Oracle DBMS_XPLAN包
DBMS_XPLAN 包的解释和关键点
DBMS_XPLAN 包是 Oracle 数据库中一个重要的工具,它允许数据库管理员和开发人员以各种方式显示 SQL 语句的执行计划,这对于 SQL 优化和性能诊断至关重要。以下是主要函数及其描述:
用于显示执行计划的主要函数
- display
-
- 目的: 显示存储在指定计划表中的执行计划。
- 参数:
-
-
table_name(默认值'PLAN_TABLE'): 计划表的名称。statement_id(可选): 标识 SQL 语句的 ID。format(默认值'TYPICAL'): 输出计划的格式。filter_preds(可选): 用于过滤计划表内容的谓词。
-
- display_cursor
-
- 目的: 显示当前或最后执行的 SQL 语句的执行计划。
- 参数:
-
-
sql_id(可选): 指定 SQL 语句的sql_id。cursor_child_no(默认值0): 指定游标的子号。format(默认值'TYPICAL'): 输出计划的格式。
-
- display_awr
-
- 目的: 显示存储在 AWR(自动工作负载库)中的执行计划。
- 参数:
-
-
sql_id: 指定 SQL 语句的sql_id。plan_hash_value(可选): 指定特定的执行计划。db_id(可选): 指定特定数据库的 ID。format(默认值'TYPICAL'): 输出计划的格式。
-
- display_sqlset
-
- 目的: 显示存储在 SQL 调优集中 SQL 语句的执行计划。
- 参数:
-
-
sqlset_name: SQL 调优集的名称。sql_id: 指定 SQL 语句的sql_id。plan_hash_value(可选): 指定特定的执行计划。format(默认值'TYPICAL'): 输出计划的格式。sqlset_owner(可选): SQL 调优集的拥有者,默认是当前用户。
-
- display_sql_plan_baseline
-
- 目的: 显示 SQL 计划基线中的执行计划。
- 参数:
-
-
sql_handle(可选): 标识 SQL 语句的句柄。plan_name(可选): 指定特定计划的名称。format(默认值'TYPICAL'): 输出计划的格式。
-
内部使用的私有函数和过程
这些函数和过程用于内部用途,主要用于数据准备和格式验证,不需要公开文档。
- prepare_records: 准备记录的内部过程。
- validate_format: 验证用户格式的内部函数。
- format_size, format_number: 格式化数字和大小的函数。
- format_time_s: 格式化时间(秒)的函数。
- prepare_plan_xml_query: 为查询构建 XML 版本的辅助函数。
- build_plan_xml: 生成 XML 版本的执行计划。
- display_plan: 以 CLOB 格式返回执行计划。
比较执行计划的支持函数
这些函数用于比较不同执行计划,通常返回任务 ID,供后续报告生成使用。
- diff_plan_outline: 比较两个通过指定轮廓生成的 SQL 计划。
- diff_plan: 比较参考计划和目标计划。
- diff_plan_sql_baseline: 比较 SQL 计划基线中的两个计划。
- diff_plan_cursor: 比较从指定游标子号生成的两个 SQL 计划。
- diff_plan_awr: 比较通过指定计划哈希值生成的两个 SQL 计划。
- get_plandiff_report_xml: 构建差异报告的 XML 版本。
示例代码
显示存储在计划表中的执行计划
SET LINESIZE 150
SET PAGESIZE 2000
SELECT * FROM TABLE(dbms_xplan.display);显示当前或最后执行的 SQL 语句的执行计划
SET LINESIZE 150
SET PAGESIZE 2000
SELECT * FROM TABLE(dbms_xplan.display_cursor);显示存储在 AWR 中的执行计划
SET LINESIZE 150
SET PAGESIZE 2000
SELECT t.*
FROM dba_hist_sqltext ht,TABLE(dbms_xplan.display_awr(ht.sql_id, NULL, NULL, '-PREDICATE +ALIAS')) t
WHERE ht.sql_text LIKE '%sAleS%';函数
create or replace package dbms_xplan AUTHID CURRENT_USER as--- --------------------------------------------------------------------------- DBMS_XPLAN CONSTANTS SECTION--- --------------------------------------------------------------------------- The following constants designate the flags returned in the bit vector--- from the COMPARE_QUERY_PLANS function.UNKNOWN_DIFF_CLASS CONSTANT NUMBER := POWER(2,31);--- --------------------------------------------------------------------------- DBMS_XPLAN PUBLIC FUNCTIONS SECTION--- ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ OVERVIEW------ This package defines several table functions which can be used to--- display execution plans.------ - DISPLAY is generally used to display the execution plan produced--- by an EXPLAIN PLAN command; you can either display the most--- recent explained statement, or the statement for a specific--- statement id.------ In addition, this table function can also be used to display--- any plan (with or without statistics) stored in a table as--- long as the columns of this table are named the same as--- columns of the plan_table (or v$sql_plan_statistics_all if--- statistics are included).--- A predicate on the specified table can be used to select rows--- of the plan to display.------ - DISPLAY_CURSOR displays the execution plans for one or several--- cursors in the shared SQL area, depending on a filter--- criteria. It can display the plan for the last executed--- statement, the current (if session is active) or last--- executed statement (if session is inactive) of a specific--- session, or all cursors matching an arbitrary criteria--- defined via SQL. In addition to the explain plan, various--- plan statistics (e.g. io, memory and timing) can be--- reported (based on the v$sql_plan_statistics_all views).------ Specific cursors are identified by SQL_ID and optionally a--- SQL_CHILD_NUMBER.------ The DEFAULT without any parameters shows the last executed--- statement of the session.------ NOTE: To use the DISPLAY_CURSOR functionality, the calling--- user must have SELECT privilege on V$SQL_PLAN_STATISTICS_ALL,--- V$SQL, and V$SQL_PLAN. By default, only the select_catalog--- role has the SELECT privilege on these views.------ - DISPLAY_AWR displays the execution plans for SQL statements stored in--- the Automatic Workload Repository (AWR).--- NOTE: To use the DISPLAY_AWR functionality, the calling user--- must have SELECT prvilege on DBA_HIST_SQL_PLAN and--- DBA_HIST_SQLTEXT. By default, select privilige for these--- views is granted to the select_catalog role.------ - DISPLAY_SQLSET displays the execution plans for SQL statements stored--- in a SQL tuning set.--- NOTE: To use the DISPLAY_SQLSET functionality, the calling--- user must have SELECT prvilege on ALL_SQLSET_PLANS and--- ALL_SQLSET_STATEMENTS. By default, select privilige for these--- views is granted to the public role.------ - DISPLAY_SQL_PLAN_BASELINE displays one or more execution plans for--- the specified sql_handle of a SQL statement. If plan_name is--- specified denoting a single plan then that plan is displayed.--- The plan information stored in the SQL management base is--- used to generate and display the plan. It is possible that--- the stored plan id may not match up with the plan id of the-- generated plan. A plan id mismatch means that the stored plan--- is not reproducible. Such a plan is deemed invalid by the--- optimizer and ignored when the corresponding SQL statement is-- compiled and a cursor is built. When plan id mismatch occurs--- a note saying 'the plan is invalid' is shown in the notes--- section of the plan.--- NOTE: To use DISPLAY_SQL_PLAN_BASELINE function, the calling--- user must have SELECT prvilege on DBA_SQL_PLAN_BASELINES--- view. By default, SELECT privilege on this view is granted--- to the SELECT_CATALOG_ROLE.--------- For example:--- To show the last explained statement--- explain plan for select ename, deptno--- from emp e, dept d--- where e.deptno = d.deptno;--- select * from table(dbms_xplan.display);------ To show the last executed statement of your session--- select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor);------ See more detailed examples below------ SECURITY------ The execution privilege on this package is granted to PUBLIC.--- The display procedures of this package are run under the caller--- security.--------- PROCEDURES AND FUNCTIONS------ function display(table_name varchar2 default 'PLAN_TABLE',--- statement_id varchar2 default null,--- format varchar2 default 'TYPICAL',--- filter_preds varchar2 default null)------ - table_name:--- specifies the table name where the plan is stored. This--- parameter defaults to "PLAN_TABLE" which is the default--- plan table for the explain plan. If NULL is specified,--- the default of 'PLAN_TABLE' will be taken into account.--- The parameter is case insensitive.------ - statement_id:--- specifies the statement id of the plan to display. This--- parameter defaults to NULL. If no statement_id is defined,--- the most recent explained statement in <table_name> will--- be displayed, assuming that the "filter_preds" parameter is--- NULL (its default).------ - format:--- Determines what information stored in the plan will be--- shown. The format string can use the following predefined--- three formats, each representing a common use case:------ 'BASIC': Display only the minimum set of information, i.e. the--- operation id, the operation name and its option------ 'TYPICAL': This is the default. Display most information--- of the explain plan (operation id, name and option,--- #rows, #bytes and optimizer cost). Pruning,--- parallel and predicate information are only--- displayed when applicable. Excludes only PROJECTION,--- ALIAS and REMOTE SQL information (see below).------ 'ALL': Maximum user level, like typical with additional--- informations (PROJECTION, ALIAS and information about--- REMOTE SQL if the operation is distributed).------ For finer control on the display output, the following keywords--- can be added to the above three standard format to customize their--- default behavior. Each keyword either represents a logical group--- of plan table columns (e.g. PARTITION) or logical additions to the--- base plan table output (e.g. PREDICATE). Format keywords must--- be separated by either a comma or a space:------ ROWS: if relevant, shows number of rows estimated by the optimizer------ BYTES: if relevant, shows number of bytes estimated by the--- optimizer------ COST: if relevant, shows optimizer cost information------ PARTITION: If relevant, shows partition pruning information------ PARALLEL: If relevant, shows PX information (distribution method--- and table queue information)------ PREDICATE: If relevant, shows the predicate section------ PROJECTION: If relevant, shows the projection section------ ALIAS: If relevant, shows the "Query Block Name / Object Alias"--- section------ REMOTE: If relevant, shows the information for distributed query--- (e.g. remote from serial distribution and remote SQL)------ NOTE: If relevant, shows the note section of the explain plan.------ Format keywords can be prefixed by the sign '-' to exclude the--- specified information. For example, '-PROJECTION' exclude--- projection information.------ Finally, if the target plan table (see "table_name" parameter) also--- stores plan statistics columns (e.g. it is a table used to capture--- the content of the fixed view v$sql_plan_statistics_all), then--- additional format keywords can be used to specify which class of--- statistics to display. These additionnal format keywords are IOSTATS,--- MEMSTATS, ALLSTATS and LAST described along with the display_cursor()--- table function (see below).------ Example:--- - use 'ALL -PROJECTION -NOTE' to display everything except the--- projection and note sections.------ - use 'TYPICAL PROJECTION' to display using the typical format--- with the additional projection section (which is normally excluded--- under the typical format). Since typical is default, using--- simply 'PROJECTION' is equivalent.------ - use '-BYTES -COST -PREDICATE' to display using the typical--- format but excluding optimizer cost and byte estimates--- as well as the predicate section.------ - use 'BASIC ROWS' to display basic information with the--- additional number of rows estimated by the optimizer.--------- - filter_preds: SQL filter predicate(s) to restrict the set of rows--- selected from the table where the plan is stored. When--- value is NULL (the default), the plan displayed--- corresponds to the last executed explain plan.------ For example:------ filter_preds=>'plan_id = 10'------ "filter_preds" can reference any column of the table--- where the plan is stored and can contain any SQL--- construct (e.g. sub-query, function calls...).------ WARNING: Application developers should expose this--- parameter to end-users only after careful--- consideration since it could expose the application--- to SQL injection. Indeed, "filter_preds" can--- potentially reference any table or execute any server--- function for which the database user invoking the--- table function has privileges.------ --------------------------------------------------------------------------- function display_cursor(sql_id varchar2 default null,--- cursor_child_no integer default 0,--- format varchar2 default 'TYPICAL')------ - sql_id:--- specifies the sql_id value for a specific SQL statement, as--- shown in V$SQL.SQL_ID, V$SESSION.SQL_ID, or--- V$SESSION.PREV_SQL_ID. If no sql_id is specified, the last--- executed statement of the current session is shown.------ - cursor_child_no:--- specifies the child number for a specific sql cursor, as shown in--- V$SQL.CHILD_NUMBER or in V$SESSION.SQL_CHILD_NUMBER,--- V$SESSION.PREV_CHILD_NUMBER. This input parameter is only--- considered when sql_id is set.------ If not specified, all child cursors for the specified sql_id are--- displayed.------ - format:--- The format string has the same meaning as that for the regular--- display() table function (see format description above). In--- addition, the following four format keywords are introduced--- to support the various plan statistics columns available--- in v$sql_plan_statistics_all.------ These keywords can also be used by the display() table function--- assuming that the specified table has the same statistics columns--- available in v$sql_plan_statistics_all.------ IOSTATS: Assuming that basic plan statistics are--- collected when SQL statements are executed (either by--- using the gather_plan_statistics hint or by setting the--- parameter statistics_level to ALL), this format will show--- IO statistics for all (or only for the last as shown below)--- executions of the cursor.------ MEMSTATS: Assuming that PGA memory management is enabled (i.e--- pga_aggregate_target parameter is set to a non 0 value),--- this format allows to display memory management--- statistics (e.g. execution mode of the operator, how--- much memory was used, number of bytes spilled to--- disk, ...). These statistics only apply to memory--- intensive operations like hash-joins, sort or some bitmap--- operators.------ ALLSTATS: A shortcut for 'IOSTATS MEMSTATS'------ LAST: By default, plan statistics are shown for all executions of--- the cursor. The keyword LAST can be specified to see only--- the statistics for the last execution.--------- Also, the following two formats are still supported for backward--- compatibility:------ 'RUNSTATS_TOT': Same as 'IOSTATS', i.e. displays IO statistics--- for all executions of the specified cursor.--- 'RUNSTATS_LAST': Same as 'IOSTATS LAST', i.e. displays the runtime--- statistics for the last execution of the cursor.--------- PRIVILEGES:--- - To use the DISPLAY_CURSOR functionality, the calling--- user must have SELECT privilege on V$SQL_PLAN_STATISTICS_ALL,--- V$SQL, and V$SQL_PLAN, otherwise it will show an appropriate--- error message.------ - Unless used in DEFAULT mode to display the last executed--- statement, all internal SQL statements of this package and--- the calling SQL statement using this table function will be--- suppressed.------ --------------------------------------------------------------------------- function display_awr(sql_id varchar2,--- plan_hash_value integer default null,--- db_id integer default null,--- format varchar2 default 'TYPICAL')------ - sql_id:--- specifies the sql_id value for a SQL statement having its plan(s)--- stored in the AWR. You can find all stored SQL statements by--- querying DBA_HIST_SQL_PLAN.------ - plan_hash_value:--- identifies a specific stored execution plan for a SQL statement.--- Optional parameter. If suppressed, all stored execution plans are--- shown.------ - db_id:--- identifies the plans for a specific dabatase. If this parameter is--- omitted, it will be defaulted to the local database identifier.------ - format:--- The format string has the same meaning as that for the regular--- display() table function (see format description above).------ --------------------------------------------------------------------------- function display_sqlset(sqlset_name varchar2,--- sql_id varchar2,--- plan_hash_value integer default null,--- format varchar2 default 'TYPICAL',--- sqlset_owner varchar2 default null)------ - sqlset_name:--- specified the name of the SQL tuning set.------ - sql_id:--- specifies the sql_id value for a SQL statement having its plan(s)--- stored in the SQL tuning set. You can find all stored SQL--- statements by querying USER/DBA/ALL_SQLSET_PLANS or table function--- SELECT_SQLSET from package dbms_sqltune.------ - plan_hash_value:--- identifies a specific stored execution plan for a SQL statement.--- Optional parameter. If suppressed, all stored execution plans are--- shown.------ - format:--- The format string has the same meaning as that for the regular--- display() table function (see format description above).------ - sqlset_owner:--- Specifies the owner of the SQL tuning set. The default is the--- name of the current user.------ --------------------------------------------------------------------------- function display_sql_plan_baseline(--- sql_handle varchar2 default NULL,--- plan_name varchar2 default NULL,--- format varchar2 default 'TYPICAL')------ - sql_handle:--- SQL statement handle. It identifies the SQL statement whose plans--- are to be explained and displayed. If NULL then PLAN_NAME must be--- specified.--- You can find SQL plan baselines created for various SQL statements--- by querying DBA_SQL_PLAN_BASELINES catalog view.------ - plan_name:--- Plan name. It identifies a specific plan to be explained and--- displayed. Default NULL means all plans associated with identified--- SQL statement to be explained and displayed. If NULL then--- sql_handle must be specified.------ - format:--- The format string has the same meaning as that for the regular--- display() table function (see format description above).------ --------------------------------------------------------------------------- Examples DBMS_XPLAN.DISPLAY():------ 1/ display the last explain plan stored in the plan table:------ set linesize 150--- set pagesize 2000--- select * from table(dbms_xplan.display);--------- 2/ display from the plan table "my_plan_table":------ set linesize 150--- set pagesize 2000--- select * from table(dbms_xplan.display('my_plan_table'));--------- 3/ display minimum plan table:------ set linesize 150--- set pagesize 2000--- select * from table(dbms_xplan.display(null, null,'basic'));--------- 4/ display all information in plan table, excluding projection:------ set linesize 150--- set pagesize 2000--- select * from table(dbms_xplan.display(null, null,--- 'all -projection'));--------- 5/ display the plan whose statement_id is 'foo':------ set linesize 150--- set pagesize 2000--- select * from table(dbms_xplan.display('plan_table', 'foo'));--------- 6/ display statpack plan for hash_value=76725 and snap_id=245------ set linesize 150--- set pagesize 2000--- select * from table(dbms_xplan.display('stats$sql_plan', null,--- 'all', 'hash_value=76725 and snap_id=245'));------ --------------------------------------------------------------------------- Examples DBMS_XPLAN.DISPLAY_CURSOR():------ 1/ display the currently or last executed statement--- (this will also show the usage of this package)------ set linesize 150--- set pagesize 2000--- select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor);--------- 2/ display the currently or last executed statement of session id 9--- (it will return 'no rows selected' for any SQL statement using--- this package)------ - Identify the sql_id and the child_number in--- a separate SQL statement and use them as parameters for--- DISPLAY_CUSRSOR()------ SQL> select prev_sql_id, prev_child_number--- from v$session where sid=9;------ PREV_SQL_ID PREV_CHILD_NUMBER--- ------------- -------------------- f98t6zufy04g5 0------ set linesize 150--- set pagesize 2000--- select *--- from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor('f98t6zufy04g5', 0));------ - Alternatively, you can combine the two statements into one------ set linesize 150--- set pagesize 2000--- select t.*--- from v$session s,--- table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(s.prev_sql_id,--- s.prev_child_number)) t--- where s.sid=9;------ NOTE: the table deriving the input parameters for--- DBMS_XPLAN.DISPLAY_CURSOR() must be the FIRST (left-side)--- table(s) in the select statement relative to the table function--------- 3/ display all cursors containing the case sensisitve string 'FoOoO',--- excluding SQL parsed by SYS------ set linesize 150--- set pagesize 2000--- select t.*--- from v$sql s,--- table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(s.sql_id,--- s.child_number)) t--- where s.sql_text like '%FoOoO%' and s.parsing_user_id <> 0;--------- 4/ display all information about all cursors containing the case--- insensitive string 'FOO', including SQL parsed by SYS------ set linesize 150--- set pagesize 2000--- select t.*--- from v$sql s,--- table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(s.sql_id,--- s.child_number, 'ALL')) t--- where upper(s.sql_text) like '%FOO%';--------- 5/ display the last executed runtime statistics for all cursors--- containing the case insensitive string 'sales', including SQL--- parsed by SYS------ set linesize 150--- set pagesize 2000--- select t.*--- from v$sql s,--- table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(s.sql_id, s.child_number,--- 'ALLSTATS LAST')) t--- where lower(s.sql_text) like '%sales%';--------- 6/ display the aggregated runtime statistics for all cursors containing--- the case sensitive string 'sAleS' and were parsed by user SH------ set linesize 150--- set pagesize 2000--- select t.*--- from v$sql s, dba_users u,--- table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(s.sql_id, s.child_number,--- 'RUNSTATS_TOT')) t--- where s.sql_text like '%sAleS%'--- and u.user_id=s.parsing_user_id--- and u.username='SH';------ --------------------------------------------------------------------------- Examples DBMS_XPLAN.DISPLAY_AWR():------ 1/ display all stored plans in the AWR containing--- the case sensitive string 'sAleS'. Don't display predicate--- information but add the query block name / alias section.------ set linesize 150--- set pagesize 2000--- select t.*--- from dba_hist_sqltext ht,--- table(dbms_xplan.display_awr(ht.sql_id, null, null,--- '-PREDICATE +ALIAS')) t--- where ht.sql_text like '%sAleS%';------ NOTE: the table deriving the input parameters for--- DBMS_XPLAN.DISPLAY_AWR() must be the FIRST (left-side)--- table(s) in the select statement relative to the table--- function.------ --------------------------------------------------------------------------- Examples DBMS_XPLAN.DISPLAY_SQLSET():------ 1/ display all stored plans for a given statement in the SQL tuning set--- named 'my_sts' owner by the current user (the caller).------ set linesize 150--- set pagesize 2000--- select *--- from table(dbms_xplan.display_sqlset('my_sts',--- 'gcfysssf6hykh',--- null,--- 'ALL -NOTE -PROJECTION')) t------ --------------------------------------------------------------------------- Examples DBMS_XPLAN.DISPLAY_SQL_PLAN_BASELINE():------ 1/ display all plans of a SQL statement identified by the sql handle--- 'SYS_SQL_b1d49f6074ab95af' using TYPICAL format.------ set linesize 150--- set pagesize 2000--- select t.*--- from table(dbms_xplan.display_sql_plan_baseline(--- 'SYS_SQL_b1d49f6074ab95af')) t;------ 2/ display all plans of one or more SQL statements containing the--- string 'HR2' using BASIC format.------ set linesize 150--- set pagesize 2000--- select t.*--- from (select distinct sql_handle from dba_sql_plan_baselines--- where sql_text like '%HR2%') pb,--- table(dbms_xplan.display_sql_plan_baseline(pb.sql_handle, null,--- 'basic')) t;------ NOTE: the table deriving the input parameters for--- DBMS_XPLAN.DISPLAY_SQL_PLAN_BASELINE() must be the first--- (left-side) table in the select statement relative to the--- table function.------ --------------------------------------------------------------------------- display from PLAN_TABLEfunction display(table_name varchar2 default 'PLAN_TABLE',statement_id varchar2 default null,format varchar2 default 'TYPICAL',filter_preds varchar2 default null)return dbms_xplan_type_tablepipelined;-- display from V$SQL_PLAN (or V$SQL_PLAN_STATISTICS_ALL)function display_cursor(sql_id varchar2 default null,cursor_child_no integer default 0,format varchar2 default 'TYPICAL')return dbms_xplan_type_tablepipelined;-- display from AWRfunction display_awr(sql_id varchar2,plan_hash_value integer default null,db_id integer default null,format varchar2 default 'TYPICAL')return dbms_xplan_type_tablepipelined;-- display from SQL tuning setfunction display_sqlset(sqlset_name varchar2,sql_id varchar2,plan_hash_value integer default null,format varchar2 default 'TYPICAL',sqlset_owner varchar2 default null)return dbms_xplan_type_tablepipelined;-- display from SQL plan baselinefunction display_sql_plan_baseline(sql_handle varchar2 default null,plan_name varchar2 default null,format varchar2 default 'TYPICAL')return dbms_xplan_type_tablepipelined;------------------------------------------------------------------------------ ---------------------------------------------------------------------- ---- ---- The folloing section of this package contains functions and procedures ---- which are for INTERNAL use ONLY. PLEASE DO NO DOCUMENT THEM. ---- ---- ---------------------------------------------------------------------- -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- private procedure, used internallyfunction prepare_records(plan_cur IN sys_refcursor,i_format_flags IN binary_integer)return dbms_xplan_type_tablepipelined;-- private function to validate the user format (used internally)function validate_format(hasPlanStats IN boolean,format IN VARCHAR2,format_flags OUT BINARY_INTEGER)return boolean;FUNCTION format_size(num number)RETURN varchar2;FUNCTION format_number(num number)RETURN varchar2;FUNCTION format_size2(num number)RETURN varchar2;FUNCTION format_number2(num number)RETURN varchar2;---- formats a number representing time in seconds using the format HH:MM:SS.-- This function is internal to this package--function format_time_s(num number)return varchar2;---- This is a helper function to build the XML version of the text of the-- select query that is run before the display display function to retrieve-- and display the execution plan of a SQL.-- All this function does it to wrap a given query, used to fetch a plan, by-- XML construct. The goal is to maintain ONE and SINGLE version of the XML-- format we use for the plan table.---- This function is also called by prvtspai.sql in sqltune directory.-- table_query : query to fetch plan from a plan table--FUNCTION prepare_plan_xml_query(plan_query IN VARCHAR2) -- query to fetch plan tableRETURN VARCHAR2;---- This function builds the xml version of an explain plan.-- The function queries the caller specified plan table and format the-- resulting plan lines into XML before returning them to the caller.---- table_name : name of the table or view that stores the plan-- statement_id: identifier of the sql statement in the plan table-- plan_id : identifier of the sql plan in the plan table. Currently-- used by sql replay only. SQL replay is used to produce plans-- for SQL stored in sql tuning set using plan_ids and so-- we need to be able to share the query we use to get the plans.-- format : format of the plan output. See description in-- function display-- filter_preds: predicate to filter the content of the plan table-- plan_tag : caller specified name of the root element in the plan xml-- tree. by default it is set to 'xplan'-- report_ref : optional report reference. Needed only to generate-- xml of the servelet.--function build_plan_xml(table_name in varchar2 default 'PLAN_TABLE',statement_id in varchar2 default NULL,plan_id in number default NULL,format in varchar2 default 'TYPICAL',filter_preds in varchar2 default NULL,plan_tag in varchar2 default 'plan',report_ref in varchar2 default NULL)return xmltype;---- This function returns an explain plan in a CLOB format.-- The function queries the caller specified plan table, generate the-- resulting plan lines into XML and then calls the XML reporting framework-- the produce and return the plan as a CLOB.---- table_name : name of the table or view that stores the plan-- statement_id: identifier of the sql statement in the plan table-- format : format of the plan output. See description in-- function display-- filter_preds: predicate to filter the content of the plan table-- type : type of output. Possible values are:-- TEXT (default), HTML, ACTIVE, or XML.--function display_plan(table_name in varchar2 default 'PLAN_TABLE',statement_id in varchar2 default NULL,format in varchar2 default 'TYPICAL',filter_preds in varchar2 default NULL,type in varchar2 default 'TEXT')return clob;----------------------------- diff_plan_outline ---------------------------------- This function compares two sql plans generated by the given outlines-- The job is done via a SQLDiag task and the function returns the task_id---- PARAMETERS:-- sql_text (IN) - text of the SQL statement-- outline1 (IN) - outline - for base plan-- outline2 (IN) - outline - for target plan-- user_name (IN) - the parsing schema name-- default to current user---- RETURN:-- task_id: can be used to retrieve the report of findings later------------------------------------------------------------------------------function diff_plan_outline(sql_text in clob,outline1 in clob,outline2 in clob,user_name in varchar2 := NULL)return varchar2;----------------------------- diff_plan ----------------------------------------- This function compares two sql plans-- reference plan: implicitly defined-- target plan: a plan generated by the given outline---- The job is done via a SQLDiag task and the function returns the task_id---- PARAMETERS:-- sql_text (IN) - text of the SQL statement-- outline (IN) - used to generate the target plan-- user_name (IN) - the parsing schema name-- default to current user---- RETURN:-- task_id: can be used to retrieve the report of findings later------------------------------------------------------------------------------function diff_plan(sql_text in clob,outline in clob,user_name in varchar2 := NULL)return varchar2;----------------------------- diff_plan_sql_baseline ----------------------------- This function compares two given sql plans (specified via plan_names)-- The job is done via a SQLDiag task and the function returns the task_id---- PARAMETERS:-- baseline_plan_name1 (IN) - plan name - base-- baseline_plan_name2 (IN) - plan name - target---- RETURN:-- task_id: can be used to retrieve the report of findings later------------------------------------------------------------------------------function diff_plan_sql_baseline(baseline_plan_name1 in varchar2,baseline_plan_name2 in varchar2)return varchar2;----------------------------- diff_plan_cursor ----------------------------------- This function compares two sql plans derived from the given cursor child #-- The job is done via a SQLDiag task and the function returns the task_id---- PARAMETERS:-- sql_id (IN) - sql id to specify a SQL statement-- cursor_child_num1 (IN) - child number - for base plan-- cursor_child_num2 (IN) - child number - for target plan---- RETURN:-- task_id: can be used to retrieve the report of findings later------------------------------------------------------------------------------function diff_plan_cursor(sql_id IN VARCHAR2,cursor_child_num1 IN NUMBER,cursor_child_num2 IN NUMBER)return varchar2;----------------------------- diff_plan_awr -------------------------------------- This function compares two sql plans specified by the given plan hash ids-- The job is done via a SQLDiag task and the function returns the task_id---- PARAMETERS:-- sql_id (IN) - sql id to specify a SQL statement-- plan_hash_value1 (IN) - base plan-- plan_hash_value1 (IN) - target plan---- RETURN:-- task_id: can be used to retrieve the report of findings later------------------------------------------------------------------------------function diff_plan_awr(sql_id IN VARCHAR2,plan_hash_value1 IN NUMBER,plan_hash_value2 IN NUMBER)return varchar2;--++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++----++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++---- ------------------------------------------ ---- PLAN DIFF SUPPORT FUNCTIONS ---- ------------------------------------------ ----++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++----++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++-------------------------------- get_report_xml ---------------------------------- NAME:-- get_report_xml---- DESCRIPTION:-- This function builds the entire report in XML.---- PARAMETERS:-- report_ref (IN) - the report reference string that-- identifies this report-- tid (IN) - task ID-- method (IN) - method of comparing, eg, 'outline'-- RETURN:-- the report in XML------------------------------------------------------------------------------FUNCTION get_plandiff_report_xml(report_ref IN VARCHAR2 := NULL,tid IN NUMBER,method IN VARCHAR2)RETURN XMLTYPE;end dbms_xplan;
相关文章:

Oracle DBMS_XPLAN包
DBMS_XPLAN 包的解释和关键点 DBMS_XPLAN 包是 Oracle 数据库中一个重要的工具,它允许数据库管理员和开发人员以各种方式显示 SQL 语句的执行计划,这对于 SQL 优化和性能诊断至关重要。以下是主要函数及其描述: 用于显示执行计划的主要函数…...

【ffmpeg命令入门】分离音视频流
文章目录 前言音视频交错存储概念为什么要进行音视频交错存储:为什么要分离音视频流: 去除音频去除视频 总结 前言 FFmpeg 是一款强大的多媒体处理工具,广泛应用于音视频的录制、转换和流媒体处理等领域。它支持几乎所有的音频和视频格式&am…...
小红书笔记评论采集全攻略:三种高效方法教你批量导出
摘要: 本文将深入探讨如何利用Python高效采集小红书平台上的笔记评论,通过三种实战策略,手把手教你实现批量数据导出。无论是市场分析、竞品监测还是用户反馈收集,这些技巧都将为你解锁新效率。 一、引言:小红书数据…...
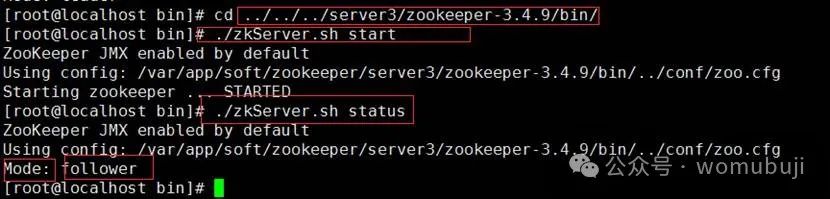
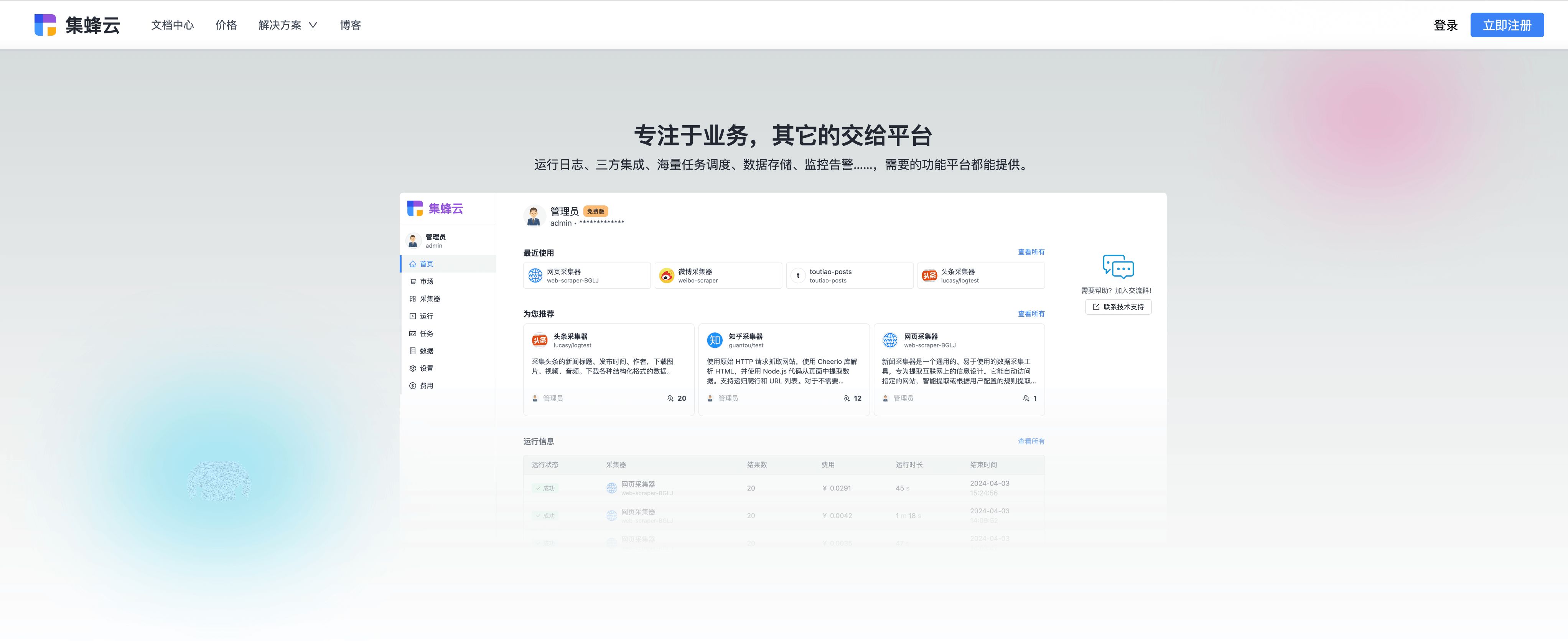
实战:ZooKeeper 操作命令和集群部署
ZooKeeper 操作命令 ZooKeeper的操作命令主要用于对ZooKeeper服务中的节点进行创建、查看、修改和删除等操作。以下是一些常用的ZooKeeper操作命令及其说明: 一、启动与连接 启动ZooKeeper服务器: ./zkServer.sh start这个命令用于启动ZooKeeper服务器…...

linux运维一天一个shell命令之 top详解
概念: top 命令是 Unix 和类 Unix 操作系统(如 Linux、macOS)中一个常用的系统监控工具,它提供了一个动态的实时视图,显示系统的整体性能信息,如 CPU 使用率、内存使用情况、进程列表等。 基本用法 root…...
大模型微调:参数高效微调(PEFT)方法总结
PEFT (Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning) 参数高效微调是一种针对大模型微调的技术,旨在减少微调过程中需要调整的参数量,同时保持或提高模型的性能。 以LORA、Adapter Tuning 和 Prompt Tuning 为主的PEFT方法总结如下 LORA 论文题目:LORA:…...

Spark+实例解读
第一部分 Spark入门 学习教程:Spark 教程 | Spark 教程 Spark 集成了许多大数据工具,例如 Spark 可以处理任何 Hadoop 数据源,也能在 Hadoop 集群上执行。大数据业内有个共识认为,Spark 只是Hadoop MapReduce 的扩展(…...

WPF多语言国际化,中英文切换
通过切换资源文件的形式实现中英文一键切换 在项目中新建Language文件夹,添加资源字典(xaml文件),中文英文各一个。 在资源字典中写上想中英文切换的字符串,需要注意,必须指定key值,并且中英文…...
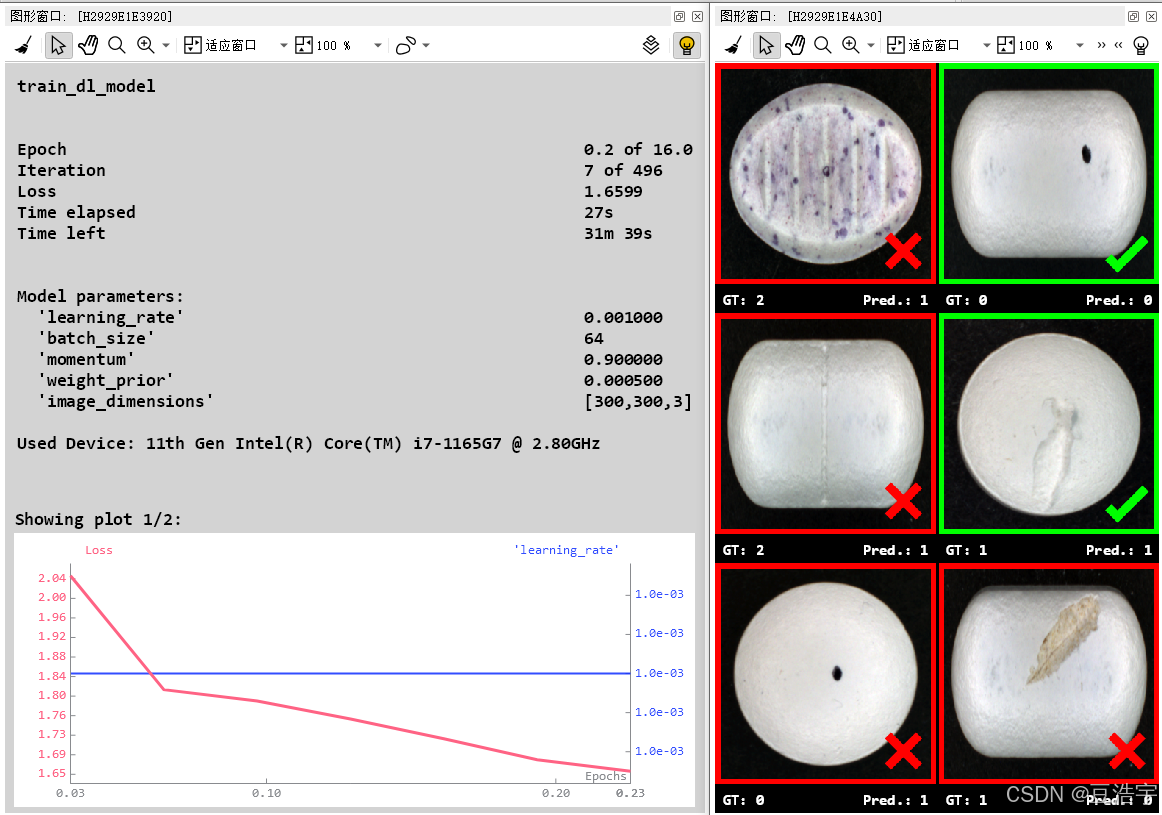
Halcon深度学习分类模型
1.Halcon20之后深度学习支持CPU训练模型,没有money买显卡的小伙伴有福了。但是缺点也很明显,就是训练速度超级慢,推理效果也没有GPU好,不过学习用足够。 2.分类模型是Halcon深度学习最简单的模型,可以用在物品分类&…...

洗地机哪种牌子好?洗地机排行榜前十名公布
洗地机市场上品牌琳琅满目,每个品牌都有其独特的魅力和优势。消费者在选择时,往往会根据自己的实际需求、预算以及对产品性能的期望来做出决策。因此,无论是哪个品牌的洗地机,只要能够满足用户的清洁需求,提供便捷的操…...

C++中的虚函数与多态机制如何工作?
在C中,虚函数和多态机制是实现面向对象编程的重要概念。 虚函数是在基类中声明的函数,可以在派生类中进行重写。当基类的指针或引用指向派生类的对象时,通过调用虚函数可以实现动态绑定,即在运行时确定要调用的函数。 多态是指通…...

《LeetCode热题100》---<哈希三道>
本篇博客讲解 LeetCode热题100道中的哈希篇中的三道题。分别是 1.第一道:两数之和(简单) 2.第二道:字母异位词分组(中等) 3.第三道:最长连续序列(中等) 第一道࿱…...
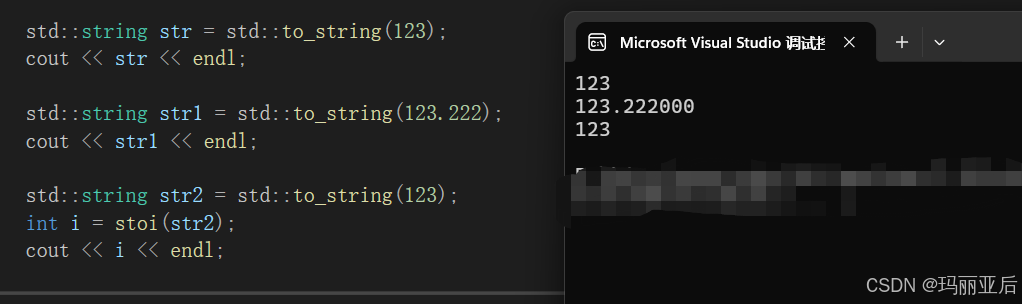
秒懂C++之string类(下)
目录 一.接口说明 1.1 erase 1.2 replace(最好别用) 1.3 find 1.4 substr 1.5 rfind 1.6 find_first_of 1.7 find_last_of 二.string类的模拟实现 2.1 构造 2.2 无参构造 2.3 析构 2.4.【】运算符 2.5 迭代器 2.6 打印 2.7 reserve扩容 …...
github简单地操作
1.调节字体大小 选择options 选择text 选择select 选择你需要的参数就可以了。 2.配置用户名和邮箱 桌面右键,选择git Bash Here git config --global user.name 用户名 git config --global user.email 邮箱名 3.用git实现代码管理的过程 下载别人的项目 git …...
模型改进-损失函数合集
模版 第一步在哪些地方做出修改: 228行 self.use_wiseiouTrue 230行 self.wiou_loss WiseIouLoss(ltypeMPDIoU, monotonousFalse, inner_iouTrue, focaler_iouFalse) 238行 wiou self.wiou_loss(pred_bboxes[fg_mask], target_bboxes[fg_mask], ret_iouFalse…...
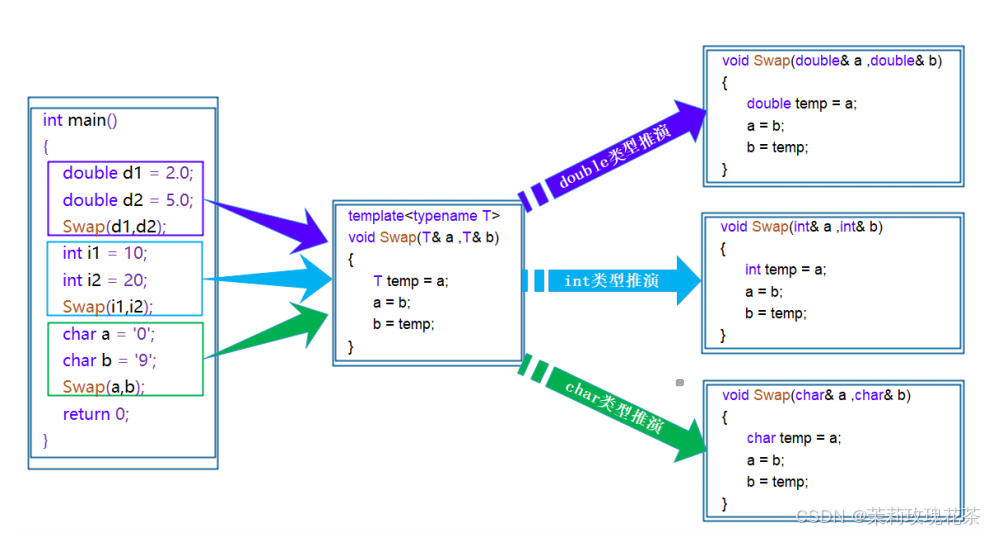
C++模板(初阶)
1.引入 在之前的笔记中有提到:函数重载(特别是交换函数(Swap)的实现) void Swap(int& left, int& right) {int temp left;left right;right temp; } void Swap(double& left, double& right) {do…...

下面关于Date类的描述错误的一项是?
下面关于Date类的描述错误的一项是? A. java.util.Date类下有三个子类:java.sql.Date、java.sql.Timestamp、java.sql.Time; B. 利用SimpleDateFormat类可以对java.util.Date类进行格式化显示; C. 直接输出Date类对象就可以取得日…...
【Python面试题收录】Python编程基础练习题①(数据类型+函数+文件操作)
本文所有代码打包在Gitee仓库中https://gitee.com/wx114/Python-Interview-Questions 一、数据类型 第一题(str) 请编写一个Python程序,完成以下任务: 去除字符串开头和结尾的空格。使用逗号(","&#…...
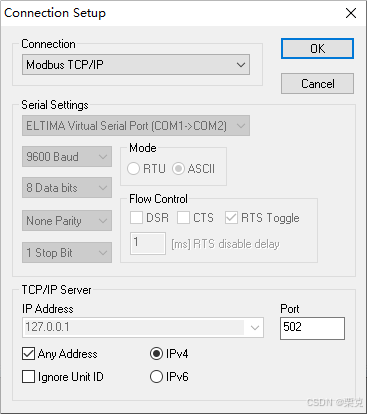
C# Nmodbus,EasyModbusTCP读写操作
Nmodbus读写 两个Button控件分别为 读取和写入 分别使用控件的点击方法 ①引用第三方《NModbus4》2.1.0版本 全局 public SerialPort port new SerialPort("COM2", 9600, Parity.None, 8, (StopBits)1); ModbusSerialMaster master; public Form1() port.Open();…...

spark常用参数调优
目录 1.set spark.grouping.sets.reference.hivetrue;2.set spark.locality.wait.rack0s3.set spark.locality.wait0s;4.set spark.executor.memoryOverhead 2G;5.set spark.sql.shuffle.partitions 1000;6.set spark.shuffle.file.buffer 256k7. set spark.reducer.maxSizeInF…...
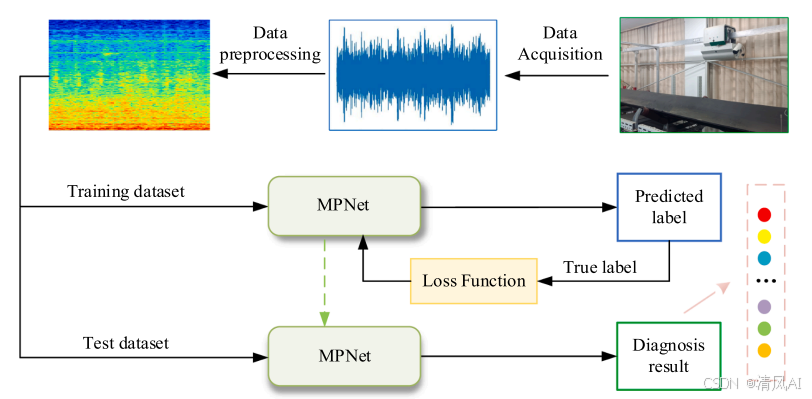
MPNet:旋转机械轻量化故障诊断模型详解python代码复现
目录 一、问题背景与挑战 二、MPNet核心架构 2.1 多分支特征融合模块(MBFM) 2.2 残差注意力金字塔模块(RAPM) 2.2.1 空间金字塔注意力(SPA) 2.2.2 金字塔残差块(PRBlock) 2.3 分类器设计 三、关键技术突破 3.1 多尺度特征融合 3.2 轻量化设计策略 3.3 抗噪声…...

基于距离变化能量开销动态调整的WSN低功耗拓扑控制开销算法matlab仿真
目录 1.程序功能描述 2.测试软件版本以及运行结果展示 3.核心程序 4.算法仿真参数 5.算法理论概述 6.参考文献 7.完整程序 1.程序功能描述 通过动态调整节点通信的能量开销,平衡网络负载,延长WSN生命周期。具体通过建立基于距离的能量消耗模型&am…...
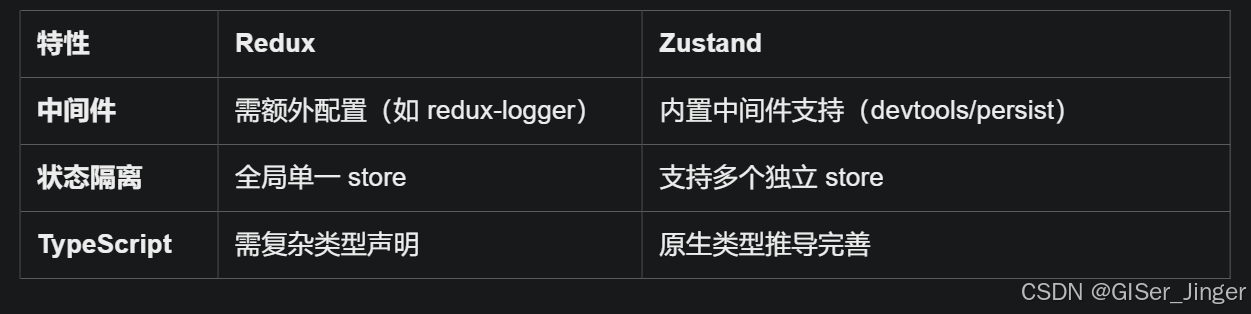
Zustand 状态管理库:极简而强大的解决方案
Zustand 是一个轻量级、快速和可扩展的状态管理库,特别适合 React 应用。它以简洁的 API 和高效的性能解决了 Redux 等状态管理方案中的繁琐问题。 核心优势对比 基本使用指南 1. 创建 Store // store.js import create from zustandconst useStore create((set)…...
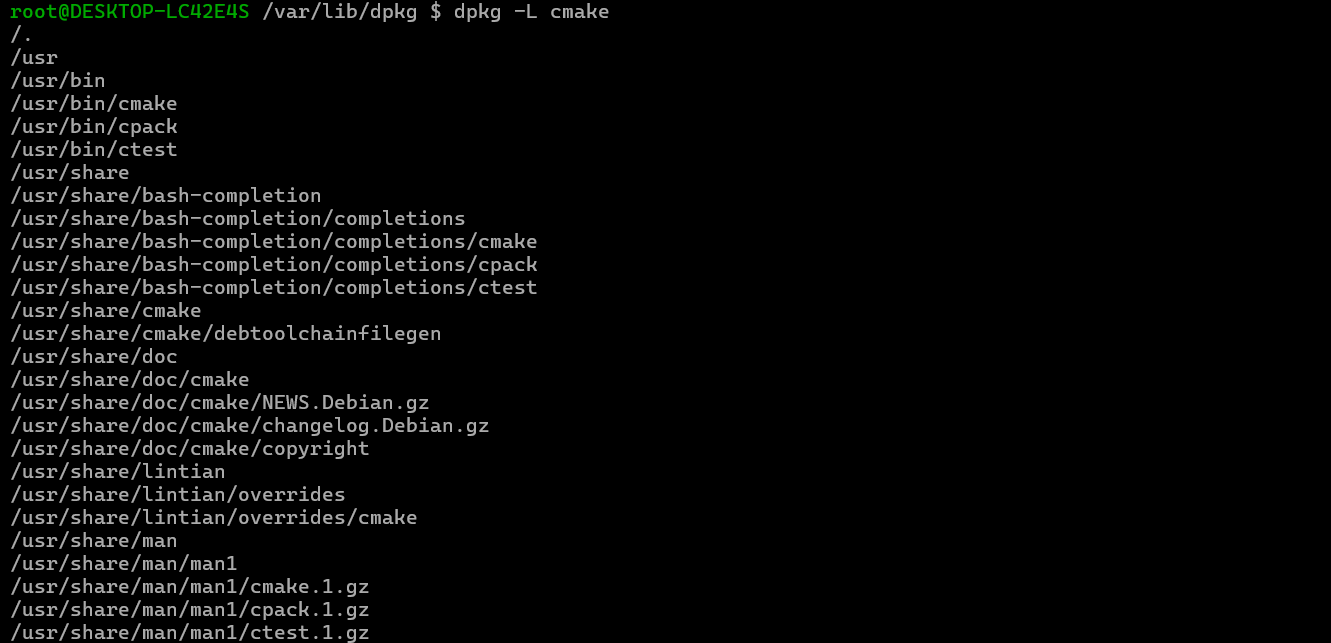
Debian系统简介
目录 Debian系统介绍 Debian版本介绍 Debian软件源介绍 软件包管理工具dpkg dpkg核心指令详解 安装软件包 卸载软件包 查询软件包状态 验证软件包完整性 手动处理依赖关系 dpkg vs apt Debian系统介绍 Debian 和 Ubuntu 都是基于 Debian内核 的 Linux 发行版ÿ…...
vscode(仍待补充)
写于2025 6.9 主包将加入vscode这个更权威的圈子 vscode的基本使用 侧边栏 vscode还能连接ssh? debug时使用的launch文件 1.task.json {"tasks": [{"type": "cppbuild","label": "C/C: gcc.exe 生成活动文件"…...

鸿蒙中用HarmonyOS SDK应用服务 HarmonyOS5开发一个医院挂号小程序
一、开发准备 环境搭建: 安装DevEco Studio 3.0或更高版本配置HarmonyOS SDK申请开发者账号 项目创建: File > New > Create Project > Application (选择"Empty Ability") 二、核心功能实现 1. 医院科室展示 /…...
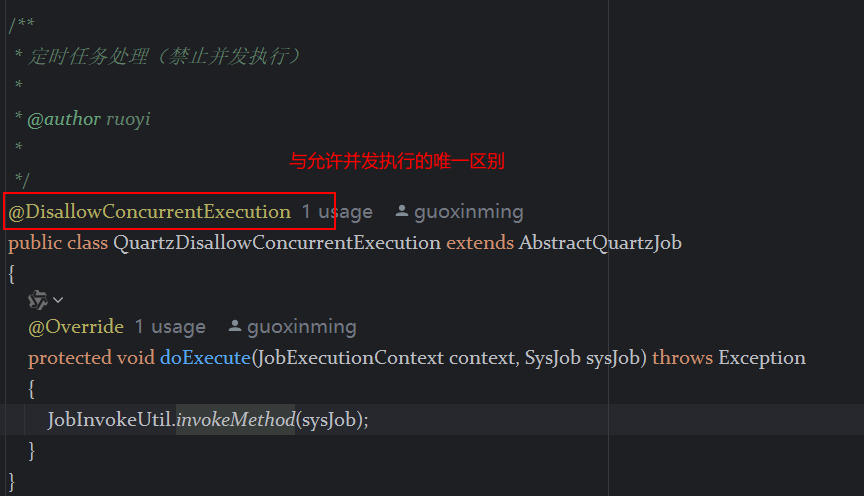
定时器任务——若依源码分析
分析util包下面的工具类schedule utils: ScheduleUtils 是若依中用于与 Quartz 框架交互的工具类,封装了定时任务的 创建、更新、暂停、删除等核心逻辑。 createScheduleJob createScheduleJob 用于将任务注册到 Quartz,先构建任务的 JobD…...
:滤镜命令)
ffmpeg(四):滤镜命令
FFmpeg 的滤镜命令是用于音视频处理中的强大工具,可以完成剪裁、缩放、加水印、调色、合成、旋转、模糊、叠加字幕等复杂的操作。其核心语法格式一般如下: ffmpeg -i input.mp4 -vf "滤镜参数" output.mp4或者带音频滤镜: ffmpeg…...

第25节 Node.js 断言测试
Node.js的assert模块主要用于编写程序的单元测试时使用,通过断言可以提早发现和排查出错误。 稳定性: 5 - 锁定 这个模块可用于应用的单元测试,通过 require(assert) 可以使用这个模块。 assert.fail(actual, expected, message, operator) 使用参数…...
uniapp微信小程序视频实时流+pc端预览方案
方案类型技术实现是否免费优点缺点适用场景延迟范围开发复杂度WebSocket图片帧定时拍照Base64传输✅ 完全免费无需服务器 纯前端实现高延迟高流量 帧率极低个人demo测试 超低频监控500ms-2s⭐⭐RTMP推流TRTC/即构SDK推流❌ 付费方案 (部分有免费额度&#x…...
