B站C#刘铁猛笔记
C#——刘铁猛笔记
类、名称空间(简述)
类(class)是构成程序的主体
名称空间(namespace)以树形结构组织类(其他类型)
名称空间:名称空间是用来组织和管理类、接口、结构体等类型的逻辑容器。它可以帮助开发人员避免命名冲突,将相关的类型组织在一起,提高代码的可读性和可维护性。名称空间可以嵌套使用,形成层次结构。在C#中,使用namespace关键字来定义名称空间。
打个比方:
在一个图书馆中,每本书都会有它专属的类放置在一个特定的位置上,那么名称空间就相当于一个图书馆,类就相当于书的类。不同的图书馆有些书的类一样,但其所含书本不一样,因此名称空间也能防止类的名字冲突。
当程序中的一个名称空间中,想要使用另一个名称空间的某一个方法时,需要在程序中名称空间的外部使用using引用所需的名称空间,或者在该名称空间中写出所需名称空间的限定名称。
namespace HelloWorld
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Console.WriteLine("Hello, World!");}}
}
当引用的名称空间中有两种或两种以上的名称空间中包含同名的类,使用这个类时也需要写出限制性名称。
类库
类库引用时使用名称空间的物理基础,使用名称空间时,可以点开References(引用)来检查是否有包含该名称空间的类库(类库简称dll)
在C#中,类库(Class Library)指的是一组封装了一些相关功能的类、接口和其他类型的集合。类库通常用于封装通用的功能,以便在多个应用程序中重复使用。类库可以包含各种类型的功能,例如数据结构、算法、I/O操作、网络通信、图形界面控件等。C#本身提供了一些标准的类库,如.NET Framework中的类库,它包含了大量的基本功能和工具类,用于支持C#程序的开发。除了使用.NET Framework提供的类库之外,开发人员也可以自己编写类库,以封装自己的功能并在不同的项目中重复使用。这样可以提高代码的复用性,降低开发成本,同时也有利于代码的维护和管理。在C#中,类库通常以DLL(Dynamic Link Library)的形式存在,可以通过引用的方式在C#项目中使用。通过引用类库,开发人员可以轻松地使用其中封装的功能,而无需关心具体的实现细节,从而提高开发效率并降低代码的重复编写。一个类库可以包含一个或多个名称空间,用于组织其中的类型。
黑盒引用(无法看源代码)
黑盒引用(Black Box Reference):指的是只能通过接口或基类来引用对象的方式。在黑盒引用中,只能访问对象的公共成员或通过接口暴露的方法,而无法直接访问对象的私有成员或实现细节。这种引用方式更加封装和安全,符合面向对象编程的封装原则。
-
引用一个类库时,右击reference
-
引用一个类库时,它可能受限于更底层的类库,因此引用时还需要引用其更底层的类库,为了避免这个麻烦,可以引用NuGet,类似于一个类库包。
白盒引用
白盒引用(White Box Reference):指的是可以直接访问对象的私有成员或实现细节的引用方式。在白盒引用中,可以直接访问对象的所有成员,包括私有成员和实现细节。这种引用方式可能会破坏对象的封装性,增加耦合度,不利于代码的维护和扩展。
引用自己已有的项目,此时需要将该项目添加到自己的solution里面,之后再右击reference,再solution里勾选该类库。
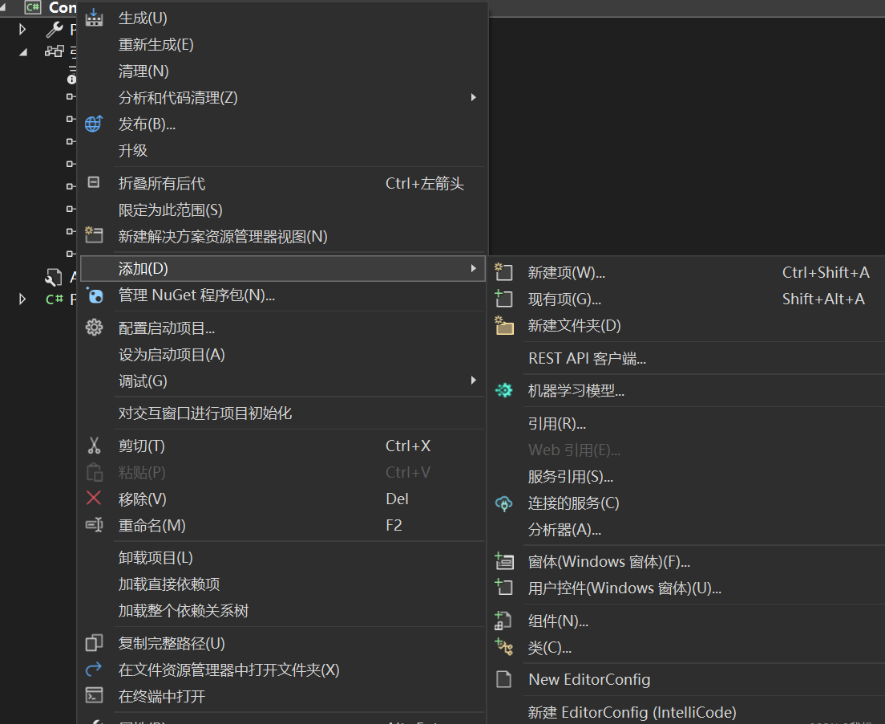
图中有新建项和现有项,若要使用新建项,在打开时就要选择class library项目。
总的来说,黑盒引用更符合面向对象编程的封装和抽象原则,而白盒引用则更容易导致代码的耦合和依赖性。在设计和编写代码时,应该尽量使用黑盒引用,只暴露必要的接口和方法,避免直接暴露对象的内部实现细节。
依赖关系
在C#中,依赖关系指的是一个类或对象在实现功能时依赖于另一个类或对象的情况。依赖关系是面向对象编程中的一个重要概念,它描述了一个对象使用另一个对象提供的功能或服务的情况。依赖关系通常体现在类之间的关联或调用关系上。当一个类需要使用另一个类的功能时,它就会依赖于这个类。这种依赖关系可以通过构造函数注入、属性注入或方法参数传递等方式来实现。依赖关系的存在可以带来一些好处,如提高代码的复用性、降低耦合度、便于单元测试等。但如果依赖关系设计不当,可能会导致代码的脆弱性、难以维护和扩展等问题。在实际开发中,我们通常会借助依赖注入(Dependency Injection)等技术来管理和解决类之间的依赖关系,以提高代码的可维护性和灵活性。通过合理设计和管理依赖关系,可以使代码更加模块化、可测试和可扩展。
类、对象、类与对象的关系
类
类(Class)是一种模板或蓝图,用于描述对象的属性和行为。类定义了对象的结构和行为,包括属性(字段)和方法。在C#中,类是定义对象的基本单位,通过类可以创建对象的实例。
对象
在C#中,对象(Object)是类的实例化(Instance)结果,是内存中的一个具体实体,具有属性和行为。对象是类的具体化,通过实例化类可以创建对象。对象在内存中占据一定的空间,包含了类中定义的属性和方法的具体数值和实现。
类与对象的关系

- 类是对象的模板,定义了对象的属性和行为,描述了对象的结构。
- 对象是类的实例化结果,是类的具体实体,具有类定义的属性和行为。
- 通过类可以创建多个对象,每个对象都是类的一个实例,但它们在内存中是独立存在的,各自拥有自己的属性值。
- 类定义了对象的结构和行为,而对象是类的具体化,实际应用中我们操作的是对象。
简单来说,就是你自己写了一个类,这个类就像一个概念一样,它包含着一些用来形容这个概念的东西,你想要使用这个类时候,你就需要创建一个对象,之后用这个对象来进行你后续的操作。
比如你写了一个飞机的类,但这个类是个概念,你能开概念吗?肯定不行,你要开的是飞机这个机器,所以你就要创建一个飞机开。
类的三大成员

前三个后面会详细说明
小知识–使用MSDN文档
把光标移到你所使用的类上,按f1键

静态成员与非静态成员

静态成员是属于类的成员,而不是属于类的实例(对象)的成员。静态成员可以被类的所有实例共享,可以通过类名直接访问,不需要创建类的实例。在内存中,静态成员只有一份拷贝,被所有实例共享。非静态成员则是属于类的实例(对象)的成员,每个对象都有自己的一份。非静态成员需要通过对象来访问,每个对象都有自己的非静态成员的拷贝。
构成c#的语言的基本元素:关键字,操作符,标识符,标识符号,文本,注释。
小知识–声明变量和类时名称的要求
声明变量时变量名采用驼峰命名法,即首单词字母要小写,后续单词字母大写
声明一个类时名称时,单词都要大写
类型
什么是类型

强类型语言、弱类型语言
强类型指的是声明的变量是什么类型,以后它就是什么类型,弱类型指声明的变量可以是多个类型
-
强类型语言是指在编程时要求严格定义变量的数据类型,不允许不同类型之间的隐式转换。
-
在强类型语言中,变量的数据类型必须在编译时就确定,并且不会发生自动类型转换。
-
强类型语言通常具有更严格的类型检查,能够在编译时捕获一些潜在的类型错误。
-
弱类型语言是指在编程时对变量的数据类型要求较为灵活,允许不同类型之间的隐式转换。
-
在弱类型语言中,变量的数据类型通常可以在运行时动态确定,允许自动类型转换。
-
弱类型语言通常具有更灵活的类型系统,但也可能导致一些难以发现的类型错误。
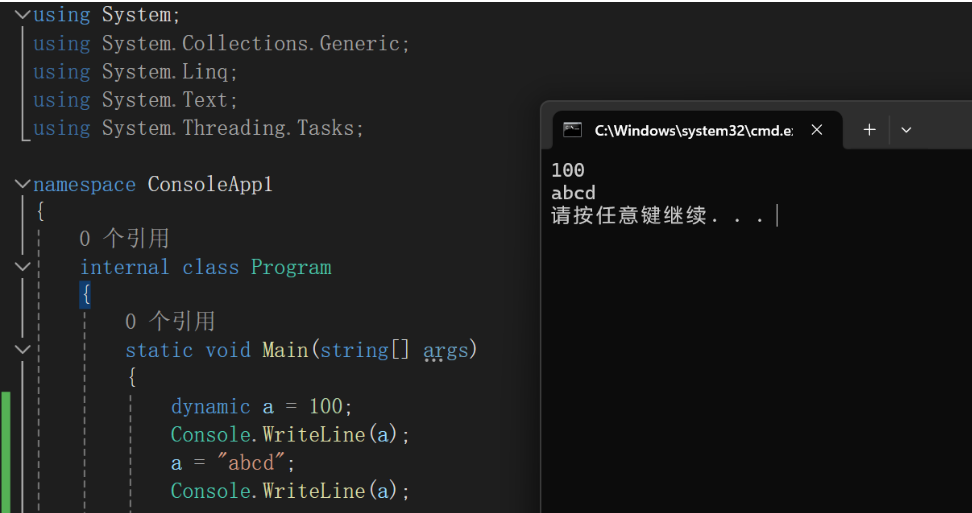
小知识–c#中用dynamic定义的变量可以让该变量在不同时刻赋任何类型的值。
namespace DynamicSample
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){dynamic myVar = 100;Console.WriteLine(myVar);myVar = "Mr.Okay!";Console.WriteLine(myVar);}}
}
类型在C#语言中的作用


C#语言的类型系统–五大数据类型

变量

变量是以变量名为对应的内存地址为起点,以其数据类型所要求的存储空间为长度的一块内存区域(变量名中要么存储的是值类型的值,或者引用类型的地址)。
静态变量
- 静态变量属于类,而不是类的特定实例。
- 静态变量在类加载时被初始化,只有一份存储空间,所有类的实例共享同一份静态变量。
- 静态变量使用static关键字声明,在内存中存储在静态存储区域。
- 可以通过类名直接访问静态变量,无需实例化对象。
- 通常用于存储类级别的信息,如常量、计数器等。
实例变量
- 实例变量属于类的实例(对象),每个对象都有自己的实例变量副本。
- 实例变量在创建对象时被分配内存空间,并随着对象的销毁而释放。
- 实例变量不使用static关键字声明,每个对象都有自己的实例变量。
- 必须通过对象实例来访问实例变量。
数组元素
数组元素(Array Element):数组是一种数据结构,用于存储相同类型的多个元素。数组元素指的是数组中的单个数据项,通过索引访问。例如,对于整型数组 int[] numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};,numbers[0] 表示数组 numbers 中的第一个元素,其值为 1。
值参数
值参数(Value Parameter):值参数是一种参数传递方式,将参数的值传递给方法。在方法内部对值参数的修改不会影响到原始值。在方法签名中,参数前没有 ref 或 out 关键字的参数均为值参数。
引用参数
引用参数(Reference Parameter):引用参数是一种参数传递方式,将参数的引用传递给方法,使得在方法内部对参数的修改会影响到原始值。在方法签名中,参数前加上 ref 关键字表示引用参数。
输出参数
输出参数(Output Parameter):输出参数是一种特殊的引用参数,用于从方法中返回多个值。在方法签名中,参数前加上 out 关键字表示输出参数,调用方法时必须为输出参数赋值。
局部变量
局部变量(Local Variable):局部变量是在方法、构造函数或代码块内部声明的变量,只在声明的作用域内有效。局部变量在声明时必须初始化,可以在声明时或稍后赋值。
值类型、引用类型声明的变量在内存中的分配
值类型在内存分配的时候会根据该类型所需的空间来分配字节,引用类型在内存分配的时候只会分配四个字节,没有引用实例时该字节的二进制都是零,当创建实例后会把堆内存的地址放进该变量中,在堆内存中分配空间时才会计算该变量真正所需要的空间。
变量的默认值
成员变量分配好空间后不赋值时会自动都赋值成0,但本地变量不赋值会报错。
装箱和拆箱
装箱:当一个引用类型的变量发现赋予的值时放在栈上的值类型的值,那么其会在堆中的一个空位置上存储这个值,并把该位置的地址赋值给引用类型的变量上。
-
装箱是将值类型转换为引用类型的过程。
-
当将值类型赋值给一个对象类型(如 object)时,会发生装箱操作,将值类型的数据包装在一个堆分配的对象中。
-
装箱会导致性能开销,因为需要在堆上分配内存来存储值类型的数据,并且需要进行数据复制。
拆箱:当一个值类型的变量发现赋予的值时引用类型,那么其会根据地址找到该值赋给自己
- 拆箱是将引用类型转换为值类型的过程。
- 当从对象类型(如 object)中获取值类型数据时,需要进行拆箱操作,将包装在对象中的数据提取出来转换为值类型。
- 拆箱需要进行类型检查和数据复制,可能会导致性能开销。
方法
方法的由来

方法的声明与调用
 当一个函数以类的成员出现时简称为方法
当一个函数以类的成员出现时简称为方法
构造器

什么是构造器
在 C# 中,构造器(Constructor)是一种特殊类型的方法,用于在创建类的实例(对象)时初始化对象的状态。构造器的作用是初始化对象的成员变量、属性或执行其他必要的初始化操作。以下是构造器的一些特点:
命名与特点:
-
构造器的名称与类名相同。
-
构造器没有返回类型,包括 void。
-
构造器可以重载,即同一个类可以有多个不同参数列表的构造器。
初始化对象:
- 在实例化对象时,构造器会被自动调用,用于初始化对象的状态。
- 构造器可以初始化对象的成员变量、属性,或执行其他必要的初始化操作。
默认构造器:
- 如果没有显式定义构造器,C# 会提供一个默认构造器(无参数构造器),用于初始化对象。
- 如果显式定义了带参数的构造器,但没有定义无参数构造器,那么默认构造器就不会被提供。
对象的创建
当通过 new 关键字创建一个类的实例时,会在内存中分配一块空间来存储该对象的数据。这个空间包括对象的字段、属性和方法等信息。
构造器的调用
在对象创建的过程中,会调用构造器来初始化对象的各个部分。构造器可以有多个重载形式,根据参数列表的不同进行选择调用。
内存分配
在调用构造器之前,系统会先为对象分配内存空间。构造器负责对这块内存空间进行初始化,包括对字段、属性等成员变量的赋值操作。
构造器的执行顺序
如果类的继承关系中包含父类和子类,构造器的执行顺序是先执行父类的构造器,然后执行子类的构造器。这确保了对象的所有部分都能得到正确的初始化。
构造器的作用
构造器可以用来初始化对象的状态,进行一些必要的设置操作,确保对象在创建后处于一个合理的状态。
快捷生成构造器
//创建构造器快捷键
//ctor 按两下tab键
public Student(int initId,string initName)
{}
声明无参数构造器(也可以称作默认构造器)
namespace ConstructorExample
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Student stu2 = new Student();Console.WriteLine(stu2.ID);Console.WriteLine(stu2.Name);}}class Student{//创建构造器快捷键//ctor 按两下tab键public Student(){this.ID = 1;this.Name = "No name";}public int ID;public string Name;}
}声明带参数的构造器(实例化一个对象时必须对构造器内的成员赋值)
为了防止声明一个类时忘记对其字段赋值,可以使用带参数的构造函数。
namespace ConstructorExample
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Student stu = new Student(2,"Mr.Okay");Console.WriteLine(stu.ID);Console.WriteLine(stu.Name);}}class Student{//声明public Student(int initId, string initName){this.ID = initId;this.Name = initName;}public int ID;public string Name;}
}重载

什么是重载
方法的重载(Method Overloading)是指在同一个类中可以定义多个具有相同名称但参数列表不同的方法。通过方法重载,可以在同一个类中使用相同的方法名来执行不同的操作,根据传入的参数列表的不同来确定调用哪个方法。
比如Console.WriteLine就是一种重载,可以输出多种类型
小知识–Debug操作

设置断点,当摁f5时会在设置的断点处停止运行
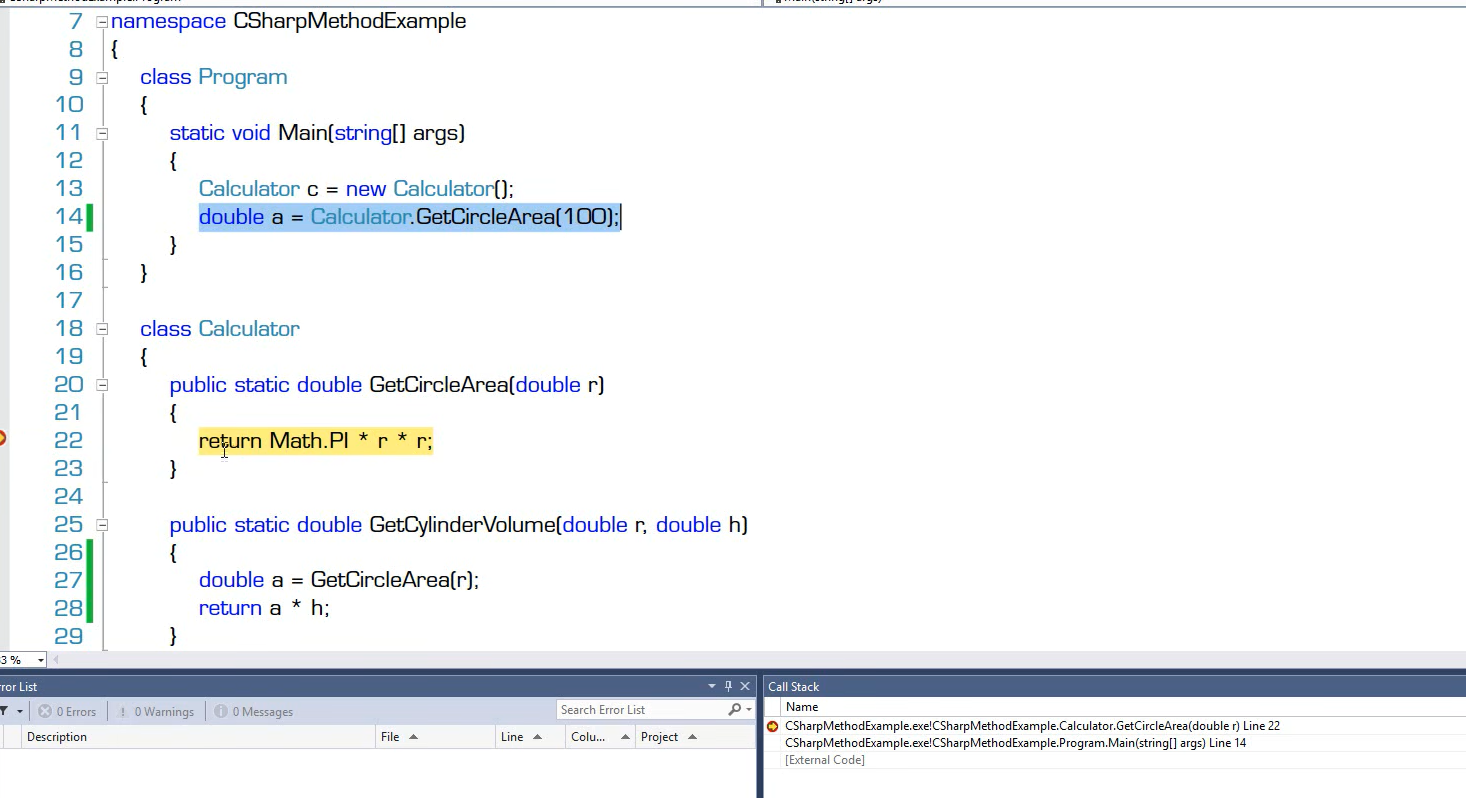
此时调用堆栈中第一行是该函数,第二行是调用该函数的位置
Step-in是一个语句一个语句进行,Step-over是若该断点在是一个调用函数,直接返回调用函数后的结果,Steo-out是寻找调用该函数的地方。
操作符

越靠上的操作符优先级越高,越靠下的操作符优先级越低
什么是操作符?

操作符不能脱离与它关联的数据类型
namespace CreateOperator
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){int x = 5;int y = 4;int z = x / y;Console.WriteLine(z);double a = 5.0;double b = 4.0;double c = a / b;Console.WriteLine(c);}}
}
演示结果
2
Mr.Okay
请按任意键继续. . .
简记法
namespace CreateOperator
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Person person1 = new Person();Person person2 = new Person();person1.Name = "Dear";person2.Name = "Dear's wife";List<Person> nation = person1+ person2;foreach(var p in nation){Console.WriteLine(p.Name);}}}//创建一个类型class Person{public string Name;//public static List<Person> GetMarry(Person p1, Person p2)//简记法————如下public static List<Person> operator +(Person p1, Person p2){List<Person> people = new List<Person>();people.Add(p1);people.Add(p2);for(int i = 0; i < 11; i++){Person child = new Person();child.Name = p1.Name + "&" + p2.Name + "s child";people.Add(child);}return people;}}
}演示结果
Dear
Dear's wife
Dear&Dear's wifes child
Dear&Dear's wifes child
Dear&Dear's wifes child
Dear&Dear's wifes child
Dear&Dear's wifes child
Dear&Dear's wifes child
Dear&Dear's wifes child
Dear&Dear's wifes child
Dear&Dear's wifes child
Dear&Dear's wifes child
Dear&Dear's wifes child
请按任意键继续. . .
优先级与运算顺序

同优先级操作符从左到右
列如:
namespace OperatorPriority
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){int x;x = 3 + 4 + 5;Console.WriteLine(x);}}
}
结果
12
请按任意键继续. . .
带有赋值功能的操作符的运算顺序都是从右向左
代码:
namespace OperatorPriority
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){int x = 100;int y = 200;int z = 300;x += y += z;Console.WriteLine(x);Console.WriteLine(y);Console.WriteLine(z);}}
}600
500
300
请按任意键继续. . .
外层命名空间的子集命名空间(静态成员属于类)
各个操作符的作用
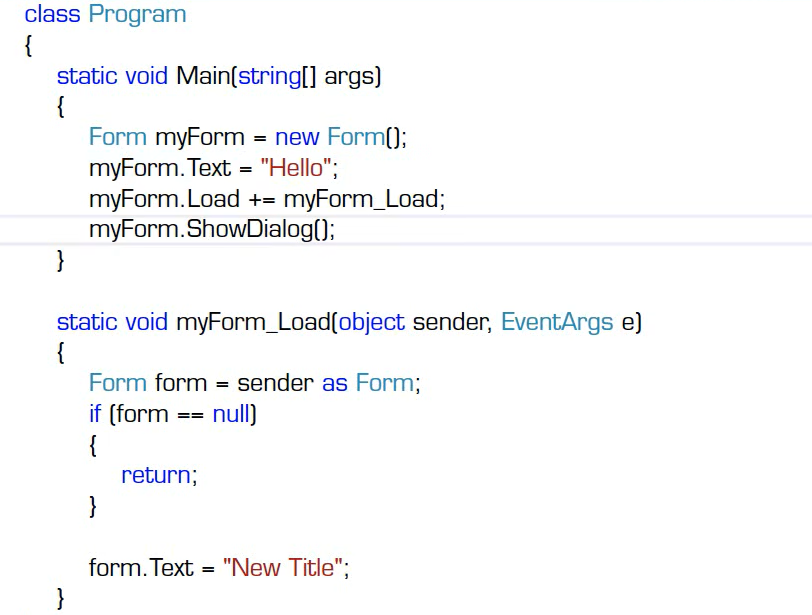
x.y 操作符:访问外层名称空间中的子名称空间,访问名称空间中的类型,访问类型中的静态成员,访问对象的成员。
//System.IO.File.Create("D:\\HelloWorld.text");
Form myForm = new Form();
myForm.Text = "Hello,World!";
myForm.ShowDialog();
f(x) 操作符:方法调用
a[x] 操作符:元素访问操作符
new 操作符:在内存中构造一个类型的实例,并且立刻调用这个实例的实例构造器(或初始化器),如果在new操作符有赋值符号时,会把该实例的内存地址赋给该变量。
在C#中,并不是构造类型时都需要使用new操作符,c#会在常用的类型构建实例时省去new操作符。
new操作符也可用于方法的继承和派生(让子类隐藏父类)
typeof 操作符:查看一个类型的内部结构
enum 枚举类型
default 操作符:获取一个类型的默认值
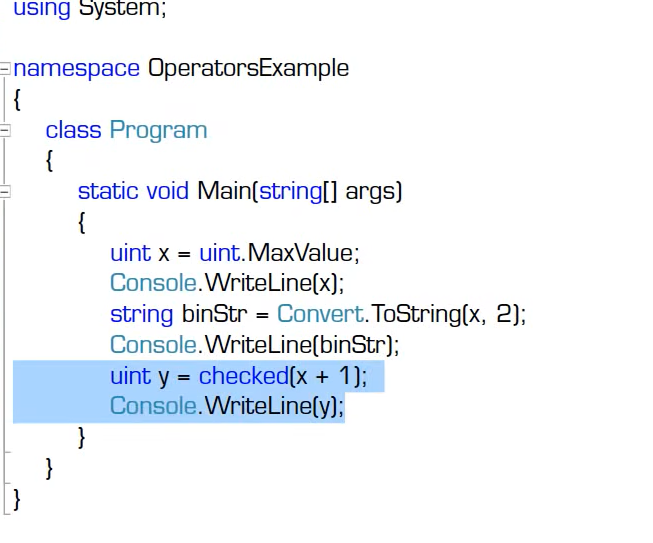
checked 操作符:用于检测程序运行时有没有类型溢出
unchecked 操作符:不检测程序运行时有没有类型溢出
checked和unchecked不仅有操作符用法,还有上下文用法
delegate 操作符:一般用于委托,在当作操作符时是用来声明匿名方法,该方法是只执行一次
委托——代码演示:
namespace OperatorsExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){//委托Calculator c = new Calculator();Action myAction = new Action(c.PrintHello);myAction();}}class Calculator{public void PrintHello(){Console.WriteLine("Hello");}}
}结果:Hello
default类型

var关键字 功能 帮忙声明隐式声明变量
namespace OperatorsExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){//Dictionary类里的value值类型是StudentDictionary<string,Student> stuDic = new Dictionary<string, Student>();for(int i = 1;i<= 100; i++){Student stu = new Student();stu.Name = "s_" + i.ToString();stu.Score = 100 + i;stuDic.Add(stu.Name, stu);}Student number6 = stuDic["s_6"];Console.WriteLine(number6.Score);}}class Student{public string Name;public int Score;}
}new 操作符:在内存中构造一个类型的实例,并且立刻调用这个实例的实例构造器(或初始化器),如果在new操作符有赋值符号时,会把该实例的内存地址赋给该变量。
new操作符和var关键字的用法:是为匿名类型创建对象,用隐式类型变量来引用实例
namespace OperatorsExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Form myForm = new Form() { Text = "Hello" };//是为匿名类型创建对象,用隐式类型变量来引用实例var person = new { Name = "Qi", Age = 21 };Console.WriteLine(person.Name);Console.WriteLine(person.Age);Console.WriteLine(person.GetType().Name);}}
}
拓展类与类之间的继承
namespace OperatorsExample
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Student stu = new Student();stu.Report();CsStudent csStu = new CsStudent();csStu.Report();}}class Student{public void Report(){Console.WriteLine("I'm a student");}}class CsStudent : Student{//重写 子类隐藏父类new public void Report(){Console.WriteLine("I'm CS student");}}
}
检查异常

delegate 操作符:一般用于委托,在当作操作符时是用来声明匿名方法,该方法是只执行一次
改进为
->操作符
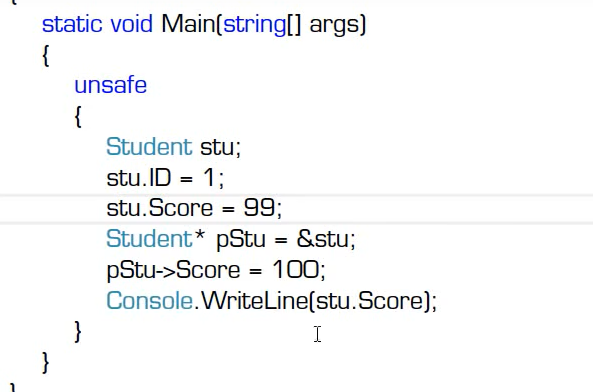

下去自己练习
类型转换
sizeof 操作符:用于查询结构体类型的字节长度,其也可以检测自定义的结构体类型的字节长度,但要放在不安全的上下文中。
& 操作符:取地址操作符,取某个对象的地址。
- 操作符:找到指针所指向的变量
~ 操作符:取反操作符。
- 操作符:取反操作后+1。
(T)x 操作符:强制转换操作符
<< >> 操作符:<< 操作符补进来的都是0,>>操作符正数补进来的是0,负数补进来的是1
is 操作符:用于检测一个对象是不是某一类型
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Security.Permissions;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ConsoleApp1
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Student stu = new Student();bool res = stu is Student;Console.WriteLine(res);//TrueStudent stu2 = null;res = stu2 is Student;Console.WriteLine(res);//falseres = stu is Animal;Console.WriteLine(res);//TrueHuman human = new Human();res = human is Student;Console.WriteLine(res);//False}}class Animal{public void Eat(){Console.WriteLine("Eating...");}}class Human : Animal{public void Think(){Console.WriteLine("Thinking...");}}class Student:Human{public void Study(){Console.WriteLine("I want to play");}}}
as 操作符(强制类型转化)
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Security.Permissions;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ConsoleApp1
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){object o = new Student();Student stu = o as Student;//如果o是Student类型,那么就把该地址赋值给stu,否则赋值null;if(stu!=null){stu.Study();}}}class Animal{public void Eat(){Console.WriteLine("Eating...");}}class Human : Animal{public void Think(){Console.WriteLine("Thinking...");}}class Student:Human{public void Study(){Console.WriteLine("I want to play");}}}
?? 操作符:通常情况下值类型不能赋值null,但Nullable<数据类型>声明的变量可以,或者在值类型后加一个? 。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Security.Permissions;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ConsoleApp1
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Nullable<int> x = null;int? y = null;Console.WriteLine(x);Console.WriteLine(x.HasValue);x = x ?? 1;//如果x是null值,那就把x赋值成1;Console.WriteLine(x);}}}
?: 操作符:if,else的简写
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Security.Permissions;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ConsoleApp1
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){int x = 80;string s = String.Empty;s = x >= 60 ? "Pass" : "False";//如果真就返回:前面的值,否则返回:后面的值Console.WriteLine(s);}}}
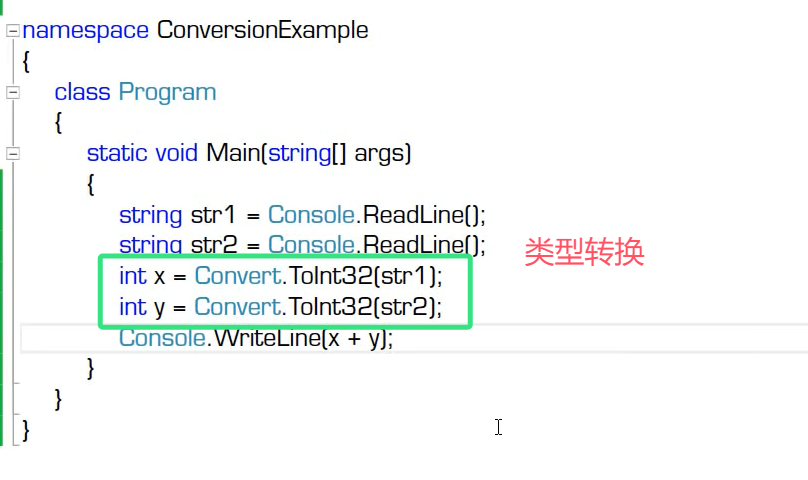
类型转换

隐式类型转换
代码演示:
namespace ConversionExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){int x = int.MaxValue;//小往大转就隐式long y = x;Console.WriteLine(y);}}
}
结果
2147483647
请按任意键继续. . .

子类向父类转换
namespace ConversionExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Teacher t = new Teacher();Human h = t;Animal a = h;a.Eat();}}class Animal{public void Eat(){Console.WriteLine("Eating...");}}class Human : Animal{public void Think(){Console.WriteLine("Who I am?");}}class Teacher : Human{public void Teach(){Console.WriteLine("I teach programming");}}
}显示类型转换
显示类型转换就是在转换对象中构造一个目标类型对象的构造器
namespace ConversionExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Stone stone = new Stone();stone.Age = 5000;//隐式类型转换 Monkey wukongSun = stone;Monkey wukongSun = (Monkey)stone;Console.WriteLine(wukongSun.Age);}}class Stone{public int Age;//隐式类型转换 public static implicit operator Monkey(Stone stone)//显示类型转换public static explicit operator Monkey(Stone stone){Monkey m = new Monkey();m.Age = stone.Age/500;return m;}}class Monkey {public int Age;}}tips:将explici改成implicit后就能把显式类型转变成隐式类型。

表达式
表达式是一种专门求值的语法实体,可以有一个或多个操作数和零个或多个操作符组成


访问事件 An event access
索引访问表达式

语句

c#语句的定义

参考c#定义文档
虚线以上需要熟练使用

const常量的值是不能够被改变的
字段

C语言参考
代码小记:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace DataMemberExample
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){List<Student> stuList = new List<Student>();for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++){Student stu = new Student();stu.Age = 24;stu.Score = i;stuList.Add(stu);}int totalAge = 0;int totalScore = 0; foreach(var stu in stuList)//在一组中一个一个迭代{totalAge += stu.Age;totalScore += stu.Score;}Student.AverageAge = totalAge / Student.Amount;Student.AverageScore = totalScore / Student.Amount; Student.ReportAmount();Student.ReportAverageAge();Student.ReportAverageScore();}}class Student{public int Age;//实例字段,创建的对象可用的成员变量public int Score;public readonly int id=100;//声明一个动态只读字段,只有一次机会对其赋值,就是在它的构造器中//如果在创建的对象中没有对id进行赋值,那么id的值就是100,否则就是在构造器中赋予的值public static readonly Color WColor = new Color() { red = 0, blue = 0, green = 0 };//声明一个静态只读字段public static int AverageAge;//静态字段,仅类可用public static int AverageScore;public static int Amount;public Student(){Student.Amount++;}public static void ReportAmount(){Console.WriteLine(Student.Amount);}public static void ReportAverageAge(){Console.WriteLine(Student.AverageAge);}public static void ReportAverageScore(){Console.WriteLine(Student.AverageScore);}}
}静态只读字段也不能被复制 功能只能被实例保存
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Xml.Schema;namespace DataMemberExample
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Console.WriteLine(Brush.DefaultColor.Red);Console.WriteLine(Brush.DefaultColor.Green);Console.WriteLine(Brush.DefaultColor.Blue);//静态初始化之后不能被赋值//Brush.DefaultColor = new Color() { Red = 0, Green = 0, Blue = 0 };}}struct Color{public int Red;public int Green;public int Blue;}class Brush{//public static readonly Color DefaultColor = new Color() { Red = 0, Green = 0, Blue = 0 };//静态构造函数里静态构造器public static readonly Color DefaultColor;static Brush(){Brush.DefaultColor = new Color() { Red = 0, Green = 0, Blue = 0 };}}
}实例字段的初始化时机实在创建一个对象的时候进行,静态字段的初始化时机实在运行环境加载该数据类型的时候,并且静态字段的初始化执行一次,即第一次被加载的时候。
set与get方法
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace PropertyExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Student stu1 = new Student();stu1.Age = 20;Student stu2 = new Student();stu2.Age = 20;Student stu3 = new Student();stu3.Age = 200;int avgAge = (stu1.Age + stu2.Age + stu3.Age) / 3;Console.WriteLine(avgAge);}}class Student{public int Age;}
}改进之后的方法 set与get方法
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace PropertyExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Student stu1 = new Student();stu1.SetAge(20);Student stu2 = new Student();stu2.SetAge(20);Student stu3 = new Student();stu3.SetAge(80);int avgAge = (stu1.GetAge() + stu2.GetAge() + stu3.GetAge()) / 3;Console.WriteLine(avgAge);}}class Student{//public int Age;private int age;public int GetAge(){return this.age;}public void SetAge(int value){if(value >= 0 && value <= 120){this.age = value;}else{throw new Exception("Age value has error.");}}}
}演化
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data.SqlTypes;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace PropertyExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){try{Student stu1 = new Student();stu1.Age = 20;Student stu2 = new Student();stu2.Age = 20;Student stu3 = new Student();stu3.Age = 20;int avgAge = (stu1.Age + stu2.Age + stu3.Age) / 3;Console.WriteLine(avgAge);}catch (Exception ex){Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);}}}class Student {//public int Age;private int age;public int Age{get{return this.age;}set{if (value >= 0 && value <= 120){this.age = value;}else{throw new Exception("Age value has error");}}}public int GetAge(){return this.age;}public void SetAge(int value){if(value >= 0 && value <= 120){this.age = value; }else{throw new Exception("Age value has error.");}}}
}属性
什么是属性

属性的声明
静态属性
静态属性(Static Property)是属于类本身的属性,而不是类的实例。可以通过类名直接访问静态属性,而不需要创建类的实例。静态属性在整个应用程序中只有一份副本,可以用于存储类级别的信息。
实例属性
实例属性(Instance Property)是指属于类的实例(对象)的属性。每个类的实例都有自己的一组属性值,这些属性值可以在实例化对象后进行访问和修改。实例属性与静态属性不同,静态属性属于类本身,而实例属性属于类的实例。
只读属性
只读属性(Read-only Property)是指只提供了 Get 访问器的属性,即只能读取属性值,不能修改。只读属性在初始化后不能再被修改,可以用于提供对象的只读视图。
属性也是一种语法
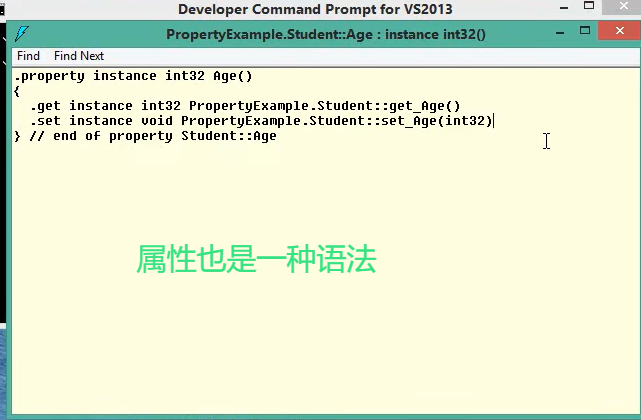
声明属性时 快捷键:propfull 再按两下tab键
//声明属性时 快捷键:propfull 再按两下tab键private int myVar;public int MyProperty{get { return myVar; }set { myVar = value; }}
静态属性报出异常
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data.SqlTypes;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace PropertyExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){try{Student.Amount = -100;//抛异常Console.WriteLine(Student.Amount);}catch (Exception ex){Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);}}}class Student {//public int Age;private int age;public int Age//属性(实例属性){get//用于返回成员变量的值{return this.age;}set//用于设置成员变量的值{if (value >= 0 && value <= 120)//上下文关键词,value就是传进来的值,不需要声明{this.age = value;}else{throw new Exception("Age value has error");}}}private static int amount;public static int Amount//静态属性{get { return amount; }set {if (value >= 0){Student.amount = value;}else{throw new Exception("Amount has error");}}}}
}结果:
Amount has error
请按任意键继续. . .
动态计算值的属性
主动计算canwork的值
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data.SqlTypes;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace PropertyExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){try{Student stu1 = new Student();stu1.Age = 16;Console.WriteLine(stu1.CanWork);}catch (Exception ex){Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);}}}class Student {private int age;public int Age{get { return age; }set { age = value; }}private bool canWork;public bool CanWork //动态计算值的属性,并且是主动计算这个值{get{if (this.age >= 18){return true;}else{return false;}}}
被动
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data.SqlTypes;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace PropertyExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){try{Student stu1 = new Student();stu1.Age = 12;Console.WriteLine(stu1.CanWork);}catch (Exception ex){Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);}}}class Student {private int age;public int Age{get { return age; }set { age = value;//被动引用时this.CalcumateCanWork();}}private bool canWork;public bool CanWork //动态计算值的属性,并且是主动计算这个值{get{return canWork;}}//以下是被动计算private void CalcumateCanWork(){if (this.age >= 16){this.canWork=true;}else{this.canWork=false;}}}
}索引器

什么是索引器
在C#中,索引器(Indexer)是一种特殊的属性,允许类的实例像数组一样通过索引来访问和设置对象的元素。通过索引器,可以为类提供类似数组的访问方式,使得对象可以像集合一样进行索引访问。索引器通常用于实现集合类或类似集合的数据结构,使得可以通过类似数组的语法来访问对象的元素。索引器可以定义多个重载版本,每个版本可以接受不同数量或类型的参数,以便支持不同的索引方式。相关代码
public class MyCollection
{private string[] data = new string[3];// 索引器的定义public string this[int index]{get { return data[index]; }set { data[index] = value; }}
}class Program
{static void Main(){MyCollection collection = new MyCollection();// 设置索引器的值collection[0] = "Item 1";collection[1] = "Item 2";collection[2] = "Item 3";// 获取索引器的值并输出Console.WriteLine(collection[0]);Console.WriteLine(collection[1]);Console.WriteLine(collection[2]);}
}
代码演示:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace IndexerExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Student stu = new Student();stu["Math"] = 90;var mathScore = stu["Math"];Console.WriteLine(mathScore);}}//索引器声明class Student{private Dictionary<string, int> scoreDictionary = new Dictionary<string, int>();public int? this[String subject]{get{if (this.scoreDictionary.ContainsKey(subject)){return this.scoreDictionary[subject];}else{return null;}}set{if(value.HasValue == false){throw new Exception("Score cannot be null.");}if (this.scoreDictionary.ContainsKey(subject)){this.scoreDictionary[subject] = value.Value;}else{this.scoreDictionary.Add(subject, value.Value);}}}}
}常量

参数
传值参数
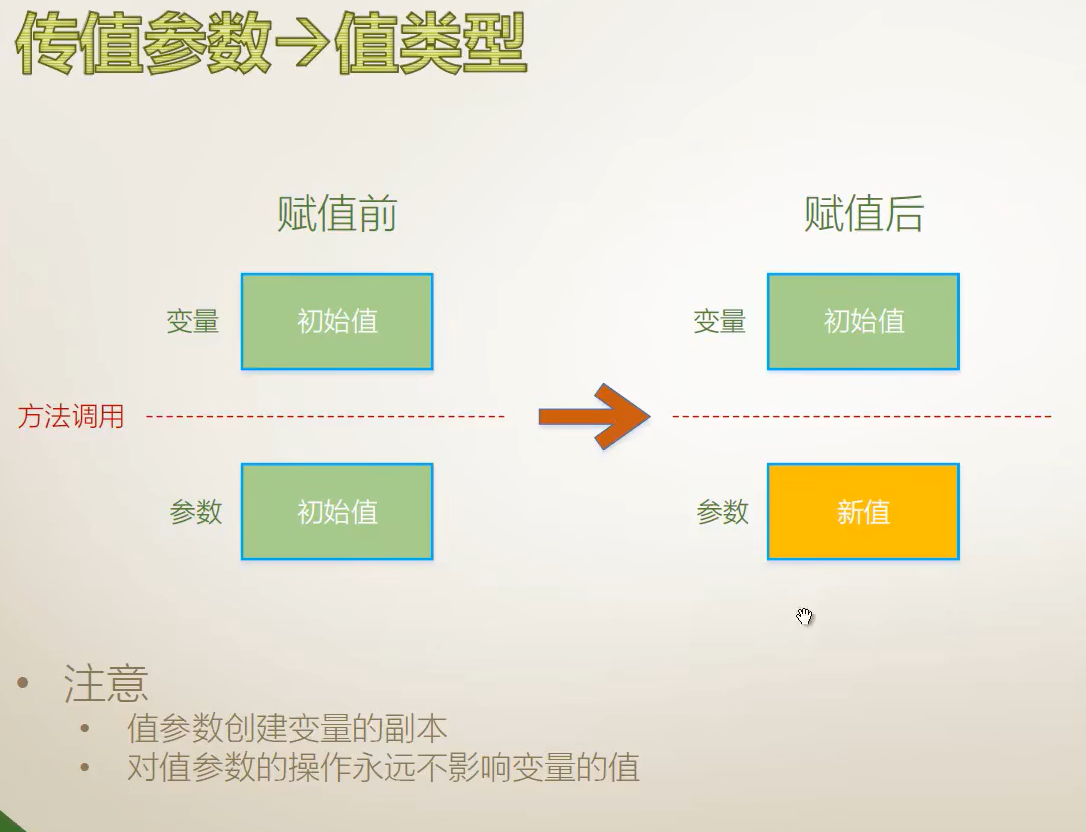
传值参数(值类型)
声明时不带修饰符的形参是值形参。一个值形参对应于一个局部变量,只是它的初始值来自该方法调用所提供的相应实参。
当形参是值形参时,方法调用中的对应实参必须是表达式,并且它的类型可以隐式转换(第 6.1 节)为形参的类型。
允许方法将新值赋给值参数。这样的赋值只影响由该值形参表示的局部存储位置,而不会影响在方法调用时由调用方给出的实参。
代码演示:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ParametersExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){//实例方法,先创建方法的实例Student stu = new Student();int y = 100;stu.AddOne(y);Console.WriteLine(y);}}//方法声明class Student{public void AddOne(int x)//x参数是传值参数,传进来的值会在方法体内部有一个副本,改变的是副本的值,并不会影响方法体外的值 {x = x + 1;Console.WriteLine(x);}}
}传值参数(引用类型)
创建新对象
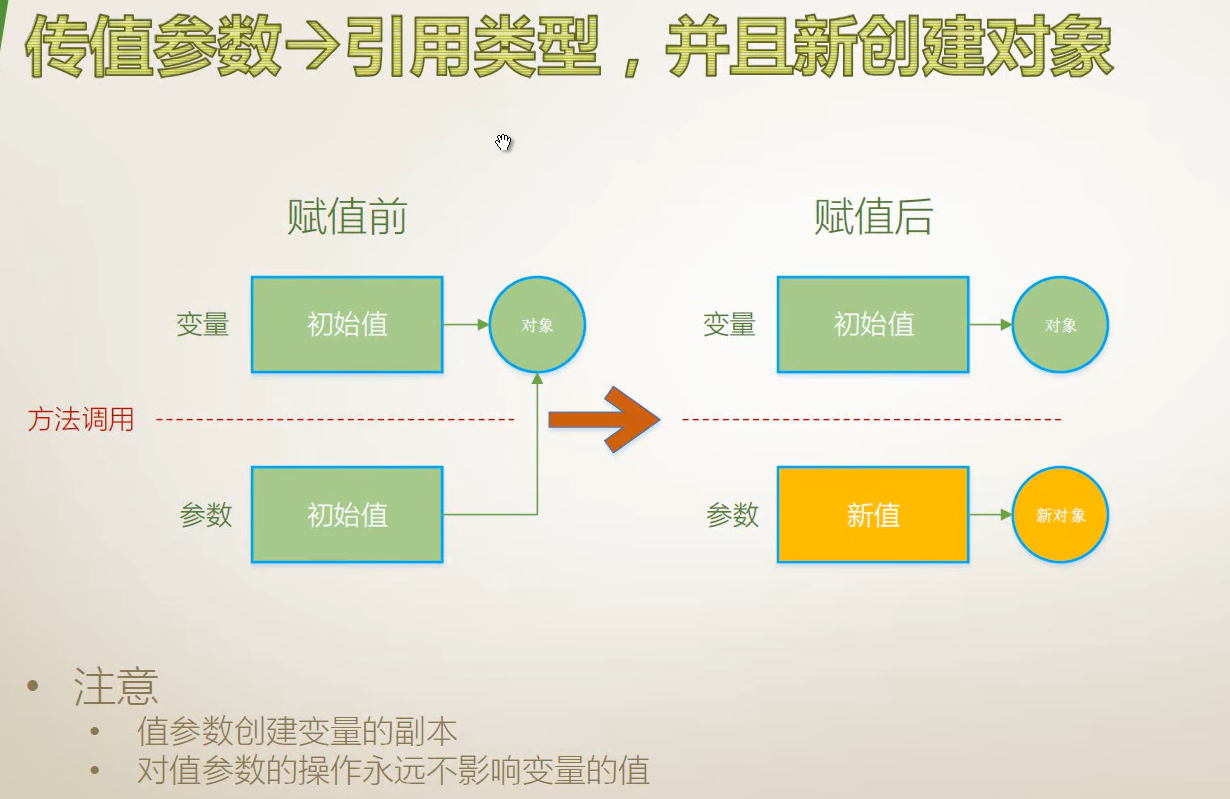
不创建对象
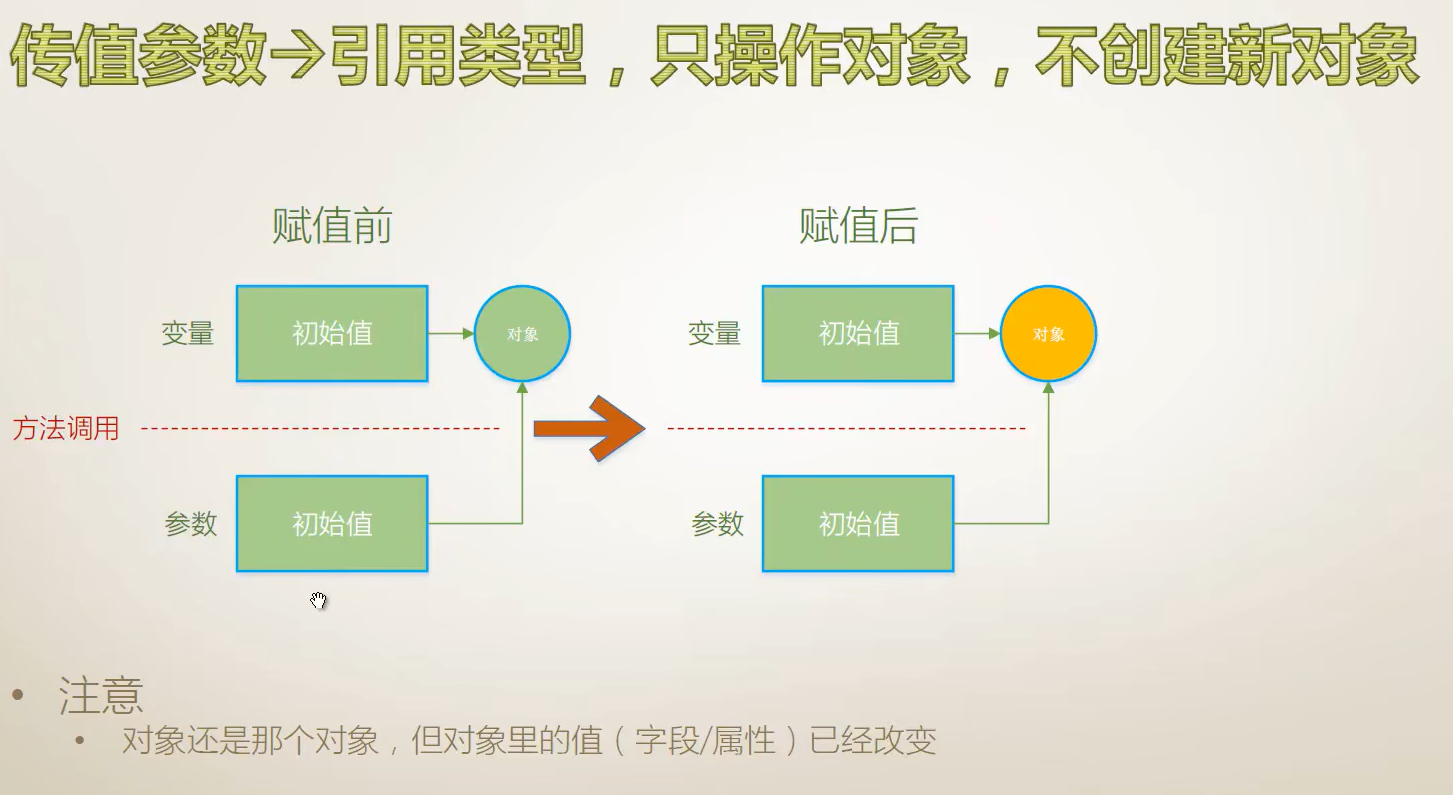
代码演示:
创建对象
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ParametersExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Student stu = new Student() { Name = "Tim" };SomeMethod(stu);//打印出来是Tom 因为参数传进来时,SomeMethod方法给Name赋了一个新值,所以打印出来的是TomConsole.WriteLine(stu.Name);//这个是方法外部变量所引用的实例没有变}//生成一个静态声明的方法static void SomeMethod(Student stu){stu = new Student() { Name = "Tom" };Console.WriteLine(stu.Name);}}//方法声明class Student{public string Name { get; set; }//简化声明的属性}
}不创建对象
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ParametersExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Student stu = new Student() { Name = "Tim" };UpdateObject(stu);Console.WriteLine("HashCode={0},Name={1}",stu.GetHashCode(),stu.Name);}//生成一个静态声明的方法static void UpdateObject(Student stu){stu.Name = "Tom";//副作用,side-effectConsole.WriteLine("HashCode={0},Name={1}",stu.GetHashCode(),stu.Name);}}//方法声明class Student{public string Name { get; set; }//简化声明的属性}
}结果
HashCode=46104728,Name=Tom
HashCode=46104728,Name=Tom
请按任意键继续. . .
传值参数的代码解释
引用参数

引用参数(值类型)
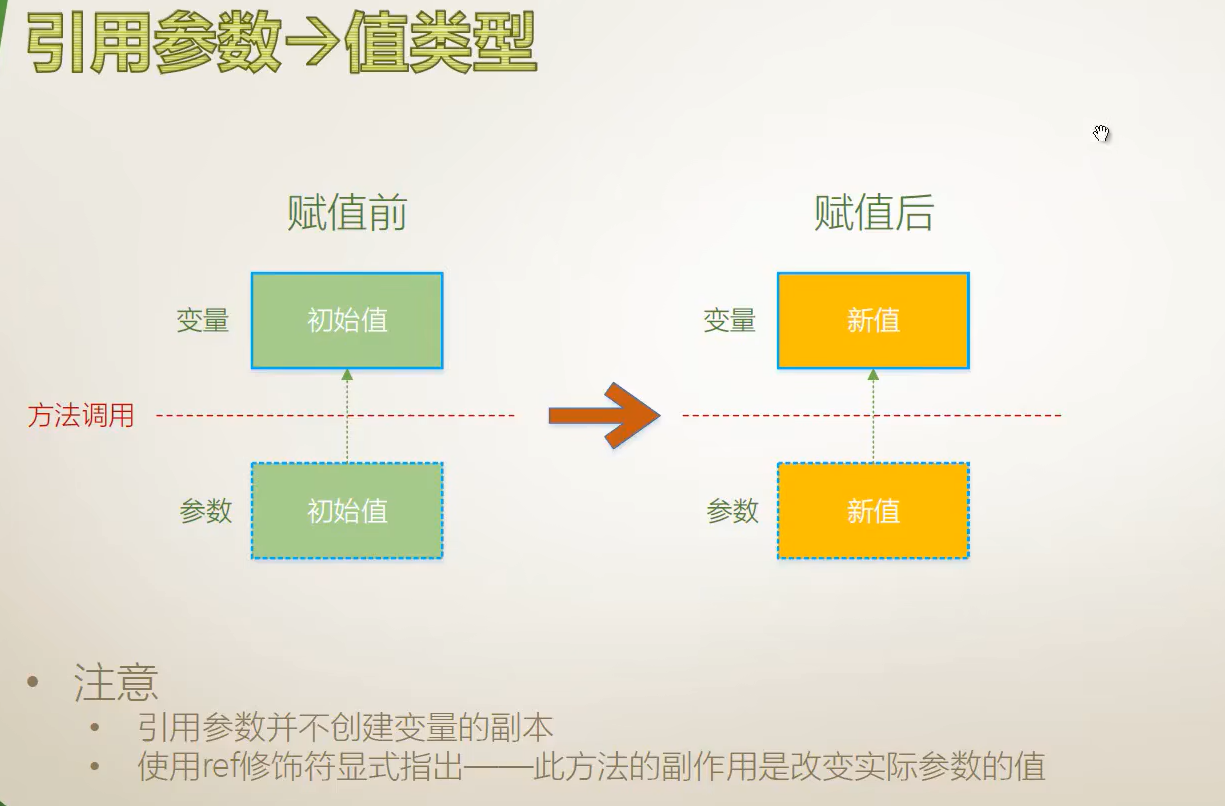
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ParametersExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){int y = 1;IWantSideEffect(ref y);Console.WriteLine(y);}static void IWantSideEffect(ref int x){x = x + 100;}}
}传值参数(引用类型)
创建新对象
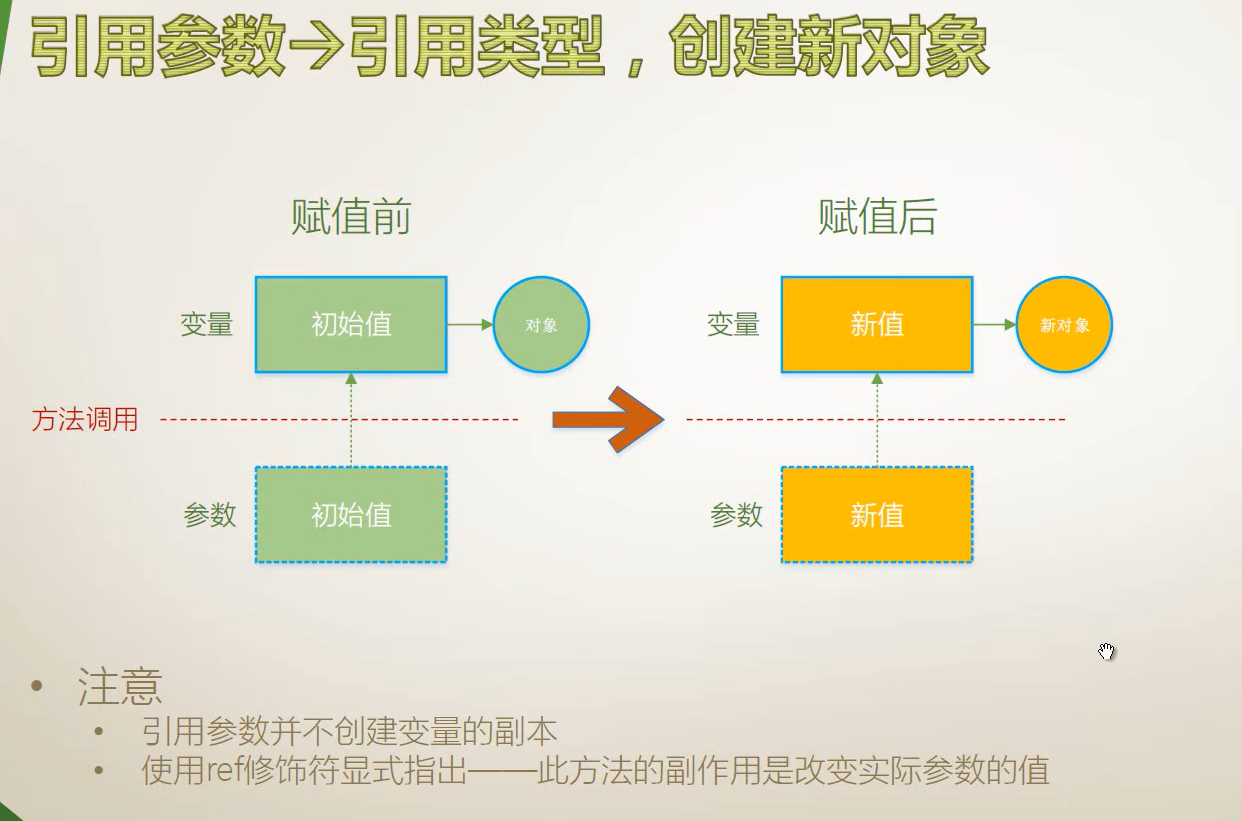
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data.SqlTypes;
using System.Linq;
using System.Security.Permissions;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ParametersExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Student outterStu = new Student() { Name = "Tim" };Console.WriteLine("HashCode={0},Name={1}", outterStu.GetHashCode(), outterStu.Name);Console.WriteLine("------------------------------");IWantSideEffect(ref outterStu);//方法体外部的变量HashCode的值和内部的属性Console.WriteLine("HashCode={0},Name={1}", outterStu.GetHashCode(), outterStu.Name);}static void IWantSideEffect(ref Student stu){stu = new Student() { Name = "Tom" };Console.WriteLine("HashCode={0},Name={1}",stu.GetHashCode(),stu.Name);}}class Student{public string Name { get; set; }}}不创建新对象
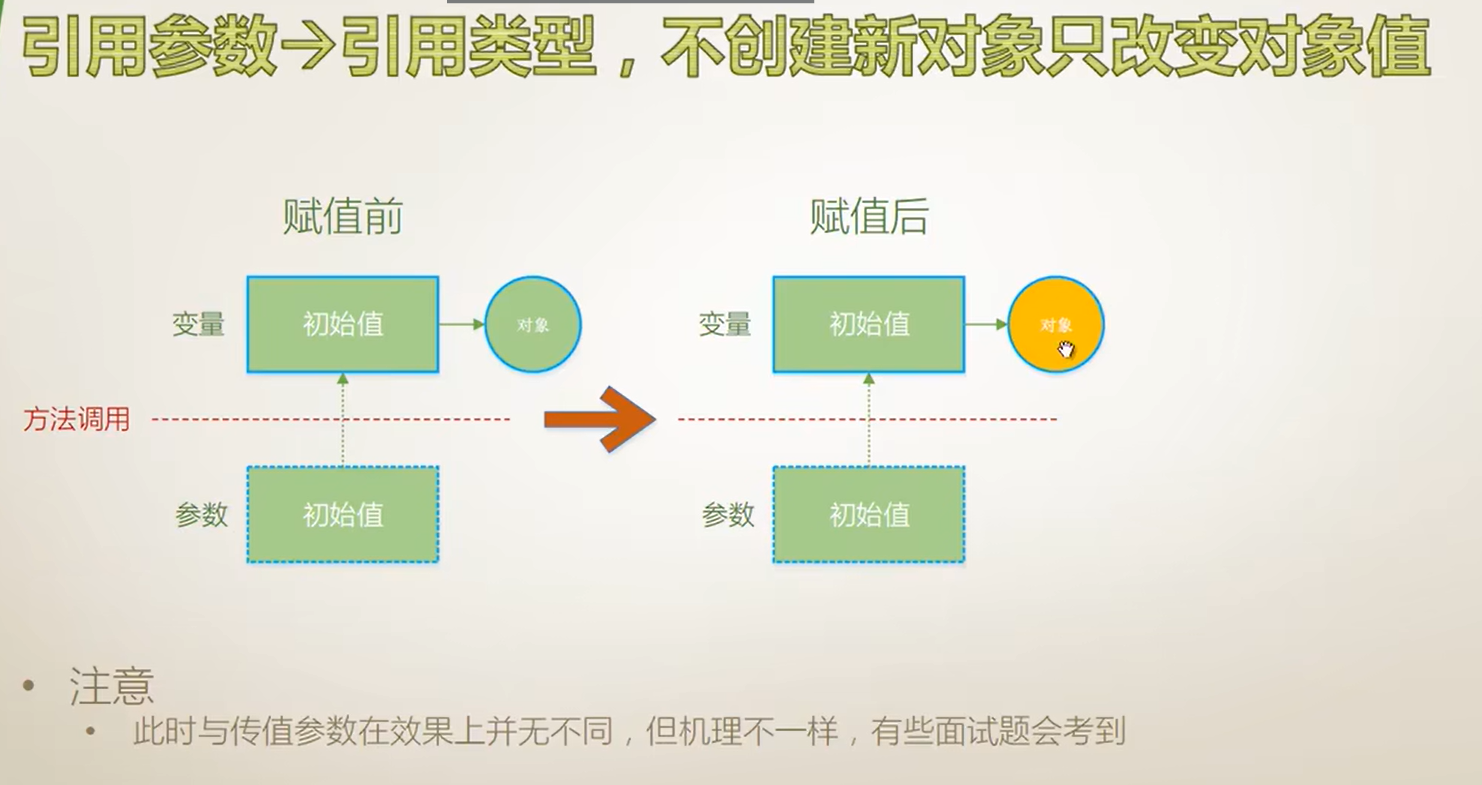

引用参数的代码解释
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data.SqlTypes;
using System.Linq;
using System.Security.Permissions;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ParametersExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){//对象的HashCode自始至终一直都没有改变,只是对值发生了改变Student outterStu = new Student() { Name = "Tim" };Console.WriteLine("HashCode={0},Name={1}", outterStu.GetHashCode(), outterStu.Name);Console.WriteLine("------------------------------");//SomeSideEffect(ref outterStu);//和值参数进行对比--值参数SomeSideEffect(outterStu);//方法体外部的变量HashCode的值和内部的属性Console.WriteLine("HashCode={0},Name={1}", outterStu.GetHashCode(), outterStu.Name);}//值参数的形参stu和实参outterStu所指向的地址是不同的,但他们所指向的地址中存储着相同类型的地址,即实例在堆内存中的地址.//引用参数的形参stu和实参outterStu多指向的是同一个地址,并且他们都存储着对象在堆内存中的地址.//static void SomeSideEffect(ref Student stu)//值参数static void SomeSideEffect(Student stu){stu.Name = "Tom";Console.WriteLine("HashCode={0},Name={1}",stu.GetHashCode(),stu.Name);}}class Student{public string Name { get; set; }}
}输出形参
有副作用的。。。。
用 out 修饰符声明的形参是输出形参。类似于引用形参,输出形参不创建新的存储位置。相反,输出形参表示的存储位置恰是在该方法调用中作为实参给出的那个变量所表示的存储位置。
当形参为输出形参时,方法调用中的相应实参必须由关键字 out 并后接一个与形参类型相同的 variable-reference(第 5.3.3 节)组成。变量在可以作为输出形参传递之前不一定需要明确赋值,但是在将变量作为输出形参传递的调用之后,该变量被认为是明确赋值的。
在方法内部,与局部变量相同,输出形参最初被认为是未赋值的,因而必须在使用它的值之前明确赋值。
在方法返回之前,该方法的每个输出形参都必须明确赋值(在方法体之内必须要有明确的赋值)。
声明为分部方法(第 10.2.7 节)或迭代器(第 10.14 节)的方法不能有输出形参。
输出参数(值类型)
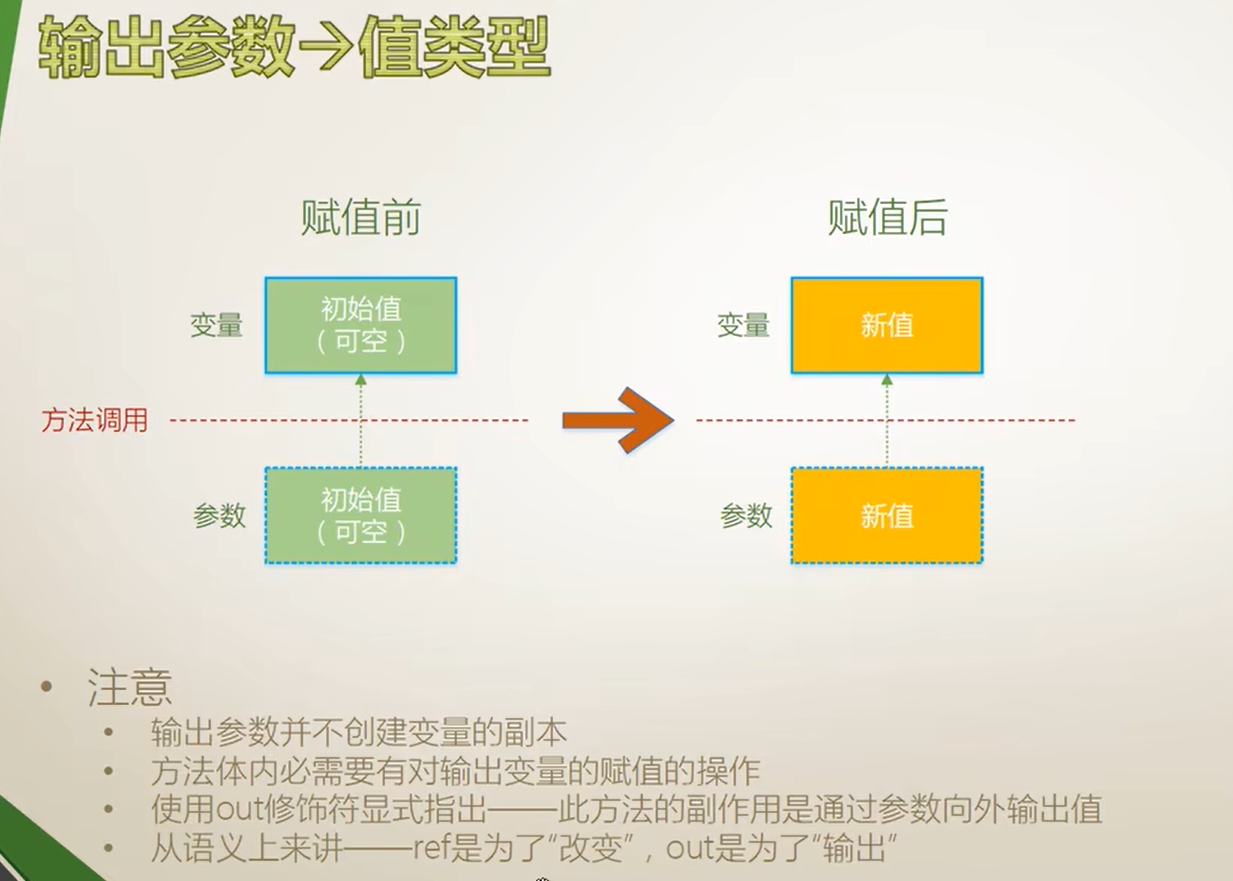
代码演示:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data.SqlTypes;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.Security.Permissions;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ParametersExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(String[] args){Console.WriteLine("Please input first number.");string arg1 = Console.ReadLine();double x = 0;//准备bool类型的变量来接收返回值bool b1 = double.TryParse(arg1, out x);//tryparse解析文本是否为double类型,即直接把内容输出给x?,并返回一个bool值if (b1 == false){Console.WriteLine("input error!");return;//return作用:上面如果输入错误,就直接结束不用执行下面一步了}Console.WriteLine("Please input second number");string arg2 = Console.ReadLine();double y = 0;bool b2 = double.TryParse(arg2, out y);if(b2 == false){Console.WriteLine("input error!");return;}//两次解析都结束了,说明拿到了两个double的值。double z = x + y;Console.WriteLine("{0}+{1}={2}",x,y,z);}}
}值类型输出参数
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data.SqlTypes;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.Security.Permissions;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ParametersExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(String[] args){double x = 0;//数字是正确的,换成字符串//bool b = DoubleParser.TryParse("789", out x);//结果790bool b = DoubleParser.TryParse("ABC", out x);//0if (b == true){Console.WriteLine(x + 1);}else{Console.WriteLine(x);}}}class DoubleParser{public static bool TryParse(string input,out double result){try{result = double.Parse(input);return true;}catch{result = 0;return false;}}}
}输出参数(引用类型)
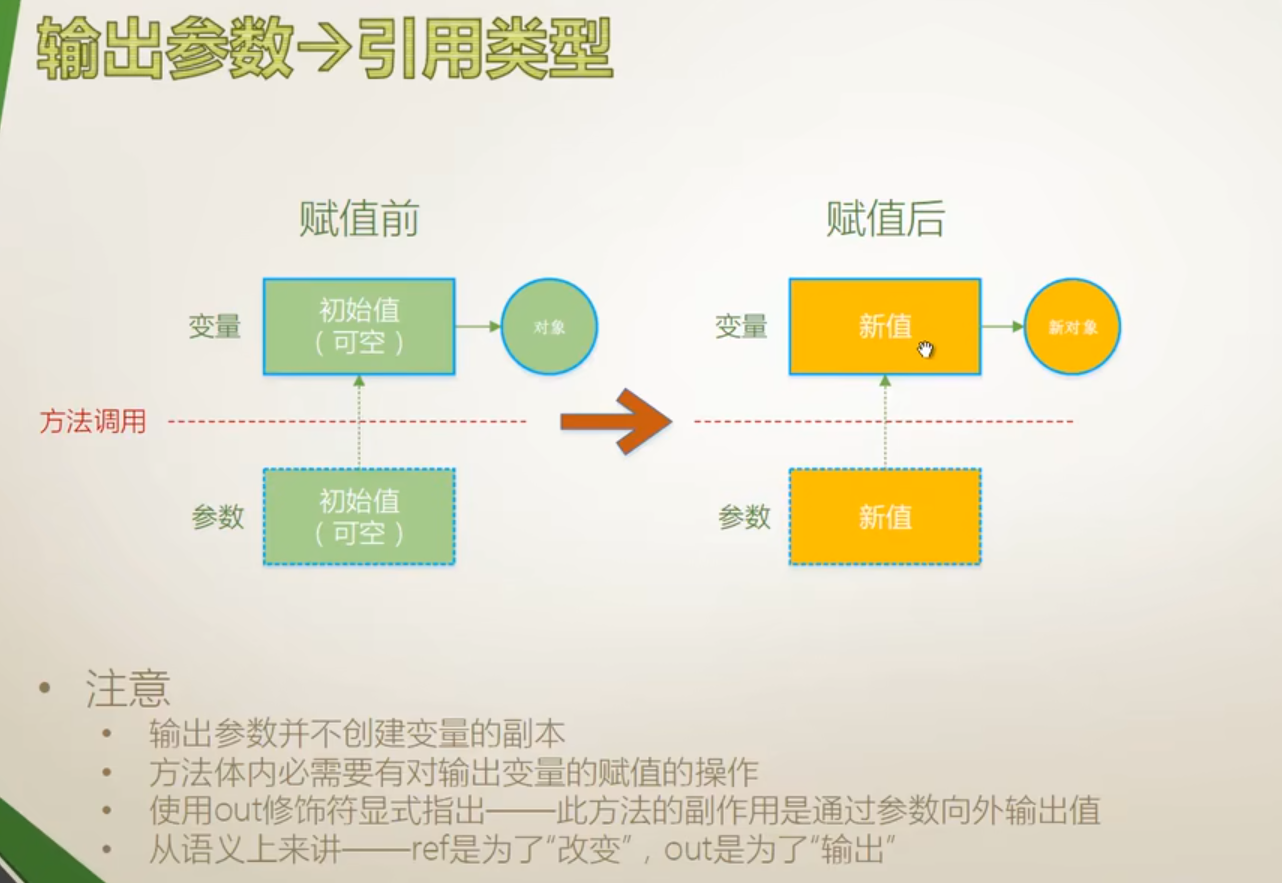
引用类型输出参数
代码演示:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data.SqlTypes;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.Security.Permissions;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ParametersExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(String[] args){Student stu = null;bool b = StudentFactory.Create("Tim", 34, out stu);if(b == true){Console.WriteLine("Student {0}, age is {1}",stu.Name,stu.Age);}}}class Student{public int Age { get; set; }public string Name { get; set; }}//工厂模式class StudentFactory{public static bool Create(string stuName, int stuAge, out Student result){result = null;if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(stuName)){return false;}if (stuAge < 20 || stuAge > 80){return false;}//result接收result = new Student() { Name = stuName, Age = stuAge };return true;}}}数组参数

代码演示:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data.SqlTypes;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.Security.Permissions;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ParametersExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(String[] args){//为了调用CalculateSum方法,需要先声明一个数组,显得语法啰嗦,可以加int[] myIntArray = new int[] { 1, 2, 3 };int result = CalculateSum(myIntArray);Console.WriteLine(result);//6//一下操作也可以,但需要再方法中加一个修饰词paramsint result1 = CalculateSum1(2,3,4);Console.WriteLine(result1);//9//String类型有个实例方法split()可以分割字符串string str = "Tim;Tom,Yaqi.Lisa";string[] result = str.Split(';',',','.');foreach(var name in result)//列表无法精确的只能通过遍历,并且数组的空间是固定的{Console.WriteLine(name);}}static int CalculateSum(int[] intArray){int sum = 0;foreach(var item in intArray){sum += item;}return sum;}static int CalculateSum1(params int[] intArray){int sum = 0;foreach(var item in intArray){sum += item;}return sum;}}}
String类型有个实例方法split()可以分割字符串
具名参数
- 参数的位子不再受约束
两个优点
- 提高了代码的可读性
- 当我们为参数加上名字之后,参数的位置就不会受参数的顺序的约束了,即参数的位置不受参数顺序的约束
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data.SqlTypes;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.Security.Permissions;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ParametersExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(String[] args){//不具名参数PrintInfo("Tim", 34);//具名参数//两个优点//1.提高了代码的可读性//2.当我们为参数加上名字之后,参数的位置就不会受参数的顺序的约束了,即参数的位置不受参数顺序的约束PrintInfo(age: 34, name: "tim");PrintInfo(name: "Tim", age: 34);}static void PrintInfo(string name,int age){Console.WriteLine("Hello {0}, you are {1}",name,age);}}}可选参数
- 参数因为具有默认值而变得“可选”
- 不推荐使用可选参数
代码演示:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data.SqlTypes;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.Security.Permissions;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ParametersExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(String[] args){PrintInfo();}static void PrintInfo(string name="Tim",int age=34)//参数在方法中已声明,具有默认值{Console.WriteLine("Hello {0}, you are {1}",name,age);}}
}
拓展方法(this参数)
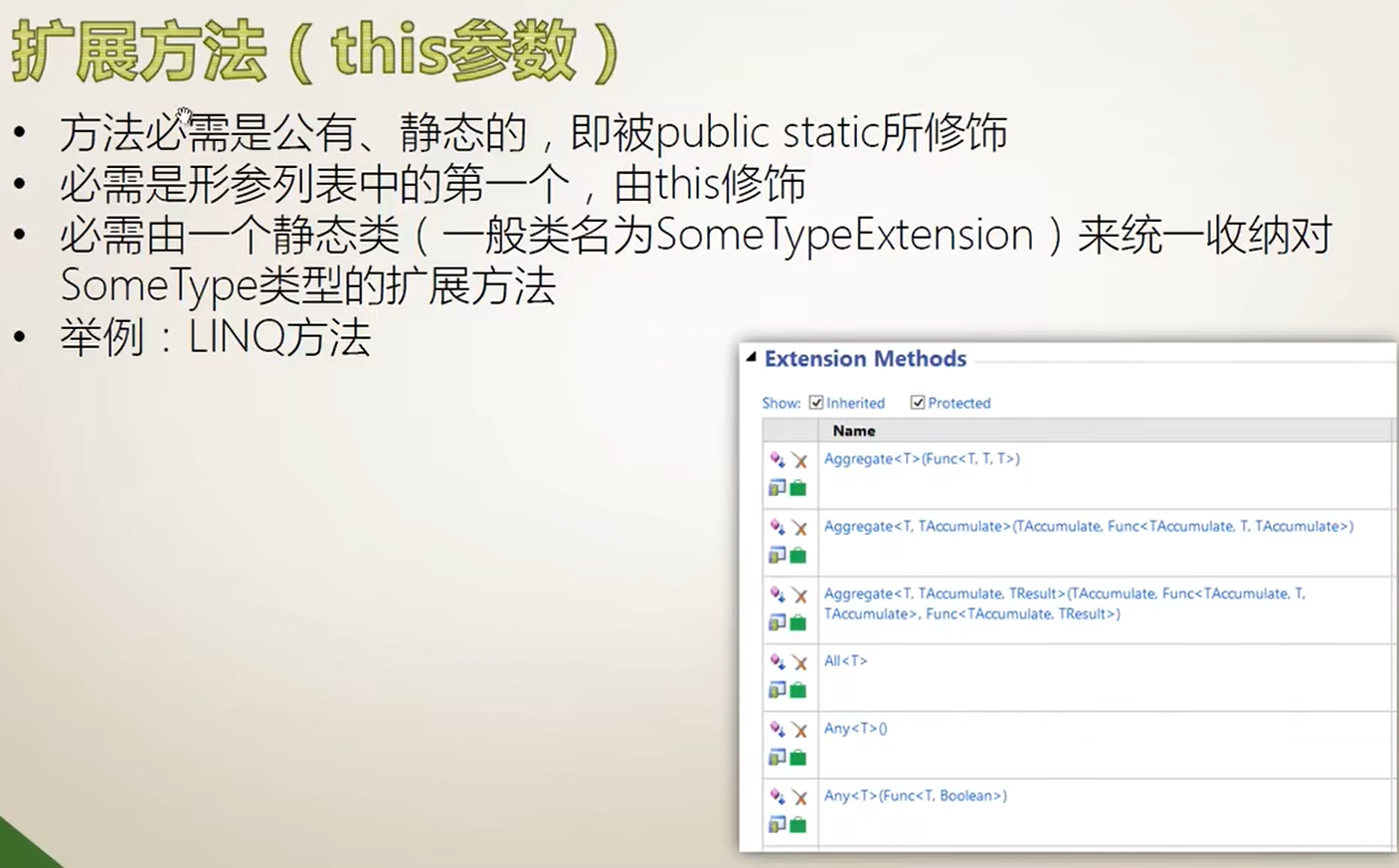
代码演示:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data.SqlTypes;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.Security.Permissions;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ParametersExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(String[] args){double x = 3.14159;double y = Math.Round(x,4);//3.1416Console.WriteLine(y);double z = x.Round(4);Console.WriteLine(z);//3.1416}}static class DoubleExtension{public static double Round(this double input, int digits){double result = Math.Round(input, digits);return result;}}
}LINQ方法
代码演示:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data.SqlTypes;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.Security.Permissions;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ParametersExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(String[] args){List<int> myList = new List<int>() { 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, };bool result = myList.All(i => i > 10);//LINQ方法--拓展方法--All--属于Enumerable静态类Console.WriteLine(result);}static bool AllGreaterThanTen(List<int> list)//集合中所有值大于10{foreach(var item in list){if (item <= 10){return false;}}return true;}}}
小结:

委托
什么是委托
在C#中,委托(Delegate)是一种类型,用于表示对一个或多个方法的引用。委托可以看作是函数指针的类型安全版本,它允许将方法作为参数传递、存储和调用。委托可以用于实现事件处理、回调函数、多播委托等功能。委托的定义类似于方法的签名,它指定了方法的返回类型和参数列表。通过委托,可以将一个方法绑定到委托实例上,然后通过委托实例调用该方法。委托可以是单播的(绑定一个方法)或多播的(绑定多个方法)
代码演示:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Security.Policy;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace DelegateExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Calculator cal = new Calculator();Action act = new Action(cal.Report);}}class Calculator{public void Report(){Console.WriteLine("I have 3 methods");}public int Add(int a,int b){int result = a + b;return result;}public int Sub(int a,int b){int result = a - b;return result;}}
}代码
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Security.Policy;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace DelegateExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Calculator cal = new Calculator();Action act = new Action(cal.Report);cal.Report();act.Invoke();act();Func<int, int, int> func1 = new Func<int, int, int>(cal.Add);Func<int, int, int> func2 = new Func<int, int, int>(cal.Sub);int x = 100;int y = 200;int z = 0;//z = func1.Invoke(x, y);//间接调用z = func1(x, y);//使用委托时都有指针的写法Console.WriteLine(z);//z = func2.Invoke(x, y);//间接调用z = func2(x, y);Console.WriteLine(z);}}class Calculator{public void Report(){Console.WriteLine("I have 3 methods");}public int Add(int a,int b){int result = a + b;return result;}public int Sub(int a,int b){int result = a - b;return result;}}
}委托的声明(自定义委托)

代码演示:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Security.Policy;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace DelegateExample
{public delegate double Calc(double a, double b);//声明自定义委托类型//自定义委托类型,可以放在类里,也可以放在类外//放在类外是所有的类都可以使用//放在类里是只能这个类使用internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Calculator cal = new Calculator();Calc calc1 = new Calc(cal.Add);Calc calc2 = new Calc(cal.Sub);Calc calc3 = new Calc(cal.Mul);Calc calc4 = new Calc(cal.Div);//通过委托间接调用方法double a = 100;double b = 200;double c = 0;//仿指针就把.Invoke 去掉c = calc1.Invoke(a, b);Console.WriteLine(c);c = calc2.Invoke(a, b);Console.WriteLine(c);c = calc3.Invoke(a, b);Console.WriteLine(c);c = calc4.Invoke(a, b);Console.WriteLine(c);}}class Calculator{public double Add(double a, double b){return a + b;}public double Sub(double a,double b){return a-b;}public double Mul(double a, double b){return a * b;}public double Div(double a, double b){return a / b;}}
}委托的一般使用


模板方法: 模板方法是一种设计模式,其中定义了一个算法的框架,而具体步骤的实现由子类来完成。在C#中,可以使用委托来实现模板方法。父类定义一个包含委托作为参数的模板方法,子类实现具体的方法并将其作为委托传递给父类的模板方法。这样可以在父类中定义算法的框架,而具体步骤的实现由子类决定。回调方法: 回调方法是一种机制,其中一个方法将另一个方法作为参数传递,以便在适当的时候调用该方法。在C#中,可以使用委托来实现回调方法。一个常见的应用是事件处理,其中事件触发时会调用注册的委托方法。通过回调方法,可以实现事件驱动的编程模型,让不同部分之间实现解耦合。自己设置断点理解
模版方法:代码
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel.Design.Serialization;
using System.Linq;
using System.Security.Policy;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace DelegateExample
{public delegate double Calc(double a, double b);internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){ProductFactory productFactory = new ProductFactory();WrapFactory wrapFactory = new WrapFactory();Func<Product> func1 = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakePizza);Func<Product> func2 = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakeToyCar);Box box1 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(func1);Box box2 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(func2);Console.WriteLine(box1.Product.Name);Console.WriteLine(box2.Product.Name);}}class Product{public string Name { get; set; }}class Box{public Product Product { get; set; }}//工厂类--工厂类里有个装盒子的方法,返回值是(Box盒子),需要用到的参数是(返回值为Product的委托)class WrapFactory{public Box WrapProduct(Func<Product> getProduct){Box box = new Box();Product product = getProduct.Invoke();//间接调用,没有通过方法直接调用,而是通过一个委托去调用box.Product = product;return box;}}//生产各种产品的工厂类class ProductFactory{public Product MakePizza(){Product product = new Product();product.Name = "Pizza";return product;}public Product MakeToyCar(){Product product = new Product();product.Name = "ToyCar";return product;}}
}
用接口的方法写
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel.Design.Serialization;
using System.Linq;
using System.Security.Policy;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace DelegateExample
{public delegate double Calc(double a, double b);internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){IProductFactory pizzaFactory = new PizzaFactory();IProductFactory toycarFactory = new ToyCarFactory();WrapFactory wrapFactory = new WrapFactory();Box box1 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(pizzaFactory);Box box2 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(toycarFactory);Console.WriteLine(box1.Product.Name);Console.WriteLine(box2.Product.Name);}}//接口interface IProductFactory{Product Make();}class PizzaFactory:IProductFactory{public Product Make(){Product product = new Product();product.Name = "Pizza";return product;}}class ToyCarFactory : IProductFactory{public Product Make(){Product product = new Product();product.Name = "ToyCar";return product;}}class Product{public string Name { get; set; }}class Box{public Product Product { get; set; }}//工厂类--工厂类里有个装盒子的方法,返回值是(Box盒子),需要用到的参数是(返回值为Product的委托)class WrapFactory{public Box WrapProduct(IProductFactory productFactory){Box box = new Box();Product product = productFactory.Make();//间接调用,没有通过方法直接调用,而是通过一个委托去调用box.Product = product;return box;}}
}回调方法:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel.Design.Serialization;
using System.Linq;
using System.Security.Policy;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace DelegateExample
{public delegate double Calc(double a, double b);internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){ProductFactory productFactory = new ProductFactory();WrapFactory wrapFactory = new WrapFactory();Func<Product> func1 = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakePizza);Func<Product> func2 = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakeToyCar);Logger logger = new Logger();Action<Product> log = new Action<Product>(logger.Log);Box box1 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(func1,log);Box box2 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(func2,log);Console.WriteLine(box1.Product.Name);Console.WriteLine(box2.Product.Name);}}//创建一个日志class Logger{public void Log(Product product){Console.WriteLine("Product '{0}' created at {1}.price is{2}.",product.Name,DateTime.UtcNow,product.Price);}}class Product{public string Name { get; set; }public double Price { get; set; }}class Box{public Product Product { get; set; }}//工厂类--工厂类里有个装盒子的方法,返回值是(Box盒子),需要用到的参数是(返回值为Product的委托)class WrapFactory{public Box WrapProduct(Func<Product> getProduct, Action<Product> logCallback){Box box = new Box();Product product = getProduct.Invoke();//间接调用,没有通过方法直接调用,而是通过一个委托去调用if (product.Price >= 50)//大于等于50的记录{logCallback(product);}box.Product = product;return box;}}//生产各种产品的工厂类class ProductFactory{public Product MakePizza(){Product product = new Product();product.Name = "Pizza";product.Price = 12;return product;}public Product MakeToyCar(){Product product = new Product();product.Name = "ToyCar";product.Price = 99;return product;}}
}滥用委托

委托的高级使用
多播委托:
多播委托是一种特殊类型的委托,它可以包含多个目标方法的引用。多播委托允许将多个方法绑定到同一个委托实例上,当该委托被调用时,所有绑定的方法都会被依次执行。多播委托使用加法运算符 '+' 来添加方法,使用减法运算符 '-' 来移除方法。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel.Design.Serialization;
using System.Linq;
using System.Security.Policy;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace DelegateExample
{public delegate double Calc(double a, double b);internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Student stu1 = new Student() { ID = 1, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow };Student stu2 = new Student() { ID = 2, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Green };Student stu3 = new Student() { ID = 3, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Red };Action action1 = new Action(stu1.DoHomework);//一个委托封装一个方法的形式称为单播委托Action action2 = new Action(stu2.DoHomework);Action action3 = new Action(stu3.DoHomework);action1.Invoke();action2.Invoke();action3.Invoke();action1 += action2;// 用一个委托封装多个方法的形式称为多播委托action1 += action3;action1.Invoke();//结果相同}}class Student{public int ID { get; set; }public ConsoleColor PenColor { get; set; }public void DoHomework(){for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){Console.ForegroundColor = this.PenColor;Console.WriteLine("Student {0} doing homework {1} hour(s).", this.ID, i);Thread.Sleep(1000);}}}
}同步调用
同步调用是指在调用方法时,程序会等待该方法执行完毕并返回结果后再继续执行后续代码。在同步调用中,调用方会阻塞等待被调用方法的完成,直到被调用方法返回结果后才能继续执行。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace MultiThreadExample
{public delegate double Calc(double a, double b);internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Student stu1 = new Student() { ID = 1, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow };Student stu2 = new Student() { ID = 2, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Green };Student stu3 = new Student() { ID = 3, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Red };//同步调用--直接stu1.DoHomework();stu2.DoHomework();stu3.DoHomework();//第二种同步调用--典型的间接同步调用Action action1 = new Action(stu1.DoHomework);Action action2 = new Action(stu2.DoHomework);Action action3 = new Action(stu3.DoHomework);action1.Invoke();//单播委托action2.Invoke();action2.Invoke();action1 += action2;//多播action1 += action3;action1.Invoke();for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Cyan;Console.WriteLine("Main thread {0}", i);Thread.Sleep(1000);}}}class Student{public int ID { get; set; }public ConsoleColor PenColor { get; set; }public void DoHomework(){for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){Console.ForegroundColor = this.PenColor;Console.WriteLine("Student {0} doing homework {1} hour(s).", this.ID, i);Thread.Sleep(1000);}}}
}
异步调用
异步调用是指在调用方法时,程序不会等待被调用方法执行完毕,而是继续执行后续代码。被调用方法会在另一个线程或任务中执行,并在执行完毕后通知调用方或执行回调方法。异步调用可以提高程序的性能和响应性,特别适用于需要长时间执行的操作,如网络请求、文件读写等。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace MultiThreadExample
{public delegate double Calc(double a, double b);internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Student stu1 = new Student() { ID = 1, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow };Student stu2 = new Student() { ID = 2, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Green };Student stu3 = new Student() { ID = 3, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Red };Action action1 = new Action(stu1.DoHomework);Action action2 = new Action(stu2.DoHomework);Action action3 = new Action(stu3.DoHomework);action1.BeginInvoke(null, null);//隐式异步调用action2.BeginInvoke(null, null);action3.BeginInvoke(null, null);Console.WriteLine("---------------------------");Thread thread1 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(stu1.DoHomework));Thread thread2 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(stu2.DoHomework));Thread thread3 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(stu3.DoHomework));thread1.Start();thread2.Start();thread3.Start();//显式异步调用Console.WriteLine("------------------------------");Task task1 = new Task(new Action(stu1.DoHomework));Task task2 = new Task(new Action(stu2.DoHomework));Task task3 = new Task(new Action(stu3.DoHomework));task1.Start();task2.Start();task3.Start();//使用task的显式异步调用for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Cyan;Console.WriteLine("Main thread {0}", i);Thread.Sleep(1000);}}}class Student{public int ID { get; set; }public ConsoleColor PenColor { get; set; }public void DoHomework(){for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){Console.ForegroundColor = this.PenColor;Console.WriteLine("Student {0} doing homework {1} hour(s).", this.ID, i);Thread.Sleep(1000);}}}
}事件
什么是事件

在C#中,事件是一种特殊的委托,用于实现发布-订阅模式。事件提供了一种机制,使一个对象可以通知其他对象发生了特定的动作或状态变化,而其他对象可以订阅该事件以在事件发生时执行相应的操作。

事件的应用
vs里面 小方块–方法 小扳手–属性 小闪电–事件
一个事件有两个处理器的时候 --代码演示
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Timers;namespace EventExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Timer timer = new Timer();timer.Interval = 1000;Boy boy = new Boy();Girl girl = new Girl();timer.Elapsed += boy.Action;//事件订阅者 += 操作符 +=操作符左边:事件 +=操作符右边:事件处理器timer.Elapsed += girl.Action;timer.Start();Console.ReadLine();}}class Boy{//alt+enter自动生成事件处理器--Action方法internal void Action(object sender, ElapsedEventArgs e){Console.WriteLine("Jump!");}}class Girl{internal void Action(object sender, ElapsedEventArgs e){Console.WriteLine("Sing!");}}
}演示结果:
Jump!
Sing!
Jump!
Sing!
Jump!
Sing!
事件的应用一星
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Timers;using System.Windows.Forms;namespace EventExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Form form = new Form();//事件拥有着Controller controller = new Controller(form);//事件的响应者form.ShowDialog();}}class Controller{private Form form;//构造器快捷键 ctorpublic Controller(Form form){if(form != null){this.form = form;this.form.Click += this.FormClicked;//this--代表Controller的实例 - - - 事件 - - 事件订阅}}private void FormClicked(object sender, EventArgs e)//事件的处理器{this.form.Text = DateTime.Now.ToString();}}}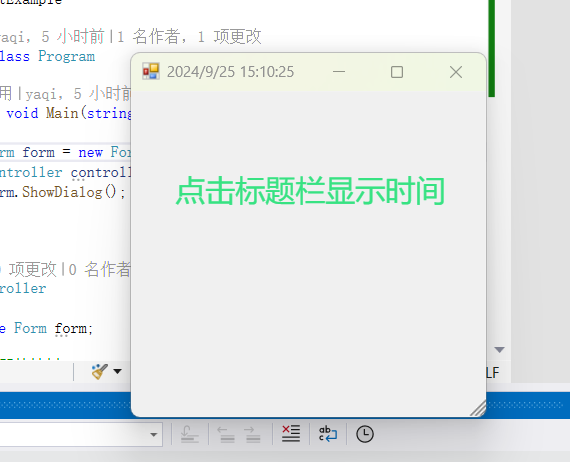
事件的应用二星
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Timers;using System.Windows.Forms;namespace EventExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){MyForm form = new MyForm();//form事件的拥有着,事件的响应者也就是事件的拥有着myForm的实例form.Click += form.formClicked;//事件click事件 -- 事件的订阅 +=操作符form.ShowDialog();}}class MyForm : Form//派生 {internal void formClicked(object sender, EventArgs e)//事件处理器{this.Text = DateTime.Now.ToString();}}}事件的应用三星
代码演示
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
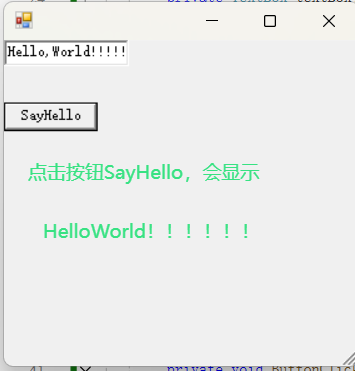
using System.Timers;using System.Windows.Forms;namespace EventExample
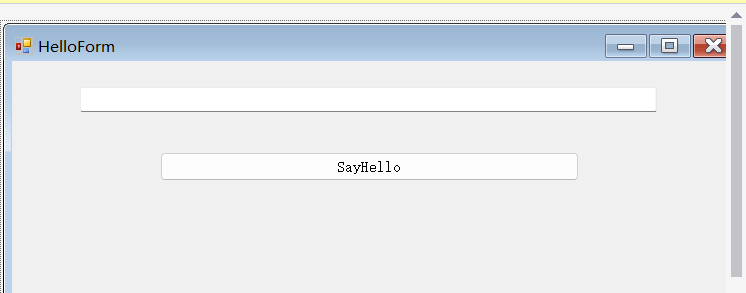
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){MyForm form = new MyForm();form.ShowDialog();}}class MyForm : Form // 派生MyForm 继承 Form类{private TextBox textBox;private Button button;//创建一个构造函数public MyForm()//事件的响应者 MyForm的对象 {this.textBox = new TextBox();this.button = new Button();//事件的响应者是MyForm,事件的拥有者是button和textButtonthis.Controls.Add(this.button);this.Controls.Add(this.textBox);this.button.Click += this.ButtonClicked;//事件的订阅this.button.Text = "SayHello";this.button.Top = 50;}private void ButtonClicked(object sender, EventArgs e)//事件处理器ButtonClicked处理器方法{this.textBox.Text = "Hello,World!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!";}}}结果:
WindowsForm例子:
Form1.Designer.cs
namespace FormsApp1
{partial class Myform{/// <summary>/// 必需的设计器变量。/// </summary>private System.ComponentModel.IContainer components = null;/// <summary>/// 清理所有正在使用的资源。/// </summary>/// <param name="disposing">如果应释放托管资源,为 true;否则为 false。</param>protected override void Dispose(bool disposing){if (disposing && (components != null)){components.Dispose();}base.Dispose(disposing);}#region Windows 窗体设计器生成的代码/// <summary>/// 设计器支持所需的方法 - 不要修改/// 使用代码编辑器修改此方法的内容。/// </summary>private void InitializeComponent(){this.myTextBox = new System.Windows.Forms.TextBox();this.myButton = new System.Windows.Forms.Button();this.SuspendLayout();// // myTextBox// this.myTextBox.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(68, 26);this.myTextBox.Margin = new System.Windows.Forms.Padding(4, 4, 4, 4);this.myTextBox.Name = "myTextBox";this.myTextBox.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(577, 25);this.myTextBox.TabIndex = 0;// // myButton// this.myButton.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(148, 91);this.myButton.Margin = new System.Windows.Forms.Padding(4, 4, 4, 4);this.myButton.Name = "myButton";this.myButton.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(419, 29);this.myButton.TabIndex = 1;this.myButton.Text = "SayHello";this.myButton.UseVisualStyleBackColor = true;this.myButton.Click += new System.EventHandler(this.ButtionClick);// // Myform// this.AutoScaleDimensions = new System.Drawing.SizeF(8F, 15F);this.AutoScaleMode = System.Windows.Forms.AutoScaleMode.Font;this.ClientSize = new System.Drawing.Size(725, 408);this.Controls.Add(this.myButton);this.Controls.Add(this.myTextBox);this.Margin = new System.Windows.Forms.Padding(4, 4, 4, 4);this.Name = "Myform";this.Text = "HelloForm";this.ResumeLayout(false);this.PerformLayout();}#endregionprivate System.Windows.Forms.TextBox myTextBox;private System.Windows.Forms.Button myButton;}
}Form1.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;namespace FormsApp1
{public partial class Myform : Form{public Myform(){InitializeComponent();}private void ButtionClick(object sender, EventArgs e){this.myTextBox.Text = "HelloWorld!";}}
}
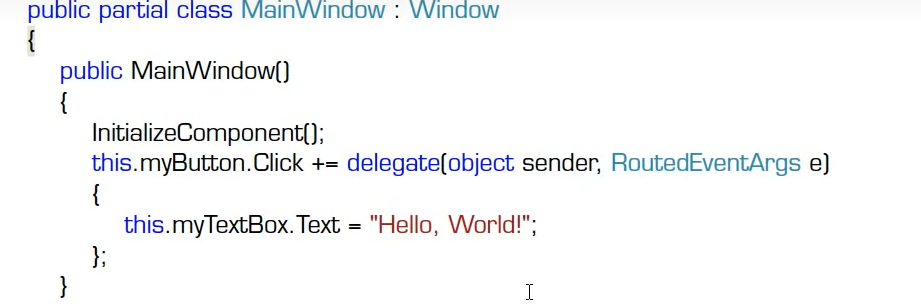
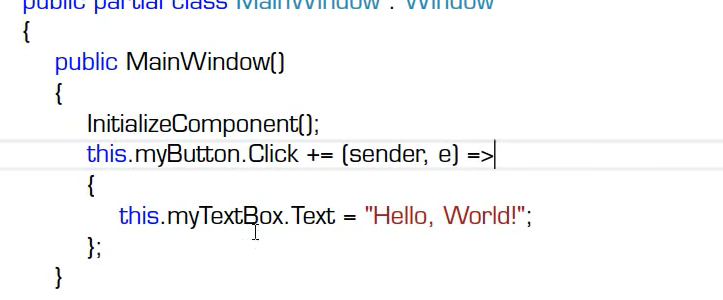
一个事件处理器是可以被重用的

一个小例子
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;namespace WinFormExample
{public partial class Form1 : Form{public Form1(){InitializeComponent();// this.button3.Click += this.ButtionClicked;//挂接事件处理器的方法一//挂接方式二//this.button3.Click += new EventHandler(this.ButtionClicked);//事件处理器处理的是button的click事件,那么新建的这个委托包着的这个方法也一定是具有和button的click事件相同约束的方法//挂接方式三--过时了--匿名方法/* this.button3.Click += delegate (object sender, EventArgs e){this.textBox1.Text = "haha!";};*/// 挂接方法三--现在的写法--Lambda表达式this.button3.Click += (object sender, EventArgs e)=>{this.textBox1.Text = "haha!";};}private void ButtionClicked(object sender, EventArgs e){if(sender == this.button1){this.textBox1.Text = "Hello";}if(sender == this.button2){this.textBox1.Text = "World";}if(sender == this.button3){this.textBox1.Text = "Mr.Okay";}}}
}Wpf演示代码教程
<Window x:Class="WpfApp2.MainWindow"xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"xmlns:local="clr-namespace:WpfApp2"mc:Ignorable="d"Title="MainWindow" Height="450" Width="800"><Grid><TextBox x:Name="textBox1" HorizontalAlignment="Center" Height="23" Margin="0,10,0,0" TextWrapping="Wrap" Text="TextBox" VerticalAlignment="Top" Width="780"></TextBox><Button x:Name="button1" Content="Click me" Margin="10,38,10,0" VerticalAlignment="Top" /></Grid>
</Window>using System.Text;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using System.Windows.Data;
using System.Windows.Documents;
using System.Windows.Input;
using System.Windows.Media;
using System.Windows.Media.Imaging;
using System.Windows.Navigation;
using System.Windows.Shapes;namespace WpfApp2
{/// <summary>/// Interaction logic for MainWindow.xaml/// </summary>public partial class MainWindow : Window{public MainWindow(){InitializeComponent();this.button1.Click += this.ButtionClicked;//传统的方法 - - 委托 this.button1.Click += new RoutedEventHandler(this.ButtionClicked);}private void ButtionClicked(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e){this.textBox1.Text = "Hello World!";}}
}
事件声明
委托

事件声明的完整格式
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace EventExample1
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){//声明一个customerCustomer customer = new Customer();Waiter waiter = new Waiter();customer.Order += waiter.Action;//使用Action方法作为Order事件的处理器customer.Action();customer.PayTheBill();}}//声明一个基础的数据类型//如果某个类的用途是作为EventArgs来用的话 -- 派生EventArgspublic class OrderEventArgs:EventArgs{public string DishName { get; set; }public string size { get; set; }}//声明一个委托类型 -- 跟所有的类平级的类型//customer的访问性低于委托的访问性 -- 需要把class都声明成publicpublic delegate void OrderEventHandler(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e );//EventHandler后缀 -- 专门用来设置委托事件的//委托类型嵌套到class里面//服务员是事件处理器public class Customer{private OrderEventHandler orderEventHandler;//用来存储和引用时间处理器的//声明事件格式public event OrderEventHandler Order{add//事件处理器的添加器{this.orderEventHandler += value;}remove//事件处理器的移除器{this.orderEventHandler -= value;}}public double Bill { get; set; }//事件是基于委托的两层意思 //第一层:事件需要委托类型来做一个约束。约束既规定事件能发送什么样的消息给响应者,这就决定了事件响应者的事件处理器,必须能够和这个约束匹配上,才能够订阅这个事件。//第二层:第二层意思:当事件响应者向事件拥有者提供了能够匹配这个事件的事件处理器之后,需要把事件处理器保存或者记录下来。能够记录或者说引用方法的任务,只有委托类型的实例能够做到。//能够记录或者说引用方法的任务-- 委托类型的实例能够存储事件响应者提供的响应方法public void PayTheBill(){Console.WriteLine("I will pay ${0}",this.Bill);}public void WalkIn(){Console.WriteLine("Walk into the restaurant");}public void SitDown(){Console.WriteLine("Sit down");}public void Think(){for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){Console.WriteLine("Let me think ...");Thread.Sleep(1000);}if (this.orderEventHandler != null){OrderEventArgs e = new OrderEventArgs();e.DishName = "Kongpao Chicken";e.size = "large";this.orderEventHandler.Invoke(this, e);}}public void Action(){Console.ReadLine();this.WalkIn();this.SitDown();this.Think(); }}//事件的响应者public class Waiter{public void Action(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e){//处理Order事件Console.WriteLine("I will serve you the dish - {0}",e.DishName);double price = 10;switch (e.size){case "small":price = price * 0.5;break;case "large":price = price * 1.5;break;default:break;}customer.Bill += price;}}
}简化声明背后的秘密
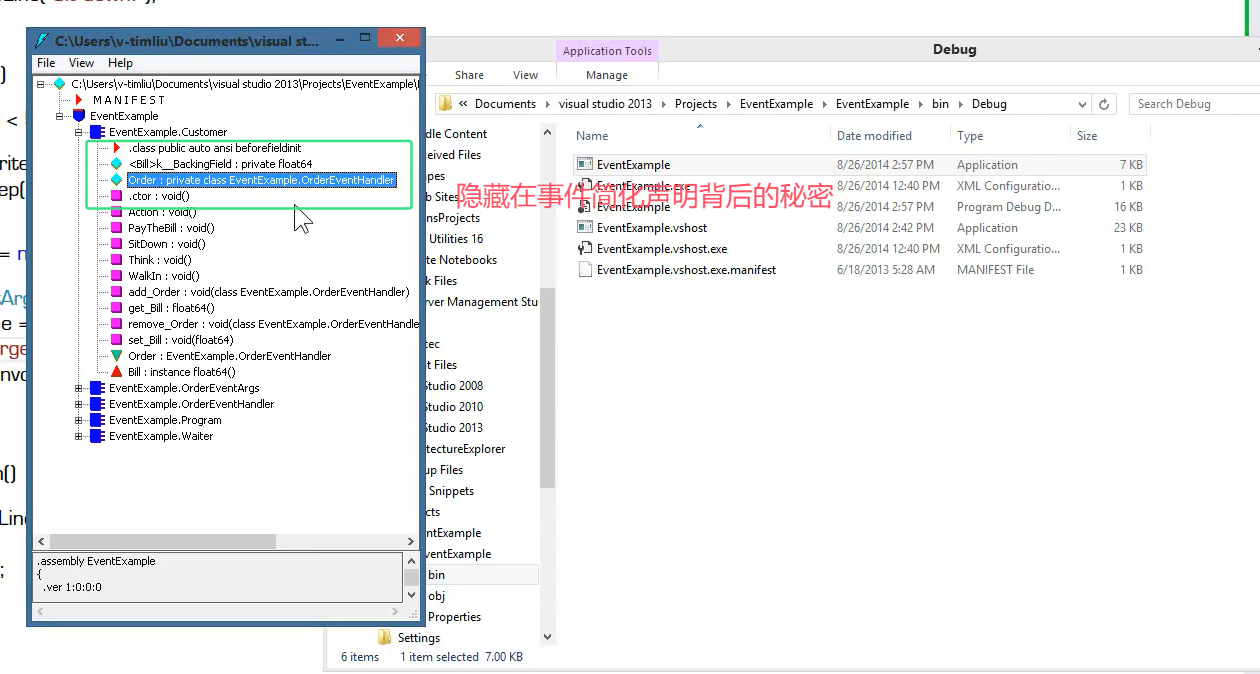
事件的声明

事件声明简化版
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace EventExample1
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){//声明一个customerCustomer customer = new Customer();Waiter waiter = new Waiter();customer.Order += waiter.Action;//使用Action方法作为Order事件的处理器customer.Action();customer.PayTheBill();}}//声明一个基础的数据类型//如果某个类的用途是作为EventArgs来用的话 -- 派生EventArgspublic class OrderEventArgs:EventArgs{public string DishName { get; set; }public string size { get; set; }}//声明一个委托类型 -- 跟所有的类平级的类型//customer的访问性低于委托的访问性 -- 需要把class都声明成publicpublic delegate void OrderEventHandler(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e );//EventHandler后缀 -- 专门用来设置委托事件的//委托类型嵌套到class里面//服务员是事件处理器public class Customer{//简化声明 -- 事件声明public event OrderEventHandler Order;public double Bill { get; set; }//事件是基于委托的两层意思 //第一层:事件需要委托类型来做一个约束。约束既规定事件能发送什么样的消息给响应者,这就决定了事件响应者的事件处理器,必须能够和这个约束匹配上,才能够订阅这个事件。//第二层:第二层意思:当事件响应者向事件拥有者提供了 能够匹配这个事件的事件处理器之后,需要把事件处理器保存或者记录下来。能够记录或者说引用方法的任务,只有委托类型的实例能够做到。//能够记录或者说引用方法的任务-- 委托类型的实例能够存储事件响应者提供的响应方法public void PayTheBill(){Console.WriteLine("I will pay ${0}",this.Bill);}public void WalkIn(){Console.WriteLine("Walk into the restaurant");}public void SitDown(){Console.WriteLine("Sit down");}public void Think(){for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){Console.WriteLine("Let me think ...");Thread.Sleep(1000);}if (this.Order != null){OrderEventArgs e = new OrderEventArgs();e.DishName = "Kongpao Chicken";e.size = "large";this.Order.Invoke(this, e);}}public void Action(){Console.ReadLine();this.WalkIn();this.SitDown();this.Think(); }}//事件的响应者public class Waiter{public void Action(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e){//处理Order事件Console.WriteLine("I will serve you the dish - {0}",e.DishName);double price = 10;switch (e.size){case "small":price = price * 0.5;break;case "large":price = price * 1.5;break;default:break;}customer.Bill += price;}}
}借刀杀人
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace EventExample1
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Console.ReadLine();//声明一个customerCustomer customer = new Customer();Waiter waiter = new Waiter();customer.Order += waiter.Action;//使用Action方法作为Order事件的处理器//customer.Action();OrderEventArgs e = new OrderEventArgs();e.DishName = "Manhanquanxi";e.Size = "large"; OrderEventArgs e2 = new OrderEventArgs();e2.DishName = "Beer";e2.Size = "large";Customer badGuy = new Customer();badGuy.Order += waiter.Action;//借刀杀人badGuy.Order.Invoker(customer, e);badGuy.Order.Invoke(customer, e2);customer.PayTheBill();}}//声明一个基础的数据类型//如果某个类的用途是作为EventArgs来用的话 -- 派生EventArgspublic class OrderEventArgs:EventArgs{public string DishName { get; set; }public string Size { get; set; }}//声明一个委托类型 -- 跟所有的类平级的类型//customer的访问性低于委托的访问性 -- 需要把class都声明成publicpublic delegate void OrderEventHandler(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e );//EventHandler后缀 -- 专门用来设置委托事件的//委托类型嵌套到class里面//服务员是事件处理器public class Customer{//简化声明 -- 事件声明public event OrderEventHandler Order;public double Bill { get; set; }//事件是基于委托的两层意思 //第一层:事件需要委托类型来做一个约束。约束既规定事件能发送什么样的消息给响应者,这就决定了事件响应者的事件处理器,必须能够和这个约束匹配上,才能够订阅这个事件。//第二层:第二层意思:当事件响应者向事件拥有者提供了 能够匹配这个事件的事件处理器之后,需要把事件处理器保存或者记录下来。能够记录或者说引用方法的任务,只有委托类型的实例能够做到。//能够记录或者说引用方法的任务-- 委托类型的实例能够存储事件响应者提供的响应方法public void PayTheBill(){Console.WriteLine("I will pay ${0}",this.Bill);}public void WalkIn(){Console.WriteLine("Walk into the restaurant");}public void SitDown(){Console.WriteLine("Sit down");}public void Think(){for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){Console.WriteLine("Let me think ...");Thread.Sleep(1000);}if (this.Order != null){OrderEventArgs e = new OrderEventArgs();e.DishName = "Kongpao Chicken";e.Size = "large";this.Order.Invoke(this, e);}}public void Action(){Console.ReadLine();this.WalkIn();this.SitDown();this.Think(); }}//事件的响应者public class Waiter{public void Action(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e){//处理Order事件Console.WriteLine("I will serve you the dish - {0}",e.DishName);double price = 10;switch (e.Size){case "small":price = price * 0.5;break;case "large":price = price * 1.5;break;default:break;}customer.Bill += price;}}
}借刀杀人 正确的代码
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace EventExample1
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Console.ReadLine();//声明一个customerCustomer customer = new Customer();Waiter waiter = new Waiter();customer.Order += waiter.Action;//使用Action方法作为Order事件的处理器//customer.Action();OrderEventArgs e = new OrderEventArgs();e.DishName = "Manhanquanxi";e.Size = "large"; OrderEventArgs e2 = new OrderEventArgs();e2.DishName = "Beer";e2.Size = "large";Customer badGuy = new Customer();badGuy.Order += waiter.Action;//借刀杀人badGuy.Order.Invoker(customer, e);badGuy.Order.Invoke(customer, e2);customer.PayTheBill();}}//声明一个基础的数据类型//如果某个类的用途是作为EventArgs来用的话 -- 派生EventArgspublic class OrderEventArgs:EventArgs{public string DishName { get; set; }public string Size { get; set; }}//声明一个委托类型 -- 跟所有的类平级的类型//customer的访问性低于委托的访问性 -- 需要把class都声明成publicpublic delegate void OrderEventHandler(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e );//EventHandler后缀 -- 专门用来设置委托事件的//委托类型嵌套到class里面//服务员是事件处理器public class Customer{//简化声明 -- 事件声明public event OrderEventHandler Order;public double Bill { get; set; }//事件是基于委托的两层意思 //第一层:事件需要委托类型来做一个约束。约束既规定事件能发送什么样的消息给响应者,这就决定了事件响应者的事件处理器,必须能够和这个约束匹配上,才能够订阅这个事件。//第二层:第二层意思:当事件响应者向事件拥有者提供了 能够匹配这个事件的事件处理器之后,需要把事件处理器保存或者记录下来。能够记录或者说引用方法的任务,只有委托类型的实例能够做到。//能够记录或者说引用方法的任务-- 委托类型的实例能够存储事件响应者提供的响应方法public void PayTheBill(){Console.WriteLine("I will pay ${0}",this.Bill);}public void WalkIn(){Console.WriteLine("Walk into the restaurant");}public void SitDown(){Console.WriteLine("Sit down");}public void Think(){for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){Console.WriteLine("Let me think ...");Thread.Sleep(1000);}if (this.Order != null){OrderEventArgs e = new OrderEventArgs();e.DishName = "Kongpao Chicken";e.Size = "large";this.Order.Invoke(this, e);}}public void Action(){Console.ReadLine();this.WalkIn();this.SitDown();this.Think(); }}//事件的响应者public class Waiter{public void Action(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e){//处理Order事件Console.WriteLine("I will serve you the dish - {0}",e.DishName);double price = 10;switch (e.Size){case "small":price = price * 0.5;break;case "large":price = price * 1.5;break;default:break;}customer.Bill += price;}}
}
EventHanlder委托代码:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime;
using System.Runtime.Remoting.Channels;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace EventExample1
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Console.ReadLine();//声明一个customerCustomer customer = new Customer();Waiter waiter = new Waiter();customer.Order += waiter.Action;//使用Action方法作为Order事件的处理器customer.Action();customer.PayTheBill();}}//声明一个基础的数据类型//如果某个类的用途是作为EventArgs来用的话 -- 派生EventArgspublic class OrderEventArgs : EventArgs{public string DishName { get; set; }public string Size { get; set; }}//声明一个委托类型 -- 跟所有的类平级的类型//customer的访问性低于委托的访问性 -- 需要把class都声明成public//public delegate void OrderEventHandler(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e);//EventHandler后缀 -- 专门用来设置委托事件的//委托类型嵌套到class里面//服务员是事件处理器public class Customer{//简化声明 -- 事件声明//public OrderEventHandler Order;public EventHandler Order;//EventArgs被继承了啊,前边的object又是基类,基类可以被所有类继承啊public double Bill { get; set; }//事件是基于委托的两层意思 //第一层:事件需要委托类型来做一个约束。约束既规定事件能发送什么样的消息给响应者,这就决定了事件响应者的事件处理器,必须能够和这个约束匹配上,才能够订阅这个事件。//第二层:第二层意思:当事件响应者向事件拥有者提供了 能够匹配这个事件的事件处理器之后,需要把事件处理器保存或者记录下来。能够记录或者说引用方法的任务,只有委托类型的实例能够做到。//能够记录或者说引用方法的任务-- 委托类型的实例能够存储事件响应者提供的响应方法public void PayTheBill(){Console.WriteLine("I will pay ${0}", this.Bill);}public void WalkIn(){Console.WriteLine("Walk into the restaurant");}public void SitDown(){Console.WriteLine("Sit down");}public void Think(){for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){Console.WriteLine("Let me think ...");Thread.Sleep(1000);}if (this.Order != null){OrderEventArgs e = new OrderEventArgs();e.DishName = "Kongpao Chicken";e.Size = "large";this.Order.Invoke(this, e);}}public void Action(){Console.ReadLine();this.WalkIn();this.SitDown();this.Think();}}//事件的响应者public class Waiter{public void Action(Object sender, EventArgs e){//类型转换Customer customer = sender as Customer;OrderEventArgs orderInfo = e as OrderEventArgs;//处理Order事件Console.WriteLine("I will serve you the dish - {0}", orderInfo.DishName);double price = 10;switch (orderInfo.Size){case "small":price = price * 0.5;break;case "large":price = price * 1.5;break;default:break;}customer.Bill += price;}}
}Order加Event专门出发事件
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime;
using System.Runtime.Remoting.Channels;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace EventExample1
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Console.ReadLine();//声明一个customerCustomer customer = new Customer();Waiter waiter = new Waiter();customer.Order += waiter.Action;//使用Action方法作为Order事件的处理器customer.Action();customer.PayTheBill();}}//声明一个基础的数据类型//如果某个类的用途是作为EventArgs来用的话 -- 派生EventArgspublic class OrderEventArgs : EventArgs{public string DishName { get; set; }public string Size { get; set; }}//声明一个委托类型 -- 跟所有的类平级的类型//customer的访问性低于委托的访问性 -- 需要把class都声明成public//public delegate void OrderEventHandler(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e);//EventHandler后缀 -- 专门用来设置委托事件的//委托类型嵌套到class里面//服务员是事件处理器public class Customer{//简化声明 -- 事件声明//public OrderEventHandler Order;public EventHandler Order;//EventArgs被继承了啊,前边的object又是基类,基类可以被所有类继承啊public double Bill { get; set; }//事件是基于委托的两层意思 //第一层:事件需要委托类型来做一个约束。约束既规定事件能发送什么样的消息给响应者,这就决定了事件响应者的事件处理器,必须能够和这个约束匹配上,才能够订阅这个事件。//第二层:第二层意思:当事件响应者向事件拥有者提供了 能够匹配这个事件的事件处理器之后,需要把事件处理器保存或者记录下来。能够记录或者说引用方法的任务,只有委托类型的实例能够做到。//能够记录或者说引用方法的任务-- 委托类型的实例能够存储事件响应者提供的响应方法public void PayTheBill(){Console.WriteLine("I will pay ${0}", this.Bill);}public void WalkIn(){Console.WriteLine("Walk into the restaurant");}public void SitDown(){Console.WriteLine("Sit down");}public void Think(){for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){Console.WriteLine("Let me think ...");Thread.Sleep(1000);}this.OnOrder("Kongpao Chicken", "large");}protected void OnOrder(string dishName,string size){if (this.Order != null){OrderEventArgs e = new OrderEventArgs();e.DishName = dishName;e.Size = size;this.Order.Invoke(this, e);}}public void Action(){Console.ReadLine();this.WalkIn();this.SitDown();this.Think();}}//事件的响应者public class Waiter{public void Action(Object sender, EventArgs e){//类型转换Customer customer = sender as Customer;OrderEventArgs orderInfo = e as OrderEventArgs;//处理Order事件Console.WriteLine("I will serve you the dish - {0}", orderInfo.DishName);double price = 10;switch (orderInfo.Size){case "small":price = price * 0.5;break;case "large":price = price * 1.5;break;default:break;}customer.Bill += price;}}
}
类
什么是类
类是一种数据结构:它可以包含数据成员(常量和字段)、函数成员(方法、属性、事件、索引器、运算符、实例构造函数、静态构造函数和析构函数)以及嵌套类型。类类型支持继承,继承是一种机制,它使派生类可以对基类进行扩展和专用化。
类也是一种数据类型:自定义的引用类型。
类代表现实世界中的种类
构造器
在C#中,析构器(Destructor)是一种特殊的方法,用于在对象被销毁时执行清理操作。析构器与构造函数相对应,构造函数用于对象的初始化,而析构器用于对象的清理。析构器在对象被垃圾回收器回收时自动调用,用于释放对象所占用的资源。需要注意的是,析构器不能被显式调用,它只会在对象被垃圾回收器回收时自动调用。析构器通常用于释放非托管资源,如文件句柄、数据库连接等,以确保资源被正确释放,避免内存泄漏。然而,在C#中,由于引入了垃圾回收机制,程序员通常不需要显式地编写析构器来释放资源。推荐使用IDisposable接口和Dispose方法来进行资源释放,以便更加灵活地管理资源的生命周期。通过实现IDisposable接口,可以在Dispose方法中释放资源,并在不再需要对象时手动调用该方法。总之,析构器是C#中的一种特殊方法,用于在对象被销毁时执行清理操作。然而,由于垃圾回收机制的存在,通常建议使用IDisposable接口和Dispose方法来管理资源的释放。代码演示:
using System;namespace HelloClass{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Student stu = new Student(1, "Yaqi");//实例stu.Report();}}//构造函数和析构函数//c与c++ 会产生内存泄漏:可以动态使用的内存越来越少 栈溢出:内存栈区的使用空间被用光class Student {//自定义的引用类型public Student(int id,string name) { //实例构造器this.ID = id;this.Name = name;}//析构器 -- 析构函数~Student() {Console.WriteLine("Bye bye! Release the system resources...");}public int ID { get; set; }public string Name { get; set; }public void Report() {Console.WriteLine($"I'm #{ID} student,my name is {Name}.");}}
}类的使用
- 一个类最多只能有一个基类,一个类在声明时有了sealed的修饰后,该类就不能当作基类。
- 一个父类可以创建一个子类对象,但是该对象的不能使用子类特有的方法
- 子类的访问级别不能超过父类的访问级别
- 横向扩展是对类成员的扩充,纵向扩展是对类成员的版本的更新
反射例子 – 科普
类的第二个方面
using System;namespace HelloClass{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Type t = typeof(Student);//引用一个类型类object o= Activator.CreateInstance(t, 1, "Yaqi");//前面两行代码 反射的一个机制Student stu = o as Student;//升级dynamic stu1 = Activator.CreateInstance(t, 1, "Yaqi");Console.WriteLine(stu.Name);Console.WriteLine(stu1.Name);}}//构造函数和析构函数//c与c++ 会产生内存泄漏:可以动态使用的内存越来越少 栈溢出:内存栈区的使用空间被用光class Student {//自定义的引用类型public Student(int id,string name) { //实例构造器this.ID = id;this.Name = name;}//析构器 -- 析构函数~Student() {Console.WriteLine("Bye bye! Release the system resources...");}public int ID { get; set; }public string Name { get; set; }public void Report() {Console.WriteLine($"I'm #{ID} student,my name is {Name}.");}}
}第三种方法:
using System;namespace HelloClass{internal class Program{//现实世界当中的一个事物static void Main(string[] args){Student s1 = new Student(1, "Yaqi");Student s2 = new Student(2, "Pang");Console.WriteLine(Student.Amount);}}//构造函数和析构函数//c与c++ 会产生内存泄漏:可以动态使用的内存越来越少 栈溢出:内存栈区的使用空间被用光class Student {//自定义的引用类型public static int Amount { get; set; }static Student(){//静态构造器 -- 来初始化静态成员Amount = 100;}public Student(int id,string name) { //实例构造器this.ID = id;this.Name = name;Amount++;}//析构器 -- 析构函数~Student() {Amount--;}public int ID { get; set; }public string Name { get; set; }public void Report() {Console.WriteLine($"I'm #{ID} student,my name is {Name}.");}}
}类的声明

类的声明基础知识
using System;namespace HelloClass{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){}class Student{//成员类 -- 是Program的成员类}}
}namespace MyNs {//类声明在名称空间内class Theacher { }
}//把类放在所有的名词空间之外 -- 声明在全局名称空间
class Computer {
}C++ .h文件类的声明 .cpp类的定义 声明和定义分开的
说hello
#pragma once
class Student
{
public:Student();~Student();void SayHello();
};#include "iostream"
#include "Student.h"
Student::Student() {}Student::~Student() {}void Student::SayHello() {std::cout <<"Hello!"<< std::endl;
}
// HelloCpp.cpp : 此文件包含 "main" 函数。程序执行将在此处开始并结束。
//#include <iostream>
#include "Student.h"
int main()
{Student* stu = new Student();stu->SayHello();return 0;
}// 运行程序: Ctrl + F5 或调试 >“开始执行(不调试)”菜单
// 调试程序: F5 或调试 >“开始调试”菜单// 入门使用技巧:
// 1. 使用解决方案资源管理器窗口添加/管理文件
// 2. 使用团队资源管理器窗口连接到源代码管理
// 3. 使用输出窗口查看生成输出和其他消息
// 4. 使用错误列表窗口查看错误
// 5. 转到“项目”>“添加新项”以创建新的代码文件,或转到“项目”>“添加现有项”以将现有代码文件添加到项目
// 6. 将来,若要再次打开此项目,请转到“文件”>“打开”>“项目”并选择 .sln 文件c++声明和定义放到一起
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
class Student
{//声明和定义放到一起.h里面
public:Student() {}~Student() {}void SayHello() {std::cout << "Hello!" << std::endl;}
};类的修饰符

访问级别
-
private:private是最低级别的访问修饰符,表示私有的,只能在当前类内部访问。使用private修饰的成员或方法只能在定义它们的类内部使用,对外部是不可见的。
-
protected:protected修饰符表示受保护的,只能在当前类及其派生类中访问。使用protected修饰的成员或方法可以在定义它们的类内部以及继承它们的子类中使用,对外部是不可见的。
-
internal:internal修饰符表示内部的,只能在当前程序集中访问。使用internal修饰的类、成员或方法可以在同一个程序集中的任何地方访问,但对于其他程序集是不可见的。
-
protected internal:protected internal是protected和internal的组合,表示受保护且内部的,可以在当前程序集以及派生类中访问。使用protected internal修饰的成员或方法可以在同一个程序集中的任何地方以及继承它们的子类中使用,对于其他程序集是不可见的。
访问主要了解public和internal
引用依赖
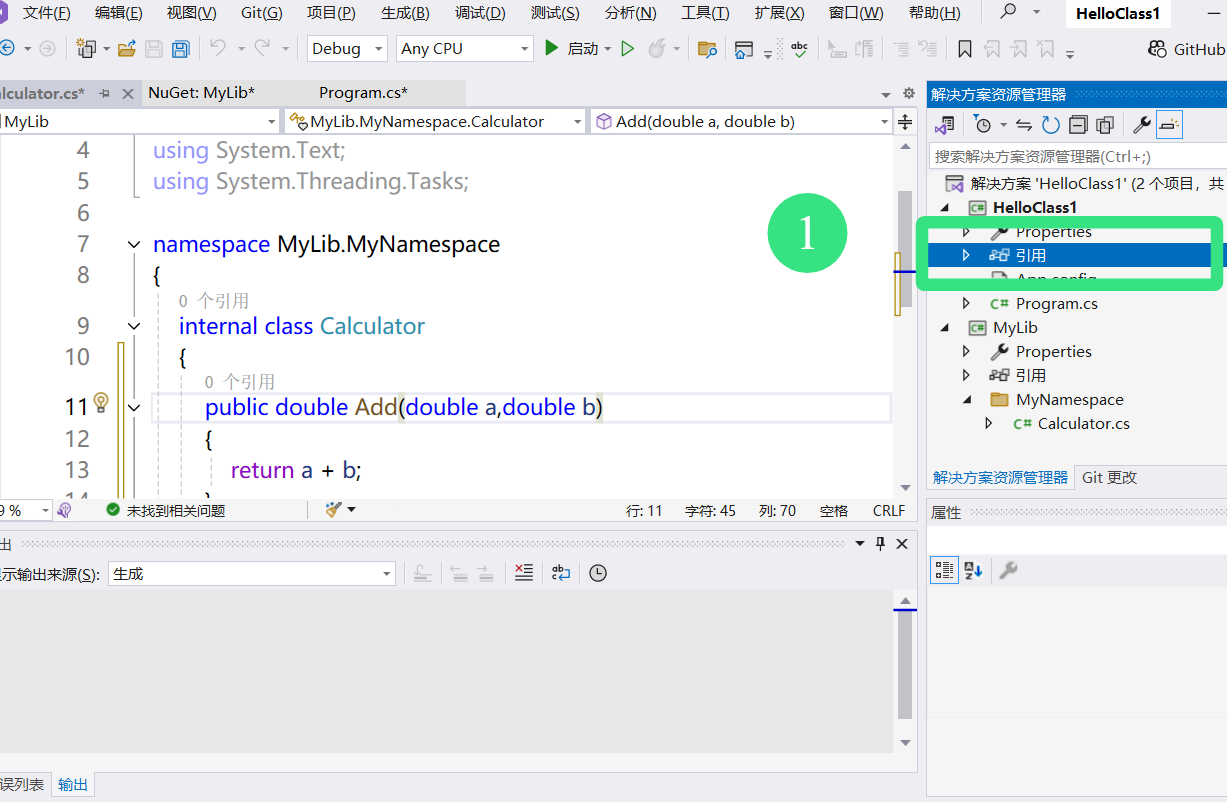
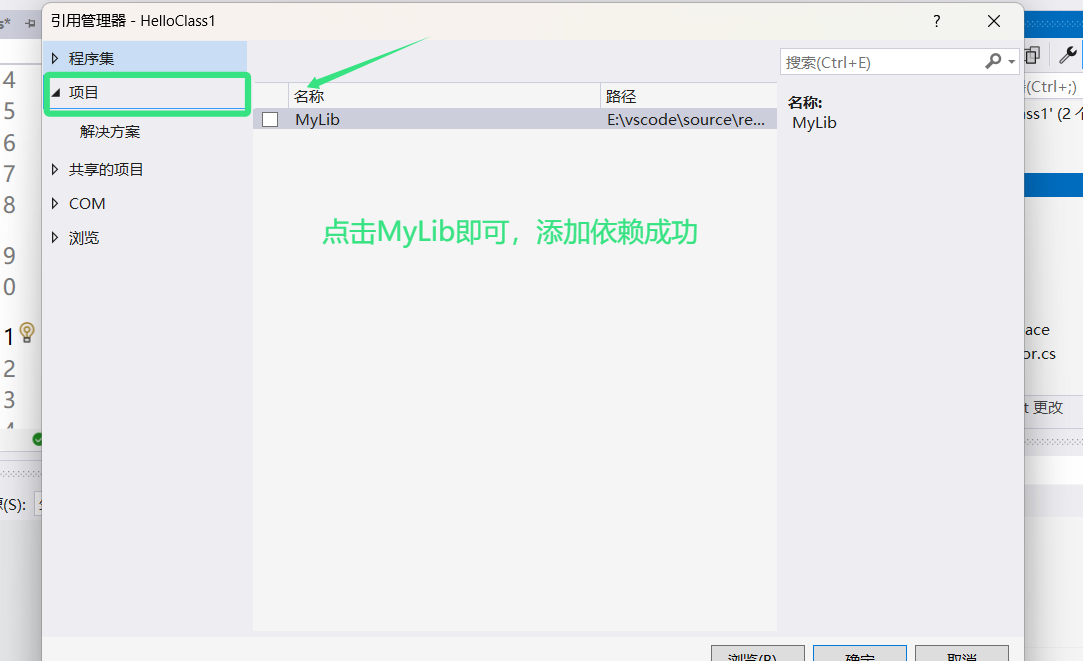
代码演示:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;namespace MyLib.MyNamespace
{public class Calculator{public double Add(double a,double b){return a + b;}}
}using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using MyLib.MyNamespace;namespace HelloClass1
{internal class Program {static void Main(string[] args){Calculator calc = new Calculator();double res = calc.Add(1.1, 2.2);Console.WriteLine(res);}}
}using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using MyLib.MyNamespace;namespace MyLib.MyNamespace2
{internal class Student{public Calculator calculator { get; set; }//Assembly}
}访问级别
private:private是最低级别的访问修饰符,表示私有的,只能在当前类内部访问。使用private修饰的成员或方法只能在定义它们的类内部使用,对外部是不可见的。protected:protected修饰符表示受保护的,只能在当前类及其派生类中访问。使用protected修饰的成员或方法可以在定义它们的类内部以及继承它们的子类中使用,对外部是不可见的。internal:internal修饰符表示内部的,只能在当前程序集中访问。使用internal修饰的类、成员或方法可以在同一个程序集中的任何地方访问,但对于其他程序集是不可见的。protected internal:protected internal是protected和internal的组合,表示受保护且内部的,可以在当前程序集以及派生类中访问。使用protected internal修饰的成员或方法可以在同一个程序集中的任何地方以及继承它们的子类中使用,对于其他程序集是不可见的。面向对象OOP
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace HelloOOp
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args) {Type t = typeof(Car);Type tb = t.BaseType;Type tTop = tb.BaseType;Console.WriteLine(tTop.BaseType == null);}}class Vehicle:Object { }class Car : Vehicle { }
}类的继承

在面向对象编程中,类的继承是一种机制,允许一个类(称为子类或派生类)继承另一个类(称为父类、基类或超类)的属性和方法。通过继承,子类可以获得父类的特性,包括字段、属性、方法等,而不需要重复编写相同的代码。在类的继承中,子类可以扩展或修改父类的功能,也可以添加自己的特有属性和方法。这种继承关系形成了类之间的层次结构,使得代码更加模块化、可复用和易于维护。
类的继承主要有以下特点
代码复用:子类可以重用父类的代码,避免重复编写相似的功能。
扩展功能:子类可以在不改变父类的情况下,添加新的属性和方法,实现功能的扩展。
方法重写:子类可以重写父类的方法,以实现不同的行为,实现多态性。
继承链:可以通过多层继承形成类的继承链,实现更复杂的类之间的关系。
代码演示:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace HelloOOp
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args) {//可以用一个父类类型的变量来引用子类类型的实例Vehicle vehicle = new Car();Object o1 = new Vehicle();Object o2 = new Car();}}//父类是子类的子集,子类是父类的超集//可以用一个父类类型的变量来引用子类类型的实例class Vehicle:Object { }class Car : Vehicle { }
}继承的本质是派生类在基类已有的成员的基础之上对基类进行的横向或者纵向的拓展横向扩展:对类成员个数的扩充纵向扩展:对类成员的版本或者说是对类成员的重写
子类对父类的全盘继承,类成员只能增加不能移除的特点
看一个字段方法按F12 进去 再按Ctrl - 返回
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace HelloAccess{internal class Program{//子类对父类的全盘继承,类成员只能增加不能移除的特点static void Main(string[] args){RaceCar recaCar = new RaceCar();recaCar.GetType}}class Vehicle {public string Owner { get; set; }}class Car : Vehicle { }class RaceCar : Car { }
}什么是基类对象,基类对象是怎么构造出来的
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace HelloAccess{internal class Program{//static void Main(string[] args){Car car = new Car();Console.WriteLine(car.Owner);}}class Vehicle {public Vehicle(){this.Owner = "N/A"; //基类断点先被触发}public string Owner { get; set; }}//先构造基类 再子类class Car : Vehicle {public Car(){this.Owner = "Car Owner";}public void ShowOwner(){Console.WriteLine(base.Owner);//只能够访问上一级}}}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace HelloAccess{internal class Program{//static void Main(string[] args){Car car = new Car("Yaqi");Console.WriteLine(car.Owner);}}class Vehicle {public Vehicle(string owner) {this.Owner = owner;}public string Owner { get; set; }}//先构造基类 再子类class Car : Vehicle{//第一个方法/* public Car():base("N/A"){this.Owner = "Car Owner";*/public Car(string owner) : base(owner)//注意:因为在基类构造器里已经把owner的值设置为owner参数的值了,所以我们不必要再在Car的构造器里再设置一遍了。让Car的构造器空着就可以了。{}}
}public:类成员的访问级别是以类的级别为上限的
MyLib
using System;namespace MyLib
{//类成员的访问级别是以类的访问级别为上限的public class Vehicle {public string Owner { get; set; }} public class Car : Vehicle {public void ShowOwner() {Console.WriteLine(base.Owner);}}}主程序
using System;
using MyLib;namespace HelloAccess{internal class Program{//static void Main(string[] args){Vehicle vehicle = new Vehicle();vehicle.Owner = "Yaqi";Console.WriteLine(vehicle.Owner);}}
}
internal访问级别:是把类成员的访问级别限制在同一个程序集这个范围之内
using System;namespace MyLib
{public class Vehicle {internal string Owner { get; set; }//internal访问级别是把类成员的访问级别限制在同一个程序集这个范围之内//在MyLib这个项目当中其它类当中去访问Owner属性,在其它项目当中不可以} public class Car : Vehicle {public void ShowOwner() {Console.WriteLine(base.Owner);}}
}
private:用private修饰类成员时,类成员被限制在类体内
using System;namespace MyLib
{public class Vehicle {private int _rpm;public void Accelerate() {_rpm += 1000;}public int Speed { get { return _rpm / 100; } }//Speed属性实际是_rpm字段的外部包装器} public class Car : Vehicle {}}using System;
using MyLib;namespace HelloAccess{internal class Program{//static void Main(string[] args){Car car = new Car();car.Accelerate();car.Accelerate();Console.WriteLine(car.Speed);}}}public是一个平面,protected是一条线,private是一个点当protectde与internal一起修饰时,他俩是或的关系,既可以被继承链上的类访问也可以被程序集内的其他类访问
using System;namespace MyLib
{public class Vehicle {protected int _rpm;//protected internal也能访问Burn 意思是对所有继承该类或在该程序集内声明的类可访问,访问级别仅次于publicprivate int _fuel;public void Refuel() {_fuel = 100;}protected void Burn(int fuel) {//既不想把Burn()方法暴露给外界引发错误的调用,有需要能够被car子类访问_fuel -= fuel;}public void Accelerate() {Burn(1);_rpm += 1000;}public int Speed { get { return _rpm / 100; } }//Speed属性实际是_rpm字段的外部包装器} public class Car : Vehicle {public void TurboAccelerate() {Burn(2);//油耗_rpm += 3000;}}
}using System;
using MyLib;namespace HelloAccess{internal class Program{//static void Main(string[] args){Bus bus = new Bus();//当protectde与internal一起修饰时,他俩是或的关系,既可以被继承链上的类访问也可以被程序集内的其他类访问//protected internal也能访问Burn 意思是对所有继承该类或在该程序集内声明的类可访问,访问级别仅次于publicbus.SlowAccelerate();Console.WriteLine(bus.Speed);}}class Bus : Vehicle { public void SlowAccelerate() {Burn(1);_rpm += 500; }}
}
重写
上节课讲的
重写(Override):重写是指在派生类中重新实现(覆盖)基类中的虚拟方法或抽象方法。当一个派生类继承自一个基类,并且想要修改基类中已有的虚拟方法或抽象方法的实现时,可以使用重写。通过重写,派生类可以提供自己的实现逻辑,而不改变方法的签名。在C#中,使用override关键字来标记重写的方法。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace OverrideExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Vehicle v = new RaseCar();//当我们用父类变量去引用一个子类实例的时候,调用被重写的成员时,总是能够调到这个继承链上最新的版本Car c = new RaseCar();//引用的是RaseCar的实例c.Run();//Rase car is runningv.Run();//Rase car is running}}//隐藏和重写class Vehicle{private int _speed;private virtual int Speed{get { return _speed; }set { _speed = value; }}public virtual void Run() {//虚函数 -- 可被重写的 -- 名存实亡Console.WriteLine("I'm running");_speed = 100;}}class Car : Vehicle {private int _rpm;public override int Speed {get { return _rpm / 100; }set { _rpm = value * 100; } }public override void Run() {Console.WriteLine("Car is running!");_rpm = 5000;}}class RaseCar : Car {public override void Run(){Console.WriteLine("Rase car is running");}}
}属性成员也是可以被重写的
类的继承
- 类成员的“横向扩展”(成员越来越多)
- 类成员的“纵向扩展”(行为改变,版本增高)
- 类成员的隐藏(不常用)
- 重写与隐藏发生条件:函数成员,可见,签名一致
多态
基于重写机制(virtual —> override)
函数成员的具体行为(版本)由对象决定
回顾:c#语言的变量和对象都是有类型的,所以会有”代差“
多态
当谈到多态时,通常是指在继承关系中,父类的引用可以指向子类的对象,并且根据实际对象的类型来调用相应的方法。这样可以实现不同对象的统一处理,提高代码的灵活性和可扩展性。
pycharm
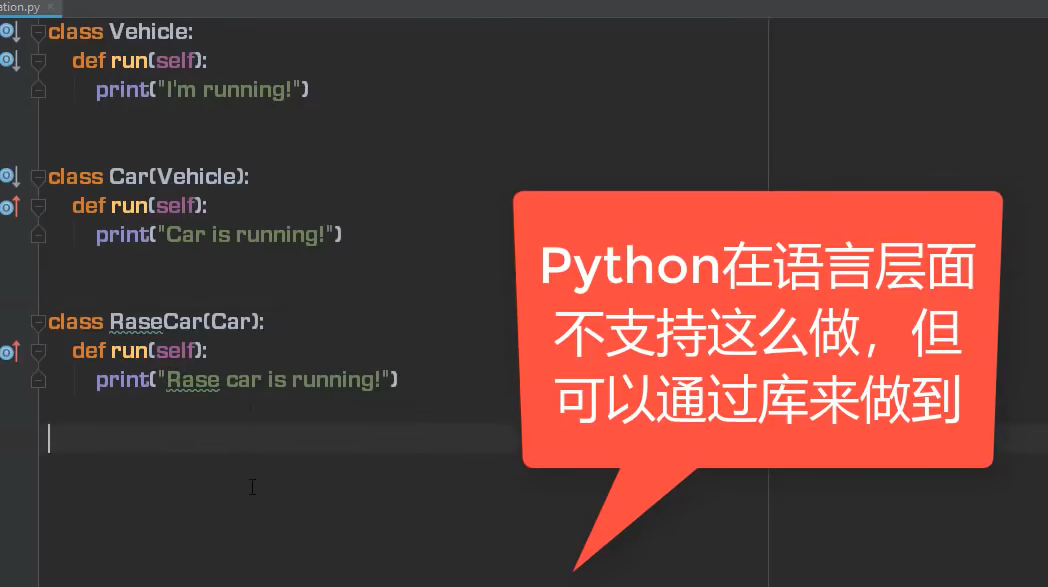
抽象类和接口
为做基类而生的“抽象类”与“开放/关闭原则”

什么是抽象类
定义:抽象类是一种不能被实例化的类,其中可以包含抽象成员(方法、属性),子类必须实现这些抽象成员才能被实例化。
特点:抽象类可以包含普通成员和抽象成员,子类必须实现所有的抽象成员才能实例化。
用途:抽象类通常用于定义一些通用的行为或属性,以便让子类共享这些行为或属性。
一个类里如果有抽象方法或者抽象成员时,那么这个类也要被abstract修饰
抽象类是专门做基类而生
代码解释
using System;
using System.Collections.Concurrent;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
using System.Security.Permissions;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Timers;
using System.Threading;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){var vb=new Vechicle();//会报错,因为抽象类不能创建实例var car=new Car();var rcar=new RaceCar();}}abstract class VechicleBase//纯虚类(全都是抽象成员){abstract public void Work();abstract public void Stop();abstract public void AddOil();}abstract class Vehicle : VechicleBase//由于继承的抽象类中只完成了两个方法,还有一个抽象方法被继承下来,因此此类//还需要被abstract修饰{public override void AddOil()//注意也要用override修饰{Console.WriteLine("Add and Fill");}public override void Stop(){Console.WriteLine("Stopped!");}}class Car : Vehicle//完成了所有的方法,没有抽象方法,因此不需要被abstract修饰{public override void Work(){Console.WriteLine("this car is working");}}class RaceCar : Vehicle{public override void Work(){Console.WriteLine("this racecar is working");}}
}
接口
定义:接口是一种抽象类型,其中只包含成员的声明,而没有实现。类可以实现一个或多个接口,实现接口的类必须实现接口中定义的所有成员。
特点:接口只包含成员的声明,不包含实现。类可以实现多个接口,但只能继承一个类。
用途:接口用于定义类应该具有的行为,使得不同类可以共享相同的接口。
using System;
using System.Collections.Concurrent;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
using System.Security.Permissions;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Timers;
using System.Threading;
using System.IO.Ports;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){var car = new Car();var rcar = new RaceCar();}}interface VechicleBase//纯虚类也可用接口实现{//要求成员都被abstract public 修饰,因此就不需要在声明时用abstract public修饰void Work();void Stop();void AddOil();}abstract class Vehicle : VechicleBase{public void Stop(){Console.WriteLine("Stopped!");}public void AddOil()//注意此时不要用override修饰(注意和抽象区分,抽象的要加override),但可以用virtual修饰,以便可以被子类修改{Console.WriteLine("Add and Fill");}abstract public void Work();//保留一个为实现的方法,让子类去实现,因此需要用abstract修饰}class Car : Vehicle//完成了所有的方法,没有抽象方法,因此不需要被abstract修饰{public override void Work()//用override修饰,因为基类Vehicle中Work用了abstract修饰{Console.WriteLine("this car is working");}}class RaceCar : Vehicle{public override void Work(){Console.WriteLine("this racecar is working");}}
}
接口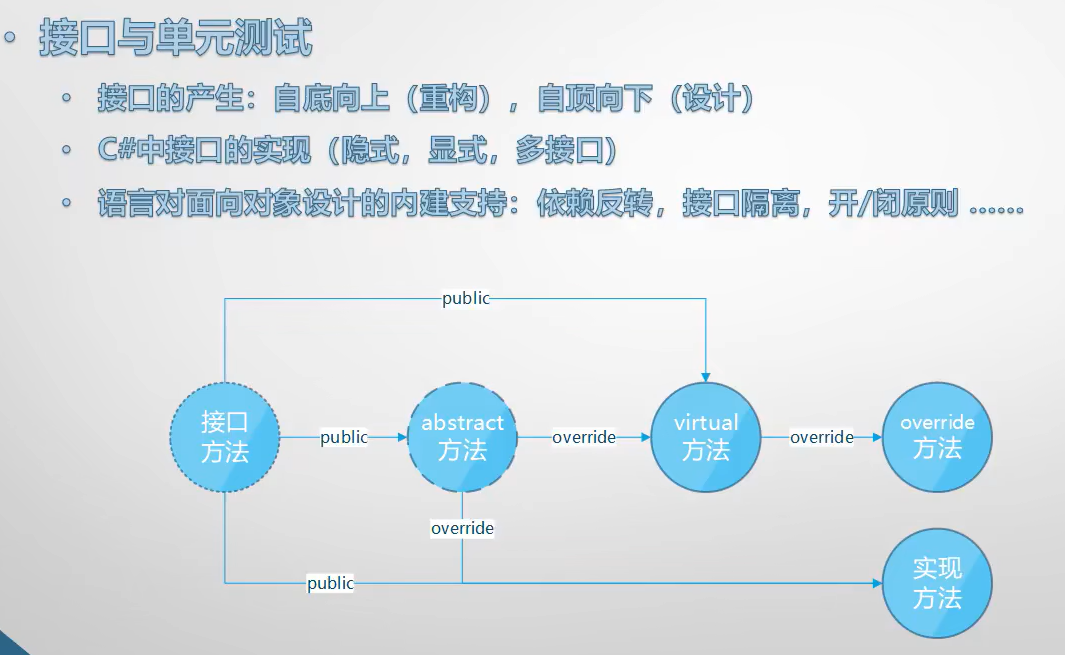
代码演示
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace InterfaceExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){//供方int[] nums1 = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };ArrayList nums2 = new ArrayList{ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };Console.WriteLine(Sum(nums1));Console.WriteLine(Avg(nums1));Console.WriteLine(Sum(nums2));Console.WriteLine(Avg(nums2));}//接口的使用//需方static int Sum(IEnumerable nums){int sum = 0;foreach (var n in nums) sum += (int)n;return sum;}static double Avg(IEnumerable nums){int sum = 0; double count = 0;foreach (var n in nums) { sum += (int)n; count++; }//强制类型转换return sum / count;//平均值}}
}使用接口的好处:
实现多态性:接口可以定义一组方法的规范,不同的类可以实现相同的接口并提供自己的实现。这样,可以通过接口类型引用对象,实现不同对象之间的统一访问方式,从而实现多态性。解耦:接口可以将接口定义和实现分离,使得类之间的耦合度降低。当一个类实现了某个接口,只需要关注接口规定的方法,而不需要关心具体的实现细节。增加灵活性:通过接口,可以在不改变类的继承关系的情况下,为类添加额外的功能。一个类可以实现多个接口,从而获得不同接口的功能。统一规范:接口可以定义一组规范,让不同的类都实现这些规范,从而保证这些类具有相同的行为。这样可以提高代码的可读性和可维护性。便于扩展:当需要为一个类添加新的功能时,可以通过实现新的接口来扩展该类的功能,而不需要修改原有的类结构。
紧耦合
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace InterfaceExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){var engine = new Engine();var car = new Car(engine);car.Run(3);Console.WriteLine(car.Speed);}}class Engine{public int PRM { get; private set; }public void Work(int gas){this.PRM = 1000 * gas;}}class Car{ private Engine _engine;public Car(Engine engine){_engine = engine;}public int Speed { get; private set; }public void Run(int gas){_engine.Work(gas);this.Speed = _engine.PRM / 100;}}
}代码随记
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace InterfaceExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){var user = new PhoneUser(new NokiaPhone());user.UsePhone();//NokiaPhone//解耦合可替换//我的一个理解:把接口看成父类,用父类类型的变量去引用子类的实例,实现类似多态的效果(从已学内容迁移,逻辑不严谨勿喷) var user1 = new PhoneUser(new EricssonPhone());user1.UsePhone();}}//接口interface IPhone{void Dail();void PickUp();void Send();void Receive();}//创建类class PhoneUser{private IPhone _phone;public PhoneUser(IPhone phone){_phone = phone;}public void UsePhone(){_phone.Dail();_phone.PickUp();_phone.Send();_phone.Receive();}}class NokiaPhone : IPhone{public void Dail(){Console.WriteLine("Nokia calling,,,");}public void PickUp(){Console.WriteLine("Hello! This is Tim!");}public void Receive(){Console.WriteLine("Ericsson ring,,,");}public void Send(){Console.WriteLine("Good evering...");}}class EricssonPhone : IPhone{public void Dail(){Console.WriteLine("Ericsson calling,,,");}public void PickUp(){Console.WriteLine("Hello! This is Tim!");}public void Receive(){Console.WriteLine("Ericsson ring,,,");}public void Send(){Console.WriteLine("Good evering...");}}
}自顶向下,逐步求精
设计模式
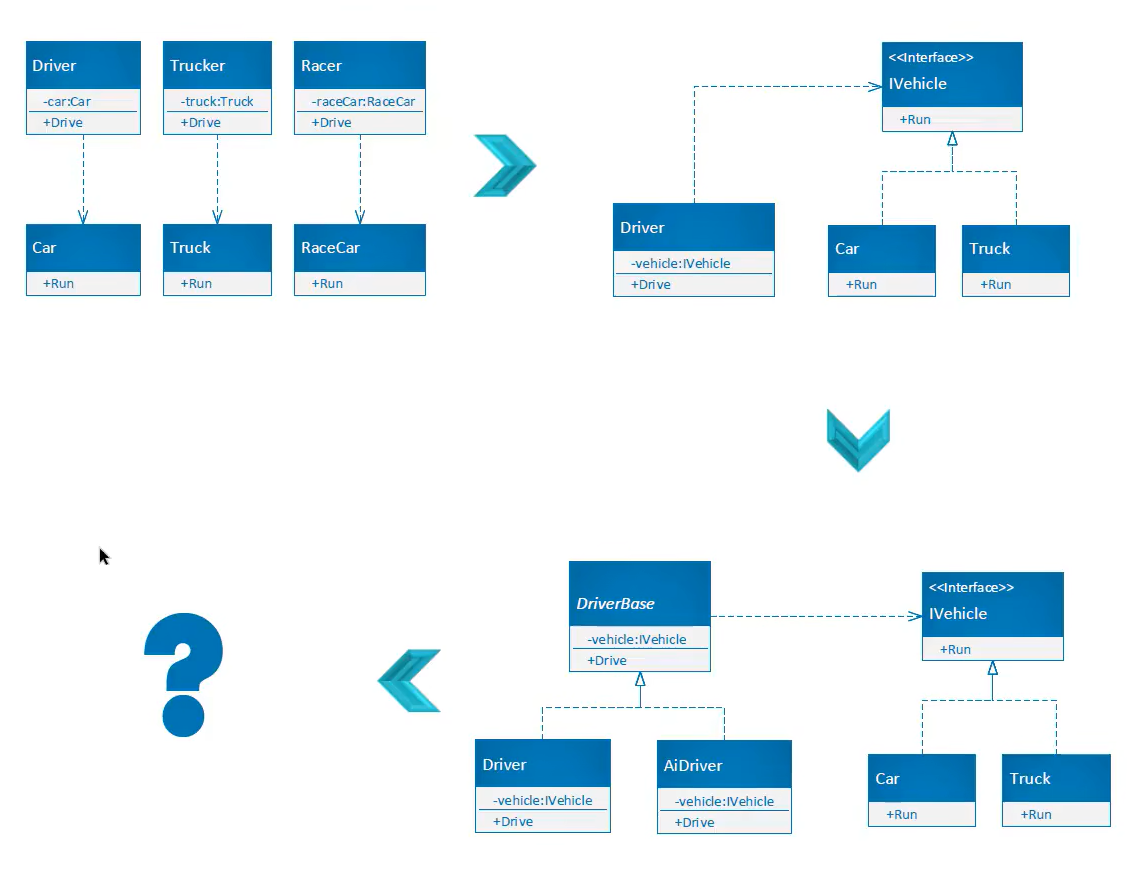
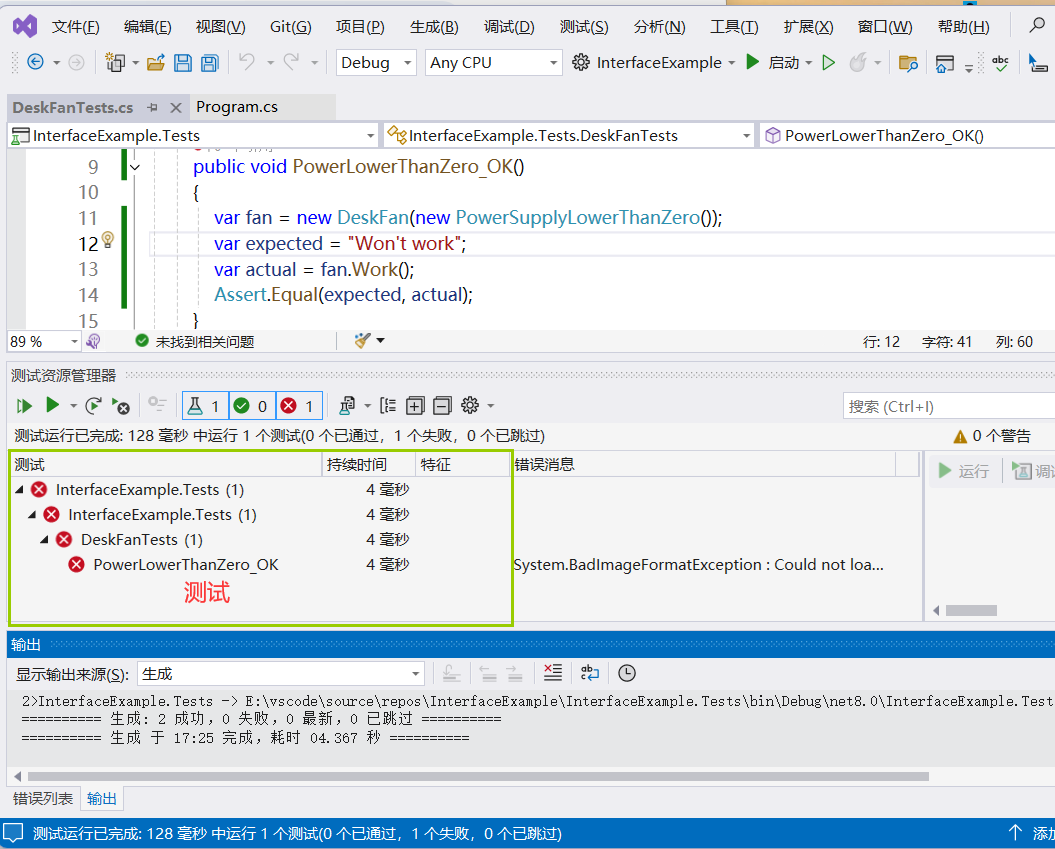
using Microsoft.VisualStudio.TestTools.UnitTesting;
using System;namespace InterfaceExample.Tests
{public class DeskFanTests{[Fact]public void PowerLowerThanZero_OK(){var fan = new DeskFan(new PowerSupplyLowerThanZero());var expected = "Won't work";var actual = fan.Work();Assert.Equals(expected, actual);}}class PowerSupplyLowerThanZero : IPowerSupply{public int GetPower(){return 0;}}
}
依赖反转 接口在单元测试中的应用
主程序
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace InterfaceExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){var fan = new DeskFan(new PowerSupply());Console.WriteLine(fan.Work());}}//解耦接口public interface IPowerSupply{int GetPower();}public class PowerSupply:IPowerSupply{public int GetPower(){return 0;//标准电源}}//电扇public class DeskFan{private IPowerSupply _powerSupply;public DeskFan(IPowerSupply powerSupply){_powerSupply = powerSupply;}public string Work(){int power = _powerSupply.GetPower();if (power <=0){return "Won't work.";}else if (power < 100){return "Slow";}else if (power < 200){return "Work fine";}else{return "Warning";}}}
}单元测试
using Microsoft.VisualStudio.TestTools.UnitTesting;
using System;
using System.ComponentModel;namespace InterfaceExample.Tests
{[TestClass]//特征public class DeskFanTest{[TestMethod]//特征public void PowerLowerThanZero_OK(){var fan = new DeskFan(new PowerSupplyLowerThanZero());var expected = "Won't work.";var actual = fan.Work();Assert.AreEqual(expected, actual);}[TestMethod]public void PowerHigherThan200_Warning(){var fan = new DeskFan(new PowerSupplyHigherThan200());var expected = "Warning";var actual = fan.Work();Assert.AreEqual(expected, actual);}}class PowerSupplyLowerThanZero : IPowerSupply{public int GetPower(){return 0;}}class PowerSupplyHigherThan200 : IPowerSupply{public int GetPower(){return 220;}}
}改进测试单元 省空间–费时间

重载virtual搭配override使用,抽象类用virtual修饰方法,子类重载用override
接口隔离
以下将会用三个例子来讲述接口隔离的用法
例子一
第一个例子,一对夫妻,妻子开车把车开坏了,那怎么办呢,丈夫就给妻子买了一个坦克,不仅开不坏,开能开炮,妻子学会了开坦克,但不能忘了开车对吧,下面的代码就会出现妻子会开坦克忘记怎么开车的情形
代码演示:
using System;
using System.Xml.Serialization;namespace IspExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){var driver = new Driver(new Car());var driver1 = new Driver(new HeavyTank());driver1.Drive();//new Car()在内存创建了Car类型实例,传参给IVehicle类型形参,即将Car实例地址传给IVehicle类型变量,又因Car为IVehicle的子类,满足里式转换。driver.Drive();}}class Driver{private Ivehicle _vehicle;public Driver(Ivehicle vehicle){_vehicle = vehicle;}public void Drive(){_vehicle.Run();}}interface Ivehicle{void Run();}class Car : Ivehicle{public void Run(){Console.WriteLine("Car is running...");}}class Truck : Ivehicle{public void Run(){Console.WriteLine("Truck is running...");}}interface ITank:Ivehicle,Iw{void Fire();void Run();}class LightTank : ITank{public void Fire(){Console.WriteLine("Boom!");}public void Run(){Console.WriteLine("Ka ka ka ...");}}class MediumTank : ITank{public void Fire(){Console.WriteLine("Boom!!");}public void Run(){Console.WriteLine("Ka! ka! ka !...");}}class HeavyTank : ITank{public void Fire(){Console.WriteLine("Boom!!!");}public void Run(){Console.WriteLine("Ka!! ka!! ka !!...");}}
}使用接口隔离的优点(代码解释)
using System;
using System.Xml.Serialization;namespace IspExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){var driver = new Driver(new Car());var driver1 = new Driver(new HeavyTank());driver1.Drive();//new Car()在内存创建了Car类型实例,传参给IVehicle类型形参,即将Car实例地址传给IVehicle类型变量,又因Car为IVehicle的子类,满足里式转换。driver.Drive();}}class Driver{private Ivehicle _vehicle;public Driver(Ivehicle vehicle){_vehicle = vehicle;}public void Drive(){_vehicle.Run();}}interface Ivehicle{void Run();}class Car : Ivehicle{public void Run(){Console.WriteLine("Car is running...");}}class Truck : Ivehicle{public void Run(){Console.WriteLine("Truck is running...");}}interface IWeapon{void Fire();//开炮...}interface ITank:Ivehicle,IWeapon {//一个类只能有一个基类,但一个接口可以有多个基接口,//因此一个类就能有多个接口}class LightTank : ITank{public void Fire(){Console.WriteLine("Boom!");}public void Run(){Console.WriteLine("Ka ka ka ...");}}class MediumTank : ITank{public void Fire(){Console.WriteLine("Boom!!");}public void Run(){Console.WriteLine("Ka! ka! ka !...");}}class HeavyTank : ITank{public void Fire(){Console.WriteLine("Boom!!!");}public void Run(){Console.WriteLine("Ka!! ka!! ka !!...");}}
}例子二
第二个例子:传给调用者的大接口由多个原本设计很好的小接口合并而来,例如Trunk是由IWeapon和IVehicle合并而来的,本来要传一个小接口进来,最后传进了一个大接口,这就有可能把原来合格的提供者挡在门外
把Driver的字段类型IVehicle改为ITank的话,构造器里面的参数类型也要改成ITank类型,这时能够作为类型服务者的类只有三个lightITank,MediumTank ,HeavyTank. 而Car和Trunk类型的实例被拒之门外了。

例子
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
using System.Security.Policy;namespace IspExample2
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){int[] nums1 = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };ArrayList nums2 = new ArrayList() { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };var nums3 = new ReadOnlyCollection(nums1);Console.WriteLine(Sum(nums1));Console.WriteLine(Sum(nums2));Console.WriteLine(Sum(nums3));//有点类似与金字塔形状,这个设计微软分为了好几层,也是因为这个接口的命名就容易让人产生误解,理解起来就有点绕。//第二层 中间层 IEnumerator 是属于对内约束的接口 或则说内层 他要求能够被迭代的类下 你想以怎样的逻辑方式去迭代 是具体方法的实现//第三层 底层 以此下推 需要一个能实现IEnumerator接口的内部类 去实现IEnumerator中写好的具体方法 (至于为何要是内部类,我理解应该是为了封装,也是一种设计原则)//第三层 底层 以此下推 需要一个能实现IEnumerator接口的内部类 去实现IEnumerator中写好的具体方法 (至于为何要是内部类,我理解应该是为了封装,也是一种设计原则)}//求和static int Sum(IEnumerable nums){int sum = 0;foreach (var n in nums){sum += (int)n;}return sum;}class ReadOnlyCollection : IEnumerable{private int[] _array;public ReadOnlyCollection(int[] array){_array = array;}public IEnumerator GetEnumerator(){return new Enumerator(this);}//成员类public class Enumerator : IEnumerator{private ReadOnlyCollection _collection;private int _head;public Enumerator(ReadOnlyCollection collection){_collection = collection;_head = -1;}public object Current{get{object o = _collection._array[_head];return o;}}public bool MoveNext(){if (++_head < _collection._array.Length){return true;}else{return false;}}public void Reset(){throw new NotImplementedException();}}}}
}第二个开胃菜
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace IspExample3
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){IKiller killer = new WarmKiller();killer.Kill();//例子不是表达写了显式 人就能去调用。 这是隐藏封装的概念,像例子里Kill的方法不能在大街上就别人看见,直到收到任务时你自己显式的去调用//var wk = killer as WarmKiller;//gentleman方法var wk = (WarmKiller)killer;//强制类型转化wk.Love();}}interface IGentleman{void Love();}interface IKiller{void Kill();}class WarmKiller : IGentleman, IKiller{public void Love(){Console.WriteLine("I will love you for ever ...");}void IKiller.Kill()//显示的实现,只有把这个类的实例当做IKiller类的实例来用的时候// 换句话说,只有我们拿一个IKiller类型变量来引用WarmKiller类型实例的时候,这个方法才能够被调用{Console.WriteLine("Let me kill the enemy ...");}}
}简单了解一下依赖
using System;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Xml.Serialization;namespace IspExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){ITank tank = new HeavyTank();// =============华丽的分割线========var t = tank.GetType();object o = Activator.CreateInstance(t);MethodInfo fireMi = t.GetMethod("Fire");MethodInfo runMi = t.GetMethod("Run");fireMi.Invoke(o,null);runMi.Invoke(o, null);}}class Driver{private Ivehicle _vehicle;public Driver(Ivehicle vehicle){_vehicle = vehicle;}public void Drive(){_vehicle.Run();}}interface Ivehicle{void Run();}class Car : Ivehicle{public void Run(){Console.WriteLine("Car is running...");}}class Truck : Ivehicle{public void Run(){Console.WriteLine("Truck is running...");}}interface IWeapon{void Fire();//开炮...}interface ITank:Ivehicle,IWeapon {//一个类只能有一个基类,但一个接口可以有多个基接口,//因此一个类就能有多个接口}class LightTank : ITank{public void Fire(){Console.WriteLine("Boom!");}public void Run(){Console.WriteLine("Ka ka ka ...");}}class MediumTank : ITank{public void Fire(){Console.WriteLine("Boom!!");}public void Run(){Console.WriteLine("Ka! ka! ka !...");}}class HeavyTank : ITank{public void Fire(){Console.WriteLine("Boom!!!");}public void Run(){Console.WriteLine("Ka!! ka!! ka !!...");}}
}反射:依赖注入

依赖程序包
什么是反射
反射(Reflection)是一种强大的机制,允许程序在运行时获取类型的信息、访问和操作程序集中的成员(如字段、属性、方法等),以及动态创建对象和调用方法。反射可以让程序在运行时动态地探查、调用和修改程序的结构。通过反射,可以实现以下功能:获取类型信息:可以通过反射获取类型的信息,如类的名称、命名空间、基类、接口、字段、属性、方法等。
创建对象:可以通过反射动态创建对象,无需在编译时知道具体类型。
调用方法和属性:可以通过反射调用对象的方法和属性,包括公共和非公共成员。
修改字段和属性:可以通过反射修改对象的字段和属性的值。
动态加载程序集:可以在运行时动态加载和使用程序集。
反射在以下场景中非常有用:框架和库的设计:可以通过反射实现插件机制,动态加载和调用插件。
序列化和反序列化:可以通过反射实现对象的序列化和反序列化。
单元测试:可以通过反射实现测试框架,动态调用测试方法。
虽然反射提供了很大的灵活性,但由于其性能相对较低,应该谨慎使用,避免过度使用反射导致性能问题。在实际应用中,应根据具体需求和场景来选择是否使用反射。
代码演示
using System;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Xml.Serialization;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;namespace IspExample
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){var sc = new ServiceCollection();//依赖注入,改一处就可以sc.AddScoped(typeof(ITank), typeof(HeavyTank));//ITank是静态类型,而typeof(ITank)是动态类型sc.AddScoped(typeof(Ivehicle), typeof(Car));sc.AddScoped<Driver>();var sp = sc.BuildServiceProvider();// ============= 华丽的分割线==========//ITank tank = sp.GetService<ITank>();//tank.Fire();//tank.Run();var driver = sp.GetService<Driver>();driver.Drive();}}class Driver{private Ivehicle _vehicle;public Driver(Ivehicle vehicle){_vehicle = vehicle;}public void Drive(){_vehicle.Run();}}interface Ivehicle{void Run();}class Car : Ivehicle{public void Run(){Console.WriteLine("Car is running...");}}class Truck : Ivehicle{public void Run(){Console.WriteLine("Truck is running...");}}interface IWeapon{void Fire();//开炮...}interface ITank:Ivehicle,IWeapon {//一个类只能有一个基类,但一个接口可以有多个基接口,//因此一个类就能有多个接口}class LightTank : ITank{public void Fire(){Console.WriteLine("Boom!");}public void Run(){Console.WriteLine("Ka ka ka ...");}}class MediumTank : ITank{public void Fire(){Console.WriteLine("Boom!!");}public void Run(){Console.WriteLine("Ka! ka! ka !...");}}class HeavyTank : ITank{public void Fire(){Console.WriteLine("Boom!!!");}public void Run(){Console.WriteLine("Ka!! ka!! ka !!...");}}
}最后一节课!!!!!!!!
泛型适用于很多,如下
类型膨胀
此时出现了一个问题:类型膨胀
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace HelloGeneric
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Apple apple = new Apple() { Color = "Red" };AppleBox box = new AppleBox() { Cargo = apple };Console.WriteLine(box.Cargo.Color);//拿一本书Book book = new Book() { Name = "New Book" };BookBox bookBox = new BookBox() { Cargo = book };Console.WriteLine(bookBox.Cargo.Name);//现在代码已经出现问题了,类型膨胀}}class Apple{public string Color { get; set; }}class Book{public string Name { get; set; }}class AppleBox//盒子里边的货物{public Apple Cargo { get; set; }}class BookBox{public Book Cargo { get; set; }}
}成员膨胀
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace HelloGeneric
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Apple apple = new Apple() { Color = "Red" };Book book = new Book() { Name = "New Book" };Box box1 = new Box() { Apple = apple };Box box2 = new Box() { Book = book };//成员膨胀}}class Apple{public string Color { get; set; }}class Book{public string Name { get; set; }}//一个盒子class Box{public Apple Apple { get; set; }public Book Book { get; set; }//...}}泛型(完美解决上述困扰)

泛型类
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace HelloGeneric
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Apple apple = new Apple() { Color = "Red" };Book book = new Book() { Name = "New Book" };Box<Apple> box1 = new Box<Apple>() { Cargo = apple };Box<Book> box2 = new Box<Book>() { Cargo = book };//泛型类在经过特化之后,它里面凡是使用到类型参数的地方都是强类型的Console.WriteLine(box1.Cargo.Color);Console.WriteLine(box2.Cargo.Name);}}class Apple{public string Color { get; set; }}class Book{public string Name { get; set; }}//一个盒子class Box<TCargo>//泛型,作为一种临时的数据类型{public TCargo Cargo { get; set; }}
}泛型接口
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace HelloGeneric
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Student<ulong> student = new Student<ulong>();student.ID = 100000000000001;student.Name = "Yaqi";Console.WriteLine(student.Name);}}interface IUnique<TId>{TId ID { get; set; }}class Student<TId> : IUnique<TId>{public TId ID { get; set; }public string Name { get; set; }}
}
接口二:这个类在继承泛型接口的时候就指定了接口类型
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace HelloGeneric
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Student student = new Student();student.ID = 1000000000001;}}interface IUnique<TId>{TId ID { get; set; }}class Student: IUnique<ulong>//实现接口时就把泛型的类型特化掉{public ulong ID { get; set; }}
}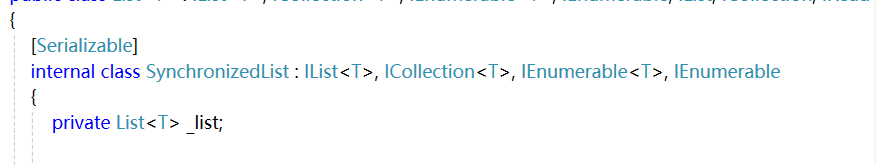
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;namespace HelloGeneric
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){//左边的IList<>是接口,右边的List实现了这个接口//接口必须通过接口实现类对象 对象来使用List<int> list = new List<int>();for(int i = 1; i <= 100; i++)//打印1--100{list.Add(i);}foreach(var item in list){Console.WriteLine(item);}}}
}
带有不止一个类型参数的泛型接口和泛型类
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;namespace HelloGeneric
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){//带有不止一个类型参数的泛型接口和泛型类IDictionary<int, string> dict = new Dictionary<int, string>();dict[1] = "Yaqi";dict[2] = "Qq";Console.WriteLine($"Student #1 is{dict[1]}");Console.WriteLine($"Student #2is{dict[2]}");}}}泛型方法
泛型方法在调用时的类型参数的自动推断
把这两个数组合并到一起
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;namespace HelloGeneric
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){int[] a = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };int[] b = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };double[] aa = { 1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.5, 5.5 };double[] bb = { 1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.5, 5.5, 6.66 };var result = Zip(a, b);//泛型方法在调用时候的类型参数的自动推断Console.WriteLine(string.Join(",", result));var result1 = Zip(aa, bb);Console.WriteLine(string.Join(",", result1));}static T[] Zip<T>(T[] a, T[] b) // a or b not null{T[] zipped = new T[a.Length + b.Length];int ai = 0, bi = 0;int zi = 0;do{if (ai < a.Length) zipped[zi++] = a[ai++];if (bi < b.Length) zipped[zi++] = b[bi++];} while (ai < a.Length || bi < b.Length);return zipped;}}}泛型委托
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;namespace HelloGeneric
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Action<string> a1 = Say;a1.Invoke("Yaqi");//使用委托 -- 间接调用Action<int> a2 = Mul;a2(1);//Hello,Yaqi//100Func<double, double, double> func1 = Add;var result1 = func1(100.1, 200.2);Console.WriteLine(result1);//lambda表达式就是简化代码Func<double, double, double> func2 = (double a, double b) => { return a + b; };//简化//Func<double, double, double> func2 = (a,b) => { return a + b; };var result2 = func1(100.1, 200.2);Console.WriteLine(result2);}//泛型委托static void Say(string str){Console.WriteLine($"Hello,{str}");}static void Mul(int x){Console.WriteLine(x*100);}static int Add(int a,int b){return a + b;}static double Add(double a,double b){return a + b;}}
}部分类
在C#中,部分类(Partial Classes)是一种允许将一个类的定义分散在多个文件中的特性。通过部分类,可以将一个类的定义拆分成多个部分,每个部分可以位于不同的文件中,便于组织和管理大型类。部分类允许将一个类的定义分成多个部分,每个部分使用partial关键字进行标记。所有部分类的定义必须处于同一个命名空间中。当编译器编译时,会将所有部分类的定义合并为一个完整的类。
枚举类型
- 人为限定取值范围的整数
- 整数值的对应
- 比特位式用法
什么是枚举类型
枚举类型是一种数据类型,用于定义一个变量只能取特定值中的一个。在许多编程语言中,枚举类型允许程序员定义一组命名的常量,这些常量在程序中可以被使用。枚举类型通常用于表示一组相关的常量或选项,以便代码更易读且更易维护。
枚举类型的bit位用法
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data.SqlTypes;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace HelloEnum
{internal class Program{public static void Main(string[] args){Person person = new Person();person.Level = Level.Employee;Person boss = new Person();boss.Level = Level.Boss;Person student = new Person();student.Level = Level.Student;student.Name = "Yaqi";//比特位式用法student.Skill = Skill.Drive | Skill.Cook | Skill.Program | Skill.Teach;Console.WriteLine((student.Skill&Skill.Cook) ==Skill.Cook);//TrueConsole.WriteLine(boss.Level>person.Level); // TrueConsole.WriteLine(Level.Employee); //EmployeeConsole.WriteLine(Level.Manager);Console.WriteLine(Level.Boss);Console.WriteLine(Level.BigBoss);Console.WriteLine((int)Level.Employee); //0Console.WriteLine((int)Level.Manager); //1Console.WriteLine((int)Level.Boss); //2Console.WriteLine((int)Level.BigBoss); //3}}enum Level {//未赋值的情况下Student,Employee=100, //0 复制100Manager, //1 101//显示设置后面依次递增,遇到新的显示设置又开始新递增Boss = 300, //2 复制300BigBoss , //3 301}enum Skill{Drive =1,Cook = 2,Program = 4,Teach = 8,}class Person{public int ID { get; set; }public string Name { get; set; }public Level Level { get; set; }public Skill Skill { get; set; }}
}结构体
- 值类型,可装/拆箱
- 可实现接口,不能派生自类/结构体
- 不能有显示无参构造器
- 结构体没有自己的基类,不能由其他结构体类型或者类类型派生而来
什么是结构体
结构体(Struct)是一种用户自定义的数据类型,用于组合不同类型的数据成员。结构体允许程序员将多个相关的数据字段打包在一起,以便作为一个单独的实体进行处理。在许多编程语言中,结构体通常用于表示一种自定义的数据结构,其成员可以包含不同的数据类型,但没有方法。
结构体和类的区别
定义方式:结构体(Struct)通常用于定义轻量级的数据结构,其成员变量可以包含不同的数据类型,但没有方法。
类(Class)用于定义更复杂的数据结构,可以包含成员变量和方法。
默认访问修饰符:结构体的成员变量默认为public,可以直接访问。
类的成员变量默认为private,需要通过方法来访问。
继承:类支持继承,一个类可以派生出子类,子类可以继承父类的成员变量和方法。
结构体不支持继承。
内存分配:结构体是值类型,它们在栈上分配内存,赋值时是复制整个对象。
类是引用类型,它们在堆上分配内存,赋值时是复制对象的引用。
实例化:结构体可以直接实例化,不需要使用new关键字。
类需要使用new关键字来实例化对象。
代码演示
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data.SqlTypes;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace HelloEnum
{internal class Program{public static void Main(string[] args){Student stu1= new Student() { ID = 101, Name = "Q" };//装箱:把值类型的值在堆内存中开辟空间,存入值,然后把堆内存地址的二进制给引用变量//object obj = stu1;//开箱//Student stu2 = (Student) obj;//Console.WriteLine($"#{stu2.ID} Name:{stu2.Name}");//如果是引用类型,stu1是new了一个实例,而stu2是通过stu1赋值的,那么就是将stu1的地址传给了stu2,通过stu2可以改变stu1的值。Student stu2 = stu1;stu1.ID = 1001;stu2.Name = "q";//Console.WriteLine($"#{stu2.ID} Name:{stu2.Name}");stu1.Speak();Student student = new Student(1, "Yaqi");student.Speak();}}interface ISpeak{void Speak();}//结构体//结构体类型不能够拥有显示的无参构造器/*public Student(){}*/struct Student:ISpeak{//public Student() {} -- 显示的无参构造器public Student(int id, string name){this.ID = id;this.Name = name;}public int ID { get; set; }public string Name { get; set; }public void Speak(){Console.WriteLine($"I'm #{this.ID} student {this.Name}");}}}相关文章:

B站C#刘铁猛笔记
C#——刘铁猛笔记 类、名称空间(简述) 类(class)是构成程序的主体 名称空间(namespace)以树形结构组织类(其他类型) 名称空间:名称空间是用来组织和管理类、接口、结构…...

如何使用信号发生器产生正弦波并用数字示波器进行测量
使用信号发生器产生正弦波并用数字示波器进行测量的步骤如下: 1. 准备工作 所需设备 信号发生器数字示波器探头(通常为10X衰减探头)BNC电缆和适配器(如果需要) 2. 设置信号发生器 连接 使用BNC电缆将信号发生器的…...
XJ04、消费金融|授信基本概念及其流程设计
银行是经营风险的特殊行业,而银行授信则与银行业务和风险天然相伴。它是银行与客户建立业务关系的起点,也是银行风险管理的关键环节和核心要素。若要了解银行业务,就得先了解银行的授信业务;若要理解银行经营,就得先理…...

儿童预防接种预约微信小程序springboot+论文源码调试讲解
2相关技术 2.1微信小程序 小程序是一种新的开放能力,开发者可以快速地开发一个小程序。小程序可以在微信内被便捷地获取和传播,同时具有出色的使用体验。尤其拥抱微信生态圈,让微信小程序更加的如虎添翼,发展迅猛。 2.2 MYSQL数据…...

nginx 修改配置
如果你的后端服务在不同的端口上运行,但静态资源访问路径相同,你可以使用 Nginx 的 location 配置来将请求转发到不同的后端服务,同时处理静态文件。这里有几种常见的方式: 方案 1: 基于路径的配置 如果所有服务的静态资源路径相…...

孤岛架构在安全性方面
孤岛架构在安全性方面的考虑主要涉及如何确保每个孤岛的安全性,同时维护整个系统的安全。 关键的安全性考虑: 1. 数据隔离和访问控制 数据隔离:每个孤岛应该有独立的数据存储,以确保数据隔离。这有助于防止数据泄露和未经授权的…...

COSCon'24 志愿者招募令:共创开源新生活!
亲爱的开源爱好者们, 第九届中国开源年会(COSCon24)即将在北京中关村国家自主创新示范区会议中心于2024年11月2日至3日隆重举行。今年的主题是“Open Source, Open Life|开源新生活”,旨在探索开源技术如何在各个领域推…...

vscode使用make编译c的问题
问题1:makefile:2: *** missing separator. Stop vscode的配置问题,看这哥们的文章即可:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_57464986/article/details/134220676 问题2:创建makefile文件 直接创建文件名为“makefile”的文件即可&#x…...

管家婆财贸ERP BB019.操作员制单日期控制
最低适用版本: 财贸系列 20.0 插件简要功能说明: 定制操作员权限功能,根据服务器日期控制系统单据新增和修改更多细节描述见下方详细文档 插件操作视频: 进销存类定制插件--操作员制单日期控制 插件详细功能文档: …...

从 Vue 2 到 Vue 3:全面升级指南
🌈个人主页:前端青山 🔥系列专栏:Vue篇 🔖人终将被年少不可得之物困其一生 依旧青山,本期给大家带来Vuet篇专栏内容:Vue-从 Vue 2 到 Vue 3:全面升级指南 前言 随着前端技术的不断发展,Vue.j…...

Apache paimon表操作实战-5
维表Join Paimon支持Lookup Join语法,它用于从 Paimon 查询的数据来补充维度字段。要求一个表具有处理时间属性,而另一个表由查找源连接器支持。 Paimon 支持 Flink 中具有主键的表和append-only的表查找联接。以下示例说明了此功能。 USE CATALOG fs_catalog; CREATE TABL…...

阿里云用STS上传oss的完整程序执行流程图 和前端需要哪些参数uniapp
H5 微信小程序可用的前端直传阿里云OSS(STS临时凭证前端签名)直接下载插件 下面是原理说明: 明白了,我来详细说明前端上传文件到阿里云OSS需要携带的具体参数: 从服务器获取的 STS 凭证: // 这些参数需要从你的后端服务器获…...

决策树方法根据指定条件筛选方案
代码功能说明 条件类:Condition 类用于定义每个条件的范围,并提供一个方法 is_satisfied 来检查输入值是否满足该条件。 算法选择器类:AlgorithmSelector 类负责应用条件并记录不满足的条件。它提供方法 apply_condition 用于更新可用算法&a…...

多特征变量序列预测(四) Transformer-BiLSTM风速预测模型
往期精彩内容: 时序预测:LSTM、ARIMA、Holt-Winters、SARIMA模型的分析与比较 全是干货 | 数据集、学习资料、建模资源分享! EMD、EEMD、FEEMD、CEEMD、CEEMDAN的区别、原理和Python实现(一)EMD-CSDN博客 EMD、EEM…...

【开源免费】基于SpringBoot+Vue.JS蜗牛兼职平台 (JAVA毕业设计)
本文项目编号 T 034 ,文末自助获取源码 \color{red}{T034,文末自助获取源码} T034,文末自助获取源码 目录 一、系统介绍1.1 平台架构1.2 管理后台1.3 用户网页端1.4 技术特点 二、演示录屏三、启动教程四、功能截图五、文案资料5.1 选题背景…...

Ajax笔记
介绍 Ajax是一种网页开发技术,全称是Asynchronous JavaScript and XML(异步JavaScript和XML)。作用如下: 数据交换:可以通过Ajax给服务器发送请求,并获取服务器响应的数据。即前端动态的发送Ajax到服务器端…...

软考:缓存分片和一致性哈希
缓存分片技术是一种将数据分散存储在多个节点上的方法,它在分布式缓存系统中尤为重要。这项技术的核心目的是提高系统的性能和可扩展性,同时确保数据的高可用性。以下是缓存分片技术的一些关键点: 数据分片:缓存分片涉及将数据分成…...

3109 体验积分值
经验值:1200 时间限制:1000毫秒 内存限制:128MB 合肥市第34届信息学竞赛(2017年) 不许抄袭,一旦发现,直接清空经验! 题目描述 Description 卡卡西和小朋友们做完了烧脑的数字游…...

初识jsp
学习本章节前建议先安装Tomcat web服务器:tomcat下载安装及配置教程_tomcat安装-CSDN博客 1、概念 我的第一个JSP程序: 在WEB-INF目录之外创建一个index.jsp文件,然后这个文件中没有任何内容。将上面的项目部署之后,启动服务器…...

Ansible 的脚本 --- playbooks剧本
playbooks 本身由以下各部分组成 (1)Tasks:任务,即通过 task 调用 ansible 的模板将多个操作组织在一个 playbook 中运行 (2)Vars:变量 (3)Templates:模板 &a…...
7.4.分块查找
一.分块查找的算法思想: 1.实例: 以上述图片的顺序表为例, 该顺序表的数据元素从整体来看是乱序的,但如果把这些数据元素分成一块一块的小区间, 第一个区间[0,1]索引上的数据元素都是小于等于10的, 第二…...

深入剖析AI大模型:大模型时代的 Prompt 工程全解析
今天聊的内容,我认为是AI开发里面非常重要的内容。它在AI开发里无处不在,当你对 AI 助手说 "用李白的风格写一首关于人工智能的诗",或者让翻译模型 "将这段合同翻译成商务日语" 时,输入的这句话就是 Prompt。…...
)
React Native 导航系统实战(React Navigation)
导航系统实战(React Navigation) React Navigation 是 React Native 应用中最常用的导航库之一,它提供了多种导航模式,如堆栈导航(Stack Navigator)、标签导航(Tab Navigator)和抽屉…...

学校时钟系统,标准考场时钟系统,AI亮相2025高考,赛思时钟系统为教育公平筑起“精准防线”
2025年#高考 将在近日拉开帷幕,#AI 监考一度冲上热搜。当AI深度融入高考,#时间同步 不再是辅助功能,而是决定AI监考系统成败的“生命线”。 AI亮相2025高考,40种异常行为0.5秒精准识别 2025年高考即将拉开帷幕,江西、…...
如何在网页里填写 PDF 表格?
有时候,你可能希望用户能在你的网站上填写 PDF 表单。然而,这件事并不简单,因为 PDF 并不是一种原生的网页格式。虽然浏览器可以显示 PDF 文件,但原生并不支持编辑或填写它们。更糟的是,如果你想收集表单数据ÿ…...

动态 Web 开发技术入门篇
一、HTTP 协议核心 1.1 HTTP 基础 协议全称 :HyperText Transfer Protocol(超文本传输协议) 默认端口 :HTTP 使用 80 端口,HTTPS 使用 443 端口。 请求方法 : GET :用于获取资源,…...

什么是VR全景技术
VR全景技术,全称为虚拟现实全景技术,是通过计算机图像模拟生成三维空间中的虚拟世界,使用户能够在该虚拟世界中进行全方位、无死角的观察和交互的技术。VR全景技术模拟人在真实空间中的视觉体验,结合图文、3D、音视频等多媒体元素…...
【Veristand】Veristand环境安装教程-Linux RT / Windows
首先声明,此教程是针对Simulink编译模型并导入Veristand中编写的,同时需要注意的是老用户编译可能用的是Veristand Model Framework,那个是历史版本,且NI不会再维护,新版本编译支持为VeriStand Model Generation Suppo…...

数据结构:递归的种类(Types of Recursion)
目录 尾递归(Tail Recursion) 什么是 Loop(循环)? 复杂度分析 头递归(Head Recursion) 树形递归(Tree Recursion) 线性递归(Linear Recursion)…...

C++--string的模拟实现
一,引言 string的模拟实现是只对string对象中给的主要功能经行模拟实现,其目的是加强对string的底层了解,以便于在以后的学习或者工作中更加熟练的使用string。本文中的代码仅供参考并不唯一。 二,默认成员函数 string主要有三个成员变量,…...
