鸿蒙修饰符
文章目录
- 一、引言
- 1.1 什么是修饰符
- 1.2 修饰符在鸿蒙开发中的重要性
- 1.3 修饰符的作用机制
- 二、UI装饰类修饰符
- 2.1 @Styles修饰符
- 2.1.1 基本概念和使用场景
- 2.1.2 使用示例
- 2.1.3 最佳实践
- 2.2 @Extend修饰符
- 2.2.1 基本概念
- 2.2.2 使用示例
- 2.2.3 @Extend vs @Styles 对比
- 2.2.4 使用建议
- 三、组件类修饰符
- 3.1 @Component修饰符
- 3.1.1 基本概念
- 3.1.2 @Component vs 普通函数对比
- 3.1.3 基础使用示例
- 3.1.4 高级特性
- 3.1.5 最佳实践
- 3.1.6 性能优化建议
- 3.2 @BuilderParam修饰符
- 3.2.1 基本概念
- 3.2.2 使用场景
- 3.2.3 注意事项与最佳实践
- 四、状态管理类修饰符
- 4.1 @State修饰符
- 4.1.1 基本概念
- 4.1.2 使用规则
- 4.1.3 @State注意事项和最佳实践
- 4.2 @Prop修饰符
- 4.2.1 基本概念
- 4.2.2 使用示例
- 4.2.3 @Prop vs 普通变量对比
- 4.2.4 @Prop的高级用法
- 4.2.5 最佳实践
- 4.3 @Link修饰符
- 4.3.1 基本概念
- 4.3.2 使用示例
- 4.3.3 @Link vs @Prop 对比
- 4.3.4 @Link最佳实践
- 4.4 @Provide/@Consume修饰符
- 4.4.1 基本概念
- 4.4.2 基础用法
- 4.4.3 高级特性
- 4.4.4 使用建议与最佳实践
- 4.5 @Watch修饰符
- 4.5.1 基本概念
- 4.5.2 基础用法
- 4.5.3 高级用法
- 4.5.4 @Watch使用场景
- 4.5.5 最佳实践
- 4.5.6 @Watch注意事项
- 4.6 @Observed/@ObjectLink修饰符
- 4.6.1 基本概念
- 4.6.2 基础用法
- 4.6.3 关键点
- 4.6.4 实际应用示例
- 4.6.5 注意事项
- 对比
- 1. 使用场景对比
- 2. 具体示例对比
- 3. 特点对比
- @State
- @Prop
- @Link
- @Observed/@ObjectLink
- 4. 数据同步方式对比
一、引言
在HarmonyOS(鸿蒙)应用开发中,修饰符(Decorator)是一个极其重要的概念。它们不仅能够简化开发过程,还能提供强大的功能扩展性。本文将深入探讨鸿蒙中的各类修饰符,帮助开发者更好地理解和使用这些工具。本文主要介绍@Styles,@Extend,@Builder,@Component,@BuilderParam,@State,@Prop,@Link,@Provide,@Watch,@Observed等等。
1.1 什么是修饰符
修饰符是一种特殊的语法元素,用@符号作为标识,可以用来修饰类、方法、属性等代码元素,为其添加额外的行为或特性。在鸿蒙开发中,修饰符主要用于以下几个方面:
- UI样式定义和复用
- 组件声明和管理
- 状态管理和数据同步
- 组件间通信
1.2 修饰符在鸿蒙开发中的重要性

1.3 修饰符的作用机制
修饰符在编译时会被转换为特定的代码,它们主要通过以下机制发挥作用:
- 装饰器模式: 在不改变原有代码结构的情况下,动态地给对象添加新的功能
- 编译时转换: 将声明式的代码转换为命令式代码
- 运行时注入: 在运行时为目标对象注入额外的行为
二、UI装饰类修饰符
2.1 @Styles修饰符
2.1.1 基本概念和使用场景
@Styles修饰符用于定义可复用的样式集合,类似于Web开发中的CSS类。它可以:
- 提取共同样式,实现复用
- 保持代码整洁
- 统一管理样式
2.1.2 使用示例
// 定义全局样式
@Styles function globalStyles() {.width('100%').height(100).backgroundColor('#f5f5f5').padding(20)
}// 使用样式
@Entry
@Component
struct StylesDemo {build() {Column() {Text('Hello').fontSize(20).globalStyles()Text('World').fontSize(16).globalStyles()}}
}
2.1.3 最佳实践
样式分类管理
// 按功能分类样式
@Styles function cardStyles() {.width('100%').padding(15).borderRadius(8).backgroundColor(Color.White)
}@Styles function buttonStyles() {.width(120).height(40).borderRadius(20).backgroundColor('#007DFF')
}
2.2 @Extend修饰符
2.2.1 基本概念
@Extend用于扩展现有组件的样式和行为,创建具有特定样式的新组件类型。
2.2.2 使用示例
// 扩展Text组件
@Extend(Text) function primaryText() {.fontSize(16).fontColor('#333333').fontWeight(FontWeight.Medium)
}// 扩展Button组件
@Extend(Button) function primaryButton(color:Color) {.width(200).height(50).backgroundColor('#007DFF').fontColor(color)
}@Entry
@Component
struct TestCase {build() {Column({ space: 20 }) {Text('这是普通文本').primaryText()Button('点击按钮').primaryButton(Color.White)}.height('100%').width('100%')}
}
2.2.3 @Extend vs @Styles 对比
| 特性 | @Extend | @Styles |
|---|---|---|
| 使用对象 | 特定组件 | 任意组件 |
| 复用性 | 只能用于指定的组件类型 | 可以应用于任何组件 |
| 类型安全 | 更强的类型检查 | 相对宽松 |
| 适用场景 | 组件定制化 | 通用样式复用 |
| 是否能接收参数 | 是 | 否 |
2.2.4 使用建议
-
选择合适的场景
- 需要创建特定样式的组件变体时,使用@Extend
- 需要跨组件复用样式时,使用@Styles
-
命名规范
// 好的命名示例
@Extend(Text) function primaryText() {}
@Extend(Text) function warningText() {}
@Extend(Button) function roundButton() {}// 避免的命名方式
@Extend(Text) function txt() {}
@Extend(Button) function btn() {}
三、组件类修饰符
3.1 @Component修饰符
3.1.1 基本概念
@Component是鸿蒙开发中最核心的修饰符之一,用于声明自定义组件。它将一个struct转换为可重用的UI组件,具有以下特点:
- 必须包含build()方法
- 支持组件生命周期
- 可以包含状态变量
- 支持组件间通信
3.1.2 @Component vs 普通函数对比
| 特性 | @Component | 普通函数 |
|---|---|---|
| 状态管理 | 支持@State等状态修饰符 | 不支持状态管理 |
| 生命周期 | 有完整生命周期 | 没有生命周期 |
| 重渲染机制 | 响应式更新 | 需手动处理更新 |
| 使用场景 | 复杂UI组件 | 简单功能封装 |
3.1.3 基础使用示例
import { promptAction } from '@kit.ArkUI';@Entry
@Component
struct TestCase {// 组件私有状态
@State counter: number = 0// 生命周期函数aboutToAppear() {promptAction.showToast({message:'Component is about to appear'})}aboutToDisappear() {promptAction.showToast({message:'Component is about to disappear'})}build() {Column() {Text(`计数器: ${this.counter}`).fontSize(20).fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)Button('增加').onClick(() => {this.counter++}).margin(10)}.width('100%').padding(20)}
}
3.1.4 高级特性
1. 组件参数传递
@Component
struct AdvancedComponent {// 从父组件接收的属性@Prop title: string@State private description: string = ''build() {Column({ space: 10 }) {Text(this.title).fontSize(24)TextInput({ placeholder: '请输入描述' }).onChange((value: string) => {this.description = value})}}
}
2. 组件插槽(Slot)
@Component
struct SlotComponent {@BuilderParam content: () => voidbuild() {Column() {this.content()}.width('100%').backgroundColor('#f5f5f5')}
}// 使用组件插槽
@Component
struct ParentComponent {build() {SlotComponent() {Row() {Text('自定义内容')Image('icon.png')}}}
}
3.1.5 最佳实践
- 组件拆分原则
// 好的实践:功能单一,职责明确
@Component
struct UserAvatar {@Prop userName: string@Prop avatarUrl: stringbuild() {Stack() {Image(this.avatarUrl).width(50).height(50).borderRadius(25)Text(this.userName[0]).fontSize(20).fontColor(Color.White)}}
}// 使用组件
@Component
struct UserProfile {build() {Row() {UserAvatar({userName: "张三",avatarUrl: "avatar.png"})Text("其他信息")}}
}
- 生命周期使用建议
@Component
struct LifecycleComponent {@State private data: any = {}aboutToAppear() {// 初始化数据,订阅事件this.initData()}aboutToDisappear() {// 清理资源,取消订阅this.cleanUp()}private initData() {// 数据初始化逻辑}private cleanUp() {// 清理逻辑}build() {// UI渲染}
}
3.1.6 性能优化建议
- 状态管理优化
@Component
struct OptimizedComponent {// 使用私有变量存储不需要响应式更新的数据private staticData: string = 'static'// 只将需要触发更新的数据声明为@State@State dynamicData: number = 0build() {Column() {// 静态内容Text(this.staticData)// 动态内容Text(`${this.dynamicData}`)}}
}
- 条件渲染优化
@Component
struct ConditionalComponent {@State loading: boolean = true@State data: Array<string> = []build() {Column() {if (this.loading) {LoadingSpinner()} else {ForEach(this.data, (item) => {DataItem({ content: item })})}}}
}
3.2 @BuilderParam修饰符
3.2.1 基本概念
@BuilderParam用于声明自定义构建函数参数,使组件能够接收和渲染自定义内容。
3.2.2 使用场景
- 自定义列表项渲染
@Component
struct MainPage {
@State items: string[] = ['项目1', '项目2', '项目3']
@Builder myItemBuilder(item: string):void{}
@BuilderParam itemBuilder: (item: string) => void = this.myItemBuilderbuild() {List() {ForEach(this.items, (item:string,idx:number) => {ListItem() {this.itemBuilder(item)}})}}
}// 使用示例
@Entry
@Component
struct TestCase {build() {Column(){MainPage({itemBuilder: (item:string) => {Row() {Text(item).width('100%').height('100%').backgroundColor(Color.Pink)}}})}}
}
- 可定制化容器组件
@Component
struct Container {@BuilderParam header?: () => void@BuilderParam content: () => void@BuilderParam footer?: () => voidbuild() {Column() {if (this.header) {this.header()}this.content()if (this.footer) {this.footer()}}}
}
3.2.3 注意事项与最佳实践
- 参数命名规范
// 推荐的命名方式
@BuilderParam headerBuilder: () => void
@BuilderParam contentBuilder: () => void
@BuilderParam footerBuilder: () => void// 不推荐的命名方式
@BuilderParam hdr: () => void
@BuilderParam cnt: () => void
- 性能考虑
@Component
struct PerformanceOptimizedList {// 使用私有变量缓存不常变化的构建函数@Builder myStaticBuilder() :void{Text('Static Content')
}@BuilderParam private staticBuilder:()=>void = this.myStaticBuilder@BuilderParam dynamicBuilder: () => voidbuild() {Column() {// 静态内容this.staticBuilder()// 动态内容this.dynamicBuilder()}}
}
四、状态管理类修饰符
4.1 @State修饰符
4.1.1 基本概念
@State是鸿蒙应用中最基础的状态管理修饰符,用于组件内部状态管理。当@State装饰的变量发生变化时,框架会自动重新渲染相关UI。
4.1.2 使用规则
- 基本语法
interface IUser{name: string,age: number
}// 使用示例
@Entry
@Component
struct TestCase {// 基础类型@State count: number = 0// 对象类型@State user: IUser = {name: 'tata',age: 25}// 数组类型@State list: string[] = ['item1', 'item2']build() {Column({ space: 20 }) {// 使用状态变量Text(`Count: ${this.count}`)Button('Add').onClick(() => {this.count++})Text(`User: ${this.user.name}, ${this.user.age}`)Button('Update User').onClick(() => {// 对象更新要使用新对象this.user = {name:this.user.name,age: this.user.age + 1}})}}
}
4.1.3 @State注意事项和最佳实践
- 状态初始化
@Component
struct StateInitDemo {// ✅ 推荐:直接初始化@State counter1: number = 0// ⚠️ 不推荐:延迟初始化可能导致问题@State counter2: numberaboutToAppear() {// 延迟初始化可能导致首次渲染问题this.counter2 = 0}
}
- 状态粒度控制
@Component
struct StateGranularityDemo {// ❌ 错误:粒度过大@State entirePage: {header: object,content: object,footer: object}// ✅ 正确:适当的状态粒度@State headerConfig: object@State contentList: array@State footerVisible: booleanbuild() {Column() {// UI实现}}
}
4.2 @Prop修饰符
4.2.1 基本概念
@Prop用于父子组件间的单向数据传递,子组件通过@Prop接收父组件传递的数据。
4.2.2 使用示例
// 子组件
@Component
struct ChildComponent {@Prop count: number // 接收父组件传递的数值@Prop message: string // 接收父组件传递的字符串build() {Column() {Text(`Count: ${this.count}`)Text(`Message: ${this.message}`)}}
}// 父组件
@Component
struct ParentComponent {@State parentCount: number = 0@State parentMessage: string = 'Hello'build() {Column() {// 传递属性给子组件ChildComponent({count: this.parentCount,message: this.parentMessage})Button('Update Parent').onClick(() => {this.parentCount++this.parentMessage = 'Updated'})}}
}
4.2.3 @Prop vs 普通变量对比
@Component
struct PropComparisonDemo {// @Prop装饰的变量@Prop propValue: number// 普通变量normalValue: numberbuild() {Column() {// @Prop变量会响应父组件的更新Text(`Prop Value: ${this.propValue}`)// 普通变量不会响应更新Text(`Normal Value: ${this.normalValue}`)}}
}
| 特性 | @Prop变量 | 普通变量 |
|---|---|---|
| 数据流向 | 单向(父到子) | 无数据流 |
| 响应更新 | 自动响应 | 不响应 |
| 可修改性 | 本地可修改但不影响父组件 | 可以自由修改 |
| 使用场景 | 父子组件通信 | 组件内部数据 |
4.2.4 @Prop的高级用法
- 默认值处理
@Component
struct PropDefaultDemo {// 使用装饰器提供默认值@Prop defaultValue: number = 100build() {Column() {Text(`Value: ${this.defaultValue}`)}}
}
- 属性监听与处理
@Component
struct PropWatchDemo {@Prop @Watch('onCountChange') count: number@State localCount: number = 0onCountChange() {// 当@Prop值变化时执行this.localCount = this.count * 2}build() {Column() {Text(`Prop Count: ${this.count}`)Text(`Local Count: ${this.localCount}`)}}
}
4.2.5 最佳实践
- 属性命名规范
@Component
struct PropNamingDemo {// ✅ 推荐:语义化命名@Prop isVisible: boolean@Prop userName: string@Prop itemCount: number// ❌ 避免:模糊的命名@Prop flag: boolean@Prop str: string@Prop num: number
}
- 类型安全
@Component
struct PropTypeDemo {// ✅ 推荐:明确的类型定义@Prop items: Array<{id: number,name: string}>// ❌ 避免:使用any类型@Prop data: any
}
4.3 @Link修饰符
4.3.1 基本概念
@Link修饰符用于实现父子组件间的双向数据绑定。与@Prop不同,@Link装饰的变量在子组件中的修改会同步回父组件。
4.3.2 使用示例
// 子组件
@Component
struct LinkChildComponent {@Link countValue: number // 双向绑定数据build() {Column() {Text(`Count: ${this.countValue}`)Button('在子组件中修改').onClick(() => {this.countValue++ // 修改会影响父组件})}}
}// 父组件
@Entry
@Component
struct TestCase {@State parentCount: number = 0build() {Column() {Text(`Parent Count: ${this.parentCount}`)LinkChildComponent({ countValue: $parentCount })Button('在父组件中修改').onClick(() => {this.parentCount++})}}
}
4.3.3 @Link vs @Prop 对比
| 特性 | @Link | @Prop |
|---|---|---|
| 数据流向 | 双向 | 单向(父到子) |
| 子组件修改 | 直接影响父组件 | 不影响父组件 |
| 使用场景 | 需要子组件修改父组件状态 | 只需要展示父组件数据 |
| 语法标记 | 变量名 | 变量名 |
4.3.4 @Link最佳实践
- 合理使用场景
@Component
struct FormComponent {// ✅ 适合使用@Link的场景:表单数据@Link formData: {username: string,password: string}build() {Column() {TextInput({ placeholder: '用户名' }).onChange((value) => {this.formData.username = value})TextInput({ placeholder: '密码' }).type(InputType.Password).onChange((value) => {this.formData.password = value})}}
}
- 避免过度使用
@Component
struct OptimizedComponent {// ✅ 只对需要双向绑定的数据使用@Link@Link editableData: string// ✅ 只读数据使用@Prop@Prop readOnlyData: string// ✅ 组件内部状态使用@State@State localState: number = 0build() {Column() {// 实现UI}}
}
4.4 @Provide/@Consume修饰符
4.4.1 基本概念
@Provide和@Consume用于实现跨组件层级的数据共享,避免多层props传递(即"prop drilling"问题)。
4.4.2 基础用法
interface IUser{name:string,role:string
}
// 顶层组件
@Entry
@Component
struct TestCase {@Provide('theme') theme: string = 'light'@Provide('user') userInfo:IUser = {name: 'tata',role: 'admin'}build() {Column() {ConsumerComponent()}}
}// 消费组件(可以是任意层级的子组件)
@Component
struct ConsumerComponent {@Consume('theme') theme: string@Consume('user') userInfo: IUserbuild() {Column() {Text(`Current Theme: ${this.theme}`)Text(`User: ${this.userInfo.name}`)}}
}
4.4.3 高级特性
- 使用别名
@Component
struct AdvancedProvider {@Provide('systemTheme') theme: string = 'light'
}@Component
struct AdvancedConsumer {// 使用别名访问共享数据@Consume('systemTheme') currentTheme: stringbuild() {Column() {Text(`Theme: ${this.currentTheme}`)}}
}
- 多层级数据共享
@Component
struct AppRoot {@Provide('globalState') userInfo:IUser = {name:'tata',role:'admin'}build() {Column() {// 可以被任意深度的子组件访问DeepNestedComponent()}}
}
4.4.4 使用建议与最佳实践
- 合理的数据粒度
// ✅ 推荐:适当的粒度
@Component
struct GoodProvider {@Provide('userSettings') settings: UserSettings@Provide('appTheme') theme: Theme
}// ❌ 避免:过大的共享范围
@Component
struct BadProvider {@Provide('entireAppState') state: AppState
}
- 性能优化
@Component
struct OptimizedProvider {// 将频繁变化的数据和稳定数据分开@Provide('staticConfig') staticConfig: Config // 稳定数据@Provide('dynamicState') dynamicState: State // 变化数据build() {Column() {// 实现UI}}
}
- 错误处理
@Component
struct SafeConsumer {@Consume('data') data?: DataType // 使用可选类型build() {Column() {if (this.data) {// 安全地使用数据Text(this.data.toString())} else {// 提供后备UIText('数据未就绪')}}}
}
4.5 @Watch修饰符
4.5.1 基本概念
@Watch用于监听状态变量的变化,当被监听的状态发生改变时,会触发相应的回调函数。
4.5.2 基础用法
// 顶层组件
@Entry
@Component
struct TestCase {@State @Watch('onCountChange') count: number = 0@State message: string = ''onCountChange() {this.message = `计数变为 ${this.count.toString()}`}build() {Column({ space: 20 }) {Text(`Current count: ${this.count}`)Text(this.message)Button('Increment').onClick(() => {this.count++})}}
}4.5.3 高级用法
- 监听多个属性
@Component
struct MultiWatchDemo {@State @Watch('onScoreChange') score: number = 0@State @Watch('onScoreChange') bonus: number = 0// 监听多个数值变化onScoreChange() {console.info(`Total: ${this.score + this.bonus}`)}build() {Column() {// UI实现}}
}
- 条件监听
@Component
struct ConditionalWatchDemo {@State @Watch('onValueChange') value: number = 0@State isEnabled: boolean = trueonValueChange(newValue: number, oldValue: number) {if (this.isEnabled) {// 只在启用状态下处理变化this.handleValueChange(newValue, oldValue)}}private handleValueChange(newVal: number, oldVal: number) {// 处理逻辑}build() {Column() {Switch().checked(this.isEnabled).onChange((value: boolean) => {this.isEnabled = value})}}
}
4.5.4 @Watch使用场景
- 表单验证
@Component
struct FormValidationDemo {@State @Watch('validateEmail') email: string = ''@State emailError: string = ''validateEmail(newValue: string) {const emailRegex = /^[^\s@]+@[^\s@]+\.[^\s@]+$/if (!emailRegex.test(newValue)) {this.emailError = '请输入有效的邮箱地址'} else {this.emailError = ''}}build() {Column({ space: 10 }) {TextInput({ placeholder: '请输入邮箱' }).onChange((value: string) => {this.email = value})if (this.emailError) {Text(this.emailError).fontSize(12).fontColor(Color.Red)}}}
}
- 数据同步
@Component
struct DataSyncDemo {@State @Watch('syncToServer') localData: IUser = {}async syncToServer(newValue: IUser) {try {await this.saveToServer(newValue)console.info('Data synced successfully')} catch (error) {console.error('Sync failed:', error)}}private async saveToServer(data: object) {// 实现服务器同步逻辑}build() {Column() {// UI实现}}
}
4.5.5 最佳实践
- 性能优化
@Component
struct WatchOptimizationDemo {@State @Watch('onDataChange') data: IUser = {name:'tata',role:'admin'}// ✅ 优化:添加防抖处理private debounceTimer: number = -1onDataChange() {if (this.debounceTimer !== -1) {clearTimeout(this.debounceTimer)}this.debounceTimer = setTimeout(() => {this.processDataChange(this.data)this.debounceTimer = -1}, 300)}private processDataChange(data: IUser) {// 处理数据变化}build() {Column() {// UI实现}}
}- 错误处理
@Component
struct WatchErrorHandlingDemo {@State @Watch('onDataChange') data: IUser = {name:'tata',role:'admin'}onDataChange() {try {// 数据验证if (!this.isValidData(this.data)) {throw new Error('Invalid data format')}// 处理数据this.processData(this.data)} catch (error) {console.error('Error in watch handler:', error)// 恢复到之前的值// 显示错误提示this.showError(error.message)}}private isValidData(data: IUser): boolean {// 实现数据验证逻辑return true}private processData(data: IUser) {// 处理数据}private showError(message: string) {// 显示错误提示}build() {Column() {// UI实现}}
}
4.5.6 @Watch注意事项
- 避免无限循环
@Component
struct WatchCycleDemo {@State @Watch('onValueChange') value1: number = 0@State @Watch('onValue2Change') value2: number = 0// ❌ 错误:可能导致无限循环onValueChange() {this.value2++ // 触发value2的watch}onValue2Change() {this.value1++ // 触发value1的watch}// ✅ 正确:添加循环保护private updateCount: number = 0private readonly MAX_UPDATES: number = 3onSafeValueChange() {if (this.updateCount < this.MAX_UPDATES) {this.updateCount++this.value2++} else {this.updateCount = 0}}
}
- 同步与异步处理
@Component
struct WatchAsyncDemo {@State @Watch('onDataChange') data: object = {}// ✅ 处理异步操作async onDataChange(newValue: object) {try {await this.validateData(newValue)await this.saveData(newValue)} catch (error) {console.error('Async operation failed:', error)}}private async validateData(data: object): Promise<void> {// 异步数据验证}private async saveData(data: object): Promise<void> {// 异步保存数据}build() {Column() {// UI实现}}
}
- @Watch 回调函数实际上不支持有效的参数传递
- 回调函数中第一个参数是被监听属性的名称字符串
4.6 @Observed/@ObjectLink修饰符
4.6.1 基本概念
@Observed和@ObjectLink是用于对象类型数据的响应式管理修饰符:
- @Observed:将一个类标记为可观察对象
- @ObjectLink:用于在组件间建立对象的引用关系,实现对象级别的双向同步
4.6.2 基础用法
// 定义可观察类
@Observed
class Student {name: stringage: numberscores: number[]constructor(name: string, age: number) {this.name = namethis.age = agethis.scores = []}
}// 父组件
@Component
struct ParentComponent {// 创建可观察对象实例@State student: Student = new Student('tata', 18)build() {Column() {// 传递给子组件StudentCard({ studentInfo: this.student })Button('修改信息').onClick(() => {this.student.age++this.student.scores.push(100)})}}
}// 子组件
@Component
struct StudentCard {// 使用ObjectLink引用父组件的对象@ObjectLink studentInfo: Studentbuild() {Column() {Text(`姓名: ${this.studentInfo.name}`)Text(`年龄: ${this.studentInfo.age}`)ForEach(this.studentInfo.scores, (score:number) => {Text(`分数: ${score}`)})}}
}
4.6.3 关键点
- 类级别装饰器
// ✅ 正确:整个类使用 @Observed
@Observed
class Model {property1: stringproperty2: number
}// ❌ 错误:不能装饰属性
class WrongModel {@Observed property: string // 这是错误的用法
}
- 嵌套对象处理
@Observed
class Parent {child: Child // 如果 Child 需要观察,Child 类也需要使用 @Observed 装饰器
}@Observed
class Child {name: string
}
- 数组处理
@Observed
class TodoList {items: Array<TodoItem> // TodoItem 类需要使用 @ObservedaddItem(item: TodoItem) {this.items.push(item)}
}@Observed
class TodoItem {content: stringcompleted: boolean
}
4.6.4 实际应用示例
// 定义观察类
@Observed
class Profile {name: stringage: numberconstructor(name: string, age: number) {this.name = namethis.age = age}
}// 父组件
@Component
struct ProfileManager {@State profile: Profile = new Profile('tata', 25)build() {Column() {// 传递给子组件ProfileEditor({ userProfile: this.profile })ProfileDisplay({ userProfile: this.profile })}}
}// 编辑组件
@Component
struct ProfileEditor {@ObjectLink userProfile: Profilebuild() {Column() {Button('修改年龄').onClick(() => {this.userProfile.age++ // 直接修改将触发更新})}}
}// 显示组件
@Component
struct ProfileDisplay {@ObjectLink userProfile: Profilebuild() {Column() {Text(`姓名: ${this.userProfile.name}`)Text(`年龄: ${this.userProfile.age}`)}}
}
4.6.5 注意事项
- @Observed 只能用于类声明
- 不能用于装饰类的属性
- 嵌套对象如需响应式,需要分别使用 @Observed 装饰器
- 配合 @ObjectLink 使用来实现组件间的数据同步
- 观察对象的属性修改会自动触发相关组件的更新
对比
让我详细对比这些修饰符的区别:
1. 使用场景对比
| 修饰符 | 使用对象 | 数据流向 | 使用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| @State | 基本类型/对象/数组 | 组件内部 | 管理组件内部状态 |
| @Prop | 基本类型/对象/数组 | 父 -> 子 | 父组件向子组件传递数据 |
| @Link | 基本类型/对象/数组 | 双向 | 父子组件双向数据同步 |
| @Observed/@ObjectLink | 类实例 | 多组件共享 | 复杂对象的响应式管理 |
2. 具体示例对比
// @State:组件内部状态管理
@Component
struct StateExample {@State count: number = 0 // 组件内部状态build() {Column() {Text(`Count: ${this.count}`)Button('Add').onClick(() => this.count++)}}
}// @Prop:单向数据流
@Component
struct PropExample {@Prop title: string // 从父组件接收数据build() {Text(this.title)}
}// @Link:双向数据绑定
@Component
struct LinkExample {@Link message: string // 与父组件双向绑定build() {TextInput({ text: this.message }).onChange((value: string) => {this.message = value // 修改会影响父组件})}
}// @Observed:对象响应式
@Observed
class User {name: stringage: numberconstructor(name: string, age: number) {this.name = namethis.age = age}
}@Component
struct ObservedExample {@State user: User = new User('tata', 25)build() {Column() {UserCard({ userInfo: this.user }) // 传递给子组件}}
}@Component
struct UserCard {@ObjectLink userInfo: User // 引用观察对象build() {Column() {Text(`Name: ${this.userInfo.name}`)Button('Age++').onClick(() => {this.userInfo.age++ // 直接修改对象属性})}}
}
3. 特点对比
@State
- 用于组件内部状态管理
- 值变化会触发组件重新渲染
- 可以管理任何类型的数据
@State count: number = 0
@State user: Object = {}
@State list: string[] = []
@Prop
- 实现单向数据流
- 子组件不能直接修改父组件数据
- 父组件数据变化会更新子组件
// 父组件
@State title: string = 'Hello'
// 子组件使用
@Prop title: string
@Link
- 实现双向数据绑定
- 子组件可以直接修改数据
- 数据变化双向同步
// 父组件
@State message: string = ''
// 子组件使用
@Link message: string
@Observed/@ObjectLink
- 用于复杂对象的响应式管理
- 自动跟踪对象属性变化
- 支持多组件共享和同步
@Observed
class Model {// 整个类的属性都会被观察
}@ObjectLink model: Model // 引用观察对象
4. 数据同步方式对比
// @State:组件内直接修改
@State value: number = 0
this.value = 1 // 直接赋值// @Prop:不能直接修改
@Prop title: string
this.title = 'new' // ❌ 错误// @Link:双向同步
@Link count: number
this.count++ // ✅ 会同步到父组件// @Observed:对象属性修改
@ObjectLink user: User
this.user.name = 'new name' // ✅ 自动触发更新

相关文章:

鸿蒙修饰符
文章目录 一、引言1.1 什么是修饰符1.2 修饰符在鸿蒙开发中的重要性1.3 修饰符的作用机制 二、UI装饰类修饰符2.1 Styles修饰符2.1.1 基本概念和使用场景2.1.2 使用示例2.1.3 最佳实践 2.2 Extend修饰符2.2.1 基本概念2.2.2 使用示例2.2.3 Extend vs Styles 对比2.2.4 使用建议…...

springboot359智慧草莓基地管理系统(论文+源码)_kaic
毕 业 设 计(论 文) 题目:智慧草莓基地管理系统 摘 要 现代经济快节奏发展以及不断完善升级的信息化技术,让传统数据信息的管理升级为软件存储,归纳,集中处理数据信息的管理方式。本智慧草莓基地管理系统就…...

单片机位数对性能会产生什么影响?!
单片机的位数是指其处理器核心的位宽,通常以比特(bit)为单位。常见的位数有8位、16位、32位和64位等。 单片机位数越高,处理器能够处理的数据量越大,性能也相应提高。 以下是对单片机位数对性能影响的详细分析&#…...

stm32内部高速晶振打开作为主时钟
首先建议你别这么干,因为内部晶振特别容易受温度等外界影响,很容易卡死或堵死程序 我是因为没画外部晶振电路,所以只能开内部晶振来作为时钟 适用于stm32f103系列 把下面的代码换掉源文件里的时钟源配置 /* 开启HSI 即内部晶振时钟 */RCC…...

【分页查询】.NET开源 ORM 框架 SqlSugar 系列
.NET开源 ORM 框架 SqlSugar 系列 【开篇】.NET开源 ORM 框架 SqlSugar 系列【入门必看】.NET开源 ORM 框架 SqlSugar 系列【实体配置】.NET开源 ORM 框架 SqlSugar 系列【Db First】.NET开源 ORM 框架 SqlSugar 系列【Code First】.NET开源 ORM 框架 SqlSugar 系列【数据事务…...

【CSS in Depth 2 精译_061】9.4 CSS 中的模式库 + 9.5 本章小结
当前内容所在位置(可进入专栏查看其他译好的章节内容) 【第九章 CSS 的模块化与作用域】 ✔️ 9.1 模块的定义 9.1.1 模块和全局样式9.1.2 一个简单的 CSS 模块9.1.3 模块的变体9.1.4 多元素模块 9.2 将模块组合为更大的结构 9.2.1 模块中多个职责的拆分…...

惠普电脑切换默认F1至F12快捷键,FN切换
发现新买的惠普电脑,按F1至F12发现是快捷功能键,而按fnF1至F12才是windows的功能键和正常我自己使用的电脑刚好相反,实在太不方便了。 解决办法需要进入biso里面去把功能键模式选中给关掉,才能恢复回来...

计算机的错误计算(一百七十)
摘要 回复一中学生来信,探讨 MATLAB 关于算式 的计算问题。 在计算机的错误计算(一百三十二)中,我们探讨了手持式计算器关于算式 的计算问题。一中学生来信询问该算式在数学软件中是否会出错。 例1. 在 MATLAB 中计算 . 首…...

Python `async def` 函数中使用 `yield` 和 `return` 的区别
Python async def 函数中使用 yield 和 return 的区别 1. return 的使用示例代码输出结果解释 2. yield 的使用示例代码输出结果解释 3. 总结 在 Python 中,async def 函数用于定义异步函数,这些函数可以在执行过程中暂停和恢复,通常与 await…...

JAVA修饰符
JAVA 修饰符...

Java 单例模式:深度解析与应用
在软件开发领域,设计模式是解决常见设计问题的有效方案,而单例模式作为创建型设计模式中的一员,其重要性不容小觑。它能够确保一个类仅有一个实例,并提供全局访问点,这一特性在资源管理、配置信息读取、线程池管理以及…...

软件质量保证——单元测试之白盒技术
笔记内容及图片整理自XJTUSE “软件质量保证” 课程ppt,仅供学习交流使用,谢谢。 程序图 程序图定义 程序图P(V,E),V是节点的集合(节点是程序中的语句或语句片段),E是有向边的集合…...

Vue0-生命周期-03
生命周期 生命周期指定就是一个对象从创建到销毁的整个过程。 Vue也是有的 完整的Vue周期包含8个阶段。 Vue官方生命周期流程图: 那这有什么用呢?我们可以在指定阶段做特殊的事件。 这些方法伴随生命周期的进行自动执行。 <!DOCTYPE html> <…...

Flutter:页面滚动
1、单一页面,没有列表没分页的,推荐使用:SingleChildScrollView() return Scaffold(backgroundColor: Color(0xffF6F6F6),body: SingleChildScrollView(child: _buildView()) );2、列表没分页,如购物车页,每个item之间…...
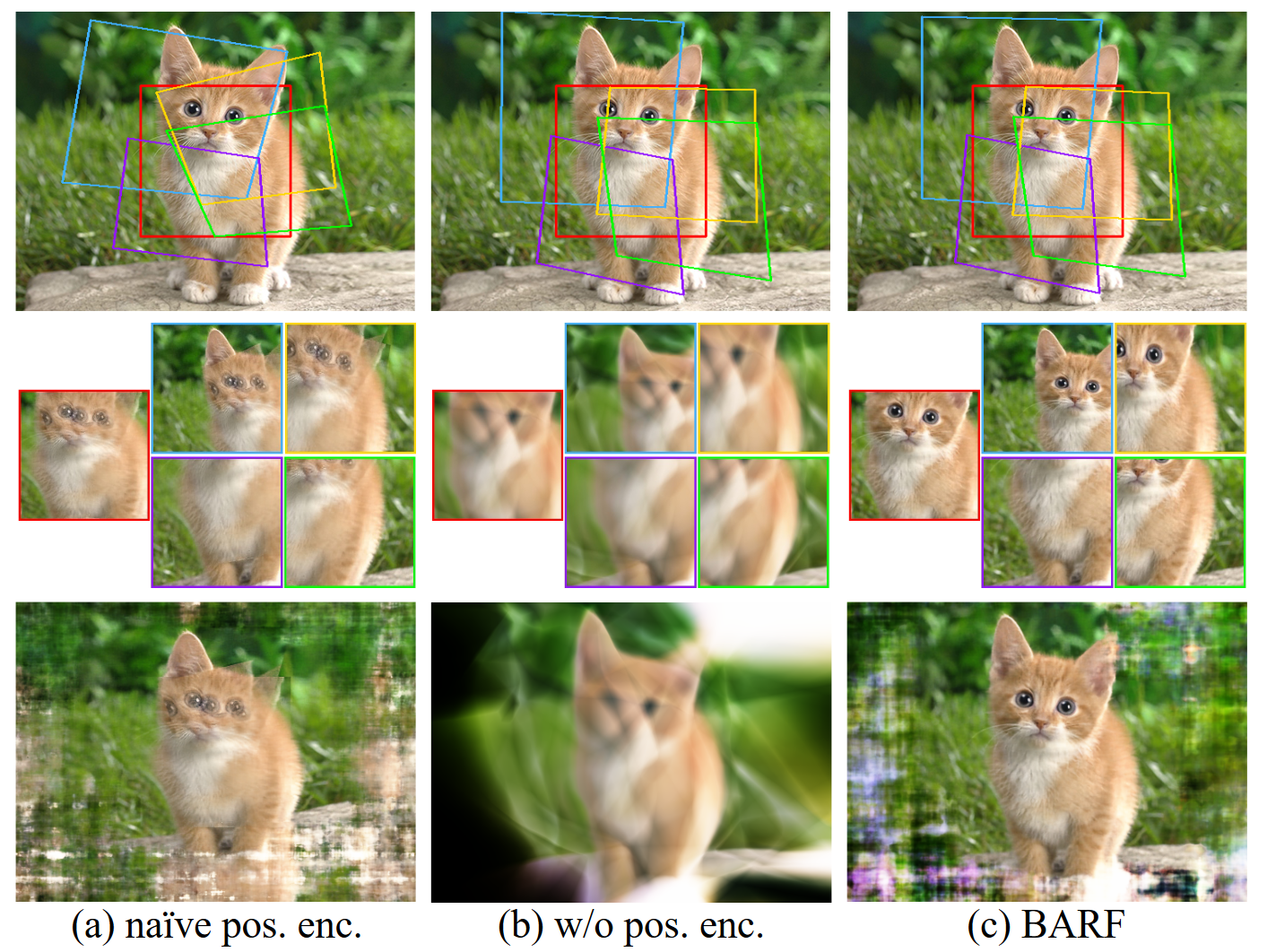

【CameraPoseRefinement】以BARF为例介绍三维重建中的位姿优化
文章目录 IntroductionApproachPlanar Image Alignment(2D)Neural Radiance Fields (3D)Bundle-Adjusting Neural Radiance Fields Experiment平面图像对齐的定性实验合成场景上的定量实验 Introduction 在计算机视觉三维重建中,求解3D场景的表示和定位给定的相机帧…...

YOLO系列论文综述(从YOLOv1到YOLOv11)【第13篇:YOLOv10——实时端到端物体检测】
YOLOv10 1 摘要2 网络结构3 YOLOv1-v10对比 YOLO系列博文: 【第1篇:概述物体检测算法发展史、YOLO应用领域、评价指标和NMS】【第2篇:YOLO系列论文、代码和主要优缺点汇总】【第3篇:YOLOv1——YOLO的开山之作】【第4篇:…...

多数元素
多数元素 给定一个大小为 n 的数组 nums ,返回其中的多数元素。多数元素是指在数组中出现次数 大于 ⌊ n/2 ⌋ 的元素。 你可以假设数组是非空的,并且给定的数组总是存在多数元素。 示例 1: 输入:nums [3,2,3] 输出ÿ…...

EasyDSS视频推拉流技术的应用与安防摄像机视频采集参数
安防摄像机的视频采集参数对于确保监控系统的有效性和图像质量至关重要。这些参数不仅影响视频的清晰度和流畅度,还直接影响存储和网络传输的需求。 安防摄像机图像效果的好坏,由DSP处理器和图像传感器sensor决定,如何利用好已有的硬件资源&…...

在CentOS7上更换为阿里云源
在CentOS 7上更换为阿里云YUM源可以通过以下步骤进行: 备份当前的YUM源配置文件 sudo mv /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo.backup 下载阿里云的YUM源配置文件 sudo curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo http://mirr…...

小程序跳转到本页面并传参
const pages getCurrentPages(); const currentPage pages[pages.length - 1]; // 当前页面路由 const route currentPage.route; // 当前页面参数 const options currentPage.options;// 构建新的 URL 参数 const newOptions {...options,// newParam: newValue }; // 你…...
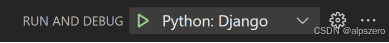
使用VSCode开发Django指南
使用VSCode开发Django指南 一、概述 Django 是一个高级 Python 框架,专为快速、安全和可扩展的 Web 开发而设计。Django 包含对 URL 路由、页面模板和数据处理的丰富支持。 本文将创建一个简单的 Django 应用,其中包含三个使用通用基本模板的页面。在此…...
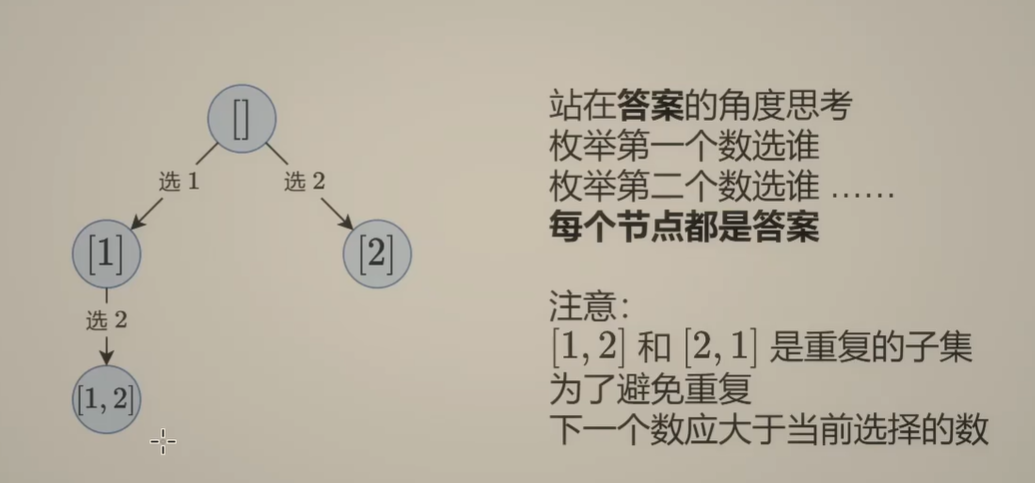
Day131 | 灵神 | 回溯算法 | 子集型 子集
Day131 | 灵神 | 回溯算法 | 子集型 子集 78.子集 78. 子集 - 力扣(LeetCode) 思路: 笔者写过很多次这道题了,不想写题解了,大家看灵神讲解吧 回溯算法套路①子集型回溯【基础算法精讲 14】_哔哩哔哩_bilibili 完…...

安宝特方案丨XRSOP人员作业标准化管理平台:AR智慧点检验收套件
在选煤厂、化工厂、钢铁厂等过程生产型企业,其生产设备的运行效率和非计划停机对工业制造效益有较大影响。 随着企业自动化和智能化建设的推进,需提前预防假检、错检、漏检,推动智慧生产运维系统数据的流动和现场赋能应用。同时,…...
)
IGP(Interior Gateway Protocol,内部网关协议)
IGP(Interior Gateway Protocol,内部网关协议) 是一种用于在一个自治系统(AS)内部传递路由信息的路由协议,主要用于在一个组织或机构的内部网络中决定数据包的最佳路径。与用于自治系统之间通信的 EGP&…...

JVM垃圾回收机制全解析
Java虚拟机(JVM)中的垃圾收集器(Garbage Collector,简称GC)是用于自动管理内存的机制。它负责识别和清除不再被程序使用的对象,从而释放内存空间,避免内存泄漏和内存溢出等问题。垃圾收集器在Ja…...
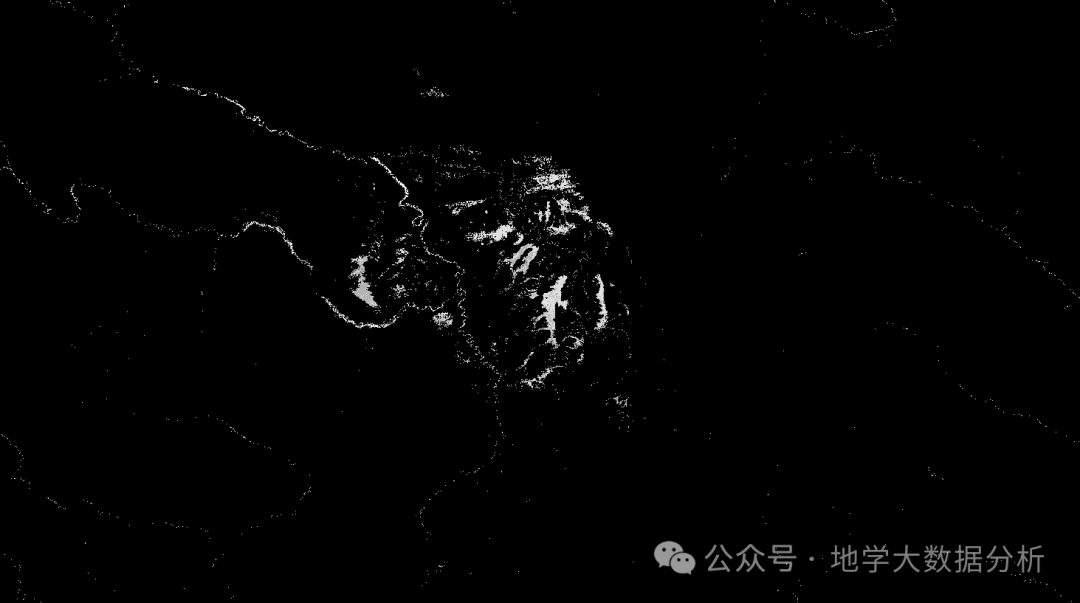

全球首个30米分辨率湿地数据集(2000—2022)
数据简介 今天我们分享的数据是全球30米分辨率湿地数据集,包含8种湿地亚类,该数据以0.5X0.5的瓦片存储,我们整理了所有属于中国的瓦片名称与其对应省份,方便大家研究使用。 该数据集作为全球首个30米分辨率、覆盖2000–2022年时间…...
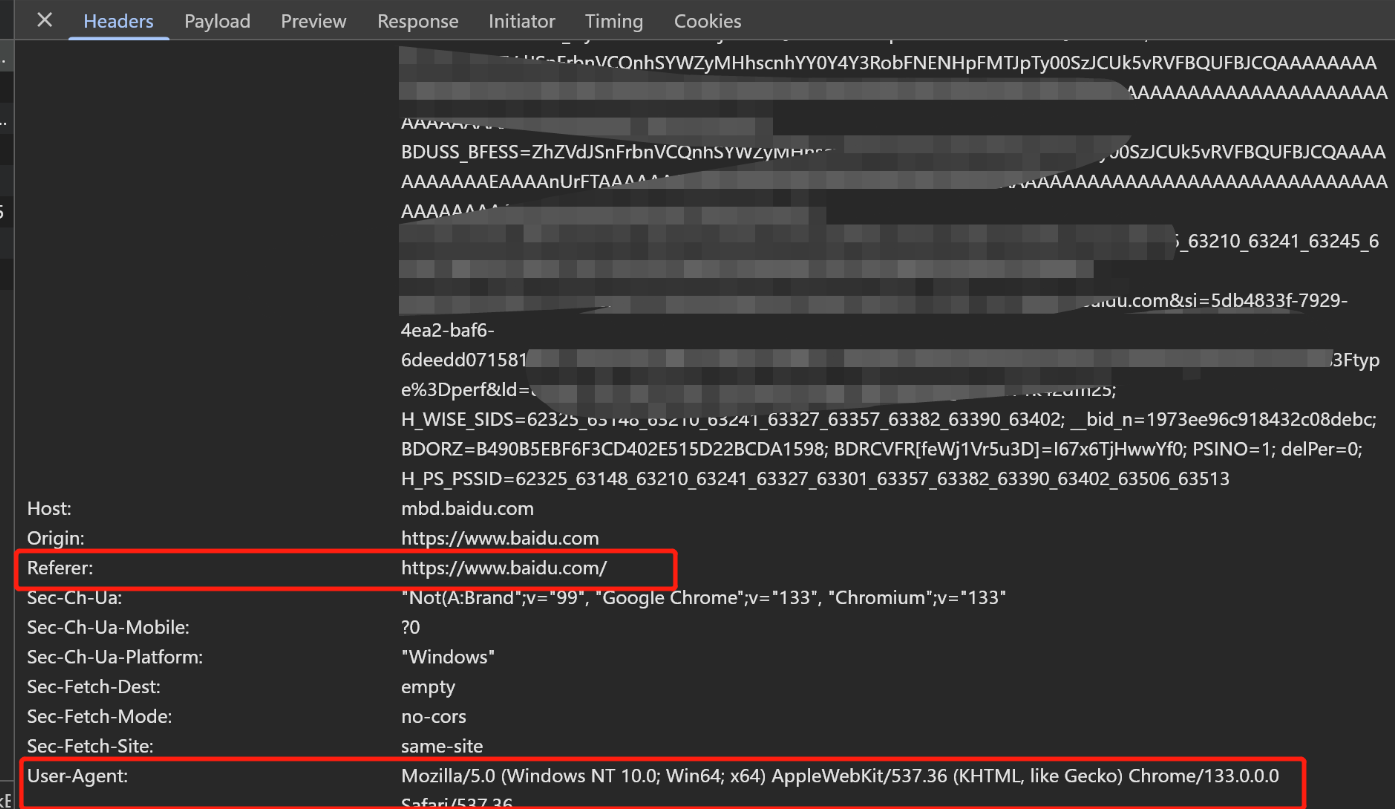
Python爬虫(一):爬虫伪装
一、网站防爬机制概述 在当今互联网环境中,具有一定规模或盈利性质的网站几乎都实施了各种防爬措施。这些措施主要分为两大类: 身份验证机制:直接将未经授权的爬虫阻挡在外反爬技术体系:通过各种技术手段增加爬虫获取数据的难度…...

Rust 异步编程
Rust 异步编程 引言 Rust 是一种系统编程语言,以其高性能、安全性以及零成本抽象而著称。在多核处理器成为主流的今天,异步编程成为了一种提高应用性能、优化资源利用的有效手段。本文将深入探讨 Rust 异步编程的核心概念、常用库以及最佳实践。 异步编程基础 什么是异步…...

多模态大语言模型arxiv论文略读(108)
CROME: Cross-Modal Adapters for Efficient Multimodal LLM ➡️ 论文标题:CROME: Cross-Modal Adapters for Efficient Multimodal LLM ➡️ 论文作者:Sayna Ebrahimi, Sercan O. Arik, Tejas Nama, Tomas Pfister ➡️ 研究机构: Google Cloud AI Re…...
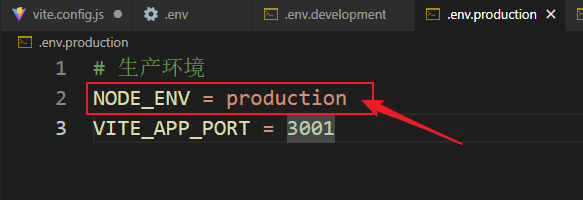
vue3+vite项目中使用.env文件环境变量方法
vue3vite项目中使用.env文件环境变量方法 .env文件作用命名规则常用的配置项示例使用方法注意事项在vite.config.js文件中读取环境变量方法 .env文件作用 .env 文件用于定义环境变量,这些变量可以在项目中通过 import.meta.env 进行访问。Vite 会自动加载这些环境变…...
