPort, rtpSink, udpSink,streamBitrate, mediaSource,rtpGroupsock, rtcpGroupsock);}
}createNewStreamSource函数加上OnDemandServerMediaSubsession类是不是很熟悉?对的OnDemandServerMediaSubsession就是我们自定义的用于实现createNewStreamSource函数的类H264LiveVideoServerMediaSubssion的父类;因为createNewStreamSource在OnDemandServerMediaSubsession中是纯虚函数,因此该处调用的就是我们自定义的createNewStreamSource函数;
因此在startPlaying函数中将fSource赋值为createNewStreamSource的返回值;我们再看一下createNewStreamSource函数吧:
FramedSource* H264LiveVideoServerMediaSubssion::createNewStreamSource(unsigned clientSessionId, unsigned& estBitrate)
{/* Remain to do : assign estBitrate */estBitrate = 1000; // kbps, estimate//创建视频源H264FramedLiveSource* liveSource = H264FramedLiveSource::createNew(envir(), Server_datasize, Server_databuf, Server_dosent);if (liveSource == NULL){return NULL;}// Create a framer for the Video Elementary Stream:return H264VideoStreamFramer::createNew(envir(), liveSource);
}则fSource就是H264VideoStreamFramer::createNew(envir(), liveSource); 因此getNextFrame函数中运行的doGetNextFrame就是H264VideoStreamFramer中的doGetNextFrame函数;
等等!发现问题没有:这个并不是我们自定义的H264FramedLiveSource类中获取视频帧的函数doGetNextFrame;这是为什么呢?
别急!返回值中H264VideoStreamFramer::createNew(envir(), liveSource); 将doGetNextFrame的类对象liveSource传递进了H264VideoStreamFramer类中;而liveSource最终赋值给了StreamParser类中成员变量fInputSource和FramedFilter类的成员变量fInputSource;更多细节参考我的另一篇文章;
接着往下说:H264VideoStreamFramer中的doGetNextFrame函数会调用MPEGVideoStreamFramer中的doGetNextFrame函数;在这个函数中有一个ensureValidBytes1第一次调用了自定义的函数doGetNextFrame
void StreamParser::ensureValidBytes1(unsigned numBytesNeeded) {
.
.
.fInputSource->getNextFrame(&curBank()[fTotNumValidBytes],maxNumBytesToRead,afterGettingBytes, this,onInputClosure, this);throw NO_MORE_BUFFERED_INPUT;
}这里仅仅是对流的解析;下面才是真正获取视频流:
void H264or5Fragmenter::afterGettingFrame(void* clientData, unsigned frameSize,unsigned numTruncatedBytes,struct timeval presentationTime,unsigned durationInMicroseconds) {H264or5Fragmenter* fragmenter = (H264or5Fragmenter*)clientData;fragmenter->afterGettingFrame1(frameSize, numTruncatedBytes, presentationTime,durationInMicroseconds);
}void H264or5Fragmenter::afterGettingFrame1(unsigned frameSize,unsigned numTruncatedBytes,struct timeval presentationTime,unsigned durationInMicroseconds) {fNumValidDataBytes += frameSize;fSaveNumTruncatedBytes = numTruncatedBytes;fPresentationTime = presentationTime;fDurationInMicroseconds = durationInMicroseconds;// Deliver data to the client:doGetNextFrame();
}void H264or5Fragmenter::doGetNextFrame() {if (fNumValidDataBytes == 1) {// We have no NAL unit data currently in the buffer. Read a new one:fInputSource->getNextFrame(&fInputBuffer[1], fInputBufferSize - 1,afterGettingFrame, this,FramedSource::handleClosure, this);} else {...}
}afterGettingFrame函数才是真正调用doGetNextFrame的函数?那么afterGettingFrame是在哪里被调用的呢?
看一下fSource->getNextFrame函数:
fInputSource->getNextFrame(fOutBuf->curPtr(), fOutBuf->totalBytesAvailable(),afterGettingFrame, this, ourHandleClosure, this);这里第三个参数就调用了afterGettingFrame函数,再看看getNextFrame函数实现;上面已经写过了 为了方便理解这里再写下:
void FramedSource::getNextFrame(unsigned char* to, unsigned maxSize,afterGettingFunc* afterGettingFunc,void* afterGettingClientData,onCloseFunc* onCloseFunc,void* onCloseClientData) {// Make sure we're not already being read:if (fIsCurrentlyAwaitingData) {envir() << "FramedSource[" << this << "]::getNextFrame(): attempting to read more than once at the same time!\n";envir().internalError();}fTo = to;fMaxSize = maxSize;fNumTruncatedBytes = 0; // by default; could be changed by doGetNextFrame()fDurationInMicroseconds = 0; // by default; could be changed by doGetNextFrame()fAfterGettingFunc = afterGettingFunc;fAfterGettingClientData = afterGettingClientData;fOnCloseFunc = onCloseFunc;fOnCloseClientData = onCloseClientData;fIsCurrentlyAwaitingData = True;doGetNextFrame();
}afterGettingFrame被赋值给了fAfterGettingClientData指针;那么fAfterGettingClientData指针什么时候被调用的?
回望doGetNextFrame的实现,每次读完流都会调用:
afterGetting(this);
//函数实现
void FramedSource::afterGetting(FramedSource* source) {source->nextTask() = NULL;source->fIsCurrentlyAwaitingData = False;// indicates that we can be read again// Note that this needs to be done here, in case the "fAfterFunc"// called below tries to read another frame (which it usually will)if (source->fAfterGettingFunc != NULL) {(*(source->fAfterGettingFunc))(source->fAfterGettingClientData,source->fFrameSize, source->fNumTruncatedBytes,source->fPresentationTime,source->fDurationInMicroseconds);}
}afterGetting的函数实现中就调用了fAfterGettingFunc指针;这就使doGetNextFrame形成了闭环:

至此函数doGetNextFrame的执行流程已经全部解析完毕,后续还会继续更新关于doGetNextFrame函数获取的帧数据是怎么处理和发送的,H264VideoStreamFramer中的doGetNextFrame函数和MPEGVideoStreamFramer中的doGetNextFrame函数都是什么作用!期待的话关注我,了解最新动态!
该文章持续更新!如果有错误或者模糊的地方欢迎留言探讨!
相关文章:

live555 rtsp服务器实战之doGetNextFrame
live555关于RTSP协议交互流程 live555的核心数据结构值之闭环双向链表 live555 rtsp服务器实战之createNewStreamSource live555 rtsp服务器实战之doGetNextFrame live555搭建实时播放rtsp服务器 注意:该篇文章可能有些绕,最好跟着文章追踪下源码&…...

Nginx系列-3 servername优先级和location优先级和常用正则表达式
1.正则表达式和分组 由于Nginx配置文件中经常出现正则表达式,因此本章节专门对常见的正则表达式进行简单介绍。 [1] 开始与结束 ^表示匹配输入字符串的开始 $表示匹配输入字符串的结束[2] 匹配次数 ?表示匹配0次或者1次 表示匹配1次或多次 *表示匹配0从或多次…...

python—爬虫爬取电影页面实例
下面是一个简单的爬虫实例,使用Python的requests库来发送HTTP请求,并使用lxml库来解析HTML页面内容。这个爬虫的目标是抓取一个电影网站,并提取每部电影的主义部分。 首先,确保你已经安装了requests和lxml库。如果没有安装&#x…...

实现图片拖拽和缩小放大功能。
1. 前言 不知道各位前端小伙伴蓝湖使用的多不多,反正我是经常在用,ui将原型图设计好后上传至蓝湖,前端开发人员就可以开始静态页面的的编写了。对于页面细节看的不是很清楚可以使用滚轮缩放后再拖拽查看,还是很方便的。于是就花了…...

昇思25天学习打卡营第18天|munger85
DCGAN生成漫画头像 首先肯定是下载训练数据,而这些训练数据就是一些卡通头像。后来我们会看到这个具体的头像 就像其他的数据集目录一样,它是由一些目录和这个目录下面的文件组成的数据集。 有相当多的图片。所以可以训练出来比较好的效果。 图片的处理…...

nginx配置文件说明
Nginx的配置文件说明 Nginx配置文件的主要配置块可以分为三个部分:全局配置块(events和http块),events块和http块。这三个部分共同定义了Nginx服务器的整体行为和处理HTTP请求的方式。 全局配置块: 包含了影响Nginx服…...

用不同的url头利用Python访问一个网站,把返回的东西保存为txt文件
这个需要调用requests模块(相当于c的头文件) import requests 还需要一个User-Agent头(这个意思就是告诉python用的什么系统和浏览器) Google Chrome(Windows): Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64…...

一文掌握Prometheus实现页面登录认证并集成grafana
一、接入方式 以保护Web站点的访问控制,如HTTP 服务器配置中实现安全的加密通信和身份验证,保护 Web 应用程序和用户数据的安全性。 1.1 加密密码 通过httpd-tools工具包来进行Web站点加密 yum install -y httpd-tools方式一:通过htpasswd生…...

欢迎来到 Mint Expedition:Web3 和 NFT 的新时代开始
7 月 15 日,Mint Expedition 正式开启,作为 Mint 生态系统的旗舰项目,将彻底变革 Web3 和 NFT 去中心化应用! Mint Expedition 是 Mint 的最新航程,延续了 Mint Forest 的成功。Mint Forest 吸引了超过 41.4 万独立用…...

针对环境构图的全局一致性扫描点云数据对齐(Graph SLAM)
本算法是一个经典的,针对SLAM(simultaneous localization and mapping 即时定位与地图构建)问题而提出的算法。该算法的提出者是Feng Lu和Evangelos Milios,他们在本算法中开创了通过全局优化方程组以减少约束引入的误差来进一步优…...

Matlab学习笔记01 - 基本数据类型
Matlab学习笔记01 - 基本数据类型 1、数据类型转换2、矩阵2.1 访问单个矩阵元素2.2 访问多个矩阵元素2.3 矩阵转置 3、字符与字符串4、数值与字符串5、元胞数组 1、数据类型转换 十进制转十六进制字符串‘FF’ >> hex2dec(3ff)ans 1023十进制转十六进制字符串 >>…...

基于重要抽样的主动学习不平衡分类方法ALIS
这篇论文讨论了数据分布不平衡对分类器性能造成的影响,并提出了一种新的有效解决方案 - 主动学习框架ALIS。 1、数据分布不平衡会影响分类器的学习性能。现有的方法主要集中在过采样少数类或欠采样多数类,但往往只采用单一的采样技术,无法有效解决严重的类别不平衡问题。 2、论…...

Python爬虫(基本流程)
1. 确定目标和范围 明确需求:确定你需要从哪些网站抓取哪些数据。合法性:检查目标网站的robots.txt文件,了解哪些内容可以被抓取。数据范围:确定爬取数据的起始和结束点,比如时间范围、页面数量等。 2. 选择合适的工…...

primeflex教学笔记20240720, FastAPI+Vue3+PrimeVue前后端分离开发
练习 先实现基本的页面结构: 代码如下: <template><div class"flex p-3 bg-gray-100 gap-3"><div class"w-20rem h-12rem bg-indigo-200 flex justify-content-center align-items-center text-white text-5xl">…...
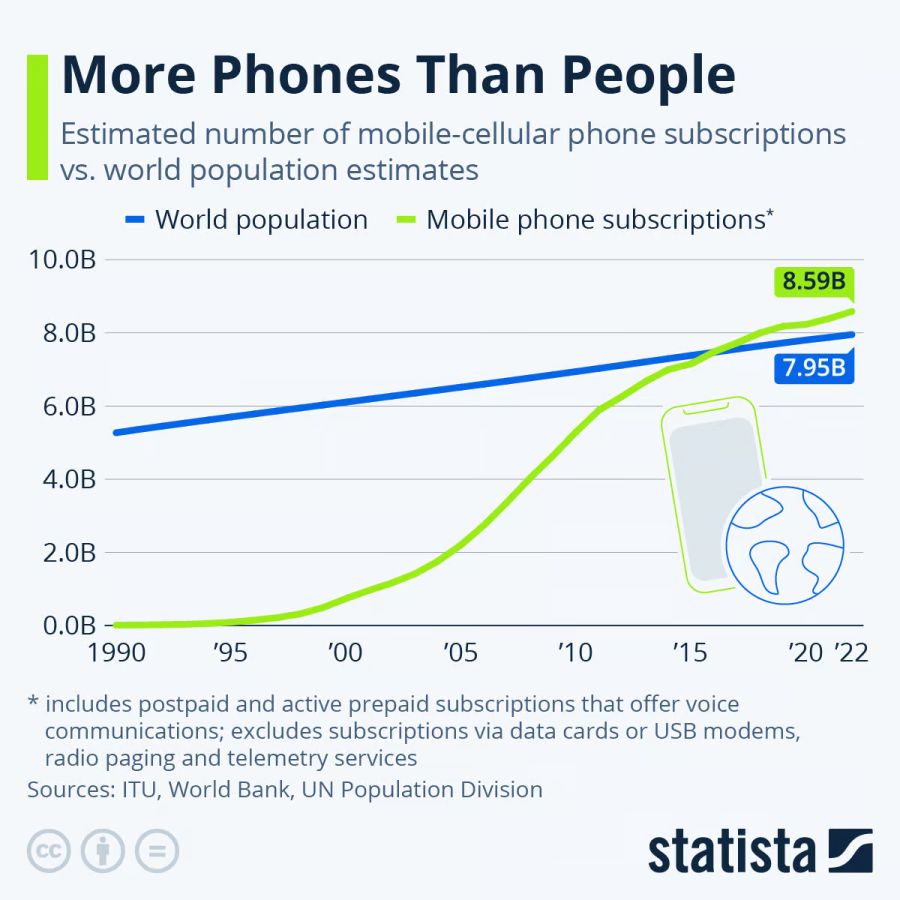
移动设备安全革命:应对威胁与解决方案
移动设备已成为我们日常工作和家庭生活中不可或缺的工具,然而,对于它们安全性的关注和投资仍然远远不够。本文深入分析了移动设备安全的发展轨迹、目前面临的威胁态势,以及业界对于这些安全漏洞响应迟缓的深层原因。文中还探讨了人们在心理层…...

【C语言】 链表实现学生管理系统(堆区开辟空间)
总体思路都能写出来,问题是感觉稍微比之前的麻烦一些,在刚开始创建结构体的时候,并没有去按照链表的思路去写,导致写成了顺序表,后面就一直纠结空间怎么开辟。 链表是由一个头节点和其它申请出来的小节点连起来的&…...

STM32实战篇:按键(外部输入信号)触发中断
功能要求 将两个按键分别与引脚PA0、PA1相连接,通过按键按下,能够触发中断响应程序(不需明确功能)。 代码流程如下: 实现代码 #include "stm32f10x.h" // Device headerint main() {//开…...

Android SurfaceView 组件介绍,挖洞原理详解
文章目录 组件介绍基本概念关键特性使用场景 SurfaceHolder介绍主要功能使用示例 SurfaceView 挖洞原理工作机制 使用SurfaceView展示图片示例创建一个自定义的 SurfaceView类在 Activity 中使用 ImageSurfaceView注意事项效果展示 组件介绍 在 Android 开发中,Sur…...

day2加餐 Go 接口型函数的使用场景
文章目录 问题价值使用场景其他语言类似特性 问题 在 动手写分布式缓存 - GeeCache day2 单机并发缓存 这篇文章中,有一个接口型函数的实现: // A Getter loads data for a key. type Getter interface {Get(key string) ([]byte, error) }// A Getter…...

摄像头 RN6752v1 视频采集卡
摄像头 AHD倒车摄像头比较好,AHD英文全名Analog High Definition,即模拟高清,拥有比较好的分辨率与画面质感。 RN6752v1 GQW AKKY2 usb 采集卡 FHD(1080p)、HD(720p)和D1(480i&am…...

oracle与MySQL数据库之间数据同步的技术要点
Oracle与MySQL数据库之间的数据同步是一个涉及多个技术要点的复杂任务。由于Oracle和MySQL的架构差异,它们的数据同步要求既要保持数据的准确性和一致性,又要处理好性能问题。以下是一些主要的技术要点: 数据结构差异 数据类型差异ÿ…...
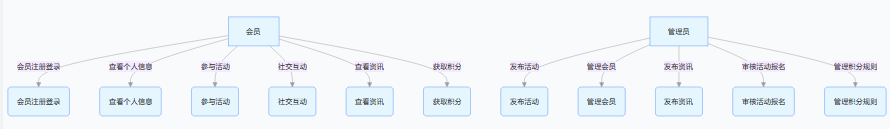
SpringBoot+uniapp 的 Champion 俱乐部微信小程序设计与实现,论文初版实现
摘要 本论文旨在设计并实现基于 SpringBoot 和 uniapp 的 Champion 俱乐部微信小程序,以满足俱乐部线上活动推广、会员管理、社交互动等需求。通过 SpringBoot 搭建后端服务,提供稳定高效的数据处理与业务逻辑支持;利用 uniapp 实现跨平台前…...

rnn判断string中第一次出现a的下标
# coding:utf8 import torch import torch.nn as nn import numpy as np import random import json""" 基于pytorch的网络编写 实现一个RNN网络完成多分类任务 判断字符 a 第一次出现在字符串中的位置 """class TorchModel(nn.Module):def __in…...

Go 语言并发编程基础:无缓冲与有缓冲通道
在上一章节中,我们了解了 Channel 的基本用法。本章将重点分析 Go 中通道的两种类型 —— 无缓冲通道与有缓冲通道,它们在并发编程中各具特点和应用场景。 一、通道的基本分类 类型定义形式特点无缓冲通道make(chan T)发送和接收都必须准备好࿰…...

【Nginx】使用 Nginx+Lua 实现基于 IP 的访问频率限制
使用 NginxLua 实现基于 IP 的访问频率限制 在高并发场景下,限制某个 IP 的访问频率是非常重要的,可以有效防止恶意攻击或错误配置导致的服务宕机。以下是一个详细的实现方案,使用 Nginx 和 Lua 脚本结合 Redis 来实现基于 IP 的访问频率限制…...
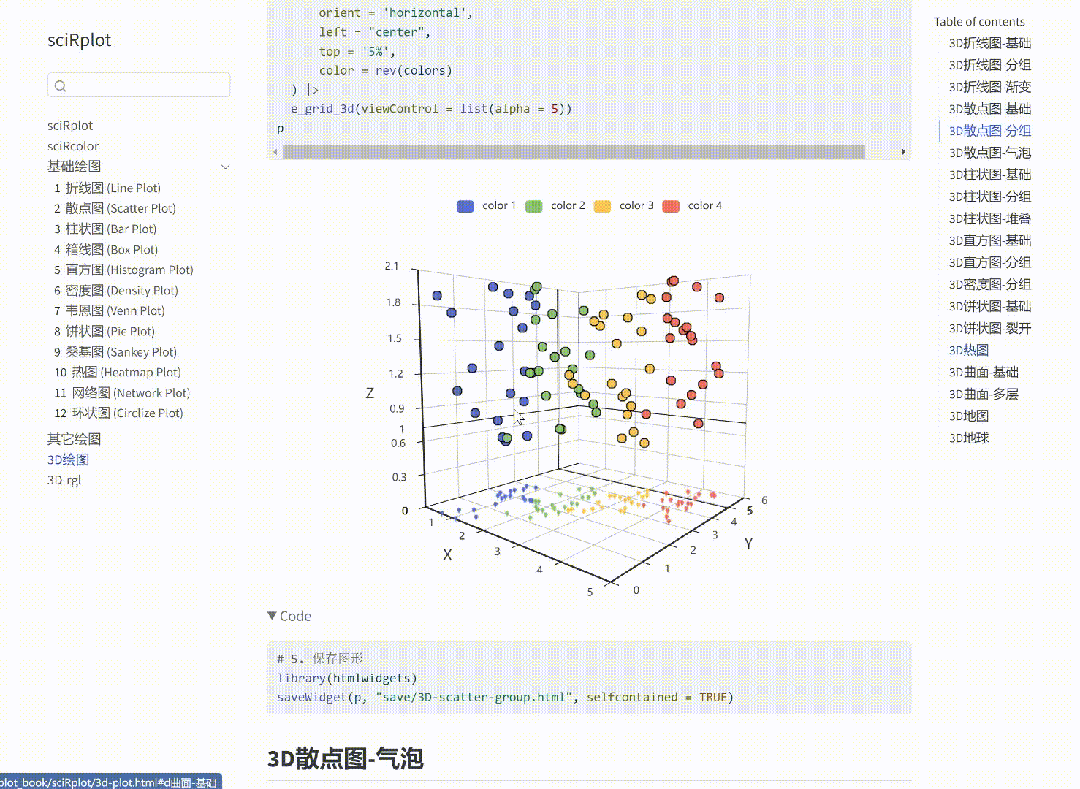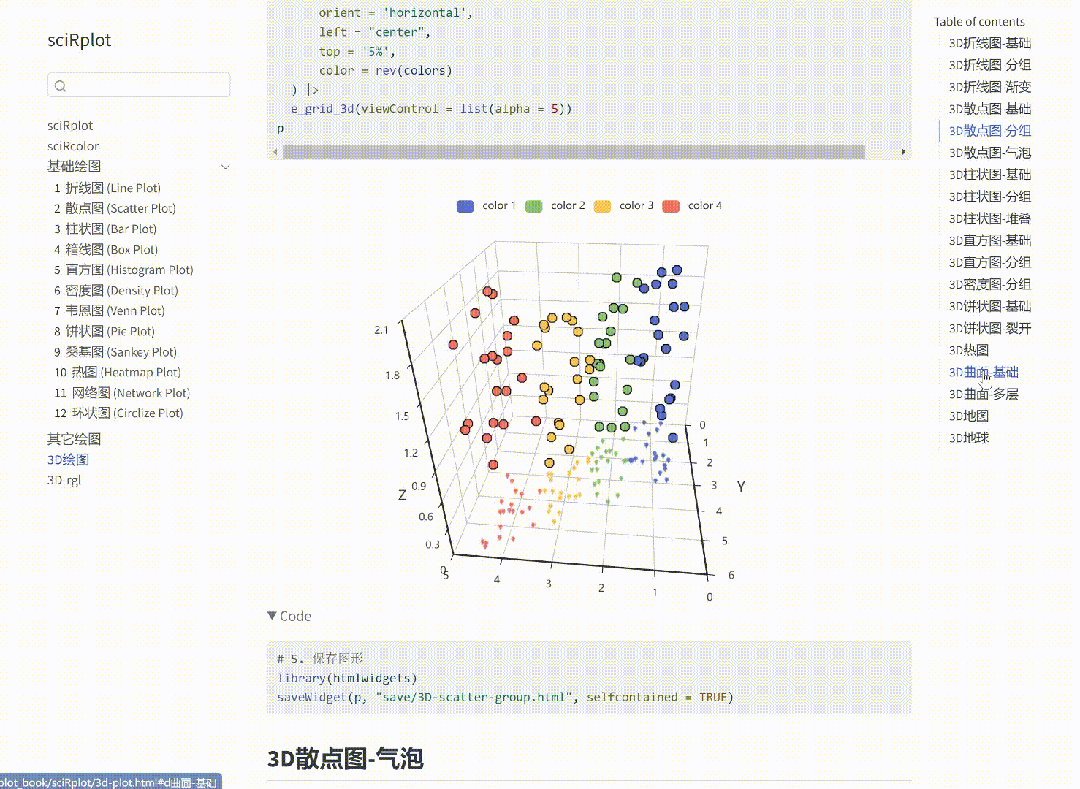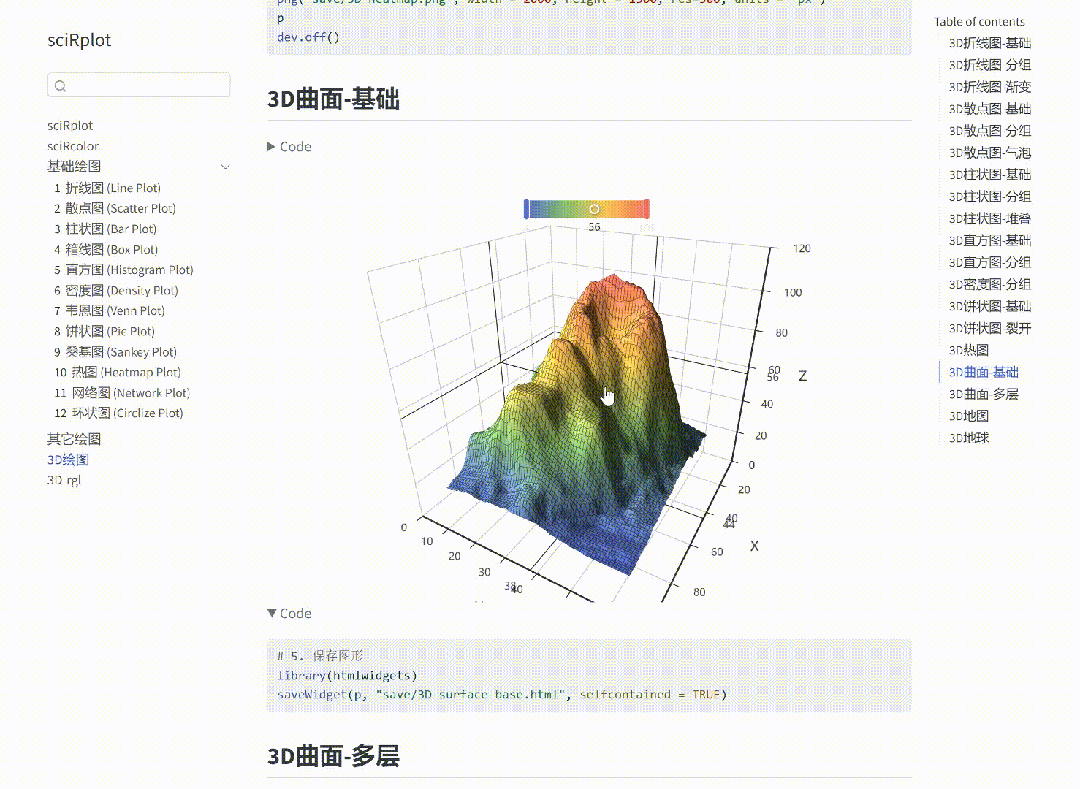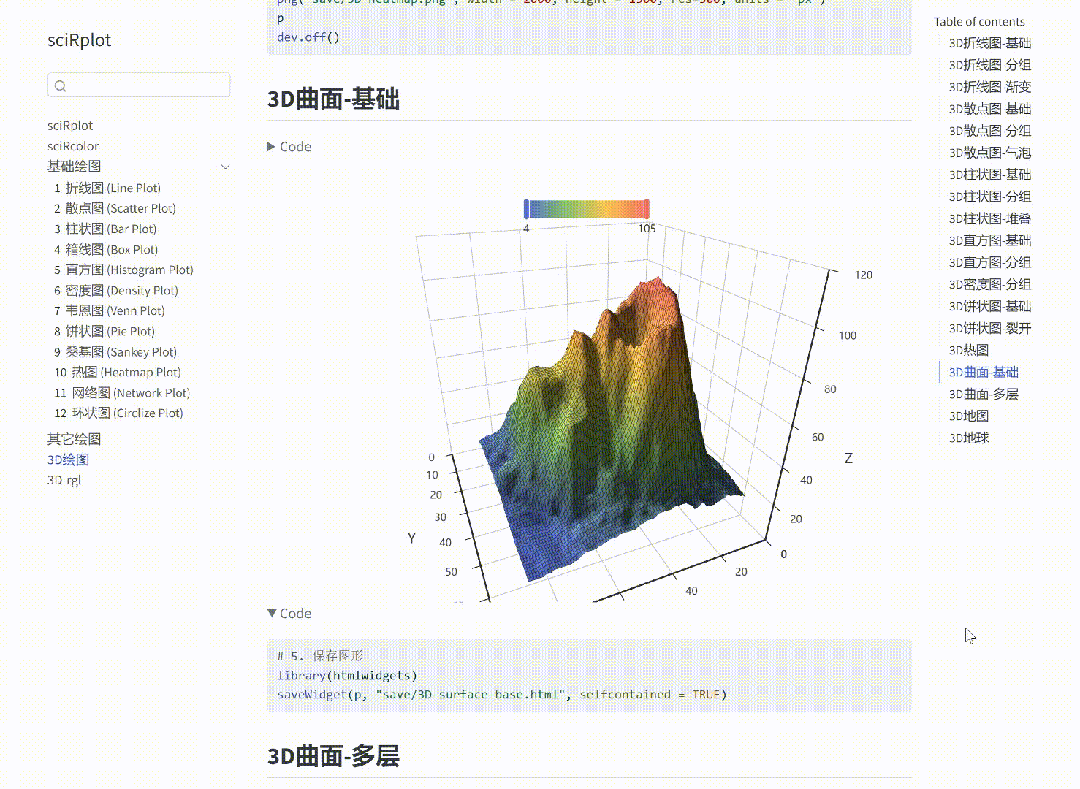
R 语言科研绘图第 55 期 --- 网络图-聚类
在发表科研论文的过程中,科研绘图是必不可少的,一张好看的图形会是文章很大的加分项。 为了便于使用,本系列文章介绍的所有绘图都已收录到了 sciRplot 项目中,获取方式: R 语言科研绘图模板 --- sciRplothttps://mp.…...
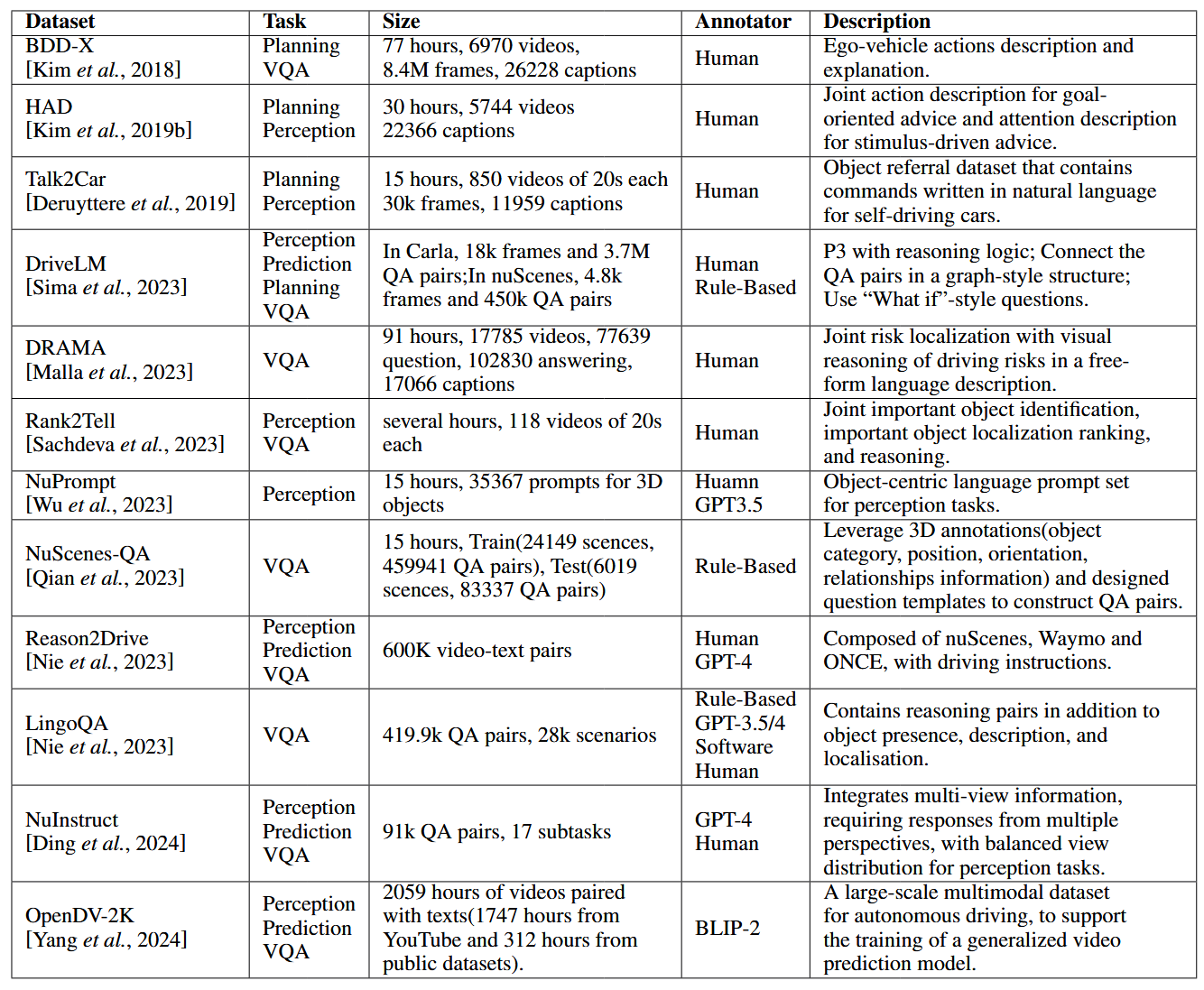
论文阅读:LLM4Drive: A Survey of Large Language Models for Autonomous Driving
地址:LLM4Drive: A Survey of Large Language Models for Autonomous Driving 摘要翻译 自动驾驶技术作为推动交通和城市出行变革的催化剂,正从基于规则的系统向数据驱动策略转变。传统的模块化系统受限于级联模块间的累积误差和缺乏灵活性的预设规则。…...
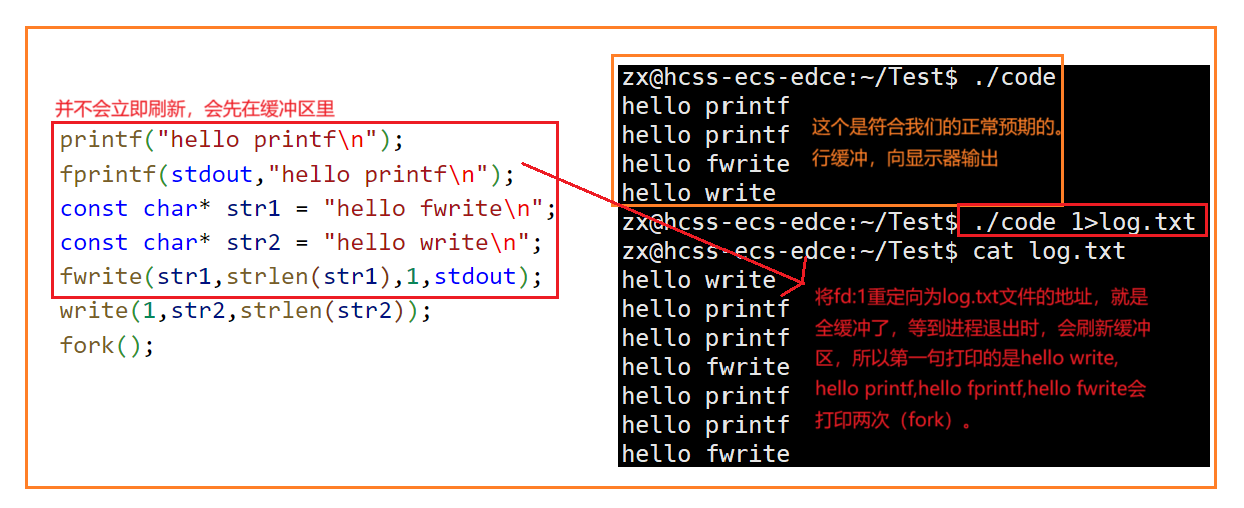
Linux中《基础IO》详细介绍
目录 理解"文件"狭义理解广义理解文件操作的归类认知系统角度文件类别 回顾C文件接口打开文件写文件读文件稍作修改,实现简单cat命令 输出信息到显示器,你有哪些方法stdin & stdout & stderr打开文件的方式 系统⽂件I/O⼀种传递标志位…...

人工智能 - 在Dify、Coze、n8n、FastGPT和RAGFlow之间做出技术选型
在Dify、Coze、n8n、FastGPT和RAGFlow之间做出技术选型。这些平台各有侧重,适用场景差异显著。下面我将从核心功能定位、典型应用场景、真实体验痛点、选型决策关键点进行拆解,并提供具体场景下的推荐方案。 一、核心功能定位速览 平台核心定位技术栈亮…...
Java后端检查空条件查询
通过抛出运行异常:throw new RuntimeException("请输入查询条件!");BranchWarehouseServiceImpl.java // 查询试剂交易(入库/出库)记录Overridepublic List<BranchWarehouseTransactions> queryForReagent(Branch…...
