Android Retrofit 框架注解定义与解析模块深度剖析(一)
一、引言
在现代 Android 和 Java 开发中,网络请求是不可或缺的一部分。Retrofit 作为 Square 公司开源的一款强大的类型安全的 HTTP 客户端,凭借其简洁易用的 API 和高效的性能,在开发者社区中广受欢迎。Retrofit 的核心特性之一便是通过注解来定义 HTTP 请求,这种方式使得代码更加清晰、易读且易于维护。本文将深入 Retrofit 框架的源码,对其注解定义与解析模块进行全面且细致的分析,揭示其背后的实现原理。
二、Retrofit 框架概述
2.1 Retrofit 的基本工作流程
Retrofit 的主要工作流程可以概括为以下几个步骤:
- 定义服务接口:开发者使用注解定义一个接口,该接口包含了各种 HTTP 请求方法。
- 创建 Retrofit 实例:通过
Retrofit.Builder构建 Retrofit 实例,配置请求的基础 URL、转换器工厂、调用适配器工厂等。 - 创建服务代理对象:使用 Retrofit 实例创建服务接口的代理对象。
- 发起请求:调用服务代理对象的方法发起 HTTP 请求,并处理响应结果。
2.2 注解在 Retrofit 中的作用
注解在 Retrofit 中扮演着至关重要的角色,它们用于描述 HTTP 请求的各个方面,包括请求方法(如 GET、POST 等)、请求路径、请求参数、请求头、请求体等。通过注解,开发者可以以一种声明式的方式定义请求,而无需编写繁琐的网络请求代码。
三、Retrofit 注解的定义
3.1 HTTP 请求方法注解
3.1.1 @GET 注解
java
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;/*** 表示 HTTP GET 请求的注解*/
@Documented
// 该注解只能应用于方法上
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
// 该注解在运行时保留,以便通过反射获取
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface GET {/*** 指定请求的相对路径* @return 请求的相对路径,默认为空字符串*/String value() default "";
}
@GET 注解用于标记一个方法为 HTTP GET 请求,value 属性用于指定请求的相对路径。例如:
java
public interface ApiService {@GET("users/{id}")Call<User> getUser(@Path("id") int userId);
}
3.1.2 其他 HTTP 请求方法注解
除了 @GET 注解,Retrofit 还提供了 @POST、@PUT、@DELETE、@HEAD、@OPTIONS 和 @PATCH 等注解,它们的定义方式与 @GET 注解类似,只是用于不同的 HTTP 请求方法。
3.2 请求路径与参数注解
3.2.1 @Path 注解
java
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;/*** 用于替换 URL 中占位符的注解*/
@Documented
// 该注解只能应用于方法的参数上
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
// 该注解在运行时保留
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Path {/*** 指定 URL 中的占位符名称* @return 占位符名称*/String value();/*** 指定是否对参数进行 URL 编码,默认为 false* @return 是否进行 URL 编码*/boolean encoded() default false;
}
@Path 注解用于替换 URL 中的占位符,例如在上面的 getUser 方法中,@Path("id") 表示将 userId 参数的值替换到 URL 中的 {id} 占位符处。
3.2.2 @Query 和 @QueryMap 注解
java
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;/*** 用于添加查询参数到 URL 中的注解*/
@Documented
// 该注解只能应用于方法的参数上
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
// 该注解在运行时保留
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Query {/*** 指定查询参数的名称* @return 查询参数的名称*/String value();/*** 指定是否对参数进行 URL 编码,默认为 false* @return 是否进行 URL 编码*/boolean encoded() default false;
}import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;/*** 用于添加多个查询参数到 URL 中的注解*/
@Documented
// 该注解只能应用于方法的参数上
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
// 该注解在运行时保留
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface QueryMap {/*** 指定是否对参数进行 URL 编码,默认为 false* @return 是否进行 URL 编码*/boolean encoded() default false;
}
@Query 注解用于添加单个查询参数到 URL 中,@QueryMap 注解用于添加多个查询参数。例如:
java
public interface ApiService {@GET("search")Call<List<Item>> search(@Query("keyword") String keyword, @Query("page") int page);@GET("search")Call<List<Item>> searchWithMap(@QueryMap Map<String, String> queryParams);
}
3.2.3 @Header 和 @HeaderMap 注解
java
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;/*** 用于添加请求头的注解*/
@Documented
// 该注解只能应用于方法的参数上
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
// 该注解在运行时保留
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Header {/*** 指定请求头的名称* @return 请求头的名称*/String value();
}import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;/*** 用于添加多个请求头的注解*/
@Documented
// 该注解只能应用于方法的参数上
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
// 该注解在运行时保留
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface HeaderMap {
}
@Header 注解用于添加单个请求头,@HeaderMap 注解用于添加多个请求头。例如:
java
public interface ApiService {@GET("data")Call<Data> getData(@Header("Authorization") String token);@GET("data")Call<Data> getDataWithMap(@HeaderMap Map<String, String> headers);
}
3.2.4 @Body 注解
java
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;/*** 用于指定请求体的注解*/
@Documented
// 该注解只能应用于方法的参数上
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
// 该注解在运行时保留
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Body {
}
@Body 注解用于指定请求体,通常用于 POST、PUT 等请求。例如:
java
public interface ApiService {@POST("users")Call<User> createUser(@Body User user);
}
3.2.5 @FormUrlEncoded、@Field 和 @FieldMap 注解
java
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;/*** 用于标记表单编码请求的注解*/
@Documented
// 该注解只能应用于方法上
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
// 该注解在运行时保留
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface FormUrlEncoded {
}import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;/*** 用于添加表单字段的注解*/
@Documented
// 该注解只能应用于方法的参数上
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
// 该注解在运行时保留
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Field {/*** 指定表单字段的名称* @return 表单字段的名称*/String value();/*** 指定是否对参数进行 URL 编码,默认为 false* @return 是否进行 URL 编码*/boolean encoded() default false;
}import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;/*** 用于添加多个表单字段的注解*/
@Documented
// 该注解只能应用于方法的参数上
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
// 该注解在运行时保留
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface FieldMap {/*** 指定是否对参数进行 URL 编码,默认为 false* @return 是否进行 URL 编码*/boolean encoded() default false;
}
@FormUrlEncoded 注解用于标记一个方法为表单编码请求,@Field 注解用于添加单个表单字段,@FieldMap 注解用于添加多个表单字段。例如:
java
public interface ApiService {@FormUrlEncoded@POST("login")Call<LoginResponse> login(@Field("username") String username, @Field("password") String password);@FormUrlEncoded@POST("login")Call<LoginResponse> loginWithMap(@FieldMap Map<String, String> fields);
}
3.2.6 @Multipart、@Part 和 @PartMap 注解
java
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;/*** 用于标记多部分请求的注解*/
@Documented
// 该注解只能应用于方法上
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
// 该注解在运行时保留
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Multipart {
}import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;/*** 用于添加多部分请求中的一个部分的注解*/
@Documented
// 该注解只能应用于方法的参数上
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
// 该注解在运行时保留
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Part {/*** 指定部分的名称* @return 部分的名称*/String value() default "";
}import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;/*** 用于添加多部分请求中的多个部分的注解*/
@Documented
// 该注解只能应用于方法的参数上
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
// 该注解在运行时保留
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface PartMap {
}
@Multipart 注解用于标记一个方法为多部分请求,@Part 注解用于添加多部分请求中的一个部分,@PartMap 注解用于添加多部分请求中的多个部分。多部分请求常用于文件上传等场景。例如:
java
public interface ApiService {@Multipart@POST("upload")Call<UploadResponse> uploadFile(@Part("file"; filename="image.jpg"") RequestBody file);@Multipart@POST("upload")Call<UploadResponse> uploadFiles(@PartMap Map<String, RequestBody> files);
}
3.3 其他注解
3.3.1 @Headers 注解
java
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;/*** 用于添加多个请求头的注解*/
@Documented
// 该注解只能应用于方法上
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
// 该注解在运行时保留
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Headers {/*** 指定请求头的数组* @return 请求头的数组*/String[] value();
}
@Headers 注解用于在方法上添加多个请求头。例如:
java
public interface ApiService {@Headers({"Content-Type: application/json","Authorization: Bearer token123"})@GET("data")Call<Data> getData();
}
四、Retrofit 注解的解析
4.1 解析入口:ServiceMethod 类
ServiceMethod 是 Retrofit 中解析注解的核心类,它负责将接口方法上的注解信息解析为实际的 HTTP 请求信息。以下是 ServiceMethod 类的部分源码:
java
abstract class ServiceMethod<T> {/*** 解析接口方法上的注解,创建 ServiceMethod 实例* @param retrofit Retrofit 实例* @param method 接口方法* @param <T> 响应类型* @return ServiceMethod 实例*/static <T> ServiceMethod<T> parseAnnotations(Retrofit retrofit, Method method) {// 创建 RequestFactory.Builder 实例,用于构建 RequestFactoryRequestFactory.Builder requestFactoryBuilder = new RequestFactory.Builder(retrofit, method);// 解析请求方法和路径相关的注解requestFactoryBuilder.parseMethodAnnotation(method.getAnnotations());// 获取方法的参数类型Type[] parameterTypes = method.getGenericParameterTypes();// 获取方法的参数注解Annotation[][] parameterAnnotationsArray = method.getParameterAnnotations();// 遍历方法的每个参数for (int p = 0; p < parameterTypes.length; p++) {// 解析参数的注解requestFactoryBuilder.parseParameter(p, parameterTypes[p], parameterAnnotationsArray[p]);}// 构建 RequestFactory 实例RequestFactory requestFactory = requestFactoryBuilder.build();// 获取方法的返回类型Type returnType = method.getGenericReturnType();if (Utils.hasUnresolvableType(returnType)) {throw methodError(method,"Method return type must not include a type variable or wildcard: %s", returnType);}if (returnType == void.class) {throw methodError(method, "Service methods cannot return void.");}// 创建 CallAdapter 实例,用于将 Call 对象转换为其他类型CallAdapter<T, ?> callAdapter = createCallAdapter(retrofit, method, returnType, requestFactory);// 获取响应类型Type responseType = callAdapter.responseType();if (Utils.hasUnresolvableType(responseType)) {throw methodError(method, "Call return type must not include a type variable or wildcard: %s", returnType);}// 创建 Converter 实例,用于将响应数据转换为指定类型Converter<ResponseBody, T> responseConverter =createResponseConverter(retrofit, method, responseType);// 获取 OkHttpClient 实例okhttp3.Call.Factory callFactory = retrofit.callFactory();// 创建 ServiceMethod 实例return new HttpServiceMethod<>(callFactory, requestFactory, callAdapter, responseConverter);}/*** 创建 CallAdapter 实例* @param retrofit Retrofit 实例* @param method 接口方法* @param returnType 方法的返回类型* @param requestFactory 请求工厂* @param <T> 响应类型* @return CallAdapter 实例*/private static <T> CallAdapter<T, ?> createCallAdapter(Retrofit retrofit, Method method, Type returnType, RequestFactory requestFactory) {try {// 通过 Retrofit 实例获取 CallAdapter.Factory 列表,并调用其 get 方法创建 CallAdapter 实例return (CallAdapter<T, ?>) retrofit.callAdapter(returnType, method.getAnnotations());} catch (RuntimeException e) {throw methodError(method, e, "Unable to create call adapter for %s", returnType);}}/*** 创建响应转换器实例* @param retrofit Retrofit 实例* @param method 接口方法* @param responseType 响应类型* @param <T> 响应类型* @return 响应转换器实例*/private static <T> Converter<ResponseBody, T> createResponseConverter(Retrofit retrofit, Method method, Type responseType) {try {// 通过 Retrofit 实例获取 Converter.Factory 列表,并调用其 responseBodyConverter 方法创建响应转换器实例return retrofit.responseBodyConverter(responseType, method.getAnnotations());} catch (RuntimeException e) {throw methodError(method, e, "Unable to create converter for %s", responseType);}}/*** 抽象方法,用于执行请求* @param args 方法参数* @return 响应结果*/abstract @Nullable T invoke(Object[] args);
}
parseAnnotations 方法是解析的入口,它接收 Retrofit 实例和 Method 实例作为参数,通过以下步骤完成注解解析:
- 创建
RequestFactory.Builder实例,用于构建RequestFactory。 - 调用
requestFactoryBuilder.parseMethodAnnotation方法解析请求方法和路径相关的注解。 - 遍历方法的每个参数,调用
requestFactoryBuilder.parseParameter方法解析参数的注解。 - 构建
RequestFactory实例。 - 获取方法的返回类型,并创建
CallAdapter实例,用于将Call对象转换为其他类型。 - 获取响应类型,并创建
Converter实例,用于将响应数据转换为指定类型。 - 获取
OkHttpClient实例,并创建ServiceMethod实例。
4.2 解析请求方法和路径注解:RequestFactory.Builder.parseMethodAnnotation 方法
java
static final class Builder {// 存储请求方法(如 GET、POST 等)private String httpMethod;// 存储请求是否需要请求体private boolean hasBody;// 存储请求的相对路径private String relativeUrl;// 存储请求的请求头private okhttp3.Headers headers;// 存储路径中的占位符名称private List<String> relativeUrlParamNames;// 标记是否为多部分请求private boolean isMultipart;// 标记是否为表单编码请求private boolean isFormEncoded;/*** 解析请求方法和路径相关的注解* @param annotations 方法上的注解数组*/void parseMethodAnnotation(Annotation[] annotations) {for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {if (annotation instanceof HttpMethod) {// 如果注解是 HttpMethod 类型(如 @GET、@POST 等)HttpMethod httpMethodAnnotation = (HttpMethod) annotation;// 获取请求方法this.httpMethod = httpMethodAnnotation.value();// 判断是否需要请求体this.hasBody = httpMethodAnnotation.hasBody();String path = httpMethodAnnotation.path();if (!path.isEmpty()) {// 检查路径是否以 / 开头if (path.startsWith("/")) {throw methodError(method, "@%s path must not start with /: %s",httpMethodAnnotation.annotationType().getSimpleName(), path);}this.relativeUrl = path;// 解析路径中的占位符this.relativeUrlParamNames = parsePathParameters(path);}} else if (annotation instanceof Headers) {// 如果注解是 Headers 类型String[] headersToParse = ((Headers) annotation).value();if (headersToParse.length == 0) {throw methodError(method, "@Headers annotation is empty.");}// 解析请求头this.headers = parseHeaders(headersToParse);} else if (annotation instanceof Multipart) {// 如果注解是 Multipart 类型if (this.hasBody) {throw methodError(method, "Only one encoding annotation is allowed.");}this.isMultipart = true;this.hasBody = true;} else if (annotation instanceof FormUrlEncoded) {// 如果注解是 FormUrlEncoded 类型if (this.hasBody) {throw methodError(method, "Only one encoding annotation is allowed.");}this.isFormEncoded = true;this.hasBody = true;}}if (httpMethod == null) {throw methodError(method, "HTTP method annotation is required (e.g., @GET, @POST, etc.).");}}/*** 解析路径中的占位符* @param path 请求路径* @return 占位符名称列表*/private static List<String> parsePathParameters(String path) {// 定义正则表达式,用于匹配路径中的占位符Matcher m = PARAM_URL_REGEX.matcher(path);List<String> patterns = new ArrayList<>();while (m.find()) {String name = m.group(1);if (name == null) {continue;}if (patterns.contains(name)) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("URL path "" + path + "" has duplicate param "" + name + "".");}patterns.add(name);}return patterns;}/*** 解析请求头* @param headers 请求头数组* @return OkHttp 的 Headers 实例*/private static okhttp3.Headers parseHeaders(String[] headers) {okhttp3.Headers.Builder builder = new okhttp3.Headers.Builder();for (String header : headers) {int colon = header.indexOf(':');if (colon == -1 || colon == 0 || colon == header.length() - 1) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Headers value must be in the form "Name: Value". Found: "" + header + """);}String name = header.substring(0, colon).trim();String value = header.substring(colon + 1).trim();builder.add(name, value);}return builder.build();}
}
parseMethodAnnotation 方法遍历方法上的所有注解,根据注解的类型进行不同的处理:
- 如果注解是
HttpMethod类型(如@GET、@POST等),获取请求方法、判断是否需要请求体,并解析路径中的占位符。 - 如果注解是
Headers类型,解析请求头。 - 如果注解是
Multipart类型,标记为多部分请求。 - 如果注解是
FormUrlEncoded类型,标记为表单编码请求。
4.3 解析参数注解:RequestFactory.Builder.parseParameter 方法
java
static final class Builder {// 存储参数处理器数组private ParameterHandler<?>[] parameterHandlers;/*** 解析方法参数的注解* @param p 参数索引* @param parameterType 参数类型* @param annotations 参数上的注解数组*/void parseParameter(int p, Type parameterType, @Nullable Annotation[] annotations) {if (annotations == null) {throw parameterError(method, p, "No Retrofit annotation found.");}ParameterHandler<?> result = null;for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {// 创建参数处理器ParameterHandler<?> annotationAction = parseParameterAnnotation(p, parameterType, annotations, annotation);if (annotationAction == null) {continue;}if (result != null) {throw parameterError(method, p, "Multiple Retrofit annotations found, only one allowed.");}result = annotationAction;}if (result == null) {throw parameterError(method, p, "No Retrofit annotation found.");}// 将参数处理器添加到参数处理器数组中parameterHandlers[p] = result;}/*** 解析单个参数注解* @param p 参数索引* @param type 参数类型* @param annotations 参数上的注解数组* @param annotation 当前要解析的注解* @return 参数处理器*/private @Nullable ParameterHandler<?> parseParameterAnnotation(int p, Type type, Annotation[] annotations, Annotation annotation) {if (annotation instanceof Path) {// 如果注解
4.3 解析参数注解:RequestFactory.Builder.parseParameter 方法(续)
java
static final class Builder {// 存储参数处理器数组private ParameterHandler<?>[] parameterHandlers;/*** 解析方法参数的注解* @param p 参数索引* @param parameterType 参数类型* @param annotations 参数上的注解数组*/void parseParameter(int p, Type parameterType, @Nullable Annotation[] annotations) {if (annotations == null) {throw parameterError(method, p, "No Retrofit annotation found.");}ParameterHandler<?> result = null;for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {// 创建参数处理器ParameterHandler<?> annotationAction = parseParameterAnnotation(p, parameterType, annotations, annotation);if (annotationAction == null) {continue;}if (result != null) {throw parameterError(method, p, "Multiple Retrofit annotations found, only one allowed.");}result = annotationAction;}if (result == null) {throw parameterError(method, p, "No Retrofit annotation found.");}// 将参数处理器添加到参数处理器数组中parameterHandlers[p] = result;}/*** 解析单个参数注解* @param p 参数索引* @param type 参数类型* @param annotations 参数上的注解数组* @param annotation 当前要解析的注解* @return 参数处理器*/private @Nullable ParameterHandler<?> parseParameterAnnotation(int p, Type type, Annotation[] annotations, Annotation annotation) {if (annotation instanceof Path) {// 如果注解是 Path 类型Path path = (Path) annotation;// 检查路径中是否包含该占位符if (!relativeUrlParamNames.contains(path.value())) {throw parameterError(method, p, "@Path parameter "" + path.value()+ "" not found in relative URL "" + relativeUrl + """);}// 检查参数类型是否为基本类型或字符串if (Utils.hasUnresolvableType(type)) {throw parameterError(method, p,"@Path parameter type must not include a type variable or wildcard: %s", type);}// 创建 PathParameterHandler 实例return new ParameterHandler.Path<>(path.value(), path.encoded(),converterFactory.stringConverter(type, annotations, retrofit));} else if (annotation instanceof Query) {// 如果注解是 Query 类型Query query = (Query) annotation;// 检查参数类型是否为基本类型或字符串if (Utils.hasUnresolvableType(type)) {throw parameterError(method, p,"@Query parameter type must not include a type variable or wildcard: %s", type);}// 创建 QueryParameterHandler 实例return new ParameterHandler.Query<>(query.value(), query.encoded(),converterFactory.stringConverter(type, annotations, retrofit));} else if (annotation instanceof QueryMap) {// 如果注解是 QueryMap 类型if (!Map.class.isAssignableFrom(Utils.getRawType(type))) {throw parameterError(method, p, "@QueryMap parameter type must be Map.");}Type keyType = Utils.getSupertype(type, Map.class, String.class);if (keyType != String.class) {throw parameterError(method, p, "@QueryMap keys must be of type String: %s", type);}Type valueType = Utils.getSupertype(type, Map.class, Object.class);// 创建 QueryMapParameterHandler 实例return new ParameterHandler.QueryMap<>(converterFactory.stringConverter(valueType, annotations, retrofit));} else if (annotation instanceof Header) {// 如果注解是 Header 类型Header header = (Header) annotation;// 检查参数类型是否为基本类型或字符串if (Utils.hasUnresolvableType(type)) {throw parameterError(method, p,"@Header parameter type must not include a type variable or wildcard: %s", type);}// 创建 HeaderParameterHandler 实例return new ParameterHandler.Header<>(header.value(),converterFactory.stringConverter(type, annotations, retrofit));} else if (annotation instanceof HeaderMap) {// 如果注解是 HeaderMap 类型if (!Map.class.isAssignableFrom(Utils.getRawType(type))) {throw parameterError(method, p, "@HeaderMap parameter type must be Map.");}Type keyType = Utils.getSupertype(type, Map.class, String.class);if (keyType != String.class) {throw parameterError(method, p, "@HeaderMap keys must be of type String: %s", type);}Type valueType = Utils.getSupertype(type, Map.class, Object.class);// 创建 HeaderMapParameterHandler 实例return new ParameterHandler.HeaderMap<>(converterFactory.stringConverter(valueType, annotations, retrofit));} else if (annotation instanceof Body) {// 如果注解是 Body 类型if (isFormEncoded || isMultipart) {throw parameterError(method, p,"@Body parameters cannot be used with form or multi - part encoding.");}// 创建 BodyParameterHandler 实例return new ParameterHandler.Body<>(converterFactory.requestBodyConverter(type, annotations, methodAnnotations, retrofit));} else if (annotation instanceof Field) {// 如果注解是 Field 类型if (!isFormEncoded) {throw parameterError(method, p, "@Field parameters can only be used with form encoding.");}Field field = (Field) annotation;// 检查参数类型是否为基本类型或字符串if (Utils.hasUnresolvableType(type)) {throw parameterError(method, p,"@Field parameter type must not include a type variable or wildcard: %s", type);}// 创建 FieldParameterHandler 实例return new ParameterHandler.Field<>(field.value(), field.encoded(),converterFactory.stringConverter(type, annotations, retrofit));} else if (annotation instanceof FieldMap) {// 如果注解是 FieldMap 类型if (!isFormEncoded) {throw parameterError(method, p, "@FieldMap parameters can only be used with form encoding.");}if (!Map.class.isAssignableFrom(Utils.getRawType(type))) {throw parameterError(method, p, "@FieldMap parameter type must be Map.");}Type keyType = Utils.getSupertype(type, Map.class, String.class);if (keyType != String.class) {throw parameterError(method, p, "@FieldMap keys must be of type String: %s", type);}Type valueType = Utils.getSupertype(type, Map.class, Object.class);// 创建 FieldMapParameterHandler 实例return new ParameterHandler.FieldMap<>(converterFactory.stringConverter(valueType, annotations, retrofit));} else if (annotation instanceof Part) {// 如果注解是 Part 类型if (!isMultipart) {throw parameterError(method, p, "@Part parameters can only be used with multipart encoding.");}Part part = (Part) annotation;String partName = part.value();if (!"".equals(partName) && !partName.endsWith(";")) {partName = partName + ";";}// 创建 PartParameterHandler 实例return new ParameterHandler.Part<>(partName,converterFactory.requestBodyConverter(type, annotations, methodAnnotations, retrofit));} else if (annotation instanceof PartMap) {// 如果注解是 PartMap 类型if (!isMultipart) {throw parameterError(method, p, "@PartMap parameters can only be used with multipart encoding.");}if (!Map.class.isAssignableFrom(Utils.getRawType(type))) {throw parameterError(method, p, "@PartMap parameter type must be Map.");}Type keyType = Utils.getSupertype(type, Map.class, String.class);if (keyType != String.class) {throw parameterError(method, p, "@PartMap keys must be of type String: %s", type);}Type valueType = Utils.getSupertype(type, Map.class, Object.class);// 创建 PartMapParameterHandler 实例return new ParameterHandler.PartMap<>(converterFactory.requestBodyConverter(valueType, annotations, methodAnnotations, retrofit));}return null;}
}
4.3.1 详细解析逻辑
-
@Path注解解析:- 首先,从
Path注解中获取占位符名称,检查该占位符是否存在于之前解析得到的relativeUrlParamNames列表中。如果不存在,会抛出异常,确保路径占位符的正确性。 - 接着,检查参数类型是否包含不可解析的类型变量或通配符。如果存在,也会抛出异常,因为
@Path参数类型应该是基本类型或字符串。 - 最后,创建
ParameterHandler.Path实例,该实例负责处理路径占位符的替换。converterFactory.stringConverter方法用于创建一个将参数类型转换为字符串的转换器,以便将参数值正确地替换到路径中。
- 首先,从
-
@Query注解解析:- 对于
Query注解,同样会检查参数类型是否包含不可解析的类型变量或通配符。 - 然后创建
ParameterHandler.Query实例,该实例会将参数值作为查询参数添加到 URL 中。converterFactory.stringConverter用于将参数值转换为字符串形式。
- 对于
-
@QueryMap注解解析:- 先检查参数类型是否为
Map类型,如果不是会抛出异常。 - 接着检查
Map的键类型是否为String类型,若不是也会抛出异常。 - 最后创建
ParameterHandler.QueryMap实例,该实例会将Map中的键值对作为查询参数添加到 URL 中。converterFactory.stringConverter用于将Map的值转换为字符串。
- 先检查参数类型是否为
-
@Header注解解析:- 检查参数类型是否包含不可解析的类型变量或通配符。
- 创建
ParameterHandler.Header实例,该实例会将参数值作为请求头添加到请求中。converterFactory.stringConverter用于将参数值转换为字符串形式的请求头值。
-
@HeaderMap注解解析:- 检查参数类型是否为
Map类型,以及Map的键类型是否为String类型。 - 创建
ParameterHandler.HeaderMap实例,该实例会将Map中的键值对作为请求头添加到请求中。converterFactory.stringConverter用于将Map的值转换为字符串形式的请求头值。
- 检查参数类型是否为
-
@Body注解解析:- 检查当前请求是否为表单编码或多部分请求,如果是则抛出异常,因为
@Body参数不能与表单或多部分编码同时使用。 - 创建
ParameterHandler.Body实例,该实例会将参数作为请求体发送。converterFactory.requestBodyConverter用于将参数类型转换为RequestBody类型,以便进行网络传输。
- 检查当前请求是否为表单编码或多部分请求,如果是则抛出异常,因为
-
@Field注解解析:- 检查当前请求是否为表单编码请求,如果不是则抛出异常,因为
@Field参数只能用于表单编码请求。 - 检查参数类型是否包含不可解析的类型变量或通配符。
- 创建
ParameterHandler.Field实例,该实例会将参数值作为表单字段添加到请求体中。converterFactory.stringConverter用于将参数值转换为字符串形式的表单字段值。
- 检查当前请求是否为表单编码请求,如果不是则抛出异常,因为
-
@FieldMap注解解析:- 检查当前请求是否为表单编码请求,以及参数类型是否为
Map类型,Map的键类型是否为String类型。 - 创建
ParameterHandler.FieldMap实例,该实例会将Map中的键值对作为表单字段添加到请求体中。converterFactory.stringConverter用于将Map的值转换为字符串形式的表单字段值。
- 检查当前请求是否为表单编码请求,以及参数类型是否为
-
@Part注解解析:- 检查当前请求是否为多部分请求,如果不是则抛出异常,因为
@Part参数只能用于多部分请求。 - 处理
Part注解的value属性,确保其格式正确。 - 创建
ParameterHandler.Part实例,该实例会将参数作为多部分请求的一部分添加到请求体中。converterFactory.requestBodyConverter用于将参数类型转换为RequestBody类型。
- 检查当前请求是否为多部分请求,如果不是则抛出异常,因为
-
@PartMap注解解析:- 检查当前请求是否为多部分请求,以及参数类型是否为
Map类型,Map的键类型是否为String类型。 - 创建
ParameterHandler.PartMap实例,该实例会将Map中的键值对作为多部分请求的多个部分添加到请求体中。converterFactory.requestBodyConverter用于将Map的值转换为RequestBody类型。
- 检查当前请求是否为多部分请求,以及参数类型是否为
4.4 创建 RequestFactory 实例
在完成所有参数注解的解析后,会调用 RequestFactory.Builder 的 build 方法来构建 RequestFactory 实例:
java
RequestFactory build() {return new RequestFactory(this);
}
RequestFactory 类封装了所有解析得到的请求信息,包括请求方法、请求路径、请求头、请求体等,后续会根据这些信息创建实际的 Request 对象。
4.5 创建 CallAdapter 和 Converter 实例
在 ServiceMethod.parseAnnotations 方法中,还会创建 CallAdapter 和 Converter 实例:
java
// 创建 CallAdapter 实例,用于将 Call 对象转换为其他类型
CallAdapter<T, ?> callAdapter = createCallAdapter(retrofit, method, returnType, requestFactory);
// 获取响应类型
Type responseType = callAdapter.responseType();
if (Utils.hasUnresolvableType(responseType)) {throw methodError(method, "Call return type must not include a type variable or wildcard: %s", returnType);
}// 创建 Converter 实例,用于将响应数据转换为指定类型
Converter<ResponseBody, T> responseConverter =createResponseConverter(retrofit, method, responseType);
4.5.1 CallAdapter 实例创建
createCallAdapter 方法通过 Retrofit 实例的 callAdapter 方法从 CallAdapter.Factory 列表中查找合适的 CallAdapter.Factory,并调用其 get 方法创建 CallAdapter 实例。CallAdapter 的作用是将 Call 对象转换为其他类型,例如将 Call<Response> 转换为 Observable<Response> 等,以支持不同的异步编程模型。
4.5.2 Converter 实例创建
createResponseConverter 方法通过 Retrofit 实例的 responseBodyConverter 方法从 Converter.Factory 列表中查找合适的 Converter.Factory,并调用其 responseBodyConverter 方法创建 Converter 实例。Converter 的作用是将 ResponseBody 转换为指定的响应类型,例如将 JSON 数据转换为 Java 对象。
4.6 创建 ServiceMethod 实例
最后,根据前面解析得到的信息,创建 ServiceMethod 实例:
java
// 获取 OkHttpClient 实例
okhttp3.Call.Factory callFactory = retrofit.callFactory();
// 创建 ServiceMethod 实例
return new HttpServiceMethod<>(callFactory, requestFactory, callAdapter, responseConverter);
HttpServiceMethod 是 ServiceMethod 的具体实现类,它负责执行实际的 HTTP 请求,并处理响应结果。在 invoke 方法中,会根据 RequestFactory 创建 Request 对象,使用 OkHttpClient 发送请求,然后通过 CallAdapter 和 Converter 处理响应。
java
final class HttpServiceMethod<ResponseT, ReturnT> extends ServiceMethod<ReturnT> {private final okhttp3.Call.Factory callFactory;private final RequestFactory requestFactory;private final CallAdapter<ResponseT, ReturnT> callAdapter;private final Converter<ResponseBody, ResponseT> responseConverter;HttpServiceMethod(okhttp3.Call.Factory callFactory, RequestFactory requestFactory,CallAdapter<ResponseT, ReturnT> callAdapter,Converter<ResponseBody, ResponseT> responseConverter) {this.callFactory = callFactory;this.requestFactory = requestFactory;this.callAdapter = callAdapter;this.responseConverter = responseConverter;}@Override@Nullable ReturnT invoke(Object[] args) {// 创建 OkHttp 的 Request 对象Request request = requestFactory.create(args);// 创建 OkHttp 的 Call 对象okhttp3.Call call = callFactory.newCall(request);// 调用 CallAdapter 的 adapt 方法将 Call 对象转换为指定类型return callAdapter.adapt(new OkHttpCall<>(request, callFactory, responseConverter));}
}
五、注解解析后的使用
当 ServiceMethod 实例创建完成后,就可以使用它来发起 HTTP 请求了。在调用服务接口的方法时,实际上是调用 ServiceMethod 的 invoke 方法:
java
public interface ApiService {@GET("users/{id}")Call<User> getUser(@Path("id") int userId);
}// 创建 Retrofit 实例
Retrofit retrofit = new Retrofit.Builder().baseUrl("https://api.example.com/").addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create()).build();// 创建服务代理对象
ApiService apiService = retrofit.create(ApiService.class);// 发起请求
Call<User> call = apiService.getUser(1);
call.enqueue(new Callback<User>() {@Overridepublic void onResponse(Call<User> call, Response<User> response) {if (response.isSuccessful()) {User user = response.body();// 处理响应数据} else {// 处理请求失败}}@Overridepublic void onFailure(Call<User> call, Throwable t) {// 处理请求异常}
});
在上述代码中,apiService.getUser(1) 实际上调用了 ServiceMethod 的 invoke 方法,该方法会根据之前解析得到的注解信息创建 Request 对象,使用 OkHttpClient 发送请求,并通过 CallAdapter 和 Converter 处理响应结果。
六、总结
Retrofit 的注解定义与解析模块是其核心功能之一,通过使用注解,开发者可以以一种简洁、声明式的方式定义 HTTP 请求。在解析过程中,Retrofit 利用 Java 的反射机制,在运行时获取方法和参数上的注解信息,并根据注解类型进行相应的处理。具体步骤包括解析请求方法和路径注解、解析参数注解、创建 RequestFactory、CallAdapter 和 Converter 实例,最终创建 ServiceMethod 实例来执行实际的 HTTP 请求。这种设计使得 Retrofit 具有高度的灵活性和可扩展性,开发者可以通过自定义 CallAdapter.Factory 和 Converter.Factory 来满足不同的需求。同时,注解的使用也使得代码更加清晰、易读和易于维护,提高了开发效率。
相关文章:
)
Android Retrofit 框架注解定义与解析模块深度剖析(一)
一、引言 在现代 Android 和 Java 开发中,网络请求是不可或缺的一部分。Retrofit 作为 Square 公司开源的一款强大的类型安全的 HTTP 客户端,凭借其简洁易用的 API 和高效的性能,在开发者社区中广受欢迎。Retrofit 的核心特性之一便是通过注…...

项目上传到Gitee过程
在gitee上新建一个仓库 点击“克隆/下载”获取仓库地址 电脑上要装好git 在电脑本地文件夹右键“Git Bash Here” 依次执行如下命令 git init git remote add origin https://gitee.com/qlexcel/stm32-simple.git git pull origin master git add . git commit -m ‘init’…...

DeepSeek R1在医学领域的应用与技术分析(Discuss V1版)
DeepSeek R1作为一款高性能、低成本的国产开源大模型,正在深刻重塑医学软件工程的开发逻辑与应用场景。其技术特性,如混合专家架构(MoE)和参数高效微调(PEFT),与医疗行业的实际需求紧密结合,推动医疗AI从“技术驱动”向“场景驱动”转型。以下从具体业务领域需求出发,…...

数学之快速幂-数的幂次
题目描述 给定三个正整数 N,M,P,求 输入描述 第 1 行为一个整数 T,表示测试数据数量。 接下来的 T 行每行包含三个正整数 N,M,P。 输出描述 输出共 T 行,每行包含一个整数,表示答案。 输入输出样例 示例 1 输入 3 2 3 7 4…...

git subtree管理的仓库怎么删除子仓库
要删除通过 git subtree 管理的子仓库,可以按照以下步骤操作: 1. 确认子仓库路径 首先确认要删除的子仓库的路径,假设子仓库路径为 <subtree-path>。 2. 从主仓库中移除子仓库目录 使用 git rm 命令删除子仓库的目录: …...

学习资料电子版 免费下载的网盘网站(非常全!)
我分享一个私人收藏的电子书免费下载的网盘网站(学习资料为主): link3.cc/sbook123 所有资料都保存在网盘了,直接转存即可,非常的便利! 包括了少儿,小学,初中,中职&am…...

SpringMVC-全局异常处理
文章目录 1. 全局异常处理2. 项目异常处理方案2.1 异常分类2.2 异常解决方案2.3 异常解决方案具体实现 1. 全局异常处理 问题:当我们在SpingMVC代码中没有对异常进行处理时,三层架构的默认处理异常方案是将异常抛给上级调用者。也就是说Mapper层报错会将…...

基于Spring Boot的宠物健康顾问系统的设计与实现(LW+源码+讲解)
专注于大学生项目实战开发,讲解,毕业答疑辅导,欢迎高校老师/同行前辈交流合作✌。 技术范围:SpringBoot、Vue、SSM、HLMT、小程序、Jsp、PHP、Nodejs、Python、爬虫、数据可视化、安卓app、大数据、物联网、机器学习等设计与开发。 主要内容:…...

【Linux内核系列】:深入理解缓冲区
🔥 本文专栏:Linux 🌸作者主页:努力努力再努力wz ★★★ 本文前置知识: 文件系统以及相关系统调用接口 输入以及输出重定向 那么在此前的学习中,我们了解了文件的概念以及相关的系统调用接口,并…...

Python开发Scikit-learn面试题及参考答案
目录 如何用 SimpleImputer 处理数据集中的缺失值? 使用 StandardScaler 对数据进行标准化的原理是什么?与 MinMaxScaler 有何区别? 如何用 OneHotEncoder 对类别型特征进行编码? 解释特征选择中 SelectKBest 与 VarianceThreshold 的应用场景。 如何通过 PolynomialFe…...
在算法竞赛中的常见用法和注意事项)
~(取反)在算法竞赛中的常见用法和注意事项
在算法竞赛中,取反符号 ~ 主要用于按位取反操作,其功能是对整数的二进制表示逐位取反(0 变 1,1 变 0)。以下是 ~ 在算法竞赛中的常见用法和注意事项: 1. 按位取反的基本用法 ~ 对整数的二进制表示进行取反…...
)
C++ MySQL 常用接口(基于 MySQL Connector/C++)
C MySQL 常用接口(基于 MySQL Connector/C) 1. 数据库连接 接口: sql::mysql::MySQL_Driver *driver; sql::Connection *con;作用: 用于创建 MySQL 连接对象。 示例: driver sql::mysql::get_mysql_driver_insta…...

本地部署 OpenManus 保姆级教程(Windows 版)
一、环境搭建 我的电脑是Windows 10版本,其他的没尝试,如果大家系统和我的不一致,请自行判断,基本上没什么大的出入啊。 openManus的Git地址:https://github.com/mannaandpoem/OpenManus 根据官网的两种安装推荐方式如…...

【Pandas】pandas Series compare
# Pandas2.2 Series ## Computations descriptive stats |方法|描述| |-|:-------| |Series.compare(other[, align_axis, ...])|用于比较两个 Series| ### pandas.Series.compare pandas.Series.compare 方法用于比较两个 Series,并返回一个包含差异的 DataFram…...

基于DeepSeek的智慧医药系统(源码+部署教程)
运行环境 智慧医药系统运行环境如下: 前端: HTMLCSS后端:Java AIGCDeepseekIDE工具:IDEA技术栈:Springboot HTMLCSS MySQL 主要角色 智慧医药系统主要分为两个角色。 游客 尚未进行注册和登录。具备登录注册、…...

如何为服务设置合理的线程数
1. 首先,要确定最大线程数的限制因素。通常,线程数量受限于内存、CPU和操作系统限制。比如,每个线程都需要一定的栈内存,默认情况下Java线程的栈大小是1MB(64位系统可能更大),所以如果内存不足&…...

Unity--Cubism Live2D模型使用
了解LIVE2D在unity的使用--前提记录 了解各个组件的作用 Live2D Manuals & Tutorials 这些文件都是重要的控制动画参数的 Cubism Editor是编辑Live2D的工具,而导出的数据的类型,需要满足以上的条件 SDK中包含的Cubism的Importer会自动生成一个Pref…...

Vue.js 3 的设计思路:从声明式UI到高效渲染机制
目录 一、声明式UI与虚拟DOM的灵活性 二、渲染器:虚拟DOM到真实DOM的桥梁 三、组件的本质与实现 四、编译与运行时的协同优化 五、性能与可维护性的权衡 总结 Vue.js 3 作为新一代前端框架,其设计理念在声明式UI描述、虚拟DOM优化、组件化架构…...

部署前后端项目
部署项目 liunx 软件安装 软件安装方式 在Linux系统中,安装软件的方式主要有四种,这四种安装方式的特点如下: 建议nginx、MySQL、Redis等等使用docker安装,会很便捷,这里只演示JDK、ngxin手动的安装 安装JDK 上述我…...

Vue Diff算法原理深度解析:如何高效更新虚拟DOM?
文章目录 1. 为什么需要Diff算法?2. Diff算法核心原则3. 核心流程图解4. 核心代码实现(简化版)5. Key的重要性示例6. 算法优化策略7. 时间复杂度优化8. 与其他框架的对比9. 总结 1. 为什么需要Diff算法? 在Vue的响应式系统中&…...
网络编程(Modbus进阶)
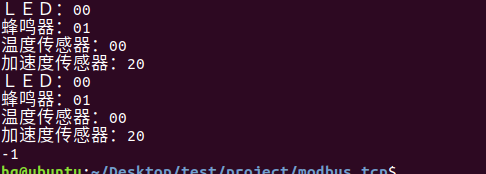
思维导图 Modbus RTU(先学一点理论) 概念 Modbus RTU 是工业自动化领域 最广泛应用的串行通信协议,由 Modicon 公司(现施耐德电气)于 1979 年推出。它以 高效率、强健性、易实现的特点成为工业控制系统的通信标准。 包…...
UE5 学习系列(二)用户操作界面及介绍
这篇博客是 UE5 学习系列博客的第二篇,在第一篇的基础上展开这篇内容。博客参考的 B 站视频资料和第一篇的链接如下: 【Note】:如果你已经完成安装等操作,可以只执行第一篇博客中 2. 新建一个空白游戏项目 章节操作,重…...

手游刚开服就被攻击怎么办?如何防御DDoS?
开服初期是手游最脆弱的阶段,极易成为DDoS攻击的目标。一旦遭遇攻击,可能导致服务器瘫痪、玩家流失,甚至造成巨大经济损失。本文为开发者提供一套简洁有效的应急与防御方案,帮助快速应对并构建长期防护体系。 一、遭遇攻击的紧急应…...

Ubuntu系统下交叉编译openssl
一、参考资料 OpenSSL&&libcurl库的交叉编译 - hesetone - 博客园 二、准备工作 1. 编译环境 宿主机:Ubuntu 20.04.6 LTSHost:ARM32位交叉编译器:arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc-11.1.0 2. 设置交叉编译工具链 在交叉编译之前&#x…...
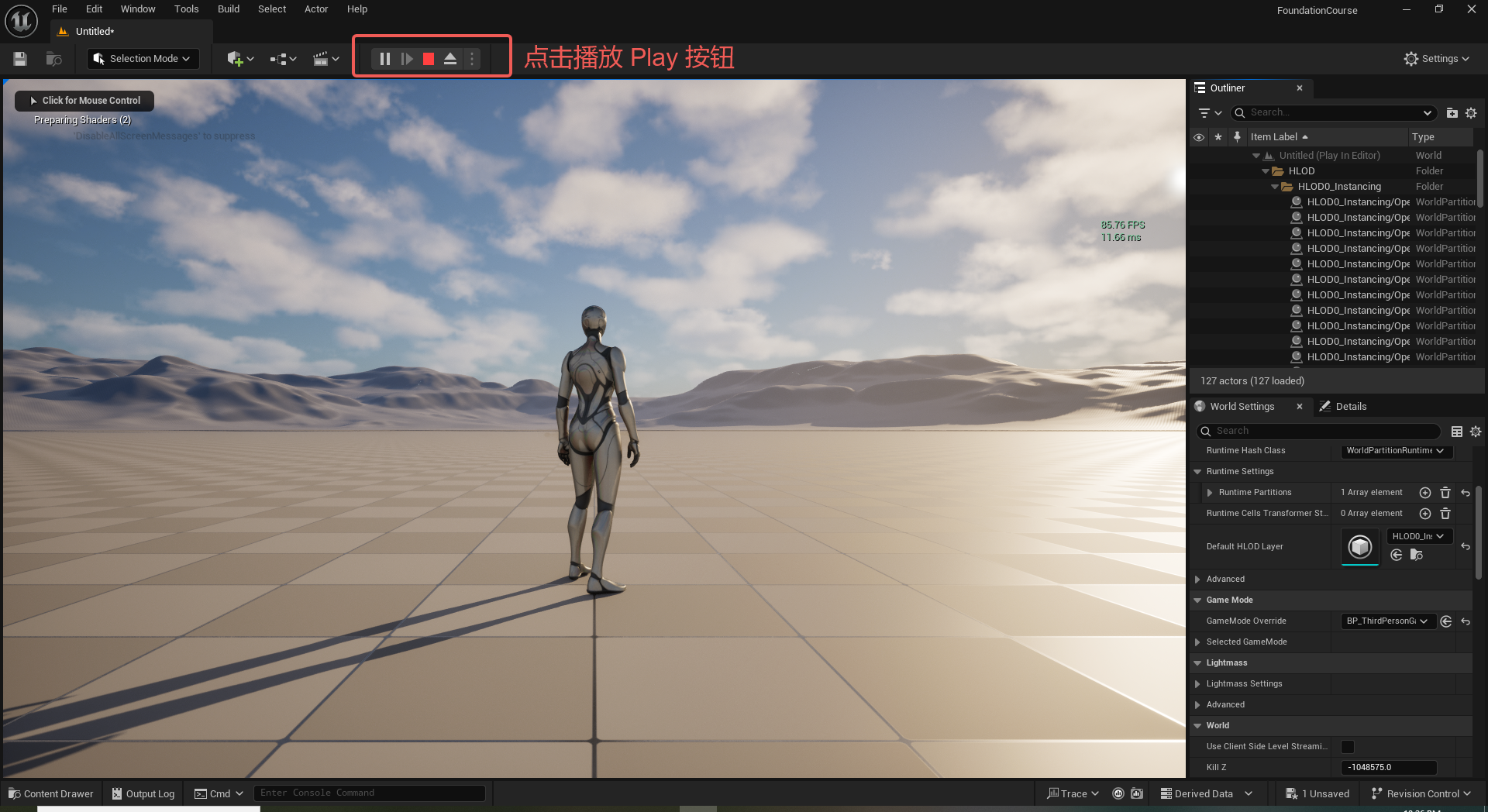
阿里云ACP云计算备考笔记 (5)——弹性伸缩
目录 第一章 概述 第二章 弹性伸缩简介 1、弹性伸缩 2、垂直伸缩 3、优势 4、应用场景 ① 无规律的业务量波动 ② 有规律的业务量波动 ③ 无明显业务量波动 ④ 混合型业务 ⑤ 消息通知 ⑥ 生命周期挂钩 ⑦ 自定义方式 ⑧ 滚的升级 5、使用限制 第三章 主要定义 …...
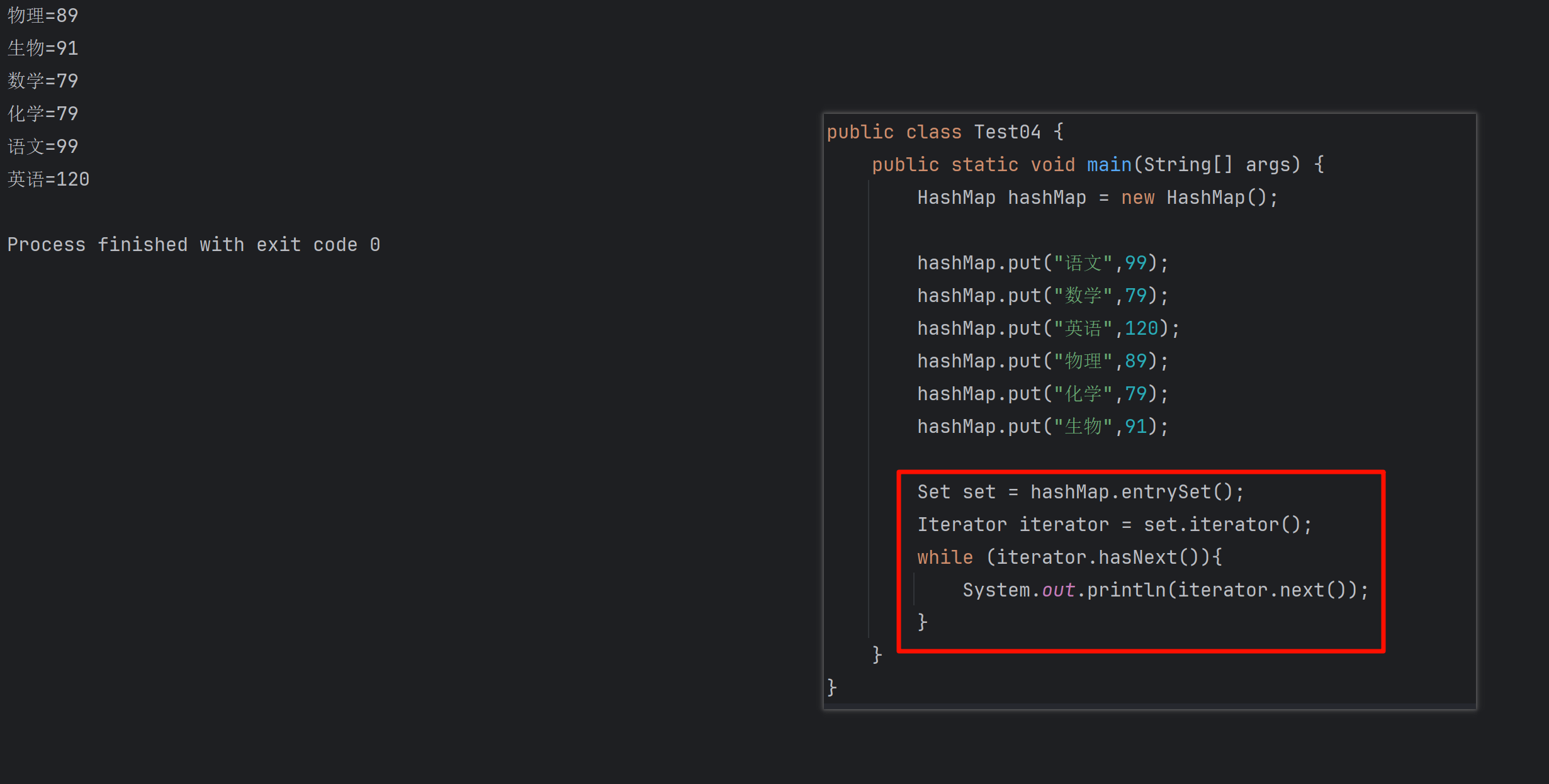
遍历 Map 类型集合的方法汇总
1 方法一 先用方法 keySet() 获取集合中的所有键。再通过 gey(key) 方法用对应键获取值 import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Set;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {HashMap hashMap new HashMap();hashMap.put("语文",99);has…...

高危文件识别的常用算法:原理、应用与企业场景
高危文件识别的常用算法:原理、应用与企业场景 高危文件识别旨在检测可能导致安全威胁的文件,如包含恶意代码、敏感数据或欺诈内容的文档,在企业协同办公环境中(如Teams、Google Workspace)尤为重要。结合大模型技术&…...
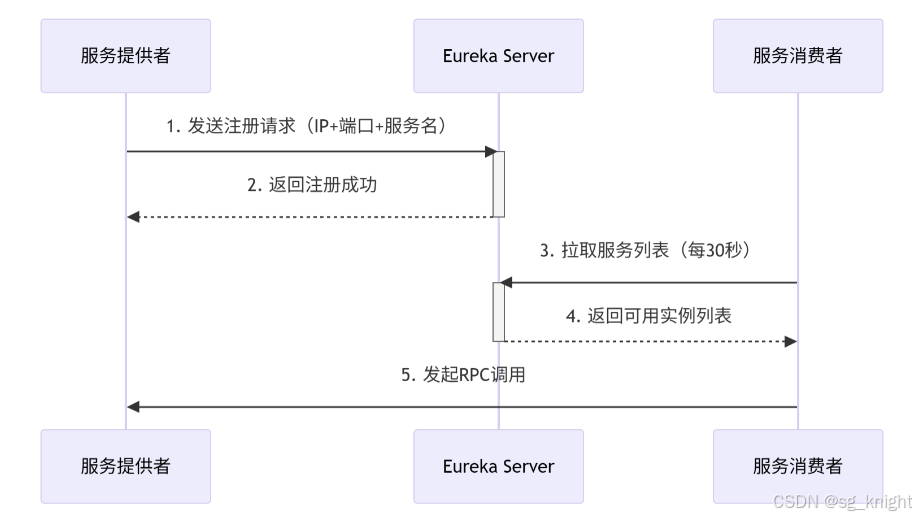
Springcloud:Eureka 高可用集群搭建实战(服务注册与发现的底层原理与避坑指南)
引言:为什么 Eureka 依然是存量系统的核心? 尽管 Nacos 等新注册中心崛起,但金融、电力等保守行业仍有大量系统运行在 Eureka 上。理解其高可用设计与自我保护机制,是保障分布式系统稳定的必修课。本文将手把手带你搭建生产级 Eur…...
C++:多态机制详解
目录 一. 多态的概念 1.静态多态(编译时多态) 二.动态多态的定义及实现 1.多态的构成条件 2.虚函数 3.虚函数的重写/覆盖 4.虚函数重写的一些其他问题 1).协变 2).析构函数的重写 5.override 和 final关键字 1&#…...
集成 Mybatis-Plus 和 Mybatis-Plus-Join)
纯 Java 项目(非 SpringBoot)集成 Mybatis-Plus 和 Mybatis-Plus-Join
纯 Java 项目(非 SpringBoot)集成 Mybatis-Plus 和 Mybatis-Plus-Join 1、依赖1.1、依赖版本1.2、pom.xml 2、代码2.1、SqlSession 构造器2.2、MybatisPlus代码生成器2.3、获取 config.yml 配置2.3.1、config.yml2.3.2、项目配置类 2.4、ftl 模板2.4.1、…...
