移情别恋c++ ദ്ദി˶ー̀֊ー́ ) ——14.哈希(2)(模拟实现)
1.概念介绍
1.1开散列
开散列(Open Hashing),也叫链地址法,是一种解决哈希冲突的方法。每个哈希表槽位保存一个链表,所有散列到同一位置的元素都存储在该链表中。当插入元素发生冲突时,将新元素添加到相应槽位的链表末尾。

1.2闭散列
闭散列(Closed Hashing),也叫开放地址法,是一种解决哈希冲突的方法。当插入元素发生冲突时,通过寻找下一个空槽位来存储冲突元素,常见策略包括1.线性探测、2.二次探测等,不使用链表存储冲突元素。

2.模拟实现
2.1闭散列模拟实现
1.枚举——status
enum status //使用枚举保存数据的“状态”,如果为EMPTY,DELETE则可以插入
{EMPTY,//记得EMPTY要写在最上面,这样,系统默认的构造函数才会将s初始化为EMPTYEXIST,DELETE
};2.数组中的元素——hashdata
template<class K,class V>
struct hashdata
{pair<K, V> data; //数据status s; //状态
};3.将key元素转化为可计算的形式——hashfunc
为了确定元素应当插入到哪个位置,需要把key取出来
template<class K>
struct hashfunc //因为key不一定是整形,如果能强制转换成整形,那就要转换
{size_t operator()(const K& key){return size_t(key); }
};单独为string类写一份:
template<>
struct hashfunc<string> //单独为k=string写一份,还记得嘛,这是模板的特化!!!!!!!这样,在初始化hashtable时就不用再传仿函数模板参数了
{size_t operator()(const string& key){size_t flag = 0;;for (auto e : key){flag *= 31;//这一步可以保证abc,acb的flag不同,防止第一步就发生冲突flag += e;//本质是遍历整个string并使每个字母的ascii码相加,当然也可以使用其他的方式}return flag;}
};模板特化相关知识:移情别恋c++ ദ്ദി˶ー̀֊ー́ ) ——9.模板进阶-CSDN博客
4.容器——hashtable
私有成员:
private:vector<hashdata<K,V>> table;size_t num=0;//储存的关键字的个数2.2.hashtable的功能实现
1.初始化
hashtable()
{table.resize(10);
}2.插入!!!!!!
bool insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{if (find(kv.first)){return false;}//负载因子,指关键字个数在总size中的占比,(越大代表发生hash冲突的概率越大)普遍超出0.7时就要扩容了,扩容需要重新开一份空间!!!!!!!!!因为映射关系被打乱了if (num * 10 / table.size() == 7)//这里很巧妙{size_t newsize = table.size() * 2;hashtable<K, V,hash> newtable;newtable.table.resize(newsize);//遍历旧表for (size_t i = 0; i < table.size();i++){if (table[i].s == EXIST){newtable.insert(table[i].data);}}table.swap(newtable.table);//记得交换一下}hash hf;//1.线性探测(解决hash冲突的方法)size_t position = hf(kv.first) % table.size();//应用映射公式 hash(key) = key % capacity (注意!!!!!这里要用table.size(),而不是table.capacity(),所以要除余while ((table[position]).s == EXIST)//如果当前的位置非空,则往后顺延一位!!!!!!{position++;position %= table.size();//positin走到底后回到0}table[position].data = kv;table[position].s= EXIST;++num;return true;
}3.查找
hashdata<K, V>* find(const K& key)//查找是从确定的初始位置查找到nullptr!!!!!结束,因为没到nullptr前,都有可能是因为冲突导致数据后移
{hash hf;size_t position =hf(key)% table.size();while (table[position].s != EMPTY){if (table[position].data.first == key&& table[position].s==EXIST){return &table[position];}position++;position %= table.size();}return NULL;
}4.删除
bool erase(const K& key)
{hashdata<K, V>* ret = find(key);if (ret){ret->s = DELETE;--num;return true;}else{return false;}
}2.3开散列模拟实现
开散列存储的本质是指针数组
1.数组中的元素——hashnode
template<class T>
struct hashnode
{T data; //数据hashnode* next;hashnode(T kv):data(kv),next(nullptr){}};2. 容器——hashtable
私有成员:
private:vector<node*> table;size_t num = 0;};2.4.hashtable内容实现
1.初始化
hashtable()
{table.resize(10);
}2.析构函数
~hashtable()
{for (size_t i = 0; i < table.size(); i++){node* cur = table[i];while (cur){node* next = cur->next;delete cur;cur = next;}table[i] = nullptr;//最后置空}}3.查找
node* find(const K& key)
{hash hf;typeoft tt;size_t position = hf(key) % table.size();node* cur = table[position];while (cur){if (tt(cur->data)== key)return cur;cur = cur->next;}return nullptr;
}4.插入
bool insert(const T& kv)
{hash hf;typeoft tt;if (find(tt(kv)))return true;if (num == table.size())//当负载因子等于1时要扩容{vector<node*> newtable;newtable.resize(table.size()* 2, nullptr);//遍历旧表for (size_t i = 0; i < table.size(); i++){node* cur = table[i];while (cur){node* next = cur->next;size_t newposition = hf(tt(cur->data)) % newtable.size();cur->next = newtable[newposition];newtable[newposition] = cur;cur = next;}table[i] = nullptr;//数据原来的位置处一定要置空,否则会因为二次析构产生问题}table.swap(newtable);//直接交换两个哈希桶(底层指针的交换)}size_t position = hf(tt(kv)) % table.size();node* newnode = new node(kv);node* cur = table[position];//头插newnode->next = cur;table[position] = newnode;num++;}3. 迭代器的设置(以开散列为例)!!!!!!!!
1.hsiterator的设置与功能
//前置声明,因为哈希表用到了迭代器,迭代器也用到了哈希表,这叫做相互依赖,需要做前置声明
template<class K, class T, class typeoft, class hash >
class hashtable;template<class K, class T,class ref,class ptr, class typeoft,class hash=hashfunc<K>>
struct hsiterator
{typedef hashnode<T> node;const hashtable< K, T, typeoft, hash> &point;//这里使用引用是为了防止析构影响原来的tabletypedef hsiterator<K, T,ref,ptr, typeoft,hash> Self;node* _node;size_t place;hsiterator(node* node_, const hashtable< K, T, typeoft, hash> &_point,size_t _place):_node(node_),point(_point),place(_place){}Self operator++(){if (_node->next)//如果—_node->next不为空,那么桶里面还有数据,走next{_node = _node->next;}else //如果为空,那么需要走到下一个桶{typeoft tt;hash hf;//size_t head = hf(tt(_node->data)) % point.table.size();//找到初始位置,方便转移至下一个桶++place;while (place < point.table.size()){if (point.table[place]){_node = point.table[place];break;}else{place++;}}if (place == point.table.size()){_node = nullptr;}return *this;}}ref operator*(){return _node->data;}ptr operator->(){return &_node->data;}bool operator!=(const Self& s){return _node != s._node;}
};2.hashtable中对hsiterator的封装
template<class K, class T, class ref, class ptr,class typeoft,class hash>
friend struct hsiterator;//这里设置了友元,这样,hsiterator就可以直接取到hashtable的private成员table数组了typedef hsiterator<K, T,T&,T*, typeoft, hash> iterator;//普通迭代器
typedef hsiterator<K, T, const T&, const T*, typeoft, hash> const_iterator;//const迭代器iterator begin()
{for (size_t i = 0; i < table.size(); i++){if (table[i])return iterator(table[i], *this, i);}return end();
}iterator end()
{return iterator(nullptr, *this, -1);//-1是随便给的
}4.unorderedmap&&unorderedset封装
1.取出K元素(仿函数)
struct setkeyoft //仿函数
{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};2.迭代器封装
set的iterator全部使用const迭代器:
typedef typename hashtable<K,K,setkeyoft>::const_iterator iterator;typedef typename hashtable<K,K,setkeyoft>::const_iterator const_iterator;
/* iterator begin(){return table.begin();}iterator end(){return table.end();}*/const_iterator begin()const{return table.begin();}const_iterator end() const{return table.end();}map的迭代器正常分类使用:
typedef typename hashtable<K, pair<const K, V>, setkeyoft>::iterator iterator;
typedef typename hashtable<K, pair<const K, V>, setkeyoft>::const_iterator const_iterator;iterator begin()
{return table.begin();
}iterator end()
{return table.end();
}const_iterator begin() const
{return table.begin();
}const_iterator end() const
{return table.end();
}5.代码全览
1.hash.h
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;namespace close_address//闭散列
{enum status //使用枚举保存数据的“状态”,如果为EMPTY,DELETE则可以插入{EMPTY,//记得EMPTY要写在最上面,这样,系统默认的构造函数才会将s初始化为EMPTYEXIST,DELETE};template<class K,class V>struct hashdata{pair<K, V> data; //数据status s; //状态};template<class K>struct hashfunc //因为key不一定是整形,如果能强制转换成整形,那就要转换{size_t operator()(const K& key){return size_t(key); }};template<>struct hashfunc<string> //单独为k=string写一份,还记得嘛,这是模板的特化!!!!!!!这样,在初始化hashtable时就不用再传仿函数模板参数了{size_t operator()(const string& key){size_t flag = 0;;for (auto e : key){flag *= 31;//这一步可以保证abc,acb的flag不同,防止第一步就发生冲突flag += e;//本质是遍历整个string并使每个字母的ascii码相加,当然也可以使用其他的方式}return flag;}};//struct hashfuncstring //这是单独为string类写的转换仿函数//{// size_t operator()(const string& key)// {// size_t flag = 0;;// for (auto e : key)// {// flag *= 31;//这一步可以保证abc,acb的flag不同// flag += e;//本质是遍历整个string并使每个字母的ascii码相加,当然也可以使用其他的方式// }// return flag;// }//};template<class K,class V,class hash=hashfunc<K>>//这里hash直接给了缺省值,如果K可以转化,就可以在初始化的时候可以不给hash的模板参数class hashtable{public:hashtable(){table.resize(10);}hashdata<K, V>* find(const K& key)//查找是从确定的初始位置查找到nullptr!!!!!结束,因为没到nullptr前,都有可能是因为冲突导致数据后移{hash hf;size_t position =hf(key)% table.size();while (table[position].s != EMPTY){if (table[position].data.first == key&& table[position].s==EXIST){return &table[position];}position++;position %= table.size();}return NULL;}bool insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){if (find(kv.first)){return false;}//负载因子,指关键字个数在总size中的占比,(越大代表发生hash冲突的概率越大)普遍超出0.7时就要扩容了,扩容需要重新开一份空间!!!!!!!!!因为映射关系被打乱了if (num * 10 / table.size() == 7)//这里很巧妙{size_t newsize = table.size() * 2;hashtable<K, V,hash> newtable;newtable.table.resize(newsize);//遍历旧表for (size_t i = 0; i < table.size();i++){if (table[i].s == EXIST){newtable.insert(table[i].data);}}table.swap(newtable.table);//记得交换一下}hash hf;//1.线性探测(解决hash冲突的方法)size_t position = hf(kv.first) % table.size();//应用映射公式 hash(key) = key % capacity (注意!!!!!这里要用table.size(),而不是table.capacity(),所以要除余while ((table[position]).s == EXIST)//如果当前的位置非空,则往后顺延一位!!!!!!{position++;position %= table.size();//positin走到底后回到0}table[position].data = kv;table[position].s= EXIST;++num;return true;}bool erase(const K& key){hashdata<K, V>* ret = find(key);if (ret){ret->s = DELETE;--num;return true;}else{return false;}}void print(){for (size_t i = 0; i < table.size(); i++){if (table[i].s == EXIST){//printf("[%d]->%d\n", i, table[i].data.first);cout << "[" << i << "]->" << table[i].data.first << endl;}else if (table[i].s == EMPTY){//printf("[%d]->空余\n", i);cout << "[" << i << "]->空余" << endl;}else{//printf("[%d]->删除\n", i);cout << "[" << i << "]->删除" << endl;}}}private:vector<hashdata<K,V>> table;size_t num=0;//储存的关键字的个数};void test1(){hashtable<int, int> it;int a[] = { 4,14,24,34,5,7,1 };for (auto e : a){it.insert(make_pair(e, e));}it.insert(make_pair(3, 3));it.insert(make_pair(3, 3));it.insert(make_pair(-3, -3));it.print();cout << endl;it.erase(3);it.print();}void test2(){hashtable<string, int> it;string arr[] = { "香蕉","苹果" ,"西瓜" ,"苹果" ,"香蕉" ,"香瓜" ,"苹果" ,"香蕉" };for (auto e : arr){auto f = it.find(e);//hashdata<K,V>*if (f){f->data.second++;}else{it.insert(make_pair(e, 1));}}it.print();}
}namespace open_address//开散列
{template<class K>struct hashfunc //因为key不一定是整形,如果能强制转换成整形,那就要转换{size_t operator()(const K& key){return size_t(key);}};template<>struct hashfunc<string> //还记得嘛,这是模板的特化!!!!!!!这样,在初始化hashtable时就不用再传仿函数模板参数了{size_t operator()(const string& key){size_t flag = 0;;for (auto e : key){flag *= 31;//这一步可以保证abc,acb的flag不同,防止第一步就发生冲突flag += e;//本质是遍历整个string并使每个字母的ascii码相加,当然也可以使用其他的方式}return flag;}};template<class T>struct hashnode{T data; //数据hashnode* next;hashnode(T kv):data(kv),next(nullptr){}};//前置声明,因为哈希表用到了迭代器,迭代器也用到了哈希表,这叫做相互依赖,需要做前置声明template<class K, class T, class typeoft, class hash >class hashtable;template<class K, class T,class ref,class ptr, class typeoft,class hash=hashfunc<K>>struct hsiterator{typedef hashnode<T> node;const hashtable< K, T, typeoft, hash> &point;//这里使用引用是为了防止析构影响原来的tabletypedef hsiterator<K, T,ref,ptr, typeoft,hash> Self;node* _node;size_t place;hsiterator(node* node_, const hashtable< K, T, typeoft, hash> &_point,size_t _place):_node(node_),point(_point),place(_place){}Self operator++(){if (_node->next)//如果—_node->next不为空,那么桶里面还有数据,走next{_node = _node->next;}else //如果为空,那么需要走到下一个桶{typeoft tt;hash hf;//size_t head = hf(tt(_node->data)) % point.table.size();//找到初始位置,方便转移至下一个桶++place;while (place < point.table.size()){if (point.table[place]){_node = point.table[place];break;}else{place++;}}if (place == point.table.size()){_node = nullptr;}return *this;}}ref operator*(){return _node->data;}ptr operator->(){return &_node->data;}bool operator!=(const Self& s){return _node != s._node;}};template<class K, class T, class typeoft ,class hash = hashfunc<K>>class hashtable{public:typedef hashnode<T> node;template<class K, class T, class ref, class ptr,class typeoft,class hash>friend struct hsiterator;//这里设置了友元,这样,hsiterator就可以直接取到hashtable的private成员table数组了typedef hsiterator<K, T,T&,T*, typeoft, hash> iterator;//普通迭代器typedef hsiterator<K, T, const T&, const T*, typeoft, hash> const_iterator;//const迭代器iterator begin(){for (size_t i = 0; i < table.size(); i++){if (table[i])return iterator(table[i], *this, i);}return end();}iterator end(){return iterator(nullptr, *this, -1);//-1是随便给的}const_iterator begin()const{for (size_t i = 0; i < table.size(); i++){if (table[i])return const_iterator(table[i], *this, i);}return end();}const_iterator end() const{return const_iterator(nullptr, *this, -1);//-1是随便给的}hashtable(){table.resize(10);}~hashtable(){for (size_t i = 0; i < table.size(); i++){node* cur = table[i];while (cur){node* next = cur->next;delete cur;cur = next;}table[i] = nullptr;//最后置空}}node* find(const K& key){hash hf;typeoft tt;size_t position = hf(key) % table.size();node* cur = table[position];while (cur){if (tt(cur->data)== key)return cur;cur = cur->next;}return nullptr;}bool insert(const T& kv){hash hf;typeoft tt;if (find(tt(kv)))return true;if (num == table.size())//当负载因子等于1时要扩容{vector<node*> newtable;newtable.resize(table.size()* 2, nullptr);//遍历旧表for (size_t i = 0; i < table.size(); i++){node* cur = table[i];while (cur){node* next = cur->next;size_t newposition = hf(tt(cur->data)) % newtable.size();cur->next = newtable[newposition];newtable[newposition] = cur;cur = next;}table[i] = nullptr;//数据原来的位置处一定要置空,否则会因为二次析构产生问题}table.swap(newtable);//直接交换两个哈希桶(底层指针的交换)}size_t position = hf(tt(kv)) % table.size();node* newnode = new node(kv);node* cur = table[position];//头插newnode->next = cur;table[position] = newnode;num++;}bool erase(const K& key){hash hf;typeoft tt;size_t position = hf(key) % table.size();node* cur = table[position];node* prev = nullptr;while (cur){if (tt(cur->data) == key){if (prev){prev->next = cur->next;delete cur;num--;}else{table[position] = nullptr;num--;}return true;}prev = cur;cur = cur->next;}return false;}private:vector<node*> table;size_t num = 0;};}2.myunorderedmap.h
#include"hash.h"using namespace open_address;namespace zone
{template<class K, class V>class unorderedmap{public:struct setkeyoft{const K& operator()(const pair<const K, V>& key){return key.first;}};typedef typename hashtable<K, pair<const K, V>, setkeyoft>::iterator iterator;typedef typename hashtable<K, pair<const K, V>, setkeyoft>::const_iterator const_iterator;iterator begin(){return table.begin();}iterator end(){return table.end();}const_iterator begin() const{return table.begin();}const_iterator end() const{return table.end();}bool insert(const pair<K,V>& key){return table.insert(key); }private:hashtable<K, pair<const K,V>, setkeyoft> table;};void testmap(){unorderedmap<string, string> it;it.insert(make_pair("sort","排序"));it.insert(make_pair("right","右"));it.insert(make_pair("left","左"));it.insert(make_pair("middle","中"));for (auto e : it){e.second += 'x';//map的value可改变,但key不能改变cout << e.first<<' '<<e.second<<endl;//记得加一个.first,因为重载的operator*,只会取得data,在map中就是pair<k,v>,所以要用.first取得key}}}3.myunorderedset.h
#include"hash.h"using namespace open_address;namespace zone
{template<class K>class unorderedset{public:struct setkeyoft //仿函数{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};typedef typename hashtable<K,K,setkeyoft>::const_iterator iterator;typedef typename hashtable<K,K,setkeyoft>::const_iterator const_iterator;/* iterator begin(){return table.begin();}iterator end(){return table.end();}*/const_iterator begin()const{return table.begin();}const_iterator end() const{return table.end();}bool insert(const K& key){return table.insert(key);}private:hashtable<K,K, setkeyoft> table;};void testset(){unorderedset<int> it;it.insert(2);it.insert(3);it.insert(14);it.insert(24);it.insert(34);unorderedset<int>::iterator arr = it.begin();while (arr != it.end()){//*arr += 5;//set的key不可修改cout << *arr << endl;++arr;}}}
相关文章:

移情别恋c++ ദ്ദി˶ー̀֊ー́ ) ——14.哈希(2)(模拟实现)
1.概念介绍 1.1开散列 开散列(Open Hashing),也叫链地址法,是一种解决哈希冲突的方法。每个哈希表槽位保存一个链表,所有散列到同一位置的元素都存储在该链表中。当插入元素发生冲突时,将新元素添加到相应…...
的生命周期及其对应用程序性能的影响)
请描述一下JVM(Java虚拟机)的生命周期及其对应用程序性能的影响
1、请描述一下JVM(Java虚拟机)的生命周期及其对应用程序性能的影响。 JVM(Java虚拟机)的生命周期主要涉及以下几个阶段:加载、验证、准备、解析、执行、卸载。每个阶段都有其特定的作用和影响。 加载:JVM…...

展会邀约|加速科技与您相约IC China 2024!
第二十一届中国国际半导体博览会( IC China 2024)将于 2024 年11月18日—11月20日在北京国家会议中心举行。加速科技将携高性能测试机ST2500EX、ST2500E、eATE及全系测试解决方案亮相E2馆B150展位。博览会期间,将同期举办"半导体产业前沿…...

鸿蒙中服务卡片数据的获取和渲染
1. 2.在卡片中使用LocalStorageProp接受传递的数据 LocalStorageProp("configNewsHead") configNewsHeadLocal: ConfigNewsHeadInfoItem[] [] 注意:LocalStorageProp括号中的为第一步图片2中的键 3.第一次在服务卡片的第一个卡片中可能会获取不到数据…...

运维篇-修复centos7无法下载docker问题
修复centos7无法下载docker问题 1、安装docker时报错2、docker无法下载镜像 1、安装docker时报错 linux的centos系统,安装docker时会报错 –> Finished Dependency Resolution Error: Package: glibc-2.17-307.el7.1.i686 (base) Requires: glibc-common 2.17…...

【论文阅读】WaDec: Decompiling WebAssembly Using Large Language Model
论文阅读笔记:WaDec: Decompiling WebAssembly Using Large Language Model 1. 来源出处 论文标题: WaDec: Decompiling WebAssembly Using Large Language Model作者: Xinyu She, Yanjie Zhao, Haoyu Wang会议: 39th IEEE/ACM International Conference on Automated Softwar…...

redis类型介绍
1. 字符串(String): • 简介:最基础的数据类型,可以存储任何形式的字符串,包括文本数据和数字数据。 • 常用操作:SET、GET、INCR、DECR等。 2. 列表(List): …...

kubernetes如何配置默认存储
如果不想每次都创建PV,希望k8s集群中能够配置号默认存储,然后根据你的PVC自动创建PV,就需要安装一个默认存储,也就是storageclass 什么是storageclass Kubernetes提供了一套可以自动创建PV的机制,即:Dyna…...

【微服务】Spring AI 使用详解
目录 一、前言 二、Spring AI 概述 2.1 什么是Spring AI 2.2 Spring AI 特点 2.3 Spring AI 带来的便利 2.4 Spring AI 应用领域 2.4.1 聊天模型 2.4.2 文本到图像模型 2.4.3 音频转文本 2.4.4 嵌入大模型使用 2.4.5 矢量数据库支持 2.4.6 数据工程ETL框架 三、Sp…...
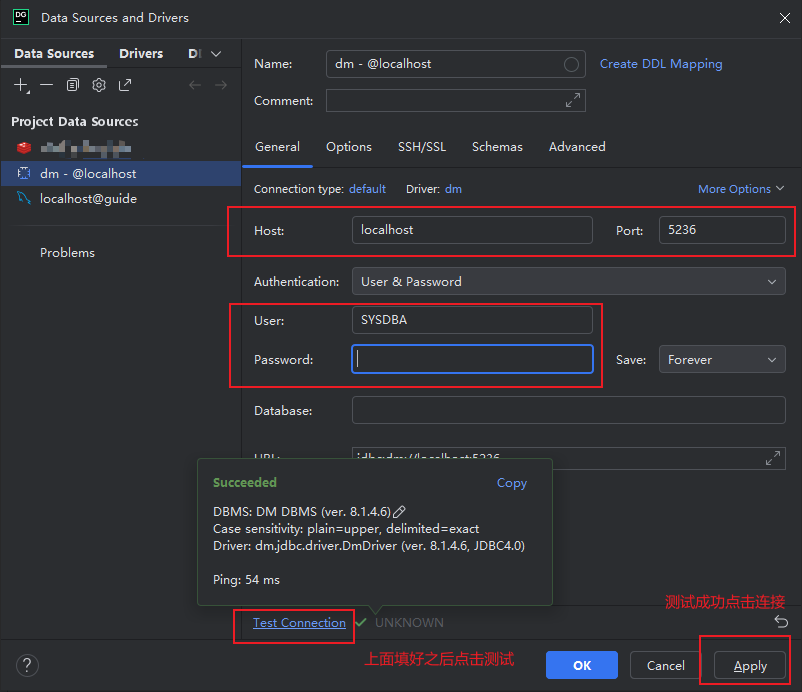
DataGrip 连接 dm
参考链接 使用DataGrip链接达梦数据库_datagrip连接达梦数据库-CSDN博客 下载 jdbc 驱动包 第一种 通过链接下载:下载 第二种【特指 window 安装包】 在达梦安装包 iso 文件里面 source/drivers/jdbc 将驱动添加进 DataGrip 选中 jdbc 驱动包,然后选…...

数据库监控工具DBdoctor v3.2.4.3版本发布,新增对openGauss、Vastbase G100的支持!
新引擎扩展 新增对openGauss数据库的支持:支持对openGauss数据库的SQL审核、实例巡检、性能洞察、锁透视、根因诊断、基础监控、索引推荐、存储分析; 新增对Vastbase G100数据库的支持:支持对Vastbase G100数据库的SQL审核、实例巡检、性能洞…...

Git 常用命令大全与详解
Git 是一种广泛使用的分布式版本控制系统。无论是管理个人项目还是进行团队协作,掌握 Git 的常用命令都是开发者必备的技能之一。本文将介绍一些常用的 Git 命令,并对其进行详细说明。 1. 基础命令 初始化仓库 git init:在当前目录下初始化…...

执行flink sql连接clickhouse库
手把手教学,flink connector打通clickhouse大数据库,通过下发flink sql,来使用ck。 组件版本jdk1.8flink1.17.2clickhouse23.12.2.59 1.背景 flink官方不支持clickhouse连接器,工作中难免会用到。 2.方案 利用GitHub大佬提供…...

什么是C++中的友元函数和友元类?
友元函数(Friend Function)和 友元类(Friend Class)是用于控制类的访问权限的机制。这允许特定的函数或类访问另一个类的私有成员和保护成员,打破了 C 的封装性规则。 友元函数 定义 友元提供了不同类的成员函数之间…...
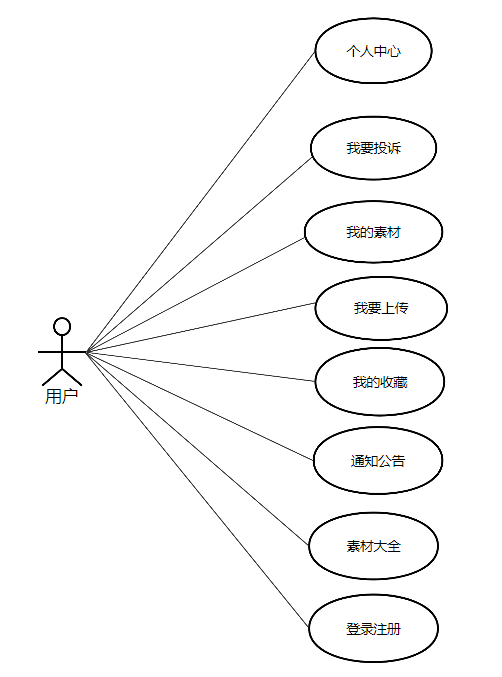
基于Spring Boot+Vue的多媒体素材管理系统的设计与实现
一.系统开发工具与环境搭建 1.系统设计开发工具 后端使用Java编程语言的Spring boot框架 项目架构:B/S架构 运行环境:win10/win11、jdk17 前端: 技术:框架Vue.js;UI库:ElementUI; 开发工具&…...

Inpaint-Web:纯浏览器端实现的开源图像处理工具
之前在刷短视频的时候,经常看到一些情侣在景区拍照,结果被路人“抢镜”。有时男朋友会拿出手机,帮忙把那些路人“P”掉,简直是既贴心又有趣。最近我在逛 GitHub 时,发现了一个可以在浏览器端删除照片中部分内容的纯前端…...

商业物联网详细指南:优势与挑战
物联网是信息技术行业最具前景的领域之一。为什么它如此热门呢?原因在于全球连接性。设备可以像人群一样相互协作。正如我们所知,协作能显著提高生产力。 物联网对普通用户和企业都有益处。许多日常流程可以通过传感器、扫描仪、摄像头和其他设备实现自…...

如何在项目中用elementui实现分页器功能
1.在结构部分复制官网代码: <template> 标签: 这是 Vue 模板的根标签,包含所有的 HTML 元素和 Vue 组件。 <div> 标签: 这是一个普通的 HTML 元素,包裹了 el-pagination 组件。它没有特别的意义,只是为了确保 el-pagi…...

Nginx参数配置-笔记
文章目录 upstream实现后台应用服务负载均衡&高可用proxy_set_header参数 upstream实现后台应用服务负载均衡&高可用 角色IPnginx172.168.110.2后端应用服务1172.168.110.3后端应用服务2172.168.110.4后端应用服务3(备用)172.168.110.5 示例如下: upstre…...

衡量神经网络表征相似度
目录 1.中心核对齐技术(CKA)2.Hilbert-Schmidt independence criterion(HSIC)HSIC的计算步骤:HSIC的性质:应用:矩阵中心化操作对于单个数据集的中心化对于两个数据集的中心化(例如,用于HSIC)Python代码示例1.中心核对齐技术(CKA) CKA通过计算两个表征的Gram矩阵(即…...
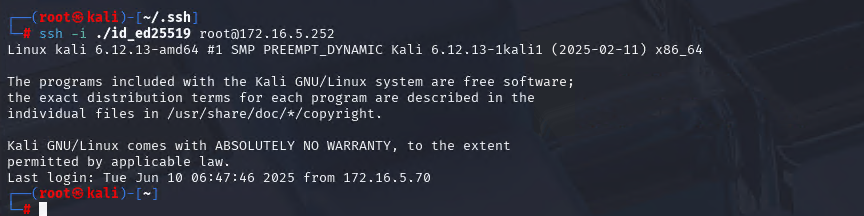
Xshell远程连接Kali(默认 | 私钥)Note版
前言:xshell远程连接,私钥连接和常规默认连接 任务一 开启ssh服务 service ssh status //查看ssh服务状态 service ssh start //开启ssh服务 update-rc.d ssh enable //开启自启动ssh服务 任务二 修改配置文件 vi /etc/ssh/ssh_config //第一…...

Python:操作 Excel 折叠
💖亲爱的技术爱好者们,热烈欢迎来到 Kant2048 的博客!我是 Thomas Kant,很开心能在CSDN上与你们相遇~💖 本博客的精华专栏: 【自动化测试】 【测试经验】 【人工智能】 【Python】 Python 操作 Excel 系列 读取单元格数据按行写入设置行高和列宽自动调整行高和列宽水平…...
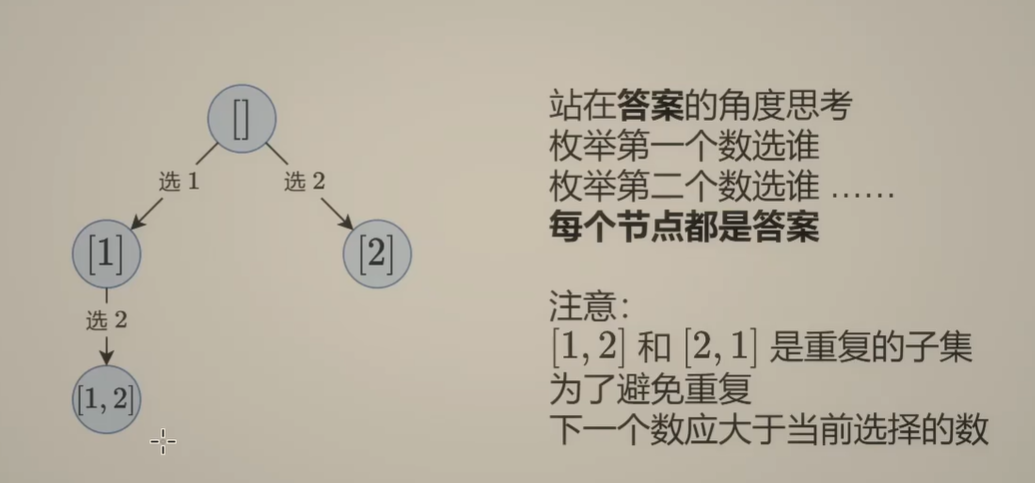
Day131 | 灵神 | 回溯算法 | 子集型 子集
Day131 | 灵神 | 回溯算法 | 子集型 子集 78.子集 78. 子集 - 力扣(LeetCode) 思路: 笔者写过很多次这道题了,不想写题解了,大家看灵神讲解吧 回溯算法套路①子集型回溯【基础算法精讲 14】_哔哩哔哩_bilibili 完…...

Opencv中的addweighted函数
一.addweighted函数作用 addweighted()是OpenCV库中用于图像处理的函数,主要功能是将两个输入图像(尺寸和类型相同)按照指定的权重进行加权叠加(图像融合),并添加一个标量值&#x…...

渲染学进阶内容——模型
最近在写模组的时候发现渲染器里面离不开模型的定义,在渲染的第二篇文章中简单的讲解了一下关于模型部分的内容,其实不管是方块还是方块实体,都离不开模型的内容 🧱 一、CubeListBuilder 功能解析 CubeListBuilder 是 Minecraft Java 版模型系统的核心构建器,用于动态创…...
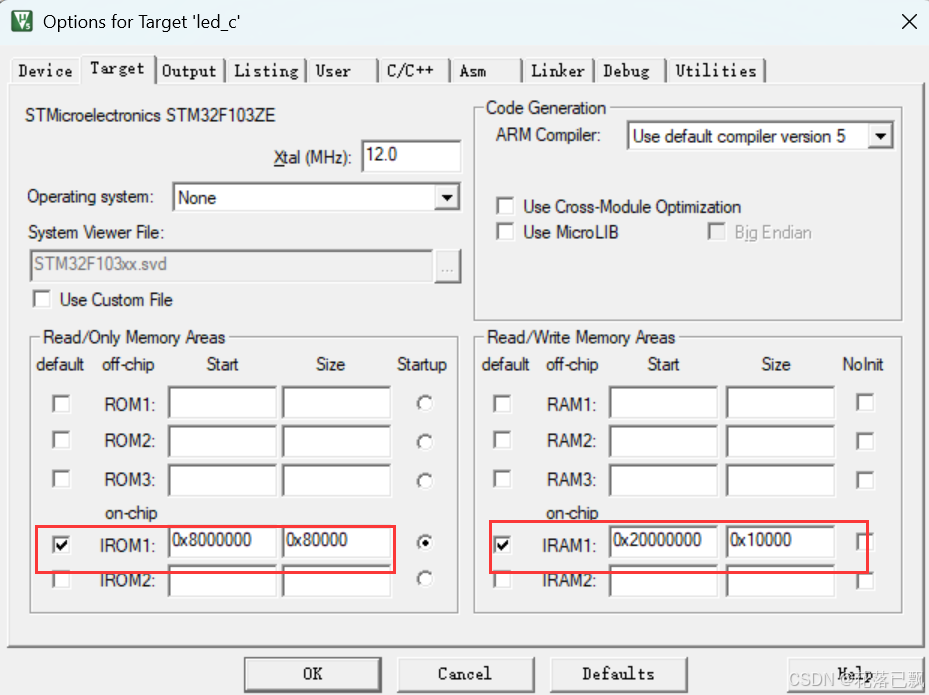
Keil 中设置 STM32 Flash 和 RAM 地址详解
文章目录 Keil 中设置 STM32 Flash 和 RAM 地址详解一、Flash 和 RAM 配置界面(Target 选项卡)1. IROM1(用于配置 Flash)2. IRAM1(用于配置 RAM)二、链接器设置界面(Linker 选项卡)1. 勾选“Use Memory Layout from Target Dialog”2. 查看链接器参数(如果没有勾选上面…...
2025 后端自学UNIAPP【项目实战:旅游项目】6、我的收藏页面
代码框架视图 1、先添加一个获取收藏景点的列表请求 【在文件my_api.js文件中添加】 // 引入公共的请求封装 import http from ./my_http.js// 登录接口(适配服务端返回 Token) export const login async (code, avatar) > {const res await http…...

TRS收益互换:跨境资本流动的金融创新工具与系统化解决方案
一、TRS收益互换的本质与业务逻辑 (一)概念解析 TRS(Total Return Swap)收益互换是一种金融衍生工具,指交易双方约定在未来一定期限内,基于特定资产或指数的表现进行现金流交换的协议。其核心特征包括&am…...

高防服务器能够抵御哪些网络攻击呢?
高防服务器作为一种有着高度防御能力的服务器,可以帮助网站应对分布式拒绝服务攻击,有效识别和清理一些恶意的网络流量,为用户提供安全且稳定的网络环境,那么,高防服务器一般都可以抵御哪些网络攻击呢?下面…...
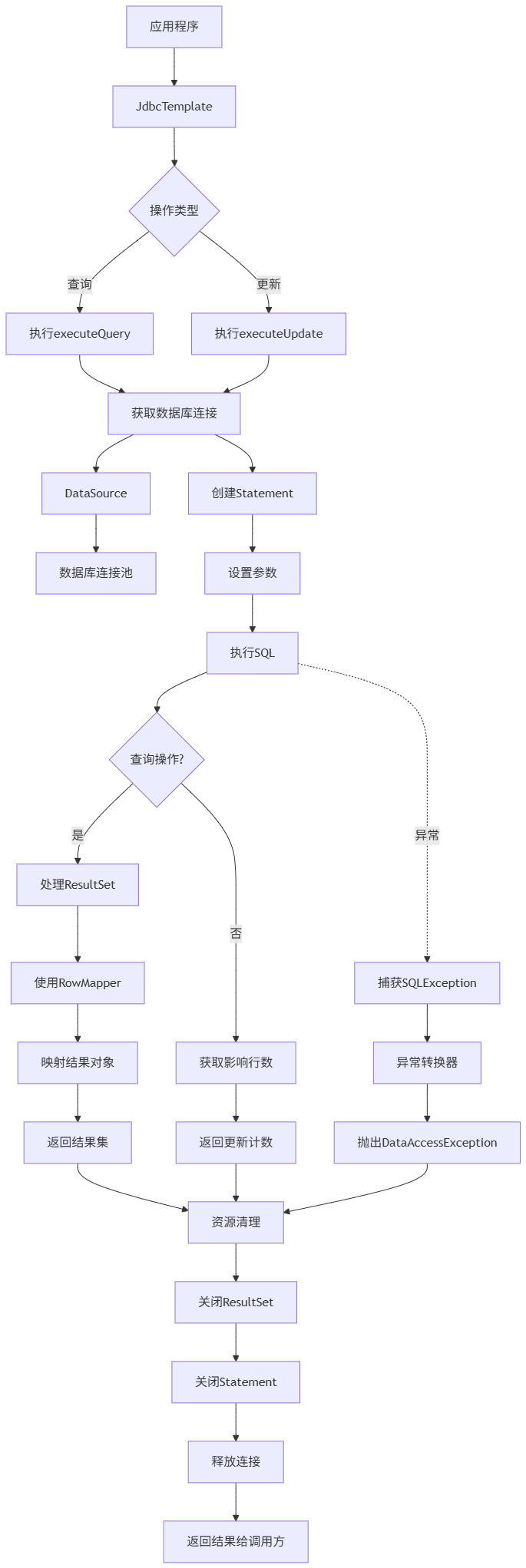
Spring数据访问模块设计
前面我们已经完成了IoC和web模块的设计,聪明的码友立马就知道了,该到数据访问模块了,要不就这俩玩个6啊,查库势在必行,至此,它来了。 一、核心设计理念 1、痛点在哪 应用离不开数据(数据库、No…...
