第二十七章 java并发常见知识内容(CompletableFuture)
JAVA重要知识点
- CompletableFuture
- 常见函数式编程操作
- 创建 CompletableFuture
- 静态工厂方法
- 处理异步结算的结果
- 异常处理
- 组合 CompletableFuture
- thenCompose() 和 thenCombine() 区别
- 并行运行多个 CompletableFuture
CompletableFuture
Java 8 才被引入的一个非常有用的用于异步编程的类。
CompletableFuture 同时实现了 Future 和 CompletionStage 接口。
public class CompletableFuture<T> implements Future<T>,
CompletionStage<T> {
}
CompletableFuture 除了提供了更为好用和强大的 Future 特性之外,还提供了函数式编程的能力。
Future 接口有 5 个方法:
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) :尝试取消执行任务。
boolean isCancelled() :判断任务是否被取消。
boolean isDone() : 判断任务是否已经被执行完成。
get() :等待任务执行完成并获取运算结果。
get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) :多了一个超时时间。
CompletionStage 接口中的方法比较多,CompletableFuture 的函数式能力就是这个接口赋予的。从这个接口的方法参数你就可以发现其大量使用了 Java8 引入的函数式编程。
常见函数式编程操作
创建 CompletableFuture
常见的创建 CompletableFuture 对象的方法如下:
- 通过 new 关键字。
- 基于 CompletableFuture 自带的静态工厂方法:runAsync() 、supplyAsync() 。
new关键字:
通过 new 关键字创建 CompletableFuture 对象这种使用方式可以看作是将 CompletableFuture 当做 Future 来使用。
举例:
创建一个结果值类型为 RpcResponse< Object > 的 CompletableFuture,可以把 resultFuture 看作是异步运算结果的载体。
CompletableFuture<RpcResponse<Object>> resultFuture = new CompletableFuture<>();
调用 complete() 方法为其传入结果,这表示 resultFuture 已经被完成了:
// complete() 方法只能调用一次,后续调用将被忽略。
resultFuture.complete(rpcResponse);
可以通过 isDone() 方法来检查是否已经完成:
public boolean isDone() {return result != null;
}
获取异步计算的结果也非常简单,直接调用 get() 方法即可。调用 get() 方法的线程会阻塞直到 CompletableFuture 完成运算。
rpcResponse = completableFuture.get();
如果已经知道计算的结果的话,可以使用静态方法 completedFuture() 来创建 CompletableFuture :
CompletableFuture<String> future =
CompletableFuture.completedFuture("hello!");
assertEquals("hello!", future.get());completedFuture() 方法底层调用的是带参数的 new 方法,只不过,这个方法不对外暴露:
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> completedFuture(U value) {return new CompletableFuture<U>((value == null) ? NIL : value);
}静态工厂方法
supplyAsync和runAsync可以帮助封装计算逻辑:
static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier);
// 使用自定义线程池(推荐)
static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor);
static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable);
// 使用自定义线程池(推荐)
static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor);runAsync() 方法接受的参数是 Runnable ,这是一个函数式接口,不允许返回值。当你需要异步操作且不关心返回结果的时候可以使用 runAsync() 方法。
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Runnable {public abstract void run();
}supplyAsync() 方法接受的参数是 Supplier< U > ,这也是一个函数式接口,U 是返回结果值的类型。
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Supplier<T> {/*** Gets a result.** @return a result*/T get();
}
需要异步操作且关心返回结果的时候,可以使用 supplyAsync() 方法。举例如下:
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> System.out.println("hello!"));
future.get();// 输出 "hello!"
CompletableFuture<String> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "hello!");
assertEquals("hello!", future2.get());处理异步结算的结果
获取到异步计算的结果之后,还可以对其进行进一步的处理,比较常用的方法有下面几个:
thenApply()
thenAccept()
thenRun()
whenComplete()
thenApply() 方法接受一个 Function 实例,用它来处理结果。方法源码如下:
// 沿用上一个任务的线程池
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApply(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn) {return uniApplyStage(null, fn);
}//使用默认的 ForkJoinPool 线程池(不推荐)
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn) {return uniApplyStage(defaultExecutor(), fn);
}
// 使用自定义线程池(推荐)
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn, Executor executor) {return uniApplyStage(screenExecutor(executor), fn);
}
thenApply() 方法使用示例如下:
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("hello!").thenApply(s -> s + "world!");
assertEquals("hello!world!", future.get());
// 这次调用将被忽略。
future.thenApply(s -> s + "nice!");
assertEquals("hello!world!", future.get());
流式调用如下:
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("hello!").thenApply(s -> s + "world!").thenApply(s -> s + "nice!");
assertEquals("hello!world!nice!", future.get());如果不需要从回调函数中获取返回结果,可以使用 thenAccept() 或者 thenRun()。这两个方法的区别在于 thenRun() 不能访问异步计算的结果。
thenAccept() 方法的参数是 Consumer<? super T> 。源码如下:
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action) {return uniAcceptStage(null, action);
}public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action) {return uniAcceptStage(defaultExecutor(), action);
}public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action,Executor executor) {return uniAcceptStage(screenExecutor(executor), action);
}解释上述代码:Consumer 属于消费型接口,它可以接收 1 个输入对象然后进行“消费”。接口源码如下:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Consumer<T> {void accept(T t);default Consumer<T> andThen(Consumer<? super T> after) {Objects.requireNonNull(after);return (T t) -> { accept(t); after.accept(t); };}
}thenRun() 的方法是的参数是 Runnable。如下:
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRun(Runnable action) {return uniRunStage(null, action);
}public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action) {return uniRunStage(defaultExecutor(), action);
}public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action,Executor executor) {return uniRunStage(screenExecutor(executor), action);
}
thenAccept() 和 thenRun() 使用示例如下:
CompletableFuture.completedFuture("hello!").thenApply(s -> s + "world!").thenApply(s -> s + "nice!").thenAccept(System.out::println);//hello!world!nice!CompletableFuture.completedFuture("hello!").thenApply(s -> s + "world!").thenApply(s -> s + "nice!").thenRun(() -> System.out.println("hello!"));//hello!上述两个方法结合起来后使用举例如下:
CompletableFuture.completedFuture("hello!").thenApply(s -> s + "world!").thenApply(s -> s + "nice!").thenAccept(System.out::println);//hello!world!nice!CompletableFuture.completedFuture("hello!").thenApply(s -> s + "world!").thenApply(s -> s + "nice!").thenRun(() -> System.out.println("hello!"));//hello!whenComplete() 的方法的参数是 BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> 。
public CompletableFuture<T> whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action) {return uniWhenCompleteStage(null, action);
}public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action) {return uniWhenCompleteStage(defaultExecutor(), action);
}
// 使用自定义线程池(推荐)
public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action, Executor executor) {return uniWhenCompleteStage(screenExecutor(executor), action);
}BiConsumer 可以接收 2 个输入对象然后进行“消费”
@FunctionalInterface
public interface BiConsumer<T, U> {void accept(T t, U u);default BiConsumer<T, U> andThen(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> after) {Objects.requireNonNull(after);return (l, r) -> {accept(l, r);after.accept(l, r);};}
}whenComplete() 使用示例如下:
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "hello!").whenComplete((res, ex) -> {// res 代表返回的结果// ex 的类型为 Throwable ,代表抛出的异常System.out.println(res);// 这里没有抛出异常所有为 nullassertNull(ex);});
assertEquals("hello!", future.get());
异常处理
通过 handle() 方法来处理任务执行过程中可能出现的抛出异常的情况:
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> handle(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn) {return uniHandleStage(null, fn);
}public <U> CompletableFuture<U> handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn) {return uniHandleStage(defaultExecutor(), fn);
}public <U> CompletableFuture<U> handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn, Executor executor) {return uniHandleStage(screenExecutor(executor), fn);
}举例实践如下:
CompletableFuture<String> future= CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {if (true) {throw new RuntimeException("Computation error!");}return "hello!";
}).handle((res, ex) -> {// res 代表返回的结果// ex 的类型为 Throwable ,代表抛出的异常return res != null ? res : "world!";
});
assertEquals("world!", future.get());还可以通过 exceptionally() 方法来处理异常情况:
CompletableFuture<String> future= CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {if (true) {throw new RuntimeException("Computation error!");}return "hello!";
}).exceptionally(ex -> {System.out.println(ex.toString());// CompletionExceptionreturn "world!";
});
assertEquals("world!", future.get());
可以使用 completeExceptionally() 方法为其赋值,令 CompletableFuture 的结果就是异常:
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = new CompletableFuture<>();
// ...
completableFuture.completeExceptionally(new RuntimeException("Calculation failed!"));
// ...
completableFuture.get(); // ExecutionException组合 CompletableFuture
可以使用 thenCompose() 按顺序链接两个 CompletableFuture 对象:
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenCompose(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn) {return uniComposeStage(null, fn);
}public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenComposeAsync(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn) {return uniComposeStage(defaultExecutor(), fn);
}public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenComposeAsync(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn,Executor executor) {return uniComposeStage(screenExecutor(executor), fn);
}thenCompose() 方法使用示例如下:
CompletableFuture<String> future= CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "hello!").thenCompose(s -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> s + "world!"));
assertEquals("hello!world!", future.get());类似的还有 thenCombine() 方法, thenCombine() 同样可以组合两个 CompletableFuture 对象:
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture= CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "hello!").thenCombine(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "world!"), (s1, s2) -> s1 + s2).thenCompose(s -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> s + "nice!"));
assertEquals("hello!world!nice!", completableFuture.get());thenCompose() 和 thenCombine() 区别
- thenCompose() 可以两个 CompletableFuture 对象,并将前一个任务的返回结果作为下一个任务的参数,它们之间存在着先后顺序。
- thenCombine() 会在两个任务都执行完成后,把两个任务的结果合并。两个任务是并行执行的,它们之间并没有先后依赖顺序。
并行运行多个 CompletableFuture
可以通过 CompletableFuture 的 allOf()这个静态方法来并行运行多个 CompletableFuture 。
实际项目中,需要并行运行多个互不相关的任务,这些任务之间没有依赖关系,可以互相独立地运行。比说要读取处理 6 个文件,这 6 个任务都是没有执行顺序依赖的任务,但是需要返回给用户的时候将这几个文件的处理的结果进行统计整理。像这种情况我们就可以使用并行运行多个 CompletableFuture 来处理。
CompletableFuture<Void> task1 =CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{//自定义业务操作});
......
CompletableFuture<Void> task6 =CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{//自定义业务操作});
......CompletableFuture<Void> headerFuture=CompletableFuture.allOf(task1,.....,task6);try {headerFuture.join();} catch (Exception ex) {......}
System.out.println("all done. ");allOf() 方法会等到所有的 CompletableFuture 都运行完成之后再返回
Random rand = new Random();
CompletableFuture<String> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(1000 + rand.nextInt(1000));} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {System.out.println("future1 done...");}return "abc";
});
CompletableFuture<String> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(1000 + rand.nextInt(1000));} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {System.out.println("future2 done...");}return "efg";
});调用 join() 后可以让程序等future1 和 future2 都运行完了之后再继续执行:
CompletableFuture<Void> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.allOf(future1, future2);
completableFuture.join();
assertTrue(completableFuture.isDone());
System.out.println("all futures done...");输出如下:
future1 done...
future2 done...
all futures done...anyOf() 方法不会等待所有的 CompletableFuture 都运行完成之后再返回,只要有一个执行完成即可!
CompletableFuture<Object> f = CompletableFuture.anyOf(future1, future2);
System.out.println(f.get());输出:
可能是:
future2 done...
efg
也可能是:
future1 done...
abc相关文章:
)
第二十七章 java并发常见知识内容(CompletableFuture)
JAVA重要知识点CompletableFuture常见函数式编程操作创建 CompletableFuture静态工厂方法处理异步结算的结果异常处理组合 CompletableFuturethenCompose() 和 thenCombine() 区别并行运行多个 CompletableFutureCompletableFuture Java 8 才被引入的一个非常有用的用于异步编…...

Qt扫盲-QMake 使用概述
QMake 使用概述一、概述二、简单开始三、使应用程序可调试1. 添加平台特定的源文件2. 如果文件不存在,停止qmake3. 检查多个条件一、概述 本教程教你qmake的基础知识。qmake 其实就是一个自动化编译的流程控制文件,也是Qt程序的生成makefile的工具&…...
Spring Cloud之Zuul
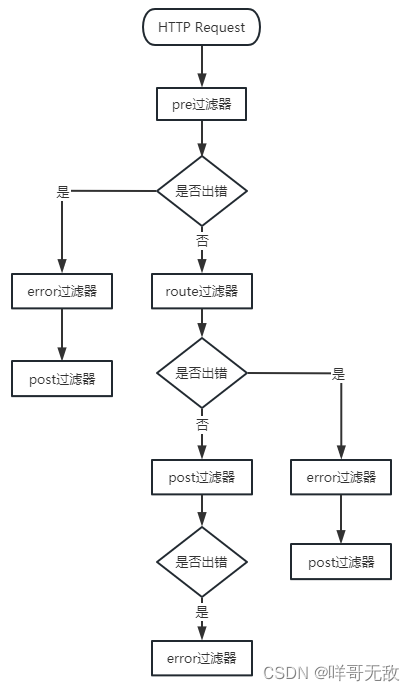
目录 简介 Zuul中的过滤器 过滤器的执行流程 使用过滤器 route过滤器的默认三种配置 路由到服务 路由到url地址 转发给自己 自定义过滤器 简介 Zuul是Netflix开源的微服务网关,主要功能是路由转发和过滤器,其原理也是一系列filters࿰…...
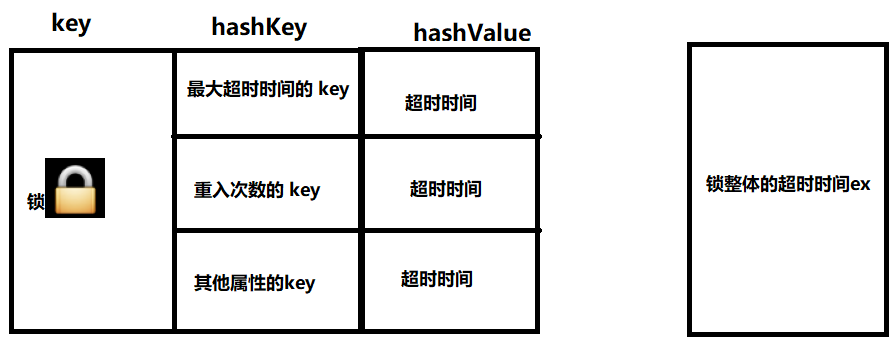
为什么要有分布式锁?
Redis避坑指南:为什么要有分布式锁?作者:京东保险 张江涛1、为什么要有分布式锁?JUC提供的锁机制,可以保证在同一个JVM进程中同一时刻只有一个线程执行操作逻辑;多服务多节点的情况下,就意味着有…...
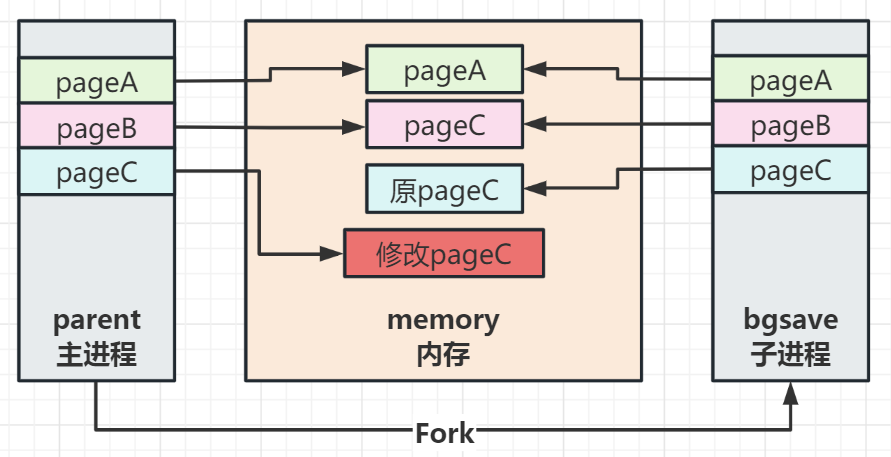
【Redis】Redis持久化之RDB详解(Redis专栏启动)
📫作者简介:小明java问道之路,2022年度博客之星全国TOP3,专注于后端、中间件、计算机底层、架构设计演进与稳定性建工设优化。文章内容兼具广度深度、大厂技术方案,对待技术喜欢推理加验证,就职于知名金融公…...

Retinanet网络与focal loss损失
参考代码:https://github.com/yhenon/pytorch-retinanet 1.损失函数 1)原理 本文一个核心的贡献点就是 focal loss。总损失依然分为两部分,一部分是分类损失,一部分是回归损失。 在讲分类损失之前,我们来回顾一下二…...

Spring事务的失效场景
事务失效场景 方法用private或final修饰 Spring底层使用了AOP,而AOP的实现方式有两种,分别是JDK动态代理和CGLIB,JDK动态代理是实现抽象接口,CGLIB是继承父类,无论哪种方式,都需要重写方法来进行方法增强,而…...

芯动联科在科创板IPO过会:拟募资10亿元,金晓冬为实际控制人
2月13日,上海证券交易所披露的信息显示,安徽芯动联科微系统股份有限公司(下称“芯动联科”)获得科创板上市委会议审议通过。据贝多财经了解,芯动联科于2022年6月24日在科创板递交招股书。 本次冲刺上市,芯…...
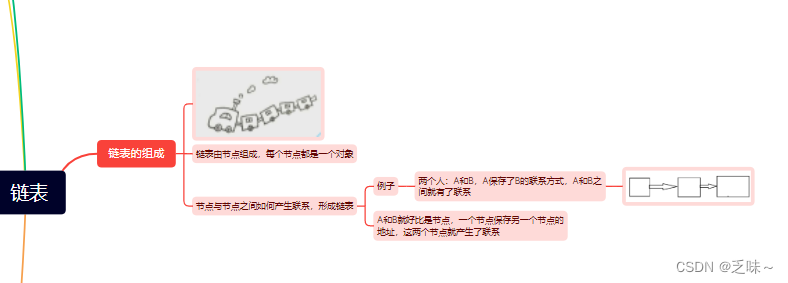
数据结构之单链表
一、链表的组成 链表是由一个一个的节点组成的,节点又是一个一个的对象, 相邻的节点之间产生联系,形成一条链表。 例子:假如现在有两个人,A和B,A保存了B的联系方式,这俩人之间就有了联系。 A和…...

儿子跟妈妈关系不好怎么办?这里有解决办法!
15岁的男孩子正处于青春期,很多男孩都傲慢自大,听不进去别人的建议,以自己为中心,认为自己能处理好自己的事情,不想听父母的唠叨。母亲面对青春期的孩子也是举手无措,语气不好,会让孩子更叛逆。…...

论文投稿指南——中文核心期刊推荐(植物保护)
【前言】 🚀 想发论文怎么办?手把手教你论文如何投稿!那么,首先要搞懂投稿目标——论文期刊 🎄 在期刊论文的分布中,存在一种普遍现象:即对于某一特定的学科或专业来说,少数期刊所含…...

华科万维C++章节练习4_6
【程序设计】 题目: 编程输出下列图形,中间一行英文字母由输入得到。 A B B B C C C C C D D D D D D D C C C C C B B B A 开头空一格,字母间空两格…...

详解子网技术
一 : Internet地址 Intemet实质上是把分布在世界各地的各种网络如计算机局域网和广域网、数字数据通信网以及公用电话交换网等互相连接起来而形成的超级网络。但是 , 网络的物理地址给Internet统一全网地址带来两个方面的问题: 第一,物理地址是物理网络技术的一种…...
chatGTP的全称Chat Generative Pre-trained Transformer
chatGPT,有时候我会拼写为:chatGTP,所以知道这个GTP的全称是很有用的。 ChatGPT全名:Chat Generative Pre-trained Transformer ,中文翻译是:聊天生成预训练变压器,所以是GPT,G是生…...
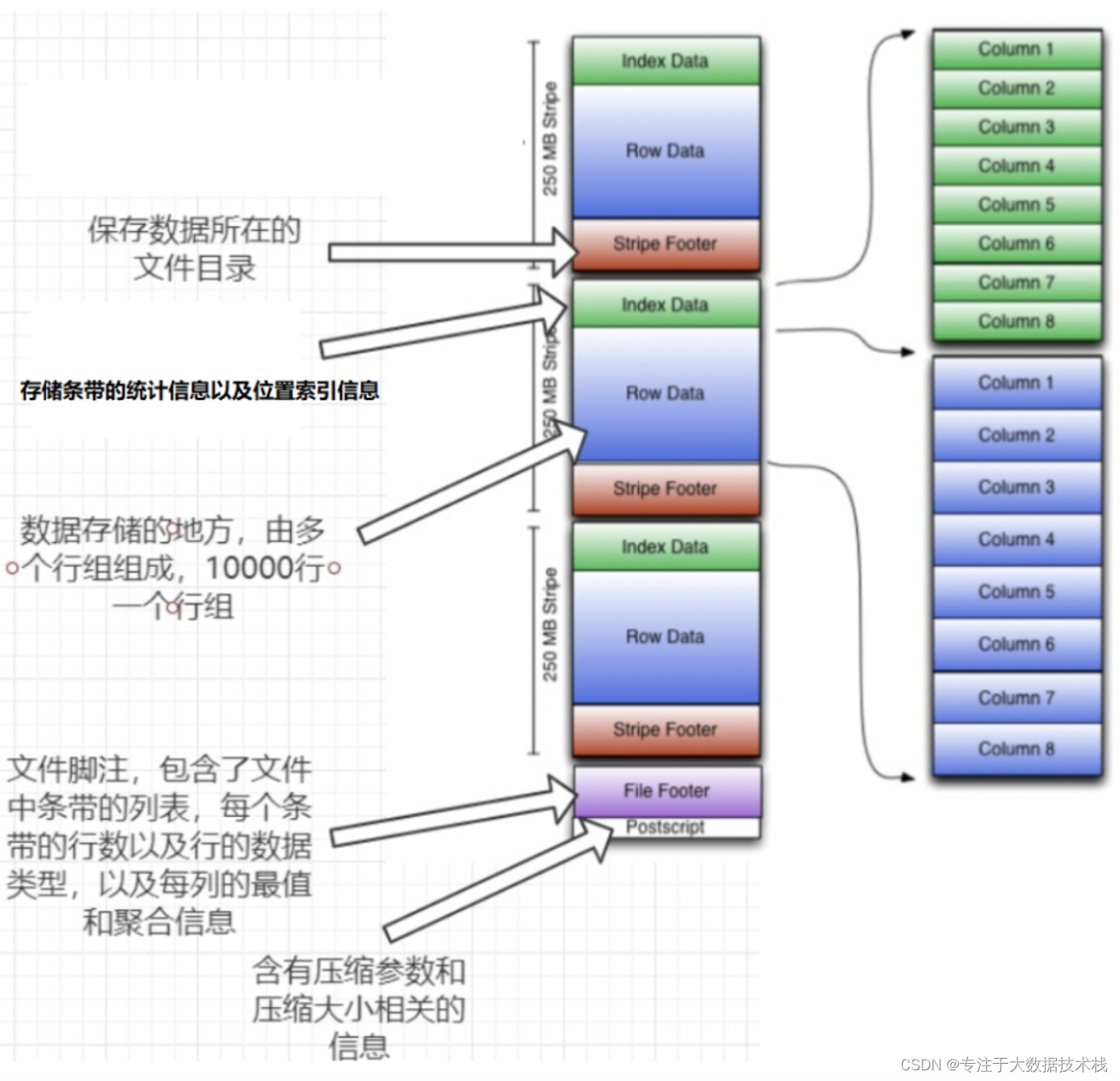
hive数据存储格式
1、Hive存储数据的格式如下: 存储数据格式存储形式TEXTFILE行式存储SEQUENCEFILE行式存储ORC列式存储PARQUET列式存储 2、行式存储和列式存储 解释: 1、上图左面为逻辑表;右面第一个为行式存储,第二个温列式存储; …...
mysql数据库备份与恢复
mysql数据备份: 数据备份方式 物理备份: 冷备:.冷备份指在数据库关闭后,进行备份,适用于所有模式的数据库热备:一般用于保证服务正常不间断运行,用两台机器作为服务机器,一台用于实际数据库操作应用,另外…...

《NFL橄榄球》:辛辛那提猛虎·橄榄1号位
辛辛那提猛虎(英语:Cincinnati Bengals),又译辛辛那提孟加拉虎,是一支职业美式橄榄球球队位于俄亥俄州辛辛那提。他们现时为美联北区的其中一支球队,他们在1968年加入美国橄榄球联合会,并在1970…...

2、线程、块和网格
目录一、线程、块、网格概念二、代码分析2.1 打印第一个线程块的第一线程2.2 打印当前线程块的当前线程2.3 获取当前是第几个线程一、线程、块、网格概念 CUDA的软件架构由网格(Grid)、线程块(Block)和线程(Thread&am…...
C++ 算法主题系列之贪心算法的贪心之术
1. 前言 贪心算法是一种常见算法。是以人性之念的算法,面对众多选择时,总是趋利而行。 因贪心算法以眼前利益为先,故总能保证当前的选择是最好的,但无法时时保证最终的选择是最好的。当然,在局部利益最大化的同时&am…...
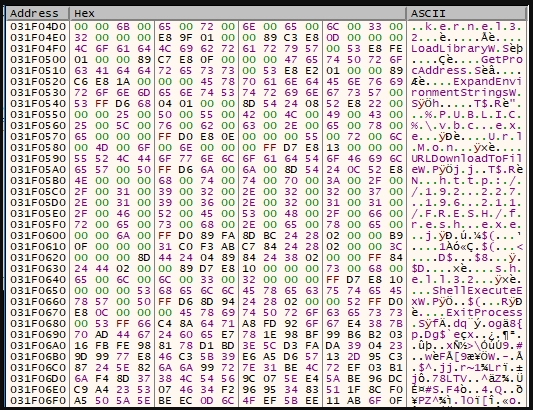
请注意,PDF正在传播恶意软件
据Bleeping Computer消息,安全研究人员发现了一种新型的恶意软件传播活动,攻击者通过使用PDF附件夹带恶意的Word文档,从而使用户感染恶意软件。 类似的恶意软件传播方式在以往可不多见。在大多数人的印象中,电子邮件是夹带加载了恶…...
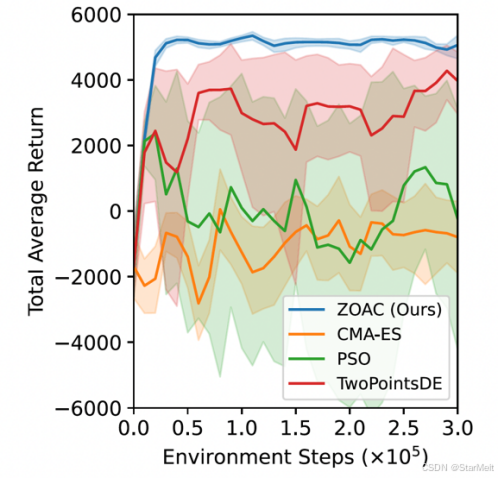
突破不可导策略的训练难题:零阶优化与强化学习的深度嵌合
强化学习(Reinforcement Learning, RL)是工业领域智能控制的重要方法。它的基本原理是将最优控制问题建模为马尔可夫决策过程,然后使用强化学习的Actor-Critic机制(中文译作“知行互动”机制),逐步迭代求解…...

五年级数学知识边界总结思考-下册
目录 一、背景二、过程1.观察物体小学五年级下册“观察物体”知识点详解:由来、作用与意义**一、知识点核心内容****二、知识点的由来:从生活实践到数学抽象****三、知识的作用:解决实际问题的工具****四、学习的意义:培养核心素养…...
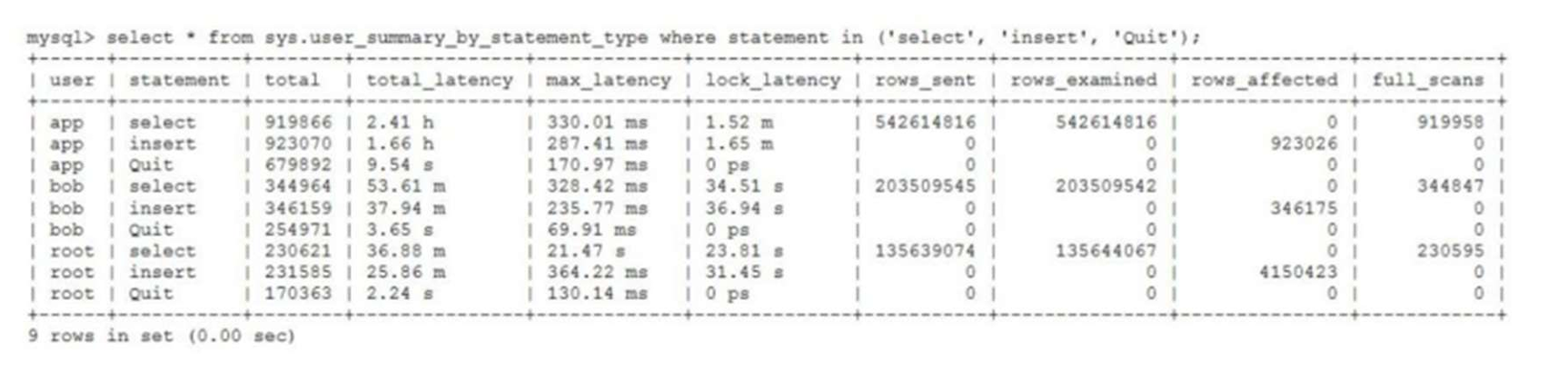
MySQL 8.0 OCP 英文题库解析(十三)
Oracle 为庆祝 MySQL 30 周年,截止到 2025.07.31 之前。所有人均可以免费考取原价245美元的MySQL OCP 认证。 从今天开始,将英文题库免费公布出来,并进行解析,帮助大家在一个月之内轻松通过OCP认证。 本期公布试题111~120 试题1…...

HTML前端开发:JavaScript 常用事件详解
作为前端开发的核心,JavaScript 事件是用户与网页交互的基础。以下是常见事件的详细说明和用法示例: 1. onclick - 点击事件 当元素被单击时触发(左键点击) button.onclick function() {alert("按钮被点击了!&…...

成都鼎讯硬核科技!雷达目标与干扰模拟器,以卓越性能制胜电磁频谱战
在现代战争中,电磁频谱已成为继陆、海、空、天之后的 “第五维战场”,雷达作为电磁频谱领域的关键装备,其干扰与抗干扰能力的较量,直接影响着战争的胜负走向。由成都鼎讯科技匠心打造的雷达目标与干扰模拟器,凭借数字射…...

爬虫基础学习day2
# 爬虫设计领域 工商:企查查、天眼查短视频:抖音、快手、西瓜 ---> 飞瓜电商:京东、淘宝、聚美优品、亚马逊 ---> 分析店铺经营决策标题、排名航空:抓取所有航空公司价格 ---> 去哪儿自媒体:采集自媒体数据进…...

稳定币的深度剖析与展望
一、引言 在当今数字化浪潮席卷全球的时代,加密货币作为一种新兴的金融现象,正以前所未有的速度改变着我们对传统货币和金融体系的认知。然而,加密货币市场的高度波动性却成为了其广泛应用和普及的一大障碍。在这样的背景下,稳定…...

听写流程自动化实践,轻量级教育辅助
随着智能教育工具的发展,越来越多的传统学习方式正在被数字化、自动化所优化。听写作为语文、英语等学科中重要的基础训练形式,也迎来了更高效的解决方案。 这是一款轻量但功能强大的听写辅助工具。它是基于本地词库与可选在线语音引擎构建,…...

重启Eureka集群中的节点,对已经注册的服务有什么影响
先看答案,如果正确地操作,重启Eureka集群中的节点,对已经注册的服务影响非常小,甚至可以做到无感知。 但如果操作不当,可能会引发短暂的服务发现问题。 下面我们从Eureka的核心工作原理来详细分析这个问题。 Eureka的…...
)
安卓基础(aar)
重新设置java21的环境,临时设置 $env:JAVA_HOME "D:\Android Studio\jbr" 查看当前环境变量 JAVA_HOME 的值 echo $env:JAVA_HOME 构建ARR文件 ./gradlew :private-lib:assembleRelease 目录是这样的: MyApp/ ├── app/ …...
