coco(json)、yolo(txt)、voc(xml)标注格式的相互转换
一般都是用labeleme进行标注 标注格式都是json
然后根据不同的格式进行数据标注转换:
1.逐个json转xml:
当我们在使用数据集训练计算机视觉模型时,常常会遇到有的数据集只给了单个的json annotation文件,而模型所需要的annotation是基于每个图片的xml annotation文件
# translate coco_json to xml
import os
import time
import json
import pandas as pd
from tqdm import tqdm
from pycocotools.coco import COCOdef trans_id(category_id):names = []namesid = []for i in range(0, len(cats)):names.append(cats[i]['name'])namesid.append(cats[i]['id'])# print('id:{1}\t {0}'.format(names[i], namesid[i]))index = namesid.index(category_id)return indexroot = r'' # 你下载的 COCO 数据集所在目录
dataType = '2019'
anno = r'' # annotation json 文件所在位置
xml_dir = r'' # 导出的xml文件所在的位置coco = COCO(anno) # 读文件
cats = coco.loadCats(coco.getCatIds()) # 这里loadCats就是coco提供的接口,获取类别# Create anno dir
dttm = time.strftime("%Y%m%d%H%M%S", time.localtime())
# if os.path.exists(xml_dir):
# os.rename(xml_dir, xml_dir + dttm)
# os.mkdir(xml_dir)with open(anno, 'r') as load_f:f = json.load(load_f)imgs = f['images'] # json文件的img_id和图片对应关系 imgs列表表示多少张图cat = f['categories']
df_cate = pd.DataFrame(f['categories']) # json中的类别
df_cate_sort = df_cate.sort_values(["id"], ascending=True) # 按照类别id排序
categories = list(df_cate_sort['name']) # 获取所有类别名称
print('categories = ', categories)
df_anno = pd.DataFrame(f['annotations']) # json中的annotationfor i in tqdm(range(len(imgs))): # 大循环是images所有图片xml_content = []file_name = imgs[i]['file_name'] # 通过img_id找到图片的信息height = imgs[i]['height']img_id = imgs[i]['id']width = imgs[i]['width']# xml文件添加属性xml_content.append("<annotation>")xml_content.append(" <folder>VOC2007</folder>")xml_content.append(" <filename>" + file_name.split('/')[1].split('.')[0] + '.jpg' + "</filename>")xml_content.append(" <size>")xml_content.append(" <width>" + str(width) + "</width>")xml_content.append(" <height>" + str(height) + "</height>")xml_content.append(" </size>")xml_content.append(" <segmented>0</segmented>")# 通过img_id找到annotationsannos = df_anno[df_anno["image_id"].isin([img_id])] # (2,8)表示一张图有两个框for index, row in annos.iterrows(): # 一张图的所有annotation信息bbox = row["bbox"]category_id = row["category_id"]# cate_name = categories[trans_id(category_id)]cate_name = cat[category_id-1]['name']# add new objectxml_content.append("<object>")xml_content.append("<name>" + cate_name + "</name>")xml_content.append("<pose>Unspecified</pose>")xml_content.append("<truncated>0</truncated>")xml_content.append("<difficult>0</difficult>")xml_content.append("<bndbox>")xml_content.append("<xmin>" + str(int(bbox[0])) + "</xmin>")xml_content.append("<ymin>" + str(int(bbox[1])) + "</ymin>")xml_content.append("<xmax>" + str(int(bbox[0] + bbox[2])) + "</xmax>")xml_content.append("<ymax>" + str(int(bbox[1] + bbox[3])) + "</ymax>")xml_content.append("</bndbox>")xml_content.append("</object>")xml_content.append("</annotation>")x = xml_contentxml_content = [x[i] for i in range(0, len(x)) if x[i] != "\n"]### list存入文件xml_path = os.path.join(xml_dir, file_name.replace('.jpg', '.xml'))with open(xml_path, 'w+', encoding="utf8") as f:f.write('\n'.join(xml_content))xml_content[:] = []2.逐个xml转txt:
# xml_to_yolo_txt.py
# 此代码和VOC_KITTI文件夹同目录
import os
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
# 这里的类名为我们xml里面的类名,顺序a按照Readme文件,或者也可以不考虑顺序
# 其中thermal类别比rgb类别多了dog和deer,生成txt注意区分 # 我统一都写成thermal的类别了
class_names = ['person','bike','car','motor', 'bus', 'train','truck','light','hydrant', 'sign','dog','deer','skateboard','stroller', 'scooter', 'other vehicle']
# class_names = ['person','bike','car','motor', 'bus', 'train','truck','light','hydrant', 'sign',
# 'skateboard','stroller','scooter','other vehicle' ]
# xml文件路径
path = 'G:/红外数据集-FLIR2/FLIR2_yolo_xml/images_rgb_val/data/'
# 转换一个xml文件为txt
def single_xml_to_txt(xml_file):tree = ET.parse(os.path.join(path, xml_file))root = tree.getroot()# 保存的txt文件路径txt_file = os.path.join('G:/红外数据集-FLIR2/FLIR2_yolo_txt/images_rgb_val/data/', xml_file.split('.')[0]+'.txt')with open(txt_file, 'w') as txt_file:for member in root.findall('object'):#filename = root.find('filename').textpicture_width = int(root.find('size')[0].text)picture_height = int(root.find('size')[1].text)class_name = member[0].text# 类名对应的indexclass_num = class_names.index(class_name)box_x_min = int(member[4][0].text) # 左上角横坐标box_y_min = int(member[4][1].text) # 左上角纵坐标box_x_max = int(member[4][2].text) # 右下角横坐标box_y_max = int(member[4][3].text) # 右下角纵坐标# 转成相对位置和宽高x_center = float(box_x_min + box_x_max) / (2 * picture_width)y_center = float(box_y_min + box_y_max) / (2 * picture_height)width = float(box_x_max - box_x_min) / picture_widthheight = float(box_y_max - box_y_min) / picture_height# print(class_num, x_center, y_center, width, height)txt_file.write(str(class_num) + ' ' + str(x_center) + ' ' + str(y_center) + ' ' + str(width) + ' ' + str(height) + '\n')
# 转换文件夹下的所有xml文件为txt
def dir_xml_to_txt(path):files = os.listdir(path)for xml_file in files:single_xml_to_txt(xml_file)
dir_xml_to_txt(path)
3. 逐个json转txt (生成coco数据集/yolo数据集格式)
(1.) 这里首先对xx.jpg,xx.json统一成coco格式,生成instances_train2017/instances_val2017
定义lables.txt是:(注意_background_是-1)
_background_
person
car
bicycle
UAV
motorcycle
xxx目录结构:
|-- images
| |--- 1.jpg
| |--- 1.json
| |--- 2.jpg
| |--- 2.json
| |--- .......
|-- labelmejson2coco.py
|-- labels.txt(2)labelmejson2coco.py文件,整理成coco数据集格式
# 命令行执行: python labelme2coco.py --input_dir images --output_dir coco --labels labels.txt
# 输出文件夹必须为空文件夹import argparse
import collections
import datetime
import glob
import json
import os
import os.path as osp
import sys
import uuid
import imgviz
import numpy as np
import labelme
import cv2
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splittry:import pycocotools.mask
except ImportError:print("Please install pycocotools:\n\n pip install pycocotools\n")sys.exit(1)def to_coco(args, label_files, train):# 创建 总标签datanow = datetime.datetime.now()data = dict(info=dict(description=None,url=None,version=None,year=now.year,contributor=None,date_created=now.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.%f"),),licenses=[dict(url=None, id=0, name=None, )],images=[# license, url, file_name, height, width, date_captured, id],type="instances",annotations=[# segmentation, area, iscrowd, image_id, bbox, category_id, id],categories=[# supercategory, id, name],)# 创建一个 {类名 : id} 的字典,并保存到 总标签data 字典中。class_name_to_id = {}for i, line in enumerate(open(args.labels).readlines()):class_id = i - 1 # starts with -1class_name = line.strip() # strip() 方法用于移除字符串头尾指定的字符(默认为空格或换行符)或字符序列。if class_id == -1:assert class_name == "_background_" # _background_:0, class1:1, ,,continueclass_name_to_id[class_name] = class_iddata["categories"].append(dict(supercategory=None, id=class_id, name=class_name, ))if train:out_ann_file = osp.join(args.output_dir, "annotations", "instances_train2017.json")else:out_ann_file = osp.join(args.output_dir, "annotations", "instances_val2017.json")for image_id, filename in enumerate(label_files):label_file = labelme.LabelFile(filename=filename)base = osp.splitext(osp.basename(filename))[0] # 文件名不带后缀if train:out_img_file = osp.join(args.output_dir, "train2017", base + ".jpg")else:out_img_file = osp.join(args.output_dir, "val2017", base + ".jpg")print("| ", out_img_file)# ************************** 对图片的处理开始 *******************************************# 将标签文件对应的图片进行保存到对应的 文件夹。train保存到 train2017/ test保存到 val2017/img = labelme.utils.img_data_to_arr(label_file.imageData) # .json文件中包含图像,用函数提出来# 对数据进行增强,图像数据本身不会随图像的变换而变换。所以直接在json文件里面使用图像的ID作为键,将图像和标注数据进行匹配和关联。如果裁剪就用下面代码# image_path = os.path.join(filename).replace('.json', '.jpg')# img = cv2.imread(image_path)imgviz.io.imsave(out_img_file, img) # 将图像保存到输出路径# ************************** 对图片的处理结束 *******************************************# ************** ************ 对标签的处理开始 *******************************************# 读取原始的JSON文件 # 如果裁剪下面这两行就取消掉with open(filename, 'r') as f:data_json = json.load(f)data["images"].append(dict(license=0,url=None,file_name=osp.relpath(out_img_file, osp.dirname(out_ann_file)),# out_img_file = "/coco/train2017/1.jpg"# out_ann_file = "/coco/annotations/annotations_train2017.json"# osp.dirname(out_ann_file) = "/coco/annotations"# file_name = ..\train2017\1.jpg out_ann_file文件所在目录下 找 out_img_file 的相对路径height=img.shape[0], # 如果裁剪就用img调用width=img.shape[1],# height=data_json['imageHeight'],# width=data_json['imageWidth'],date_captured=None,id=image_id,))masks = {} # for areasegmentations = collections.defaultdict(list) # for segmentationfor shape in label_file.shapes:points = shape["points"]label = shape["label"]group_id = shape.get("group_id")shape_type = shape.get("shape_type", "polygon")mask = labelme.utils.shape_to_mask(img.shape[:2], points, shape_type)if group_id is None:group_id = uuid.uuid1()instance = (label, group_id)if instance in masks:masks[instance] = masks[instance] | maskelse:masks[instance] = maskif shape_type == "rectangle":(x1, y1), (x2, y2) = pointsx1, x2 = sorted([x1, x2])y1, y2 = sorted([y1, y2])points = [x1, y1, x2, y1, x2, y2, x1, y2]else:points = np.asarray(points).flatten().tolist()segmentations[instance].append(points)segmentations = dict(segmentations)for instance, mask in masks.items():cls_name, group_id = instanceif cls_name not in class_name_to_id:continuecls_id = class_name_to_id[cls_name]mask = np.asfortranarray(mask.astype(np.uint8))mask = pycocotools.mask.encode(mask)area = float(pycocotools.mask.area(mask))bbox = pycocotools.mask.toBbox(mask).flatten().tolist()data["annotations"].append(dict(id=len(data["annotations"]),image_id=image_id,category_id=cls_id,segmentation=segmentations[instance],area=area,bbox=bbox,iscrowd=0,))# ************************** 对标签的处理结束 *******************************************# ************************** 可视化的处理开始 *******************************************if not args.noviz:labels, captions, masks = zip(*[(class_name_to_id[cnm], cnm, msk)for (cnm, gid), msk in masks.items()if cnm in class_name_to_id])viz = imgviz.instances2rgb(image=img,labels=labels,masks=masks,captions=captions,font_size=15,line_width=2,)out_viz_file = osp.join(args.output_dir, "visualization", base + ".jpg")imgviz.io.imsave(out_viz_file, viz)# ************************** 可视化的处理结束 *******************************************with open(out_ann_file, "w") as f: # 将每个标签文件汇总成data后,保存总标签data文件json.dump(data, f)# 主程序执行
def main():parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(formatter_class=argparse.ArgumentDefaultsHelpFormatter)parser.add_argument("--input_dir", help="input annotated directory", default=r"E:/老师和教研室相关/揭榜挂帅挑战杯/海陆/")parser.add_argument("--output_dir", help="output dataset directory", default=r"E:/老师和教研室相关/揭榜挂帅挑战杯/海陆/coco")parser.add_argument("--labels", help="labels file", default='E:/老师和教研室相关/揭榜挂帅挑战杯/海陆/0labels.txt')parser.add_argument("--noviz", help="no visualization", action="store_true")args = parser.parse_args()if osp.exists(args.output_dir):print("Output directory already exists:", args.output_dir)sys.exit(1)os.makedirs(args.output_dir)print("| Creating dataset dir:", args.output_dir)if not args.noviz:os.makedirs(osp.join(args.output_dir, "visualization"))# 创建保存的文件夹if not os.path.exists(osp.join(args.output_dir, "annotations")):os.makedirs(osp.join(args.output_dir, "annotations"))if not os.path.exists(osp.join(args.output_dir, "train2017")):os.makedirs(osp.join(args.output_dir, "train2017"))if not os.path.exists(osp.join(args.output_dir, "val2017")):os.makedirs(osp.join(args.output_dir, "val2017"))# 获取目录下所有的.jpg文件列表# feature_files = glob.glob(osp.join(args.input_dir, "*.jpg"))feature_files = glob.glob(osp.join(args.input_dir, "*.png"))print('| Image number: ', len(feature_files))# 获取目录下所有的joson文件列表label_files = glob.glob(osp.join(args.input_dir, "*.json"))print('| Json number: ', len(label_files))# feature_files:待划分的样本特征集合 label_files:待划分的样本标签集合 test_size:测试集所占比例# x_train:划分出的训练集特征 x_test:划分出的测试集特征 y_train:划分出的训练集标签 y_test:划分出的测试集标签x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(feature_files, label_files, test_size=0.3, random_state=1)print("| Train number:", len(y_train), '\t Value number:', len(y_test))# 把训练集标签转化为COCO的格式,并将标签对应的图片保存到目录 /train2017/print("—" * 50)print("| Train images:")to_coco(args, y_train, train=True)# 把测试集标签转化为COCO的格式,并将标签对应的图片保存到目录 /val2017/print("—" * 50)print("| Test images:")to_coco(args, y_test, train=False)if __name__ == "__main__":print("—" * 50)main()print("—" * 50)coco数据集格式如下:
|-- annotations
| |--- instances_train2017.json
| |--- instances_val2017.json
|-- train2017
| |--- 2.jpg
| |--- 5.jpg
| |--- .......
|-- val2017
| |--- 1.jpg
| |--- 3.jpg
| |--- .......
|-- visualization
| |--- 1.jpg
| |--- 2.jpg
| |--- ....... (3) cocojson2yolotxt 是对统一的coco格式利用instances_train2017/instances_val2017形成yolo的txt格式
这里得 classes.txt 没有_background_ 只有自己设定的类别
#COCO 格式的数据集转化为 YOLO 格式的数据集
#--json_path 输入的json文件路径
#--save_path 保存的文件夹名字,默认为当前目录下的labels。import os
import json
from tqdm import tqdm
import argparseparser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
#这里根据自己的json文件位置,换成自己的就行
parser.add_argument('--json_path', default='F:/CutLER-main/output/imagenet_train_fixsize480_tau0.2_N3.json',type=str, help="input: coco format(json)")
#这里设置.txt文件保存位置
parser.add_argument('--save_path', default='F:/CutLER-main/output/yolo_my_mask/labels/', type=str, help="specify where to save the output dir of labels")
arg = parser.parse_args()def convert(size, box):dw = 1. / (size[0])dh = 1. / (size[1])x = box[0] + box[2] / 2.0y = box[1] + box[3] / 2.0w = box[2]h = box[3]
#round函数确定(xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax)的小数位数x = round(x * dw, 6)w = round(w * dw, 6)y = round(y * dh, 6)h = round(h * dh, 6)return (x, y, w, h)if __name__ == '__main__':json_file = arg.json_path # COCO Object Instance 类型的标注ana_txt_save_path = arg.save_path # 保存的路径data = json.load(open(json_file, 'r'))if not os.path.exists(ana_txt_save_path):os.makedirs(ana_txt_save_path)id_map = {} # coco数据集的id不连续!重新映射一下再输出!with open(os.path.join(ana_txt_save_path, 'classes.txt'), 'w') as f:# 写入classes.txtfor i, category in enumerate(data['categories']):f.write(f"{category['name']}\n")id_map[category['id']] = i# print(id_map)#这里需要根据自己的需要,更改写入图像相对路径的文件位置。list_file = open(os.path.join(ana_txt_save_path, 'train2017.txt'), 'w')for img in tqdm(data['images']):filename = img["file_name"]img_width = img["width"]img_height = img["height"]img_id = img["id"]head, tail = os.path.splitext(filename)ana_txt_name = head + ".txt" # 对应的txt名字,与jpg一致f_txt = open(os.path.join(ana_txt_save_path, ana_txt_name), 'w')for ann in data['annotations']:if ann['image_id'] == img_id:box = convert((img_width, img_height), ann["bbox"])f_txt.write("%s %s %s %s %s\n" % (id_map[ann["category_id"]], box[0], box[1], box[2], box[3]))f_txt.close()#将图片的相对路径写入train2017或val2017的路径list_file.write('./images/train2017/%s.jpg\n' %(head))list_file.close()
(4) cocojson2yolotxt_seg 是对统一的coco格式利用instances_train2017/instances_val2017形成yolo-segment的txt格式,用于实例分割的,最好一般都用这个来转换
import os
import json
import shutildef write_yolo_txt_file(txt_file_path, label_seg_x_y_list):if not os.path.exists(txt_file_path):with open(txt_file_path, "w") as file:for element in label_seg_x_y_list:file.write(str(element) + " ")file.write('\n')else:with open(txt_file_path, "a") as file:for element in label_seg_x_y_list:file.write(str(element) + " ")file.write('\n')def read_json(in_json_path, img_dir, target_dir):with open(in_json_path, "r", encoding='utf-8') as f:# json.load数据到变量json_datajson_data = json.load(f)# print(len(json_data['annotations']))# print(len(json_data['images']))# print(len(json_data['categories']))for annotation in json_data['annotations']: # 遍历标注数据信息# print(annotation)category_id = annotation['category_id']image_id = annotation['image_id']for image in json_data['images']: # 遍历图片相关信息if image['id'] == image_id:width = image['width'] # 图片宽height = image['height'] # 图片高img_file_name = image['file_name'] # 图片名称img_file_name = img_file_name.split('/')[-1]filename = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(img_file_name))[0]# img_file_name=img_file_name[:-4]# txt_file_name = img_file_name.split('.')[0] + '.txt'txt_file_name = filename + '.txt' # 要保存的对应txt文件名break# print(width,height,img_file_name,txt_file_name)segmentation = annotation['segmentation'] # 图像分割点信息[[x1,y1,x2,y2,...,xn,yn]]seg_x_y_list = [i / width if num % 2 == 0 else i / height for num, i inenumerate(segmentation[0])] # 归一化图像分割点信息label_seg_x_y_list = seg_x_y_list[:]label_seg_x_y_list.insert(0, category_id) # 图像类别与分割点信息[label,x1,y1,x2,y2,...,xn,yn]# print(label_seg_x_y_list)# 写txt文件txt_file_path = target_dir + txt_file_name# print(txt_file_path)write_yolo_txt_file(txt_file_path, label_seg_x_y_list)# # 选出txt对应img文件# img_file_path = img_dir + img_file_name# # print(img_file_path)# shutil.copy(img_file_path, target_dir)if __name__ == "__main__":img_dir = 'E:/老师和教研室相关/揭榜挂帅挑战杯/海陆/yolo/images/train2017/'target_dir = 'E:/老师和教研室相关/揭榜挂帅挑战杯/海陆/yolo/labels/train2017/'if not os.path.exists(target_dir):os.mkdir(target_dir)in_json_path = 'E:/老师和教研室相关/揭榜挂帅挑战杯/海陆/coco/annotations/instances_train2017.json'read_json(in_json_path, img_dir, target_dir)4.逐个txt转json
注意这里面lcassesname 要txt里面的目标类别对应,判断对应的标签名称,写入json文件中
import os
import json
import base64
import cv2def read_txt_file(txt_file):with open(txt_file, 'r') as f:lines = f.readlines()data = []for line in lines:line = line.strip().split()class_name = line[0]bbox = [coord for coord in line[1:]]data.append({'class_name': class_name, 'bbox': bbox})return datadef convert_to_labelme(data, image_path, image_size):labelme_data = {'version': '4.5.6','flags': {},'shapes': [],'imagePath': json_image_path,'imageData': None,'imageHeight': image_size[0],'imageWidth': image_size[1]}for obj in data:dx = obj['bbox'][0]dy = obj['bbox'][1]dw = obj['bbox'][2]dh = obj['bbox'][3]w = eval(dw) * image_size[1]h = eval(dh) * image_size[0]center_x = eval(dx) * image_size[1]center_y = eval(dy) * image_size[0]x1 = center_x - w/2y1 = center_y - h/2x2 = center_x + w/2y2 = center_y + h/2if obj['class_name'] == '0': #判断对应的标签名称,写入json文件中label = str('People')elif obj['class_name'] == '1': #判断对应的标签名称,写入json文件中label = str('Car')elif obj['class_name'] == '2': #判断对应的标签名称,写入json文件中label = str('Bus')elif obj['class_name'] == '3': #判断对应的标签名称,写入json文件中label = str('Lamp')elif obj['class_name'] == '4': #判断对应的标签名称,写入json文件中label = str('Motorcycle')elif obj['class_name'] == '5': #判断对应的标签名称,写入json文件中label = str('Truck')shape_data = {'label': label,'points': [[x1, y1], [x2, y2]],'group_id': None,'shape_type': 'rectangle','flags': {}}labelme_data['shapes'].append(shape_data)return labelme_datadef save_labelme_json(labelme_data, image_path, output_file):with open(image_path, 'rb') as f:image_data = f.read()labelme_data['imageData'] = base64.b64encode(image_data).decode('utf-8')with open(output_file, 'w') as f:json.dump(labelme_data, f, indent=4)# 设置文件夹路径和输出文件夹路径
txt_folder = r"G:/datasets/yolo_M3FD_Detection/labels" # 存放txt文件的文件夹路径
output_folder = r"G:/datasets/yolo_M3FD_Detection/jsons/"
img_folder = r"G:/datasets/yolo_M3FD_Detection/ir/"# 创建输出文件夹
if not os.path.exists(output_folder):os.makedirs(output_folder)# 遍历txt文件夹中的所有文件
for filename in os.listdir(txt_folder):if filename.endswith('.txt'):# 生成对应的输出文件名output_filename = os.path.splitext(filename)[0] + '.json'# 读取txt文件txt_file = os.path.join(txt_folder, filename)data = read_txt_file(txt_file)# 设置图片路径和尺寸# image_filename = os.path.splitext(filename)[0] + '.jpg' # 图片文件名与txt文件名相同,后缀为.jpgimage_filename = os.path.splitext(filename)[0] + '.png' # 图片文件名与txt文件名相同,后缀为.jpg# image_path = os.path.join(img_folder, image_filename)image_path = os.path.join(image_filename) # 直接文件名 方便后面json转换# image_size = (1280, 720) # 根据实际情况修改json_image_path = image_path.split('\\')[-1]print("image_path:", image_path)image_path_folder = os.path.join(img_folder, image_filename)image_size = cv2.imread(image_path_folder).shape# 转化为LabelMe格式labelme_data = convert_to_labelme(data, image_path, image_size)# 保存为LabelMe JSON文件output_file = os.path.join(output_folder, output_filename)save_labelme_json(labelme_data, image_path_folder, output_file)5.逐个txt转coco的json
相当于直接把coco的数据集instances格式弄出来
import os
import json
import cv2
import random
import time
from PIL import Image# 生成全部的Json_all 分train/val/test
coco_format_save_path='G:datasets/yolo_ir_jz/jsons/test/' #要生成的标准coco格式标签所在文件夹
yolo_format_classes_path='G:datasets/yolo_ir_jz/classes.txt' #类别文件,一行一个类
yolo_format_annotation_path='G:datasets/yolo_ir_jz/labels/test/' #yolo格式标签所在文件夹
img_pathDir='G:datasets/yolo_ir_jz/images/test/' #图片所在文件夹with open(yolo_format_classes_path,'r') as fr: #打开并读取类别文件lines1=fr.readlines()
# print(lines1)
categories=[] #存储类别的列表
for j,label in enumerate(lines1):label=label.strip()categories.append({'id':j+1,'name':label,'supercategory':'None'}) #将类别信息添加到categories中
# print(categories)write_json_context=dict() #写入.json文件的大字典
write_json_context['info']= {'description': '', 'url': '', 'version': '', 'year': 2024, 'contributor': 'gc', 'date_created': '2024-09-27'}
write_json_context['licenses']=[{'id':1,'name':None,'url':None}]
write_json_context['categories']=categories
write_json_context['images']=[]
write_json_context['annotations']=[]#接下来的代码主要添加'images'和'annotations'的key值
imageFileList=os.listdir(img_pathDir) #遍历该文件夹下的所有文件,并将所有文件名添加到列表中
for i,imageFile in enumerate(imageFileList):imagePath = os.path.join(img_pathDir,imageFile) #获取图片的绝对路径image = Image.open(imagePath) #读取图片,然后获取图片的宽和高W, H = image.sizeimg_context={} #使用一个字典存储该图片信息#img_name=os.path.basename(imagePath) #返回path最后的文件名。如果path以/或\结尾,那么就会返回空值img_context['file_name']=imageFileimg_context['height']=Himg_context['width']=Wimg_context['date_captured']='2024-09-27'img_context['id']=i #该图片的idimg_context['license']=1img_context['color_url']=''img_context['flickr_url']=''write_json_context['images'].append(img_context) #将该图片信息添加到'image'列表中txtFile=imageFile[:5]+'.txt' #获取该图片获取的txt文件with open(os.path.join(yolo_format_annotation_path,txtFile),'r') as fr:lines=fr.readlines() #读取txt文件的每一行数据,lines2是一个列表,包含了一个图片的所有标注信息for j,line in enumerate(lines):bbox_dict = {} #将每一个bounding box信息存储在该字典中# line = line.strip().split()# print(line.strip().split(' '))class_id,x,y,w,h=line.strip().split(' ') #获取每一个标注框的详细信息class_id,x, y, w, h = int(class_id), float(x), float(y), float(w), float(h) #将字符串类型转为可计算的int和float类型xmin=(x-w/2)*W #坐标转换ymin=(y-h/2)*Hxmax=(x+w/2)*Wymax=(y+h/2)*Hw=w*Wh=h*Hbbox_dict['id']=i*10000+j #bounding box的坐标信息bbox_dict['image_id']=ibbox_dict['category_id']=class_id+1 #注意目标类别要加一bbox_dict['iscrowd']=0height,width=abs(ymax-ymin),abs(xmax-xmin)bbox_dict['area']=height*widthbbox_dict['bbox']=[xmin,ymin,w,h]bbox_dict['segmentation']=[[xmin,ymin,xmax,ymin,xmax,ymax,xmin,ymax]]write_json_context['annotations'].append(bbox_dict) #将每一个由字典存储的bounding box信息添加到'annotations'列表中name = os.path.join(coco_format_save_path,"train"+ '.json')
with open(name,'w') as fw: #将字典信息写入.json文件中json.dump(write_json_context,fw,indent=2)6.根据txt划分yolo数据集格式
训练集:验证集:测试集 (7:2:1) 比例可以自己定义
import os, shutil, random
from tqdm import tqdm"""
标注文件是yolo格式(txt文件)
训练集:验证集:测试集 (7:2:1)
"""def split_img(img_path, label_path, split_list):try:Data = 'G:\datasets/yolo_my_enhance'# Data是你要将要创建的文件夹路径(路径一定是相对于你当前的这个脚本而言的)# os.mkdir(Data)train_img_dir = Data + '/images/train'val_img_dir = Data + '/images/val'test_img_dir = Data + '/images/test'train_label_dir = Data + '/labels/train'val_label_dir = Data + '/labels/val'test_label_dir = Data + '/labels/test'# 创建文件夹os.makedirs(train_img_dir)os.makedirs(train_label_dir)os.makedirs(val_img_dir)os.makedirs(val_label_dir)os.makedirs(test_img_dir)os.makedirs(test_label_dir)except:print('文件目录已存在')train, val, test = split_listall_img = os.listdir(img_path)all_img_path = [os.path.join(img_path, img) for img in all_img]# all_label = os.listdir(label_path)# all_label_path = [os.path.join(label_path, label) for label in all_label]train_img = random.sample(all_img_path, int(train * len(all_img_path)))train_img_copy = [os.path.join(train_img_dir, img.split('\\')[-1]) for img in train_img]train_label = [toLabelPath(img, label_path) for img in train_img]train_label_copy = [os.path.join(train_label_dir, label.split('\\')[-1]) for label in train_label]for i in tqdm(range(len(train_img)), desc='train ', ncols=80, unit='img'):_copy(train_img[i], train_img_dir)_copy(train_label[i], train_label_dir)all_img_path.remove(train_img[i])val_img = random.sample(all_img_path, int(val / (val + test) * len(all_img_path)))val_label = [toLabelPath(img, label_path) for img in val_img]for i in tqdm(range(len(val_img)), desc='val ', ncols=80, unit='img'):_copy(val_img[i], val_img_dir)_copy(val_label[i], val_label_dir)all_img_path.remove(val_img[i])test_img = all_img_pathtest_label = [toLabelPath(img, label_path) for img in test_img]for i in tqdm(range(len(test_img)), desc='test ', ncols=80, unit='img'):_copy(test_img[i], test_img_dir)_copy(test_label[i], test_label_dir)def _copy(from_path, to_path):shutil.copy(from_path, to_path)def toLabelPath(img_path, label_path):img = img_path.split('\\')[-1]label = img.split('.jpg')[0] + '.txt'return os.path.join(label_path, label)if __name__ == '__main__':img_path = 'G:/datasets/yolo_my_enhance/yolo_my_enhance' # 你的图片存放的路径(路径一定是相对于你当前的这个脚本文件而言的)label_path = './YoloLabels' # 你的txt文件存放的路径(路径一定是相对于你当前的这个脚本文件而言的)split_list = [0.7, 0.2, 0.1] # 数据集划分比例[train:val:test]split_img(img_path, label_path, split_list)
相关文章:
、yolo(txt)、voc(xml)标注格式的相互转换)
coco(json)、yolo(txt)、voc(xml)标注格式的相互转换
一般都是用labeleme进行标注 标注格式都是json 然后根据不同的格式进行数据标注转换: 1.逐个json转xml: 当我们在使用数据集训练计算机视觉模型时,常常会遇到有的数据集只给了单个的json annotation文件,而模型所需要的annotation是基于每…...
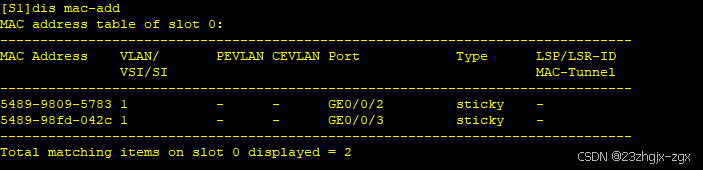
以太网交换安全:端口安全
一、端口安全介绍 端口安全是一种网络设备防护措施,通过将接口学习到的动态MAC地址转换为安全MAC地址(包括安全动态MAC和Sticky MAC),阻止除安全MAC和静态MAC之外的主机通过本接口和设备通信,从而增强设备的安全性。以…...
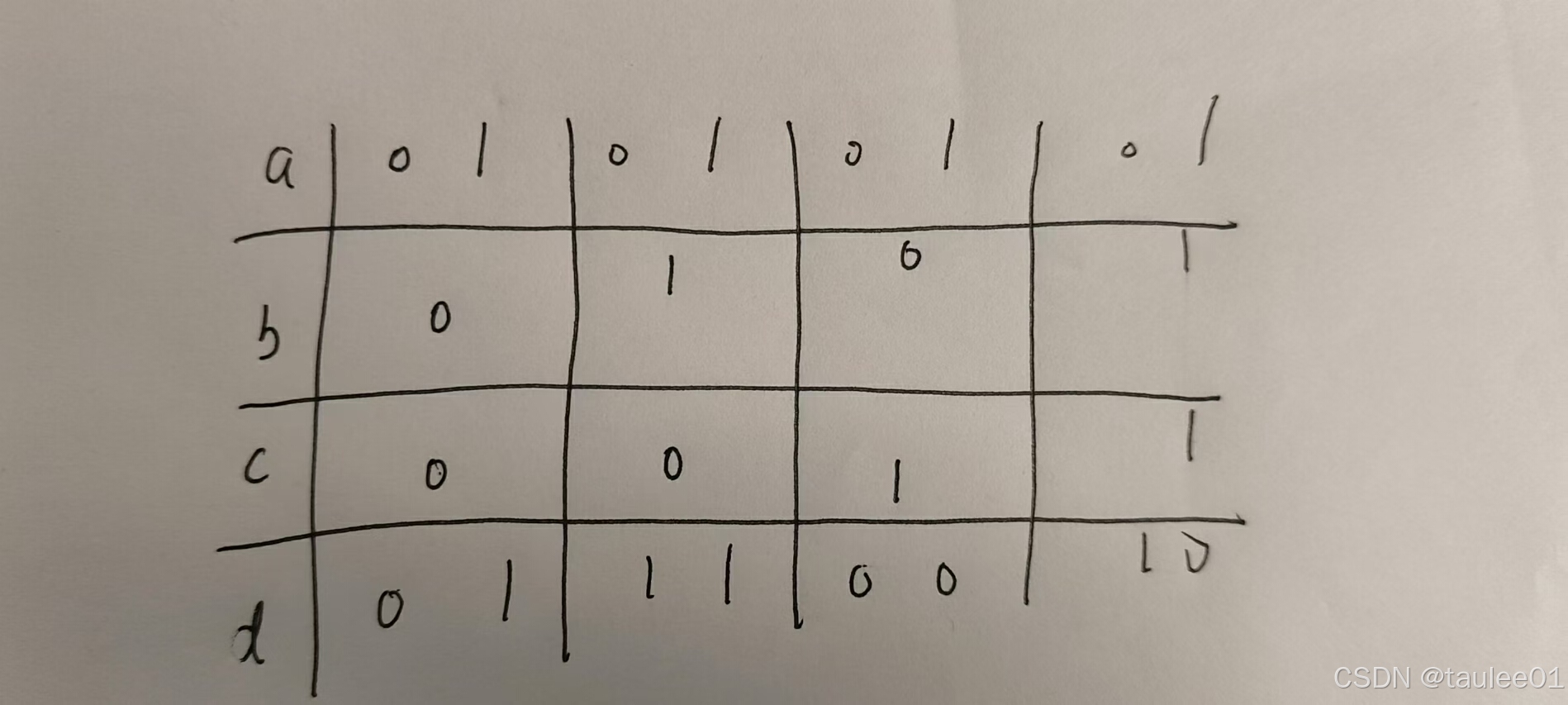
[题解] Codeforces Round 976 (Div. 2) A ~ E
A. Find Minimum Operations 签到. void solve() {int n, k;cin >> n >> k;if (k 1) {cout << n << endl;return;}int ans 0;while (n) {ans n % k;n / k;}cout << ans << endl; }B. Brightness Begins 打表发现, 翻转完后的序列为: 0…...
【零基础入门产品经理】学习准备篇 | 需要学一些什么呢?
前言: 零实习转行产品经理经验分享01-学习准备篇_哔哩哔哩_bilibili 该篇内容主要是对bilibili这个视频的观后笔记~谢谢美丽滴up主友情分享。 全文摘要:如何在0实习且没有任何产品相关经验下,如何上岸产品经理~ 目录 一、想清楚为什么…...

第四届机器人、自动化与智能控制国际会议(ICRAIC 2024)征稿
第四届机器人、自动化与智能控制国际会议(ICRAIC 2024)由湖南第一师范学院主办,南京师范大学、山东女子学院、爱迩思出版社(ELSP)协办。 大会将专注于机器人、数字化、自动化、人工智能等技术的开发和融合,…...
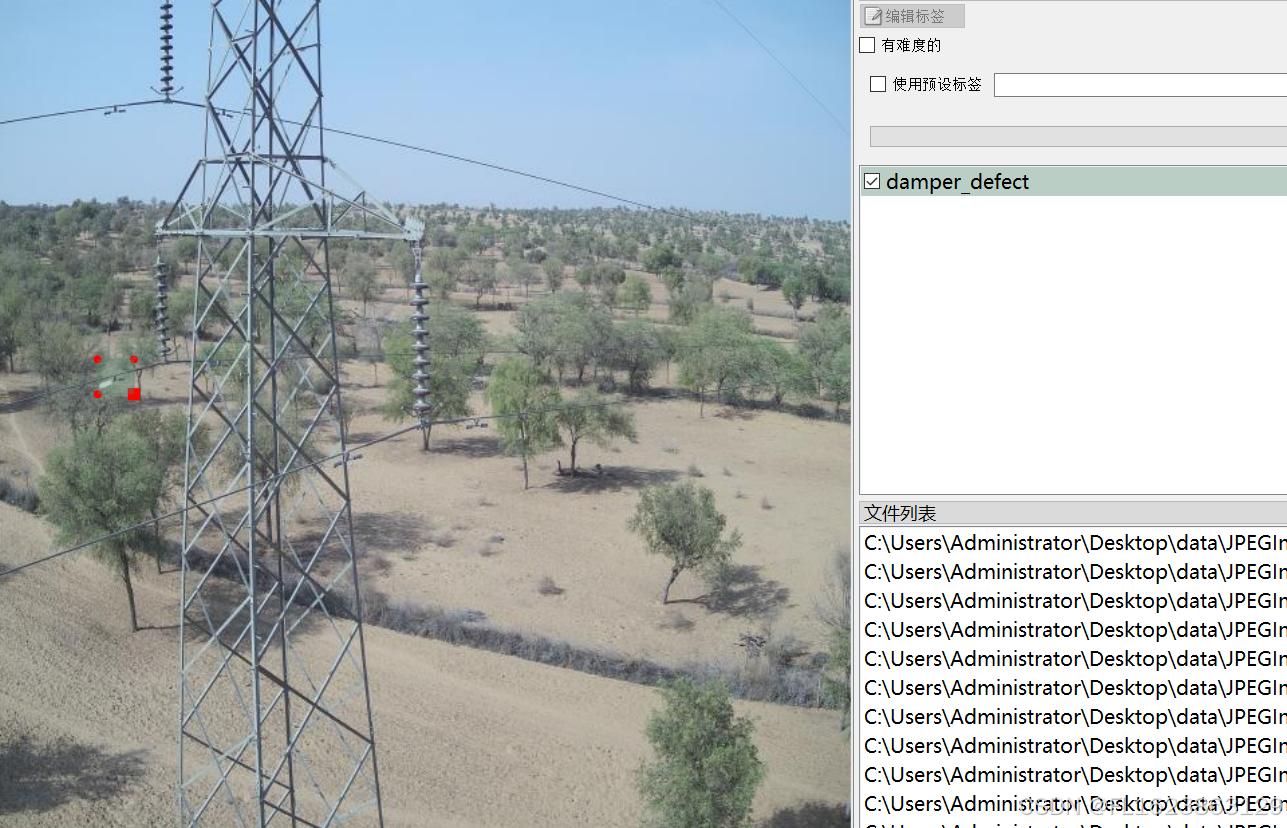
[数据集][目标检测]电力场景防震锤缺陷检测数据集VOC+YOLO格式705张1类别
重要说明:防震锤缺陷图片太难找,数据集里面存在大量单一场景图片,请仔细查看图片预览谨慎下载,此外数据集均为小目标检测,如果训练map偏低属于正常现象 数据集格式:Pascal VOC格式YOLO格式(不包含分割路径…...

【SpringBoot】
目录 一、Spring Boot概要 1. SpringBoot介绍 2. SpringBoot优点 3. SpringBoot缺点 4. 时代背景-微服务 二、Spring Boot 核心配置 1. Spring Boot配置文件分类 1.1 application.properties 1.2 application.yml 1.3 小结 2. YAML概述 3. YAML基础语法 3.1 注意事…...
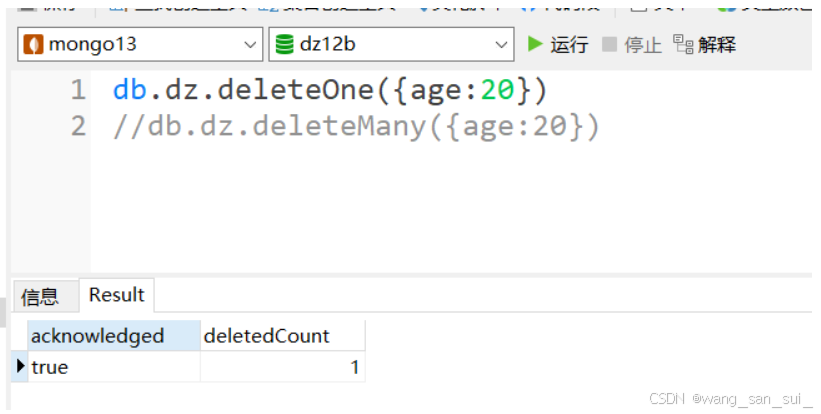
Linux操作系统中MongoDB
1、什么是MongoDB 1、非关系型数据库 NoSQL,泛指非关系型的数据库。随着互联网web2.0网站的兴起,传统的关系数据库在处理web2.0网站,特别是超大规模和高并发的SNS类型的web2.0纯动态网站已经显得力不从心,出现了很多难以克服的问…...

2、.Net 前端框架:OpenAuth.Net - .Net宣传系列文章
OpenAuth.Net 是一个开源的身份验证框架,由开发者 Yubaolee 创建,它旨在简化 Web 应用和服务的安全授权过程。这个框架以其强大的功能和易用性,为开发人员提供了一种高效的方式来处理用户认证和授权问题。 OpenAuth.Net 的关键特性包括&#…...
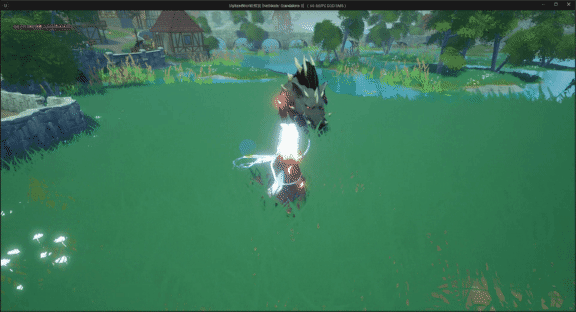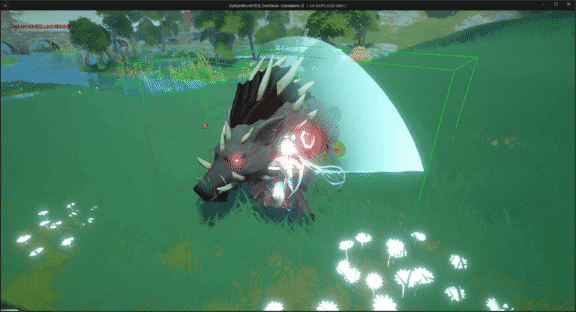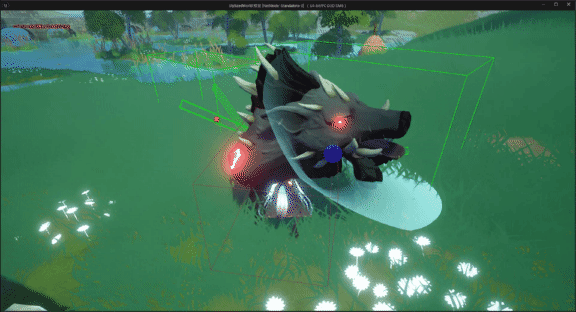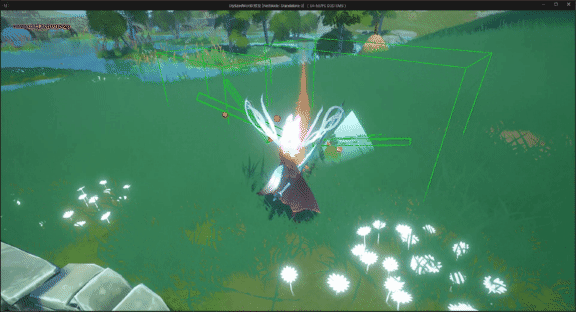
unreal engine5制作动作类游戏时,我们使用刀剑等武器攻击怪物或敌方单位时,发现攻击特效、伤害等没有触发
UE5系列文章目录 文章目录 UE5系列文章目录前言一、问题分析二、解决方法1. 添加项目设置碰撞检测通道2.玩家角色碰撞设置3.怪物角色碰撞预设 最终效果 前言 在使用unreal engine5制作动作类游戏时,我们使用刀剑等武器攻击怪物或敌方单位时,发现攻击特效…...
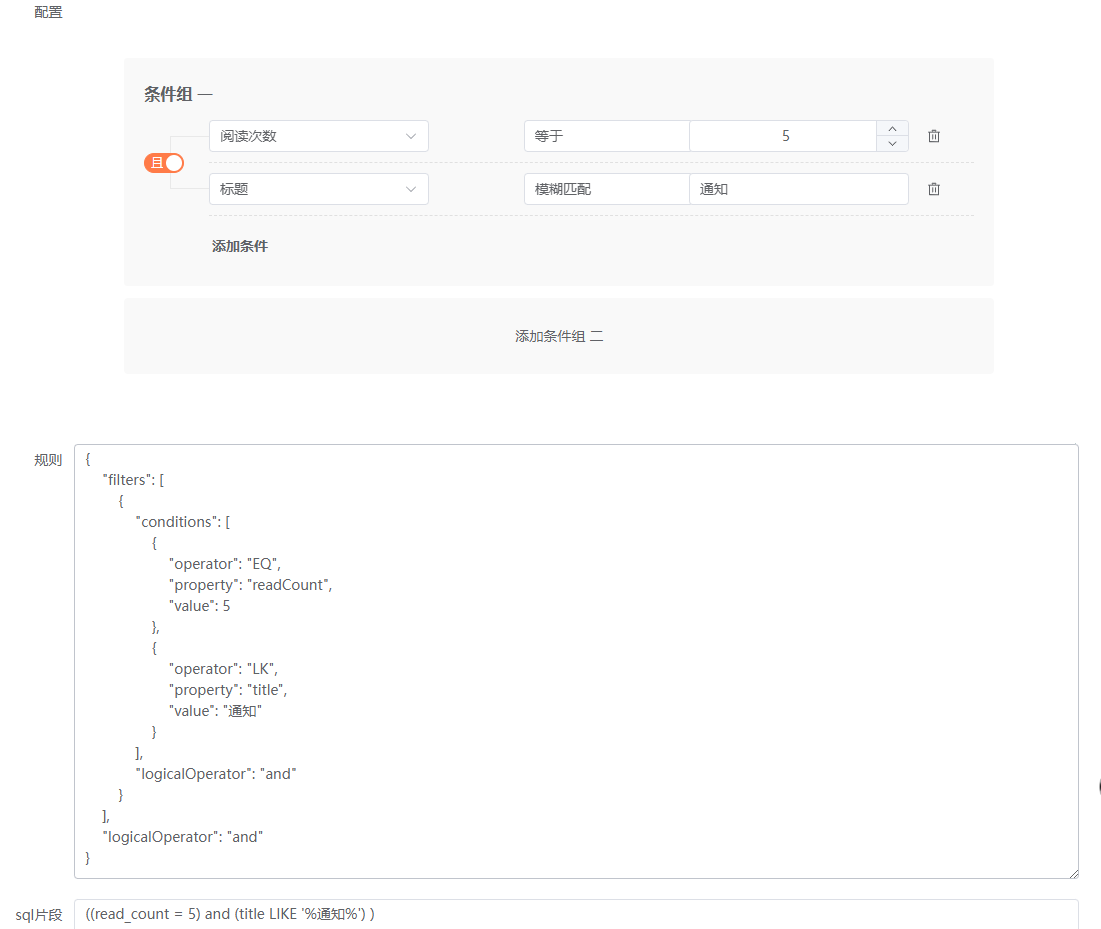
数据权限的设计与实现系列11——前端筛选器组件Everright-filter集成功能完善2
筛选条件数据类型完善 文本类 筛选器组件给了一个文本类操作的范例,如下: Text: [{label: 等于,en_label: Equal,style: noop},{label: 等于其中之一,en_label: Equal to one of,value: one_of,style: tags},{label: 不等于,en_label: Not equal,v…...

C++ 游戏开发
C游戏开发 C 是一种高效、灵活且功能强大的编程语言,因其性能和控制能力而在游戏开发中被广泛应用。许多著名的游戏引擎,如 Unreal Engine、CryEngine 和 Godot 等,都依赖于 C 进行核心开发。本文将详细介绍 C 在游戏开发中的应用࿰…...
)
【历年CSP-S复赛第一题】暴力解法与正解合集(2019-2022)
P5657 [CSP-S2019] 格雷码P7076 [CSP-S2020] 动物园P7913 [CSP-S 2021] 廊桥分配P8817 [CSP-S 2022] 假期计划 P5657 [CSP-S2019] 格雷码 暴力50分 #include<bits/stdc.h> #define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0) #define int long long #d…...

基于PyQt5和SQLite的数据库操作程序
基于PyQt5和SQLite的数据库操作程序:功能解析 在现代办公和数据处理中,数据库操作是不可或缺的一部分。然而,传统的数据库管理工具往往界面复杂,操作繁琐,对于非专业人士来说存在一定的学习曲线。为了解决这个问题,我们开发了一款基于PyQt5和SQLite的数据库操作程序。该…...
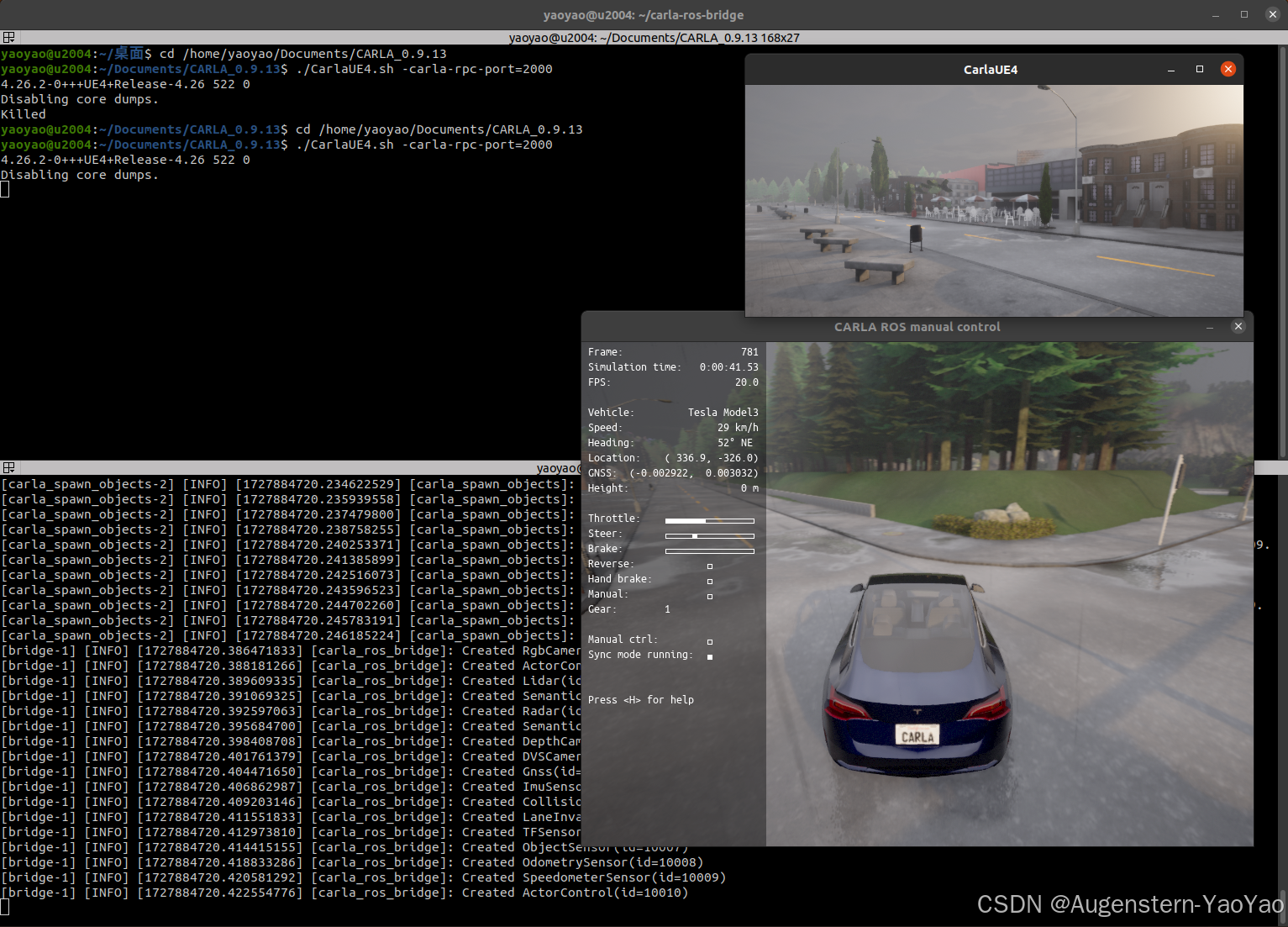
在Ubuntu 20.04中安装CARLA
0. 引言 CARLA (Car Learning to Act) 是一款开源自动驾驶模拟器,其支持自动驾驶系统全管线的开发、训练和验证(Development, Training, and Validation of autonomous driving systems)。Carla提供了丰富的数字资产,例如城市布局…...
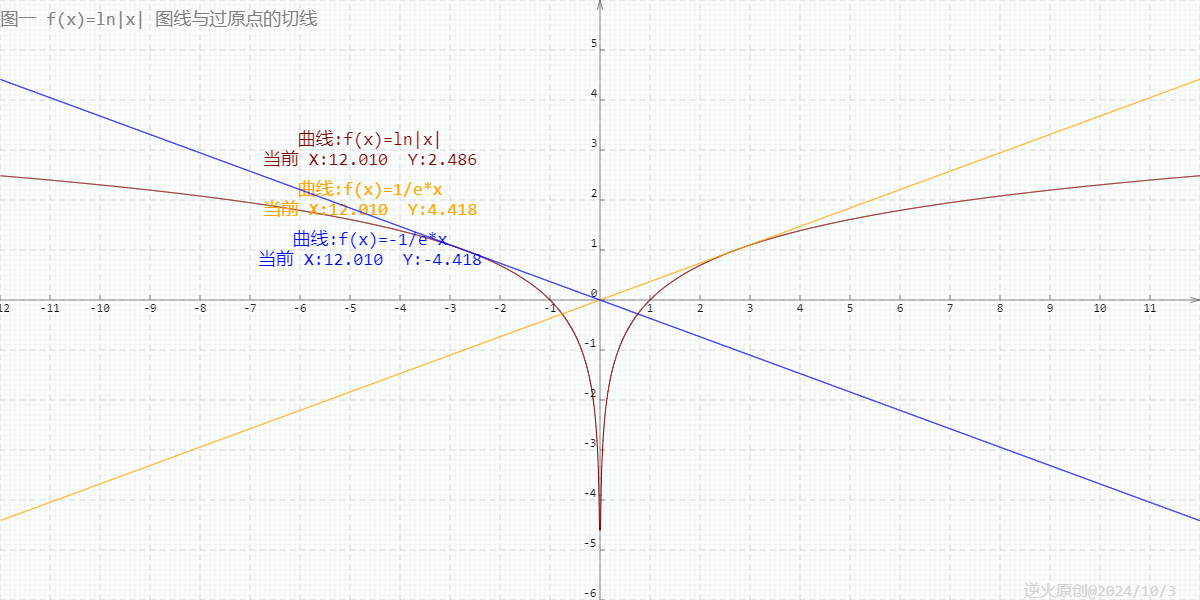
【高中数学/对数/导数】曲线y=ln|x|过坐标原点的两切线方程为?
【问题】 曲线yln|x|过坐标原点的两切线方程为?(高考真题) 【出处】 《高考数学 函数与导数题型解题研究》P5第8题 中原教研工作室编著 【解答】 yln|x|的图线分两部分,y轴左边的部分是ylnx的镜像 所以知ylnx上切线过原点的…...

Qt CMake
使用 CMake 构建 CMake 是一款用于简化跨不同平台开发项目的构建流程的工具。 CMake 可自动生成构建系统,如 Makefile 和 Visual Studio 项目文件。 CMake 是一个第三方工具,有自己的文档。 本主题介绍如何在 Qt 5 中使用 CMake 3.1.0。 开始使用 CMak…...
制造企业各部门如何参与生产成本控制与管理?
国内制造业的分量可不轻,从日常生活用品到高端工业设备,中国制造几乎涵盖了各个领域。 不过很多制造业企业在管理方面确实存在一些难题:成本控制不容易,产品质量并不稳定,生产周期也常常较长。 一、中国制造业生产管…...
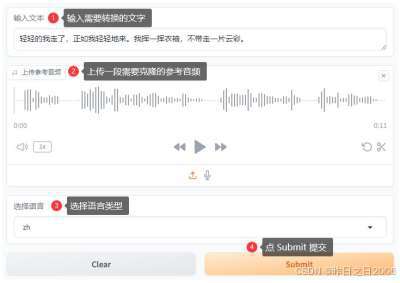
FireRedTTS - 小红书最新开源AI语音克隆合成系统 免训练一键音频克隆 本地一键整合包下载
小红书技术团队FireRed最近推出了一款名为FireRedTTS的先进语音合成系统,该系统能够基于少量参考音频快速模仿任意音色和说话风格,实现独特的音频内容创造。 FireRedTTS 只需要给定文本和几秒钟参考音频,无需训练,就可模仿任意音色…...
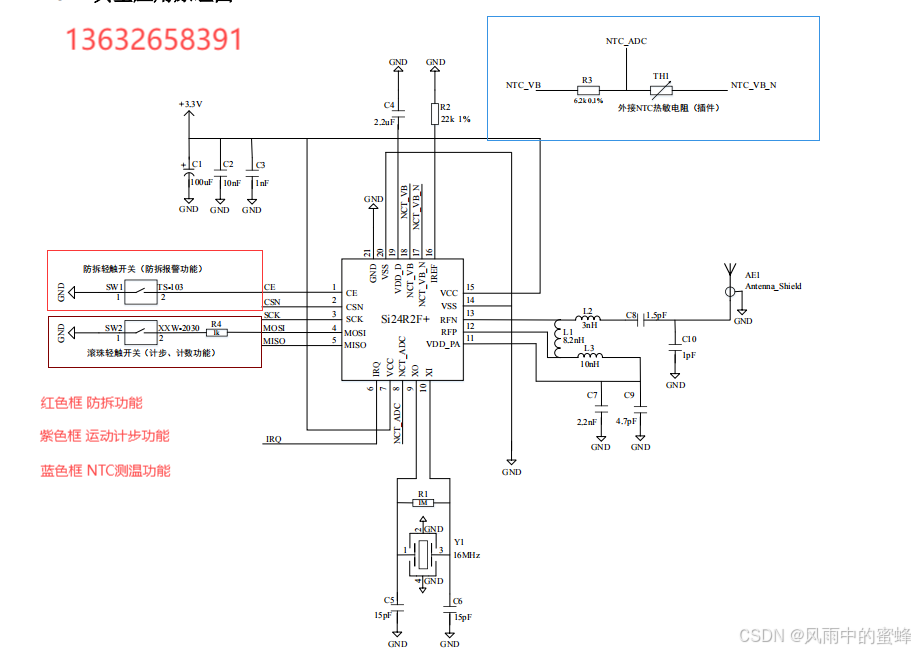
活体检测标签之2.4G有源RFID--SI24R2F+
首先从客户对食品安全和可追溯性的关注切入,引出活体标签这个解决方案。接着分别阐述活体标签在动物养殖和植物产品方面的应用,强调其像 “身份证” 一样记录重要信息,让客户能够了解食品的来源和成长历程,从而放心食用。最后呼吁…...
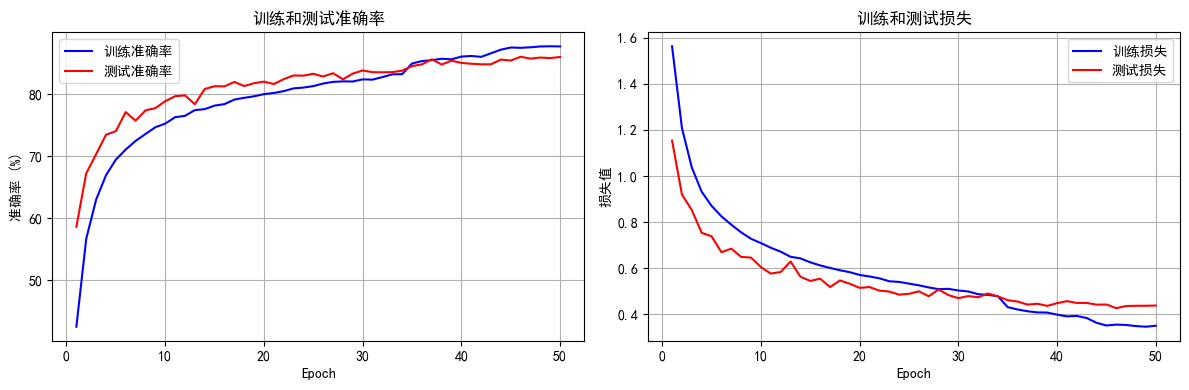
python打卡day49
知识点回顾: 通道注意力模块复习空间注意力模块CBAM的定义 作业:尝试对今天的模型检查参数数目,并用tensorboard查看训练过程 import torch import torch.nn as nn# 定义通道注意力 class ChannelAttention(nn.Module):def __init__(self,…...
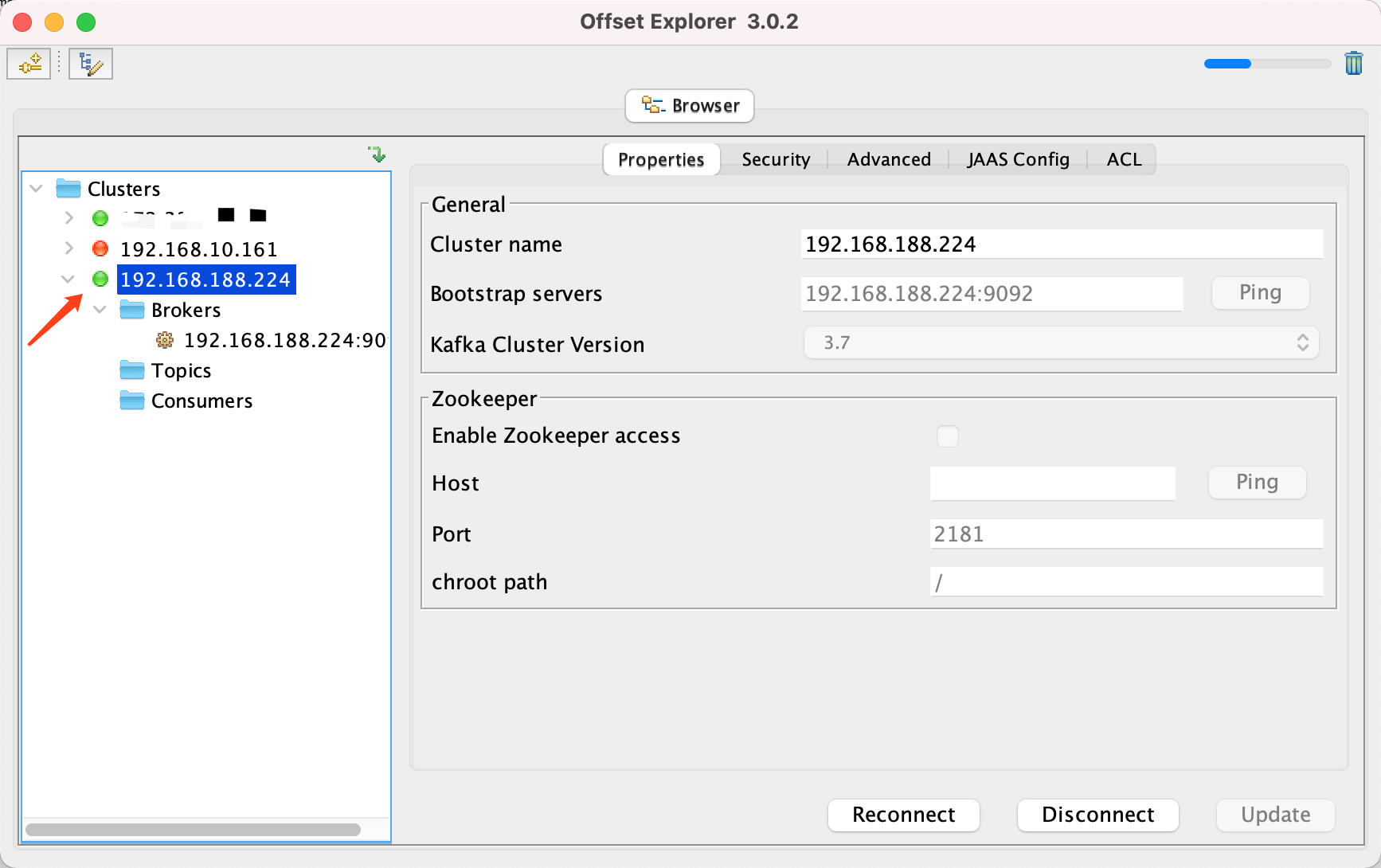
Docker 运行 Kafka 带 SASL 认证教程
Docker 运行 Kafka 带 SASL 认证教程 Docker 运行 Kafka 带 SASL 认证教程一、说明二、环境准备三、编写 Docker Compose 和 jaas文件docker-compose.yml代码说明:server_jaas.conf 四、启动服务五、验证服务六、连接kafka服务七、总结 Docker 运行 Kafka 带 SASL 认…...
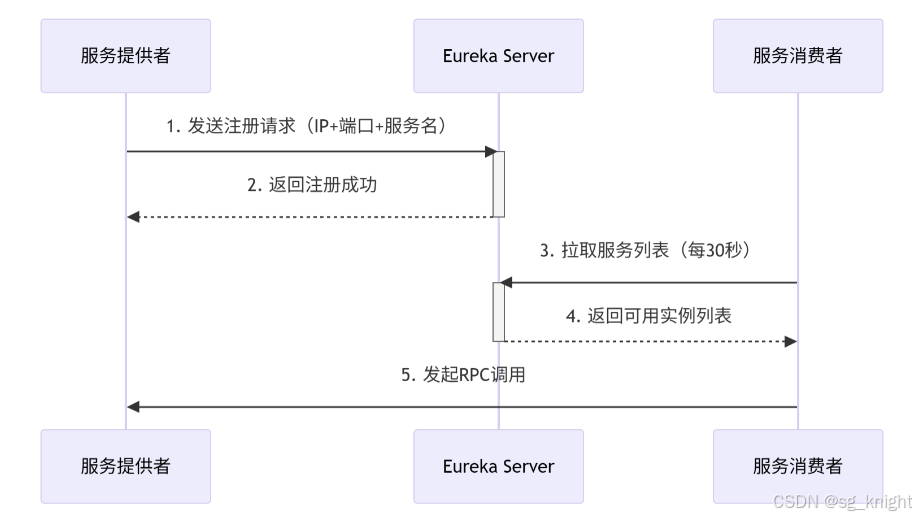
Springcloud:Eureka 高可用集群搭建实战(服务注册与发现的底层原理与避坑指南)
引言:为什么 Eureka 依然是存量系统的核心? 尽管 Nacos 等新注册中心崛起,但金融、电力等保守行业仍有大量系统运行在 Eureka 上。理解其高可用设计与自我保护机制,是保障分布式系统稳定的必修课。本文将手把手带你搭建生产级 Eur…...
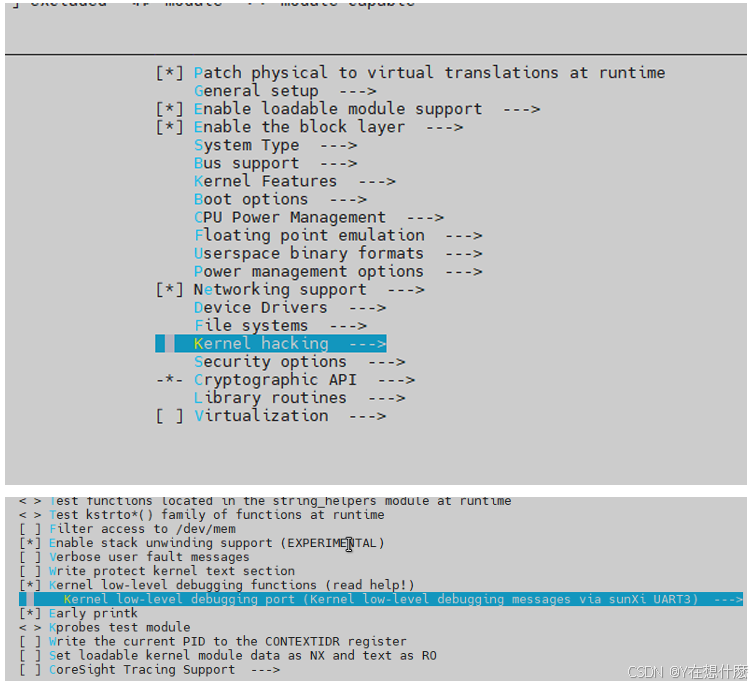
全志A40i android7.1 调试信息打印串口由uart0改为uart3
一,概述 1. 目的 将调试信息打印串口由uart0改为uart3。 2. 版本信息 Uboot版本:2014.07; Kernel版本:Linux-3.10; 二,Uboot 1. sys_config.fex改动 使能uart3(TX:PH00 RX:PH01),并让boo…...

CMake控制VS2022项目文件分组
我们可以通过 CMake 控制源文件的组织结构,使它们在 VS 解决方案资源管理器中以“组”(Filter)的形式进行分类展示。 🎯 目标 通过 CMake 脚本将 .cpp、.h 等源文件分组显示在 Visual Studio 2022 的解决方案资源管理器中。 ✅ 支持的方法汇总(共4种) 方法描述是否推荐…...

go 里面的指针
指针 在 Go 中,指针(pointer)是一个变量的内存地址,就像 C 语言那样: a : 10 p : &a // p 是一个指向 a 的指针 fmt.Println(*p) // 输出 10,通过指针解引用• &a 表示获取变量 a 的地址 p 表示…...
32单片机——基本定时器
STM32F103有众多的定时器,其中包括2个基本定时器(TIM6和TIM7)、4个通用定时器(TIM2~TIM5)、2个高级控制定时器(TIM1和TIM8),这些定时器彼此完全独立,不共享任何资源 1、定…...
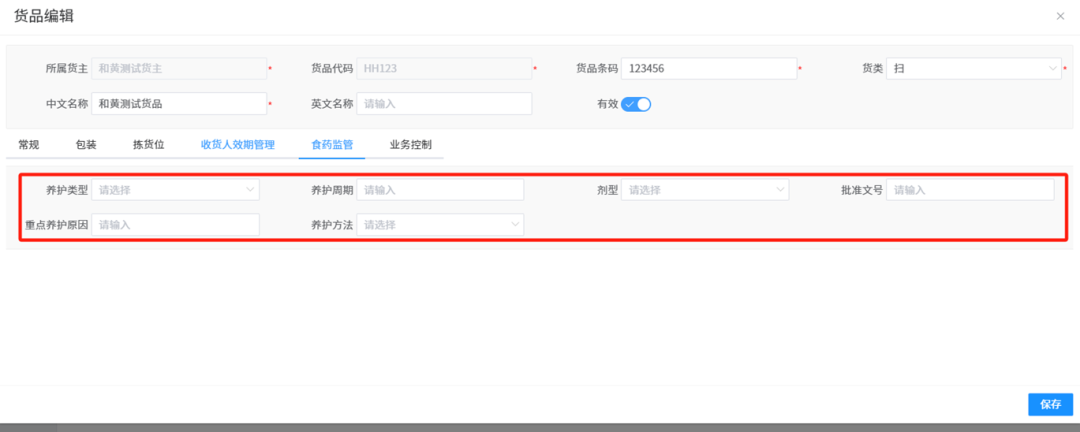
针对药品仓库的效期管理问题,如何利用WMS系统“破局”
案例: 某医药分销企业,主要经营各类药品的批发与零售。由于药品的特殊性,效期管理至关重要,但该企业一直面临效期问题的困扰。在未使用WMS系统之前,其药品入库、存储、出库等环节的效期管理主要依赖人工记录与检查。库…...

英国云服务器上安装宝塔面板(BT Panel)
在英国云服务器上安装宝塔面板(BT Panel) 是完全可行的,尤其适合需要远程管理Linux服务器、快速部署网站、数据库、FTP、SSL证书等服务的用户。宝塔面板以其可视化操作界面和强大的功能广受国内用户欢迎,虽然官方主要面向中国大陆…...

[特殊字符] Spring Boot底层原理深度解析与高级面试题精析
一、Spring Boot底层原理详解 Spring Boot的核心设计哲学是约定优于配置和自动装配,通过简化传统Spring应用的初始化和配置流程,显著提升开发效率。其底层原理可拆解为以下核心机制: 自动装配(Auto-Configuration) 核…...
