S变换matlab实现
S变换函数
function [st,t,f] = st(timeseries,minfreq,maxfreq,samplingrate,freqsamplingrate)
% S变换
% Code by huasir @Beijing 2025.1.10
% Reference is "Localization of the Complex Spectrum: The S Transform"
% from IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 44., number 4, April 1996, pages 998-1001.
%% 函数的输出和输出
% Input
% * timeseries: 待进行S变换的信号向量
% * minfreq: 时频分布结果中的最小频率,对应频率轴的最小值(默认值为0)
% * maxfreq: 时频分布结果中的最大频率,对应频率轴的最大值(默认值为奈奎斯特频率)
% * samplingrate: 两个采样点之间的采样时间间隔(默认为1)
% * freqsamplingrate:频率分辨率(默认为1)
% Output
% * st: Stockwell变换的结果,行对应频率,列对应时刻,
% * t: 包含采样时刻的时间向量
% * f: 频率向量
%% 以下参数可按需调整
% * [verbose]: 如果为真,则打印函数运行中所有的提示信息
% * [removeedge]:如果为真,则删除最小二乘拟合的抛物线,并在时间序列的边缘放置一个5%的hanning锥
% 通常情况下,这是个不错的选择。
% * [analytic_signal]: 如果时间序列是实数值,则取它的解析信号并进行S变换
% * [factor]: 局部化高斯的宽度因子,例如,一个周期为10s的正弦信号具有宽度因子*10s的高斯窗口。
% 通常使用的因子为1,有些情况下为了得到更好的频率分辨率,可以采用3。
% *****All frequencies in (cycles/(time unit))!******
% Copyright (c) by huasir
% $Revision: 1.0 $ $Date: 2025/01/10 $
% 这是保存函数默认值的S变换封装器
TRUE = 1;
FALSE = 0;
%%% 默认参数 [有特殊需求的情况下进行更改]
verbose = TRUE;
removeedge= FALSE;
analytic_signal = FALSE;
factor = 1;
%%% 默认参数设置结果
%% 开始进行输入变量检查
% 首先确保输入的时间序列是有效值,否则,返回帮助信息
if verbose disp(' '),end % i like a line left blank if nargin == 0 % nargin为输入参数的个数,nargin=0,表示无输入if verbose disp('No parameters inputted.'),end st_help t=0;,st=-1;,f=0; return
end % 如果输入数据为行向量的话,将它调整为列向量
if size(timeseries,2) > size(timeseries,1) timeseries=timeseries';
end % 确保输入数据为1维向量,而不是矩阵
if size(timeseries,2) > 1 error('Please enter a *vector* of data, not matrix') return
elseif (size(timeseries)==[1 1]) == 1 error('Please enter a *vector* of data, not a scalar') return
end % 输入变量不全的情况下采用默认值if nargin == 1 %只有1个输入变量minfreq = 0; maxfreq = fix(length(timeseries)/2); samplingrate=1; freqsamplingrate=1;
elseif nargin==2 %2个输入变量maxfreq = fix(length(timeseries)/2); samplingrate=1; freqsamplingrate=1; [ minfreq,maxfreq,samplingrate,freqsamplingrate] = check_input(minfreq,maxfreq,samplingrate,freqsamplingrate,verbose,timeseries);
elseif nargin==3 samplingrate=1; freqsamplingrate=1; [ minfreq,maxfreq,samplingrate,freqsamplingrate] = check_input(minfreq,maxfreq,samplingrate,freqsamplingrate,verbose,timeseries);
elseif nargin==4 freqsamplingrate=1; [ minfreq,maxfreq,samplingrate,freqsamplingrate] = check_input(minfreq,maxfreq,samplingrate,freqsamplingrate,verbose,timeseries);
elseif nargin == 5 [ minfreq,maxfreq,samplingrate,freqsamplingrate] = check_input(minfreq,maxfreq,samplingrate,freqsamplingrate,verbose,timeseries);
else if verbose disp('Error in input arguments: using defaults'),end minfreq = 0; maxfreq = fix(length(timeseries)/2); samplingrate=1; freqsamplingrate=1;
end
if verbose disp(sprintf('Minfreq = %d',minfreq)) disp(sprintf('Maxfreq = %d',maxfreq)) disp(sprintf('Sampling Rate (time domain) = %d',samplingrate)) disp(sprintf('Sampling Rate (freq. domain) = %d',freqsamplingrate)) disp(sprintf('The length of the timeseries is %d points',length(timeseries))) disp(' ')
end
%END OF INPUT VARIABLE CHECK % If you want to "hardwire" minfreq & maxfreq & samplingrate & freqsamplingrate do it here % calculate the sampled time and frequency values from the two sampling rates
t = (0:length(timeseries)-1)*samplingrate;
spe_nelements =ceil((maxfreq - minfreq+1)/freqsamplingrate) ;
f = (minfreq + [0:spe_nelements-1]*freqsamplingrate)/(samplingrate*length(timeseries));
if verbose disp(sprintf('The number of frequency voices is %d',spe_nelements)),end % The actual S Transform function is here:
st = strans(timeseries,minfreq,maxfreq,samplingrate,freqsamplingrate,verbose,removeedge,analytic_signal,factor);
% this function is below, thus nicely encapsulated %WRITE switch statement on nargout
% if 0 then plot amplitude spectrum
if nargout==0 if verbose disp('Plotting pseudocolor image'),end pcolor(t,f,abs(st))
end return %^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
%^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
%^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
%^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
%^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ function st = strans(timeseries,minfreq,maxfreq,samplingrate,freqsamplingrate,verbose,removeedge,analytic_signal,factor);
% Returns the Stockwell Transform, STOutput, of the time-series
% Code by R.G. Stockwell.
% Reference is "Localization of the Complex Spectrum: The S Transform"
% from IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 44., number 4,
% April 1996, pages 998-1001.
%
%-------Inputs Returned------------------------------------------------
% - are all taken care of in the wrapper function above
%
%-------Outputs Returned------------------------------------------------
%
% ST -a complex matrix containing the Stockwell transform.
% The rows of STOutput are the frequencies and the
% columns are the time values
%
%
%----------------------------------------------------------------------- % Compute the length of the data.
n=length(timeseries);
original = timeseries;
if removeedge if verbose disp('Removing trend with polynomial fit'),end ind = [0:n-1]'; r = polyfit(ind,timeseries,2); fit = polyval(r,ind) ; timeseries = timeseries - fit; if verbose disp('Removing edges with 5% hanning taper'),end sh_len = floor(length(timeseries)/10); wn = hanning(sh_len); if(sh_len==0) sh_len=length(timeseries); wn = 1&[1:sh_len]; end % make sure wn is a column vector, because timeseries is if size(wn,2) > size(wn,1) wn=wn'; end timeseries(1:floor(sh_len/2),1) = timeseries(1:floor(sh_len/2),1).*wn(1:floor(sh_len/2),1); timeseries(length(timeseries)-floor(sh_len/2):n,1) = timeseries(length(timeseries)-floor(sh_len/2):n,1).*wn(sh_len-floor(sh_len/2):sh_len,1); end % If vector is real, do the analytic signal if analytic_signal if verbose disp('Calculating analytic signal (using Hilbert transform)'),end % this version of the hilbert transform is different than hilbert.m % This is correct! ts_spe = fft(real(timeseries)); h = [1; 2*ones(fix((n-1)/2),1); ones(1-rem(n,2),1); zeros(fix((n-1)/2),1)]; ts_spe(:) = ts_spe.*h(:); timeseries = ifft(ts_spe);
end % Compute FFT's
tic;vector_fft=fft(timeseries);tim_est=toc;
vector_fft=[vector_fft,vector_fft];
tim_est = tim_est*ceil((maxfreq - minfreq+1)/freqsamplingrate) ;
if verbose disp(sprintf('Estimated time is %f',tim_est)),end % Preallocate the STOutput matrix
st=zeros(ceil((maxfreq - minfreq+1)/freqsamplingrate),n);
% Compute the mean
% Compute S-transform value for 1 ... ceil(n/2+1)-1 frequency points
if verbose disp('Calculating S transform...'),end
if minfreq == 0 st(1,:) = mean(timeseries)*(1&[1:1:n]);
else st(1,:)=ifft(vector_fft(minfreq+1:minfreq+n).*g_window(n,minfreq,factor));
end %the actual calculation of the ST
% Start loop to increment the frequency point
for banana=freqsamplingrate:freqsamplingrate:(maxfreq-minfreq) st(banana/freqsamplingrate+1,:)=ifft(vector_fft(minfreq+banana+1:minfreq+banana+n).*g_window(n,minfreq+banana,factor));
end % a fruit loop! aaaaa ha ha ha ha ha ha ha ha ha ha
% End loop to increment the frequency point
if verbose disp('Finished Calculation'),end %%% end strans function %------------------------------------------------------------------------
function gauss=g_window(length,freq,factor) % Function to compute the Gaussion window for
% function Stransform. g_window is used by function
% Stransform. Programmed by Eric Tittley
%
%-----Inputs Needed--------------------------
%
% length-the length of the Gaussian window
%
% freq-the frequency at which to evaluate
% the window.
% factor- the window-width factor
%
%-----Outputs Returned--------------------------
%
% gauss-The Gaussian window
% vector(1,:)=[0:length-1];
vector(2,:)=[-length:-1];
vector=vector.^2;
vector=vector*(-factor*2*pi^2/freq^2);
% Compute the Gaussion window
gauss=sum(exp(vector)); %----------------------------------------------------------------------- %^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^%
function [ minfreq,maxfreq,samplingrate,freqsamplingrate] = check_input(minfreq,maxfreq,samplingrate,freqsamplingrate,verbose,timeseries)
% this checks numbers, and replaces them with defaults if invalid % if the parameters are passed as an array, put them into the appropriate variables
s = size(minfreq);
l = max(s);
if l > 1 if verbose disp('Array of inputs accepted.'),end temp=minfreq; minfreq = temp(1);; if l > 1 maxfreq = temp(2);,end; if l > 2 samplingrate = temp(3);,end; if l > 3 freqsamplingrate = temp(4);,end; if l > 4 if verbose disp('Ignoring extra input parameters.'),end end; end if minfreq < 0 | minfreq > fix(length(timeseries)/2); minfreq = 0; if verbose disp('Minfreq < 0 or > Nyquist. Setting minfreq = 0.'),end end if maxfreq > length(timeseries)/2 | maxfreq < 0 maxfreq = fix(length(timeseries)/2); if verbose disp(sprintf('Maxfreq < 0 or > Nyquist. Setting maxfreq = %d',maxfreq)),end end if minfreq > maxfreq temporary = minfreq; minfreq = maxfreq; maxfreq = temporary; clear temporary; if verbose disp('Swapping maxfreq <=> minfreq.'),end end if samplingrate <0 samplingrate = abs(samplingrate); if verbose disp('Samplingrate <0. Setting samplingrate to its absolute value.'),end end if freqsamplingrate < 0 % check 'what if freqsamplingrate > maxfreq - minfreq' case freqsamplingrate = abs(freqsamplingrate); if verbose disp('Frequency Samplingrate negative, taking absolute value'),end end % bloody odd how you don't end a function %^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^%
function st_help
disp(' ')
disp('st() HELP COMMAND')
disp('st() returns - 1 or an error message if it fails')
disp('USAGE:: [localspectra,timevector,freqvector] = st(timeseries)')
disp('NOTE:: The function st() sets default parameters then calls the function strans()')
disp(' ')
disp('You can call strans() directly and pass the following parameters')
disp(' **** Warning! These inputs are not checked if strans() is called directly!! ****')
disp('USAGE:: localspectra = strans(timeseries,minfreq,maxfreq,samplingrate,freqsamplingrate,verbose,removeedge,analytic_signal,factor) ')disp(' ')
disp('Default parameters (available in st.m)')
disp('VERBOSE - prints out informational messages throughout the function.')
disp('REMOVEEDGE - removes the edge with a 5% taper, and takes')
disp('FACTOR - the width factor of the localizing gaussian')
disp(' ie, a sinusoid of period 10 seconds has a ')
disp(' gaussian window of width factor*10 seconds.')
disp(' I usually use factor=1, but sometimes factor = 3')
disp(' to get better frequency resolution.')
disp(' ')
disp('Default input variables')
disp('MINFREQ - the lowest frequency in the ST result(Default=0)')
disp('MAXFREQ - the highest frequency in the ST result (Default=nyquist')
disp('SAMPLINGRATE - the time interval between successive data points (Default = 1)')
disp('FREQSAMPLINGRATE - the number of frequencies between samples in the ST results')
% end of st_help procedure
S逆变换函数
function [ts] = inverse_st(st)
% Returns the inverse of the Stockwell Transform of the REAL_VALUED timeseries.
% Reference is "Localization of the Complex Spectrum: The S Transform"
% from IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 44., number 4, April 1996, pages 998-1001.
%
%-------Inputs Needed------------------------------------------------
%
% S-Transform matrix created by the st.m function
%-------Optional Inputs ------------------------------------------------
% none
%-------Outputs Returned------------------------------------------------
%
% ts -a REAL-VALUED time series
%--------Additional details----------------------- % sum over time to create the FFT spectrum for the positive frequencies
stspe = sum(st,2); % get st matrix dimensions
[nfreq,ntimes] = size(st);
if rem(ntimes ,2) ~= 0 % odd number of points, so nyquist point is not aliased, so concatenate % the reversed spectrum to create the negative frequencies % drop the DC value negspe = fliplr(stspe(2:nfreq)');
else % even number of points % therefore drop the first point (DC) and the last point (aliased nyqusit freq) negspe = fliplr(stspe(2:nfreq-1)');
end % using symmetry of FFT spectrum of a real signal, recreate the negative frequencies from the positie frequencies fullstspe = [conj(stspe') negspe]; % the time series is the inverse fft of this
ts = ifft(fullstspe);
% and take the real part, the imaginary part will be zero.
ts = real(ts); 相关文章:

S变换matlab实现
S变换函数 function [st,t,f] st(timeseries,minfreq,maxfreq,samplingrate,freqsamplingrate) % S变换 % Code by huasir Beijing 2025.1.10 % Reference is "Localization of the Complex Spectrum: The S Transform" % from IEEE Transactions on Signal Proc…...

Springboot——钉钉(站内)实现登录第三方应用
文章目录 前言准备1、创建钉钉应用,并开放网页应用2、配置网页应用各项参数发布版本 前端改造后端逻辑1、获取应用免登录 Access_token2、通过免登录 Access_token 和 Auth_Code 获取对应登录人信息 注意事项 前言 PC端的钉钉中工作台,增加第三方应用&a…...

基于深度学习算法的AI图像视觉检测
基于人工智能和深度学习方法的现代计算机视觉技术在过去10年里取得了显著进展。如今,它被广泛用于图像分类、人脸识别、图像中物体的识别等。那么什么是深度学习?深度学习是如何应用在视觉检测上的呢? 什么是深度学习? 深度学习是…...

cJson——序列化格式json和protobuf对比
cJson——序列化格式json和protobuf对比 1. 更小的消息体积2. 更快的序列化与反序列化速度3. 类型安全4. 向后和向前兼容性5. 更低的带宽消耗6. 高效的编码方式7. 易于跨语言支持8. 支持复杂的数据结构9. 更好的支持大型数据交换总结 Protocol Buffers (Protobuf) 和 JSON 都是…...

搭建一个fastapi的项目,调用ollama服务
1. 项目结构 my_project/ │ ├── app/ │ ├── main.py # FastAPI应用的入口 │ ├── services/ # 包含服务逻辑 │ │ └── ollama_service.py │ ├── models/ # 定义数据模型 │ │ └── response.py │ ├─…...
)
Wireshark编译手册(Windows)
以下是对 Wireshark 官方文档中“Windows 平台的设置和构建说明”部分的翻译和总结: 2.2. Windows 平台 本节提供了在 Windows 上进行 Wireshark 开发的快速设置指南,包含推荐的配置。 2.2.1. 使用 Microsoft Visual Studio 注意:除非您非…...

在高德地图上加载3DTilesLayer图层模型/天地瓦片
1. 引入必要的库 Three.js:一个用于创建和显示3D图形的JavaScript库。vuemap/three-layer:一个Vue插件,它允许你在高德地图中添加Three.js图层。vuemap/layer-3dtiles:一个用于处理3D Tiles格式数据的Vue插件,可以用来…...

深入浅出负载均衡:理解其原理并选择最适合你的实现方式
负载均衡是一种在多个计算资源(如服务器、CPU核心、网络链接等)之间分配工作负载的技术,旨在优化资源利用率、提高系统吞吐量和降低响应时间。负载均衡的实现方式多种多样,以下是几种常见的实现方式: 1. 硬件负载均衡&…...

STM32的存储结构
STM32F103 芯片是基于 ARM Cortex-M3 内核的微控制器,它集成了多种类型的存储器,每种存储器都有其特定的作用和存储对象。以下是关于 STM32F103 中 Flash、ROM 和 SRAM 的详细介绍: 1. Flash Memory (闪存) 作用:Flash 是非易失性…...

@SneakyThrows 注解详解
SneakyThrows 注解详解 1. 基本介绍 SneakyThrows 是 Lombok 提供的注解,用于简化异常处理,自动生成 try-catch 代码块,将检查型异常转换为非检查型异常。 2. 使用对比 2.1 传统写法 public String readFile(String path) {try {return …...

js监测页面可见性
监测切换页面 检测页面的可见性状态document.visibilityState:document.hiddenvisibilitychange 事件 js 检测页面切换至别的应用 检测页面的可见性状态 在JavaScript中,你可以使用Page Visibility API来检测页面的可见性状态。这个API提供了一组接口,允…...

Android wifi常见问题及分析
参考 Android Network/WiFi 那些事儿 前言 本文将讨论几个有意思的网络问题,同时介绍 Android 上常见WiFi 问题的分析思路。 网络基础Q & A 一. 网络分层缘由 分层想必大家很熟悉,是否想过为何需要这样分层? 网上大多都是介绍每一层…...

EFCore HasDefaultValueSql
今天小伙伴在代码中遇到了有关 HasDefaultValue 的疑问,这里整理澄清下... 在使用 Entity Framework Core (EFCore) 配置实体时,HasDefaultValue 方法会为数据库列设置一个默认值。该默认值的行为取决于以下条件: 1. 配置 HasDefaultValue 的…...

Win10微调大语言模型ChatGLM2-6B
在《Win10本地部署大语言模型ChatGLM2-6B-CSDN博客》基础上进行,官方文档在这里,参考了这篇文章 首先确保ChatGLM2-6B下的有ptuning AdvertiseGen下载地址1,地址2,文件中数据留几行 模型文件下载地址 (注意࿱…...

什么叫区块链?怎么保证区块链的安全性?
区块链(Blockchain)是一种分布式数据库或账本技术,它通过去中心化的方式记录交易或其他数据,并确保这些记录是安全、透明和不可篡改的。区块链最初是作为比特币(Bitcoin)加密货币的基础技术而被公众所知&am…...

一、智能体强化学习——强化学习基础
1.1 强化学习与深度学习的基本概念 1.1.1 强化学习的核心思想 什么是强化学习? 强化学习(Reinforcement Learning, RL):指在与环境(Environment)的反复交互中,智能体(Agent&#x…...

【DES加密】
什么是DES DES(Data Encryption Standard) 是一种对称加密算法。它的设计目标是提供高度的数据安全性和性能。 DES的概念 DES使用56位的密钥和64位的明文块进行加密。DES算法的分组大小是64位,因此,如果需要加密的明文长度不足64位,需要进…...

.NET中的框架和运行环境
在.NET生态系统中,框架和运行环境是两个不同的概念,它们各自扮演着重要的角色。 下面我将分别介绍.NET中的框架和运行环境,并解释它们之间的区别。 .NET 框架(Frameworks) 框架提供了一套预定义的类库、工具和服务&…...

探索微软 M365 安全:全方位守护数字世界
在当今这个科技呈井喷式飞速发展,数字化浪潮以汹涌澎湃、锐不可当之势席卷全球的时代,企业与个人仿若置身于一片浩瀚无垠、信息奔涌的海洋之中,尽情畅享着技术革新所带来的无穷无尽便利。然而,恰如平静海面下潜藏着暗礁与汹涌暗流,网络安全问题恰似隐匿在暗处、随时可能给…...

深入探索AI核心模型:CNN、RNN、GAN与Transformer
在人工智能的飞速发展中,众多深度学习模型和算法不断涌现,推动了许多领域的进步。特别是在图像识别、自然语言处理、生成建模等方向,AI模型的应用越来越广泛。本文将介绍几种最常用的AI模型,包括卷积神经网络(CNN&…...

内存分配函数malloc kmalloc vmalloc
内存分配函数malloc kmalloc vmalloc malloc实现步骤: 1)请求大小调整:首先,malloc 需要调整用户请求的大小,以适应内部数据结构(例如,可能需要存储额外的元数据)。通常,这包括对齐调整,确保分配的内存地址满足特定硬件要求(如对齐到8字节或16字节边界)。 2)空闲…...
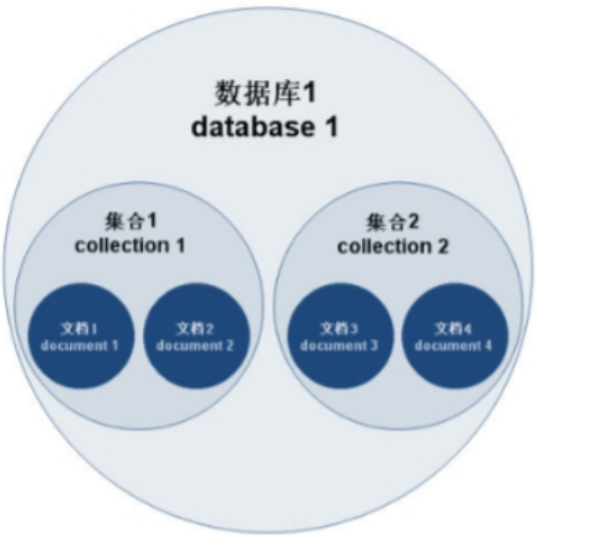
MongoDB学习和应用(高效的非关系型数据库)
一丶 MongoDB简介 对于社交类软件的功能,我们需要对它的功能特点进行分析: 数据量会随着用户数增大而增大读多写少价值较低非好友看不到其动态信息地理位置的查询… 针对以上特点进行分析各大存储工具: mysql:关系型数据库&am…...
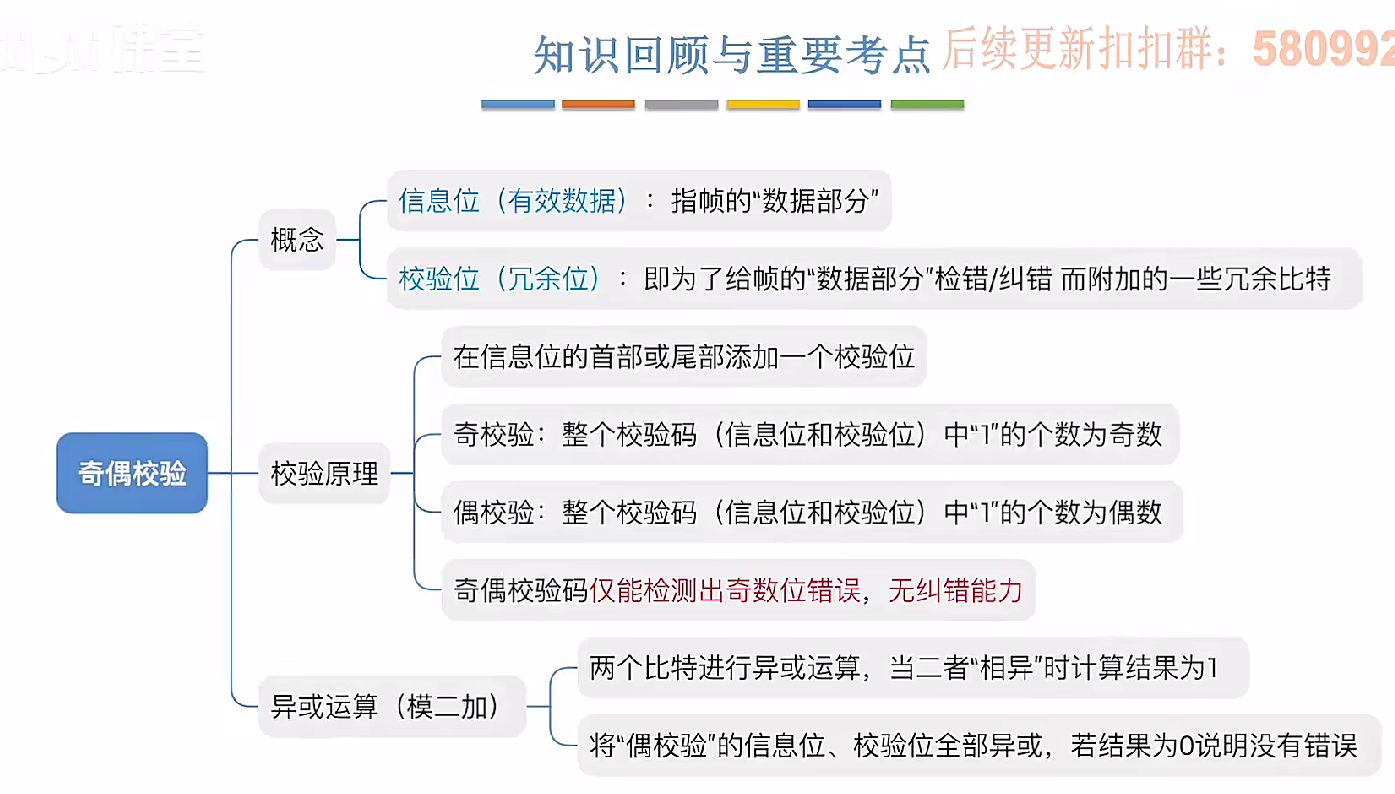
3.3.1_1 检错编码(奇偶校验码)
从这节课开始,我们会探讨数据链路层的差错控制功能,差错控制功能的主要目标是要发现并且解决一个帧内部的位错误,我们需要使用特殊的编码技术去发现帧内部的位错误,当我们发现位错误之后,通常来说有两种解决方案。第一…...
从深圳崛起的“机器之眼”:赴港乐动机器人的万亿赛道赶考路
进入2025年以来,尽管围绕人形机器人、具身智能等机器人赛道的质疑声不断,但全球市场热度依然高涨,入局者持续增加。 以国内市场为例,天眼查专业版数据显示,截至5月底,我国现存在业、存续状态的机器人相关企…...
可以参考以下方法:)
根据万维钢·精英日课6的内容,使用AI(2025)可以参考以下方法:
根据万维钢精英日课6的内容,使用AI(2025)可以参考以下方法: 四个洞见 模型已经比人聪明:以ChatGPT o3为代表的AI非常强大,能运用高级理论解释道理、引用最新学术论文,生成对顶尖科学家都有用的…...
中的KV缓存压缩与动态稀疏注意力机制设计)
大语言模型(LLM)中的KV缓存压缩与动态稀疏注意力机制设计
随着大语言模型(LLM)参数规模的增长,推理阶段的内存占用和计算复杂度成为核心挑战。传统注意力机制的计算复杂度随序列长度呈二次方增长,而KV缓存的内存消耗可能高达数十GB(例如Llama2-7B处理100K token时需50GB内存&a…...

在web-view 加载的本地及远程HTML中调用uniapp的API及网页和vue页面是如何通讯的?
uni-app 中 Web-view 与 Vue 页面的通讯机制详解 一、Web-view 简介 Web-view 是 uni-app 提供的一个重要组件,用于在原生应用中加载 HTML 页面: 支持加载本地 HTML 文件支持加载远程 HTML 页面实现 Web 与原生的双向通讯可用于嵌入第三方网页或 H5 应…...
详细解析)
Caliper 负载(Workload)详细解析
Caliper 负载(Workload)详细解析 负载(Workload)是 Caliper 性能测试的核心部分,它定义了测试期间要执行的具体合约调用行为和交易模式。下面我将全面深入地讲解负载的各个方面。 一、负载模块基本结构 一个典型的负载模块(如 workload.js)包含以下基本结构: use strict;/…...

Docker拉取MySQL后数据库连接失败的解决方案
在使用Docker部署MySQL时,拉取并启动容器后,有时可能会遇到数据库连接失败的问题。这种问题可能由多种原因导致,包括配置错误、网络设置问题、权限问题等。本文将分析可能的原因,并提供解决方案。 一、确认MySQL容器的运行状态 …...

前端开发者常用网站
Can I use网站:一个查询网页技术兼容性的网站 一个查询网页技术兼容性的网站Can I use:Can I use... Support tables for HTML5, CSS3, etc (查询浏览器对HTML5的支持情况) 权威网站:MDN JavaScript权威网站:JavaScript | MDN...
