一文讲清springboot所有注解
Spring Boot 注释是提供有关 Spring 应用程序信息的元数据。
基于 Spring 构建,涵盖其所有功能,
Spring Boot 因其生产就绪环境而迅速成为开发人员的最爱,它允许开发人员直接专注于逻辑,而无需配置和设置的麻烦。
Spring Boot 是一个基于微服务的框架,允许在最短的时间内创建可用于生产的应用程序。
以下是 Spring Boot 的一些主要特性:
它避免了 Spring 中繁重的 XML 配置。
它提供了易于维护和创建 REST 端点的功能。
它包括一个嵌入式 Tomcat 服务器。
部署非常容易;WAR 和 JAR 文件可以轻松部署到 Tomcat 服务器。
Spring Boot 注释通常位于包org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure和org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition中,对于使用 Spring Boot 至关重要。
常见的 Spring Boot 注解、其用途和示例
1.@SpringBoot应用程序:
此注释用于启动 Spring Boot 应用程序。
它结合了三个注解:@Configuration、@EnableAutoConfiguration 和 @ComponentScan。
例子:
@SpringBootApplication
public class MyApplication {public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(MyApplication.class, args);}
}
2.@RestController:
该注解表明该类是一个 RESTful 控制器,结合了@Controller 和@ResponseBody。
例子:
@RestController
public class MyController {@GetMapping("/hello")public String hello() {return "Hello, World!";}
}
此注释在 Spring 4 中引入,它消除了使用 @ResponseBody 注释控制器类中的每个请求处理方法的需要。
我们来看一下比较:
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/api/v1")
public class EmployeeController {@Autowiredprivate EmployeeRepository employeeRepository;@GetMapping("/employees")public @ResponseBody List<Employee> getAllEmployees() {return employeeRepository.findAll();}@GetMapping("/employees/{id}")public @ResponseBody ResponseEntity<Employee> getEmployeeById(@PathVariable(value = "id") Long employeeId)throws ResourceNotFoundException {Employee employee = employeeRepository.findById(employeeId).orElseThrow(() -> new ResourceNotFoundException("Employee not found for this id :: " + employeeId));return ResponseEntity.ok().body(employee);}@PostMapping("/employees")public @ResponseBody Employee createEmployee(@Valid @RequestBody Employee employee) {return employeeRepository.save(employee);}@PutMapping("/employees/{id}")public @ResponseBody ResponseEntity<Employee> updateEmployee(@PathVariable(value = "id") Long employeeId,@Valid @RequestBody Employee employeeDetails) throws ResourceNotFoundException {Employee employee = employeeRepository.findById(employeeId).orElseThrow(() -> new ResourceNotFoundException("Employee not found for this id :: " + employeeId));employee.setEmailId(employeeDetails.getEmailId());employee.setLastName(employeeDetails.getLastName());employee.setFirstName(employeeDetails.getFirstName());final Employee updatedEmployee = employeeRepository.save(employee);return ResponseEntity.ok(updatedEmployee);}@DeleteMapping("/employees/{id}")public @ResponseBody Map<String, Boolean> deleteEmployee(@PathVariable(value = "id") Long employeeId)throws ResourceNotFoundException {Employee employee = employeeRepository.findById(employeeId).orElseThrow(() -> new ResourceNotFoundException("Employee not found for this id :: " + employeeId));employeeRepository.delete(employee);Map<String, Boolean> response = new HashMap<>();response.put("deleted", Boolean.TRUE);return response;}
}
在此示例中,每个返回值都用@ResponseBody注释。
为了在我们的示例中使用 @RestController,我们需要用 @RestController 替换 @Controller,并从每个方法中删除 @ResponseBody。生成的类应如下所示:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1")
public class EmployeeController {@Autowiredprivate EmployeeRepository employeeRepository;@GetMapping("/employees")public List<Employee> getAllEmployees() {return employeeRepository.findAll();}@GetMapping("/employees/{id}")public ResponseEntity<Employee> getEmployeeById(@PathVariable(value = "id") Long employeeId)throws ResourceNotFoundException {Employee employee = employeeRepository.findById(employeeId).orElseThrow(() -> new ResourceNotFoundException("Employee not found for this id :: " + employeeId));return ResponseEntity.ok().body(employee);}@PostMapping("/employees")public Employee createEmployee(@Valid @RequestBody Employee employee) {return employeeRepository.save(employee);}@PutMapping("/employees/{id}")public ResponseEntity<Employee> updateEmployee(@PathVariable(value = "id") Long employeeId,@Valid @RequestBody Employee employeeDetails) throws ResourceNotFoundException {Employee employee = employeeRepository.findById(employeeId).orElseThrow(() -> new ResourceNotFoundException("Employee not found for this id :: " + employeeId));employee.setEmailId(employeeDetails.getEmailId());employee.setLastName(employeeDetails.getLastName());employee.setFirstName(employeeDetails.getFirstName());final Employee updatedEmployee = employeeRepository.save(employee);return ResponseEntity.ok(updatedEmployee);}@DeleteMapping("/employees/{id}")public Map<String, Boolean> deleteEmployee(@PathVariable(value = "id") Long employeeId)throws ResourceNotFoundException {Employee employee = employeeRepository.findById(employeeId).orElseThrow(() -> new ResourceNotFoundException("Employee not found for this id :: " + employeeId));employeeRepository.delete(employee);Map<String, Boolean> response = new HashMap<>();response.put("deleted", Boolean.TRUE);return response;}
}
有了这个注解,代码的可读性就大大提高了。
3.@RequestMapping:
此注解用于将 Web 请求映射到特定的处理程序方法。它可以在类或方法级别应用。
例子:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class MyController {@GetMapping("/hello")public String hello() {return "Hello, World!";}
}
4.@Autowired:
此注解用于 Spring bean 中的自动依赖注入。它可以应用于字段、构造函数或方法。
简单来说它有两个作用:
@Autowired 注释用于自动注入 Bean。
@Autowired 注解用于构造函数注入、setter 注入和字段注入。
例子:
@Service
public class MyService {private MyRepository repository;
@Autowiredpublic MyService(MyRepository repository) {this.repository = repository;}
}
另一个例子:
@Autowired
private EmployeeRepository employeeRepository;
5.@Component:
@Component 注释在 Spring 框架中用于将某个类标记为 Spring 管理的组件。
它允许 Spring 自动扫描并实例化它,使其可通过依赖注入在应用程序中使用。
通常用于表示业务逻辑层、持久层、控制器等,它允许 Spring 管理它们的生命周期并注入依赖项。
简单来说,@Component注解用于标记一个类为Spring管理的组件。
例子:
@Component
public class MyComponent {// ...
}
6.@Service:
此注解用于表明某个类是 Spring bean 的一个特殊类型,通常用于业务逻辑。通常称为服务层。
例子:
@Service
public class MyService {// ...
}
更多Spring Boot注解及其详解。
7.@Repository:
该注解用来表明某个类是特殊类型的Spring bean,通常用于数据库访问。
例子:
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class UserRepository {
public void saveUser(User user) {// Implement logic to save user to database}
public User getUserById(Long id) {// Implement logic to retrieve user by ID from databasereturn null;}
// Other data access methods...
}
在这个例子中,UserRepository该类被标记了@Repository,表明它是一个由Spring容器管理的数据访问组件,用于执行与用户数据相关的持久化操作。
有些人可能不太熟悉这个注释,但@Repository 与@Controller、@Service 和@Component 一样,表示该对象应该由 Spring 管理。
@Repository 用于持久层接口,将其中一个实现类分配给 Spring 管理。
它和MyBatis的@Mapper比较类似,在程序中,MyBatis需要在编译时找到对应的mapper并生成代理类,以实现数据库查询功能。
@Mapper和@Repository都用于持久层接口上。
即使没有这个注解,我们经常也看不到错误,因为 Spring 的配置文件中包含一个MapperScannerConfigurer可以扫描持久层接口并创建实现类供 Spring 管理的 bean。
类似地,在主应用程序类中添加@MapperScan 可以达到相同的效果MapperScannerConfigurer。
8.@Configuration:
此注解用于将类声明为配置类。它通常与使用 @Bean 注解的方法结合使用。
例子:
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import com.companyname.projectname.customer.CustomerService;
import com.companyname.projectname.order.OrderService;
@Configuration
public class Application {
@Beanpublic CustomerService customerService() {return new CustomerService();}
@Beanpublic OrderService orderService() {return new OrderService();}
}
上述AppConfig类相当于以下 Spring XML:
<beans><bean id="customerService" class="com.companyname.projectname.CustomerService"/><bean id="orderService" class="com.companyname.projectname.OrderService"/>
</beans>
该注解一般用于配置Swagger、MyBatis等属性。
9.@Value:
此注释用于将属性文件或其他来源的值注入到 Spring bean 中。
例子:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MyComponent {
@Value("${my.property}")private String myProperty;
public void displayPropertyValue() {System.out.println("The value of my.property is: " + myProperty);}
}
在此示例中,@Value(“${my.property}”)将 Spring 属性的值注入到myProperty字段中。
假设应用程序的配置文件中有一个名为“my.property”的属性,
它的值将被注入到myProperty字段中。此注释通常用于代码生成器中,以避免硬编码值。
10.@EnableAutoConfiguration:
此注解启用了 Spring Boot 的自动配置机制,该机制根据类路径依赖项和属性来配置应用程序。
例子:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAutoConfiguration
public class MyApplication {// ...
}
使用@EnableAutoConfiguration:
Spring Boot 根据项目的依赖项和配置自动配置各种应用程序组件,例如数据源,JPA 和 Web 组件。
该类MyService将被Spring容器自动扫描和管理。
没有@EnableAutoConfiguration:
开发人员需要手动配置各种应用程序组件,增加了开发工作量。
该类MyService不会被自动扫描,并且必须为 Spring 容器管理明确配置。
要排除特定的自动配置类,exclude可以使用@EnableAutoConfiguration 属性:
例子:
@EnableAutoConfiguration(excludeName = {"org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafAutoConfiguration","org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration"
})
11.@GetMapping、@PostMapping、@PutMapping、@DeleteMapping:
这些注解用于将特定的 HTTP 方法映射到处理程序方法。它们是相应 HTTP 方法的快捷方式。
例子:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class MyController {@GetMapping("/hello")public String hello() {return "Hello, World!";}@PostMapping("/data")public void saveData(@RequestBody Data data) {// Save data}
}
12.@PathVariable:
该注解用于将方法参数绑定到URL路径变量。
方法参数名称和 URL 变量匹配的示例:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class MyController {@GetMapping("/users/{id}")public User getUser(@PathVariable Long id) {// Retrieve user by given ID}
}
具有不同方法参数名称和 URL 变量的示例:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class MyController {@GetMapping("/users/{id}")public User getUser(@PathVariable("id") Long userId) {// Retrieve user by given ID}
}
13.@RequestParam:
该注解用于将方法参数与请求参数绑定。
例子:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class MyController {@GetMapping("/users")public List<User> getUsers(@RequestParam("status") String status) {// Retrieve users by given status}
}
@RequestParam和@PathVariable之间的区别:
参数:
用于从查询参数中获取值。
查询参数通常通过符号后的 URL 传递?(例如?name=John&age=25)。
在方法参数中使用指定参数名,Spring自动注入相应的值。
适用于简单数据类型以及使用 的 GET 或 POST 请求application/x-www-form-urlencoded。
例子:
@GetMapping("/users")
public String getUserByName(@RequestParam("name") String name) {// Retrieve user by namereturn "User name: " + name;
}
概括:
@PathVariable:用于从URL路径获取值。
@RequestParam:用于从 URL 查询参数中获取值。
14.@RequestBody:
此注解用于将请求主体绑定到方法参数。它通常用于 RESTful API 中接收 JSON 或 XML 负载。
例子:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class MyController {@PostMapping("/users")public void createUser(@RequestBody User user) {// Create a new user}
}
在这个例子中,Spring 根据 自动将请求体转换为对象User。Content-Type如果请求的Content-Type为application/json,则请求体可能如下所示:
{"name": "xiaou","age": 25
}
@RequestParam和@RequestBody之间的区别:
参数:
用于查询参数,通常是简单数据类型。
适用于处理带有查询参数的表单提交或 GET 请求。
例子:
@GetMapping("/users")
public String getUserByName(@RequestParam("name") String name) {// Retrieve user by namereturn "User name: " + name;
}
@RequestBody:
用于请求主体,通常是复杂数据类型(例如 JSON 或 XML)。
适合处理具有大型或复杂负载的 POST 请求。
例子:
@PostMapping("/users")
public String createUser(@RequestBody User user) {// Process received user objectreturn "User created: " + user.toString();
}
概括:
@PathVariable:用于从URL路径中获取参数。
@RequestParam:用于从URL查询字符串中获取参数。
@RequestBody:用于从HTTP请求体中获取参数。
15.@Qualifier:
该注解用于指定当有多个相同类型的bean时,应该注入哪个bean。
例子:
@Component("fooFormatter")
public class FooFormatter implements Formatter {public String format() {return "foo";}
}@Component("barFormatter")
public class BarFormatter implements Formatter {public String format() {return "bar";}
}@Component
public class FooService {@Autowired@Qualifier("fooFormatter")private Formatter formatter;// Additional code
}
在此示例中,@Qualifier(“fooFormatter”)确保fooFormatterbean 被注入到FooService。
16.@ConditionalOnProperty:
此批注用于根据属性的值有条件地启用或禁用 bean 或配置。
例子:
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "my.feature.enabled", havingValue = "true")
public class MyConfiguration {// Configuration that is enabled only if my.feature.enabled is true
}
17.@Scheduled:
此注解用于以固定间隔安排方法的执行。
例子:
@Component
public class MyScheduler {@Scheduled(fixedDelay = 5000)public void doSomething() {// Task executed at fixed intervals}
}
18.@Cacheable、@CachePut、@CacheEvict:
这些注释用于缓存方法结果。它们分别允许您缓存方法返回值、更新缓存或从缓存中逐出条目。
例子:
@Service
public class MyService {@Cacheable("users")public User getUserById(Long id) {// Retrieve user from database}@CachePut("users")public User updateUser(User user) {// Update user in database and cache}@CacheEvict("users")public void deleteUser(Long id) {// Delete user from database and cache}
}
网络注释
1.@CookieValue:
用于从 HTTP 请求中提取特定的 Cookie 值。
例子:
@GetMapping("/showUser")
public String showUser(@CookieValue("username") String username) {// Logic using the extracted cookie valuereturn "User: " + username;
}
2.@ModelAttribute:
用于将请求参数绑定到模型对象,通常用于将表单数据传递给处理程序方法。
例子:
@PostMapping("/saveUser")
public String saveUser(@ModelAttribute User user) {// Logic to save userreturn "redirect:/users";
}
3.@ResponseStatus:
用于指定处理程序方法或异常的 HTTP 状态代码。
例子:
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND)
public class ResourceNotFoundException extends RuntimeException {// Custom exception
}@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {@ExceptionHandler(ResourceNotFoundException.class)@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND)public String handleResourceNotFoundException() {return "resourceNotFound";}
}
4.@ExceptionHandler:
用于定义控制器中的方法来处理特定的异常。
例子:
@Controller
public class MyController {@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)public ModelAndView handleException(Exception ex) {ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView("error");modelAndView.addObject("errorMessage", ex.getMessage());return modelAndView;}
}
数据注释
1.@Entity:
用于将某个类标记为 JPA 实体,通常映射到数据库表。
例子:
@Entity
@Table(name = "employees")
public class Employee {// Entity attributes and methods
}
2. @Table:
用于指定实体映射到的表的详细信息。
例子:
@Entity
@Table(name = "products", schema = "inventory")
public class Product {// Entity attributes and methods
}
3.@Id:
用于指定实体的主键。
例子:
@Entity
@Table(name = "employees")
public class Employee {@Idprivate Long id;// Other attributes and methods
}
4.@GeneratedValue:
用于指定主键的生成策略。
例子:
@Entity
@Table(name = "employees")
public class Employee {@Id@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)private Long id;// Other attributes and methods
}
5.@Column:
用于指定字段映射到的列的详细信息。
例子:
@Entity
@Table(name = "employees")
public class Employee {@Id@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)private Long id;@Column(name = "emp_name", length = 50, nullable = false)private String name;// Other attributes and methods
}
6.@Transient:
用于指定某个字段不应持久保存到数据库中。
例子:
@Entity
@Table(name = "employees")
public class Employee {@Id@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)private Long id;@Column(name = "emp_name", length = 50, nullable = false)private String name;@Transientprivate transientField;// Other attributes and methods
}
7.@PersistenceContext:
用于注入EntityManager用于管理实体持久性操作。
@Service
public class EmployeeService {@PersistenceContextprivate EntityManager entityManager;// Other methods
}
8.@Query:
此批注用于声明自定义 JPQL(Java 持久性查询语言)查询。
它可以在 Repository 接口或实体类中的方法上使用。
例子:
@Repository
public interface EmployeeRepository extends JpaRepository<Employee, Long> {@Query("SELECT e FROM Employee e WHERE e.department = ?1")List<Employee> findByDepartment(Department department);
}9.@NamedQuery:
此批注用于在实体类上声明命名查询。
命名查询是预定义的 JPQL 查询,可以在多个地方引用。
例子:
@Entity
@NamedQuery(name = "Employee.findAll", query = "SELECT e FROM Employee e")
public class Employee {// Entity attributes and methods
}
10.@Param:
此注释用于引用JPQL查询中的命名参数。
@Query它在注释中以及查询字符串中的命名参数中使用。
例子:
@Repository
public interface EmployeeRepository extends JpaRepository<Employee, Long> {@Query("SELECT e FROM Employee e WHERE e.department = :dept")List<Employee> findByDepartment(@Param("dept") Department department);
}
11.@JoinTable:
此注解用于指定实体之间多对多关系的连接表的详细信息。
例子:
@Entity
public class Student {@ManyToMany@JoinTable(name = "student_course",joinColumns = @JoinColumn(name = "student_id"),inverseJoinColumns = @JoinColumn(name = "course_id"))private List<Course> courses;// Other attributes and methods
}
12.@JoinColumn:
此批注用于指定实体关联的外键列,通常用于多对一或一对一关系。
例子:
@Entity
public class Employee {@ManyToOne@JoinColumn(name = "department_id")private Department department;// Other attributes and methods
}
验证注解
这些注释通常在 Bean Validation(JSR-380)规范的上下文中使用,以验证
JavaBean 属性。
1.@Valid:
此注解用于指示嵌套对象的属性也应进行验证。它通常用于确保复杂对象的所有属性都经过验证。
例子:
public class Address {@NotNullprivate String street;// Other attributes and methods
}public class User {@Validprivate Address address;// Other attributes and methods
}
2.@NotNull:
此注解用于验证属性值不为空。它通常适用于String,Collection,Map或基本数据类型。
例子:
public class User {@NotNullprivate String username;// Other attributes and methods
}
3.@Size:
此注解用于验证属性值的大小是否在指定范围内。它可以应用于 String、Collection、Map 或数组属性。
例子:
public class User {@Size(min = 2, max = 50)private String name;// Other attributes and methods
}
4.@Min:
此注释用于验证属性值是否大于或等于指定的最小值。它通常用于数字属性。
例子:
public class User {@Min(18)private int age;// Other attributes and methods
}
5.@Max:
此注释用于验证属性值是否小于或等于指定的最大值。它通常用于数字属性。
例子:
public class User {@Max(100)private int age;// Other attributes and methods
}
6.@Email:
此注解用于验证属性值是否符合电子邮件地址的格式。它通常应用于字符串属性。
例子:
public class User {@Emailprivate String email;// Other attributes and methods
}
7.@Pattern:
此批注用于验证属性值是否与指定的正则表达式模式匹配。它允许自定义验证规则。
例子:
public class User {@Pattern(regexp = "^[A-Za-z0-9]+$")private String username;// Other attributes and methods
}
安全注解
这些注释通常用于 Spring Security 和 OAuth2 框架,用于配置与安全相关的功能和授权机制。
1.EnableWebSecurity:
启用 Spring Security 的 Web 安全支持。
它通常放在配置类中,以指示 Spring Boot 应用程序应该使用 Spring Security。
例子:
@EnableWebSecurity
@Configuration
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {// Configure security rules, etc.
}
2.@Configuration:
表示某个类是配置类。它通常与其他注解一起使用,定义 bean 并配置应用程序的各种功能。
例子:
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {// Define beans, etc.
}
3.@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity:
启用全局方法级安全性。它可以配置PreAuthorize、PostAuthorize、Secured和RolesAllowed注释。
例子:
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)
@Configuration
public class MethodSecurityConfig extends GlobalMethodSecurityConfiguration {// Configure method-level security rules
}
4.@PreAuthorize:
用于在执行方法之前执行授权检查。它允许使用 Spring 表达式语言 (SpEL) 来指定访问规则。
例子:
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ROLE_ADMIN')")
public void deleteUser(User user) {// Logic for deleting a user
}
5.@PostAuthorize:
用于在执行方法后执行授权检查。它允许使用 Spring 表达式语言 (SpEL) 来指定访问规则。
例子:
@PostAuthorize("returnObject.owner == authentication.name")
public Object findDocument() {// Logic for returning a document
}
6.@Secured:
用于限制对方法的访问,指定调用该方法所需的角色。
例子:
@Secured("ROLE_ADMIN")
public void deleteUser(User user) {// Logic for deleting a user
}
7.@RolesAllowed:
用于限制对方法的访问,指定调用该方法所需的角色。
例子:
@RolesAllowed("ROLE_ADMIN")
public void deleteUser(User user) {// Logic for deleting a user
}
8.@EnableOAuth2Client, @EnableResourceServer, @EnableAuthorizationServer:
这些注释用于 OAuth2 配置,启用 OAuth2 客户端、资源服务器和授权服务器功能。它们通常放置在配置类上。
例子:
@Configuration
@EnableOAuth2Client
public class OAuth2ClientConfig {// Configure OAuth2 client
}@Configuration
@EnableResourceServer
public class ResourceServerConfig extends ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter {// Configure resource server
}@Configuration
@EnableAuthorizationServer
public class AuthorizationServerConfig extends AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter {// Configure authorization server
}
测试注解
这些注释通常用于 JUnit 和 Spring Framework 中的测试相关功能。
1. @RunWith:
用于指定 JUnit 4 中的测试运行器。在 JUnit 5 中,它已被取代@ExtendWith。
例子:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
public class MySpringTest {// Test code
}
2.@SpringBootTest:
用于启动完整的 Spring 应用程序上下文以进行集成测试。它会自动配置应用程序上下文。
例子:
@SpringBootTest
public class MyIntegrationTest {// Integration test code
}
3.@WebMvcTest:
用于对 Spring MVC 应用程序进行单元测试。它仅加载与 Web 相关的组件,例如控制器和过滤器。
例子:
@WebMvcTest(UserController.class)
public class UserControllerTest {// Controller unit test code
}
4.@DataJpaTest:
用于执行 JPA 持久层的单元测试。它会自动配置内存数据库(例如 H2)并扫描@Entity注释。
例子:
@DataJpaTest
public class UserRepositoryTest {// JPA 单元测试代码
}
5.@DataJpaTest:
用于执行 Spring RestTemplate 或 WebClient 客户端的单元测试。它会自动配置 RestTemplate 或 WebClient bean。
例子:
@RestClientTest(MyRestClient.class)
public class MyRestClientTest {// Rest 客户端单元测试代码
}
6.@MockBean:
用于创建模拟对象并将其注入 Spring 上下文。它替代 Spring bean 进行单元测试。
例子:
@SpringBootTest
public class MyServiceTest {@MockBean private SomeDependency mockDependency; // 单元测试代码
}
7.@AutoConfigureMockMvc:
用于在 Spring MVC 测试中自动配置 MockMvc。它用于模拟对控制器的请求。
例子:
@WebMvcTest (UserController.class)
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
public class UserControllerTest { @Autowired private MockMvc mockMvc; // 控制器测试代码
}
8.@Test、@Before、@After、@BeforeEach、@AfterEach、@BeforeAll、@AfterAll:
用于JUnit测试方法的生命周期管理。@Test标记一个测试方法,而其他注解在测试方法之前或之后执行特定的操作。
例子:
@Test
public void testSomething () {// 测试方法
} @BeforeEach
public void setUp () {// 每个测试方法之前的操作
} @AfterEach
public void teaDown () {// 每个测试方法之后的操作
}
- @RestClientTest:
用于指定测试类或测试方法的自定义名称。它用于生成更有意义的测试报告。
例子:
@Test
@DisplayName ( "测试用户注册功能" )
public void testUserRegistration () {// 测试方法
}
10.@Disabled:
用于禁用测试类或测试方法。在调试或开发过程中需要暂时跳过某些测试时使用。
例子:
@Test
@Disabled("Temporarily disabled, waiting for fix")
public void testSomething() {// Test method
}
11.@ParameterizedTest、@ValueSource、@CsvSource:
用于参数化测试,允许相同的测试方法使用不同的参数运行多次。@ValueSource指定单个参数值的列表,而@CsvSource指定多个参数值。
例子:
@ParameterizedTest
@ValueSource(strings = {"apple", "banana", "orange"})
public void testFruit(String fruit) {// Test method with different fruit parameters
}@ParameterizedTest
@CsvSource({"apple, 1", "banana, 2", "orange, 3"})
public void testFruit(String fruit, int count) {// Test method with different fruit and count parameters
}
12.@ExtendWith:
用于扩展测试运行时的功能,例如参数解析和条件评估。
例子:
@ExtendWith(MyExtension.class)
public class MyTest {// 测试方法
}
消息注释
这些注释通常用于 Spring 框架的 JMS(Java 消息服务)消息传递功能,简化了 JMS 消息的生成和使用。
1.@EnableJms:
启用 JMS 功能。通常放置在配置类上以激活对 JMS 相关注释的支持。
例子:
@Configuration
@EnableJms
public class AppConfig { // 其他配置代码
}
2.@JmsListener:
声明一个方法作为 JMS 消息监听器,用于接收 JMS 消息。它可以指定要监听的队列或主题。
例子:
@JmsListener (destination = "myQueue" )public void acceptMessage ( String message ) {// 处理收到的消息
}
3.@SendTo:
指定消息处理方法中回复消息的目标。通常与 一起使用@JmsListener。
例子:
@JmsListener (destination = "inputQueue" )@SendTo ( "outputQueue" )
public String handleMessage (String message) {// 处理消息并返回结果
}
4.@MessageMapping:
标识用于处理特定目标消息的方法。通常与 Spring 的 WebSocket 支持一起使用来处理 WebSocket 消息。
例子:
@MessageMapping ( "/hello" )@SendTo ( "/topic/greetings" )
public Greeting Greeting (HelloMessage message) {// 处理消息并返回结果
}
5.@Payload:
指定JMS消息处理方法中的payload参数,用于获取JMS消息内容。
例子:
@JmsListener (destination = "myQueue" )
public void acceptMessage ( @Payload String message) {// 处理消息
}
6.@Header:
指定JMS消息处理方法中的header参数,用于获取JMS消息头信息。
例子:
@JmsListener (destination = "myQueue" )
public void acceptMessage ( @Header ( "X-Custom-Header" ) String customHeader) {// 处理消息头
}
面向方面编程 (AOP) 注释
这些注释通常用于 Spring 框架的面向方面编程 (AOP),以模块化横切关注点。
1.@Aspect:
定义一个方面,封装横切逻辑。方面是一个包含切入点和建议的类。
例子:
@Aspect
@Component
public class LoggingAspect { // 方面类的实现
}
2.@Pointcut:
定义切入点,指定应应用方面逻辑的位置。同一个切入点可在多个建议中重复使用。
例子:
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))")
private void serviceLayer () {}
3.@Before:
定义一个前置建议,在方法执行之前执行。它在连接点之前运行。
例子:
@Before("serviceLayer()")
public void beforeAdvice () {// 之前建议的逻辑
}
4.@After:
定义一个后续通知,在方法执行后执行(无论方法结果如何)。它在连接点之后运行。
例子:
@After("serviceLayer()")
public void afterAdvice () {// 后续建议的逻辑
}
5.@AfterReturning:
定义返回建议,在方法成功返回后执行。它仅当方法正常返回时运行。
例子:
@AfterReturning (pointcut = "serviceLayer()" , returned = "result" )public void afterReturningAdvice ( Object result ) {// 返回建议的逻辑
}
6.@AfterThrowing:
定义一个抛出通知,在方法抛出异常后执行。它仅当方法抛出异常时运行。
例子:
@AfterThrowing (pointcut = "serviceLayer()" , throwing = "exception" )public void afterThrowingAdvice ( Exception exception ) {// 抛出建议的逻辑
}
7.@Around:
定义一个环绕通知,在方法执行之前和之后执行。它控制方法的执行。
例子:
@Around("serviceLayer()")
public Object aroundAdvice (ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {// 执行前逻辑Object result = joinPoint.proceed(); // 执行被建议的方法// 执行后逻辑return result;
}
以下注释很少使用,因此简要总结。
执行器注释
这些注释用于启用和定制 Spring Boot Actuator,它为应用程序提供监控和管理功能。
这些注释用于启用和定制 Spring Boot Actuator,它为应用程序提供监控和管理功能。
@EnableActuator:
启用Spring Boot Actuator模块,提供应用程序监控和管理功能。
@Endpoint:
创建自定义端点,允许您公开自定义监控和管理端点。
例子:
@Endpoint(id = "customEndpoint")
public class CustomEndpoint {@ReadOperationpublic String read() {return "Custom Read Operation";}
}
@RestControllerEndpoint:
创建一个 REST 样式的端点以用作 REST 控制器。
例子:
@RestControllerEndpoint(id = "customRestEndpoint")
public class CustomRestEndpoint {@GetMapping("/custom")public String custom() {return "Custom REST Endpoint";}
}
@ReadOperation:
指定处理端点中的 GET 请求的方法。
@WriteOperation:
指定处理端点中的 POST 请求的方法。
@DeleteOperation:
指定处理端点中的 DELETE 请求的方法。
配置属性注释
这些注释用于将配置属性映射到 Java Bean。
@ConfigurationProperties:
将配置文件中的属性映射到 Java Bean。
例子:
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "app" )
public class AppProperties {private String name;private String version; // Getters 和 setters
}
@ConstructorBinding:
将配置属性绑定到构造函数参数,通常与一起使用@ConfigurationProperties。
@Validated:
标记配置属性类以进行验证,通常与 JSR-380(Bean 验证)一起使用。
国际化和本地化
@EnableMessageSource:启用消息源处理,通常用于国际化和本地化。
@EnableWebMvc:启用 Spring MVC 功能,通常在配置类上使用以启用对 Spring MVC 的支持。
@LocaleResolver:解析请求中的区域信息。
@MessageBundle:指定国际化消息资源文件的基础名称。
@MessageSource:检索消息资源,通常与一起使用@Autowired。
日志记录和监控
@Slf4j,@Log4j2,@Log:
简化不同日志框架(SLF4J、Log4j2、JDK Logging)的记录器的创建。
例子:
@Slf4j
public class MyService {public void doSomething () { log.info ( "正在做某事" ) ; }
}
@Timed、@Counted、@ExceptionMetered:
添加指标来监控方法执行时间、调用次数和异常。
数据验证
@NotNull,@NotBlank,@Email,@Size,@Pattern:
验证字段是否为非空、非空白、电子邮件格式、大小范围和正则表达式模式匹配。
@Positive,@PositiveOrZero,@Negative,@NegativeOrZero:
验证数字是正数、非负数、负数还是非正数。
GraphQL 注释
@GraphQLApi:将一个类标记为 GraphQL API 类。
@GraphQLQuery、@GraphQLMutation、@GraphQLSubscription:定义 GraphQL 查询、变异和订阅。
@GraphQLArgument、@GraphQLContext、@GraphQLNonNull、@GraphQLInputType、@GraphQLType:定义 GraphQL 参数、上下文、非空类型、输入类型和类型。
集成注释
@IntegrationComponentScan:扫描集成组件。
@MessagingGateway、@Transformer、@Splitter、@Aggregator、@ServiceActivator、@InboundChannelAdapter、@OutboundChannelAdapter、@Router、@BridgeTo:配置并定义集成组件。
Flyway 数据库迁移
@FlywayTest:测试 Flyway 数据库迁移。
@FlywayTestExtension:扩展Flyway测试功能。
@FlywayTestExtension.Test、@FlywayTestExtension.BeforeMigration、@FlywayTestExtension.AfterMigration:标记测试方法并在迁移之前和之后执行。
JUnit 5 注释
@ExtendWith:扩展 JUnit 5 功能。
@TestInstance:配置测试实例的生命周期。
@TestTemplate:指定测试模板方法。
@DisplayNameGeneration:自定义生成测试显示名称的策略。
@Nested:创建嵌套测试类。
@Tag:根据标签标记要运行的测试。
@DisabledOnOs、@EnabledOnOs、@DisabledIf、@EnabledIf:根据条件启用或禁用测试。
API 文档注释
@Api、@ApiOperation、@ApiParam、@ApiModel、@ApiModelProperty:定义并描述 API 文档详细信息。
异常处理注解
@ControllerAdvice:定义全局异常处理程序。
@ExceptionHandler:处理特定的异常。
GraphQL 注释(附加)
@GraphQLSchema、@GraphQLQueryResolver、@GraphQLMutationResolver、@GraphQLSubscriptionResolver、@GraphQLResolver:定义 GraphQL 模式和解析器。
服务器发送事件 (SSE) 注释
@SseEmitter:创建一个 SSE 事件发射器。
@SseEventSink:注入 SSE 事件接收器。
WebFlux 注释
@RestController、@GetMapping、@PostMapping、@PutMapping、@DeleteMapping、@PatchMapping:定义 WebFlux RESTful 控制器和请求映射。
计量注释
@Timed:测量方法执行时间。
@Counted:计算方法调用次数。
@Gauge:将方法公开为衡量指标。
@ExceptionMetered:测量方法异常率。
概括
这不是一份非常详尽的清单。Spring Boot 为各种模块和功能提供了大量注释。
有关完整列表和详细用法,请参阅官方 Spring Boot 文档和模块特定指南。
本摘要涵盖了常用的注释,但包括了您在典型项目中可能遇到的几乎所有注释。
相关文章:

一文讲清springboot所有注解
Spring Boot 注释是提供有关 Spring 应用程序信息的元数据。 基于 Spring 构建,涵盖其所有功能, Spring Boot 因其生产就绪环境而迅速成为开发人员的最爱,它允许开发人员直接专注于逻辑,而无需配置和设置的麻烦。 Spring Boot 是一…...

pytest测试专题 - 1.1 运行pytest
<< 返回目录 1 pytest学习笔记 - 1.1 运行pytest 1.1 运行pyest 在命令行执行pytest --help usage: pytest [options] [file_or_dir] [file_or_dir] [...] ... ...1.1.1 pytest不携带参数 pytest不带参数时,会扫描当前目录下的所有目录、子目录中符合测试用…...

Java多线程——线程池的使用
线程饥饿死锁 在单线程的Executor中,如果任务A将任务B提交给同一个Executor,并且等待任务B的结果,就会引发死锁线程池中所有正在执行任务的线程由于等待其他仍处于工作队列中的任务而阻塞 执行时间较长的任务 执行时间较长的任务不仅会造成…...

NO.15十六届蓝桥杯备战|while循环|六道练习(C++)
while循环 while语法形式 while 语句的语法结构和 if 语句⾮常相似,但不同的是 while 是⽤来实现循环的, if 是⽆法实现循环的。 下⾯是 while 循环的语法形式: //形式1 while ( 表达式 )语句; //形式2 //如果循环体想包含更多的语句&a…...

DeepSeek 从入门到精通学习指南,2025清华大学《DeepSeek从入门到精通》正式发布104页pdf版超全解析
DeepSeek 是一款强大的 AI 搜索引擎,广泛应用于企业级数据检索和分析。无论您是初学者还是有经验的用户,掌握 DeepSeek 的使用都能为您的工作带来极大的便利。本文将从入门到精通,详细介绍如何学习和使用 DeepSeek。 链接: https://pan.baid…...

2025年SEO自动优化工具
随着2025年互联网的快速发展,越来越多的企业和个人意识到,拥有一个排名靠前的网站对于吸引客户、增加流量、提高转化率至关重要。而要想让自己的网站脱颖而出,获得更多曝光,最重要的一项工作就是进行SEO优化。传统的SEO优化方式通…...

KEPServerEX 的接口类型与连接方式的详细说明
目录 一、KEPServerEX 核心架构 二、KEPServerEX 支持的接口类型 三、KEPServerEX 支持的连接类型 1. 通用工业协议 2. 品牌专属协议 3. 行业专用协议 4. 数据库与文件接口 四、配置示例 1. 接口配置(以OPC UA为例) 2. 连接配置(以…...

AGI时代的认知重塑:人类文明的范式转移与思维革命
文章目录 引言:站在文明转型的临界点一、认知危机:当机器开始理解世界1.1 AGI的本质突破:从模式识别到世界建模1.2 人类认知的脆弱性暴露二、认知革命:重构思维的四个维度2.1 元认知升级:从直觉思维到二阶观察2.2 混合智能:人机认知回路的构建2.3 认知安全:防御机器思维…...

OmniManip:以目标为中心的交互基元作为空间约束实现通用机器人操作
25年1月来自北大、北大-智元实验室和智元机器人公司的论文“OmniManip: Towards General Robotic Manipulation via Object-Centric Interaction Primitives as Spatial Constraints”。 开发能够在非结构化环境中进行操作的通用机器人系统是一项重大挑战。虽然视觉-语言模型 …...

论文第二次阅读笔记
摘要学习 存在问题:目前流行的图神经网络仅通过欧几里得几何及其相关的向量空间操作来建模数据,存在局限性 我们通过提出一种数学上有根据的图卷积网络(GCN)的推广,将其扩展到常曲率空间(或其乘积空间),从而填补了这一空白。 一是引入一种统一的形式主义,可以在所有常…...

【Android开发AI实战】选择目标跟踪基于opencv实现——运动跟踪
文章目录 【Android 开发 AI 实战】选择目标跟踪基于 opencv 实现 —— 运动跟踪一、引言二、Android 开发与 AI 的融合趋势三、OpenCV 简介四、运动跟踪原理(一)光流法(二)卡尔曼滤波(三)粒子滤波 五、基于…...

系统漏洞扫描服务:安全风险识别与防护指南
系统安全的关键在于漏洞扫描服务,此服务能迅速发现潜在的安全风险。借助专业的扫描工具和技术,它确保系统稳定运作。以下将简要介绍这一服务的主要特点。 扫描原理 系统漏洞扫描服务依赖两种主要手段:一是通过漏洞数据库进行匹配࿰…...

2.Excel:滨海市重点中学的物理统考考试情况❗(15)
目录 NO12 1.数据透视表 2. 3.sum函数 4.sumifs客观/主观平均分 5.sumifs得分率 6.数字格式修改 NO3/4/5 sumifs某一组数据相加,某一范围,某一范围的具体点向下拖拉,锁定列;向左右,锁定行F4&#x…...

使用 React 16+Webpack 和 pdfjs-dist 或 react-pdf 实现 PDF 文件显示、定位和高亮
写在前面 在本文中,我们将探讨如何使用 React 16Webpack 和 pdfjs-dist 或 react-pdf 库来实现 PDF 文件的显示、定位和高亮功能。这些库提供了强大的工具和 API,使得在 Web 应用中处理 PDF 文件变得更加容易。 项目设置 首先,我们需要创建…...

驱动开发系列35 - Linux Graphics GEM Buffer Object 介绍
一:概述 在 Linux 内核中,DRM(Direct Rendering Manager)模块 是用于管理显示硬件和图形渲染的核心框架。它负责协调用户空间应用程序(例如 X Server、Wayland Compositors、Mesa 等)和 GPU 硬件之间的通信,是 Linux 图形子系统的重要组成部分。 GEM (Graphics Executio…...

Java常见的异常类有哪些?
对应异常: 空指针 → NullPointerException数据库 → SQLException数组越界 → IndexOutOfBoundsException文件丢失 → FileNotFoundExceptionIO问题 → IOException强制转 → ClassCastException方法找不到 → NoSuchMethodException数组类型错 → ArrayStoreExce…...

清华大学新闻与传播学院沈阳团队出品的《DeepSeek:从入门到精通》104页PDF
前言 本机运行DeepSeek R1大模型文章如下: Windows电脑本地部署运行DeepSeek R1大模型(基于Ollama和Chatbox)【保姆级万字教程】在Windows计算机部署DeepSeek大模型,给在实验室无外网的同事们用(基于Ollama和OpenWebUI…...

增量hdfs数据追平
1、假设客户只改了最近的分区。他不会去修改历史的分区表,如果大量改历史的分区表,那纯纯把hive当mysql用了。这样我们就只能找出变动的表,然后删除,重新迁移。 2、此处是确保他们不会大量改历史分区,只有少部分改&am…...

Linux高并发服务器开发 第十七天(管道缓存区查询大小 管道的优劣 命名管道mkfifo 建立释放映射区mmap/munmap 匿名映射 进程间的通信)
目录 1.pipe管道读写行为 1.1例题:实现父子进程 ls | wc -l 1.2兄弟进程 ls | wc -l 2.管道缓存区 2.1命令查询 2.2函数查询 3.pipe管道的优劣 4.命名管道 fifo 5.mmap 5.1文件进程间通信 5.2建立、释放映射区 5.3匿名映射 6.进程间通信 6.1父子进间通…...

C语言常见概念
目录 第一个C语言程序 main函数 写法: printf和库函数 printf()函数 库函数 关键字 字符和ASCII码表 字符串和\0 转义字符 语句 注释 注释的两种形式 第一个C语言程序 #include<stdio.h>//第一个c语言程序 int main() {printf("Hello World…...
)
React Native 开发环境搭建(全平台详解)
React Native 开发环境搭建(全平台详解) 在开始使用 React Native 开发移动应用之前,正确设置开发环境是至关重要的一步。本文将为你提供一份全面的指南,涵盖 macOS 和 Windows 平台的配置步骤,如何在 Android 和 iOS…...
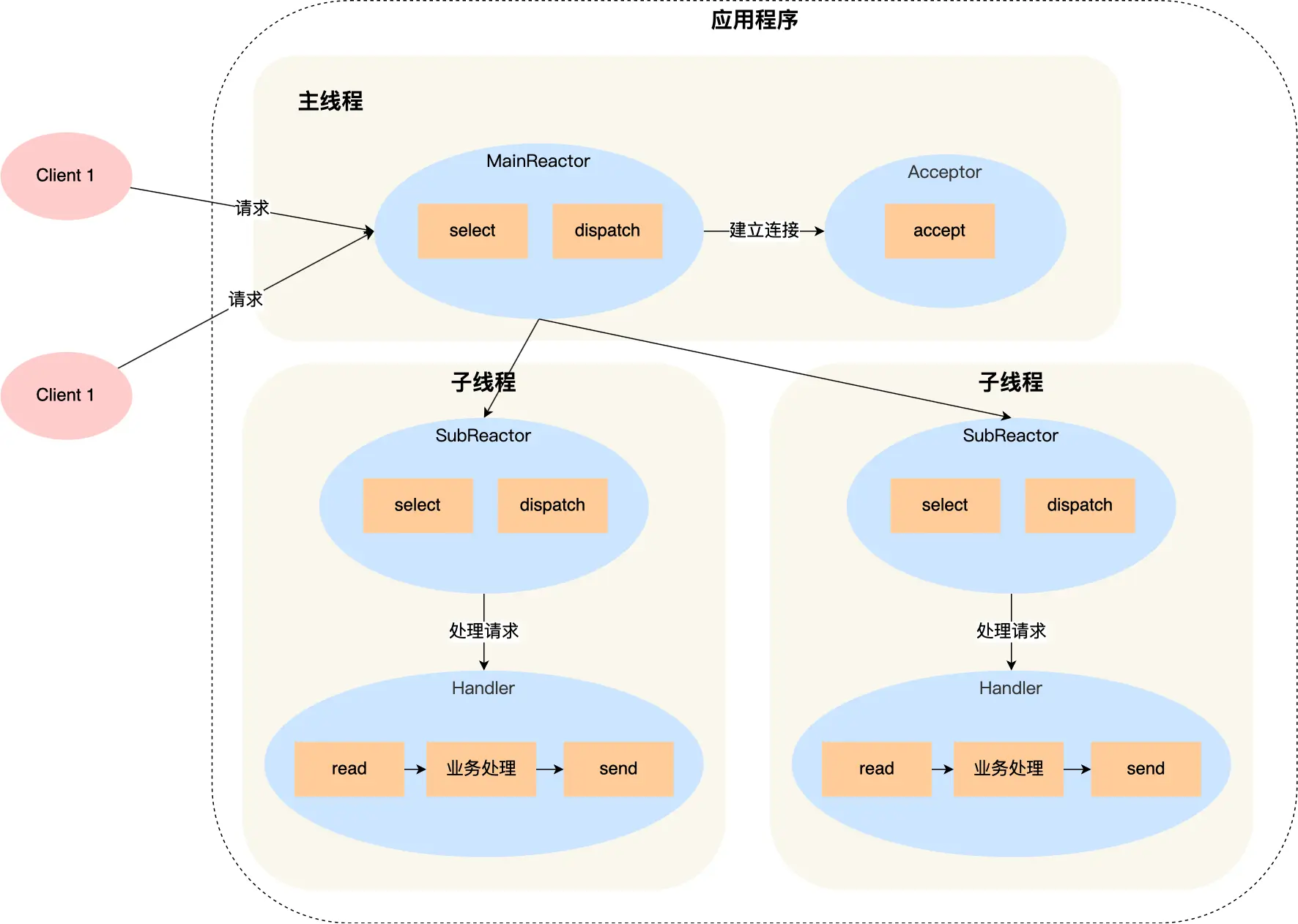
select、poll、epoll 与 Reactor 模式
在高并发网络编程领域,高效处理大量连接和 I/O 事件是系统性能的关键。select、poll、epoll 作为 I/O 多路复用技术的代表,以及基于它们实现的 Reactor 模式,为开发者提供了强大的工具。本文将深入探讨这些技术的底层原理、优缺点。 一、I…...

全面解析各类VPN技术:GRE、IPsec、L2TP、SSL与MPLS VPN对比
目录 引言 VPN技术概述 GRE VPN 3.1 GRE封装结构 3.2 GRE的应用场景 GRE over IPsec 4.1 GRE over IPsec封装结构 4.2 为什么使用GRE over IPsec? IPsec VPN 5.1 IPsec传输模式(Transport Mode) 5.2 IPsec隧道模式(Tunne…...
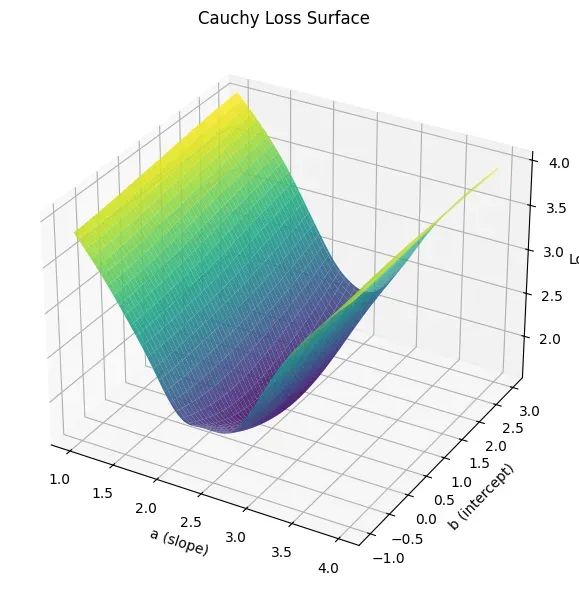
让回归模型不再被异常值“带跑偏“,MSE和Cauchy损失函数在噪声数据环境下的实战对比
在机器学习的回归分析中,损失函数的选择对模型性能具有决定性影响。均方误差(MSE)作为经典的损失函数,在处理干净数据时表现优异,但在面对包含异常值的噪声数据时,其对大误差的二次惩罚机制往往导致模型参数…...
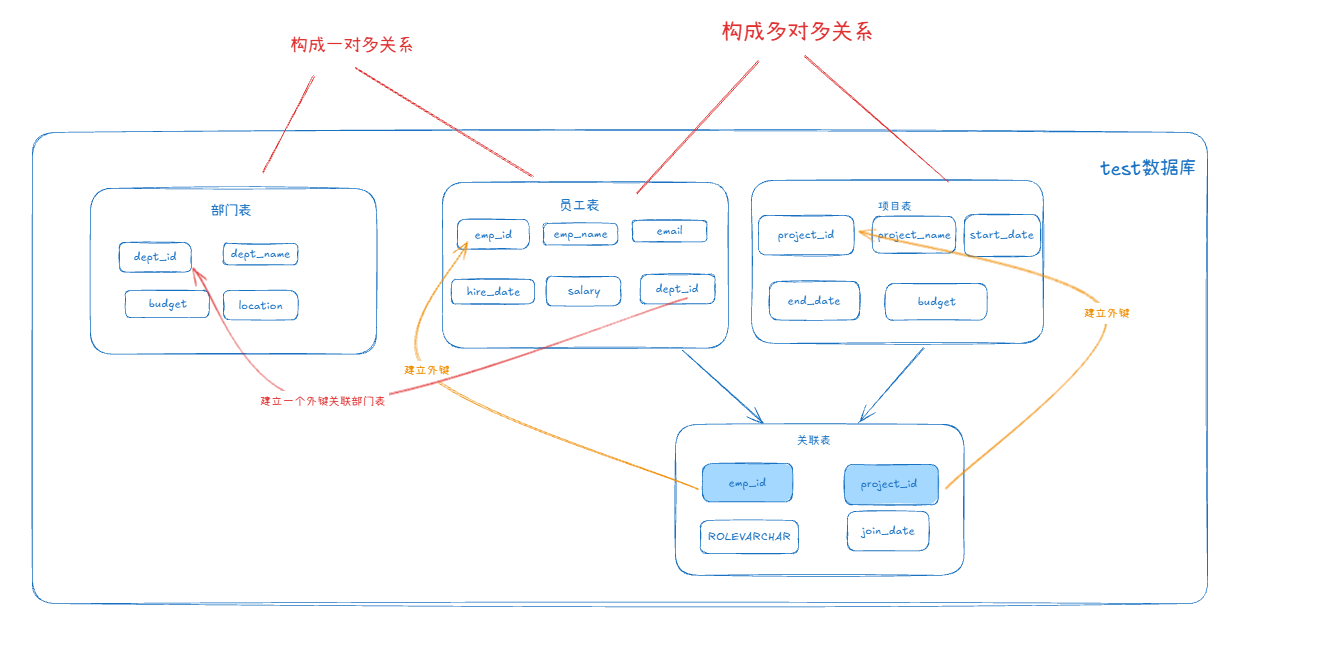
MySQL 知识小结(一)
一、my.cnf配置详解 我们知道安装MySQL有两种方式来安装咱们的MySQL数据库,分别是二进制安装编译数据库或者使用三方yum来进行安装,第三方yum的安装相对于二进制压缩包的安装更快捷,但是文件存放起来数据比较冗余,用二进制能够更好管理咱们M…...
)
华为OD最新机试真题-数组组成的最小数字-OD统一考试(B卷)
题目描述 给定一个整型数组,请从该数组中选择3个元素 组成最小数字并输出 (如果数组长度小于3,则选择数组中所有元素来组成最小数字)。 输入描述 行用半角逗号分割的字符串记录的整型数组,0<数组长度<= 100,0<整数的取值范围<= 10000。 输出描述 由3个元素组成…...

消防一体化安全管控平台:构建消防“一张图”和APP统一管理
在城市的某个角落,一场突如其来的火灾打破了平静。熊熊烈火迅速蔓延,滚滚浓烟弥漫开来,周围群众的生命财产安全受到严重威胁。就在这千钧一发之际,消防救援队伍迅速行动,而豪越科技消防一体化安全管控平台构建的消防“…...
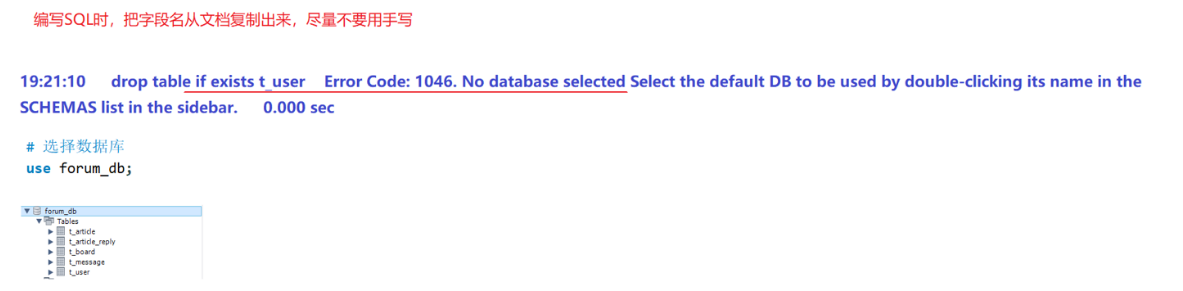
篇章二 论坛系统——系统设计
目录 2.系统设计 2.1 技术选型 2.2 设计数据库结构 2.2.1 数据库实体 1. 数据库设计 1.1 数据库名: forum db 1.2 表的设计 1.3 编写SQL 2.系统设计 2.1 技术选型 2.2 设计数据库结构 2.2.1 数据库实体 通过需求分析获得概念类并结合业务实现过程中的技术需要&#x…...

Monorepo架构: Nx Cloud 扩展能力与缓存加速
借助 Nx Cloud 实现项目协同与加速构建 1 ) 缓存工作原理分析 在了解了本地缓存和远程缓存之后,我们来探究缓存是如何工作的。以计算文件的哈希串为例,若后续运行任务时文件哈希串未变,系统会直接使用对应的输出和制品文件。 2 …...

Qt的学习(二)
1. 创建Hello Word 两种方式,实现helloworld: 1.通过图形化的方式,在界面上创建出一个控件,显示helloworld 2.通过纯代码的方式,通过编写代码,在界面上创建控件, 显示hello world; …...
