PostgreSQL的学习心得和知识总结(一百五十六)|auto_explain — log execution plans of slow queries
目录结构
注:提前言明 本文借鉴了以下博主、书籍或网站的内容,其列表如下:
1、参考书籍:《PostgreSQL数据库内核分析》
2、参考书籍:《数据库事务处理的艺术:事务管理与并发控制》
3、PostgreSQL数据库仓库链接,点击前往
4、日本著名PostgreSQL数据库专家 铃木启修 网站主页,点击前往
5、参考书籍:《PostgreSQL指南:内幕探索》,点击前往
6、参考书籍:《事务处理 概念与技术》
7、auto_explain pg官方手册在线文档,点击前往
8、auto_explain 中文手册在线文档,点击前往
1、本文内容全部来源于开源社区 GitHub和以上博主的贡献,本文也免费开源(可能会存在问题,评论区等待大佬们的指正)
2、本文目的:开源共享 抛砖引玉 一起学习
3、本文不提供任何资源 不存在任何交易 与任何组织和机构无关
4、大家可以根据需要自行 复制粘贴以及作为其他个人用途,但是不允许转载 不允许商用 (写作不易,还请见谅 💖)
5、本文内容基于PostgreSQL master源码开发而成
auto_explain — log execution plans of slow queries
- 文章快速说明索引
- 功能实现背景说明
- 功能实现源码解析

文章快速说明索引
学习目标:
做数据库内核开发久了就会有一种 少年得志,年少轻狂 的错觉,然鹅细细一品觉得自己其实不算特别优秀 远远没有达到自己想要的。也许光鲜的表面掩盖了空洞的内在,每每想到于此,皆有夜半临渊如履薄冰之感。为了睡上几个踏实觉,即日起 暂缓其他基于PostgreSQL数据库的兼容功能开发,近段时间 将着重于学习分享Postgres的基础知识和实践内幕。
学习内容:(详见目录)
1、auto_explain — log execution plans of slow queries
学习时间:
2024年10月20日 16:20:13
学习产出:
1、PostgreSQL数据库基础知识回顾 1个
2、CSDN 技术博客 1篇
3、PostgreSQL数据库内核深入学习
注:下面我们所有的学习环境是Centos8+PostgreSQL master +Oracle19C+MySQL8.0
postgres=# select version();version
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------PostgreSQL 18devel on x86_64-pc-linux-gnu, compiled by gcc (GCC) 8.5.0 20210514 (Red Hat 8.5.0-21), 64-bit
(1 row)postgres=##-----------------------------------------------------------------------------#SQL> select * from v$version; BANNER Oracle Database 19c EE Extreme Perf Release 19.0.0.0.0 - Production
BANNER_FULL Oracle Database 19c EE Extreme Perf Release 19.0.0.0.0 - Production Version 19.17.0.0.0
BANNER_LEGACY Oracle Database 19c EE Extreme Perf Release 19.0.0.0.0 - Production
CON_ID 0#-----------------------------------------------------------------------------#mysql> select version();
+-----------+
| version() |
+-----------+
| 8.0.27 |
+-----------+
1 row in set (0.06 sec)mysql>
功能实现背景说明
当我们向 PostgreSQL 发送一个 SQL 语句时,该语句的执行方式如下图所示:

当使用 EXPLAIN 命令时,PostgreSQL 仅返回估计执行计划,即优化器认为对提供的 SQL 语句最有效的执行计划 (该语句并未真正执行)。另一方面,如果我们运行 EXPLAIN ANALYZE (PostgreSQL 会运行该语句),因此我们将获得实际执行计划,其中还包含执行计划中每个操作的时间信息。但是在调查生产系统上的慢速查询时,我们可能会面临几个挑战:
- 出于安全原因,我们可能不被允许在生产系统上运行查询,因此,在这种情况下,我们不能简单地运行 EXPLAIN ANALYZE 命令来获取实际执行计划
- 即使我们有权运行 EXPLAIN ANALYZE 命令,我们也可能会观察到与客户抱怨的计划不同的计划
auto_explain模块提供了一种方式来自动记录慢速语句的执行计划,而不需要手工运行EXPLAIN。这在大型应用中追踪未被优化的查询时有用。
该模块没有提供 SQL 可访问的函数。要使用它,简单地将它载入服务器。你可以把它载入到一个单独的会话:
LOAD 'auto_explain';
你必须作为超级用户来这样做。更典型的用法是通过在postgresql.conf的session_preload_libraries或shared_preload_libraries参数中包括auto_explain将它预先载入到某些或者所有会话中。然后你就可以追踪那些出乎意料地慢的查询,而不管它们何时发生。当然为此会付出一些额外的负荷作为代价。
上面是官方文档的描述,但是通常情况下使用它有更明显的原因:
您想知道 PostgreSQL 查询为什么很慢吗?那么
EXPLAIN ANALYZE是一个很好的起点。正如上面所说,查询可能依赖于其他服务器活动,可能需要一段时间才能运行,并且可能会随时间而变化。
因此,分析慢查询的更好解决方案是获取 PostgreSQL 在运行相关查询时使用的实际执行计划。
于是,如果您想查看最慢查询的实际执行计划,auto_explain就是您需要的工具。
在本人的数据库内核开发中auto_explain的使用非常多 但是从来没有深入看一下其源码实现。接下来 我们将研究它的作用、如何配置它,如何使用这些日志来加快查询速度,以及它的源码解析。
它的使用和配置都非常简单,官方文档和其他人的博客都已经介绍地很详细,我这里不再赘述。直接上干货:

该插件代码非常简单,只有auto_explain.c编出的动态库 因此只需加载即可使用!
功能实现源码解析
原理上分为两部分:GUC和HOOK 如下:
// contrib/auto_explain/auto_explain.c/** Module load callback*/
void
_PG_init(void)
{/* Define custom GUC variables. */...MarkGUCPrefixReserved("auto_explain");/* Install hooks. */prev_ExecutorStart = ExecutorStart_hook;ExecutorStart_hook = explain_ExecutorStart;prev_ExecutorRun = ExecutorRun_hook;ExecutorRun_hook = explain_ExecutorRun;prev_ExecutorFinish = ExecutorFinish_hook;ExecutorFinish_hook = explain_ExecutorFinish;prev_ExecutorEnd = ExecutorEnd_hook;ExecutorEnd_hook = explain_ExecutorEnd;
}
| 参数 | PostgreSQL 默认值 | 建议设置(根据需要) |
|---|---|---|
| auto_explain.log_min_duration | -1 | 100 |
| auto_explain.log_parameter_max_length | -1 | -1 |
| auto_explain.log_analyze | Off | On |
| auto_explain.log_timing | On (with log_analyze) | On |
| auto_explain.log_buffers | Off | On |
| auto_explain.log_verbose | Off | On |
| auto_explain.log_triggers | Off | Off |
| auto_explain.log_nested_statements | Off | Off |
| auto_explain.log_settings (v12) | Off | Off |
| auto_explain.log_wal (v13) | Off | Off |
| auto_explain.log_format | TEXT | JSON |
| auto_explain.log_level | LOG | LOG |
| auto_explain.sample_rate | 1 | 1 |
这些参数的作用不再赘述 根据需要自行设置即可。接下看一下相关HOOK,如下:
ExecutorStart_hook
A hook called at the beginning of any execution of any query plan
ExecutorStart_hook is a hook which is called at the beginning of any execution of any query plan.ExecutorStart_hook was added in PostgreSQL 8.4.
ExecutorRun_hook
A hook which is called at any plan execution, after ExecutorStart
ExecutorRun_hook is a hook which is called at any plan execution, after ExecutorStart.ExecutorRun_hook was added in PostgreSQL 8.4.
ExecutorFinish_hook
A hook called after the last ExecutorRun call
ExecutorFinish_hook is a hook which is called after the last ExecutorRun call.ExecutorFinish_hook was added in PostgreSQL 9.1.
ExecutorEnd_hook
A hook which is called at the end of execution of any query plan
ExecutorEnd_hook is a hook which is called at the end of execution of any query plan.ExecutorEnd_hook was added in PostgreSQL 8.4.
若是有小伙伴对其他HOOK感兴趣,可以看一下本人之前的博客:
- PostgreSQL的学习心得和知识总结(八十六)|深入理解PostgreSQL数据库HOOK技术及开源hooks文档介绍,点击前往
这段时间偶然看到了HashData的一篇博客,里面扼要地介绍了执行器的操作流程,如下:
在数据库内核层面,执行器的操作流程可以概括为四个关键阶段,它们依次是:
ExecutorStart、ExecutorRun、ExecutorFinish和ExecutorEnd。这四个阶段在执行器和算子之间建立了紧密的关联,并各自扮演着不同的角色。

注:对此感兴趣的小伙伴可以看一下这篇博客:
- PostgreSQL技术内幕(十六)如何写一个执行器算子?
一、
ExecutorStart:主要负责初始化各个算子的状态。以SQL语句select * from table order by i limit 2;为例:
- ExecutorStart会首先创建一个包含所有执行所需信息的执行器状态(Estate)
- 随后,通过InitPlan来初始化Plan State树,为接下来的执行做好准备。在这个过程中,ExecInitNode函数发挥着关键作用,它根据节点的类型(如limit、sort或scan)进行相应的初始化操作。这个过程是层层递进的,确保每个节点或算子的信息和私有状态都被正确设置。
// src/backend/executor/execMain.c/* ----------------------------------------------------------------* ExecutorStart** This routine must be called at the beginning of any execution of any* query plan* 任何查询计划执行开始时都必须调用此例程** Takes a QueryDesc previously created by CreateQueryDesc (which is separate* only because some places use QueryDescs for utility commands). The tupDesc* field of the QueryDesc is filled in to describe the tuples that will be* returned, and the internal fields (estate and planstate) are set up.* 采用先前由 CreateQueryDesc 创建的 QueryDesc(之所以单独创建,是因为有些地方使用 QueryDesc 作为实用程序命令)。* QueryDesc 的 tupDesc 字段被填充以描述将返回的元组,并且内部字段(estate 和 planstate)被设置。** eflags contains flag bits as described in executor.h.** NB: the CurrentMemoryContext when this is called will become the parent* of the per-query context used for this Executor invocation.* 注意:调用此方法时,CurrentMemoryContext 将成为此 Executor 调用所使用的每个查询上下文的父级。** We provide a function hook variable that lets loadable plugins* get control when ExecutorStart is called. Such a plugin would* normally call standard_ExecutorStart().* 我们提供了一个函数钩子变量,让可加载插件在调用 ExecutorStart 时获得控制权。* 这样的插件通常会调用 standard_ExecutorStart()。** ----------------------------------------------------------------*/
void
ExecutorStart(QueryDesc *queryDesc, int eflags)
{/** In some cases (e.g. an EXECUTE statement or an execute message with the* extended query protocol) the query_id won't be reported, so do it now.** Note that it's harmless to report the query_id multiple times, as the* call will be ignored if the top level query_id has already been* reported.*/pgstat_report_query_id(queryDesc->plannedstmt->queryId, false);if (ExecutorStart_hook)(*ExecutorStart_hook) (queryDesc, eflags);elsestandard_ExecutorStart(queryDesc, eflags);
}void
standard_ExecutorStart(QueryDesc *queryDesc, int eflags)
{.../** Build EState, switch into per-query memory context for startup.*/estate = CreateExecutorState();queryDesc->estate = estate;.../** Initialize the plan state tree*/InitPlan(queryDesc, eflags);...
}
详细如下:

然后看一下这里的钩子函数,如下:
/** ExecutorStart hook: start up logging if needed*/
static void
explain_ExecutorStart(QueryDesc *queryDesc, int eflags)
{/** At the beginning of each top-level statement, decide whether we'll* sample this statement. If nested-statement explaining is enabled,* either all nested statements will be explained or none will.* 在每个顶级语句的开头,决定是否要对此语句进行采样。* 如果启用了嵌套语句解释,则将解释所有嵌套语句,或者不解释任何嵌套语句。** When in a parallel worker, we should do nothing, which we can implement* cheaply by pretending we decided not to sample the current statement.* If EXPLAIN is active in the parent session, data will be collected and* reported back to the parent, and it's no business of ours to interfere.* 在并行工作进程中,我们不应该做任何事情,我们可以通过假装决定不对当前语句进行采样来廉价地实现这一点。* 如果 EXPLAIN 在父会话中处于活动状态,则将收集数据并报告回父会话,我们无权干涉。*/if (nesting_level == 0){if (auto_explain_log_min_duration >= 0 && !IsParallelWorker())current_query_sampled = (pg_prng_double(&pg_global_prng_state) < auto_explain_sample_rate); // 这块决定是否要采样elsecurrent_query_sampled = false;}if (auto_explain_enabled()){/* Enable per-node instrumentation iff log_analyze is required. */// 当且仅当需要 log_analyze 时,才启用每个节点的检测。if (auto_explain_log_analyze && (eflags & EXEC_FLAG_EXPLAIN_ONLY) == 0){if (auto_explain_log_timing)queryDesc->instrument_options |= INSTRUMENT_TIMER;elsequeryDesc->instrument_options |= INSTRUMENT_ROWS;if (auto_explain_log_buffers)queryDesc->instrument_options |= INSTRUMENT_BUFFERS;if (auto_explain_log_wal)queryDesc->instrument_options |= INSTRUMENT_WAL;}}if (prev_ExecutorStart)prev_ExecutorStart(queryDesc, eflags);elsestandard_ExecutorStart(queryDesc, eflags);if (auto_explain_enabled()){/** Set up to track total elapsed time in ExecutorRun. Make sure the* space is allocated in the per-query context so it will go away at* ExecutorEnd.* 设置以跟踪 ExecutorRun 中的总耗时。* 确保在每个查询上下文中分配空间,以便它在 ExecutorEnd 时消失。*/if (queryDesc->totaltime == NULL){MemoryContext oldcxt;oldcxt = MemoryContextSwitchTo(queryDesc->estate->es_query_cxt);queryDesc->totaltime = InstrAlloc(1, INSTRUMENT_ALL, false);MemoryContextSwitchTo(oldcxt);}}
}#define auto_explain_enabled() \(auto_explain_log_min_duration >= 0 && \(nesting_level == 0 || auto_explain_log_nested_statements) && \current_query_sampled)
小结一下上面函数的处理逻辑:
- 决定是否要采样
- 我们这里默认 auto_explain_enabled 是开启的,那么当启用auto_explain_log_analyze时,才启用每个节点的检测
- 执行其他HOOK或标准ExecutorStart
- #3 完成之后,设置跟踪 ExecutorRun 中的总耗时
注意第4步中的INSTRUMENT_ALL,如下:
// src/include/executor/instrument.h/* Flag bits included in InstrAlloc's instrument_options bitmask */
typedef enum InstrumentOption
{INSTRUMENT_TIMER = 1 << 0, /* needs timer (and row counts) */INSTRUMENT_BUFFERS = 1 << 1, /* needs buffer usage */INSTRUMENT_ROWS = 1 << 2, /* needs row count */INSTRUMENT_WAL = 1 << 3, /* needs WAL usage */INSTRUMENT_ALL = PG_INT32_MAX
} InstrumentOption;
二、
ExecutorRun:初始化完成后,执行器进入运行阶段,通过ExecutorRun来实现算子的运行。此阶段类似于一个外循环,不断从下游获取数据,直到数据全部处理完毕。这个过程主要是通过调用不同的访问方法来执行的,每个访问方法都对应一个函数指针。在初始化阶段,这些函数指针已被设置好,并在运行阶段被调用。
/* ----------------------------------------------------------------* ExecutorRun** This is the main routine of the executor module. It accepts* the query descriptor from the traffic cop and executes the* query plan.** ExecutorStart must have been called already.** If direction is NoMovementScanDirection then nothing is done* except to start up/shut down the destination. Otherwise,* we retrieve up to 'count' tuples in the specified direction.* 如果方向为 NoMovementScanDirection,则除了启动/关闭目的地外不执行任何操作。* 否则,我们将在指定方向上检索最多“count”个元组。** Note: count = 0 is interpreted as no portal limit, i.e., run to* completion. Also note that the count limit is only applied to* retrieved tuples, not for instance to those inserted/updated/deleted* by a ModifyTable plan node.* 注意:count = 0 表示没有入口限制,即运行至完成。* 还请注意,计数限制仅适用于检索到的元组,而不适用于由修改表计划节点插入/更新/删除的元组。** There is no return value, but output tuples (if any) are sent to* the destination receiver specified in the QueryDesc; and the number* of tuples processed at the top level can be found in* estate->es_processed. The total number of tuples processed in all* the ExecutorRun calls can be found in estate->es_total_processed.* 没有返回值,但输出元组(如果有)会发送到 QueryDesc 中指定的目标接收器;* 并且可以在 estate->es_processed 中找到在顶层处理的元组数量。* 可以在 estate->es_total_processed 中找到在所有 ExecutorRun 调用中处理的元组总数。** We provide a function hook variable that lets loadable plugins* get control when ExecutorRun is called. Such a plugin would* normally call standard_ExecutorRun().* 我们提供了一个函数钩子变量,让可加载插件在调用 ExecutorRun 时获得控制权。* 这样的插件通常会调用 standard_ExecutorRun()。** ----------------------------------------------------------------*/
void
ExecutorRun(QueryDesc *queryDesc,ScanDirection direction, uint64 count,bool execute_once)
{if (ExecutorRun_hook)(*ExecutorRun_hook) (queryDesc, direction, count, execute_once);elsestandard_ExecutorRun(queryDesc, direction, count, execute_once);
}void
standard_ExecutorRun(QueryDesc *queryDesc,ScanDirection direction, uint64 count, bool execute_once)
{.../* Allow instrumentation of Executor overall runtime */if (queryDesc->totaltime)InstrStartNode(queryDesc->totaltime); // 记录开始时刻的...sendTuples = (operation == CMD_SELECT ||queryDesc->plannedstmt->hasReturning);if (sendTuples)dest->rStartup(dest, operation, queryDesc->tupDesc);.../** run plan*/if (!ScanDirectionIsNoMovement(direction)){if (execute_once && queryDesc->already_executed)elog(ERROR, "can't re-execute query flagged for single execution");queryDesc->already_executed = true;ExecutePlan(estate,queryDesc->planstate,queryDesc->plannedstmt->parallelModeNeeded,operation,sendTuples,count,direction,dest,execute_once);}.../** shutdown tuple receiver, if we started it*/if (sendTuples)dest->rShutdown(dest);if (queryDesc->totaltime)InstrStopNode(queryDesc->totaltime, estate->es_processed); // diff上面 记录差值...
}
注1:关于上面sendTuples这块的这里不再赘述,有兴趣的小伙伴可以去去查看一下本人之前的博客:
- PostgreSQL的学习心得和知识总结(一百四十四)|深入理解PostgreSQL数据库之sendTuples的实现原理及功能修改,点击前往
注2:上面真正的核心ExecutePlan函数的处理(循环直到我们处理完计划中适当数量的元组。),如下所示:

接下来看一下此处的钩子函数,如下:
/** ExecutorRun hook: all we need do is track nesting depth*/
static void
explain_ExecutorRun(QueryDesc *queryDesc, ScanDirection direction,uint64 count, bool execute_once)
{nesting_level++;PG_TRY();{if (prev_ExecutorRun)prev_ExecutorRun(queryDesc, direction, count, execute_once);elsestandard_ExecutorRun(queryDesc, direction, count, execute_once);}PG_FINALLY();{nesting_level--;}PG_END_TRY();
}
这里比较简单:仅需要做的就是跟踪嵌套深度。
三、
ExecutorFinish:为确保信息的完整性和后续分析的便利性,在ExecutorRun和ExecutorEnd之间,特别引入了ExecutorFinish阶段。在ExecutorFinish阶段,执行器会进行一些统计信息的收集、时间的记录以及相关的清理工作。
/* ----------------------------------------------------------------* ExecutorFinish** This routine must be called after the last ExecutorRun call.* It performs cleanup such as firing AFTER triggers. It is* separate from ExecutorEnd because EXPLAIN ANALYZE needs to* include these actions in the total runtime.* 此例程必须在最后一次 ExecutorRun 调用之后调用。* 它执行清理工作,例如触发 AFTER 触发器。* 它与 ExecutorEnd 是分开的,因为 EXPLAIN ANALYZE 需要将这些操作包含在总运行时中。** We provide a function hook variable that lets loadable plugins* get control when ExecutorFinish is called. Such a plugin would* normally call standard_ExecutorFinish().** ----------------------------------------------------------------*/
void
ExecutorFinish(QueryDesc *queryDesc)
{if (ExecutorFinish_hook)(*ExecutorFinish_hook) (queryDesc);elsestandard_ExecutorFinish(queryDesc);
}void
standard_ExecutorFinish(QueryDesc *queryDesc)
{EState *estate;MemoryContext oldcontext;/* sanity checks */Assert(queryDesc != NULL);estate = queryDesc->estate;Assert(estate != NULL);Assert(!(estate->es_top_eflags & EXEC_FLAG_EXPLAIN_ONLY));/* This should be run once and only once per Executor instance */Assert(!estate->es_finished);/* Switch into per-query memory context */oldcontext = MemoryContextSwitchTo(estate->es_query_cxt);/* Allow instrumentation of Executor overall runtime */if (queryDesc->totaltime)InstrStartNode(queryDesc->totaltime);/* Run ModifyTable nodes to completion */// 运行完修改表节点ExecPostprocessPlan(estate);/* Execute queued AFTER triggers, unless told not to */// 执行排队的 AFTER 触发器,除非被告知不要执行if (!(estate->es_top_eflags & EXEC_FLAG_SKIP_TRIGGERS))AfterTriggerEndQuery(estate);if (queryDesc->totaltime)InstrStopNode(queryDesc->totaltime, 0);MemoryContextSwitchTo(oldcontext);estate->es_finished = true;
}
和上面一样,ExecutorFinish 钩子:同样仅需要做的就是跟踪嵌套深度。
四、
ExecutorEnd:执行器ExecutorEnd阶段,负责逐层结束下游节点的执行。这个过程是通过调用每个节点的结束函数(endplan)来实现的,该函数会识别到具体的节点类型,并调用相应的结束方法。在结束过程中,执行器会销毁每个节点的状态信息,释放资源。
/* ----------------------------------------------------------------* ExecutorEnd** This routine must be called at the end of execution of any* query plan* 必须在任何查询计划执行结束时调用此例程** We provide a function hook variable that lets loadable plugins* get control when ExecutorEnd is called. Such a plugin would* normally call standard_ExecutorEnd().** ----------------------------------------------------------------*/
void
ExecutorEnd(QueryDesc *queryDesc)
{if (ExecutorEnd_hook)(*ExecutorEnd_hook) (queryDesc);elsestandard_ExecutorEnd(queryDesc);
}void
standard_ExecutorEnd(QueryDesc *queryDesc)
{EState *estate;MemoryContext oldcontext;/* sanity checks */Assert(queryDesc != NULL);estate = queryDesc->estate;Assert(estate != NULL);/** Check that ExecutorFinish was called, unless in EXPLAIN-only mode. This* Assert is needed because ExecutorFinish is new as of 9.1, and callers* might forget to call it.*/Assert(estate->es_finished ||(estate->es_top_eflags & EXEC_FLAG_EXPLAIN_ONLY));/** Switch into per-query memory context to run ExecEndPlan*/oldcontext = MemoryContextSwitchTo(estate->es_query_cxt);ExecEndPlan(queryDesc->planstate, estate);/* do away with our snapshots */UnregisterSnapshot(estate->es_snapshot);UnregisterSnapshot(estate->es_crosscheck_snapshot);/** Must switch out of context before destroying it*/MemoryContextSwitchTo(oldcontext);/** Release EState and per-query memory context. This should release* everything the executor has allocated.*/FreeExecutorState(estate);/* Reset queryDesc fields that no longer point to anything */queryDesc->tupDesc = NULL;queryDesc->estate = NULL;queryDesc->planstate = NULL;queryDesc->totaltime = NULL;
}
以上面SQL为例,我们调试一下这里:
postgres=# \d+ t1Table "public.t1"Column | Type | Collation | Nullable | Default | Storage | Compression | Stats target | Description
--------+---------+-----------+----------+---------+---------+-------------+--------------+-------------id | integer | | | | plain | | |
Access method: heappostgres=#
postgres=# explain (analyze, verbose)select * from t1 order by id limit 2;QUERY PLAN
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Limit (cost=25.00..25.01 rows=2 width=4) (actual time=0.200..0.201 rows=2 loops=1)Output: id-> Sort (cost=25.00..27.50 rows=1000 width=4) (actual time=0.199..0.200 rows=2 loops=1)Output: idSort Key: t1.idSort Method: top-N heapsort Memory: 25kB-> Seq Scan on public.t1 (cost=0.00..15.00 rows=1000 width=4) (actual time=0.012..0.105 rows=1000 loops=1)Output: idPlanning Time: 0.057 msExecution Time: 0.213 ms
(10 rows)postgres=#
下面是ExecutorStart阶段:
ExecInitSeqScan(SeqScan * node, EState * estate, int eflags)
ExecInitNode(Plan * node, EState * estate, int eflags)
ExecInitSort(Sort * node, EState * estate, int eflags)
ExecInitNode(Plan * node, EState * estate, int eflags)
ExecInitLimit(Limit * node, EState * estate, int eflags)
ExecInitNode(Plan * node, EState * estate, int eflags)
InitPlan(QueryDesc * queryDesc, int eflags)
standard_ExecutorStart(QueryDesc * queryDesc, int eflags)
ExecutorStart(QueryDesc * queryDesc, int eflags)
PortalStart(Portal portal, ParamListInfo params, int eflags, Snapshot snapshot)
exec_simple_query(const char * query_string)
...
下面是ExecutorRun阶段:
ExecSeqScan(PlanState * pstate)
ExecProcNodeFirst(PlanState * node)
ExecProcNode(PlanState * node)
ExecSort(PlanState * pstate)
ExecProcNodeFirst(PlanState * node)
ExecProcNode(PlanState * node)
ExecLimit(PlanState * pstate)
ExecProcNodeFirst(PlanState * node)
ExecProcNode(PlanState * node)
ExecutePlan(EState * estate, PlanState * planstate, _Bool use_parallel_mode, CmdType operation, _Bool sendTuples, uint64 numberTuples, ScanDirection direction, DestReceiver * dest, _Bool execute_once)
standard_ExecutorRun(QueryDesc * queryDesc, ScanDirection direction, uint64 count, _Bool execute_once)
ExecutorRun(QueryDesc * queryDesc, ScanDirection direction, uint64 count, _Bool execute_once)
PortalRunSelect(Portal portal, _Bool forward, long count, DestReceiver * dest)
PortalRun(Portal portal, long count, _Bool isTopLevel, _Bool run_once, DestReceiver * dest, DestReceiver * altdest, QueryCompletion * qc)
exec_simple_query(const char * query_string)
...
如上SQL是一个比较简单的查询,ExecutorFinish阶段并未做什么。
下面是ExecutorEnd阶段:
ExecEndSeqScan(SeqScanState * node)
ExecEndNode(PlanState * node)
ExecEndSort(SortState * node)
ExecEndNode(PlanState * node)
ExecEndLimit(LimitState * node)
ExecEndNode(PlanState * node)
ExecEndPlan(PlanState * planstate, EState * estate)
standard_ExecutorEnd(QueryDesc * queryDesc)
ExecutorEnd(QueryDesc * queryDesc)
PortalCleanup(Portal portal)
PortalDrop(Portal portal, _Bool isTopCommit)
exec_simple_query(const char * query_string)
...

接下来看一下此处的钩子函数,如下:
/** ExecutorEnd hook: log results if needed*/
static void
explain_ExecutorEnd(QueryDesc *queryDesc)
{if (queryDesc->totaltime && auto_explain_enabled()){MemoryContext oldcxt;double msec;/** Make sure we operate in the per-query context, so any cruft will be* discarded later during ExecutorEnd.* 确保我们在每个查询上下文中进行操作,因此任何多余的内容都会在 ExecutorEnd 期间被丢弃。*/oldcxt = MemoryContextSwitchTo(queryDesc->estate->es_query_cxt);/** Make sure stats accumulation is done. (Note: it's okay if several* levels of hook all do this.)* 确保统计数据累积已完成。(注意:如果几级钩子都这样做也没关系。)*/InstrEndLoop(queryDesc->totaltime);/* Log plan if duration is exceeded. */msec = queryDesc->totaltime->total * 1000.0;if (msec >= auto_explain_log_min_duration){ExplainState *es = NewExplainState();es->analyze = (queryDesc->instrument_options && auto_explain_log_analyze);es->verbose = auto_explain_log_verbose;es->buffers = (es->analyze && auto_explain_log_buffers);es->wal = (es->analyze && auto_explain_log_wal);es->timing = (es->analyze && auto_explain_log_timing);es->summary = es->analyze;/* No support for MEMORY *//* es->memory = false; */es->format = auto_explain_log_format;es->settings = auto_explain_log_settings;ExplainBeginOutput(es);ExplainQueryText(es, queryDesc);ExplainQueryParameters(es, queryDesc->params, auto_explain_log_parameter_max_length);ExplainPrintPlan(es, queryDesc);if (es->analyze && auto_explain_log_triggers)ExplainPrintTriggers(es, queryDesc);if (es->costs)ExplainPrintJITSummary(es, queryDesc);ExplainEndOutput(es);/* Remove last line break */if (es->str->len > 0 && es->str->data[es->str->len - 1] == '\n')es->str->data[--es->str->len] = '\0';/* Fix JSON to output an object */if (auto_explain_log_format == EXPLAIN_FORMAT_JSON){es->str->data[0] = '{';es->str->data[es->str->len - 1] = '}';}/** Note: we rely on the existing logging of context or* debug_query_string to identify just which statement is being* reported. This isn't ideal but trying to do it here would* often result in duplication.*/ereport(auto_explain_log_level,(errmsg("duration: %.3f ms plan:\n%s",msec, es->str->data),errhidestmt(true)));}MemoryContextSwitchTo(oldcxt);}if (prev_ExecutorEnd)prev_ExecutorEnd(queryDesc);elsestandard_ExecutorEnd(queryDesc);
}
小结一下上面函数逻辑,如下:
- 结束此次总统计:将每个周期的统计数据累加为总数
- 如果超出持续时间则记录该计划
- 开辟一个NewExplainState对象,并根据指定进行填充关键bool值;然后构造计划文本
- 根据指定级别进行ereport
- 之后才走ExecutorEnd逻辑
相关文章:

PostgreSQL的学习心得和知识总结(一百五十六)|auto_explain — log execution plans of slow queries
目录结构 注:提前言明 本文借鉴了以下博主、书籍或网站的内容,其列表如下: 1、参考书籍:《PostgreSQL数据库内核分析》 2、参考书籍:《数据库事务处理的艺术:事务管理与并发控制》 3、PostgreSQL数据库仓库…...

数据结构模板代码合集(不完整)
P3368 【模板】树状数组 2 #include <bits/stdc.h> using namespace std; const int maxn 5e5 7;int n, m, s, t; int ans; int a[maxn]; struct node{int l, r;int num; }tr[maxn * 4];void build(int p, int l, int r){tr[p] {l, r, 0};if(l r){tr[p].num a[l];r…...

shell脚本语法详解
目录 shell语法基础 指定shell解析器 注释 运行 变量 定义变量 引用变量 清除变量值 从键盘获取值 输入单值 添加输入提示语 读取多值 编辑 定义只读变量 环境变量 设置环境变量与查看环境变量 特殊变量 三种引号的作用与区别 小括号与大括号 参数传递 位…...

2021亚洲机器学习会议:面向单阶段跨域检测的域自适应YOLO(ACML2021)
原文标题:Domain Adaptive YOLO for One-Stage Cross-Domain Detection 中文标题:面向单阶段跨域检测的域自适应YOLO 1、Abstract 域转移是目标检测器在实际应用中推广的主要挑战。两级检测器的域自适应新兴技术有助于解决这个问题。然而,两级…...

面试题:描述在前端开发中,如何利用数据结构来优化页面渲染性能,并给出一个具体的示例。
在前端开发中,优化页面渲染性能是提升用户体验的关键之一。合理地使用数据结构可以有效地减少DOM操作的次数、提高数据处理的效率,从而加快页面的渲染速度。以下是一些策略,并给出一个具体的示例。 1. 使用合适的数据结构 数组与对象&#…...

微积分复习笔记 Calculus Volume 1 - 3.2 he Derivative as a Function
3.2 The Derivative as a Function - Calculus Volume 1 | OpenStax...

html 轮播图效果
轮播效果: 1、鼠标没有移入到banner,自动轮播 2、鼠标移入:取消自动轮播、移除开始自动轮播 3、点击指示点开始轮播到对应位置 4、点击前一个后一个按钮,轮播到上一个下一个图片 注意 最后一个图片无缝滚动,就是先克隆第一个图片…...
 too many SQL variables异常)
Android Room(SQLite) too many SQL variables异常
SQLiteException 一、解决办法1. 修改数据库语句2. 分批执行 二、问题根源 转载请注明出处: https://blog.csdn.net/hx7013/article/details/143198862 在使用 Room 或其他基于 SQLite 的 ORM 框架时,批量操作如 IN 或 NOT IN 查询可能会触发 android.database.sqli…...

sentinel原理源码分析系列(八)-熔断
限流为了防止过度使用资源造成系统不稳,熔断是为了识别出”坏”资源,避免好的资源受牵连(雪崩效应),是保证系统稳定性的关键,也是资源有效使用的关键,sentinel熔断插槽名称Degrade(降级),本人觉得应该改为熔…...
——开阔眼界,不做井底之蛙)
安全见闻(4)——开阔眼界,不做井底之蛙
内容预览 ≧∀≦ゞ 安全见闻四:操作系统安全机制深度解析声明操作系统机制1. 注册表2. 防火墙3. 自启动与计划任务4. 事件日志5. 内核驱动与设备驱动6. 系统服务7. 进程与线程8. 系统编程 从操作系统机制看病毒设计1. 自启动:病毒如何在系统启动时运行&a…...

(二十二)、k8s 中的关键概念
文章目录 1、总体概览2、第一层:物理机、集群、Node、Pod 之间的关系2、第二层:命名空间 Namespace3、定义4、控制平面(Control Plane)5、特别的概念 Service6、Deployment 经过 之前几篇文章对 k8s 的实践,结合实践&…...

python基础综合案例(数据可视化-地图可视化)
1.基础地图使用 注意写名字的时候要写全名,比如上海市不能写出上海,不然看不到数据 鼠标点击即可看到数据 设置属性的时候不要忘记导包 # 演示地图可视化的基础使用 from pyecharts.charts import Map from pyecharts.options import VisualMapOpts # 准…...

基于SpringBoot足球场在线预约系统的设计与实现
💗博主介绍💗:✌在职Java研发工程师、专注于程序设计、源码分享、技术交流、专注于Java技术领域和毕业设计✌ 温馨提示:文末有 CSDN 平台官方提供的老师 Wechat / QQ 名片 :) Java精品实战案例《700套》 2025最新毕业设计选题推荐…...

操作系统笔记(二)进程,系统调用,I/O设备
什么是进程? 一个正在执行的程序一个包含运行一个程序所需要的所有信息的容器进程的信息保存在一个进程表中( Process Table)。进程表中的每一项对应一个进程,称为进程控制块(Process control block,PCB)。 PCB信息包括: 用户ID(UID)、进程ID(PID)…...

DevOps实践:在GitLab CI/CD中集成静态分析Helix QAC的工作原理与优势
基于云的GitLab CI/CD平台使开发团队能够简化其CI/CD流程,并加速软件开发生命周期(SDLC)。 将严格的、基于合规性的静态分析(如Helix QAC所提供)作为新阶段添加到现有的GitLab CI/CD流程中,将进一步增强SD…...

前端面试题-token的登录流程、JWT
这是我的前端面试题的合集的第一篇,后面也会更新一些笔试题目。秋招很难,也快要结束了。但是,不要放弃,一起加油^_^ 一、token的登录流程 1.客户端用账号密码请求登录 2.服务端收到请求,需要去验证账号密码 3.验证成…...

【软考高级架构】关于分布式数据库缓存redis的知识要点汇总
一.分布式数据库的含义 分布式数据库缓存指的是在高并发的环境下,为了减轻数据库的压力和提高系统响应时间,在数据库系统和应用系统之间增加一个独立缓存系统。 二.常见的缓存技术 (1)MemCache: Memcache是一个高性能的分布式的内…...
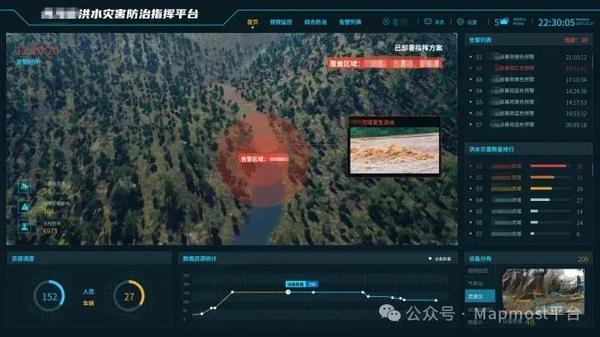
构建自然灾害预警决策一体化平台,筑牢工程安全数字防线
近年来,国家和部委也强调了要切实加强地质灾害监测预警。作为国内智慧应急领域的先行者,Mapmost持续探索利用数字孪生技术,推进自然灾害风险预警精细化,强化对监测数据的综合分析和异常信息研判处置。建立健全区域风险预警与隐患点…...

随机题两题
逆序对 题目 给定一个数组,求其中有多少逆序对,要求时间复杂度不超过nlogn。 思路 使用归并排序的分治思想,将数组递归地分为左右两部分。在合并两个有序子数组时,若左侧数组中的某个数大于右侧数组中的某个数,则可…...

信息安全工程师(69)数字水印技术与应用
前言 数字水印技术是一种在数字媒体中嵌入特定信息的技术,这些信息可以是版权信息、元数据等。 一、数字水印技术的定义与原理 数字水印技术(Digital Watermarking)是将一些标识信息(即数字水印)直接嵌入数字载体&…...

超短脉冲激光自聚焦效应
前言与目录 强激光引起自聚焦效应机理 超短脉冲激光在脆性材料内部加工时引起的自聚焦效应,这是一种非线性光学现象,主要涉及光学克尔效应和材料的非线性光学特性。 自聚焦效应可以产生局部的强光场,对材料产生非线性响应,可能…...
Linux 文件类型,目录与路径,文件与目录管理
文件类型 后面的字符表示文件类型标志 普通文件:-(纯文本文件,二进制文件,数据格式文件) 如文本文件、图片、程序文件等。 目录文件:d(directory) 用来存放其他文件或子目录。 设备…...

Admin.Net中的消息通信SignalR解释
定义集线器接口 IOnlineUserHub public interface IOnlineUserHub {/// 在线用户列表Task OnlineUserList(OnlineUserList context);/// 强制下线Task ForceOffline(object context);/// 发布站内消息Task PublicNotice(SysNotice context);/// 接收消息Task ReceiveMessage(…...
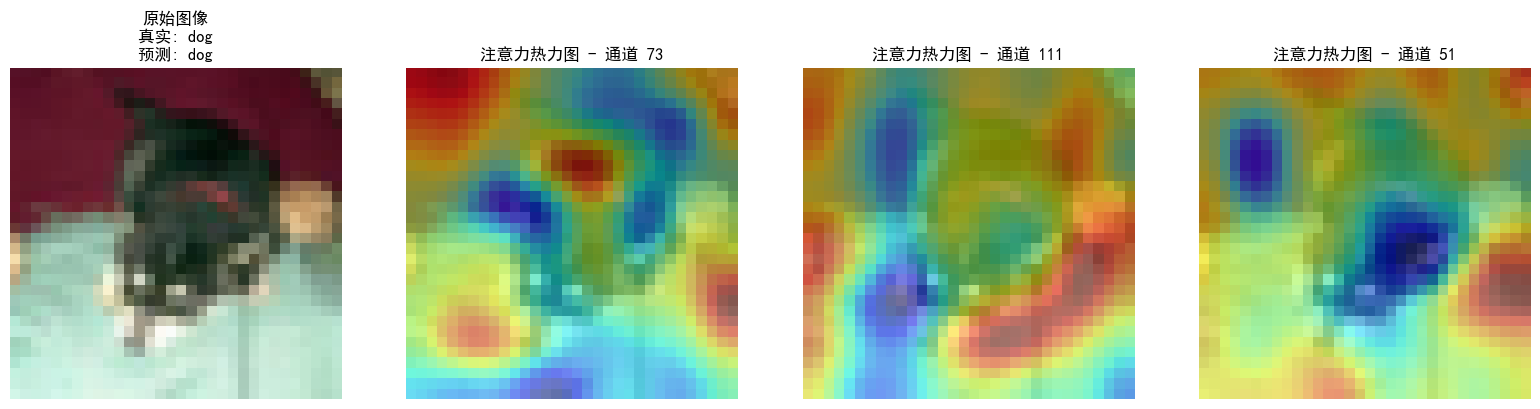
DAY 47
三、通道注意力 3.1 通道注意力的定义 # 新增:通道注意力模块(SE模块) class ChannelAttention(nn.Module):"""通道注意力模块(Squeeze-and-Excitation)"""def __init__(self, in_channels, reduction_rat…...
Cinnamon修改面板小工具图标
Cinnamon开始菜单-CSDN博客 设置模块都是做好的,比GNOME简单得多! 在 applet.js 里增加 const Settings imports.ui.settings;this.settings new Settings.AppletSettings(this, HTYMenusonichy, instance_id); this.settings.bind(menu-icon, menu…...

如何为服务器生成TLS证书
TLS(Transport Layer Security)证书是确保网络通信安全的重要手段,它通过加密技术保护传输的数据不被窃听和篡改。在服务器上配置TLS证书,可以使用户通过HTTPS协议安全地访问您的网站。本文将详细介绍如何在服务器上生成一个TLS证…...
Mac软件卸载指南,简单易懂!
刚和Adobe分手,它却总在Library里给你写"回忆录"?卸载的Final Cut Pro像电子幽灵般阴魂不散?总是会有残留文件,别慌!这份Mac软件卸载指南,将用最硬核的方式教你"数字分手术"࿰…...
ardupilot 开发环境eclipse 中import 缺少C++
目录 文章目录 目录摘要1.修复过程摘要 本节主要解决ardupilot 开发环境eclipse 中import 缺少C++,无法导入ardupilot代码,会引起查看不方便的问题。如下图所示 1.修复过程 0.安装ubuntu 软件中自带的eclipse 1.打开eclipse—Help—install new software 2.在 Work with中…...

NFT模式:数字资产确权与链游经济系统构建
NFT模式:数字资产确权与链游经济系统构建 ——从技术架构到可持续生态的范式革命 一、确权技术革新:构建可信数字资产基石 1. 区块链底层架构的进化 跨链互操作协议:基于LayerZero协议实现以太坊、Solana等公链资产互通,通过零知…...

Java 二维码
Java 二维码 **技术:**谷歌 ZXing 实现 首先添加依赖 <!-- 二维码依赖 --><dependency><groupId>com.google.zxing</groupId><artifactId>core</artifactId><version>3.5.1</version></dependency><de…...
